- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Chonggang General Hospital, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Infectious Diseases, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Infectious Diseases (Ministry of Education), Institute for Viral Hepatitis, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 4Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Background and aims: HCV genotype (GT) 3 is associated with rapid liver disease progression. However, the liver disease progression and its risk factors in patients with HCV GT 3 infection after sustained virological response (SVR) following direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) remain unclear. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the liver disease progression of patients with GT 3 after SVR.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of patients with HCV infection who achieved SVR by DAAs. The clinical outcome was overall liver disease progression (OLDP), defined as newly diagnosed compensated liver cirrhosis, decompensated liver cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma. The incidence of OLDP was evaluated by Kaplan−Meier analysis. Cox regression analysis identified the risk factors for OLDP.
Results: A total of 409 patients (46.9% GT3) were followed for 43.7 (32.9, 58.7) months. The incidence of OLDP was higher in patients with GT 3 (4.63/100PY) than non-GT 3 (0.60/100PY; P < 0.001). According to Cox multivariate analysis, GT 3 was significantly associated with OLDP (HR 6.41, 95% CI 1.82 - 22.56; P=0.004). The predictors of OLDP in patients with GT 3 were HCV recurrence (HR 12.15, 95% CI 3.18 - 46.46; P < 0.001) and FIB-4 > 3.25 (HR 16.40, 95% CI 1.03 - 39.81; P = 0.046) at baseline.
Conclusion: HCV GT 3-infected patients remain at a higher risk of OLDP even after achieving SVR by DAAs, especially patients with advanced liver fibrosis and at high risk for reinfection or virological late relapse.
Introduction
The World Health Organization estimated that 57.8 million people were living with chronic HCV infection in 2019 and were at risk of subsequent complications, including liver decompensation and hepatocellular cancer (HCC). China currently has the highest number of individuals infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the world (Cui et al., 2023). In previous studies, the most common genotype (GT) of HCV worldwide was genotype (GT) 1 (46%), followed by GT 3 (22%) (Gower et al., 2014). The proportion of GT 3 was 38.7% in southwest China, followed by 13.69% in South China and 11.11% in Northwest China, and the proportion of GT 3 has been increasing each year (Zhou et al., 2009; Chan et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2017; Polaris Observatory HCV Collaborators, 2017; Cui et al., 2023).
Compared with other genotypes, GT 3 is associated with a lower rate of sustained virological response (SVR) and a higher risk of hepatic fibrosis progression and HCC in patients with HCV (Kanwal et al., 2014; Chan et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2020; Wang and Wei, 2021). A study conducted in the United States found that patients infected with GT 3 had a higher risk of end-stage liver disease (ESLD), HCC, and liver-related death compared to those infected with genotype 1. Specifically, these patients had a 1.1-fold increased risk of ESLD, a 2.1-fold increased risk of HCC, and a 1.4-fold increased risk of liver-related death (McMahon et al., 2017). A study conducted in China found that GT 3, particularly subtype 3b, was linked to faster liver disease progression (Wu et al., 2020). However, most conducted on this topic were focused on regions where GT 1 is predominant and the number of GT 3 patients were relatively few in these studies. Therefore, further studies are necessary for regions with high GT 3 prevalence.
In addition, the risk of liver disease progression attributable to HCV infection is decreased by the achievement of sustained virological response (SVR) after direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), which are highly effective in curing more than 90% of patients of all genotypes (Manns et al., 2017; Nagaoki et al., 2020). However, achieving SVR does not equate to complete elimination of the risk of liver disease progression (Semmler et al., 2022). Currently, there is limited data on liver disease progression for GT 3 patients after receiving DAA treatment and achieving SVR.
Therefore, this retrospective cohort study aimed to investigate the influence of GT 3 on liver disease progression for HCV patients who achieved SVR. We hypothesized that GT 3 were associated with worse liver disease progression in HCV patients after SVR following DAA therapy. The findings of this study are significant for formulating appropriate treatment and follow-up strategies for these patients.
Methods
Study design and participants
This was a retrospective cohort study of adults (≥18 years) with HCV infection who achieved SVR with DAA treatment at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University in China. The patients were treated between August 2015 and September 2021 and followed up through November 2023. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) diagnosed with HCV infection; (2) received DAA regimens, which included one of the following: sofosbuvir, sofosbuvir/daclatasvir, sofosbuvir/ledipasvir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, elbasvir/grazoprevir, or glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in combination with or without ribavirin (RBV); (3) achieved SVR 12, defined as having undetectable HCV RNA levels for at least 12 weeks after treatment (Yoshida et al., 2015). The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) failed to achieve SVR; (2) coinfected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); (3) had a history of HCC and liver transplantation or diagnosed with HCC within 6 months after the end of treatment (EOT); (4) lacked clear genotype results. The choice of the regimens was decided by the physician according to drug policies and clinical practice guidelines at the time of treatment initiation. Patients were followed up every 6 to 12 months after the end of treatment (EOT) until they experienced overall liver disease progression (OLDP) (Kanwal et al., 2014), liver transplantation, or died. This study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee.
Data collection
The following laboratory data at baseline and follow-up visits were collected from the medical records for analysis: anti-HCV, HCV-RNA, HCV genotype, HBV core antibody (anti-HBc), Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index; Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) score, white blood cell (WBC), hemoglobin (HB), platelet count (PLT), Albumin (ALB), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and international normalized ratio (INR). The demographic data included age, sex, diabetes status, hypertension status, and alcohol intake. The results of imaging, including abdominal ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR), transient elastography (FibroScan®, Echosens, Paris, France), and liver pathology, were collected.
Assessment of variables and outcomes
In this study, the HCV patients were divided into the GT 3 group and the non-GT 3 group. Non-GT 3 included GT1, GT 2, GT 4, and GT 6, except for GT 5 which was not detected. HCV recurrence was defined as patients who achieved SVR 12 but were detected with HCV RNA above the detection limit at least once during the follow-up period. OLDP included newly diagnosed compensated liver cirrhosis (CLC), decompensated liver cirrhosis (DLC), or HCC (Kanwal et al., 2014). In this study, three patients died of gastrointestinal bleeding, one patient died of severe pneumonia, and two patients died because of accidents during FUP. One patient diagnosed with CLC before DAA treatment underwent liver transplantation. Thus, death and liver transplantation were excluded from our analyses of OLDP.
