- 1Beijing Minhai Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
- 2Center for Infectious Disease Research, Department of Basic Medical Science, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a pathogenic bacterium that causes infections such as pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media, and bacteremia. The prevention of pneumococcal disease by vaccination has become more urgent due to increased antibiotic resistance. Pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides (CPS) are effective vaccine antigens that stimulate the host to produce protective antibodies. S. pneumoniae serotype 14 is one of most prevalent types in Latin America and across the world. However, the yield of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 CPS from existing fermentation processes remains low and requires improvement. In this study, various aspects of the fermentation process were optimized to improve pneumococcal growth and polysaccharide productivity, including feed medium, cultivation gas environment, fermentation pH, and temperature. A simplified purification method was also developed to obtain pure CPS, including ultrafiltration, acid and ethanol precipitation, diafiltration, and lyophilization. These fermentation optimizations significantly enhanced the optical density of pneumococcal bacterial cultures and increased fermentation yields to 2.4–2.6 g/L—significantly higher than previously achieved. Furthermore, the test results of pure CPS could meet the requirements in the European Pharmacopoeia (11th edition). These optimizations provide valuable insights into the nutritional requirements and impact of varying fermentation process parameters on pneumococcal growth and CPS productivity, thus contributing to the development of a more efficient and cost-effective method for the production of pneumococcal CPS—essential for manufacturing vaccines against pneumococcal infections.
1 Introduction
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a lancet-shaped, Gram-positive, facultative anaerobic bacterium with more than 100 known serotypes; it causes human diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media, and bacteremia, with children under 5 years of age the most susceptible population (Al-Jumaili et al., 2023; Paton and Trappetti, 2019; Weiser et al., 2018). With its increasing antibiotic resistance, vaccination to prevent pneumococcal infection is increasingly emphasized (Fitzgerald and Waterer, 2019; Guo and Qiao, 2021; Lees et al., 2017; Morais et al., 2019; Weiser et al., 2018). Pathogenic factors of S. pneumoniae include pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides (CPS), hemolysins, and surface proteins, among which CPS is the key virulence factor (Kadioglu et al., 2008). CPS on bacterial surfaces not only protect bacteria from being cleared by mucus in the nasal cavity (Hamaguchi et al., 2018; Hyams et al., 2010) but also shield bacterial surface structures, thus protecting bacteria from attack by neutrophils, macrophages, and antibodies. However, CPS as effective antigens can stimulate the host to produce protective antibodies (Avery and Heidelberger, 1925; Avery et al., 1925). Hence, CPS of highly virulent serotypes are formulated into widely used pneumococcal vaccines (Jones and Currie, 1991; Talaga et al., 2002). S. pneumoniae serotype 14 is one of the most prevalent in Latin America and around the world, and it presents high levels of antibiotic resistance. In existing fermentation processes, the yield of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 CPS remains low and needs improvement.
In the manufacturing process of CPS, the fermentation of S. pneumoniae is a critical step affecting CPS yield. Microbial fermentation is a very complex system influenced by many factors, including strain selection, medium composition, feed medium composition, fermentation pH and temperature, aeration and stirring, and modes of operation such as batch, fed-batch, or continuous culture (Degeest and De Vuyst, 1999; Gonçalves et al., 2014; Grobben et al., 1997; Gururao et al., 2018; Jain and Maithal, 2011; Zeidan et al., 2017). Moreover, the synthesis of CPS by S. pneumoniae is regulated by multiple factors through a complex metabolic pathway. Studies have shown that there is no simple correlation between the concentration of S. pneumoniae cells and the yield of CPS, which indicates that the optimal growth conditions for S. pneumoniae do not necessarily result in the highest production of CPS (Gonçalves et al., 2002; Henriques et al., 2006; Leal et al., 2011; Marthos et al., 2015; Restrepo et al., 2005).
Although S. pneumoniae disease and new vaccines have been extensively studied, few studies have seemed to investigate the factors affecting CPS productivity and optimizing CPS production. Moreover, most fermentation research has been conducted in flasks, which do not reproduce large-scale conditions. The cultivation conditions of bacterial growth and CPS productivity have been investigated for serotypes 1 (Marthos et al., 2015), 4 (Kim et al., 1996), 5 (Li et al., 2024), 6B (Gonçalves et al., 2007), 14 (Leal et al., 2011; Massaldi et al., 2010), and 23F (Gonçalves et al., 2002). Jain and Maithal (2011) described a fermentation medium and process for S. pneumoniae where the biomass of serotype 14 S. pneumoniae could reach 0.9–15.0 (OD600nm), with a polysaccharide yield of 0.2–0.25 g/L. In Leal et al. (2011), the yield of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 CPS increased by 30% and reached 185.2 mg/L after optimization of the medium and culture process (Leal et al., 2011). Desai and colleagues found that by using an improved chemically defined medium, the optical density (OD600) of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 could reach 6.8, with a fermentation yield of up to 1.1 g/L (Gururao et al., 2018). Patents disclose that after a series of process optimizations, the batchwise fermentation yield of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 CPSs reached 450 mg/L, and the yield for fed-batch fermentation could reach 1,100 mg/L (Vinayak et al., 2017). The perfusion mode in fermentation could greatly enhance the growth density of S. pneumoniae by cycling the culture through a perfusion system and removing spent medium and waste products. Fermentation operating in perfusion mode could achieve an optical density up to 30 (OD600), with a corresponding CPS yield up to 2.2 g/L (Gururao et al., 2018). However, due to the complexity of operation, the high cost of materials, and the potential contamination risk in the external perfusion system during circulation, batchwise or fed-batch fermentation modes are preferred in actual production processes.
In addition, CPS as antigens must meet strict quality standards in pneumococcal vaccines, including high immunogenicity and adequate safety. Quality control requirements related to vaccine safety include residual protein, nucleic acid, pyrogenic substances, and chemical reagents associated with purification (Jones, 2015; Jones and Currie, 1991; Morais et al., 2018; Talaga et al., 2002). Current mainstream techniques for purifying polysaccharides include a precipitation-based approach where acid precipitation is utilized alone or in conjunction with organic solvent precipitation to remove impurities (Bahler et al., 2008; Cano et al., 1980; Jung et al., 2011; Lee et al., 2020; Li et al., 2016) and the absorption of impurities by silica particles or the flocculation of impurities (Macha et al., 2014; Venkat et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2014; Zhu et al., 2021). Generally, purification through precipitation is achieved by a complex labor-intensive purification process. Chromatography-based approaches include ion-exchange (Venkat et al., 2022; Zanardo et al., 2016), hydrophobic, mixed-mode (Kapre and Datta, 2020), size-exclusion (Jin et al., 2014), and affinity methods (Suárez et al., 2001). However, chromatography purification is typically expensive. Enzymatic hydrolysis, such as protease and nuclease (Gonçalves et al., 2003; Keming et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2015), is also usually expensive and requires validation for the removal of enzymes.
Therefore, we have undertaken this study to determine the fermentation process parameters that could influence pneumococcal growth and CPS production with the aim of improving the CPS yield of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 fermentation. In addition, a simplified downstream purification process was developed to obtain pure CPS, and tests were conducted to investigate the quality of pure CPS according to the European Pharmacopeia (11th ed.).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial strains
S. pneumoniae serotype 14 strain (CMCC 31608) was purchased from the National Center for Medical Culture Collections. The lyophilized strain was used to establish a master seed lot and a working seed lot. Tests were conducted to verify the characteristics of the strain by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control of China.
