- 1Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
- 2Department of Forestry, Wildlife and Fisheries, Institute of Agriculture, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Knoxville, TN, United States
- 3Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Marine Life Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China
- 4Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Agriculture, AL-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
- 5Laboratory of Biotechnology, Department of Microbiology, Agricultural Research Center (ARC), Animal Health Research Institute (AHRI), Zagazig, Egypt
- 6Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Enterococcus faecalis, a common inhabitant of the feline gastrointestinal tract, has emerged as a significant pathogen causing urinary tract infections (UTIs) in domestic cats. The rise of multidrug-resistant E. faecalis strains and their propensity to form biofilms pose significant challenges in treatment. This study investigated the antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of hexagonal zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alone and in combination with streptomycin and Moringa oleifera leaf extract (MOLe) against multidrug-resistant E. faecalis isolates from feline UTIs.
Methods: Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed using the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. Biofilm formation was assessed using the crystal violet assay, and biofilm-associated genes (sprE, gelE, fsrABC) were detected by PCR. ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs (streptomycin-loaded ZnONPs), and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs (streptomycin and MOLe-loaded ZnONPs) were characterized using FTIR, DLS, TEM, and SEM. The antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of the synthesized nanoparticles were evaluated through time-kill assays, well diffusion assays, and gene expression analysis.
Results: A high prevalence of multidrug resistance was observed among the E. faecalis isolates, with significant resistance to ampicillin, vancomycin, and streptomycin. Characterization studies revealed the successful encapsulation of streptomycin and MOLe within the ZnONPs.In vitro assays demonstrated that Str/MOLe@ZnONPs exhibited potent antibacterial and antibiofilm activities against the tested E. faecalis strains, significantly reducing bacterial growth and biofilm formation.
Discussion: The emergence of multidrug-resistant E. faecalis strains necessitates the development of novel therapeutic strategies. This study demonstrates the promising potential of ZnONPs, particularly those loaded with streptomycin and MOLe, in combating biofilm-forming E. faecalis. The synergistic effects of the combined formulation may offer a novel approach to overcome antibiotic resistance and improve the treatment outcomes of E. faecalis UTIs in domestic cats.
1 Introduction
Enterococci are widespread bacteria that are causally to the development of severe urinary tract infections (Weese et al., 2011; Kajihara et al., 2015). Enterococci are often found in cats, and dogs serve as a reservoir for transmitting these bacteria to people (Kataoka et al., 2014; Jackson et al., 2009; Ossiprandi and Zerbini, 2015). The excessive and disorganized use of antibacterial medication has resulted in a rise of drug-resistant E. faecalis strains, rendering most medications ineffective against this bacterium (Oguttu et al., 2021). Bacteria acquire resistance to aminoglycosides because their cell wall has insufficient permeability, making these antibiotics ineffective when used individually (García-Solache and Rice, 2019). Furthermore, the ability of these bacteria to form biofilms makes bacteria more resistant to antibiotics (Pereira et al., 2014). Therefore, there is an urgency for developing new anti-enterococcal therapeutic drugs.
Moringaoleifera Lam (MOL) is rich in nutrient components, such as essential amino acids, oleic acids, vitamins, and minerals. MOL is well-known for its uses in medicine, including the treatment of a variety of illnesses, the control of the immunological system, and the manifestation of anti-oxidant, anti-diabetic, and anti-cancer qualities (Dhakad et al., 2019). MOL is a plant that may be consumed as a vegetable, and it also has the potential to be used as a medication to cure a broad variety of diseases (Xiao et al., 2020). The extracts of MOL have been observed to contain a phytochemical composition which includes alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, tannins, triterpenoids, and steroids (El-Mohamedy and Abdalla, 2014). Numerous studies have shown that various extracts from various tissues of MOL demonstrated antibacterial activities against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, for example, fresh leaf juice against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus (Ahmed et al., 2023).
Nanoparticles (NPs) are increasingly used as an alternative to antibiotics (Wang et al., 2017; Ali et al., 2023; El-Demerdash et al., 2023b; Abd El-Emam et al., 2024), as zinc oxide (ZnO) showed antimicrobial activity (Raghunath and Perumal, 2017; Dawwam et al., 2022), against both Gram-positive (Guo et al., 2015), and Gram-negative bacteria (Liu et al., 2009; Reddy et al., 2014; Guo et al., 2015).Recent studies have shown progress in the combination use of antibiotics with nanoparticles, resulting in a synergistic impact. Research on the mechanism of action of combining nanoparticles (NPs) with antibiotics indicates that the increased antibacterial effect may result from a chemical interaction between the NPs and antibiotics. Enhancing antibiotics using nanoparticles decreases the need for high medication doses, lowers toxicity to human cells, and restores their capacity to combat resistant microorganisms (Selvaraj et al., 2019). Nanoparticles combined with antibiotics have boosted the amount of antibiotics at the site where bacteria and antibiotics interact. This combination has improved the binding of antibiotics to bacteria and prevented bacterial efflux pumps from working, resulting in a more effective conjugation. The nanoparticle-antibiotic combination is intended as a substitute for resistant bacteria. Nano-conjugates show a significant enhancement in their biological effectiveness compared to unbound antibiotic molecules (Allahverdiyev et al., 2011). Previous studies have shown an advantageous enhancement in the antibacterial efficacy of streptomycin when paired with nanoparticles, with improvements ranging from(30–87.5%) (Nishanthi et al., 2019; Salar et al., 2015; Aremu et al., 2021).Furthermore, the combination of ZnONPs with antibiotics demonstrated a potential approach that significantly altered the resistance characteristics of multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa strains (El-Telbany et al., 2022), and showed an antibiofilm effect against S. aureus (Abdelghafar et al., 2022).
Recent studies have shown that targeting quorum-sensing genes, such as fsr, could be a promising approach for developing new anti-enterococcal therapies (Tang et al., 2015; Desouky et al., 2013; Singh and Nakayama, 2014; Shojima and Nakayama, 2014). Additionally, ZnONPs have been demonstrated to inhibit quorum-sensing in various bacteria, including P. aeruginosa (Ali et al., 2020; El-Telbany et al., 2022), S.aureus (Abdelghafar et al., 2022), and C. violaceum (Kamli et al., 2021). This study aimed to evaluate the antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of hexagonal ZnONPs synthesized using Moringa oleifera leaf extract and loaded with streptomycin against E. faecalis isolated from urinary tract infections in pet cats.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Samples, isolation and identification of E. faecalis
A total of 100 pet cats (50 male, and 50 female), were chosen for urine sample collection at the Animal Health Research Institute in Zagazig, Egypt. The cats had urinary clinical symptoms such as inappropriate urination, extensive licking of the genital region, and frequent and/or protracted efforts to pee. Urine samples were immediately delivered to the laboratory for culture and antibiotic susceptibility testing within 1 hour and kept in cold boxes. The study was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki by the World Medical Association and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University (approval number ZU-IACUC/2/F/215/2023). E. faecalis strains were routinely cultivated on Bile EsculinAzide Agar (Thermo Scientific., L and smear, The Netherlands) (Ew and Microbiology, 1997). All presumptive E. faecalis isolates with typical black to brown colonies were confirmed by E. faecalis primers targeted by the ddl gene as described previously (Dutka-Malen et al., 1995).
2.2 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (Kamli et al.)
Antimicrobial susceptibility was evaluated on Mueller–Hinton agar using the disc diffusion method following CLSI guidelines (CLSI, 2023). Examined were 11 standard antimicrobial discs from Oxoid, Cambridge, UK, representing 8 antimicrobial categories, including aminoglycosides [streptomycin (S; 10 µg), carbapenemes[Imipenem (IMP;10 µg),andmeropenem (MEM; 10 µg)], Fluoroquinolones [Levofloxacin(LEV; 5 µg) and ciprofloxacin (CIP; 5 µg)],glycopeptide [Vancomycin (VA;30 µg), and Teicoplanin (TEC;30 µg)], glycylcycline[Tigecycline (TGC;15 µg)],penicillins [ampicillin (AM; 10 µg)], oxazolidones [lenzolid (LNZ; 30 µg)], and tetracyclines [doxycycline (DO; 30 µg)]. The multiple antimicrobial resistance (MAR)indexes were computed as previously described (Tambekar et al., 2006). Pandrug-resistance refers to resistance to all antimicrobial agents, extensive drug resistance is resistance to all classes of antimicrobial agents except 2 or fewer, and multidrug-resistance indicates resistance to three or more classes of antimicrobial agents, as detailed in previous reports (Magiorakos et al., 2012).
2.3 Biofilm formation, and detection of the gelE, sprE, and fsr (A, B, C) genes by conventional polymerase chain reaction
All E. faecalis isolates were checked for biofilm production using crystal violet assay and compared with the control strain (E. faecalisATCC 29212,and E. faecalisATCC 51299) as previously described (Kafil et al., 2013; Mathur et al., 2006).The optical density (OD) was measured at a wavelength of 570nm. The isolates were classified into several categories based on their OD values: strong biofilm formers (OD570> 2), medium biofilm formers (OD570 > 1 but <2), weak biofilm formers (OD570> 0.5 but <1), and non-biofilm formers (OD570 ≤ 0.5) (Mohamed et al., 2004; El-Demerdash et al., 2023b). E. faecalis isolates underwent DNA extraction using the QIAamp DNA Mini kit from Qiagen, Gmbh, and Hilden, Germany, following the manufacturer’s instructions. The isolates were analyzed for the presence of gelatinase (gelE), serine protease (sprE) and quorum-sensing for gene locus (fsr; A, B, C) using previously designed primers (Dutka-Malen et al., 1995; Popović et al., 2018; Nakayama et al., 2002).The PCR assays used DNA from E. faecalis ATCC 29212 and E. faecalis ATCC 51299, with sterile saline used as positive and negative controls, respectively.
2.4 Extraction of biochemical compounds of MOLe
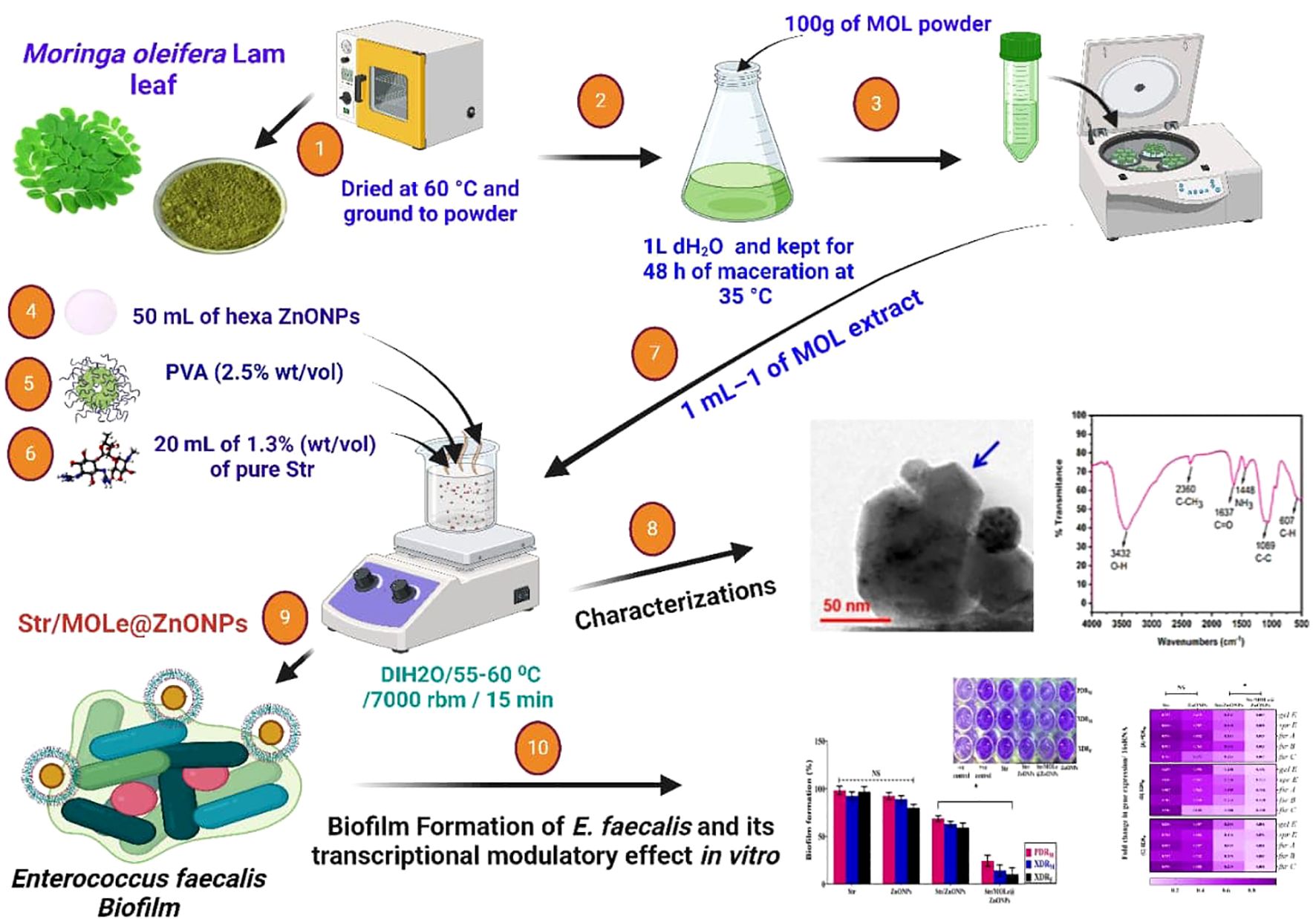
Briefly, the leaves of moringa oleifera leaves were washed with distilled water, dried, and ground into a fine powder. 100 g of the powder was soaked in 1000 mL of distilled water for 48 hours at 35°C. The mixture was then filtered, and the supernatant was obtained after centrifugation at 9,000xg for 10 minutes. The supernatant was diluted for foliar application.
2.5 Synthesis of exo-capsulation hexagonal Str/MOLe@ZnONPs
2.5.1 Deposition of hexagonal ZnONPs
ZnONPs were synthesized using a hydrothermal technique including Zn(NO3)2·6H2O and NaOH precursors, as outlined in the published work (Fiedot-Tobola et al., 2018). A 0.6 M solution of zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O) in aqueous ethanol was stirred continuously for 45 minutes to dissolve the salt. Similarly, a 1 M aqueous ethanol solution of NaOH was prepared. The zinc nitrate hexahydrate solution was then slowly added to the NaOH solution dropwise over 25 minutes while stirring vigorously. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour at a constant temperature. The precipitate was allowed to settle overnight and then separated by centrifugation. The zinc oxide nanoparticles were washed four times with distilled water and ethanol and dried in an air atmosphere at 90°C.
