- 1State Key Laboratory of Advanced Special Steel and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced Ferrometallurgy and School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
- 2Center for Hydrogen Metallurgy Technology, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
- 3Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
- 4School of Materials Science, Shanghai Dianji University, Shanghai, China
The two-dimensional MAX phases with compositional diversity are promising functional materials for electrochemical energy storage. Herein, we report the facile preparation of the Cr2GeC MAX phase from oxides/C precursors by the molten salt electrolysis method at a moderate temperature of 700°C. The electrosynthesis mechanism has been systematically investigated, and the results show that the synthesis of the Cr2GeC MAX phase involves electro-separation and in situ alloying processes. The as-prepared Cr2GeC MAX phase with a typical layered structure shows the uniform morphology of nanoparticles. As a proof of concept, Cr2GeC nanoparticles are investigated as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, which deliver a good capacity of 177.4 mAh g−1 at 0.2 C and excellent cycling performance. The lithium-storage mechanism of the Cr2GeC MAX phase has been discussed based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations. This study may provide important support and complement to the tailored electrosynthesis of MAX phases toward high-performance energy storage applications.
Highlights
• Cr2GeC nanoparticles were first prepared from oxides/C precursors by molten salt electrolysis.
• The electrosynthesis mechanism of Cr2GeC involving electro-separation and in situ alloying processes has been investigated systematically.
• The as-prepared Cr2GeC nanoparticles as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries deliver an impressive capacity of up to 177.4 mAh g−1 at 0.2 C.
1 Introduction
The MAX phases are ternary lamellar-structure transition metal carbides and/or nitrides with a general formula of Mn+1AXn, where M is an early transition metal; A is an A-group element; X is C and/or N; and n is 1, 2, or 3 (Barsoum, 2000; Sokol et al., 2019; Fatima et al., 2020). In recent years, MAX phases have received widespread attention due to their superior physical and chemical properties, such as excellent thermal/electrical conductivity (Jin et al., 2020), thermal-shock resistance (Li et al., 2014), high-temperature oxidation resistance (Drouelle et al., 2020), and mechanical properties (Tan et al., 2021). The bulk MAX phases were commonly synthesized by hot pressing and spark plasma sintering (Ghasali et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). The molten salt electrolysis method as a simple and economical strategy has broad appeal for the fabrication of MAX phase powders. Oxides or even multi-component ores and graphite powders can be used as raw materials to synthesize MAX phase powders by molten salt electrolysis. Molten salt as an ionic solvent facilitates the mass transfer and nucleation/growth processes, resulting in finer and more homogeneous particle products (Liu et al., 2013; Li et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022). Up until now, some MAX phases (V2AlC, Ti3AlC2, V4AlC3, Cr2AlC, etc.) have been synthesized using the molten salt electrolysis method (Amr, 2016; Liu et al., 2020; Pang et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2022).
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are one of the most widely used electrochemical energy storage devices due to the advantages of high energy density, high Coulombic efficiency, and long service life (Kim et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2020). Energy storage materials have been continuously investigated to support the development of high-performance LIBs. MAX phases with special laminated structures and excellent metal conductivities have been considered as potential lithium-storage hosts (Xu et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2018; Luan et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2019). Xu et al. investigated the reversible electrochemical intercalation behavior of Li ions in Ti2SC and Ti3SiC2 MAX phases and concluded that particle size has an important influence on the electrochemical properties of MAX phases. The nanoscale Ti2SC delivered the initial reversible capacity of about 80 mAh g−1 (at 4 C), which increases to about 180 mAh g−1 after 1,000 cycles (Xu et al., 2016). Chen et al. confirmed that partially etched Ti3AlC2 has potential as an anode for high-capacity LIBs through the alloying of Al with Li (Chen et al., 2018). Li et al. prepared the V2SnC MAX phase with a high weight capacity of 490 mAh g−1 (volume capacity of 570 mAh cm−3) via the molten salt method, and a charge storage mechanism involving dual redox reactions of V2C–Li and Sn–Li was proposed (Li et al., 2021). In general, MAX phases have attracted increasing attention for applications as Li-storage anodes.
Ge, with an excellent Li ion diffusion rate and high electrical conductivity, has been considered a promising anode material candidate for LIBs (Hu et al., 2016). However, the volume expansion (about ∼250% for Li15Ge4) of Ge during the Li insertion/extraction process severely hampers its energy storage properties. Cr2GeC is one of the MAX phases, and the A-layer atom is Ge. The stable Cr2GeC MAX phase is expected to take advantage of the two-dimensional structural properties of the MAX phase and the Li-storage property of metallic Ge. If the typical alloying mechanism of Li15Ge4 in the Cr2GeC MAX phase is considered as the basis, the theoretical capacity can reach 535 mAh g–1 (Xu et al., 2016). In this work, Cr2GeC nanoparticles were easily prepared by molten salt electrolysis of oxides/C precursors and evaluated as anode materials for LIBs for the first time. The results show that the as-prepared Cr2GeC with a refined particle size delivers a high rate and excellent cycling performance, exhibiting an attractive Li storage capacity.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Molten salt electrosynthesis of Cr2GeC
Commercial Cr2O3 (3 μm, 99.5%, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), GeO2 (500 nm, 99.9%, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), graphite powders (10 nm, 99.8%, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) with different molar ratios (1:1:1, 1:2:1, 1:3:1, and 1:4:1), and 10 wt% polyvinyl butyral (PVB, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) were mixed by ball-milling at 300 r/min for 5 h to prepare the powdered Cr2O3/GeO2/C precursor. About 0.5 g of the obtained mixed powders were pressed under 10 MPa to fabricate a Cr2O3/GeO2/C disc (10 mm in diameter). The Cr2O3/GeO2/C disc was wrapped by nickel foam and fixed on a Mo wire (2 mm in diameter, Shanghai Non-Ferrous Metals (Group) Co., Ltd.) to form the Cr2O3/GeO2/C cathode system. A high-purity graphite rod (5 mm in diameter, 99.999%, Shanghai Carbon Co., Ltd.) fixed with the Mo wire was used as the anode. CaCl2 and NaCl (Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.) were commonly baked at 300–400°C for 24–48 h and then used as electrolytes in a 1:1 M ratio. The electrodes and mixed salts were assembled in a corundum crucible to form an electrolytic cell, which was then placed in an electrolysis furnace sealed on one end. High-purity Ar gas was continuously introduced into the electrolytic furnace to create an inert atmosphere. The electrolysis furnace temperature was then ramped up to 700°C with a heating rate of 5°C/min. Pre-electrolysis was then performed between two graphite rods (5 mm in diameter, 99.999%, Shanghai Carbon Co., Ltd.) at 2.0 V for 2–5 h to eliminate residual purities in molten salts. A constant voltage of 3.0 V was applied between the Cr2O3/GeO2/C cathode and the graphite anode for pre-set times. After electrolysis, the obtained electrolytic samples were washed with deionized water to remove solid salts and then, dried at 100°C in a vacuum drying oven for further characterization.