2.2 Reagent and equipment
2.2.1 Reagent
2.2.1.1 Solid medium
The solid medium included soy peptone (Thermo Fisher Scientific), dipotassium hydrogen phosphate and tryptophan (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), L-cysteine hydrochloride and tyrosine (Tianjin Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.), and agar powder (Beijing Aoboxing Biotechnology Co., Ltd.).
2.2.1.2 Liquid medium
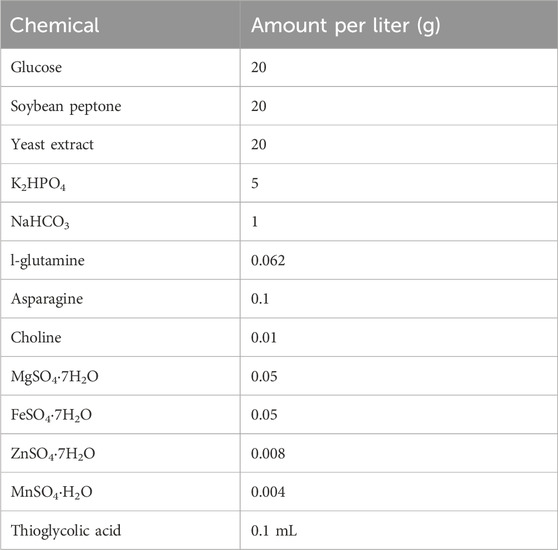
The liquid medium included glutamine (Hebei Bailingwei Ultrafine Materials Co., Ltd.), L-asparagine, choline chloride, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, ferrous sulfate and zinc sulfate heptahydrates, thioglycolic acid (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), soy peptone, yeast extract (Thermo Fisher Scientific), glucose (Shandong Saint-Show Technology & Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), and sodium hydroxide (Chengdu Huayu Pharmaceutical Excipients Co., Ltd.). The components of the fermentation culture medium are listed in Table 1.
2.2.1.3 Inactivation
DOC (SIGMA-ALDRICH).
2.2.1.4 Purification
For CPS purification, we used acetic acid (Chengdu Huayu Pharmaceutical Excipients Co., Ltd.), disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate (Hunan Jiudian Hongyang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), sodium chloride (Hubei Wuhuan Salt Industry Group Co., Ltd.), calcium chloride (Beijing Yanjing Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), sodium hydroxide (Chengdu Huayu Pharmaceutical Excipients Co., Ltd.), anhydrous sodium acetate, and anhydrous ethanol (Nanjing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.).
2.2.2 Equipment
2.2.2.1 Fermentation
The fermentation equipment consisted of a 15-L microbial bioreactor (Shanghai Bailun Biotechnology), CO2 incubator (Thermo Fisher), UV–visible spectrophotometer (Beijing Puxi Technology), biological safety cabinet (Suzhou Antai Air Technology), XB43 microscope (Olympus), bioprocess analyzer (Shenzhen Hillman Biotechnology), vacuum freeze dryer (Shanghai Dongfulong), biochemical incubator (Qingdao Haier Biomedical Co., Ltd.), and high-speed centrifuge (Thermo Fisher).
2.2.2.2 Purification
The purification equipment consisted of a magnetic stirrer (Shanghai Meiyingpu Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd.), electronic balance (Mettler Toledo), electronic platform scale (Mettler Toledo), multiparameter tester (Mettler Toledo), high-speed centrifuges (Thermo Fisher), and ultrafiltration membranes (Millipore).
2.3 Bioreactor fermentation
Frozen stock culture (1 mL) from working seed lot was used to inoculate solid medium and was cultured in a CO2 incubator for 9–15 h (with a CO2 concentration of 10% and a cultivation temperature of 36°C). The strain was then inoculated to a 3-L flask containing 1 L of liquid medium; the flask was incubated at 36°C and 90 rpm to obtain an optical density (OD) of 0.4–0.6 at 600 nm. When the OD600 of the culture reached 0.4–0.6, it was transferred at an inoculation volume of 5–10% into bioreactors containing the fermentation medium. Lab-scale fed-batch fermentations were carried out in a 15-L bioreactor with a working volume of 10 L.
Bioreactor cultivation was conducted under 10% CO2 atmosphere (0.1 vvm), 100% CO2 atmosphere (0.1 vvm), and 100% nitrogen atmosphere (0.1 vvm).
Bioreactor cultivation pH was controlled by adding 5 M NaOH at pH 6.0, pH 6.4, pH 6.8, and pH 7.2.
Bioreactor cultivation temperature was maintained at 35°C, 36°C, 37°C, 38°C, and 39°C.
The agitation speed was maintained using a mechanically driven impeller (90 rpm).
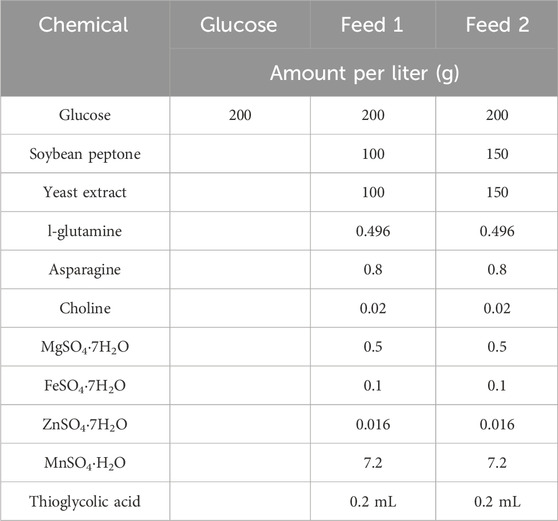
During the fed-batch fermentation process, a continuous feed medium (with different components—Table 2) was used to maintain the glucose concentration above 5 g/L in the fermentation system. At various intervals during cultivation, samples were taken to measure optical density at 600 nm and analyze glucose concentration.
2.3.1 Fermentation time
The CPS are synthesized extensively during the logarithmic phase of S. pneumoniae growth (Morais et al., 2018), and the CPS titer normally reaches maximum at the end of the stationary phase or the early stage of the decline phase (Gonçalves et al., 2006; Gonçalves et al., 2002; Li et al., 2024). Moreover, prolonged fermentation in the decline phase would lead to gradual degradation of CPS (Crinean, 2014; Massaldi et al., 2010), which is detrimental to their quality (Loetscher et al., 1992; Qiong et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2006; Zhao et al., 2012). Therefore, all fermentation experiments were terminated in the early stage of the decline phase to achieve high CPS yield and quality.
In the final stage of fermentation, the fermentation broth was treated with 0.1% DOC and stirred for 40 min and then incubated at 4°C for 12 h for sterilization. After cell lysis, polysaccharide in the supernatant was measured for CPS yield (samples were centrifuged to obtain pellets and supernatants).
2.4 Purification of CPS
A simplified purification process was developed, involving ultrafiltration and diafiltration to remove small molecular impurities, followed by acid and alcohol precipitation to eliminate protein and nucleic acid impurities, and finally diafiltration and lyophilization to obtain purified polysaccharide.
