
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell. Neurosci., 07 April 2025
Sec. Cellular Neuropathology
Volume 19 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2025.1536028
This article is part of the Research TopicCurrent Topics of Stem Cells and Cell Derivations to Treat Central Nervous System InjuryView all 3 articles
Stroke is characterized with high morbidity, mortality and disability all over the world, and one of its core pathologies is blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction. BBB plays a crucial physiological role in protecting brain tissues and maintaining homeostasis in central nervous system (CNS). BBB dysfunction serves as a key factor in the development of cerebral edema, inflammation, and further neurological damage in stroke patients. Currently, stem cells and their derived exosomes have shown remarkable potential in repairing the damaged BBB and improving neurological function after stroke. Stem cells repair the integrity of BBB through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, angiogenesis and regulation of intercellular signaling mechanisms, while stem cell-derived exosomes, as natural nanocarriers, further enhance the therapeutic effect by carrying active substances such as proteins, RNAs and miRNAs. This review will present the latest research advances in stem cells and their exosomes in stroke treatment, as well as the challenges of cell source, transplantation timing, dosage, and route of administration in clinical application, aiming to discuss their mechanisms of repairing BBB integrity and potential for clinical application, and proposes future research directions. Stem cells and exosomes are expected to provide new strategies for early diagnosis and precise treatment of stroke, and promote breakthroughs in the field of stroke.
Stroke refers to an acute disease in which blood flowing to the brain is disrupted due to sudden rupture or blockage of cerebral blood vessels, which can induce death of brain cells and damage to brain tissue. It can be categorized into ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke (Campbell and Khatri, 2020). As reported by the World Health Organization, stroke is recognized as the third leading cause of mortality on a global scale and is among the most significant contributors to prolonged disability. As indicated by data from 2024, approximately 795,000 patients have strokes annually, including around 610,000 with initial attacks and 185,000 with recurrent strokes (Martin et al., 2024). Stroke is more common in aged people, with the greatest incidence observed in individuals aged 65 and above. As the global population continues to age, stroke is expected to show a rising incidence, posing considerable strain on public health and healthcare systems.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) serves as a permeability barrier composed mainly of brain microvascular endothelial cells, astrocytes, pericytes, and basement membranes. Primarily, it safeguards the brain from detrimental substances while maintaining the stability of the intracerebral environment. Upon an occurrence of a stroke, the integrity of the BBB is compromised, resulting in augmented extracellular fluid exudate and an intensified inflammatory response, which further exacerbates the neurological damage (Ghori et al., 2022). Disruption of the BBB has been demonstrated to be closely associated with the prognosis of stroke (Ng et al., 2022), and restoring the function of BBB is deemed as a pivotal strategy for improving the prognosis of stroke patients.
Stem cells, with advanced self-renewal capacity and multidirectional differentiation potential, have been extensively utilized in regenerative medicine and tissue repair recently. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles, with diameters of about 30–150 nm, and are secreted by stem cells. They are capable of carrying various bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, and participate in intercellular signaling and material exchange (Rashed et al., 2017). Stem cell-derived exosomes exhibit a potential application in playing neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative effects, particularly in the context of stroke treatment. In this regard, stem cell-derived exosomes may promote the repair of neurological injury by modulating the function of BBB (Jian et al., 2019).
Despite stem cell transplantation has demonstrated a certain degree of safety, its efficacy is still not fully validated. Stem cell therapy faces several challenges, such as choice of cell source, timing of transplantation, dosage, and route of administration, all of which can impact final therapeutic outcomes (Park et al., 2020; Anthony et al., 2022; Wang Y. et al., 2024). As a developing therapeutic strategy, the mechanisms through which stem cells and exosomes function are not entirely understood, and there are ongoing issues related to standardizing their production and targeted delivery methods (Li et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022). In addition, the lack of sufficiently large-scale randomized controlled trials during the clinical testing phase raises concerns about the real-world effectiveness of these therapies (Chen et al., 2024). While stem cells and their derived exosomes show potential for treating stroke, they still face various challenges, including uncertainties about their efficacy, complexities in the production process, and standardization issues in clinical applications. Therefore, this article intends to provide a review of literature on stroke associated BBB studies and to examine the potential therapeutic role of stem cells and their exosomes on stroke, and then summarize the current research progress and propose the future research directions.
Ischemic stroke represents the most prevalent form of stroke, constituting 62.4% of all new stroke cases globally in 2019, as reported by the 2019 GBD study (Martin et al., 2024). The etiology of ischemic stroke is predominantly attributed to a decrease or cessation of cerebral blood flow, often precipitated by the narrowing or occlusion of blood vessels resulting from thrombosis or atherosclerosis. The TOAST classification system further categorizes ischemic stroke into various sub-types, including large-artery atherosclerosis, cardiac embolism, small-vessel occlusion, acute stroke of other determined etiology, and stroke of undetermined etiology (Adams et al., 1993).
In the context of ischemic stroke, the onset of hypoxia precipitates a disruption in cellular metabolism, culminating in cellular death and subsequent brain tissue damage. The pathogenesis of ischemic stroke is associated with a variety of factors, including vascular endothelial dysfunction, inflammatory response, and changes in blood rheology. Within 24 h of the onset of ischemia, brain tissues exhibit a substantial inflammatory response, accompanied by a significant escalation in pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, such as IL-1β and TNF-α, which further exacerbate brain injury (Ramiro et al., 2018). Ischemic stroke also triggers oxidative stress, which leads to the production of free radicals that damage cell membranes and DNA, thereby exacerbating cell death (Allen and Bayraktutan, 2009). Furthermore, research has identified a correlation between blood biomarkers, such as D-dimer and C-reactive protein, in patients with ischemic strokes and the underlying mechanisms of stroke. These biomarkers have been shown to be indicative of the pathophysiological status of different ischemic strokes (Katan and Elkind, 2018).
The classification of hemorrhagic stroke principally encompasses two distinct categories: intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). According to the 2019 GBD study, ICH accounts for 27.9%, and SAH accounts for 9.7% (Martin et al., 2024). ICH is defined as the accumulation of blood in the brain tissue, with underlying causes including high blood pressure, ruptured cerebral aneurysms, and blood disorders. SAH, characterized by the entry of blood into the subarachnoid space of the meninges, is typically caused by a ruptured aneurysm. Research has demonstrated that patients afflicted with hemorrhagic stroke frequently exhibit a suboptimal prognosis and an elevated risk of recurrence. Consequently, the timely identification and management of risk factors are of paramount importance (Banerjee et al., 2020; Williams et al., 2023).
With regard to the underlying mechanisms, the occurrence of ICH is typically accompanied by the rupture of blood vessels and the leakage of blood, resulting in direct and secondary damage to brain tissue. Following the hemorrhage, the formation of a hematoma results in an increase in local pressure. The hemoglobin breakdown products within the hematoma can trigger secondary injury, leading to ischemia and cerebral edema in the surrounding brain tissue (Chen et al., 2021). Concurrent studies have demonstrated a close correlation between the activation of inflammatory responses and neuronal death, with the subsequent release of inflammatory mediators exacerbating brain injury (Dong et al., 2024).
Significant disparities in the incidence and clinical manifestation of stroke have been observed between sexes. Research has demonstrated that the overall incidence of stroke is consistently higher in males compared to females, particularly within younger and middle-aged demographics (Thomas et al., 2021). However, hormonal changes after menopause significantly increase the risk of stroke in women, and common risk factors such as hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and diabetes mellitus are more prevalent in women (Wassertheil-Smoller et al., 2003). Women have been shown to have a more unfavorable stroke prognosis, as indicated by higher mortality and functional impairment rates (Branyan and Sohrabji, 2020). This may be attributable to a number of factors, including their advanced age at the time of onset, the presence of more concomitant illnesses, and the tendency to present with more atypical symptoms compared to men, which can result in delays in diagnosis and treatment. Consequently, there is an imperative to comprehend gender-related disparities to facilitate the development of customized prevention and treatment strategies for diverse patient populations.
The incidence of stroke also varies significantly across age groups. Research has demonstrated a positive correlation between age and stroke incidence, with a notable surge observed among individuals aged 65 and above. According to the 2019 data, the age distribution of stroke shows a significant peak, concentrated in the 70+ age group, where the incidence is generally higher in men than in women (GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators, 2021). Although stroke incidence is lower in younger individuals (under 50 years of age), recent studies have documented an increase in stroke events in this demographic due to lifestyle changes and an elevated risk profile (Ekker et al., 2018). This distribution pattern underscores the necessity for the development of suitable prevention and intervention strategies that are tailored to address the shifting stroke incidence across diverse age groups.
Animal models play a critical role in ischemic stroke research because of their ability to mimic the physiological and pathological features of human stroke (Figure 1). Transient or permanent intraluminal lesion occlusion, middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and thromboembolic models are the most commonly used models to simulate human ischemic stroke. These models can effectively reproduce the major physiological changes and pathological processes of ischemic stroke. MCAO models are the main models used to study ischemic stroke, and studies have shown that they can be used not only to evaluate the efficacy of new therapies, but also to study the mechanisms of neuroprotection after stroke (Li and Zhang, 2021). The reproducibility and controllability of the MCAO model make it an important tool for drug screening and mechanistic studies. The reproducibility and controllability of the MCAO model make it an important tool for drug screening and mechanistic studies. In recent years, researchers have optimized the model, such as using microcatheter technology for local embolization, to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of the model (Komatsu et al., 2021). In addition to the commonly used rodents, larger animal models such as pigs and non-human primates have been used in ischemic stroke research, which are considered more clinically relevant due to the similarity of their brain structure to humans and are better able to mimic the pathophysiology of stroke in humans (Taha et al., 2022). Using these animal models, researchers can explore new therapeutic strategies for ischemic stroke and evaluate the safety and efficacy of drugs, thereby advancing translational clinical research.
Hemorrhagic stroke research also relies on animal models, particularly to study the pathological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of hemorrhagic stroke. Common animal models include spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage models, collagenase-induced hemorrhage models, and blood injection models that mimic the pathology of human hemorrhagic stroke (Chen et al., 2021; Li and Zhang, 2021). Studies have shown that the use of these models can be effective in evaluating the potential of novel drugs to reduce post-hemorrhagic brain injury and improve functional outcomes. In addition, alterations in the microenvironment after hemorrhagic stroke have been found to be closely related to the inflammatory response, providing new ideas for the development of novel therapies (Harjunpää et al., 2024). Through in-depth study of animal models, scientists can better understand the mechanism of hemorrhagic stroke and provide a theoretical basis for clinical treatment.
The development of in vitro models has provided another effective tool for preclinical stroke research, and the combination of cellular models and in vitro experiments is playing an increasingly important role in stroke research. In recent years, advances in cell culture technology, particularly the advent of three-dimensional cell culture systems, have allowed researchers to better mimic the in vivo microenvironment and thus improve the prediction of drug responses. Using human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived organoid models, researchers can recapitulate the pathological features of neurodegenerative diseases in vitro to assess the efficacy and safety of new drugs. These models allow researchers to study cellular responses to ischemia and hemorrhage in a controlled environment, providing insight into the mechanisms of stroke (Pang et al., 2024). In vitro culture models of human neurons or glial cells can be used to simulate physiological changes in cells after ischemia or hemorrhage and to assess the effects of drugs on cell survival and function. In addition, the combination of using co-culture models of multiple cell types can better simulate the microenvironment in the brain and help to study cell-cell interactions and their role in stroke (Song et al., 2021). This combination of cellular modeling and in vitro experiments not only improves the reproducibility and reliability of studies, but also provides an important experimental basis for the development of new therapies and advances in stroke research (Van Breedam and Ponsaerts, 2022). Despite the advantages of in vitro models, they are still not a complete replacement for animal models because the in vitro environment cannot fully mimic the complex cellular interactions and signaling that occur under physiological conditions (Peng et al., 2021).
After ischemic stroke occurs, activation of the complement system can lead to a series of inflammatory responses that further exacerbate brain tissue damage. Excessive activation of complement leads to disruption of the blood-brain barrier, further exacerbating neuronal damage and death. The levels of complement components such as C3 and C5 are significantly elevated after ischemia, which enhances the local inflammatory response by promoting the infiltration and activation of inflammatory cells (Ma et al., 2019). C3a and C5a, as the key effectors of complement activation, are able to induce the activation of microglia and promote the release of inflammatory factors, which aggravate the brain tissue injury and attract more immune cells to reach the injury site (Ahmad et al., 2019; Couch et al., 2023).
After the onset of hemorrhagic stroke, the activation of complement can exacerbate the inflammatory response and cerebrovascular permeability, which can lead to the exacerbation of secondary brain damage. Elevated complement component C4 is strongly correlated with the severity of neurological deficits, suggesting that complement may serve as a biomarker for prognostic assessment in hemorrhagic stroke (Wu et al., 2023). Complement activation has also been associated with the formation of perihematomal edema, which is considered to be one of the important factors in the poor prognosis after hemorrhagic stroke (Hatchell et al., 2023).