2.2 Lithium-storage performance tests of Cr2GeC
The two-electrode CR2032-type coin cell was fabricated to evaluate the lithium-storage performance of the as-prepared Cr2GeC. In detail, a slurry made by mixing 80 wt% Cr2GeC as active materials, 10 wt% acetylene black (Taiyuan Lizhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd.), and 10 wt% polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF, Taiyuan Lizhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd.) in N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP, Taiyuan Lizhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd.) was coated on a Cu foil; then, the obtained Cu foil coated with the slurry was dried under vacuum at 80°C for 10 h. The disc-shaped electrodes (12 mm in diameter) were cut off from the dried Cu foil. In addition, the lithium metal foil, 1.0 M LiPF6, and the polypropylene membrane (Taiyuan Lizhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd.) were used as the counter electrode, electrolyte, and separator, respectively. The coin cells were assembled in an argon glovebox.
2.3 Material characterization
The phase composition of the samples was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker D8 Advance). The morphology, microstructure, and elemental distribution of the samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEOL JSM-6700F), transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100F), and the affiliated energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). A Bio-Logic HCP-803 electrochemical workstation was used to record the current–time curve of the electrolysis process and cyclic voltammetry curves of the fabricated coin cell. The charge–discharge tests of coin cells were carried out on a NEWARE CT-4000 battery test system. For computational details, all density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed using the Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package (VASP). The generalized gradient approximation (GGA) developed by Perdew, Burke, and Ernzerhof (PBE) was used as the exchange-correlation potential. The cutoff energy is set to 400 eV. A Monkhorst–Pack grid of 6 × 6 × 6 was used for bulk lattice optimization, and a Monkhorst–Pack grid of 3 × 3 × 1 was used for slabs. Electronic and ionic optimizations were performed using a self-consistent field (SCF) energy criterion of 10–4 eV and a maximum force of 0.001 eV/Å. The 2 × 2 × 1 supercell of the Cr2GeC (010) slab contains 38 atoms, where the bottom three atomic layers were fixed. A vacuum layer of 15 Å was used to prevent the interaction between the near slabs.
3 Results and discussion
Cr2O3/GeO2/C used as a cathode was directly electrolyzed to prepare Cr2GeC in molten CaCl2–NaCl. Theoretical analyses of Cr2O3, GeO2, CaCl2, and NaCl were first performed based on Gibbs free energy, and the calculated temperature-dependent decomposition voltage plots are shown in Figure 1A. The results show that the applied voltage of 3.0 V is sufficient to electrochemically separate the oxygen from the oxides (Cr2O3 and GeO2) in the cathode at a wide temperature range below 1,000°C, in the case of avoiding the decomposition of chloride molten salts. Theoretically, oxygen ions ionized from cathodic Cr2O3 and GeO2 and discharged at the anode at the applied voltage. The in situ alloying reaction between the electrochemically reduced metals Cr, Ge, and C was expected to induce the formation of Cr2GeC. Figures 1B and C show the schematic of this electrolysis process and the crystal structure of the Cr2GeC MAX phase.
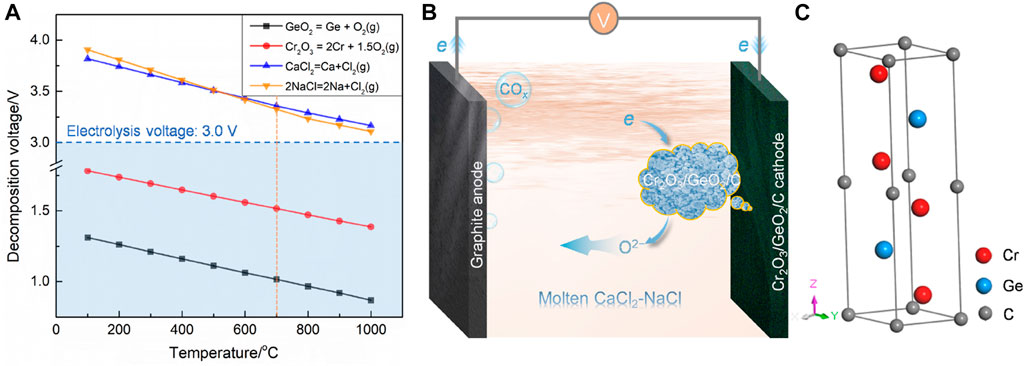
FIGURE 1. (A) Temperature-dependent theoretical decomposition voltages of Cr2O3, GeO2, CaCl2, and NaCl. (B) Schematic diagram of the electrolysis process. (C) Crystal structure of Cr2GeC.