2.5.2 Str-coated hexagonal ZnONPs
A solution of PVA at a concentration (2.5% wt/vol) was applied onto 50 ml of hexa ZnONPs while being vigorously stirred with a powerful magnetic at 1000 rpm for 15 h at 25 to 27°C and a pH of 7.2. This process followed the emulsion-coacervation technique (Sharaf et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2006),with some alterations. Next, 20 mL of 1.3% (wt/vol) solution of pure Str in deionized water was agitated for 10 min and then poured over PVA-ZnONPs. The mixture was then rapidly swirled for 15 min at the same temperature as before. The excess uncoated PVA polymers and any other medications were eliminated from the Str/ZnONPs using several rounds of centrifugation(Centrifuge 5427 R) at 7,000 rpm for 15 min, each time with additional ddH2O, followed by drying in a vacuum for 24 h 55-60°C.
2.5.3 Exo-capsulation hexagonal Str/MOLe@ZnONPs
About 0.2 mg of Str/ZnONPs were dissolved in 30 mL–1 of dH2O at 70-80°C for 30 min. 0.5ml of tween 20 was added to the mixture, which was then agitated at 300 rbm for 15 min at 50°C to preactivate lignin. 1 mL of MOLe at a concentration of 1mg mL–1 was added drop by drop and subjected to a homogenizer (Heidolph, DIAX 900) for 10 min at 30000 rpm. Subsequently, a high-intensity ultrasonic horn (Hielscher Ultrasound Homogenizer UIP1000, 20 kHz, 50% amplitude, Ti-horn) was used for 1 hour at 50°C to create the Str/MOLe@ZnONPs. The mixture was centrifuged at 18,000 rpm for 20 min to remove unreacted molecules in the supernatant. The particle was concentrated fivefold in deionized water before being resuspended. Subsequently, low-intensity ultrasound was used to disperse the particles. The NPs were finally centrifuged at 500g for 10 min to eliminate bigger aggregates. The Str/MOLe@ZnONPs were kept at 4°C.
2.6 Characterizations of exo-capsulation hexagonal Str/MOLe@ZnONPs
DLS was used to assess formulation particle size and ζ-potential charge means (Malvern Instruments, UK). 3 ml of bareZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs were diluted in deionized water, put in a cell cuvette, and measured four times to estimate the size, and three ζ-potential charge the mean ± SD (Sharaf et al., 2021). The optical properties of the nanopowders (ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs) were analyzed using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in KBr pellets. The particle size and morphology of the samples were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (JCM-7000 Neo Scope™ Benchtop TEM; JEOL, Japan).
2.7 Antibacterial activities
2.7.1 Agar well diffusion assay
The antibacterial effects of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and MOLe@ZnONPs were evaluated against E. faecalis isolates with high antimicrobial resistance profiles (PDR[isolate code 21], and XDR [isolate code 32,and 34]) and strong biofilm production. The results were compared to streptomycin discs (10 µg, Oxoid, Cambridge, UK). Bacterial suspensions in sterile saline were adjusted to a concentration of 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL and cultured on Mueller–Hinton (MH) agar. Wells were created in the agar plates, and 100 µL of each chemical was added to each well. Sterile water served as the negative control. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours, and the zones of growth inhibition were measured to assess the antimicrobial effectiveness of the tested drugs (Wang et al., 2010).
2.7.2 Minimum inhibitory concentration, and minimum bactericidal concentration
The minimal inhibitory concentration was identified using microbroth dilution techniques. The concentrations of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str were diluted in a two-fold manner from 1 to 1024 μg/mL. They were then mixed with a standardized inoculum solution and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) was defined as the lowest concentration at which no visible growth was observed. The Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) was determined by culturing 10 μL of each clear well on Mueller-Hinton agar plates and identifying the lowest concentration that resulted in a 99.9% reduction in the initial inoculum after overnight incubation (Baek and An, 2011). The tolerance levels of E. faecalis against Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Strwere assessed using a specific formula: Tolerance = MBC/MIC as previously described (May et al., 1998).
2.7.3 Time-kill assay
A single colony of E. faecalis was cultured in BHI broth at 37°C overnight. The bacterial cells were then collected by centrifugation at 6000 x g for 10 minutes and resuspended in the lowest inhibitory concentration of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str. At 0, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h, samples were collected, and colonies were counted. The number of viable cells was determined as colony-forming units per mL (CFU/mL) using the drop plate technique with a 10-fold serial dilution in saline. The diluted solution was then dropped into MHA plates and incubated at 37°C for 24 h (Tan et al., 2019).
2.7.4 Biofilm formation
Subinhibitory concentrations (1/2 × MIC) of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str, along with an antibiotic-free medium as a negative control, were used to evaluate their effect on E. faecalis formation. Biofilms were measured by crystal violet testing, according to established protocols (Mathur et al., 2006). The optical density of the biofilm mass was quantified using a microplate ELISA reader (Huma Reader HS, Wiesbaden, Germany) at a wavelength of 590 nm. The experiments were conducted in triplicate. Any influence of nanoparticles on the measurement was subtracted from the absorbance caused by the samples. The average result was then presented with ± SD. The biofilm development was assessed in triplicate in separate trials and expressed as the ratio of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str compared to the untreated negative control.
2.8 Gene expression related to virulence in biofilm culture
qRT-PCR was performed on biofilm cultures treated with sub-inhibitory doses of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str, as well as an untreated control. RNA was extracted using the QIAampRNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen) and treated with DNase I to remove genomic DNA. Real-time PCR amplification was performed using HERA SYBR® Green RT-qPCR Master Mix (Willowfort) and novel primers (Table 1) designed for the gelE,sprE, and quorum-sensing fsr (A, B, C) virulence genes. Primers were designed using Primer3 and FastPCR software, optimized for specificity and sensitivity using touchdown PCR, and validated experimentally. The 16S rRNA gene was used as an internal control. PCR conditions were as follows: reverse transcription at 50°C for 30 minutes, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 15 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 30 seconds, and extension at 72°C for 30 seconds. The relative expression of target genes was calculated using the 2^-ΔΔCt method and normalized to the 16S rRNA gene (Yuan et al., 2006; Massol-Deya et al., 1995).
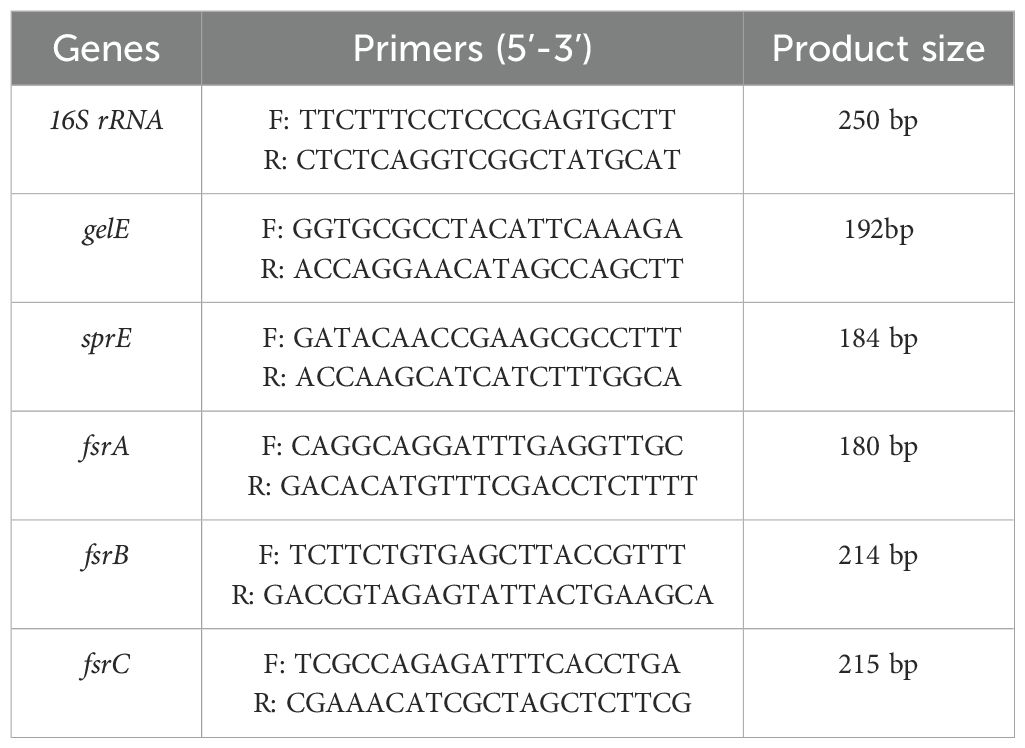
Table 1. Novel primers for gene expression analysis of biofilm-associated genes in Enterococcus faecalis (Syper-green real time PCR assay).
2.9 Statistical analysis
Each experiment was performed in triplicate, and all results are shown as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical significance was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (P < 0.05). Analyzes were performed using SAS 9.4 for Windows x64 by the SAS Institute and graphical results were plotted using GraphPad Prism software (version 8, GraphPad Inc. Software).
3 Result
3.1 Occurrence of E. faecalis, and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns
The general prevalence of E. faecalis was 14% as reported in Supplementary Table S1. 16% of the 50 female samples included E. faecalis, whereas 12% of the 50 urine samples from male companion cats had E. faecalis.
The antimicrobial susceptibilities of E. faecalis isolates were determined in vitro (Supplementary Tables S2, S3; Figure 1A). All isolates were 100% resistant to Teicoplanin and Linezolid. High resistance rates were observed for Tigecycline (87.5% and 83.3%) and Ampicillin (100% and 83.3%) in E. faecalis isolates from female and male sources, respectively. Lower resistance rates were detected for both ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin (12.5% and 16.6%) in E. faecalis isolates from females and males, respectively. Notably, E. faecalis isolates showed high resistance rates to both Imipenem and meropenem, reaching 35.7%. Additionally, 64.2% of isolated E. faecalis species were resistant to vancomycin, while 42.8% were resistant to streptomycin.
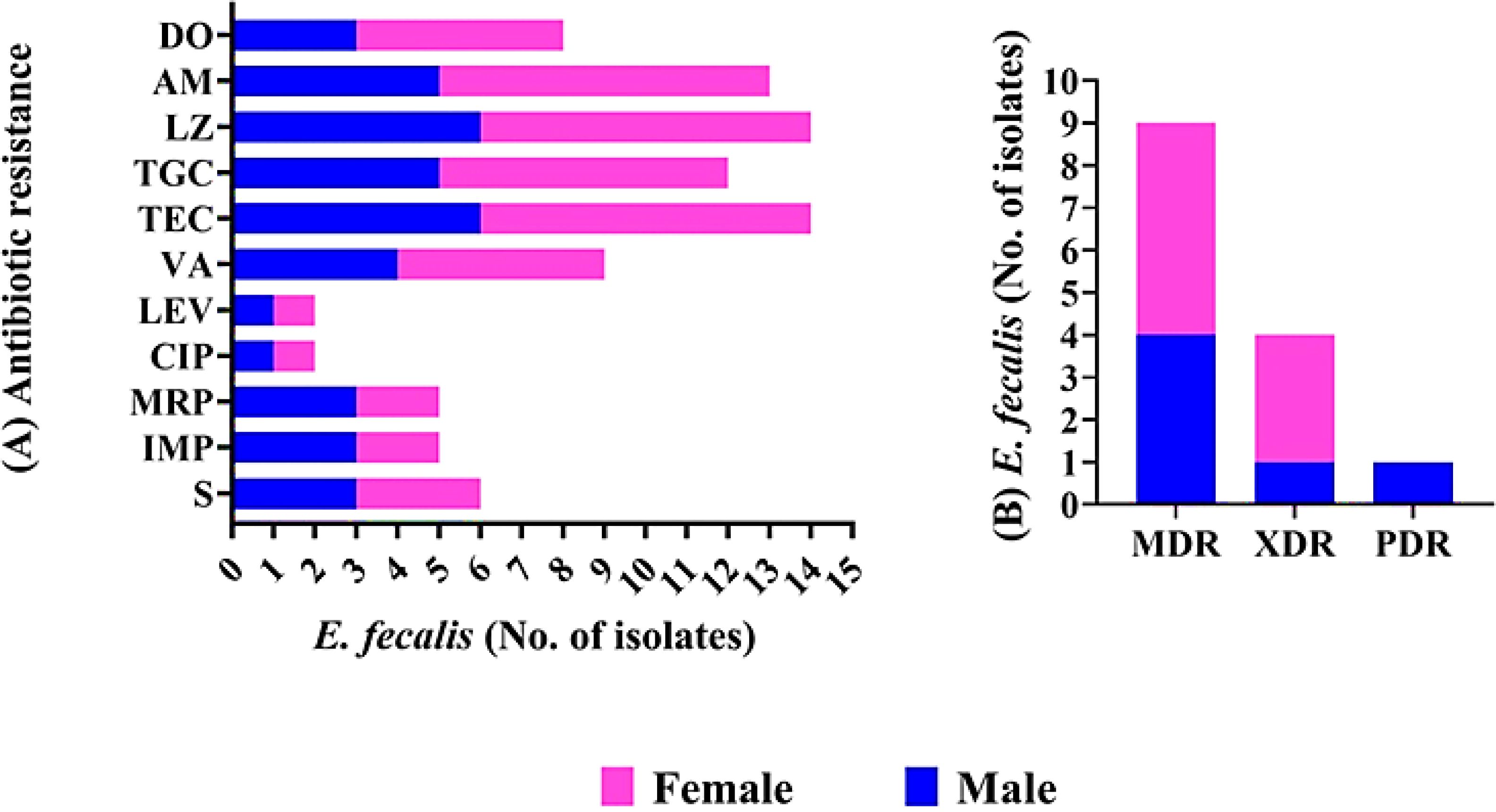
Figure 1. Antimicrobial resistance pattern of E. fecalis isolated from female, and male pet cats. (A) The patterns of antimicrobial resistance are shown for streptomycin (S), Imipenem (IMP), meropenem (MEM), Levofloxacin (LEV), ciprofloxacin (CIP),Vancomycin (VA), Teicoplanin (TEC), Tigecycline (TGC),ampicillin (AM), lenzolid (LNZ), and doxycycline (DO). (B) Presence of MDR, XDR, and PDR classifications in E. fecalis.
The investigation of the antibiogram in Supplementary Table S3 indicated that E. faecalis isolates showed resistance to 5–11 antimicrobial drugs, with MARs ranging from 0.45 to 1.00, and displayed 12 unique resistance patterns. PDR, XDR, and MDR patterns were identified in the studied isolates as shown in Supplementary Table S3, Table 2; Figure 1B. None of the isolates examined were completely susceptible to all antibiotics tested. One out of 14 E. faecalis isolates showed pan-drug resistance patterns [isolate code 21], being resistant to all antimicrobial drugs tested (7.1%). Four of the isolates tested (28.5%) had XDR characteristics [isolate code 9,11,32,and 34]. However, 9 of E. faecalis showed MDR patterns[isolate code 3,5,6,7,10,14,16, 24,and 45] (64.2%). Regarding the isolation source, five, and three E. faecalis isolated from female origin exhibited MDR[isolate code 6,10,16,24,and 45] and XDR [isolate code 9,11,and 34] profiles, respectively, while the PDR [isolate code 21] E. faecalis isolates originated from male origin.
