- 1The College of Veterinary Medicine, Southwest University, Chongqing, China
- 2Animal Epidemic Prevention and Control Center of Rongchang, Chongqing, China
- 3Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 4State Key Laboratory for Animal Disease Control and Prevention, College of Veterinary Medicine, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
Brucellosis is a serious zoonosis caused by Brucella spp. infection, which not only seriously jeopardizes the health of humans and mammals, but also causes huge economic losses to the livestock industry. Brucella is a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium that relies primarily on its virulence factors and a variety of evolved survival strategies to replicate and proliferate within cells. Currently, the mechanisms of autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis in Brucella-infected hosts are not fully understood and require further research and discussion. This review focuses on the relationship between Brucella and autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis to provide the scientific basis for revealing the pathogenesis of Brucella.
1 Introduction
Brucellosis is a prevalent, chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Brucella. So far, twelve Brucella species have been isolated and identified. There are six classical species: Brucella melitensis (B. melitensis), Brucella abortus (B. abortus), Brucella suis (B. suis), Brucella ovis (B. ovis), Brucella canis (B. canis) and Brucella neotoma (B. neotoma) (Roop et al., 2021). The species show a high degree of similarity at the genetic level but differ in host preference, zoonotic risk, and virulence (Suárez-Esquivel et al., 2020). B. melitensis, B. abortus, B. suis, B. canis, and B. ovis are some of the more well-studied Brucella species that have sickened goats and sheep, cattle, pigs, dogs, and sheep, respectively (Roop et al., 2021). Animals infected with Brucella can cause abortion, infertility, and reduced productivity. B. melitensis, B. abortus, B. suis, and B. canis are pathogenic to humans. B. melitensis is the most virulent to humans, followed by B. suis, and the weakest is B. abortus (Deng et al., 2019). People often become ill through direct contact with tissues or blood from diseased animals or through accidental ingestion of products (e.g., dairy products) from infected animals. The common symptoms include undulant fever, sweating, fatigue, anorexia, and joint pain (de Figueiredo et al., 2015a).
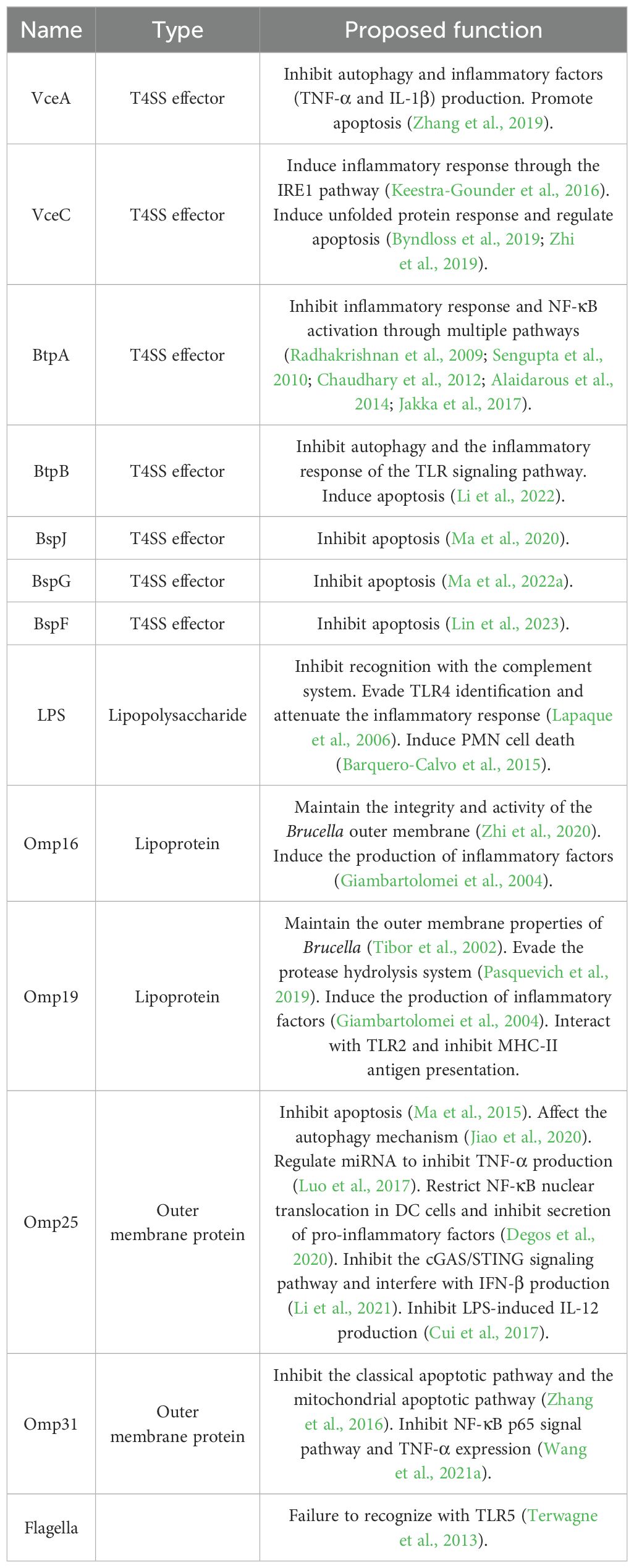
Brucella has evolved various survival strategies to escape killing by host cells, such as stimulating autophagy after invasion of the host, forming autophagosome-like structures, and preventing lysosomal fusion to allow proliferation, as have Legionella pneumophila and Porphyromonas gingivalis (Dorn et al., 2002). Autophagy is an innate immune mechanism of the host cell that maintains cellular homeostasis by removing damaged proteins and organelles from the host cell. Some pathogens have evolved strategies that in turn utilize autophagy mechanisms to survive inside cells. T4SS is an important virulence factor of Brucella, which secretes effectors such as RicA, VceA, VecC, BtpA, BtpB, BspJ, BspG, BspA, BspB, BspC, BspE, BspF, BPE005, BPE123, BPE043, BPE275, and SepA. VceA and BtpB can regulate autophagy (Zhang et al., 2019; Li et al., 2022). Several autophagy proteins are involved in intracellular replication in Brucella: WIPI and ATG9 are involved in the formation of replicative Brucella-containing vacuole (rBCV) (Taguchi et al., 2015), and Beclin1 and ATG14L are involved in the formation of autophagic BCV (aBCV) (Starr et al., 2012). When pathogenic microorganisms infect the organism, host cells may promote the maturation and secretion of certain inflammatory factors that initiate natural immune responses and inflammation, contributing to the host’s immune defense against the pathogen. We discussed several pathways of inflammatory response triggered by Brucella invasion of the host: VceC triggers an inflammatory response by inducing an unfolded protein response (UPR) (de Jong et al., 2013; Keestra-Gounder et al., 2016); Inflammatory responses triggered by the inflammasomes NLRP3 and AIM2 (Gomes et al., 2013; Costa Franco et al., 2019); Other pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) of Brucella, such as LPS, major outer membrane proteins, and lipoproteins, trigger inflammatory responses via the TLR pathway. At the same time, Brucella uses virulence factors (e.g., BtpA, BtpB, Omp25, etc.) to hinder pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and evade host innate immunity. Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is an autonomous, orderly death of the organism that occurs under genetic regulation. Strongly virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibits apoptosis and weakly virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis promotes apoptosis (Zhai et al., 2019). Similar to M. tuberculosis, Brucella can also promote or inhibit apoptosis under different conditions and establish a persistent infection by regulating apoptosis. Brucella can infect professional phagocytes as well as non-professional phagocytes. Inhibition of apoptosis in infected cells seems to be beneficial to Brucella (de Figueiredo et al., 2015b), but there is no definitive answer to date. Some virulence factors of Brucella have pro- or inhibitory effects on apoptosis. Omp25 and Omp31 are the major outer membrane proteins of Brucella. BspJ, BspG, BspF, Omp25, and Omp31 inhibit apoptosis (Ma et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2016; Ma et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2022a; Lin et al., 2023). VceA and BtpB promote apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2019; Li et al., 2022). VceC inhibits or promotes apoptosis through different pathways (Byndloss et al., 2019; Zhi et al., 2019).
The mechanisms of autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis in Brucella-infected hosts have not been fully and systematically elucidated. This paper focuses on the relationship between Brucella and autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis, laying the foundation for further unraveling the pathogenic mechanism of Brucella.
2 Pathogenesis of Brucella
2.1 Intracellular transport
Brucella is capable of infecting both professional and non-professional phagocytes. Upon entering the host cell, Brucella is “trapped” in a compartment, forming a membrane-enclosed structure called a Brucella-containing vacuole (BCV). Most BCVs fuse with lysosomes and 90% of internal Brucella are hydrolyzed and killed. However, it is not clear how the remaining 10% escapes killing by the host. At 10-30 minutes post-infection, BCV acquires early endosomal markers such as EEA-1 (early endosomal antigen 1) and the small GTPase Rab5 (Pizarro-Cerdá et al., 1998; Chaves-Olarte et al., 2002). Early endosomal markers present on BCVs are gradually replaced by late endosomal markers (the lysosome-associated membrane protein LAMP1 and the small GTPase Rab7) at 4 hours post-infection (Celli et al., 2003; Starr et al., 2008). Over time, the endosomes mature and acidify (pH reaches 4 to 4.5), at which point the BCVs are referred to as endosomal-containing Brucella vacuoles (eBCVs). BCV acidification is required for Brucella survival and replication (Porte et al., 1999). eBCV has been shown to interact with COPII-coated structures at functional endoplasmic reticulum exit sites (ERES) (Celli et al., 2005). At 8-12 hours post-infection, eBCV gradually loses endosomal markers and acquires ER-derived membranes. Meanwhile, eBCV acquired ER membrane markers such as calcium-binding protein and Sec61β. These vacuoles have structural and functional properties of the ER that provide conditions for the growth and replication of Brucella, at which point the BCVs are referred to as replicative Brucella-containing vacuoles (rBCVs). Brucella undergoes extensive replication in rBCV, which is eventually captured in autophagosome-like structures and becomes autophagic BCV (aBCV). At this point, aBCV stops maturing and kills cells (Figure 1) (Jiao et al., 2021). We now have a preliminary understanding of the intracellular cycle of Brucell. However, the underlying mechanisms of each stage of Brucella development within the cell have not been fully explained.