After the aforementioned theoretical analysis, the electrosynthesis of the target Cr2GeC was first attempted using Cr2O3/GeO2/C with a molar ratio of 1:1:1 in molten CaCl2–NaCl at a relatively moderate temperature of 700°C. However, the XRD result (Figure 2A) shows that the electrolytic sample contains mixed phases of Cr2GeC, Cr7C3, and Cr3C2, indicating a significant loss of the Ge content. Therefore, excess GeO2 was further supplied into the cathode to compensate for the loss of Ge. The samples obtained by the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C precursors with different molar ratios of 1:2:1, 1:3:1, and 1:4:1 were further analyzed by XRD. It can be confirmed that Cr2GeC can be synthesized from Cr2O3/GeO2/C with a molar ratio of 1:2:1, while a further increase in the GeO2 content (i.e., cases of 1:3:1 and 1:4:1) results in the generation of metallic Ge as the second phase in Cr2GeC. On this basis, the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C with a molar ratio of 1:2:1 was further analyzed to understand the formation of the Cr2GeC MAX phase. Figure 2B shows XRD patterns of the samples obtained through the electrolysis of the Cr2O3/GeO2/C cathode (with a molar ratio of 1:2:1) at 700°C for different times. The results show that Ge, CaCr2O4, and Ca2GeO4 appeared in the cathode after 0.5 h of electrolysis. The generation of CaCr2O4 and Ca2GeO4 is caused by combination reactions between Cr2O3, GeO2, Ca2+, and O2−, which has been confirmed in previous works (Rong et al., 2014; Pang et al., 2018). CaCr2O4 and Ca2GeO4 as intermediate phases can also be electrochemically reduced to the corresponding metals of Cr and Ge. With the extension of electrolysis time to 2 h, the target Cr2GeC MAX phase accompanied by a portion of Ge, CaCr2O4, Cr3C2, and Cr7C3 was detected. This result also indicates that the reduction of GeO2 and/or Ca2GeO4 is faster compared to that of CaCr2O4. Furthermore, the reaction between Cr and C is also thermodynamically advantageous, leading to the formation of Cr3C2 and Cr7C3. It should be noted that no significant characteristic peak of C was detected due to the use of amorphous structured graphite powder. The final product after electrolysis for 3 h was detected to be the Cr2GeC MAX phase. In addition, some weak Cr3C2 and Cr7C3 characteristic peaks are still present in the XRD pattern due to the loss of Ge during electrolysis. It is inferred that the loss of the Ge content comes from the electrochemically reduced Ge and the intermediate product of Ca2GeO4. The former (Ge) in the nano state usually has a low melting point to enter the molten salt, and the latter (Ca2GeO4) has a certain solubility in molten salts (Wu and Yang, 2001; Zou et al., 2020). Therefore, excess GeO2 is necessary for molten salt electrosynthesis of the Cr2GeC MAX phase from Cr2O3/GeO2/C.
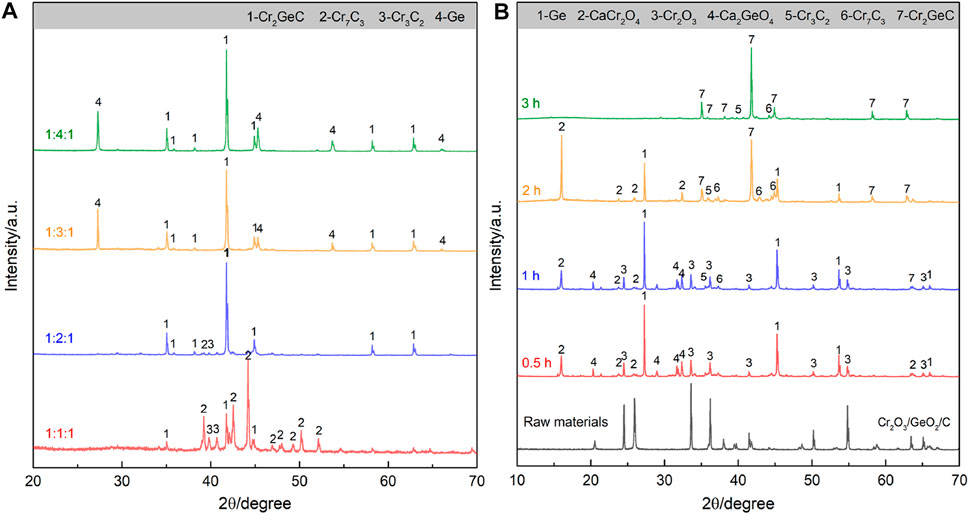
FIGURE 2. (A) XRD patterns of the samples obtained by the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C with different molar ratios (1:1:1, 1:2:1, 1:3:1, and 1:4:1) at 700°C for 3 h. (B) XRD patterns of the samples obtained by the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C (with a molar ratio of 1:2:1) at 700°C for different times.
As the synthesis conditions of Cr2GeC have been confirmed, the morphological variation of cathodic samples obtained at different electrolysis conditions was further investigated by SEM. Figure 3A shows the SEM image of the raw Cr2O3/GeO2/C precursor, illustrating a mixture of particles with inhomogeneous size morphologies. The larger particles are Cr2O3 with a size of about 3 μm, while the nanoparticles are GeO2 and C. After 0.5 h of electrolysis (Figure 3B), irregular particles up to 5 μm in size and tiny nodular nanoparticles appeared in the cathode sample, which corresponds to Cr2O3, CaCr2O4, Ca2GeO4, and Ge based on the XRD results. The nodular nanoparticles in the field of view became more numerous with the extension of the electrolysis time to 1 h, as shown in Figure 3C. After 3 h of electrolysis, the obtained sample is the Cr2GeC MAX phase, showing a uniform morphology of nanoparticles (Figure 3D). The magnified SEM image (Figure 3E) shows that the as-prepared Cr2GeC has a clear layered structure. The apparent characteristic peaks of Cr, Ge, and C were detected by EDS, as shown in Figure 3F. The SEM images of the samples obtained by the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C with different molar ratios at 700°C for 3 h are shown in Figures 3G–I. In the case of insufficient GeO2 addition (i.e., Cr2O3/GeO2/C with a molar ratio of 1:1:1), the products are Cr2GeC, Cr7C3, and Cr3C2 mixtures, thus showing a mixed irregular sintered morphology (Figure 3G). However, with the increase of the GeO2 content (i.e., Cr2O3/GeO2/C with molar ratios of 1:3:1 and 1:4:1), sintered clusters appeared in the electrolytic samples due to the generation and growth of Ge from excessive GeO2, and the increase in the Ge content enables this phenomenon to become more apparent, as shown in Figures 3H, I.
