- 1Department of Immunology, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT, United States
- 2Department of Public Health Sciences, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT, United States
Background: Contributions of leukocytes to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) defense have been reported extensively. However, it remains unclear whether there are different leukocyte responses to ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and its variants.
Methods: We analyzed peripheral blood leukocyte and subtype concentrations from 575 COVID-19 patients and 950 non-COVID-19 subjects registered at the University of Connecticut John Dempsey Hospital between 2020 and 2022, which covers the ancestral strain, Delta, and Omicron variants.
Results: We found that neutrophils, immature granulocytes, and monocytes were elevated, and lymphocytes were reduced after infection. These hyperactive neutrophils/immature granulocytes and suppressed lymphocytes/monocytes were associated with poorer prognosis in ancestral strain infection. Different from the ancestral strain, hyperactive immature granulocytes were not shown in the decedents of Delta infection, and immature granulocyte concentration was not observed to be associated with mortality. In Omicron infection, suppressed lymphocytes and monocytes were not shown in the decedents, and lymphocyte/monocyte concentrations were not associated with mortality.
Conclusions: Our findings provided insights into different leukocyte immune responses to ancestral SARS-CoV-2, Delta, and Omicron variants.
Introduction
Since the first report of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in December 2019 (Zhang et al., 2020), the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has caused more than 769 million cases and 6.9 million deaths worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) dashboard (accessed 30/08/2023). The heterogeneous disease courses of COVID-19 range from mild to severe and even fatal outcomes (Hu et al., 2021). To better prevent and control COVID-19, researchers put huge effort into identifying clinical characteristics and infectious mechanisms. Numerous variants have occurred worldwide because of the high genetic recombination and mutation of coronaviruses (Aleem et al., 2023). Five dominant variants were defined by the WHO, including Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), Delta (B.1.617.2), and Omicron (B.1.1.529) (Aleem et al., 2023). The Delta variant predominantly occurred from May 1, 2021, and was quickly overtaken by the Omicron variant in December 2021 (Lambrou et al., 2022). Although the Omicron variant presented an increased transmission compared to previous variants (Kumar et al., 2022), it is reported that Omicron has less pathogenic potential, which may partly explain the reduced morbidity of COVID-19 in 2022 (Zhang HP. et al., 2023). Thus, the SARS-CoV-2 variants may have different pathogenesis compared with the ancestral strain.
The COVID-19 pathology results from not only the viral infection but also abnormal immune responses. Previous studies have shown that blood leukocyte concentrations are associated with COVID-19 progression and prognosis, such as substantially higher concentrations of neutrophils (Kasine et al., 2022) and immature neutrophils (Obermayer et al., 2021), highly dysregulated monocytes (Schulte-Schrepping et al., 2020), and a lower concentration of lymphocytes (Zhang et al., 2021). However, it remains unclear whether the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and its variants have different effects on the immune system, resulting in differences in peripheral blood leukocytes. Therefore, we analyzed the 2020–2022 hematology test data from the University of Connecticut (UConn) John Dempsey Hospital to examine the associations between leukocytes and leukocyte subtypes and the morbidity and mortality of different types of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our investigation shed light on the tendency of immunity to vary; this information is a precondition for identifying diagnostic markers and therapeutic strategies targeting COVID-19 in the future.
Materials and methods
Study population and data collection
The unidentified participants were randomly enrolled from the electronic databases of the UConn John Dempsey Hospital in Farmington, Connecticut, from 2020 to 2022. Here, we leverage the hospital database to build a clinical study on patients infected with COVID-19 from March 2020 to December 2022, as well as a group of non-COVID-19 controls who were annual physical examination patients with no symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection within 2 weeks before the examination. Please note that it is possible that there could be asymptomatic COVID-19 individuals in the group of non-COVID-19 controls. An automated Sysmex XN-3000 analyzer was used to measure the peripheral blood white blood cell (leukocyte) counts.
Patient demographics, including survival, age, sex, COVID-19 vaccination status, corticosteroid use, and comorbid conditions, were recorded during hospital admissions and summarized in Table 1. Comorbidities include chronic lung diseases, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer. Clinical hematology testing was performed one or several times after hospital admissions, and we summarized patients’ first-time results of leukocyte and subtype counts in peripheral blood (Figures 1, 2). The concentrations of neutrophils, immature granulocytes, lymphocytes, and monocytes were calculated based on the total leukocyte counts (leukocyte count × percentage of subtype/100). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants (Lambrou et al., 2022), we approximately divided the patients into three groups: 1) ancestral strain infection from March to June 2020; 2) Delta variant infection from July to December 2021; and 3) Omicron variant infection from January to December 2022.
