- Laboratory Department, The People’s Hospital of Leshan, Leshan, China
Objective: Bacterial vaginosis is a disease caused by vaginal microecology disorder, which seriously affects female health. At present, there are many drugs to treat BV, and this study aims to compare the efficacy and safety of multiple drugs for BV through a network meta-analysis (NMA).
Methods: All studies were sourced from PubMed and Embase databases from the establishment date to April 13, 2023. We evaluated the clinical cure success rate and adverse effects (abnormal increase in vaginal discharge, external genital irritation, and vulvar itching) and performed subgroup analyses of the clinical cure success rate for different modes of administration. All statistical analyses were performed using R and STATA 14.0 software for network meta-analysis.
Results: We included 42 studies that met the criteria, involving a total of 8382 patients. Network meta-analysis results showed that metronidazole and secnidazole had a higher rate of adverse reactions than placebo (RR 7.06; 95%-CI 2.61-19.10, RR 4.03; 95%-CI 1.63-9.98), the adverse reaction rate of probiotics group was lower than that of metronidazole group (RR 0.44; 95%-CI 0.21-0.93). The clinical cure rate of oral ornidazole was better than clindamycin (RR 16.08; 95%-CI 1.72-150.47), Secnidazole (RR 8.17; 95%-CI 1.66-40.25) and probiotics. Direct meta-analysis results showed that ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than Secnidazole (RR 1.22; 95%-CI 1.10-1.34), oral ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than Secnidazole (RR 1.23; 95%-CI 1.11-1.36). The clinical cure rate of vaginal application of sucrose was better than metronidazole (RR 1.12; 95%-CI 1.03-1.21) and metronidazole had a lower clinical cure rate than probiotics (RR 0.68; 95%-CI 0.52-0.88).
Conclusions: The results of this systematic review and network meta-analysis suggest that ornidazole may be an effective alternative for the treatment of BV, and that sucrose and probiotics are potential BV treatments that need to be validated by more high-quality clinical studies in the future.
Introduction
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a disease caused by an imbalance of vaginal microecology (Coudray and Madhivanan, 2020). Vaginal flora is one of the most important defense mechanisms for reproductive function and maintaining a healthy environment. Healthy vaginal flora is composed of anaerobic bacteria and aerobic bacteria, with Lactobacillus as the dominant microorganism, which can inhibit the growth and colonization of pathogenic microorganisms through the production of lactic acid, H2O2, etc (Bautista et al., 2016; Ding et al., 2021). However, the environment of bacterial vaginitis has changed from a mixed environment dominated by lactobacilli to one of overgrowth of Gardnerella vaginalis and other anaerobic bacteria (e.g., Atopobium vaginae, Bacteroides spp and Ureaplasma urealyticum), and the clinical symptoms are generally vaginal discharge, vaginal odor, pruritus in the perineal area, and elevated vaginal pH (Smith and Ravel, 2017; Abou Chacra et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2021). The prevalence of BV ranges from 20-60% between different countries, with the highest prevalence in sub-Saharan Africa (Bautista et al., 2016).BV can increase the risk of contracting many sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG), Trichomonas vaginalis (TV), and herpes simplex virus-2 (HSV-2), among others (Gardella et al., 2017; Smith and Ravel, 2017; Paavonen and Brunham, 2020).In addition, BV is associated with adverse reproductive health outcomes such as preterm birth, miscarriage, infections, cervicitis, urethritis, salpingitis, and urinary tract infections, which significantly affect women’s health (Hillier et al., 1995; Leitich and Kiss, 2007; Baisley et al., 2009; Coudray and Madhivanan, 2020; Ravel et al., 2021).
In the 2015 guidelines for the management of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended BV treatment with metronidazole or clindamycin (Workowski and Bolan, 2015). By 2018, topical or oral metronidazole for 5-7 days or vaginal clindamycin for 7 days became the first-line treatment option for BV recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) (Sherrard et al., 2018). Although the treatment is effective, excessive use of metronidazole and clindamycin can also cause side effects such as gastrointestinal reactions and allergic reactions (Menard, 2011; Ayinde and Ross, 2023). Several antibiotic drugs (tinidazole, metronidazole, ofloxacin, Secnidazole, etc.) and non-antibiotic drugs (sucrose, probiotics, etc.) are effective in the treatment of BV, and some of them have been or are in clinical phase I or Phase II randomized controlled trials (Donders et al., 2014). As an effective component of single small-molecule oligosaccharides, sucrose can selectively promote the growth of inherently beneficial lactobacilli in the vagina, lower vaginal pH, regulate the vaginal flora, and thus inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria (Lidbeck and Nord, 1993; Xiao et al., 2015).In addition, probiotic therapy is also considered to be one of the feasible ways to treat BV. However, there is currently no literature system evaluating their effectiveness and safety in the treatment of BV. This study selected eight alternative drugs for the treatment of BV and used a network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare efficacy and safety in the treatment of BV to determine which antibiotic was the best alternative to metronidazole.
NMA is a statistical technique that allows multiple treatments to be compared in the same meta-analysis and is based on meta-analysis techniques for weighted combined analysis. This approach allows for a combination of direct and indirect comparisons, where indirect comparisons can compare interventions that have not previously been compared in a randomized controlled trial, as well as comparing more than two interventions. And ranked in order of effect size to address differences in treatment effects among multiple complex interventions, providing an important reference for policymakers to develop clinical guidelines.
Method
Search strategy
We systematically searched potentially eligible studies in PubMed and EMBASE databases using a combination of medical subject title (MeSH) descriptors and free text terms (as of October 2023). Designed to search the following categories: “bacterial vaginitis”, “metronidazole”, “Clindamycin”, “Probiotics” and “placebo”. In addition, references for all included studies were manually searched and a meta-analysis was performed on the same topic to obtain additional eligible studies (see table in Supplementary Materials).
Selection criteria
Articles included in this study must meet the following criteria: 1. Randomized controlled trial (RCT) or observational studies published in English; 2. The subjects were patients diagnosed with BV; 3. The effects of the treatment drugs for BV were compared with each other; 4. Primary outcomes included clinical cure rate and incidence of adverse reactions. In addition, reviews, editorials, conference abstracts, and case reports were excluded from the final dataset.
Data extraction
For each included study, data extraction was performed by two independent examiners using standardized data extraction tables, and the relevant study characteristics extracted included: 1. The first author; 2. Year of publication; 3. Research type; 4. Disease type; 5. Basic information of the patient; 6. Type of treatment (antibiotics, metronidazole, probiotics, or placebo); 7. Medication information (medication method, dosage, and duration); 8. Prognosis and curative effect (clinical cure rate); 9. Adverse reactions.
Outcome indicator
We considered two primary outcomes, clinical cure and adverse event (AE), in a network meta-analysis. Criteria for clinical cure include: (A) Vaginal pH ≤4.5; (B) Normal vaginal discharge, negative olfactory test; (C) Normal vaginal microbiota, the clue cells were less than 20% of the total epithelial cells in the saline tablet. Finally, safety, i.e. the incidence of adverse events, was assessed. An adverse event is defined as any adverse medical event associated with the use of a drug. The most common adverse reactions included abnormally increased vaginal discharge, enhanced vaginal odor, external genital irritation, and genital itching.
Quality evaluation
The quality of the included studies was assessed by two independent reviewers based on the tools provided by the Cochrane Manual, and differences were resolved by two independent reviewers through discussion with a third reviewer, if necessary. Finally, Review Manager 5.4 software was used to generate the bias risk graph.
Statistical analysis
Two outcome measures, clinical cure rate and incidence of adverse reactions, were evaluated by Bayesian network meta-analysis. In addition, a subgroup analysis of two different treatments in the clinical cure rate measure, oral and vaginal application, was performed to compare the effectiveness and safety of various drugs for the treatment of BV. Stata 14.0 software and R software were used for statistical analysis of the data. We analyzed all the data using a random effects model to obtain relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI), comparing the efficacy and safety of various drugs in a given population. A random-effects network meta-analysis was then performed, which was used to directly and indirectly compare the efficacy of various drugs. Funnel plots were drawn to evaluate publication bias in the included literature. This study is registered with PROSPERO, number CRD42023454041.
