- Medical Molecular Microbiology and Antibiotic Resistance Laboratory (MMARLab), Department of Biomedical and Biotechnological Sciences (BIOMETEC), University of Catania, Catania, Italy
Background: The use of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus spp. is a potential innovative approach to fight antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Klebsiella pneumoniae is one of the most concerning multi drug-resistant (MDR) pathogens, and its ability to colonize the human gut is considered to be the main reason for recurrent infections in critically ill patients.
Methods: In this study, Lactobacillus gasseri 1A-TV, already described for its probiotic activity, was characterized at the genomic level. Moreover, its cell-free supernatant (CFS) was tested for antimicrobial activity against extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)- and carbapenemase (KPC)-producing K. pneumoniae clinical isolates.
Results: Whole-genome sequencing showed that the L. gasseri 1A-TV genome was of 2,018,898 bp in size with 34.9% GC content, containing 1,937 putative protein coding sequences, 55 tRNA, and 4 rRNA detected by RAST and classified in 20 functional groups by Cluster of Orthologous Genes (COG). BAGEL4 (BActeriocin GEnome minimal tooL) and the antiSMASH 7.0 pipeline identified two bacteriocin biosynthetic gene clusters (BBGCs), namely, BBGC1 that comprises two class IIc bacteriocins including gassericin A-like bacteriocin, and BBGC2 carrying the class III bacteriocin helveticin J. Strikingly, 1A-TV CFS inhibited the growth of all K. pneumoniae isolates only after 8 h of incubation, showing a bactericidal effect at 24 h and interfering, even at lower concentrations, with the biofilm production of biofilm-producer strains independently of a bactericidal effect. NMR analysis of CFS identified and quantified several metabolites involved in carbohydrate metabolism and amino acid metabolism, and organic acids like ethanol, lactate, acetate, and succinate. Finally, in vitro assays of 1A-TV showed significant co-aggregation effects against carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae, namely, strains 1, 2, 3, and 7.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the antimicrobial activity of 1A-TV as a probiotic candidate or its CFS as a natural bioproduct active against MDR K. pneumoniae strains, underlining the importance of novel therapeutic strategies for prevention and control of ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae colonization.
1 Introduction
The global burden of antimicrobial resistance has become a major health concern (Aslam et al., 2018; Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators, 2022) and Klebsiella pneumoniae is one of the most concerning multidrug -resistant (MDR) pathogens involved in hospital-acquired infections thanks to its wide resistome and mobilome. Colonization and carriage of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae (CRKP) are considered to be the main reason for recurrent infections in critically ill patients (Kontopoulou et al., 2019); therefore, decolonization of CRKP could reduce the secondary and recurrent infections. K. pneumoniae biofilm formation on catheters and internal devices of hospitalized patients can also be another agent of colonization in different districts, invasive infections, and treatment failure (Wang et al., 2020). In fact, extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)- and carbapenemase (KPC)-producing K. pneumoniae has a greater ability to produce biofilms compared to non-ESBL- and KPC-producing strains, conferring a further advantage to the MDR strains in terms of persistence in the host and resistance of the effect of the antibiotics (Sabença et al., 2023).
In light of the above, several studies have reported beneficial effects exerted by novel strategies based on probiotics as preventive therapy against MDR pathogens, in order to guarantee a better outcome to hospitalized and immunocompromised patients. The use of probiotics could be valuable to re-establish a healthy microbiota and ultimately homeostasis (Davison and Wischmeyer, 2019); in fact, dysbiosis of the microbiota, often exacerbated by antibiotic treatment, is one of the causes of MDR pathogen colonization (Alagna et al., 2020), whereas a balanced state is necessary to prevent the onset of infections and other non-infectious pathological conditions (Gomaa, 2020). Moreover, the health-promoting effects are due to not only the viability of probiotics but also certain biomolecules produced by probiotics such as postbiotics, which could be useful in preventing the risks of using live bacteria while still exerting their beneficial effects to the host (Aggarwal et al., 2022). Recently, the International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) defined postbiotics as “preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host” (Salminen et al., 2021). Postbiotics are metabolic and/or structural microbial compounds such as cell-free supernatants (CFSs), bacterial lysates, vitamins, cell wall fragments, peptides, and teichoic acid that have the ability to confer health-promoting effects to the host.
In this context, lactobacilli belong to the lactic acid bacteria (LAB) group are promising candidates to human health; thus, they are often employed for their beneficial effects (Pace et al., 2015; Seddik et al., 2017). Lactobacillus antimicrobial activity is exerted through different mechanisms, such as the stimulation of host immune system, competition for binding sites and nutrients with pathogens, and the production of inhibitory compounds like organic acids, hydrogen peroxide, and bacteriocins. The antagonistic activity of lactobacilli has been demonstrated to act against a wide spectrum of pathogens, suggesting a promising future for alternative strategies in fighting infection (Chen et al., 2021; Scillato et al., 2021).
In our previous study, we firstly characterized the strain Lactobacillus gasseri 1A-TV for its excellent ability to interfere and co-aggregate with urogenital pathogens and the 1A-TV CFS also exerted a strong antimicrobial activity, supported by the production of D- and L-lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and bacteriocin production (Scillato et al., 2021).
Considering the potential use of L. gasseri 1A-TV in the prevention and/or treatment of infections associated with MDR K. pneumoniae, this study is focused on the antimicrobial effects exerted by 1A-TV CFS as a postbiotic against ESBL- and KPC-producing K. pneumoniae.
In order to address this, we used the whole-genome sequencing of L. gasseri 1A-TV combined with a genome mining tool to identify biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs); likewise, we investigated the antimicrobial activity of 1A-TV against ESBL- and KPC-producing K. pneumoniae by using killing curve assay and we evaluated its anti-biofilm and co-aggregating ability versus the pathogen strains.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial strains and culture conditions
L. gasseri 1A-TV was grown in de Man Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) broth and agar plates (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) at 37°C for 48 h in anaerobic conditions, using the GasPak™ EZ Anaerobe Pouch System (BD, New Jersey, USA).
In this study, we used seven K. pneumoniae clinical strains from our microbial bank at the MMARLab, previously characterized for their MDR profiles, and selected for their clinical and epidemiological characteristics (Table 1) (Gona et al., 2011, Gona et al., 2019; Mezzatesta et al., 2011). A non-resistant strain was added as control, Kbp7. They comprised the following: (i) Two KPC-producing strains belonging to ST258, isolated from hospitalized patients in two different hospitals in Catania as previously described (Mezzatesta et al., 2011); these strains were isolated from central venous catheter for patient 2 (renamed Kbp1) and from bloodstream for patient 8 (Kbp4 in this study). (ii) Two co-producing NDM-OXA-48 KP belonging to ST101, strain KP730 and KP723 as previously reported (Gona et al., 2019), renamed Kbp2 and Kbp3, respectively; both were isolated from patients of the neonatal intensive care unit of the University Hospital of Catania and belonged to two different epidemiological clusters by the Core Genome MLST (Kbp2 cluster A, Kbp3 cluster C). (iii) Two ESBL-producing strains ST307, isolated from patients 2 and 6 as previously reported (Gona et al., 2011) and named Kbp5 and Kbp6, respectively; Kbp 5 and Kbp6 were responsible for severe urinary tract infections in the renal transplant unit. MLST for K. pneumoniae isolates was performed as previously described (Mezzatesta et al., 2011), and STs were assigned by the MLST Pasteur website (http://www.pasteur.fr/mlst). In addition, minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of amikacin and colistin were performed by the microdilution method interpreted according to EUCAST guidelines v.14.0. (https://www.eucast.org). Fosfomycin MIC was performed by the agar dilution method described by CLSI. All ESBL- and KPC-producing K. pneumoniae were also resistant to colistin. All strains were grown on MacConkey agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and aerobically incubated at 37°C overnight.