The complement system plays an important role in nerve injury by regulating apoptosis, affecting blood-brain barrier integrity, and promoting axonal remodeling. Complement activation leads to an increased inflammatory response in neuronal cells, releasing a variety of proinflammatory factors that bind to specific receptors, promoting microglia activation, increasing neuroinflammatory responses, and ultimately leading to neuronal apoptosis (Kakarla et al., 2021). Elevated levels of complement cleavage products, such as C3a and C5a, are directly proportional to the degree of disruption of the blood-brain barrier, and inhibition of complement can significantly reduce the extent of blood-brain barrier damage and inflammatory response, and improved neurological function (Holste et al., 2021). Complement components C1q and C3 play a facilitating role in axonal remodeling and influence neural repair and regeneration (Kanmogne and Klein, 2021). Thus, regulation of the complement system may provide new strategies for the treatment of nerve injury.
There is a complex interaction between the complement system and inflammatory factors. Complement component C1 inhibitors and other anti-inflammatory factors can inhibit excessive inflammatory responses after ischemia and promote tissue repair and regeneration (Ma et al., 2019). Activation of complement components C3 and C5 can stimulate macrophages and other immune cells to release pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn promote further complement activation. While the production of C3a and C5a promotes the infiltration of inflammatory cells, they can also play an anti-inflammatory role by modulating the polarization state of macrophages and promoting the production of M2-type macrophages (Alawieh et al., 2020). This interaction is not only significant in the acute phase, but may also play an important role in the recovery process after stroke, affecting the ability of nerve repair and regeneration.
Existing treatment strategies for hemorrhagic stroke, current treatment strategies mainly include measures such as surgery to control bleeding and reduce intracranial pressure. The complexity of the surgery and the overall health status of the patient also affects the outcome of postoperative recovery, and some patients may face a higher risk of mortality and complications after surgery (Al-Kawaz et al., 2020). In ischemic stroke the main reliance is on thrombolytic therapy and mechanical retrieval of thrombus. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA), is now widely recognized as a thrombolytic therapy treatment. Thrombolysis works best usually within 3–4.5 h of symptom onset (Wang et al., 2019). Prompt thrombolysis significantly reduces patient disability and mortality. Beyond this time window, treatment is significantly less effective and may even lead to greater risk (Bangad et al., 2023; Jazayeri et al., 2024). Mechanical thrombectomy provides a better treatment option for patients with large vessel occlusions, but its effectiveness also decreases over time (Albers et al., 2021; Yeo et al., 2021). In addition, anticoagulants in the available pharmacological treatments may have bleeding complications in some patients, especially in high-risk patients, while others may fail to achieve the desired anticoagulant effect (Huang et al., 2015; Paciaroni et al., 2015).
These traditional therapies often only address the symptoms and fail to repair the damaged nerve tissue at the root of the problem, and may be accompanied by certain side effects, which makes it especially important to find new treatments. Stem cell therapy has achieved favorable results in preclinical and early clinical studies by promoting nerve regeneration, inhibiting inflammatory response and improving blood supply, among other mechanisms. Therefore, incorporating stem cell and exosome therapies into the comprehensive treatment program of stroke can bring new hope and better therapeutic results for patients.
Although the pathophysiological mechanisms of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke are different, both emphasize the importance of dysregulated cellular signaling pathways in stroke pathogenesis. In the study of these signaling pathways, it has been found that various factors including inflammatory response, oxidative stress, apoptosis, neuronal regeneration and excitotoxicity are closely related to post-stroke dysfunction and BBB damage. These signaling pathways are not only intertwined, but may also exhibit different functions at different time points after stroke. Specific details are shown in the table below (Table 1). How effectively these signaling pathways are regulated in future research and clinical interventions will be key to improving prognosis after stroke.
Blood-brain barrier is a natural barrier between the brain and circulatory system. BBB is composed of tightly connected endothelial cells, basement membranes, pericytes, and peduncles of astrocytes, forming a complex and highly regulated system. The primary function of BBB is to modulate the flow of substances into and out of the brain, safeguard the central nervous system (CNS) from harmful substances, and permit the passage of essential nutrients and metabolites. As report, BBB is the largest interface for molecular blood-brain exchange (Nag and Begley, 2005). BBB integrity is of paramount importance for maintaining normal functions of nervous system. On the other hand, damaged structure and impaired function of BBB can result in neuronal damage and neurological dysfunction.
Tight junctions in brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) are protein complexes that facilitate the adhesion of neighboring barrier cells. Based on subcellular localization, tight junctions can be categorized into transmembrane proteins and cytoplasmic proteins. Tight junction transmembrane proteins between neighboring cells bind to each other through extracellular loops, forming a “zipper” structure that closes the paracellular gap. Cytoplasmic proteins, on the other hand, act as bridges connecting transmembrane proteins and cytoskeletal proteins, forming a complete meshwork that provides structural support for maintaining BBB integrity. The BBB achieves its selective permeability through tight junctions among barrier cells, thereby influencing exchange of substances between blood and cerebrospinal fluid (Banks et al., 2021). Furthermore, absence of pericytes results in the loss of BBB integrity during embryogenesis (Daneman et al., 2010). Laminin in astrocytes regulates pericyte differentiation and maturation and induces/maintains tight junction protein expression in endothelial cells, thereby promoting BBB integrity (Yao et al., 2014). The interaction between pericytes and astrocytes stabilizes the function of BBB and greatly contributes to maintaining BBB integrity.
The mechanism of BBB injury at the onset of stroke is multifactorial, involving neuroinflammatory responses, oxidative stress, cytokine release, and apoptosis (Figure 2).
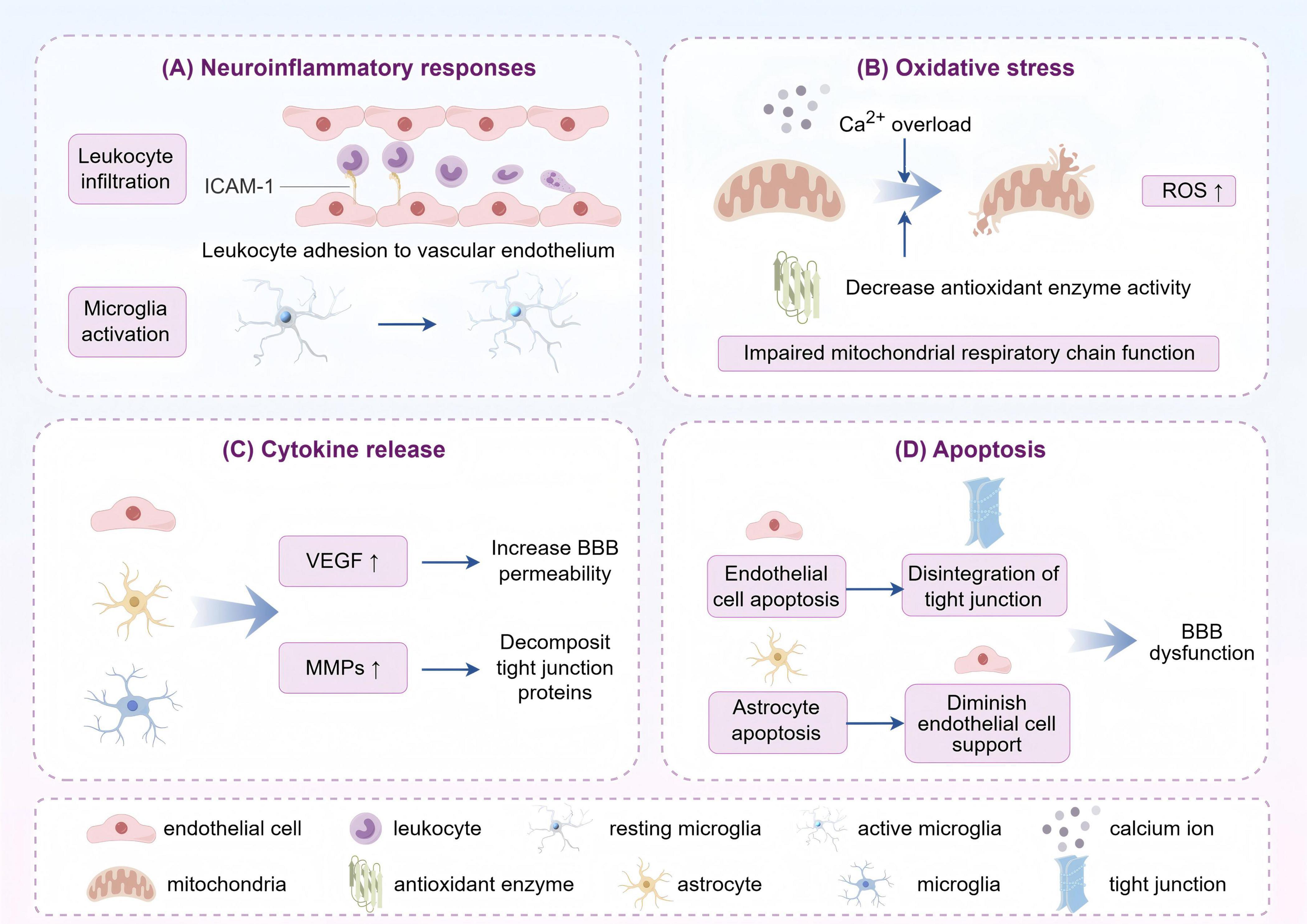
Figure 2. The primary mechanisms of post-stroke blood-brain barrier (BBB) impairment can be categorized as follows: (A) Inflammatory response: leukocyte infiltration and microglia activation after stroke release inflammatory mediators that damage the endothelial cells and tight junctions of the BBB and increase its permeability. (B) Oxidative stress: stroke leads to impaired energy metabolism in the brain, elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and impaired antioxidant defense system. ROS attack the components of the BBB, destroying its structure and function. (C) Cytokine release: after stroke, cytokines such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are released, the former activating relevant receptors to open tight junctions, and the latter degrading extracellular matrix and tight junction proteins to disrupt the integrity of the BBB. (D) Apoptosis: stroke-induced factors induce apoptosis or abnormal function of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells and astrocytes, leading to structural disintegration and destabilization of the BBB (by Figdraw).
In the aftermath of a stroke, structure and function of BBB change substantially, predominantly manifested as decreased expression of tight junctions and an augmentation in permeability of endothelial cells. During the acute phase of ischemia, microglia are activated to secrete cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which further exacerbate the destruction of BBB (Guo et al., 2023). Furthermore, neuronal hypoxia and metabolic imbalance impair the function of endothelial cells, which aggravates BBB dysfunction and promotes the formation of brain edema. For example, after acute ischemic stroke, inadequate O2 delivery will occur due to insufficient blood flow, which in turn leads to ATP deficiency and ion transport dysfunction, thereby causing excessive glutamate release and contributing to astrocyte swelling (Sun et al., 2019). Meanwhile, intracellular Ca2+ overload induces mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction, allowing a rapid increase in reactive oxygen species, which swiftly inhibits antioxidant defenses and give rise to further tissue damage (Rodrigo et al., 2013; Jiang et al., 2018). BBB disruption can give profound influence on neurological function. Accordingly, safeguarding the structural integrity and function of BBB represents a crucial strategy for enhancing stroke prognosis and facilitating neurological recovery (Guo et al., 2023).
Blood-brain barrier damage after ischemic stroke is usually a gradual process, whereas hemorrhagic stroke can cause significant damage in a short period of time. After hemorrhagic stroke, local inflammation and cellular damage due to direct entry of blood components into brain tissue and hematoma formation further exacerbate BBB destruction, leading to more severe cerebral edema and neurological deficits (Shtaya et al., 2021). As the hematoma expands, the release of hemoglobin and other blood components triggers a strong local inflammatory response that further activates microglia and other immune cells, releasing large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines that lead to endothelial cell apoptosis and an increase in blood-brain barrier permeability, resulting in increased cerebral edema and neuronal cell death, and ultimately affecting the neurological recovery of the patient (Alsbrook et al., 2023).
Stem cells have achieved extensive utilization in medicine, including regenerative medicine, tissue engineering and the disease treatment which are currently attracting significant attention in modern medical science due to their promising potential. According to their origin, stem cells can be categorized into embryonic stem cells (ESC), mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), neural stem cells (NSC), hematopoietic stem cells, and so on. Each type of stem cell differs in biological properties, application potential and clinical prospects (Figure 3). The capacity of stem cells to self-renew and differentiate in multiple directions makes them well-suited to replacing damaged or dead neurons, secreting neurotrophic factors, regulating immune responses, and promoting endogenous neurogenesis, thereby improving pathological conditions. In recent years, there have been notable successes in utilizing stem cell therapy in CNS-related diseases (Ying et al., 2023). To illustrate, MSCs have been demonstrated to effectively inhibit ferroptosis and facilitate functional recovery following spinal cord injury through mitochondrial transfer, exhibiting robust regenerative capacity and safety (Yao et al., 2023). Furthermore, research on using stem cells to treat neurodegenerative diseases and traumatic brain injury is advancing, with numerous trials yielding positive outcomes (Sivandzade and Cucullo, 2021; Zhou et al., 2024). Despite the promising outlook for stem cell therapy, it is still confronted with significant challenges, including ethical concerns, the standardization of cell sources, and the long-term safety of the therapy (Nazim and Ahmad, 2023).