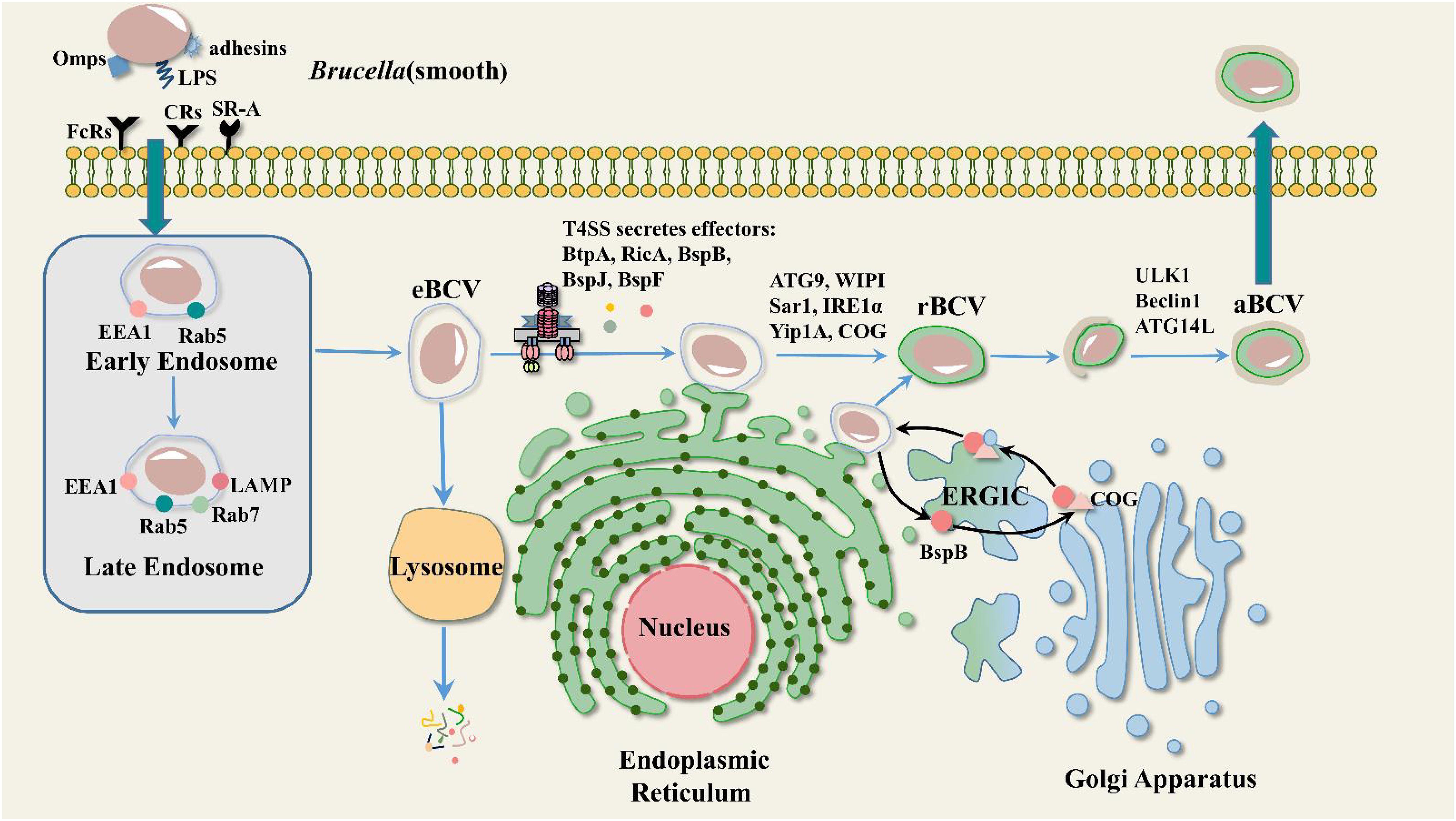
Figure 1. Mode of intracellular transport of Brucella. Heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) and LPS from Smooth Brucella bind to prion protein (PrPc) and class A scavenger receptor (SR-A) on lipid rafts, respectively, and thus enter the cell, where they pass through three phases: eBCV, rBCV, and aBCV. EEA1, LAMP, Rab5, and Rab7 are involved in eBCV maturation. ATG9, WIPI, Sar1, IRE1α, Yip1A, and COG are involved in rBCV formation. The T4SS effector BspB is transported to the Golgi via the ER-to-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), where it binds to the conserved oligomeric Golgi (COG) complex and facilitates the transport of Golgi membrane-derived vesicles to the BCV. ULK1, Beclin1, and ATG14L are involved in aBCV formation.
2.2 Virulence factor of Brucella: T4SS
T4SS is an important virulence factor for Brucella, which plays an important role in the intracellular replication of Brucella (de Jong and Tsolis, 2012). T4SS is encoded by the virB operon, and the functional virB system is present in all Brucella species and remains highly conserved (O’Callaghan et al., 1999). The virB system consists of virB1-virB12 proteins, which can be divided into four groups according to their functions: the ATPases (virB4 and virB11), the core components (virB6-virB10), the surface-exposed components (virB2 and virB5), and the other components (virB1 and virB12) (Xiong et al., 2021). Numerous studies have shown that virB is essential for persistent Brucella infection in various host cells (Hong et al., 2000; Comerci et al., 2001; den Hartigh et al., 2004). Salcedo, S.P. et al. investigated the ability of different Brucella strains to infect the human trophoblast and, as expected, the replication of B. melitensis 16M in JEG cells was completely dependent on virB. Surprisingly, the B. abortus virB mutant was able to replicate at a low level in JEG cells (Salcedo et al., 2013), suggesting that this replication of B. abortus has an incomplete dependence on the virB type IV secretion system, and the exact mechanism that generates this incomplete dependence is not clear and requires further validation. B. abortus A19 was more adaptable to harsh environments (strong acidic and high-salt) in the presence of virB (Deng et al., 2022), this experimental result explains that virB facilitates the invasion of Brucella spp. into host cells, adapts to the intracellular complexity, and enhances bacterial survival. In addition, the virB mutant strain enhanced autophagy, up-regulated IL-6, and down-regulated IL-10 expression in macrophages compared to the B. abortus A19 parental strain.
virB T4SS can secrete effectors such as RicA, VceA, VecC, BtpA, BtpB, BspJ, BspG, BspA, BspB, BspC, BspE, BspF, BPE005, BPE123, BPE043, BPE275, and SepA, which can enter the host cells to function. Based on previous studies, the role of T4SS effectors can be divided into two aspects: One is affecting the formation of rBCV and the other is affecting the virulence of Brucella (Xiong et al., 2021). RicA was the first effector reported to interact with the small GTPase Rab2. RicA-deficient mutants showed no significant change in virulence among infected mice or HeLa cells (Ke et al., 2015), suggesting that RicA may not play a major role in the intracellular parasitism of Brucella. However, in HeLa cells, the B. abortus RicA mutant loses the late endosomal marker LAMP1 earlier than the wild-type strain, which facilitates the RicA mutant to reach the ER faster and establish a replicative ecological niche (de Barsy et al., 2011). Rab2 is important for rBCV biogenesis and bacterial replication. However, RicA may have a negative impact on Rab2 function, so that B. abortus RicA mutants proliferate faster in host cells. Meanwhile, it has been found that effector BspB attenuates the negative regulation of Rab2 function by RicA (Smith et al., 2020). Mutants deficient in SepA invaded macrophages more efficiently but significantly reduced Brucella replication capacity at an early stage, suggesting that SepA may play an integral role in the early stages of Brucella infection (Döhmer et al., 2014). SepA-deficient strains had a defect in excluding LAMP1, suggesting that SepA may have a role in inhibiting the fusion of BCVs with lysosomes (Ke et al., 2015). It is not clear why Brucella deficient in SepA invades macrophages more efficiently. Quorum sensing (QS) is a regulatory system that allows microorganisms to sense changes in population density for gene expression regulation. VjbR and BlxR are two regulators of QS. It was found that VjbR mutants down-regulated the expression of virB operon and flagellar genes, suggesting that VjbR contributes to B. melitensis survival by regulating Brucella virulence factors (Delrue et al., 2005). In one study (Brambila-Tapia and Pérez-Rueda, 2014), VjbR activated genes associated with persistent infection (e.g., intracellular trafficking, vesicular transport) and defense mechanisms; BlxR inhibits the expression of genes related to metabolism (e.g., energy production and conversion), which facilitates bacterial adaptation to the intracellular environment. GntR10 is a transcriptional regulator of Brucella. Deletion of GntR10 resulted in down-regulation of VjbR and BlxR expression, affecting the expression of T4SS effectors (BspE and BspF) and ultimately inhibiting NF-κB activation (Li et al., 2023).
3 Brucella mediates autophagy
3.1 Autophagy is involved in the intracellular survival of Brucella
There have been a number of reports suggesting that the reproduction of Brucella spp. in the host is inextricably linked to autophagy. Guo, F., and colleagues hold the view that autophagy benefits the intracellular survival of Brucella (Guo et al., 2012). In B. melitensis 16M-infected mouse macrophages, they observed a rise in the expression of the autophagy marker LC3-II and the formation of autophagosomes. Moreover, Brucella replication was significantly reduced after treatment with the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine. A similar phenomenon occurred in mouse RAW264.7 macrophages infected by B. suis (Dong et al., 2023) i.e., B. suis invasion up-regulated LC3-II expression, and additionally, the autophagy-lysosomal pathway positively promoted Brucella proliferation. These researchers point out that autophagy may also serve bacteria as a form of self-protection. However, Hamer, I.’s experiments (Hamer et al., 2014) showed that B. abortus and B. melitensis do not induce macroautophagy in mouse embryonic fibroblasts to reach their replicative niche or to stimulate their replication. Differences in cell types may be one reason for the variability.
3.2 VceA and BtpB inhibit autophagy
Autophagy is an innate immune mechanism of the host cell, and Brucella effectors may disrupt host cell homeostasis by inhibiting autophagy. VceA, one of the first substrates identified in Brucella T4SS, is regulated by VjbR and remains highly conserved among all sequenced Brucella genes (de Jong et al., 2008). In preliminary studies, it was observed that VceA mutant strains enhanced autophagy, but the role played by VceA in the autophagy process needs to be further investigated. Zhang, J.’s team (Zhang et al., 2019) found that infection of human trophoblast cells by B. abortus VceA mutant strains resulted in increased expression of ATG5 and LC3-II, and decreased levels of P62 and LC3-I expression. They observed the expression of P62 protein under immunofluorescence microscopy and found that the number of P62 protein focal points was significantly reduced in the mutant strain group. In addition, the number of autophagosomes was increased in the VceA knockout group under electron microscopy. It is therefore hypothesized that VceA may have a role in inhibiting autophagy. Li, J et al. found that deletion of BtpB resulted in increased LC3-II expression, decreased P62, and accumulation of autophagic lysosomes (Li et al., 2022). This suggests that BtpB also has an inhibitory effect on autophagy. Brucella Omp25 affects macrophage autophagy (Jiao et al., 2020), but the molecular mechanism is unknown.
3.3 Autophagy proteins (WIPI1, ATG9, ULK1, Beclin1) are involved in Brucella intracellular replication
Autophagy proteins play an important role in autophagy genesis (Table 1). Taguchi, Y.’s experiments confirmed that cells knocking down the expression of the autophagosome nucleation protein WIPI1 and the autophagy protein ATG9 had significantly lower ER membrane-derived large vacuole production (Taguchi et al., 2015). This suggests that WIPI1 and ATG9 are involved in rBCV biogenesis. In addition to this, the autophagy proteins ULK1 and Beclin1 are involved in Brucella intracellular parasitism. ULK1 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a key role in the initiation of autophagy and serves as a homologue of yeast Atg1 in mammals. Five ULK1 homologs have been identified, and they are ULK1, ULK2, ULK3, ULK4, and STK36, of which only ULK1 and ULK2 are widely believed to be involved in the regulation of the conventional autophagy signaling pathway (Zachari and Ganley, 2017). In the absence of serum, neuronal autophagy was induced by simulating an environment with low potassium concentrations, and the results showed that ULK1 was required, whereas ULK2 was not (Lee and Tournier, 2011). There are also several experiments confirming that ULK1 is indispensable and that the absence of ULK1 is sufficient to disrupt the onset of conventional autophagy (Chan et al., 2007), whereas ULK2 acts as a surrogate or compensatory for the impairment of ULK1 function in this process (Zachari and Ganley, 2017). ULK1 and ULK2 interact with the same core components and share a high degree of similarity in their protein kinase domains, i.e. 52% protein sequence and 78% homology. It is unclear why ULK1 dominates the autophagy pathway. In yeast, the Atg1 complex consists of Atg1, Atg11, Atg13, Atg17, Atg29, Atg31. In mammals, the components of the ULK1 complex are ULK1, ATG13, ATG101, FIP200, (200 kDa focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein)/RB1CC1. Interaction of ATG13 and FIP200/RB1CC1 with ULK1 helps enhance the activity and stability of ULK1 kinase (Ganley et al., 2009). During conventional autophagy, when the organism is in an abnormal (e.g., starvation) state, mTORC1 activity is inhibited and AMPK activates ULK1 activity by phosphorylating (Kim et al., 2011). Beclin1 is one of the important components of class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3P), and although it is an important regulator of autophagy initiation, its specific mechanism of action remains poorly studied. Pandey, A. et al. found that in autophagy-deficient cells (including deletion or inactivation of ULK1, Beclin1, and ATG9a), intracellular transport and replication of B. melitensis 16M is severely disrupted (Pandey et al., 2018). However, in B. abortus-invaded HeLa cells (Starr et al., 2012), depletion of ULK1 and Beclin1 did not affect Brucella abortus delivery to the ER and bacterial replication but significantly reduced aBCV production. The two studies yielded markedly disparate findings with regard to the impact of ULK1 and Beclin1 deletions on rBCV biogenesis and Brucella replication. Differential behavior of Brucella in macrophages and non-phagocytes (e.g., HeLa) has been demonstrated. Thus, differences in cell models may be one of the possibilities for producing different results. Nevertheless, the results of both Pandey, A. and Starr point out that ULK1 and Beclin1 have an effect on Brucella parasitism. However, the effect of ULK1- and Beclin1-mediated autophagy mechanisms on Brucella still needs to be further studied.