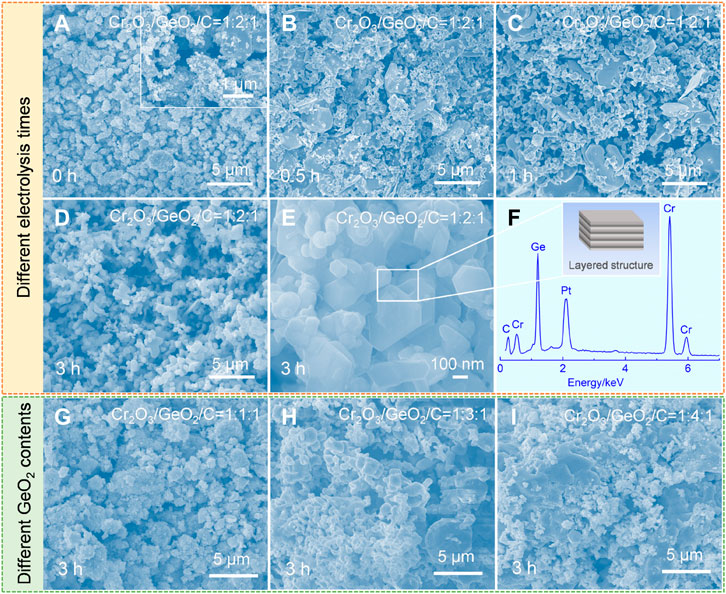
FIGURE 3. (A–F) SEM images and EDS spectra of the samples obtained by the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C with a molar ratio of 1:2:1 at 700°C for different times. (A) 0 h (i.e., raw material). (B) 0.5 h. (C) 1 h. (D,E) 3 h. (F) EDS spectra corresponding to (E). (G,I) SEM images of the samples obtained by the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C with different molar ratios: (G) 1:1:1, (H) 1:3:1, and (I) 1:4:1.
Figure 4A shows the typical current–time curve of the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C at 3.0 V. The current value rose to 1.2 A at the brief initial electrolysis stage i and then, gradually decreased to about 0.2 A within 1 h (stage ii). Subsequently, electrolysis remained in a relatively stable current state until the end of electrolysis (stage iii). The current variation during electrolysis can be explained by the three-phase interlines (3PIs) mechanism (Xiao et al., 2006; Xiao and Wang, 2014). The increase of the active surface area coming from the electrochemical reduction of GeO2 results in a sharp increase in current. As the 3PIs propagate into the interior of the cathode, the electrolysis process is controlled by oxygen-ion diffusion in the molten salts contained in the cathodic pores, resulting in a decrease in the current. The subsequent stable current value is obtained due to the exhaustion of oxygen in the cathode. The current efficiency (η) of this electrolysis process was calculated to be about 38.4% according to the following equation (Ge et al., 2015). This was expected to further improve the current efficiency by optimizing electrolysis systems:
where n is the number of transferred electrons, F is the Faraday constant, m is the metal mass obtained by electrolysis, C is the charge passed during electrolysis, and M is the relative atomic mass of Cr2O3 and GeO2.
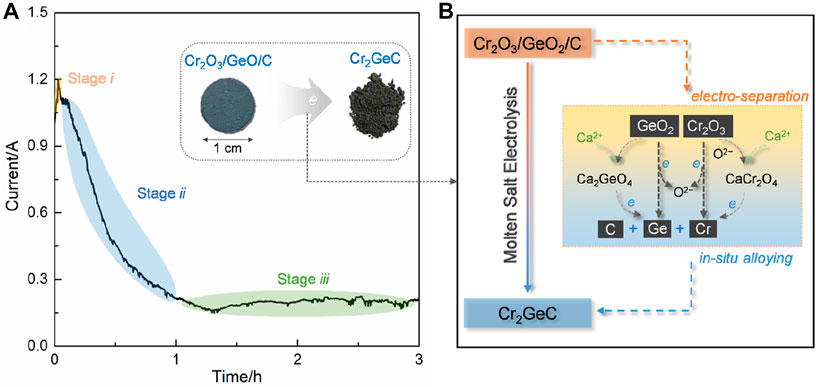
FIGURE 4. (A) Typical current–time curve recorded during the electrolysis of Cr2O3/GeO2/C under 3.0 V at 700°C; the insets are the photographs of the Cr2O3/GeO2/C disc and obtained Cr2GeC powders. (B) Schematic of the electrochemical synthesis mechanism of Cr2GeC from Cr2O3/GeO2/C.
The electrochemical synthesis mechanism of the Cr2GeC MAX phase from Cr2O3/GeO2/C was proposed based on the aforementioned analysis, and the corresponding schematic is shown in Figure 4B. GeO2 in the cathode was preferentially reduced to metal Ge by reaction (2), as confirmed by the XRD results (Figure 2). In addition, Ca2GeO4 and CaCr2O4 as intermediate products were generated through combination reactions between Ca2+, O2−, GeO2, and Cr2O3 by reactions (3)–(4) during electrolysis, wherein O2− is derived from the electrolysis of the oxides (GeO2 and Cr2O3) and the residual O2− in the molten salts. These oxides were also successively electrochemically reduced to metals Cr and Ge through reactions (2) and (5)–(7). As a result, the as-generated Cr and Ge can in situ react with C to form Cr2GeC by reaction (8). In general, the electrosynthesis of the Cr2GeC MAX phase involves the electro-separation of oxides and in situ alloying of Cr, Ge, and C.