Results
Study selection
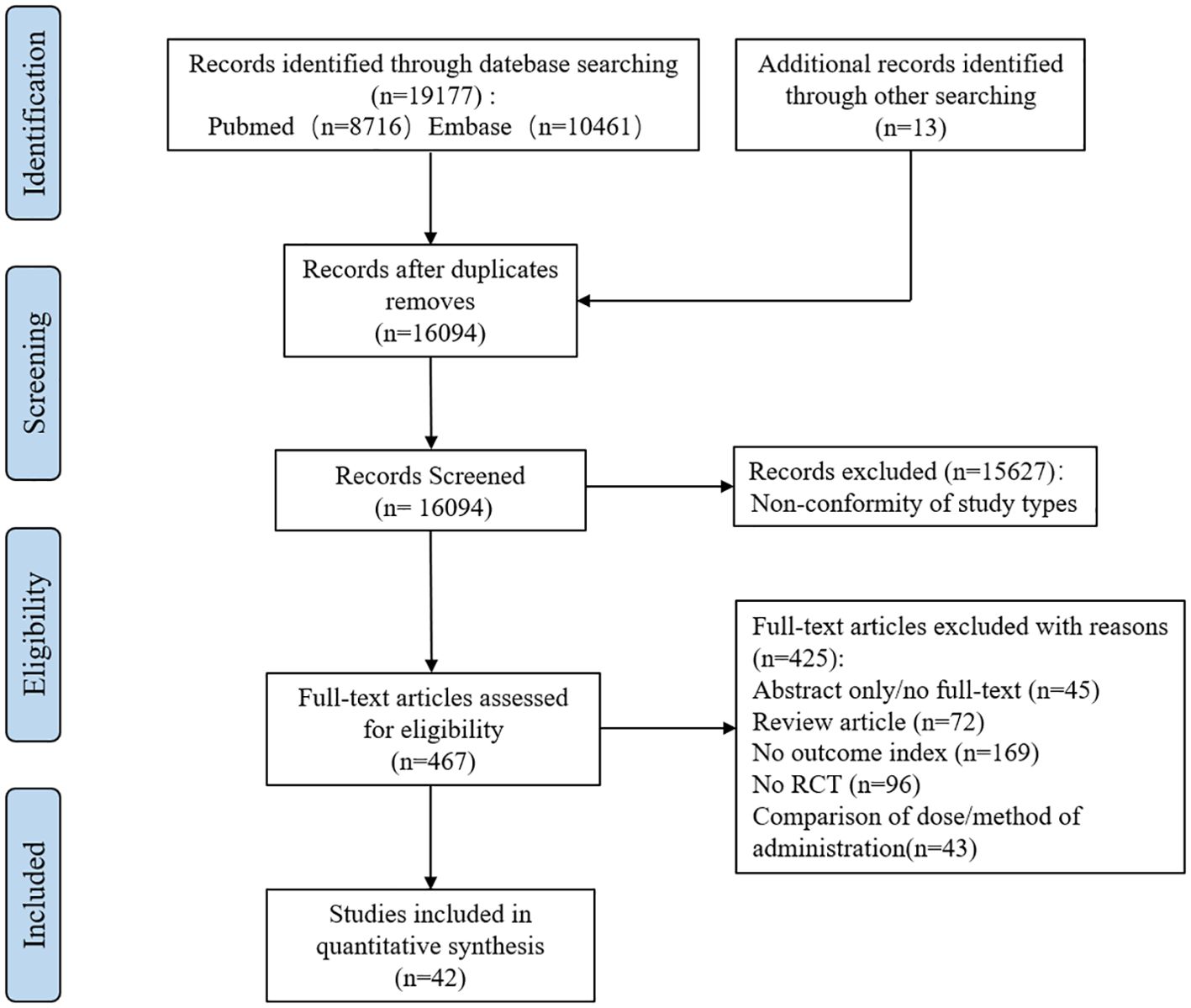
We searched PubMed and Embase databases for a total of 19177 potentially relevant articles. After excluding 3083 duplicate articles, the full text of 467 articles was obtained by reading titles and abstracts. A full review of the literature resulted in the inclusion of 42 eligible studies that met the criteria (see Figure 1).
Study characteristics
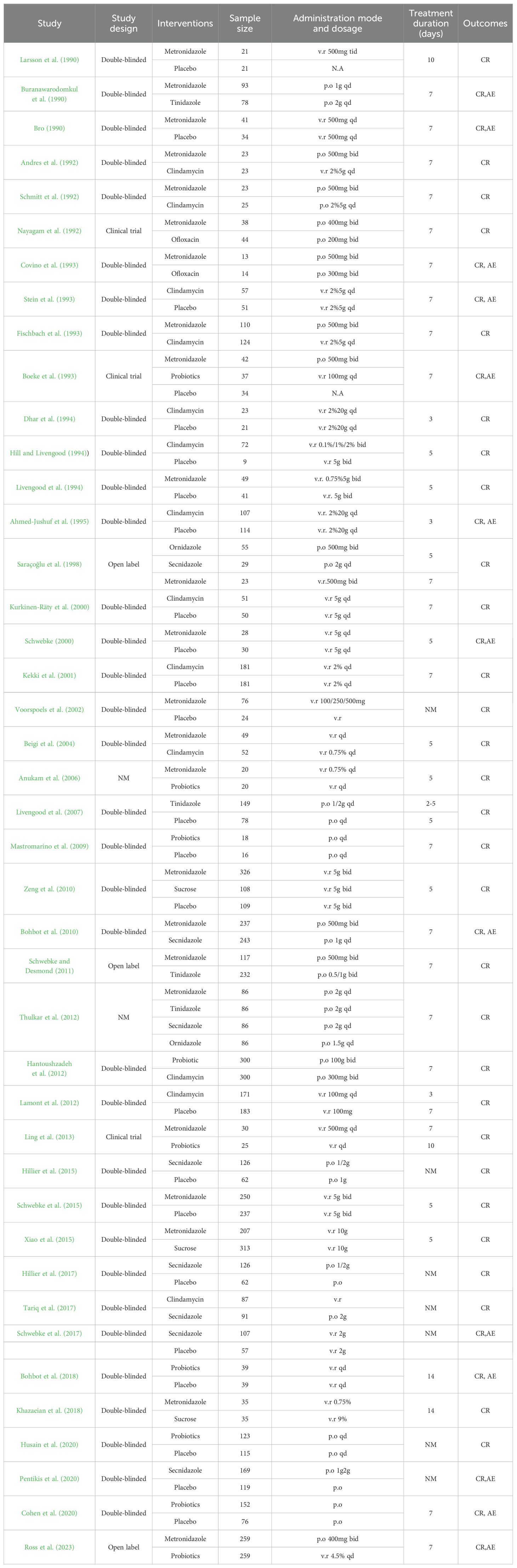
The main features of the included study (see Table 1) included a total of 8,382 subjects in 42 articles, all of whom were diagnosed with BV. In patients with BV, a total of eight drugs and a placebo were evaluated for monotherapy.
Deviation risk assessment
Of the 42 studies included, 39 were explicitly RCT studies. Three of the studies were non-RCT and double-blind, with a high risk of bias. Overall, all references included in this study had a low to moderate risk of bias (See Supplementary Figures S1, S2).
