
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Cell. Neurosci., 26 February 2025
Sec. Cellular Neurophysiology
Volume 19 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2025.1540989
Introduction: Profilin 2 (PFN2) is an actin binding protein highly expressed in the brain that participates in actin dynamics. It has been shown in vitro and in vivo that in neurons it functions both post-synaptically to shape and maintain dendritic arborizations and spine density and plasticity, as well as pre-synaptically to regulate vesicle exocytosis. PFN2 was also found in protein complexes with proteins that have been implicated in or are causative of autism spectrum disorder.
Methods: We employ a genetically engineered knock-out mouse line for Pfn2 that we previously generated to study the mouse social, vocal and motor behavior in comparison to wild type control littermates. We also study neuronal physiology in the knock-out mouse model by means of cellular and field electrophysiological recordings in cerebellar Purkinje cells and in the Schaffer collaterals. Lastly, we study anatomical features of the cerebellum using immunofluorescence stainings.
Results: We show that PFN2 deficiency reproduces a number of autistic-like phenotypes in the mouse, such as social behavior impairment, stereotypic behavior, altered vocal communication, and deficits in motor performance and coordination. Our studies correlate the behavioral phenotypes with increased excitation/inhibition ratio in the brain, due to brain-wide hyperactivity of glutamatergic neurons and increased glutamate release not compensated by enhanced GABAergic neurotransmission. Consequently, lack of PFN2 caused seizures behavior and age-dependent loss of cerebellar Purkinje cells, comorbidities observed in a subset of autistic patients, which can be attributed to the effect of excessive glutamatergic neurotransmission.
Discussion: Our data directly link altered pre-synaptic actin dynamics to autism spectrum disorder in the mouse model and support the hypothesis that synaptic dysfunctions that asymmetrically increase the excitatory drive in neuronal circuits can lead to autistic-like phenotypes. Our findings inspire to consider novel potential pathways for therapeutic approaches in ASD.
Since the last two decades the relevant role of the actin cytoskeleton for the development and function of the nervous system has been extensively studied. Both growth cone dynamics and neurite extension (for a review see Omotade et al., 2017), as well as synaptic plasticity (for a review see Cingolani and Goda, 2008), have been shown to depend on actin dynamics. Actin binding proteins (ABP) are key factors that convey extracellular cues to actin cytoskeleton rearrangements. Only a few ABPs have been genetically linked to neurodevelopmental or neurological disorders in humans, either through copy number variation (CNV) or single nucleotide variation (SNV) and microdeletions, including: inverted formin 2 (IFN2) (Boyer et al., 2011; Mademan et al., 2013), profilin 1 (PFN1) (Wu et al., 2012; Smith et al., 2015), the cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 1 and 2 (CYFIP1 and CYFIP2) (Oguro-Ando et al., 2015; Nakashima et al., 2018; Peng et al., 2018), spectrin beta III (SPTBN2) (Avery et al., 2017), microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 (MACF1) (Dobyns et al., 2018), dystonin (DST) (Fortugno et al., 2019). The relevance of ABPs in neurodevelopmental and neurophysiological processes has also been assessed in mouse models, which have shown phenotypes ranging from neuronal cell migration impairment to neuronal development defects, as well as to alterations in synaptic maturation, connectivity and plasticity (Soderling et al., 2003; Grove et al., 2004; Bellenchi et al., 2007; Pilo Boyl et al., 2007; Bozdagi et al., 2012; Pathania et al., 2014; Han et al., 2015; Di Domenico et al., 2021; Klemz et al., 2021). Often these mouse models displayed certain anatomical or physiological conditions typical of neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), intellectual disability, schizophrenia, and epilepsy (Soderling et al., 2003; Bozdagi et al., 2012; Han et al., 2015; Davenport et al., 2019), however, the behavioral phenotypes were mild possibly due to heterozygosity, or to compensatory mechanisms, or to functional redundancy of paralogs, or because deletion of the specific gene occurred too late in brain development.
The profilin 2 (Pfn2) conventional knock-out (ko) mouse model (Pfn2−/−) is viable and has been already shown to display synaptic, physiological, and behavioral phenotypes typical of neurodevelopmental disorders (Gareus et al., 2006; Pilo Boyl et al., 2007). The Pfn2 ko mouse model has two distinct features when compared to other ABPs knock-out models: (1) PFN2 function seems to be mainly restricted to regulating actin dynamics at the synapse, both in pre-synaptic boutons and in dendritic spines (Ackermann and Matus, 2003; Pilo Boyl et al., 2007), the neuronal compartment that has been recently proposed to be a hotspot for mental disorders (Yan et al., 2016); and (2) in this mouse model, PFN2 is absent during the entire embryonic development without resulting in pre-natal or juvenile lethality (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007; Di Domenico et al., 2021), as happens for many ABPs knock-out mouse models. The viability of Pfn2−/− mice can be explained by the restricted expression and function of PFN2, which only starts in post-mitotic neurons around embryonic day 12.5, and to a partial compensatory effect from its paralog, profilin 1 (Di Domenico et al., 2021). This combination of factors allows the study of the knock-out phenotype, which originates during embryonic development, in adult and aging mice. Functionally PFN2 is a small 14 kDa protein that forms a 1:1 complex with globular (G-) actin (profilactin) and accelerates the ADP to ATP exchange that primes G-actin to polymerization (Gieselmann et al., 1995; Paul and Pollard, 2009). In principle, this allows profilin 2 to coordinate the rate, place, and type of actin polymerization through the interaction with numerous specific actin nucleation and elongation factors (Krause et al., 2003; Faix and Grosse, 2006; Pollard, 2007) via its poly-L-proline (PLP) binding domain.
The human genomic locus 3q25-27, encompassing the PFN2 gene, has been linked to autism spectrum disorder in two past studies on Finnish families in Scandinavia and the USA (AUTS2, now, due to a nomenclature overlap, renamed AUTS8, OMIM: 607373) (Auranen et al., 2002; Coon et al., 2005), but until now no gene inactivating SNVs, CNVs, or microdeletions affecting specifically the PFN2 gene have been reported in exome sequencing studies. The absence of a clear association of the ASD phenotype to any of the genes included in the 3q25-27 human locus together with the findings on the specific synaptic function of PFN2 has prompted us to revisit a potential role of profilin 2 in autistic-like behavior. The core ASD traits are defined by the DSM-5 guidelines (American Psychiatric Association, 2013) as: (i) Social interaction deficits; (ii) Repetitive, ritualistic, and stereotyped behavior. In this work we show that the Pfn2 ko mouse presents with deficits in both these core traits. In addition, we investigate comorbid traits that often accompany the main autistic phenotype, in particular vocal communication, that we studied in the mouse pups, and motor coordination. We find that these behaviors are robustly altered in the Pfn2−/− mouse model, which could therefore represent an interesting in vivo model to study or validate one possible pathway causing autism spectrum disorder.
Pfn2 mutants are born in Mendelian ratio but in heterozygous breeding pairs we noted delayed growth of the Pfn2−/− pups compared to Pfn+/− and wt control littermates in larger size litters, suggesting a competitive disadvantage during rearing. Genotyping at weaning age (P21-P25) showed a reduced mendelian ratio to about 22% for Pfn2−/− animals (Figure 1A), pointing to a mortality rate of Pfn2−/− pups before weaning that was not observed in Pfn2+/− and wt control littermates (Figure 1B).
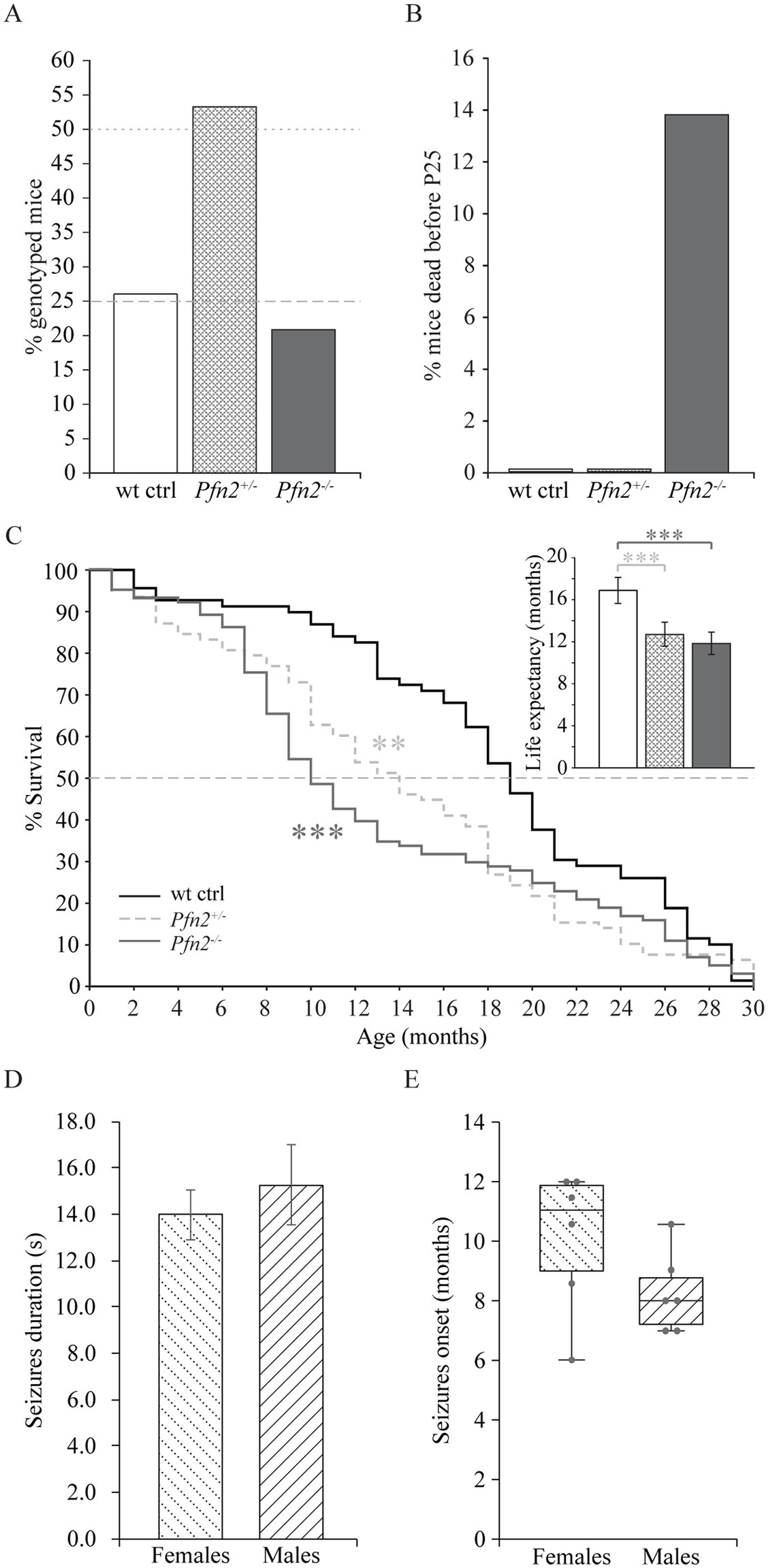
Figure 1. Reduced survival before weaning and shorter life expectancy of Pfn2−/− mice. (A) In Pfn2+/− matings, fewer Pfn2−/− offspring mice were found than expected from Mendelian ratio (dashed and dotted gray lines) at weaning (P21-P25). N = 47 wt, N = 97 Pfn2+/−, and N = 38 Pfn2−/− genotyped animals from 24 litters. (B) Pre-weaning loss of Pfn2−/− pups. Offspring were genotyped at P8, when all genotypes obeyed the Mendelian ratio, and followed until weaning (P25): 14% of Pfn2−/− mice died during this period, but no wt and Pfn2+/− mice. N = 76 wt ctrl, N = 178 Pfn2+/−, N = 75 Pfn2−/− P8 animals. (C) Kaplan–Meier plot of survival data shows higher mortality rate of Pfn2−/− mice between 6 and 14 months of age with an intermediate phenotype for Pfn2+/− mice (Peto-Prentice generalized Wilcoxon test: Pfn2−/− vs. wt ctrl, p < 0.001; Pfn2+/− vs. wt ctrl, p = 0.001). The median survival (dotted line in the graph) was 10 months for Pfn2−/− mice, 14 months for Pfn2+/− and 19 months for wt controls. Inset shows life expectancy (average life span) for each genotype, 12.9 ± 0.8 months for Pfn2−/− mice, 13.8 ± 0.9 months for Pfn2+/− and 18.3 ± 1.0 months for wt controls (two-tailed t-test: Pfn2−/− vs. wt ctrl mice, p < 0.0001; Pfn2+/− vs. wt ctrl mice, p = 0.0008). N = 69 wt ctrl, N = 78 Pfn2+/−, N = 101 Pfn2−/− animals. (D) Average duration of seizures in male and female Pfn2 ko mice. No difference was detected (two-sided t-test, p = 0.5384). (E) Box plot representation of the seizures onset for male and female Pfn2 ko mice, with single units per group indicated by the gray dots and horizontal bar indicating median. A tendential earlier onset in males was observed (Mann–Whitney U-test, p = 0.1467). N = 70 Pfn2−/− mice. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.