Exosomes are nanosized vesicles secreted by cells, usually between 30 and 150 nm in diameter, and are widely found in a variety of biological fluids. These tiny vesicles contain biologically active molecules such as proteins, lipids, and RNA. Their specific markers include transmembrane proteins (CD9, CD63, CD81) and heat shock proteins (HSP70). In consideration of their pivotal function in intercellular communication, exosomes can transmit information and regulate the function of target cells (Bebelman et al., 2018). Exosomes were firstly introduced in the early 1980s, with the description of small vesicles formed during the maturation of reticulocytes. These vesicles were proposed to play a role in selective externalization and removal of transferrin receptors (Pan and Johnstone, 1983; Johnstone et al., 1987). These years, exosomes are recognized to serve as carriers that facilitate intercellular communication through exchange of proteins and genetic material. The intrinsic characterizations of exosomes in regulating various intracellular pathways enhance their use in therapeutics in tumors, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative diseases (Katakowski et al., 2013; Perets et al., 2019; Chen H.-X. et al., 2020; Zhong et al., 2023). Through rigorous scientific inquiry into exosomes, researchers aspire to devise innovative therapeutic strategies leveraging these naturally occurring nanoscale carriers. Strategies for exosome isolation mainly include ultracentrifugation (the most commonly used), gel filtration, magnetic bead method, etc. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of purity, yield, and operational complexity, and the appropriate method needs to be selected according to the research needs (Figure 4). However, the complex heterogeneity of exosomes and the standardization of isolation and purification techniques still require further investigation to facilitate their clinical utilization (Li et al., 2017; Vargas-Rodríguez et al., 2023; Yang H. et al., 2023). The composition of exosomes has been demonstrated to vary depending on the state of their parent cells, with those from different sources exhibiting disparate biological effects (Théry et al., 2002). This article will focus on the role of stem cell-derived exosomes on BBB damage.
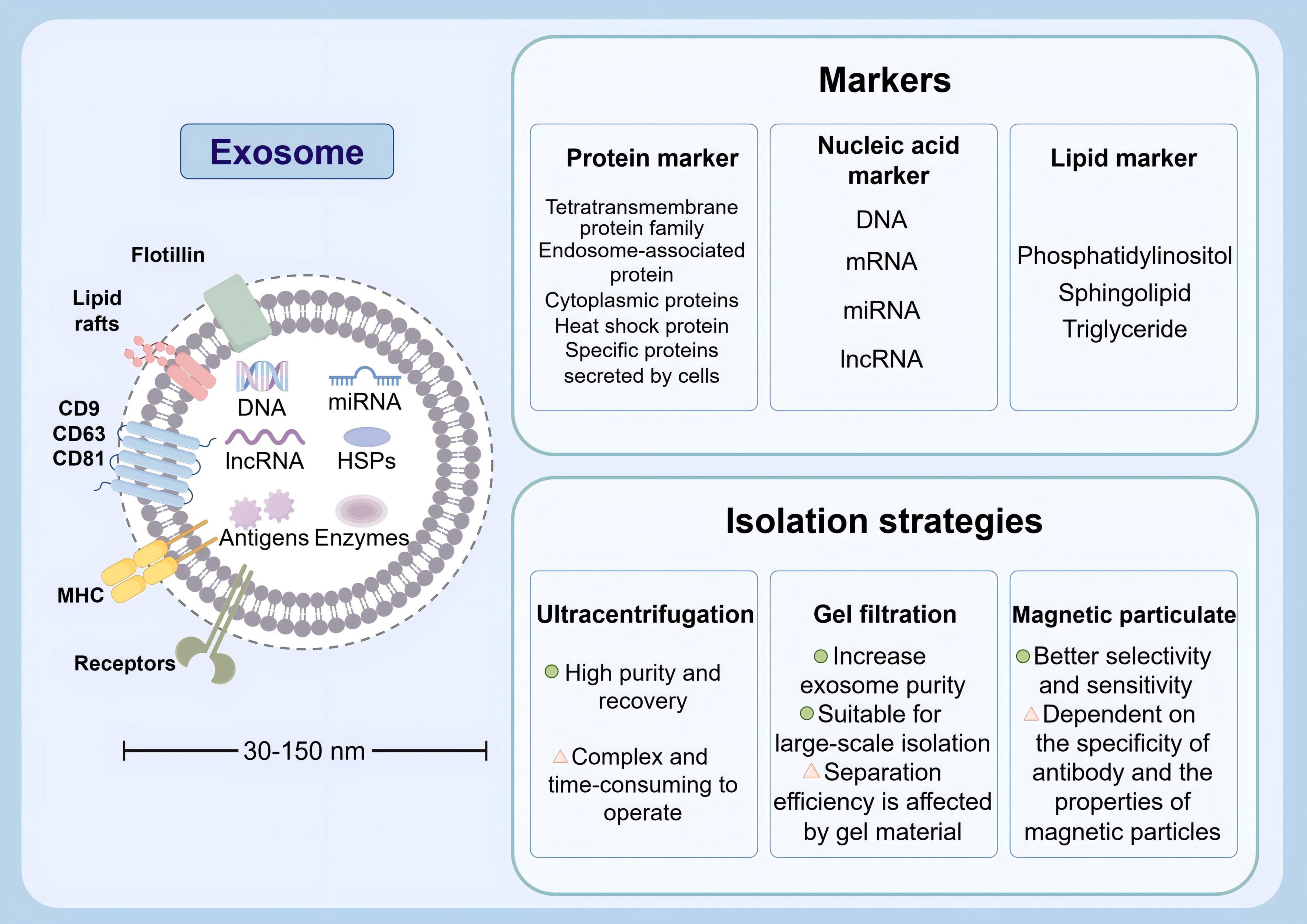
Figure 4. Physical characteristics, various markers and isolation strategies of exosomes (by Figdraw).
Using stem cells to treat stroke is emerges as a topic of growing interest in neuroscience. A substantial body of evidence from scientific studies has demonstrated that various sources of stem cells, including mesenchymal stem cells and neural stem cells, exhibit possibility to enhance neuronal repair and facilitate neurovascular repair following a stroke (Boese et al., 2020; Do et al., 2021; Hamblin and Lee, 2021; Hamblin et al., 2021; Yoshida et al., 2021; Datta et al., 2022; Kvistad et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023). These findings have been corroborated through in vivo and in vitro experimentation (Table 2).
In the context of stroke therapy, stem cells can be administrated through three routes: intravenous (IV), intra-arterial (IA), and intranasal (IN). IN route, which offers numerous advantages over the other two pathways, was firstly proposed in 2013 in research focusing on ischemic stroke (Wei et al., 2013; Table 3).
Intranasal delivery enables stem cells to traverse the olfactory epithelium and gain access to the space in close proximity to the ostium of the turbinate. Subsequently, the cells enter the subarachnoid space through an extension of the olfactory filaments as they traverse the sieve plate. The specific histological features of these nasal structures facilitate the direct entry of cells into the brain (Galeano et al., 2018; Li et al., 2022). The IN delivery is non-invasive, has relatively simple administration procedures, and will not cause additional harm to patients. Consequently, patients can tolerate high-frequency administration through IN route (Chau et al., 2018). However, the unique and complex structure of the nasal cavity, along with its blood circulation, active enzymes, and defense mechanisms, creates significant challenges for delivering drugs to the brain through IN route (Miyake and Bleier, 2015). As a result, further preclinical studies are essential to provide sufficient safety and efficacy data. This research is crucial to confirm that stem cells can effectively reach the targeted areas of the brain when administered intranasally, paving the way for future clinical trials.
In addition to their use as a therapeutic modality, human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) can be derived to mimic the characteristics of the human BBB for application in brain and organoid models. In vitro BBB modeling can reproduce both physiological and pathological states of BBB. Consequently, BBB modeling represents a valuable instrument for elucidating disease etiology and a foundation for evaluating prospective pharmaceutical agents. As a result, it has been utilized to anticipate the permeability of CNS drugs (Aday et al., 2016; Yan et al., 2021).
Human pluripotent stem cells can be differentiated into BMECs, pericytes and astrocytes, which can be jointly applied with in vitro BBB models. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)-derived BMECs exhibit a mixture of endothelial and epithelial characteristics at the transcriptional level and lack the expressions of key endothelial adhesion molecules, such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-2, which mediate the interaction between immune cells and BBB, as reported before (Nishihara et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2021). Consequently, researchers have devised the extended endothelial cell culture method (EECM) to iPSCs into BMECs with comparable morphology, barrier properties, and expression of endothelial adhesion molecules to those of primary human BMECs. BMEC-like cells reproduce numerous functional and molecular characteristics of BMECs in vivo, thus becoming a crucial instrument for elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms behind dysfunction of BBB and identifying novel therapeutic targets for BBB injury (Lippmann et al., 2020; Matsuo et al., 2023).
The iPSC-derived BBB model is a straightforward, two-dimensional structural representation of neurovascular unit (NVU) cells that does not form intricate three-dimensional structures in specific brain regions. In contrast, the microfluidic BBB-on-chip model reproduces more complex structure and function of BBB in vivo by integrating multiple iPSC-derived cells so as to simulate the multicellular structure of BBB in vitro. The model can precisely control various factors, including three-dimensional vessel-like structures, cell-cell interactions, cell-ECM interactions, substrate stiffness, and mechanical shear (Yan et al., 2021). In comparison to conventional models, it offers advantages in terms of cell permeability imaging and real-time monitoring of trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) values (Srinivasan et al., 2015). Therefore, the combination of iPSC technology with microfluidics can serve as an instrument with great promise for mechanobiological studies and drug screening.
The interaction of stem cells with the immune system of the host is of equal importance in the process of recovery from a stroke. Stem cells have the capacity to modulate the function of local immune cells and alter the composition of the immune microenvironment, thereby promoting neuroprotection and regeneration (Verma et al., 2022). MSCs are also capable of influencing the immune microenvironment by modulating the function of macrophages, promoting tissue repair and regeneration (Manneken and Currie, 2023). This remodeling of the immune microenvironment has been shown to play a pivotal role in mitigating inflammation while promoting the formation of new blood vessels and the regeneration of nerve cells, thereby leading to significant improvements in functional recovery after stroke (Dekoninck and Blanpain, 2019). These observations underscore the potential of stem cell therapy in providing novel therapeutic approaches and strategies for BBB repair following stroke.
Stem cells have been shown to modulate the inflammatory response by secreting a variety of cytokines and exosome, which are the focus of immune mechanisms that promote the repair of BBB.
Disruption of BBB is well accepted as a significant contributing factor to the damage and dysfunction of brain tissue in the aftermath of a stroke. Stem cells are capable of repairing the damaged BBB through a variety of mechanisms, primarily through anti-inflammatory effects, antioxidant effects, regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and modulation of intercellular communication.
Ischemic foci in the aftermath of an acute ischemic stroke may release a considerable number of inflammatory cytokines, the accumulation of which represents a primary trigger for the destruction of BBB. Additionally, these factors can facilitate the recruitment of peripheral neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes, which contribute to leukocyte infiltration and further promote inflammation, thereby leading to nerve damage and formation of a pro-inflammatory vicious cycle.
Numerous studies have identified mechanisms through which stem cells inhibit inflammatory responses when repairing damaged BBB tissue. The administration of human amniotic membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells has been demonstrated to dose-dependently ameliorate neurological deficits caused by cerebral infarction. This is achieved by inhibiting the conversion of inflammatory cytokines from anti-inflammatory (M2-type) to pro-inflammatory (M1-type) in combination with by reducing the disruption of BBB and apoptosis in peri-infarcted areas (Yoshida et al., 2021). The inflammatory response occurring at BBB increases the absorption of VEGF by the endothelial cells in the brain. This process not only promotes the formation of new blood vessels, known as angiogenesis, but also raises the permeability of BBB itself (Croll et al., 2004). The transplantation of MSCs through gap junction-mediated cell-cell interactions has been demonstrated to inhibit VEGF uptake by brain endothelial cells in vitro, which in turn suppressed the inflammatory response in the brain (Kikuchi-Taura et al., 2021).
The nuclear transcription factor NF-κB acts as a regulatory factor with multiple transcriptional roles in a variety of cells in brain tissue. NF-κB is activated during cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury, and the resulting NF-κB activation exacerbates cerebral ischemic injury through multiple different mechanisms, including promotion of inflammation, induction of apoptosis, and mediation of free radical damage (Huang et al., 2010). In an animal model of spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC)-secreted TSG-6 has been demonstrated to ameliorate injury of BBB by regulating activated astrocytes, which is achieved by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway (Tang et al., 2021). An investigator in 2022 initially identified that MSC treatment through IA route after stroke exerted neuroprotective effects by modulating SIRT-1-mediated NF-κB pathways to attenuate inflammatory vesicle signaling and apoptosis (Sarmah et al., 2022). Aquaporin 4 (AQP4), the primary water channel protein in the mammalian brain, is found in astrocytes throughout the central nervous system and can control neurological water homeostasis. Besides, it shows an elevated expression in cerebral ischemia (Manley et al., 2000; Verkman et al., 2017). Furthermore, the investigator observed that administration of MSCs through IA route could modulate AQP4 by regulating expression of Protein kinase C-δ (PKC δ), thereby attenuating post-stroke edema (Datta et al., 2022). PKC δ exerts a significant regulatory effect on disruption of BBB following neuroinflammation, which is exacerbated by the downregulation of adhesion molecule expression and endothelial cell injury.