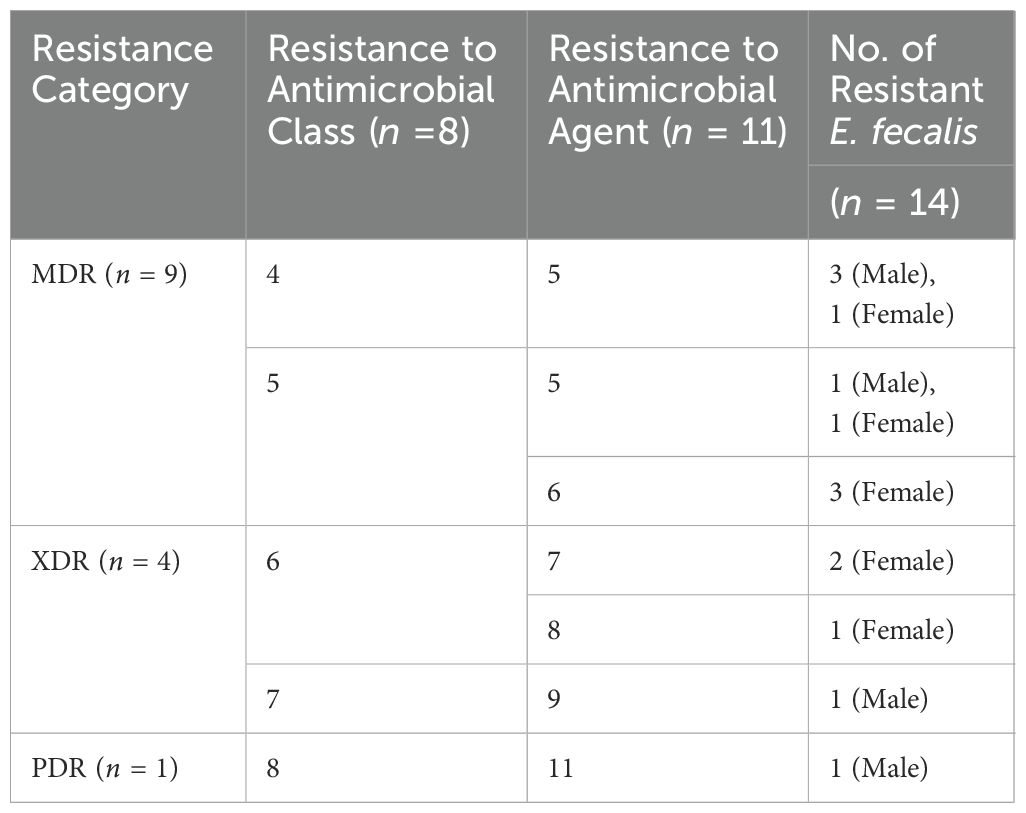
Table 2. The presence of multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and pandrug-resistant (PDR) categories in E. faecalis isolates from female and male pet cats.
3.2 Biofilm formation and virulence determinants of E. faecalis isolates
E. faecalis isolates were tested for biofilm formation by using the crystal violet staining method (Supplementary Table S3; Figure 2A), in which 3(3/14 = 21.4%), and 7(7/14 = 50%) isolates are strong biofilm producer[isolate code 21,32,and 34], and moderate biofilm producer[isolate code 6,7,9,10,16,24,and45] respectively. On the other hand, only one isolate isn`t producing biofilm (1/14 = 7.1%) [isolate code 3], and 3 isolates are weak producer (21.4%) [isolate code 5,11,and 14]. Of note, the overall E. faecalis isolated from female origin showed biofilm producer with the highest number exhibited moderate biofilm producer (6/8 = 75%) [isolate code 6,9,10,16,24,and 45].While, most E. faecalis isolated from male origin showed strong [isolate code 21, and 32] and weak biofilm producer [isolate code 5,and14] (2 isolate for each). Moreover, two E. faecalis isolates from male origin showed moderate [isolate code 7] and none biofilm producer [isolate code 3] (1 isolate for each).
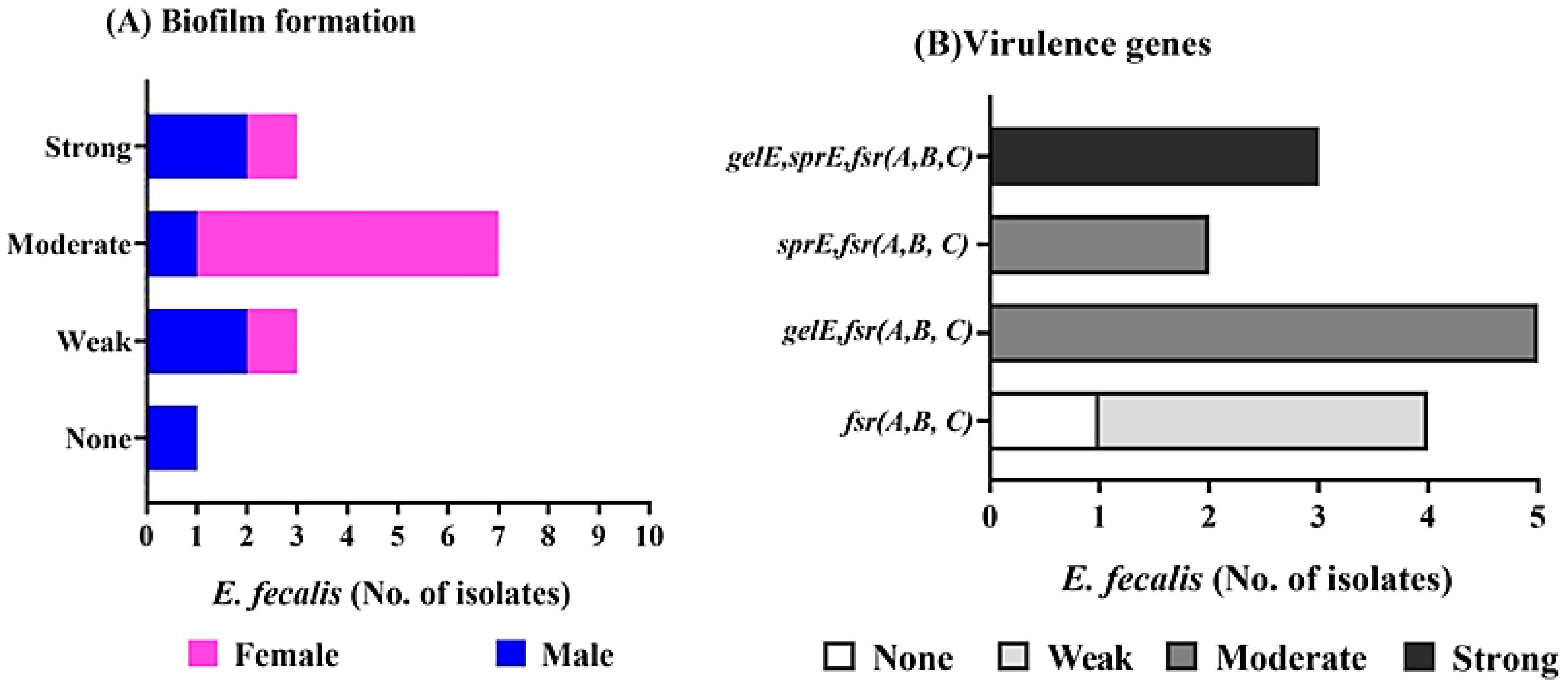
Figure 2. Biofilm formation, and virulence determinant genes of E. fecalis isolated from female, and male pet cats. (A) Determination of biofilm formation by crystal violet stain showing none, strong, moderate, and weak biofilm producers. (B) Detection of the gelE, sprE, and fsr (A,B,C) genes by PCR, and its correlation with biofilm formation.
PCR analysis was performed to identify genes related to virulence and biofilm formation, including gelE, sprE, and fsrABC (Supplementary Table S3; Figure 2B). All 13 biofilm-producing isolates were positive for the fsrABC gene locus [isolate code 5,6,7,9,10,11,14,16,21,24,32,34 and 45], resulting in expected DNA fragments of 740, 566, and 1343 bp, respectively (Figure 3). The gelE gene was detected in 8 (8/13 = 61.5%) biofilm-forming isolates [isolate code 7,9,10,21,24,32,34, and 45], including 3 strong biofilm producers [isolate code 21,32, and 34] and 5 moderate biofilm producers [isolate code 7, 9, 10, 24, and 45]. The sprE gene was detected in 5 E. faecalis isolates[isolate code 6, 16, 21, 32, and 34], including 3 strong biofilm producers [isolate code 21,32, and 34] and 2 moderate biofilm producers [isolate code 6, and 16]. Isolates lacking gelE and sprE genes, despite the presence of fsrABC, exhibited weak or no biofilm formation [isolate code 3,5,11 and 14].
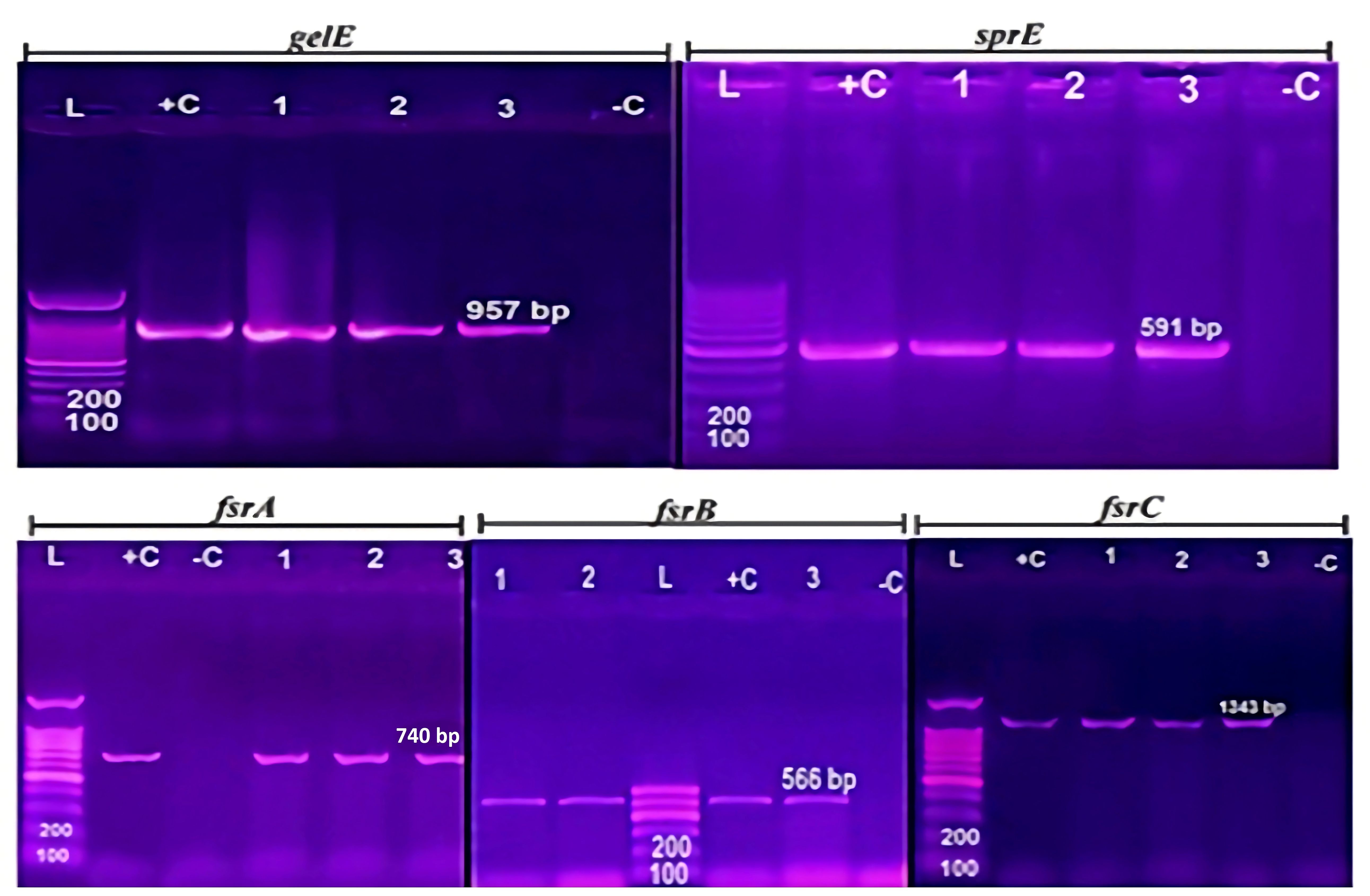
Figure 3. Agarose gel electrophoresis of biofilm genes gelE, sprE, and fsr (A,B,C): DNA ladder (100 bp), control positive and control negative (DNase water) are shown in each lane by L,C+, and C-. The same tested E. fecalis isolates [isolate code 21,32, and 34] are shown in 1, 2, 3 lanes. The biofilm genes gelE, sprE, and fsr (A,B,C) of all E. fecalis isolates are provided in Supplementary Table S3.
3.3 Characterization of hexagonal zinc oxide nanocapsulation
3.3.1 Surface morphology analysis
Size, shape and surface morphological structure of nanoparticles were studied using TEM, the results are shown in Figures 4A–C and 4a–c at 100 and 50 nm, respectively. The produced formulations have varied morphological surfaces, according to TEM. The ZnONPs formed were hexagonal and agglomerated, with an average size ~60 nm (see blue arrow, Figure 4Aa). After loading the antibiotic, TEM images were showed several gaps/bumps on the surface of Str/ZnONPs with an average size ~200 nm (see yellow arrow, Figure 4Bb), which decreased by a large percentage after coating and capsulating the surface with MOLe with a smooth surface with an average size ~250nm of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs (see white arrow, Figure 4Cc). High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HTEM) (Supplementary Figure S2A) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern in Supplementary Figure S2B exhibits concentric rings of bright spots confirming the preferential orientation and highly crystalline nature of ZnONPs. whereas (101), (102), (110), and (103) planes correspond to the wurtzite structure of ZnO. This confirms the formation of NC and corroborates with the FTIR results.