These findings prompted us to investigate survival and life expectancy of Pfn2−/− mice through a standard survival analysis. The Kaplan–Meier plot showed a significant mortality of Pfn2−/− mice between 7 and 13 months (Peto-Prentice test, p < 0.001), with the median survival halved compared to wt littermate controls (Figure 1C). Interestingly, Pfn2 heterozygote mice displayed an intermediate phenotype, with significantly reduced survival compared to wt controls (p = 0.001), indicating a gene dosage effect on mouse survival. As a consequence, life expectancy (average life span) of both Pfn2−/− and heterozygote mice was significantly reduced by 30 and 25%, respectively (Figure 1C, inset).
Premature mortality has been reported in autism spectrum disorder (Hirvikoski et al., 2016). One associated cause is epilepsy, in a recent study found in 12% of individuals with autism (Lukmanji et al., 2019). In a small-scale study (N = 70 Pfn2−/− mice) we observed spontaneous, sensory induced, seizures in 12.5% of Pfn2−/− mice, irrespective of their sex. The seizures were tonic or tonic–clonic, had an average length of 14 s in females and 15 s in males (Figure 1D), and the mice typically recovered within 60–120 s. The seizures’ onset was tendentially earlier in male mutant mice (8 months) than in females (11 months, Figure 1E). Since the onset of seizures coincides with the period of higher mortality of the Pfn2−/− mice, we suspect that they might contribute to their reduced life expectancy.
The competitive disadvantage of Pfn2−/− pups during rearing hinted at altered social behavior, either in the relationship of the mutant pups with the mother or with the other littermates for successful breastfeeding. To study sociability more in detail, we addressed two established behaviors in adult mice: maternal behavior of Pfn2−/− mice toward the pups and social interactions of Pfn2−/− male mice.
Maternal behavior was found severely affected in Pfn2−/− mice. Nest building was almost absent in Pfn2−/− females (Supplementary Figure 1) and when Pfn2−/− mothers were allowed as single parents to rear their litters, all pups were lost irrespectively of the pups’ genotype (Table 1, top part). Interestingly, with the cohabitation of a wt or Pfn2+/− father, all litters of Pfn2−/− mothers could be rescued and survived. However, only about half of the litters survived when both parents were Pfn2−/− animals (Table 1, bottom part). One possible reason for the rearing deficit of Pfn2−/− mothers was a severely compromised pup retrieval behavior: when challenged to retrieve P7 pups dispersed in the cage, wt mothers quickly collected all pups within 7 min back into the nest (Figure 2A). Instead, Pfn2−/− mothers never retrieved a single pup within the maximally allowed experimental time (30 min). Thus, Pfn2−/− dams completely lacked pup rearing behavior.
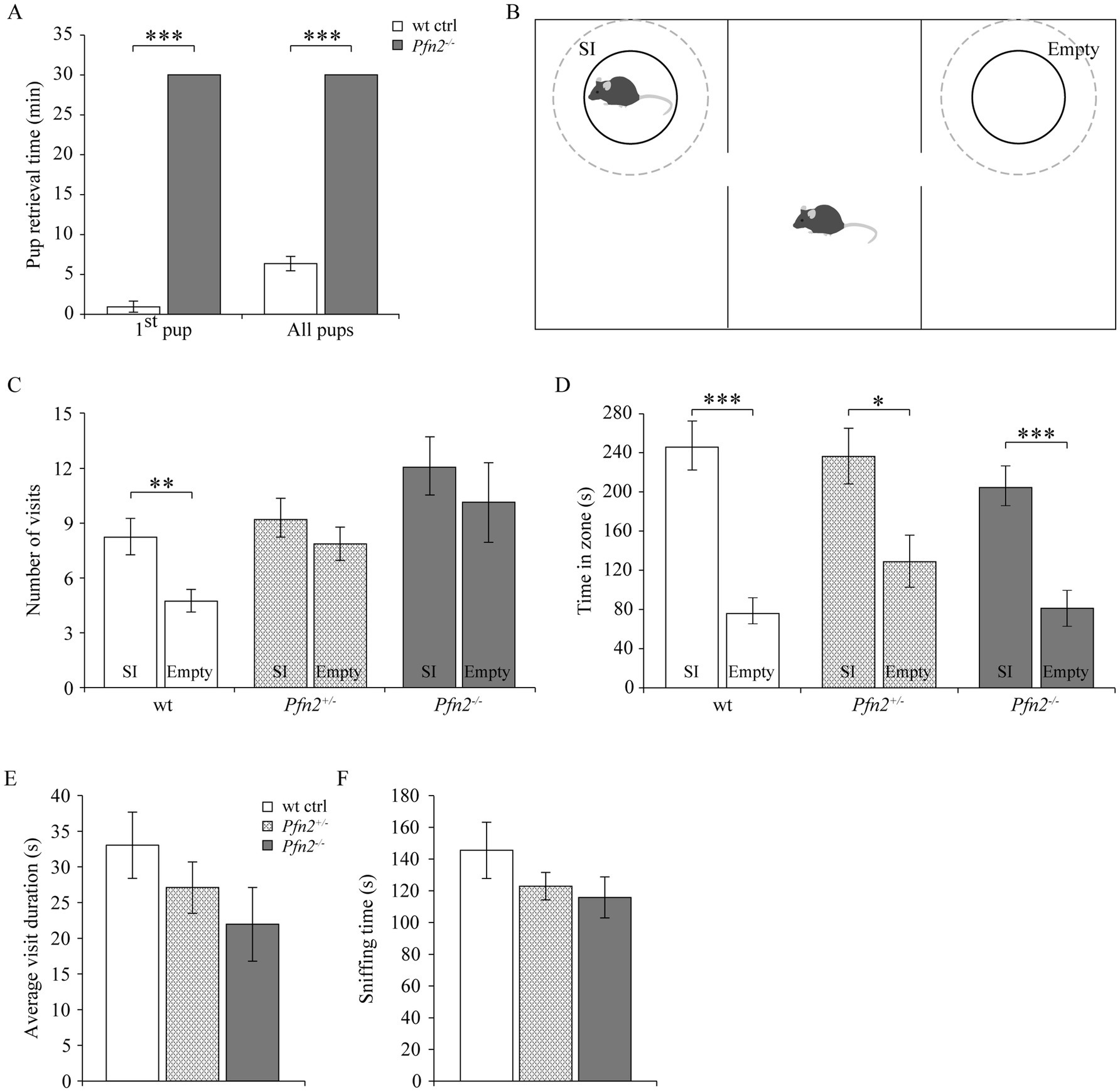
Figure 2. Maternal and social behavior are impaired in Pfn2−/− mice. (A) Maternal behavior: pup retrieval by Pfn2−/− females was completely missing within the experimental time of 30 min, while on average wt control females retrieved the first pup within 1 min (0.8 ± 0.7 min) and the entire litter in 6.2 ± 0.9 min (one-sided t-test, p < 0.001 for both tests). N = 5 wt ctrl and N = 7 Pfn2−/− females. (B) Schematic of the 3-chambered social interaction test. Dashed circles delimit the SI (Social Interaction) zone hosting in our set-up a novel juvenile (~P25) mouse to control for the hyper-excitability of Pfn2−/− mice, and the Empty zone used for social behavior quantification. (C) By number of visits, Pfn2−/− and Pfn2+/− mice showed no significant preference for the SI zone compared to the Empty zone (two-sided t-test, p = 0.4683 and p = 0.3276, respectively) while wt control mice showed a significant preference for the SI zone (two-sided t-test p = 0.0098), indicating social interaction impairment in mutant and heterozygous mice. (D) By the time spent socializing, all genotypes spent more time in the SI zone than in the Empty zone, although Pfn2−/− mice showed the least preference. (E) On average Pfn2−/− mice spent less time per visit in the SI zone compared to wt control mice. Heterozygous mice performed in the middle. (F) Sniffing in the SI zone was reduced in Pfn2 mutant mice compared to wt controls. N = 8 wt ctrl, N = 7 Pfn2+/− and N = 9 Pfn2−/−. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.
Suspecting a general social interaction deficit upon reduction of profilin 2 levels, we applied to adult male mice the Social Interaction paradigm in the 3-chambered maze to assess adult sociability (Figure 2B) (Moy et al., 2007). When social interaction between the adult test mouse and a stranger juvenile was assessed, Pfn2−/− mice showed a mild reduction of sociability. Only wt controls showed a significant preference for the Social interaction (SI) zone in terms of number of visits (SI: 8 ± 1 vs. Empty: 5 ± 1), while both Pfn2+/− (SI: 9 ± 1 vs. Empty: 8 ± 1) and Pfn2−/− (SI: 12 ± 2 vs. Empty: 10 ± 2) mice failed to do so (Figure 2C). Wt control mice also showed the highest preference for the social compartment when measuring the time spent in the SI zone compared to the Empty zone (Figure 2D), although also Pfn2−/− and Pfn2+/− mice showed some degree of preference for the SI compartment. The average visit duration of Pfn2−/− mice to the stranger juvenile mouse was tendentially reduced compared to wt controls (Figure 2E), as well as the average sniffing time (Figure 2F). In addition, the interaction of Pfn2−/− mice with the stranger juvenile mouse was qualitatively very different from control mice: direct nose contacts of Pfn2−/− mice with the juvenile mouse were rare, with the mutant mice mostly running around and over the metal enclosure. In a previous study (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007) we reported a striking increase of novelty-seeking behavior in Pfn2−/− mice, which spent more time than wt control littermates to explore novel objects. We suspect that this phenotype might have masked the social behavior in our set-up, where the juvenile mouse has represented an interesting novel object due to its immature sociability and its motility, triggering a novelty-seeking behavior in the Pfn2−/− mice.
Ritualistic and repetitive behavior, accompanied by resistance to changes, is the second core symptom that characterizes ASD and can be measured in mouse models for ASD as stereotypic behavior (Peça et al., 2011; Schmeisser et al., 2012). We therefore assessed an array of stereotypic behaviors in control and Pfn2 mutant mice after transfer into a novel cage. In this context, no significant differences were observed for self-grooming and digging. However, Pfn2−/− animals showed significantly higher occurrence of circling, and wall leaning stereotypies compared to Pfn2+/− and wt control mice (Figure 3A), indicating a stronger susceptibility to repetitive behavior. Also jerking, a tic-like stereotypic behavior that can have both physiologic or pathologic origin, was significantly increased in Pfn2−/− mice (Figure 3A).

Figure 3. Stereotypic and repetitive behavior is increased in Pfn2−/− mice. (A) Five stereotypic behaviors were measured after transfer in a novel cage environment. Circling (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0442), wall leaning (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0273) and jerking (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0015) were increased in Pfn2−/− mice compared to wt controls, grooming and digging were not changed. N = 10 wt ctrl, N = 11 Pfn2+/− and N = 15 Pfn2−/− mice. (B,C) Y-Maze: spontaneous alternation (SPA) exploration strategy was diminished in Pfn2−/− mice compared to wt controls (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0159) in favor of same arm return (SAR) exploration, performed by 50% of the Pfn2−/− mice (one-sample t-test, p = 0.0122), indicative of a resistance to changes in the mutants. (D) Latency to start exploring the maze by entering the first arm was higher in Pfn2−/− animals compared to wt controls (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0409). N = 11 wt ctrl, N = 10 Pfn2−/− animals. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.
Complementary to this general compulsive behavior, we evaluated the resistance to changes in Pfn2−/− mice, using a more sophisticated paradigm. For this purpose, we tested the animals in a Y-maze set-up, where mice typically explore the arms of the maze in sequential order (spontaneous alternation, SPA). Pfn2−/− mice displayed decreased SPA (Figure 3B), and while in our experiment no control mouse ever returned to the same arm (SAR), about 50% of the tested Pfn2−/− mice showed this repetitive behavior (Figure 3C). Pfn2−/− mutants also showed a marked deficit in decision making, as suggested by the longer latency to initiate exploration (Figure 3D). These data suggest a propensity to repetitive behavior and an increased resistance to changes in Pfn2−/− mice.
