- 1Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Sivas Cumhuriyet University, Sivas, Türkiye
- 2Department of Medical Biochemistry, Trabzon Kanuni Health Practice and Research Hospital, Trabzon Faculty of Medicine, University of Health Sciences, Trabzon, Türkiye
- 3Department of Medical Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Karadeniz Technical University, Trabzon, Türkiye
- 4Department of Hematology, Mengücek Gazi Education and Research Hospital, Erzincan, Türkiye
- 5Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
- 6Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Jordan
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is one of the most prevalent hematological malignancies. miRNAs play roles in cancer initiation and progression in various cancer types by post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. The aim of this study is to investigate the mechanisms in the development and progression of acute myeloid leukemia and to identify potential target genes and miRNAs by bioinformatic analysis. miRNA expression profiles were obtained from the GSE51908 dataset on the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). GEO2R was used to identify differentially expressed miRNAs. The diagnostic and overall survival effects of the identified miRNA were determined using ROC analysis and Kaplan-Meier curve, respectively. Putative miRNA targets were determined based on miRWalk and miRDB tools. The expression change and overall survival analysis of the identified target gene were analyzed by Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA). Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks of the target gene were determined using STRING and GeneMANIA. Functional enrichment analysis was performed using the DAVID program. 24 DE-miRNAs were identified, including 16 upregulated and 8 downregulated genes. miR-342-5p expression had significantly shorter survival than those in higher expression control group (p = 0.0001), and its AUC value to discriminate AML from control groups was 0.795. High expression of MDM4 predicts an unfavorable prognosis in AML patients. The MDM4 gene was determined to be associated with decreased survival rates. According to KEGG results, microRNAs, p53 signaling pathway, and cell cycle are associated with AML development. The current study based on the GEO database, miR-342-5p/MDM4/p53 axis AML may provide new therapeutic targets.
1 Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by the accumulation of immature blast cells due to the inhibition of normal hematopoiesis, and aberrant proliferation and differentiation of immature myeloid hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow (BM) (Xin et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2020). It is the most prevalent variety of acute leukemia in adults and has a high morbidity and mortality rate (Cheng et al., 2020; Juliusson et al., 2012). Tumor formation in AML is highly complex and is associated with various gene mutations (Cheng et al., 2020). In recent years, there have been advances in genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic studies of AML (Kirtonia et al., 2022). Although these studies have improved our understanding of AML, its pathogenesis has not yet been completely elucidated (Liu et al., 2019). AML affects numerous organs, including the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and central nervous system, and has a poor prognosis (Cheng et al., 2020). AML can be treated with chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, cell therapy, biological immunotherapy, and gene-targeted therapy, although the success rate of treatment is not that high (Xin et al., 2022). Despite the evolving treatment options, the ineffectiveness of chemotherapy and the lack of information on the molecular pathogenesis of AML of the disease still remain a problem (Kirtonia et al., 2022). The majority of patients experience a relapse after obtaining complete remission, and some even dies (Cheng et al., 2020). Accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and efficient treatment of AML depend on the identification and development of therapeutic targets (Liu et al., 2019). It is predicted that studies on the pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of AML may have important clinical application value (Cheng et al., 2020). For this purpose, revealing the potential roles of non-coding RNAs, especially in AML, will be crucial in terms of understanding the molecular pathways related to AML development, chemotherapeutic response, and relapse. Previous studies have shown the role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the pathogenesis of cancers, including AML (Kirtonia et al., 2022).
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are highly conserved small non-coding RNA molecules, usually 18–24 nucleotides long, acting as negative post transcriptional regulation of gene expression (He and Hannon, 2004). The abnormal expression of miRNAs is associated with a variety of diseases, including cancer, and offers crucial information on the molecular pathophysiology of the diseases (O’Brien et al., 2018). miRNAs are dysregulated levels in AML and are crucial for the development or repression of the disease (Fletcher et al., 2022). Through alterations in proximity to the oncogenic genomic area, epigenetic modifications, inappropriate targeting of miRNA promoter regions by altered transcription factors or oncoproteins, and processing of deregulated miRNAs, these molecules could be involved in the pathogenesis of AML (Liu et al., 2019). Depending on the molecular pathways of the mRNA they target, miRNAs exhibit either oncogenic or tumor-suppressive properties (Otmani and Lewalle, 2021). There are many miRNAs involved in the development of AML, one of which is miR-342 (Fletcher et al., 2022; Journal et al., 2019; Expression et al., 2022). Abnormal expression of miR-342 has been observed in various types of cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, cervical cancer, lung cancer, etc.) and has been associated with tumor development and proliferation (Gao et al., 2017; Li X. et al., 2014; Zhao and Zhang, 2015). miR-342 functions as a tumor suppressor in AML (Journal et al., 2019). However, the molecular mechanisms involved in miR-342 underlying the pathogenesis of AML remain unclear. Identifying the potential target of miR-342 and the associated biological pathways may suggest the miR-342 is a new potential therapeutic target in AML patients.
Murine double minute (MDM) proteins are overexpressed in a various of cancer types, and they primarily exhibit their oncogenic properties by inhibiting the p53 tumor suppressor (Li and Lozano, 2013). It also modulates and responds to many signaling networks (Wade et al., 2013). Both MDM2 (murine double minute 2) and MDM4 (murine double minute 4, also know as MDMX) form a heterodimer that closely regulates p53 function (Eskandari et al., 2021). MDM4 binds p53 to induce transcriptional inactivation and thus inhibits p53 function. Experimental evidence showed that p53 is kept inactive in the cytoplasm at high levels by interactions with MDM4. Further investigation of p53 in AML cell lines OCI/AML-2 (AML2) is mostly due to cytoplasmic and MDM4 binding (Tan B. X. et al., 2014). It is crucial to disrupt the MDM-p53 relationship in order to activate p53 while developing effective therapeutic approaches for tumor therapy. Therefore, scientists have focused on the roles of MDM4 as a negative regulators of the p53 tumor suppressor (Li and Lozano, 2013).
Microarray analysis can be used to identify miRNA changes in AML (Candia et al., 2015). Based on these data, new and functional miRNAs can be identified by bioinformatic analysis. In recent years, bioinformatics analysis has been used in oncology research to identify genetic alterations and new potential cancer-related biomarkers (Sheng et al., 2021). Few studies have been conducted to analyze the prognostic lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA (Wang et al., 2019) and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA (Lv et al., 2018) ceRNA network in AML (Cheng et al., 2020).
