- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University (The Second People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province), Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Qujing Hospital of Kunming Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Qujing), Qujing, Yunnan, China
- 3Department of General Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University (The Second People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province), Kunming, Yunnan, China
Klebsiella michiganensis is an emerging hospital-acquired bacterial pathogen, particularly strains harboring plasmid-mediated carbapenemase genes. Here, we recovered and characterized a multidrug-resistant strain, blaKPC-2–producing Klebsiella michiganensis LS81, which was isolated from the abdominal drainage fluid of a clinical patient in China, and further characterized the co-harboring plasmid. K. michiganensis LS81 tested positive for the blaKPC-2 genes by PCR sequencing, with blaKPC-2 located on a plasmid as confirmed by S1 nuclease pulsed-field gel electrophoresis combined with Southern blotting. In the transconjugants, the blaKPC-2 genes were successfully transferred to the recipient strain E. coli EC600. Whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis confirmed that this strain belongs to sequence type 196 (ST196), with a complete genome comprising a 5,926,662bp circular chromosome and an 81,451bp IncM2 plasmid encoding blaKPC-2 (designated pLS81-KPC). The IncM2 plasmid carried multiple β-lactamase genes such as blaTEM-1B, blaCTX-M-3, and blaKPC-2 inserted in truncated Tn6296 with the distinctive core structure ISKpn27–blaKPC-2–ISKpn6. A comparison with 46 K. michiganensis genomes available in the NCBI database revealed that the closest phylogenetic relative of K. michiganensis LS81 is a clinical isolate from a wound swab in the United Kingdom. Ultimately, the pan-genomic analysis unveiled a substantial accessory genome within the strain, alongside significant genomic plasticity within the K. michiganensis species, emphasizing the necessity for continuous surveillance of this pathogen in clinical environments.
Introduction
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) infections are characterized by increased prevalence, severe disease manifestations, longer hospital stays, higher healthcare costs, and increased mortality rates compared to susceptible carbapenem infections, thereby exacerbating a considerable global burden (Perez and Bonomo, 2019). In the 2024 updated WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, CRE is classified as a critical group due to their ability to transfer resistance genes, which have been an urgent and continuous threat to global public health. An important mechanism for carbapenem resistance in CRE is the production of carbapenemases such as K. pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC). KPC is a class A serine β-lactamase that belongs to group 2f in the Bush classification. KPC-2 is the most commonly identified variant that can efficiently hydrolyze all β-lactam antimicrobials, including carbapenems (Ding et al., 2023). The drastic increase in antibiotic-resistant strains exacerbates the failure to cure, posing a significant challenge to clinical anti-infective treatments.
Klebsiella michiganensis is an emerging species of pathogenic Klebsiella, one of the nine species of Klebsiella oxytoca complex (Yang et al., 2022). K. michiganensis has continued to spread in clinical settings, colonizing patients and causing nosocomial infections since it was first discovered in a toothbrush holder in 2012 (Saha et al., 2013). The clonal background of clinical isolates of K. michiganensis remains poorly understood and accurate species identification relies on genome sequencing and analysis. The chromosome-encoded OXY-type β-lactamase in K. michiganensis confers resistance to amino- and carboxy-penicillins. This species also acquires extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) and carbapenemases through horizontal gene transfer (HGT), similar to other Enterobacteriaceae (Campos-Madueno et al., 2021). They also cause infections with severe clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients and can even lead to the outbreaks of clonal isolates (Chapman et al., 2020).
Carbapenemase genes can be horizontally transferred between resistant and susceptible strains via transposons and conjugative plasmids, enabling the rapid spread of resistance genes among Enterobacteriaceae and contributing to increasing CRE infections. Tn4401 is a removable element that commonly carries the blaKPC-2 gene in Europe, Brazil, and the United States (Furlan et al., 2023). In Asia, blaKPC-2 is mainly located on different variants of Tn1721-like transposons (Tang et al., 2017). Typical transposons Tn4401 and Tn1721, both members of the Tn3 family, have been demonstrated to mobilize the blaKPC-2 at high transposition frequencies (Tang et al., 2022). Here, we characterized a blaKPC-2–producing IncM2 plasmid harboring transposon ΔTn6296 in K. michiganensis LS81 recovered from a patient at a university-affiliated hospital in China. The ability of this strain to transfer the blaKPC-2 genes was assessed by conjugation experiments. The genetic structure and location of the resistance genes on the IncM2 plasmid were analyzed through S1 nuclease pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (S1-PFGE) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS). Our comparison with the whole-genome sequence available from NCBI of K. michiganensis strains carrying blaKPC-2 aimed to discern the driving force behind the blaKPC-2 IncM2 plasmids.
Materials and methods
Patient characteristics and strain screening
A 65-year-old Chinese man admitted to the Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University (Kunming, China) with no history of travel outside China was diagnosed with severe pneumonia in 2021, and strain LS81 was isolated in the clinical laboratory from this patient’s abdominal drainage fluid in February. Klebsiella oxytoca was initially identified as the pathogen from his culture by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS) (Bruker Daltonik GmbH, Bremen, Germany).
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing and carbapenemase-producing organism characterization
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of cefoperazone-sulbactam, piperacillin-tazobactam, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, ceftazidime,ceftriaxone, cefepime, ertapenem, imipenem, amikacin, levofloxacin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and cefuroxime was done using the bioMérieux VITEK2. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values were interpreted according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute document M100-S32 (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2022). Quality control was conducted using the E. coli ATCC 25922 and K. pneumoniae ATCC BAA-1705. The modified carbapenem inactivation method (mCIM) in conjunction with the EDTA-modified carbapenem inactivation method (eCIM) test was utilized for phenotypic detection of carbapenemase enzymes. PCR amplification was employed to identify major carbapenemase resistance genes (blaKPC-2, blaNDM-1, blaOXA-48, blaVIM-2, and blaIMP).