ASD typically emerge within the first 2 years after birth and crying behavior of babies is the first way of communication in humans. Atypical crying behavior has been reported in incipient ASD infants, often resulting in a negative response of the mother (Esposito and Venuti, 2009). In mouse newborns, up to 8–9 days after birth, “crying” behavior is an important communication pathway, triggered by separation distress. Separated pups emit ultrasonic calls in the 30–110 kHz frequency range to attract their mother’s attention. We monitored ultrasonic vocalizations (USV) from P7 pups and found increased number of USVs in Pfn2−/− pups compared to wt controls (Figure 4A, medians Pfn2−/− males: 592, wt males: 165; Pfn2−/− females: 990, wt females: 311 calls/5 min). Similar observations have been reported in other mouse models of autism (Scattoni et al., 2009; Tsai et al., 2012). Detailed analysis of the USV traces revealed that, despite Pfn2−/− and wt control littermates displaying a collection of vocalizations of similar shape and frequency, Pfn2−/− pups communicated with a more monotonous vocalization pattern, with persistent use of long (20–90 ms), sometimes interrupted, calls in the middle range of US frequencies (<70–75 kHz) and rather flat frequency modulation (examples shown in Figure 4B). Pfn2−/− male and female pups showed, respectively, a 6- and 4-fold median increase of this type of “flat calls” compared to wt control littermates (Figure 4C, medians Pfn2−/− males: 144, wt males: 22.5; Pfn2−/− females: 216, wt females: 49 flat calls/5 min). In Pfn2−/− mutants these “flat calls” were often arranged in particularly long trains of calls that were uniformly spaced (with a regular inter-call interval of 150 ± 10 ms, see Supplementary Figure 2) and more intense (<−50 dB, darker gray tone). In comparison to wt control littermates, Pfn2−/− male and female pups presented significantly higher number of long trains of calls composed of more than 10 of these monotonous “flat calls” (Figure 4D). About 50% of Pfn2 mutant pups presented one or more very long trains of over 20 “flat calls,” while none of the control mice showed this behavior (call train example in Supplementary Figure 2). Vocalization patterns are usually made of groups of 2 or 3 closely spaced calls (with short inter-call intervals, <50 ms), within which frequency variations and harmonics are seen. We observed an increased group size and extended group of calls duration in both Pfn2−/− males and females compared to wt control littermates (Figures 4E,F).

Figure 4. The ultrasonic vocalization pattern in Pfn2−/− pups is more monotonous. (A) Box plot representing the total number of US calls from P5-P7 Pfn2−/− and wt control pups isolated from the nest in 5 min recording time. The median for Pfn2−/− pups is more than 3-fold the median of wt controls (Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.0642 for males and p = 0.0083 for females). (B) Graphic representation of two sample flat call traces, one continuous and one interrupted. Of note the uniform frequency below 70 kHz and the length (90–100 ms). (C) Box plot representing the number of flat calls from Pfn2−/− and wt control pups in 5 min recording time. The median for Pfn2−/− pups is about 6-fold the median of controls in males and 4-fold in females (Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.0231 for males; p = 0.0051 for females). (D) The number of trains with more than 10 calls per mouse was strongly increased in Pfn2 mutants compared to wt controls (Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.0062 for males; p = 0.0120 for females). (E) The average size of the group of calls (number of shorter calls with inter-call time < 50 ms) was increased in Pfn2−/− compared to wt control pups (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0087 for males; p = 0.0298 for females). (F) The average duration of group of calls was higher in Pfn2−/− compared to wt control pups (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0351 for males; p = 0.0542 for females). N = 16 wt ctrl and N = 11 Pfn2−/− males, N = 13 wt ctrl and N = 12 Pfn2−/− females. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.
In summary, Pfn2−/− pups appeared to be in distress when separated from the mother and engaged in a despair calling behavior with increased calling and reduced frequency modulation (monotony) compared to control pups.
In addition to the core symptoms and the possible communication deficits, impaired motor coordination is often found as a comorbidity in ASD (Fournier et al., 2010). We tested basic motor performance and coordination in Pfn2−/− mice using a fixed rotation speed RotaRod paradigm, while we assessed motor learning by constantly increasing the rotation speed. In older Pfn2 mutants, motor performance and coordination at fixed low rotation speed was significantly impaired (Figures 5A,B), while younger mutant mice did not show significant deficits (Figures 5C,D). Motor learning, on the other hand, was unaffected at all ages in Pfn2−/− mice, in line with previous findings in the conditioned learning paradigm (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007). Thus, Pfn2−/− mice showed an age dependent impairment of motor performance that could depend on impaired coordination.
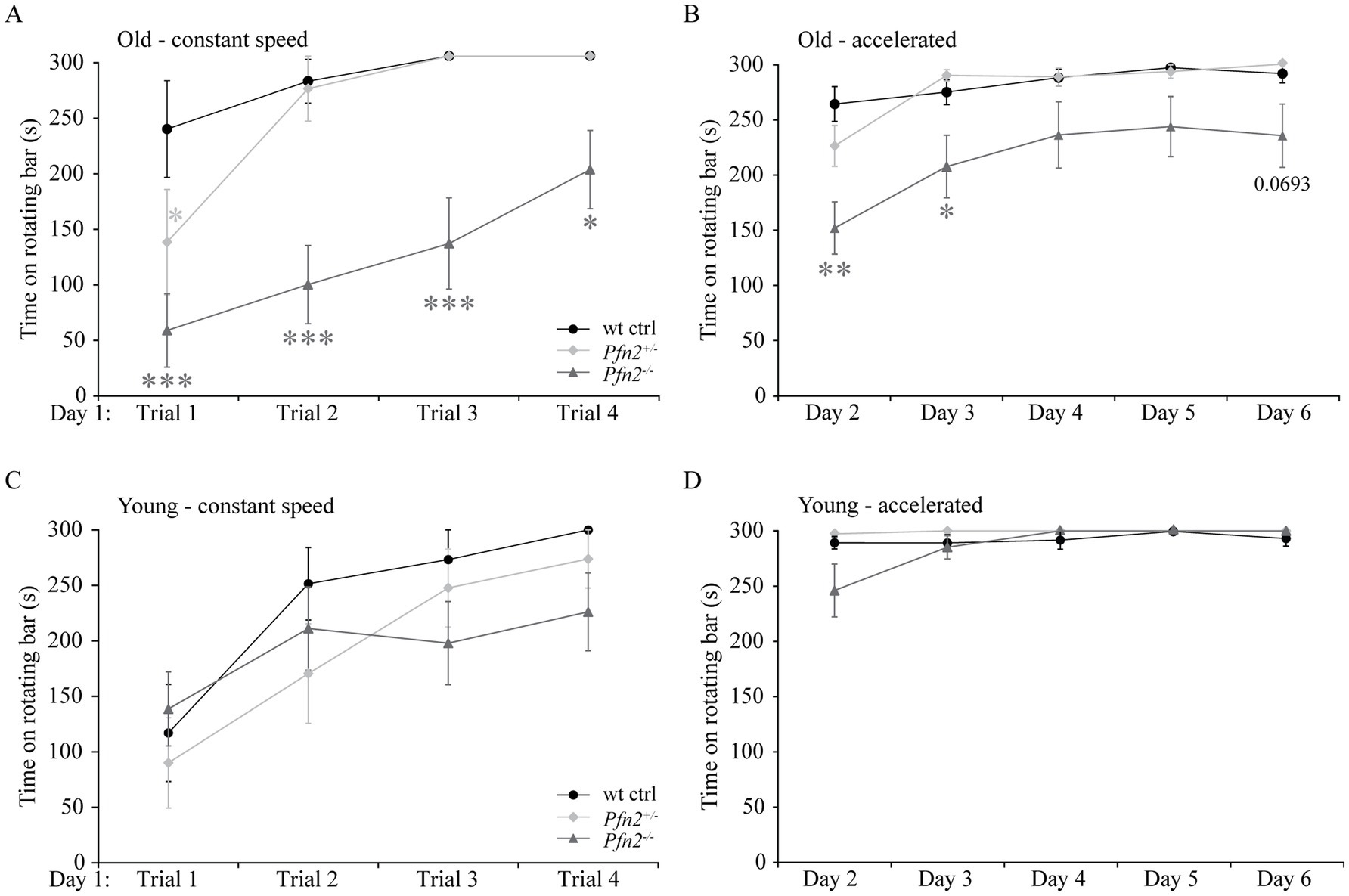
Figure 5. Motor performance decreases with age in Pfn2−/− mice. (A) Old (6–8 months) Pfn2−/− mice showed lower performance on a RotaRod (constant speed, 3 rpm) than wt controls (two-way ANOVA with repeated measures, genotype effect F(2, 25) = 19.09, p < 0.0001; Tukey’s post-hoc test for Pfn2−/− vs. wt control: Trial 1, p = 0.0001; Trial 2. p = 0.0001; Trial 3, p = 0.0004; and Trial 4, p = 0.0487). Pfn2+/− mice showed a motor deficit only in Trial 1 (p = 0.0425). (B) Old Pfn2−/− mice also showed lower performance on a RotaRod in an accelerated rotation paradigm (3–30 rpm in 300 s: two-way ANOVA with repeated measures, genotype effect F(2, 25) = 6.285, p = 0.0061; Tukey’s post-hoc test for Pfn2−/− vs. wt control: Day 2, p < 0.0001; Day 3, p = 0.0224; Day 6, p = 0.0693). Notably, motor learning remained unaffected [Day effect F(4, 100) = 22.68, p < 0.0001]. (C) In young mice (3–5 months) no significant differences were seen between Pfn2−/−, Pfn2+/− and wildtype mice in the performance at constant speed, as well as (D) in the accelerated Rotarod mode. Represented data are the average of the best performances of the day ± SEM. Old mice, N = 9 wt ctrl and Pfn2−/−, N = 10 Pfn2+/−; young mice N = 11 per genotype. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.
Coordination skills were further investigated with the Hanging test, which addresses both muscle strength and coordination between legs and body. The performance of Pfn2−/− mice was markedly impaired at both young (Figure 6A) and older age (Figure 6B). In the group of older mice, the Pfn2+/− animals showed a gene dosage-dependent intermediate phenotype.

Figure 6. Motor coordination is reduced in Pfn2−/− mice. (A) In the Hanging test young (3–5 months) Pfn2−/− mice showed deficits compared to wt controls (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0004) and Pfn2+/− mice (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0018). (B) Older mice (6–8 months) performed in general less well than young mice, but Pfn2−/− mutants again displayed significant coordination impairment compared to wt controls (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0103) and to Pfn2+/− mice (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0207). Heterozygous mice showed an age dependent loss of coordination ability. (C) Independently of the mouse age, muscle strength of the forelimbs was significantly reduced in both Pfn2−/− mice (two-sided t-test, p < 0.0001) and Pfn2+/− mice (two-sided t-test, p < 0.0001) compared to wt controls. When all 4 limbs were engaged, only Pfn2−/− mice were found impaired (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0003), while Pfn2+/− mice performed similarly to wt controls (two-sided t-test, p = 0.0002 Pfn2+/− vs. Pfn2−/− mice). Same animals as in Figure 5 were used. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.
To discriminate between muscle strength and coordination, we measured the mice grip strength. While gripping only with the forelimbs depends exclusively on the muscle control and strength, when the mice are allowed to grip with all four limbs, the coordination between fore- and hindlimbs affects the gripping strength. Both Pfn2−/− and Pfn2+/− mice showed about 20% less pulling strength with their forelimbs (Figure 6C, left), suggesting a mild deficit in muscle strength. However, grip strength with all four limbs was reduced only in Pfn2−/− mice (Figure 6C, right), while Pfn2+/− animals were comparable to wt controls, suggesting that the main motor function affected by loss of PFN2 was coordination.
Coordination issues could be spotted already at very early age (i.e., at P10) in Pfn2−/− mice by the characteristic hindlimb clasping when gently lifted by the tail instead of the normal hindlimb outward splaying (Supplementary Figure 3A), a phenotype typically present in mouse models with motor coordination and/or ataxia issues and cerebellar dysfunction (Lalonde and Strazielle, 2011; Yerger et al., 2022). Interestingly, the gait quality was only mildly affected in a foot-printing assay, where we only observed a slightly shorter pace (Supplementary Figure 3B).
Since motor coordination largely depends on cerebellar function, we studied Purkinje cell physiology in Pfn2−/− mice.
Purkinje cells (PC) are large inhibitory neurons of the cerebellar cortex organized in a monolayer between the inner granule cells and the external molecular layer, in which they extend their large dendritic arbors. These arbors receive extensive excitatory input from parallel and climbing fibers that generate dense trains, respectively, of simple and complex spikes (Sugimori and Llinás, 1990; Ghez and Thach, 2010). The central part of the cerebellum comprising the vermis region, the spinocerebellum, has been shown to regulate motor execution (Ghez and Thach, 2010).
We performed electrophysiological studies on Purkinje cells. Spontaneous excitatory post-synaptic currents (sEPSCs) recorded from PCs showed a significant leftward shift of the cumulative probability of the inter-event intervals in Pfn2−/− mice, indicating a significant increase of the sEPSCs frequency (Figure 7A), while their amplitude distribution did not change significantly (not shown). Moreover, the paired-pulse ratio (PPR) between pairs of stimuli on parallel fibers with increasing inter-stimulus interval (ISI) was significantly reduced in Pfn2−/− cells between 10 and 50 ms paired-pulse (PP) intervals (Figure 7B), indicative of an altered short-term synaptic plasticity that we can attribute to higher release probability of glutamatergic vesicles, since we have shown in a previous work that synaptic density is not altered in Pfn2−/− mice (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007). To confirm the increased excitatory input from parallel fibers onto PCs, two additional experiments were performed. First, we studied the effect of PFN2 depletion when manipulating the release probability by increasing the extracellular [Ca2+] from 2 mM, in standard control ACSF conditions, to 4 mM. In these conditions, the increase of EPSCs amplitude was 22% larger in Pfn2−/− than wt neurons (Figure 7C, Pfn2−/−: 2.75 ± 0.25 vs. wt: 2.27 ± 0.24-fold increase), indicating that PCs in Pfn2−/− animals experience higher excitatory stimulation. In a second experiment, frequency-dependent plasticity of the parallel fiber-PC synapse was analyzed. Increasing the frequency of stimulation from 0.05 to 0.2 Hz produced a mild potentiation of the EPSCs in both Pfn2−/− and wt control cells (Figure 7D), however, an additional frequency increase up to 1 Hz produced potentiation only in wt control neurons but not in Pfn2−/− cells that reached a plateau at much lower stimulation frequency than wt controls (Figure 7D, linear regressions, dotted lines). These results support the previous findings of a higher basal probability of glutamate release in Pfn2−/− glutamatergic neurons.