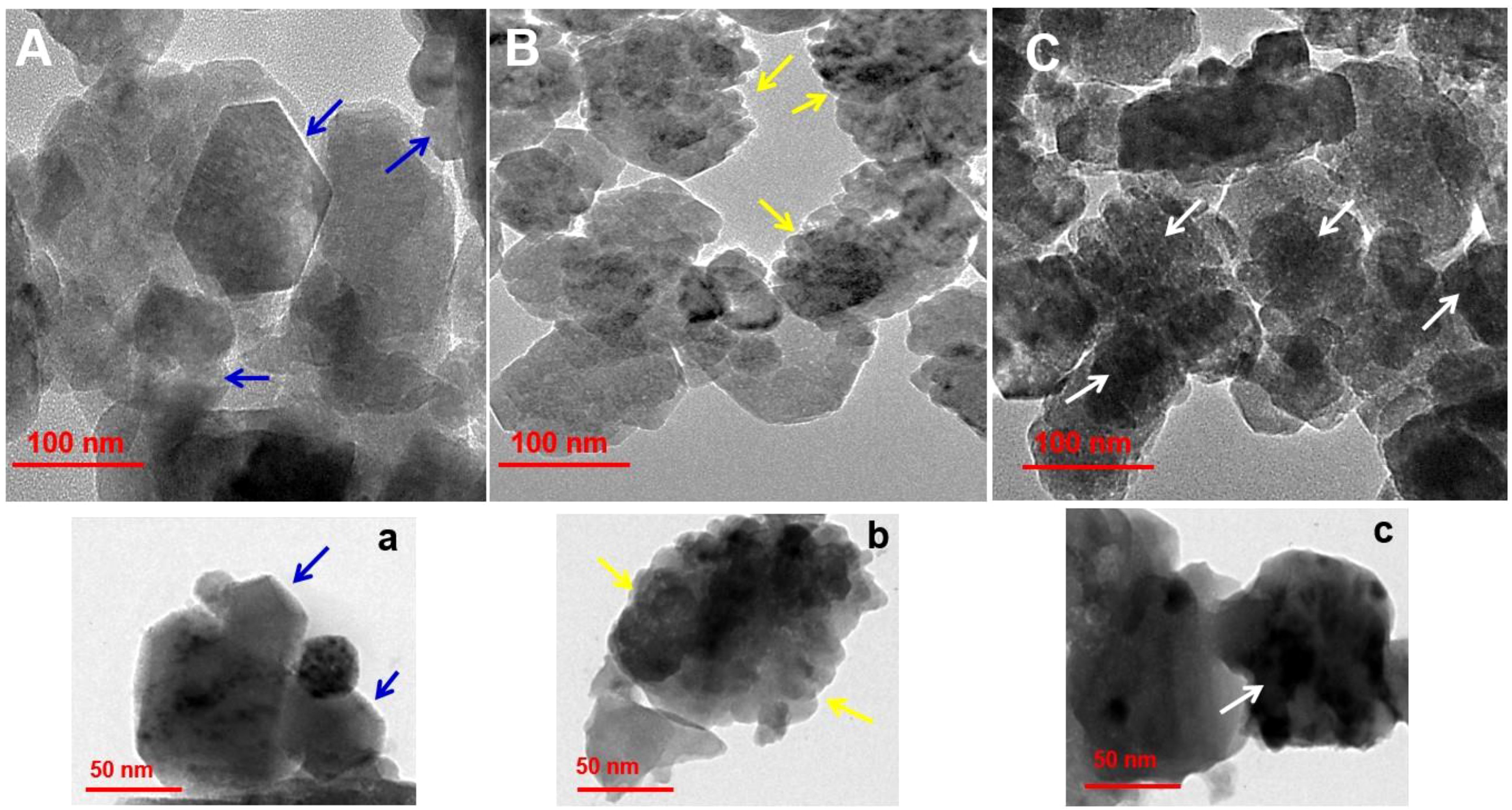
Figure 4. Surface morphology analysis by of (A-a) ZnONPs, (B-b) Str/ZnONPs and (C-c) Str/MOLe@ZnONPs by TEM. Arrow symbol highlights specific features of the nanoparticles.
Furthermore, the nanoparticles were analyzed by SEM to determine their dimensions, geometry, and surface morphology. The morphologies of ZnONPs are significantly influenced by Str and MOLe. The nanosynthesized formulas have a spherical, hexacrystalline structure of ZnONPs (see blue arrow Figure 5A), besides, agglomerated in clusters with rough in appearance of each Str/ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPswith an average particle size from 50 to 260 nm, as confirmed by their precise structural properties (see yellow and white arrow Figures 5B, C).
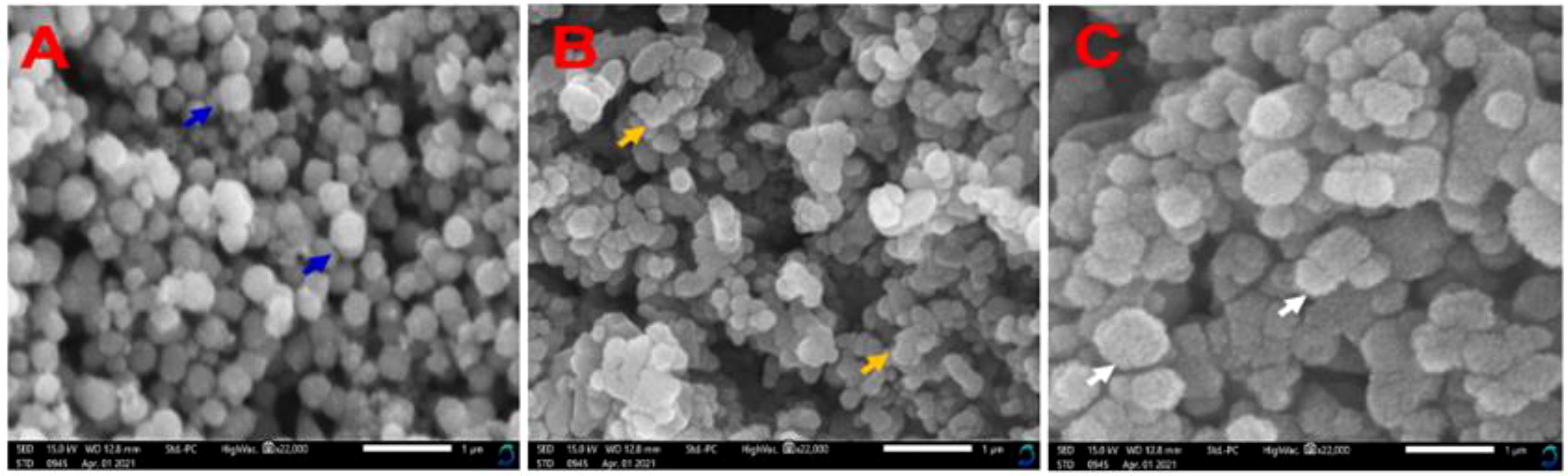
Figure 5. SEM analysis of nanocapsulation synthesized (A) ZnONPs, (B) Str/ZnONPs and (C) Str/MOLe@ZnONPs at Magnification: ×22,000 (1µm). Arrow symbol highlights specific features of the nanoparticles.
3.3.2 DLS
DLS was used to evaluate the particle size (PS), polydispersity index (PDI), and ζ-potential of ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs. The average results of all the calculations demonstrated a distribution of PS in nanometers, the findings are included in Table 3 and visually shown in Supplementary Figure S1. The results obtained from DLS analysis indicated that the nanoparticles had average diameters of around 65.9 ± 3.57nm,199.3 ± 12.93nm and 271.4 ± 19.10nm, with corresponding PDI of 0.326 ± 0.037, 0.690± 0.12and 0.142 ± 0.05for ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, respectively (Supplementary Figures S1A, C). The results indicated that the incorporation of Str and the application of a MOLe coating led to an augmentation in the dimensions of ZnONPs. The ζ-potential values of nanoparticles are often used to assess their stability. In this study, the ζ-potential values of ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs were found to be –19.8± 0.22mV,–29.1± 0.12, and –33.1 ± 0.55mV, as shown in (Figures 5A–C). Row Coloration Data (RCD) was clarified tree formulations by three variables (size, PDI and ζ-potential) where the first and second component were (94.9 - 2.2%), (96.3-1.9%) and (97.3-3.9%) of ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs the total variance (99.2%) during analysis (107 µs), as score plot carve (Supplementary Figure S1G–I).
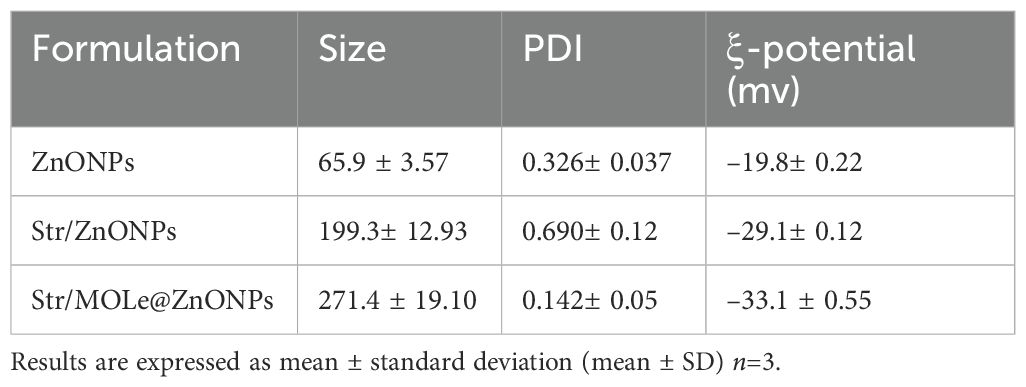
Table 3. Characteristics the mean size (Z-average), polydispersity index (PDI), ξ-potential to different nano-formulation.
3.3.3 FTIR
FTIR analysis is a successful method for illustrating the chemical composition of synthesized substances. The FTIR spectra were analyzed at a scan range of 4000 –500 cm-1 to determine the functional groups that were involved in the synthesis of ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs were depicted in Figure 6. In this investigation, FTIR spectrum of synthesized ZnONPs showed the peak at 481 cm-1 corresponds to the absorption of the Zn–O bond, the bands at 3485, 2424, 1629, 1395, and 742 cm-1 correspond to the bonds O–H, C = O, C = C, C–O, and C–H, respectively, as shown in Figures 6A, B showed the greatest peaks in the FTIR spectrum of Str/ZnONPs at 3495 cm-1 correspond to O–H stretching vibrations of phenols, The FTIR spectral bands at 1609 cm-1 is assigned to –C=C stretching of functional group, the maximum at 1399 cm-1 corresponds to C-H stretching vibrations of the alkene group. Other brief peaks between 500 and 800 cm-1 have been ascribed to the presence of metal–oxygen (Zn–O). However, Figure 6C showed the FTIR absorption spectra of biosynthesized, vacuum-dried Str/MOLe@ZnONPs revealed the presence of bonds due to O–H stretching (around 3,432 cm-1) and C–CH3 stretching (around 2,360 cm-1). The FTIR spectrum revealed a C=O-corresponding absorption band at 1,637 cm-1. The bands seen at 1448 cm-1 are attributed to the modes of vibration of the amino group (NH3). A band at 1089 cm-1indicated C=C elongation. The bands evident between 500 and 650 cm-1 denoted the presence of the R–CH group. The FTIR spectra of synthetic M. oleifera leaf extract are shown in (Supplementary Figure S3A), the highest FT-IR peaks at 3490 cm1 in the MOLe FTIR spectrum are attributed to the O–H stretching vibrations of phenols. The peak observed at 2090 cm-1 corresponds to the C-H stretching and bending vibrations. At 1670 cm-1, the active C=O stretching vibrations. The FTIR spectrum of streptomycin (Str) was observed to contain absorption bands at 3345, 2180, 1451, 1030, and 850 cm-1 due to the N-H in the amino group, C-H, CH2 group, C–N stretching, and C–C group, respectively (Supplementary Figure S3B).
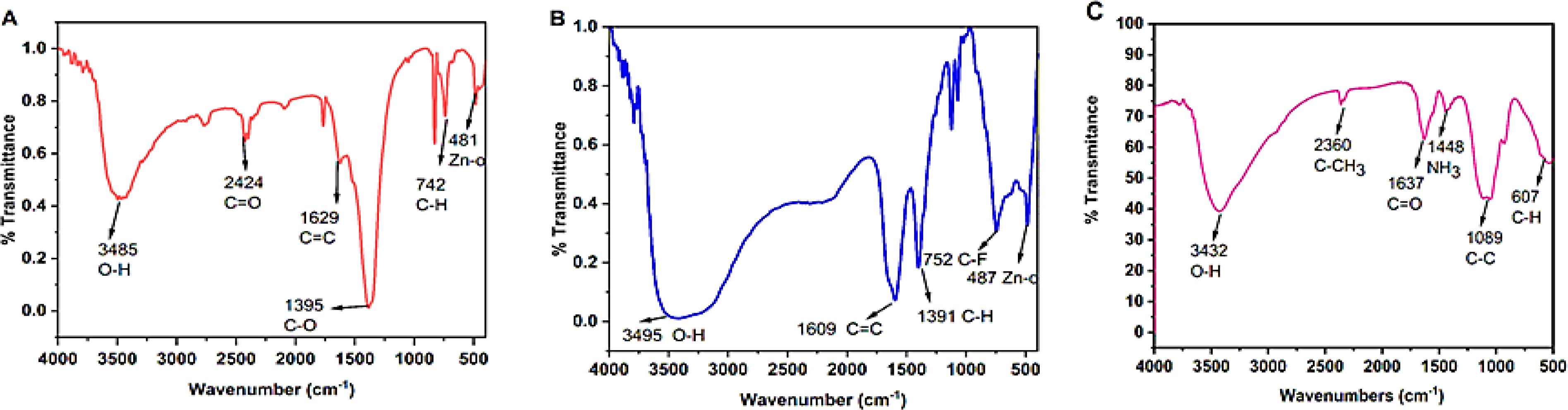
Figure 6. FTIR spectra analyzed the synthesis of (A) ZnONPs, (B) Str/ZnONPs and (C) Str/MOLe@ZnONPs.
3.4 Antimicrobial activities
3.4.1 Antibacterial activity against planktonic E. faecalis cells
Three E. faecalis isolates, two categorized as extensively drug-resistant (XDR) [isolate code 32, and 34] and one as pan drug-resistant (PDR) [isolate code 21], originating from both male (2 isolates) [isolate code 21, and 32] and female (1 isolate) [isolate code 34] sources, were tested for susceptibility to Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and MOLe@ZnONPs. Their resistance to at least 7 antimicrobial agents and strong biofilm production were considered. The evaluation included measuring inhibition zone diameters and determining minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values (Figure 7; Supplementary Table S4). The findings indicated a notable difference in the inhibitory zone size among Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, streptomycin, and unloaded MOLe@ZnONPs (p<0.05). The Str/MOLe@ZnONPs exhibited the highest antibacterial activity, with an inhibition zone diameter of up to 40mm (Figure 7). This efficacy was reflected in the low recorded MICs (≤ 16 μg/mL) (Supplementary Table S4) compared with 35 mm diameter inhibition zones of Str/ZnONPs, and MICs (≤ 32 μg/mL). Furthermore, the MBC values of Strand Str/MOLe@ZnONPs were two-fold higher than MIC values with a tolerance equal to 2 indicating their bactericidal effect. While, both of MOLe@ZnONPs, and Str antibiotic alone didn`t show significant inhibition of the growth with MICs ≤ 64, and 256 μg/mL, respectively (Figure 7; Supplementary Table S4).