The microstructure of the synthesized Cr2GeC MAX phase was further investigated by TEM. Figure 5A distinctly shows the TEM image of the as-prepared Cr2GeC powder and the inset is its corresponding selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern. Evidently, Cr2GeC exhibits a nanoscale irregular shape with a particle size of about 100 nm. In addition, Cr2GeC nanoparticles show an interconnected morphology because of the sintering effect during the molten salt electrolysis process. The SAED pattern reveals the typical hexagonal property of the Cr2GeC MAX phase. From the high-resolution TEM image shown in Figure 5B, the as-prepared Cr2GeC reveals the evident layers along the (0001) crystallographic direction. The regular lattice-resolved image commonly confirms periodic crystal structures (Zhao et al., 2022). An EDS analysis was further performed to investigate the element distribution of Cr2GeC nanoparticles. The obtained EDS mapping results are shown in Figures 5C–F. It can be seen that elements Cr, Ge, and C show a uniform distribution and have a good overlap with the particles shown in the TEM image (Figure 5C), demonstrating the homogeneity of the as-prepared Cr2GeC nanoparticles.
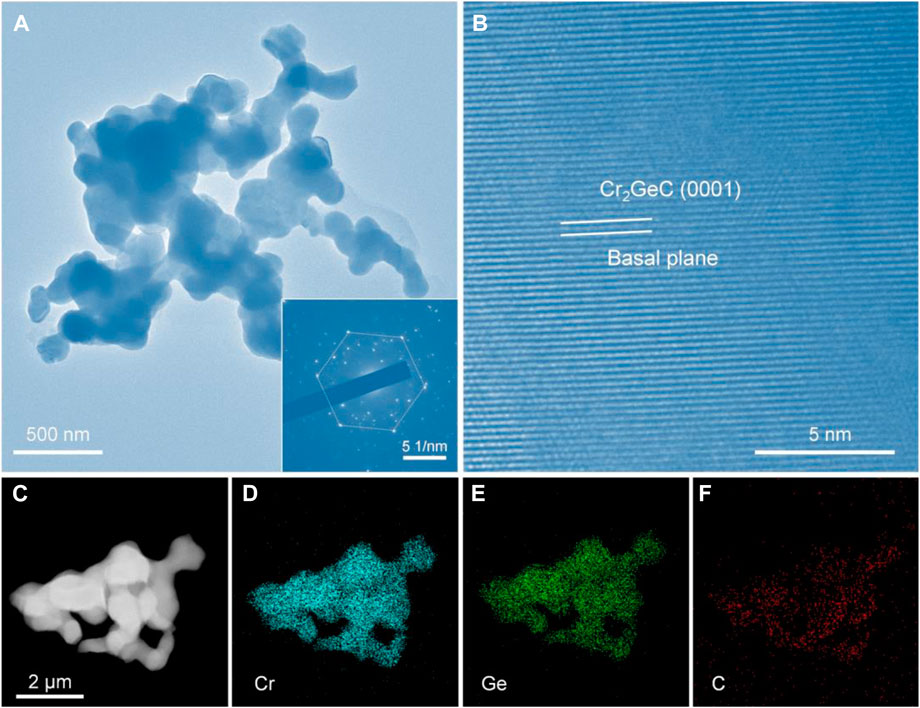
FIGURE 5. (A) TEM and (B) high-resolution TEM images of the as-prepared Cr2GeC; the inset in (A) is its corresponding selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern. (C) TEM and (D–F) are the corresponding EDS mappings of Cr2GeC nanoparticles.
To evaluate the lithium-storage performance of the as-prepared Gr2GeC MAX phase, Gr2GeC nanoparticles were used as anode materials to assemble lithium coin cell batteries for electrochemical tests. Figure 6A shows cyclic voltammetry curves in terms of lithium storage for the first three cycles in the potential range of 0.01–3.0 V with a sweep rate of 0.1 mV s−1. It can be seen that several reduction peaks within 0.01–1.0 V appeared only in the first cycle, which may be due to the formation of an irreversible solid electrolyte interface (SEI) phase or the incompletely reversible intercalation of Li in the MAX phase structure (Ren et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2016). The charge–discharge curves and the rate performance of the as-prepared Gr2GeC nanoparticles at various current densities are shown in Figures 6B and C. The discharge capacities of Cr2GeC are 177.4, 153.5, 112.4, 94.4, 85.7, and 67.6 mAh g−1 at current densities of 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 5 C, respectively. The Gr2GeC MAX phase exhibits excellent rate capacities for Li-storage. The discharge capacity can recover up to 220.1 mAh g−1 upon the reduction of the current rate to 0.2 C, which is superior to the initial discharge capacity of 177.4 mAh g−1. In addition, the as-prepared Gr2GeC was cycled at a high current density of 1 C for 200 cycles to investigate the cycling performance of Cr2GeC. As shown in Figure 6D, the initial discharge capacity of the Cr2GeC electrode is 116.4 mAh g−1, which increased to 129.8 mAh g−1 after 200 cycles and the capacity remained at about 100%. The decreasing size of Gr2GeC MAX phase particles and the expansion of two-dimensional structures that are caused by the Ge–Li (de) alloying reaction during (de) lithiation are believed to be responsible for the increase of the capacity during cycling (Li et al., 2021). The aforementioned results visually reveal that the as-prepared Cr2GeC nanoparticle can facilitate fast and stable lithium storage. Table 1 shows the comparison of the lithium-storage performance of the synthesized Cr2GeC and other reported MAX phase materials (Xu et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2018; Luan et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2019; Li et al., 2021). It can be seen that the as-prepared Cr2GeC also presents promising lithium-storage performance. The energy storage properties exhibited by MAX phase materials are exciting, and molten salt electrolysis provides a facile and controllable strategy for the synthesis of the MAX phase toward energy storage applications.