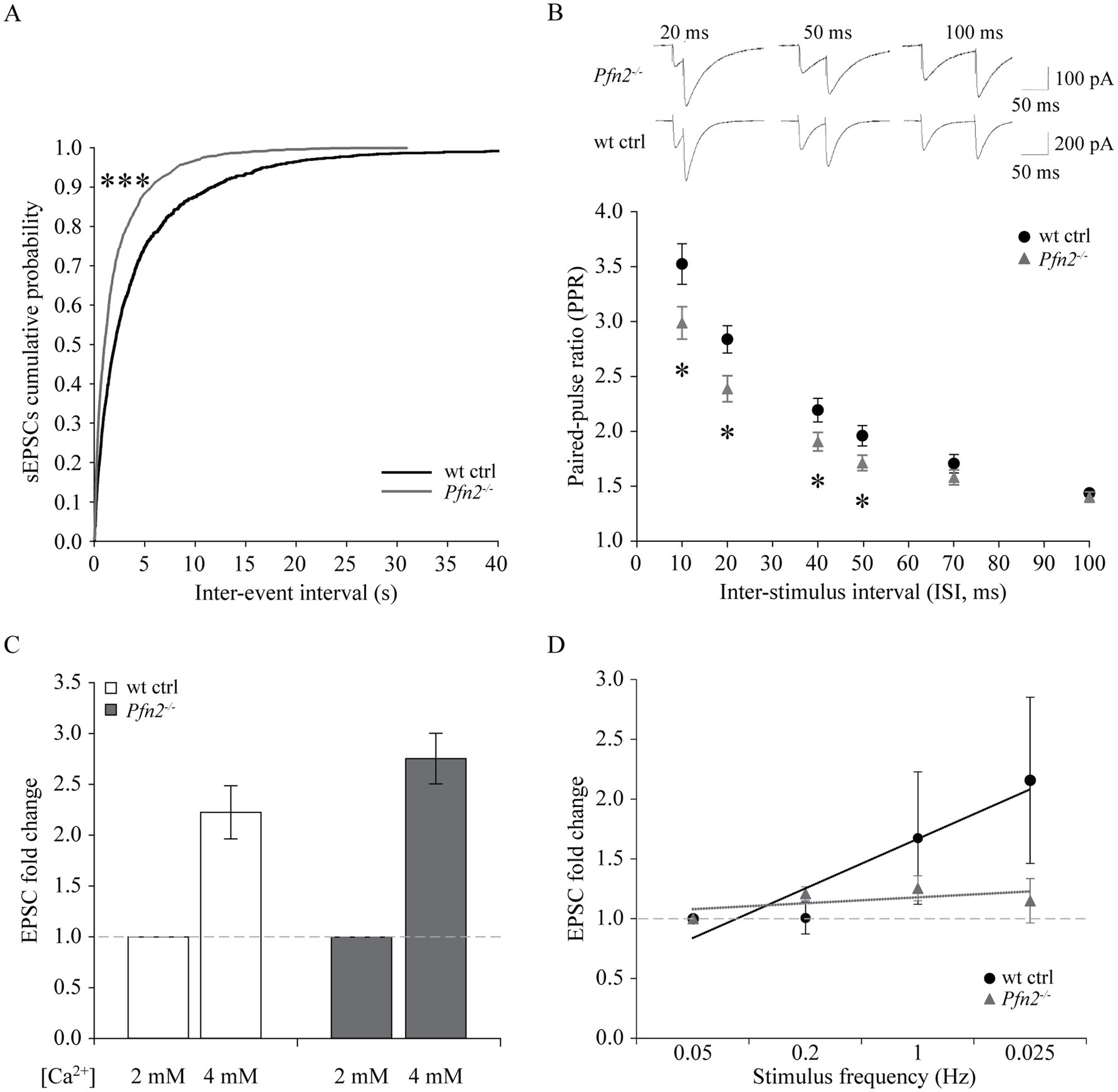
Figure 7. Increased glutamatergic input into Purkinje cells of Pfn2−/− mice. (A) Percentage cumulative frequency graphs of the average inter-event interval (IEI) distribution of sEPSCs recorded in PCs. The leftward shift for Pfn2−/− neurons indicates higher percentage of small IEIs, equivalent to increased frequency of events (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, p < 0.001). N/n = 2/4 wt ctrl, N/n = 3/6 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. (B) Paired-pulse ratio (PPR) of parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses at different inter-stimulus intervals (ISI: 10, 20, 40, 50, 70, 100 ms). At ISI ≤ 50 ms, Pfn2−/− neurons showed significantly reduced PPR compared to wt control, indicating higher probability of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Upper traces: sample traces of Pfn2−/− and wt control neurons at different ISI. N/n = 3/8 wt ctrl and N/n = 4/10 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. (C) Hyper-excitability of Pfn2−/− neurons in response to extracellular calcium increase. Raising the [Ca2+] from 2 to 4 mM increased the EPSCs by 2.75 ± 0.25-fold in Pfn2−/− neurons, but only by 2.22 ± 0.26-fold in wt control neurons. Dotted line marks the normalized value for [Ca2+] = 2 mM. N/n = 2/6 wt ctrl and N/n = 2/6 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. (D) Normalized frequency-dependent plasticity of evoked EPSCs increasing the stimulation from 0.05 Hz to 1 Hz. Stimulation was then reduced to 0.025 Hz to test the maintenance of the potentiation. Pfn2−/− neurons showed potentiation of EPSCs at 0.2 Hz stimulation but immediately reached a low plateau, while wt control neurons further potentiated their response up to 1 Hz stimulation and maintained it during the final low Hz stimulation. Linear regression analysis shows the different slope of the wt and Pfn2−/− neurons facilitation (respectively, black and grey dotted lines). The dashed grey line indicates the normalized level at the initial 0.05 Hz stimulation. N/n = 2/3 wt ctrl and N/n = 2/3 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001.
In summary, our results showed that PFN2 is regulating cerebellar physiology by restraining the glutamatergic input in PCs from afferent projections. The findings in the cerebellum are in line with our previous observations in striatum (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007), strengthening the point that PFN2 has a critical function in limiting glutamatergic release in the CNS.
PCs of the cerebellum are a class of neurons particularly vulnerable to excessive glutamatergic input due to their double connectivity with parallel and climbing fibers. Excitotoxicity is predominantly a glutamate-dependent event, mediated by NMDA receptors, which, in conditions of dysregulated glutamate homeostasis, cause excessive and/or prolonged rises in intracellular calcium that trigger neuronal cell death pathways (for a review, see Armada-Moreira et al., 2020). The increased glutamatergic output observed in profilin 2 knock-out mice led us to investigate the structure of the PC layer in 4 and 10 months old Pfn2−/− mice in spinocerebellar slices, the time points aligning with the motor coordination experiments previously described. At 4 months the PC layer in Pfn2−/− mice was essentially normal (Figure 8A), showing no significant difference in the linear density of PCs compared to wt controls (Figure 8B). At this age motor performance was not affected. However, at 10 months of age we observed severe changes in Pfn2 mutant mice: the PC layer in the central part of the cerebellum was highly disorganized, with long stretches completely devoid of PC cell bodies (Figure 8C), resulting in significantly reduced linear PC density (Figure 8D, Pfn2−/−: 2.27 ± 0.23 vs. wt: 4.60 ± 0.17 cells/100 μm). Severe motor coordination and performance deficits were indeed present at this age. These findings also suggest that PCs in Pfn2−/− mice are slowly lost throughout life.
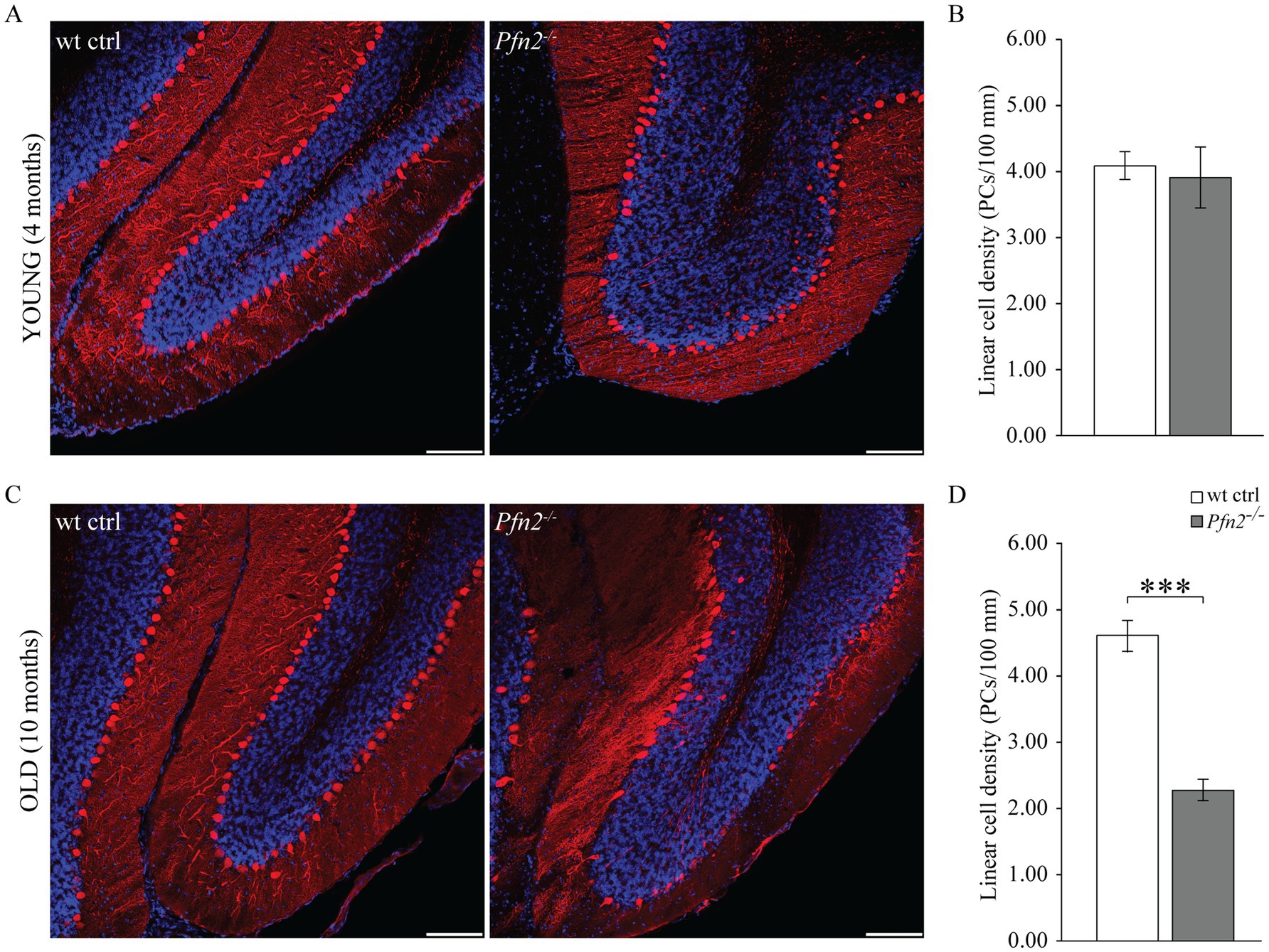
Figure 8. Age dependent loss of Purkinje cells in Pfn2−/− mice. (A) Sample confocal microscopy images of cerebellar folia from 4 months old wt control (left) and Pfn2−/− (right) mice, using calbindin antibodies (red) to specifically identify Purkinje cells and DAPI (blue) for the nuclei to highlight the granule cell layer. (B) Quantification of the linear cell density of Purkinje cells in 4 months old mice: no difference between Pfn2−/− and wt ctrl mice was found. (C) Sample confocal microscopy images of cerebellar folia from 10 months old wt control (left) and Pfn2−/− (right) mice. Large patches of PCs were lost in Pfn2−/− compared to wt control mice. (D) Quantification of the linear cell density of Purkinje cells in 8–10 months old mice: significantly reduced density in Pfn2−/− mice compared to controls (two-sided t-test, p = 2.6*10−8). Scale bar 100 μm. Quantification of N = 3 wt ctrl and N = 3 Pfn2−/− 4 months old and 8–10 months old mice, from at least 2 stained sagittal spinocerebellar slices per mouse. ***p ≤ 0.001.
