- 1Institute of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, Sichuan Agricultural University, Wenjiang, China
- 2Avian Disease Research Center, College of Veterinary Medicine of Sichuan Agricultural University, Wenjiang, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Animal Disease and Human Health of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Agricultural University, Wenjiang, China
A Corrigendum on
Autophagy Is a Potential Therapeutic Target Against Duck Tembusu Virus Infection in Vivo
By Hu Z, Pan Y, Cheng A, Zhang X, Wang M, Chen S, Zhu D, Liu M, Yang Q, Wu Y, Zhao X, Huang J, Zhang S, Mao S, Ou X, Yu Y, Zhang L, Liu Y, Tian B, Pan L, Rehman MU, Yin Z and Jia R (2020). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10:155. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00155
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3 as published. This figure contains the wrong slides of microscopy. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions in any way. The original article has been updated.
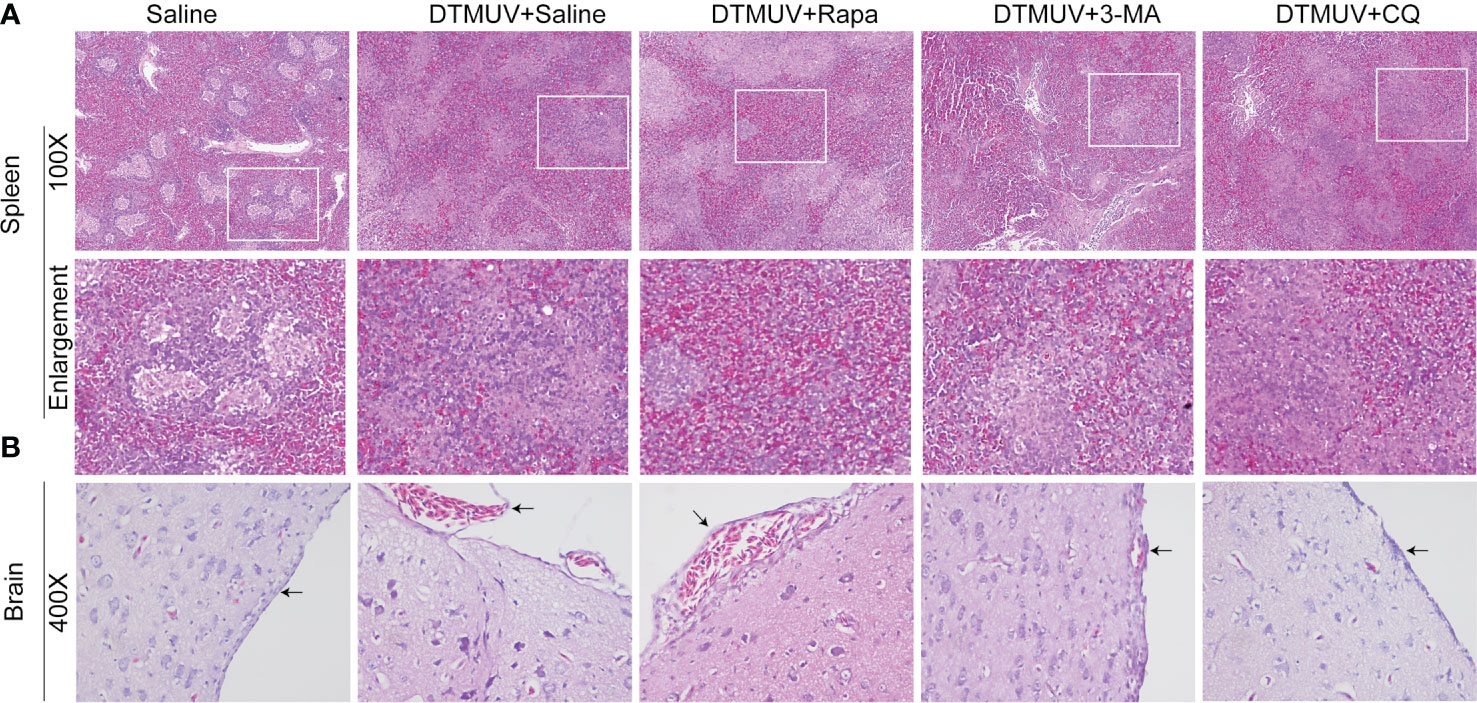
Figure 3 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of cells in the spleens (A) and the brains (B) of ducks infected with DTMUV in the absence or presence of either Rapa, 3-MA, or CQ, respectively. Treatment with saline was used as the control. Images shown were representative from five ducks in each group. The images were with 100X magnification for spleens and 400X for brains. Black arrows: blood cells in the meninx.
Keywords: DTMUV, autophagy, spleen, brain, tissue damage, replication, immune response
Citation: Hu Z, Pan Y, Cheng A, Zhang X, Wang M, Chen S, Zhu D, Liu M, Yang Q, Wu Y, Zhao X, Huang J, Zhang S, Mao S, Ou X, Yu Y, Zhang L, Liu Y, Tian B, Pan L, Rehman MU, Yin Z and Jia R (2021) Corrigendum: Autophagy Is a Potential Therapeutic Target Against Duck Tembusu Virus Infection in Vivo. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11:641825. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.641825
Received: 15 December 2020; Accepted: 28 January 2021;
Published: 19 February 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Layla Kamareddine, Qatar University, Qatar
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Pan, Cheng, Zhang, Wang, Chen, Zhu, Liu, Yang, Wu, Zhao, Huang, Zhang, Mao, Ou, Yu, Zhang, Liu, Tian, Pan, Rehman, Yin and Jia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anchun Cheng, Y2hlbmdhbmNodW5AdmlwLjE2My5jb20=; Renyong Jia, amlhcnlAc2ljYXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhiqiang Hu1,2,3†
Zhiqiang Hu1,2,3† Anchun Cheng
Anchun Cheng Mingshu Wang
Mingshu Wang Dekang Zhu
Dekang Zhu Mafeng Liu
Mafeng Liu Shaqiu Zhang
Shaqiu Zhang Sai Mao
Sai Mao Xumin Ou
Xumin Ou Bin Tian
Bin Tian Leichang Pan
Leichang Pan Mujeeb Ur Rehman
Mujeeb Ur Rehman Zhongqiong Yin
Zhongqiong Yin Renyong Jia
Renyong Jia