- 1Department of Biotechnology and Laboratory Science in Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 2Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan
- 3Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 4School of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, College of Medical Science and Technology, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 5Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 6School of Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan
Introduction: The rpoE-chrR pair is a regulatory system used by photosynthetic microorganisms to overcome singlet oxygen stress. rpoE and chrR encode the sigma factor σE and anti-sigma factor ChrR, respectively. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, an opportunistic pathogen, is a multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterium. Although it is not a photosynthetic microorganism, a rpoE-chrR homolog (smlt2377-smlt2378) was found in the S. maltophilia genome. In this study, we aimed to assess the significance of σEc-ChrR pair in oxidative stress alleviation and antibiotic susceptibility of S. maltophilia KJ.
Methods: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to validate the presence of operon. The contribution of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon to oxidative stress alleviation and antibiotic susceptibility was evaluated using mutant constructs and stress-tolerance assays. RNA-seq transcriptome assay of wild-type KJ, KJΔChrR (chrR mutant), and KJΔChrRΔRpoEc (chrR/rpoEc double mutant) was performed to reveal the σEc regulon.
Results: The rpoEc-chrR pair and downstream chrA formed an operon. Inactivation of chrR upregulated the expression of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in an σEc- and ChrA-dependent manner. σEc activation contributed to superoxide tolerance and increased β-lactam susceptibility but did not affect the tolerance to singlet oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Transcriptome analysis revealed that expression of the nine-gene cluster, smlt2375-smlt2367, was significantly upregulated in KJΔChrR and reverted to the wild-type level in KJΔChrRΔRpoEc. smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster was located upstream of the rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and divergently transcribed, seeming to be involved in membrane lipid modification. Deletion of smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster from the chromosome of KJΔChrR reverted the superoxide tolerance and β-lactam susceptibility to the wild-type level.
Discussion: The rpoEc-chrR pair of S. maltophilia was involved in superoxide tolerance and β-lactam susceptibility. Notably, a novel regulatory circuit involving rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster was revealed.
1 Introduction
Pathogens frequently encounter various stressors imposed by host cells, such as iron depletion, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and envelope-damaging agents (Sun and Zhou, 2018). Bacteria have evolved various mechanisms to deal with such environmental stresses (Marles-Wright and Lewis, 2007). One mechanism involves the reversible association of different σ factors with the bacterial core RNA polymerase (RNAP) to control the expression of discrete sets of genes in response to stress-related signals (Helmann, 2002).
RNAP is an essential transcriptional enzyme. Bacterial core RNAP has five subunits: αI, αII, β, β‘, and ω. The sigma (σ) factor binds to the core RNAP to form a holoenzyme. Sigma factor is a transcription initiation factor that facilitates the specific binding of RNAP to gene promoters. Bacteria usually have one housekeeping σ factor (σD) and an array of alternative σ factors possessing different promoter-recognition properties to regulate the subsets of genes necessary for survival under specific environmental conditions or stress responses (Gruber and Gross, 2003). The number of σ factors varies among bacteria, possibly related to their habitat and metabolism. The sigma factors are classified into two distinct families: σ70 and σ54. The σ70 family members are further divided into four groups: group 1 comprising primary factors and groups 2–4 consisting of alternative factors with specialized functions (Davis et al., 2017).
Extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors, the largest and most diverse group of alternative sigma factors, belong to group 4 of the σ70 families (Mascher, 2023). Several mechanisms responsible for the regulation of ECF sigma factor activity have been described. In general, these activities are inhibited by anti-σ factors. In response to stimuli, anti-σ factors use diverse mechanisms to release σ factors that then bind to the core enzyme and drive the transcription of an array of genes. The subset of genes regulated in this manner is referred to as the regulon. The genes encoding ECF σ factor and anti-σ factor are generally organized in an operon (Paget, 2015). The most representative model is the RpoE/RseA model of Escherichia coli. RseA, an anti-σE factor, is an integral cytoplasmic membrane protein with a C-terminal extracytoplasmic sensory domain and an N-terminal intracellular inhibitory domain that binds to cognate σE protein. Upon challenge with stimuli, RseA is subsequently hydrolyzed by a two-step intramembrane proteolysis, and σE is released to trigger the transcription of responsive genes (Ho and Ellermeier, 2012). In addition to the inner membrane anti-σE factor, an example of cytoplasmic anti-σ factor is discovered in the phototrophic alpha-proteobacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. In this microorganism, σE-ChrR pair is a regulatory system to alleviate the singlet oxygen stress. Under unstressed conditions, σE binds to the anti-σ factor ChrR, which maintains σE in an inactive state. Singlet oxygen acts as a signal that is sensed in an unidentified manner and leads to σE release, thereby inducing the expression of σE regulon to alleviate singlet oxygen stress (Donohue, 2019).
Singlet oxygen, one of the ROS, is the primary agent of photo-oxidative stress in photosynthetic microorganisms. In these microorganisms, singlet oxygen is generated by energy transfer from the excited pigments of the photosystems (Sharma et al., 2012). A singlet oxygen molecule can react with a wide range of cellular macromolecules to cause damage (Triantaphylides and Hayaux, 2009). Interestingly, singlet oxygen is also produced in non-photosynthetic microorganisms because cellular cofactors, such as flavins, rhodopsins, quinones, and porphyrins, serve as photosensitizers. To face the singlet oxygen stress, microorganisms have evolved several mechanisms to alleviate singlet oxygen-mediated stress, including quenchers (such as carotenoids) and scavengers (such as glutathione) (Glaeser et al., 2011).
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a ubiquitous environmental bacterium that acts as an opportunistic pathogen causing various clinical conditions, mainly pulmonary and bloodstream infections (Sánchez, 2015). From the external to the host environment, S. maltophilia is subjected to various stresses, including nutrient unavailability, oxidative stress, osmotic stress, and iron-depletion; therefore, it has evolved various mechanisms to adapt to the dynamic environment (Huang et al., 2014; Lin et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2018; Jair et al., 2019; Huang et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020a, 2020; Pan et al., 2022; Shih et al., 2022; Liao et al., 2022). S. maltophilia is intrinsically resistant to several antibiotics as it possesses various determinants contributing to antibiotic resistance, such as β-lactamases, efflux pumps, and aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (Mojica et al., 2022). These defense mechanisms make the treatment of S. maltophilia infections challenging. S. maltophilia is intrinsically resistant to most β-lactams due to the chromosomally encoded L1 and L2 β-lactamases. Among β-lactams, ceftazidime (CAZ) and ticarcillin-clavulanic acid are the only ones suitable for treating S. maltophilia infections. L1 and L2 β-lactamases inducible expression in S. maltophilia is linked to the disturbance of peptidoglycan (PG) homeostasis (Mojica et al., 2022), similar to AmpC expression in Enterobacter cloacea, Citrobacter freundii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Jacoby, 2009). In addition to β-lactamase, non-β-lactamase-mediated β-lactam resistance in S. maltophilia has also been reported. For example, loss-of-function of PhoPQ two-component regulatory system increases the outer membrane permeability, which leads to increased β-lactam susceptibility of S. maltophilia (Huang et al., 2021).
Some stress-alleviation systems contribute to antibiotic resistance (Shin et al., 2020). We reported that the smeU1VWU2X operon, which encodes an RND-type efflux pump, not only alleviates menadione (MD)-mediated oxidative stress but also contributes to antibiotic resistance in S. maltophilia (Wu et al., 2018). Furthermore, formaldehyde detoxification system FadRACB participates in the alleviation of oxidative stress and fluoroquinolone resistance in S. maltophilia (Li et al., 2020b). A genome-wide survey revealed that S. maltophilia K279a harbors the rpoE-chrR pair (Crossman et al., 2008), although it is not a photosynthetic microorganism. This observation raised our curiosity about the significance of the rpoE-chrR system in S. maltophilia. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the role of the σE-ChrR pair of S. maltophilia in oxidative stress alleviation and antibiotic susceptibility.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial strains, plasmids, and primers
The strains, plasmids and primers used in this study are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2 Reverse transcription-PCR and operon verification
DNA-free RNA was prepared from S. maltophilia KJΔChrR cells and reverse transcribed into cDNA using the ChrA-C primer (Supplementary Table S1). cDNA was used as the template for PCR using the primer sets of RpoEcQ-F/R, ChrRQ-F/R, and ChrAQ-F/R (Supplementary Table S1). The ChrAQ-F/R primer sets were used as a control for DNA contamination check.
2.3 In-frame deletion mutation construction
In-frame deletion mutants were constructed using allelic replacement strategy as described previously (Yang et al., 2009). Two DNA fragments flanking the deleted region were amplified by PCR and subsequently cloned into pEX18Tc to generate pΔRpoEc, pΔChrR, and pΔChrA. The primer sets used were RpoEcN-F/R and RpoEcC-F/R for pΔRpoEc, RpoEcC-F/R and ChrRC-F/R for pΔChrR, as well as ChrRC-F/R and ChrAC-F/R for pΔChrA (Supplementary Table S1). The resulting pEX18Tc-derived constructs were transported to S. maltophilia strain by conjugation. Transconjugants selection and mutants confirmation were performed as described previously (Yang et al., 2009). The double and triple mutants were constructed from the single mutant sequentially using the same protocol.