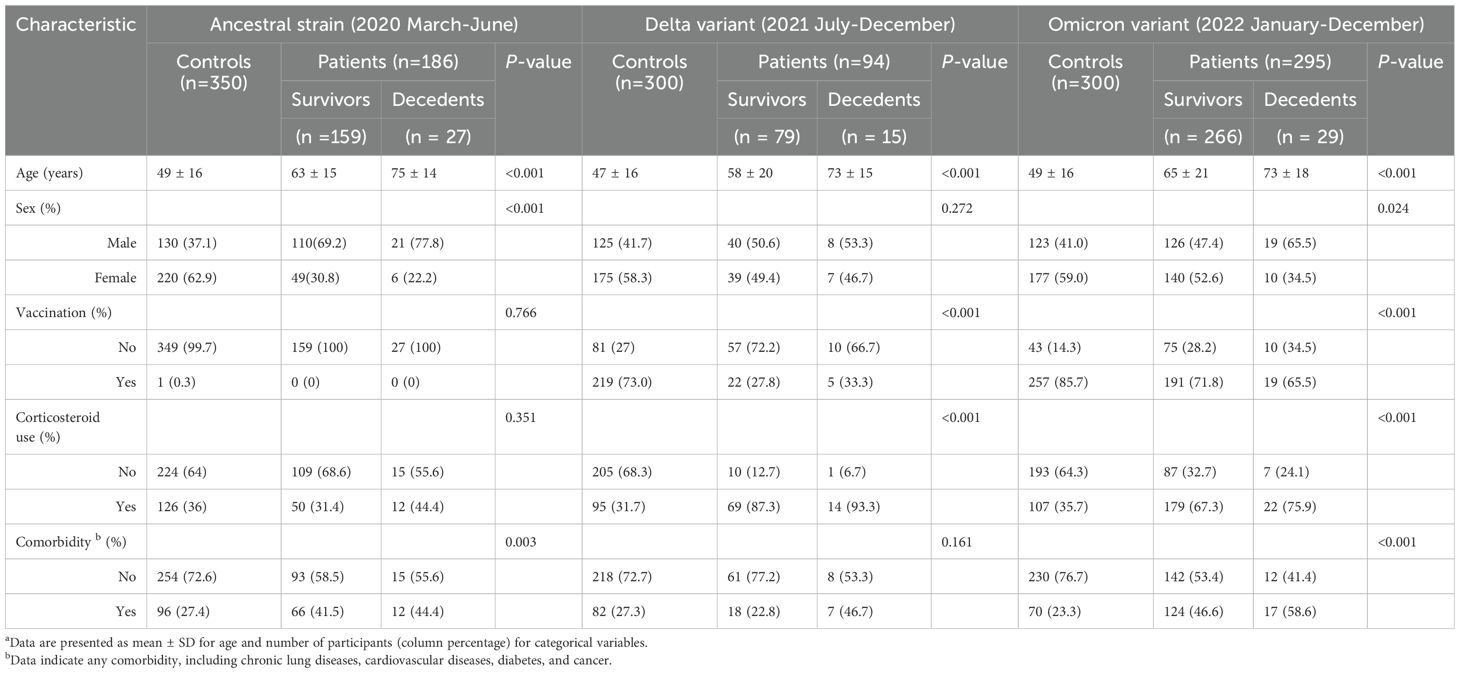
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of participants a.
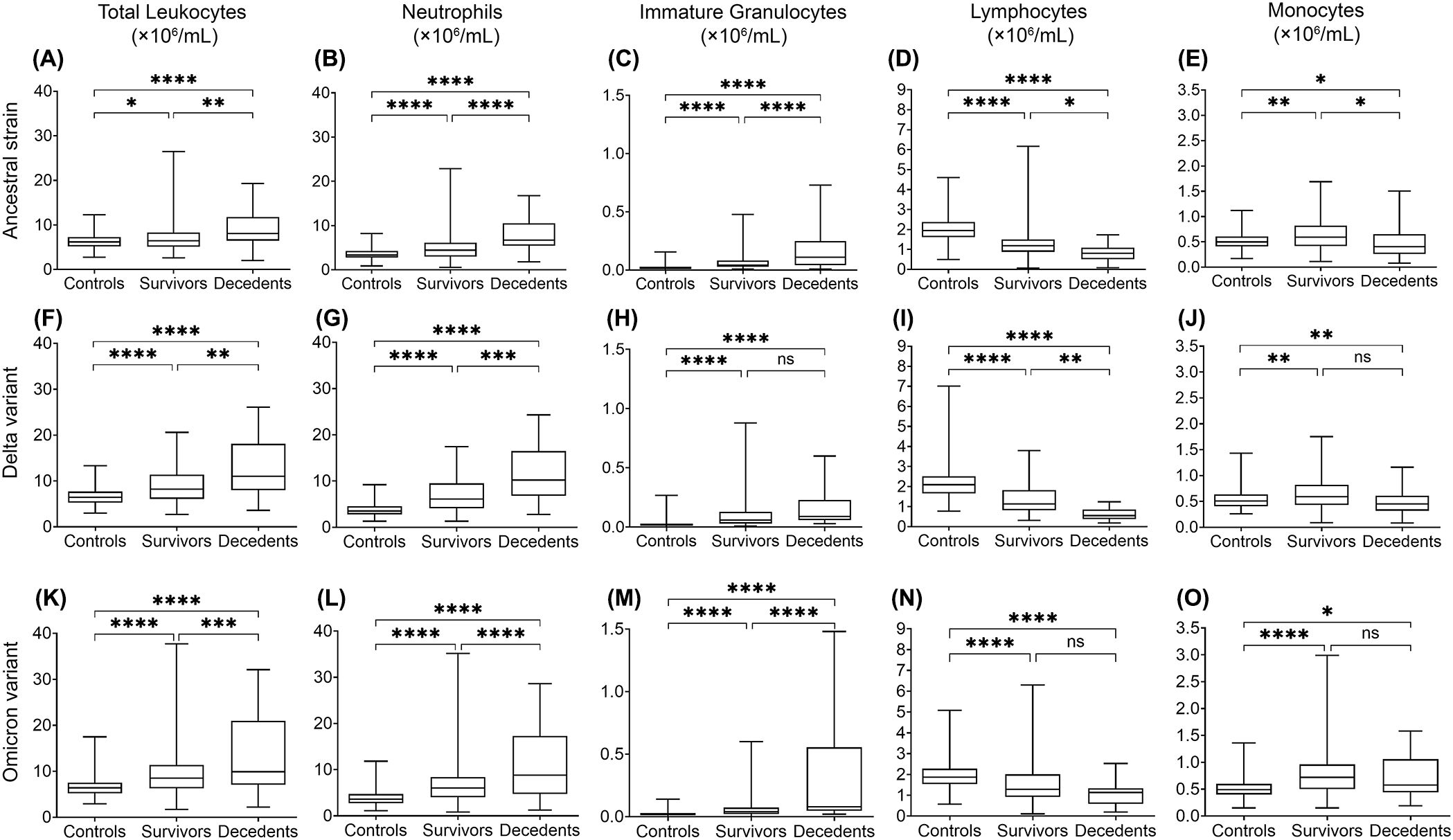
Figure 1. Multiple linear regression analysis of leukocyte levels in COVID-19 survivors and decedents compared to non-COVID-19 control subjects for 2020 (mainly ancestral strain), 2021 (mainly Delta variant), and 2022 (mainly Omicron variant). Total leukocytes (A, F, K), neutrophils (B, G, L), immature granulocytes (C, H, M), lymphocytes (D, I, N), and monocytes (E, J, O) indicate changes of significant difference in 2020 (A-E), 2021 (F-J) and 2022 (K-O). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ns, P>0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
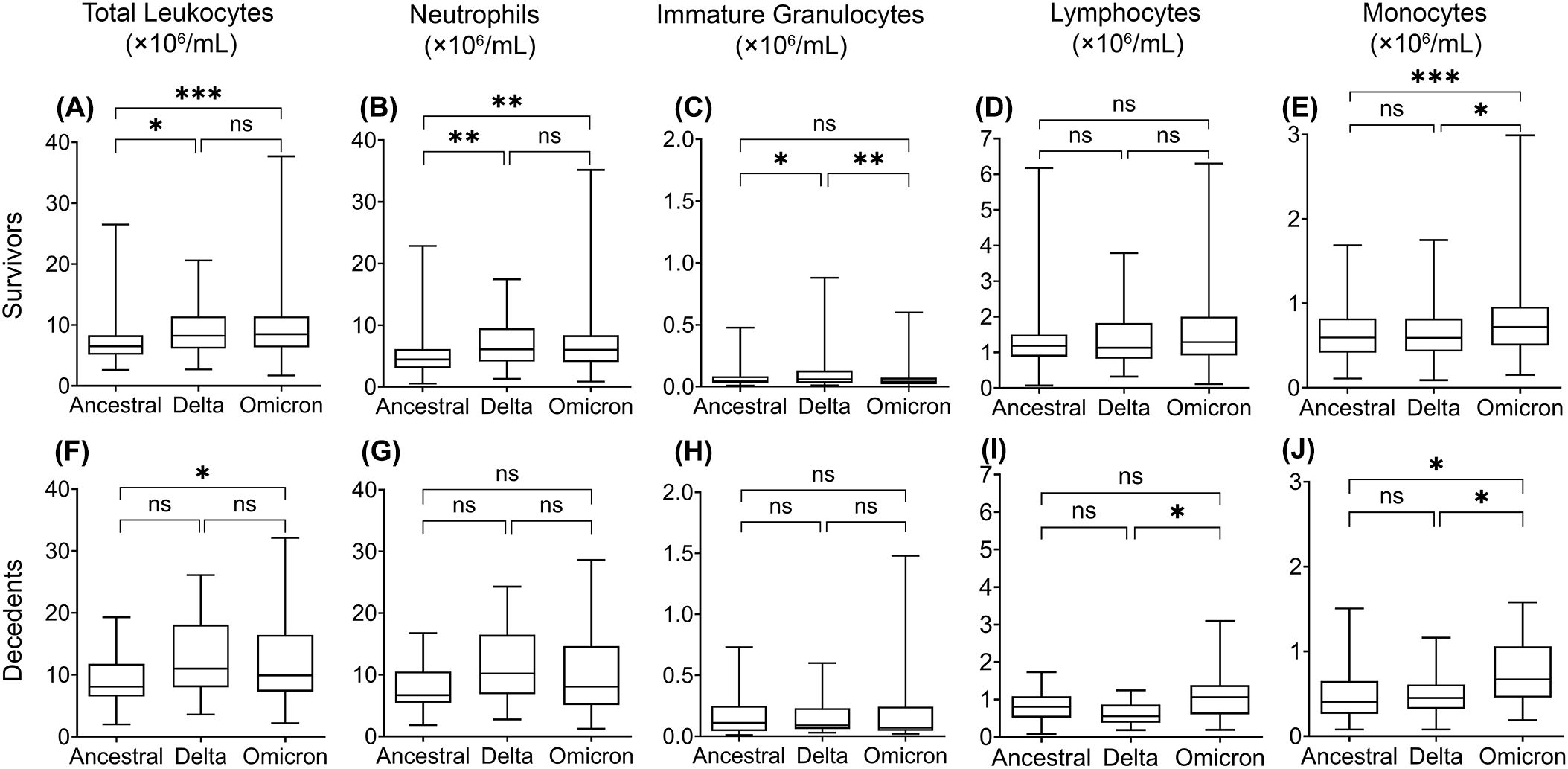
Figure 2. Multiple linear regression analysis of leukocyte levels in COVID-19 survivors (upper) and decedents (lower) infected with the ancestral strain, Delta variant, and Omicron variant. Total leukocytes (A, F), neutrophils (B, G), immature granulocytes (C, H), lymphocytes (D, I), and monocytes (E, J). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ns, P>0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Statistical analysis
To further understand the physiological and immunopathological differences among the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strain, the Delta variant, and the Omicron variant, we analyzed the 2020, 2021, and 2022 data separately. The COVID-19 patients were divided into two groups - COVID-19 survivors and decedents. Sex, age, COVID-19 vaccination status, corticosteroid usage, and comorbid conditions were compared statistically between non-COVID-19 controls and COVID-19 patients each year. The two-sample t-test was used to compare continuous variables. The chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to examine the relationships between leukocytes and their subtypes with COVID-19 disease outcomes during the three years following adjustment for age, sex, COVID-19 vaccination, corticosteroid use, and comorbid conditions.