Conjugl transfer and location of blaKPC-2 gene
The transferability of the blaKPC-2 gene was determined by the broth mating conjugal method, using the previously described protocol with some adjustments (Prah et al., 2021). The LS81 strain was mixed with rifampicin-resistant E. coli EC600 in a volume ratio of 1:2, with LS81 as donor strain and E. coli EC600 as recipient strain. The plates were incubated at 35°C overnight, and transconjugants were selected on Mueller-Hinton agar plates containing rifampicin (600 μg/mL) and imipenem (1 μg/mL; Solarbio, Beijing, China). PCR sequencing confirmed the presence of the plasmid carrying blaKPC-2. To determine the location of the blaKPC-2 gene in the LS81 strain, we performed pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) after S1 restriction enzyme digestion. This was followed by Southern blotting with a digoxigenin-labeled KPC-2 gene probe to localize and fingerprint the plasmid, based on a previous report with some modifications (Bi et al., 2018). DNA isolation was conducted on 1% agarose gel (SeaKem Gold) in 0.5× Tris-borate-EDTA buffer (TBE) in the CHEF-Mapper XA system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) for 18 h, under the following conditions: field strength of 6 V/cm², angles of 120°, initial switching time of 2.2 s, final pulse time of 63.8 s, and temperature of 14°C.
Whole-genome sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted by SDS extraction combined with column purification. The LS81 strain’s whole genome was sequenced by both Illumina Novaseq 6000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, United States) and Oxford Nanopore PromethION 24 (Nanopore, Oxford, United Kingdom) sequencing technology platforms. Unicycler (Wick et al., 2017) assembled high-accuracy Illumina reads (Q30 > 85%) to obtain high-quality bacterial genome backbones and Nanopore data connected high-quality contig, and Pilon (Walker et al., 2014) was used to correct assembled genomes.
Genome component prediction, sequence annotation, and protein classification
RAST 2.0 (Overbeek et al., 2014) combined with BLAST database against UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot (The UniProt Consortium, 2023) and RefSeq (O’leary et al., 2016) databases was used to predict open reading frames and pseudogenes. Annotation of resistance genes, multilocus sequence typing (MLST), and plasmid replicon types was done using bioinformatics tools from the Center for Genomic Epidemiology (Zankari et al., 2012). Plasmids were analyzed for removable element information using ISfinder (Siguier et al., 2006) and Tn Number Registry (Tansirichaiya et al., 2019). Finally, the data were visualized using software R version 4.0.4 and Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) 1.1 to further map the genetic background.
Phylogenetic analysis
To explore the global genomic epidemiology of K. michiganensis strains carrying blaKPC-2, we conducted phylogenetic analysis between strain LS81 and other K. michiganensis strains carrying blaKPC-2, using data from the NCBI GenBank database to 6 May 2024. We obtained genome sequences and strain metadata for 993 isolates of K. michiganensis, of which 49 strains were found to carry blaKPC-2 resistance gene. After excluding three potentially contaminated strains, we conducted a phylogenetic analysis on the remaining 46 strains (Supplementary Table S1). Klebsiella pneumoniae HS11286 was used as an outgroup in the analysis because of its close phylogenetic group. OrthoFinder (Emms and Kelly, 2015) clustered protein sequences into orthologous protein families, screened 2,924 single-copy gene families for phylogenetic analysis, and used MAFFT (Katoh et al., 2019) to align protein sequences, iteratively comparing 1,000 replicates. TrimAI (Capella-Gutiérrez et al., 2009) trimmed sequences and SeqKit (Shen et al., 2024) integrated with these trimmed alignment results of 2,924 protein families into a super-sequence matrix, finally, Iqtree2 (Minh et al., 2020) constructed a maximum likelihood tree.
Data availability
All reads generated in this study were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database. The genome sequences of the K. michiganensis LS81 chromosome and plasmid pLS81-KPC were submitted to GenBank with the accession numbers CP089448 and CP089449. The phylogenetic analysis used Klebsiella pneumoniae HS11286 as the outgroup genome, with the NCBI RefSeq assembly number GCF_000240185.1.
Results
Bacterial identification, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and conjugal transfer of blaKPC-2
Strain LS81 was found to be mCIM-positive and eCIM-negative. Subsequently, the blaKPC-2 gene was identified in this strain through sequencing of the PCR-positive products. It was initially misidentified as K. oxytoca by MALDI-TOF/MS and finally reclassified as K. michiganensis by WGS. In accordance with the CLSI breakpoint criteria, strain LS81 was resistant to almost all β-lactam antibiotics tested, including carbapenems (imipenem), cefuroxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefepime, cefoperazone-sulbactam, piperacillin-tazobactam, and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, whereas it was susceptible to quinolones (amikacin and levofloxacin) and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Table 1). Conjugl transfer showed that strain LS81 successfully transferred blaKPC-2 into E. coli EC600, as confirmed by PCR sequencing. The transconjugate was the blaKPC-2–encoding E. coli EC600 (designated H-LS81), which had similar antibiotic resistance to strain LS81 (Table 1).