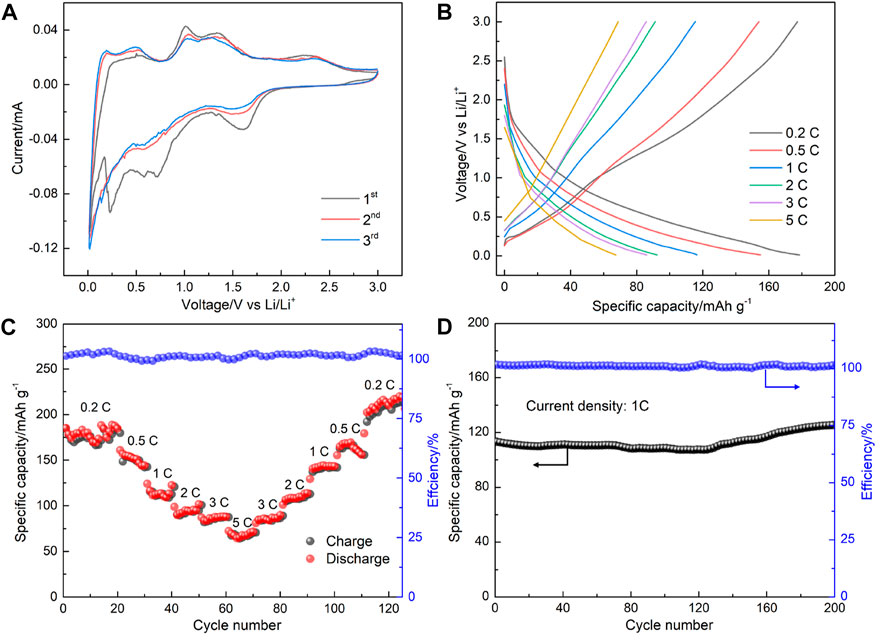
FIGURE 6. (A) Cyclic voltammetry curves at the first, second, and third cycle at 0.1 mV s−1 in the potential range of 0.01–3.0 V. (B) Galvanostatic charge–discharge curves of the fabricated cell at the current densities range of 0.2–5 C. (C) Capacities and Coulombic efficiency at different current densities. (D) Cycling performance of the Cr2GeC electrode at 1°C for 200 cycles.
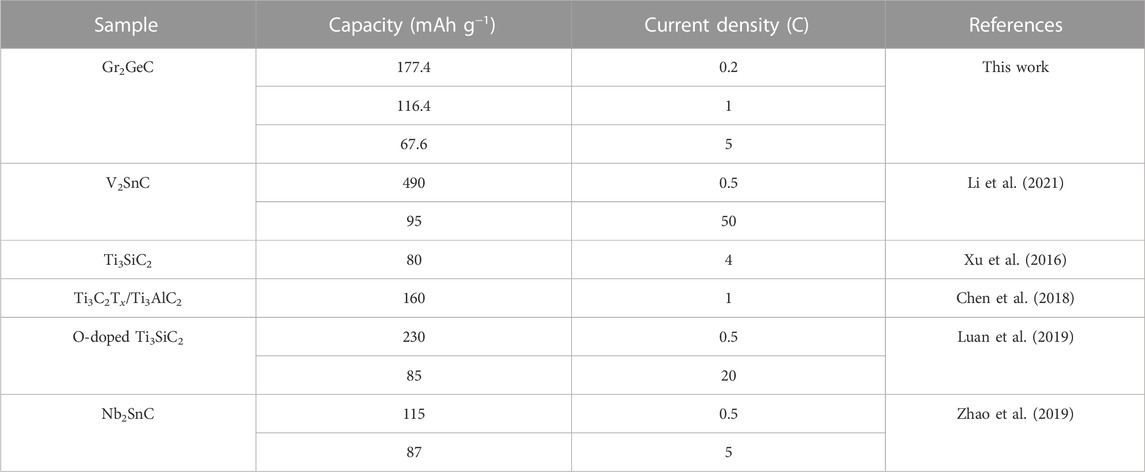
TABLE 1. Comparison of the lithium-storage performance of synthesized Cr2GeC and other reported MAX phase materials.
The DFT calculations were performed to preliminarily understand the Li-storage mechanism of Cr2GeC. The interaction between Li ions and Cr2GeC surfaces was investigated to evaluate the Li-storage behavior of Cr2GeC at the atomic scale. As shown in Figures 7A and B, different adsorption sites for Li adsorption were investigated, leading to two stable adsorption configurations. The adsorption energies for Ge and Cr sites are −1.34 eV and −0.69 eV, respectively. The results indicate that the reaction between the Ge atom and the Li ion is more favored. In addition, Bader charge analysis and charge redistribution were performed to further gain a deeper understanding of their adsorption behaviors. The change of the Bader charge in surface elements shows the interaction between the Cr2GeC and Li cation. Ge gains 0.019|e| when the Li cation is adsorbed on this site, indicating that Ge–Li reactions are preferred, which occur and contribute to the redox capacity. The side view of charge redistribution for the same isosurface value (2 × 10−3 electrons/bohr−3) is shown in Figures 7C and D. The yellow/blue color represents the charge accumulation/depletion, suggesting a strong interaction between Li and Ge, which is in accordance to the adsorption energies. The DFT calculation result reveals that Li storage may be caused by Li–Ge alloying at the edges of Cr2GeC nanoparticles.