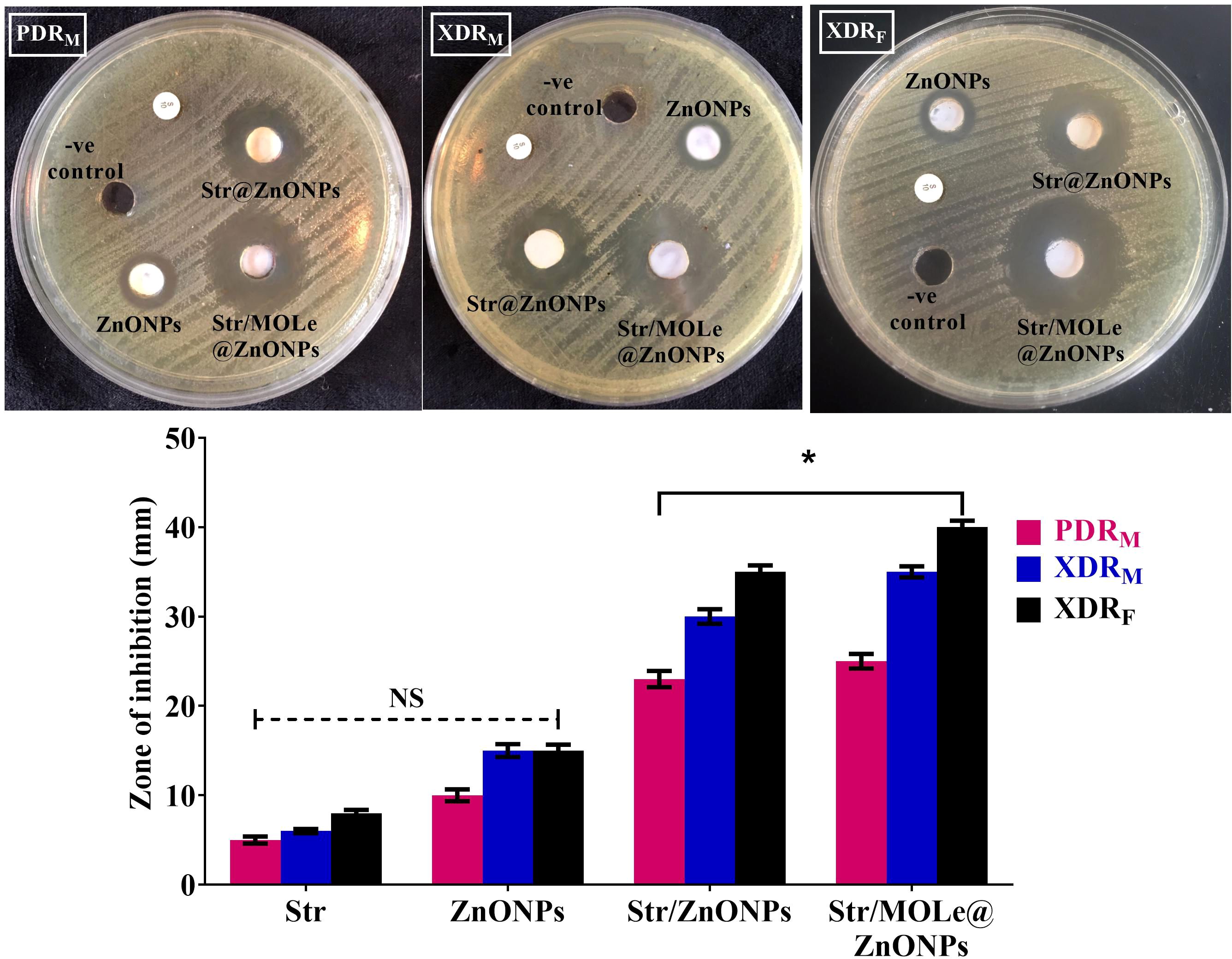
Figure 7. The inhibition zone of ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs compared with Str were determined by in vitro of E. fecalis bacterial growth by agar well diffusion assay; extensively drug-resistant isolate of female origin (XDRF; isolate code 34), extensively drug-resistant isolate of male origin (XDRM; isolate code 32), and pandrug-resistant isolate of male origin (PDRM; isolate code 21). Each column represents the average ± standard deviation of three separate studies along with illustrative visuals. *Signifies statistically significant differences (P< 0.05), whereas NS indicates non-significant differences (P> 0.05) in comparison to the control group.
The time-kill assay was assessed by culturing the E. faecalis isolate (exhibited PDR pattern; isolate code 21) under MIC- concentration of streptomycin, and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs and evaluating the number of viable bacteria (Figure 8). The viable bacteria count reduced from 10^6 CFU/mL to 10^4 CFU/mL after 4 hours of treatment with Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, and further dropped to 10^2 CFU/mL after 16 hours (Figure 8). The number of live bacteria reduced progressively to 10^5 CFU/mL after 16h of treatment with Str/ZnONPs. The findings showed that Str/MOLe@ZnONPs had bactericidal effects in a short period. On the other hand, both MOLe@ZnONPs and Str antibiotic alone didn`t show a significant reduction in the number of viable bacteria with a slight increase in the number of viable counts turned from zero point till 16 h incubation.
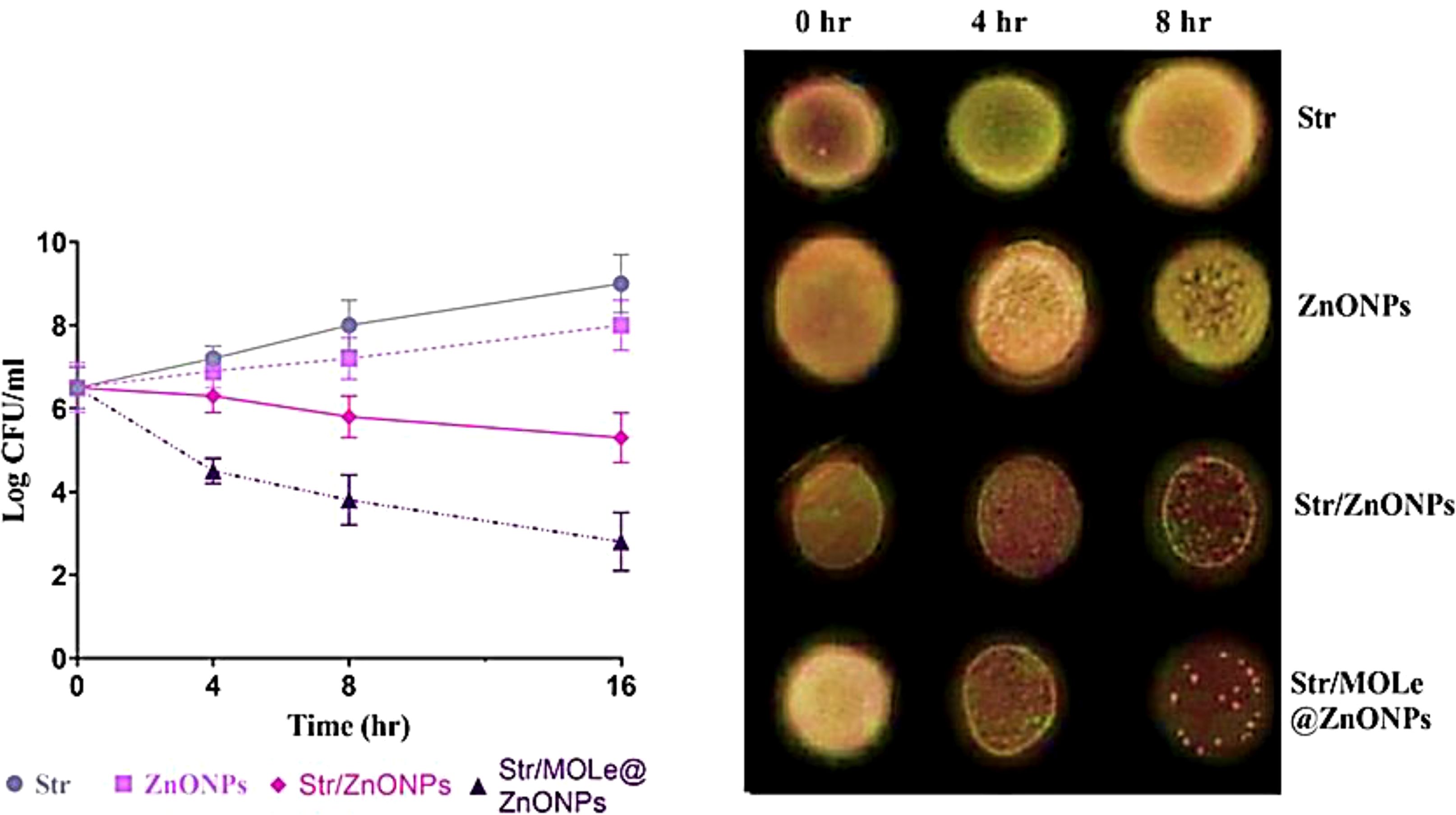
Figure 8. The time-kill curve and the bactericidal mechanism of ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs compared with Str at time point 0, 4, 8, 16 h on pandrug-resistant E. faecalis isolate of male origin (PDRM; isolate code 21). Each column indicates the mean ± SD from the three independent trials. Bacterial cultures from the MIC test were deposited on agar plates and incubated for 24 hours. The decrease in viable cell counts was observed at 0, 4, and 8 h.
3.4.2 Anti-biofilm activity of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs
CV staining showed that with sub-inhibitory concentration of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, the biomass of biofilm was completely inhibited and the percentage biofilm formation ranged from 10-24% in treated isolates compared with the untreated (Positive controls)(p<0.05) (Figure 9). While, a moderate effect of Str/ZnONPs on biofilms were detected with a percentage ranged from 59-68% in treated biofilm mass (p<0.05). However, both of MOLe@ZnONPs, and streptomycin antibiotic alone didn`t show any detectable ability to reduce the biofilm mass with a range of 80–92%,and 92-98%, respectively (p>0.05).
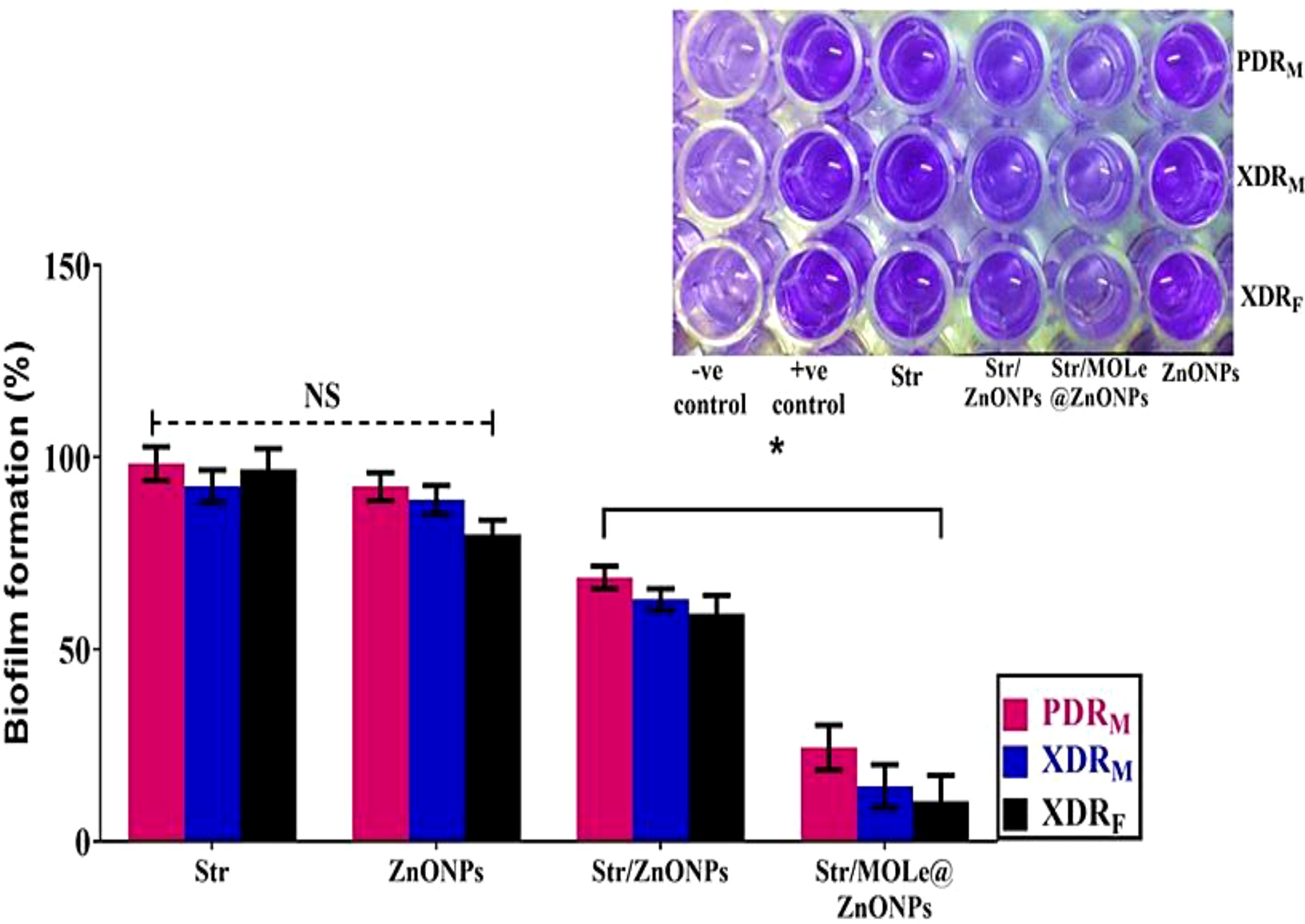
Figure 9. The biofilms formation by the crystal violet staining measuring at OD600 of extensively drug-resistant E. fecalis isolate of female origin (XDRF; isolate code 34), extensively drug-resistant E. fecalis isolate of male origin (XDRM; isolate code 32), and pandrug-resistant E. fecalis isolate of male origin (PDRM; isolate code 21) treated with ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs compared with Str. The columns demonstrate the mean ± SD of three independent experiments along with representative images. A greater intensity of the violet color indicates increased biofilm formation. “*” denotes statistically significant differences (P< 0.05), while “NS” indicates non-significant differences (P > 0.05) in comparison with the control sample.
To investigate the mechanism by which Str/MOLe@ZnONPs inhibit the biofilm formation of E. faecalis, real-time qRT-PCR was used to determine the expression of gelatinase (gelE), serine protease (sprE),and quorum-sensing fsr gene locus(fsr;A,B,C) virulence genes (Figure 10). The more vulnerable down-regulatory effect was detected in Str/MOLe@ZnONPs treated biofilm producer E. faecalis isolates as compared with the control group (P< 0.05). In which, the results showed that the fold change in gelE, sprE, and fsr; A, B, and C gene expression in PDR-treated E. faecalis [isolate code 21] were 0.06,0.032,0.015,0.043, and 0.05 respectively. Moreover, Str/ZnONPs showed a moderate, and significant down-regulatory effect on gelE, sprE, and fsr; A, B, and C genes expression compared with the control group (P< 0.05). On the other hand, both MOLe@ZnONPs, and streptomycin antibiotic alone didn`t significantly decrease the expression level of gelE,sprE, and fsr; A, B, C genes in treated E. faecalis isolates (P> 0.05).