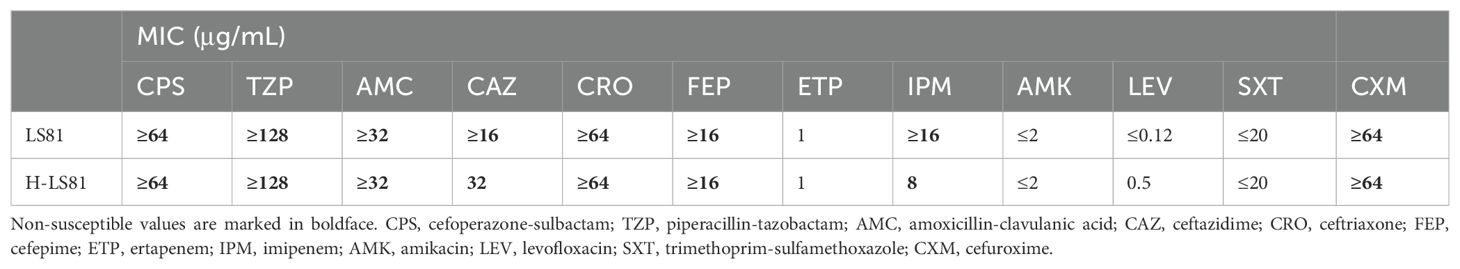
Table 1. Minimum inhibitory concentration(MIC) of antimicrobials for K. michiganensis LS81 and transconjugant H-LS81.
Genomics features of K. michiganensis LS81
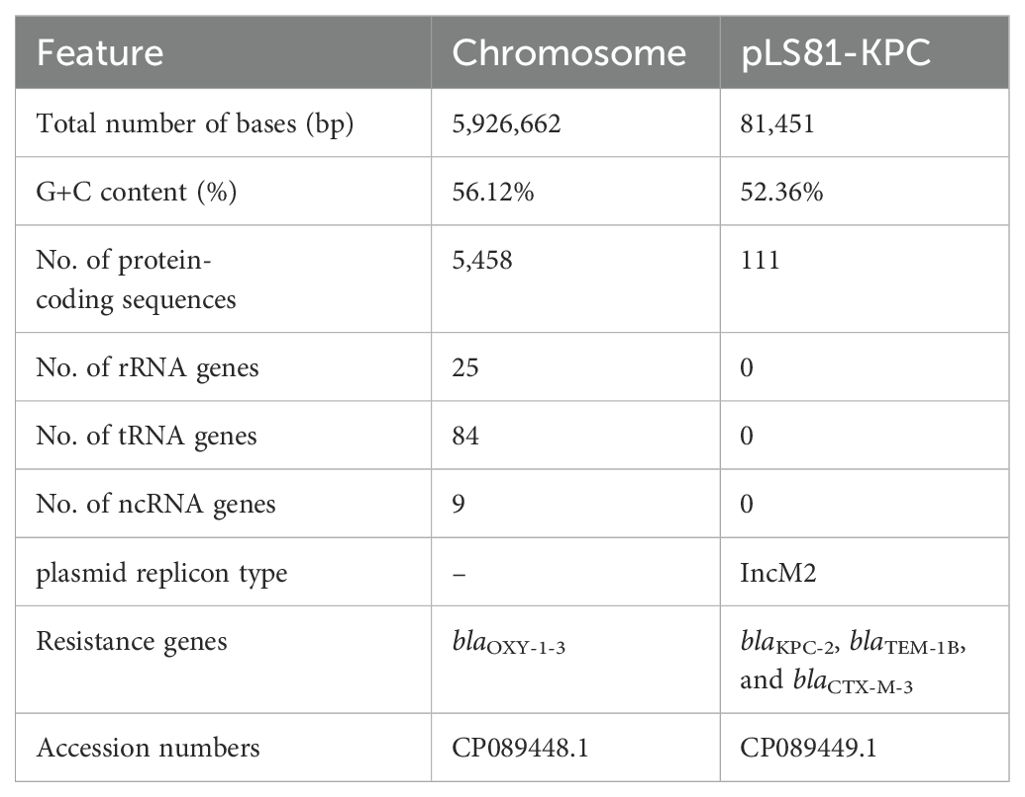
Accurate species identification depends on genome sequencing and analysis. The genome of K. michiganensis LS81 consists of a circular chromosome of 592662 bp and a plasmid. The average G+C content of the chromosomes was 56.12%, which contained 5,458 protein-coding genes, 25 ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), and 84 transfer RNAs (tRNAs). Screening for drug resistance gene information revealed that the chromosome contains the blaOXY-1-3 gene and that the plasmid pLS81-KPC carries the β-lactam antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs): blaKPC-2, blaTEM-1B, and blaCTX-M-3 (Table 2).
Characterization of plasmid pLS81-KPC
S1-PFGE and Southern blotting showed the blaKPC-2 gene located on a plasmid of approximately ~80-kb (Supplementary Figure S1). WGS confirmed that the pLS81-KPC plasmid was a circular DNA of 81,451-bp with 111 open reading frames and an average G+C content of 52.36%. The replication initiation region is composed of the repABC family, and the stable region is mainly composed of an independent part of the long 27.2-kb segment, including pemI, pemK, mucA, mucB, parA, and parB. The conjugation transfer region consists of two distant tra regions (22.8-kb) and a trb region (4.7-kb) of different lengths (Figure 1A). Incompatibility plasmid classification showed that pLS81-KPC is an IncM2-type plasmid, having the same replication subtype as the reference plasmid pCTX-M3 (accession number: AF550415), two plasmids with 77% coverage, 99% nucleotide consistency, and the stable region and the conjugation transfer region were essentially the same (Figure 1B). The exogenous insertion region of pLS81-KPC was mainly composed of two antibiotic-resistant regions: the blaKPC-2 region and ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-3 unit. Located between the repABC replication initiation region and the trb plasmid conjugation transfer region, the full length of the blaKPC-2 region is about 16.7-kb. In the ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-3 transposable unit, because there is no obvious site selection for ISEcp1 insertion, they move as an integral mobile element, facilitating blaCTX-M spread and replication. The blaKPC-2 gene lies between ISKpn27 and ISKpn6, forming an ISKpn27–blaKPC-2–ISKpn6 core structure. As Tn1722-3′ is truncated, it forms a variant of Tn6296; the ΔTn6296 transposon constituted the core genetic environment of blaKPC-2 (Figure 1C).