CLC was defined by one of the following criteria: (1) liver biopsy confirming cirrhosis (Metavir or Ishak score); (2) gastroesophageal varices in endoscopy; (3) liver stiffness measurement cutoff >14.6 kPa; (4) imaging studies showing signs of portal hypertension; and (5) laboratory data consistent with 2 out of 4 requirements in the absence of other explanations: PLT <100×10^9/L, serum ALB <35 g/L, INR >1.3, and APRI ≥2 (Tang et al., 2023). DLC was defined as the presence of ascites, variceal bleeding, and/or hepatic encephalopathy on the basis of cirrhosis (Xu et al., 2020). The diagnosis of HCC was based on hepatic histology, AFP, typical CT imaging, or MR imaging findings (Zhou et al., 2023). The diagnosis of fatty liver was based on ultrasound, CT, or MR. Alcohol abuse was defined as the consumption of >50 g/d of alcohol.
Statistical analysis
All datasets were estimated for normality of variance using the Kolmogorov−Smirnov test (S−K test). Continuous variables are described as the mean (standard deviation) and median (interquartile range [IQR]) according to the normality of the distribution. This study applied the chi-squared (χ²) test or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. Student’s t-test (P≥0.05 in the S-K test) or Mann−Whitney U test (P<0.05 in the S-K test) was used for continuous variables according to their normality of distribution to compare baseline characteristics.
The occurrence of OLDP was expressed per 100 patient-years (/100PY) and evaluated based on Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and compared between two groups by the Log-rank test. Significant risk factors linked to OLDP were evaluated through univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. The risk factors were expressed as hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. Statistical analysis was performed using R version 4.3.0.
Results
Patient characteristics
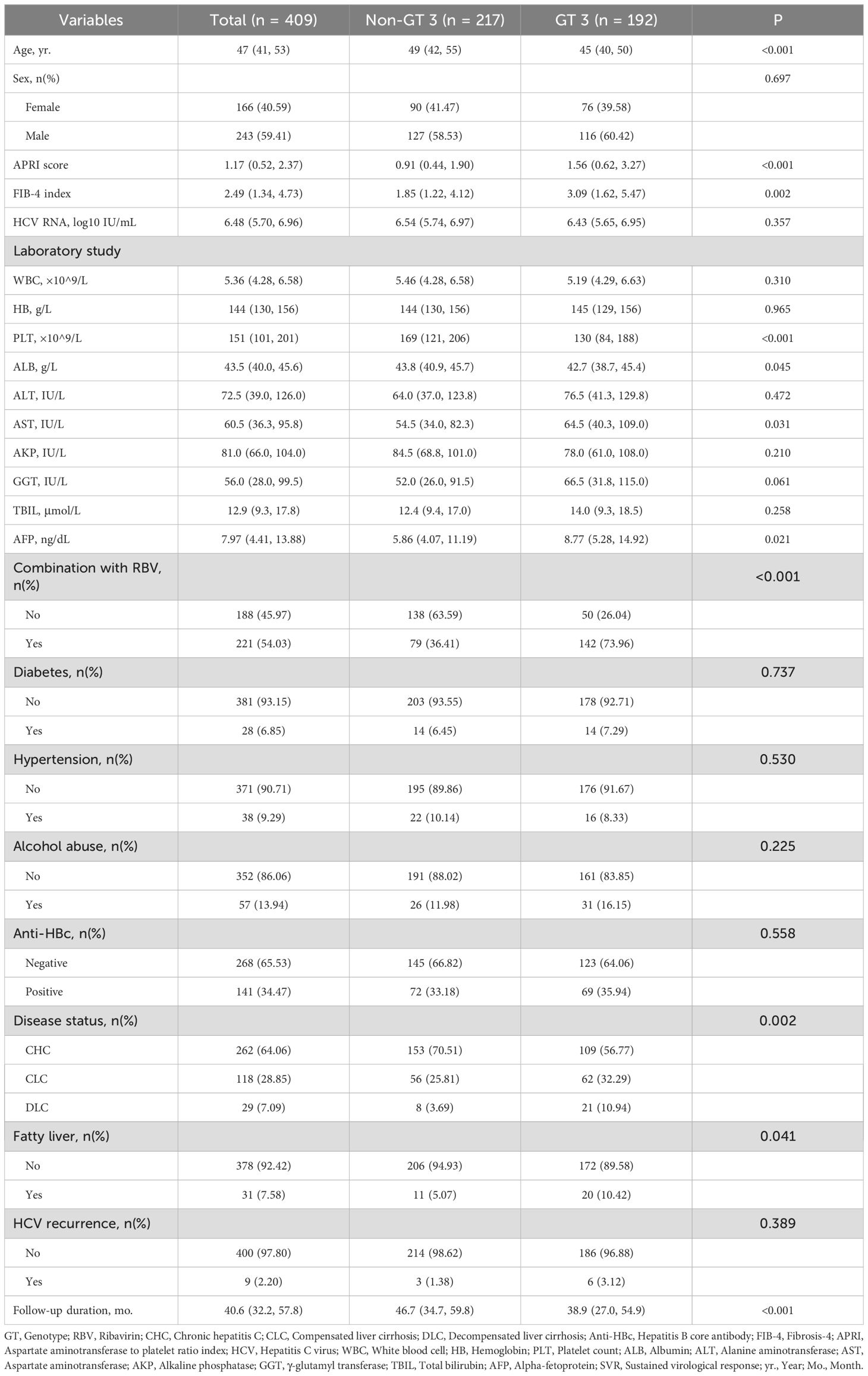
From 585 patients who received DAA treatment, 409 patients were included in the current study after strict screening (Figure 1). In Table 1, 192 (46.9%) patients were divided into the GT 3 group. In the GT 3 group, 94 (49.0%) patients were infected with subtype 3b, and 81 (42.2%) patients were infected with subtype 3a. Additionally, in the non-GT 3 group, the genotypes included GT1 (51/217, 23.5%), GT2 (29/217, 13.4%), GT4 (1/217, 0.5%), and GT6 (136/217, 62.7%) (Supplementary Table S1). Compared with the non-GT 3 group, patients with GT 3 were with younger age, lower PLT, higher AFP, higher FIB-4, higher APRI scores, increased risk of baseline cirrhosis and HCV reoccurrence (P<0.05; Table 1).