1. After sterilization, the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 30 min to collect the supernatant, which was ultrafiltered using 100-kDa membrane to obtain concentrated ultrafiltrate, and diafiltered to remove small molecules and impurities.
2. Acetic acid was added to the concentrate to adjust the pH to 4.00; after thorough mixing, it was left to stand at 2–8°C for 2 h, and then the supernatant was collected by centrifugation.
3. The supernatant obtained from the previous step was adjusted back to pH 6.0–7.0 using 5M NaOH solution. Disodium hydrogen phosphate was added to a concentration of 10 mmol/L, monosodium dihydrogen phosphate to a concentration of 10 mmol/L, sodium chloride to a concentration of 1.0 mol/L, anhydrous sodium acetate to a concentration of 0.9 mol/L, and calcium chloride to a concentration of 0.35 mol/L. After being fully dissolved, acetic acid was added to adjust the pH to 5.40. Then, 20% (v/v) of anhydrous ethanol was added according to the volume of the solution, thoroughly mixed, and left to stand at 2–8°C for 3–24 h before the supernatant was collected by centrifugation.
4. The supernatant was ultrafiltered using 100 kDa membrane to obtain a polysaccharide-enriched ultrafiltrate; the concentrated ultrafiltrate was then lyophilized and collected.
2.5 Structural identity and conformity of CPS by 1H NMR spectroscopy
Analysis of the CPS by 1H NMR spectroscopy (Bruker, Avance III 400 and 600) was conducted at the Beijing Center for Physical and Chemical Analysis, Beijing, China. Prior to analysis, the CPS samples were freeze-dried and reconstituted to a final concentration of 2–4 mg/mL in deuterium oxide. In 1H NMR data, splitting patterns are indicated as follows: “s” for singlet, “d” for doublet, “t” for triplet, “q” for quartet, “m” for multiplet, and “br” for broad singlet. NMR chemical shifts (δ) are reported in parts per million (ppm), and coupling constants (J) are reported in Hertz (Hz).
2.6 Analysis of samples
The polysaccharide content of serotype 14 was determined based on the rate nephelometric method using specific antisera obtained from Statens Serum Institute (Copenhagen, Denmark) according to the immunochemical method (2.7.1) in the European Pharmacopoeia (11th edition). The purified CPS from type 14 were subjected to tests according to the European Pharmacopoeia (11th edition), including protein (2.5.16), nucleic acids (2.5.17), total nitrogen (2.5.9), phosphorus (2.5.18), molecular size (2.2.30), and hexosamines (2.5.20). Protein was determined by the Lowry method.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of feed medium composition on growth profile and productivity
With the increase of biomass and consumption of nutrients in the fermentation process, glucose solution is typically supplemented into a fermentation broth to maintain the essential sufficient carbon source in fed-batch fermentation. However, S. pneumoniae is a fastidious microorganism, and various nitrogen sources are expected to support the growth of pneumococcal bacteria and CPS synthesis. Moreover, transition metals such as zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn) serve as cofactors in many bacterial proteins involved in critical cellular processes; it has been demonstrated that increased Mn/Zn ratios could facilitate CPS production via Mn-dependent activation of the phosphoglucomutase Pgm (McFarland et al., 2021). Therefore, manganese concentration was increased in feed medium to enhance the Mn/Zn ration. Fermentation in a 15-L bioreactor with a working volume of 10 L was conducted to investigate the effects of varying components of feed medium on pneumococcal growth and CPS synthesis.
Standard operating parameters were utilized at this stage: fermentation temperature was maintained at 37°C, pH was fixed at 7.2, and agitation speed was controlled at 90 rpm following Gonçalves et al. (2006), Jain and Maithal (2011), Leal et al. (2011), and Massaldi et al. (2010), with 10% inoculation volume employed in these fermentation experiments. Nitrogen, proven to support pneumococcal growth and polysaccharide synthesis (Gonçalves et al., 2006; Gonçalves et al., 2002; Carvalho et al., 2013), was applied at this stage. Lab-scale fermentations were carried out in batchwise mode without feeding medium, as well as fed-batch mode during which different types of feed medium were continuously supplemented into the bioreactor to keep the glucose concentration in the fermentation broth above 5 g/L.
As demonstrated in Figure 1, a short lag phase was apparent, and S. pneumoniae cultures reached climax at approximately 3.5 h with 10% inoculation volume applied. It is obvious that feed medium composition exerted a huge effect on growth curves, and feed medium supplemented with nitrogen source rather than pure carbon could support much higher pneumococcal growth. The maximum optical density for feed medium 2 was almost double that of pure glucose feed medium. Correspondingly, CPS yields for the four fermentation experiments were 0.42 g/L (batch mode), 0.67 g/L (glucose), 1.46 g/L (feed medium 1), and 1.72 g/L (feed medium 2). These results demonstrated that feed medium supplemented with nitrogen source and Mn transition metals could significantly promote pneumococcal bacteria growth and CPS synthesis.
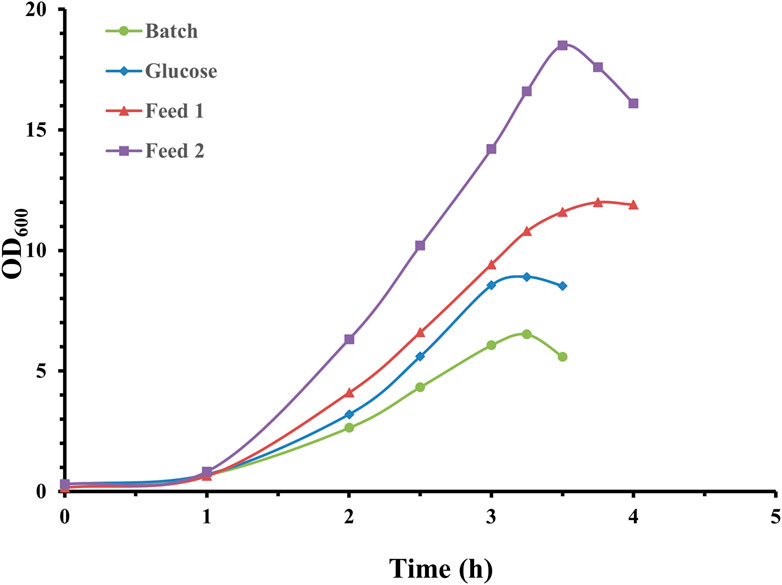
Figure 1. Time profile of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 batch and fed-batch cultivation with different feed medium composition. Fermentation growth profile in batchwise mode indicated by green circles; fermentation growth profile with glucose feeding indicated by blue diamonds; fermentation growth profile with feed 1 indicated by red triangles; fermentation growth profile with feed 2 indicated by purple squares.
An even more concentrated feed medium (200 g/L soy peptone and 200 g/L yeast extract) was also investigated in fed-batch fermentation, but not successfully due to solubility issues during feed medium preparation. In addition, the CPS yield for fed-batch operation with this thick feed medium was only 1.38 g/L, similar to the yield obtained with feed medium 1. This is probably due to the increased osmolality of fermentation broth, which may inhibit cellular growth and CPS synthesis. Therefore, feed medium 2 was selected to investigate cultivation gas, fermentation pH, and temperature.