The aim of this study is to investigate the mechanisms underlying the development of AML, potential target genes, and new potential biomarkers for AML prognosis through miRNA-associated mRNA network in silico analysis. We focus on the mir342-5p/MDM4/p53 network given these findings because it may present exciting opportunities for comprehending the underlying molecular process and for cancer therapy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Microarray data
The dataset we used for this study was downloaded from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo) (Edgar et al., 2002). In the present study miRNAs expression profile data of GSE51908 based on the platform of GPL8786 (Affymetrix Multispecies miRNA-1 Array) were obtained from the GEO database, which was deposited by Civin Candia et al. (2015), Tan Y. S. et al. (2014). GSE51908 dataset includes 190 samples (AML cell lines and patient samples, B ALL cell lines and Patient samples, T ALL cell lines and patient samples, normal B cells, granulocytes, normal monocytes, T cells and CD34+ cells). In this study, we selected 42 sample for AML (AML cell lines and patient sample) and 50 control (normal B cells, normal granulocytes, normal monocytes, normal T cells and normal CD34+ cells from human peripheral blood of normal healthy individuals) from GSE51908 datasets.
2.2 Data processing
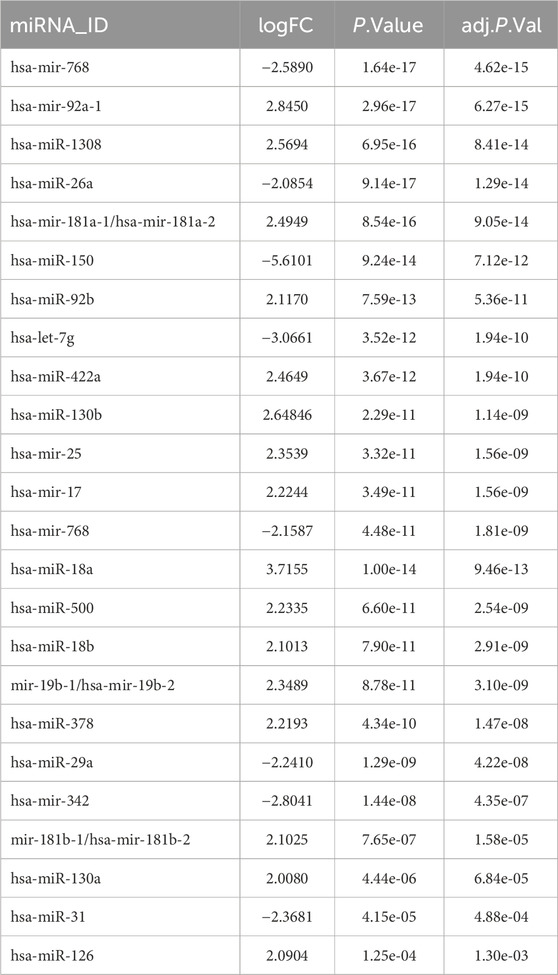
GEO2R (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/geo2r) was used to identify differentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRNAs) in the microarray datasets between the AML and control groups (Bao and Jiang, 2019). A large number of experimental datasets are included in GEO2R, and false-positive rates are modified using an adjusted P-value (adj. P). For the purpose of choosing DE-miRNAs, the adjusted p-value cut-off was set at p < 0.05 and llogFCl>2.
2.3 Prediction of miRNA targets
The miRWalk database (http://mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/search_mirnas Version 3.0) was used to estimate the targets of the overlapping genes among miRNA datasets. MiRWalk is an intuitive interface that generates predicted and verified miRNA binding sites. To improve the precision of miRNA target prediction, the miRDB and miRTarBase methods in the miRWalk database were used (Sticht et al., 2018). Only target genes that were recognized by both databases were used to choose putative mRNAs. Additionally, AML cell lines (HL-60 and KG-1 cells) used the online database miRDB to estimate the targets of miRNA (Chen and Wang, 2020).
2.4 Differential expression of genes in AML and healthy tissue
Based on information from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx), the interactive web program Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) provides a variety of visualization and analysis capabilities for gene expression. Using the gene expression profiling database GEPIA (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/), we identified changes in the expression of identified genes between AML and healthy tissue (Tang et al., 2017).
2.5 Survival analysis
Using TCGA data from AML, GEPIA’s online tool was used to carry out a survival analysis of MDM4 (Tang et al., 2017). In order to assess and compare the survival rates of AML to death, Kaplan-Meier analysis and the log-rank test were employed to generate survival curves. To calculate and compare the overall survival (OS) of AML with control groups, the Cox proportional hazards regression model was employed. The hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and log rank P-value were evaluated.
2.6 Construction of protein-protein interactions (PPI) network
The STRING database is a protein-protein association network that provides all known and predicted information about the direct (physical) and indirect (functional) relationships that occur between different proteins (Szklarczyk et al., 2011). Another online resource, GeneMANIA is a database consisting of an intuitive interface for gene function predictions and interactions of genes with each other (Warde-farley et al., 2010). The PPI network of MDM4-associated target genes was established by the STRING (http://www.string-db.org/) (Szklarczyk et al., 2011), and GeneMANIA (http://genemania.org/) database (Warde-farley et al., 2010).
2.7 Functional enrichment analysis
The Gene Ontology (GO) resource is a free public resource that explains how genes move in biological systems and provides information about cellular location, molecular functions, and biological processes (Gene et al., 2011). The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) contains a wide variety of databases, including analysis of genome sequences, biological functions, diseases, drugs, and chemicals (Kanehisa and Goto, 2000). The Database for Annotation Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/ Version 6.8) software was used to analyze GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the potential activities of chosen genes (MDM4, MDMD2, and p53) (Huang et al., 2007). The cut-off value was set as P < 0.05.
2.8 Statistical analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (version 23.0; IBM Corp. Armonk, NY, United States) was used to conduct the statistical analyses. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to evaluate the distribution of the variables. The examination of two independent variables with non-normal distributions was determined using the Mann-Whitney U test. On Medcalc software version 19.1 (Medcalc software BVBA, Belgium), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were examined.