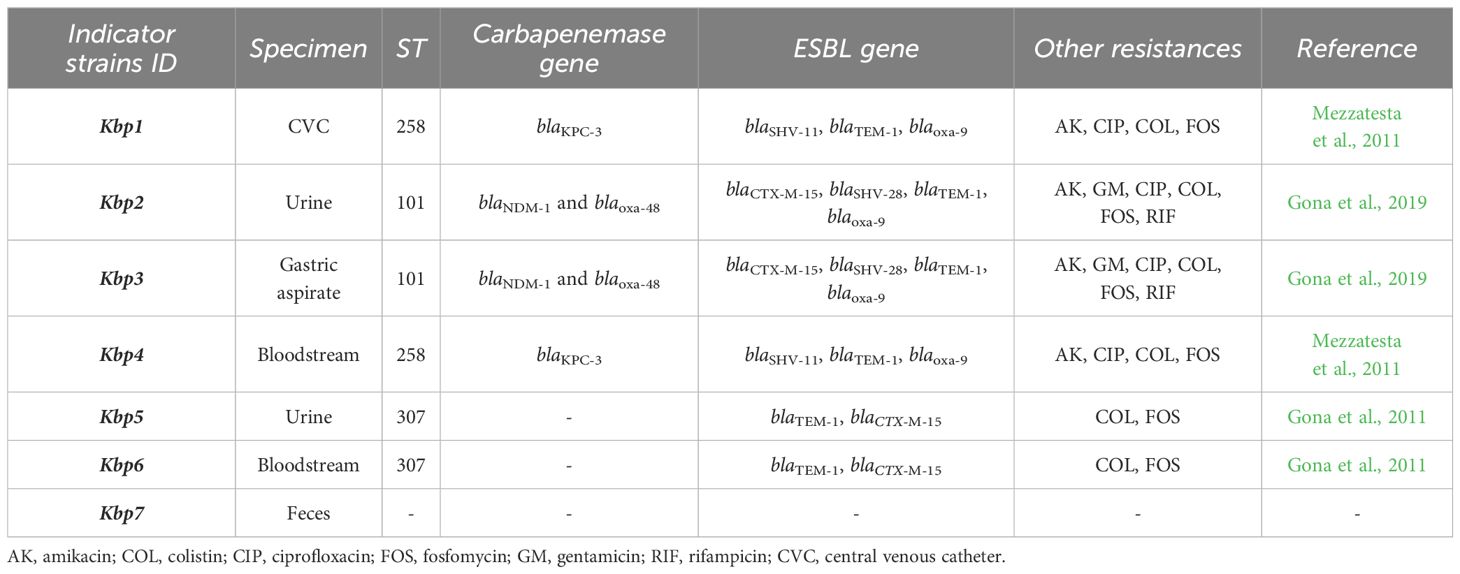
Table 1. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance profile of K. pneumoniae clinical isolates described in this study.
2.2 Whole-genome sequencing, assembly, and annotation
L. gasseri 1A-TV genomic DNA was extracted using the PureLink™ Genomic DNA Mini Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, then it was quantified by a Qubit 2.0 fluorometer (dsDNA HS assay, Invitrogen, USA) and quality assessed by a Nanodrop2000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Genomic libraries were prepared with a Nextera XT DNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina, USA) and sequenced by the Illumina MiSeq platform following the manufacturer’s protocol (Ravi et al., 2018). The raw data were provided as paired-end reads (2 × 250 Read Length) with a 258× coverage and their quality was checked using Trimmomatic (Bolger et al., 2014), while the genome was assembled by SPAdes v3.14.0 through the MEGA annotator pipeline (Bankevich et al., 2012). The genome annotation was performed with Prokka v. 1.13 (Seemann, 2014) (Supplementary Data Sheet S1), whereas rRNA and tRNA gene predictions were performed with RNAmmer v1.2 (Lagesen et al., 2007) and tRNAscan-SE v1.21, respectively (Lowe and Eddy, 1997). Rapid annotation using subsystem technology (RAST) was also applied for microbial genome annotation to identify different subsystems in the genome defined as “a set of functional roles” connected to specific genes of the available annotated genome (Aziz et al., 2008). Furthermore, the database of Cluster of Orthologous Genes (COG) was used for a summary of functional annotation (Galperin et al., 2021).
2.3 Genomic data accession number
The L. gasseri 1A-TV genomic reads have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) SRA database under SUB14624849, with BioProject accession number PRJNA1140194.
2.4 In silico prediction of bacteriocin biosynthetic gene clusters
Microbial genome mining was obtained using the antiSMASH 7.0 pipeline (antibiotic and Secondary Metabolite Analysis SHell) to predict classic and novel BGCs coding for secondary metabolites (Blin et al., 2023) and BAGEL4 (BActeriocin GEnome minimal tooL) to identify ribosomal synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) (van Heel et al., 2018). The amino acid sequences of the core peptides identified within the BGCs were further analyzed by the CD search tool.
2.5 Determination of antimicrobial activity
The inhibitory activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV was firstly tested against seven K. pneumoniae strains shown in Table 1, using a deferred antagonism test, an assay typically used to investigate the production of bacteriocins and then quantified by the agar spot test (Siroli et al., 2017; Scillato et al., 2021). For the agar spot assay, 5 µL of 1A-TV broth cultures was spotted on the surface of MRS soft agar plates (1.2%) and incubated anaerobically for 48 h at 37°C. An overnight culture of indicator strains (100 μL; approximately 107 CFU/mL) was mixed with Brain Heart Infusion soft agar (0.7%) (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and poured over the plate where lactobacilli were spotted, as previously described (Scillato et al., 2021). Antagonistic activity was assessed by measuring diameters of inhibition zones and expressed as follows: no inhibition (−); diameter between 1 and 3 mm (+); diameter between 3 and 6 mm (++); diameter between 6 and 10 mm (+++); diameter > 10 mm (++++).
2.6 Auto-aggregation and co-aggregation assays
Auto-aggregation and co-aggregation activities were determined using our previous protocol with some modifications (Scillato et al., 2021; Vertillo Aluisio et al., 2022). Overnight cultures of L. gasseri 1A-TV and K. pneumoniae were centrifuged at 3,000 g for 15 min at 4°C, and the pellets were washed twice and resuspended in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich) to obtain a final concentration of 107 CFU/mL. For auto-aggregation assay, 4 mL of each suspension was incubated at room temperature with a shaker at 200 rpm, whereas for the co-aggregation assay, 2 mL of 1A-TV and 2 mL of each indicator suspension were mixed and incubated in the same conditions. The optical density of bacterial suspensions was measured at 600 nm at T0 and after 5 h of incubation (T5). Suspensions were dispensed in a 96-well plate at T0 and T5, and OD600 readings were attained with a microplate reader (BioTek Synergy™ HTX). For T5 readings, each sample was centrifuged at 650 g for 2 min to precipitate aggregated bacteria before dispending the 96-well plate.
Auto-aggregation percentage was then calculated as:
Co-aggregation percentage was calculated as:
where AT0 is the absorbance value at time 0, and AT5 is the absorbance value after 5 h of incubation.
The co-aggregation percentage of L. gasseri 1A-TV with K. pneumoniae has been considered significant when it is higher than auto-aggregation percentage of each pathogenic strain. Each assay was performed in triplicate.
2.7 Cell-free supernatant preparation
CFS of L. gasseri 1A-TV was prepared as previously described (Scillato et al., 2021). 1A-TV was inoculated in MRS broth at 37°C for 48 h, then the broth culture was centrifuged at 7,000 g for 30 min at 4°C and the supernatant was filtered with a 0. 22-µm membrane. pH values of CFS were measured by a pH meter (pH 50+DHS Benchtop pH Meter).
2.8 CFS 1H-NMR analysis
1H-NMR analysis was performed to determine the metabolic profile of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS. 1A-TV CFS (630 μL; OD600 ≈ 1.6) was added to 70 μL of a buffer solution, pH 7.4 [1.5 M K2HPO4, 100% (v/v) D2O, NaN3 2 mM, TMSP 5.8 mM]. The final mix (600 μL) was used for the acquisition of the NMR spectra. This analysis was performed using a Bruker IVDr 600 MHz (Bruker BioSpin) operating at the Larmor proton frequency of 600.13 MHz, equipped with a 2H PATXI H/C/decoupling probe 5 mm N and an automatic refrigerated sample changer (SampleJet). The temperature was adjusted to 300 ± 0.1 K with a BTO 2000 thermocouple. The signals were assigned by comparing their chemical shift and multiplicity with the Chenomx software data bank (Chenomx Inc., Canada, ver 8.02). To estimate the reproducibility, 1A-TV CFS NMR analysis was performed three times and MRS free was used as control.
2.9 In vitro antimicrobial activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS
A time-killing assay was performed to evaluate the in vitro inhibitory activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS against K. pneumoniae strains as previously described (Scillato et al., 2021). The kinetic growth of indicator strains in the presence of CFS was tested at different time intervals: 0, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h; viable microbial cell counts (CFU/mL) on Mueller Hinton (MH) agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) were determined according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute guidelines (7.17.2 Time-Kill Assay 7.17 tests to assess bactericidal activity, 2024). For the assay, K. pneumoniae indicators were used at 3 × 105 CFU/mL in 10 mL of broth containing 5 mL of cation-adjusted Mueller Hinton broth (BD, New Jersey, USA) and 5 mL of CFS (1:1 ratio). The control growth of indicator strains was assessed by inoculating 10 mL of fresh medium containing MH-MRS broth (1:1). The CFU/mL values of each indicator strain were recorded as log10 reduction of the total count of CFU/mL in the original inoculum and the bactericidal activity was defined as a reduction of at least 99.9% (≥ 3 log10) (approved guideline M26-A, CLSI). This experiment was repeated in triplicate.