3.2 Effect of cultivation gas environment on growth profile and productivity
Research has shown that most isolates of S. pneumoniae are a mixture of T-type (transparent) and O-type (opaque) colonies. O-type S. pneumoniae can significantly upregulate the expression of CPS in an anaerobic environment, increasing the expression level of CPS 5.2–10.6 times, while the yield of T-type colonies remains consistently low. This difference in yield is related to the expression level of CPS encoding proteins, especially CpsD tyrosine kinase (Li et al., 2017; Weiser et al., 2001). It has been shown that the cultivation of S. pneumoniae serotype 19F was significantly influenced by environmental conditions, with 5% CO2 atmosphere environment during cultivation enhancing CPS production 3.5 fold (Jalali and Tarahomjoo, 2015). Moreover, nitrogen has also been proven to support high pneumococcal growth and CPS synthesis (Gonçalves et al., 2006; Gonçalves et al., 2002; Carvalho et al., 2013; Gonçalves et al., 2002; Weiser Jeffrey, 2001).
This study investigated various cultivation gas environments, including 10% CO2 (Jain and Maithal, 2011), 100% CO2 (Gonçalves et al., 2002), and nitrogen. Feed medium 2 was employed according to previous optimization of feed medium. Fermentation temperature was set at 37°C, agitation speed was fixed at 90 rpm, fermentation pH was controlled at 7.2, and 10% inoculation volume was applied in this series of fermentation experiments.
As seen in Figure 2, a complete anaerobic cultivation environment is beneficial for the growth of pneumococcal bacteria, and both cultivation gas environments (100% CO2 and nitrogen) could support the growth of pneumococcal bacteria to approximately 18 (OD600), with a nitrogen gas environment slightly higher than 100% CO2. The gaps in biomass were also reflected in CPS yields, which were 1.08 g/L (10% CO2), 1.56 g/L (100% CO2), and 1.72 g/L (100% nitrogen) for the three cultivation gas environments.
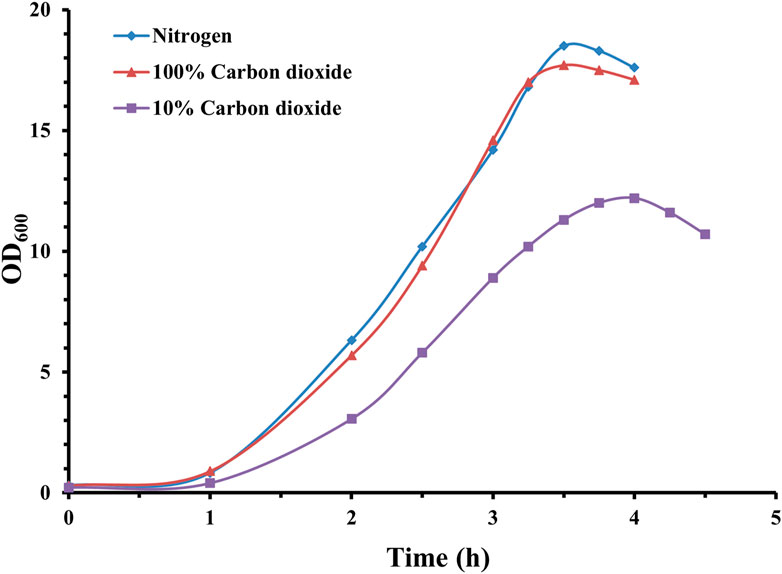
Figure 2. Time profile of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 fed-batch cultivation under different cultivation gas environments. Fermentation growth profile in nitrogen environment indicated by blue diamonds; fermentation growth profile in 100% CO2 environment indicated by red triangles; fermentation growth profile in 10% CO2 environment indicated by purple squares.
Both 100% CO2 and nitrogen demonstrated similar pneumococcal growth profiles. However, probably due to the continuous dissolving of CO2 into the cultivation medium, inhibiting pneumococcal growth and CPS synthesis, 100% nitrogen cultivation environment could facilitate a higher level of CPS synthesis, which is consistent with Gonçalves et al. (2002).
3.3 Effect of fermentation pH on growth profile and productivity
According to Leal et al. (2011), the cultivation pH is a highly important variable in S. pneumoniae fermentation; a four-fold increase in polysaccharide productivity was achieved with pH optimization in cultivation (Leal et al., 2011). Hugo and colleagues also indicated that pH control is critical for cell growth and CPS production, and pH maintenance above 6 could enhance productivity (Massaldi et al., 2010). Therefore, four fermentation pH setpoints—6.0, 6.4, 6.8, and 7.2—were carefully chosen to investigate the effect of fermentation pH on pneumococcal growth and CPS productivity in this study.
In this series of fermentation experiments, 5% inoculation volume was employed instead of 10% to examine the effect of inoculation volume on maximal pneumococcal bacterial density. Feed medium 2 was employed according to previous optimization of feed medium. A nitrogen cultivation environment was applied according to the optimal cultivation gas environment. The fermentation temperature was set at 37°C, and the agitation speed was fixed at 90 rpm.
As demonstrated in Figure 3, fermentation with 5% inoculation volume exhibited similar maximal bacterial density with 10% inoculation volume. However, due to the smaller inoculation volume, a longer lag and exponential phase (approximately 5 h) was evident.
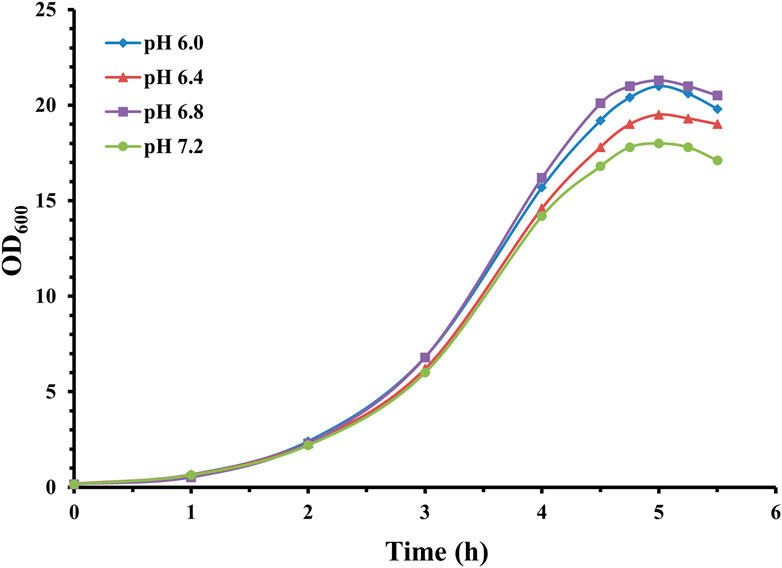
Figure 3. Time profile of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 fed-batch cultivation with different fermentation pHs. Fermentation growth profile at pH 6.0 indicated by blue diamonds; fermentation growth profile at pH 6.4 indicated by red triangles; fermentation growth profile at pH 6.8 indicated by purple squares; fermentation growth profile at pH 7.2 indicated by green circles.
