- 1Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
- 2Ningbo Institute of Life and Health Industry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, China
- 3Department of General Surgery (Hepatic, Anal-canal, Gastrointestinal), Ningbo Zhenhai People’s Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Introduction: Candida albicans, a human fungal pathogen, multiplies to invade body cells and causes fungal diseases in the condition of insufficient body's immune function. Early detection of C. albicans is required to guide appropriate prevention and treatment.
Methods: The purpose of this study was to establish a C. albicans assay based on newly developed closed dumbbell-mediated isothermal amplification (CDA) to achieve rapid and simple point of care diagnostic. The CDA technique was carried out by specific primers targeting at the conserved C. albicans ITS2 gene. All primers were selected and evaluated by real-time fluorescence monitoring and endpoint visual judgement indicated by hydroxy naphthol blue (HNB). Optimal primers and accelerate primers (out primers and loop primers) were designed and selected after confirmation of the fundamental CDA primers to achieve more efficient CDA reaction for C. albicans detection (CA-OL-CDA).
Results: After establishment of the assay, 9 non-Candida albicans strains, including 3 Candida species were tested to negative by adopting the established CA-OL-CDA assay, indicated high specificity. The limit of detection of Candida albicans DNA by CA-OL-CDA assay was 6.2×10-6 ng/μL of DNA (10 copies/μL), 10-fold more sensitive than real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR).
Discussion: The CA-OL-CDA assay exhibited advantages of high specificity, sensitivity, simpler and more efficient operation. In addition, the CA-OL-CDA method holds potential in on-site detection for C. albicans using color shift by adopting the reaction mixture based on HNB.
1 Introduction
Candida albicans is the most prevalent human fungal pathogen and a commensal in a large portion of the population, colonizing the oral, gastrointestinal, and reproductive tracts asymptomatically (Wall et al., 2019; Ho et al., 2021; Wakade et al., 2021). Usually, C. albicans could invade body cells and cause disease under abnormal immune function conditions (Kadosh, 2016; Bertolini et al., 2019; Lopes and Lionakis, 2022). As reported in the United States, approximately 70% of women may suffer from C. albicans vaginal infection during their lifetime (Nyirjesy et al., 2022). In addition, burn wounds may contribute to candidiasis via high colonization and infection by C. albicans (Fidel et al., 1999; Wisplinghoff et al., 2004; von Müller et al., 2020; Brandenburg et al., 2021). Moreover, various predispositions lead to the occurrence of candidiasis, including AIDS, steroid therapy, organ and tissue transplantation, cancer therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics (Hsu et al., 2021; Kumwenda et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022). Therefore, it is significant to detect C. albicans accurately for the prevention, control, and7nbsp;efficient treatment of the disease caused by this conditioned pathogen.
Currently, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has been the most commonly used method for the diagnosis of C. albicans (Wahyuningsih et al., 2000). However, PCR detection proved relatively complex to some field conditions and special environments because of expensive thermocycles, well-trained operators, and gel electrophoresis instruments (Farrar and Wittwer, 2015). In recent years, various isothermal amplification techniques that offer alternative approaches to the well-established PCR-based methods for C. albicans detection have been developed, such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), polymerase spiral reaction (PSR), and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) (Jiang et al., 2016; Noguchi et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2021). Among the isothermal amplification methods discussed above, owing to the advantages of high specificity, simplicity, high sensitivity, and rapid accumulation of targeted DNA, LAMP and the modified LAMP method have been adopted for commercial assays (Noguchi et al., 2017; Lin et al., 2021; Ou et al., 2021; Tu et al., 2024). However, the drawbacks of LAMP lie in its sophisticated, cumbersome, and complex primer design, which makes further expansion and application inconvenient (Gonçalves Dda et al., 2014; Mao et al., 2018; Gomez-Gutierrez and Goodwin, 2022). Thus, a novel isothermal nucleic acid amplification method that has a simpler primer design and is more cost-effective for the rapid and sensitive detection of C. albicans is needed.
Closed dumbbell-mediated isothermal amplification (CDA) is based on self-primer-mediated single nucleic acid annealing and extending, which was characterized by efficiency, high sensitivity, and high specificity (Gui et al., 2022; Mao et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2024). In this study, the conserved internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2), a region between 5.8S and 28S ribosomal DNA of C. albicans, was selected as the target for specific identification and amplification. The specificity and sensitivity of the developed CDA were compared with those of real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) under similar conditions. In addition, we also successfully assessed the practical application of the CDA assay in real-time fluorescence and on-site visible detection of C. albicans with 100% sensitivity and specificity. All results showed that the established CDA assay for C. albicans identification had the potential to achieve efficient, rapid, accurate, and visible on-site detection.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics statement
Ethical approval, including the waiver of informed consent of the clinical strains and samples collected in the laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, was granted by the Ethics Committee of Clinical Investigation in the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, under approval number 2024-096A-02. The research conformed to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. The study involved no more than minimal risk to subjects, and no personal information was obtained.
2.2 Isolation of DNA of strains
Thirty clinical isolates of C. albicans were collected from July 2023 to August 2024 by the research team from the laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, and various non-C. albicans clinical isolates and strains were listed. Standard strains of C. albicans (CICC 1965), Candida glabrata (BNCC 337348), Candida parapsilosis (BNCC 337317), Candida tropicalis (BNCC 186815), Klebsiella pneumoniae (BNCC 361251), Escherichia coli (CGMCC, 1.12883), Staphylococcus aureus (CGMCC: 1.6750), Salmonella typhimurium (CGMCC: 1.1190), Listeria monocytogenes (CGMCC: 1.9144), Vibrio parahaemolyticus (CGMCC: 1.1997), and Shigella sonnei (CVCC 3926) were obtained from the China Center of Industrial Culture Collection (CICC), the BeNa culture Collection (BNCC), the China Gene Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the China Veterinary Culture Collection Center (CVCC). Candida strains were cultured in yeast peptone dextrose (YPD) medium (Li et al., 2021), and Escherichia coli strains were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium (Jira et al., 2018). DNA was extracted from bacteria liquid at 180 rpm for 24 h using DNA purification kits (TIANGEN, Shanghai) and stored at −20°C.
2.3 CA-CDA primer design
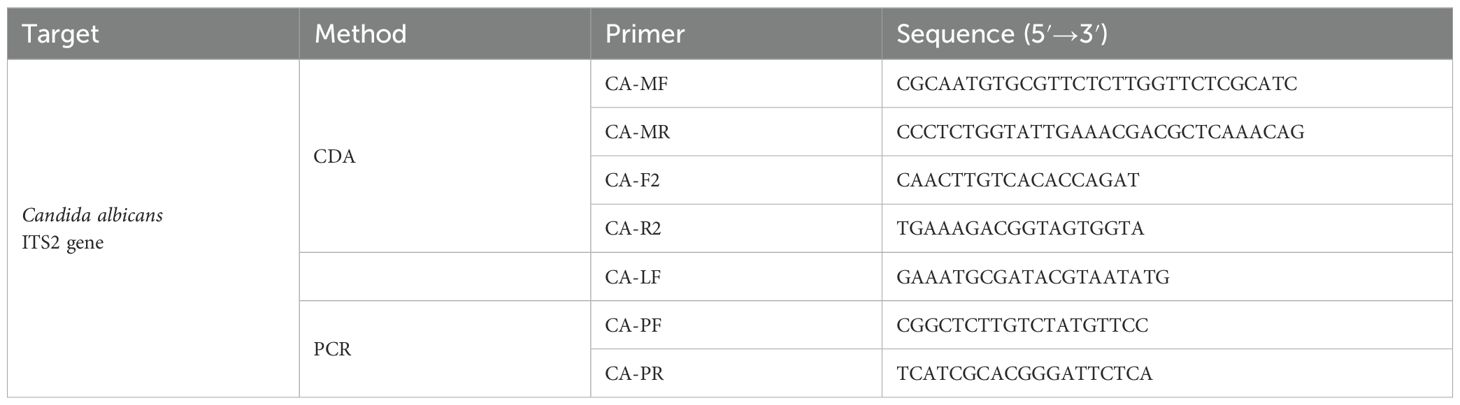
Four pairs of primers of C. albicans CDA (CA-CDA) were designed targeting the specific conserved sequences of the ITS2 region (Accession No. MT193530.1) after BLAST on the NCBI GenBank database using the DNAMAN Version 8.0 software (Supplementary Table 1). The situation of CA-CDA primers on ITS2 sequences is shown in Figure 1A. The F1, R1, and M sequences are abbreviations for “forward 1”, “reverse 1”, and “middle”, respectively. Sites with a lowercase “c” stand for “complementary”. M is the middle of F1c and R1, separated into M1 and M2. Under this system, the forward primer (MF) contains sequences complementary to M1 (M1c) and sequences complementary to F1c (F1). The backward primer (MR) contains sequences (M2) complementary to M2c and R1. To achieve further optimization, external primers (F2 and R2) and loop primers (LF) are designed to accelerate the CDA reaction. The location of all CA-CDA primers used in this study is marked with different colors, as shown in Figure 1B. The primer sequences are listed in Table 1 and synthesized by BGI Bioengineering Technical Services Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China).