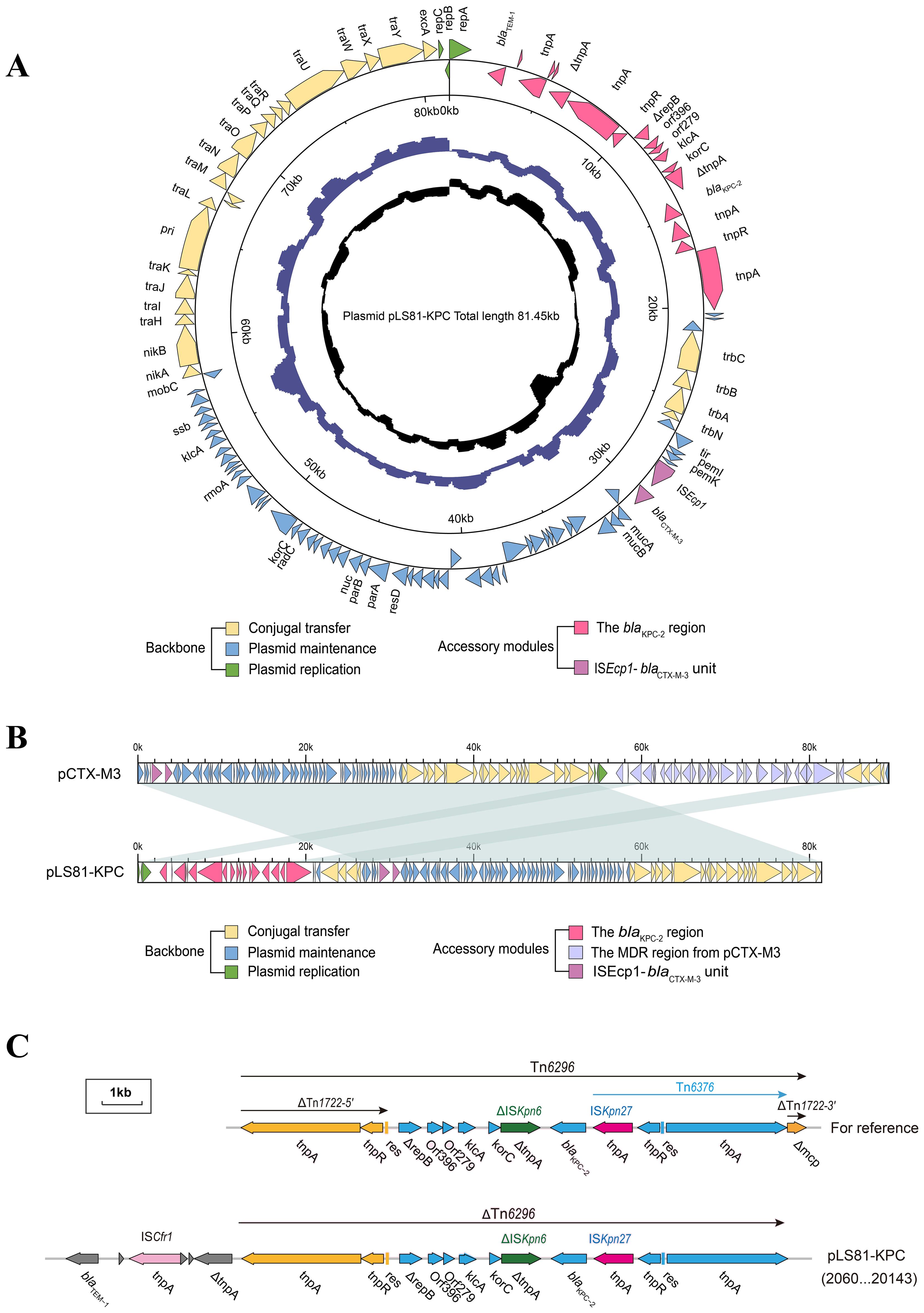
Figure 1. Genes are indicated by arrows; backbone and accessory modules are colored differently. Shading denotes regions of homology (>95% nucleotide identity). (A) Circular map of pLS81-KPC. The intermediate ring and the innermost ring represent the GC content and the GC-skew [(G − C)/(G + C)]. (B) Linear comparison of the IncM2 plasmids pLS81-KPC and pCTX-M3. (C) Linear comparison of the Tn6296 and the genetic structure surrounding the blaKPC-2 region in the plasmids pLS81-KPC.
Phylogenetic trees of carrying blaKPC-2K. michiganensis
To correlate the genetic information of K. michiganensis strains carrying blaKPC-2, phylogenetic tree analysis based on protein sequences was performed to further explore their population structure, evolutionary relationships, and internal genome structure. We collected 46 K. michiganensis genomes that had average nucleotide identity (ANI) values of ≥95% based on K. michiganensis reference strain THO-011. A total of 46 K. michiganensis hosts from 32 Homo sapiens, 13 environments, and one food are shown in Figure 2 and Supplementary Table S1. They came from different countries, mainly from China (n = 22), followed by Germany (n = 9), the USA (n = 7), the United Kingdom (n = 3), and Ecuador (n = 2), the remaining three strains were from Brazil, the Czech Republic, and Canada, and dated from 1997 to 2023. Phylogenetic analysis showed that K. michiganensis carrying blaKPC-2 could be divided into two major clades on the tree, with the second clade further subdivided into two subclades. It is noteworthy that K. michiganensis LS81 and ARGID_31165 share a common ancestral node, show an unequivocal bootstrap value of 100% through the neighbor-joining analysis, and indicate that K. michiganensis LS81 may have evolved from a subspecies of this strain, ARGID_31165 from a homo sapiens wound swab from the United Kingdom 2019. Further analysis of the genomic information showed that, except for blaKPC-2, K. michiganensis LS81 and ARGID_31165 contained blaOXY and blaTEM-1 genes, but, as different variants, they had no common plasmid replicon type and MLST type.

Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella michiganensis LS81 and 45 other K. michiganensis isolates based on core genomes. Klebsiella pneumoniae HS11286 used as outgroup in analysis. The figure provides information on the antimicrobial resistance genes, host, country, date of collection, and MLST type of these strains. Detailed information on the isolates included in this study is summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
We detected 152 plasmids with 35 subtypes of inc gene variants, grouped into 11 different types: IncF, IncH, IncN, IncM, IncU, IncX, IncP, IncC, IncR, IncQ, and Col; the most frequently detected inc types were IncFII, IncFIB, and IncN (Supplementary Table S1). We investigated the drug resistance profiles of K. michiganensis strains and identified a total of 44 resistance genes (Figure 2). Except for the blaKPC-2 gene, blaOXY is prevalent in all strains (46/46) and exists as blaOXY variants (blaOXY-1, blaOXY-2, and blaOXY-5), followed by sul1 in sulfonamide (35/46). blaCTX-M, blaTEM, blaOXA, and blaSHV were detected in 36 strains as major ARGs for ESBLs. We screened for the gene encoding carbapenem resistance, and 11 strains even carried other carbapenemase genes such as blaIMP-4, blaNDM-1, and blaNDM-5.
Discussion
The increasing prevalence and spread of the carbapenem resistance gene blaKPC-2 poses a serious threat to public health, the blaKPC-2 gene has been widely detected in different hosts. In recent years, other Enterobacteriaceae strains producing KPC-2 have been identified, including Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter freundii, Serrella marcescens, and Protesus mirabilis (Stewardson et al., 2019). K. michiganensis can colonize in the skin, mouth, intestines, and respiratory tract of healthy individuals and patients, and it is considered an opportunistic pathogen causing clinical infections. The extant studies highlight its critical clinical importance as a nosocomial pathogen, particularly in patients with underlying conditions causing multiple infections (Meng et al., 2022). Research has reported a propensity for K. michiganensis to cause bloodstream infections in immunocompromised individuals and severe, potentially fatal gastrointestinal damage in premature infants (Chen et al., 2020).
Nonetheless, research into the full pathological implications of K. michiganensis remains limited. Owing to the capacity of MALDI-TOF/MS to rapidly identify the species level of pathogenic microorganisms, its application in clinical microbiology laboratories has proliferated in recent years. However, the reference spectra for these novel bacterial species may be absent from most laboratories’ MALDI-TOF/MS databases, complicating the differentiation of each species within the K. oxytoca complex. In some cases, distinguishing K. michiganensis from the K. oxytoca complex requires reliance on genomic analysis techniques such as WGS, which are not readily available in standard clinical laboratories, posing a significant challenge to accurate Klebsiella species identification. As K. michiganensis is often mistakenly identified as K. oxytoca, it is conceivable that some clinical conditions ostensibly due to K. oxytoca may actually be caused by K. michiganensis.
The blaKPC-2 gene can be transferred by plasmids, transposons, integrons and so on, and the critical step is HGT of mobile genetic elements (MGEs) around this determinant. Plasmids are MGEs that can replicate independently of the chromosome, and many carry genes encoding beneficial phenotypes for the survival of host strains, such as antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and virulence (Grodner et al., 2024). The IncM2 plasmid carrying blaKPC-2 in K. michiganensis LS81 could be autonomously transferred into E. coli EC600, the resistance phenotype of the conjugate was obtained by the pLS81-KPC plasmid. It is noteworthy that K. michiganensis LS81 and the transconjugant H-LS81 have similar drug resistance, and the transconjugant strain once cloned will pose significant clinical challenges.
Conjugative plasmids are considered to be the primary vectors for the dissemination of AMR because of their ability to transfer horizontally between bacteria, ensure their stability through toxin-antitoxin and distribution systems, and offset their own fitness costs through mutation (Partridge et al., 2018). Among the 46 blaKPC-2–producing K. michiganensis genomes included in our study, 35 different plasmid subtypes were detected, with the most common Inc types being IncFII, IncFIB, and IncN. Similar to the report on the K. oxytoca complex, blaKPC-2 is mainly found on IncN or IncF plasmids (Yang et al., 2022). The diversity of plasmid backgrounds in these isolates may provide opportunities for blaKPC-2 exchange between different plasmid families. IncL/M plasmids were previously classified in the same incompatibility group, but, after verification that they were compatible with each other, IncL and IncM plasmids were separated into two different incompatibility groups with an overall nucleotide identity of about 94% (Getino et al., 2022). IncM plasmid poses a threat due to its broad host range and increasing prevalence in clinical, animal, and environmental isolate (Rozwandowicz et al., 2018). In our study, K. michiganensis pLS81-KPC carrying blaCTX-M3 had almost the same stable region and conjugal transfer region as the IncM2 reference plasmid pCTX-M3, derived from a Citrobacter freundii isolate from Poland (Gołebiewski et al., 2007). As reported, the IncM pCTX-M-3 plasmid can even combine with other plasmid systems to exhibit more complex replication and transfer behavior, while the range of recipients of its conjugation system is broad, including α-, β-, and γ-proteobacteria and also Firmicutes (Kern-Zdanowicz, 2021).