With regard to modulation of immune system and inflammatory response, the transplantation of MSCs following transient MCAO in ICR mice demonstrated a reduction in IgG leakage in brain parenchyma and a reversal of gap formation of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 in tight junctions (Cheng et al., 2018). Upregulated IL-6 contributes to exacerbation of neuroinflammation in CNS-associated disorders. MSCs have been demonstrated to effectively suppress IL-6 secreted and released from immune cells. This is attributed to secretion of anti-inflammatory factors, including IL-10 and TGF-β, by activated microglia, astrocytes, and immune cells that have infiltrated the CNS. In addition, MSCs promote the production of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which exert an additional suppressive effect on secretion of IL-6 and contribute to reduction in neuroinflammation by playing an additional inhibitory role (Negi and Griffin, 2020; Kerkis et al., 2024). Neural stem cells (NSCs) may also mitigate ischemic injury by inhibiting a plethora of pro-inflammatory mediators. Above studies illustrate the pivotal role of disparate sources of stem cells in restoring the integrity and function of BBB following cerebral ischemia by modulating the extracellular microenvironment and attenuating neuroinflammation (Hamblin and Lee, 2021).
Increasing evidence indicates that oxidative stress-mediated damage to BBB is crucial in pathogenesis of various neurological disorders (Song et al., 2020). In this case, the antioxidant effects of MSCs following transplantation may become a promising strategy in repairing damage of BBB. In an in vitro cellular model of MCAO, CCR2-overexpressing MSCs demonstrated the capacity to restore BBB integrity by inhibiting degradation of tight junctions and excess ROS production. It can be attributed to partial mediation by redox-regulated peroxiredoxin-4 (PRDX4), a member of the PRDX antioxidant family, in restoring BBB integrity. Additionally, overexpression of CCR2 resulted in enhanced homing ability of MSCs (Huang et al., 2018). Moreover, Nrf2 emerges as a significant transcription factor governing antioxidant defense mechanisms, and the Nrf2 pathway is activated in astrocytes to safeguard themselves and their neighboring neurons from oxidative damage. After stimulation by oxidative stress, Nrf2 is released from Keap1 and transported to the nucleus. The RNAs and expressions of Nrf2 and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were upregulated in astrocytes co-cultured with BMSCs. Additionally, MSC transplantation was observed to enhance the secretion of other antioxidant enzymes, such as HO-1, which were significantly ameliorated by the Cx43/Nrf2 signaling pathway, enhanced the antioxidant effects of astrocytes, and prevented them from apoptosis (Chen X. et al., 2020).
An additional potential mechanism through which MSCs facilitate repair of BBB is modulating MMP activity (Klein and Bischoff, 2011). MMPs have been observed to degrade tight junctions in early stages following cerebral ischemia or cerebral hemorrhage. In particular, the upregulation of MMP9 has been demonstrated to promote neuroinflammation, which in turn leads to the destruction of BBB (Yang and Rosenberg, 2011; Kurzepa et al., 2014). The administration of transplanted MSCs following MCAO inhibited MMP9 upregulation, attenuated neuroinflammation, and weakened neutrophil infiltration through downregulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (Cheng et al., 2018). Furthermore, controlling MMP9 upregulation has been demonstrated to promote downregulation of AQP4 and PKC δ, which in turn attenuates vasogenic cerebral edema and thereby protects the nerves (Datta et al., 2022). In addition, MMP9 has been reported to degrade ZO-1. Some studies of hNSC transplantation in mice with cerebral ischemia found that downregulating MMP9 could improve ZO-1 degradation, which is conductive to maintaining the integrity of BBB (Hamblin and Lee, 2021). Notably, a study has proved an association between elevated MMP8 concentrations in serum and an increased risk of small vessel stroke (Jia et al., 2021). In a model of acute cerebral infarction, transplantation of BMSC resulted in a decrease in MMP8 level in cerebrospinal fluid, leading to a reduction in the size of ischemic lesions and an improvement in neurological outcome (Bai et al., 2024).
After ischemic stroke, the Wnt signaling pathway is believed to play a crucial role in regulating neovascularization and repairing the damaged BBB (Tran et al., 2016). Research indicates that activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway encourages endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and lumen formation, which enhances neovascularization and improves blood flow to the brain (Fang et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024). In the early stages following ischemic, the Wnt signaling pathway facilitates neovascularization by promoting the release of pro-angiogenic factors, such as VEGF, from endothelial cells while simultaneously inhibiting anti-angiogenic factors like endogenin. Additionally, this pathway can activate the AKT signaling pathway by reducing the expression of negative regulators, such as phosphatase and tensin homolog, which is vital for maintaining BBB integrity (Cheng et al., 2023). In summary, the neovascularization triggered by the activation of the Wnt signaling pathway after a stroke not only aids in repairing the damaged BBB but also enhances the oxygen and nutrient supply to brain tissues, thereby fostering neurological recovery. Furthermore, transplanted MSCs secrete Wnt signaling-related ligands such as Wnt3a and Wnt7a, which activate the Wnt signaling pathway in endothelial cells. These Wnt signaling molecules promote the proliferation, differentiation, and migration of vascular endothelial cells, leading to vascular neovascularization and the repair of BBB (Lippmann et al., 2012).
In vivo and in vitro experiments in a rat model of MCAO demonstrated that treatment with MSCs promoted angiogenesis and vascular stabilization, while reducing BBB leakage. This was achieved through the facilitation of communication between BMECs and astrocytes via the VEGF/flk1 and angiopoietin 1 (Ang1)/Tie2 pathways (Zacharek et al., 2007; Yamaguchi et al., 2022). Furthermore, MSCs safeguard neural stem cells from neurotoxic agents by transferring functional mitochondria into damaged cells (Babenko et al., 2018; Paliwal et al., 2018).
There are increasing elucidation focusing on potential of using exosomes as mediators of intercellular communication in stroke therapy. Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles released by cells that contain different biologically active molecules, like proteins, mRNAs, miRNAs, and other components. The combinations of these molecules reflect the properties and physiological states of the cells from which they originate. Therefore, exosomes serve not only important mediators of intercellular communication but also perform varying functions within an organism (Mathivanan et al., 2011). The distinctive characteristics of exosomes have been significantly concerned due to their possibility of being applied in clinic treatment, particularly in the context of CNS diseases, where they may serve as biomarkers and carriers for diagnosis of agents (Liu et al., 2019; Figure 5).
Following a stroke, some exosomes derived from brain cells have been observed to cause detriment on the nervous system and they can traverse BBB and enter the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore, those in bodily fluids may serve as biomarkers in diagnosing stroke and its prognosis, offering a non-invasive means of assessment (Li et al., 2018; Otero-Ortega et al., 2019). Numerous recent studies have indicated that microRNAs in exosomes may represent potential biomarkers for diagnosis of ischemic stroke (Jiang et al., 2022). What’s more, prior research has indicated that plasma-derived exosomes miRNAs, including miR-21-5p and miRNA-30a-5p, can be undertaken as biomarkers assisting in diagnosing ischemic stroke and differentiating its stage. This offers clinicians a novel reference for early determination of ischemic stroke and potential insights into the utility of biomarkers for thrombolytic therapy (Wang et al., 2018). Cerebrovascular disease represents a significant cause of stroke in Asian children and young adults. Expressions of several miRNAs, including miR-574-5p, miR-3679-5p, miR-6165, and miR-6760-5p, changed in exosomes targeting cerebrospinal fluid sources from moyamoya disease patients (Wang et al., 2020). In an earlier study, dysregulated miRNAs were also found to be closely associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage (Zheng et al., 2012). In conclusion, further attention is required to research focusing on ascertaining the use of exosomes as biomarkers to enhance their immediate diagnostic value for stroke.
Exosome therapy offers enhanced safety and convenience compared to traditional cell therapy, and can mitigate the risks associated with cell transplantation (Larson et al., 2024). However, exosomes derived from disparate sources exhibit disparate mechanisms and effects when they are applied for stroke treatment. Exosomes from BMSCs can protect nerves by modulating immune cell responses. Besides, exosomes contribute to polarization of microglia and macrophages toward M2-type while suppressing astrocyte activation. Additionally, exosomes can speed up myelination, thereby promoting neurovascular regeneration and protecting the nerves (Chai et al., 2024). Furthermore, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs)-derived exosomes exhibit anti-inflammatory role and inhibitory effect on oxidative stress production in the presence of ischemia-reperfusion injury (Chen et al., 2016). After the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was loaded into NSC-derived exosomes, rats middle cerebral artery occlusion possessed BDNF-hNSC-Exos, which significantly enhances cell survival and facilitates endogenous NSCs differentiating into neurons, while concurrently controlling microglia activation (Zhang et al., 2023). Given the impact of cell type specificity on the biological properties of exosomes, it is imperative to identify the optimal source of exosomes for stroke treatment.
Currently, development of biomedical nanomaterials technology has transferred people’s attention to exploring various nanotechnology approaches for delivery of drugs to treat neurological complications. Actually, exosomes emerge as one such approach. Nanomedicines based on exosomes can encapsulate neuroprotective agents and anti-inflammatory compounds, which can penetrate BBB so as to deliver bioactive drugs to target cells with precision. Exosomes possess a unique cellular tropism and remarkable specificity in delivering drugs. In certain instances, exosomes achieve receptor-mediated tissue targeting through the modification of specific ligands on their surface (Zhang et al., 2022; Singh et al., 2024).
The clinical translation of exosome therapy is still confronted with numerous challenges, including the standardization of exosome preparation, dosage control, optimization of routes of administration, and the assessment of long-term safety. It is increasingly essential to investigate the specific mechanisms of exosomes in stroke treatment and develop more efficacious therapeutic strategies based on exosomes.
Exosomes exert a pivotal role in physiological regulation of BBB through intricate communication among a multitude of cell types. Major mechanisms include repairing tight junctions, regulating miRNAs and reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis. There is mounting evidence to suggest that exosomes facilitate some crucial cellular communication processes by providing target cells with required functional proteins, metabolites, and nucleic acids, thereby influencing the BBB integrity after a stroke (Valadi et al., 2007; Men et al., 2019).
To illustrate, the neuronal release of miR-132-containing exosomes, which released by neurons and internalized and transported to vascular endothelial cells, could regulated through direct targeting of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by regulate vascular endothelial cadherin expression, enhance BBB integrity, which has been supported by previous studies (Xu et al., 2017). In addition, astrocyte-derived exosomes have also been demonstrated to contribute to maintaining function of BBB through releasing paracrine factors that regulate permeability and resistance of BMECs (Osaid et al., 2023). Furthermore, BMECs promote the formation of chemotactic gradients through exosome- and nanovesicle-mediated paracrine signaling, which induces the generation of nanotube structures and optimizes alignment of tight junctions among BMECs. This is critical for the robustness of BBB.
In the MCAO mice model, the researchers observed that exosomes exerted a protective effect by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy in BMECs, as well as preserving the expressions of some tight junctions. Furthermore, exosomes enriched with MSC-derived miR-132-3p can reduce ROS production and BMEC apoptosis while maintaining the expressions of tight junctions, thereby conferring antioxidant and BBB protective benefits. This may be attributed to the inhibition of RASA1 expression by miR-132-3p in exosomes, which in turn activates the Ras/PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway (Pan et al., 2020). Exosomes have the potential to exert therapeutic effects by influencing BBB integrity following a stroke through modulation of multiple signaling pathways. A study investigating mice with ICH has demonstrated that hiPSC-NSC-Exos could reduce MCP-1 to release from astrocytes by over activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby attenuating BBB disruption and ameliorating neurological deficits (Wang et al., 2025). Conversely, evidence suggests that stroke-induced damage to BBB is closely associated with exosomes containing the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19, which are released by astrocytes. These exosomes can impair the function of BBB and even induce its dysfunction by downregulating expression of tight junctions through the lncRNA H19/miR-18a/VEGF signaling axis (Wang J. et al., 2022). In summary, these studies indicate that therapy using exosomes may enhance BBB integrity in stroke patients by regulating pertinent signaling pathways.
In nerve repair following stroke, stem cell therapy has been shown to promote nerve regeneration by supplying new neurons or support cells. Additionally, the reprogramming of glial cells has been observed to potentially generate endogenous support for nerve regeneration, with the combination of these approaches demonstrating the potential to enhance nerve repair (Tang et al., 2023; Williamson et al., 2023). Glial cells are capable of transforming into functional neurons under specific physiological and pathological conditions, a process that involves several key mechanisms (Figure 6). A comprehensive examination of these mechanisms offers novel insights and potential therapeutic strategies for neural repair after stroke.
Dynamic regulation of transcription factors is one of the central mechanisms of cellular reprogramming after stroke. Using specific transcription factors, such as Ascl1, NeuroD1 and Myt1l, glial cells can be effectively converted into functional neurons (Liang et al., 2023). Overexpression of NeuroD1 effectively promotes the differentiation of NG2 glial cells into neurons, a process that is closely related to the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway (Wei et al., 2023). However, it has also been found that NeuroD1 does not effectively transform microglia into neurons, but rather induces apoptosis (Rao et al., 2021). SOX2, an important transcription factor, is able to regulate the properties of neural stem cells and promote the transformation of microglia and astrocytes into neurons (Hagey et al., 2022).
Signaling pathways play an equally important role in the reprogramming of glial cells into induced neurons. In the aftermath of ischemic injury, the hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathway has been shown to promote metabolic reprogramming of glial cells, thereby enhancing their tolerance to ischemia and promoting neuronal survival (Madai et al., 2024). The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway has also been found to be closely associated with glial proliferation and transformation, and in particular, the activation of this pathway under the regulation of ADAR1 can promote the transformation of astrocytes into neurons (Cai et al., 2023). The response of astrocytes in inflammatory environments also affects their reprogramming ability through specific signaling pathways, suggesting that intercellular signaling is critical in this process (Zhou et al., 2022).