2.10 Measurement of bactericidal activity of CFS
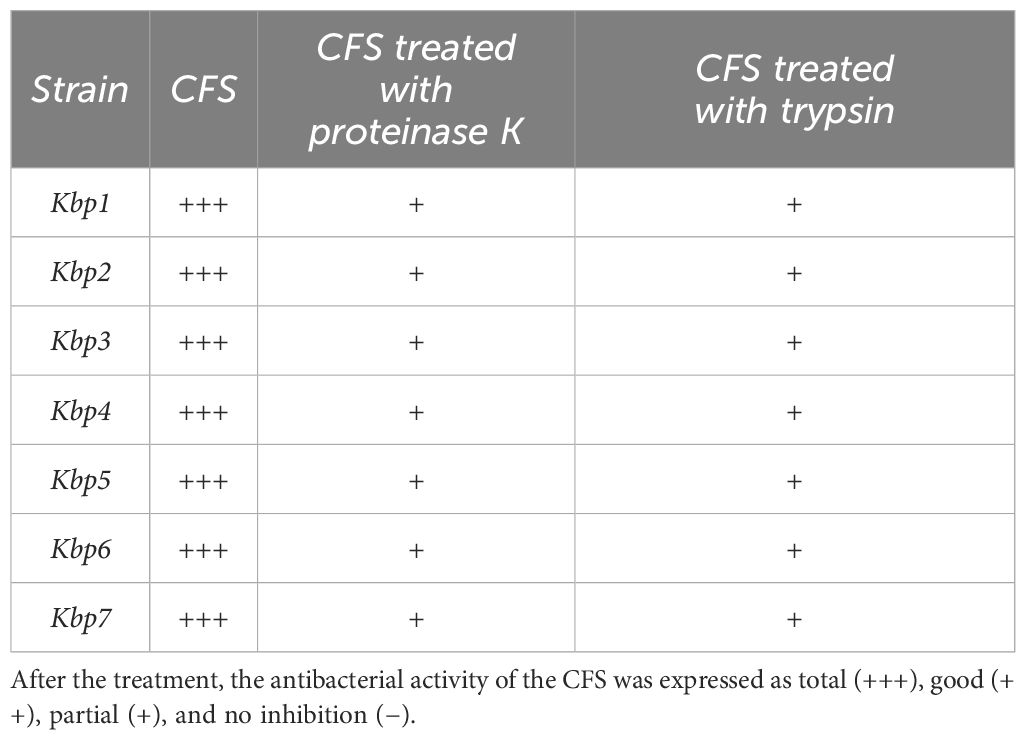
The sensitivity of the CFS to enzymatic activity was assayed by trypsin (E. C.3.4.21.4, type II) and proteinase K (E. C. 3.4.21.64) at pH 7.5 (100 mM Tris-HCl buffer). Aliquots of the CFS were incubated (1:1 v/v) with enzyme solutions (1 mg/mL) and their respective controls at 37°C for 2 h under aerobic conditions (Scillato et al., 2021). After proteolytic enzyme treatments, the antibacterial activity of the CFS was performed by antagonism experiments in 96-well plates using the indicator strains at 3 × 105 CFU/mL. After incubation for 24 h at 37°C, the bactericidal effects were estimated by a turbidimetric method with Microplate Reader (BioTek Synergy™ H1) system using OD600 for bacterial strains. All experiments were repeated three times.
2.11 K. pneumoniae biofilm formation
The crystal violet staining method was used to test biofilm production of K. pneumoniae indicators as previously described with some modifications (Raras et al., 2019; El-Mokhtar et al., 2020). K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603 was used as control for the biofilm production (Ochońska et al., 2021).
Briefly, overnight cultures of K. pneumoniae in LB broth were diluted 1:100 and dispensed in a 96-well plate (200 µL per well). After 24 h of incubation at 37°C, the plate was washed thrice with 200 μL of distilled water and air-dried. Then, 100 μL of 0.2% crystal violet was added to each well, incubated for 20 min, and then discarded. The plate was washed thrice with distilled water, air-dried, then 200 μL of 95% ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich) was added to each well. After 30 min of incubation, the intensity of crystal violet was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader (BioTek Synergy™ HTX). Based on OD570 values, the isolates with OD570< 0.120 were considered as weak biofilm producers, those with OD570 0.120–0.240 had intermediate biofilm formation ability, and isolates with OD570 > 0.240 were classified as strong biofilm producers, as previously described (Maldonado et al., 2007).
2.12 Biofilm inhibition assay
To investigate the effect of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS on K. pneumoniae biofilm production, only strong biofilm producers were used as indicators. The assay was performed in a 96-well plate as aforementioned with the addition of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS at scalar concentrations starting from a 1:1 ratio (50% of CFS), then the plate was incubated for 24 h at 37°C. To estimate inhibition of biofilm formation with CFS treatment, the following formula was applied: =
where C denotes the OD570 values of wells without CFS treatment, T represents the OD570 values of treated wells, and B indicates the OD570 values of negative control, as previously described (El-Mokhtar et al., 2020).
To evaluate whether the antibiofilm effect was simultaneously associated with the bactericidal activity of 1A-TV CFS, the same assay was performed in another 96-well plate without crystal violet staining to obtain viable microbial cell counts (CFU/mL). After 24 h of incubation, the cultures were removed from each well, serially diluted and plated on MH agar for determination of viable microbial cell counts. All experiments were performed in at least three independent assays.
2.13 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by using GraphPad Prism 8 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), and results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments.
For the co-aggregation assays, ANOVA with Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) test was applied to determine significant differences. For time-killing assays, the two-way ANOVA test with the Geisser–Greenhouse correction was applied to compare growth curves in treated and untreated conditions. For biofilm inhibition assays, two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used. In all cases, p-value was expressed as follows: * p< 0.05, ** p< 0.01, and *** p< 0.001.
3 Results
3.1 Genome annotation and genome mining for biosynthetic gene clusters
The whole-genome sequencing of L. gasseri 1A-TV showed a single chromosome of 2,018,898 bp in size with a 34.9% GC content, composed of 14 contigs with an N50 value of 352,766. The genome carried 1,951 coding sequences (CDSs), 55 tRNA, and 4 rRNA by RAST annotation. The COG database assigned 1,763 protein-coding genes to 20 different functional categories (Figure 1), such as clustering in transport and metabolism of different macromolecules, energy production and conversion, secondary metabolite biosynthesis, and cell functions. Genome mining using both antiSMASH v.7.0 and BAGEL4 identified two putative bacteriocin biosynthetic gene clusters (BBGCs), namely, BBGC1 (contig_1 RiPP-like) located in contig 1 (from 37,767 to 48,215 nt) that contained two bacteriocin belonging to IIc class, and BBGC2 located in contig 2 (from 10.357 to 31348 nt) carrying the bacteriocin helveticin J of class III. In particular, antiSMASH v.7.0 identified nine putative proteins in the bacteriocin cluster BBGC1, of which six were involved in the bacteriocin biosynthetic process: (i) two class IIc bacteriocins, namely, bacteriocin leader domain-containing protein (ctg1_38; PF10439) and gassericin A-like bacteriocin (ctg1_39, PF10439); (ii) two ABC transporter-related protein (ctg1_35 and ctg1_36; PF00005); (iii) immunity protein (ctg1_40); and (iv) one bacterial extracellular solute-binding protein (ctg_141, PF13416) (Figures 2A, B; Supplementary Data Sheet S2). Furthermore, the antiSMASH cluster blast showed identical genetic organization of gassericin-S BGC from L. gasseri (BGC0001601) including two bacteriocins (gasA and gasX) and immunity protein (gasI) as shown in Figure 2C (Kasuga et al., 2019). BBGC2 was detected only by BAGEL4 and identified the bacteriocin helveticin J as the core peptide and two bacteriocin ABC transporters (PF00005), which may be involved in the transport of the bacteriocin across the membrane (Supplementary Data Sheet S3).
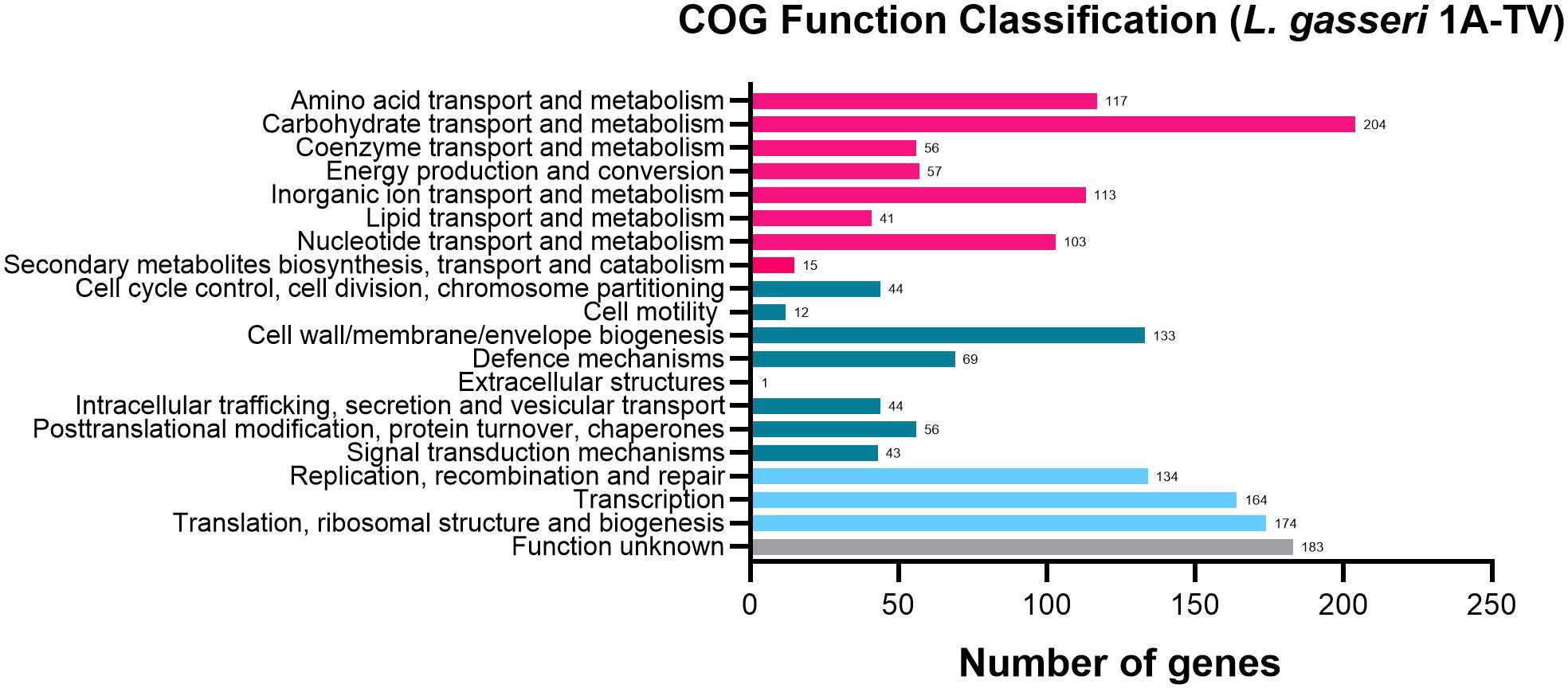
Figure 1. 1A-TV genome analyzed by Cluster of Orthologous Genes (COG) and divided into functional categories: in red, the genes linked to metabolism; in dark green, the cellular functions; and in light blue, the genes involved in information through clusters of orthologous genes (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/cog-project/).