Interestingly, we also observed in Pfn2−/− cerebella the presence of calbindin positive cells in the internal granular layer (Figures 8A,C right panels), which hint to a late neurodevelopmental migration defect, conceivable according to the proven function of profilins in cell motility (Zhou et al., 2019).
The etiology of ASD remains largely unknown, but one hypothesis suggests it could be based on a shift of the excitation/inhibition (E/I) ratio in the brain or in select neuronal circuits (Rubenstein and Merzenich, 2003; Lee et al., 2017). We previously documented increased glutamatergic transmission in Pfn2−/− mice, through higher glutamatergic vesicle exocytosis (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007), and we provided additional findings in this work supporting the possibility that a general increase of the glutamatergic neurotransmission not counterbalanced by an increase of GABAergic inhibition could underlie the autistic-like traits of Pfn2−/− mice. In order to prove this, inhibition needs to be measured. The CA3-CA1 Schaffer collaterals in the hippocampus are a well-characterized brain circuit to address the balance between excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs. We first analyzed excitatory transmission in this circuit using three different paradigms. We recorded miniature excitatory post-synaptic currents (mEPSCs) from CA1 pyramidal neurons, and then, while blocking GABAA receptors, we measured the paired-pulse ratio (PPR) and calculated the input–output (I-O) relation in the Schaffer collaterals pathway. Glutamatergic transmission, similarly to all other previously tested circuits, was increased also in the hippocampus of Pfn2−/− mice: mEPSCs were significantly more frequent in Pfn2−/− mice compared to wt controls, as indicated by the leftward shift of the cumulative curve for the inter-event intervals (Figure 9A), with only a mild reduction in their amplitude (Supplementary Figure 4A). By means of extracellular field recordings we showed that the paired-pulse ratio at 40 ms ISI was reduced by 40% (Figure 9B, Pfn2−/− 3.08 ± 0.30 vs. wt 1.80 ± 0.18) while the I-O relation was significantly increased in Pfn2−/− mice compared to control littermates (Figure 9C), indicating that for a similar number of stimulated pre-synaptic fibers, Pfn2−/− mice exhibited an increased post-synaptic response. There was no difference in the stimulation intensity to obtain the same fiber volley in the two genotypes (Supplementary Figure 4B), therefore similar numbers of pre-synaptic fibers responded to the same stimulation level.
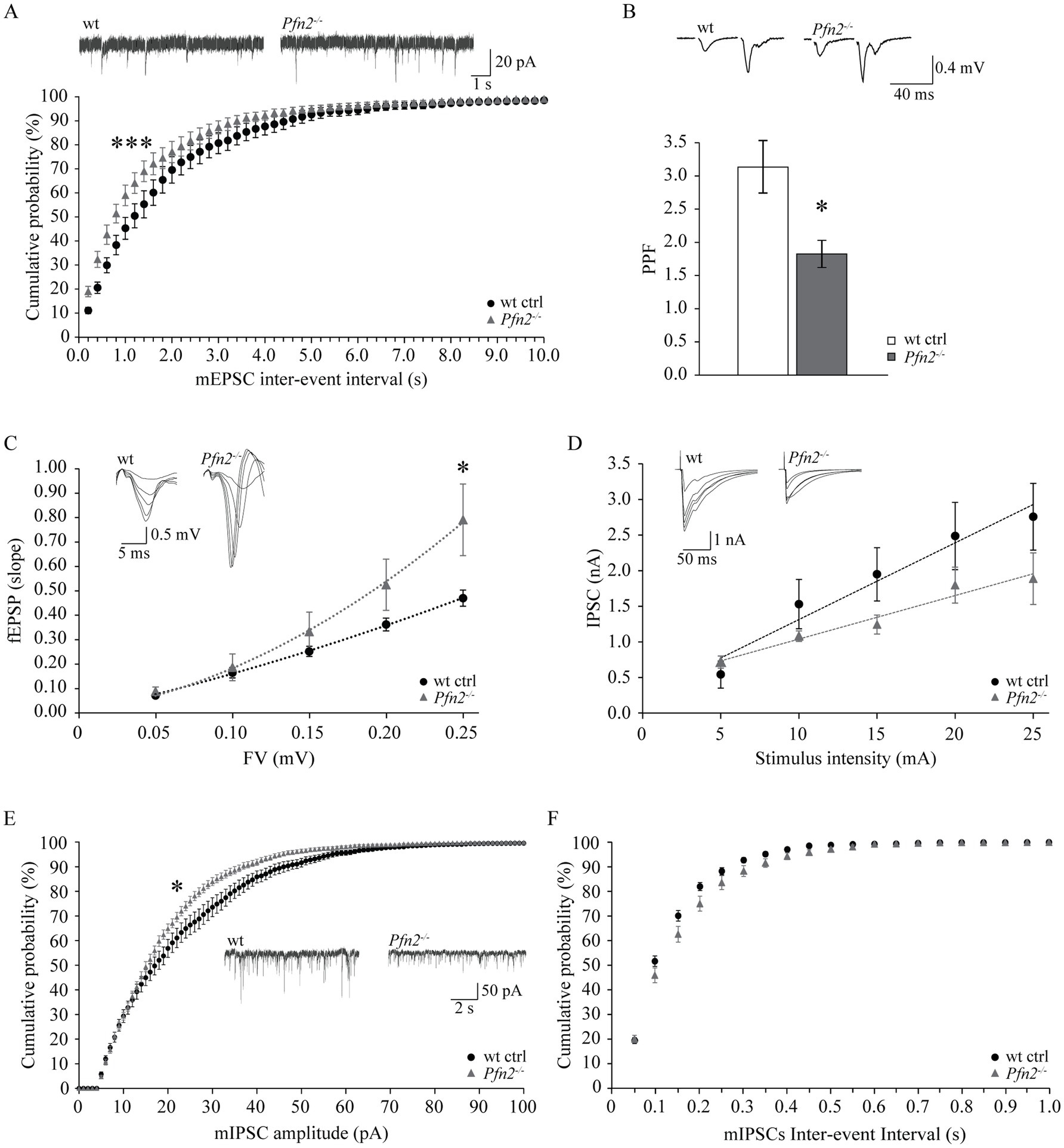
Figure 9. Increased ratio of excitatory versus inhibitory synaptic inputs in the hippocampus of Pfn2−/− mice. (A) Percentage cumulative frequency plot of the inter-event intervals distributions of mEPSCs recorded in CA3 neurons showed increased frequency of events in Pfn2−/− compared to wt control mice (Kolmogorov–Smirnov p = 0.001). Upper traces, sample mEPSCs traces. N/n = 4/7 wt ctrl and N/n = 3/8 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. (B) Field PPR with 40 ms inter-stimulus interval in the Schaffer collaterals of Pfn2−/− mice was significantly reduced by ca. 40% compared to wt controls (two-sided t-test p = 0.0102), indicating higher vesicle exocytosis probability. Upper traces: sample fEPSC response traces with 40 ms ISI. N/n = 6/15 wt ctrl and N/n = 5/9 Pfn2−/− mice/slices. (C) fEPSP input–output (I-O) relation in the Schaffer collaterals was increased in Pfn2−/− mice compared to wt controls, indicating a stronger excitatory transmission. Polynomial regression analysis (dotted lines) shows the higher I-O relation in Pfn2−/− slices compared to wt controls (y = 8.6734x2 + 0.9515x for Pfn2−/− mice, y = 1.9042x2 + 1.4053x for wt mice). Upper traces: superimposed traces from a sample recording at increasing fiber volley. N/n = 7/19 ctrl and N/n = 7/14 Pfn2−/− mice/slices. (D) IPSC I-O relation showed a mild decrease of the inhibitory synaptic transmission in Pfn2−/− pyramidal neurons compared to wt controls. Upper traces: superimposed traces from a sample recording at increasing stimulus intensity. N/n = 3/6 wt and N/n = 3/5 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. (E) Percentage cumulative frequency plot of the amplitudes of mIPSCs shows a significant decrease of inhibitory transmission in Pfn2−/− mice compared to wt littermate controls (Kolmogorov–Smirnov, p = 0.025). Inset traces: sample mIPSCs traces. (F) No difference was found in the inter-event interval of mIPSCs between Pfn2−/− and wt control mice, as shown by the cumulative probability plot. N/n = 3/10 wt and N/n = 4/10 Pfn2−/− mice/cells. *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001.
Next, we studied inhibitory transmission in the same circuit, measuring miniature inhibitory post-synaptic currents (mIPSCs) in CA1 pyramidal neurons and calculating the I-O relation while blocking AMPA receptors. Contrary to the excitatory drive that was clearly increased, the inhibitory transmission was unchanged or mildly reduced. In the input–output relation experiment, Pfn2−/− pyramidal neurons showed a tendential loss of GABA-dependent currents (Figure 9D), which was confirmed by a significant decrease in the amplitudes of mIPSCs (Figure 9E) with no change in mIPSCs frequencies (Figure 9F), suggesting a prevalent post-synaptic defect in CA1 pyramidal neurons, where PFN2 was shown to interact with gephyrin scaffolds and was proposed to regulate receptor densities (Giesemann et al., 2003; Murk et al., 2012). Overall our data indicate that in Pfn2−/− mice excitatory synaptic inputs are increased while inhibitory synaptic inputs are reduced, thereby suggesting a shift of the E/I balance toward excessive excitation.
In this work we report three important findings based on the constitutive Pfn2 knock-out mouse model: (1) that lack of PFN2 causes a variety of autistic-like phenotypes; (2) that increased glutamate release in Pfn2−/− mice alters excitatory synaptic connectivity in multiple circuits, suggesting that this is a general defect of all glutamatergic synapses lacking PFN2; (3) that inhibitory neurotransmission is not upregulated to counterbalance the increased glutamatergic drive in Pfn2−/− mice, thus suggesting a net increase of the excitation/inhibition ratio.
The conventional knock-out of Pfn2 produces conspicuous deficits in maternal/paternal behavior, vocal communication, and motor coordination, with an age-dependent effect on motor performance that correlates with the loss of Purkinje cells in the cerebellum. Therefore, the phenotypic spectrum ranges from core symptoms to common comorbidities of ASD, including epileptic seizures, measured in about 12.5% of the mutant mice. In recent years, whole-exome sequencing (WES) studies of ever larger cohorts of autism patients have uncovered a significant number of genes causative of ASD, which appear to be involved in a wide spectrum of cellular functions (De Rubeis et al., 2014; Iossifov et al., 2014; Satterstrom et al., 2020). Nevertheless, many more genes are thought to be involved, with variable degree of impact on autism risk, according to estimations based on statistical simulations and the development of more powerful statistical tools to analyze the mutations discovered by WES, which integrate polygenicity and protein interactions networks (Neale et al., 2012; Sanders et al., 2012; He et al., 2013; De Rubeis et al., 2014). Consensus is emerging that the ultimate physiological target of the mutations is either synaptic function or brain circuit development, in particular through cortical neurons specification (Baudouin, 2014; Fromer et al., 2014; Satterstrom et al., 2020). The human gene PROFILIN 2 has not yet appeared in WES studies of genomes of ASD patients. However, current knowledge on PFN2 function in brain, as well as the data presented in this work, would support its standing as a risk gene for neurological disorders, including ASD. In the mouse, PFN2 function appears to be mainly restricted to regulating synaptic activity (Ackermann and Matus, 2003; Gareus et al., 2006; Pilo Boyl et al., 2007) and to maintaining dendritic arborization (Michaelsen et al., 2010; Di Domenico et al., 2021), thus clearly taking part in the shaping of neuronal connectivity. Moreover, profilin 2 has been shown to interact with a number of ligands and to participate in signaling pathways that have been implicated in ASD. For example, the small RHO GTPases regulate actin dynamics in developing neurons and indeed have been implicated as additional ASD risk genes in models that cluster genes strongly associated to and co-expressed with discovered ASD causing genes in key tissues, such as mid-fetal pre-frontal and somato-sensory cortex (De Rubeis et al., 2014). The RHOA pathway, involving the downstream effector kinase ROCK (RHO-associated coiled-coil containing kinase), regulates in very specific ways dendrite sprouting, extension, and ramification, as well as axon branching during early and late neuronal development (Bito et al., 2000; Nakayama et al., 2000; Ohnami et al., 2008) and can therefore affect the establishment of correct neuronal connectivity. ROCK kinase has been shown to specifically interact with PFN2 (Witke et al., 1998; Da Silva et al., 2003) and the RHOA/ROCK pathway to act through phosphorylation of PFN2 to limit early neurite sprouting of cultured mouse hippocampal neurons (Da Silva et al., 2003). On the other hand, the RAC1 pathway functions by activating the WAVE regulatory complex (WRC), a molecular machine that promotes actin nucleation to form branched actin networks (Pollard, 2007) essential for axonal branching and growth-cone dynamics (Spillane et al., 2011; Miguel-Ruiz and Letourneau, 2014), dendritic branching (Stürner et al., 2019), as well as spine sprouting, structure, and potentiation (Korobova and Svitkina, 2010). CYFIP1 and NCKAP1 that are part of the WRC, are both established ASD risk genes. PFN2 is found in complexes with the two CYFIP paralogues (Witke et al., 1998) and ultimately takes part in the actin polymerization process initiated by the WRC, recruited as profilactin moiety, a 1:1 PFN2-G-actin complex. Thus, copy number variation (CNV) or single nucleotide variation (SNV) in the PFN2 gene could well contribute through numerous pathways to alterations in neuronal development and physiology, ultimately leading to ASD.