4 Inflammatory mechanisms of host invasion by Brucella
4.1 VceC induces inflammatory responses
Like VceA, VceC is conserved in all sequenced Brucella genes, and its C-terminal 20 amino acids are essential for the translocation of VceC into the host cell (de Jong et al., 2008). VceC translocates to the ER through its structural advantage and binds to the ER chaperone immunoglobulin GRP78 to cause ER stress, inducing an unfolded protein response (UPR) as well as ultimately leading to an inflammatory response (de Jong et al., 2013; Keestra-Gounder et al., 2016). The UPR has three signaling pathways involving three important ER transmembrane proteins: inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PEPK), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) (Schröder and Kaufman, 2005). VceC-triggered inflammatory responses are mainly realized through the IRE1α pathway (Keestra-Gounder et al., 2016). The IRE1α pathway is activated in a time-dependent manner during Brucella infection, and activated IRE1α translocates TRAF2 to the ER membrane, which subsequently sends signals to activate the NF-κB pathway, eventually inducing an inflammatory response (Figure 2) (Taguchi et al., 2015; Caruso and Núñez, 2016; Keestra-Gounder et al., 2016). Notably, the process of NF-κB activation requires the support of NOD1 and NOD2 signaling molecules with the activity of the adaptor protein RIP2. NOD1 and NOD2 are two members of the NOD-like receptors (NLRs) family of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that sense bacterial peptidoglycan (PGN)-derived fragments to induce pro-inflammatory responses (Caruso and Núñez, 2016). In contrast, NOD1 and NOD2 were shown to be irrelevant to PGN stimulation during VceC-induced inflammation. Although NOD1 and NOD2 play an important role in ER stress-induced inflammatory responses, it has been found that these receptors do not affect Brucella parasitism in mice (Oliveira et al., 2012). B. abortus infected normal (C57BL/6), NOD1-deficient, NOD2-deficient, and RIP2-deficient mice, respectively, and there was no difference in the bacterial numbers in the spleens of the four groups, suggesting that NOD1, NOD2, and RIP2 are dispensable for the intracellular survival of B.abortus. The second is that NOD1 and NOD2 are not the root cause of host cell (trophoblast) death. Infection of pregnant mice lacking NOD1 and NOD2 with B. abortus did cause suppression of the inflammatory response and increased pup survival compared to pregnant wild-type mice (Keestra-Gounder et al., 2016). However, the TUNEL assay of placental sections from B. abortus-infected NOD1- and NOD2-deficient mice as well as control mice showed no significant difference in the number of trophoblast cell deaths between the two groups, indicating that NOD1 and NOD2 do not play a role in trophoblast cell death (Byndloss et al., 2019).
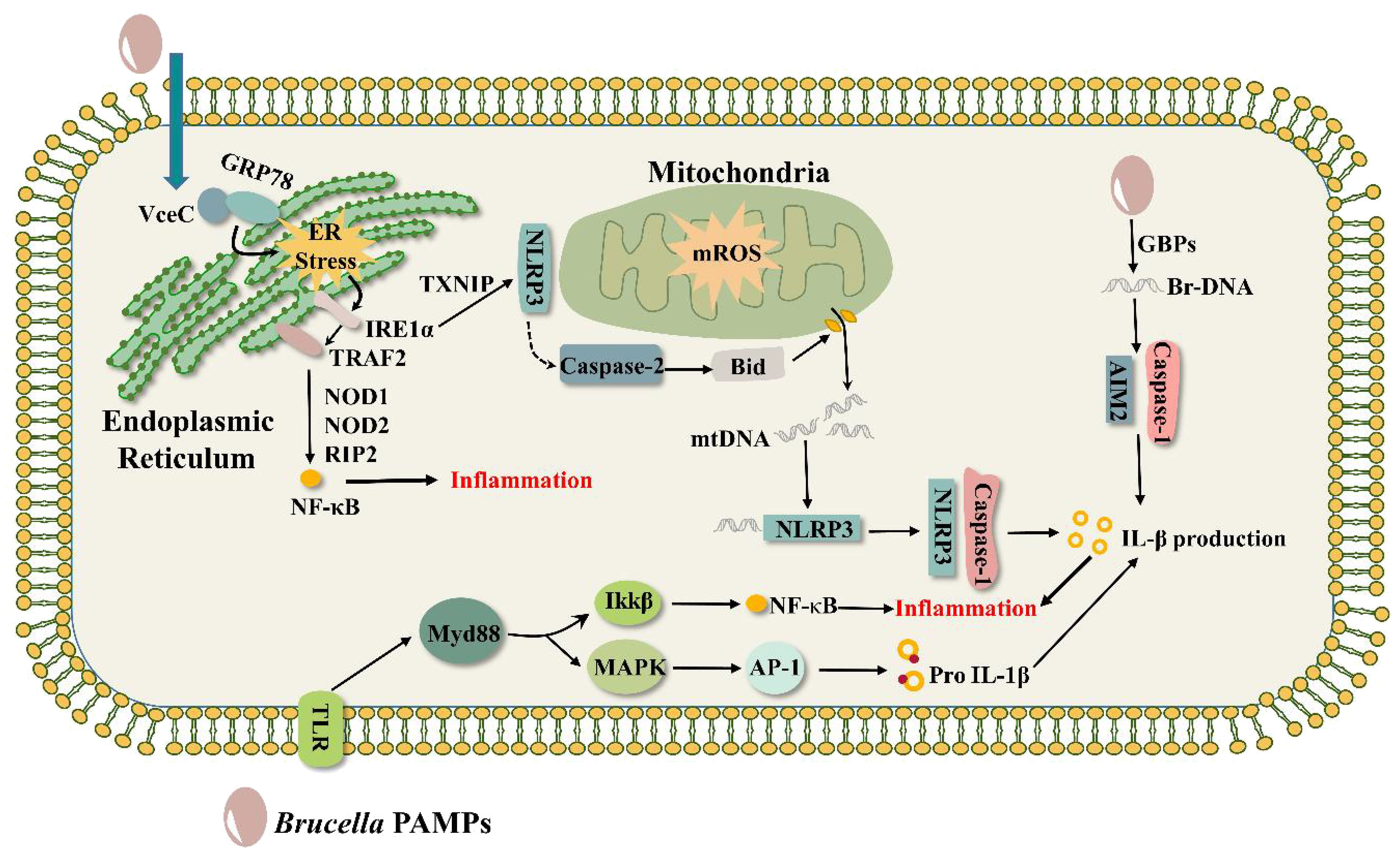
Figure 2. Brucella triggers inflammatory responses. VceC binds to the ER chaperone immunoglobulin GRP78 to trigger ER stress, activates the IRE1α, translocates TRAF2 to the ER membrane, and activates the NF-κB pathway with the support of the signaling molecules NOD1, NOD2, and the adaptor protein RIP2, inducing an inflammatory response. AIM2 recognizes Brucella DNA in the presence of the guanylate-binding protein GBP and activates the inflammatory response of the caspase-1 pathway. During ER stress, IRE1α is activated to recruit TXNIP and NLRP3 in mitochondria to participate in mitochondrial ROS. At the same time, NLRP3 activates Caspase-2 to make the BH3 protein Bid a truncated active form, induces the release of DNA from mitochondria, and DNA interacts with NLRP3 to activate the inflammatory response of the Caspase-1 pathway. Other pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) of Brucella, such as LPS, major outer membrane proteins, and lipoproteins, trigger inflammatory responses via the TLR pathway.
4.2 BtpA and BtpB regulate the inflammatory response
BtpA and BtpB are known to inhibit the host’s innate immune response and regulate the inflammatory response. BtpA, which is not present in B. suis, contains a TIR domain at its C-terminus, and the TIR domain is an important component of toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated innate immunity. BtpA is similar to the TIR domain adapter protein MAL and can compete with MAL for TLR4. Meanwhile, BtpA interacts with MAL to reduce MAL phosphorylation and eventually reduces TLR4 and TLR2-mediated activation of the NF-κB pathway (Radhakrishnan et al., 2009; Sengupta et al., 2010; Alaidarous et al., 2014). In addition, BtpA can interact with the TIR domain-containing adapter protein MyD88 to influence the inflammatory response (Chaudhary et al., 2012). BtpA attenuates LPS-induced pyroptosis and inflammatory cytokine secretion by ubiquitination and degradation of caspase-1, 4, 11 in mouse and human macrophages (Jakka et al., 2017). BtpA inhibits caspase- 4/11-mediated inflammation, which is the far-reaching inspiration for the development of therapeutic drugs targeting LPS-induced septicemia. BtpB is present in all sequenced Brucella species and, similar to BtpA, also contains a TIR domain that can function accordingly by interfering with TLR signaling. In addition, Brucella flagella can evade TLR5 recognition to limit innate immune recognition (Terwagne et al., 2013).
4.3 Inflammatory responses triggered by NLRP3 and AIM2
It has been shown that ASC inflammasomes, mainly NLRP3 and AIM2, can sense Brucella and regulate caspase 1-mediated inflammation (Figure 2) (Gomes et al., 2013), ultimately influencing Brucella pathogenesis. Generally, the C-terminus of AIM2 senses pathogen DNA, and its N-terminal pyrin domain binds to the N-terminus of ASC, while the C-terminal CARD domain of ASC binds to the procaspase-1. Formation of the DNA-AIM2-ASC-pro-Caspase-1 complex, the AIM2 inflammasome, regulates IL-1β maturation and secretion through activation of caspase-1 (Hornung et al., 2009). It was found that AIM2 recognizes Brucella DNA (Costa Franco et al., 2019) and that guanylate-binding protein (GBP) plays an important role in this process (Costa Franco et al., 2018), possibly by killing Brucella so that the DNA is released in large quantities for AIM2 binding. NLRP3 crosstalks with the ER stress IRE1α pathway for cytokine IL-1β secretion and pyroptosis (Bronner et al., 2015). T4SS effectors (VceC, BtpA, BspL), Yip1A (a host factor), and STING activate the IRE1α axis of the UPR (de Jong et al., 2013; Smith et al., 2013; Taguchi et al., 2015; Guimarães et al., 2019; Luizet et al., 2021), but it is not clear whether they can act directly on NLRP3-triggered inflammatory responses. During Brucella infection, IRE1α is activated to recruit TXNIP and NLRP3 in mitochondria to engage in mitochondrial ROS. Simultaneously, NLRP3 activates Caspase-2 to process the BH3-only protein BID into its truncated active form, which subsequently induces the creation of a pore in the mitochondrial membrane and the release of mitochondrial DNA. DNA binds to NLRP3 and promotes the formation of the NLRP3-ASC-Caspase-1 complex, eventually leading to IL-1β production (Shin and Argon, 2015; Marim et al., 2017). Mice with AIM2, NLRP3, and ASC deletions were more susceptible to B. abortus compared to wild-type strain (Gomes et al., 2013; Tupik et al., 2020), suggesting that multiple ASC-dependent inflammasomes attenuate Brucella pathogenesis and contribute to host protection from infection. Surprisingly, AIM2 and NLRP3 were dispensable for controlling Brucella joint burdens, but Caspase-1 and Caspase-11 caused arthritis and apoptosis to control Brucella joint infection. In addition to this, LPS can also induce caspase-11-mediated pyroptosis (Lacey et al., 2018).
4.4 cGAS-STING pathway induces type I interferon production
The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling pathway is strongly associated with various inflammatory diseases (Decout et al., 2021). STING is an important DNA sensor that does not recognize whole DNA but can directly recognize cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) of bacterial origin. So, STING usually works through two different mechanisms. On the one hand, STING directly recognizes CDN (e.g., c-di-GMP) and induces an intracellular immune response. On the other hand, DNA from pathogenic microorganisms is released into the host cytoplasm (Burdette et al., 2011). cGAS recognizes and binds to the DNA, catalyzes the production of cGAMP, activates STING, and ultimately induces the expression of genes such as type I interferons and pro-inflammatory cytokines (Ishikawa et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2013). In recent years, researchers have found that STING plays an important role in controlling Brucella infection in vitro and in vivo, while cGAS is dispensable (Costa Franco et al., 2018; Alonso Paiva IM et al., 2023). Costa Franco et al. found that Brucella DNA is not only dependent on STING to induce expression of innate immunity genes (IFN-β and GBP), but also induces STING translocation from the ER to the perinuclear region. In addition, they observed that IRF3 and the P65 subunit of NF-κB were phosphorylated and translocated into the nucleus, a process that is also STING-dependent. These results suggest that Brucella invasion of host cells also induces the STING pathway. This study also demonstrates that Brucella produces the second messenger c-di-GMP to activate the STING pathway directly. They propose that Brucella first produces c-di-GMP, which induces initial STING signaling and activation of type I IFN and GBP. GBP binds to BCV, BCV lyses and releases Brucella DNA. cGAS recognizes the DNA and produces cGAMP, which further amplifies the STING signal. It is undeniable that STING plays an important role in defense against Brucella infection, but the mechanism of the cGAS-STING axis in Brucella infection needs to be further validated, and how GBP and BCV binding induces BCV lysis is unclear. The researchers found that Omp25 is dependent on ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of cGAS, inhibits activation of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway, and interferes with the production of IFN-β, thereby evading host innate immunity mechanisms (Li et al., 2021).