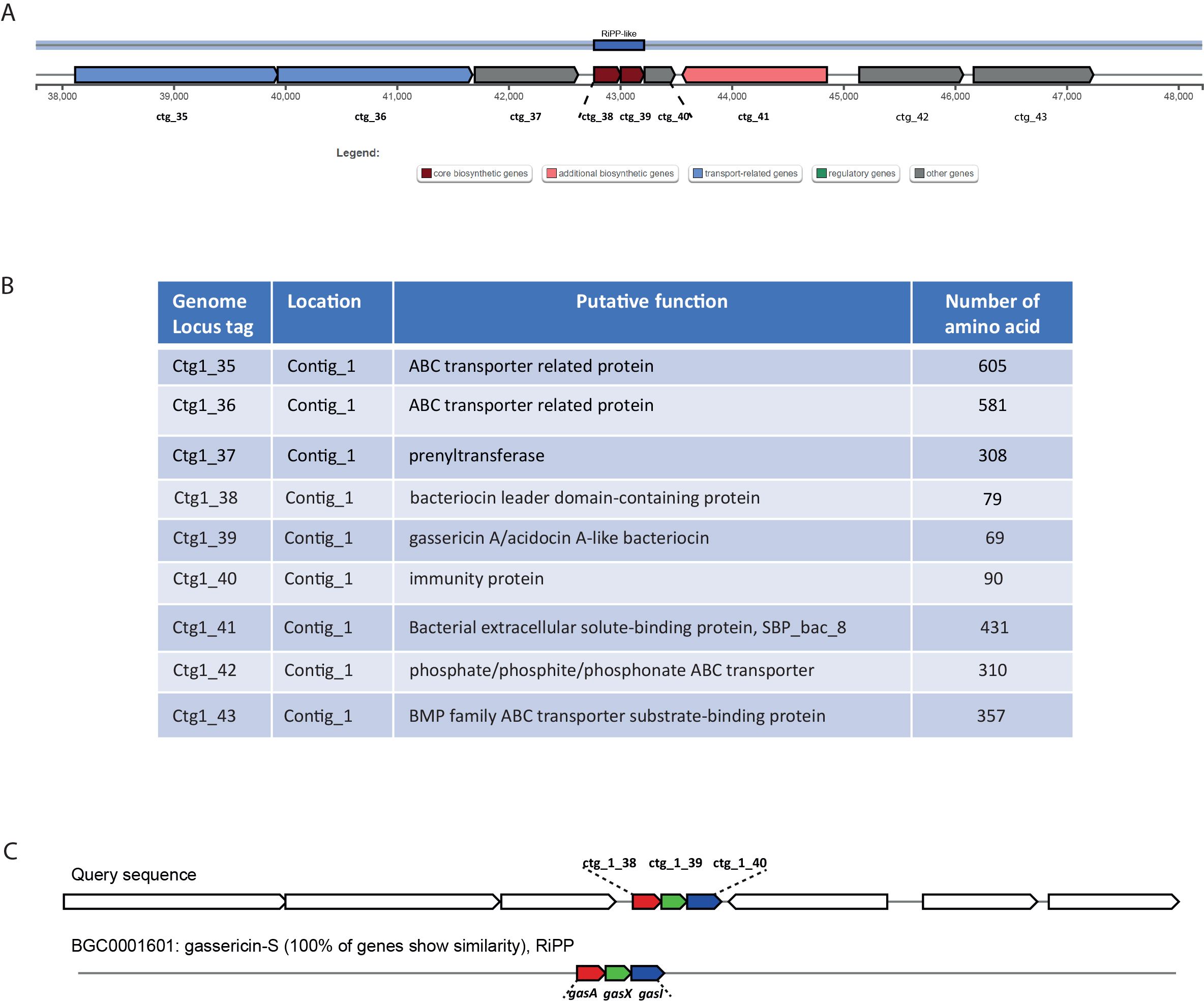
Figure 2. (A) Genetic map of the bacteriocin cluster BBGC1 identified by antiSMASH. The bacteriocin cluster comprises nine putative proteins, of which six are involved in the bacteriocin biosynthetic process, ctg1_38 and ctg1_39 encoding for two bacteriocins belonging to class IIc. (B) Genetic organization of cluster BBGC1, including nine locus tags with their putative function. (C) Comparison between 1A-TV BBGC1 and gassericin-S BGC1 in Lactobacillus gasseri carrying gasA, gasX, and gasI genes.
3.2 Anti-Klebsiella activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV
The effect of antagonistic activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV against seven MDR K. pneumoniae strains evaluated by the deferred antagonism test (Supplementary Figure 1) and quantified by the agar spot test demonstrated a total inhibition of the seven indicator strains with diameters of inhibition zones > 10 mm (++++) for all seven indicator strains (Figure 3).
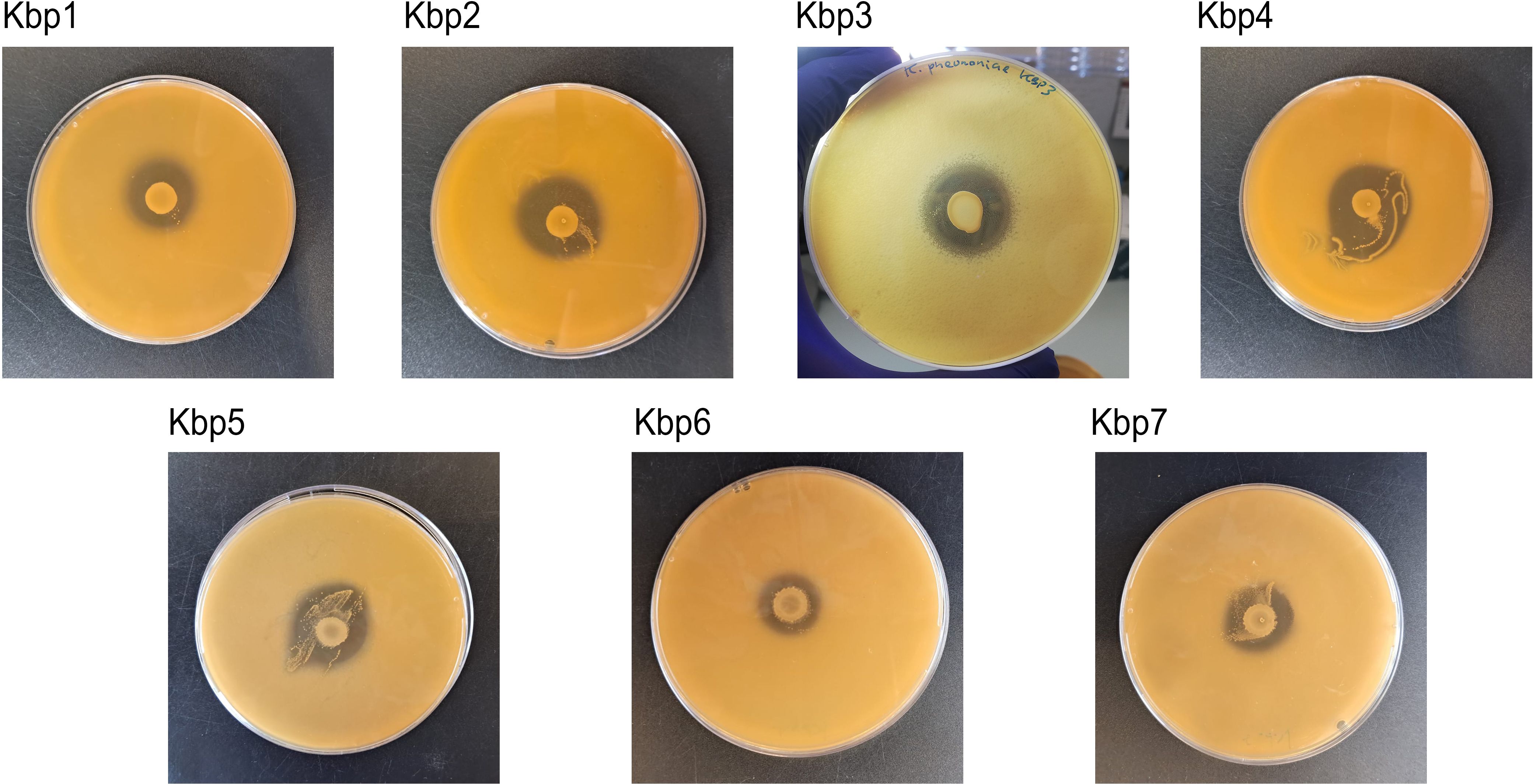
Figure 3. Agar spot test for each strain of K. pneumoniae. Strong antagonistic activity of 1A-TV was confirmed for all strains, with a diameter of inhibition zone > 10 mm.