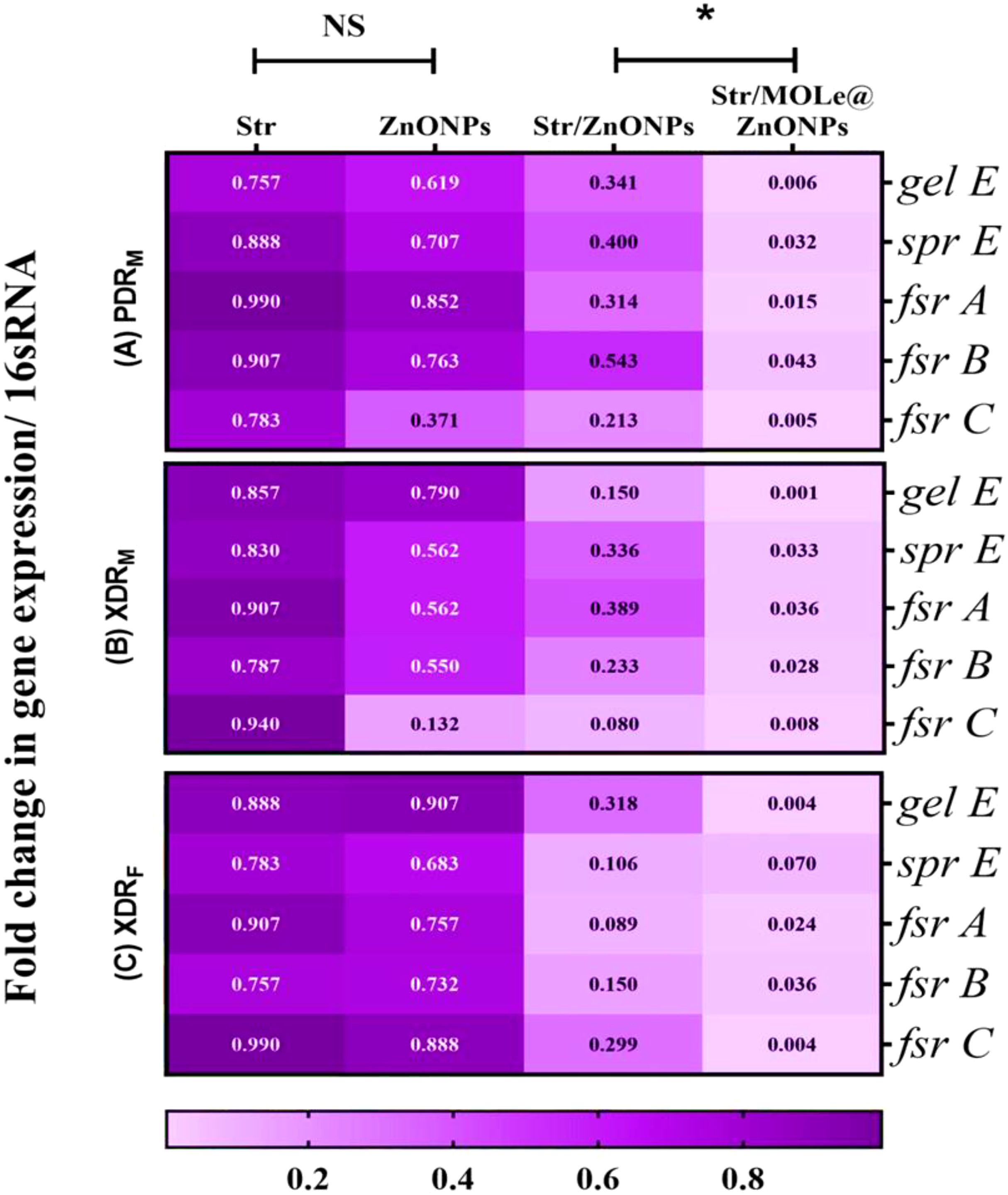
Figure 10. Heatmap of the relative gene expression of gelE, sprE, and fsr (A,B,C) upon treated with ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs and Str/MOLe@ZnONPs compared with Str; extensively drug-resistant E. fecalis isolate of female origin (XDRF; isolate code 34), extensively drug-resistant E. fecalis isolate of male origin (XDRM; isolate code 32), and pandrug-resistant E. fecalis isolate of male origin (PDRM; isolate code 21). Gene expression levels were determined using the ΔΔCT method and shown as fold change. 16S rRNA served as the endogenous control. The scale color indicates the level of down-regulation; associated genes with high levels of down-regulation are represented by the light mauve color, whereas genes with low level of down-regulation are represented by the deep mauve color. Each statistic represents the mean of three separate experiments. “*” indicates statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), while “NS” indicates non-significant changes (P > 0.05) in comparison with the control group.
4 Discussion
Historically, pets have been identified as a potential source of resistant microorganisms that might convey this resistance to humans (Kataoka et al., 2014; Jackson et al., 2009; Ossiprandi and Zerbini, 2015). Cats and dogs often carry antimicrobial drug-resistant enterococci which act as a source of these resistant microbes for humans. Enterococci often result in intricate urinary tract infections (Weese et al., 2011; Kajihara et al., 2015). The present study examined a 14% incidence rate of E. faecalis in urinary tract infections of domestic cats, with the majority of isolates coming from female cats, as previously reported (Oguttu et al., 2021). Drug-resistant E. faecalis strains have been on the rise, rendering many medications ineffective against infections caused by these bacteria (Oguttu et al., 2021). The research revealed a resistance level of 42.8% against aminoglycosides, which may be anticipated since Enterococci are naturally resistant to different doses of aminoglycosides, making them unsuitable for use as standalone treatments. The significant resistance to streptomycin at a high dose shown in recent investigations (Oguttu et al., 2021; Tumpa et al., 2022; Kristich et al., 2014).Worth noting, the increased resistance levels of 92.8% against ampicillin, compared with previously reported 41% (Oguttu et al., 2021). Previous investigation on the antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococci has confirmed the global rise of multi-drug resistant enterococci, especially to vancomycin (Werner et al., 2008). Despite the previously observed 28% resistance against vancomycin, alarming 64.2% of isolated E. faecalis species were resistant to vancomycin reported in this study.
Enterococcus species are inherently resistant and tolerant, and have the ability to quickly develop resistance to almost every antimicrobial agent used in clinical settings (Kristich et al., 2014).Therefore, we presented information on several drug resistance patterns (n = 12-pattern), with 64.2%, 28.5%, and 7.1% of the isolates showing MDR, XDR, and PDR categories, respectively. This resistance level was lower than what was previously mentioned (Oguttu et al., 2021; Tumpa et al., 2022).
Biofilms formation by Enterococci contribute to its virulence that allows the bacteria to irreversibly attached to urinary catheters (Costerton, 2001; Dautle et al., 2003), resistance to antibiotics (Mohamed et al., 2004).There was obvious association with higher prevalence of biofilm-forming strains and the sample source(urine and stool samples) (Hashem et al., 2017), and more than half of urinary tract infection isolated bacteria were biofilm producers (Akhter et al., 2014). Because of previously described superiority of using crystal Violet biofilm assay as a phenotypic detection of the biofilm-forming entercococcal clinical isolates (Sindhanai et al., 2016; Hassan et al., 2011). Our work demonstrated the using of already-established crystal violet assays to detect a higher frequency of biofilm forming E. fecalis than previously reported (Hashem et al., 2017), Another study team observed that 34% of their isolates developed powerful biofilms, 49% produced moderate biofilms, and 17% developed weak biofilms (Sindhanai et al., 2016).
The gelE gene encodes gelatinase activity, which is identified as the first crucial stage in the biofilm formation process. It serves as a trigger for bacterial surface adhesion and enhances the aggregation of microcolony cells (Hancock and Perego, 2004). GelE expression is positively regulated by the fsr locus controlled by quorum sensing (Nakayama et al., 2001; Qin et al., 2001).The fecal streptococci regulator (fsr) locus consists of three genes: fsrA, fsrB, and fsrC. It is a well-characterized quorum sensing system that controls E. faecalis biofilm formation and gene expression in reaction to high cell population densities (Miller and Bassler, 2001; Hancock and Perego, 2004). This locus is situated next to two genes that encode virulence factors: one encodes a gelatinase (gelE) and the other a serine protease (sprE). A prior work highlighted the significance of integrating patterns of the gelE/fsrA, B locus genes using genome screening and subsystem analysis to predict gelatinase activity linked with biofilm formation (Hashem et al., 2017).
All E. faecalis isolates were examined for the presence of biofilm-associated genes fsr, gelE, and sprE. The gelE gene was detected in 61.5% of biofilm-forming isolates. Previous studies have reported the presence of the gelE gene in 100%, 94%, 88%, and 92% of Enterococcus isolates (Hashem et al., 2017; Roberts et al., 2004; Mohamed and Murray, 2005; Sedgley et al., 2005). These reports, together with our findings, verify that gelE is crucial for biofilm development.
Potent biofilm-forming strains were found to possess the complete fsrABC gene locus, along with gelE and sprE genes. Conversely, a reduction in biofilm formation was associated with the absence of gelE and sprE genes. These findings align with previous research demonstrating that the absence of fsr and/or gelatinase activity leads to reduced biofilm development (Mohamed et al., 2004). Increased use of antimicrobials leads to serious the development of enterococci resistance. Besides, the high resistance of Enterococcus to aminoglycoside renders the use of this antibiotic as a single agent (García-Solache and Rice, 2019). Accordingly, investigation of new antimicrobial agents is an ultimate need (Cegelski et al., 2008; Lallo da Silva et al., 2019; Essawi et al., 2020; El-Demerdash et al., 2023a; Ebrahem et al., 2024).
Nanomaterials provide potential solutions that circumvent typical antibiotic resistance mechanisms (Wang et al., 2017; Abd El-Emam et al., 2023; Hashem et al., 2024; Saad et al., 2024). Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) do not have any adverse effects on health status (Sruthi et al., 2018), they show antibacterial properties against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (Raghunath and Perumal, 2017; Liu et al., 2009; Reddy et al., 2014; Guo et al., 2015). TEM examination was used to analyze the surface morphology of the nanoformulations established in the investigation. The study was conducted at a decreased magnification scale of 50 and 100 nm. TEM analysis revealed distinct morphological surfaces in the produced formulations, resulting in materials with diameters ranging from 70 nm for ZnONPs, 200 nm for MOLe@ZnONPs, and 250 nm for Str/MOLe@ZnONPs.However, the addition of individual or dual drug caused no significant difference in the structure or morphology of the nanoparticles other than increased size within the nanoparticles. The increase in the size of nanoparticles upon drug loading was a clear indication of the successful drug trapping within the nanoparticles (Guo and Sun, 2020).
The findings of our study align with those of Chaudhary et al. (2019), who also observed a hexagonal form in the manufactured ZnO nanoparticles utilizing Aloe vera peel extract (Chaudhary et al., 2019). In addition, Salam et al. (2014) conducted a study in which they generated zinc oxide nanoparticles using a leaf extract from O. basilicum L. var. purpurascens Benth.-Lamiaceae. The researchers discovered that the nanoparticles exhibited a hexagonal (wurtzite) form and had a size of less than 50 nm. Divya et al. (2013) documented the presence of both spherical and hexagonal morphologies in zinc oxide nanoparticles that were generated using H. rosa-sinensis as the precursor.
However, the drug-loaded nanoparticles have higher zeta potential negative values because of the basicity of drugs which imparts a negative charge to the nanoparticles. The agglomeration of ZnO observed in the SEM and TEM supported the zeta potential and PDI readings (Abrahamse et al., 2017).
Nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution (PDI < 0.5) are often desired for biomedical applications. The DLS size and PDI of the synthesized nanoformulations ranged from 60 nm to 274 nm (Krug and Wick, 2011). Particles with a ζ-potential value above ±30 mV are generally considered more stable (Ali et al., 2018).The decrease in the negative ζ-potential charge observed in this study may be attributed to the ionization of hydroxyl groups (–OH) in the capping moieties at alkaline pH (Nava et al., 2011). This reduced negative charge indicates the successful loading of Str and MOLe onto the nanoparticles, which was confirmed by FTIR analysis (Asgari et al., 2014; Sawant and Bamane, 2018; Kumar et al., 2014; Nabiyouni et al., 2011).
For targeted biofilm delivery, it is crucial to extend the presence of the medicine over the microbial surface. Furthermore, we demonstrated the antibacterial efficacy of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, Str/ZnONPs, and MOLe@ZnONPs against XDR and PDR E. faecalis isolates. The strains chosen for further testing using the in vitro agar well diffusion technique, MIC, and MBC tests were those exhibiting a robust biofilm-forming characteristic and resistance to a minimum of 7 antimicrobial agents. The study found that the mixture of ZnONPs with Str and MOLe had notable anti-enterococcal effects, with a growth inhibition zone of up to 40mm, MICs of < 16 μg/mL, and a quick decline in viable bacteria to 102 CFU/mL after 16 hours. These findings are supported by previous studies that assessed the inhibitory action of Str/ZnONPs, such as aminoglycosides-meropenem is a promising technique that significantly altered the resistance profile of multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa strains by reducing MICs (El-Telbany et al., 2022; Fadwa et al., 2021). Meanwhile, a previous report showed a bacteriostatic rate of zinc oxide nanoparticles against E. faecalis (Bohan, 2018), our study reported the MIC of the Str/MOLe@ZnONPswere higher than those found in previous studies that using curcumin green synthesis of ZnONPsfor E. faecalis (El-Kattan et al., 2022; Sangani et al., 2015; Shinde, 2015; Aflatoonian et al., 2017). It is noteworthy that the combination of Streptomycin and ZnONPs exhibited heightened antibacterial efficacy against E. faecalis. The primary focus of the current study is on the observation that E. faecalis, which exhibited resistance to streptomycin, displays a significant increase in susceptibility to the same antibiotic with co-administration with nanoparticles. This specific insight provides opportunities to address the present dilemma of antibiotic resistance and effectively battle antimicrobial infections via mitigation strategies (Ghaffar et al., 2022).
Combining metal oxide nanoparticles, such as zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs), with antibiotics like streptomycin (Str) offers a promising approach to enhance antibiotic efficacy and overcome bacterial resistance. ZnONPs can improve the delivery and effectiveness of Str by increasing its binding to bacterial cells, inhibiting efflux pump activity, and disrupting bacterial membranes (Kotrange et al., 2021). Additionally, ZnONPs can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which further enhances Str’s bactericidal effects.
Previous studies have demonstrated significant improvements in antibacterial activity when combining Str with nanoparticles, with efficacy increases of up to 87.5% reported (Nishanthi et al., 2019; Salar et al., 2015; Aremu et al., 2021). This synergistic approach holds potential for combating antibiotic resistance in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (Raghunath and Perumal, 2017; Liu et al., 2009; Reddy et al., 2014; Guo et al., 2015).