2.4 Singlet oxygen tolerance test
Tert-Butyl hydroperoxide (tBOOH) and Rose Bengal (RB) were used for the generation of single oxygen. The tBOOH reacts with peroxynitrite to generate singlet oxygen (Di Mascio et al., 1997). Rose Bengal is a UV/VIS absorbing molecule capable of absorbing and using light energy to excite oxygen to singlet oxygen (DeRosa and Crutchley, 2002). For cell viability, the logarithmic-phase bacterial cells tested of 2 × 105 CFU/μL were 10-fold serially diluted. Five microliters of the bacterial suspension were spotted onto the LB agar with and without tBOOH or RB as indicated. For the RB test, two plates were prepared. One plate was covered with foil seal to create “dark” conditions in which little or no singlet oxygen is produced. The other plate was kept in the light, representing the singlet oxygen-stressed condition. After 18-h incubation at 37°C, the bacterial viability was imaged. For growth curve, overnight culture was inoculated into LB broth with and without tBOOH or RB at an initial OD450 of 0.15. Bacterial growth was monitored for 24 h.
2.5 Menadione and antibiotic tolerance assay
For cell viability, the logarithmic-phase bacterial cells of 2×105 CFU/μL were serially 10-fold diluted. Five microliter bacterial aliquot was spotted onto LB agar with and without MD or antibiotic as indicated. After a 24-h incubation at 37˚C, the cell viabilities were recorded. For growth curve, overnight culture was inoculated into LB broth with and without MD or antibiotic at an initial OD450 of 0.15. Bacterial growth was monitored for 24 h.
2.6 Construction of a rpoEc promoter–xylE transcriptional fusion, pRpoEcxylE
For the construction of a transcriptional fusion of the rpoEc promoter with a promoterless xylE gene, the 356-bp DNA segment upstream of rpoEc was PCR-amplified using rpoEcN-F/R primer pair (Supplementary Table S1) and cloned into pXylE (Chen et al., 2011) to generate pRpoEcxylE.
2.7 Catechol-2,3-dioxygenase activity determination
C23O, encoded by xylE, can convert catechol to an intensely yellow products, which can be spectrophotometrically quantified. One unit of enzyme activity (Uc) was defined as the amount of enzyme that converts 1 nmol of catechol per minute. The specific activity (Uc/OD450) of the enzyme was defined as units per OD450 unit of cells. All data were reported from experiments performed in triplicate.
2.8 Transcriptome analysis
Overnight cultures of KJ, KJΔChrR, and KJΔChrRΔRpoEc were inoculated into fresh LB broth at an initial OD450 of 0.15. After 5-h culture at 37°C, total RNA was prepared for RNAseq transcriptome analysis. RNA isolation, rRNA depletion, adapter-ligated cDNA library, and cDNA sequencing were carried out as described previously (Wu et al., 2022). The sequencing reads were mapped to the genome of K279a (Crossman et al., 2008). The total number of reads per gene was normalized by transcripts per kilobase million (TPM). The RNA-seq data have been deposited in GenBank under BioProject accession numbers SAMN41918898 for KJ, SAMN41918899 for KJΔChrR, and SAMN41918900 for KJΔChrRΔRpoEc.
2.9 Quantitative real-time-PCR
RNA was isolated from logarithmical phase bacterial cells and converted to cDNA using the High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Real-time PCR was performed using the TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) and an ABI Prism 7000 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems). The primer sets used are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The 16S rRNA was used to normalize the gene expressions. Fold change was calculated using the ΔΔCT method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001). Three biological replicates were performed.
3 Results
3.1 Smlt2377/Smlt2378 is a σE/ChrR homolog in S. maltophilia
The σE-ChrR pair homologs are distributed among α-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria, such as R. sphaeroides, Vibrionaceae, and Pseudomonas (Glaeser et al., 2011). To identify the σE-ChrR homolog in S. maltophilia, we performed BLASTP analysis using P. aeruginosa ChrR (accession No. CRR21278) as the query. The search results revealed a single candidate, Smlt2378, showing 94% protein identity with P. aeruginosa ChrR (Figure 1A). Next, genomic organization surrounding smlt2378 was surveyed. smlt2377 encoded an ECF σ factor, demonstrating that the σE-ChrR pair is conserved in S. maltophilia. Eleven base pairs downstream of smlt2378 and in the same orientation, a third open reading frame of 693 bp (Smlt2379) was identified (Figure 1B). smlt2379 encoded a 23.6-kDa cytoplasmic protein with an NAD(P)-binding domain that highly functioned as an oxidoreductase. Genomic organization strongly suggested the presence of the smlt2377-smlt2378-smlt2379 operon, which was verified via reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (Figure 1C). Based on the results presented in this study, we designated smlt2377-smlt2378-smlt2379 as rpoEc-chrR-chrA. Next, we examined the conservation of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in S. maltophilia. Among the 12 strains surveyed, all harbored this operon, indicating high conservation of the rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in S. maltophilia. In addition, we also noticed that there are nine genes (smlt2375-smlt2367) located upstream of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and divergently transcribed (Figure 1D). This genomic organization highly suggested that the nine genes may form an operon and regulated by σEc, which will be further expounded later.
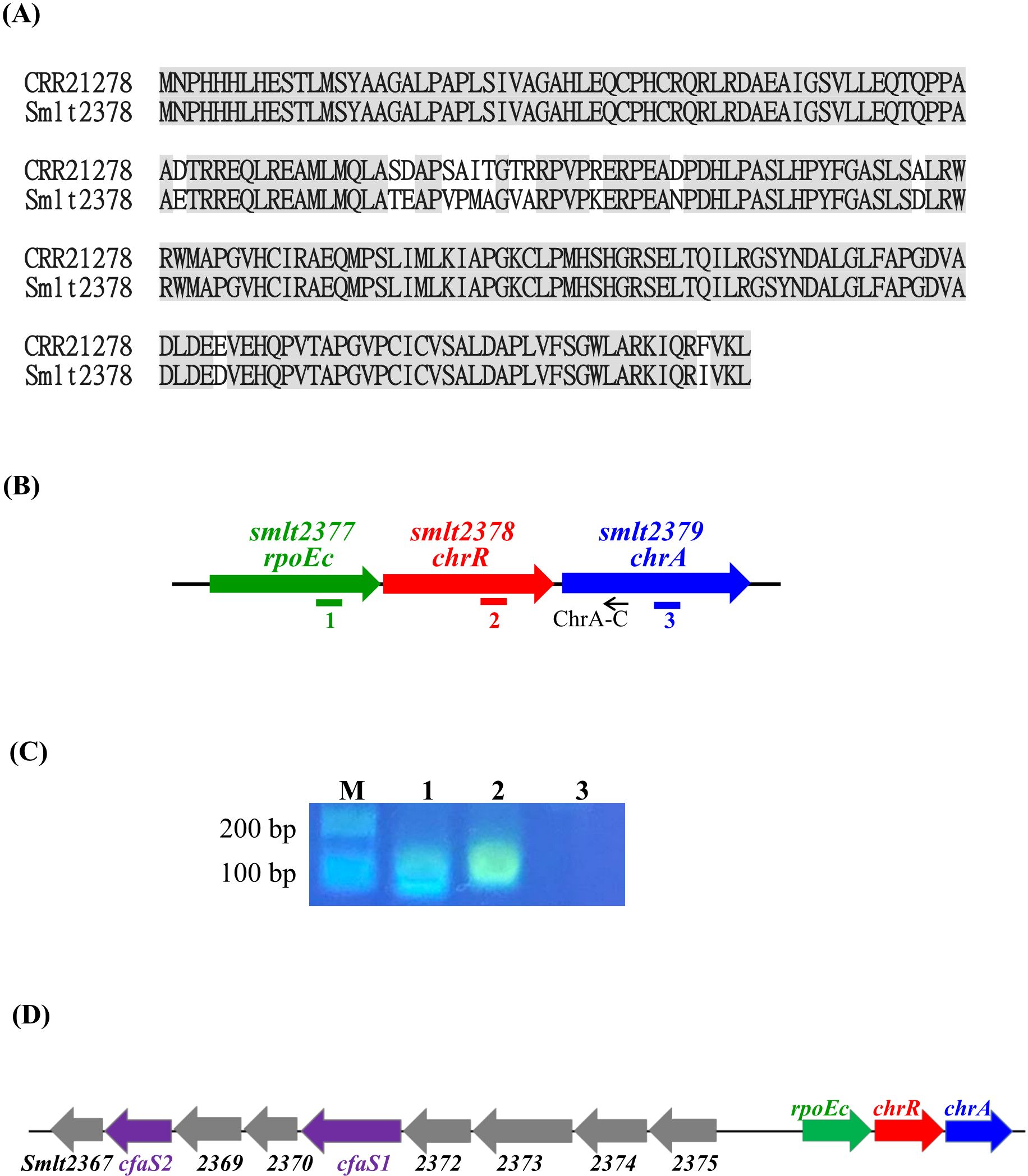
Figure 1. Characterization of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon. (A) Protein sequences alignment of P. aeruginosa ChrR (accession No. CRR21278) and S. maltophilia ChrR (Smlt2378). Protein sequence alignment was carried out using Needleman-Wunsch global alignment. The same amino acid residues are marked in gray. (B) Genetic organization of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon. The orientation of the genes is indicated by arrows. The small black arrow indicates the position of the ChrA-C primer used for reverse transcription. Solid bars labeled as 1-3 represent the positions of PCR amplicons correspondent with the labels in (C). (C) Verification of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon. Overnight culture of S. maltophilia KJΔChrR was inoculated into fresh LB with an initial OD450 of 0.15 and grown for 5 h. The cDNAs were obtained by reverse transcription using the primer ChrA-C. cDNA (100 ng) was used as the template for PCR. The PCR amplicons were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide. Lane 1, PCR amplicon generated by RpoEcQ-F and RpoEcQ-R; lane 2, PCR amplicon generated by ChrRQ-F and ChrRQ-R; lane 3, PCR amplicon generated by ChrAQ-F and ChrAQ-R. The ChrAQ-F/R primers were used as a control for DNA contamination check. (D) Genetic organization of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and the divergently transcribed nine genes, smlt2375-smlt2367.