In this study, the values for the area under the curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of predictors. In comparing the prognostic accuracy for AML response with miR-342-5p expression levels, AUC value was calculated from the ROC curve using the Medcalc program. P values were two-sided, and statistical significance was defined as ≤0.05.
3 Results
To identify DE-miRNAs, a comparison between AML and normal control groups were performed by GEO2R, and a total of 250 miRNAs were identified between AML and normal samples. 24 De-miRNAs (16 upregulated and 8 downregulated) (Table 1) were identified from the GSE51908, using adjusted p < 0.05 and llogFCl>2 for DE-miRNAs selection. Volcano plot, visually demonstrating of DE-miRNAs is shown in Figure 1A. Box data normalization (Figure 1C) and scatter plots of miR-342-5p (Figure 1B) are shown in Figure 1.
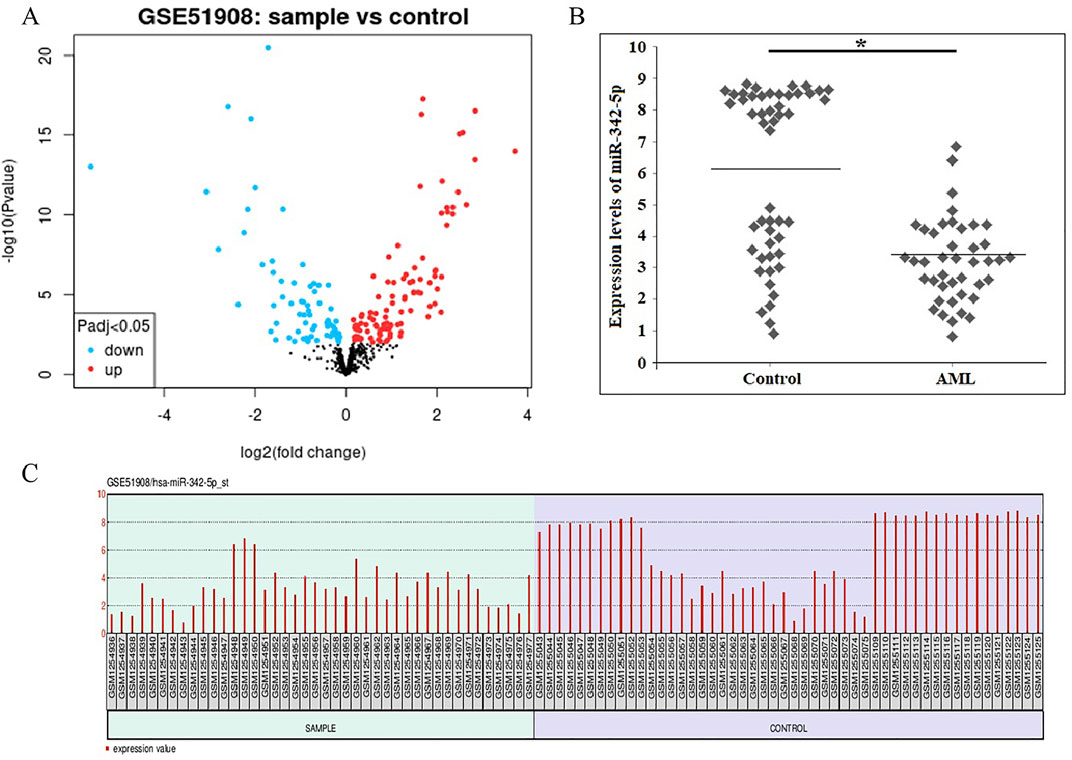
Figure 1. (A) Volcano plots showing the amount of De-miRNAs that are differentially expressed in AML when compared to normal controls. The blue dots show miRNAs that are downregulated, and the red dots show those that are upregulated. (B) The scatter plots of miR-342-5p were shown to distinguish Control and AML groups was determined using data from GSE51908. The line indicates the mean value of control and AML groups. Mann Whitney U-test, *P-value = 0.0001. (C) Box data normalization plots of the miR-342-5p. x coordinate represents samples; Y coordinate represents gene expression values.
The levels of miR-342-5p were significantly different between control and AML groups (p = 0.0001). To determine the power of miR-342-5p expression levels to distinguish patients with AML from control, the ROC analysis was performed. Values for AUC, sensitivity, specificity and cut-off points for miR-342-5p shown in Figure 2A. miR-342-5p showed significantly higher AUC values (AUC = 0.795, p = 0.0001). The cut-off of miR-342-5p was 6.85.
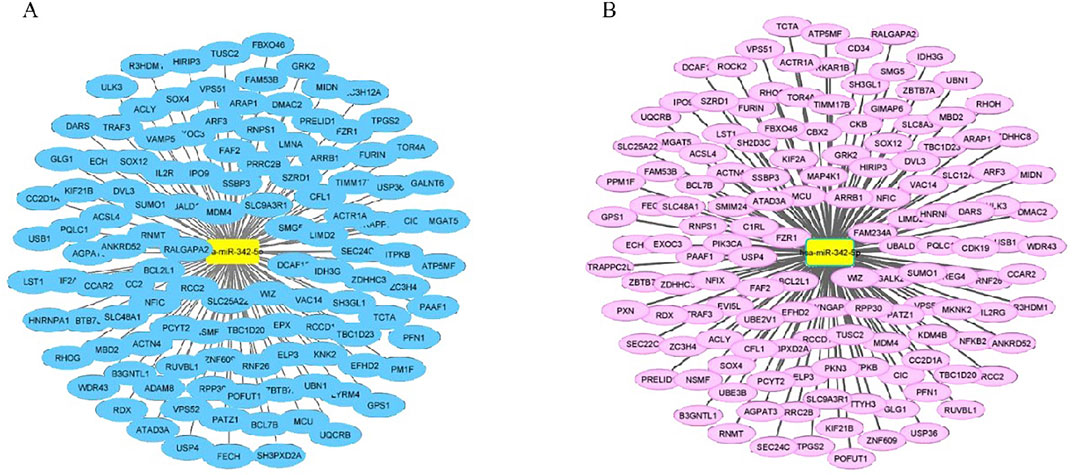

Figure 2. Prediction of miRNA targets from miRDB in HL-60 and KG-1 cells. (A) There are 119 predicted targets for hsa-miR-342-5p with expression level ≥ 5 in cell line HL-60. (B) There are 141 predicted targets for hsa-miR-342-5p with expression level ≥ 5 in cell line KG-1. In addition, those with a target score greater than 50 in all cells were selected. miR-342-5p and putative mRNAs and visualized using by Cytoscape software 3.8.