4.5 Lipopolysaccharide regulates inflammation and controls host immunity
LPS is closely related to inflammation. B. melitensis, B. abortus, as well as B. suis express smooth LPS (S-LPS), which consists of lipid A, core oligosaccharide, and polysaccharide O-chain. B. ovis and B. canis become naturally rough LPS (R-LPS) due to lack of O-chain. The presence of the O-chain protects Brucella from damage by host cell cationic peptides, oxygen metabolites, and complement (Cardoso et al., 2006). The LPS O-chain interacts with the lipid raft on the host cell surface, allowing Brucella to enter the cell and delaying fusion with lysosomes to promote Brucella survival (Porte et al., 2003). O-chain also inhibits phagocytic apoptosis (Fernandez-Prada et al., 2003), which favors bacterial survival by avoiding host cell apoptosis. Unlike Enterobacteriaceae, the lipid A portion of Brucella and Ochrobactrum anthropi is recognized by TLR4 only at high concentrations, eliciting biochemical signals, whereas TLR-1, TLR-2, and TLR-6, as well as their heterodimeric combinations, are not (Dueñas et al., 2004). Compared to rough strains, lipid A of smooth Brucella was more able to trigger TLR4 in CHO cells and was more advantageous in inducing dendritic cell maturation (Campos et al., 2004). Brucella lipid A has ultra-long-chain fatty acids (ULCFAs) and is structurally different from typical lipid A. The typical lipid A activates innate immune defenses by binding to TLR4 and the TLR4 25-kDa co-receptor MD-2 (Meng et al., 2010). ULCFAs may result in Brucella’s ability to bind to TLR4 being greatly attenuated and failing to stimulate a strong inflammatory response (Lapaque et al., 2006), which serves as a way for Brucella to conceal itself and escape killing (Conde-Álvarez et al., 2012). The lipid A portion of B. abortus induces the death of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), and the dead PMNs are removed by phagocytosis. At the same time, Brucella carried by PMNs may be transferred to other organs for the next round of proliferation (Barquero-Calvo et al., 2015). This manner of PMN death not only facilitates a safe pathway for Brucella to spread in host cells but also hinders the pro-inflammatory signaling pathway. LPS core connects O polysaccharide and lipid A. WadA, WadB, WadC, and WadD are Brucella LPS core glycosyltransferases involved in assembling the LPS core branching structure (Shi et al., 2022). Moreover, WadC gene mutation caused increased binding of TLR4 to MD-2 (Conde-Álvarez et al., 2012; Gil-Ramírez et al., 2014; Soler-Lloréns et al., 2014; Salvador-Bescós et al., 2018). In conclusion, the LPS core helps Brucella to evade the host immune system and favors its survival.
4.6 Physiologic functions of outer membrane proteins
Lipoproteins are key mediators of the pro-inflammatory response induced by Brucella (Giambartolomei et al., 2004). Brucella strains produce three outer membrane lipoproteins: Omp10, Omp16, and Omp19. Omp16 has a peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein (Pal) domain that is highly conserved in Brucella. Inactivation of Omp16 damages the integrity and activity of the Brucella outer membrane, resulting in decreased intracellular survival of Brucella in macrophages (Zhi et al., 2020). Some researchers have noted that while Omp10 and Omp19 are not essential genes for Brucella intracellular survival in vitro, Omp10 mutants lead to a significant attenuation of Brucella survival in mice and Omp19 inactivation alters Brucella outer membrane properties (Tibor et al., 2002). After B. abortus infects the host via the oral cavity, Omp19 protects the bacteria from gastrointestinal proteases and lysosomal proteases. Not only that, Omp19 has a protective role for the outer membrane protein Omp25, preventing Omp25 from being degraded by proteases (Pasquevich et al., 2019). Lipid-modified Omp16 and Omp19 in B. abortus induced macrophages to produce TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-12, with the involvement of TLR2 (Giambartolomei et al., 2004). In conclusion, Omp10, Omp16, and Omp19 are essential for the survival of Brucella.
4.7 Omp25 inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory factors
Omp25 is an outer membrane protein of Brucella. Omp25 can manipulate innate immunity to establish chronic infections (Degos et al., 2020). In vitro, Omp25 of B. abortus binds directly to the SLAMF1 receptor on the surface of dendritic cells (DCs), restricting NF-κB nuclear translocation and inhibiting the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors, although this does not affect intracellular replication and transport of Brucella abortus. In vivo, Omp25 binding to SLAMF1 does not affect Brucella replication during the acute infection phase but favors bacterial persistent survival. The researchers also found that Omp25 inhibited LPS-induced IL-12 production in human monocytes (Cui et al., 2017). Omp25 inhibition of TNF-α was associated with Omp25-induced miRNAs in B. suis-infected porcine and mouse macrophages (Luo et al., 2017). On the one hand, the relevant miRNAs acted on the 3’UTR region of TNF-α to inhibit TNF-α production at the transcriptional level; on the other hand, the miRNAs targeted IRAK1 and TRAF6 proteins to prevent the NF-κB signaling pathway from being activated, thus reducing TNF-α production, which ultimately favored Brucella survival.
5 Brucella regulates apoptosis
5.1 Brucella infection promotes or inhibits apoptosis
Brucella infection promotes apoptosis (Table 2). B. Melitensis 16M infection induces apoptosis via ROS (Li et al., 2016). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are the second messengers of apoptosis. When cells receive pro-apoptotic signals, ROS production increases, calcium influx increases, Bax up-regulates, and the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opens, activating the trypsin, which leads to cell death (Sun et al., 2016). It has been shown that S-type Brucella inhibits apoptosis and R-type Brucella promotes apoptosis. Compared to R-type Brucella, O-polysaccharide (OPS) was present in the outer membrane of S-type Brucella. It has been proposed (Fernandez-Prada et al., 2003) that OPS prevents the death of macrophages (the preferred target of Brucella intracellular replication), which ultimately favors Brucella survival; Brucella deficient in OPS not only leads to the death of the bacteria itself, but also promotes phagocytic apoptosis. The complement system is a multimolecular system composed of many types of proteins, and the host can activate the complement pathway to clear most Gram-negative bacteria. It is known that the unique structure of Brucella OPS hinders the binding of complement factors to the cell membrane of bacteria, favoring the survival of Brucella (Barquero-Calvo et al., 2007). We speculate that OPS may prevent macrophage apoptosis by reducing the chances of Brucella being recognized by relevant host cell receptors or cytokines, just as complement factors are impeded from binding to the cell membrane of bacteria.
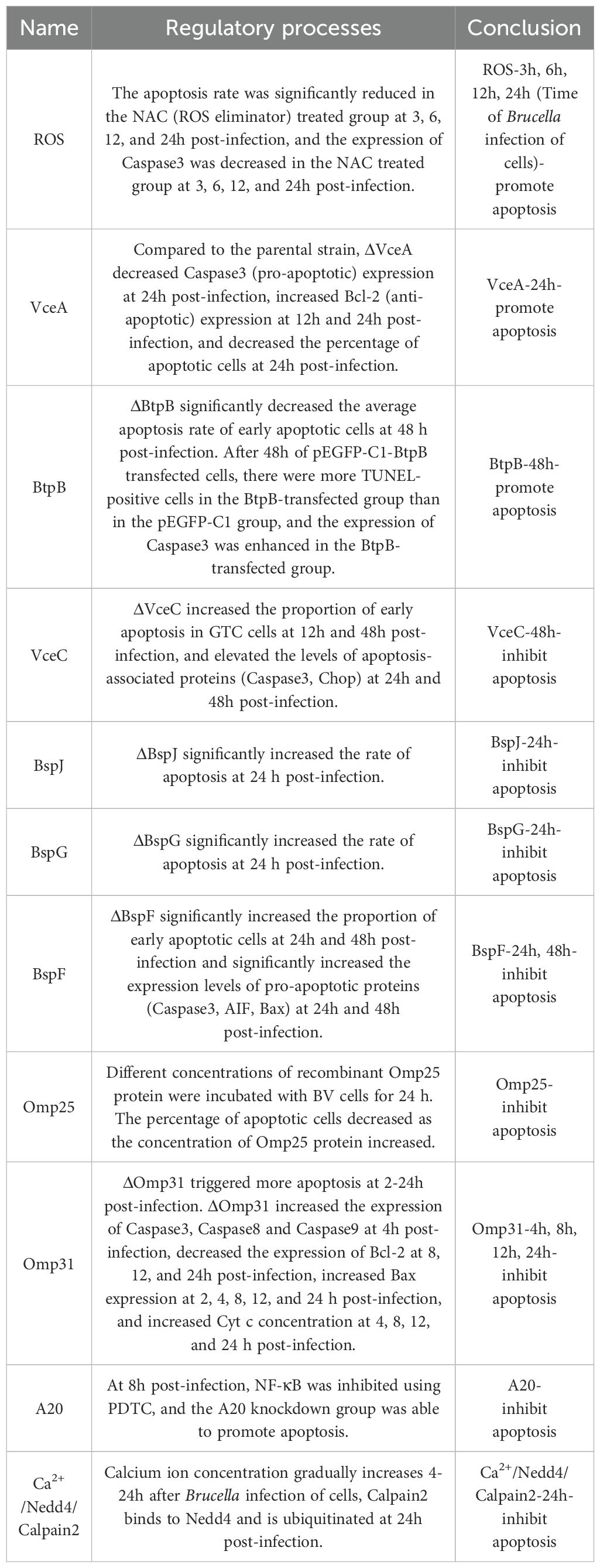
Table 2. Temporal expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins and the Brucella’s control of apoptosis.
Brucella infection inhibits apoptosis (Table 2; Figure 3). Gaidiero et al. found that B. abortus 19 infection of monocytes and lymphocytes resulted in delayed apoptosis compared to healthy controls (Galdiero et al., 2000). Tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) plays an important role in inducing apoptosis. Gross et al. found that B. suis infected human monocytes in vitro to inhibit apoptosis non-dependently with TNF-α (Gross et al., 2000). The results of these two studies suggest that Brucella invasion of host cells exhibits apoptosis inhibition, but it has not been elucidated how Brucella regulates anti-apoptotic mechanisms. In B. melitensis-infected mouse macrophages, the expression of many mitochondrion-associated genes involved in the apoptotic pathway was down-regulated (He et al., 2006). It is therefore speculated that Brucella inhibits macrophage apoptosis possibly related to the inhibition of mitochondrial gene expression involved in cytochrome C release, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane permeability. Cui, G., and colleagues found that the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4 is required for B. abortus survival in macrophages and can regulate apoptosis (Cui et al., 2014). This process can be briefly described as follows: Brucella infection leads to an increase in intracellular calcium ion concentration and activation of Nedd4, which promotes ubiquitination and degradation of calpain and inhibits the activation of caspase-3, ultimately inhibiting apoptosis. The development of calcium channel blockers or drugs that inhibit the increase of calcium ions may be a novel idea for the treatment of brucellosis. Zinc finger protein A20 is a dual inhibitor of macrophage activation and apoptosis, both promoting apoptosis and acting as an anti-apoptotic protein. A20 promotes the intracellular growth of B. abortus by inhibiting macrophage activation and apoptosis (Wei et al., 2015).