3.2 rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon barely contributes to singlet oxygen tolerance
To characterize rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon, its genes were deleted from S. maltophilia KJ, either alone or in combination, to yield KJΔRpoEc, KJΔChrR, KJΔChrA, KJΔChrRΔRpoEc, KJΔChrRΔChrA, KJΔRpoEcΔChrA, and KJΔRpoEcΔChrRΔChrA (Supplementary Table S1). These mutants exhibited no observable growth defects on LB agar (Figure 2A) or broth (data not shown).
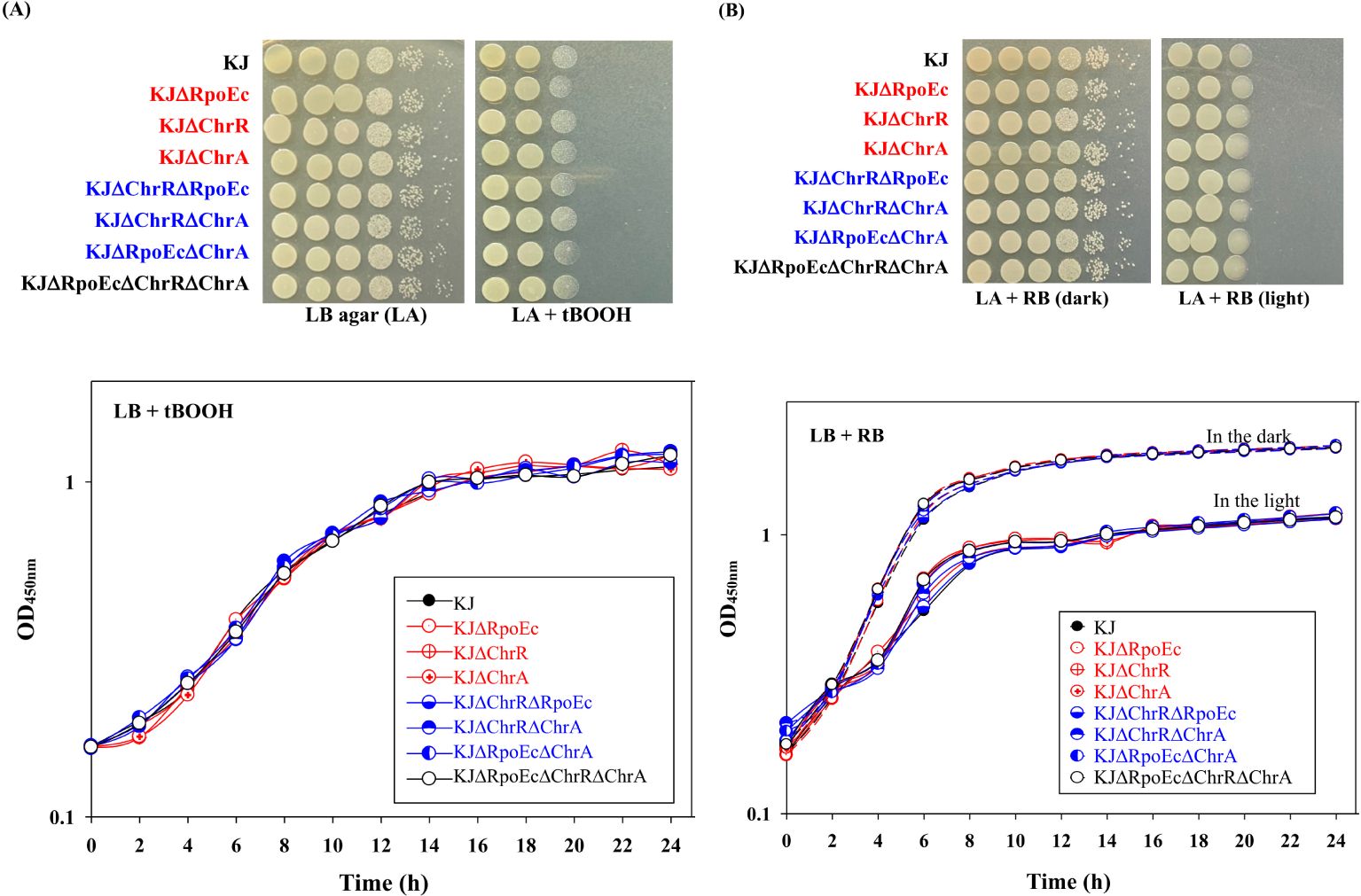
Figure 2. Role of chrEc-chrR-chrA operon in singlet oxygen tolerance. (A) tBOOH test. For cell viability, the logarithmic-phase bacterial cells tested of 2 × 105 CFU/μL were 10-fold serially diluted. Five microliters of bacterial suspension were spotted onto the LB plates with and without 500 μM tBOOH. After 18-h incubation at 37°C, the bacterial viability was imaged. For growth curve, overnight culture was inoculated into LB broth with 300 μM tBOOH at an initial OD450 of 0.15. Bacterial growth was monitored for 24 h. The image and graph are representatives of at least three replicated experiments. (B) RB test. For cell viability, the logarithmic-phase bacterial cells tested of 2 × 105 CFU/μL were 10-fold serially diluted. Five microliters of bacterial suspension were spotted onto two LB plates with 300 nM RB. One plate was covered with foil to create “dark” condition. The other plate was kept in the light. After 18-h incubation at 37°C, the bacterial viability was imaged. For growth curve, overnight culture was inoculated into LB broth with 200 nM RB at an initial OD450 of 0.15. Both dark and light culture conditions were prepared. Dash and solid lines indicate the cultures in the dark and light, respectively. Bacterial growth was monitored for 24 h. The image and graph are representatives of at least three replicated experiments.
A study on σE-ChrR pair of R. sphaeroides indicated its contribution to the singlet oxygen stress response (Anthony et al., 2004). We were interested in understanding whether the rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon played a role in the alleviation of singlet oxygen stress. Rose Bengal (RB) and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBOOH) methods were used to evaluate singlet oxygen tolerance (Di Mascio et al., 1997; Brahmachari and Karmakar, 2020). All the mutants tested displayed almost comparable viability to wild-type KJ in RB- and tBOOH-containing LB agar or broth (Figures 2A, B), indicating that rpoEc-chrR-chrA hardly contributes to singlet oxygen alleviation in our assay.
3.3 rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon contributes to superoxide tolerance
Involvement of the rpoEC-chrR-chrA operon in superoxide tolerance was assessed using an MD tolerance assay. Inactivation of chrR increased bacterial tolerance to MD, and complementation of KJΔChrR with a plasmid containing chrR reversed MD tolerance to wild-type levels (Figure 3A). Furthermore, further inactivation of rpoEc or chrA in KJΔChrR partially restored MD tolerance (Figure 3A). Thus, σEc activation increases MD tolerance, and ChrA is involved in this regulatory circuit.