Figure 1. A flowchart of patient selection. HCV, Hepatitis C virus; DAA, Direct-acting antiviral; SVR, Sustained virological response; HBV, Hepatitis B virus; HIV, Human immunodeficiency virus; HCC, Hepatocellular carcinoma; DLC, Decompensated liver cirrhosis; CHC, Chronic hepatitis C; CLC, Compensated liver cirrhosis; GT, Genotype.
Incidences of overall liver disease progression
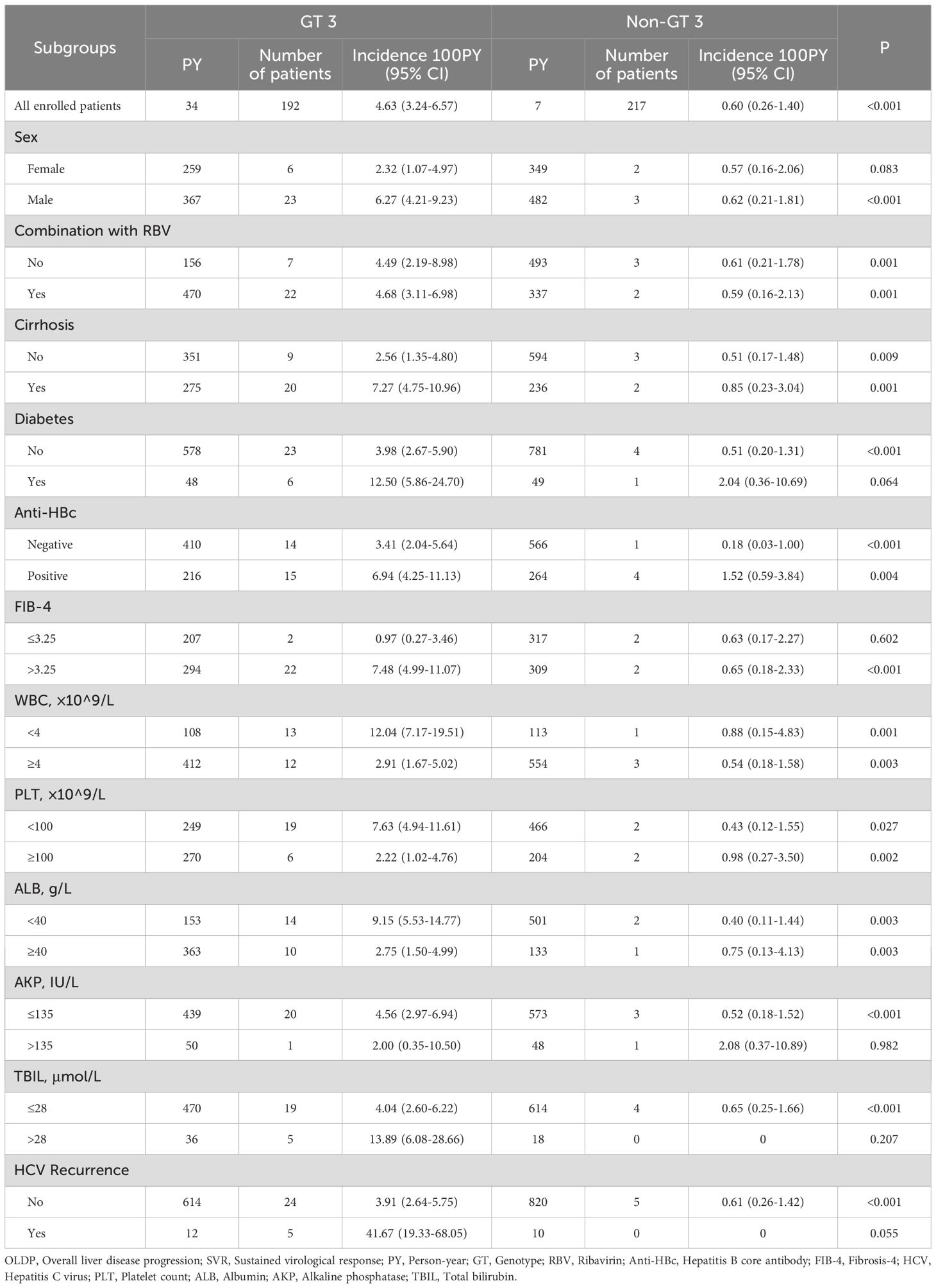
The median time from EOT to OLDP during follow-up in patients with GT 3 was shorter than that in patients with non-GT 3 (38.9 vs. 46.7 months; P<0.001; Table 1). Overall, OLDP occurred in 10 patients with CLC, 11 patients with DLC, and 20 patients with HCC. In the GT 3 group, the incidences of newly diagnosed CLC, DLC, and HCC were 3.65% (7/219), 4.17% (8/219), and 9.90% (19/219), respectively. The non-GT 3 group had lower incidences of 1.38% (3/217) for CLC and DLC, and 0.46% (1/217) for HCC. Regarding the median progression time, the GT 3 group had intervals of 11.47 months (CLC), 7.42 months (DLC), and 18.70 months (HCC), while the non-GT 3 group had 34.17 months (CLC), 25.53 months (DLC), and 48.30 months (HCC). The incidence of OLDP was higher in patients with GT 3 (4.63/100PY, 95% CI 3.24-6.57) than non-GT 3 (0.60/100PY, 95% CI 0.26-1.48; P <0.001; Table 2). The populations with high incidence of OLDP (>5.00/PY) were GT 3-infected with male, cirrhosis, diabetes, anti-HBC positive, FIB-4>3.25, WBC<4×10^9/L, PLT<100×10^9/L, ALB<40 g/L, TBIL>28μmol/L and HCV recurrence (Table 2).