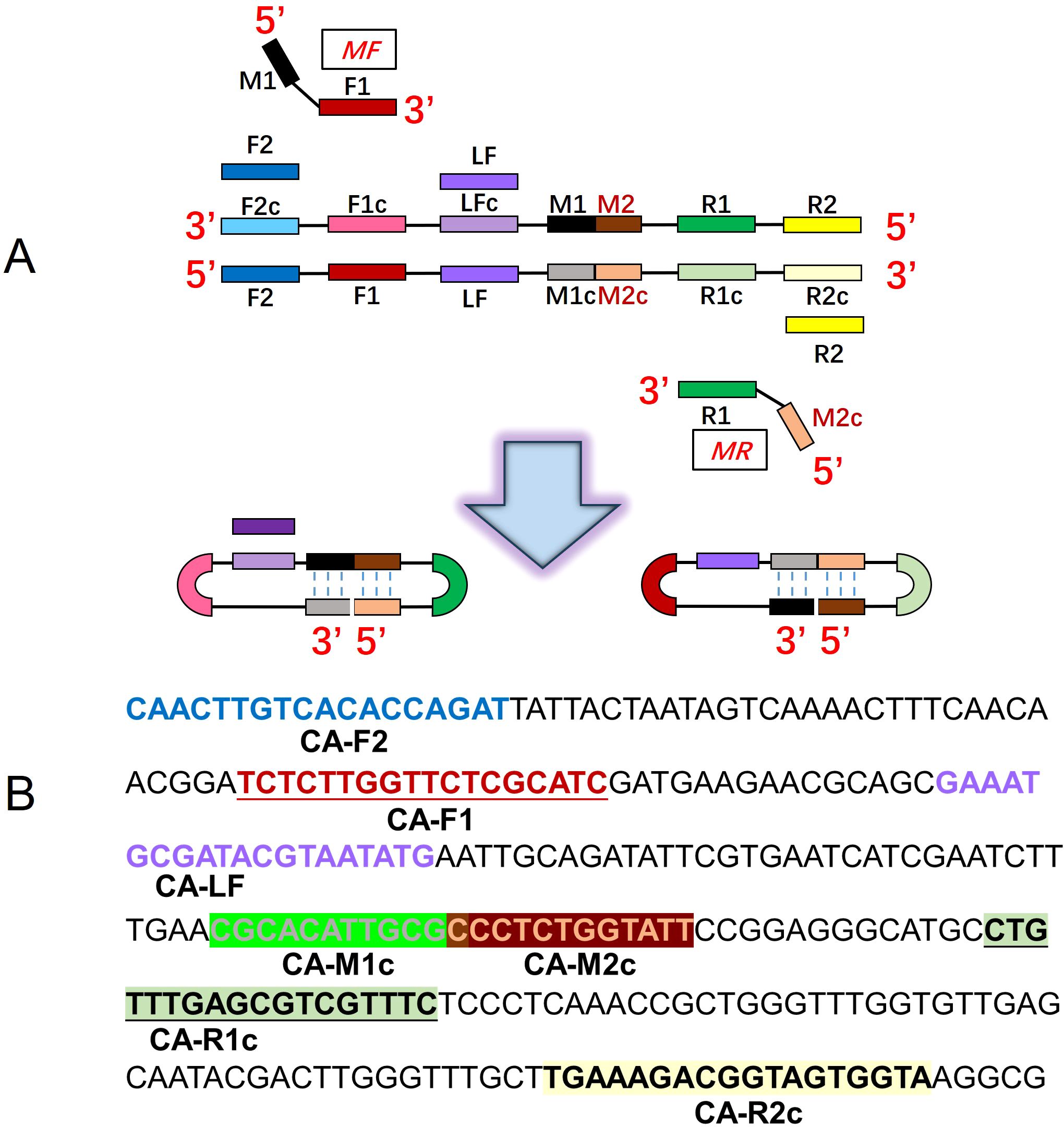
Figure 1. Principle of the closed dumbbell-mediated isothermal amplification (CDA) method. (A) Overall scheme for primers used in the CDA method. (B) Partial sequences of the C. albicans ITS2 gene were used to design primers for the CDA method.
2.4 CDA assays
CDA assays were carried out as reported by our group (Mao et al., 2022). In short, each CDA reaction was conducted in 25 μL of reaction mixture, including 12.5 μL of 2× isothermal amplification buffer [including 40 mM Tris-HCl, 20 mM KCl, 20 mM (NH4)2SO4, 16 mM MgSO4, and 0.2% Triton X-100], 1 μL of Bst 2.0 WarmStart DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs), 1 μL of MF and MR, 1 μL each of Eva green and HNB (Biotium, Hayward, CA, USA), and an appropriate amount of nucleic acid template and nuclease-free water. Finally, the reaction mixture was covered with paraffin oil (Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd.). After the addition of the accelerate primers (outer primers and loop primers) with the system of F2 (0.2 μM), R2 (0.2 μM), and LF (0.2 μM), the assay was named CA-OL-CDA. The negative control (NC) contained nuclease-free water. The reaction was incubated at 60–65°C for 60 min and 85°C for 10 min in the CFX96 Real-Time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, California, USA) and Q3 Real-Time PCR instrument (Applied Biosystems, California, USA). Using the direct visual judgment approach, the color change from purple to sky blue for positive samples was visible by the naked eye under natural light, while the negative reaction remained purple.