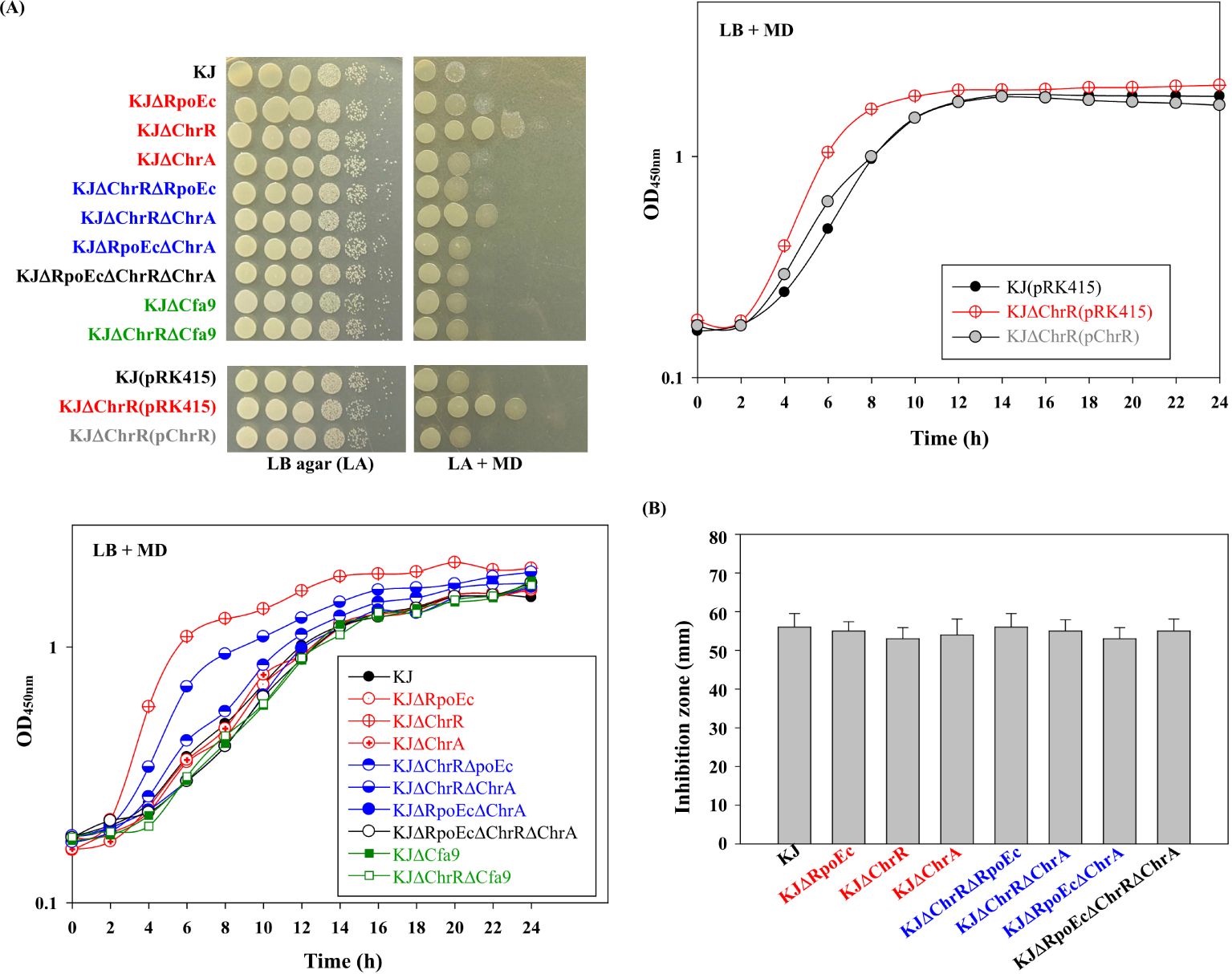
Figure 3. Role of chrEc-chrR-chrA operon in MD and H2O2 tolerance (A) Role of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in MD tolerance. For cell viability, the logarithmic-phase bacterial cells of 2 × 105 CFU/μL were 10-fold serially diluted. Bacterial aliquot (5 μL) was spotted onto LB agars without and with 50 μg/mL MD. After a 24-h incubation at 37°C, the growth of bacterial cells was observed. For growth curve, overnight culture was inoculated into LB broth with 20 μg/mL MD at an initial OD450 of 0.15. Bacterial growth was monitored for 24 h. The image and graph are representatives of at least three replicated experiments. (B) Role of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in H2O2 tolerance. The bacterial cell suspension tested was spread onto LB agar. A sterile filter paper disc with 15 μL 10% H2O2 was placed on the agar. The growth inhibition zone was measured after a 24-h incubation at 37°C. Bars represent the average values from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard deviation for triplicates.
Next, we investigated the role of rpoEC-chrR-chrA operon in H2O2 tolerance. All tested strains exhibited comparable H2O2 susceptibilities (Figure 3B), tentatively ruling out the contribution of rpoEC-chrR-chrA operon to H2O2 tolerance.
3.4 rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon contributes to CAZ susceptibility
S. maltophilia is intrinsically resistant to various antibiotics (Crossman et al., 2008). Clinically, CAZ and fluoroquinolones are the choices for the treatment of S. maltophilia infection. Stress alleviation systems can cross-protect bacteria from antibiotics (Shin et al., 2020). Therefore, we assessed the involvement of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in susceptibility to CAZ and levofloxacin (LEV) susceptibility. The viabilities of wild-type KJ and its derived mutants in MH agar or broth containing CAZ and LEV were assessed. Of the three single-deletion mutants, KJΔChrR showed compromised viability in a medium containing CAZ, and viability was restored by ChrR complementation (Figure 4). Furthermore, KJΔChrRΔRpoEc and KJΔChrRΔChrA displayed viability almost comparable to wild-type KJ (Figure 4). Collectively, ΔchrR-mediated rpoEc and chrA upregulation contributed to an increase in CAZ susceptibility. With respect to LEV susceptibility, all rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon-associated mutants displayed viability comparable to wild-type KJ (Figure 4), tentatively ruling out the involvement of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in LEV susceptibility.
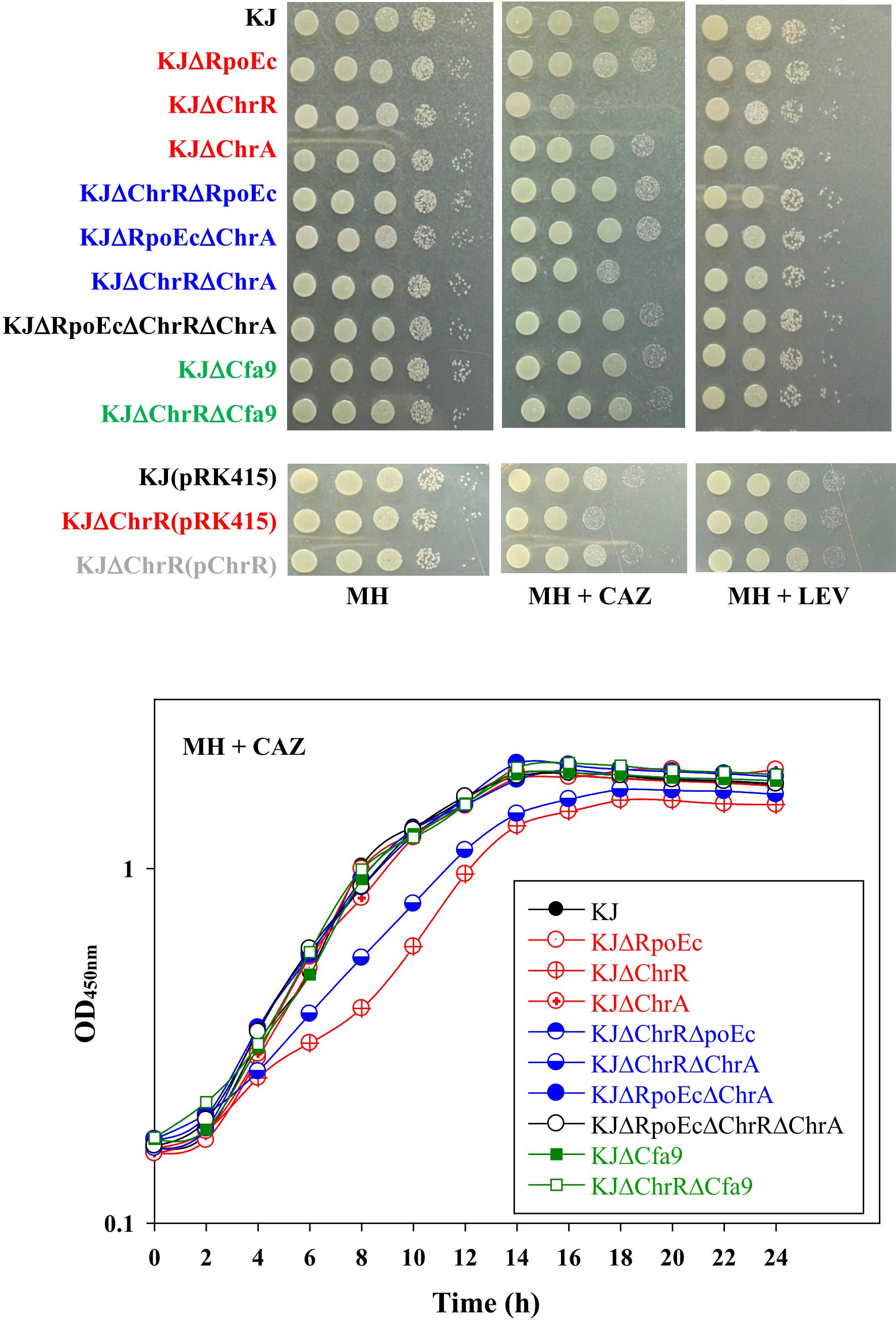
Figure 4. Role of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in antibiotic susceptibility. For cell viability, the logarithmic-phase bacterial cells (2 × 105 CFU/μL) were 10-fold serially diluted. Bacterial aliquot (5 μL) was spotted onto MH agars without and with 120 μg/mL CAZ or 0.25 μg/mL LEV. After a 24-h incubation at 37°C, the growth of bacterial cells was observed. For growth curve, overnight culture was inoculated into MH broth with 200 μg/mL CAZ at an initial OD450 of 0.15. Bacterial growth was monitored for 24 h. The image and graph are representatives of at least three replicated experiments.