The cumulative incidence of OLDP at 5 years was higher for patients with GT 3 (18.7%) than for those with non-GT 3 (3.0%; P<0.001), as was the case with CLC (7.8% vs. 2.8%, P=0.042), DLC (5.9% vs. 2.0%, P = 0.044), and HCC (12.7% vs. 1.0%, P < 0.001) (Figure 2). The cumulative incidence of OLDP in patients with GT 3 was higher than that with GT 1 (P=0.003) and GT 6 (P<0.001) (Figure 3), but there was no statistical difference from that in patients with GT 2 (P=0.215). Among 262 patients without cirrhosis, those infected with GT 3 had a higher cumulative incidence of OLDP at 5 years than those infected with non-GT 3 (11.1% vs. 2.8%; P=0.009) (Figure 4A). Patients with cirrhosis in the GT 3 group had a higher risk of OLDP than those with non-GT 3 (27.3% vs. 3.3%; P<0.001) (Figure 4B). After excluding the patients with HCV recurrence, the cumulative incidence of OLDP in GT 3 patients was statistically different from that in non-GT 3 patients (P < 0.001). There was no statistical difference in the cumulative incidence of CLC (P=0.172) and DLC (P=0.081) between the two groups. The cumulative incidence of HCC after completion of DAA treatment and SVR was statistically different between the two groups (P < 0.001).