Fermentation with varying levels of pH showed similar growth curves with different maximal optical density. Correspondingly, CPS yield was 1.49 g/L (pH 6.0), 1.92 g/L (pH 6.4), 2.55 g/L (pH 6.8), and 1.62 g/L (pH 7.2). Calculated specific CPS yield was 0.071 g/L/OD600 for pH 6.0, 0.098 g/L/OD600 for pH 6.4, 0.120 g/L/OD600 for pH 6.8, and 0.09 g/L/OD600 for pH 7.2.
These results showed that although biomass growth was slightly affected by pH within this range, the quantity of synthesized CPS varied significantly. The specific CPS production obtained at pH 6.8 is obviously higher than pH 6.4, 7.2, and 6.0. This also aligns with Henriques et al. (2006), who indicated that optimal conditions for pneumococcal bacteria growth and polysaccharide synthesis are not always the same.
3.4 Effect of fermentation temperature on growth profile and productivity
The fermentation temperature for S. pneumoniae is usually set at 36–37°C (Jain and Maithal, 2011; Suárez et al., 2001). However, few studies have investigated the effect of fermentation temperature on pneumococcal growth and CPS productivity. In this series of fermentation experiments, feed medium 2 was employed, a nitrogen cultivation environment (0.1 vvm) was applied, fermentation pH was set at 6.8, and agitation speed was fixed at 90 rpm.
As shown in Figure 4, fermentation temperatures of 36°C, 37°C, 38°C, and 39°C demonstrated significantly different growth trends and similar maximal pneumococcal density. The duration of the lag and exponential phases before reaching stationary phase is approximately 3.5 h (39°C), 4.5 h (38°C), 5 h (37°C), and 5.5 h (36°C), showing obvious differences in growth speed within this fermentation temperature range. In addition, fermentation at 35°C exhibited a much lower optical density, and the time before reaching stationary phase (6.5 h) was much longer than other fermentation temperatures.
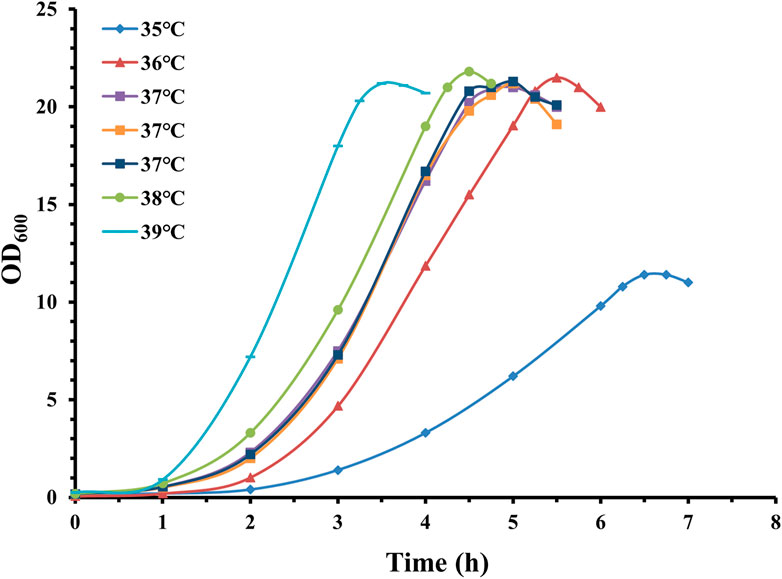
Figure 4. Time profile of S. pneumoniae serotype 14 fed-batch cultivation with different fermentation temperatures. Fermentation growth profile at 35°C indicated by blue diamonds; fermentation growth profile at 36°C indicated by red triangles. Three batches of fermentation growth profiles at 37°C indicated by purple, orange and navy squares; fermentation growth profile at 38°C indicated by green circles; fermentation growth profile at 39°C indicated by cyan bars.
Interestingly, despite obviously different growth speeds, the maximal pneumococcal density for temperatures 36°C, 37°C, 38°C, and 39°C was very similar. On the other hand, the CPS productivity was 0.98 g/L (35°C), 2.20 g/L (36°C), 2.55 g/L (37°C), 1.94 g/L (38°C), and 1.78 g/L (39°C), and the calculated specific CPS yield was 0.086 g/L/OD600 for 35°C, 0.102 g/L/OD600 for 36°C, 0.120 g/L/OD600 for 37°C, 0.089 g/L/OD600 for 38°C, and 0.084 g/L/OD600 for 39°C.
These results indicate that conditions that favor bacterial growth are not always associated with high CPS productivity, and that fermentation temperature has a profound effect on serotype 14 CPS productivity. Precise control of temperature at 37°C is beneficial for CPS fermentation titer.
3.5 Test results for pure CPS
CPS must meet strict quality standards when used as antigens, including high immunogenicity and adequate safety. Quality control requirements related to vaccine safety include residual protein, nucleic acid, pyrogenic substances, and chemical reagents associated with purification (Jones, 2015; Jones and Currie, 1991; Morais et al., 2018; Talaga et al., 2002).
This study adopted a simplified purification method for the extraction and purification of CPS from fermentation broth. This purification method included ultrafiltration, acid precipitation, alcohol precipitation, and final ultra- and diafiltration, excluding traditional CTAB precipitation and phenol extraction, as well as the costly chromatography process. Compared with the mainstream purification process, this simplified purification process saves significant cost and time. Purified CPS for serotype 14 was prepared from fermentation broth sterilized by DOC, and percentage contents of components for purified polysaccharides were analyzed according to the European Pharmacopoeia (11th Edition).
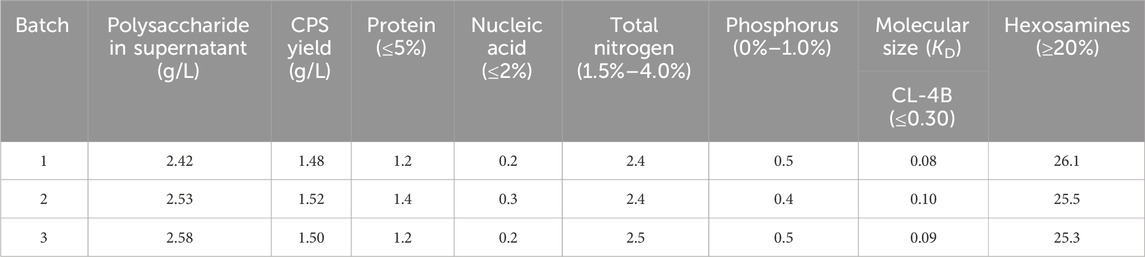
To confirm the consistency of the productivity and quality of this fermentation and purification process, three consecutive batches of 15-L bioreactor fermentation and purification were conducted utilizing feed medium 2, nitrogen gas, fermentation pH at 6.8, and temperature at 37°C (Figure 4; Table 3).
The fermentation titer for these three consecutive batches was 2.42 g/L, 2.53, and 2.58 g/L, which is an approximately four-fold increase over the fermentation titer before optimization. In the meantime, by comparing the percentage content of the components of serotype-14 refined CPS obtained after a simplified purification process, it was found that the residual protein content in the refined CPS was 1.2%–1.4%, which is significantly lower than the residual protein quality standard (5.0%). Residual nucleic acid for refined CPS was between 0.2% and 0.3%, much lower than the quality standard. All other test results could also meet the quality control standards of the European Pharmacopoeia (11th Edition).