The mechanisms responsible for CAZ susceptibility in S. maltophilia can be attributed to β-lactamase-mediated and non-β-lactamase-mediated mechanisms (Huang et al., 2021). To assess whether β-lactamase is involved in the ΔchrR-mediated CAZ susceptibility increase, CAZ-induced β-lactamase activities of KJ, KJΔChrR, KJΔChrRΔRpoEc, and KJΔChrRΔChrA were determined. All mutants tested displayed comparable CAZ-induced β-lactamase activities with wild-type KJ (Supplementary Figure S1), indicating that σEc activation-mediated increase of β-lactam susceptibility is irrelated to β-lactamase activity.
3.5 Regulation of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon expression
We constructed a PrpoEc and xylE transcriptional fusion construct, pRpoEcxylE (Supplementary Table S1), to assess the expression of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon by C23O determination. Plasmid pRpoEcxylE was transformed into the wild-type and its derived rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon-associated mutants (Supplementary Table S1) to assess the autoregulation circuit. KJ(pRpoEcxylE) exhibited moderate C23O activity, supporting the intrinsic expression of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon. Compared to that of wild-type KJ, the promoter activity of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon was significantly increased in KJΔChrR and reverted to wild-type levels in KJΔChrRΔRpoEc and KJΔChrRΔChrA (Figure 5). These results are consistent with the previous understanding of σE-ChrR system that ChrR functions as an anti-σE and σE imposes autoregulation on its own expression (Donohue, 2019). A more interesting finding is that ChrA played a positive role in ΔchrR-mediated rpoEc upregulation (Figure 5). To further clarify this, the promoter activity of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in KJΔChrA was assessed. KJΔChrA(pRpoEcxylE) displayed lower C23O activity than KJ(pRpoEcxylE) (Figure 5), supporting that ChrA plays a positive role in regulating the transcriptional expression of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon.
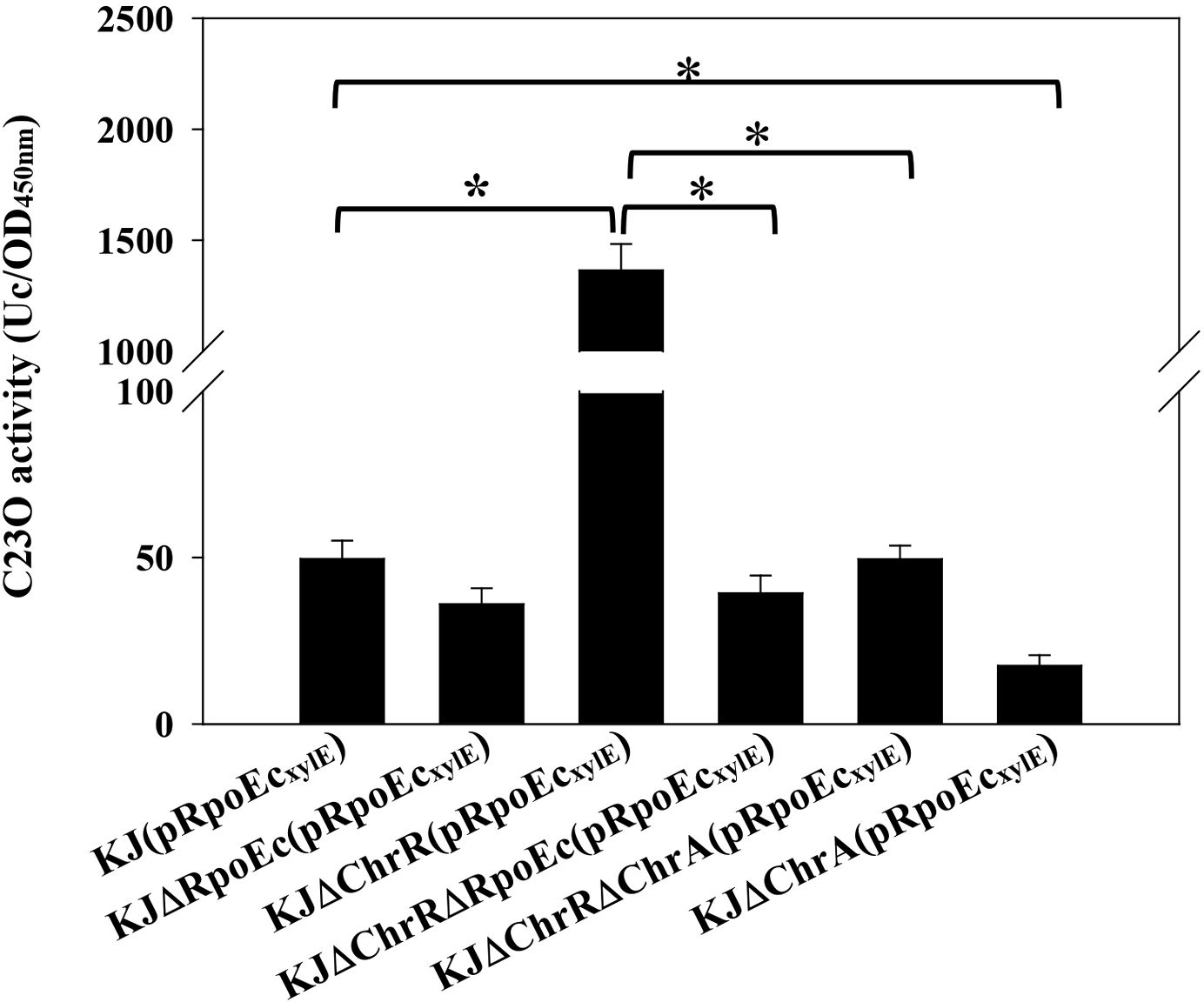
Figure 5. Regulation of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon expression. Overnight cultures of bacterial cells tested were subcultured into fresh LB broth with an initial OD450 of 0.15. After 5-h culture, the C23O activity was measured. One unit of C23O activity (Uc) was defined as the amount of C23O that converted 1 nmol of catechol per min. The C23O specific activity was expressed as Uc/OD450. Bars represent the average values from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviations for three triplicate samples. A two-sided Welch’s t-test and Bonferroni’s correction were used to determine statistical significance. *P <0.01.
Given the contribution of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon to MD tolerance (Figure 3A) and CAZ susceptibility (Figure 4), we wondered whether MD and CAZ were the stimuli that induced the expression of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon. The C23O activity expressed by KJ(pRpoEcxylE) under MD and CAZ challenges was determined. MD- and CAZ-treated KJ(pRpoEcxylE) exhibited C23O activity comparable to the untreated counterpart (Supplementary Figure S2), indicating that MD and CAZ are not the stimuli that activate σEc.
3.6 smlt2375-smlt2367 genes upregulation contributes to σEc activation-mediated increase in MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility
To elucidate the mechanism underlying the σEc activation-mediated increase in MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility, RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of wild-type KJ, KJΔChrR, and KJΔChrRΔRpoEc was performed once. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were considered significant if the change in transcripts per kilobase million (TPM) between KJ and KJΔChrR was greater than three-fold. Twenty-four DEGs were revealed (Supplementary Table S2). Of them, 23 genes were upregulated and one was downregulated in KJΔChrR (Supplementary Table S2). Furthermore, the TPM values of the 24 DEGs in KJΔChrRΔRpoEc were significantly reverted (Supplementary Table S2), indicating that these 24 genes were members of the ChrR-σE regulatory circuit. To validate the transcriptome data, we performed qRT-PCR to probe the genes rpoEc, smlt2373, smlt2382, cytB, L1, and L2. The results supported the reliability of the transcriptome results (Supplementary Figure S3). By inputting the 500-base region upstream of the 24 DEGs into the motif search program MEME (Bailey et al., 2009), we generated a putative consensus DNA-binding motif of σEc (σEc box) (Figure 6A). Figure 6B shows the putative σEc box located upstream of rpoEc and smlt2375.

Figure 6. In silico analysis of putative σEc box of S. maltophilia KJ. (A) Sequence logo of the putative σEc box of S. maltophilia. Identification of putative σEc box was performed using HEME program. The inputs included the 500-base region upstream from the 24 DEGs revealed by transcriptome analysis of KJ and KJΔChrR. (B) The intergenic region of rpoEc and smlt2375, and the putative σEc box. rpoEc and smlt2375 code σEc and a hypothetical protein, respectively. The start codon for smlt2375 and rpoEc are highlighted in blue and green, respectively. The putative σEc box of rpoEc and smlt2375 are highlighted in yellow.
As β-lactam resistance of S. maltophilia is strongly linked to PG homeostasis and β-lactamase induction (Huang et al., 2021), we checked the TPM values of L1, L2, and 37 known PG homeostasis-associated genes. No significant DEGs were identified among the 39 genes (Supplementary Table S3). β-lactamase activity and transcriptome analyses (Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S3) suggested the involvement of a non-β-lactamase mechanism in the σEc activation-mediated increase in β-lactam susceptibility.