3.3 Auto-aggregation and co-aggregation ability
The auto-aggregation and co-aggregation levels of the indicator strains are shown in Figure 4. A good ability for auto-aggregation is shown by each strain, with aggregation values ranging between 52% and 66%. Moreover, all K. pneumoniae strains co-aggregated with L. gasseri, but only for K. pneumoniae 1, 2, 3, and 7 was it statistically significant (p< 0.05), with co-aggregation values of 74.6%, 73.6%, 71.9%, and 67.8%, respectively (Supplementary Table S1).
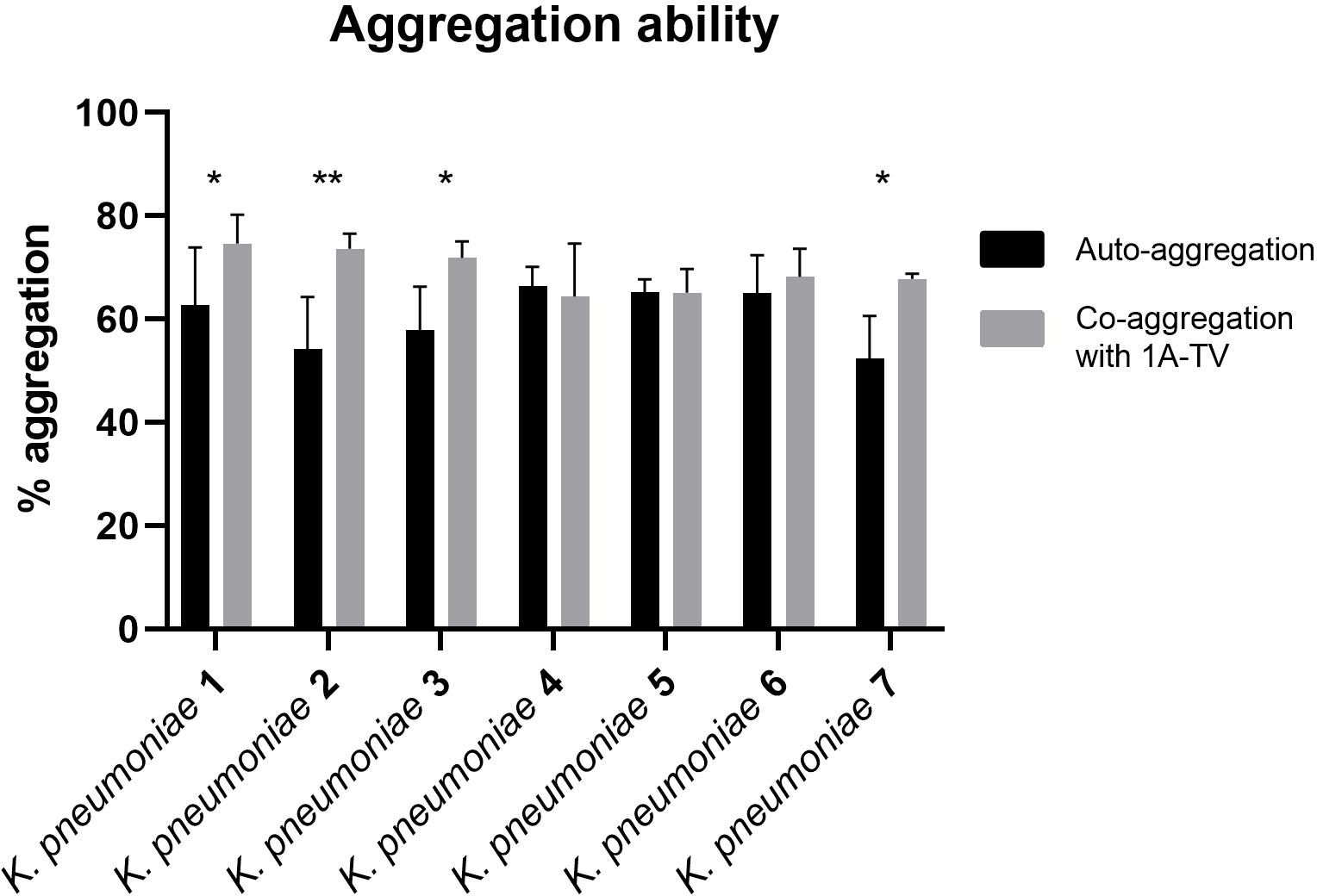
Figure 4. Auto-aggregation and co-aggregation of K. pneumoniae strains with L. gasseri 1A-TV. Co-aggregation values were considered statistically significant for strain Kbp1, Kbp2, Kbp3, and Kbp7, where ns was assigned for p -value > 0.05, * for p-value ≤ 0.05, and ** for p -value ≤ 0.01.
3.4 Metabolic profile of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS
The NMR spectra of CFS L. gasseri 1A-TV identified 25 molecules, mainly metabolites belonging to the families of organic acids, ketones, alcohols, amino acids, monosaccharides, and nucleosides, and concentrations were expressed subtracting the original quantity present in the MRS medium for each component (Supplementary Table S2). Although the 1A-TV metabolic profile included many metabolites involved in the carbohydrate metabolism and amino acid metabolism, organic acids showed the highest concentrations, including ethanol (55.68 mM), lactate (46.62 mM), and acetate (16.61 mM), followed by succinate (7.88 mM) and amino acids like alanine (0.53 mM), valine (0.13 mM), and isoleucine (0.01 mM). Lower levels of certain components compared to the original medium included statistically significant variations for citrate (−2.29 mM), malate (−1.90 mM), and threonine (−0.73 mM) levels.
3.5 Inhibition of planktonic K. pneumoniae by 1A-TV CFS and bactericidal effect
The results of time-killing assays are summed up in Figure 5. After 4, 6, and 8 h of incubation, 1A-TV CFS showed a bacteriostatic effect on all ESBL- and KPC-producing strains, with a reduction in bacterial growth of about 1 log10 compared to the initial inoculum. After 24 h of incubation, 1A-TV CFS exerted an extraordinary bactericidal effect against all indicator strains, as the bactericidal activity is defined as a reduction of at least 99.9% (≥ 3 log10) of the total count (CFU/mL) of the original inoculum (Supplementary Table S3). Statistical analysis showed that differences between treated and untreated K. pneumoniae were significant for all strains: p< 0.001 for strains 1, 2, 5, and 7, and p< 0.01 for strains 3, 4, and 6. Furthermore, proteolytic treatment of CFS with proteinase K and trypsin determined a decrease of the antibacterial activity compared to the CFS without proteolytic treatment (Table 2).