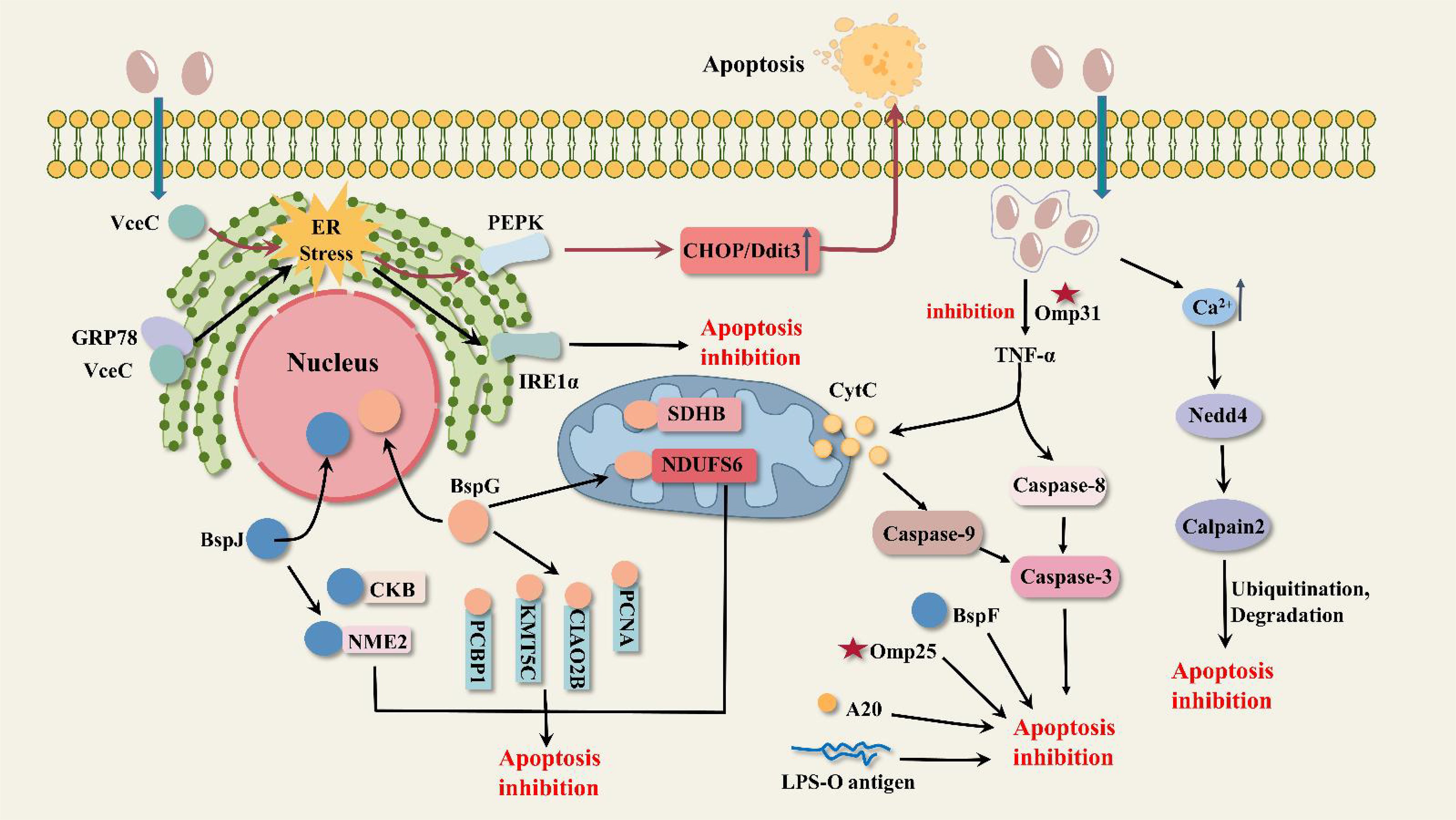
Figure 3. Possible pathways of apoptosis inhibition by Brucella. VceC triggers ER stress and activates the PEPK metabolic pathway to induce apoptosis; in addition, the activated IRE1 pathway inhibits apoptosis. BspJ interacts with host proteins NME2 and CKB to inhibit apoptosis. BspG interacts with host proteins PCBP1, KMT5C, NDUFS6, PCNA, CIAO2B, and SDHB to inhibit apoptosis. BspF inhibits apoptosis by affecting P53 expression. The outer membrane protein Omp31 inhibits the TNF-α-CytC-Caspase9 mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and the TNF-α-Caspase8-Caspase3 classical apoptotic pathway. Brucella infection leads to increased calcium ion concentration, activation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4, promotion of calpain ubiquitination and degradation, and inhibition of the Caspase-3 apoptotic pathway. The outer membrane proteins Omp25 and LPS-O polysaccharide inhibit apoptosis; zinc finger protein A20 is involved in apoptosis but is not the only factor.
5.2 VceA and BtpB promote apoptosis
In experiments with B. abortus VceA mutant strains infecting human trophoblast cells, the researchers observed a decrease in the level of cysteine-3 (an early marker of apoptosis) and an increase in the expression of Bcl-2 (an anti-apoptotic gene) (Zhang et al., 2019). This suggests that VceA may have a role in promoting apoptosis. Study shows that BtpB triggers apoptosis. In Li, J’s experiments (Li et al., 2022), BtpB plasmid was transfected into RAW264.7 cells, observing significant DNA fragmentation and a rise in caspase-3 expression, which is a typical feature of apoptosis. Moreover, flow cytometry showed that BtpB-deficient B. suis inhibited macrophage apoptosis after 48h of infection, suggesting that BtpB induces apoptosis, but its cellular targets and specific mechanisms are unknown.
5.3 VceC promotes or inhibits apoptosis through different pathways
VceC not only induces inflammatory responses but also affects host cell apoptosis. C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) is the most important apoptotic pathway mediated by the UPR. VceC regulates the apoptosis pathway of CHOP and affects Brucella proliferation in cells. M. X. Byndloss et al. found that in B. abortus-infected pregnant mice, VceC promotes CHOP production by inducing ER stress to activate the PEPK pathway, which ultimately benefits host cell death and bacterial discharge (Byndloss et al., 2019). However, F. Zhi et al. indicated that VceC interaction with GRP78 triggers the IRE1α pathway of ER stress and inhibits apoptosis in trophoblast cells of B. suis-infected goats. Moreover, VceC promoted the sustained proliferation of Brucella in host cells, which may be attributed to the inhibition of apoptosis by Brucella (Zhi et al., 2019). Therefore, there is no consensus on how VceC regulates the CHOP apoptotic pathway, and its specific mechanism still requires extensive research.
5.4 BspJ, BspG, and BspF inhibit apoptosis
BspJ and BspG are nucleomodulins of Brucella. BspJ is the first protein defined that enters the nucleus of the host cell after being secreted by B. abortus. BspJ interacts with nucleoside diphosphate kinase 2 (NME2) and creatine kinase B (CKB). NME2 and CKB are associated with energy synthesis and have inhibitory effects on apoptosis. In a B. abortus 2308 infected macrophage model (Ma et al., 2020), loss of BspJ significantly increased macrophage apoptotic rate and reduced intracellular survival of Brucella. Suggesting that BspJ may act as a potential virulence factor to protect the intracellular survival of Brucella and has a role in inhibiting apoptosis in host cells. This inhibitory effect is probably achieved by interacting with NME2 and CKB. To further validate the function of BspJ in Brucella intracellular infection, Ma, Z.’s team (Ma et al., 2022b), did a more detailed study, and they found that deletion of BspJ reduced the survival and proliferation of B. abortus in the rBCV phase. Moreover, BspJ does not affect bacterial invasion and adhesion. Additionally, loss of BspJ resulted in abnormal secretion of inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-1β, IL-10, IFN-γ, TNF-α) in host cells and mice compared to normal strains. However, it remains difficult to explain how BspJ leads to a reduction in Brucella survival and the mechanisms by which BspJ affects the level of apoptosis in host cells still require considerable research. Like BspJ, BspG inhibits apoptosis and interacts with host proteins PCBP1, KMT5C, NDUFS6, PCNA, CIAO2B, and SDHB. NDUFS6, CIAO2B, and SDHB are associated with mitochondrial energy metabolism, so it is hypothesized that BspG may enter mitochondria to mediate the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. In addition to this, the loss of BspG resulted in high levels of expression of the pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α, leading to an increase in their killing effect on host cells, which may be one of the reasons for the reduced survival of B. abortus in vitro and in vivo (Ma et al., 2022a). BspF can inhibit host cell apoptosis by attenuating the crotonylation modification of p53 and reducing the expression of p53, thus helping Brucella to survive for a long time (Lin et al., 2023). P53 plays an important role in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and the classical apoptotic pathway. In the mitochondrial pathway, P53 activates the expression of downstream genes such as Bax, PUMA, Noxa, and Bi, increases mitochondrial membrane permeability, and promotes the release of cytochrome C and ATP (Laptenko and Prives, 2006). In the classical apoptotic pathway, P53 binds to Apaf-1 and activates the caspase cascade reaction (Zhang et al., 2010).
5.5 Omp31 and Omp25 inhibit apoptosis
Omp31 and Omp25, the major outer membrane proteins of Brucella, can inhibit apoptosis. Omp31 is present in all Brucella species except B. abortus (Cloeckaert et al., 1996). In a macrophage model of B. melitensis infection, deletion of Omp31 resulted in elevated expression of TNF-α, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, Caspase-9, Bax, and Cytc, decreased expression of Bcl-2, and impaired Brucella survival (Zhang et al., 2016). It suggests that Brucella Omp31 has an inhibitory effect on the TNF-α-Caspase8-Caspase3 classical apoptotic pathway and the TNF-α-Cytc-Caspase9 mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. In BV-2 microglia, Omp31-induced autophagy achieves inhibition of TNF-α by negatively regulating the NF-κB P65 signaling pathway (Wang et al., 2021a). Omp31 or the autophagy inducer rapamycin inhibits the P65 signaling pathway proteins IκBα, P65 expression, and P65 phosphorylation, reduces the translocation of phosphor-P65 proteins to the nucleus, and ultimately decreases the level of TNF-α expression. The function that mitochondria play in the apoptotic pathway cannot be ignored, and when mitochondrial morphology is altered, such as by rupture, the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is supposed to be disrupted. However, a study (Lobet et al., 2018) showed that mitochondria undergoing fragmentation affected neither TNF-α-induced apoptosis nor bacterial replication in B. abortus. The cause of the fragmentation that occurs in mitochondria is not fully understood and is not related to DRP1, a key effector of mitochondrial fission, but may be related to insufficient mitochondrial fusion. Like Omp31, Omp25 is the major outer membrane protein of Brucella that inhibits apoptosis of BV-2 microglia, but the exact mechanism of apoptosis is unknown (Ma et al., 2015).
6 Crosstalk clues between autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis affected by Brucella
TNF-α regulates inflammatory responses and apoptosis. On the one hand, TNF-α amplifies and coordinates pro-inflammatory signaling. It binds to TNFR-1 to activate host resistance to Brucella and enhances the inflammatory response (Hop et al., 2017). On the other hand, TNF-α induces apoptosis. Inhibition of TNF-α production by Brucella virulence factors affects inflammatory responses and apoptosis. In addition, Brucella-induced autophagy seems to influence TNF-α production. Most of the inhibition of TNF-α by Brucella is related to the NF-κB signaling pathway. The NF-κB family is present in almost all cells and is involved in immune and inflammatory responses. In the cytoplasm, NF-κB dimers (e.g., NF-κB/P65) are usually in an inactivated state bound to IκB. When cells are subjected to various stimuli (e.g., TNF-α, interleukins), the IκB protein is degraded and the NF-κB dimer translocates to the nucleus to control the transcription of relevant genes (e.g., inflammatory factors and apoptosis genes) (Xiao, 2007). Brucella VceA inhibited the production of TNF-α and IL-1β, suggesting that VceA may influence the inflammatory response by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Zhang et al., 2019). In dendritic cells, Brucella Omp25 binds to SLAMF1 and inhibits NF-κB nuclear translocation thereby reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6) (Degos et al., 2020). In macrophages, Omp25 suppressed LPS-induced TNF-α production. The relevant miRNAs targeted IRAK1 and TRAF6 proteins to prevent the NF-κB signaling pathway from being activated, thus reducing TNF-α production, which ultimately favored Brucella survival (Luo et al., 2017). Brucella Omp31 may impair the TNF-α-triggered classical apoptotic pathway and the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Autophagy was shown to control the NF-κB P65 signaling pathway through the degradation of regulatory proteins (Xiao, 2007). B. melitensis Omp31 inhibits the NF-κB P65 signaling pathway by inducing autophagy, thereby reducing TNF-α protein expression (Wang et al., 2021a).
The C-JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK) is associated with autophagy and apoptosis. Internalized Brucella activates the UPR sensor IRE1α, which activates IRE1α-associated kinases (including JNK and ASK1), and then drives the activation or assembly of autophagy proteins (e.g., ULK1, Beclin1, and ATG9a). The activities of these autophagy proteins contribute to cellular membrane remodeling to support the development of replicative niches (Pandey et al., 2018). Activated JNK can phosphorylate P53 and induce P53-dependent apoptosis. B.suis S2 inhibits activation of the JNK/P53 signaling pathway to suppress apoptosis in human microglia clone 3 cells by increasing the expression of CALR protein (Wang et al., 2021b).