In view of the fact that Pfn2 is highly expressed in neurons across the entire brain (Witke et al., 1998; Da Silva et al., 2003; Pilo Boyl et al., 2007), that PFN2 is involved in pathways connected to ASD risk or ASD causing genes, as just described, and that PFN2 is mainly functioning in excitatory synaptic physiology and in a more limited way in inhibitory synaptic physiology, as shown in this work, we believe that it is not so surprising that the Pfn2 knock-out mouse reproduces a variety of autistic-like traits. In the Pfn2 knock-out mouse model the loss of maternal (and paternal) behavior was remarkably strong, while in the sociability test the deficits were less evident, most likely due to the confounding factor of the previously reported novelty-induced hyper-excitability behavior (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007). The hyper-excitability phenotype possibly also masked repetitive behavior and resistance to changes, which did not appear particularly strong in the applied behavioral paradigms, while the communication behavior of Pfn2 mutant mouse pups was significantly altered, with a pattern reminiscent of infant vocalization in ASD (Esposito and Venuti, 2009). We acknowledge that not all standard autistic-like behaviors are present or are markedly detectable in the mouse model, but it is not unusual that behavioral characterization of mouse models reveals heterogeneity in the manifestation of the autistic-like phenotypes, with some that appear stronger and others evidently mild, even among the core symptoms. The overall picture obtained for the Pfn2 ko mouse model is not uncommon when characterizing animal models of human diseases, and in particular ASD, for at least two reasons: first, animal models often exhibit only a part of the full spectrum of phenotypes seen in polygenic human diseases like autism (Neale et al., 2012; McCarroll and Hyman, 2013) because the animal models typically carry the mutation of only one gene, as in the case of the Pfn2 knockout mouse; secondly, one has to consider that inbred mice have a relatively narrow genetic background variation, therefore if in a colony the genetic background is tolerant of a specific genetic mutation for a certain behavior, there is little chance that one can find individual mice with stronger or diverse phenotypes for that behavior. As for many neurological disorders, it is unlikely that PFN2 mutations would occur homozygously in humans, however the complete Pfn2 knock-out mouse model employed in this work facilitates to discern which aspects of neuronal development, physiology, and behavior are critically affected when the gene is inactivated. Moreover, a homozygous knock-out approach in mouse helps to overcome the higher robustness of the mouse CNS compared to the more complex and therefore vulnerable human CNS in the study of these phenotypes. It is anyway remarkable that even Pfn2 heterozygous mice show intermediate phenotypes in some of the tested behaviors, strengthening the expectation of discovering CNVs or SNVs in PFN2 in humans.
Concerning the excess glutamate release in Pfn2−/− mice, we have previously reported the mechanism by which PFN2 regulates excitatory pre-synaptic terminal physiology, with loss of PFN2 increasing pre-synaptic vesicle release from excitatory synapses in the cortico-striatal pathway and therefore enhancing circuit excitation (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007). With this work we extend the study, showing that the mechanism found originally in one circuit is reasonably a general mechanism for glutamatergic neurons, since also the parallel fiber signaling in the cerebellum and the Schaffer collaterals system in the hippocampus are affected in a comparable way when PFN2 is missing, and they are very different circuits with only in common the released neurotransmitter, glutamate. Therefore, one should expect an overall increase of glutamatergic excitation over the entire central nervous system when PFN2 is below threshold. A consequence of the increased glutamatergic neurotransmission in the absence of PFN2 is the progressive loss of cerebellar Purkinje cells that we observed in Pfn2 ko mice. PCs are the most susceptible cells of the brain to excitotoxicity, due to their double innervation from glutamatergic climbing and parallel fibers (Ghez and Thach, 2010). The excitotoxicity hypothesis is supported by the fact that PC loss is progressive and starts after a few months of the mouse life, excluding a major neurodevelopmental defect. The progressive loss of PCs is also paralleled at the behavioral level by the age-dependent deterioration of the coordination phenotype, which is in line with the involvement of the Purkinje cells of the spinocerebellar region to regulate limb motor functions (Ghez and Thach, 2010). Purkinje cell loss has been found in a subset of autism patients following post-mortem analysis of their brains (Skefos et al., 2014). Unfortunately, no connection was made with the type of genetic or physiological dysfunction that caused the autism phenotype in these individuals, in particular if it could be an increased excitation/inhibition ratio.
Lastly, in this work we add an important notion to the understanding of the loss of PFN2 in the brain. When PFN2 is absent, inhibitory GABAergic neurotransmission is not affected in the same way as the excitatory, being on the contrary unaltered or post-synaptically mildly depressed in the same glutamatergic neurons that receive higher glutamatergic excitatory inputs from the CA3 region of the hippocampus. It has been since long reported the interaction of PFN2 with the inhibitory post-synaptic scaffold protein gephyrin (Giesemann et al., 2003; Murk et al., 2012), but to the best of our knowledge no follow up studies have been conducted to explore the physiological significance of this interaction. We report here for the first time one physiological outcome of disrupting the interaction between PFN2 and gephyrin: the decrease of inhibitory currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons. This reduction of post-synaptic inhibitory currents could be due to decreased clustering of GABA receptors or to their faulty assembly or function. The consequence of this finding is that the net effect of depleting PFN2 in the brain is, therefore, a likely increase of the excitation/inhibition ratio, mainly due to an increase of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the brain. The E/I imbalance has been proposed as one possible cause of ASD (Rubenstein and Merzenich, 2003), and has been already demonstrated, as proof-of-principle, by the knock-out mouse model of the eIF4E binding protein 2 (Eif4epb2) (Gkogkas et al., 2013), which showed increase in excitatory transmission, and by the knock-out of GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit (Gabrb3), which had decreased inhibitory function (DeLorey et al., 1998). The Pfn2 knock-out mouse appears to be in line with this mechanism and these other mouse models, with a particular phenotypic agreement to the first model. One probable consequence of the increase of the E/I ratio at the circuit level is the epileptic seizures phenotype that we observed in the Pfn2 ko mouse. Tonic and tonic–clonic seizures induced by sensory stimulation were found in about 12.5% of the mutant mice, starting from young to middle age, but measurement of epileptic activity in freely moving Pfn2 mutant mice might reveal a higher prevalence. Epilepsy is a comorbidity observed in a subset of ASD patients. Recent meta-analyses of studies on autistic patients have shown that in humans epilepsy has an average prevalence of 15–16%, although with higher pooled prevalence in subjects with intellectual disability (21–24%) than in those without (8–9%), and that this prevalence increases with age (Amiet et al., 2008; Woolfenden et al., 2012). Our findings in the Pfn2 ko mouse model appear mostly in line with these data. Unfortunately, nothing is known yet about the causes of epilepsy as a comorbidity of ASD in humans. Our study, as well as others (DeLorey et al., 1998; Cobos et al., 2005), suggest that one possible cause of the epileptic comorbidity might reside in synaptic dysfunctions that raise the E/I ratio.
In conclusion, the Pfn2 knock-out mouse could provide a model to study therapeutic interventions for a subset of autistic disorders dependent on increased excitation/inhibition ratio in the nervous system. According to the physiological function of PFN2 in neurons and its protein–protein interactions network, it is not unlikely that in future WES studies with even larger patients’ cohorts and more complex statistical analysis methods PFN2 might be detected as an ASD risk gene. The knock-out mouse phenotype strongly supports this possibility, since several ASD symptoms, both core and comorbid, are reproduced and are similar to those in other ASD mouse models.
The Pfn2 knock-out (Pfn2−/−) mouse model was previously described (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007). All mice used in the experiments were littermates generated by crossing heterozygous parents. Mice were socially housed with a standard 12 h light/dark cycle at 22 °C and 50–55% humidity, with free access to water and food pellets. All experiments were performed according to EU regulations (Licenses n. 19/2005-B and AZ 84–02.04.2013.A233).
Male mice 3–5-months old (“young”) were used in behavioral experiments, except where differently indicated. Mice indicated as “old” were aged 6–10 months. Maternal behavior: pregnant females were single-housed a week before delivery. Litter survival was assessed 10 days post-partum (P10). In a second approach, pregnant female and male were left together to allow cross-fostering. Maternal behavior, pup retrieval: P5 pups from Pfn2−/− and wt control females were dispersed in the cage and time for retrieval of the first pup and of the entire litter was scored up to 30 min. Social interaction: the test chamber was built according to Moy et al. (2007). The experiment consisted of two 10 min trials: first, the test animal explored a tripartite chamber containing two empty cages in the outer compartments; second, the same test animal was confronted with one empty cage and one cage containing the stranger mouse, with a modification of the original test to ensure a non-aversive context for Pfn2−/− mice that are hyper-excitable (Pilo Boyl et al., 2007): we used juvenile mice of 3.5 weeks (P25) of age as social partners. Stereotypic and repetitive behavior: self-grooming, digging, jerking, circling, and wall-leaning behavior was scored as number of events in 300 s after transfer into a novel cage. Y-maze: mice were allowed to freely explore the Y maze for 5 min and percent (%) of SPA (spontaneous alternation) and SAR (same arm return) was calculated with respect to total arm entries. Ultrasound vocalizations (USV): USVs were measured in P5-P9 male and female pups (Branchi et al., 2001). Pups were singularly taken from the mother and placed in a soundproof chamber at room temperature (22 °C) under a condenser ultrasound microphone (Avisoft Bioacoustics CM16/CMPA) connected to an UltraSoundGate 116Hb and data were collected for 300 s with the Avisoft Recorder 2.76 in 16-bit format. Analysis of USVs was performed using the Avisoft SASLab Pro software (Avisoft Bioacoustics, Berlin DE). The low frequency (<70–75 kHz) long calls (>20 ms) and the call trains (series of calls with a regular spacing of 150 ± 10 ms) were manually scored. RotaRod: an automated apparatus (TSE Systems, Germany) was used to test young (2.5–5 months) and older (5.5–8 months) mice. On the first day mice were subjected to a constant speed (3 rpm) protocol for 4 sequential trials of 300 s each with inter-trial interval of 1 h 30 min. Second, for five consecutive days mice were subjected to an incremental rotation speed paradigm (3–30 rpm) in 300 s, three times a day with inter-trial interval of 1 h 30 min; the best performance of the day was selected for every single mouse to assess motor ability, coordination and learning. Hanging: mice were hanged with the forelegs to a thin metal bar and stay time was measured. Grip: a grip strength meter (Harvard Apparatus) was used to test muscle strength of the animals. Mice were allowed to grab a metal grid with the forepaws only or with all 4 paws and were gently and constantly pulled by the tail until they lost the grip. The pulling strength was measured in Newton. Three measurements were taken for each mouse and the average was used for statistical purposes. Epileptic seizures: visible tonic and tonic–clonic seizures were triggered in a number of Pfn2−/− mice by some sudden stimulus or stressful situation. The observations in this work, for statistical reasons, come exclusively from the mice that showed the seizures upon the opening of the cage for the regular observation of the mice or the changing of the bedding. When the epileptic mouse started to become rigid, arching the back, the timer was started. Depending on the type of seizure, the mouse might remain rigid and eventually fall on one side or start convulsive movements and jumps. The timer was stopped when the mouse started to recover, as signaled by straightening and self-grooming.
4- and 10- to12-months old mice were anesthetized and perfused with 4% formaldehyde. Brains were post-fixed O/N at 4 °C. Sagittal cerebellar slices 300 μm thick were cut with a VT1000 Vibratome (Leica Microsystems, Germany) in cold PBS. Slices were stained with antibodies following standard procedures. Anti-calbindin monoclonal antibody (Sigma, Germany, 1: 500), anti-mouse Alexa546-conjugated secondary antibody (Molecular Probes, Germany, 1:400) and the nuclear dye Hoechst (Roche, Germany, 0.5 μg/mL) were used for the staining. Imaging was performed with a Leica TSE SPE Confocal Microscope (Germany) acquiring 40 μm Z-stacks.