In investigating neonatal sepsis in several low- and middle-income countries within Africa and South Asia, it has been found that diverse strains shared identical plasmid types and exhibited the same carbapenemase gene variants, indicating the potential occurrence of successful dissemination and acquisition across multiple species (Sands et al., 2021). Moreover, the discovery of identical carbapenemase ARGs across diverse plasmids substantiates the extensive dissemination of AMR (Brandt et al., 2019). In Germany, researchers observed a widespread distribution of the blaKPC-2 gene across various species, a process enabled by both intra- and inter-species HGT involving a unique IncN plasmid; this transfer also resulted in the rise of highly antibiotic-resistant bacteria that possess up to 14 additional ARGs encoded on the same plasmid (Yao et al., 2024). These findings underscore the pivotal role of MGEs in enabling the worldwide dissemination of resistance via HGT among a diverse array of bacterial species.
In genetic variation and evolution of bacteria, transposable elements play an important role. The blaKPC-2 gene is mainly located in the Tn4401 and Tn1721 transposable elements. Deletions or insertions at different sites in Tn4401 divide the gene into subtypes; there are at least nine subtypes of Tn4401a–Tn4401I, of which Tn4401a and Tn4401b are the most common (Araújo et al., 2018). The Tn1721 variant has been reported to be the dominant structure in Asia, particularly in China, and the structure of the Tn1721 variant in the blaKPC-2 epidemic is complex and diverse. In 2016, a scientific research team in China studied the genetic environment of the blaKPC-2 gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates and found that blaKPC-2 is located in two types of genetic structures, Tn1721–blaKPC-2–Tn3 and Tn1721– blaKPC-2–ΔTn3-IS26 (Shen et al., 2016). In 2022, this team again reported that transposition of the Tn1721 variant promoted the evolution and spread of the KPC-2 plasmid in Enterobacteriaceae, blaKPC-2 can be located on three different variants of Tn1721, A1-type (Tn1721-blaKPC-2), A2-type (Tn1721–blaKPC-2–IS26), and B-type (Tn1721–blaKPC-2–IRL2) (Tang et al., 2022).
Tn6296, a transposon of the Tn3 family originally identified in the Klebsiella pneumoniae plasmid pKP048 (Jiang et al., 2010). The core structure of Tn6376–blaKPC-2–ΔISKpn6-korC-klcA-orf279-orf396-ΔrepB was inserted into Tn1722, truncated and split into ΔTn1722-5′ and ΔTn1722-3′. Unlike the most common blaKPC-2–producing mobile element transposon, the Tn6296/Tn6376 chimera may have evolved by recombination of the Tn4401. Insertions and deletions in the exogenous insertion region blaKPC-2 lead to different ΔTn6296 variant structures, and different lengths of truncated Tn6296 can be observed on different plasmids. Tn6296-derived complex transposons are present in common species of Enterobacteriaceae, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae pHS062105-3 (Shanghai, China, KF623109), Klebsiella pneumoniae pVA833-92 (Santiago de Chile, Chile, CP093457), and many other bacterial species such as Serratia marcescens pKPC-2-HENAN1602 (Zhengzhou, China, CP047392) (Wang et al., 2022b), Citrobacter freundii PP10159-3 (Chongqing, China, MF072963) (Ouyang et al., 2018), Aeromonas hydrophila PK522-A-KPC and pK522-B-KPC (Taizhou, China, CP118700, CP118703) (Jing et al., 2024), Citrobacter koseri pCK1008-KPC-123 (Hangzhou, China, ON209376) (Wang et al., 2022a), Aeromonas media pE31A (Jinan, China, CP067418), and Klebsiella aerogenes pC212158-KPC_75k (Hangzhou, China, CP139398) (Li et al., 2024). Tn6296-derived complex transposons show diversity in bacterial clones carrying the blaKPC-2 gene. Notably, they share a common core structure ISKpn27–blaKPC-2–ISKpn6, we speculate that ISKpn27–blaKPC-2–ISKpn6 may be the main genetic structure in the gene microenvironment carrying blaKPC-2. These transposons not only carry the blaKPC-2 gene but can also contain other ARGs, forming complex chimeric structures for rapid adaptation and evolution under antibiotic selection pressure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study is the first to characterized a blaKPC-2–producing IncM2 plasmid pLS81-KPC harboring transposon ΔTn6296 in K. michiganensis strain in China, suggesting that it may play an important role in the dissemination of blaKPC-2 in K. michiganensis. In addition, the presence and significance of K. michiganensis in clinical pathology may be underestimated because most strains designated as K. oxytoca in research have not been subjected to accurate species identification. Consequently, this species might be implicated in diseases previously attributed to the K. oxytoca complex and other members of the genus, with the epidemiology of colonization and infection of each species in humans remaining largely uncharted. Although China is considered an endemic area for CRE, large-scale molecular epidemiological studies of the carbapenem-resistant K. oxytoca complex have been rare in China. As an emerging pathogen, K. michiganensis has relatively few reported clinical infections and its genomic characteristics and multidrug resistance profile need further investigation.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The raw data from the sequence experiment have been deposited in the database of NCBI under accession numbers CP089448 and CP089449. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).