2.5 CA-OL-CDA sensitivity and specificity analysis
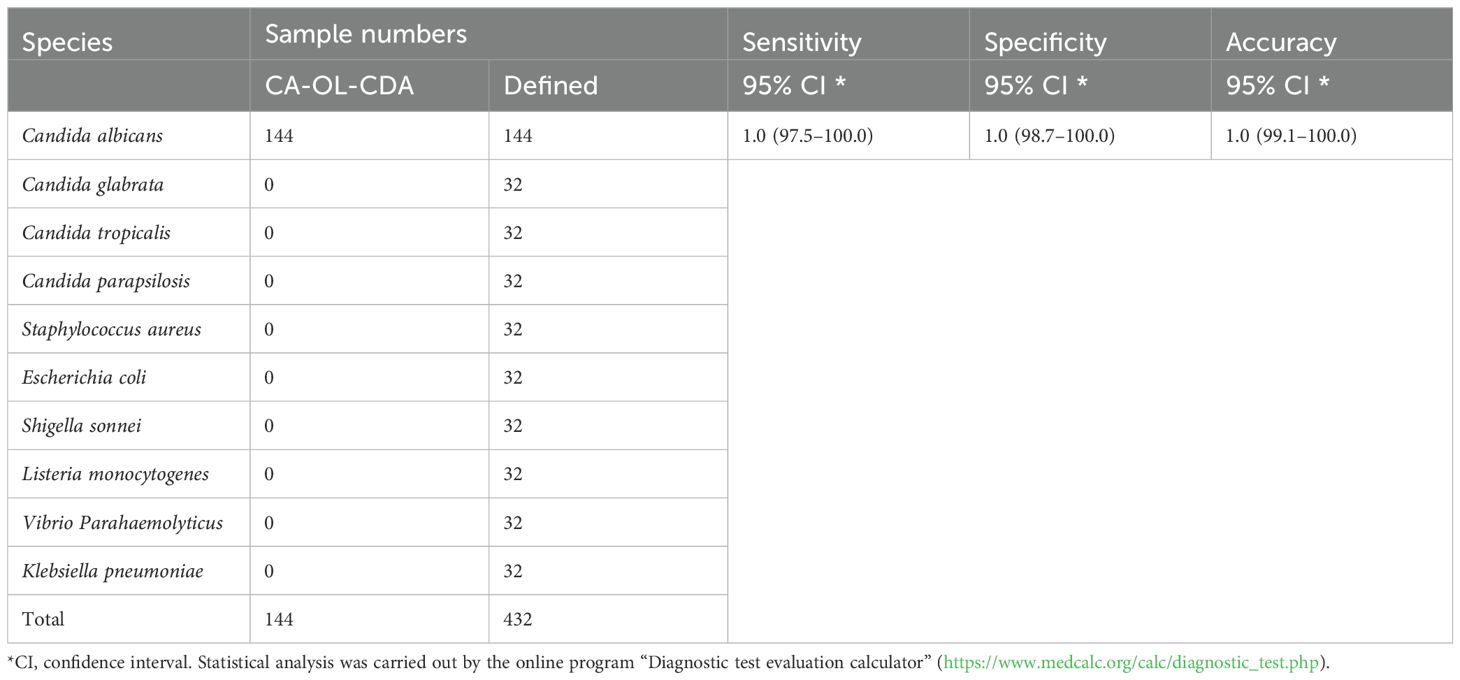
To confirm the specificity of the CA-OL-CDA assay in positive samples of C. albicans, we performed the method using three other Candida species, i.e., C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, and C. tropicalis, and six non-Candida bacteria, namely, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Shigella sonnei, Listeria monocytogenes, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. All of them were used for the specificity test after the determination of the optimal temperature of 60°C, and sterilized enzyme-free water was deemed as the negative control. The specificity of CA-OL-CDA results was obtained by analyzing the amplification curve and melting curve.
To determine the sensitivity of the CA-OL-CDA method, a 10-fold concentration dilution was prepared from the original concentration of C. albicans, and the DNA concentrations were 6.2×10−1, 6.2×10−2, 6.2×10−3, 6.2×10−4, 6.2×10−5, 6.2×10−6, and 6.2×10−7 ng/μL, respectively. The sensitivity of the CA-OL-CDA assay was repeated four times to determine the minimum value of template DNA by real-time fluorescence amplification monitoring and visual endpoint judgment. Visual judgment is usually conducted with a white paper under the tubes to avoid mistakes. Furthermore, the amplified products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
2.6 Real-time quantitative PCR reaction
The real-time qPCR assay was performed using primers F1 (5′-CGGCTCTTGTCTATGTTCC-3′) and R1 (5′-TCATCGCACGGGATTCTCA-3′) (Figure 1, Table 2). The samples of qPCR were in accordance with the CA-OL-CDA assay and as a comparison and confirmation for the CA-OL-CDA assay results. The total 50-μL volume in qPCR reaction contains 25 μL of 2× Taq PCR Mix (Sangon, Shanghai, China) and 10 mM each of primer 1 × Eva green and the DNA sample. Real-time fluorescence monitoring was carried out using the CFX96 Real-Time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, California, USA) and a Q3 Real-Time PCR instrument (Applied Biosystems, California, USA). PCR reaction procedures were set as follows: denaturation at 95°C for 2.5 min, annealing at 55°C for 30 s, and extension at 72°C for 20 s for 35 cycles. Finally, the PCR products were subjected to melting curve analysis in the same equipment.
3 Results
3.1 Design and screening of CDA primers for C. albicans
Four pairs of CA-CDA primers targeting at the conserved ITS2 gene of C. albicans were amplified to obtain the optimal primer set monitored by the amplification curve and melting curve. The cycle threshold of the CA-CDA reaction was negatively correlated to the amplification efficiency. As shown in Figure 2, the amplification curve of the CA-CDA method showed that the fourth group of primers had the best efficiency in amplification. The threshold detection time of 6.2×10−2 ng/μL of the C. albicans gene was 23 min, the melting temperature of the amplification product was 83.5°C, and the negative control showed no evidence of non-specific amplification.
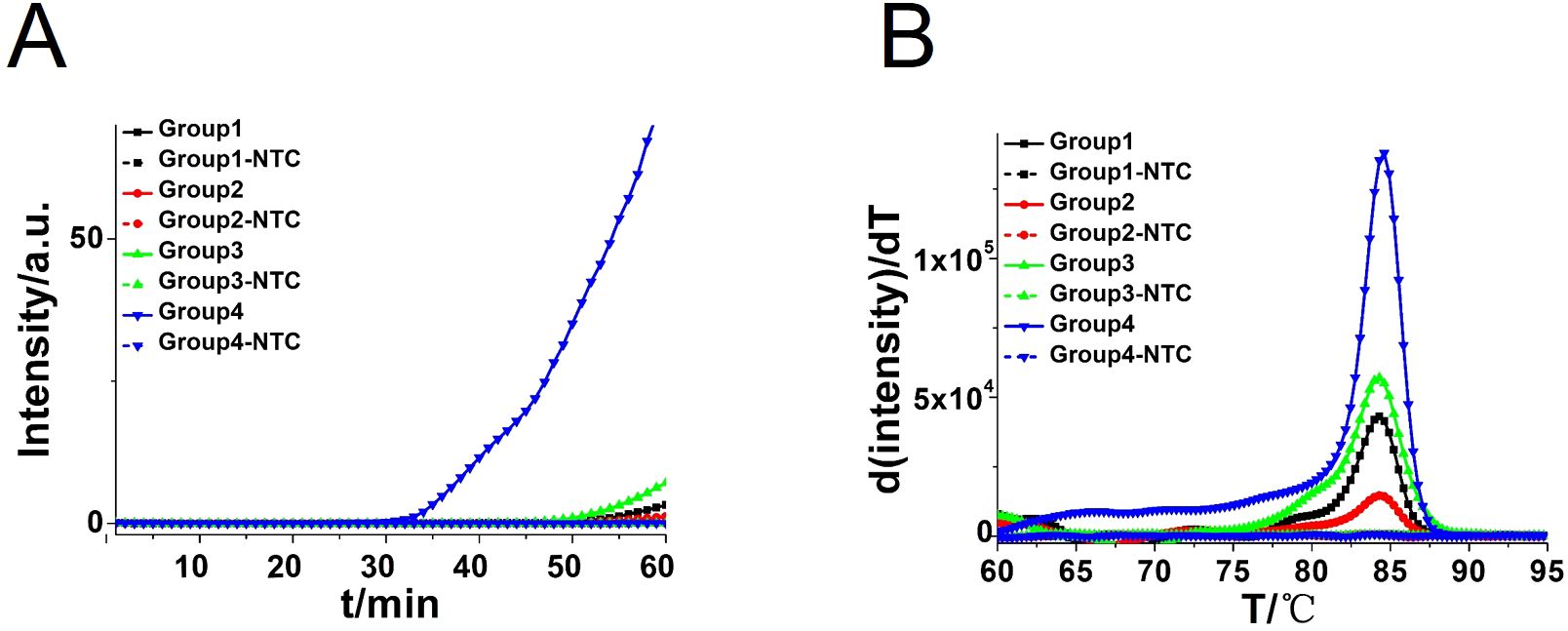
Figure 2. CDA amplification at 60°C for 60 min. (A) Real-time fluorescence of different CDA primer groups targeting the ITS2 gene; the primer groups are listed in Supplementary Table S1. (B) Melting curve analysis of CA-CDA products by real-time PCR. NTC, No template control.