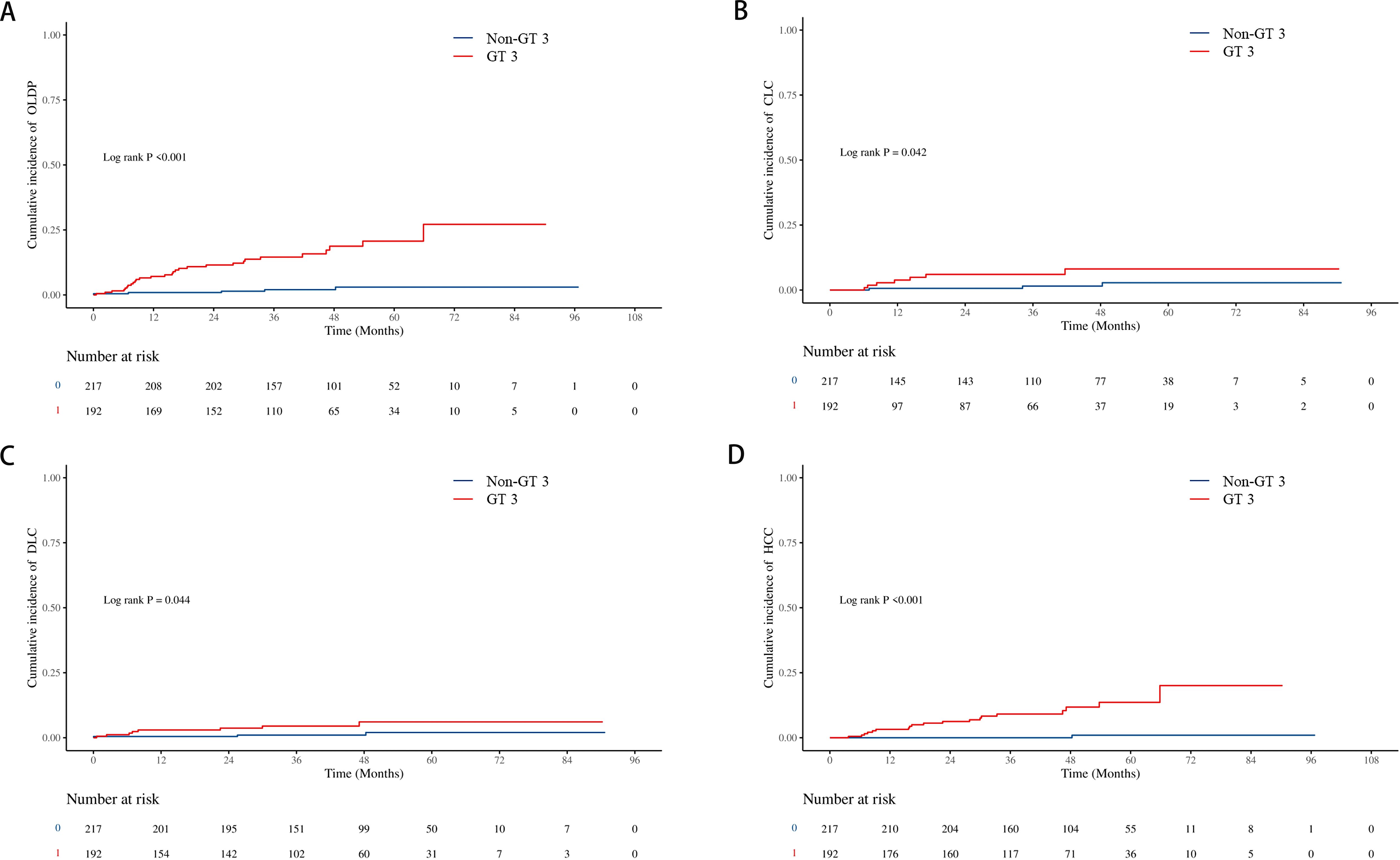
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence of liver disease progression in the GT 3 group and non-GT 3 group. (A) The cumulative incidence rates of OLDP; (B) The cumulative incidence rates of CLC; (C) The cumulative incidence rates of DLC; (D) The cumulative incidence rates of HCC. The level of significance was set at p<0.05 (Kaplan−Meier estimates). GT, genotype; OLDP, overall liver disease progression; CLC, Compensated liver cirrhosis; DLC, Decompensated liver cirrhosis; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
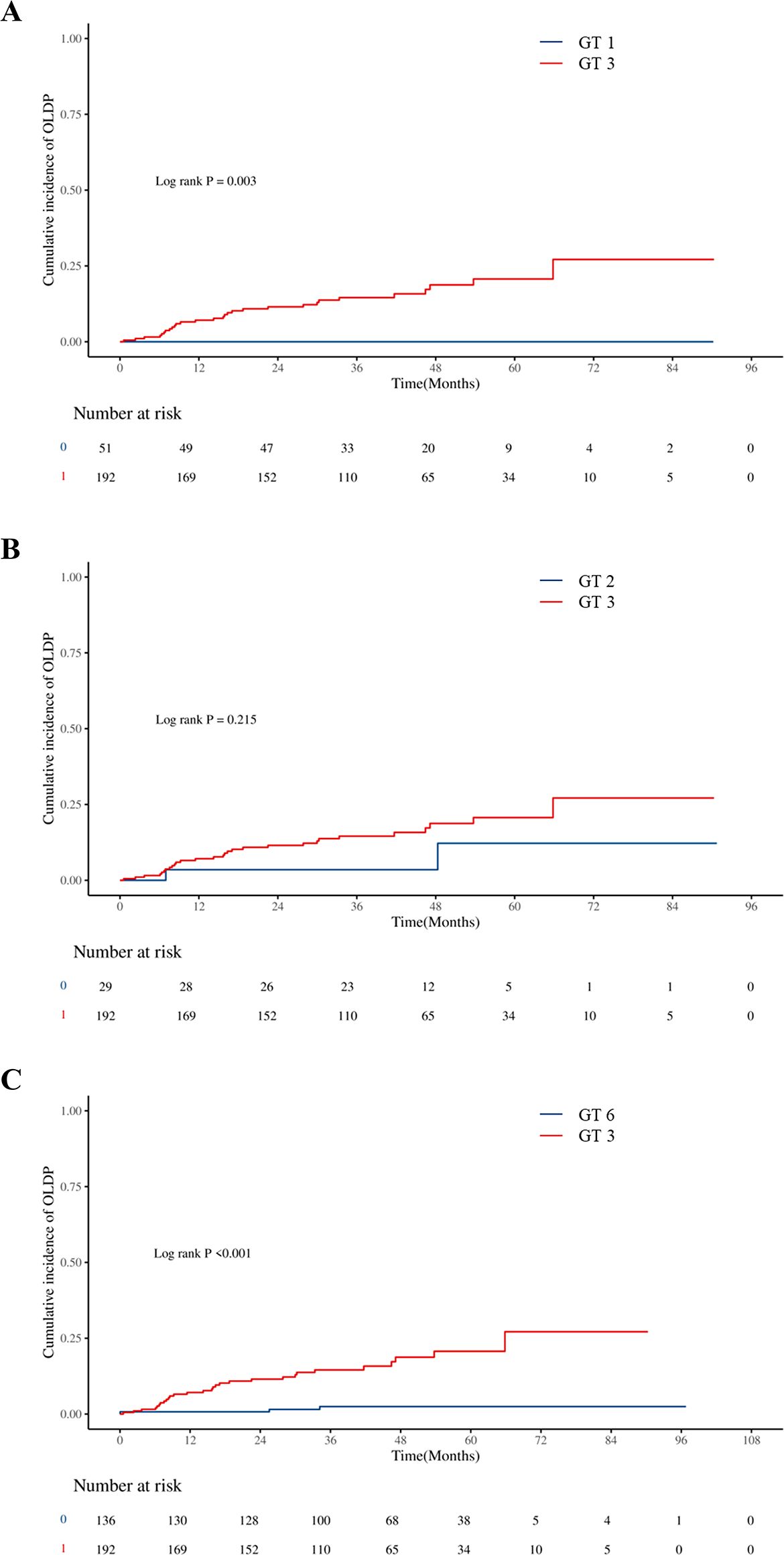
Figure 3. Cumulative incidences of liver disease progression in patients: (A) between GT 3 and GT 1, (B) between GT 3 and GT 2, and (C) between GT 3 and GT 6.
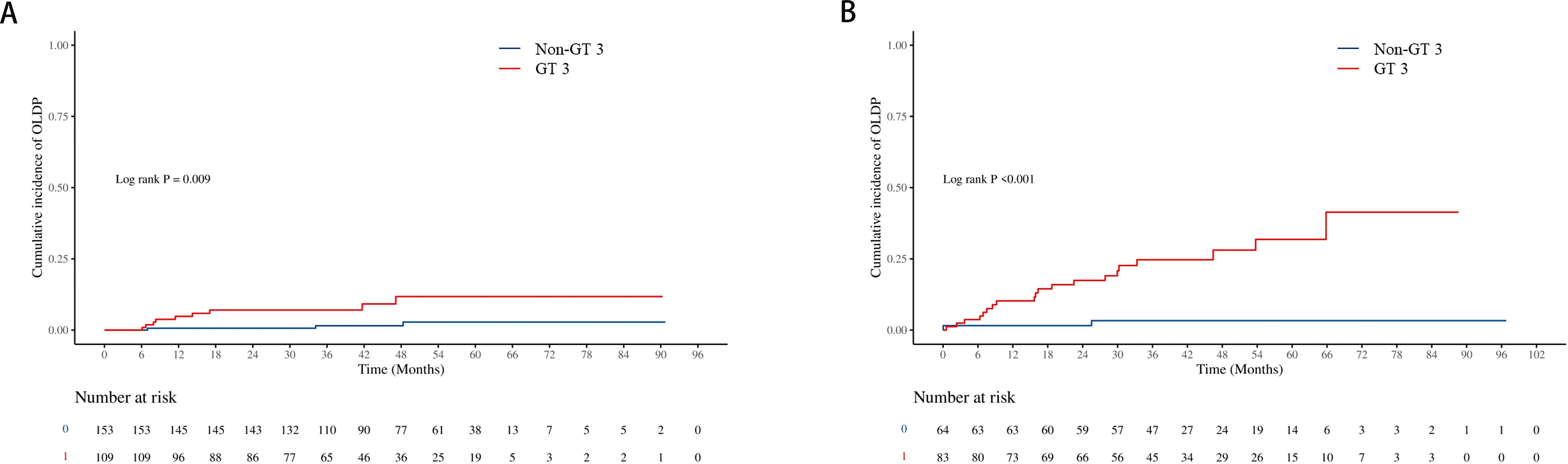
Figure 4. Cumulative incidence of OLDP according to cirrhosis status. The cumulative incidence rates of OLDP in the patients (A) without cirrhosis and (B) with cirrhosis. The level of significance was set at p<0.05 (Kaplan−Meier estimates). GT, genotype; OLDP, overall liver disease progression.