AIR and ROS are associated with autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis. The excessive ROS can be involved in the regulation of autophagy and programmed death by altering the activity of specific enzymes through redox reactions. Mitochondria are the main source of ROS. Verbeke et al. found that B. abortus induced mitophagy mediated by BNIP3L (Verbeke et al., 2023). TECPR1 is a protein that promotes the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes. AIR is an important domain of TECPR1. AIR binds to the ATG12-ATTG5 complex and then releases the Pleckstrin homology domain, which promotes autophagosome and lysosome fusion. B. melitensis 16M regulates the effects of the AIR domain on autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis through the ROS signaling pathway. In B. melitensis 16M-infected macrophages, ROS induced apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy, whereas AIR inhibited autophagosome maturation and autophagy initiation. Autophagy may negatively regulate the activation of inflammasomes and prevent inflammation (Li et al., 2016).
7 Conclusions
Brucella can manipulate autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis for intracellular replication and survival. A range of virulence factors of Brucella can modulate autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis, and play an important role in suppressing the immune response of the host cells (Table 3). In summary, Brucella has evolved some effective defense mechanisms to counteract host cell damage. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in the various survival methods of Brucella are not fully understood, and the functions of some of its virulence factors remain unclear. RicA, BtpA, BspB, BspF, and BspJ affect the biosynthesis of rBCV, but it is not clear whether other virulence factors have an effect on the biosynthesis of eBCV, rBCV, and aBCV. The specific mechanism by which VceA and BtpB inhibit autophagy is unclear. We have a preliminary understanding of the mechanisms by which VceC, BspJ, BspG, and BspF regulate apoptosis, but the mechanisms by which VceA and BtpB promote apoptosis remain unclear. The functions of certain virulence factors such as BspC, BspE, BPE005, BPE123, BPE043, and BPE275 are completely unknown. Related autophagy proteins are involved in intracellular replication in Brucella. However, the mechanism of interaction between Brucella and autophagy is not fully understood. After Brucella infection of the organism, host cells induce inflammatory responses through multiple pathways to defend against bacterial damage. We do not yet know what is the relationship between the impact of Brucella on inflammation and its chronic infection. Several effective and widely used animal vaccines have been produced, such as B. abortus S19/A19, B. melitensis Rev1, and B. suis S2. A vaccine against human brucellosis has not yet been developed; animal brucellosis vaccines are more diverse and effective, but also have drawbacks. Therefore, it is of great significance to have a comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of Brucella, which has a positive effect on the clinical development of drugs and facilitates the prevention and treatment of Brucella diseases.
Author contributions
YQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. GZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. FJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. CC: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. CM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. SW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. CF: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. BZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HJ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the State Key Laboratory for Animal Disease Control and Prevention (SKLVEB-KFKT-09), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU-KT22013), Science and Technology Major Project of Gansu Province (22ZD6NA001), Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-CSAB-202403), and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (2022NSCQ-MSX2392, cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0446).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
(2024). So Many Roads: the Multifaceted Regulation of Autophagy Induction. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30126896/ (accessed October 15, 2018).
Alaidarous, M., Ve, T., Casey, L. W., Valkov, E., Ericsson, D. J., Ullah, M. O., et al. (2014). Mechanism of bacterial interference with TLR4 signaling by Brucella Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing protein TcpB. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 654–668. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.523274
Alonso Paiva IM, A., Santos, R., Brito, C. B., Ferrero, M. C., Ortiz Wilczyñski, J. M., Silva, E. A. C., et al. (2023). Role of the cGAS/STING pathway in the control of Brucella abortus infection acquired through the respiratory route. Front. Immunol. 14, 1116811. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1116811
Barquero-Calvo, E., Chaves-Olarte, E., Weiss, D. S., Guzmán-Verri, C., Chacón-Díaz, C., Rucavado, A., et al. (2007). Brucella abortus Uses a Stealthy Strategy to Avoid Activation of the Innate Immune System during the Onset of Infection. PloS One 2, e631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000631
Barquero-Calvo, E., Mora-Cartín, R., Arce-Gorvel, V., de Diego, J. L., Chacón-Díaz, C., Chaves-Olarte, E., et al. (2015). Brucella abortus Induces the Premature Death of Human Neutrophils through the Action of Its Lipopolysaccharide. PloS Pathog. 11, e1004853. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004853
Brambila-Tapia, A. J. L., Pérez-Rueda, E. (2014). A functional and phylogenetic comparison of quorum sensing related genes in Brucella melitensis 16M. J. Microbiol. Seoul Korea. 52, 709–715. doi: 10.1007/s12275-014-3570-x
Bronner, D. N., Abuaita, B. H., Chen, X., Fitzgerald, K. A., Nuñez, G., He, Y., et al. (2015). Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates the inflammasome via NLRP3- and caspase-2-driven mitochondrial damage. Immunity. 43, 451–462. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.008
Burdette, D. L., Monroe, K. M., Sotelo-Troha, K., Iwig, J. S., Eckert, B., Hyodo, M., et al. (2011). STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic-di-GMP. Nature. 478, 515–518. doi: 10.1038/nature10429
Byndloss, M. X., Tsai, A. Y., Walker, G. T., Miller, C. N., Young, B. M., English, B. C., et al. (2019). Brucella abortus Infection of Placental Trophoblasts Triggers Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Cell Death and Fetal Loss via Type IV Secretion System-Dependent Activation of CHOP. mBio. 10, e01538–e01519. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01538-19
Campos, M. A., Rosinha, G. M. S., Almeida, I. C., Salgueiro, X. S., Jarvis, B. W., Splitter, G. A., et al. (2004). Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in induction of cell-mediated immunity and resistance to Brucella abortus infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 72, 176–186. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.1.176-186.2004
Cardoso, P. G., Macedo, G. C., Azevedo, V., Oliveira, S. C. (2006). Brucella spp noncanonical LPS: structure, biosynthesis, and interaction with host immune system. Microb. Cell Factories. 5, 13. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-5-13
Caruso, R., Núñez, G. (2016). Innate immunity: ER stress recruits NOD1 and NOD2 for delivery of inflammation. Curr. Biol. CB 26, R508–R511. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.05.021
Celli, J., de Chastellier, C., Franchini, D. M., Pizarro-Cerda, J., Moreno, E., Gorvel, J. P. (2003). Brucella evades macrophage killing via VirB-dependent sustained interactions with the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Exp. Med. 198, 545–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030088
Celli, J., Salcedo, S. P., Gorvel, J. P. (2005). Brucella coopts the small GTPase Sar1 for intracellular replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 102, 1673–1678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406873102
Chan, E. Y. W., Kir, S., Tooze, S. A. (2007). siRNA screening of the kinome identifies ULK1 as a multidomain modulator of autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 25464–25474. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703663200
Chaudhary, A., Ganguly, K., Cabantous, S., Waldo, G. S., Micheva-Viteva, S. N., Nag, K., et al. (2012). The Brucella TIR-like protein TcpB interacts with the death domain of MyD88. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 417, 299–304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.104
Chaves-Olarte, E., Guzmán-Verri, C., Méresse, S., Desjardins, M., Pizarro-Cerdá, J., Badilla, J., et al. (2002). Activation of Rho and Rab GTPases dissociates Brucella abortus internalization from intracellular trafficking. Cell Microbiol. 4, 663–676. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2002.00221.x
Cloeckaert, A., Debbarh, H. S., Vizcaíno, N., Saman, E., Dubray, G., Zygmunt, M. S. (1996). Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Brucella melitensis bp26 gene coding for a protein immunogenic in infected sheep. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 140, 139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb08327.x
Comerci, D. J., Martínez-Lorenzo, M. J., Sieira, R., Gorvel, J. P., Ugalde, R. A. (2001). Essential role of the VirB machinery in the maturation of the Brucella abortus-containing vacuole. Cell Microbiol. 3, 159–168. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2001.00102.x
Conde-Álvarez, R., Arce-Gorvel, V., Iriarte, M., Manček-Keber, M., Barquero-Calvo, E., Palacios-Chaves, L., et al. (2012). The lipopolysaccharide core of Brucella abortus acts as a shield against innate immunity recognition. PloS Pathog. 8, e1002675. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002675
Costa Franco, M. M. S., Marim, F. M., Alves-Silva, J., Cerqueira, D., Rungue, M., Tavares, I. P., et al. (2019). AIM2 senses Brucella abortus DNA in dendritic cells to induce IL-1β secretion, pyroptosis and resistance to bacterial infection in mice. Microbes Infect. 21, 85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2018.09.001
Costa Franco, M. M., Marim, F., Guimarães, E. S., Assis, N. R. G., Cerqueira, D. M., Alves-Silva, J., et al. (2018). Brucella abortus Triggers a cGAS-Independent STING Pathway To Induce Host Protection That Involves Guanylate-Binding Proteins and Inflammasome Activation. J. Immunol. Baltim Md 1950 200, 607–622. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700725
Cui, B., Liu, W., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Du, Q., Zhao, X., et al. (2017). Brucella Omp25 Upregulates miR-155, miR-21-5p, and miR-23b to Inhibit Interleukin-12 Production via Modulation of Programmed Death-1 Signaling in Human Monocyte/Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00708
Cui, G., Wei, P., Zhao, Y., Guan, Z., Yang, L., Sun, W., et al. (2014). Brucella infection inhibits macrophages apoptosis via Nedd4-dependent degradation of calpain2. Vet. Microbiol. 174, 195–205. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.08.033
de Barsy, M., Jamet, A., Filopon, D., Nicolas, C., Laloux, G., Rual, J. F., et al. (2011). Identification of a Brucella spp. secreted effector specifically interacting with human small GTPase Rab2. Cell Microbiol. 13, 1044–1058. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01601.x
Decout, A., Katz, J. D., Venkatraman, S., Ablasser, A. (2021). The cGAS–STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 21, 548–569. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00524-z
de Figueiredo, P., Ficht, T. A., Rice-Ficht, A., Rossetti, C. A., Adams, L. G. (2015a). Pathogenesis and immunobiology of brucellosis: review of Brucella-host interactions. Am. J. Pathol. 185, 1505–1517. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.003
de Figueiredo, P., Ficht, T. A., Rice-Ficht, A., Rossetti, C. A., Adams, L. G. (2015b). Pathogenesis and immunobiology of brucellosis. Am. J. Pathol. 185, 1505–1517. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.003
Degos, C., Hysenaj, L., Gonzalez-Espinoza, G., Arce-Gorvel, V., Gagnaire, A., Papadopoulos, A., et al. (2020). Omp25-dependent engagement of SLAMF1 by Brucella abortus in dendritic cells limits acute inflammation and favours bacterial persistence in vivo. Cell Microbiol. 22, e13164. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13164
de Jong, M. F., Starr, T., Winter, M. G., den Hartigh, A. B., Child, R., Knodler, L. A., et al. (2013). Sensing of bacterial type IV secretion via the unfolded protein response. mBio. 4, e00418–e00412. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00418-12
de Jong, M. F., Sun, Y. H., den Hartigh, A. B., van Dijl, J. M., Tsolis, R. M. (2008). Identification of VceA and VceC, two members of the VjbR regulon that are translocated into macrophages by the Brucella type IV secretion system. Mol. Microbiol. 70, 1378–1396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06487.x
de Jong, M. F., Tsolis, R. M. (2012). Brucellosis and type IV secretion. Future Microbiol. 7, 47–58. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.136
Delrue, R. M., Deschamps, C., Léonard, S., Nijskens, C., Danese, I., Schaus, J. M., et al. (2005). A quorum-sensing regulator controls expression of both the type IV secretion system and the flagellar apparatus of Brucella melitensis. Cell Microbiol. 7, 1151–1161. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00543.x
Deng, X., He, J., Wang, Y., Yang, Q., Yi, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Deletion of the type IV secretion system promoter VirB in Brucella abortus A19 strain attenuated the virulence of the bacteria and promotes autophagy. Can. J. Microbiol. 68, 165–176. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2021-0053
Deng, Y., Liu, X., Duan, K., Peng, Q. (2019). Research progress on brucellosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 26, 5598–5608. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180510125009
den Hartigh, A. B., Sun, Y. H., Sondervan, D., Heuvelmans, N., Reinders, M. O., Ficht, T. A., et al. (2004). Differential requirements for VirB1 and VirB2 during Brucella abortus infection. Infect. Immun. 72, 5143–5149. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5143-5149.2004
Döhmer, P. H., Valguarnera, E., Czibener, C., Ugalde, J. E. (2014). Identification of a type IV secretion substrate of Brucella abortus that participates in the early stages of intracellular survival. Cell Microbiol. 16, 396–410. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12224
Dong, B., Li, F., Wang, J., Lv, S., Miao, L., Guo, G., et al. (2023). Effect of ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy-lysosome pathway on intracellular replication of Brucella.suis. Vet. Microbiol. 280, 109699. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109699
Dorn, B. R., Dunn, W. A., Progulske-Fox, A. (2002). Bacterial interactions with the autophagic pathway. Cell Microbiol. 4, 1–10. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2002.00164.x
Dueñas, A. I., Orduña, A., Crespo, M. S., García-Rodríguez, C. (2004). Interaction of endotoxins with Toll-like receptor 4 correlates with their endotoxic potential and may explain the proinflammatory effect of Brucella spp. LPS. Int. Immunol. 16, 1467–1475. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh148
Fernandez-Prada, C. M., Zelazowska, E. B., Nikolich, M., Hadfield, T. L., Roop, R. M., Robertson, G. L., et al. (2003). Interactions between Brucella melitensis and human phagocytes: bacterial surface O-Polysaccharide inhibits phagocytosis, bacterial killing, and subsequent host cell apoptosis. Infect. Immun. 71, 2110–2119. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.2110-2119.2003
Galdiero, E., Romano Carratelli, C., Vitiello, M., Nuzzo, I., Del Vecchio, E., Bentivoglio, C., et al. (2000). HSP and apoptosis in leukocytes from infected or vaccinated animals by Brucella abortus. New Microbiol. 23, 271.