Multiple logistic regression analysis was conducted to examine the associations of mortality with leukocytes and each subtype after adjustment for sex, age, COVID-19 vaccination status, corticosteroid use, and comorbid conditions. Adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated by exponentiating the regression coefficients of each cell type. Based on the multiple logistic regression model, we calculated and plotted the predicted mortality probabilities and corresponding 95% CIs. Specifically, for each cell type, we generated a sequence of cell values across the observed range and constructed a new dataset comprising all possible combinations of these cell values, categorical covariates, and mean age. Predicted probabilities were then obtained for each combination using the prediction function in the logistic regression model. For each cell value, we calculated the mean predicted mortality probability and derived the 95% CI using the quantile function. All statistical tests were 2-sided, and a P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 9.0.0 and R version 4.4.1.
Results
This study included 575 COVID-19 patients and 950 non-COVID-19 patient controls (Table 1). Based on the published CDC results of SARS-CoV-2 variant changes (Lambrou et al., 2022), we divided the patients into three groups: 1) The ancestral strain: 186 patients from March to June 2020, which were mainly ancestral strain infection; 2) The Delta variant: 94 patients from July to December 2021, which were mainly Delta variant infection; and 3) The Omicron variant: 295 patients from January to December 2022, which were mainly Omicron variant infection. The mortality rates for each of the three groups were 14.5% (27 decedents), 16.0% (15 decedents), and 9.8% (29 decedents), respectively.
Age and sex are correlated with COVID-19
Compared with the non-COVID-19 controls, the average age was significantly higher for the COVID-19 survivors and decedents (Table 1), showing that patients hospitalized for COVID-19 are older than patients hospitalized for other issues. This is consistent with the previous studies showing that older people, especially those with comorbidities, might be more likely to be infected and have poorer prognosis (Attaway et al., 2021).
Compared with the non-COVID-19 controls, the survivors and decedents were more likely to be male. However, the sex difference was non-significant for the Delta variant group due to the small sample sizes (Table 1). The results are consistent with previous studies (Garg et al., 2020; Shrock et al., 2020; Takahashi et al., 2020; Webb Hooper et al., 2020) showing that males might be more vulnerable to COVID-19 than females. This may be because of differences in ACE2 expression (Peng et al., 2021; Viveiros et al., 2022), hormonal influences (Selek et al., 2021; Sciarra et al., 2023), immune response variations (Klein and Flanagan, 2016; Takahashi and Iwasaki, 2021; Zhao et al., 2021), and other biological or behavioral factors (Friske and Spanagel, 2023).
COVID-19 vaccination, corticosteroid use, and comorbid conditions
Vaccination status correlates with COVID-19, where COVID-19 patients have a significantly lower vaccination rate than non-COVID-19 controls (Table 1). Corticosteroid is commonly used in several respiratory diseases, including COVID-19. As expected, COVID-19 patients have a much higher percentage of corticosteroid use than non-COVID-19 controls (Table 1). There is also a higher percentage of COVID-19 patients with comorbidities than non-COVID-19 controls (Table 1), suggesting a correlation between COVID-19 and other diseases.
Higher concentrations of total leukocytes and neutrophils in COVID-19
To assess whether leukocyte responses differ between infection of ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and variants, we analyzed the concentrations of peripheral blood leukocytes and subtypes from COVID-19 patients and non-COVID-19 controls from various aspects. We performed multiple linear regression analyses to compensate for the effects of age, sex, COVID-19 vaccination, corticosteroid use, and comorbid conditions. We then compared the average leukocyte and subtype concentrations between COVID-19 survivors, decedents, and non-COVID-19 controls (Figure 1), where the ancestral strain, Delta, and Omicron variant groups were analyzed separately. In addition, we compared leukocyte differences between the three variant groups (Figure 2) in survivors or decedents. We then performed multiple logistic regression for each group separately to determine whether leukocytes or subtypes are associated with COVID-19 mortality (Table 2).