3.2 Optimization of the CA-OL-CDA primer set for C. albicans
To achieve a more efficient CDA amplification process, outer primers and loop primers were designed and verified using the previous optimal primer named CA-OL-CDA. As shown in Figure 3A, the reaction efficiency of the CDA method was improved by the addition of accelerate primers, and the threshold time of the CA-OL-CDA method for the detection of C. albicans (6.2×10−2 ng/μL) was shortened by 6 min. Furthermore, both eight positive and negative replicates were used to evaluate the repeatability of the developed assay. The results of the real-time amplification curve (Figure 3C) and the melting curve (Figure 3D) presented good repeatability. The melting curves in Figures 2B, 3D presented similar results, indicating a positive effect after the addition of accelerate primers and the absence of non-specific amplification.
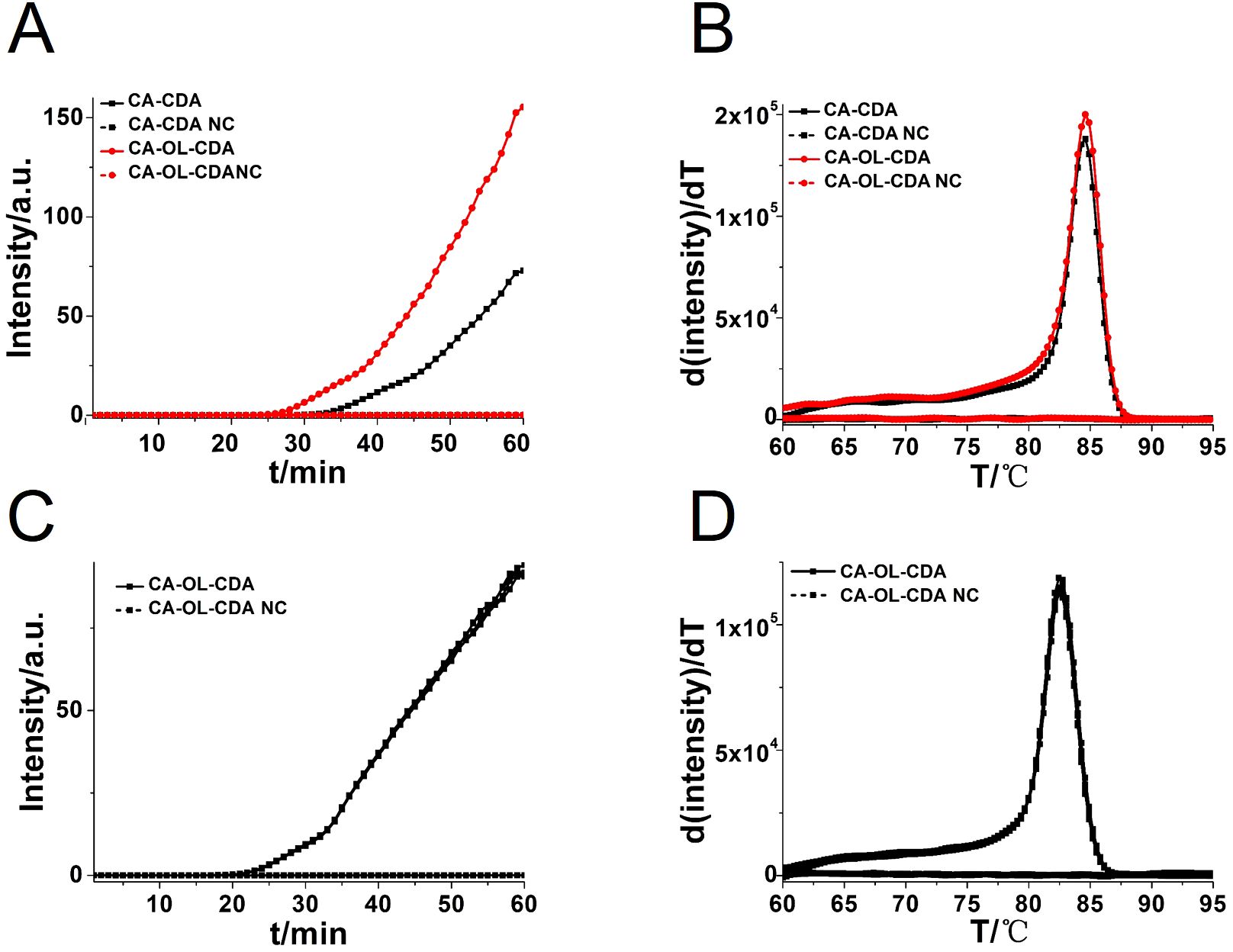
Figure 3. Real-time fluorescent amplification curves of C. albicans DNA by CA-CDA and CA-OL-CDA. (A) Amplification curve of the CA-CDA and CA-OL-CDA assay. (B) Melting curve analysis of CA-CDA and CA-OL-CDA results. (C) Amplification curve of eight repeated experiments of CA-OL-CDA. (D) Melting curve of eight repeated experiments of CA-OL-CDA. PC, positive control. NC, negative control.
In addition, the reaction temperature for the CA-OL-CDA assay of C. albicans was compared and confirmed that the optimal temperature after incubation ranged from 60 to 65°C at 1°C increments. The optimal reaction temperature for the developed CA-OL-CDA method was set at 60°C to ensure positive detection of DNA at low concentrations (Figure 4). The results of the real-time amplification curve and the melting curve further supported the good repeatability of the CA-OL-CDA assay.
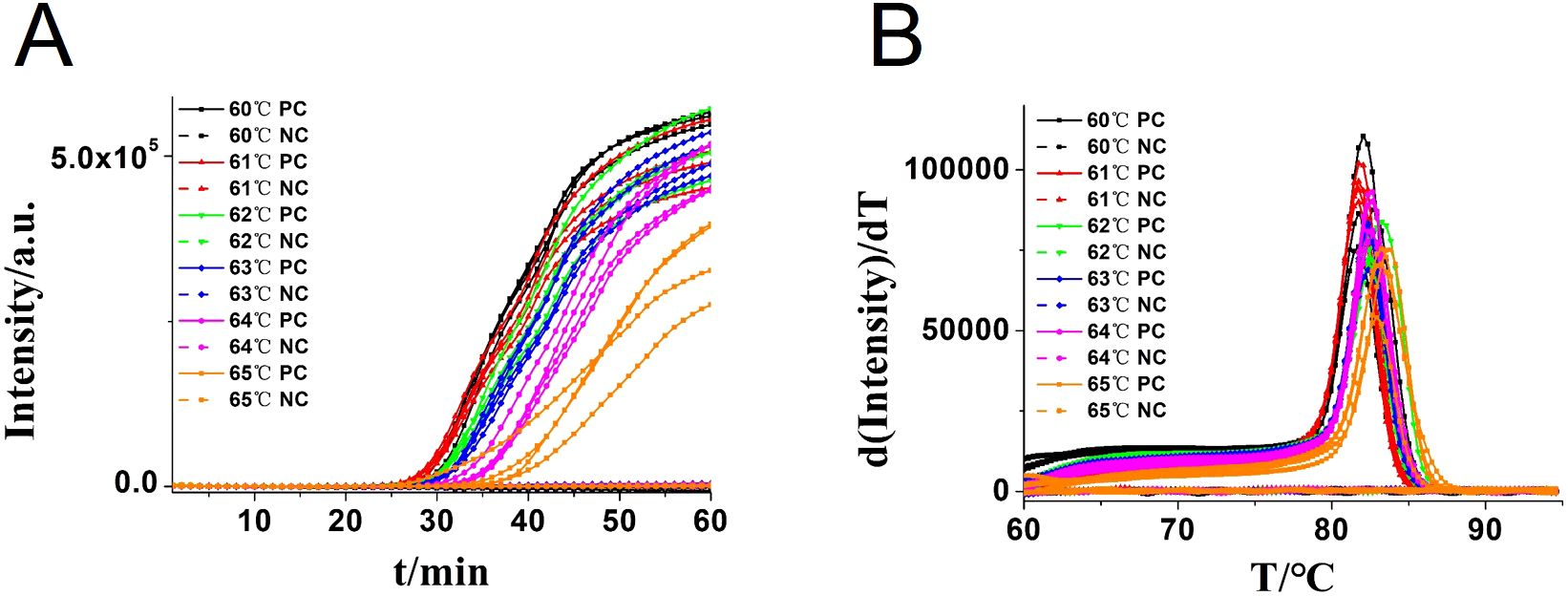
Figure 4. Real-time fluorescent amplification of CA-OL-CDA at different temperatures. (A) Amplification curve. (B) Melting curve analysis of products. Each set has four positive reactions and four negative controls (NC).