Among the identified DEGs (Supplementary Table S2), a nine-gene cluster, smlt2375-smlt2367, was the most significantly upregulated (Table 1). The nine genes were located upstream of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and divergently transcribed (Figure 1). Furthermore, these genes were simultaneously upregulated in KJΔChrR but significantly reverted in KJΔChrRΔRpoEc (Table 1). These observations strongly suggest that these nine genes form an operon regulated by σEc. The annotations and locations of the proteins encoded by smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster are summarized in Table 1. The nine-gene cluster appeared to be involved in membrane lipid modification as it encoded a fatty acid desaturase (Smlt2374), an oxidoreductase (Smlt2373), two cyclopropane-fatty-acyl phospholipid synthase (CFA synthases) (Smlt2371 and Smlt2368), and five hypothetical proteins (Table 1). To investigate the role of the nine-gene upregulation in ΔchrR-mediated increase in MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility, a nine-gene deletion mutant was constructed in wild-type KJ and KJΔChrR, yielding KJΔCfa9 and KJΔChrRΔCfa9, respectively (Supplementary Table S1). KJΔCfa9 and wild-type KJ showed comparable MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility; however, compared to those in KJΔChrR, MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility were almost reverted to wild-type levels in KJΔChrRΔCfa9 (Figures 3A, 4), indicating that smlt2375-smlt2367 genes upregulation contributes to ΔchrR-mediated increase in MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility.
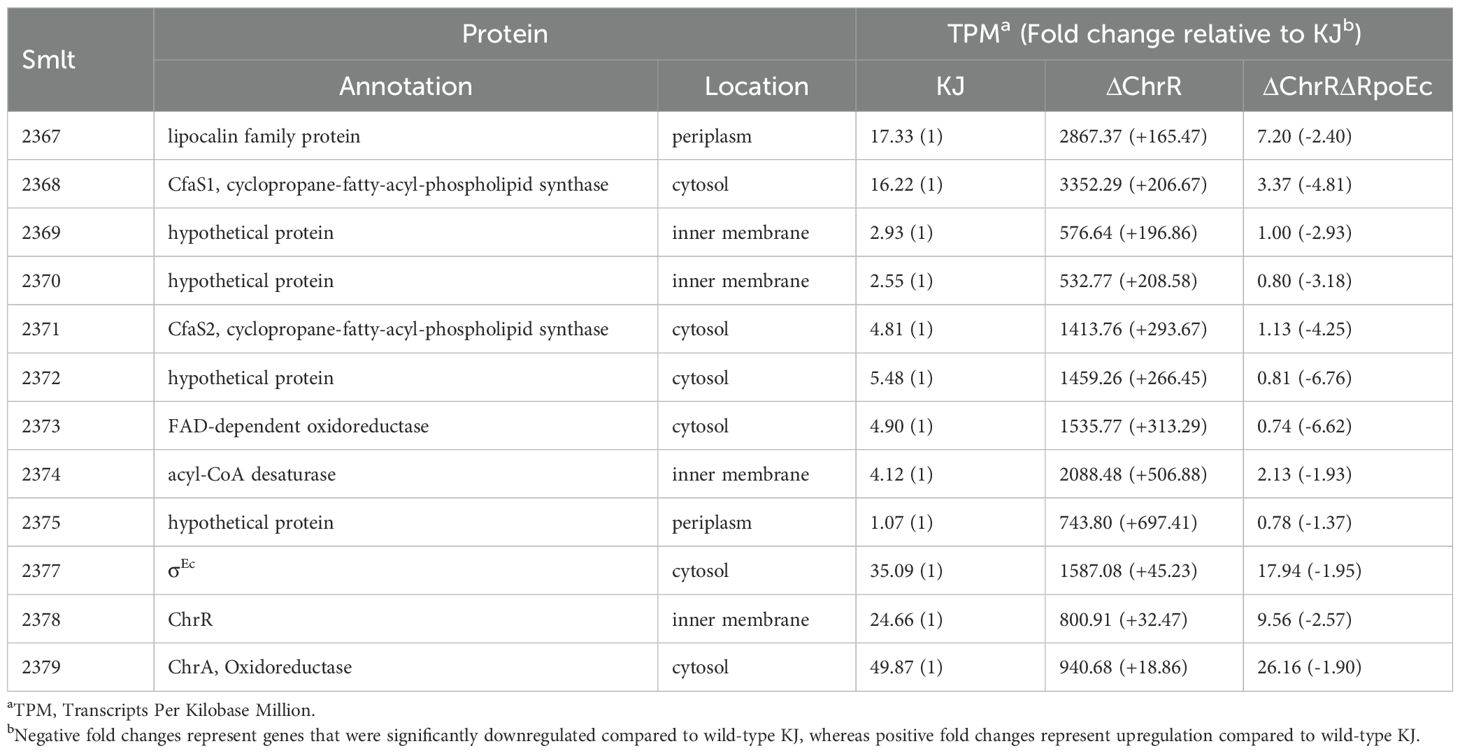
Table 1. Transcripts Per Kilobase Million (TPM) values of selected genes in KJ, KJΔChrR, and KJΔChrRΔRpoEc, revealed by transcriptome analysis.
4 Discussion
σE-ChrR system was first reported in photosynthetic microorganisms, such as R. sphaeroides, due to its role in the alleviation of stress induced by singlet oxygen, which is an inevitable by-product of photosynthesis (Anthony et al., 2004). Later, a core σE-ChrR regulon was discovered in non-photosynthetic α- and γ-proteobacteria, such as Azospirillum brasilense, Caulobacter crescentus, Shewanella oneidensis, Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, and Vibrio cholerae (Gupta et al., 2013; Lourenço and Gomes, 2009; Dai et al., 2015; Butcher et al., 2017; Tardu et al., 2017). These known σE-ChrR regulons are involved in the alleviation of singlet oxygen stress. In this study, we revealed that rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon was not involved in singlet oxygen stress alleviation but contributed to superoxide tolerance and CAZ susceptibility in S. maltophilia (Figures 2, 3A, 4). A similar function was shown earlier in A. brasilense Sp245, in which the rpoE2-chrR2 system is involved in superoxide and antibiotic tolerance (Gupta et al., 2013). Sigma E2 activation in A. brasilens Sp245 confers resistance to β-lactam and nalidixic acid (Gupta et al., 2013); however, σEc activation increases the β-lactam susceptibility of S. maltophilia (Figure 4).
The rpoE-chrR system is an effector of singlet oxygen stress, and both genes are generally organized into an operon in bacteria. Unlike the two-gene rpoE-chrR operon, rpoEc and chrR of S. maltophilia are located in the three-gene rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon (Figure 1A). Similarly, a three-gene rpoE-chrR-VC2303 operon is observed in V. cholerae (Tardu et al., 2017). The protein encoded by VC2303 is annotated as a hypothetical protein and its significance in the RpoE-ChrR system has not characterized. In this study, we verified that ChrA of S. maltophilia plays a positive role in the expression of rpoEc regulon (Figure 5). To consider the underlying mechanism responsible for ChrA function, the rsbV-rsbW-sigB-rsbX operon of Bacillus subtilis provides some ideas. sigB, rsbW, and rsbV encode the sigma factor σB, anti-σB (RsbW), and anti-anti-σB (RsbV), respectively (Kazmierczak et al., 2005). Similar to most ECF σ factors, σB autoregulates the rsbV-rsbW-sigB-rsbX operon expression. RsbX plays a negative role in σB activity through its phosphatase activity (Voelker et al., 1997). Here, inactivation of chrA decreased the expression of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon (Figure 5). As ChrA is predicted to be a cytoplasmic protein with an NAD(P)-binding domain that functions as an oxidoreductase, we speculated that ChrA plays a positive role in modulating σEc activity and this modulation may be oxidoreductase activity involved.
Transcriptome analysis revealed the genes regulated by rpoEc-chrR pair. Among the DEGs (Supplementary Table S2), three upregulated gene clusters and a downregulated gene attracted our attention, that is, smlt2375-smlt2367, smlt2382-smlt2380, yceA-cybB-yceB operon (smlt3627-smlt3629), and smlt0227. smlt2375-smlt2367 gene cluster was the most upregulated in KJΔChrR. Because of the presence of a fatty acid desaturase gene (smlt2374) and two CFA synthase genes (smlt2371 and smlt2368), smlt2375-smlt2367 gene cluster may be involved in membrane lipid modification. CFA synthase catalyzes the modification of the acyl chains of membrane phospholipids through the methylation of unsaturated fatty acyl chains to generate cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid (CFA) (Grogan and Cronan, 1997). Modification of membrane lipids by CFA synthase can alter the biophysical properties of membranes and protect cells against drastic environmental perturbations such as oxidative stress, high ionic strength, and acid stress (Grogan and Cronan, 1986, 1997; Tardu et al., 2017; Chang and Cronan, 1999; Jiang et al., 2019). Membrane lipid modification also modulates membrane permeability and fluidity, thereby altering bacterial susceptibility to antibiotics and antimicrobial peptides (Schmidt et al., 2018). Integrating our finding that β-lactamase activity is not the critical factor responsible for σEc activation-mediated increase of β-lactam susceptibility. Therefore, we speculated that the upregulation of smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster in KJΔChrR may alter membrane properties against MD-mediated oxidative stress and increase membrane permeability to CAZ, which increases MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility. smlt2382-smlt2380 gene cluster is located downstream of rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and divergently transcribed. The proteins encoded by smlt2382-smlt2380 are the members of a two-component regulatory system, including sensor kinase, response regulator, and hybrid sensor kinase/response regulator, respectively. Thus, a regulatory interconnect between rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and smlt2382-smlt2380 gene cluster highly exists. Furthermore, yceA-cybB-yceB operon is the member of rpoEc regulon. The contribution of yceA-cybB-yceB operon to MD tolerance has been reported recently (Liao et al., 2023). Therefore, the smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster upregulation may not be the sole factor leading to MD tolerance increase in KJΔChrR. The contribution of yceA-cybB-yceB operon upregulation cannot be ignored. smlt0227 is the sole downregulated DEG in KJΔChrR. The protein encoded by smlt0227 is annotated as a major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporter. MFS transporter plays a crucial role in a multitude of physiological processes and its involvement in stress tolerance and antibiotic susceptibility has been widely reported (Pao et al., 1998; Nag and Mehra, 2021).