Ganley, I. G., Lam, D. H., Wang, J., Ding, X., Chen, S., Jiang, X. (2009). ULK1.ATG13.FIP200 complex mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 12297–12305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900573200
Giambartolomei, G. H., Zwerdling, A., Cassataro, J., Bruno, L., Fossati, C. A., Philipp, M. T. (2004). Lipoproteins, not lipopolysaccharide, are the key mediators of the proinflammatory response elicited by heat-killed Brucella abortus. J. Immunol. Baltim Md 1950 173, 4635–4642. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.7.4635
Gil-Ramírez, Y., Conde-Álvarez, R., Palacios-Chaves, L., Zúñiga-Ripa, A., Grilló, M. J., Arce-Gorvel, V., et al. (2014). The identification of wadB, a new glycosyltransferase gene, confirms the branched structure and the role in virulence of the lipopolysaccharide core of Brucella abortus. Microb. Pathog. 73, 53–59. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.06.002
Gomes, M. T. R., Campos, P. C., Oliveira, F. S., Corsetti, P. P., Bortoluci, K. R., Cunha, L. D., et al. (2013). Critical role of ASC inflammasomes and bacterial type IV secretion system in caspase-1 activation and host innate resistance to Brucella abortus infection. J. Immunol. Baltim Md 1950 190, 3629–3638. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202817
Gross, A., Terraza, A., Ouahrani-Bettache, S., Liautard, J. P., Dornand, J. (2000). In vitro brucella suis infection prevents the programmed cell death of human monocytic cells. Infect. Immun. 68, 342–351. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.342-351.2000
Guimarães, E. S., Gomes, M. T. R., Campos, P. C., Mansur, D. S., dos Santos, A. A., Harms, J., et al. (2019). Brucella abortus cyclic dinucleotides trigger STING-dependent Unfolded Protein Response that favors bacterial replication. J. Immunol. Baltim Md 1950 202, 2671–2681. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801233
Guo, F., Zhang, H., Chen, C., Hu, S., Wang, Y., Qiao, J., et al. (2012). Autophagy favors Brucella melitensis survival in infected macrophages. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 17, 249–257. doi: 10.2478/s11658-012-0009-4
Hamer, I., Goffin, E., De Bolle, X., Letesson, J. J., Jadot, M. (2014). Replication of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis in fibroblasts does not require Atg5-dependent macroautophagy. BMC Microbiol. 14, 223. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0223-5
He, Y., Reichow, S., Ramamoorthy, S., Ding, X., Lathigra, R., Craig, J. C., et al. (2006). Brucella melitensis triggers time-dependent modulation of apoptosis and down-regulation of mitochondrion-associated gene expression in mouse macrophages. Infect. Immun. 74, 5035–5046. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01998-05
Hong, P. C., Tsolis, R. M., Ficht, T. A. (2000). Identification of genes required for chronic persistence of Brucella abortus in mice. Infect. Immun. 68, 4102–4107. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.4102-4107.2000
Hop, H. T., Reyes, A. W. B., Huy, T. X. N., Arayan, L. T., Min, W., Lee, H. J., et al. (2017). Activation of NF-kB-mediated TNF-induced antimicrobial immunity is required for the efficient brucella abortus clearance in RAW 264.7 cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 7, 437. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00437
Hornung, V., Ablasser, A., Charrel-Dennis, M., Bauernfeind, F., Horvath, G., Caffrey, D. R., et al. (2009). AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature. 458, 514–518. doi: 10.1038/nature07725
Ishikawa, H., Ma, Z., Barber, G. N. (2009). STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature. 461, 788–792. doi: 10.1038/nature08476
Jakka, P., Namani, S., Murugan, S., Rai, N., Radhakrishnan, G. (2017). The Brucella effector protein TcpB induces degradation of inflammatory caspases and thereby subverts non-canonical inflammasome activation in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 20613–20627. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.815878
Jiao, H., Luo, Y., Zhou, Z., Gu, G., Li, B., Li, W., et al. (2020). Integrative Bioinformatics Indentification of the Autophagic Pathway-Associated miRNA-mRNA Networks in RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells Infected with ΔOmp25 Brucella melitensis. Inflammation. 43, 532–539. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01135-6
Jiao, H., Zhou, Z., Li, B., Xiao, Y., Li, M., Zeng, H., et al. (2021). The mechanism of facultative intracellular parasitism of brucella. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 3673. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073673
Ke, Y., Wang, Y., Li, W., Chen, Z. (2015). Type IV secretion system of Brucella spp. and its effectors. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 5, 72. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00072
Keestra-Gounder, A. M., Byndloss, M. X., Seyffert, N., Young, B. M., Chávez-Arroyo, A., Tsai, A. Y., et al. (2016). NOD1 and NOD2 signalling links ER stress with inflammation. Nature. 532, 394–397. doi: 10.1038/nature17631
Kim, J., Kundu, M., Viollet, B., Guan, K. L. (2011). AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 132–141. doi: 10.1038/ncb2152
Lacey, C. A., Mitchell, W. J., Dadelahi, A. S., Skyberg, J. A. (2018). Caspase-1 and caspase-11 mediate pyroptosis, inflammation, and control of brucella joint infection. Infect. Immun. 86, e00361–e00318. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00361-18
Lapaque, N., Takeuchi, O., Corrales, F., Akira, S., Moriyon, I., Howard, J. C., et al. (2006). Differential inductions of TNF-alpha and IGTP, IIGP by structurally diverse classic and non-classic lipopolysaccharides. Cell Microbiol. 8, 401–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00629.x
Laptenko, O., Prives, C. (2006). Transcriptional regulation by p53: one protein, many possibilities. Cell Death Differ. 13, 951–961. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401916
Lee, E. J., Tournier, C. (2011). The requirement of uncoordinated 51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) and ULK2 in the regulation of autophagy. Autophagy. 7, 689–695. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.7.15450
Levine, B., Liu, R., Dong, X., Zhong, Q. (2015). Beclin orthologs: integrative hubs of cell signaling, membrane trafficking, and physiology. Trends Cell Biol. 25, 533–544. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.05.004
Li, R., Liu, W., Yin, X., Zheng, F., Wang, Z., Wu, X., et al. (2021). Brucella spp. Omp25 Promotes Proteasome-Mediated cGAS Degradation to Attenuate IFN-β Production. Front. Microbiol. 12, 702881. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.702881
Li, J., Qi, L., Diao, Z., Zhang, M., Li, B., Zhai, Y., et al. (2022). Brucella btpB manipulates apoptosis and autophagic flux in RAW264.7 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 14439. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214439
Li, Z., Wang, S., Han, J., Shi, C., Yang, G., Cui, Y., et al. (2023). Deletion of Brucella transcriptional regulator GntR10 regulated the expression of quorum sensing system and type IV secretion system effectors, which affected the activation of NF-κB. J. Proteomics 283–284, 104938. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2023.104938
Li, T., Xu, Y., Liu, L., Huang, M., Wang, Z., Tong, Z., et al. (2016). Brucella melitensis 16M regulates the effect of AIR domain on inflammatory factors, autophagy, and apoptosis in mouse macrophage through the ROS signaling pathway. PloS One 11, e0167486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167486
Lin, R., Li, A., Li, Y., Shen, R., Du, F., Zheng, M., et al. (2023). The Brucella Effector Protein BspF Regulates Apoptosis through the Crotonylation of p53. Microorganisms. 11, 2322. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092322
Lobet, E., Willemart, K., Ninane, N., Demazy, C., Sedzicki, J., Lelubre, C., et al. (2018). Mitochondrial fragmentation affects neither the sensitivity to TNFα-induced apoptosis of Brucella-infected cells nor the intracellular replication of the bacteria. Sci. Rep. 8, 5173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23483-3
Luizet, J. B., Raymond, J., Lacerda, T. L. S., Barbieux, E., Kambarev, S., Bonici, M., et al. (2021). The Brucella effector BspL targets the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway and delays bacterial egress from infected cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 118, e2105324118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2105324118
Luo, X., Zhang, X., Wu, X., Yang, X., Han, C., Wang, Z., et al. (2017). Brucella downregulates tumor necrosis factor-α to promote intracellular survival via omp25 regulation of different microRNAs in porcine and murine macrophages. Front. Immunol. 8, 2013. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.02013
Lystad, A. H., Carlsson, S. R., Simonsen, A. (2019). Toward the function of mammalian ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex in autophagy and related processes. Autophagy. 15, 1485–1486. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1618100
Ma, Z., Deng, X., Li, R., Hu, R., Miao, Y., Xu, Y., et al. (2022a). Crosstalk of Brucella abortus nucleomodulin BspG and host DNA replication process/mitochondrial respiratory pathway promote anti-apoptosis and infection. Vet. Microbiol. 268, 109414. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109414
Ma, Z., Li, R., Hu, R., Deng, X., Xu, Y., Zheng, W., et al. (2020). Brucella abortus bspJ is a nucleomodulin that inhibits macrophage apoptosis and promotes intracellular survival of brucella. Front. Microbiol. 11, 599205. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.599205
Ma, Q. L., Liu, A. C., Ma, X. J., Wang, Y. B., Hou, Y. T., Wang, Z. H. (2015). Brucella outer membrane protein Omp25 induces microglial cells in vitro to secrete inflammatory cytokines and inhibit apoptosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8, 17530–17535.