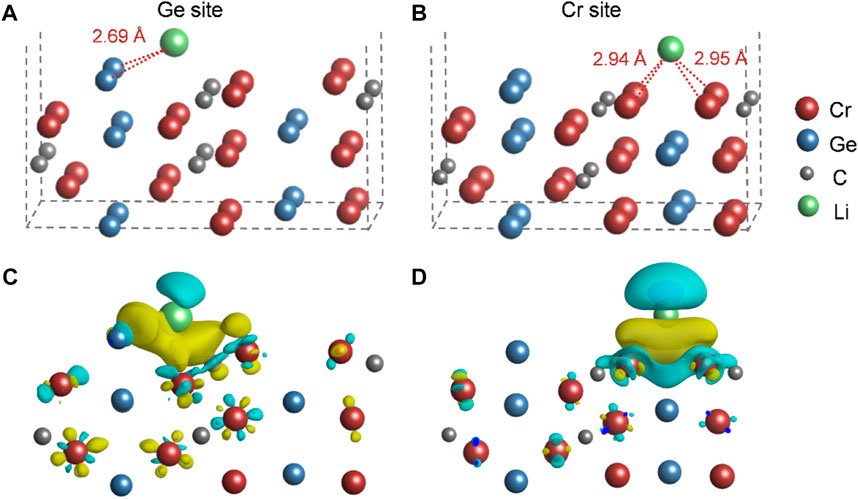
FIGURE 7. Li ion adsorption in (A) Ge and (B) Cr sites. The charge redistributions due to the interaction between Li and (C) Ge and (D) Cr sites. The yellow/blue color represents the charge accumulation/depletion, where isosurfaces refer to an isovalue of 2 × 10−3 electrons/Bohr−3.
4 Conclusion
The Cr2GeC MAX phase with a typical two-dimensional layered structure has been electrochemically synthesized in molten salts. This electrosynthesis process consumes only electrons to directly convert Cr2O3/GeO2/C into Cr2GeC at a moderate temperature of 700°C. The synthesis mechanism mainly involves the electro-separation of oxygen ions from Cr2O3/GeO2 and in situ alloying of the as-generated Cr, Ge, and C. The as-prepared Cr2GeC MAX phase shows a uniform morphology of nanoparticles with a particle size of about 100 nm. Cr2GeC nanoparticles have been further investigated as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, which showed attractive electrochemical performance with a specific capacity of 177.4 mAh g−1 at 0.2 C and excellent cycling performance. The possible lithium-storage mechanism of Cr2GeC has been discussed based on DFT calculations, whereby Ge atoms at edge sites of Cr2GeC nanoparticles undergo the (de) alloying reaction of Ge–Li.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
ZP, FT, and XX performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. JL, XZ, SC, FW, SW, XY, and QX provided valuable suggestions. GL, XL, and XZ supervised and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 52022054, 51974181, and 52004157), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 2022M712023), the Shanghai Postdoctoral Excellence Program (no. 2021159), the Shanghai Sailing Program (no. 21YF1412900), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2022YFC2906100), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (no. 21DZ1208900), and the Iron and Steel Joint Research Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation and China Baowu Steel Group Corporation Limited (no. U1860203).
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank the Program for the Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning (no. TP2019041) and the “Shuguang Program” supported by the Shanghai Education Development Foundation and the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (no. 21SG42). ZP would like to acknowledge the valuable discussions and kind help of Xin Li, who has graduated from Shanghai University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Amr, M. (2016). Abdelkader. Molten salts electrochemical synthesis of Cr2AlC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 33–42. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.09.003
Barsoum, M. W. (2000). The MN+1AXN phases: A new class of solids: Thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog. Solid St. Chem. 28 (1–4), 201–281. doi:10.1016/S0079-6786(00)00006-6
Chen, X., Zhu, Y., Zhu, X., Peng, W., Yang, L., Zhang, G., et al. (2018). Partially etched Ti3AlC2 as a promising high-capacity lithium-ion battery anode. Chemsuschem 11, 2677–2680. doi:10.1002/cssc.201801200
Drouelle, E., Gauthier-Brunet, V., Cormier, J., Villechaise, P., Sallot, P., Naimi, F., et al. (2020). Microstructure-oxidation resistance relationship in Ti3AlC2 MAX phase. J. Alloy. Compd. 82615, 154062. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154062
Fatima, M., Fatheema, J., Monir, N. B., Ahmad, H. S., Khan, B., Islam, A., et al. (2020). Nb-doped MXene with enhanced energy storage capacity and stability. Front. Chem. 8, 168. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00168
Gao, Y., Ge, J., Wang, X., Wu, T., Zhu, F., Duan, J., et al. (2022). Molten salt electrochemical synthesis of low-cost Vn+1AlCn (n=1,3) and their derived two-dimensional MXenes. Ceram. Int. 48, 17975–17980. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.222
Ge, J., Zhang, F., Jiao, H., and Jiao, S. (2015). Metallic nickel preparation by electro-deoxidation in molten sodium hydroxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, E185–E189. doi:10.1149/2.0811509jes
Ghasali, E., Reza Derakhshandeh, M., Orooji, Y., Alizadeh, M., and Ebadzadeh, T. (2021). Effects of 211 and 413 ordering on the corrosion behavior of V-Al-C MAX phases prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 4774–4787. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.03.001
Hu, Z., Zhang, S., Zhang, C., and Cui, G. (2016). High performance germanium-based anode materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 326, 34–85. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2016.08.002
Jin, S., Su, T., Hu, Q., and Zhou, A. (2020). Thermal conductivity and electrical transport properties of double-A-layer MAX phase Mo2Ga2C. Mater. Res. Lett. 8, 158–164. doi:10.1080/21663831.2020.1724204
Kim, T., Song, W., Son, D. Y., Ono, L. K., and Qi, Y. (2019). Lithium-ion batteries: Outlook on present, future, and hybridized technologies. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 2942–2964. doi:10.1039/C8TA10513H
Li, S., Li, H., Zhou, Y., and Zhai, H. (2014). Mechanism for abnormal thermal shock behavior of Cr2AlC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 1083–1088. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.12.003