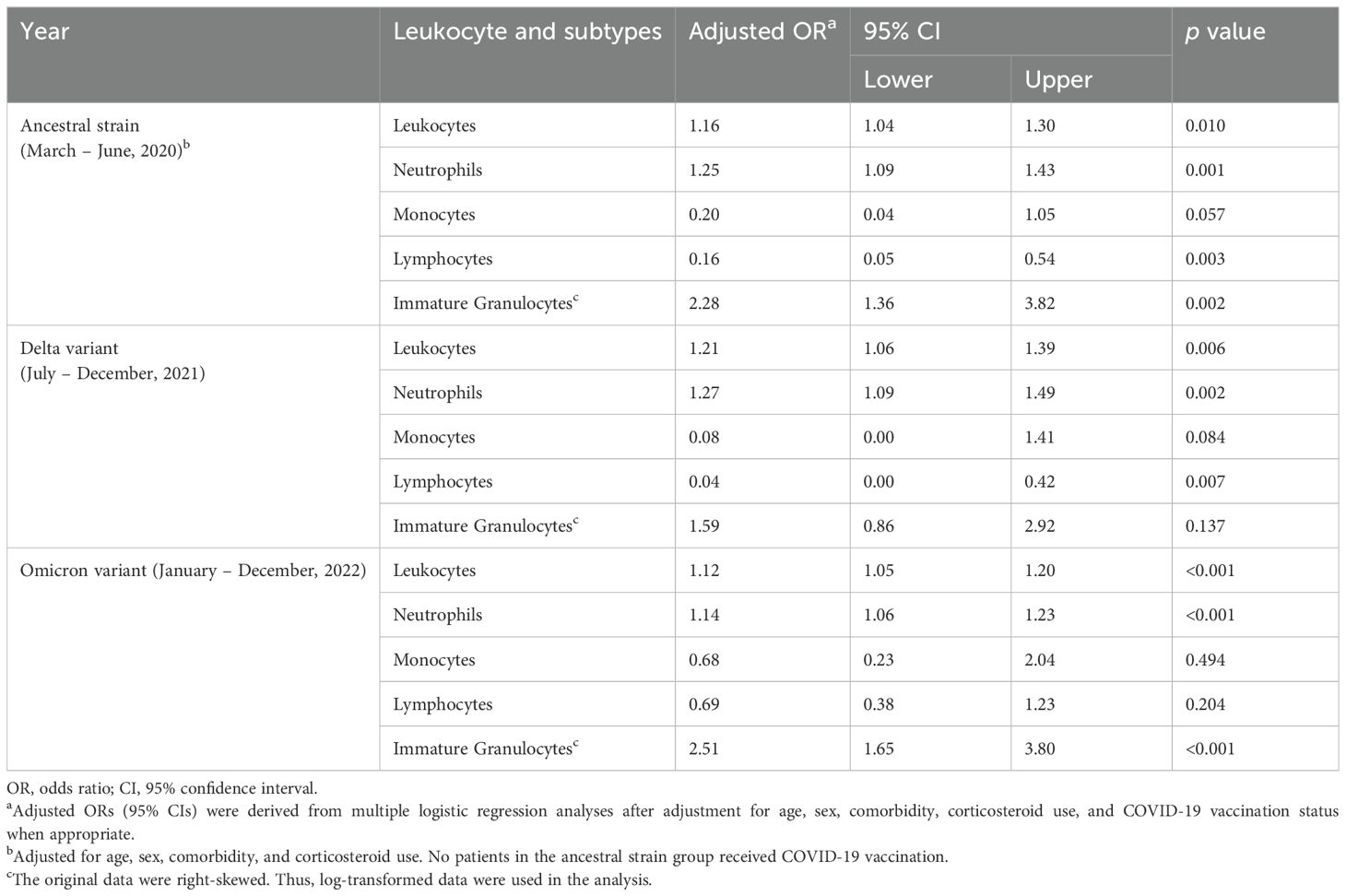
Table 2. Adjusted ORs (95% CIs) for COVID-19 mortality in relation to the concentrations of leukocytes and the subtypes, stratified by three types of COVID-19 infection.
We found that in all three groups, total leukocyte and neutrophil concentrations were significantly higher in COVID-19 survivors and further higher in COVID-19 decedents compared with the non-COVID-19 controls (Figures 1A, F, K). The higher leukocyte concentration is mainly contributed by the higher neutrophil concentration (Figures 1B, G, L) because neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes in human blood. Multiple logistic regression analyses showed that total leukocytes and neutrophils were positively associated with COVID-19 mortality (Table 2, Supplementary Figure 1A–B, F-G, K-L). These imply that the elevation of neutrophil levels may be correlated with COVID-19 pathogenesis and prognosis.
When comparing the three groups, we found that the Delta and Omicron variant survivors had significantly higher total leukocyte and neutrophil concentrations than the ancestral strain survivors (Figures 2A,B). Moreover, Omicron variant survivors also have significantly higher monocyte concentrations than the ancestral strain survivors (Figure 2E). Omicron but not Delta variant decedents showed significantly higher total leukocyte concentrations than the ancestral strain decedents (Figure 2F). This is due to the higher monocyte (Figure 2J) but not neutrophil concentration (Figure 2G).
The concentration of immature granulocytes is higher in COVID-19
The increase of immature granulocytes in peripheral blood happens in many inflammatory diseases, suggesting emergency granulopoiesis and cytokine storm (Polidoro et al., 2020; Combadiere et al., 2021; Malengier-Devlies et al., 2021). As expected, COVID-19 also showed a higher concentration of immature granulocytes in peripheral blood (Figures 1C, H, M). The COVID-19 decedents showed significantly higher peripheral blood immature granulocytes than survivors during the ancestral strain and Omicron variant infection (Figures 1C, M) but not in the Delta variant infection (Figure 1H). Consistent with this result, multiple logistic regression analyses showed that immature granulocyte concentrations are positively associated with COVID-19 mortality in the ancestral strain and Omicron variant infection but not the Delta variant infection (Table 2; Supplementary Figure 1). When comparing the three groups, we found that the Delta variant survivors had significantly higher immature granulocyte concentrations than the other two groups (Figure 2C), suggesting that the Delta variant may induce more emergency granulopoiesis. The decedents showed no difference in immature granulocyte concentrations between groups (Figure 2H).
A lower lymphocyte concentration in COVID-19
Compared with the non-COVID-19 controls, the COVID-19 patients had fewer lymphocytes in all three groups, especially for patients who died from COVID-19 (Figures 1D, I, N). The results are consistent with the previous studies (Huang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021; Belaid et al., 2022). However, the Omicron variant decedents did not show a further lower concentration of lymphocytes compared to survivors (Figure 1N). In addition, lymphocyte concentrations were negatively associated with COVID-19 mortality, although the association was non-significant for those infected with the Omicron variant (Table 2; Supplementary Figure 1D, I, N), suggesting suppression of regulatory immunity may contribute to a worse prognosis in the ancestral strain and Delta variant but not Omicron variant-caused COVID-19. This was further supported by the results that the Omicron variant decedents (Figure 2I) had higher lymphocyte concentrations than those in the Delta variant decedents. The suppression of regulatory immunity might be due to the administration of corticosteroids to the patients.