3.6 1H NMR spectra of pure CPS
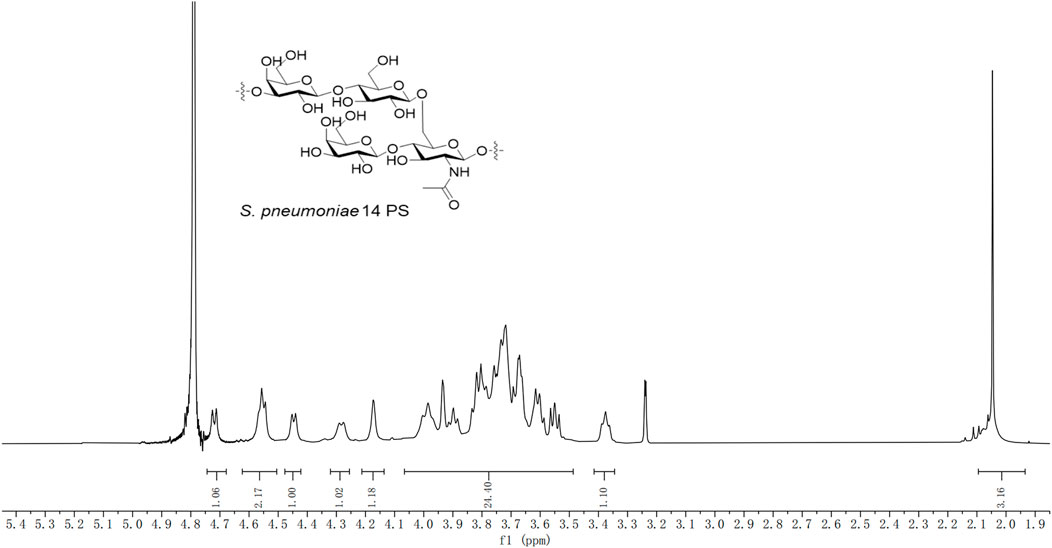
To investigate the structure of pure CPS, the 1H NMR spectra of the serotype 14 pneumococcal CPS were obtained (Figure 5). The 1H NMR spectra of the pure CPS were consistent with the 1H NMR spectra of the CPS of serotype 14 S. pneumoniae (CPS 14) reported in Brisson et al. (1997) and Louçano et al. (2020). There, the chemical shift of the anomeric proton of β-D-GlcpNAc is located at 4.73 ppm, the anomeric proton of β-D-Glcp and branched β-D-Galp is located at 4.55 ppm, the anomeric proton of the main chain β-D-Galp is located at 4.45 ppm, and the methyl hydrogen of the N-acetyl group is located at 2.05 ppm. The existence of each specific structure and the integrity of the repeating units were confirmed by 1H NMR spectra, including the main chain β-D-Galp, β-D-Glcp, β-D-GlcpNAc, and branched β-D-Galp units, as well as NHAc and others. It was clarified that the structural unit of serotype 14 refined CPS is →3)-β-D-Galp-(1→4)-β-D-Glcp-(1→6)-[β-D-Galp-(1 →4)]-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→, consistent with type 14 S. pneumoniae CPS. 1H NMR (600 MHz, deuterium oxide) δ 4.73 ppm (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1 GlcpNAc), 4.55 ppm (m, 2H, H-1 Glcp, H-1 Galp’), 4.45 ppm (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H Galp), 4.33–4.26 ppm (d, J = 9.4 Hz 1H, H-6 GlcpNAc), 4.21–4.13 ppm (m, 1H, 4-H Galp), 4.04–3.51 ppm (m, 24H), 3.42–3.34 ppm (m, 1H, 2-H Glcp), and 2.05 ppm (s, 3H, -NHAc).
4 Conclusion
CPS, as efficient pneumococcal antigens, can stimulate the host to produce protective antibodies. The CPS of highly virulent serotypes are formulated into widely used pneumococcal vaccines. S. pneumoniae serotype 14 is prevalent worldwide. However, the productivity of current fermentation processes for S. pneumoniae serotype 14 remains low and requires improvement. S. pneumoniae fermentation is a very complex system which is influenced by various factors. Moreover, the synthesis of CPS is regulated by multiple factors through a complex metabolic pathway. Little research was found into the factors that could affect pneumococcal growth and productivity.
This study explored various fermentation parameters that could influence fermentation growth and CPS synthesis; feed medium, cultivation gas environment, fermentation pH, and temperature were found to significantly affect pneumococcal growth and CPS yield, with fermentation yield increasing from 0.67 g/L to 2.5 g/L after optimization. Our research strongly validates the feasibility of these optimization strategies to improve fermentation yield, which could potentially be applied to other serotypes as well. CPS must meet strict quality standards when used as antigens, including high immunogenicity and adequate safety. Quality control requirements related to vaccine safety include residual protein, nucleic acid, pyrogenic substances, and chemical reagents associated with purification (Jones, 2015; Jones and Currie, 1991; Morais et al., 2018; Talaga et al., 2002). In this study, a simplified downstream process was developed for purifying polysaccharide to validate the quality of refined polysaccharide after the optimization of the fermentation process. Our results show that the percentage contents of components of serotype 14 bulk polysaccharide could meet the quality standards of the European Pharmacopeia (11th edition). This optimized fermentation and purification process for serotype 14 could satisfy the need for high productivity and superior quality, which could potentially be applied to the manufacture of other pneumococcal CPS.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YL: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, validation, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. YX: conceptualization and writing–review and editing. XC: investigation and writing–review and editing. YW: investigation, methodology, and writing–review and editing. JW: formal analysis, investigation, and writing–review and editing. YZ: investigation and writing–review and editing. HW: investigation, methodology, and writing–review and editing. HY: investigation and writing–review and editing. JL: conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a grant from Beijing Postdoctoral Research Foundation (Grant number: 2023-ZZ-32), Beijing, China.
Conflict of interest
Authors YL, YX, XC, YW, JW, YZ, HW, and JL were employed by Beijing Minhai Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Jumaili, A., Dawood, H. N., Ikram, D., and Al-Jabban, A. (2023). Pneumococcal disease: global disease prevention strategies with a focus on the challenges in Iraq. Int. J. Gen. Med. 16, 2095–2110. doi:10.2147/ijgm.S409476
Avery, O. T., and Heidelberger, M. (1925). Immunological relationships of cell constituents of pneumococcus: second paper. J. Exp. Med. 42 (3), 367–376. doi:10.1084/jem.42.3.367
Avery, O. T., Heidelberger, M., and Goebel, W. F. (1925). The soluble specific substance of friedlander's bacillus: paper II. chemical and immunological relationships of pneumococcus type II and of a strain of friedlander's bacillus. J. Exp. Med. 42 (5), 709–725. doi:10.1084/jem.42.5.709
Bahler, B., Douglas, H. E., and Heller, L. T.-S. (2008). Purification of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3 polysaccharides. Patent WO2008045852. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2008045852A2/en.