Clinical cure rate
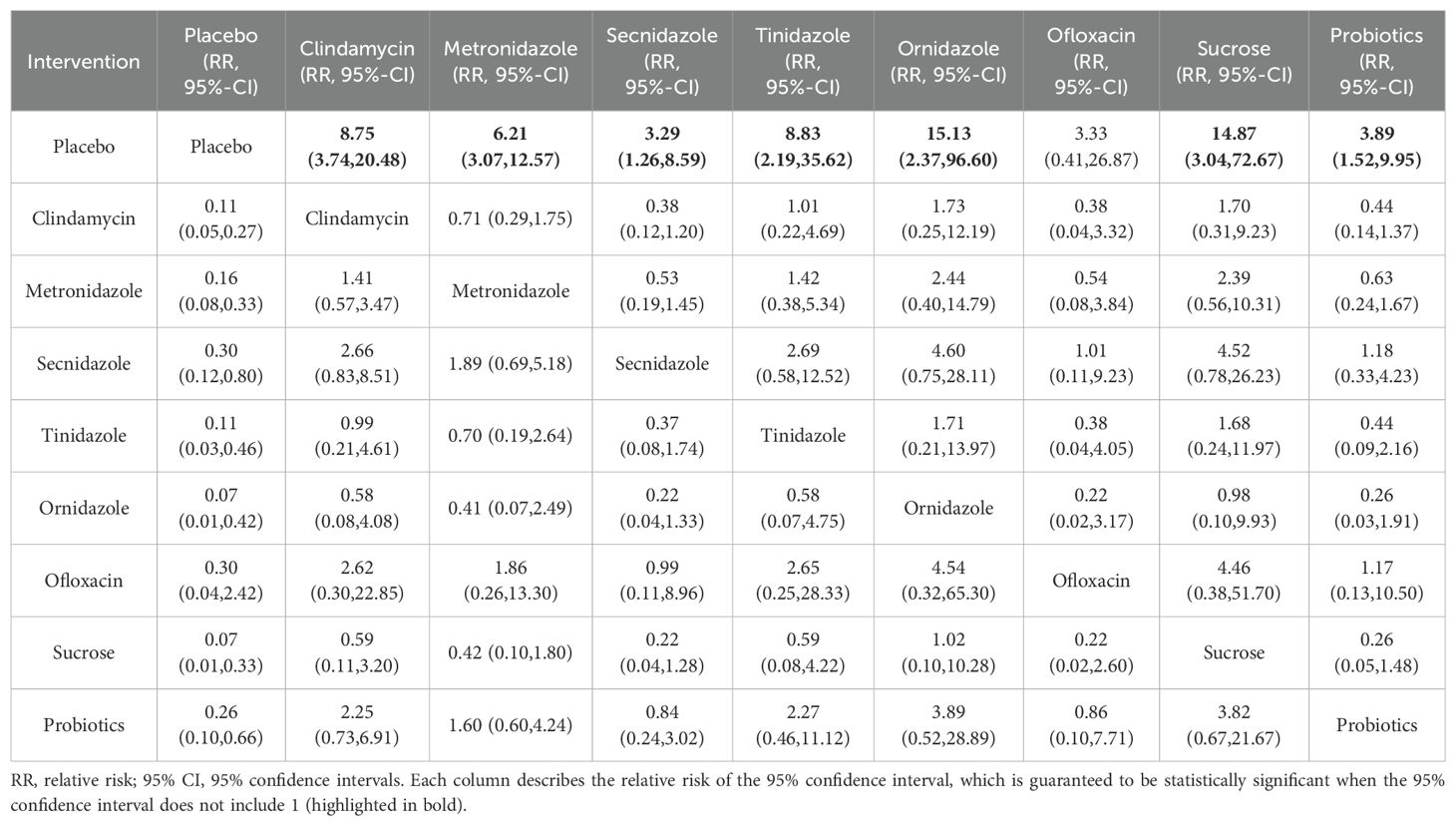
Among the 42 included articles, the clinical cure rates of 8382 subjects were evaluated, of which 4686 were cured after treatment. The results of the direct meta-analysis are shown in Supplementary Figure S3, Direct meta-analysis results showed that ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than Secnidazole (RR 1.22; 95%-CI 1.10-1.34).To further determine the direct and indirect comparative efficacy between the nine interventions, we conducted a network meta-analysis, and the network evidence graph is shown in Figure 2A. The results showed that clindamycin had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 8.75; 95%-CI 3.74-20.48), the clinical cure rate of metronidazole was better than that of placebo (RR 6.21; 95%-CI 3.07-12.57), Secnidazole had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 3.29; 95%-CI 1.26-8.59), the clinical cure rate of tinidazole was better than that of placebo (RR 8.83; 95%-CI 2.19-35.62), ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 15.13; 95%-CI 2.37-96.6), sucrose had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 14.87; 95%-CI 3.04-72.67), the clinical success rate of probiotics was better than that of placebo (RR 3.89; 95%-CI 1.52-9.95), and the remainder were not found to be statistically significant (see Table 2).
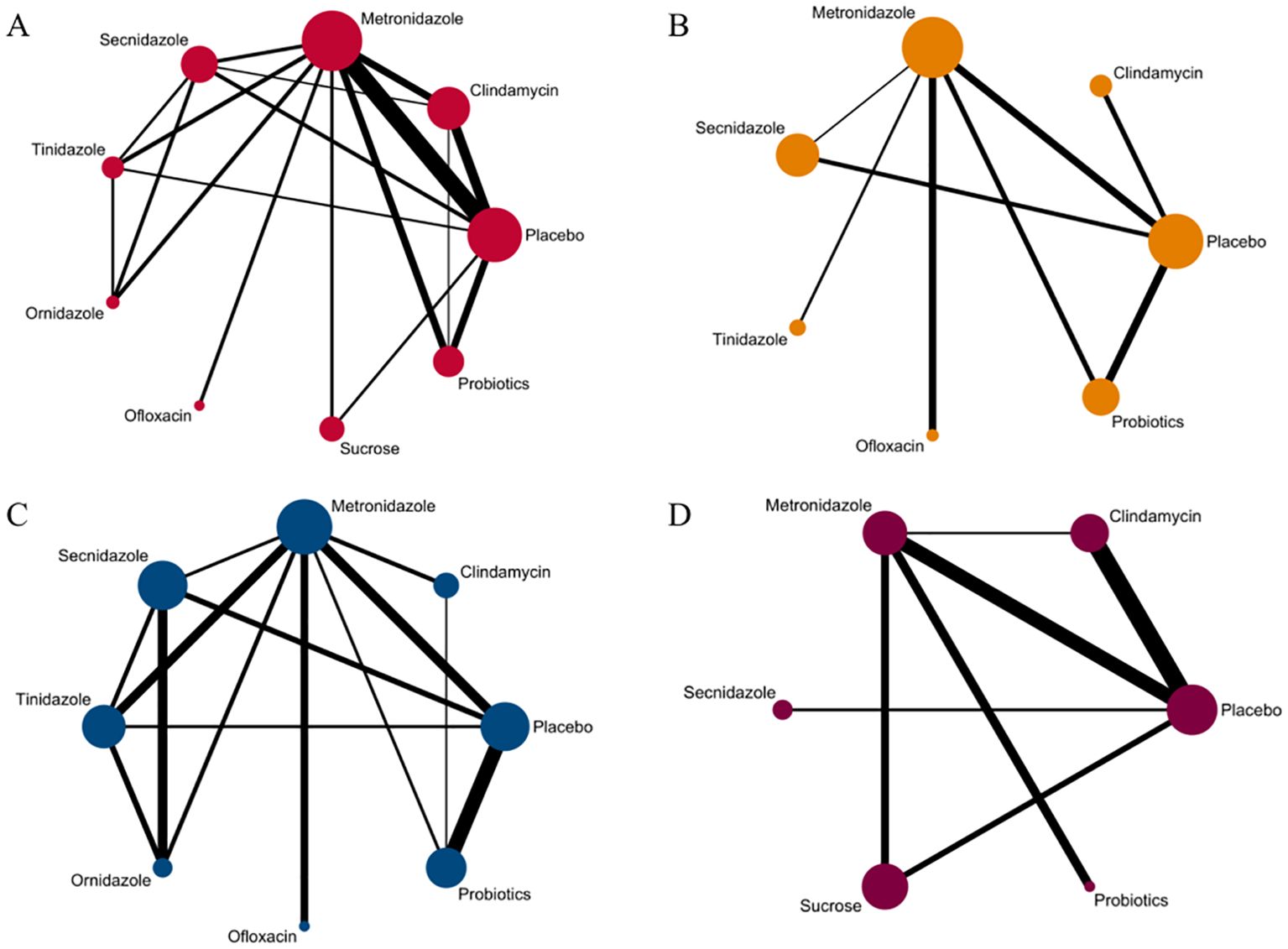
Figure 2. Network evidence graph. (A) Clinical cure rate. (B) incidence of adverse reactions. (C) Clinical cure rate of oral therapy. (D) Clinical cure rate of local vaginal administration. A graph of network evidence for the four study types, where the size of the nodes relates to the number of participants in that intervention type and the thickness of the line between interventions relates to the number of studies in that comparison.