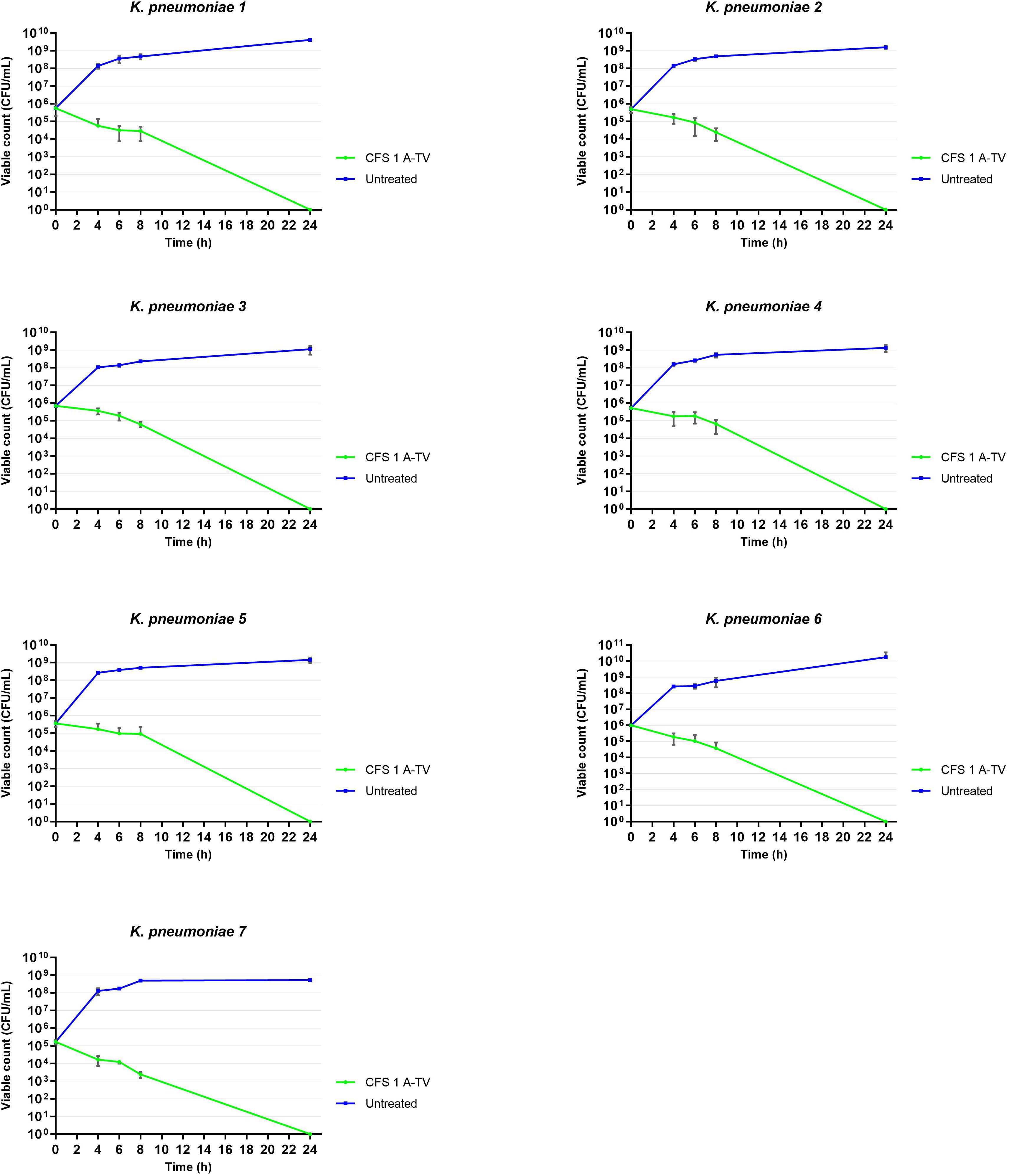
Figure 5. Time-killing curves showed the ability of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS to inhibit the growth of all indicators. After 24 h of incubation, CFS showed bactericidal activity reducing the inoculum by more than three logs. Statistical analysis showed that differences between treated and untreated K. pneumoniae were significative for all strains: p< 0.001 for strains 1, 2, 5, and 7, and p< 0.01 for strains 3, 4, and 6.
3.6 Inhibition of biofilm formation of ESBL- and KPC-producing K. pneumoniae by CFS
To evaluate the ability of 1-ATV CFS to interfere with the K. pneumoniae biofilm formation, the total biomass was evaluated by colorimetric assay using crystal violet. Only K. pneumoniae 1 (ST258, blaKPC-3, blaSHV-11, blaTEM-1, blaoxa-positive), K. pneumoniae 5 (ST307, blaTEM-1, blaCTX-M-15-positive), and K. pneumoniae 6 (ST307, blaTEM-1, blaCTX-M-15-positive) were considered strong biofilm producers with values above the threshold line (OD570 > 0.240) and were selected for biofilm inhibition testing (Figure 6A).
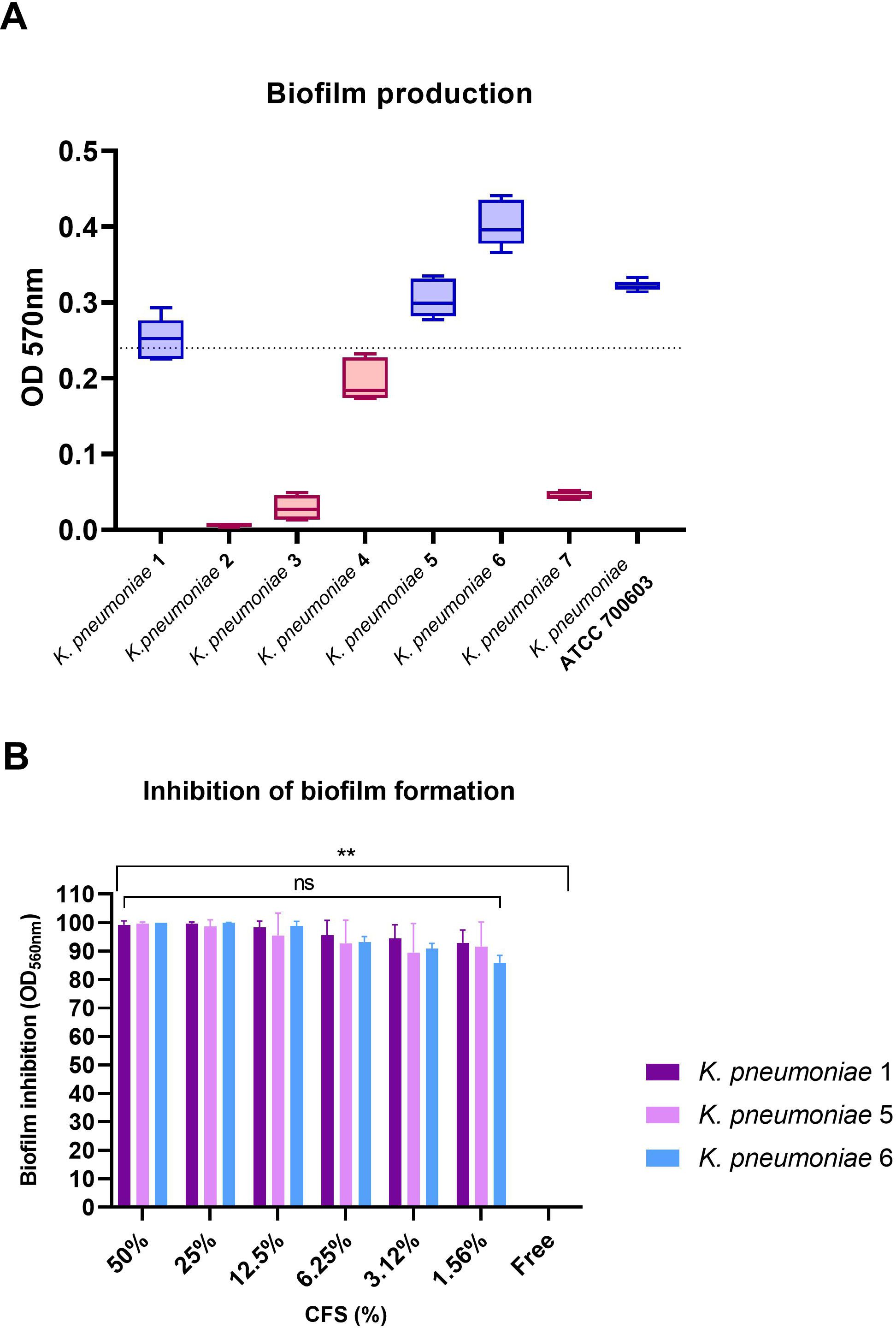
Figure 6. (A) Biofilm formation by K. pneumoniae indicator strains. Strains with values above baseline (OD570 > 0.240) were considered strong biofilm producers. (B) Inhibition of biofilm formation for biofilm producers at scalar concentrations of CFS. No statistical differences were found between CFS at different concentrations, while comparing the free control with all strains and all CFS concentrations showed statistical significance in all cases (**p< 0.01). ns, not significant.
As shown in Figure 6B, L. gasseri 1A-TV CSF was able to determine a high percentage of biofilm inhibition (from 100% to 95% inhibition) for all K. pneumoniae strains tested at different concentrations, and only at lower concentrations (from 6.25% to 1.56%) was inhibition just slightly reduced with high values from 93% to 86% compared to the free control (Supplementary Table S4). Importantly, no statistical difference was found among the scalar concentrations of CFS. When scalar concentrations of CFS and free control were compared, a statistical difference was found (p< 0.01) for all strains and all concentrations analyzed.
Moreover, viability was assessed after treatment with CFS at scalar concentrations (Supplementary Figure 2): At higher concentrations, CFS inhibited K. pneumoniae growth, despite the higher inoculum compared to time-killing assays, and at concentrations from 12.5% to 1.56% of CFS, all strains had a viable count ranging between 108 and 1011 CFU/mL, but biofilm formation was still inhibited (Supplementary Table S5).
4 Discussion
The emergence of CRKP represents a serious threat to public health, especially for critically ill and immunocompromised patients, and its fecal carriage can represent a risk factor for the onset of infections; therefore, intestinal clearance of CRKP could prevent CRKP infections. Several studies have reported beneficial effects exerted by novel strategies based on probiotics such as lactobacilli against MDR pathogens. The wide spectrum of valuable properties yielded by probiotics is associated with their ability to reinforce the dynamic equilibrium of the resident microbiota, which is an important tool to counteract “dysbiosis” in the host, maintain mucosal integrity, and prevent infection (Stavropoulou and Bezirtzoglou, 2020). In particular, antagonistic mechanisms carried out by probiotics can comprise colonization of the host epithelium, interference of pathogen adhesion, and direct co-aggregation with pathogens, all hindering host mucosa colonization; likewise, release of inhibitory substances and metabolites can interfere with growth and biofilm formation of pathogens (Sanders et al., 2019).