Loss of monocytes is associated with poor prognosis in the ancestral strain and Delta variant infection
We found that COVID-19 survivors had significantly higher monocyte concentrations than non-COVID-19 controls (Figures 1E, J, O). However, the situation was different for the decedents. Compared with the non-COVID-19 controls, the monocyte concentration in the decedents was significantly higher in the Omicron variant infection (Figure 1O) but significantly lower in the ancestral strain infection (Figure 1E) and the Delta variant infection (Figure 1J). Additionally, monocyte concentrations were negatively associated with COVID-19 mortality, although the association was less significant in the Omicron variant infection (Table 2; Supplementary Figure 1), suggesting the failed induction of monocyte immunity might be involved in the prognosis of the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and Delta variant but not Omicron variant caused COVID-19. By comparing the groups, we found the Omicron variant survivors (Figure 2E) and decedents (Figure 2J) had significantly higher monocyte concentrations than those in the ancestral strain and Delta variant infection, implying a possibility that the Omicron variant may have less capacity to suppress monocyte immunity.
Discussion
The ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strain has a high pathogenicity, lethality, and genetic variability (Schwab et al., 2023). In the past three years, many variants have been identified. Their lethality seems decreased but exhibits higher transmissibility, including Delta and Omicron variants (Liu and Rocklov, 2021; Chavda et al., 2022). Investigating human immune regulation in response to SARS-CoV-2 variant infection is crucial to understanding further how the elevated inflammatory signaling has contributed to COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. Many studies have focused on the dysregulation of leukocyte response and consequent immunopathology triggered by SARS-CoV-2 (Jimenez and Torres Arias, 2022; Islam et al., 2023). Neutrophilia, hyperactive immature granulocytes, and lymphopenia were usually seen in severe COVID-19 patients (Huang et al., 2020; Tan et al., 2020; Aschenbrenner et al., 2021; Sinha et al., 2022; Almendro-Vazquez et al., 2023; Nasrollahi et al., 2023; Rice et al., 2023). They may cause an excessive inflammatory response to SARS-CoV-2 (Polidoro et al., 2020; Qin et al., 2020; Root-Bernstein, 2023), which is thought to be the main contributor to the death of COVID-19 patients (Mehta et al., 2020). However, no clear illumination exists about the comparison among leukocyte subtypes responding to ancestral strain and its variants during the last three years. Our study compared the distinct leukocyte responses to ancestral SARS-CoV-2, Delta, and Omicron in COVID-19 survivors and decedents.
We were able to show different peripheral blood leukocyte subtype patterns between the ancestral strain, Delta variant, and Omicron variant infection, which may help us understand the difference in immune responses between the SARS-CoV-2 variants. Although COVID-19 patients in all years showed higher concentrations of myeloid cell populations (neutrophils, immature granulocytes, and monocytes) and lower concentrations of adaptive immune lymphocytes compared to non-COVID-19 controls, COVID-19 survivors and decedents show different patterns. In the ancestral strain infection, a significantly higher concentration of neutrophils and immature granulocytes and a lower concentration of lymphocytes and monocytes were shown in decedents compared to survivors, suggesting hyperactivation of neutrophils/granulocytes and suppression of lymphocytes/monocytes may contribute to mortality in ancestral COVID-19. In the Delta variant infection, compared to the ancestral strain infection, a higher concentration of immature granulocytes was not significantly observed in decedents compared to survivors. This is because the Delta variant survivors already induced a high number of immature granulocytes. In the Omicron variant infection, unlike the ancestral strain infection, lower concentrations of lymphocytes and monocytes were not significantly observed in decedents compared to survivors. Actually, Omicron decedents had higher amounts of lymphocytes and monocytes compared to those in the ancestral strain and Delta variant infection. These imply that the mortality observed from the Omicron variant infection might not be due to the inhibition of lymphocytes and monocytes. Detail mechanisms remain for further investigation.
One important finding is the involvement and changes of monocytes during infection of the ancestral strain and different variants. Studies have indicated that the monocyte population is a trigger and target in the progression of severe COVID-19 disease (Schulte-Schrepping et al., 2020; Ahern et al., 2022; Zhang PP. et al., 2023). Studies showed classic monocytes reduced in COVID-19 cases, while increased activated monocyte subsets may impact pulmonary function in COVID-19 convalescents (Payen et al., 2020; Park et al., 2023). However, these studies did not address whether monocyte responses differ in patients infected with ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strain and variants; here, we provide some insights into this question and suggest further investigation. According to these findings, blood monocyte tests could represent a promising routine tool for monitoring the progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection, clinical prognosis of COVID-19, and therapeutic targeting throughout hospitalization.
One pitfall of our research is that we assume patients from 2020 March-June as the ancestral strain infection, patients from 2021 July-December as the Delta variant infection, and patients from 2022 January-December as the Omicron variant infection based on previous published CDC results (Lambrou et al., 2022). This is due to the feasibility limitation of sequencing on all our patients, and this is the best way we can analyze existing patient data and discover differences between ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Meanwhile, although we considered COVID-19 vaccination, corticosteroid use, and comorbidities, we did not have data on lifestyle risk factors and genetic factors, and we could not control for the influences of these factors. The number of decedents in each type of infection is small, which may partly explain the non-significant associations for decedents.
Conclusion
Collectively, our study demonstrated different responses of leukocytes, both innate and adaptive immune cells, to ancestral SARS-CoV-2, the Delta variant, and the Omicron variant, indicating their roles in COVID-19 infection and mortality. By studying the correlation changes in leukocyte subtypes between the three types of infection, we can better evaluate the prognosis of COVID-19 patients at admission.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation. Raw and analyzed quantification data have been deposited in the Harvard Dataverse repository (https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataverse/COVID-19_2025).
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because we acquired de-identified patient information in our hospital database. After consorting with our IRB, this process does not need IRB approval. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements because we did not have direct contact with patients.