We ranked the drugs according to their probability of clinical cure success (See Figure 3A). The results showed that sucrose (73.3%) ranked first, followed by ornidazole (73.1%), Clindamycin (62.5%), Tinidazole (62.4%), metronidazole (53%), probiotics (40.7%), ofloxacin (38%), Secnidazole (36.4%) and placebo (10.4%). See Supplementary Figure S11 for the ranking cumulative probability of all treatment drugs.
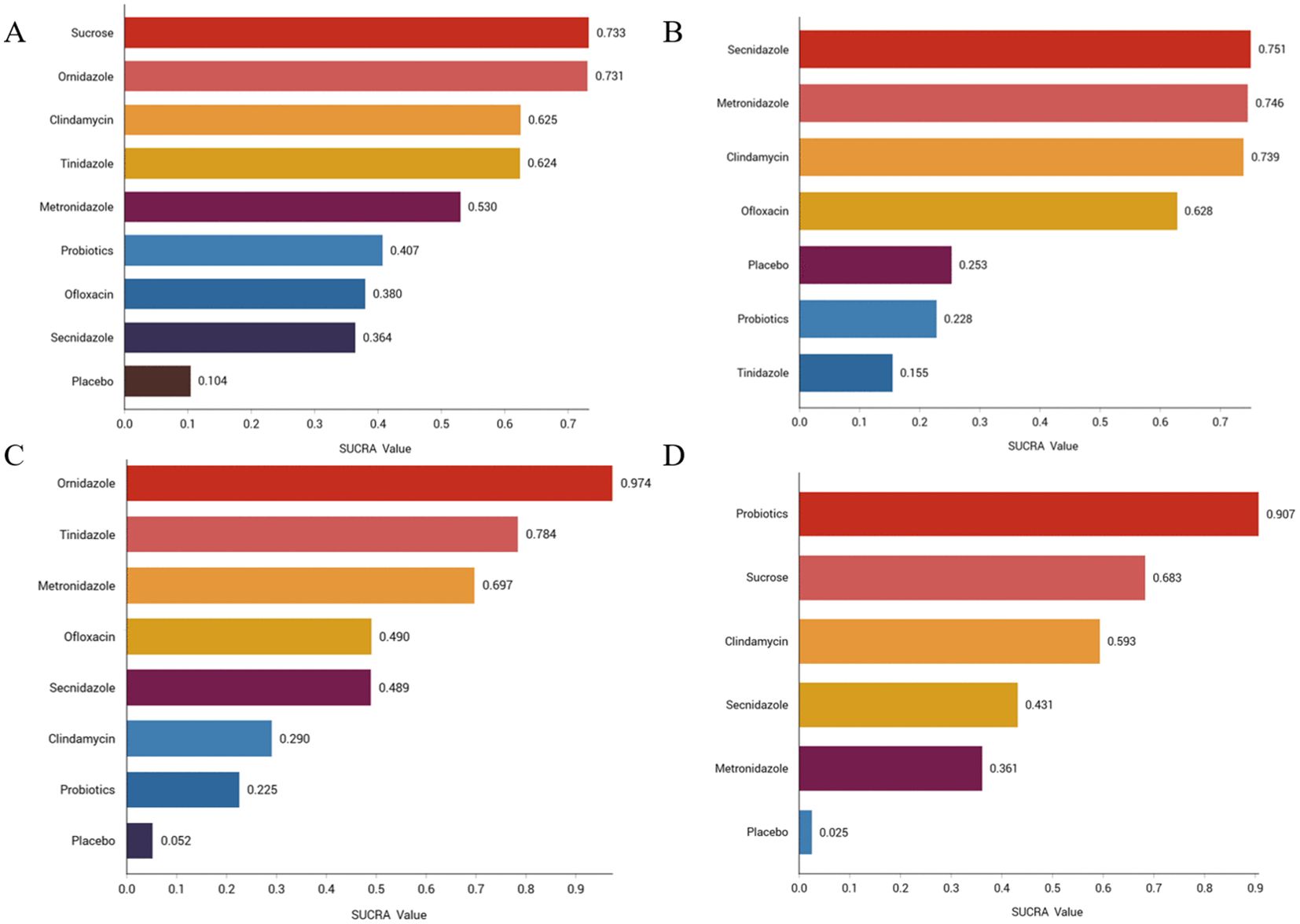
Figure 3. Efficacy and safety rankings of drugs used to treat BV (A) Clinical cure rate (B) Incidence of adverse reactions (C) Clinical cure rate of oral therapy (D) Clinical cure rate of local vaginal administration. SUCRA: Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve.
Adverse effects rate
Among the 42 included articles, a total of 13 articles evaluated 2524 subjects adverse reactions, of which 811 had adverse reactions. The results of the direct meta-analysis are shown in Supplementary Figure S4. To further determine the direct and indirect comparative efficacy of these six antibiotics, we conducted a network meta-analysis, and the network evidence graph is shown in Figure 2B. The evidence map, which directly or indirectly compared the therapeutic effects of six interventions, showed that metronidazole had a higher rate of adverse reactions than placebo (RR 2.14; 95%-CI 1.03-4.42), secnidazole had a higher adverse reaction rate than placebo (RR 2.20; 95%-CI 1.09-4.46), the adverse reaction rate of probiotics was lower than that of metronidazole (RR 0.44; 95%-CI 0.21-0.93), and no statistical significance was found in the comparison of the remaining drugs (See Table 3).
We ranked antibiotics according to their probability of adverse effects (See Figure 3B). The results showed that Secnidazole (75.1%) ranked first place, followed by metronidazole (74.6%), Clindamycin (73.9%), ofloxacin (62.8%), placebo (25.3%), probiotics (22.8%), tinidazole (22.8%). The ranking cumulative probability of all drug treatments is plotted in Supplementary Figure S12.
Clinical cure rate of oral drugs in patients with BV
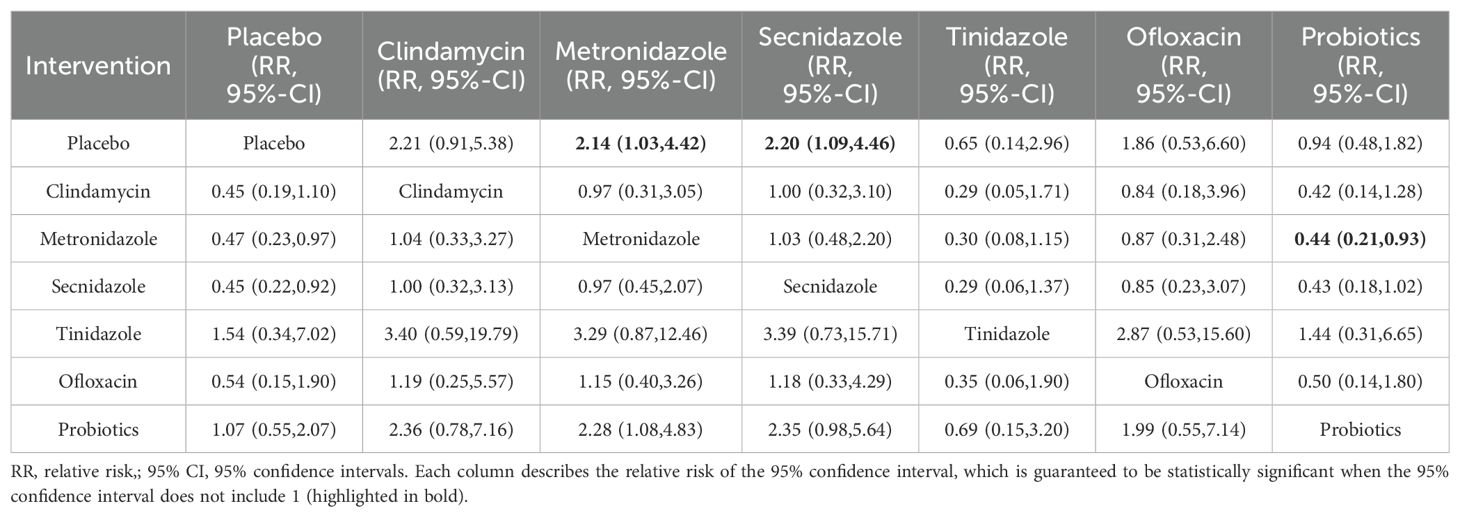
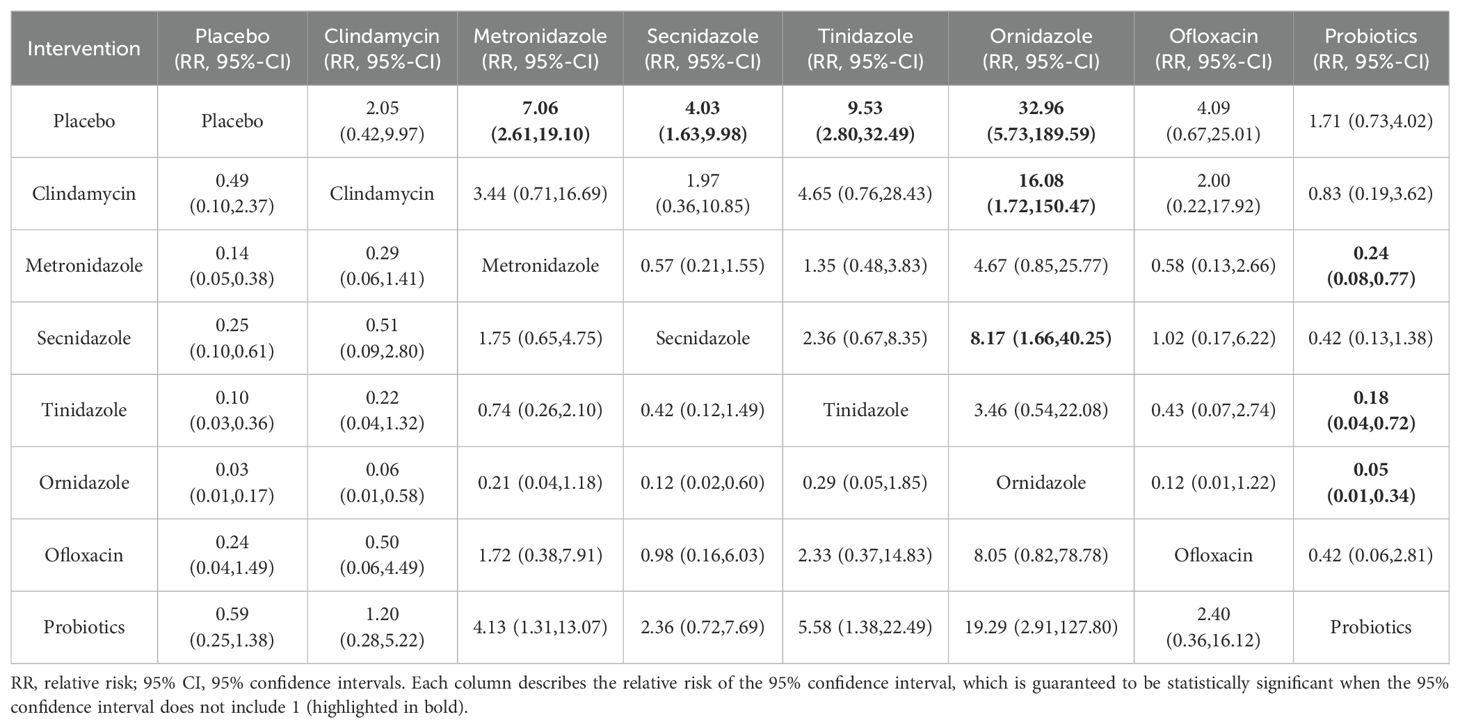
Among the 42 publications included, 19 evaluated the clinical cure rate of 3788 subjects with BV with oral drugs, of whom 2312 were successfully cured. To further determine the direct and indirect comparative efficacy of these eight interventions, we conducted a network meta-analysis, and the network evidence graph is shown in Figure 2C. The results of the direct meta-analysis are shown in Supplementary Figure S5, the clinical cure rate of ornidazole was better than Secnidazole (RR 1.23; 95%-CI 1.11-1.36). The evidence map, which directly or indirectly compared the therapeutic effects of eight interventions, showed that