Acute hippocampal brain slices were obtained from P16-P24 mice. Animals were anesthetized with isoflurane, decapitated, the brains removed from the skull and placed into cold (4 °C) artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF: 130 mM NaCl, 2.75 mM KCl, 1.43 mM MgSO4, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 1.1 mM NaH2PO4, 28.8 mM NaHCO3, 11 mM Glucose), pH 7.3–7.4, 315–325 mOsm/L and gassed with carbogen (95% O2, 5% CO2). The hippocampi were dissected and transversally cut in 400 μM slices with a vibratome (Leica VT1200S) in chilled and carbogenated ACSF. Slices were then equilibrated in slice-chambers containing ACSF continuously gassed with carbogen for 30 min at 32 °C and subsequently stored at room temperature in ACSF. All recordings were done at room temperature (21–23 °C) in a recording chamber continuously perfused by carbogenated ACSF. If necessary, drugs were added to the ACSF. Recordings were obtained using 2–4 MΩ glass electrodes (Science Products GB150TF-8P, Hoffenheim, Germany) filled with intracellular solution and a Multiclamp 700B amplifier (Axon Instruments), and data were digitized using a Digidata 1322A (Axon Instruments). mIPSCs: miniature inhibitory post-synaptic currents (mIPSCs) were recorded from CA1 pyramidal neurons at −70 mV holding potential for 10 min and analyzing 2 min (ca. 120 events) in the middle region of the recording, using a high chloride intracellular solution containing (in mM): 90 CsCl, 20 Cs-gluconate, 8 NaCl, 2 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 1 EGTA, and 2 QX-314, pH 7.2 (290 mOsM/L). mIPSCs were recorded in ASCF supplemented with NBQX (10 μM) to block AMPA receptors and TTX (0.2 μM) to block action potentials. Evoked IPSCs: IPSCs were evoked with a stimulation electrode placed ca. 100 μm away from the soma of the recorded pyramidal cell. The position of the stimulation electrode was adjusted such that the smallest stimulus (5 μA) elicited a current of ca. 500 pA. mEPSCs: mEPSCs were recorded from CA1 pyramidal neurons in acute hippocampal brain slices at a holding potential of −70 mV, for at least 10 min to make sure that 120 events could be analyzed using the following intracellular solution (in mM): 150 Cs-gluconate, 8 NaCl, 2 MgATP, 10 HEPES, 0.2 EGTA and 5 QX-314 ([2-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino]2-oxoethyl]-triethylazanium bromide), pH 7.2 (290 mOsM/L). mEPSCs were recorded in ASCF supplemented with picrotoxin (PTX, 100 μM) to block GABAA receptors, tetrodotoxin (TTX, 0.2 μM) to block action potentials and trichlormethiazide (TCM, 250 μM) to increase mEPSC frequency. fEPSCs: fEPSP were recorded from acute hippocampal slices, disconnecting the Schaffer collaterals cutting with a scalpel in the CA3 area to prevent recurrent spontaneous excitation. Schaffer collaterals after the cut were stimulated and synaptic responses were recorded in the stratum radiatum of the CA1 region, using glass microelectrodes filled with ACSF. fEPSCs were recorded in ASCF supplemented with picrotoxin (PTX, 100 μM) to block GABAA receptors. Before the experiment was started, recordings were registered for 20 min until fEPSP reached a stable baseline. For PPF experiments Schaffer collaterals were stimulated with a stimulus interval of 40 ms. For the input–output relation, the input was the amplitude of the fiber volley representing the strength of the action potential arriving from the Schaffer collaterals; the output was defined as the slope of the resulting fEPSP. Fiber volley amplitudes of 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2 and 0.25 mV were evoked and the resulting fEPSC plotted. All data were analyzed using Clampfit 10.2 (Molecular Devices), a custom written Matlab routine (MathWorks), and GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software). Values are given as means ± SEM.
Parasagittal cerebellar slices (250 μm) were prepared from 1-month old mice and immersed in ice-cold gassed (95% O2, 5% CO2) sucrose-based artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) containing: 87 mM NaCl, 75 mM sucrose, 2 mM KCl, 7 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 25 mM NaHCO3, 1.2 mM NaH2PO4 and 10 mM glucose, pH 7.4, 300–305 mOsm. Slices were then allowed to recover for at least 1 h at RT in standard ACSF (125 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1.2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM CaCl2, 25 mM NaHCO3, 1.2 mM NaH2PO4 and 10 mM glucose) before measurement. In high [Ca2+] experiments, [Ca2+] concentration was raised to 4 mM and Mg2+ concentration was adjusted to 1 mM. Patch-clamp recording: whole-cell patch-clamp recordings on PCs were performed with a Multiclamp 700B amplifier (Molecular Devices, USA) using glass electrodes (3–4 MΩ) pulled with a vertical puller (PC-10, Narishige, Japan). Intracellular solution (140 mM Cs-Methanesulfonate, 10 mM Hepes, 0.5 mM EGTA, 2 mM MgATP, 0.3 mM Na3GTP, 2 mM MgCl2) was adjusted to 295–300 mOsm, pH 7.2. Signals were acquired with the DigiData-1440A (AutoMate Scientific, USA) amplifier using pCLAMP-v10 software and analyzed off-line with Clamp-fit 10 program (Axon Instruments, USA). Excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) were recorded clamping the cell at −70 mV. Spontaneous EPSCs were recorded during an initial 10 min baseline period followed by application of bicuculline (10 μM, Sigma Aldrich, USA) for 15 min. A concentric bipolar stimulating electrode (SNE-100 × 50 mm long Hugo Sachs Elektronik - Harvard Apparatus GmbH, Germany) was placed in the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex for parallel fiber stimulation. Series resistance (Rs) was not compensated during voltage-clamp experiments to avoid increased electrical noise in the trace. Rs was constantly monitored over time and recordings in which it changed more than 20% were discarded. For Paired-Pulse experiments, pairs of stimuli were applied every 20 s. Stimulus was delivered through an A320R Isostim Stimulator/Isolator (WPI, USA). PPR was calculated as the ratio between the amplitude evoked by the second stimulus (A2) and the amplitude of the first (A1; A2/A1).
In behavioral tests one-way ANOVA or two-way ANOVA with repeated-measures in one factor were applied to assess statistical differences, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. Unpaired two-tailed t-Student’s test was used on two sets of data with normal distributions, while the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test for independent measures was used if distributions were not normal. Input–output experiments were subjected to regression analysis. Events and amplitudes frequency distributions were compared with the non-parametric Kolmogorov–Smirnov two-sample test by stochastically sampling a select number of values from each cell of the same genotype to produce a single distribution per genotype and reiterating the process 20 times, selecting at the end the highest p value resulting from all the comparisons. Kaplan-Mayer survival curves were analyzed applying the non-parametric Peto-Prentice generalized Wilcoxon test.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The animal study was approved by the Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz (LANUV)NRW, 45610 Recklinghausen. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
WW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MD: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AN: Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. VS: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. PP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by EMBL and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), through the SFB1089 collaborative research center and the SPP1464 priority program to WW; by the Bonner Forum Biomedizin (BFB) grant 56/10 to PPB.
We are thankful to Fabrizio Eusebi, who passed away during the course of this study, for supporting our collaboration with his expertise and resources. We thank Valeria Berno, Mumna al Banchaabouchi and Karin Gale from EMBL-Rome for technical help. A big thank you to all the animal caretakers, who made the work with the mice easy and smooth, and to our lab technical staff.
AN was employed by the Biogen Inc.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncel.2025.1540989/full#supplementary-material
Ackermann, M., and Matus, A. (2003). Activity-induced targeting of profilin and stabilization of dendritic spine morphology. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 1194–1200. doi: 10.1038/nn1135
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association.
Amiet, C., Gourfinkel-An, I., Bouzamondo, A., Tordjman, S., Baulac, M., Lechat, P., et al. (2008). Epilepsy in autism is associated with intellectual disability and gender: evidence from a meta-analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 64, 577–582. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.04.030
Armada-Moreira, A., Gomes, J. I., Pina, C. C., Savchak, O. K., Gonçalves-Ribeiro, J., Rei, N., et al. (2020). Going the extra (synaptic) mile: excitotoxicity as the road toward neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 14:90. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00090
Auranen, M., Vanhala, R., Varilo, T., Ayers, K., Kempas, E., Ylisaukko-oja, T., et al. (2002). A genome wide screen for autism-spectrum disorders: evidence for a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 3q25-27. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 777–790. doi: 10.1086/342720
Avery, A. W., Thomas, D. D., and Hays, T. S. (2017). β-III-spectrin spinocerebellar ataxia type 5 mutation reveals a dominant cytoskeletal mechanism that underlies dendritic arborization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, E9376–E9385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707108114
Baudouin, S. J. (2014). Heterogeneity and convergence: the synaptic pathophysiology of autism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 39, 1107–1113. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12498
Bellenchi, G. C., Gurniak, C. B., Perlas, E., Middei, S., Ammassari-Teule, M., and Witke, W. (2007). N-cofilin is associated with neuronal migration disorders and cell cycle control in the cerebral cortex. Genes Dev. 21, 2347–2357. doi: 10.1101/gad.434307
Bito, H., Furuyashiki, T., Ishihara, H., Shibasaki, Y., Ohashi, K., Mizuno, K., et al. (2000). A critical role for a rho-associated kinase, p160ROCK, in determining axon outgrowth in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuron 26, 431–441. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81175-7
Boyer, O., Nevo, F., Plaisier, E., Funalot, B., Gribouval, O., Benoit, G., et al. (2011). INF2 mutations in Charcot–Marie–tooth disease with Glomerulopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2377–2388. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1109122
Bozdagi, O., Sakurai, T., Dorr, N., Pilorge, M., Takahashi, N., and Buxbaum, J. D. (2012). Haploin sufficiency of Cyfip1 produces fragile X-like phenotypes in mice. PLoS One 7:e42422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042422
Branchi, I., Santucci, D., and Alleva, E. (2001). Ultrasonic vocalisation emitted by infant rodents: a tool for assessment of neurobehavioural development. Behav. Brain Res. 125, 49–56. doi: 10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00277-7
Cingolani, L. A., and Goda, Y. (2008). Actin in action: the interplay between the actin cytoskeleton and synaptic efficacy. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 344–356. doi: 10.1038/nrn2373
Cobos, I., Calcagnotto, M. E., Vilaythong, A. J., Thwin, M. T., Noebels, J. L., Baraban, S. C., et al. (2005). Mice lacking Dlx1 show subtype-specific loss of interneurons, reduced inhibition and epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1059–1068. doi: 10.1038/nn1499
Coon, H., Matsunami, N., Stevens, J., Miller, J., Pingree, C., Camp, N. J., et al. (2005). Evidence for linkage on chromosome 3q25-27 in a large autism extended pedigree. Hum. Hered. 60, 220–226. doi: 10.1159/000090546
Da Silva, J. S., Medina, M., Zuliani, C., Di Nardo, A., Witke, W., and Dotti, C. G. (2003). RhoA/ROCK regulation of neuritogenesis via profilin IIa-mediated control of actin stability. J. Cell Biol. 162, 1267–1279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200304021
Davenport, E. C., Szulc, B. R., Drew, J., Taylor, J., Morgan, T., Higgs, N. F., et al. (2019). Autism and schizophrenia-associated CYFIP1 regulates the balance of synaptic excitation and inhibition. Cell Rep. 26, 2037–2051. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.092
De Rubeis, S., He, X., Goldberg, A. P., Poultney, C. S., Samocha, K., Ercument Cicek, A., et al. (2014). Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature 515, 209–215. doi: 10.1038/nature13772
DeLorey, T. M., Handforth, A., Anagnostaras, S. G., Homanics, G. E., Minassian, B. A., Asatourian, A., et al. (1998). Mice lacking the beta3 subunit of the GABAA receptor have the epilepsy phenotype and many of the behavioral characteristics of Angelman syndrome. J. Neurosci. 18, 8505–8514. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-20-08505.1998
Di Domenico, M., Jokwitz, M., Witke, W., and Pilo Boyl, P. (2021). Specificity and redundancy of profilin 1 and 2 function in brain development and neuronal structure. Cells 10:2310. doi: 10.3390/cells10092310
Dobyns, W. B., Aldinger, K. A., Ishak, G. E., Mirzaa, G. M., Timms, A. E., Grout, M. E., et al. (2018). MACF1 mutations encoding highly conserved zinc-binding residues of the GAR domain cause defects in neuronal migration and axon guidance. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 103, 1009–1021. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.10.019
Esposito, G., and Venuti, P. (2009). Comparative analysis of crying in children with autism, developmental delays, and typical development. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabl. 24, 240–247. doi: 10.1177/1088357609336449
Faix, J., and Grosse, R. (2006). Staying in shape with formins. Dev. Cell 10, 693–706. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.05.001
Fortugno, P., Angelucci, F., Cestra, G., Camerota, L., Ferraro, A. S., Cordisco, S., et al. (2019). Recessive mutations in the neuronal isoforms of DST, encoding dystonin, lead to abnormal actin cytoskeleton organization and HSAN type VI. Hum. Mutat. 40, 106–114. doi: 10.1002/humu.23678
Fournier, K. A., Hass, C. J., Naik, S. K., Lodha, N., and Cauraugh, J. H. (2010). Motor coordination in autism spectrum disorders: a synthesis and meta-analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 40, 1227–1240. doi: 10.1007/s10803-010-0981-3
Fromer, M., Pocklington, A. J., Kavanagh, D. H., Williams, H. J., Dwyer, S., Gormley, P., et al. (2014). De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nature 506, 179–184. doi: 10.1038/nature12929
Gareus, R., Di Nardo, A., Rybin, V., and Witke, W. (2006). Mouse profilin 2 regulates endocytosis and competes with SH3 ligand binding to dynamin 1. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 2803–2811. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503528200
Ghez, C., and Thach, W. T. (2010). “The cerebellum” in Principles on neural science. eds. E. Kandel, J. Schwartz, and T. Jessell (New York, NY: McGraw-Hill), 832–852.