Ma, Z., Yu, S., Cheng, K., Miao, Y., Xu, Y., Hu, R., et al. (2022b). Nucleomodulin BspJ as an effector promotes the colonization of Brucella abortus in the host. J. Vet. Sci. 23, e8. doi: 10.4142/jvs.21224
Marim, F. M., Franco, M. M. C., Gomes, M. T. R., Miraglia, M. C., Giambartolomei, G. H., Oliveira, S. C. (2017). The role of NLRP3 and AIM2 in inflammasome activation during Brucella abortus infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 39, 215–223. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0581-1
Matoba, K., Kotani, T., Tsutsumi, A., Tsuji, T., Mori, T., Noshiro, D., et al. (2020). Atg9 is a lipid scramblase that mediates autophagosomal membrane expansion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 27, 1185–1193. doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-00518-w
Meng, J., Lien, E., Golenbock, D. T. (2010). MD-2-mediated ionic interactions between lipid A and TLR4 are essential for receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 8695–8702. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.075127
Nishida, Y., Arakawa, S., Fujitani, K., Yamaguchi, H., Mizuta, T., Kanaseki, T., et al. (2009). Discovery of Atg5/Atg7-independent alternative macroautophagy. Nature. 461, 654–658. doi: 10.1038/nature08455
O’Callaghan, D., Cazevieille, C., Allardet-Servent, A., Boschiroli, M. L., Bourg, G., Foulongne, V., et al. (1999). A homologue of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirB and Bordetella pertussis Ptl type IV secretion systems is essential for intracellular survival of Brucella suis. Mol. Microbiol. 33, 1210–1220. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01569.x
Oliveira, F. S., Carvalho, N. B., Zamboni, D. S., Oliveira, S. C. (2012). Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-1 and -2 play no role in controlling Brucella abortus infection in mice. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 861426. doi: 10.1155/2012/861426
Pandey, A., Lin, F., Cabello, A. L., da Costa, L. F., Feng, X., Feng, H. Q., et al. (2018). Activation of host IRE1α-dependent signaling axis contributes the intracellular parasitism of brucella melitensis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 8, 103. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00103
Pasquevich, K. A., Carabajal, M. V., Guaimas, F. F., Bruno, L., Roset, M. S., Coria, L. M., et al. (2019). Omp19 enables brucella abortus to evade the antimicrobial activity from host’s proteolytic defense system. Front. Immunol. 10, 1436. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01436
Pizarro-Cerdá, J., Méresse, S., Parton, R. G., van der Goot, G., Sola-Landa, A., Lopez-Goñi, I., et al. (1998). Brucella abortus transits through the autophagic pathway and replicates in the endoplasmic reticulum of nonprofessional phagocytes. Infect. Immun. 66, 5711–5724. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5711-5724.1998
Polson, H. E. J., de Lartigue, J., Rigden, D. J., Reedijk, M., Urbé, S., Clague, M. J., et al. (2010). Mammalian Atg18 (WIPI2) localizes to omegasome-anchored phagophores and positively regulates LC3 lipidation. Autophagy. 6, 506–522. doi: 10.4161/auto.6.4.11863
Porte, F., Liautard, J. P., Köhler, S. (1999). Early acidification of phagosomes containing Brucella suis is essential for intracellular survival in murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 67, 4041–4047. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.4041-4047.1999
Porte, F., Naroeni, A., Ouahrani-Bettache, S., Liautard, J. P. (2003). Role of the Brucella suis lipopolysaccharide O antigen in phagosomal genesis and in inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 71, 1481–1490. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1481-1490.2003
Proikas-Cezanne, T., Takacs, Z., Dönnes, P., Kohlbacher, O. (2015). WIPI proteins: essential PtdIns3P effectors at the nascent autophagosome. J. Cell Sci. 128, 207–217. doi: 10.1242/jcs.146258
Radhakrishnan, G. K., Yu, Q., Harms, J. S., Splitter, G. A. (2009). Brucella TIR domain-containing protein mimics properties of the toll-like receptor adaptor protein TIRAP. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 9892–9898. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805458200
Roop, R. M., Barton, I. S., Hopersberger, D., Martin, D. W. (2021). Uncovering the hidden credentials of brucella virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR. 85, e00021–e00019. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-19
Salcedo, S. P., Chevrier, N., Lacerda, T. L. S., Ben Amara, A., Gerart, S., Gorvel, V. A., et al. (2013). Pathogenic brucellae replicate in human trophoblasts. J. Infect. Dis. 207, 1075–1083. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit007
Salvador-Bescós, M., Gil-Ramírez, Y., Zúñiga-Ripa, A., Martínez-Gómez, E., de Miguel, M. J., Muñoz, P. M., et al. (2018). WadD, a new brucella lipopolysaccharide core glycosyltransferase identified by genomic search and phenotypic characterization. Front. Microbiol. 9, 2293. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02293
Schröder, M., Kaufman, R. J. (2005). The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74, 739–789. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074134
Sengupta, D., Koblansky, A., Gaines, J., Brown, T., West, A. P., Zhang, D., et al. (2010). Subversion of innate immune responses by Brucella through the targeted degradation of the TLR signaling adapter, MAL. J. Immunol. Baltim Md 1950 184, 956–964. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902008
Shi, B., Li, X., Li, B., Zheng, N., Li, M., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Construction and evaluation of the brucella double gene knock-out vaccine strain MB6 Δbp26ΔwboA (RM6). Zoonoses. 2, 971. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0031
Shin, S., Argon, Y. (2015). Stressed-out endoplasmic reticulum inflames the mitochondria. Immunity. 43, 409–411. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.027
Smith, E. P., Cotto-Rosario, A., Borghesan, E., Held, K., Miller, C. N., Celli, J. (2020). Epistatic interplay between type IV secretion effectors engages the small GTPase rab2 in the brucella intracellular cycle. mBio. 11, e03350–e03319. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03350-19
Smith, J. A., Khan, M., Magnani, D. D., Harms, J. S., Durward, M., Radhakrishnan, G. K., et al. (2013). Brucella induces an unfolded protein response via TcpB that supports intracellular replication in macrophages. PloS Pathog. 9, e1003785. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003785
Soler-Lloréns, P., Gil-Ramírez, Y., Zabalza-Baranguá, A., Iriarte, M., Conde-Álvarez, R., Zúñiga-Ripa, A., et al. (2014). Mutants in the lipopolysaccharide of Brucella ovis are attenuated and protect against B. ovis infection mice. Vet. Res. 45, 72. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0072-0
Starr, T., Child, R., Wehrly, T. D., Hansen, B., Hwang, S., López-Otin, C., et al. (2012). Selective subversion of autophagy complexes facilitates completion of the Brucella intracellular cycle. Cell Host Microbe 11, 33–45. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.12.002
Starr, T., Ng, T. W., Wehrly, T. D., Knodler, L. A., Celli, J. (2008). Brucella intracellular replication requires trafficking through the late endosomal/lysosomal compartment. Traffic Cph Den. 9, 678–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00718.x
Suárez-Esquivel, M., Chaves-Olarte, E., Moreno, E., Guzmán-Verri, C. (2020). Brucella genomics: macro and micro evolution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7749. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207749
Sun, X. L., Chen, B. Y., Zhao, H. K., Cheng, Y. Y., Zheng, M. H., Duan, L., et al. (2016). Gas1 up-regulation is inducible and contributes to cell apoptosis in reactive astrocytes in the substantia nigra of LPS and MPTP models. J. Neuroinflammation. 13, 180. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0643-2
Sun, L., Wu, J., Du, F., Chen, X., Chen, Z. J. (2013). Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type-I interferon pathway. Science. 339:786–791. doi: 10.1126/science.1232458
Taguchi, Y., Imaoka, K., Kataoka, M., Uda, A., Nakatsu, D., Horii-Okazaki, S., et al. (2015). Yip1A, a novel host factor for the activation of the IRE1 pathway of the unfolded protein response during Brucella infection. PloS Pathog. 11, e1004747. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004747
Tanida, I., Ueno, T., Kominami, E. (2004). LC3 conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36, 2503–2518. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.05.009
Terwagne, M., Ferooz, J., Rolán, H. G., Sun, Y. H., Atluri, V., Xavier, M. N., et al. (2013). Innate immune recognition of flagellin limits systemic persistence of Brucella. Cell Microbiol. 15, 942–960. doi: 10.1111/cmi.2013.15.issue-6
Tibor, A., Wansard, V., Bielartz, V., Delrue, R. M., Danese, I., Michel, P., et al. (2002). Effect of omp10 or omp19 deletion on Brucella abortus outer membrane properties and virulence in mice. Infect. Immun. 70, 5540–5546. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5540-5546.2002
Tooze, S. A., Jefferies, H. B. J., Kalie, E., Longatti, A., McAlpine, F. E., McKnight, N. C., et al. (2010). Trafficking and signaling in mammalian autophagy. IUBMB Life. 62, 503–508. doi: 10.1002/iub.v62:7
Tupik, J. D., Coutermarsh-Ott, S. L., Benton, A. H., King, K. A., Kiryluk, H. D., Caswell, C. C., et al. (2020). ASC-Mediated Inflammation and Pyroptosis Attenuates Brucella abortus Pathogenesis Following the Recognition of gDNA. Pathog. Basel Switz. 9, 1008. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9121008
Valverde, D. P., Yu, S., Boggavarapu, V., Kumar, N., Lees, J. A., Walz, T., et al. (2019). ATG2 transports lipids to promote autophagosome biogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 218, 1787–1798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201811139
Velikkakath, A. K. G., Nishimura, T., Oita, E., Ishihara, N., Mizushima, N. (2012). Mammalian Atg2 proteins are essential for autophagosome formation and important for regulation of size and distribution of lipid droplets. Mol. Biol. Cell. 23, 896–909. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e11-09-0785
Verbeke, J., Fayt, Y., Martin, L., Yilmaz, O., Sedzicki, J., Reboul, A., et al. (2023). Host cell egress of Brucella abortus requires BNIP3L-mediated mitophagy. EMBO J. 42, e112817. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112817
Wang, Z., Wang, G., Wang, Y., Liu, Q., Li, H., Xie, P., et al. (2021a). Omp31 of brucella inhibits NF-κB p65 signaling pathway by inducing autophagy in BV-2 microglia. Neurochem. Res. 46, 3264–3272. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03429-4
Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Yang, H., Guo, J., Wang, Z. (2021b). Doxycycline induces apoptosis of brucella suis S2 strain-infected HMC3 microglial cells by activating calreticulin-dependent JNK/p53 signaling pathway. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.640847
Webber, J. L., Young, A. R. J., Tooze, S. A. (2007). Atg9 trafficking in Mammalian cells. Autophagy. 3, 54–56. doi: 10.4161/auto.3419
Wei, P., Cui, G., Lu, Q., Yang, L., Guan, Z., Sun, W., et al. (2015). A20 promotes Brucella intracellular growth via inhibition of macrophage cell death and activation. Vet. Microbiol. 175, 50–57. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.11.006
Weidberg, H., Shvets, E., Shpilka, T., Shimron, F., Shinder, V., Elazar, Z. (2010). LC3 and GATE-16/GABARAP subfamilies are both essential yet act differently in autophagosome biogenesis. EMBO J. 29, 1792–1802. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.74
Xiao, G. (2007). Autophagy and NF-κB fight for fate. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 18, 233–243. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.04.006
Xiong, X., Li, B., Zhou, Z., Gu, G., Li, M., Liu, J., et al. (2021). The virB system plays a crucial role in brucella intracellular infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 13637. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413637
Zachari, M., Ganley, I. G. (2017). The mammalian ULK1 complex and autophagy initiation. Essays Biochem. 61, 585–596. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170021
Zhai, W., Wu, F., Zhang, Y., Fu, Y., Liu, Z. (2019). The immune escape mechanisms of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 340. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020340
Zhang, J., Li, M., Li, Z., Shi, J., Zhang, Y., Deng, X., et al. (2019). Deletion of the type IV secretion system effector vceA promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis in brucella-infected human trophoblast cells. Curr. Microbiol. 76, 510–519. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01651-6
Zhang, X. P., Liu, F., Wang, W. (2010). Coordination between cell cycle progression and cell fate decision by the p53 and E2F1 pathways in response to DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 31571–31580. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.134650
Zhang, K., Wang, H., Guo, F., Yuan, L., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., et al. (2016). OMP31 of Brucella melitensis 16M impairs the apoptosis of macrophages triggered by TNF-α. Exp. Ther. Med. 12, 2783–2789. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3655
Zhi, F., Zhou, D., Bai, F., Li, J., Xiang, C., Zhang, G., et al. (2019). VceC mediated IRE1 pathway and inhibited CHOP-induced apoptosis to support brucella replication in goat trophoblast cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 4104. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174104
Keywords: Brucella, intracellular survival, autophagy, inflammation, apoptosis
Citation: Qin Y, Zhou G, Jiao F, Cheng C, Meng C, Wang L, Wu S, Fan C, Li J, Zhou B, Chu Y and Jiao H (2024) Brucella mediates autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis to escape host killing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1408407. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408407
Received: 28 March 2024; Accepted: 26 September 2024;
Published: 23 October 2024.
Edited by:
Xihui Shen, Northwest A&F University, ChinaReviewed by:
Mingxing Tian, Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaYating Wen, University of South China, China
Copyright © 2024 Qin, Zhou, Jiao, Cheng, Meng, Wang, Wu, Fan, Li, Zhou, Chu and Jiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bo Zhou, aG90dGFuazMyMTBAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Yuefeng Chu, Y2h1eXVlZmVuZ0BjYWFzLmNu; Hanwei Jiao, amlhb2hhbndlaUBzd3UuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yaqiong Qin
Yaqiong Qin Gengxu Zhou
Gengxu Zhou Fengyuan Jiao1†
Fengyuan Jiao1† Yuefeng Chu
Yuefeng Chu Hanwei Jiao
Hanwei Jiao