Li, S., Song, J., Che, Y., Jiao, S., He, J., and Yang, B. (2022). Advances in molten salt synthesis of non-oxide materials. Energy Environ. Mater. 0, 1–13. doi:10.1002/eem2.12339
Li, Y., Ma, G., Shao, H., Xiao, P., Lu, J., Xu, J., et al. (2021). Electrochemical lithium storage performance of molten salt derived V2SnC MAX phase. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 158. doi:10.1007/s40820-021-00684-6
Liu, P., Hou, Z., Hu, M., Hu, L., Tang, R., Wu, H., et al. (2020). Electro-synthesis of ultrafine V2AlC MAX-phase and its conversion process towards two-dimensional V2CTX. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 122501. doi:10.1149/1945-7111/aba401
Liu, X., Fechlera, N., and Antonietti, M. (2013). Salt melt synthesis of ceramics, semiconductors and carbon nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 8237–8265. doi:10.1039/C3CS60159E
Luan, S., Zhou, J., Xi, Y., Han, M., Wang, D., Gao, J., et al. (2019). High lithium-ion storage performance of Ti3SiC2 MAX by oxygen doping. ChemistrySelect 4, 5319–5321. doi:10.1002/slct.201900328
Pang, Z., Zou, X., Li, S., Tang, W., Xu, Q., and Lu, X. (2020). Molten salt electrochemical synthesis of ternary carbide Ti3AlC2 from titanium-rich slag. Adv. Eng. Mater. 22, 1901300. doi:10.1002/adem.201901300
Pang, Z., Zou, X., Zheng, Kai, Li, S., Wang, S., Hsu, H. Y., et al. (2018). Sustainable synthesis of Cr7C3, Cr2AlC, and their derived porous carbons in molten salts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 16607–16615. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03837
Ren, C. E., Zhao, M. Q., Makaryan, T., Halim, J., Boota, M., Kota, S., et al. (2016). Porous two-dimensional transition metal carbide (MXene) flakes for high-performance Li-ion storage. ChemElectroChem 3, 689–693. doi:10.1002/celc.201600059
Rong, L., He, R., Wang, Z., Peng, J., Jin, X., and George Chen, Z. (2014). Investigation of electrochemical reduction of GeO2 to Ge in molten CaCl2-NaCl. Electrochim. Acta 147, 352–359. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2014.09.107
Sokol, M., Natu, V., Kota, S., and Michel, W. B. (2019). On the chemical diversity of the MAX phases. Trends Chem. 1 (2), 210–223. doi:10.1016/j.trechm.2019.02.016
Tan, Y., Xia, Y., Teng, Z., Chen, C., Zhou, X., and Zhang, H. (2021). Synthesis and enhanced mechanical properties of compositionally complex MAX phases. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 4658–4665. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.03.027
Wu, Y., and Yang, P. (2001). Melting and welding semiconductor nanowires in nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 13, 520–523. doi:10.1002/1521-4095(200104)13:7<520::AID-ADMA520>3.0.CO;2-W
Xiao, W., Jin, X., Deng, Y., Wang, D., Hu, X., and George Chen, Z. (2006). Electrochemically driven three-phase interlines into insulator compounds: Electroreduction of solid SiO2 in molten CaCl2. ChemPhysChem 7, 1750–1758. doi:10.1002/cphc.200600149
Xiao, W., and Wang, D. (2014). The electrochemical reduction processes of solid compounds in high temperature molten salts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 3215–3228. doi:10.1039/C3CS60327J
Xu, J., Zhao, M. Q., Wang, Y., Yao, W., Chen, C., Anasori, B., et al. (2016). Demonstration of Li-ion capacity of MAX phases. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 1094–1099. doi:10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00488
Zhang, Z., Duan, X., Jia, D., Zhou, Y., and van der Zwaag, S. (2021). On the formation mechanisms and properties of MAX phases: A review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 3851–3878. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.02.002
Zhao, Q., Hu, L., Li, W., Liu, C., Jiang, M., and Shi, J. (2020). Recovery and regeneration of spent lithium-ion batteries from new energy vehicles. Front. Chem. 8, 807. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00807
Zhao, S., Chen, L., Xiao, H., Huang, J., Li, Y., Qian, Y., et al. (2022). Phase transformation and amorphization resistance in high-entropy MAX phase M2SnC (M = Ti, V, Nb, Zr, Hf) under in-situ ion irradiation. Acta Mater 238, 118222. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2022.118222
Zhao, S., Dall’Agnese, Y., Chu, X., Zhao, X., Gogotsi, Y., and Gao, Y. (2019). Electrochemical interaction of Sn-containing MAX phase (Nb2SnC) with Li-ions. ACS Energy Lett. 4, 2452–2457. doi:10.1021/acsenergylett.9b01580
Keywords: MAX phase, Cr2GeC, molten salt electrosynthesis, lithium-ion batteries, energy storage
Citation: Pang Z, Tian F, Xiong X, Li J, Zhang X, Chen S, Wang F, Li G, Wang S, Yu X, Xu Q, Lu X and Zou X (2023) Molten salt electrosynthesis of Cr2GeC nanoparticles as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Front. Chem. 11:1143202. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1143202
Received: 12 January 2023; Accepted: 06 February 2023;
Published: 17 February 2023.
Edited by:
Jianxun Song, Zhengzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Handong Jiao, Beijing Institute of Technology, ChinaLiwen Hu, Chongqing University, China
Copyright © 2023 Pang, Tian, Xiong, Li, Zhang, Chen, Wang, Li, Wang, Yu, Xu, Lu and Zou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhongya Pang, emhvbmd5YXBhbmdAc2h1LmVkdS5jbg==; Guangshi Li, bGdzQHNodS5lZHUuY24=; Xingli Zou, eGx6b3VAc2h1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhongya Pang
Zhongya Pang Feng Tian1,2†
Feng Tian1,2† Xiaolu Xiong
Xiaolu Xiong