Author contributions
JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. GW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HH: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Formal analysis, Validation. HL: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Formal analysis, Validation. XL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. DD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 82360409), by the Top Experts training Project for the Academy and Technology in Yunnan province (grant number: 202305AC160072), and by the Association Foundation Program of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department and Kunming Medical University (grant number: 202201AY070001-267).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ming He (Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Kunming Medical University, Kunming, Yunnan Province, China) and Hong Shi (Yunnan Key Laboratory of Primate Biomedical Research, Institute of Primate Translational Medicine, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, Yunnan Province, China) for their assistance with data analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1492700/full#supplementary-material
References
Araújo, B. F., Royer, S., Campos, P. A., Ferreira, M. L., Gonçalves, I. R., MaChado, L. G., et al. (2018). Insights into a novel Tn4401 deletion (Tn4401i) in a multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical strain belonging to the high-risk clonal group 258 producing KPC-2. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 52, 525–527. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.08.011
Bi, R., Kong, Z., Qian, H., Jiang, F., Kang, H., Gu, B., et al. (2018). High Prevalence of blaNDM Variants Among Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli in Northern Jiangsu Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02704
Brandt, C., Viehweger, A., Singh, A., Pletz, M. W., Wibberg, D., Kalinowski, J., et al. (2019). Assessing genetic diversity and similarity of 435 KPC-carrying plasmids. Sci. Rep. 9, 11223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47758-5
Campos-Madueno, E. I., Sigrist, T., Flückiger, U. M., Risch, L., Bodmer, T., Endimiani, A. (2021). First report of a blaVIM-1 metallo-β-lactamase-possessing Klebsiella michiganensis. J. Global Antimicrob. Resist. 25, 310–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.03.027
Capella-Gutiérrez, S., Silla-Martínez, J. M., Gabaldón, T. (2009). trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics. 25, 1972–1973. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
Chapman, P., Forde, B. M., Roberts, L. W., Bergh, H., Vesey, D., Jennison, A. V., et al. (2020). Genomic investigation reveals contaminated detergent as the source of an extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing klebsiella michiganensis outbreak in a neonatal unit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58, e01980-19. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01980-19
Chen, Y., Brook, T. C., Soe, C. Z., O’neill, I., Alcon-Giner, C., Leelastwattanagul, O., et al. (2020). Preterm infants harbour diverse Klebsiella populations, including atypical species that encode and produce an array of antimicrobial resistance- and virulence-associated factors. Microb. Genom. 6, e000377. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000377
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2022). Performance standard for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: Twenty-fourth informational supplement M100-S32 (Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI).
Ding, L., Shen, S., Chen, J., Tian, Z., Shi, Q., Han, R., et al. (2023). Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase variants: the new threat to global public health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 36, e0000823. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00008-23
Emms, D. M., Kelly, S. (2015). OrthoFinder: solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy. Genome Biol. 16, 157. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0721-2
Furlan, J. P. R., Da Silva Rosa, R., Ramos, M. S., Dos Santos, L. D. R., Lopes, R., Savazzi, E. A., et al. (2023). Genetic plurality of blaKPC-2-harboring plasmids in high-risk clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae of environmental origin. Sci. Total Environ. 881, 163322. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163322
Getino, M., López-Díaz, M., Ellaby, N., Clark, J., Ellington, M. J., La Ragione, R. M. (2022). A broad-host-range plasmid outbreak: dynamics of incL/M plasmids transferring carbapenemase genes. Antibiotics (Basel). 11, 1641. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111641
Gołebiewski, M., Kern-Zdanowicz, I., Zienkiewicz, M., Adamczyk, M., Zylinska, J., Baraniak, A., et al. (2007). Complete nucleotide sequence of the pCTX-M3 plasmid and its involvement in spread of the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase gene blaCTX-M-3. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 3789–3795. doi: 10.1128/aac.00457-07
Grodner, B., Shi, H., Farchione, O., Vill, A. C., Ntekas, I., Diebold, P. J., et al. (2024). Spatial mapping of mobile genetic elements and their bacterial hosts in complex microbiomes. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 2262–2277. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01735-5
Jiang, Y., Yu, D., Wei, Z., Shen, P., Zhou, Z., Yu, Y. (2010). Complete nucleotide sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae multidrug resistance plasmid pKP048, carrying blaKPC-2, blaDHA-1, qnrB4, and armA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 3967–3969. doi: 10.1128/aac.00137-10
Jing, Y., Yu, S., Li, Z., Ma, J., Wang, L., Yu, L., et al. (2024). Coexistence of a novel chromosomal integrative and mobilizable element Tn7548 with two blaKPC-2-carrying plasmids in a multidrug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila strain K522 from China. J. Global Antimicrob. Resist. 37, 157–164. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.03.006
Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J., Yamada, K. D. (2019). MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 20, 1160–1166. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx108
Kern-Zdanowicz, I. (2021). pCTX-M3-structure, function, and evolution of a multi-resistance conjugative plasmid of a broad recipient range. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4606. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094606
Li, X., Li, C., Zhou, L., Wang, Q., Yao, J., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Global phylogeography and genomic characterization of blaKPC and blaNDM-positive clinical Klebsiella aerogenes isolates from China 2016-2022. Sci. Total Environ. 923, 171560. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171560
Meng, H., Wang, S., Tang, X., Guo, J., Xu, X., Wang, D., et al. (2022). Respiratory immune status and microbiome in recovered COVID-19 patients revealed by metatranscriptomic analyses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1011672