Signaling pathways such as Wnt, Notch, and TGF-β play key roles in the interactions between stem cells and glial cells (Azadian et al., 2023). The Wnt signaling pathway promotes the transition of glial cells to neurons by regulating their proliferation and differentiation (Freese et al., 2010). Notch signaling, on the other hand, plays an important role in maintaining the stem cell self-renewal and inhibits over-differentiation, which is essential for glial cell reprogramming (Zhou et al., 2010). In addition, the TGF-β signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating the inflammatory response and regeneration of glial cells, affecting their ability to transform into neurons. The interplay of these signaling mechanisms not only affects stem cell fate decisions, but also plays an important role in damage repair in the nervous system. Exosomes are enriched with miRNAs that modulate multiple signaling pathways, which in turn affect glial cell fate (Vahidinia et al., 2024). Exosomes affect glial cell proliferation and differentiation by regulating NF-κB and mTOR pathways (Szpakowski et al., 2023). Studies have shown that exosomes from mouse embryonic neural stem cells promote neural stem cell differentiation and inhibit their downstream target gene Hes1 by translocating miR-9, which in turn promotes neuron generation (Yuan et al., 2021). The modulation of these signaling pathways exerts a direct influence on cell survival and function, in addition to its involvement in the process of cell reprogramming. This provides a novel framework for the exploration of therapeutic targets for post-stroke neurological repair.
The influence of the cellular microenvironment on the reprogramming of glial cells into induced neurons cannot be ignored. Inflammatory factors in the microenvironment such as IL-1β and TNF-α are able to promote the transformation of glial cells, leading to their transformation to neurons (Liang et al., 2023). Cytokines and signaling molecules in the inflammatory microenvironment also affect the reprogramming capacity of glial cells, and chronic low-grade inflammation can promote the supply of lactate to neurons but also impair its utilization efficiency (Wang Y. et al., 2022). In addition, interactions between astrocytes and microglia can regulate each other’s functions by secreting specific cytokines, thereby affecting the efficiency of cellular reprogramming (Tang et al., 2024). VEGF can promote astrocyte to neuron transformation through activation of the MAPK/Erk signaling pathway, suggesting the importance of the cellular microenvironment in the reprogramming process (Lei et al., 2023).
Comparison of stem cell therapy with reprogramming of glial cells into neurons provides new perspectives on neurological repair after stroke. Despite the challenges facing each of these two fields, their combination may provide more effective options for future therapeutic strategies.
Recently, regenerative medicine and molecular biology have developed swiftly, which enables significant advancement for research on using stem cell and exosome therapies in stroke treatment. Such therapies in stroke treatment have been explored in a number of ways, including as therapeutic modalities, drug carriers and in vitro BBB modeling. It is imperative not to underestimate the significance of stem cells and exosomes in restoring BBB integrity following a stroke. The importance of stem cells and their exosomes in restoring BBB integrity after stroke cannot be overlooked.
As research into the use of stem cells and exosomes in neural repair continues, more evidences are emerging that these cells have beneficial effects on inflammation, apoptosis and neural regeneration. This suggests the significant potential of exosomes in repairing damaged BBB. In addition to reducing neuronal damage by regulating the microenvironment, exosomes can also promote recruitment and activation of endogenous stem cells, thereby assisting in the restoration of the function of damaged BBB.
While some articles have supported the role of stem cell exosomes in repairing BBB, it is imperative to acknowledge the discrepancies in perspectives across studies and the heterogeneity of research methodologies. It is recommended that future research concentrate on the systematic validation of the mechanism of action of stem cell exosomes, exploration of their effects in different stroke models, and the resolution of key issues such as the extraction and purification of stem cells and exosomes, cell sources, immune rejection, potential risk of tumor formation, and optimal routes of administration. Moreover, future research should concentrate on the creation of standardized therapeutic regimens. Meanwhile, clinical trials must be conducted with greater rigor to verify the safety and efficacy of these therapies through multicenter clinical trials. Only in this way, it will provide more compelling evidence for the clinical application of stem cell exosomes.
Advancement of these strategies to strengthen the specificity of targeting sites of neuroinflammation is imperative in the context of the complex architecture of the CNS, which requires the integration of advanced medical technologies and innovative engineering approaches, so that guarantee that stem cells or exosomes loaded with agents for treatments are efficiently and precisely delivered to the target brain region. To further the development of this field, it is essential to engage in multidisciplinary collaboration, integrating the resources of experts in diverse fields, including basic research, clinical application, and bioengineering. This approach enables a comprehensive examination of the biological properties and potential applications of stem cells and exosomes, spanning the full research continuum from fundamental biology to clinical translation.
In conclusion, studying stem cells and exosomes in repairing BBB after stroke is of significant scientific value and clinical significance. With further research and technological advancement, future studies will provide new insights and methodologies for early diagnosis of stroke, precise targeted therapy, and improved prognosis of stroke patients. Therefore, it is anticipated to achieve new developments in this field, which will lead to more effective treatment options for stroke patients.
XF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JL: Validation, Writing – review and editing. SY: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. JJ: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. QZ: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. TZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. ZX: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Jilin Province Health Research Talent Special Project (2021SCZ33 and 2024SCZ29).
We thank all our colleagues in the institute for their assistance and propose throughout the research.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adams, H. P., Bendixen, B. H., Kappelle, L. J., Biller, J., Love, B. B., Gordon, D. L., et al. (1993). Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24, 35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.1.35
Aday, S., Cecchelli, R., Hallier-Vanuxeem, D., Dehouck, M. P., and Ferreira, L. (2016). Stem cell-based human blood-brain barrier models for drug discovery and delivery. Trends Biotechnol. 34, 382–393. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.01.001
Ahmad, S., Bhatia, K., Kindelin, A., and Ducruet, A. F. (2019). The role of complement C3a receptor in stroke. Neuromol. Med. 21, 467–473. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08545-7
Ahn, S. Y., Chang, Y. S., Sung, S. I., and Park, W. S. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cells for severe intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants: Phase I dose-escalation clinical trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 7, 847–856. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0219
Alawieh, A. M., Langley, E. F., Feng, W., Spiotta, A. M., and Tomlinson, S. (2020). Complement-dependent synaptic uptake and cognitive decline after stroke and reperfusion therapy. J. Neurosci. 40, 4042–4058. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2462-19.2020
Albers, G. W., Lansberg, M. G., Brown, S., Jadhav, A. P., Haussen, D. C., Martins, S. O., et al. (2021). Assessment of optimal patient selection for endovascular thrombectomy beyond 6 hours after symptom onset: A pooled analysis of the AURORA database. JAMA Neurol. 78, 1064–1071. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.2319
Al-Kawaz, M. N., Hanley, D. F., and Ziai, W. (2020). Advances in therapeutic approaches for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurotherapeutics 17, 1757–1767. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00902-w
Allen, C. L., and Bayraktutan, U. (2009). Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke 4, 461–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-4949.2009.00387.x
Alsbrook, D. L., Di Napoli, M., Bhatia, K., Biller, J., Andalib, S., Hinduja, A., et al. (2023). Neuroinflammation in acute ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 23, 407–431. doi: 10.1007/s11910-023-01282-2
Anthony, S., Cabantan, D., Monsour, M., and Borlongan, C. V. (2022). Neuroinflammation, stem cells, and stroke. Stroke 53, 1460–1472. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036948
Azadian, S., Doustmohammadi, A., Naseri, M., Khodarahmi, M., Arab, S. S., Yazdanifar, M., et al. (2023). Reconstructing the cell-cell interaction network among mouse immune cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 120, 2756–2764. doi: 10.1002/bit.28431
Babenko, V. A., Silachev, D. N., Popkov, V. A., Zorova, L. D., Pevzner, I. B., Plotnikov, E. Y., et al. (2018). Miro1 enhances mitochondria transfer from multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MMSC) to neural cells and improves the efficacy of cell recovery. Molecules 23:687. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030687
Bai, Y., Du, Y., Yang, Y., Wälchli, T., Constanthin, P. E., and Li, F. (2024). Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction increases BBB permeability and promotes stem cell–induced regeneration of stroke by downregulating MMP8. Cell Transplant 33:09636897231223293. doi: 10.1177/09636897231223293
Balaganapathy, P., Baik, S.-H., Mallilankaraman, K., Sobey, C. G., Jo, D.-G., and Arumugam, T. V. (2018). Interplay between notch and p53 promotes neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 38, 1781–1795. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17715956
Balch, M. H. H., Nimjee, S. M., Rink, C., and Hannawi, Y. (2020). Beyond the brain: The systemic pathophysiological response to acute ischemic stroke. J. Stroke 22, 159–172. doi: 10.5853/jos.2019.02978
Banerjee, G., Wilson, D., Ambler, G., Hostettler, I. C., Shakeshaft, C., Cohen, H., et al. (2020). Longer term stroke risk in intracerebral haemorrhage survivors. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 91, 840–845. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-323079
Bangad, A., Abbasi, M., and de Havenon, A. (2023). Secondary ischemic stroke prevention. Neurotherapeutics 20, 721–731. doi: 10.1007/s13311-023-01352-w
Banks, W. A., Reed, M. J., Logsdon, A. F., Rhea, E. M., and Erickson, M. A. (2021). Healthy aging and the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Aging 1, 243–254. doi: 10.1038/s43587-021-00043-5
Bebelman, M. P., Smit, M. J., Pegtel, D. M., and Baglio, S. R. (2018). Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 188, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.013
Boese, A. C., Eckert, A., Hamblin, M. H., and Lee, J.-P. (2020). Human neural stem cells improve early stage stroke outcome in delayed tissue plasminogen activator-treated aged stroke brains. Exp. Neurol. 329:113275. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113275
Branyan, T. E., and Sohrabji, F. (2020). Sex differences in stroke co-morbidities. Exp. Neurol. 332:113384. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113384
Cai, D., Fraunfelder, M., Fujise, K., and Chen, S.-Y. (2023). ADAR1 exacerbates ischemic brain injury via astrocyte-mediated neuron apoptosis. Redox Biol. 67:102903. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102903
Campbell, B. C. V., and Khatri, P. (2020). Stroke. Lancet 396, 129–142. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31179-X
Chai, M., Su, G., Chen, W., Gao, J., Wu, Q., Song, J., et al. (2024). Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in central nervous system diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 7481–7499. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04032-8
Chau, M. J., Deveau, T. C., Gu, X., Kim, Y. S., Xu, Y., Yu, S. P., et al. (2018). Delayed and repeated intranasal delivery of bone marrow stromal cells increases regeneration and functional recovery after ischemic stroke in mice. BMC Neurosci. 19:20. doi: 10.1186/s12868-018-0418-z
Chen, H.-X., Liang, F.-C., Gu, P., Xu, B.-L., Xu, H.-J., Wang, W.-T., et al. (2020). Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells repair a Parkinson’s disease model by inducing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 11:288. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2473-5
Chen, K.-H., Chen, C.-H., Wallace, C. G., Yuen, C.-M., Kao, G.-S., Chen, Y.-L., et al. (2016). Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke. Oncotarget 7:74537. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12902
Chen, L., Xiong, Y., Chopp, M., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Engineered exosomes enriched with select microRNAs amplify their therapeutic efficacy for traumatic brain injury and stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 18:1376601. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1376601
Chen, X., Liang, H., Xi, Z., Yang, Y., Shan, H., Wang, B., et al. (2020). BM-MSC transplantation alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury, promotes astrocytes vimentin expression, and enhances astrocytes antioxidation via the Cx43/Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8:302. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00302
Chen, Y., Chang, J., Wei, J., Feng, M., and Wang, R. (2021). Assessing the evolution of intracranial hematomas by using animal models: A review of the progress and the challenges. Metab. Brain Dis. 36, 2205–2214. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00828-y
Cheng, L., Liu, Z., and Xia, J. (2023). New insights into circRNA and its mechanisms in angiogenesis regulation in ischemic stroke: A biomarker and therapeutic target. Mol. Biol. Rep. 50, 829–840. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07949-2
Cheng, Z., Wang, L., Qu, M., Liang, H., Li, W., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate blood-brain barrier leakage after cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Neuroinflamm 15:135. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1153-1
Couch, C., Alawieh, A. M., Toutonji, A., Atkinson, C., and Tomlinson, S. (2023). Evaluating the comorbidities of age and cigarette smoking on stroke outcomes in the context of anti-complement mitigation strategies. Front. Immunol. 14:1161051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161051
Croll, S. D., Ransohoff, R. M., Cai, N., Zhang, Q., Martin, F. J., Wei, T., et al. (2004). VEGF-mediated inflammation precedes angiogenesis in adult brain. Exp. Neurol. 187, 388–402. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.02.010