Author contributions
YW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. RS: Writing – review & editing. WG: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZF: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, USA (R01-HL145454), and National Institute on Aging (The Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center Award P30-AG024832), USA, and a startup fund from UConn Health.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. Paul Appleton from UConn Health Clinical Research Center and Donna Pike from UConn Health Information Technology Services for collecting unidentified clinical hematology tests. We acknowledge Dr. Bernard L. Cook from UConn School of Medicine for their help with the scientific writing and editing of this manuscript. Raw and analyzed data is publicly available through Harvard Dataverse (https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/XNLFFR).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1508120/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | The predicted probability of COVID-19 mortality in relation to the concentrations of leukocytes and the subtypes is stratified by three types of COVID-19 infection: the ancestral strain (A, D, G, J, M), Delta variant (B, E, H, K, N), and Omicron variant (C, F, I, L, O). The gray areas indicate 95% confidence intervals in each panel.
References
Ahern, D. J., Ai, Z., Ainsworth, M., Allan, C., Allcock, A., Angus, B., et al. (2022). A blood atlas of COVID-19 defines hallmarks of disease severity and specificity. Cell 185, 916–938. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.012
Aleem, A., Akbar Samad, A. B., Vaqar, S. (2023). Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 And Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19) (Treasure Island (FL: StatPearls).
Almendro-Vazquez, P., Laguna-Goya, R., Paz-Artal, E. (2023). Defending against SARS-CoV-2: The T cell perspective. Front. Immunol. 14, 1107803. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1107803
Aschenbrenner, A. C., Mouktaroudi, M., Kramer, B., Oestreich, M., Antonakos, N., Nuesch-Germano, M., et al. (2021). Disease severity-specific neutrophil signatures in blood transcriptomes stratify COVID-19 patients. Genome Med. 13, 7. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00823-5
Attaway, A. H., Scheraga, R. G., Bhimraj, A., Biehl, M., Hatipoglu, U. (2021). Severe covid-19 pneumonia: pathogenesis and clinical management. BMJ 372, n436. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n436
Belaid, B., Lamara Mahammad, L., Mihi, B., Rahali, S. Y., Djidjeli, A., Larab, Z., et al. (2022). T cell counts and IL-6 concentration in blood of North African COVID-19 patients are two independent prognostic factors for severe disease and death. J. Leukoc. Biol. 111, 269–281. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4COVA1020-703R
Chavda, V. P., Patel, A. B., Vaghasiya, D. D. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 variants and vulnerability at the global level. J. Med. Virol. 94, 2986–3005. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27717
Combadiere, B., Adam, L., Guillou, N., Quentric, P., Rosenbaum, P., Dorgham, K., et al. (2021). LOX-1-expressing immature neutrophils identify critically-ill COVID-19 patients at risk of thrombotic complications. Front. Immunol. 12, 752612. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.752612
Friske, M. M., Spanagel, R. (2023). Chronic alcohol consumption and COVID-19 infection risk: A narrative review. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. (Hoboken) 47, 629–639. doi: 10.1111/acer.15041
Garg, S., Kim, L., Whitaker, M., O’Halloran, A., Cummings, C., Holstein, R., et al. (2020). Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 - COVID-NET, 14 states, march 1-30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 69, 458–464. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3
Hu, B., Guo, H., Zhou, P., Shi, Z. L. (2021). Characteristics of SARS-coV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 141–154. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Huang, C., Wang, Y., Li, X., Ren, L., Zhao, J., Hu, Y., et al. (2020). Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395, 497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Huang, L., Shi, Y., Gong, B., Jiang, L., Zhang, Z., Liu, X., et al. (2021). Dynamic blood single-cell immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6, 110. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00526-2
Islam, M. S., Wang, Z., Abdel-Mohsen, M., Chen, X., Montaner, L. J. (2023). Tissue injury and leukocyte changes in post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2: review of 2833 post-acute patient outcomes per immune dysregulation and microbial translocation in long COVID. J. Leukoc. Biol. 113, 236–254. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiac001
Jimenez, D., Torres Arias, M. (2022). Immunouniverse of SARS-coV-2. Immunol. Med. 45, 186–224. doi: 10.1080/25785826.2022.2066251
Kasine, T., Dyrhol-Riise, A. M., Barratt-Due, A., Kildal, A. B., Olsen, I. C., Nezvalova-Henriksen, K., et al. (2022). Neutrophil count predicts clinical outcome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: Results from the NOR-Solidarity trial. J. Intern. Med. 291, 241–243. doi: 10.1111/joim.13377
Klein, S. L., Flanagan, K. L. (2016). Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 626–638. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.90
Kumar, S., Thambiraja, T. S., Karuppanan, K., Subramaniam, G. (2022). Omicron and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2: A comparative computational study of spike protein. J. Med. Virol. 94, 1641–1649. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27526
Lambrou, A. S., Shirk, P., Steele, M. K., Paul, P., Paden, C. R., Cadwell, B., et al. (2022). Genomic surveillance for SARS-coV-2 variants: predominance of the delta (B.1.617.2) and omicron (B.1.1.529) variants - United States, June 2021-January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 71, 206–211. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7106a4
Liu, Y., Rocklov, J. (2021). The reproductive number of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is far higher compared to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus. J. Travel Med. 28, taab124. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taab124
Malengier-Devlies, B., Metzemaekers, M., Wouters, C., Proost, P., Matthys, P. (2021). Neutrophil homeostasis and emergency granulopoiesis: the example of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Front. Immunol. 12, 766620. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.766620