To further evaluate the clinical relevance of AML, the overall survival of AML patients was assessed by the Kaplan-Meier test using data from the article of Bullinger et al. (2010). Interestingly, as shown in Figure 2B, AML patients with low miR-342-5p expression had significantly shorter survival than those in higher expression control group (p = 0.0001), and its AUC value to discriminate AML from control groups was 0.795 (Figure 2A).
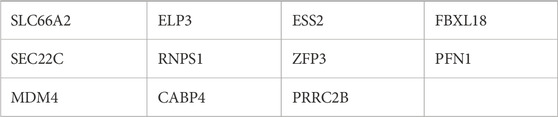
miR-342-5p in AML, potential target genes were predicted by the mirWALK database (miRDB and miRTarBase algorithms) (Table 2). Furthermore, the target genes of hsa-mir-342-5p at HL-60 and KG-1 cells were determined using miRDB (Figures 3A, B).
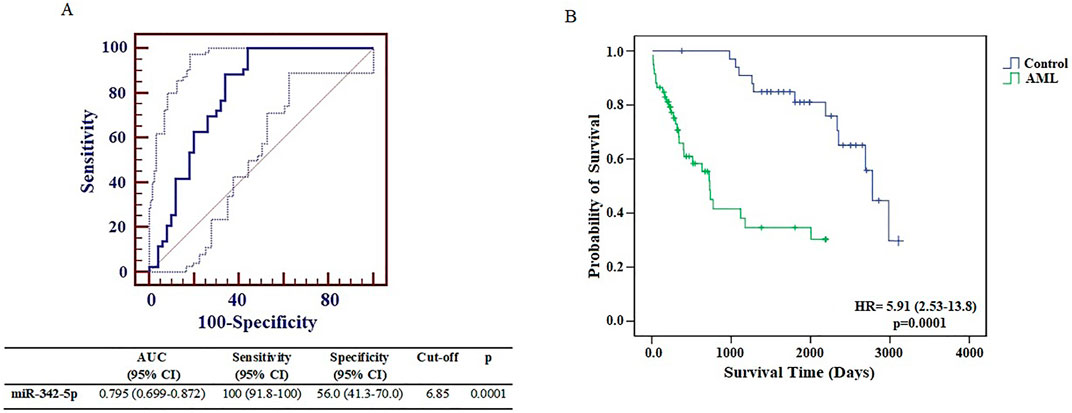
Figure 3. (A) Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of miR-342-5p expression levels in control and AML groups was determined using data from GSE51908. (B) The Kaplan–Meier survival curve of AML and Control groups. Survival analysis was performed using data from Bullinger et al. (2010).
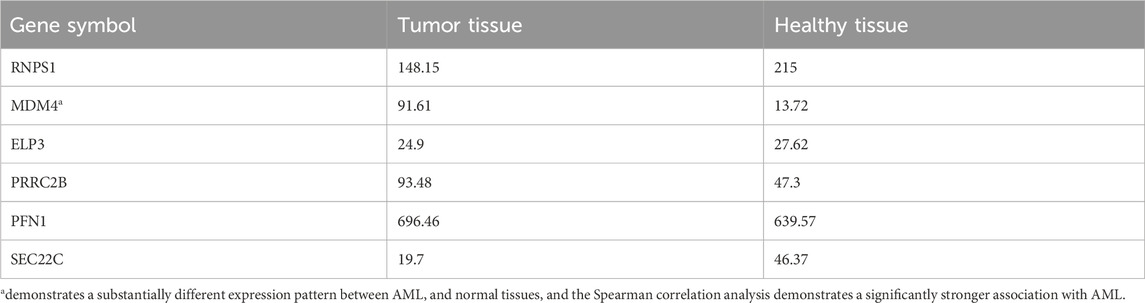
Common target genes identified in HL-60 and KG-1 cells, and the mirWALK database were selected. Target gene expression values in AML were determined using GEPIA (LAML; Acute Myeloid Leukemia) (Table 3). And also, Multi-Gene comparison was performed according to AML and TCGA normal and GTEx data (Figure 4A). MDM4 expression level is increased in tumor tissue compared to healthy tissue (Figures 4B, C).
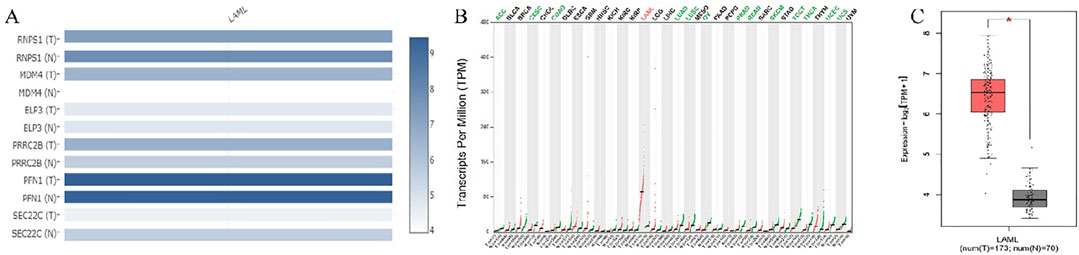
Figure 4. (A) Target genes according to expression changes in AML. (B) MDM4 was dysregulated in human cancers. (C) In AML, MDM4 expression is increased according to TCGA normal and GTEx data in GEPIA database (P = 0.01). (LAML; Acute Myeloid Leukemia).
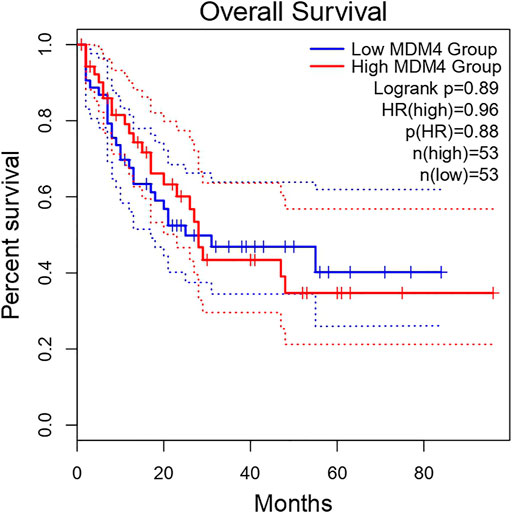
High expression of MDM4 predicts an unfavorable prognosis in AML patients. This highlights the important prognostic value of MDM4 in AML. The overall survival analysis of MDM4 is shown in Figure 5.