Daadi, M. M., Maag, A.-L., and Steinberg, G. K. (2008). Adherent self-renewable human embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cell line: Functional engraftment in experimental stroke model. PLoS One 3:e1644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001644
Daneman, R., Zhou, L., Kebede, A. A., and Barres, B. A. (2010). Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 468, 562–566. doi: 10.1038/nature09513
Datta, A., Sarmah, D., Kaur, H., Chaudhary, A., Mounica, K. L., Kalia, K., et al. (2022). Post-stroke impairment of the blood-brain barrier and perifocal vasogenic edema is alleviated by endovascular mesenchymal stem cell administration: Modulation of the PKCδ/MMP9/AQP4-Mediated Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 2758–2775. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02761-2
Datta, A., Sarmah, D., Mounica, L., Kaur, H., Kesharwani, R., Verma, G., et al. (2020). Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted pharmacotherapy. Transl. Stroke Res. 11, 1185–1202. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00806-z
Dekoninck, S., and Blanpain, C. (2019). Stem cell dynamics, migration and plasticity during wound healing. Nat. Cell. Biol. 21, 18–24. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0237-6
Do, P. T., Wu, C.-C., Chiang, Y.-H., Hu, C.-J., and Chen, K.-Y. (2021). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell therapy in blood–brain barrier preservation following ischemia: Molecular mechanisms and prospects. IJMS 22:10045. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810045
Dong, H., Wen, X., Zhang, B.-W., Wu, Z., and Zou, W. (2024). Astrocytes in intracerebral hemorrhage: Impact and therapeutic objectives. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 17:1327472. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1327472
Eckert, A., Huang, L., Gonzalez, R., Kim, H.-S., Hamblin, M. H., and Lee, J.-P. (2015). Bystander effect fuels human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells to quickly attenuate early stage neurological deficits after stroke. Stem. Cells Transl. Med. 4, 841–851. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0184
Ekker, M. S., Boot, E. M., Singhal, A. B., Tan, K. S., Debette, S., Tuladhar, A. M., et al. (2018). Epidemiology, aetiology, and management of ischaemic stroke in young adults. Lancet Neurol. 17, 790–801. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30233-3
Fang, J., Wang, Z., and Miao, C.-Y. (2023). Angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 44, 1305–1321. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01061-2
Fann, D. Y.-W., Lee, S. Y., Manzanero, S., Tang, S. C., Gelderblom, M., Chunduri, P., et al. (2013). Intravenous immunoglobulin suppresses NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal death in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis. 4:e790. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.326
Fischer, S., Wiesnet, M., Marti, H. H., Renz, D., and Schaper, W. (2004). Simultaneous activation of several second messengers in hypoxia-induced hyperpermeability of brain derived endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 198, 359–369. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10417
Fischer, U. M., Harting, M. T., Jimenez, F., Monzon-Posadas, W. O., Xue, H., Savitz, S. I., et al. (2009). Pulmonary passage is a major obstacle for intravenous stem cell delivery: The pulmonary first-pass effect. Stem. Cells Dev. 18, 683–692. doi: 10.1089/scd.2008.0253
Freese, J. L., Pino, D., and Pleasure, S. J. (2010). Wnt signaling in development and disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 38, 148–153. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.09.003
Galeano, C., Qiu, Z., Mishra, A., Farnsworth, S. L., Hemmi, J. J., Moreira, A., et al. (2018). The route by which intranasally delivered stem cells enter the central nervous system. Cell Transplantation 27:501. doi: 10.1177/0963689718754561
Gao, X., Yang, H., Xiao, W., Su, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2022). Modified exosomal SIRPα variants alleviate white matter injury after intracerebral hemorrhage via microglia/macrophages. Biomater. Res. 26:67. doi: 10.1186/s40824-022-00311-4
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators (2021). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 20, 795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
Ghori, A., Prinz, V., Nieminen-Kehlä, M., Bayerl, S. H., Kremenetskaia, I., Riecke, J., et al. (2022). Vascular endothelial growth factor augments the tolerance towards cerebral stroke by enhancing neurovascular repair mechanism. Transl. Stroke Res. 13, 774–791. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-00991-z
Guo, X., Liu, R., Jia, M., Wang, Q., and Wu, J. (2023). Ischemia reperfusion injury induced blood brain barrier dysfunction and the involved molecular mechanism. Neurochem. Res. 48, 2320–2334. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03923-x
Hagey, D. W., Bergsland, M., and Muhr, J. (2022). SOX2 transcription factor binding and function. Development 149:dev200547. doi: 10.1242/dev.200547
Hamblin, M. H., and Lee, J.-P. (2021). Neural stem cells for early ischemic stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:7703. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147703
Hamblin, M. H., Murad, R., Yin, J., Vallim, G., and Lee, J.-P. (2021). Modulation of gene expression on a transcriptome-wide level following human neural stem cell transplantation in aged mouse stroke brains. Exp. Neurol. 347:113913. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113913
Hao, X., Bai, Y., Li, W., and Zhang, M. (2024). Phloretin attenuates inflammation induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage through regulation of the TLR2/MyD88/NF-kB pathway. Sci. Rep. 14:26583. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77671-5
Harjunpää, H., Tallberg, R., Cui, Y., Guenther, C., Liew, H.-K., Seelbach, A., et al. (2024). β2-Integrins regulate microglial responses and the functional outcome of hemorrhagic stroke in vivo. J. Immunol. 213, 519–525. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300815
Hatchell, D., Alshareef, M., Vasas, T., Guglietta, S., Borucki, D., Guo, C., et al. (2023). A role for P-selectin and complement in the pathological sequelae of germinal matrix hemorrhage. J. Neuroinflammation 20, 143. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02828-4
Hicks, A. U., Lappalainen, R. S., Narkilahti, S., Suuronen, R., Corbett, D., Sivenius, J., et al. (2009). Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursor cells and enriched environment after cortical stroke in rats: Cell survival and functional recovery. Eur. J. Neurosci. 29, 562–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06599.x
Holste, K., Xia, F., Garton, H. J. L., Wan, S., Hua, Y., Keep, R. F., et al. (2021). The role of complement in brain injury following intracerebral hemorrhage: A review. Exp. Neurol. 340:113654. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113654
Hu, K., Gao, Y., Chu, S., and Chen, N. (2022). Review of the effects and mechanisms of microglial autophagy in ischemic stroke. Int. Immunopharmacol. 108:108761. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108761
Huang, B., Yang, X.-D., Lamb, A., and Chen, L.-F. (2010). Posttranslational modifications of NF-κB: Another layer of regulation for NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell. Signalling 22, 1282–1290. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.03.017
Huang, X., Moreton, F. C., Kalladka, D., Cheripelli, B. K., MacIsaac, R., Tait, R. C., et al. (2015). Coagulation and fibrinolytic activity of tenecteplase and alteplase in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 46, 3543–3546. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011290
Huang, Y., Wang, J., Cai, J., Qiu, Y., Zheng, H., Lai, X., et al. (2018). Targeted homing of CCR2-overexpressing mesenchymal stromal cells to ischemic brain enhances post-stroke recovery partially through PRDX4-mediated blood-brain barrier preservation. Theranostics 8, 5929–5944. doi: 10.7150/thno.28029
Jaillard, A., Hommel, M., Moisan, A., Zeffiro, T. A., Favre-Wiki, I. M., Barbieux-Guillot, M., et al. (2020). Autologous mesenchymal stem cells improve motor recovery in subacute ischemic stroke: A randomized clinical trial. Transl. Stroke Res. 11, 910–923. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00787-z
Jazayeri, S. B., Ghozy, S., Hemmeda, L., Bilgin, C., Elfil, M., Kadirvel, R., et al. (2024). Risk of hemorrhagic transformation after mechanical thrombectomy without versus with IV thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 45, 1246–1252. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8307
Jha, N. K., Chen, W.-C., Kumar, S., Dubey, R., Tsai, L.-W., Kar, R., et al. (2022). Molecular mechanisms of developmental pathways in neurological disorders: A pharmacological and therapeutic review. Open Biol. 12:210289. doi: 10.1098/rsob.210289
Jia, Y., Guo, D., Zhang, K., Yang, P., Zang, Y., Sun, L., et al. (2021). Causal associations of serum matrix metalloproteinase-8 level with ischaemic stroke and ischaemic stroke subtypes: A mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Neurol. 28, 2543–2551. doi: 10.1111/ene.14878
Jian, Z., Liu, R., Zhu, X., Smerin, D., Zhong, Y., Gu, L., et al. (2019). The involvement and therapy target of immune cells after ischemic stroke. Front. Immunol. 10:2167. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02167
Jiang, L., Chen, W., Ye, J., and Wang, Y. (2022). Potential role of exosomes in ischemic stroke treatment. Biomolecules 12:115. doi: 10.3390/biom12010115
Jiang, X., Andjelkovic, A. V., Zhu, L., Yang, T., Bennett, M. V. L., Chen, J., et al. (2018). Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 163–164, 144–171. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.10.001
Johnstone, R. M., Adam, M., Hammond, J. R., Orr, L., and Turbide, C. (1987). Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 262, 9412–9420. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)48095-7
Kahles, T., and Brandes, R. P. (2013). Which NADPH oxidase isoform is relevant for ischemic stroke? The case for nox 2. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 18, 1400–1417. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4721
Kakarla, V., Kaneko, N., Nour, M., Khatibi, K., Elahi, F., Liebeskind, D. S., et al. (2021). Pathophysiologic mechanisms of cerebral endotheliopathy and stroke due to sars-CoV-2. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 41, 1179–1192. doi: 10.1177/0271678X20985666
Kanmogne, M., and Klein, R. S. (2021). Neuroprotective versus neuroinflammatory roles of complement: From development to disease. Trends Neurosci. 44, 97–109. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.10.003
Katakowski, M., Buller, B., Zheng, X., Lu, Y., Rogers, T., Osobamiro, O., et al. (2013). Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 335, 201–204. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.02.019
Katan, M., and Elkind, M. S. (2018). The potential role of blood biomarkers in patients with ischemic stroke: An expert opinion. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2:13. doi: 10.1177/2514183x18768050
Kerkis, I., Silva, ÁP., and Araldi, R. P. (2024). The impact of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and mesenchymal stem cell-derived IL-6 on neurological conditions. Front. Immunol. 15:1400533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1400533
Kikuchi-Taura, A., Okinaka, Y., Saino, O., Takeuchi, Y., Ogawa, Y., Kimura, T., et al. (2021). Gap junction-mediated cell-cell interaction between transplanted mesenchymal stem cells and vascular endothelium in stroke. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 39, 904–912. doi: 10.1002/stem.3360
Klein, T., and Bischoff, R. (2011). Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids 41, 271–290. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0689-x
Komatsu, T., Ohta, H., Motegi, H., Hata, J., Terawaki, K., Koizumi, M., et al. (2021). A novel model of ischemia in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion using a microcatheter and zirconia ball under fluoroscopy. Sci. Rep. 11:12806. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92321-w
Kurzepa, J., Kurzepa, J., Golab, P., Czerska, S., and Bielewicz, J. (2014). The significance of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in the ischemic stroke. Int. J. Neurosci. 124, 707–716. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2013.872102
Kvistad, C. E., Kråkenes, T., Gjerde, C., Mustafa, K., Rekand, T., and Bø, L. (2022). Safety and clinical efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell treatment in traumatic spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis and ischemic stroke - A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 13:891514. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.891514
Larson, A., Natera-Rodriguez, D. E., Crane, A., Larocca, D., Low, W. C., Grande, A. W., et al. (2024). Emerging roles of exosomes in stroke therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:6507. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126507
Laskowitz, D. T., Bennett, E. R., Durham, R. J., Volpi, J. J., Wiese, J. R., Frankel, M., et al. (2018). Allogeneic umbilical cord blood infusion for adults with ischemic stroke: Clinical outcomes from a phase I safety study. Stem. Cells Transl. Med. 7, 521–529. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0008
Lei, Y., Chen, X., Mo, J.-L., Lv, L.-L., Kou, Z.-W., and Sun, F.-Y. (2023). Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes transdifferentiation of astrocytes into neurons via activation of the MAPK/erk-Pax6 signal pathway. Glia 71, 1648–1666. doi: 10.1002/glia.24361
Li, J. J., Wang, B., Kodali, M. C., Chen, C., Kim, E., Patters, B. J., et al. (2018). In vivo evidence for the contribution of peripheral circulating inflammatory exosomes to neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 15:8. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1038-8
Li, L., Jiang, Q., Ding, G., Zhang, L., Zhang, Z. G., Li, Q., et al. (2010). Effects of administration route on migration and distribution of neural progenitor cells transplanted into rats with focal cerebral ischemia, an MRI study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 30, 653–662. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.238
Li, P., Kaslan, M., Lee, S. H., Yao, J., and Gao, Z. (2017). Progress in exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics 7:789. doi: 10.7150/thno.18133
Li, Y., and Zhang, J. (2021). Animal models of stroke. Animal Model Exp. Med. 4, 204–219. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12179
Li, Y., Tang, Y., and Yang, G.-Y. (2021). Therapeutic application of exosomes in ischaemic stroke. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 6, 483–495. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000419
Li, Y., Wu, H., Jiang, X., Dong, Y., Zheng, J., and Gao, J. (2022). New idea to promote the clinical applications of stem cells or their extracellular vesicles in central nervous system disorders: Combining with intranasal delivery. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 12:3215. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.04.001