3.3 Assessment of sensitivity of CA-OL-CDA and real-time fluorescence PCR for C. albicans
To compare the detection sensitivity of the developed CA-OL-CDA assay and real-time qPCR assay, the same concentrations of 10-fold serial dilutions of DNA of C. albicans ranging from 6.2×10−1 to 6.2×10−7 ng/μL were tested. As shown by the real-time fluorescence plot and the color change of the reaction mixture, the minimum limit of detection of C. albicans by CA-OL-CDA was 6.2 fg/μL DNA (Figures 5A, C; Supplementary Figure 1), which is 10 times more sensitive than qPCR for the detection of C. albicans (Figure 6A). The melting curve analysis of CA-OL-CDA products showed that Tm was 83.50°C, and the Tm value shift in lower concentrations may be caused by limited products in a short time. The results showed that the CA-OL-CDA assay is highly sensitive for the detection of the targeted C. albicans DNA sequence. In addition, melting curve results by CA-OL-CDA and qPCR showed no difference in Tm values (Figures 5B, 6B).
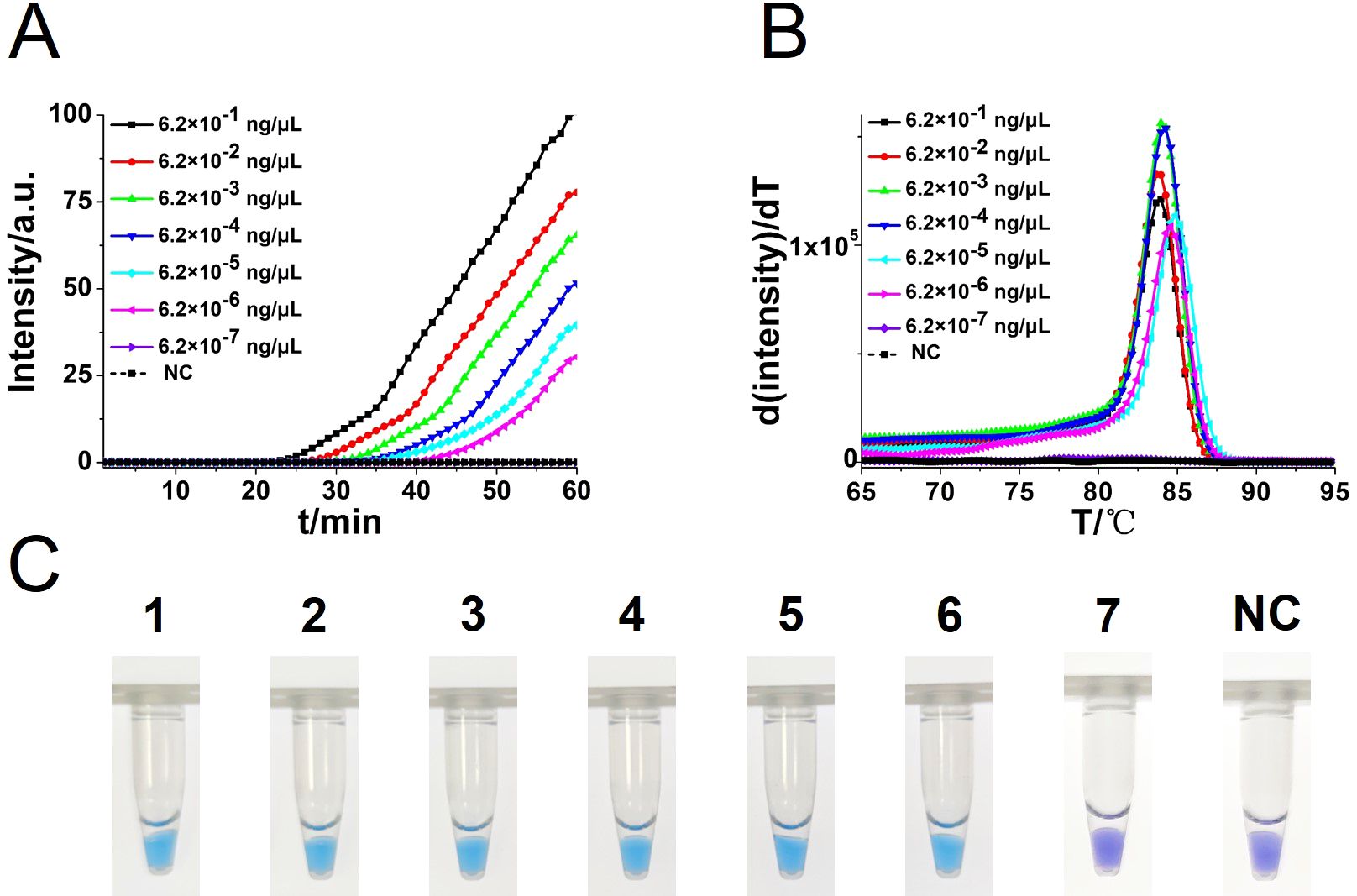
Figure 5. Sensitivity analysis of the CA-OL-CDA method was performed by real-time fluorescent monitoring and visual endpoint judgment. (A) CA-OL-CDA amplification was monitored by real-time PCR per 1 min with different concentrations of DNA. The reaction was carried out at 60°C for 60 min. (B) Melting curve analysis of C. albicans OL-CDA products after amplification of different concentrations of extracted DNA. (C) Sensitivity analysis of the CA-OL-CDA method for visual detection of C. albicans DNA. DNA concentrations were as follows: 6.2×10−1, 6.2×10−2, 6.2×10−3, 6.2×10−4, 6.2×10−5, 6.2×10−6, and 6.2×10−7 ng/μL and negative control (nuclease-free water).