The PPI network of MDM4-related target genes was obtained from the STRING and GeneMANIA database (Figures 6A, B). STRING database demonstrated that the MDM4 gene primarily interacts with TP53, MDMD2, CNSK1A1, UBE2S2, UBB, UBC, USP7, CDKN2A, ATM, and CHEK2. GeneMANIA demonstrated that mdm4 interacts with MDM2, TP53, TP73,USP2,CBLC, HGF, ABL1, CD44, CDKN2A, USP7, SMARCD2, SMARCD3, SMARCD1, BECN1, MAP2K5, PELI1, GLIS2, CDKN2B, CDK4, and FAM193A. Among the genes, especially MDMD2 and p53, which are related to cell cycle and apoptosis, were selected.

Figure 6. PPI network of potential target genes for MDM4. (A) Protein-Protein interaction results from the STRING (http://www.string-db.org/) database with mdm4 indicate the relationship of mdm4 to other major signaling pathways. (B) GeneMANIA (http://genemania.org/) database was used to construct a gene interaction network between MDM4 and other genes.
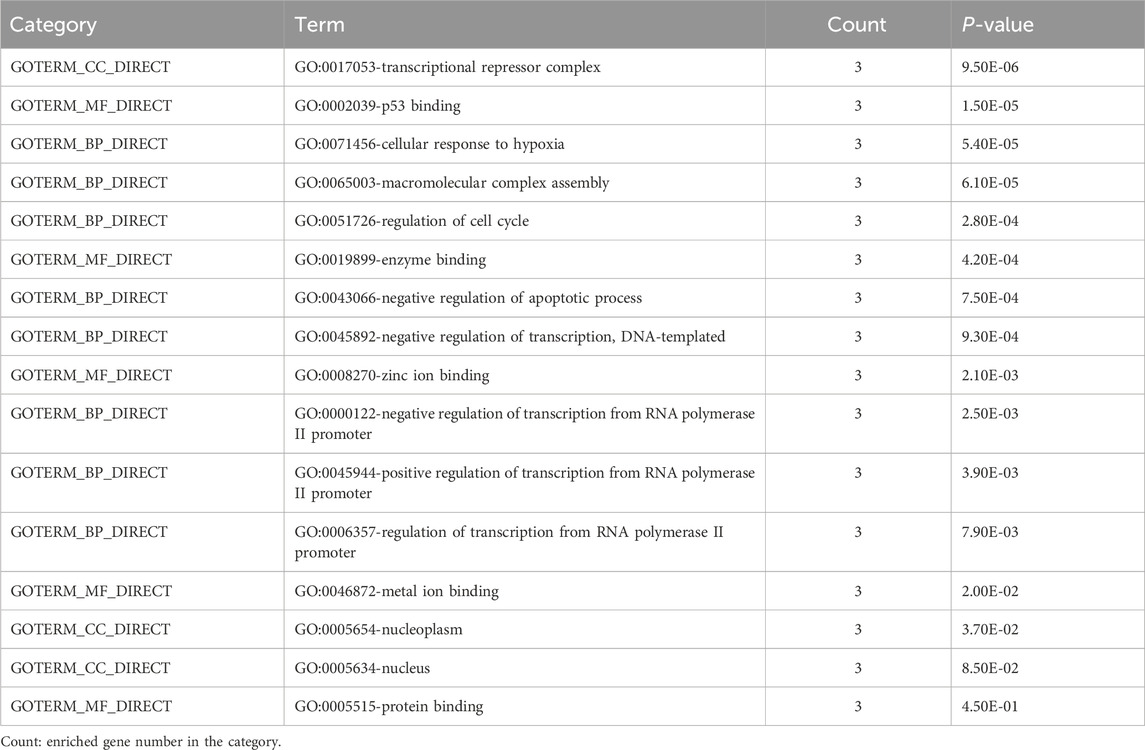
The Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway analyses were performed to better understand the pathway and process affected by the identified genes. GO terms enriched by MDM4, MDM2, and p53 genes are shown in Table 4. Three terms biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) are included in the GO ontology. The biological processes of these differentially expressed genes were primarily involved in the cellular response to hypoxia, macromolecular complex assembly, regulation of cell cycle, negative regulation of the apoptotic process, negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, and regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter. Meanwhile, the genes related to cellular components were mostly involved in transcriptional repressor complex, nucleoplasm, and nucleus. In terms of molecular function, these differential genes were mostly enriched in p53 binding, enzyme binding, zinc ion binding, metal ion binding, and protein binding.
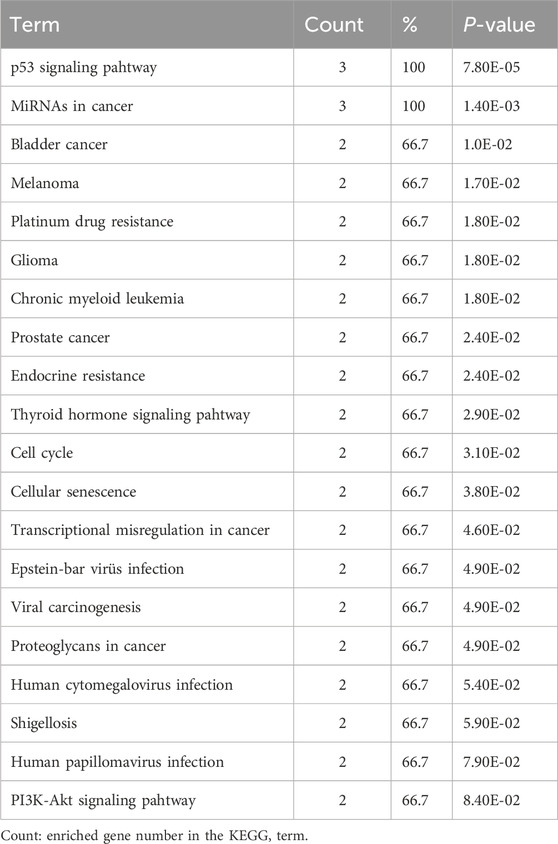
In addition, the top 20 results of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of MDM4, MDM2, and p53 genes are shown in Table 5. Among these pathways, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, microRNAs in cancer, proteoglycans in cancer, p53 signaling pathway, cellular senescence, and cell cycle are closely correlated with the development of AML.