Mehta, P., McAuley, D. F., Brown, M., Sanchez, E., Tattersall, R. S., Manson, J. J., et al. (2020). COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 395, 1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Nasrollahi, H., Talepoor, A. G., Saleh, Z., Eshkevar Vakili, M., Heydarinezhad, P., Karami, N., et al. (2023). Immune responses in mildly versus critically ill COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 14, 1077236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1077236
Obermayer, A., Jakob, L. M., Haslbauer, J. D., Matter, M. S., Tzankov, A., Stoiber, W. (2021). Neutrophil extracellular traps in fatal COVID-19-associated lung injury. Dis. Markers 2021, 5566826. doi: 10.1155/2021/5566826
Park, J., Dean, L. S., Jiyarom, B., Gangcuangco, L. M., Shah, P., Awamura, T., et al. (2023). Elevated circulating monocytes and monocyte activation in COVID-19 convalescent individuals. Front. Immunol. 14, 1151780. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1151780
Payen, D., Cravat, M., Maadadi, H., Didelot, C., Prosic, L., Dupuis, C., et al. (2020). A longitudinal study of immune cells in severe COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 11, 580250. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580250
Peng, J., Sun, J., Zhao, J., Deng, X., Guo, F., Chen, L. (2021). Age and gender differences in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expressions in oral epithelial cells. J. Transl. Med. 19, 358. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03037-4
Polidoro, R. B., Hagan, R. S., de Santis Santiago, R., Schmidt, N. W. (2020). Overview: systemic inflammatory response derived from lung injury caused by SARS-coV-2 infection explains severe outcomes in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 11, 1626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01626
Qin, C., Zhou, L., Hu, Z., Zhang, S., Yang, S., Tao, Y., et al. (2020). Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71, 762–768. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Rice, C. M., Lewis, P., Ponce-Garcia, F. M., Gibbs, W., Groves, S., Cela, D., et al. (2023). Hyperactive immature state and differential CXCR2 expression of neutrophils in severe COVID-19. Life Sci. Alliance 6, e202201658. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201658
Root-Bernstein, R. (2023). From co-infections to autoimmune disease via hyperactivated innate immunity: COVID-19 autoimmune coagulopathies, autoimmune myocarditis and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 3001. doi: 10.3390/ijms24033001
Schulte-Schrepping, J., Reusch, N., Paclik, D., Bassler, K., Schlickeiser, S., Zhang, B., et al. (2020). Severe COVID-19 is marked by a dysregulated myeloid cell compartment. Cell 182, 1419–40 e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.001
Schwab, C., Merle, U., Schirmacher, P., Longerich, T. (2023). Lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection-a comparative autopsy study focusing on COVID-19 development and virus variants. Histopathology. 83, 242–251. doi: 10.1111/his.14931
Sciarra, F., Campolo, F., Franceschini, E., Carlomagno, F., Venneri, M. A. (2023). Gender-specific impact of sex hormones on the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 6302. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076302
Selek, A., Guclu, M., Bolu, S. E. (2021). COVID-19 pandemic: what about the gonads? Hormones (Athens) 20, 259–268. doi: 10.1007/s42000-021-00277-3
Shrock, E., Fujimura, E., Kula, T., Timms, R. T., Lee, I. H., Leng, Y., et al. (2020). Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science 370, 1058. doi: 10.1126/science.abd4250
Sinha, S., Rosin, N. L., Arora, R., Labit, E., Jaffer, A., Cao, L., et al. (2022). Dexamethasone modulates immature neutrophils and interferon programming in severe COVID-19. Nat. Med. 28, 201–211. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01576-3
Takahashi, T., Ellingson, M. K., Wong, P., Israelow, B., Lucas, C., Klein, J., et al. (2020). Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes. Nature 588, 315–320. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2700-3
Takahashi, T., Iwasaki, A. (2021). Sex differences in immune responses. Science 371, 347–348. doi: 10.1126/science.abe7199
Tan, L., Wang, Q., Zhang, D., Ding, J., Huang, Q., Tang, Y. Q., et al. (2020). Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: a descriptive and predictive study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5, 33. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0148-4
Viveiros, A., Gheblawi, M., Aujla, P. K., Sosnowski, D. K., Seubert, J. M., Kassiri, Z., et al. (2022). Sex- and age-specific regulation of ACE2: Insights into severe COVID-19 susceptibility. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 164, 13–16. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.11.003
Webb Hooper, M., Napoles, A. M., Perez-Stable, E. J. (2020). COVID-19 and racial/ethnic disparities. JAMA 323, 2466–2467. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.8598
Zhang, J. J., Dong, X., Cao, Y. Y., Yuan, Y. D., Yang, Y. B., Yan, Y. Q., et al. (2020). Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 75, 1730–1741. doi: 10.1111/all.14238
Zhang, P. P., He, Z. C., Yao, X. H., Tang, R., Ma, J., Luo, T., et al. (2023). COVID-19-associated monocytic encephalitis (CAME): histological and proteomic evidence from autopsy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8, 24. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01291-6
Zhang, Q., Meng, Y., Wang, K., Zhang, X., Chen, W., Sheng, J., et al. (2021). Inflammation and antiviral immune response associated with severe progression of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 12, 631226. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.631226
Zhang, H. P., Sun, Y. L., Wang, Y. F., Yazici, D., Azkur, D., Ogulur, I., et al. (2023). Recent developments in the immunopathology of COVID-19. Allergy 78, 369–388. doi: 10.1111/all.15593
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 variant, leukocyte, neutrophil, monocyte, lymphocyte
Citation: Wu Y, Serna R, Gan W and Fan Z (2025) Different patterns of leukocyte immune responses to infection of ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1508120. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1508120
Received: 08 October 2024; Accepted: 27 March 2025;
Published: 17 April 2025.
Edited by:
Sreekanth Gopinathan Pillai, Manipal Institute of Virology, IndiaReviewed by:
Laura Pérez-Alós, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, DenmarkLaura Maggi, University of Florence, Italy
Swarandeep Singh, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Serna, Gan and Fan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhichao Fan, emZhbkB1Y2hjLmVkdQ==; Wenqi Gan, d2dhbkB1Y2hjLmVkdQ==
 Yuanyuan Wu
Yuanyuan Wu Raphael Serna
Raphael Serna Wenqi Gan
Wenqi Gan Zhichao Fan
Zhichao Fan