Minh, B. Q., Schmidt, H. A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M. D., Von Haeseler, A., et al. (2020). IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37, 1530–1534. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa015
O’leary, N. A., Wright, M. W., Brister, J. R., Ciufo, S., Haddad, D., Mcveigh, R., et al. (2016). Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D733–D745. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1189
Ouyang, J., Sun, F., Zhou, D., Feng, J., Zhan, Z., Xiong, Z., et al. (2018). Comparative genomics of five different resistance plasmids coexisting in a clinical multi-drug resistant Citrobacter freundii isolate. Infect. Drug Resist. 11, 1447–1460. doi: 10.2147/idr.S165818
Overbeek, R., Olson, R., Pusch, G. D., Olsen, G. J., Davis, J. J., Disz, T., et al. (2014). The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D206–D214. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1226
Partridge, S. R., Kwong, S. M., Firth, N., Jensen, S. O. (2018). Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 31, e00088-17. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00088-17
Perez, F., Bonomo, R. A. (2019). Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: global action required. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19, 561–562. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(19)30210-5
Prah, I., Ayibieke, A., Mahazu, S., Sassa, C. T., Hayashi, T., Yamaoka, S., et al. (2021). Emergence of oxacillinase-181 carbapenemase-producing diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Ghana. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 10, 865–873. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1920342
Rozwandowicz, M., Brouwer, M. S. M., Fischer, J., Wagenaar, J. A., Gonzalez-Zorn, B., Guerra, B., et al. (2018). Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73, 1121–1137. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx488
Saha, R., Farrance, C. E., Verghese, B., Hong, S., Donofrio, R. S. (2013). Klebsiella michiganensis sp. nov., a new bacterium isolated from a tooth brush holder. Curr. Microbiol. 66, 72–78. doi: 10.1007/s00284-012-0245-x
Sands, K., Carvalho, M. J., Portal, E., Thomson, K., Dyer, C., Akpulu, C., et al. (2021). Characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Gram-negative bacteria that cause neonatal sepsis in seven low- and middle-income countries. Nat. Microbiol. 6, 512–523. doi: 10.1038/s41564-021-00870-7
Shen, W., Sipos, B., Zhao, L. (2024). SeqKit2: A Swiss army knife for sequence and alignment processing. Imeta. 3, e191. doi: 10.1002/imt2.191
Shen, P., Zhang, Y., Li, G., Jiang, X. (2016). Characterization of the genetic environment of the blaKPC-2 gene among Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from a Chinese Hospital. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 20, 384–388. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2016.04.003
Siguier, P., Perochon, J., Lestrade, L., Mahillon, J., Chandler, M. (2006). ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, D32–D36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj014
Stewardson, A. J., Marimuthu, K., Sengupta, S., Allignol, A., El-Bouseary, M., Carvalho, M. J., et al. (2019). Effect of carbapenem resistance on outcomes of bloodstream infection caused by Enterobacteriaceae in low-income and middle-income countries (PANORAMA): a multinational prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19, 601–610. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(18)30792-8
Tang, Y., Li, G., Liang, W., Shen, P., Zhang, Y., Jiang, X. (2017). Translocation of Carbapenemase Gene blaKPC-2 both Internal and External to Transposons Occurs via Novel Structures of Tn1721 and Exhibits Distinct Movement Patterns. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61, e01151-17. doi: 10.1128/aac.01151-17
Tang, Y., Li, G., Shen, P., Zhang, Y., Jiang, X. (2022). Replicative transposition contributes to the evolution and dissemination of KPC-2-producing plasmid in Enterobacterales. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 11, 113–122. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.2013105
Tansirichaiya, S., Rahman, M. A., Roberts, A. P. (2019). The transposon registry. Mob. DNA. 10, 40. doi: 10.1186/s13100-019-0182-3
The UniProt Consortium (2023). UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D523–D531. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1052
Walker, B. J., Abeel, T., Shea, T., Priest, M., Abouelliel, A., Sakthikumar, S., et al. (2014). Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PloS One 9, e112963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112963
Wang, L., Shen, W., Zhang, R., Cai, J. (2022a). Identification of a novel ceftazidime-avibactam-resistant KPC-2 variant, KPC-123, in citrobacter koseri following ceftazidime-avibactam treatment. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.930777
Wang, X., Xiao, W., Li, L., Jing, M., Sun, M., Chang, Y., et al. (2022b). Analysis of the molecular characteristics of a blaKPC-2-harbouring untypeable plasmid in Serratia marcescens. Int. Microbiol. 25, 237–244. doi: 10.1007/s10123-021-00172-2
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L., Holt, K. E. (2017). Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PloS Comput. Biol. 13, e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595
Yang, J., Long, H., Hu, Y., Feng, Y., Mcnally, A., Zong, Z. (2022). Klebsiella oxytoca complex: update on taxonomy, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 35, e0000621. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00006-21
Yao, Y., Falgenhauer, L., Rezazadeh, Y., Falgenhauer, J., Imirzalioglu, C., Chakraborty, T. (2024). Predominant transmission of KPC-2 carbapenemase in Germany by a unique IncN plasmid variant harboring a novel non-transposable element (NTEKPC-Y). Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e0256423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02564-23
Keywords: Klebsiella michiganensis, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, whole genome sequencing, blaKPC-2 carbapenemases, ISKpn27-blaKPC-2-ISKpn6, phylogenetics
Citation: Song J-M, Long H-B, Ye M, Yang B-R, Wu G-J, He H-C, Wang J-L, Li H-W, Li X-G, Deng D-Y, Li B and Yuan W-L (2024) Genomic characterization of a blaKPC-2–producing IncM2 plasmid harboring transposon ΔTn6296 in Klebsiella michiganensis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1492700. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1492700
Received: 07 September 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 12 November 2024.
Edited by:
Mithun Rudrapal, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology and Research, IndiaReviewed by:
Johra Khan, Majmaah University, Saudi ArabiaSamiksha Garse, D.Y. Patil Deemed to be University, India
Copyright © 2024 Song, Long, Ye, Yang, Wu, He, Wang, Li, Li, Deng, Li and Yuan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: De-Yao Deng, ZGVuZ2RleWFvMjAwN0B5ZWFoLm5ldA==; Bo Li, MjI5NjU5MTQ0MEBxcS5jb20=; Wen-Li Yuan, amlhbnlhbmtlX3l3bEB5bnUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jian-Mei Song
Jian-Mei Song Hu-Bo Long
Hu-Bo Long Mei Ye
Mei Ye Bao-Rui Yang
Bao-Rui Yang Guang-Juan Wu1
Guang-Juan Wu1