4 Discussion
Acute myeloid leukemia is one of the most prevalent hematopoietic malignancies in adults (Short et al., 2018). Although significant advancements in the clinical treatment of AML, including stem cell transplantation and chemotherapies (Deng et al., 2017), the treatment is not at the desired level (Wang et al., 2022). The 5-year survival rate for AML patients is less than 15% (Zhao et al., 2015). Early diagnosis and timely intervention in patients with AML can improve their chances of survival. Cytogenetic and molecular analysis are very important in predicting the remission and survival rates of AML patients (Article et al., 2017). Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of AML, identifying new biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis, exploring new therapeutic strategies and improving the clinical outcome of AML is important (Journal et al., 2019; Article et al., 2017). Therefore, an improved understanding of the pathogenesis of AML will provide new insights into the diagnosis and treatment of AML. Recent studies have revealed that miRNAs are associated with the formation and development of AML, and play a role in the pathogenesis of AML by regulating their target genes (Fletcher et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). In order to comprehend the molecular mechanism of AML and develop new therapeutic targets for AML, it is necessary to identify unregulated miRNAs or mRNAs.
Microarray and High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) are widely used in cancer research to understand gene functions, find target molecules, and identify biomarkers for disease classification and diagnosis (Tang et al., 2017). Data obtained through experimental analysis are used in bioinformatics approaches. In particular, it is seen that bioinformatics data mining is a new trend in cancer research (Çakmak, 2022). Information on gene expression variations between normal and malignant tissues, chemical interactions, and the discovery of novel potential biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment can be obtained using bioinformatics tools (Çakmak, 2022).
The goal of the study is to identify potential target genes and important miRNAs for the diagnosis and therapy of AML by bioinformatics analysis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the relationship between AML and miR-342-5p and target genes by bioinformatics analysis in the literature. Microarray data of GSE51908 were obtained from the GEO database to identify DE-miRNAs between AML and normal control (healthy). It was determined that several miRNAs were significantly differentially expressed, especially miR-342-5p′s expression was decreased in AML (Table 1; Figure 1). miRNA expression profiles are associated with prognosis, highlighting the potential significance of miRNAs in this disease (Garzon et al., 2008).
The Kaplan-Meier general database showed that MDM4 was significantly associated with the prognosis of AML patients (Figure 5). In addition, Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to determine the survival times of the AML and control groups over miR-342-5p expression levels. Low miR-342-5p strongly predicted overall survival in AML patients. Moreover, Cox regression analysis showed that miR-342-5p expression independently provided prognostic information. Similarly, studies have shown that some miRs have a lower mortality rate and a huge effect on survival. Among the target genes of miR-10a-3p, SLC14A1, ARHGAP5, PIK3CA, it has been shown to show significant negative association with it, leading to longer survival in AML (Bullinger et al., 2010; Thanh et al., 2021). Similar to these studies, it has been shown that miR-342-5p is associated with the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with AML and has a positive effect on survival.
The findings of the ROC and overall survival studies show that miR-342-5p had diagnostic and prognostic significance in AML (Figure 2). The potential use of miRNAs as disease biomarkers has been the most common clinical use to far (Wallace and Connell, 2017). ROC analysis was performed to confirm whether the miR-342-5p can be used as one of the markers for AML. The miR-342-5p levels exhibited a significantly higher AUC value (AUC = 0.795, p = 0.0001), (Figure 2A). Based on this finding, it is concluded that miR-342-5p levels can be used as a reliable marker to evaluate AML. Previous studies revealed that plasma miR-92a, miR-143, and miR-342 could be promising biomarkers for AML (Article et al., 2017). In AML, miRNAs act as tumor suppressors or oncomiRs to affect a wide variety of leukemic processes, such as self-renewal, differentiation, proliferation, and epigenetic regulation. These molecules influence leukemic development and progression by targeting directly at the mRNA level or promoting malignancy (Wallace and Connell, 2017).
In addition to being a promising biomarker of miR-342-5p, it provides information about the molecular pathways involved in AML pathology. For this purpose, the target genes of miR-342-5p were determined using the miRwalk database. In addition, target genes identified in HL-60 and KG-1 cells and genes that are match as a result of mirwalk data were selected. Using the GEPIA database, expression analyses of these genes in AML were performed. In the GEPIA analysis, TCGA normal and database based on GTEx data in 173 AML patients and 70 healthy subjects, MDM4 expression level was higher in AML patients (Table 3; Figure 4). In addition, high expression levels of MDM4 were associated with poor overall survival (Figure 5).
Mouse Double Minute 4, which is among the target genes of miR-342-5p, has been reported to increase its expression in glioma, soft tissue sarcoma, melanoma, retinoblastoma, breast cancers and hematological malignancies (Li L. et al., 2014; Touqan et al., 2013; Furgason et al., 2015; Haupt et al., 2015; Carvajal et al., 2018). It has been stated that patients with AML have very high MDM4 expression and exhibit oncogenic activity compared to many other tumor types (Carvajal et al., 2018).
Functional enrichment analysis and PPI network were performed to identify the proteins that MDM4 is associated with in the development of AML and to reveal how these proteins function. According to the match data of the STRING, and GeneMANIA database, p53 and MDMD2 proteins were determined, especially in relation to apoptosis and cell cyle (Figures 6A, B). According to the literature, MDM4 inhibit p53 transcriptional activity by interacting with the p53 transactivation domain through its N-terminal domain (Tan B. X. et al., 2014). The tumor suppressor p53 protein, which guards the genome, triggers cell DNA repair, cell cycle arrest, senescence, and/or apoptosis pathways (Vousden and Lane, 2007). Downregulate p53, MDM2 and MDM4 are mutually dependent on one another (Badciong and Haas, 2002). MDM4 forms heterodimers with MDM2 via its RING domains and enhances the degradation of p53 by stimulating MDM2 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity (Wang et al., 2011). Loss of p53 function in stem and myeloid progenitor cells promotes the onset of leukemia (Zhao et al., 2010). In AML, TP53 mutations occur in less than 10% of patients (Kadia et al., 2016). Despite the TP53 mutations found in some subtypes of AML, MDM4 or MDM2 overexpression is the primary cause of p53 inactivation. Given the critical roles of MDM4 or MDM2, disruption of MDM4/MDM2/p53 interactions may offer a new way to restore p53 activity. Despite recent efforts to develop MDM4/MDM2 inhibitors, the desired success has not been achieved as a result of lack of affinity and dose-limiting toxicity (Carvajal et al., 2018). Therefore, targeting MDM4 with miRNA replacement therapy may be an attractive therapeutic strategy in AML.