metronidazole had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 7.06; 95%-CI 2.61-19.10, RR 4.03; 95%-CI 1.63-9.98), Secnidazole had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 4.03; 95%-CI 1.63-9.98), tinidazole had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 9.53; 95%-CI 2.80-189.59), ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 32.96; 95%-CI 5.73-189.59), the clinical cure rate of ornidazole was better than clindamycin (RR 16.08; 95%-CI 1.72-150.47), the clinical cure rate of probiotics was worse than that of metronidazole (RR 0.24; 95%-CI 0.08-0.77), ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than Secnidazole (RR 8.17; 95%-CI 1.66-40.25), the clinical cure rate of probiotics was worse than tinidazole (RR 0.18; 95%-CI 0.04-0.72), the clinical cure rate of probiotics was worse than ornidazole (RR 0.05; 95%-CI 0.01-0.34), and no statistical significance was found in the comparison of the remaining antibiotics (See Table 4).
We ranked antibiotics according to their probability in terms of clinical cure rate (See Figure 3C). The results showed that ornidazole (97.4%) ranked the first place, followed by Tinidazole (78.4%), metronidazole (69.7%), ofloxacin (49%), Secnidazole (48.9%), clindamycin (29%), probiotics (22.5%) and placebo (5.2%). The ranking cumulative probability of all drug treatments is plotted in Supplementary Figure S13.
Clinical cure rate of vaginal application of drugs in patients with BV
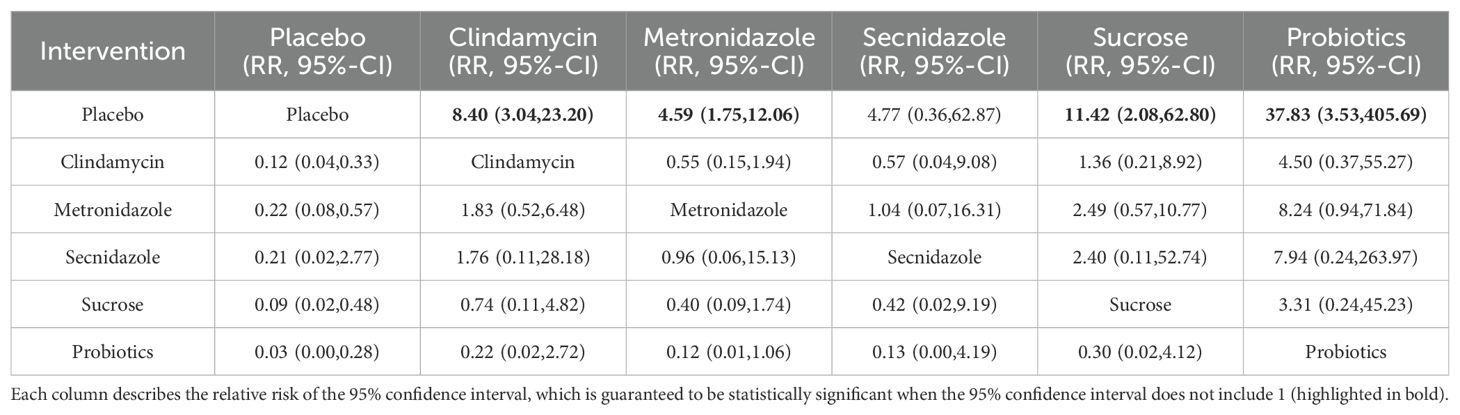
Among the 42 kinds of publications included, a total of 20 publications evaluated the clinical cure rate of 3808 cases of BV patients with vaginal application of drugs, of which 1953 cases were successfully cured. The results of the direct meta-analysis are shown in Supplementary Figure S6. The results showed that the clinical cure rate of sucrose was better than metronidazole (RR 1.12; 95%-CI 1.03-1.21), the clinical cure rate of metronidazole was worse than that of probiotics (RR 0.68; 95%-CI 0.52-0.88).To further determine the direct and indirect comparative efficacy of these six interventions, we conducted a network meta-analysis, and the network evidence graph is shown in Figure 2D. The evidence map, which directly or indirectly compared the therapeutic effects of six interventions, showed clindamycin had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 8.40; 95%-CI 3.04-23.20), the clinical cure rate of metronidazole was better than that of placebo (RR 4.59; 95%-CI 1.75-12.06), sucrose had a better clinical cure rate than placebo (RR 11.42; 95%-CI 2.08-62.80), the clinical cure rate of probiotics was superior to placebo (RR 37.83; 95%-CI 3.53-405.69) and no statistical significance was found in the comparison of the remaining antibiotics (See Table 5).