In this study, we specifically selected sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) to investigate biofilm-related effects, as these concentrations enable the detection of subtle influences on biofilm formation without inhibiting bacterial growth. This approach is consistent with previous report, which has shown that antimicrobial sub-MIC concentrations can promote biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus without affecting bacterial growth (Elawady et al., 2024). Notably, we observed a substantial reduction in biofilm biomass was noticed after exposure to a sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (sub-MIC) of Str/MOLe@ZnONPs, where the percentage of biofilm formation ranged from 10-24%. In line with other studies, proved that ZnONPs enhanced antibiofilm activity via the ability of its small size to penetrate the biofilm matrix (Fadwa et al., 2021), interfered with biofilm integrity either by interrupting exopolysaccharide synthesis (Al-Wrafy et al., 2022),or disturbing the process of biofilm formation, causing it to break apart and decompose (Abdel-Halim et al., 2022; Masák et al., 2014). Following previous reports indicated a synergistic antibiofilm effect against S. aureus of combination between ZnONPs and tested antibiotics (Abdelghafar et al., 2022).
In this study, we focused on the role of the gelE gene, which encodes a gelatinase enzyme strongly associated with biofilm formation in Enterococcus species. Gelatinase plays a crucial role in degrading extracellular matrix components, facilitating bacterial attachment and aggregation—key steps in biofilm formation (Şchiopu et al., 2023). Additionally, gelatinase can influence the modulation of virulence factors and contribute to the persistence of biofilms in hostile environments. Our results showed a decrease in the expression of gelE, along with other virulence genes, including sprE (serine protease) and the quorum-sensing fsr gene locus (fsrA, fsrB, fsrC), following treatment with ZnONPs combined with Streptomycin (Str) and MOLe.
This modulation of gelE and other virulence genes under sub-MIC concentrations suggests that these agents may interfere with key biofilm-related mechanisms, offering a potential therapeutic strategy for biofilm-associated infections. Previous research suggests that suppression of FSR quorum sensing genes may have an impact as an alternative strategy for therapeutic anti-enterococcal drug development (Tang et al., 2015; Desouky et al., 2013; Singh and Nakayama, 2014; Shojima and Nakayama, 2014). Metal oxide NPs as ZnONPs acting as QS inhibitors are promising new alternative against antibiotic resistant Gram-negative bacteria (Hayat et al., 2019).The quorum-quenching action of ZnONPs leading to reduction of biofilm regulating gene expression, and lowering the virulence efficacy, and biofilm ability of P. aeruginosa (Ali et al., 2020; El-Telbany et al., 2022), S.aureus (Abdelghafar et al., 2022), and C. violaceum (Kamli et al., 2021).
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrates the potent antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of ZnONPs combined with Str and MOLe against multidrug-resistant E. faecalis, including pan-drug-resistant isolates. The observed anti-biofilm effects are likely due to the inhibition of gelatinase (gelE), serine protease (sprE), and quorum-sensing fsr genes. These findings, supported by our gene expression analysis using novel, specifically designed primers, suggest that ZnONPs in combination therapy with traditional antibiotics and MOLe could be a promising therapeutic option for combating enterococcal infections.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University (approval number ZU-IACUC/2/F/215/2023). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was not obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study because we do not know the committee responsible for this approval.
Author contributions
AS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SR: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. FA: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. MT: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. CL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2025R114), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr Mohammed Gaber Taha, Prof. Dr. Hany Mohamed, and Prof. Dr. Mohamed Mabrouk from the Faculty of Agriculture at Al-Azhar University, Egypt, for their assistance and encouragement throughout this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1505469/full#supplementary-material
References
Abd El-Emam, M. M., El-Demerdash, A. S., Abdo, S. A., Abd-Elfatah, E. B., El-Sayed, M. M., Qelliny, M. R., et al. (2024). The ameliorative role of Aloe vera-loaded chitosan nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus induced acute lung injury: Targeting TLR/NF-$κ$B signaling pathways. Open Vet. J. 14, 416. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.38
Abd El-Emam, M. M., Mostafa, M., Farag, A. A., Youssef, H. S., El-Demerdash, A. S., Bayoumi, H., et al. (2023). The potential effects of quercetin-loaded nanoliposomes on amoxicillin/clavulanate-induced hepatic damage: Targeting the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-$κ$B signaling pathway and microbiota modulation. Antioxidants 12, 1487. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081487
Abdelghafar, A., Yousef, N., Askoura, M. (2022). Zinc oxide nanoparticles reduce biofilm formation, synergize antibiotics action and attenuate Staphylococcus aureus virulence in host; an important message to clinicians. BMC Microbiol. 22, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02658-z
Abdel-Halim, M. S., Askoura, M., Mansour, B., Yahya, G., El-Ganiny, A. M. (2022). In vitro activity of celastrol in combination with thymol against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. J. Antibiotics 75, 679–690. doi: 10.1038/s41429-022-00566-y
Abrahamse, H., Kruger, C. A., Kadanyo, S., Mishra, A. (2017). Nanoparticles for advanced photodynamic therapy of cancer. Photomed. Laser Surg. 35, 581–588. doi: 10.1089/pho.2017.4308
Aflatoonian, M., Khatami, M., Sharifi, I., Pourseyedi, S., Khatami, M., Yaghobi, H., et al. (2017). Evalution antimicrobial activity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on two standard gram positive and gram negative strains. Tehran Univ. Med. J. 75, 562–569.
Ahmed, M., Marrez, D. A., Abdelmoeen, N. M., Mahmoud, E. A., Abdel-Shakur Ali, M., Decsi, K., et al. (2023). Proximate Analysis of Moringa oleifera Leaves and the Antimicrobial Activities of Successive Leaf Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts Compared with Green Chemically Synthesized Ag-NPs and Crude Aqueous Extract against Some Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 3529. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043529
Akhter, J., Ahmed, S., Saleh, A. A., Anwar, S. (2014). Antimicrobial resistance and in vitro biofilm-forming ability of Enterococci spp. isolated from urinary tract infection in a tertiary care hospital in Dhaka. Bangladesh Med. Res. Council Bull. 40, 6–9. doi: 10.3329/bmrcb.v40i1.20320
Ali, S. G., Ansari, M. A., Alzohairy, M. A., Alomary, M. N., Jalal, M., AlYahya, S., et al. (2020). Effect of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 9, 260. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9050260
Ali, H. H., Michaux, F., Khanji, A. N., Jasniewski, J., Linder, M. (2018). Chitosan-Shea butter solid nanoparticles assemblies for the preparation of a novel nanoparticles in microparticles system containing curcumin. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 553, 359–367.
Ali, N. M., Mohamed, G. A. E., Demerdash, A. S. (2023). Impact of oral administration of chitosan–nanoparticles on oxidative stress index and gut microbiota of heat stressed broilers. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 13, 997–1003.
Al-Wrafy, F. A., Al-Gheethi, A. A., Ponnusamy, S. K., Noman, E. A., Fattah, S. A. (2022). Nanoparticles approach to eradicate bacterial biofilm-related infections: A critical review. Chemosphere 288, 132603. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132603
Aremu, O. S., Qwebani-Ogunleye, T., Katata-Seru, L., Mkhize, Z., Trant, J. F. J. S. R. (2021). Synergistic broad-spectrum antibacterial activity of Hypoxis hemerocallidea-derived silver nanoparticles and streptomycin against respiratory pathobionts. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11, 15222. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93978-z
Asgari, S., Fakhari, Z., Berijani, S. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles coated with carboxymethyl chitosan grafted sodium methacrylate. JNS 4 (1), 55–63. doi: 10.7508/jns.2014.01.007
Baek, Y.-W., An, Y.-J. (2011). Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus aureus. Sci. Total Environ. 409, 1603–1608. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.01.014
Bohan, A. J. (2018). Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nano particles against bacteria isolated from infants with urinary tract infection. Al-Mustansiriyah J. Sci. 29, 34–42. doi: 10.23851/mjs.v29i2.176
Cegelski, L., Marshall, G. R., Eldridge, G. R., Hultgren, S. J. (2008). The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 17–27. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1818
Chaudhary, A., Kumar, N., Kumar, R., Salar, R. K. J. S. A. S. (2019). Antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Aloe vera peel extract. J. Sci. Adv. Stud. 1, 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s42452-018-0144-2
CLSI (2023). CLSI M100-ED33: 2023 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd Edition. Wayne, Pennsylvania, USA.
Costerton, J. W. (2001). Cystic fibrosis pathogenesis and the role of biofilms in persistent infection. Trends Microbiol. 9, 50–52. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(00)01918-1
Dautle, M. P., Wilkinson, T. R., Gauderer, M. W. (2003). Isolation and identification of biofilm microorganisms from silicone gastrostomy devices. J. Pediatr. Surg. 38, 216–220. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2003.50046
Dawwam, G. E., Al-Shemy, M. T., El-Demerdash, A. S. (2022). Green synthesis of cellulose nanocrystal/ZnO bio-nanocomposites exerting antibacterial activity and downregulating virulence toxigenic genes of food-poisoning bacteria. Sci. Rep. 12, 1–18. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21087-6
Desouky, S. E., Nishiguchi, K., Zendo, T., Igarashi, Y., Williams, P., Sonomoto, K., et al. (2013). High-throughput screening of inhibitors targeting Agr/Fsr quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 77, 923–927. doi: 10.1271/bbb.120769
Dhakad, A. K., Ikram, M., Sharma, S., Khan, S., Pandey, V. V., Singh, A. J. P. R. (2019). Biological, nutritional, and therapeutic significance of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 33, 2870–2903. doi: 10.1002/ptr.v33.11
Divya, M., Sowmia, C., Joona, K., Dhanya, K. J. R. J. P. B. C. (2013). Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaf extract and investigation of its antimicrobial activity. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 4, 1137–1142.
Dutka-Malen, S., Evers, S., Courvalin, P. (1995). Detection of glycopeptide resistance genotypes and identification to the species level of clinically relevant enterococci by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33, 24–27. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.1.24-27.1995
Ebrahem, A. F., El-Demerdash, A. S., Orady, R. M., Nabil, N. M. (2024). Modulatory effect of competitive exclusion on the transmission of ESBL E. coli in chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 16, 1087–1098. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10095-1
El-Demerdash, A. S., Mohamady, S. N., Megahed, H. M., Ali, N. M. (2023a). Evaluation of gene expression related to immunity, apoptosis, and gut integrity that underlies Artemisia’s therapeutic effects in necrotic enteritis-challenged broilers. 3 Biotech. 13, 181. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03560-9
El-Demerdash, A. S., Orady, R. M., Matter, A. A., Ebrahem, A. F. (2023b). An alternative approach using nano-garlic emulsion and its synergy with antibiotics for controlling biofilm-producing multidrug-resistant Salmonella in chicken. Indian J. Microbiol. 63 (4), 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s12088-023-01124-2
El-Kattan, N., Emam, A. N., Mansour, A. S., Ibrahim, M. A., Abd El-Razik, A. B., Allam, K. A., et al. (2022). Curcumin-assisted green synthesis of silver and zinc oxide nanostructures and their antibacterial activity against some clinical pathogenic multi-drug resistant bacteria. RSC Adv. 12, 18022–18038. doi: 10.1039/D2RA00231K
El-Mohamedy, R. S., Abdalla, A. M. (2014). Evaluation of antifungal activity of Moringa oleifera extracts as natural fungicide against some plant pathogenic fungi in vitro. J. Adv. Res. 10, 963–982.
El-Telbany, M., Mohamed, A. A., Yahya, G., Abdelghafar, A., Abdel-Halim, M. S., Saber, S., et al. (2022). Combination of meropenem and zinc oxide nanoparticles: antimicrobial synergism, exaggerated antibiofilm activity, and efficient therapeutic strategy against bacterial keratitis. Antibiotics 11, 1374. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101374
Elawady, R., Aboulela, A. G., Gaballah, A., Ghazal, A. A., Amer, A. N. (2024). Antimicrobial Sub-MIC induces Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation without affecting the bacterial count. BMC infectious diseases 24 (1), 1–15. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09790-3
Essawi, W. M., El-Demerdash, A. S., El-Mesalamy, M. M., Abonorag, M. A. (2020). Validation of camel’s fetal fluids as antimicrobial agents. Curr. Microbiol. 77, 1399–1404. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-01945-0
Ew, K. J. C. A., Microbiology, T. O. D. (1997). The Gram-positive cocci. Part II: streptococci, enterococci, and streptococcus-like bacteria. J. Med. Microb. 577–649.