Risk factors of overall liver disease progression in all patients
In Table 3, univariate analysis results suggested that male, diabetes, HCV recurrence, FIB-4>3.25, PLT<100×10^9/L, and ALB<40 g/L at baseline were associated with OLDP risk. Furthermore, according to multivariate Cox regression analysis, the predictors of OLDP in all patients were male (HR 3.23, 95% CI 1.10 - 9.50; P=0.033), GT 3 (HR 6.41, 95% CI 1.82 – 22.56; P=0.004) and HCV recurrence (HR 7.90, 95% CI 2.35 – 26.58; P<0.001). In Supplementary Table S2, Cox regression analysis showed that the FIB-4 index (HR 6.40, 95% CI 1.03 – 39.81) and HCV recurrence (HR 12.15, 95% CI 3.18 – 46.46) are risk factors of OLDP for GT 3 patients.
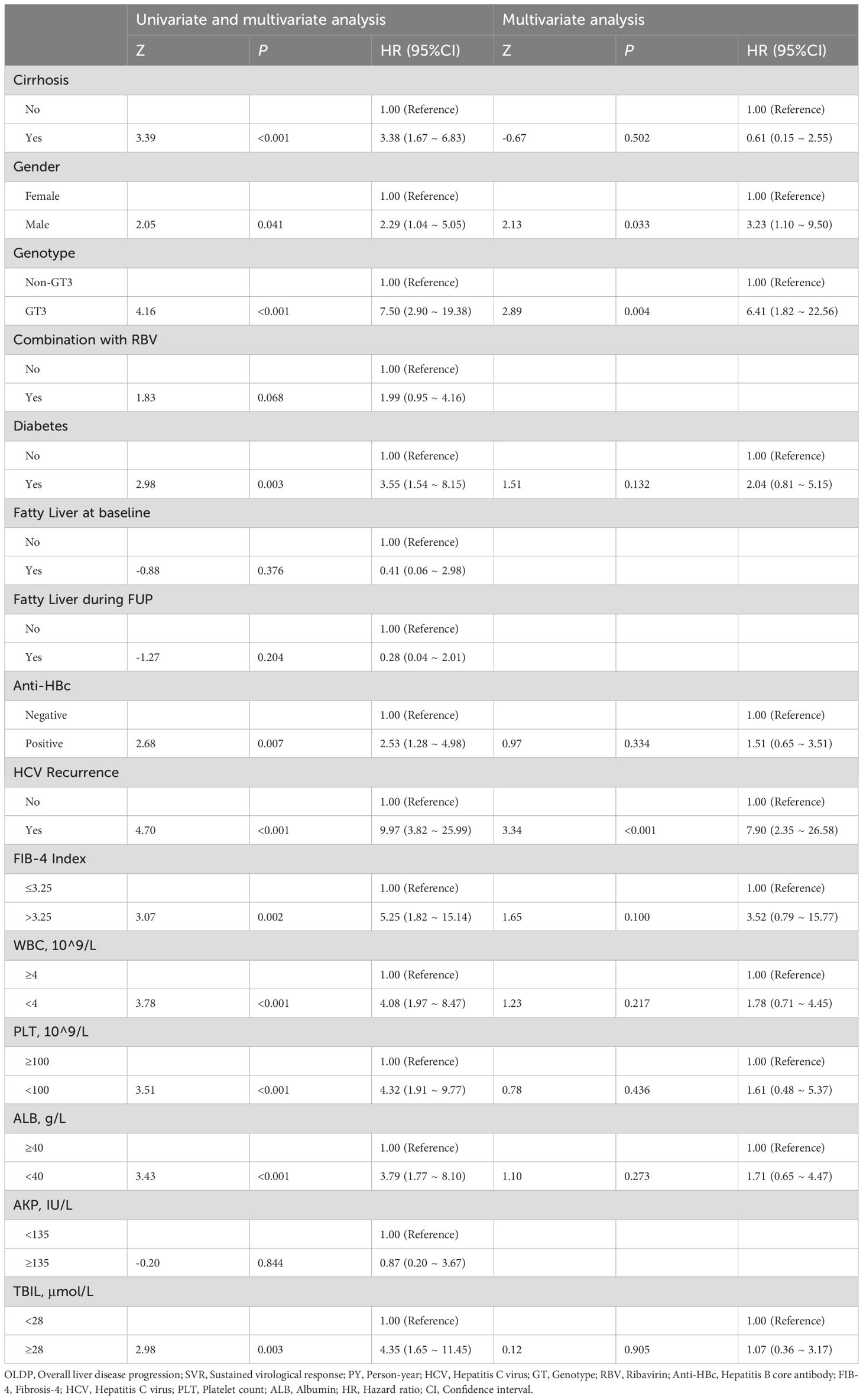
Table 3. Variables associated with OLDP in patients with all patients (univariate and multivariate analysis).
Discussion
The risk of liver disease progression was decreased after viral eradication, while this risk could not be eliminated in some patients with certain characteristics. To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the clinical outcomes of patients infected with GT 3 who achieved DAA-induced SVR. Our findings revealed that patients with GT 3 were at a higher risk of OLDP including HCC after successful DAA therapy than those with non-GT 3. In addition, we reported the post-SVR incidences of OLDP in each subgroup among patients with GT 3 and non-GT 3, which has never been reported before. Finally, we identified the risk factors of OLDP in patients with GT 3 after DAA therapy and built a model to predict this risk for clinical practice.
In our study, 46.9% of patients treated with DAAs were infected with GT 3. This proportion was higher than that in most previous studies, which reported that the proportion of patients with GT 3 was 8.3-13.8% (Ioannou et al., 2017; Nahon et al., 2018). In China, HCV GT 3 (33.1-39.4%) was more prevalent in southwest provinces, such as Yunnan, Guangxi, and Chongqing (Zhou et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2017; Tang et al., 2023). Southwestern China is a vital transit area for drug smuggling, and intravenous drug abuse has become the major risk factor for GT 3 (Ruta and Cernescu, 2015; Chen et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2020). This may explain the high prevalence of GT 3 in southwestern China. In this study, we found that the GT 3 group was younger (45 vs 49) and had a higher proportion of cirrhosis (43.2% vs 29.5%) when treated with DAAs. Patients with GT 3 had a shorter median time (38.9 vs 46.7) from EOT to experience their first event of OLDP. Similarly, a Chinese study reported a younger age and shorter duration from infection to liver disease progression in GT 3-infected patients than in patients with other genotypes (Lu et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2020).