We ranked interventions according to their probability in terms of clinical cure rates (See Figure 3D). The results showed that probiotics (90.7%) ranked first, followed by sucrose (68.3%), clindamycin (59.3%), Seknidazole (43.1%), metronidazole (36.1%), and placebo (2.5%). The ranking cumulative probability of all drug treatments is plotted in Supplementary Figure S14.
Publishes bias and inconsistency evaluations
By observing the symmetry of the funnel plot to detect publication bias, the funnel plot in this study was basically in a symmetric distribution, and no significant publication bias was found in all results, and 11 points were distributed outside the 95%CI, indicating the possible influence of small sample size. (See Supplementary Figures S15–S18).
Discussion
The NMA aims to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of monotherapy with various drugs for the treatment of BV. A NMA of clinical cure rates and adverse event rates for all 42 included studies was performed using random-effects models, and subgroup analyses were performed for two different routes of administration, oral and vaginal. To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyze a single drug for patients diagnosed with BV (Muñoz-Barreno et al., 2021). The study by Alison et al. focused on evaluating the effectiveness of antibiotics or antibiotic and probiotic combination therapy, not a comparison between single drugs (Muñoz-Barreno et al., 2021). The study by Tan et al. also only compared the effectiveness of metronidazole or metronidazole in combination with probiotics and was not a network meta-analysis (Tan et al., 2017).
In our analysis of clinical cure rates for BV, we found that most of the drugs had higher clinical cure rates than placebo, and there was no significant difference in the single comparison between the drugs. However, a further evaluation of 42 studies allowed us to identify certain therapies that worked better. SUCRA value is a method used to evaluate the effectiveness of different interventions, a higher SUCRA value indicates a better treatment outcome. According to the SUCRA value, sucrose had the highest cure rate, followed by ornidazole and clindamycin. Sucrose is the main source of glucose for the normal microbiota, reduces the pH of the growth environment of pathogenic bacteria, and effectively inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria (Lidbeck and Nord, 1993). Current studies have also shown that sucrose gel is more effective than metronidazole gel and is an effective alternative therapy (Zeng et al., 2010). However, more clinical drug comparisons, different treatment times, and long-term follow-up investigations are needed to further confirm these results. Ornidazole, a second-generation 5-nitroimidazole drug, is currently being used as a treatment for BV, and this drug has a spectrum of activity against BV-associated anaerobic microorganisms (Zhao et al., 2023). Clindamycin, which is recommended by the CDC for various first-line treatments of BV in women, has also shown good clinical cure rates (Workowski and Bolan, 2015).
In the analysis of the incidence of adverse reactions in BV, we found that the incidence of adverse reactions of metronidazole was higher than that of placebo, the main adverse effects of metronidazole include gastrointestinal symptoms, increased vaginal discharge, and itching. And that of secnidazole was higher than that of placebo, the incidence of adverse reactions to probiotics was lower than that of metronidazole (RR 0.44; 95%-CI 0.21-0.93), which is consistent with the results of relevant clinical trials (Boeke et al., 1993; Ross et al., 2023). According to the SUCRA value, we found that the lowest incidence of adverse reactions was tinidazole, followed by probiotics and placebo. The safety of probiotics has been reported in the literature, but in the literature included in this study, the evaluation of adverse reactions was less. In future studies, more adverse reactions of single drug therapy should be investigated.
This study provides more meaningful clues as we conducted a subgroup analysis of different dosing modes in cure rates and found that there was a significant difference in efficacy between oral and vaginal administration. Ornidazole had the highest probability of oral administration, followed by tinidazole and metronidazole. The results of the network meta also showed that the clinical cure rate of ornidazole was better than clindamycin (RR 16.08; 95%-CI 1.72-150.47), ornidazole had a better clinical cure rate than Secnidazole (RR 8.17; 95%-CI 1.66-40.25), the clinical cure rate of probiotics was worse than ornidazole (RR 0.05; 95%-CI 0.01-0.34), indicating that oral ornidazole has a better effect than clindamycin and probiotics, the two traditional therapeutic drugs, but there are few studies on the side effects of Ornidazole, and it is unknown whether it will cause serious adverse reactions. Metronidazole, the drug of choice for the treatment of BV, has the lowest half-life of 7.9-8.8h (Mattila et al., 1983). Other nitroimidazole drugs newly appearing in the market have different half-lives, among which Ornidazole and tinidazole have longer half-lives of 14-14.7h and 14.1-16.8h, respectively (Martin et al., 1990; Gillis et al., 1996). This makes it have a better effect on the treatment process, and a longer half-life has a better control effect on pathogenic bacteria, which is the main reason for choosing oral administration. Probiotics had the highest probability of cure with vaginal administration, followed by sucrose and clindamycin, and there was no crossover with oral drugs. Probiotic therapy has a significant effect on BV treatment. When probiotics are applied to the vagina, probiotics quickly colonize the vagina, occupying the colonization site of pathogenic bacteria, effectively reducing pathogenic bacteria, and improving the recovery rate of normal bacteria of BV (Liu and Yi, 2022).In addition, probiotics can produce a variety of antibacterial substances and lactic acid, thus inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria and stimulating the immune system through competitive adhesion to achieve therapeutic effects (Ling et al., 2013).
For the timing of the visit for the test of cure, most of the literature included in this study evaluated patients 21-30 days after the start of treatment, and a few evaluated patients 2-3 months. Differences in the time of assessment also lead to a bias in the final clinical cure rate, which generally decreases the longer the visit. As the visit time increases, the patients also face an increased risk of secondary infections, such as douching during life, sexual transmission, or failure of initial treatment to completely eradicate all the microbes that cause bacterial vaginitis, all of which can lead to reinfection of BV.
In this study, there are still some limitations: first, the sample size of individual studies is limited; Second, different selection criteria are used in individual studies. Then there was heterogeneity between studies in terms of patient populations, probiotic strains, and outcome follow-up. In the end, individual studies gave different doses. In addition, there is currently insufficient data to demonstrate significant differences between the efficacy of other drugs to treat BV, and more high-quality clinical studies are needed to verify this. And in future studies, the side effects of drug treatment should also receive more attention.
Conclusion
This systematic review and network meta-analysis is the first study to analyze a drug for the treatment of BV, and the results suggest that ornidazole may be an effective option for the treatment of BV, while sucrose and probiotics are potential BV treatments, and more clinical trial studies are needed in the future to verify this idea.