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis revealed that MDM4, MDM2, and p53 genes are associated with PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in cancer, MicroRNAs in cancer, Proteoglycans in cancer, p53 signaling pathway, cellular senescence and cell cycle. Previous studies have reported the involvement of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway (Bertacchini et al., 2015), p53 signaling (Chen and Sun, 2022), cellular senescence (Mao et al., 2022), cell cycle (Zhou et al., 2021), microRNAs in cancer (Trino et al., 2018), and proteoglycans in AML (Wu et al., 2020).
When the studies with miR-342 in the literature are examined; It has been suggested that dysregulation of the miR-342 Naa10p axis may be involved in the aggressive progression of pediatric AML. Naa10p-siRNA was reported to significantly suppress cell proliferation and increase cell apoptosis (Journal et al., 2019). Wu et al. showed that miR-342-5p is downregulated and has a significant inhibitory effect on cell proliferation in CML. miR-342-5p was shown to target the 3′-UTR domain of CCND1 and reduce its expression, and overexpression of miR-342-5p increased imatinib-induced DNA double-strand breaks and apoptosis (Wu et al., 2021). In another study, it was determined that miR-342-3p expression was decreased in the plasma of AML patients. Further studies have shown that miR-342-3p targets SOX12 and thus its mimics suppress AML cell growth, accelerate apoptosis and induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest (Wang et al., 2022).
Given all these data, miR-342-5p is thought to act as a tumor suppressor. Given that the expression of miR-342-5p is reduced in AML, miRNA replacement therapy may provide an opportunity to restore the previously lost contribution of miR-342-5p. MiR-342-5p mimics can suppress cell proliferation in AML. miR-342-5p negatively regulates MDM4 expression, modulates DNA replication signaling pathways by contributing to the hsa-mir342-5p/MDM4/p53 network and may promote apoptosis. miR-342-5p and MDM4 are thought to be targets for the treatment of AML.
This study has a few limitations; only one microarray profile was analyzed as the database of miRNA profiles is rare. Experimental validation was not performed for the biological functions and targets of the identified miRNA. Further studies are needed for the mechanism of miR-342-5p and its potential targets in the development of AML. We believe that it can be a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of AML patients and that cohort studies should be conducted on this topic.
miRNA and candidate genes associated with the pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of AML were identified using integrated bioinformatics approaches. A new miRNA-mRNA regulatory was axis identified that could improve understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of AML. These target molecules can serve as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. However, further studies are needed to confirm these predictive results.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SM: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SO: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. CH: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. OA: Investigation, Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. YA: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. FE: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MA: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The AML sequencing dataset was shared by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, for which the authors are grateful.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Article, O., Elhamamsy, A. R., Suleiman, M., Sharkawy, E., Zanaty, A. F., Ahmed, M., et al. (2017). Circulating miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342 in plasma are novel potential biomarkers for acute myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 6 (2), 77–86. doi:10.22088/acadpub.BUMS.6.2.2
Badciong, J. C., and Haas, A. L. (2002). MdmX is a RING finger ubiquitin ligase capable of synergistically enhancing Mdm2 ubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (51), 49668–49675. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208593200
Bao, M., and Jiang, G. (2019). Differential expression and functional analysis of lung cancer gene expression datasets: a systems biology perspective. Oncol. Lett. 18, 776–782. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10362
Bertacchini, J., Heidari, N., Mediani, L., Capitani, S., Shahjahani, M., Ahmadzadeh, A., et al. (2015). Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 72, 2337–2347. doi:10.1007/s00018-015-1867-5
Bullinger, L., Ehrich, M., Do, K., Schlenk, R. F., Do, H., Nelson, M. R., et al. (2010). Quantitative DNA methylation predicts survival in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 115 (3), 636–642. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-03-211003
Çakmak, E. (2022). A bioinformatics approach to identify potential biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Lung Cancer 43 (1), 6–13. doi:10.17776/csj.976510
Candia, J., Cherukuri, S., Guo, Y., Doshi, K. A., Civin, C. I., Losert, W., et al. (2015). Uncovering low-dimensional, miR-based signatures of acute myeloid and lymphoblastic leukemias with a machine-learning-driven network approach. Converg. Sci. Phys. Oncol. 1 (2), 025002. doi:10.1088/2057-1739/1/2/025002
Carvajal, L. A., Neriah, D. B., Senecal, A., Benard, L., Thiruthuvanathan, V., Yatsenko, T., et al. (2018). Dual inhibition of MDMX and MDM2 as a therapeutic strategy in leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 10 (436), eaao3003. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aao3003
Chen, Y., and Sun, L. (2022). Inhibition of NEDD8 NEDDylation induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via p53 signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 42 (8), BSR20220994. doi:10.1042/BSR20220994
Chen, Y., and Wang, X. (2020). miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, D127–D131. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz757
Cheng, Y., Su, Y., Wang, S., Liu, Y., Jin, L., Wan, Q., et al. (2020). Identification of circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competitive endogenous RNA network as novel prognostic markers for acute myeloid leukemia. Genes (Basel) 11, 868. doi:10.3390/genes11080868
Deng, L., Jiang, L., Lin, X., Tseng, K., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2017). The PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor BEZ235 suppresses proliferation and migration and reverses multidrug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Publ. Gr 38, 382–391. doi:10.1038/aps.2016.121
Edgar, R., Domrachev, M., and Lash, A. E. (2002). Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30 (1), 207–210. doi:10.1093/nar/30.1.207
Eskandari, M., Shi, Y., Liu, J., Albanese, J., Goel, S., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). The expression of MDM2, MDM4, p53 and p21 in myeloid neoplasms and the effect of MDM2/MDM4 dual inhibitor. Leuk. Lymphoma 62 (1), 167–175. doi:10.1080/10428194.2020.1817441
Expression, G., Myeloid, A., Sayed, A., and Ahmed, S. (2022). Clinical significance of MicroRNA-29a and MicroRNA-100 gene expression in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 44 (2), 391–395. doi:10.1097/MPH.0000000000002168
Fletcher, D., Guinn, B., Brown, E., Javadala, J., and Uysal-onganer, P. (2022). microRNA expression in acute myeloid leukaemia: new targets for therapy. EJHaem 3 (3), 596–608. doi:10.1002/jha2.441
Furgason, J. M., Koncar, R. F., Michelhaugh, S. K., Sarkar, F. H., Mittal, S., Sloan, A. E., et al. (2015). Whole genome sequence analysis links chromothripsis to EGFR, MDM2, MDM4, and CDK4 amplification in glioblastoma. Oncoscience 2 (7), 618–628. doi:10.18632/oncoscience.178
Gao, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., and Liao, J. (2017). Down-regulation of miR-342-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its prognostic significance. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 21 (9), 2098–2102.