Fadwa, A. O., Alkoblan, D. K., Mateen, A., Albarag, A. M. (2021). Synergistic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and various antibiotics combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinically isolated bacterial strains. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 28, 928–935. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.09.064
Fiedot-Tobola, M., Ciesielska, M., Maliszewska, I., Rac-Rumiłowska, O., Suchorska-Woźniak, P., Teterycz, H., et al. (2018). Deposition of zinc oxide on different polymer textiles and their antibacterial properties. Materials (Basel) 11, 707. doi: 10.3390/ma11050707
García-Solache, M., Rice, L. B. (2019). The Enterococcus: a model of adaptability to its environment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 32, e00058–e00018. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00058-18
Ghaffar, N., Javad, S., Farrukh, M. A., Shah, A. A., Gatasheh, M. K., Al-Munqadhi, B. M., et al. (2022). Metal nanoparticles assisted revival of Streptomycin against MDRS Staphylococcus aureus. PloS One 17, e0264588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264588
Guo, B.-L., Han, P., Guo, L.-C., Cao, Y.-Q., Li, A.-D., Kong, J.-Z., et al. (2015). The antibacterial activity of Ta-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s11671-015-1047-4
Guo, Y., Sun, Z. (2020). Investigating folate-conjugated combinatorial drug loaded ZnO nanoparticles for improved efficacy on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. J. Exp. Nanosci. 15, 390–405. doi: 10.1080/17458080.2020.1785621
Hancock, L. E., Perego, M. (2004). The Enterococcus faecalis fsr two-component system controls biofilm development through production of gelatinase. J. Bacteriol. 186, 5629–5639. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.17.5629-5639.2004
Hashem, Y. A., Amin, H. M., Essam, T. M., Yassin, A. S., Aziz, R. K. (2017). Biofilm formation in enterococci: genotype-phenotype correlations and inhibition by vancomycin. Sci. Rep. 7, 5733. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05901-0
Hashem, N. M., Essawi, W. M., El-Demerdash, A. S., El-Raghi, A. A. (2024). Biomolecule-producing probiotic bacterium Lactococcus lactis in free or nanoencapsulated form for endometritis treatment and fertility improvement in buffaloes. J. Funct. Biomater. 15, 138. doi: 10.3390/jfb15060138
Hassan, A., Usman, J., Kaleem, F., Omair, M., Khalid, A., Iqbal, M. (2011). Evaluation of different detection methods of biofilm formation in the clinical isolates. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 15, 305–311. doi: 10.1016/S1413-8670(11)70197-0
Hayat, S., Muzammil, S., Aslam, B., Siddiquie, M. H., Saqalein, M., Nisar, M. A. (2019). Quorum quenching: role of nanoparticles as signal jammers in Gram-negative bacteria. Future Microbiol. 14, 61–72. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2018-0257
Hu, F., Neoh, K., Kang, E. (2006). Synthesis and in vitro anti-cancer evaluation of tamoxifen-loaded magnetite/PLLA composite nanoparticles. Biomaterials 27, 5725–5733. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.07.014
Jackson, C., Fedorka-Cray, P., Davis, J., Barrett, J., Frye, J. (2009). Prevalence, species distribution and antimicrobial resistance of enterococci isolated from dogs and cats in the United States. J. Appl. Microbiol. 107, 1269–1278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04310.x
Kafil, H. S., Mobarez, A. M., Moghadam, M. F. (2013). Adhesion and virulence factor properties of Enterococci isolated from clinical samples in Iran. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 56, 238. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.120375
Kajihara, T., Nakamura, S., Iwanaga, N., Oshima, K., Takazono, T., Miyazaki, T., et al. (2015). Clinical characteristics and risk factors of enterococcal infections in Nagasaki, Japan: a retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 15, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1175-6
Kamli, M. R., Malik, M. A., Srivastava, V., Sabir, J. S., Mattar, E. H., Ahmad, A. (2021). Biogenic ZnO nanoparticles synthesized from Origanum vulgare abrogates quorum sensing and biofilm formation in opportunistic pathogen Chromobacterium violaceum. Pharmaceutics 13, 1743. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111743
Kataoka, Y., Umino, Y., Ochi, H., Harada, K., Sawada, T. (2014). Antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococcal species isolated from antibiotic-treated dogs and cats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 76, 1399–1402. doi: 10.1292/jvms.13-0576
Kotrange, H., Najda, A., Bains, A., Gruszecki, R., Chawla, P., Tosif, M. M. (2021). Metal and metal oxide nanoparticle as a novel antibiotic carrier for the direct delivery of antibiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 9596. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179596
Kristich, C. J., Rice, L. B., Arias, C. A. (2014). “Enterococcal infection—treatment and antibiotic resistance,” in Enterococci: from commensals to leading causes of drug resistant infection. Washington, D.C., USA: ASM Press (American Society for Microbiology Press).
Krug, H. F., Wick, P. J. A. C. I. E. (2011). Nanotoxicology: an interdisciplinary challenge. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 1260–1278. doi: 10.1002/anie.201001037
Kumar, S. R., Paulpandi, M., Manivelraja, M., Mangalaraj, D., Viswanathan, C., Kannan, S., et al. (2014). An in vitro analysis of H1N1 viral inhibition using polymer coated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4, 13409–13418. doi: 10.1039/c3ra47542e
Lallo da Silva, B., Abucafy, M. P., Berbel Manaia, E., Oshiro Junior, J. A., Chiari-Andreo, B. G., Pietro, R. C. R., et al. (2019). Relationship between structure and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 9395–9410. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S216204
Liu, Y.-J., He, L.-L., Mustapha, A., Li, H., Hu, Z., Lin, M.-S. (2009). Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Appl. Microbiol. 107, 1193–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04303.x
llahverdiyev, A. M., Kon, K. V., Abamor, E. S., Bagirova, M., Rafailovich, M. J. E. R. O. A.-I. T. (2011). Coping with antibiotic resistance: combining nanoparticles with antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 9, 1035–1052. doi: 10.1586/eri.11.121
Magiorakos, A.-P., Srinivasan, A., Carey, R. B., Carmeli, Y., Falagas, M., Giske, C., et al. (2012). Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18, 268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x
Masák, J., ČeJKOVÁ, A., Schreiberová, O., Řezanka, T. (2014). Pseudomonas biofilms: possibilities of their control. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 89, 1–14. doi: 10.1111/fem.2014.89.issue-1
Massol-Deya, A. A., Odelson, D. A., Hickey, R. F., Tiedje, J. M. (1995). Bacterial community fingerprinting of amplified 16S and 16–23S ribosomal DNA gene sequences and restriction endonuclease analysis (ARDRA). Mol. Microb. Ecol. Manual, 289–296.
Mathur, T., Singhal, S., Khan, S., Upadhyay, D., Fatma, T., Rattan, A. (2006). Detection of biofilm formation among the clinical isolates of staphylococci: an evaluation of three different screening methods. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 24, 25–29. doi: 10.1016/S0255-0857(21)02466-X
May, J., Shannon, K., King, A., French, G. (1998). Glycopeptide tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 42, 189–197. doi: 10.1093/jac/42.2.189
Miller, M. B., Bassler, B. L. (2001). Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 165–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165
Mohamed, J. A., Huang, W., Nallapareddy, S. R., Teng, F., Murray, B. E. (2004). Influence of origin of isolates, especially endocarditis isolates, and various genes on biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis. Infect. Immun. 72, 3658–3663. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.6.3658-3663.2004
Mohamed, J. A., Murray, B. E. (2005). Lack of correlation of gelatinase production and biofilm formation in a large collection of Enterococcus faecalis isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 5405–5407. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.10.5405-5407.2005
Nabiyouni, G., Barati, A., Saadat, M. (2011). Surface adsorption of polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol with variable molecular weights on zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mol. Microbiol. 41, 145–154.
Nakayama, J., Cao, Y., Horii, T., Sakuda, S., Akkermans, A. D., de Vos, W. M., et al. (2001). Gelatinase biosynthesis-activating pheromone: a peptide lactone that mediates a quorum sensing in Enterococcus faecalis. Mol. Microbiol. 41, 145–154. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02486.x
Nakayama, J., Kariyama, R., Kumon, H. (2002). Description of a 23.9-kilobase chromosomal deletion containing a region encoding fsr genes which mainly determines the gelatinase-negative phenotype of clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecalis in urine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 3152–3155. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.6.3152-3155.2002
Nava, G., Piñón, E., Mendoza, L., Mendoza, N., Quintanar, D., Ganem, A. (2011). Formulation and in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of elastic liposomes for transdermal delivery of ketorolac tromethamine. Pharmaceutics 3, 954–970. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics3040954
Nishanthi, R., Malathi, S., Palani, P. J. M. S., C, E. (2019). Green synthesis and characterization of bioinspired silver, gold and platinum nanoparticles and evaluation of their synergistic antibacterial activity after combining with different classes of antibiotics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 96, 693–707. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.050
Oguttu, J. W., Qekwna, D. N., Odoi, A. (2021). Prevalence and predictors of antimicrobial resistance among Enterococcus spp. from dogs presented at a veterinary teaching hospital, South Africa. Front. Vet. Sci. 7, 589439. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.589439
Ossiprandi, M. C., Zerbini, L. (2015). Antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococcal species isolated from Italian dogs. Antimicrob. Resist. Open Access, 35–50. doi: 10.5772/59829
Pereira, U. A., Barbosa, L. C., Maltha, C. R., Demuner, A. J., Masood, M. A., Pimenta, A. L. (2014). Inhibition of Enterococcus faecalis biofilm formation by highly active lactones and lactams analogues of rubrolides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 82, 127–138. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.05.035
Popović, N., Dinić, M., Tolinački, M., Mihajlović, S., Terzić-Vidojević, A., Bojić, S., et al. (2018). New insight into biofilm formation ability, the presence of virulence genes and probiotic potential of Enterococcus sp. dairy isolates. Front. Microbiol. 9, 78. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00078
Qin, X., Singh, K. V., Weinstock, G. M., Murray, B. E. (2001). Characterization of fsr, a regulator controlling expression of gelatinase and serine protease in Enterococcus faecalis OG1RF. J. Bacteriol. 183, 3372–3382. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.11.3372-3382.2001
Raghunath, A., Perumal, E. (2017). Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 49, 137–152. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.11.011
Reddy, L. S., Nisha, M. M., Joice, M., Shilpa, P. (2014). Antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticle against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pharm. Biol. 52, 1388–1397. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.893001
Roberts, J. C., Singh, K. V., Okhuysen, P. C., Murray, B. E. (2004). Molecular epidemiology of the fsr locus and of gelatinase production among different subsets of Enterococcus faecalis isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 2317–2320. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.5.2317-2320.2004
Saad, M. F., Elsayed, M. M., Khder, M., Abdelaziz, A. S., El-Demerdash, A. S. (2024). Biocontrol of multidrug resistant pathogens isolated from fish farms using silver nanoparticles combined with hydrogen peroxide insight to its modulatory effect. Sci. Rep. 14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58349-4
Salam, H. A., Sivaraj, R., Venckatesh, R. (2014). Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Ocimum basilicum L. var. purpurascens Benth.-Lamiaceae leaf extract. Mater. Lett. 131, 16–18. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.05.033
Salar, R. K., Sharma, P., Kumar, N. (2015). Enhanced antibacterial activity of streptomycin against some human pathogens using green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Res. Rev. J. Eng. Technol. 1, 106–115.
Sangani, M. H., Nakhaei Moghaddam, M., Forghanifard, M. M. (2015). Inhibitory effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Nanomed J 2(2), 121–128. doi: 10.7508/nmj.2015.02.004
Sawant, V., Bamane, S. (2018). PEG-beta-cyclodextrin functionalized zinc oxide nanoparticles show cell imaging with high drug payload and sustained pH responsive delivery of curcumin in to MCF-7 cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 43, 397–408. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2017.11.010
Şchiopu, P., Toc, D. A., Colosi, I. A., Costache, C., Ruospo, G., Berar, G., et al. (2023). An overview of the factors involved in biofilm production by the Enterococcus genus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 11577. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411577
Sedgley, C., Molander, A., Flannagan, S., Nagel, A., Appelbe, O., Clewell, D., et al. (2005). Virulence, phenotype and genotype characteristics of endodontic Enterococcus spp. Oral. Microbiol. Immunol. 20, 10–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2004.00180.x
Selvaraj, V., Sagadevan, S., Muthukrishnan, L., Johan, M. R., Podder, J. (2019). Eco-friendly approach in synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of optical, surface morphological and antimicrobial properties. J. Nanomater. 9, 153–162. doi: 10.1007/s40097-019-0306-9
Sharaf, M., Arif, M., Khan, S., Abdalla, M., Shabana, S., Chi, Z., et al. (2021). Co-delivery of hesperidin and clarithromycin in a nanostructured lipid carrier for the eradication of Helicobacter pyloriin vitro. Bioorg. Chem. 112, 104896. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104896
Sharaf, M., Sewid, A. H., Hamouda, H., Elharrif, M. G., El-Demerdash, A. S., Alharthi, A., et al. (2022). Rhamnolipid-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Novel Multitarget Candidate against Major Foodborne E. coli Serotypes and Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e00250–e00222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00250-22
Shinde, S. S. (2015). Antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Sci. Med. Cent. 3, 1033.
Shojima, A., Nakayama, J. (2014). Quorum sensing in gram-positive bacteria: assay protocols for staphylococcal agr and enterococcal fsr systems. Microb. Biofilms: Methods Protoc., 33–41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0467-9_3
Sindhanai, V., Avanthiga, S., Suresh Chander, V. (2016). Antibiotic susceptibility pattern of biofilm forming and biofilm non forming enterococci species. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 15, 33–37.
Singh, R. P., Nakayama, J. (2014). “Development of quorum-sensing inhibitors targeting the fsr system of Enterococcus faecalis,” in Quorum Sensing vs Quorum Quenching: A Battle with No End in Sight (Springer).
Sruthi, S., Ashtami, J., Mohanan, P. V. (2018). Biomedical application and hidden toxicity of Zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Chem. 10, 175–186. doi: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2018.09.008
Tambekar, D., Dhanorkar, D., Gulhane, S., Khandelwal, V., Dudhane, M. (2006). Antibacterial susceptibility of some urinary tract pathogens to commonly used antibiotics. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 5, 1562–1565.
Tan, F., She, P., Zhou, L., Liu, Y., Chen, L., Luo, Z., et al. (2019). Bactericidal and anti-biofilm activity of the retinoid compound CD437 against Enterococcus faecalis. Front. Microbiol. 10, 2301. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02301
Tang, W., Jimenez-Oses, G., Houk, K., van der Donk, W. A. (2015). Substrate control in stereoselective lanthionine biosynthesis. Nat. Chem. 7, 57–64. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2113
Tumpa, A., Štritof, Z., Pintarić, S. (2022). Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterococcus spp. from urine of dogs and cats in northwestern Croatia. Res. Vet. Sci. 151, 42–46. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.04.015
Wang, L., Hu, C., Shao, L. (2017). The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 1227. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S121956
Wang, Z., Lee, Y.-H., Wu, B., Horst, A., Kang, Y., Tang, Y. J., et al. (2010). Anti-microbial activities of aerosolized transition metal oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 80, 525–529. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.047
Weese, J. S., Blondeau, J. M., Boothe, D., Breitschwerdt, E. B., Guardabassi, L., Hillier, A., et al. (2011). Antimicrobial use guidelines for treatment of urinary tract disease in dogs and cats: antimicrobial guidelines working group of the international society for companion animal infectious diseases. Vet. Med. Int. 2011, 1–9. doi: 10.4061/2011/263768
Werner, G., Coque, T., Hammerum, A., Hope, R., Hryniewicz, W., Johnson, A., et al. (2008). Emergence and spread of vancomycin resistance among enterococci in Europe. Eurosurveillance 13, 19046. doi: 10.2807/ese.13.47.19046-en
Xiao, X., Wang, J., Meng, C., Liang, W., Wang, T., Zhou, B., et al. (2020). Moringa oleifera Lam and its therapeutic effects in immune disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 566783. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.566783
Keywords: Enterococcus faecalis, Moringaoleifera Lam, hexagonal nanoencapsulation, multi-drug resistance, biofilm
Citation: Sewid AH, Sharaf M, El-Demerdash AS, Ragab SM, Al-Otibi FO, Taha Yassin M and Liu C-G (2025) Hexagonal zinc oxide nanoparticles: a novel approach to combat multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecalis biofilms in feline urinary tract infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1505469. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1505469
Received: 02 October 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 24 January 2025.
Edited by:
Luminita Marutescu, University of Bucharest, RomaniaReviewed by:
Joel E. Lopez-Meza, Michoacana University of San Nicolás de Hidalgo, MexicoRodrigo Esparza, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Sewid, Sharaf, El-Demerdash, Ragab, Al-Otibi, Taha Yassin and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Azza S. El-Demerdash, ZHIuYXp6YXNhbGFoQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; ZHJhenphQGFocmkuZ292LmVn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Alaa H. Sewid1,2†
Alaa H. Sewid1,2† Mohamed Sharaf
Mohamed Sharaf Azza S. El-Demerdash
Azza S. El-Demerdash Mohamed Taha Yassin
Mohamed Taha Yassin Chen-Guang Liu
Chen-Guang Liu