Author contributions
YF: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Visualization. YG: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. QL: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YH: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. KC: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HY: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HD: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LX: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1402346/full#supplementary-material
References
Abou Chacra, L., Fenollar, F., Diop, K. (2021). Bacterial vaginosis: what do we currently know? Front. Cell. Infect Microbiol. 11, 672429. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.672429
Ahmed-Jushuf, I. H., Shahmanesh, M., Arya, O. P. (1995). The treatment of bacterial vaginosis with a 3 day course of 2% clindamycin cream: results of a multicentre, double blind, placebo controlled trial. B V Investig Group Genitourinary Med. 71, 254–256. doi: 10.1136/sti.71.4.254
Andres, F. J., Parker, R., Hosein, I., Benrubi, G. I. (1992). Clindamycin vaginal cream versus oral metronidazole in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: a prospective double-blind clinical trial. South. Med. J. 85, 1077–1080. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199211000-00006
Anukam, K. C., Osazuwa, E., Osemene, G. I., Ehigiagbe, F., Bruce, A. W., Reid, G. (2006). Clinical study comparing probiotic Lactobacillus GR-1 and RC-14 with metronidazole vaginal gel to treat symptomatic bacterial vaginosis. Microbes Infect. 8, 2772–2776. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2006.08.008
Ayinde, O., Ross, J. D. (2023). The frequency and duration of side-effects associated with the use of oral metronidazole; A prospective study of VITA trial participants. Int. J. STD AIDS 34, 897–902. doi: 10.1177/09564624231179505
Baisley, K., Changalucha, J., Weiss, H. A., Mugeye, K., Everett, D., Hambleton, I., et al. (2009). Bacterial vaginosis in female facility workers in north-western Tanzania: prevalence and risk factors. Sexual Transmit Infect 85, 370–375. doi: 10.1136/sti.2008.035543
Bautista, C. T., Wurapa, E., Sateren, W. B., Morris, S., Hollingsworth, B., Sanchez, J. L. (2016). Bacterial vaginosis: a synthesis of the literature on etiology, prevalence, risk factors, and relationship with chlamydia and gonorrhea infections. Military Med. Res. 3, 4. doi: 10.1186/s40779-016-0074-5
Beigi, R. H., Austin, M. N., Meyn, L. A., Krohn, M. A., Hillier, S. L. (2004). Antimicrobial resistance associated with the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 191, 1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.05.033
Boeke, A. J., Dekker, J. H., Van Eijk, J. T., Kostense, P. J., Bezemer, P. D. (1993). Effect of lactic acid suppositories compared with oral metronidazole and placebo in bacterial vaginosis: a randomised clinical trial. Genitourinary Med. 69, 388–392. doi: 10.1136/sti.69.5.388
Bohbot, J. M., Daraï, E., Bretelle, F., Brami, G., Daniel, C., Cardot, J. M. (2018). Efficacy and safety of vaginally administered lyophilized Lactobacillus crispatus IP 174178 in the prevention of bacterial vaginosis recurrence. J. Gynecol Obstet Hum. Reprod. 47, 81–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2017.11.005
Bohbot, J. M., Vicaut, E., Fagnen, D., Brauman, M. (2010). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis: a multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised phase III study comparing secnidazole and metronidazole. Infect. Dis. Obstet Gynecol 2010, 2010. doi: 10.1155/2010/705692
Bro, F. (1990). Metronidazole pessaries compared with placebo in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Scandinavian J. Primary Health Care 8, 219–223. doi: 10.3109/02813439008994962
Buranawarodomkul, P., Chandeying, V., Sutthijumroon, S. (1990). Seven day metronidazole versus single dose tinidazole as therapy for nonspecific vaginitis. J. Med. Assoc. Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet 73, 283–287.
Cohen, C. R., Wierzbicki, M. R., French, A. L., Morris, S., Newmann, S., Reno, H., et al. (2020). Randomized trial of lactin-V to prevent recurrence of bacterial vaginosis. New Engl. J. Med. 382, 1906–1915. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915254
Coudray, M. S., Madhivanan, P. (2020). Bacterial vaginosis-A brief synopsis of the literature. Eur. J. Obstet Gynecol Reprod. Biol. 245, 143–148. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2019.12.035
Covino, J. M., Black, J. R., Cummings, M., Zwickl, B., Mccormack, W. M. (1993). Comparative evaluation of ofloxacin and metronidazole in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Sexual Transmit Dis. 20, 262–264. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199309000-00004
Dhar, J., Arya, O. P., Timmins, D. J., Moss, S., Mukembo, S., Alawattegama, A. B., et al. (1994). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis with a three day course of 2% clindamycin vaginal cream: a pilot study. Genitourinary Med. 70, 121–123. doi: 10.1136/sti.70.2.121
Ding, C., Yu, Y., Zhou, Q. (2021). Bacterial Vaginosis: Effects on reproduction and its therapeutics. J. Gynecol obstet Hum. Reprod. 50, 102174. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2021.102174
Donders, G. G., Zodzika, J., Rezeberga, D. (2014). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis: what we have and what we miss. Expert Opin. Pharmacother 15, 645–657. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2014.881800
Fischbach, F., Petersen, E. E., Weissenbacher, E. R., Martius, J., Hosmann, J., Mayer, H. (1993). Efficacy of clindamycin vaginal cream versus oral metronidazole in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Obstet Gynecol 82, 405–410.
Gardella, C., Eckert, L., Lentz, G. (2017). “Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis,” in Comprehensive Gynecology, 7th ed (Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA).
Gillis, J. C., Wiseman, L. R., Secnidazole (1996). A review of its antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in the management of protozoal infections and bacterial vaginosis. Drugs 51, 621–638. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199651040-00007
Hantoushzadeh, S., Golshahi, F., Javadian, P., Khazardoost, S., Aram, S., Hashemi, S., et al. (2012). Comparative efficacy of probiotic yoghurt and clindamycin in treatment of bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women: a randomized clinical trial. J. Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med. 25, 1021–1024. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.614654
Hill, G. B., Livengood, C. H., 3rd (1994). Bacterial vaginosis-associated microflora and effects of topical intravaginal clindamycin. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 171, 1198–1204. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(94)90132-5
Hillier, S., Morgan, F., Waldbaum, A., Schwebke, J., Nyirjesy, P., Adetoro, N., et al. (2015). 6: A phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of single, oral doses of SYM-1219, a granule formulation containing 1 and 2 gram doses of secnidazole, for the treatment of women with bacterial vaginosis. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 213, 885. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.09.013
Hillier, S. L., Nugent, R. P., Eschenbach, D. A., Krohn, M. A., Gibbs, R. S., Martin, D. H., et al. (1995). Association between bacterial vaginosis and preterm delivery of a low-birth-weight infant. The Vaginal Infections and Prematurity Study Group. New Engl. J. Med. 333, 1737–1742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512283332604
Hillier, S. L., Nyirjesy, P., Waldbaum, A. S., Schwebke, J. R., Morgan, F. G., Adetoro, N. A., et al. (2017). Secnidazole treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 130, 379–386. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002135
Husain, S., Allotey, J., Drymoussi, Z., Wilks, M., Fernandez-Felix, B. M., Whiley, A., et al. (2020). Effects of oral probiotic supplements on vaginal microbiota during pregnancy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with microbiome analysis. BJOG: an Int. J. Obstet Gynecol 127, 275–284. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.15675
Kekki, M., Kurki, T., Pelkonen, J., Kurkinen-Räty, M., Cacciatore, B., Paavonen, J. (2001). Vaginal clindamycin in preventing preterm birth and peripartal infections in asymptomatic women with bacterial vaginosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 97, 643–648. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(01)01321-7
Khazaeian, S., Navidian, A., Navabi-Rigi, S. D., Araban, M., Mojab, F., Khazaeian, S. (2018). Comparing the effect of sucrose gel and metronidazole gel in treatment of clinical symptoms of bacterial vaginosis: a randomized controlled trial. Trials 19, 585. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2905-z
Kurkinen-Räty, M., Vuopala, S., Koskela, M., Kekki, M., Kurki, T., Paavonen, J., et al. (2000). A randomised controlled trial of vaginal clindamycin for early pregnancy bacterial vaginosis. BJOG: an Int. J. Obstet Gynecol 107, 1427–1432. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2000.tb11660.x
Lamont, R. F., Taylor-Robinson, D., Bassett, P. (2012). Rescreening for Normal vaginal microbiota in pregnancy and re-treating with clindamycin vaginal cream significantly increases cure and improvement rates. Int. J. STD AIDS 23, 565–569. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2011.011229
Larsson, P. G., Bergman, B., Forsum, U., Påhlson, C. (1990). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis in women with vaginal bleeding complications or discharge and harboring Mobiluncus. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 29, 296–300. doi: 10.1159/000293339