In terms of clinical outcomes, several cohort studies have reported GT 3 is related to a higher rate of liver disease progression, including cirrhosis and HCC, and liver-related death compared to other genotypes (Kanwal et al., 2014; McMahon et al., 2017; Lee et al., 2019). These findings are similar to our study, a higher incidence of liver disease progression was observed in patients with GT 3 in this study. The same conclusion was obtained in the subgroup analysis. Biopsy studies showed that GT 3 was demonstrated to be much more likely to increase liver steatosis than other genotypes, resulting in more rapid liver fibrosis which leads to higher incidence rates of cirrhosis and HCC (Abid et al., 2005; Probst et al., 2011). Previous studies revealed an improvement in liver steatosis in patients with GT 3 after antiviral treatment but not in patients with GT 1, which seems to indirectly explain this association (Zarębska-Michaluk, 2021). However, whether GT 3-induced liver steatosis persists after virus eradication remains unclear. We have observed that GT 3-infected patients without cirrhosis are more likely to develop new cirrhosis, while we found that fatty liver mainly diagnosed by ultrasound at baseline is not associated with liver disease progression. The reason is probably a missed diagnosis of fatty liver by ultrasound. The lack of data, including body mass index and controlled attenuation parameter, hinders further analysis of the association of GT 3 and liver steatosis after DAA therapy. Relevant studies based on DAAs are needed in the future.
Our results displayed that FIB-4 index and HCV recurrence were risk factors of OLDP for GT 3 patients. Few studies reported the effects of reinfection and late HCV recurrence on disease progression after DAA treatment. This study suggested that HCV recurrence, regardless of the cause, increased the risk of liver disease progression after SVR following DAA. High-risk behaviors (such as MSM, drug injection, etc.) that can lead to reinfection should be avoided after successful antiviral treatment. In this study, FIB-4 was used to evaluate liver fibrosis to explore the impact of liver fibrosis on the risk of liver disease progression. Among patients with FIB-4>3.25 and APRI<2, 3/58 (5.2%, 1.29/100 PY) developed HCC, and the incidence of HCC was similar to that in the study of Alessia (6/133, 1.22/100 PY) (Ciancio et al., 2023). In this study, there were 170 patients with FIB-4 > 3.25, of whom 29 were not diagnosed with cirrhosis, and 2/29 progressed to cirrhosis after antiviral treatment, which suggested that not all patients with liver fibrosis could achieve fibrosis regression after DAA treatment. Dynamic follow-up of FIB-4 and imaging is necessary. Similarly, Ioannou observed that FIB-4 continued to rise after SVR (Ioannou et al., 2019). However, unrecognized cirrhosis may be present in non-cirrhotic patients with high FIB-4, while patients diagnosed with cirrhosis and with low FIB-4 may not actually have cirrhosis. FIB-4, as a classic noninvasive diagnostic indicator for fibrosis, still has some limitations, and future studies need to combine more indicators to stratify the risk of liver disease progression after DAA therapy.
Several limitations should be noted when interpreting our findings. First, this was a retrospective study. Patients were enrolled from a single center in southwestern China, which may limit the generalizability of our results to other populations. Second, the diagnosis of cirrhosis and HCC is considerably dependent on imaging methods, which could miss the diagnosis of very early cirrhosis and HCC. Third, this study did not calculate the mortality of such a cohort, which was mainly affected by non-hepatic causes. Published research has demonstrated that DAA therapy is independently associated with a significant decrease in the risk of mortality, which may lead to a lower incidence of liver disease progression. Fourth, due to the natural of retrospective study design, the lack of BMI, LSM values, CAP scores, alcohol consumption after SVR were not analyzed in this study, which may provide more information on the liver disease progression after SVR. Finally, the patients lost to follow-up could potentially introduce bias.
Conclusion
This retrospective cohort study proved the higher risk of liver disease progression of GT 3-infected patients even if achieving SVR by successful DAA therapy. It reinforced the need for the surveillance of GT 3-infected patients after treatment, especially with FIB-4>3.25 and at the risk of HCV recurrence.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University Human Research Ethics Committee (NO. 2021593). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YX: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. CG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. NW: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision. DC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Chongqing Medical Scientific Research Key Project (Joint Project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau) (Grant number 2022ZDXM001), and the First batch of key Disciplines on Public Health in Chongqing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1510939/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
SVR, sustained virological response; CHC, chronic hepatitis C; CLC, compensated liver cirrhosis; DLC, decompensated liver cirrhosis; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; DAA, directly acting antiviral; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; GT, genotype; RBV, ribavirin; CHC, chronic hepatitis C; CLC, compensated liver cirrhosis; HBcAb, hepatitis B core antibody; FIB-4, fibrosis-4; APRI, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index; HCV, hepatitis C virus; WBC, white blood cell; HB, hemoglobin; PLT, platelet count; ALB, albumin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; AKP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; TBIL, Total bilirubin; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; LSM, liver stiffness measurement; BMI, body-mass index; CAP, controlled attenuation parameter.