Gieselmann, R., Kwiatkowski, D. J., Janmey, P. A., and Witke, W. (1995). Distinct biochemical characteristics of the two human profilin isoforms. Eur. J. Biochem. FEBS 229, 621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.0621j.x
Giesemann, T., Schwarz, G., Nawrotzki, R., Berhörster, K., Rothkegel, M., Schlüter, K., et al. (2003). Complex formation between the postsynaptic scaffolding protein gephyrin, profilin, and Mena: a possible link to the microfilament system. J. Neurosci. 23, 8330–8339. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-23-08330.2003
Gkogkas, C. G., Khoutorsky, A., Ran, I., Rampakakis, E., Nevarko, T., Weatherill, D. B., et al. (2013). Autism-related deficits via dysregulated eIF4E-dependent translational control. Nature 493, 371–377. doi: 10.1038/nature11628
Grove, M., Demyanenko, G., Echarri, A., Zipfel, P. A., Quiroz, M. E., Rodriguiz, R. M., et al. (2004). ABI2-deficient mice exhibit defective cell migration, aberrant dendritic spine morphogenesis, and deficits in learning and memory. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 10905–10922. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10905-10922.2004
Han, K., Chen, H., Gennarino, V., Richman, R., Lu, H.-C. C., and Zoghbi, H. Y. (2015). Fragile X-like behaviors and abnormal cortical dendritic spines in cytoplasmic FMR1-interacting protein 2-mutant mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 1813–1823. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu595
He, X., Sanders, S. J., Liu, L., de, S., Lim, E. T., Sutcliffe, J. S., et al. (2013). Integrated model of De novo and inherited genetic variants yields greater power to identify risk genes. PLoS Genet. 9:e1003671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003671
Hirvikoski, T., Mittendorfer-Rutz, E., Boman, M., Larsson, H., Lichtenstein, P., and Bölte, S. (2016). Premature mortality in autism spectrum disorder. Br. J. Psychiatr. J. Mental Sci. 208, 232–238. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.114.160192
Iossifov, I., O’Roak, B. J., Sanders, S. J., Ronemus, M., Krumm, N., Levy, D., et al. (2014). The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 515, 216–221. doi: 10.1038/nature13908
Klemz, A., Kreis, P., Eickholt, B. J., and Gerevich, Z. (2021). The actin binding protein drebrin helps to protect against the development of seizure-like events in the entorhinal cortex. Sci. Rep. 11:8662. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87967-5
Korobova, F., and Svitkina, T. (2010). Molecular architecture of synaptic actin cytoskeleton in hippocampal neurons reveals a mechanism of dendritic spine morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 165–176. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-07-0596
Krause, M., Dent, E. W., Bear, J. E., Loureiro, J. J., and Gertler, F. B. (2003). Ena/VASP proteins: regulators of the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19, 541–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.050103.103356
Lalonde, R., and Strazielle, C. (2011). Brain regions and genes affecting limb-clasping responses. Brain Res. Rev. 67, 252–259. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2011.02.005
Lee, E., Lee, J., and Kim, E. (2017). Excitation/inhibition imbalance in animal models of autism Spectrum disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 81, 838–847. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.05.011
Lukmanji, S., Manji, S. A., Kadhim, S., Sauro, K. M., Wirrell, E. C., Kwon, C.-S., et al. (2019). The co-occurrence of epilepsy and autism: a systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 98, 238–248. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.07.037
Mademan, I., Deconinck, T., Dinopoulos, A., Voit, T., Schara, U., Devriendt, K., et al. (2013). De novo INF2 mutations expand the genetic spectrum of hereditary neuropathy with glomerulopathy. Neurology 81, 1953–1958. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000436615.58705.c9
McCarroll, S. A., and Hyman, S. E. (2013). Progress in the genetics of polygenic brain disorders: significant new challenges for neurobiology. Neuron 80, 578–587. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.046
Michaelsen, K., Murk, K., Zagrebelsky, M., Dreznjak, A., Jockusch, B. M., Rothkegel, M., et al. (2010). Fine-tuning of neuronal architecture requires two profilin isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 15780–15785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004406107
Miguel-Ruiz, J. E. S., and Letourneau, P. C. (2014). The role of Arp2/3 in growth cone actin dynamics and guidance is substrate dependent. J. Neurosci. 34, 5895–5908. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0672-14.2014
Moy, S. S., Nadler, J. J., Young, N. B., Perez, A., Holloway, L. P., Barbaro, R. P., et al. (2007). Mouse behavioral tasks relevant to autism: phenotypes of 10 inbred strains. Behav. Brain Res. 176, 4–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.07.030
Murk, K., Wittenmayer, N., Michaelsen-Preusse, K., Dresbach, T., Schoenenberger, C.-A., Korte, M., et al. (2012). Neuronal profilin isoforms are addressed by different signalling pathways. PLoS One 7:e34167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034167
Nakashima, M., Kato, M., Aoto, K., Shiina, M., Belal, H., Mukaida, S., et al. (2018). De novo hotspot variants in CYFIP2 cause early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 83, 794–806. doi: 10.1002/ana.25208
Nakayama, A. Y., Harms, M. B., and Luo, L. (2000). Small GTPases Rac and rho in the maintenance of dendritic spines and branches in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 5329–5338. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-14-05329.2000
Neale, B. M., Kou, Y., Liu, L., Ma’ayan, A., Samocha, K. E., Sabo, A., et al. (2012). Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 485, 242–245. doi: 10.1038/nature11011
Oguro-Ando, A., Rosensweig, C., Herman, E., Nishimura, Y., Werling, D., Bill, B. R., et al. (2015). Increased CYFIP1 dosage alters cellular and dendritic morphology and dysregulates mTOR. Mol. Psychiatry 20, 1069–1078. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.124
Ohnami, S., Endo, M., Hirai, S., Uesaka, N., Hatanaka, Y., Yamashita, T., et al. (2008). Role of RhoA in activity-dependent cortical axon branching. J. Neurosci. 28, 9117–9121. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1731-08.2008
Omotade, O. F., Pollitt, S. L., and Zheng, J. Q. (2017). Actin-based growth cone motility and guidance. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 84, 4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2017.03.001
Pathania, M., Davenport, E. C., Muir, J., Sheehan, D. F., López-Doménech, G., and Kittler, J. T. (2014). The autism and schizophrenia associated gene CYFIP1 is critical for the maintenance of dendritic complexity and the stabilization of mature spines. Transl. Psychiatry 4:e374. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.16
Paul, A. S., and Pollard, T. D. (2009). Review of the mechanism of processive actin filament elongation by formins. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 66, 606–617. doi: 10.1002/cm.20379
Peça, J., Feliciano, C., Ting, J. T., Wang, W., Wells, M. F., Venkatraman, T. N., et al. (2011). Shank3 mutant mice display autistic-like behaviours and striatal dysfunction. Nature 472, 437–442. doi: 10.1038/nature09965
Peng, J., Wang, Y., He, F., Chen, C., Wu, L.-W., Yang, L.-F., et al. (2018). Novel west syndrome candidate genes in a Chinese cohort. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 24, 1196–1206. doi: 10.1111/cns.12860
Pilo Boyl, P., di, A., Mulle, C., Sassoè-Pognetto, M., Panzanelli, P., Mele, A., et al. (2007). Profilin2 contributes to synaptic vesicle exocytosis, neuronal excitability, and novelty-seeking behavior. EMBO J. 26, 2991–3002. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601737
Pollard, T. D. (2007). Regulation of actin filament assembly by Arp2/3 complex and formins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 36, 451–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.101936
Rubenstein, J. L. R., and Merzenich, M. M. (2003). Model of autism: increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2, 255–267. doi: 10.1034/j.1601-183X.2003.00037.x
Sanders, S. J., Murtha, M. T., Gupta, A. R., Murdoch, J. D., Raubeson, M. J., Willsey, A. J., et al. (2012). De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism. Nature 485, 237–241. doi: 10.1038/nature10945
Satterstrom, F. K., Kosmicki, J. A., Wang, J., Breen, M. S., de, S., An, J.-Y., et al. (2020). Large-scale exome sequencing study implicates both developmental and functional changes in the neurobiology of autism. Cell 180, 568–584. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.12.036
Scattoni, M. L., Crawley, J., and Ricceri, L. (2009). Ultrasonic vocalizations: a tool for behavioural phenotyping of mouse models of neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 33, 508–515. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.08.003
Schmeisser, M. J., Ey, E., Wegener, S., Bockmann, J., Stempel, A. V., Kuebler, A., et al. (2012). Autistic-like behaviours and hyperactivity in mice lacking ProSAP1/Shank2. Nature 486, 256–260. doi: 10.1038/nature11015
Skefos, J., Cummings, C., Enzer, K., Holiday, J., Weed, K., Levy, E., et al. (2014). Regional alterations in Purkinje cell density in patients with autism. PLoS One 9, 1–12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081255
Smith, B. N., Vance, C., Scotter, E. L., Troakes, C., Wong, C. H., Topp, S., et al. (2015). Novel mutations support a role for profilin 1 in the pathogenesis of ALS. Neurobiol. Aging 36:1602. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.10.032
Soderling, S. H., Langeberg, L. K., Soderling, J. A., Davee, S. M., Simerly, R., Raber, J., et al. (2003). Loss of WAVE-1 causes sensorimotor retardation and reduced learning and memory in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 1723–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0438033100
Spillane, M., Ketschek, A., Jones, S. L., Korobova, F., Marsick, B., Lanier, L., et al. (2011). The actin nucleating Arp2/3 complex contributes to the formation of axonal filopodia and branches through the regulation of actin patch precursors to filopodia. Dev. Neurobiol. 71, 747–758. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20907
Stürner, T., Tatarnikova, A., Mueller, J., Schaffran, B., Cuntz, H., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Transient localization of the Arp2/3 complex initiates neuronal dendrite branching in vivo. Development 146:dev171397. doi: 10.1242/dev.171397
Sugimori, M., and Llinás, R. R. (1990). Real-time imaging of calcium influx in mammalian cerebellar Purkinje cells in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 87, 5084–5088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5084
Tsai, P. T., Hull, C., Chu, Y., Greene-Colozzi, E., Sadowski, A. R., Leech, J. M., et al. (2012). Autistic-like behaviour and cerebellar dysfunction in Purkinje cell Tsc1 mutant mice. Nature 488, 647–651. doi: 10.1038/nature11310
Witke, W., Podtelejnikov, A. V., Di Nardo, A., Sutherland, J. D., Gurniak, C. B., Dotti, C., et al. (1998). In mouse brain profilin I and profilin II associate with regulators of the endocytic pathway and actin assembly. EMBO J. 17, 967–976. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.4.967
Woolfenden, S., Sarkozy, V., Ridley, G., Coory, M., and Williams, K. (2012). A systematic review of two outcomes in autism spectrum disorder – epilepsy and mortality. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 54, 306–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04223.x
Wu, C.-H., Fallini, C., Ticozzi, N., Keagle, P. J., Sapp, P. C., Piotrowska, K., et al. (2012). Mutations in the profilin 1 gene cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 488, 499–503. doi: 10.1038/nature11280
Yan, Z., Kim, E., Datta, D., Lewis, D. A., and Soderling, S. H. (2016). Synaptic actin dysregulation, a convergent mechanism of mental disorders? J. Neurosci. 36, 11411–11417. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2360-16.2016
Yerger, J., Cougnoux, A. C., Abbott, C. B., Luke, R., Clark, T. S., Cawley, N. X., et al. (2022). Phenotype assessment for neurodegenerative murine models with ataxia and application to Niemann-pick disease, type C1. Biol. Open 11:bio059052. doi: 10.1242/bio.059052
Zhou, K., Chen, J., Wu, J., Xu, Y., Wu, Q., Yue, J., et al. (2019). Profilin 2 promotes proliferation and metastasis of head and neck Cancer cells by regulating PI3K/AKT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Res. Featuring Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 27, 1079–1088. doi: 10.3727/096504019X15579146061957
Keywords: profilin 2, glutamatergic neuron hyperactivity, excitation/inhibition balance, autism spectrum disorder, seizures
Citation: Witke W, Di Domenico M, Maggi L, Di Nardo A, Stein V and Pilo Boyl P (2025) Autism spectrum disorder related phenotypes in a mouse model lacking the neuronal actin binding protein profilin 2. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 19:1540989. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1540989
Received: 06 December 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Heiko J. Luhmann, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, GermanyReviewed by:
Shatabdi Bhattacharjee, Georgia State University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Witke, Di Domenico, Maggi, Di Nardo, Stein and Pilo Boyl. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pietro Pilo Boyl, cGlldHJvLnBpbG9ib3lsQHVuaS1ib25uLmRl
†Present address: Marina Di Domenico, European Brain Research Institute-Fondazione Rita Levi Montalcini, Rome, Italy
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.