Brisson, J. R., Uhrinova, S., Woods, R. J., van der Zwan, M., Jarrell, H. C., Paoletti, L. C., et al. (1997). NMR and molecular dynamics studies of the conformational epitope of the type III group B Streptococcus capsular polysaccharide and derivatives. Biochemistry 36 (11), 3278–3292. doi:10.1021/bi961819l
Cano, F. R., Kuo, J. S. C., and Querry, M. V. (1980). Purification of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides. Patent US4242501. Available at: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/patent/US-4242501-A.
Carvalho, S. M., Kuipers, O. P., and Neves, A. R. (2013). Environmental and nutritional factors that affect growth and metabolism of the pneumococcal serotype 2 strain D39 and its nonencapsulated derivative strain R6. PLOS ONE 8 (3), e58492. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058492
Crinean, J. H. (2014). Method for controlling Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A polysaccharide molecular weight. Patent US8795689. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US8795689/en.
Degeest, B., and De Vuyst, L. (1999). Indication that the nitrogen source influences both amount and size of exopolysaccharides produced by Streptococcus thermophilus LY03 and modelling of the bacterial growth and exopolysaccharide production in a complex medium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 2863–2870. doi:10.1128/AEM.65.7.2863-2870.1999
Fitzgerald, D., and Waterer, G. W. (2019). Invasive pneumococcal and meningococcal disease. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 33 (4), 1125–1141. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2019.08.007
Gonçalves, V. M., Dias, W. O., Campos, I. B., Liberman, C., Sbrogio-Almeida, M. E., Silva, E. P., et al. (2014). Development of a whole cell pneumococcal vaccine: BPL inactivation, cGMP production, and stability. Vaccine 32 (9), 1113–1120. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.10.091
Gonçalves, V. M., Takagi, M., Carmo, T. S., Barbosa, R. M., Albani, S. M., Pinto, J. V., et al. (2007). Simple and efficient method of bacterial polysaccharides purification for vaccines production using hydrolytic enzymes and tangential flow ultrafiltration.
Gonçalves, V. M., Takagi, M., Carneiro, S. M., de Campos Giordano, R., and Tanizaki, M. M. (2006). Introduction of air in the anaerobic culture of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 23F induces the release of capsular polysaccharide from bacterial surface into the cultivation medium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 101 (5), 1009–1014. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03012.x
Gonçalves, V. M., Takagi, M., Lima, R. B., Massaldi, H., Giordano, R. C., and Tanizaki, M. M. (2003). Purification of capsular polysaccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 23F by a procedure suitable for scale-up. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 37 (Pt 3), 283–287. doi:10.1042/ba20020075
Gonçalves, V. M., Zangirolami, T. C., Giordano, R. L., Raw, I., Tanizaki, M. M., and Giordano, R. C. (2002). Optimization of medium and cultivation conditions for capsular polysaccharide production by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 23F. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 59 (6), 713–717. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1075-8
Grobben, G. J., van Casteren, W. H. M., Schols, H. A., Oosterveld, A., Sala, G., Smith, M. R., et al. (1997). Analysis of the exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus NCFB 2772 grown in continuous culture on glucose and fructose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48, 516–521. doi:10.1007/s002530051089
Guo, Y., and Qiao, L.-N. (2021). Clinical features and antibiotic sensitivity of invasive pneumococcal disease versus noninvasive pneumococcal disease in children. Zhongguo dang dai er ke za zhi = Chin. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 23 (5), 466–470. doi:10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2011125
Gururao, D. S., Allen, H. M., Patrick, K. J., R, L. D., Ellis, L. S., Arnold, L. J., et al. (2018). Media and fermentation methods for producing polysaccharides in bacterial cell culture. Patent CN108473945A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN108473945A/en.
Hamaguchi, S., Zafar, M. A., Cammer, M., and Weiser, J. N. (2018). Capsule prolongs survival of Streptococcus pneumoniae during starvation. Infect. Immun. 86 (3), e00802–e00817. doi:10.1128/iai.00802-17
Henriques, A. W. S., Jessouroun, E., Lima, E. L., and Alves, T. L. M. (2006). Capsular polysaccharide production by Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C: optimization of process variables using response surface methodology. Process Biochem. 41 (8), 1822–1828. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.03.044
Hyams, C., Camberlein, E., Cohen, J. M., Bax, K., and Brown, J. S. (2010). The Streptococcus pneumoniae capsule inhibits complement activity and neutrophil phagocytosis by multiple mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 78 (2), 704–715. doi:10.1128/iai.00881-09
Jain, R., and Maithal, K. (2011). Fermentation process for Streptococcus pneumoniae. Patent WO2011151841. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2011151841/en.
Jalali, M., and Tarahomjoo, S. (2015). Investigation of appropriate cultivation approach for capsular polysaccharide production by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19F. Am. J. Microbiol. Res. 3, 197–200. doi:10.12691/ajmr-3-6-4
Jin, Y., Sun, Q., Li, J., Zhao, Q., Li, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2014). Method for preparing Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide. Patent CN103833865A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN103833865A.
Jones, C. (2015). Glycoconjugate vaccines: the regulatory framework. Methods Mol. Biol. Clift. NJ 1331, 229–251. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2874-3_14
Jones, C., and Currie, F. (1991). Control of components of bacterial polysaccharide vaccines by physical methods. Biologicals 19 (1), 41–47. doi:10.1016/1045-1056(91)90023-d
Jung, S. J., Seo, E. S., Yun, S. I., Minh, B. N., Jin, S. D., Ryu, H. J., et al. (2011). Purification of capsular polysaccharide produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21 (7), 734–738. doi:10.4014/jmb.1010.10043
Kadioglu, A., Weiser, J. N., Paton, J. C., and Andrew, P. W. (2008). The role of Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors in host respiratory colonization and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6 (4), 288–301. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1871
Kapre, S. V., and Datta, A. K. (2020). Polysaccharide purification for vaccine production using lytic enzymes, tangential flow filtration, and multimode chromatography. Patent CN111295450A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN111295450A.
Keming, R., Xi, W., Jianhong, W., Guijie, B., and Rong, S. (2015). Purification method of streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide. Patent CN105131139A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN105131139A/en.
Kim, S. N., Min, K. K., Choi, I. H., Kim, S. W., Pyo, S. N., and Rhee, D. K. (1996). Optimization of culture conditions for production of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide type IV. Archives Pharmacal Res. 19 (3), 173–177. doi:10.1007/BF02976885
Leal, M. L. S., Pereira, D. S. G., Jessouroun, E., Couto, MAPG, and Pereira, N. (2011). Investigation of cultivation conditions for capsular polysaccharide production by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 14. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 14, 6. doi:10.2225/VOL14-ISSUE5-FULLTEXT-6
Lee, C., Chun, H. J., Park, M., Kim, R. K., Whang, Y. H., Choi, S. K., et al. (2020). Quality improvement of capsular polysaccharide in Streptococcus pneumoniae by purification process optimization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 39. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.00039
Lees, J. A., Croucher, N. J., Goldblatt, D., Nosten, F., Parkhill, J., Turner, C., et al. (2017). Genome-wide identification of lineage and locus specific variation associated with pneumococcal carriage duration. eLife 6, e26255. doi:10.7554/eLife.26255
Li, J., Wang, J., Jiao, F., and Zhang, J. R. (2017). Observation of pneumococcal phase variation in colony morphology. Bio Protoc. 7 (15), e2434. doi:10.21769/BioProtoc.2434
Li, X., Zhang, R., Xie, Y., Cheng, Z., Chen, J., and Jiang, S. (2016). Development of a procedure for purification of capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 by acidification method. Chin. J. Biol. 29 (8), 5. doi:10.13200/j.cnki.cjb.001432
Li, Y., Cao, X., Huang, X., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Jin, Q., et al. (2024). Novel manufacturing process of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides using advanced sterilization methods. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12, 1451881. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2024.1451881
Loetscher, P., Mottlau, L., and Hochuli, E. (1992). Immobilization of monoclonal antibodies for affinity chromatography using a chelating peptide. J. Chromatogr. 595 (1-2), 113–119. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(92)85151-i
Louçano, J., Both, P., Marchesi, A., Bino, Ld, Adamo, R., Flitsch, S., et al. (2020). Automated glycan assembly of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 capsular polysaccharide fragments. RSC Adv. 10 (40), 23668–23674. doi:10.1039/D0RA01803A
Macha, C., Lavanya, A. R., and Nanna, R. S. Purification of Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides using aluminium phosphate and ethanol. In, 2014.