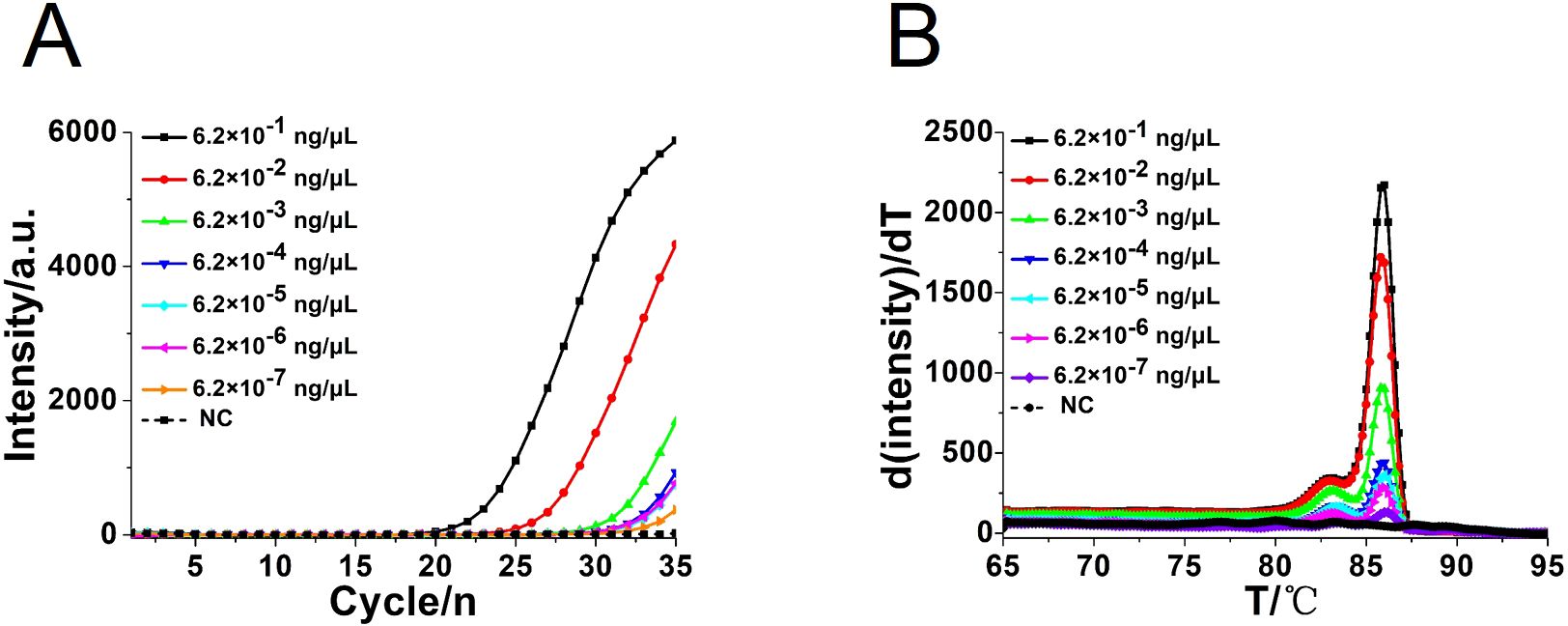
Figure 6. Real-time PCR assay for C. albicans DNA detection. (A) Real-time amplification curve. (B) Melting curve analysis of C. albicans by real-time PCR assay. NC, negative control reaction without the template.
3.4 Specificity of the CA-OL-CDA assay
To assess the specificity of the CA-OL-CDA method, C. albicans (CICC 1965) were set as a positive control. In addition, C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, and C. tropicalis and six non-Candida strains were tested. The results showed that the obtained CA-OL-CDA primers specifically identified and amplified the targeted DNA sequences (Figure 7A). Melting curve analysis showed that Tm was 83.50°C (Figure 7B), and no difference was observed between the positive control and different DNA samples, which was consistent with previous results shown in Figures 3B, D, 5B, exhibiting good reproducibility. As shown in Figures 7, 8, both real-time fluorescence plot and visual detection accurately identified C. albicans. All other strains tested negative (Table 2).
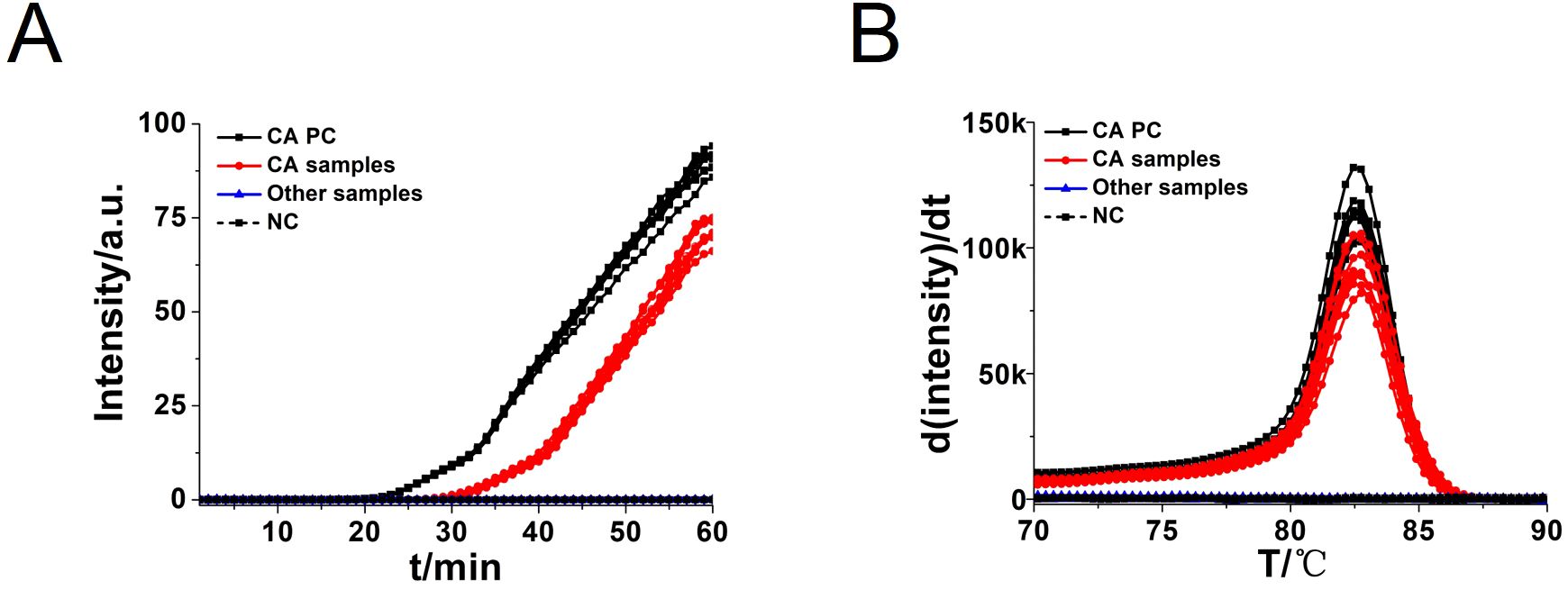
Figure 7. Real-time fluorescent amplification C. albicans OL-CDA assay. Real-time CA-OL-CDA reactions were carried out at 60°C for 60 min. (A) Real-time CA-OL-CDA for the Candida albicans positive control (CA PC), different Candida albicans samples, other samples (Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Shigella sonnei, Listeria monocytogenes, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae), and no template control (NC). (B) Melting curve analysis of CA-OL-CDA products. PC, positive control. NC, negative control.