In this study, we evaluated the antimicrobial activity of L. gasseri 1ATV against six clinical isolates selected for their multidrug resistance profiles and for the presence of carbapenemase and ESBL genes, including two ESBL-producing strains (ST 307), two KPC-producing strains (ST 258), and two co-producing NDM-OXA-48 KP (ST 101); moreover, all strains were also resistant to colistin and fosfomycin. Interestingly, four CPKP strains belong to nosocomial high-risk clones ST101 and ST258, which were associated with infections reported worldwide (Shaidullina et al., 2023). Only a few studies have characterized the activity of alternative strategies like probiotic Lactobacillus spp. against similar carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae strains (Chen et al., 2019, Chen et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2021), and even less have focused on the antimicrobial activity against biofilm formation by carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae (Chatupheeraphat et al., 2023). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the antibacterial activity of L. gasseri against ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae strains, combined with genome mining tools to obtain new insights into its anti-CRKP effects. First, L. gasseri 1A-TV exhibited excellent antimicrobial activity against all strains by using the classic methods of deferred antagonism and agar spot assays, and these results were confirmed using 1A-TV CFS. In particular, when the 1A-TV CFS activity was evaluated by time-killing tests, an extraordinary bactericidal effect was observed after 24 h of incubation against all isolates, and the antimicrobial effects decreased when the CFS was treated with either proteinase K or trypsin.
Since there is a renewed interest in alternative strategies, involving metabolic by-products of probiotic strains that could retain their bioactivity without using viable cells in patients (Vallejo-Cordoba et al., 2020), these results are very promising for future perspectives. Moreover, several studies have demonstrated the antimicrobial activity of lactobacilli CFS against a wide spectrum of pathogens, including ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa (El-Mokhtar et al., 2020).
Genome mining by antiSMASH and BAGEL4 revealed three bacteriocin genes in two different BBGCs. In BBGC1 two bacteriocins were detected and categorized as class IIc, which comprises a wide range of bactericidal bacteriocins usually produced by the Firmicutes phylum. Interestingly, one was a gassericinA/acidocin-like bacteriocin, a circular bacteriocin with a wide spectrum against food-borne pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus (Pandey et al., 2013). In BBGC2, a third bacteriocin was detected, namely, helveticin J belonging to class III, as previously described (Scillato et al., 2021), that has a bactericidal mode of action against sensitive indicators as well (Joerger and Klaenhammer, 1986). The data obtained by genome mining could suggest their potential role in the antagonistic activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV, considering that bacteriocins are believed to contribute to interspecies competition with other bacteria, including pathogens; therefore, the production of bacteriocins could represent an important antimicrobial factor (Soltani et al., 2021). Further studies need to be performed to elucidate the actual involvement of bacteriocins in the antimicrobial activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS.
We also evaluated the metabolic profiles of 1A-TV CFS by 1H-NMR analysis to measure what metabolites are produced and consumed by this strain, which included organic acids, amino acids, and metabolites of the carbohydrate pathways. 1A-TV is mainly a producer of ethanol, lactic acid, and, in minor concentration, acetic acid, with a similar ratio of lactate/acetate to other Lactobacillus spp (Parlindungan et al., 2021). Yet, when compared to other strains with inhibitory activity, like L. plantarum and L. sakei as previously reported (Parlindungan et al., 2021), the concentration of organic acids in L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS is half or even less. In particular, acetic acid produced by L. plantarum has been reported to be essential for its anticolonization effect against CRKP in mice, and it was normally produced as higher concentrations by this strain (50 mmol/L) than by 1A-TV (Yan et al., 2021). The lower concentration of organic acids in 1A-TV CFS might reinforce that the strong antimicrobial activity of this strain is particularly given by the bacteriocins it produces.
In this study, we investigated two other aspects that contribute to antibacterial effects like co-aggregation and anti-biofilm activities. In fact, multiple studies have highlighted the protective role of probiotics that, by binding pathogens into co-aggregates, can exert their inhibitory activity: co-aggregation can expose pathogens to higher concentrations of inhibitory substances and metabolites and it can also hinder biofilm formation, which is an important feature for infection and resistance to host defenses and antibiotics (Monteagudo-Mera et al., 2019). In particular, 1A-TV showed high levels of co-aggregation with all strains, with statistically significant values for K. pneumoniae 1, 2, 3, and 7 strains, with higher co-aggregation values compared to Lactobacillus delbrueckii vs. K. pneumoniae (Bnfaga et al., 2023) that might depend on strain- or species-specific aggregating factors of L. gasseri 1A-TV.
Another feature of lactobacilli CFS is the strong anti-biofilm activity that could be due to the presence of bio-surfactants and exopolysaccharides produced by these strains (Raras et al., 2019; El-Mokhtar et al., 2020). The anti-biofilm activity of L. gasseri 1A-TV CFS against K. pneumoniae strong biofilm producers (strain 1, blaKPC-3, blaSHV-11, blaTEM-1, blaoxa-positive; strain 5, blaTEM-1, blaCTX-M-15-positive; and strain 6, blaTEM-1, blaCTX-M-15-positive) is noteworthy because biofilm formation is a strategy of some organisms to persist in severe environments by promoting bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents, the immune system, and stress conditions (Piperaki et al., 2017; Chatupheeraphat et al., 2023). Furthermore, the majority of clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae are able to form biofilm (approximately 80%), even those that are ESBL or carbapenemase producers, which can lead to persistence of colonization and infection, and it can also promote the spread of antibiotic resistance (Sabença et al., 2023).
This study has potential limitations. First, despite using NMR analysis to identify and quantify different metabolites released in CFS including organic acids, amino acids, and carbohydrate metabolism, the full characterization of the bioactives present in the CFS was not clearly defined. Thus, further studies by mass spectrometry are already underway to thoroughly investigate the bioactive molecules present in CFS and to investigate their activity in antimicrobial effects. A second limitation of this study is the inclusion of only a small number of K. pneumoniae strains, which were selected because they were well-characterized at the phenotype and genotype level.
In conclusion, this work supports the efficacy of the L. gasseri 1A-TV strain in adjuvant and preventive strategies against ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae, elucidating the inhibitory effect of CFS on bacterial growth and biofilm production. Even more, the use of metabolites and products of probiotic strains, like CFS, could be the answer to the debate of using probiotics as live microorganisms that could acquire virulence or antimicrobial resistance genes, becoming a potential vehicle for the diffusion of resistance determinants to other bacteria (Imperial and Ibana, 2016). Thus, the use of active natural bioproducts opens new perspectives aimed at the prevention and control of colonization by ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
GA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. VC: Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. RS: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SS: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by EU funding within the MUR PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Disease (project no. PE00000007, INF-ACT) (CUP E63C22002090006) and by the National Research Project PRIN 2022, Project title: “Bacterial interplay in genetically engineered microbiota model devised to counteract antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae” (CUP E53D23001300006).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1471107/full#supplementary-material
References
7.17.2 Time-Kill Assay 7.17 tests to assess bactericidal activity (2024). In: Clinical microbiology procedures handbook (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Aggarwal, S., Sabharwal, V., Kaushik, P., Joshi, A., Aayushi, A., Suri, M. (2022). Postbiotics: From emerging concept to application. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.887642
Alagna, L., Palomba, E., Mangioni, D., Bozzi, G., Lombardi, A., Ungaro, R., et al. (2020). Multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria decolonization in immunocompromised patients: A focus on fecal microbiota transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 5619. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165619
Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399, 629–655. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
Aslam, B., Wang, W., Arshad, M. I., Khurshid, M., Muzammil, S., Rasool, M. H., et al. (2018). Antibiotic resistance: a rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 11, 1645–1658. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S173867
Aziz, R. K., Bartels, D., Best, A. A., DeJongh, M., Disz, T., Edwards, R. A., et al. (2008). The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9, 75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bankevich, A., Nurk, S., Antipov, D., Gurevich, A. A., Dvorkin, M., Kulikov, A. S., et al. (2012). SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19, 455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Blin, K., Shaw, S., Augustijn, H. E., Reitz, Z. L., Biermann, F., Alanjary, M., et al. (2023). antiSMASH 7.0: new and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W46–W50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad344
Bnfaga, A. A., Lee, K. W., Than, L. T. L., Amin-Nordin, S. (2023). Antimicrobial and immunoregulatory effects of Lactobacillus delbrueckii 45E against genitourinary pathogens. J. BioMed. Sci. 30, 19. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00913-7
Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M., Usadel, B. (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114–2120. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Chatupheeraphat, C., Peamchai, J., Luk-In, S., Eiamphungporn, W. (2023). Synergistic effect and antibiofilm activity of the antimicrobial peptide K11 with conventional antibiotics against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1153868