Marthos, B. V., Ferri, A. L., de Figueiredo, D. B., Zangirolami, T. C., and Gonçalves, V. M. (2015). Capsular polysaccharide production by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 1: from strain selection to fed-batch cultivation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 (24), 10447–10456. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6928-z
Massaldi, H., Bessio, M. I., Suárez, N., Texeira, E., Rossi, S., and Ferreira, F. (2010). Features of bacterial growth and polysaccharide production of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 14. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 55 (1), 37–43. doi:10.1042/ba20090218
McFarland, A. L., Bhattarai, N., Joseph, M., Winkler, M. E., and Martin, J. E. (2021). Cellular Mn/Zn ratio influences phosphoglucomutase activity and capsule production in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39. J. Bacteriol. 203 (13), e0060220. doi:10.1128/jb.00602-20
Morais, V., Dee, V., and Suárez, N. (2018). Purification of capsular polysaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae: traditional and new methods. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 6, 145. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2018.00145
Morais, V., Texeira, E., and Suarez, N. (2019). Next-generation whole-cell pneumococcal vaccine. Vaccines (Basel) 7 (4), 151. doi:10.3390/vaccines7040151
Paton, J. C., and Trappetti, C. (2019). Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide. Microbiol. Spectr. 7 (2). doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0019-2018
Qiong, C., Ji-Chun, S., Chun-E W, , Shan-Shan, W., and Qiang, Y. (2022). Current status and prospect of quality control of 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Drug Stand. China (002), 023. doi:10.19778/j.chp.2022.02.010
Restrepo, A. V., Salazar, B. E., Agudelo, M., Rodriguez, C. A., Zuluaga, A. F., and Vesga, O. (2005). Optimization of culture conditions to obtain maximal growth of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 5 (1), 34. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-5-34
Suárez, N., Fraguas, L. F., Texeira, E., Massaldi, H., Batista-Viera, F., and Ferreira, F. (2001). Production of capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 and its purification by affinity chromatography. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 (2), 969–971. doi:10.1128/aem.67.2.969-971.2001
Talaga, P., Vialle, S., and Moreau, M. (2002). Development of a high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed-amperometric detection based quantification assay for pneumococcal polysaccharides and conjugates. Vaccine 20 (19-20), 2474–2484. doi:10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00183-4
Venkat, M. R., Babu, K. V., Dev, M. N., Mahima, D., Venkateswara, R. M., and Kantam, C. (2022). Method for separation of protein and other impurities from microbial capsular polysaccharides. Patent CN107835821B. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN107835821B.
Vinayak, K. S., Kumar, J. S., and Srivastava, A. K. (2017). A novel process of cultivating bacteria for yield improvement of capsular polyoses. Patent EP2791317A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP2791317A.
Wang, J., Zhao, H., Song, D., Liang, H., Tan, J., Han, X., et al. (2015). Method for purifying pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide. Patent CN104530250A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN104530250A.
Wang, L., Wu, H., Gao, R., and Li, T. (2017). Method for purifying Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide. Patent CN107082819A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN107082819A/en.
Weiser, J. N., Bae, D., Epino, H., Gordon, S. B., Kapoor, M., Zenewicz, L. A., et al. (2001). Changes in availability of oxygen accentuate differences in capsular polysaccharide expression by phenotypic variants and clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 69 (9), 5430–5439. doi:10.1128/iai.69.9.5430-5439.2001
Weiser, J. N., Ferreira, D. M., and Paton, J. C. (2018). Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16 (6), 355–367. doi:10.1038/s41579-018-0001-8
Weiser Jeffrey, N. (2001). Modulating production of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide. Available at: https://www.surechembl.org/document/NZ-521343-A.
Xiao, L., Fang, Y., Cheng, L., and Kong, J. (2006). Advances in the development of meningococcal vaccines. Prog Microbiol Immunol 34 (1), 3. doi:10.13309/j.cnki.pmi.2006.01.014
Yuan, Y., Ruppen, M., Sun, W.-Q., Chu, L., Simpson, J., Patch, J., et al. (2014). Shortened purification process for the production of capsular Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharides. Patent US8652480. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US8652480/en.
Zanardo, R., Ferri, A., Borges, D., Kraschowetz, S., Cabrera-Crespo, J., and Gonçalves, V. (2016). Development of a new process for purification of capsular polysaccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 14. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 33, 435–443. doi:10.1590/0104-6632.20160333s20150140
Zeidan, A. A., Poulsen, V. K., Janzen, T., Buldo, P., Derkx, P. M. F., Øregaard, G., et al. (2017). Polysaccharide production by lactic acid bacteria: from genes to industrial applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 (Suppl. p_1), S168–s200. doi:10.1093/femsre/fux017
Zhao, H., Zhao, Z., and Xie, G. (2012). Progress in isolation and purification of bacterial capsular polysaccharide. Prog Microbiol Immunol 40 (2), 72–78. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-9154-9_3
Zhu, L., Cook, S. A., Mmerchant, N., and Moran, J. K. (2021). Methods for purifying bacterial polysaccharides. Patent CN113728109A. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN113728109A/en.
Keywords: capsular polysaccharide, fermentation, yield, purification, serotype 14
Citation: Li Y, Xu Y, Cao X, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao Y, Wang H, Yao H and Liu J (2024) Optimization of manufacturing process for serotype 14 pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide. Front. Chem. Eng. 6:1481257. doi: 10.3389/fceng.2024.1481257
Received: 15 August 2024; Accepted: 04 October 2024;
Published: 23 October 2024.
Edited by:
Zhuangrong Huang, Bristol Myers Squibb, United StatesReviewed by:
Yuxin Liu, Sanofi Genzyme, United StatesHaifeng Lu, East China University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Xu, Cao, Wang, Wang, Zhao, Wang, Yao and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hantian Yao, eWFvaHQyMUBtYWlscy50c2luZ2h1YS5lZHUuY24=; Jiankai Liu, bGl1amlhbmthaUBiaW9taW5oYWkuY29t
 Yuelong Li
Yuelong Li Yongxue Xu1
Yongxue Xu1 Jianlong Wang
Jianlong Wang