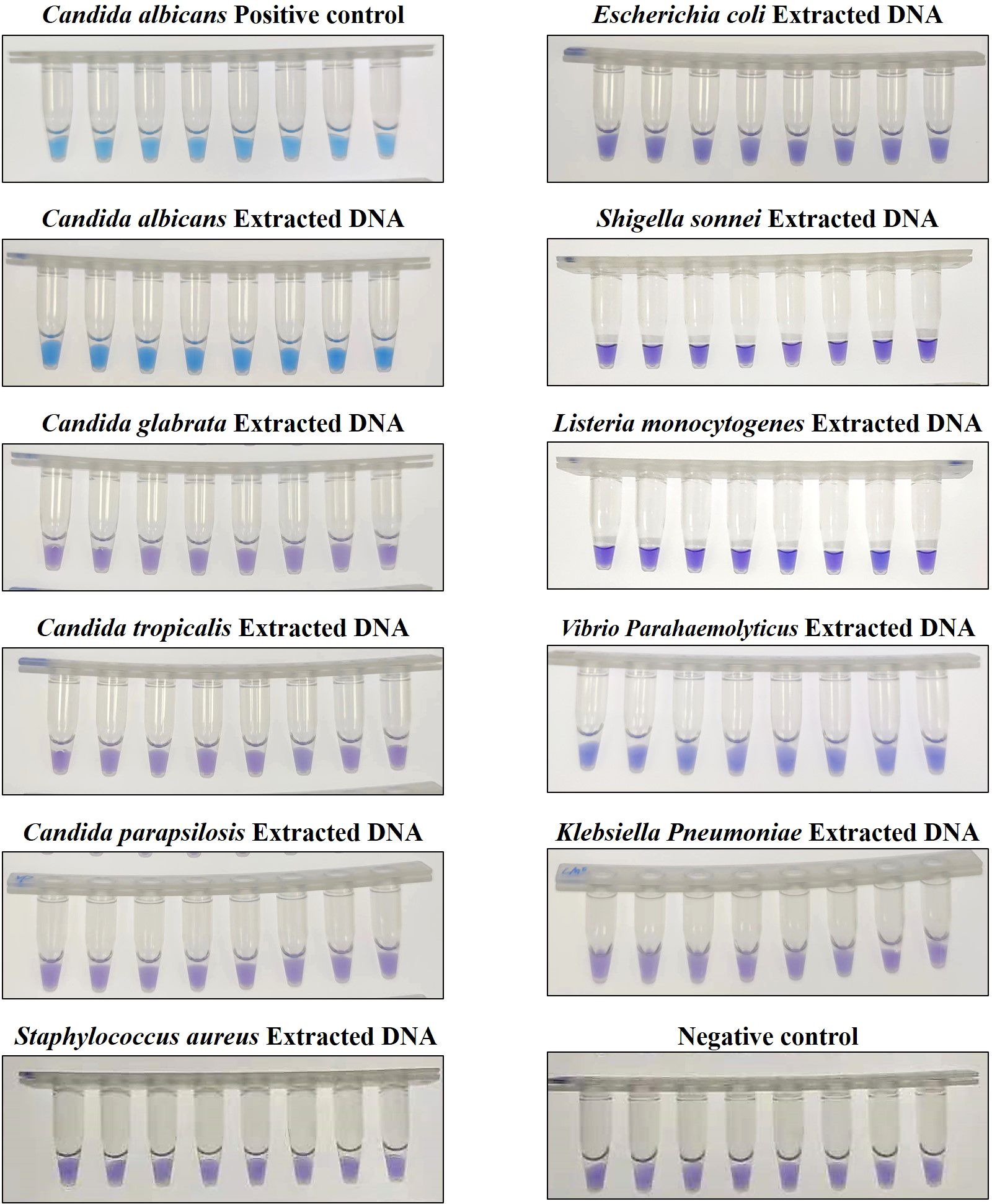
Figure 8. Endpoint colorimetric CA-OL-CDA method using HNB. Candida albicans positive controls (6.2×10−2 ng/μL of templates). Extracted DNA samples from Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Shigella sonnei, Listeria monocytogenes, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
4 Discussion
C. albicans is a frequently opportunistic pathogen of humans, with an abnormal growth under an imbalanced environment. With the widespread use of hormones, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and immunosuppressive agents, the infection rate of C. albicans has shown an increasing trend (He et al., 2021). The mortality rate due to C. albicans infections has been reported to be 40% (Gunsalus et al., 2016). Traditional molecular diagnosis methods of C. albicans are somewhat limited owing to complex operations and the lack of accuracy (Dadar et al., 2018). Thus, rapid and accurate detection of C. albicans is essential for the prompt treatment of the disease.
Commercialized CHROMagar™ Candida and germ tube production are two conventional methods for the identification of C. albicans. Both are not accurate, and even the germ tube production method occasionally provides false-negative results (Kim et al., 2002; Wohlmeister et al., 2017). Gradually, nucleic acid-based assays with the advantages of obtaining fast results and being accurate have been applied to detect C. albicans with high sensitivity and specificity (Fidler et al., 2018; Fallahi et al., 2020). In contrast, PCR has drawbacks such as high cost, inconvenience with the use of instruments, and the possibility of obtaining false-negative results via the PCR assay (sensitivity: 94.1%) (Jiang et al., 2016). In addition, the well-established LAMP has been applied to detect a variety of pathogens, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and C. albicans. However, we found that LAMP, which has a complicated primer design and provides false-positive results, was not convenient to carry out (Fallahi et al., 2020; Griffioen et al., 2020; Rivoarilala et al., 2021).
In this study, we successfully developed a CA-OL-CDA assay with high sensitivity (100%), high specificity (100%), and high accuracy that was simpler to use and more efficient for the detection of C. albicans compared with PCR-based approaches. We amplified 6.2×10−2 ng/μL of the C. albicans DNA within 60 min at isothermal 60°C with good reproducibility. Sensitivity experiments have demonstrated that the lower limit of detection of CA-OL-CDA is 6.2 fg/μL of extracted C. albicans DNA, and the detection sensitivity is 10 times lower than that of qPCR. The commercial C. albicans LAMP kits aimed at oral exfoliative cytology samples is capable of detecting 1 pg per reaction (Noguchi et al., 2017). In addition, the time required for CA-OL-CDA is shorter than that of the qPCR method. Comparison of the results obtained by the CA-OL-CDA technique and the results of real-time PCR methods for C. albicans showed that the CA-OL-CDA technique could detect C. albicans with relatively equal sensitivity and specificity to real-time PCR tests without the disadvantages of the real-time PCR method. Specificity tests revealed that the CA-OL-CDA method did not identify closely related C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, and C. tropicalis. No cross-reactivity was also observed for the six distantly related S. aureus, E. coli, S. sonnei, L. monocytogenes, V. parahaemolyticus, and K. pneumoniae. The detection result can be judged by observing the color difference of the reaction mixture, which has great potential for on-site detection. Moreover, the amplification curves, melting curve, and endpoint visual judgments of 144 batches of positive tests and 288 batches of negative tests were consistent.
5 Conclusions
A sensitive and specific CDA method for the visual detection of C. albicans was established, which can be applied for on-site detection in areas with relatively developing medical conditions. The CA-OL-CDA method may help to improve the detection efficiency and the prevention and medication of diseases caused by C. albicans.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
YAZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. XC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YEZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. FG: Resources, Writing – review & editing. GO: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RM: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration of Zhejiang Province, grant number 2022ZB324; the Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission, grant number 2022KY1113; the Ningbo Clinical Research Center for Hematologic Malignancies, grant number 2021L001; the Ningbo Public Welfare Research Project, grant number 2022S032; the Zhejiang Provincial Basic Public Welfare Research Project, grant number LBY24H180004; and the Research Foundation of Ningbo Institute of Life and Health Industry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number 2021YJY1008.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the researchers who provided the test strains.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1484089/full#supplementary-material
References
Bertolini, M., Ranjan, A., Thompson, A., Diaz, P. I., Sobue, T., Maas, K., et al. (2019). Candida albicans induces mucosal bacterial dysbiosis that promotes invasive infection. PLoS Pathog. 15, e1007717. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007717
Brandenburg, K. S., Weaver, A. J., Jr., Karna, S. L. R., Leung, K. P. (2021). The impact of simultaneous inoculation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans on rodent burn wounds. Burns 47, 1818–1832. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2021.02.025
Dadar, M., Tiwari, R., Karthik, K., Chakraborty, S., Shahali, Y., Dhama, K. (2018). Candida albicans - Biology, molecular characterization, pathogenicity, and advances in diagnosis and control - An update. Microb. Pathog. 117, 128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.02.028
Fallahi, S., Babaei, M., Rostami, A., Mirahmadi, H., Arab-Mazar, Z., Sepahvand, A. (2020). Diagnosis of Candida albicans: conventional diagnostic methods compared to the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay. Arch. Microbiol. 202, 275–282. doi: 10.1007/s00203-019-01736-7
Farrar, J. S., Wittwer, C. T. (2015). Extreme PCR: efficient and specific DNA amplification in 15-60 seconds. Clin. Chem. 61, 145–153. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.228304
Fidel, P. L., Jr., Vazquez, J. A., Sobel, J. D. (1999). Candida glabrata: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical disease with comparison to C. albicans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 12, 80–96. doi: 10.1128/cmr.12.1.80
Fidler, G., Leiter, E., Kocsube, S., Biro, S., Paholcsek, M. (2018). Validation of a simplex PCR assay enabling reliable identification of clinically relevant Candida species. BMC Infect. Dis. 18, 393. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3283-6
Gomez-Gutierrez, S. V., Goodwin, S. B. (2022). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of plant pathogens in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.857673
Gonçalves Dda, S., Cassimiro, A. P., de Oliveira, C. D., Rodrigues, N. B., Moreira, L. A. (2014). Wolbachia detection in insects through LAMP: loop mediated isothermal amplification. Parasit Vectors 7, 228. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-228
Griffioen, K., Cornelissen, J., Heuvelink, A., Adusei, D., Mevius, D., Jan van der Wal, F. (2020). Development and evaluation of 4 loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays to detect mastitis-causing bacteria in bovine milk samples. J. Dairy Sci. 103, 8407–8420. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-18035
Gui, Z., Cai, H., Wu, L., Miao, Q., Yu, J. F., Cai, T., et al. (2022). Visual closed dumbbell-mediated isothermal amplification (CDA) for on-site detection of Rickettsia raoultii. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 16, e0010747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010747