References
Abid, K., Pazienza, V., de Gottardi, A., Rubbia-Brandt, L., Conne, B., Pugnale, P., et al. (2005). An in vitro model of hepatitis C virus genotype 3a-associated triglycerides accumulation. J. Hepatol. 42, 744–751. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.12.034
Chan, A., Patel, K., Naggie, S. (2017). Genotype 3 infection: the last stand of hepatitis C virus. Drugs 77, 131–144. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0685-x
Chen, Y., Yu, C., Yin, X., Guo, X., Wu, S., Hou, J. (2017). Hepatitis C virus genotypes and subtypes circulating in Mainland China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 6, e95. doi: 10.1038/emi.2017.77
Ciancio, A., Ribaldone, D. G., Spertino, M., Risso, A., Ferrarotti, D., Caviglia, G. P., et al. (2023). Who should not be surveilled for HCC development after successful therapy with DAAS in advanced chronic hepatitis C? Results of a long-term prospective study. Biomedicines 11, 166. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010166
Cui, F., Blach, S., Manzengo Mingiedi, C., Gonzalez, M. A., Sabry Alaama, A., Mozalevskis, A., et al. (2023). Global reporting of progress towards elimination of hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 8, 332–342. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00386-7
Gower, E., Estes, C., Blach, S., Razavi-Shearer, K., Razavi, H. (2014). Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 61, S45–S57. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.027
Ioannou, G. N., Beste, L. A., Green, P. K., Singal, A. G., Tapper, E. B., Waljee, A. K., et al. (2019). Increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma persists up to 10 years after HCV eradication in patients with baseline cirrhosis or high FIB-4 scores. Gastroenterology 157, 1264–1278. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.033
Ioannou, G. N., Green, P. K., Berry, K. (2017). HCV eradication induced by direct-acting antiviral agents reduces the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. S0168-8278, 32273–32270. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.08.030
Kanwal, F., Kramer, J. R., Ilyas, J., Duan, Z., El-Serag, H. B. (2014). HCV genotype 3 is associated with an increased risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer in a national sample of U.S. Veterans with HCV. Hepatology 60, 98–105. doi: 10.1002/hep.27095
Lee, S. S., Kim, C. Y., Kim, B. R., Cha, R. R., Kim, W. S., Kim, J. J., et al. (2019). Hepatitis C virus genotype 3 was associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea. J. Viral Hepat 26, 459–465. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13047
Lu, J., Xiang, X., Cao, Z., Wang, W., Zhao, G., Tang, W., et al. (2017). Younger trend of cirrhosis incidence in genotype 3 HCV infected patients in Eastern China. J. Med. Virol. 89, 1973–1980. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24894
Manns, M. P., Buti, M., Gane, E., Pawlotsky, J.-M., Razavi, H., Terrault, N., et al. (2017). Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 3, 17006. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.6
McMahon, B. J., Bruden, D., Townshend-Bulson, L., Simons, B., Spradling, P., Livingston, S., et al. (2017). Infection with hepatitis C virus genotype 3 is an independent risk factor for end-stage liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver-related death. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatology: Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterological Assoc. 15, 431–437. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.012
Nagaoki, Y., Imamura, M., Teraoka, Y., Morio, K., Fujino, H., Ono, A., et al. (2020). Impact of viral eradication by direct-acting antivirals on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development, prognosis, and portal hypertension in hepatitis C virus-related compensated cirrhosis patients. Hepatol. Res. 50, 1222–1233. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13554
Nahon, P., Layese, R., Bourcier, V., Cagnot, C., Marcellin, P., Guyader, D., et al. (2018). Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma after direct antiviral therapy for HCV in patients with cirrhosis included in surveillance programs. Gastroenterology 155, 1436–1450.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.015
Polaris Observatory HCV Collaborators (2017). Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2, 161–176. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30181-9
Probst, A., Dang, T., Bochud, M., Egger, M., Negro, F., Bochud, P. Y. (2011). Role of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 in liver fibrosis progression–a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepatitis 18, 745–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01481.x
Ruta, S., Cernescu, C. (2015). Injecting drug use: A vector for the introduction of new hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 21, 10811–10823. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10811
Semmler, G., Meyer, E. L., Kozbial, K., Schwabl, P., Hametner-Schreil, S., Zanetto, A., et al. (2022). HCC risk stratification after cure of hepatitis C in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 76, 812–821. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.025
Tang, Q., Chen, Z., Li, H., Zhang, L., Peng, M., Zeng, Y., et al. (2023). Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis C virus genotypes in different geographical regions of Chinese mainland and a phylogenetic analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 12, 66. doi: 10.1186/s40249-023-01106-y
Wang, X., Wei, L. (2021). Direct-acting antiviral regimens for patients with chronic infection of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 in China. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 9, 419–427. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00097
Wu, N., Rao, H.-Y., Yang, W.-B., Gao, Z.-L., Yang, R.-F., Fei, R., et al. (2020). Impact of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 on liver disease progression in a Chinese national cohort. Chin. Med. J. (Engl) 133, 253–261. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000629
Xu, X.-Y., Ding, H.-G., Li, W.-G., Xu, J.-H., Han, Y., Jia, J.-D., et al. (2020). Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis (abbreviated version). World J. Gastroenterol. 26, 7088. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7088
Yoshida, E. M., Sulkowski, M. S., Gane, E. J., Herring, R. W., Ratziu, V., Ding, X., et al. (2015). Concordance of sustained virological response 4, 12, and 24 weeks post-treatment with sofosbuvir-containing regimens for hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 61, 41–45. doi: 10.1002/hep.27366
Zarębska-Michaluk, D. (2021). Genotype 3-hepatitis C virus’ last line of defense. World J. Gastroenterol. 27, 1006–1021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.1006
Zhou, J., Sun, H., Wang, Z., Cong, W., Zeng, M., Zhou, W., et al. (2023). Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition). Liver Cancer 12, 405–444. doi: 10.1159/000530495
Keywords: hepatitis C virus, direct-acting antiviral, sustained virological response, HCV genotype 3, disease progression
Citation: Ran X, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zeng C, Gong C, Wang N and Cai D (2025) Genotype 3 is linked to worse liver disease progression in hepatitis C patients even after SVR following DAA therapy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1510939. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1510939
Received: 14 October 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 03 February 2025.
Edited by:
Baibaswata Nayak, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaReviewed by:
Shalimar, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaSenthil Kumar Venugopal, South Asian University, India
Copyright © 2025 Ran, Xu, Wang, Zeng, Gong, Wang and Cai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dachuan Cai, Y3FtdWNkY0BjcW11LmVkdS5jbg==; Ni Wang, TGFab2UxMjNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
‡ORCID: Cai Dachuan’s, orcid.org/0000-0003-3269-8549
 Xiping Ran
Xiping Ran Yang Xu2†
Yang Xu2† Ni Wang
Ni Wang Dachuan Cai
Dachuan Cai