Li, Z.-M., Zhang, Z.-T., Guo, C.-J., Geng, F.-Y., Qiang, F., and Wang, L.-X. (2013). Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation for intracerebral hemorrhage—a prospective clinical observation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 115, 72–76. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.04.030
Liang, Z., Lou, Y., Hao, Y., Li, H., Feng, J., and Liu, S. (2023). The relationship of astrocytes and microglia with different stages of ischemic stroke. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 21, 2465–2480. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230718104634
Lippmann, E. S., Azarin, S. M., Kay, J. E., Nessler, R. A., Wilson, H. K., Al-Ahmad, A., et al. (2012). Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 783–791. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2247
Lippmann, E. S., Azarin, S. M., Palecek, S. P., and Shusta, E. V. (2020). Commentary on human pluripotent stem cell-based blood-brain barrier models. Fluids Barriers CNS 17:64. doi: 10.1186/s12987-020-00222-3
Liu, H., Jiang, C., Peng, J., Hu, X., and Xia, Y. (2023). Transplantation of neural stem cells-overexpressed Ku70 improves neurological deficits in a mice model of cerebral ischemia stroke. Neurochem. Res. 49, 718–731. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04065-w
Liu, J., Pang, S.-Y., Zhou, S.-Y., He, Q.-Y., Zhao, R.-Y., Qu, Y., et al. (2024). Lipocalin-2 aggravates blood-brain barrier dysfunction after intravenous thrombolysis by promoting endothelial cell ferroptosis via regulating the HMGB1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Redox Biol. 76:103342. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103342
Liu, W., Bai, X., Zhang, A., Huang, J., Xu, S., and Zhang, J. (2019). Role of exosomes in central nervous system diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 12:240. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00240
Long, J., Sun, Y., Liu, S., Yang, S., Chen, C., Zhang, Z., et al. (2023). Targeting pyroptosis as a preventive and therapeutic approach for stroke. Cell Death Discov. 9, 1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01440-y
Lu, H., Chen, S., Nie, Q., Xue, Q., Fan, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). Synaptotagmin-3 interactions with GluA2 mediate brain damage and impair functional recovery in stroke. Cell Rep. 42:112233. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112233
Lu, T. M., Houghton, S., Magdeldin, T., Durán, J. G. B., Minotti, A. P., Snead, A., et al. (2021). Pluripotent stem cell-derived epithelium misidentified as brain microvascular endothelium requires ETS factors to acquire vascular fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 118:e2016950118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2016950118
Lu, W., Wang, Y., and Wen, J. (2024). The roles of RhoA/ROCK/NF-κB pathway in microglia polarization following ischemic stroke. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 19:19. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10118-w
Ma, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., and Yang, G.-Y. (2019). Significance of complement system in ischemic stroke: A comprehensive review. Aging Dis. 10, 429–462. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0119
Madai, S., Kilic, P., Schmidt, R. M., Bas-Orth, C., Korff, T., Büttner, M., et al. (2024). Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway protects against acute ischemic stroke by reprogramming central carbon metabolism. Theranostics 14, 2856–2880. doi: 10.7150/thno.88223
Manley, G. T., Fujimura, M., Ma, T., Noshita, N., Filiz, F., Bollen, A. W., et al. (2000). Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat. Med. 6, 159–163. doi: 10.1038/72256
Manneken, J. D., and Currie, P. D. (2023). Macrophage-stem cell crosstalk: Regulation of the stem cell niche. Development 150:dev201510. doi: 10.1242/dev.201510
Martin, S. S., Aday, A. W., Almarzooq, Z. I., Anderson, C. A. M., Arora, P., Avery, C. L., et al. (2024). 2024 heart disease and stroke statistics: A report of US and global data from the American heart association. Circulation 149, e347–e913. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209
Mathivanan, S., Fahner, C. J., Reid, G. E., and Simpson, R. J. (2011). ExoCarta 2012: Database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr828
Matsuo, K., Engelhardt, B., and Nishihara, H. (2023). Differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells to brain microvascular endothelial cell-like cells with a mature immune phenotype. J. Visualized Exp. 65134. doi: 10.3791/65134
Men, Y., Yelick, J., Jin, S., Tian, Y., Chiang, M. S. R., Higashimori, H., et al. (2019). Exosome reporter mice reveal the involvement of exosomes in mediating neuron to astroglia communication in the CNS. Nat. Commun. 10:4136. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11534-w
Miyake, M. M., and Bleier, B. S. (2015). The blood-brain barrier and nasal drug delivery to the central nervous system. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 29, 124–127. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4149
Muir, K. W., Bulters, D., Willmot, M., Sprigg, N., Dixit, A., Ward, N., et al. (2020). Intracerebral implantation of human neural stem cells and motor recovery after stroke: Multicentre prospective single-arm study (PISCES-2). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 91, 396–401. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-322515
Nag, S., and Begley, D. (2005). Blood-brain barrier, exchange of metabolites and gases. Pathol. Genet. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 5, 22–29.
Nagai, N., Kawao, N., Okada, K., Okumoto, K., Teramura, T., Ueshima, S., et al. (2010). Systemic transplantation of embryonic stem cells accelerates brain lesion decrease and angiogenesis. NeuroReport 21:575. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32833a7d2c
Narasimhan, P., Liu, J., Song, Y. S., Massengale, J. L., and Chan, P. H. (2009). VEGF stimulates the ERK 1/2 signaling pathway and apoptosis in cerebral endothelial cells after ischemic conditions. Stroke 40, 1467–1473. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.534644
Nazim, S. M., and Ahmad, S. (2023). Stem cell research, regenerative medicine and challenges. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 73, S143–S147. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.AKUS-23
Negi, N., and Griffin, M. D. (2020). Effects of mesenchymal stromal cells on regulatory T cells: Current understanding and clinical relevance. Stem Cells 38, 596–605. doi: 10.1002/stem.3151
Ng, F. C., Churilov, L., Yassi, N., Kleinig, T. J., Thijs, V., Wu, T. Y., et al. (2022). Microvascular dysfunction in blood-brain barrier disruption and hypoperfusion within the infarct posttreatment are associated with cerebral edema. Stroke 53, 1597–1605. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036104
Nishihara, H., Gastfriend, B. D., Soldati, S., Perriot, S., Mathias, A., Sano, Y., et al. (2020). Advancing human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier models for studying immune cell interactions. FASEB J. 34:16693. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001507RR
Osaid, Z., Haider, M., Hamoudi, R., and Harati, R. (2023). Exosomes interactions with the blood–brain barrier: Implications for cerebral disorders and therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:15635. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115635
Otero-Ortega, L., Laso-García, F., Gómez-de Frutos, M., Fuentes, B., Diekhorst, L., Díez-Tejedor, E., et al. (2019). Role of exosomes as a treatment and potential biomarker for stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 10, 241–249. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0654-7
Paciaroni, M., Agnelli, G., Falocci, N., Caso, V., Becattini, C., Marcheselli, S., et al. (2015). Early recurrence and cerebral bleeding in patients with acute ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation: Effect of anticoagulation and its timing: the RAF study. Stroke 46, 2175–2182. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.008891
Paliwal, S., Chaudhuri, R., Agrawal, A., and Mohanty, S. (2018). Regenerative abilities of mesenchymal stem cells through mitochondrial transfer. J. Biomed. Sci. 25:31. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0429-1
Pan, B.-T., and Johnstone, R. M. (1983). Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 33, 967–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90040-5
Pan, Q., Kuang, X., Cai, S., Wang, X., Du, D., Wang, J., et al. (2020). miR-132-3p priming enhances the effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes on ameliorating brain ischemic injury. Stem Cell Res. Therapy 11:260. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01761-0
Pang, B., Wu, L., and Peng, Y. (2024). In vitro modelling of the neurovascular unit for ischemic stroke research: Emphasis on human cell applications and 3D model design. Exp. Neurol. 381:114942. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114942
Park, Y. J., Niizuma, K., Mokin, M., Dezawa, M., and Borlongan, C. V. (2020). Cell-based therapy for stroke: Musing with muse cells. Stroke 51, 2854–2862. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.030618
Peng, Y., Chu, S., Yang, Y., Zhang, Z., Pang, Z., and Chen, N. (2021). Neuroinflammatory in vitro cell culture models and the potential applications for neurological disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 12:671734. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.671734
Perets, N., Betzer, O., Shapira, R., Brenstein, S., Angel, A., Sadan, T., et al. (2019). Golden exosomes selectively target brain pathologies in neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders. Nano Letters 19, 3422–3431. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04148
Perez-Alvarez, M. J., Villa Gonzalez, M., Benito-Cuesta, I., and Wandosell, F. G. (2018). Role of mTORC1 controlling proteostasis after brain ischemia. Front. Neurosci. 12:60. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00060
Qiao, L., Huang, F., Zhao, M., Xie, J., Shi, J., Wang, J., et al. (2014). A two-year follow-up study of cotransplantation with neural stem/progenitor cells and mesenchymal stromal cells in ischemic stroke patients. Cell Transplant 23, S65–S72. doi: 10.3727/096368914X684961
Qin, C., Yang, S., Chu, Y.-H., Zhang, H., Pang, X.-W., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 7, 1–29. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01064-1
Ramiro, L., Simats, A., García-Berrocoso, T., and Montaner, J. (2018). Inflammatory molecules might become both biomarkers and therapeutic targets for stroke management. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 11:1756286418789340. doi: 10.1177/1756286418789340
Rao, Y., Du, S., Yang, B., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, R., et al. (2021). NeuroD1 induces microglial apoptosis and cannot induce microglia-to-neuron cross-lineage reprogramming. Neuron 109, 4094–4108.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.11.008
Rashed, M., Bayraktar, E., Helal, G., Abd-Ellah, M. F., Amero, P., Chavez-Reyes, A., et al. (2017). Exosomes: From garbage bins to promising therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:538. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030538
Rodrigo, R., Fernández-Gajardo, R., Gutiérrez, R., Matamala, J. M., Carrasco, R., Miranda-Merchak, A., et al. (2013). Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Novel therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 12, 698–714. doi: 10.2174/1871527311312050015
Sarmah, D., Datta, A., Kaur, H., Kalia, K., Borah, A., Rodriguez, A. M., et al. (2022). Sirtuin-1 - mediated NF-κB pathway modulation to mitigate inflammasome signaling and cellular apoptosis is one of the neuroprotective effects of intra-arterial mesenchymal stem cell therapy following ischemic stroke. Stem Cell. Rev. Rep. 18, 821–838. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10315-7
Semenza, G. L. (2009). Regulation of oxygen homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiology (Bethesda) 24, 97–106. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00045.2008
Shtaya, A., Bridges, L. R., Williams, R., Trippier, S., Zhang, L., Pereira, A. C., et al. (2021). Innate immune anti-inflammatory response in human spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 52, 3613–3623. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034673
Singh, G., Mehra, A., Arora, S., Gugulothu, D., Vora, L. K., Prasad, R., et al. (2024). Exosome-mediated delivery and regulation in neurological disease progression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 264:130728. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130728
Sivandzade, F., and Cucullo, L. (2021). Regenerative stem cell therapy for neurodegenerative diseases: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:2153. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042153
Song, G., Zhao, M., Chen, H., Zhou, X., Lenahan, C., Ou, Y., et al. (2021). The application of brain organoid technology in stroke research: Challenges and prospects. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15:646921. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.646921
Song, K., Li, Y., Zhang, H., An, N., Wei, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2020). Oxidative stress-mediated blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption in neurological diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2020:4356386. doi: 10.1155/2020/4356386
Srinivasan, B., Kolli, A. R., Esch, M. B., Abaci, H. E., Shuler, M. L., and Hickman, J. J. (2015). TEER measurement techniques for in vitro barrier model systems. J. Lab. Autom. 20, 107–126. doi: 10.1177/2211068214561025
Sun, Y., Feng, X., Ding, Y., Li, M., Yao, J., Wang, L., et al. (2019). Phased treatment strategies for cerebral ischemia based on glutamate receptors. Front. Cell Neurosci. 13:168. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00168
Szpakowski, P., Ksiazek-Winiarek, D., Czpakowska, J., Kaluza, M., Milewska-Jedrzejczak, M., and Glabinski, A. (2023). Astrocyte-derived exosomes differentially shape T cells’ immune response in MS patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:7470. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087470
Taha, A., Bobi, J., Dammers, R., Dijkhuizen, R. M., Dreyer, A. Y., van Es, A. C. G. M., et al. (2022). Comparison of large animal models for acute ischemic stroke: Which model to use? Stroke 53, 1411–1422. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036050
Tang, B., Song, M., Xie, X., Le, D., Tu, Q., Wu, X., et al. (2021). Tumor Necrosis factor-stimulated Gene-6 (TSG-6) secreted by BMSCs regulates activated astrocytes by inhibiting NF-κB Signaling pathway to ameliorate blood brain barrier damage after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurochem. Res. 46, 2387–2402. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03375-1
Tang, H., Li, Y., Tang, W., Zhu, J., Parker, G. C., and Zhang, J. H. (2023). Endogenous neural stem cell-induced neurogenesis after ischemic stroke: Processes for brain repair and perspectives. Transl. Stroke Res. 14, 297–303. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-01078-5
Tang, W., Cheng, R., Gao, M.-Y., Hu, M.-J., Zhang, L., Wang, Q., et al. (2024). A novel annexin dimer targets microglial phagocytosis of astrocytes to protect the brain-blood barrier after cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01432-3 Online ahead of print.