Gunsalus, K. T. W., Tornberg-Belanger, S. N., Matthan, N. R., Lichtenstein, A. H., Kumamoto, C. A., Mitchell, A. P. (2016). Manipulation of host diet to reduce gastrointestinal colonization by the opportunistic pathogen Candida albicans. mSphere 1, e00020–e00015. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00020-15
He, H., Wang, Y., Fan, Y., Li, C., Han, J. (2021). Hypha essential genes in Candida albicans pathogenesis of oral lichen planus: an in-vitro study. BMC Oral. Health 21, 614. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01975-5
Ho, J., Camilli, G., Griffiths, J. S., Richardson, J. P., Kichik, N., Naglik, J. R. (2021). Candida albicans and candidalysin in inflammatory disorders and cancer. Immunology 162, 11–16. doi: 10.1111/imm.13255
Hsu, S. L., Wu, C. T., Chang, Y. C., Fan, C. K., Lee, Y. J. (2021). Case report of an unusual hepatic abscess caused by Actinomyces odontolyticus in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 21, 998. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06703-6
Jiang, X., Dong, D., Bian, L., Zou, D., He, X., Ao, D., et al. (2016). Rapid detection of Candida albicans by polymerase spiral reaction assay in clinical blood samples. Front. Microbiol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00916
Jira, J., Rezek, B., Kriha, V., Artemenko, A., Matolínová, I., Skakalova, V., et al. (2018). Inhibition of E. coli growth by nanodiamond and graphene oxide enhanced by Luria-bertani medium. Nanomaterials (Basel) 8, 140. doi: 10.3390/nano8030140
Kadosh, D. (2016). Control of Candida albicans morphology and pathogenicity by post-transcriptional mechanisms. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 73, 4265–4278. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2294-y
Kim, D., Shin, W. S., Lee, K. H., Kim, K., Young Park, J., Koh, C. M. (2002). Rapid differentiation of Candida albicans from other Candida species using its unique germ tube formation at 39 degrees C. Yeast 19, 957–962. doi: 10.1002/yea.891
Kumwenda, P., Cottier, F., Hendry, A. C., Kneafsey, D., Keevan, B., Gallagher, H., et al. (2022). Estrogen promotes innate immune evasion of Candida albicans through inactivation of the alternative complement system. Cell Rep. 38, 110183. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110183
Li, Q., Liu, J., Chen, M., Ma, K., Wang, T., Wu, D., et al. (2021). Abundance interaction in Candida albicans and Candida glabrata mixed biofilms under diverse conditions. Med. Mycol 59, 158–167. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa040
Lin, X., Jin, X., Du, W., Shan, X., Huang, Q., Fu, R., et al. (2021). Quantitative and specific detection of viable pathogens on a portable microfluidic chip system by combining improved propidium monoazide (PMAxx) and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Anal. Methods 13, 3569–3576. doi: 10.1039/d1ay00953b
Liu, Z., Li, Y., Li, C., Lei, G., Zhou, L., Chen, X., et al. (2022). Intestinal Candida albicans promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by up-regulating NLRP6. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.812771
Lopes, J. P., Lionakis, M. S. (2022). Pathogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans. Virulence 13, 89–121. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.2019950
Mao, R., Qi, L., Li, J., Sun, M., Wang, Z., Du, Y. (2018). Competitive annealing mediated isothermal amplification of nucleic acids. Analyst 143, 639–642. doi: 10.1039/c7an01569k
Mao, R., Wang, T., Zhao, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, S., Cai, T. (2022). Closed dumbbell mediated isothermal amplification of nucleic acids for DNA diagnostic assays. Talanta 240, 123217. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123217
Noguchi, H., Iwase, T., Omagari, D., Asano, M., Nakamura, R., Ueki, K., et al. (2017). Rapid detection of Candida albicans in oral exfoliative cytology samples by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Oral. Sci. 59, 541–547. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.16-0717
Nyirjesy, P., Brookhart, C., Lazenby, G., Schwebke, J., Sobel, J. D. (2022). Vulvovaginal candidiasis: A review of the evidence for the 2021 centers for disease control and prevention of sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 74, S162–S168. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab1057
Ou, H., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Ma, Y., Liu, C., Jia, L., et al. (2021). Rapid detection of multiple pathogens by the combined loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology and microfluidic chip technology. Ann. Palliat Med. 10, 11053–11066. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2792
Rivoarilala, L. O., Victor, J., Crucitti, T., Collard, J. M. (2021). LAMP assays for the simple and rapid detection of clinically important urinary pathogens including the detection of resistance to 3rd generation cephalosporins. BMC Infect. Dis. 21, 1037. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06720-5
Tu, Y., Wang, Y., Jiang, H., Ren, H., Wang, X., Lv, W. (2024). A loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the rapid detection of Didymella segeticola causing tea leaf spot. J. fungi (Basel Switzerland) 10, 467. doi: 10.3390/jof10070467
von Müller, C., Bulman, F., Wagner, L., Rosenberger, D., Marolda, A., Kurzai, O., et al. (2020). Active neutrophil responses counteract Candida albicans burn wound infection of ex vivo human skin explants. Sci. Rep. 10, 21818. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78387-y
Wahyuningsih, R., Freisleben, H. J., Sonntag, H. G., Schnitzler, P. (2000). Simple and rapid detection of Candida albicans DNA in serum by PCR for diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 3016–3021. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.8.3016-3021.2000
Wakade, R. S., Huang, M., Mitchell, A. P., Wellington, M., Krysan, D. J. (2021). Intravital imaging of Candida albicans identifies differential in vitro and in vivo filamentation phenotypes for transcription factor deletion mutants. mSphere 6, e0043621. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00436-21
Wall, G., Montelongo-Jauregui, D., Vidal Bonifacio, B., Lopez-Ribot, J. L., Uppuluri, P. (2019). Candida albicans biofilm growth and dispersal: contributions to pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 52, 1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2019.04.001
Wang, F., Ge, D., Wang, L., Li, N., Chen, H., Zhang, Z., et al. (2021). Rapid and sensitive recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips for detecting Candida albicans. Anal. Biochem. 633, 114428. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2021.114428
Wisplinghoff, H., Bischoff, T., Tallent, S. M., Seifert, H., Wenzel, R. P., Edmond, M. B. (2004). Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 39, 309–317. doi: 10.1086/421946
Wohlmeister, D., Vianna, D. R. B., Helfer, V. E., Calil, L. N., Buffon, A., Fuentefria, A. M., et al. (2017). Differentiation of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, and Candida krusei by FT-IR and chemometrics by CHROMagar™ Candida. J. Microbiol. Methods 141, 121–125. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2017.08.013
Keywords: Candida albicans, point-of-care diagnostic, closed dumbbell mediated isothermal amplification, real-time fluorescence CDA, visual CDA, sensitivity, specificity
Citation: Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhong Y, Guo F, Ouyang G and Mao R (2025) Rapid and simple detection of Candida albicans using closed dumbbell-mediated isothermal amplification. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1484089. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1484089
Received: 21 August 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 03 February 2025.
Edited by:
Robert Colgrove, Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Payal Gupta, Graphic Era University, IndiaSoma Rohatgi, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, Zhong, Guo, Ouyang and Mao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guifang Ouyang, Znl5b3V5YW5nZ3VpZmFuZ0BuYnUuZWR1LmNu; Rui Mao, bXIzNzQ5QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yanli Zhang1†
Yanli Zhang1† Fei Guo
Fei Guo Guifang Ouyang
Guifang Ouyang Rui Mao
Rui Mao