Promoter activity and transcriptome assay revealed that rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon exhibited moderate expression, indicating that rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon was transcribed by σD-driven RNAP in logarithmically grown KJ cells. Under these conditions, translated σEc was sequestered via ChrR binding (Figure 7A). In the presence of stimuli, σEc was released from ChrR and activated the expression of σEc regulon. In this study, KJΔChrR mimicked the concept of σEc activation. A positive autoregulation was observed in the rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and ChrA played a positive role in this regulatory circuit. Furthermore, activated σEc upregulated the expression of smlt2375-smlt2367 gene cluster, thus increasing the MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility (Figure 7B).
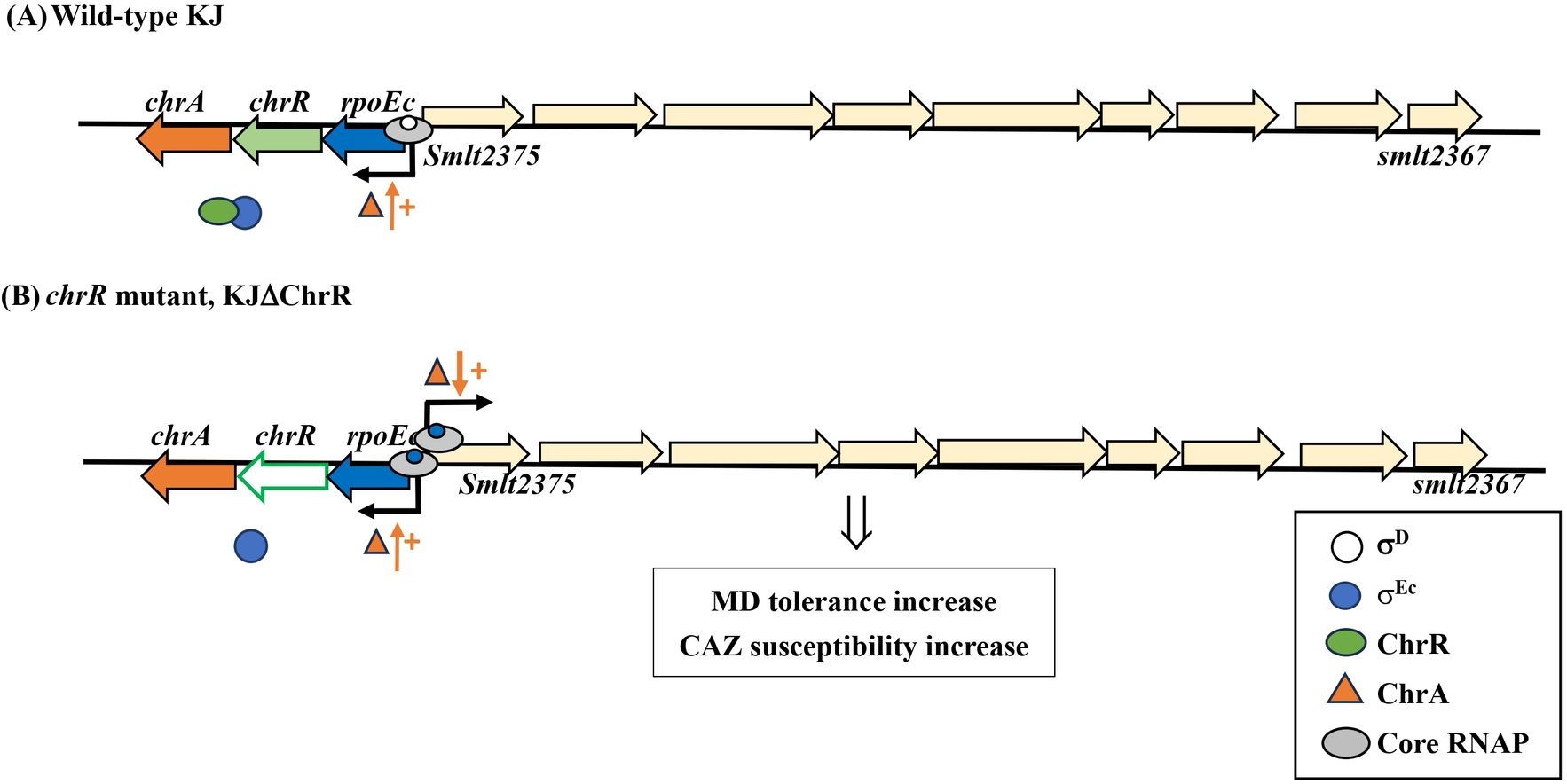
Figure 7. The proposed model for σEc activation-mediated increase in MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility. In the wild-type KJ, rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon is moderately expressed via σD-driven RNA polymerase. The σEc protein is sequestered by ChrR (A). In the chrR mutant, the free form σEc and core RNA polymerase (RNAP) form a holoenzyme, which drives the expression of σEc regulon, including rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon and smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster. ChrA protein plays a positive role in the transcriptional-level expression of σE regulon. The upregulation of smlt2375-smlt2367 cluster contributes to the σEc activation-mediated increase in MD tolerance and CAZ susceptibility (B).
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
R-HK: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. H-FL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. L-HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. T-YY: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-TL: Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. T-CY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This project has received funding from the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan (grant numbers MOST 111-2320-B-A49-025-MY3 and NSTC 112-2320-B-A49-043-MY3), the Taipei Veterans General Hospital (V112C-227 & V113C-225), and the Professor Tsuei-Chu Mong Merit Scholarship (grant number 412260001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1492008/full#supplementary-material
References
Anthony, J. R., Newman, J. D., Donohue, T. J. (2004). Interactions between the Rhodobacter sphaeroides ECF sigma factor, σE, and its anti-sigma factor, ChrR. J. Mol. Biol. 341, 345–360. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.06.018
Bailey, T. L., Boden, M., Buske, F. A., Frith, M., Grant, C. E., Clementi, L., et al. (2009). MEME suite: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W202–W208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335
Brahmachari, G., Karmakar, I. (2020). Visible light-induced and singlet oxygen-mediated photochemical conversion of 4-hydroxy-α-benzopyrones to 2-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-2-carboxamides/carboxylates using rose Bengal as a photosensitizer. J. Org. Chem. 85, 8851–8864. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00726
Butcher, B. G., Bao, Z., Wilson, J., Stodghill, P., Swingle, B., Filiatrault, M., et al. (2017). The ECF sigma factor, PSPTO_1043, in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 is induced by oxidative stress and regulates genes involved in oxidative stress response. PloS One 12, e0180340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180340
Chang, Y. Y., Cronan, J. E., Jr (1999). Membrane cyclopropane fatty acid content is a major factor in acid resistance of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 33, 249–259. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01456.x
Chen, C. H., Huang, C. C., Chung, T. C., Hu, R. M., Huang, Y. W., Yang, T. C. (2011). Contribution of resistance-nodulation-division efflux pump operon smeU1-V-W-U2-X to multidrug resistance of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 5826–5833. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00317-11
Crossman, L. C., Gould, V. C., Dow, J. M., Vernikos, G. S., Okazaki, A., Sebaihia, M., et al. (2008). The complete genome, comparative and functional analysis of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia reveals an organism heavily shielded by drug resistance determinants. Genome Biol. 9, R74. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-4-r74
Dai, J., Wei, H., Tian, C., Damron, F. H., Zhou, J., Qiu, D. (2015). An extracytoplasmic function sigma factor-dependent periplasmic glutathione peroxidase is involved in oxidative stress response of. Shewanella oneidensis. BMC Microbiol. 15, 34. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0357-0
Davis, M. C., Kesthely, C. A., Franklin, E. A., MacLellan, S. R. (2017). The essential activities of the bacterial sigma factor. Can. J. Microbiol. 63, 89–99. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2016-0576
DeRosa, M. C., Crutchley, R. J. (2002). Photosensitized singlet oxygen and its applications. Coord Chem. Rev. 223-224, 351–371. doi: 10.1016/S0010-8545(02)00034-6
Di Mascio, P., Briviba, K., Sasaki, S. T., Catalani, L. H., Medeiros, M. H., Bechara, E. J., et al. (1997). The reaction of peroxynitrite with tert-butyl hydroperoxide products singlet molecular oxygen. Biol. Chem. 378, 1071–1074.