Théry, C., Zitvogel, L., and Amigorena, S. (2002). Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 569–579. doi: 10.1038/nri855
Thomas, Q., Crespy, V., Duloquin, G., Ndiaye, M., Sauvant, M., Béjot, Y., et al. (2021). Stroke in women: When gender matters. Rev. Neurol. 177, 881–889. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2021.01.012
Tol, M., Akar, A. R., Durdu, S., Ayyildiz, E., and Ilhan, O. (2008). Comparison of different needle diameters and flow rates on bone marrow mononuclear stem cell viability: an ex vivo experimental study. Cytotherapy 10, 98–99. doi: 10.1080/14653240701762356
Tran, K. A., Zhang, X., Predescu, D., Huang, X., Machado, R. F., Göthert, J. R., et al. (2016). Endothelial β-catenin signaling is required for maintaining adult blood-brain barrier integrity and central nervous system homeostasis. Circulation 133, 177–186. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015982
Vahidinia, Z., Azami Tameh, A., Barati, S., Izadpanah, M., and Seyed Hosseini, E. (2024). Nrf2 activation: A key mechanism in stem cell exosomes-mediated therapies. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 29:30. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00551-3
Valadi, H., Ekström, K., Bossios, A., Sjöstrand, M., Lee, J. J., and Lötvall, J. O. (2007). Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 654–659. doi: 10.1038/ncb1596
Van Breedam, E., and Ponsaerts, P. (2022). Promising strategies for the development of advanced in vitro models with high predictive power in ischaemic stroke research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:7140. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137140
Vargas-Rodríguez, P., Cuenca-Martagón, A., Castillo-González, J., Serrano-Martínez, I., Luque, R. M., Delgado, M., et al. (2023). Novel therapeutic opportunities for neurodegenerative diseases with mesenchymal stem cells: The focus on modulating the blood-brain barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:14117. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814117
Velier, J. J., Ellison, J. A., Kikly, K. K., Spera, P. A., Barone, F. C., and Feuerstein, G. Z. (1999). Caspase-8 and caspase-3 are expressed by different populations of cortical neurons undergoing delayed cell death after focal stroke in the rat. J. Neurosci. 19, 5932–5941. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-14-05932.1999
Venkat, P., Zacharek, A., Landschoot-Ward, J., Wang, F., Culmone, L., Chen, Z., et al. (2020). Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells harvested from type two diabetes rats promotes neurorestorative effects after stroke in type two diabetes rats. Exp. Neurol. 334:113456. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113456
Verkman, A. S., Smith, A. J., Phuan, P., Tradtrantip, L., and Anderson, M. O. (2017). The aquaporin-4 water channel as a potential drug target in neurological disorders. Exp. Opin. Ther. Targets 21:1161. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1398236
Verma, N., Fazioli, A., and Matijasich, P. (2022). Natural recovery and regeneration of the central nervous system. Regen. Med. 17, 233–244. doi: 10.2217/rme-2021-0084
Walczak, P., Zhang, J., Gilad, A. A., Kedziorek, D. A., Ruiz-Cabello, J., Young, R. G., et al. (2008). Dual-modality monitoring of targeted intraarterial delivery of mesenchymal stem cells after transient ischemia. Stroke J. Cereb. Circulation 39:1569. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502047
Wang, C., Cheng, F., Han, Z., Yan, B., Liao, P., Yin, Z., et al. (2025). Human-induced pluripotent stem cell–derived neural stem cell exosomes improve blood–brain barrier function after intracerebral hemorrhage by activating astrocytes via PI3K/AKT/MCP-1 axis. Neural. Regen. Res. 20, 518–532. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01889
Wang, G., Wen, Y., Faleti, O. D., Zhao, Q., Liu, J., Zhang, G., et al. (2020). A panel of exosome-derived miRNAs of cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of moyamoya disease. Front. Neurosci. 14:548278. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.548278
Wang, J., Cao, B., Sun, R., Chen, Y., and Feng, J. (2022). Exosome-transported long non-coding ribonucleic acid H19 induces blood-brain barrier disruption in cerebral ischemic stroke via the H19/micro ribonucleic acid-18a/vascular endothelial growth factor axis. Neuroscience 500, 41–51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.07.028
Wang, J., Xiong, T., Wu, Q., and Qin, X. (2024). Integrated strategies for targeting arteriogenesis and angiogenesis after stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01291-4 Online ahead of print.
Wang, J., Yao, J., Liu, Y., and Huang, L. (2021). Targeting the gasdermin D as a strategy for ischemic stroke therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 188:114585. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114585
Wang, R., Zeng, J., Wang, F., Zhuang, X., Chen, X., and Miao, J. (2019). Risk factors of hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous thrombolysis with rt-PA in acute cerebral infarction. QJM Int. J. Med. 112, 323–326. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcy292
Wang, W., Li, D.-B., Li, R.-Y., Zhou, X., Yu, D.-J., Lan, X.-Y., et al. (2018). Diagnosis of hyperacute and acute ischaemic stroke: The potential utility of exosomal MicroRNA-21-5p and MicroRNA-30a-5p. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 45, 204–212. doi: 10.1159/000488365
Wang, Y., Chang, C., Wang, R., Li, X., and Bao, X. (2024). The advantages of multi-level omics research on stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 19, 1998–2003. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390959
Wang, Y., Li, J., Wang, M.-Y., Pan, Z.-Y., Li, Z.-Q., and Wang, Z.-F. (2022). Chronic microglial inflammation promotes neuronal lactate supply but impairs its utilization in primary rat astrocyte-neuron co-cultures. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 607, 28–35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.03.122
Wassertheil-Smoller, S., Hendrix, S. L., Limacher, M., Heiss, G., Kooperberg, C., Baird, A., et al. (2003). Effect of estrogen plus progestin on stroke in postmenopausal women: The women’s health initiative: A randomized trial. JAMA 289, 2673–2684. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.20.2673
Wei, M., Feng, D., Lu, Z., Hu, Z., Wu, H., Lian, Y., et al. (2023). Neurod1 mediates the reprogramming of NG2 glial into neurons in vitro. Gene Expr. Patterns 47:119305. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2023.119305
Wei, N., Yu, S. P., Gu, X., Taylor, T. M., Song, D., Liu, X.-F., et al. (2013). Delayed intranasal delivery of hypoxic-preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhanced cell homing and therapeutic benefits after ischemic stroke in mice. Cell Transplant 22, 977–991. doi: 10.3727/096368912X657251
Williams, S., Glaser, K., and Ray, B. (2023). Strokes and predictors of outcomes. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. North Am. 35, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cnc.2022.10.003
Williamson, M. R., Le, S. P., Franzen, R. L., Donlan, N. A., Rosow, J. L., Nicot-Cartsonis, M. S., et al. (2023). Subventricular zone cytogenesis provides trophic support for neural repair in a mouse model of stroke. Nat. Commun. 14:6341. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42138-0
Wu, M., Chen, K., Jiang, M., Xie, F., Cao, X., Chen, L., et al. (2023). High plasma complement C4 levels as a novel predictor of clinical outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1103278. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1103278
Xu, B., Zhang, Y., Du, X.-F., Li, J., Zi, H.-X., Bu, J.-W., et al. (2017). Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 27, 882–897. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.62
Yadava, S., Reddy, D. H., Nakka, V. P., Anusha, V. L., Dumala, N., Viswanadh, M. K., et al. (2025). Unravelling neuroregenerative and neuroprotective roles of wnt/β-catenin pathway in ischemic stroke: Insights into molecular mechanisms. Neuroscience 565, 527–547. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.12.024
Yamaguchi, T., Nishijima, M., and Kawabata, K. (2022). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3ß enhances functions of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived brain microvascular endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 45, 1525–1530. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b22-00393
Yan, L., Moriarty, R. A., and Stroka, K. M. (2021). Recent progress and new challenges in modeling of human pluripotent stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier. Theranostics 11, 10148–10170. doi: 10.7150/thno.63195
Yang, H., Zhang, H., Gu, H., Wang, J., Zhang, J., Zen, K., et al. (2023). Comparative analyses of human exosome proteomes. Protein J. 42, 365–373. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10100-0
Yang, K., Bao, T., Zeng, J., Wang, S., Yuan, X., Xiang, W., et al. (2023). Research progress on pyroptosis-mediated immune-inflammatory response in ischemic stroke and the role of natural plant components as regulator of pyroptosis: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 157:113999. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113999
Yang, Y., and Rosenberg, G. A. (2011). Blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke J. Cereb. Circulation 42:3323. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.608257
Yao, S., Pang, M., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Lin, Y., Lv, Y., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cell attenuates spinal cord injury by inhibiting mitochondrial quality control-associated neuronal ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 67:102871. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102871
Yao, Y., Chen, Z.-L., Norris, E. H., and Strickland, S. (2014). Astrocytic laminin regulates pericyte differentiation and maintains blood brain barrier integrity. Nat. Commun. 5:3413. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4413
Yavagal, D. R., Lin, B., Raval, A. P., Garza, P. S., Dong, C., Zhao, W., et al. (2014). Efficacy and dose-dependent safety of intra-arterial delivery of mesenchymal stem cells in a rodent stroke model. PLoS One 9:e93735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093735
Yeo, L. L. L., Jing, M., Bhogal, P., Tu, T., Gopinathan, A., Yang, C., et al. (2021). Evidence-based updates to thrombectomy: Targets, new techniques, and devices. Front. Neurol. 12:712527. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.712527
Yi, X., and Tang, X. (2021). Exosomes from miR-19b-3p-modified ADSCs inhibit ferroptosis in intracerebral hemorrhage mice. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9:661317. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.661317
Ying, C., Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Gao, S., Guo, X., Lin, J., et al. (2023). Stem cells in central nervous system diseases: Promising therapeutic strategies. Exp. Neurol. 369:114543. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114543
Yoshida, Y., Takagi, T., Kuramoto, Y., Tatebayashi, K., Shirakawa, M., Yamahara, K., et al. (2021). Intravenous administration of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells in the subacute phase of cerebral infarction in a mouse model ameliorates neurological disturbance by suppressing blood brain barrier disruption and apoptosis via immunomodulation. Cell Transplantation 30:9636897211024183. doi: 10.1177/09636897211024183
Yuan, P., Ding, L., Chen, H., Wang, Y., Li, C., Zhao, S., et al. (2021). Neural stem cell-derived exosomes regulate neural stem cell differentiation through miR-9-Hes1 axis. Front Cell. Dev. Biol. 9:601600. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.601600
Zacharek, A., Chen, J., Cui, X., Li, A., Li, Y., Roberts, C., et al. (2007). Angiopoietin1/Tie2 and VEGF/Flk1 induced by MSC treatment amplifies angiogenesis and vascular stabilization after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27, 1684–1691. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600475
Zhang, R., Mao, W., Niu, L., Bao, W., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). NSC-derived exosomes enhance therapeutic effects of NSC transplantation on cerebral ischemia in mice. eLife 12:e84493. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84493
Zhang, S., Chen, Q., Jin, M., Ren, J., Sun, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024). Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway through microbiota-gut-brain axis. Phytomedicine 128:155530. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155530
Zhang, T., Fang, S., Wan, C., Kong, Q., Wang, G., Wang, S., et al. (2015). Excess salt exacerbates blood-brain barrier disruption via a p38/MAPK/SGK1-dependent pathway in permanent cerebral ischemia. Sci Rep 5:16548. doi: 10.1038/srep16548
Zhang, T., Wu, P., Budbazar, E., Zhu, Q., Sun, C., Mo, J., et al. (2019). Mitophagy reduces oxidative stress via Keap1 (kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1)/Nrf2 (nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2)/PHB2 (prohibitin 2) pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 50, 978–988. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021590
Zhang, Y., Liu, Q., Zhang, X., Huang, H., Tang, S., Chai, Y., et al. (2022). Recent advances in exosome-mediated nucleic acid delivery for cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 20:279. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01472-z
Zhao, H., Li, Y., Chen, L., Shen, C., Xiao, Z., Xu, R., et al. (2019). HucMSCs-derived miR-206-knockdown exosomes contribute to neuroprotection in subarachnoid hemorrhage induced early brain injury by targeting BDNF. Neuroscience 417, 11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.07.051
Zheng, H.-W., Wang, Y.-L., Lin, J.-X., Li, N., Zhao, X.-Q., Liu, G.-F., et al. (2012). Circulating MicroRNAs as potential risk biomarkers for hematoma enlargement after intracerebral hemorrhage. CNS Neurosci Ther 18, 1003–1011. doi: 10.1111/cns.12019
Zheng, X., Ren, B., and Gao, Y. (2023). Tight junction proteins related to blood-brain barrier and their regulatory signaling pathways in ischemic stroke. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165:115272. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115272
Zhong, L., Wang, J., Wang, P., Liu, X., Liu, P., Cheng, X., et al. (2023). Neural stem cell-derived exosomes and regeneration: Cell-free therapeutic strategies for traumatic brain injury. Stem Cell Res. Therapy 14:198. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03409-1
Zhou, H., Yi, Z., Le, D., Mao, G., and Zhang, H. (2024). Intravenous administration of human chorionic membrane mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional recovery in a rat traumatic brain injury model. Neuroreport 35, 81–89. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001981
Zhou, J., Geng, Y., Su, T., Wang, Q., Ren, Y., Zhao, J., et al. (2022). NMDA receptor-dependent prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 induction in neurons promotes glial proliferation during brain development and injury. Cell Rep. 38:110557. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110557
Keywords: blood brain barrier, stroke, stem cell, exosomes, cell therapy
Citation: Fu X, Li J, Yang S, Jing J, Zheng Q, Zhang T and Xu Z (2025) Blood-brain barrier repair: potential and challenges of stem cells and exosomes in stroke treatment. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 19:1536028. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1536028
Received: 28 November 2024; Accepted: 12 March 2025;
Published: 07 April 2025.
Edited by:
Mao Pang, Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Sudhanshu P. Raikwar, Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI), United StatesCopyright © 2025 Fu, Li, Yang, Jing, Zheng, Zhang and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhuo Xu, eHV6aHVvQGpsdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.