Leitich, H., Kiss, H. (2007). Asymptomatic bacterial vaginosis and intermediate flora as risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet Gynaecol 21, 375–390. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2006
Lidbeck, A., Nord, C. E. (1993). Lactobacilli and the normal human anaerobic microflora. Clin. Infect. Dis. 16 Suppl 4, S181–S187. doi: 10.1093/clinids/16.Supplement_4.S181
Ling, Z., Liu, X., Chen, W., Luo, Y., Yuan, L., Xia, Y., et al. (2013). The restoration of the vaginal microbiota after treatment for bacterial vaginosis with metronidazole or probiotics. Microbial Ecol. 65, 773–780. doi: 10.1007/s00248-012-0154-3
Liu, H. F., Yi, N. (2022). A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of probiotics for bacterial vaginosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 26, 90–98. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202201_27752
Livengood, C. H., 3rd, Ferris, D. G., Wiesenfeld, H. C., Hillier, S. L., Soper, D. E., Nyirjesy, P., et al. (2007). Effectiveness of two tinidazole regimens in treatment of bacterial vaginosis: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 110, 302–309. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000275282.60506.3d
Livengood, C. H., 3rd, Mcgregor, J. A., Soper, D. E., Newton, E., Thomason, J. L. (1994). Bacterial vaginosis: efficacy and safety of intravaginal metronidazole treatment. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 170, 759–764. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(94)70278-0
Martin, C., Bruguerolle, B., Mallet, M. N., Condomines, M., Sastre, B., Gouin, F. (1990). Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of a single dose of ornidazole (1,000 milligrams intravenously) for antibiotic prophylaxis in colorectal surgery. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34, 1921–1924. doi: 10.1128/AAC.34.10.1921
Mastromarino, P., Macchia, S., Meggiorini, L., Trinchieri, V., Mosca, L., Perluigi, M., et al. (2009). Effectiveness of Lactobacillus-containing vaginal tablets in the treatment of symptomatic bacterial vaginosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 15, 67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02112.x
Mattila, J., Männistö, P. T., Mäntylä, R., Nykänen, S., Lamminsivu, U. (1983). Comparative pharmacokinetics of metronidazole and tinidazole as influenced by administration route. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 23, 721–725. doi: 10.1128/AAC.23.5.721
Menard, J. P. (2011). Antibacterial treatment of bacterial vaginosis: current and emerging therapies. Int. J. Women’s Health 3, 295–305. doi: 10.2147/IJWH
Muñoz-Barreno, A., Cabezas-Mera, F., Tejera, E., MaChado, A. (2021). Comparative effectiveness of treatments for bacterial vaginosis: A network meta-analysis. Antibiot (Basel Switzerland) 10, 978. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080978
Nayagam, A. T., Smith, M. D., Ridgway, G. L., Allason-Jones, E., Robinson, A. J., Stock, J. (1992). Comparison of ofloxacin and metronidazole for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Int. J. STD AIDS 3, 204–207. doi: 10.1177/095646249200300309
Paavonen, J. A., Brunham, R. C. (2020). Vaginitis in nonpregnant patients: ACOG practice bulletin number 215. Obstet Gynecol 135, 1229–1230. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003857
Pentikis, H., Adetoro, N., Tipping, D., Levy, S. (2020). An integrated efficacy and safety analysis of single-dose secnidazole 2 g in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Reprod. Sci. (Thousand Oaks Calif) 27, 523–528. doi: 10.1007/s43032-019-00048-x
Ravel, J., Moreno, I., Simón, C. (2021). Bacterial vaginosis and its association with infertility, endometritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 224, 251–257. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.019
Ross, J. D. C., Brittain, C., Anstey Watkins, J., Kai, J., David, M., Ozolins, M., et al. (2023). Intravaginal lactic acid gel versus oral metronidazole for treating women with recurrent bacterial vaginosis: the VITA randomised controlled trial. BMC Women’s Health 23, 241. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02303-5
Saraçoğlu, F., Göl, K., Sahin, I., Türkkani, B., Atalay, C., Oztopçu, C. (1998). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis with oral or vaginal ornidazole, secnidazole and metronidazole. Int. J. gynaecol obstet: Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol Obstet 62, 59–61. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7292(98)00029-0
Schmitt, C., Sobel, J. D., Meriwether, C. (1992). Bacterial vaginosis: treatment with clindamycin cream versus oral metronidazole. Obstet Gynecol 79, 1020–1023.
Schwebke, J. R. (2000). Asymptomatic bacterial vaginosis: response to therapy. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 183, 1434–1439. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.107735
Schwebke, J. R., Desmond, R. A. (2011). Tinidazole vs metronidazole for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 204, 211. e211–211. e216. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.898
Schwebke, J. R., Marrazzo, J., Beelen, A. P., Sobel, J. D. (2015). A phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study evaluating the safety and efficacy of metronidazole vaginal gel 1.3% in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Sexual Transmit Dis. 42, 376–381. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000300
Schwebke, J. R., Morgan, F. G., Jr., Koltun, W., Nyirjesy, P. (2017). A phase-3, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effectiveness and safety of single oral doses of secnidazole 2 g for the treatment of women with bacterial vaginosis. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol 217, 678.e671–678.e679. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.08.017
Sherrard, J., Wilson, J., Donders, G., Mendling, W., Jensen, J. S. (2018). 2018 European (IUSTI/WHO) International Union against sexually transmitted infections (IUSTI) World Health Organisation (WHO) guideline on the management of vaginal discharge. Int. J. STD AIDS 29, 1258–1272. doi: 10.1177/0956462418785451
Smith, S. B., Ravel, J. (2017). The vaginal microbiota, host defence and reproductive physiology. J. Physiol. 595, 451–463. doi: 10.1113/JP271694
Stein, G. E., Christensen, S. L., Mummaw, N. L., Soper, D. E. (1993). Placebo-controlled trial of intravaginal clindamycin 2% cream for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 27, 1343–1345. doi: 10.1177/106002809302701106
Tan, H., Fu, Y., Yang, C., Ma, J. (2017). Effects of metronidazole combined probiotics over metronidazole alone for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Arch. Obstet Gynecol 295, 1331–1339. doi: 10.1007/s00404-017-4366-0
Tariq, N., Basharat, A., Khan, D. H., Fahim, A., Khan, M. H. (2017). Treatment for symptomatic bacterial vaginosis: ARandomized controlled trial. J. Coll. Phys Surgeons–Pakistan: JCPSP 27, 686–689.
Thulkar, J., Kriplani, A., Agarwal, N. (2012). A comparative study of oral single dose of metronidazole, tinidazole, secnidazole and ornidazole in bacterial vaginosis. Indian J. Pharmacol. 44, 243–245. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.93859
Voorspoels, J., Casteels, M., Remon, J. P., Temmerman, M. (2002). Local treatment of bacterial vaginosis with a bioadhesive metronidazole tablet. Eur. J. obstet gynecol Reprod. Biol. 105, 64–66. doi: 10.1016/S0301-2115(02)00110-0
Workowski, K. A., Bolan, G. A. (2015). “Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015,” in MMWR Recommendations and reports: Morbidity and mortality weekly report Recommendations and reports, vol. 64, 1–137. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5885289/pdf/nihms777542.pdf
Xiao, B. B., Zhang, D., Chen, R., Shi, H. R., Xin, X. R., Wang, H. L., et al. (2015). Sucrose gel for treatment of bacterial vaginosis: a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, parallel-group, phase III clinical trial. Beijing da xue xue bao Yi xue ban = J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 47, 925–932.
Zeng, Z. M., Liao, Q. P., Yao, C., Geng, L., Feng, L. H., Shi, H. R., et al. (2010). Directed shift of vaginal flora after topical application of sucrose gel in a phase III clinical trial: a novel treatment for bacterial vaginosis. Chin. Med. J. 123, 2051–2057.
Zhao, X., Boyd, P., Dallal Bashi, Y. H., Mccoy, C. F., Karl Malcolm, R. (2023). Physicochemical considerations in the formulation development of silicone elastomer vaginal rings releasing 5-nitroimidazole drugs for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Int. J. Pharma 644, 123296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123296
Keywords: bacterial vaginosis, treatment, antibiotic, sucrose, network meta-analysis
Citation: Fan Y, Gu Y, Xian Y, Li Q, He Y, Chen K, Yu H, Deng H, Xiong L, Cui Z, Yang Y and Xiang Y (2024) Efficacy and safety of different drugs for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1402346. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1402346
Received: 17 March 2024; Accepted: 29 August 2024;
Published: 11 October 2024.
Edited by:
António Machado, Universidad San Francisco de Quito, EcuadorReviewed by:
Ninfa Ramírez Durán, Autonomus University of the State of Mexico Medicine Faculty, MexicoDavid Eschenbach, University of Washington, United States
Copyright © 2024 Fan, Gu, Xian, Li, He, Chen, Yu, Deng, Xiong, Cui, Yang and Xiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuxin Fan, ZmFueXV4aW4xOTk4QDE2My5jb20=
 Yuxin Fan
Yuxin Fan Yanhong Gu
Yanhong Gu Li Xiong
Li Xiong