Chen, C.-C., Lai, C.-C., Huang, H.-L., Huang, W.-Y., Toh, H.-S., Weng, T.-C., et al. (2019). Antimicrobial activity of lactobacillus species against carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00789
Chen, C.-C., Lai, C.-C., Huang, H.-L., Su, Y.-T., Chiu, Y.-H., Toh, H.-S., et al. (2021). Antimicrobial ability and mechanism analysis of Lactobacillus species against carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 54, 447–456. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.01.005
Davison, J. M., Wischmeyer, P. E. (2019). Probiotic and synbiotic therapy in the critically ill: State of the art. Nutrition 59, 29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.07.017
El-Mokhtar, M. A., Hassanein, K. M., Ahmed, A. S., Gad, G. F., Amin, M. M. (2020). Antagonistic Activities of Cell-Free Supernatants of Lactobacilli Against Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. F. Infect. Drug Resist. 13, 543–552. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S235603
Galperin, M. Y., Wolf, Y. I., Makarova, K. S., Vera Alvarez, R., Landsman, D., Koonin, E. V. (2021). COG database update: focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D274–D281. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1018
Gomaa, E. Z. (2020). Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113, 2019–2040. doi: 10.1007/s10482-020-01474-7
Gona, F., Bongiorno, D., Aprile, A., Corazza, E., Pasqua, B., Scuderi, M. G., et al. (2019). Emergence of two novel sequence type and 3367) NDM-1- and OXA-48-co-producing K. pneumoniae in Italy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 38, 1687–1691. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03597-w
Gona, F., Mezzatesta, M. L., Corona, D., Zerbo, D., Scriffignano, V., Stefani, S., et al. (2011). Klebsiella pneumoniae ESBL producers responsible for severe UTIs in a renal transplant unit. Infection 39, 83–85. doi: 10.1007/s15010-011-0081-0
Imperial, I. C. V. J., Ibana, J. A. (2016). Addressing the antibiotic resistance problem with probiotics: reducing the risk of its double-edged sword effect. Front. Microbiol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01983
Joerger, M. C., Klaenhammer, T. R. (1986). Characterization and purification of helveticin J and evidence for a chromosomally determined bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 481. J. Bacteriol 167, 439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.439-446.1986
Kasuga, G., Tanaka, M., Harada, Y., Nagashima, H., Yamato, T., Wakimoto, A., et al. (2019). Homologous expression and characterization of gassericin T and gassericin S, a novel class IIb bacteriocin produced by LA327. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 85 (6), eo2815–18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02815-18
Kontopoulou, K., Iosifidis, E., Antoniadou, E., Tasioudis, P., Petinaki, E., Malli, E., et al. (2019). The clinical significance of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae rectal colonization in critically ill patients: from colonization to bloodstream infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 68, 326–335. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000921
Lagesen, K., Hallin, P., Rødland, E. A., Staerfeldt, H.-H., Rognes, T., Ussery, D. W. (2007). RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 3100–3108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm160
Lowe, T. M., Eddy, S. R. (1997). tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 955–964. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.5.955
Maldonado, N., Ruiz, C., Cecilia, M., Nader-Macías, M. (2007). A simple technique to detect Klebsiella biofilm-forming-strains. Inhibitory potential of Lactobacillus fermentum CRL 1058 whole cells and products. Commun. Curr. Res. Educ. Top. Trends Appl. Microbiol. 52–59.
Mezzatesta, M. L., Gona, F., Caio, C., Petrolito, V., Sciortino, D., Sciacca, A., et al. (2011). Outbreak of KPC-3-producing, and colistin-resistant, Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in two Sicilian hospitals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 17, 1444–1447. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03572.x
Monteagudo-Mera, A., Rastall, R. A., Gibson, G. R., Charalampopoulos, D., Chatzifragkou, A. (2019). Adhesion mechanisms mediated by probiotics and prebiotics and their potential impact on human health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 6463–6472. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09978-7
Ochońska, D., Ścibik, Ł., Brzychczy-Włoch, M. (2021). Biofilm formation of clinical klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from tracheostomy tubes and their association with antimicrobial resistance, virulence and genetic diversity. Pathogens 10, 1345. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101345
Pace, F., Pace, M., Quartarone, G. (2015). Probiotics in digestive diseases: focus on Lactobacillus GG. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol 61, 273–292.
Pandey, N., Malik, R. K., Kaushik, J. K., Singroha, G. (2013). Gassericin A: a circular bacteriocin produced by lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus gasseri. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 1977–1987. doi: 10.1007/s11274-013-1368-3
Parlindungan, E., Lugli, G. A., Ventura, M., van Sinderen, D., Mahony, J. (2021). Lactic acid bacteria diversity and characterization of probiotic candidates in fermented meats. Foods 10, 1519. doi: 10.3390/foods10071519
Piperaki, E.-T., Syrogiannopoulos, G. A., Tzouvelekis, L. S., Daikos, G. L. (2017). Klebsiella pneumoniae: virulence, biofilm and antimicrobial resistance. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 36, 1002–1005. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001675
Raras, T., Firman, A., Kinanti, I., Noorhamdani, N. (2019). Anti-biofilm activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kefir against multidrug-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 13, 983–992. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.13.2.35
Ravi, R. K., Walton, K., Khosroheidari, M. (2018). MiSeq: A next generation sequencing platform for genomic analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 1706, 223–232. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7471-9_12
Sabença, C., Costa, E., Sousa, S., Barros, L., Oliveira, A., Ramos, S., et al. (2023). Evaluation of the ability to form biofilms in KPC-producing and ESBL-producing klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples. Antibiotics (Basel) 12, 1143. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12071143
Salminen, S., Collado, M. C., Endo, A., Hill, C., Lebeer, S., Quigley, E. M. M., et al. (2021). The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 649–667. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
Sanders, M. E., Merenstein, D. J., Reid, G., Gibson, G. R., Rastall, R. A. (2019). Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16, 605–616. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0173-3
Scillato, M., Spitale, A., Mongelli, G., Privitera, G. F., Mangano, K., Cianci, A., et al. (2021). Antimicrobial properties of Lactobacillus cell-free supernatants against multidrug-resistant urogenital pathogens. Microbiologyopen 10, e1173. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1173
Seddik, H. A., Bendali, F., Gancel, F., Fliss, I., Spano, G., Drider, D. (2017). Lactobacillus plantarum and its probiotic and food potentialities. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 9, 111–122. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9264-z
Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30, 2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Shaidullina, E. R., Schwabe, M., Rohde, T., Shapovalova, V. V., Dyachkova, M. S., Matsvay, A. D., et al. (2023). Genomic analysis of the international high-risk clonal lineage Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 395. Genome Med. 15, 9. doi: 10.1186/s13073-023-01159-6
Siroli, L., Patrignani, F., Serrazanetti, D. I., Parolin, C., Ñahui Palomino, R. A., Vitali, B., et al. (2017). Determination of antibacterial and technological properties of vaginal lactobacilli for their potential application in dairy products. Front. Microbiol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00166
Soltani, S., Hammami, R., Cotter, P. D., Rebuffat, S., Said, L. B., Gaudreau, H., et al. (2021). Bacteriocins as a new generation of antimicrobials: toxicity aspects and regulations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 45, fuaa039. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa039
Stavropoulou, E., Bezirtzoglou, E. (2020). Probiotics in medicine: A long debate. Front. Immunol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02192
Vallejo-Cordoba, B., Castro-López, C., García, H. S., González-Córdova, A. F., Hernández-Mendoza, A. (2020). Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: A review of current evidence and emerging trends. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 94, 1–34. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2020.06.001
van Heel, A. J., de Jong, A., Song, C., Viel, J. H., Kok, J., Kuipers, O. P. (2018). BAGEL4: a user-friendly web server to thoroughly mine RiPPs and bacteriocins. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, W278–W281. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky383
Vertillo Aluisio, G., Spitale, A., Bonifacio, L., Privitera, G. F., Stivala, A., Stefani, S., et al. (2022). Streptococcus salivarius 24SMBc Genome Analysis Reveals New Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Involved in Antimicrobial Effects on Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Microorganisms 10, 2042. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10102042
Wang, G., Zhao, G., Chao, X., Xie, L., Wang, H. (2020). The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance of klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17, 6278. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176278
Keywords: Lactobacillus gasseri, ESBL, cell-free supernatant, carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae, antimicrobial activity
Citation: Vertillo Aluisio G, Mezzatesta ML, Cafiso V, Scuderi R, Stefani S and Santagati M (2024) Cell-free supernatant of Lactobacillus gasseri 1A-TV shows a promising activity to eradicate carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae colonization. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1471107. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1471107
Received: 26 July 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 03 December 2024.
Edited by:
Govind Vediyappan, Kansas State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Rosa Del Campo, Ramón y Cajal Institute for Health Research, SpainAntónio Machado, Universidad San Francisco de Quito, Ecuador
Copyright © 2024 Vertillo Aluisio, Mezzatesta, Cafiso, Scuderi, Stefani and Santagati. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maria Santagati, bS5zYW50YWdhdGlAdW5pY3QuaXQ=
 Gaia Vertillo Aluisio
Gaia Vertillo Aluisio Maria Lina Mezzatesta
Maria Lina Mezzatesta Viviana Cafiso
Viviana Cafiso Renata Scuderi
Renata Scuderi Stefania Stefani
Stefania Stefani Maria Santagati
Maria Santagati