Donohue, T. J. (2019). Shedding light on a Group IV (ECF11) alternative σ factor. Mol. Microbiol. 112, 374–384. doi: 10.1111/mmi.v112.2
Glaeser, J., Nuss, A. M., Berghoff, B. A., Klug, G. (2011). Singlet oxygen stress in microorganisms. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 58, 141–173. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381043-4.00004-0
Grogan, D. W., Cronan, J. E. (1986). Characterization of Escherichia coli mutants completely defective in synthesis of cyclopropane fatty-acids. J. Bacteriol 166, 872–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.872-877.1986
Grogan, D. W., Cronan, J. E., Jr. (1997). Cyclopropane ring formation in membrane lipids of bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61, 429–441. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.61.4.429-441
Gruber, T. M., Gross, C. A. (2003). Multiple sigma subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090913
Gupta, N., Kumar, S., Mishra, M. N., Tripathi, A. K. (2013). A constitutively expressed pair of rpoE2-chrR2 in Azospirillum brasilense Sp7 is required for survival under antibiotic and oxidative stress. Microbiol. (Reading) 159, 205–218. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.061937-0
Helmann, J. D. (2002). The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 46, 47–110. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2911(02)46002-X
Ho, T. D., Ellermeier, C. D. (2012). Extra cytoplasmic function σ factor activation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 15, 182–188. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.01.001
Huang, Y. W., Huang, H. H., Huang, K. H., Chen, W. C., Lin, Y. T., Hsu, C. C., et al. (2019). AmpI function as an iron exporter to alleviate -lactam-mediated reactive oxygen species stress in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63, e02467–e02418. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02467-18
Huang, Y. W., Liou, R. S., Lin, Y. T., Huang, H. H., Yang, T. C. (2014). A linkage between SmeIJK efflux pump, cell envelope integrity, and σE-mediated envelope stress response in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. PloS One 9, e111784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111784
Huang, H. H., Wu, B. K., Li, L. H., Lin, Y. T., Yang, T. C. (2021). Role of the PhoPQ two-component regulatory system in the β-lactam resistance of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 76, 1480–1486. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab059
Jacoby, G. A. (2009). AmpC beta-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 22, 161–182. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00036-08
Jair, H. W., Lu, H. F., Huang, Y. W., Pan, S. Y., Lin, I. L., Huang, H. H., et al. (2019). Roles of the two-MnSOD system of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the alleviation of superoxide stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 1770. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071770
Jiang, X. J., Duan, Y., Zhou, B., Guo, Q., Wang, H., Hang, X., et al. (2019). The cyclopropane fatty acid synthase mediates antibiotic resistance and gastric colonization of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol 201, e00374–e00319. doi: 10.1128/JB.00374-19
Kazmierczak, M. J., Wiedmann, M., Boor, K. J. (2005). Alternative sigma factors and their roles in bacterial virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 69, 527–543. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.4.527-543.2005
Li, L. H., Shih, Y. L., Huang, J. Y., Wu, C. J., Huang, Y. W., Huang, H. H., et al. (2020a). Protection from hydrogen peroxide stress relies mainly on AhpCF and KatA2 in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. BioMed. Sci. 27, 37. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00631-4
Li, L. H., Wu, C. M., Lin, Y. T., Pan, S. Y., Yang, T. C. (2020b). Roles of FadRACB system in formaldehyde detoxification, oxidative stress alleviation, and antibiotic susceptibility in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 2101–2109. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa173
Liao, C. H., Ku, R. H., Li, L. H., Wu, C. M., Yang, T. C. (2023). Role of yceA-cybB-yceB operon in oxidative stress tolerance, swimming motility and antibiotic susceptibility of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 78, 1891–1899. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad179
Liao, C. H., Lu, H. F., Huang, H. H., Chen, Y., Li, L. H., Lin, Y. T., et al. (2022). The fciTABC and feoABI systems contribute to ferric citrate acquisition in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. BioMed. Sci. 29, 26. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00809-y
Lin, Y. T., Huang, Y. W., Liou, R. S., Chang, Y. C., Yang, T. C. (2014). MacABCsm, an ABC-type tripartite efflux pump of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia involved in drug resistance, oxidative and envelope stress tolerance and biofilm formation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69, 3221–3226. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku317
Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lourenço, R. F., Gomes, S. L. (2009). The transcriptional response to cadmium, organic hydroperoxide, singlet oxygen and UV-A mediated by the σE-ChrR system in Caulobacter crescentus. Mol. Microbiol. 72, 1159–1170. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06714.x
Marles-Wright, J., Lewis, R. J. (2007). Stress responses of bacteria. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 17, 755–760. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.08.004
Mascher, T. (2023). Past, present, and future of extracytoplasmic function σ factors: distribution and regulatory diversity of the third pillar of bacterial signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 77, 625–644. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-032221-024032
Mojica, M. F., Humphries, R., Lipuma, J. J., Mathers, A. J., Rao, G. G., Shelburne, S. A., et al. (2022). Clinical challenges treating Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: an update. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 4, dlac040. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlac040
Nag, A., Mehra, S. (2021). A major facilitator superfamily (MFS) efflux pump, SCO4121, from Streptomyces coelicolor with roles in multidrug resistance and oxidative stress tolerance and its regulation by a MarR regulator. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 87, e02238–e02220. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02238-20
Paget, M. S. (2015). Bacterial sigma factors and anti-sigma factors: structure, function and distribution. Biomolecules 5, 1245–1265. doi: 10.3390/biom5031245
Pan, S. Y., Shih, Y. L., Huang, H. H., Li, L. H., Lin, Y. T., Yang, T. C. (2022). The involvement of PacIRA system of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the uptake of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyochelin and intraspecies competition for iron acquisition. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 55, 273–281. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.03.001
Pao, S. S., Paulsen, I. T., Saier, M. H., Jr. (1998). Major facilitator superfamily. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62, 1–34. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.62.1.1-34.1998
Sánchez, M. B. (2015). Antibiotic resistance in the opportunistic pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Front. Microbiol. 6, 658. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00658
Schmidt, R., Yonghong, D., Hoffmann, R. (2018). Phospholipid composition of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli influences its susceptibility against antimicrobial peptide apidaecin 1b. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 90, 316–323. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2017.11.008
Sharma, P., Jha, A. B., Dubey, R. S., Pessarakli, M. (2012). Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 1–26. doi: 10.1155/2012/217037
Shih, Y. L., Wu, C. M., Lu, H. F., Li, L. H., Lin, Y. T., Yang, T. C. (2022). Involvement of the hemP-hemA-smlt0796-smlt0797 operon in hemin acquisition by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0032122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00321-22
Shin, B., Park, C., Park, W. (2020). Stress responses linked to antimicrobial resistance in Acinetobacter species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 1423–1435. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10317-z
Sun, S., Zhou, J. (2018). Molecular mechanisms underlying stress response and adaptation. Thorac. Cancer 9, 218–227. doi: 10.1111/tca.2018.9.issue-2
Tardu, M., Bulut, S., Kavakli, I. H. (2017). MerR and ChrR mediate blue light induced photo-oxidative stress response at the transcriptional level in Vibrio cholera. Sci. Rep. 7, 40817. doi: 10.1038/srep40817
Triantaphylidès, C., Havaux, M. (2009). Singlet oxygen in plants: production, detoxification and signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 14, 219–228. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2009.01.008
Voelker, U., Luo, T., Smirnova, N., Haldenwang, W. (1997). Stress activation of Bacillus subtilis sigma B can occur in the absence of sigma B negative regulator RsbX. J. Bacteriol 179, 1980–1984. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.6.1980-1984.1997
Wu, C. J., Chen, Y., Li, L. H., Wu, C. M., Lin, Y. T., Ma, C. H., et al. (2022). Roles of SmeYZ, SbiAB, and SmeDEF efflux systems in iron homeostasis of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0244821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02448-21
Wu, C. J., Chiu, T. T., Lin, Y. T., Huang, Y. W., Li, L. H., Yang, T. C. (2018). Role of smeU1VWU2X operon in alleviation of oxidative stresses and occurrence of sulfaethoxazole-trimethoprim-resistant mutants in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e02114–7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02114-17
Keywords: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, singlet oxygen, β-lactam susceptibility, oxidative stress, sigma factor
Citation: Ku R-H, Lu H-F, Li L-H, Yeh T-Y, Lin Y-T and Yang T-C (2025) Roles of the rpoEc-chrR-chrA operon in superoxide tolerance and β-lactam susceptibility of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1492008. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1492008
Received: 06 September 2024; Accepted: 17 January 2025;
Published: 04 February 2025.
Edited by:
Giancarlo Ripabelli, University of Molise, ItalyReviewed by:
Bryan Troxell, AjaxBio, LLC, United StatesJananee Jaishankar, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Ku, Lu, Li, Yeh, Lin and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tsuey-Ching Yang, dGN5YW5nQG55Y3UuZWR1LnR3
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ren-Hsuan Ku1†
Ren-Hsuan Ku1† Li-Hua Li
Li-Hua Li Ting-Yu Yeh
Ting-Yu Yeh Yi-Tsung Lin
Yi-Tsung Lin Tsuey-Ching Yang
Tsuey-Ching Yang