Garzon, R., Volinia, S., Liu, C., Fernandez-cymering, C., Palumbo, T., Pichiorri, F., et al. (2008). MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 111 (6), 3183–3189. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-07-098749
Gene, T., Consortium, O., Ashburner, M., Ball, C. A., Blake, J. A., Botstein, D., et al. (2011). Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 25 (1), 25–29. doi:10.1038/75556
Haupt, S., Buckley, D., Pang, J., Panimaya, J., Paul, P. J., Gamell, C., et al. (2015). Targeting Mdmx to treat breast cancers with wild-type p53. Cell Death Dis. 6 (7), e1821. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.173
He, L., and Hannon, G. J. (2004). MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5 (7), 522–531. doi:10.1038/nrg1379
Huang, D. W., Sherman, B. T., Tan, Q., Kir, J., Liu, D., Bryant, D., et al. (2007). DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 169–175. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm415
Journal, A. I., Wang, H., He, H., and Yang, C. (2019). miR-342 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of acute myeloid leukemia by targeting Naa10p. Nanomedicine, Biotechnol. 47 (1), 3671–3676. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1596930
Juliusson, G., Lazarevic, V., Ho, A., Hagberg, O., and Ho, M.Swedish Acute Leukemia Registry Group (2012). Acute myeloid leukemia in the real world: why population-based registries are needed. Blood 119 (17), 3890–3899. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-12-379008
Kadia, T. M., Jain, P., Ravandi, F., Garcia-manero, G., Andreef, M., Takahashi, K., et al. (2016). TP53 mutations in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: clinicomolecular characteristics, response to therapy, and outcomes. Cancer 122 (22), 3484–3491. doi:10.1002/cncr.30203
Kanehisa, M., and Goto, S. (2000). KEGG: kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28 (1), 27–30. doi:10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kirtonia, A., Ashrafizadeh, M., Zarrabi, A., Hushmandi, K., Zabolian, A., Bejandi, A. K., et al. (2022). Long noncoding RNAs: a novel insight in the leukemogenesis and drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Cell Physiol. 237 (1), 450–465. doi:10.1002/jcp.30590
Li, L., Tan, Y., Chen, X., Xu, Z., Yang, S., Ren, F., et al. (2014). MDM4 overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia patients with complex karyotype and wild-type TP53. PLoS One 9 (11), e113088. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113088
Li, Q., and Lozano, G. (2013). Molecular pathways: targeting Mdm2 and Mdm4 in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 19 (1), 34–41. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0053
Li, X., Chu, H., Lv, T., Wang, L., Kong, S., and Dai, S. (2014). miR-342-3p suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting FOXM1 in human cervical cancer. FEBS Lett. 588 (17), 3298–3307. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.07.020
Liu, Y., Cheng, Z., Pang, Y., Cui, L., Qian, T., Quan, L., et al. (2019). Role of microRNAs, circRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 12 (1), 51. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0734-5
Lv, C., Sun, L., Guo, Z., Li, H., Kong, D., Xu, B., et al. (2018). Circular RNA regulatory network reveals cell – cell crosstalk in acute myeloid leukemia extramedullary infiltration. J. Transl. Med. 16, 361. doi:10.1186/s12967-018-1726-x
Mao, Y., Xu, J., Xu, X., Qiu, J., Hu, Z., Jiang, F., et al. (2022). Comprehensive analysis for cellular senescence-related immunogenic characteristics and immunotherapy prediction of acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 987398. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.987398
O’Brien, J., Hayder, H., Zayed, Y., and Peng, C. (2018). Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 9 (AUG), 402–412. doi:10.3389/fendo.2018.00402
Otmani, K., and Lewalle, P. (2021). Tumor suppressor miRNA in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment: mechanism of deregulation and clinical implications. Front. Oncol. 15 (11), 708765. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.708765
Sheng, H., Pan, H., Yao, M., Xu, L., Lu, J., Liu, B., et al. (2021). Integrated analysis of circular RNA-associated ceRNA network reveals potential circRNA biomarkers in human breast cancer. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 1732176. doi:10.1155/2021/1732176
Short, N. J., Rytting, M. E., and Cortes, J. E. (2018). Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 392 (10147), 593–606. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31041-9
Sticht, C., De La Torre, C., Parveen, A., and Gretz, N. (2018). miRWalk: an online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS One 13, e0206239. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0206239
Szklarczyk, D., Franceschini, A., Kuhn, M., Simonovic, M., Roth, A., Minguez, P., et al. (2011). The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 561–568. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq973
Tan, B. X., Khoo, K. H., Lim, T. M., and Lane, D. P. (2014). High Mdm4 levels suppress p53 activity and enhance its half-life in acute myeloid leukaemia. Oncotarget 5 (4), 933–943. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1559
Tan, Y. S., Kim, M., Kingsbury, T. J., Civin, C. I., and Cheng, W. (2014). Regulation of RAB5C is important for the growth inhibitory effects of MiR-509 in human precursor-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS One. 9 (11), e111777. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111777
Tang, Z., Li, C., Kang, B., Gao, G., Li, C., and Zhang, Z. (2017). GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W98–W102. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx247
Thanh, T., Friedrich, V., Kristy, S., Christoph, W. W., Melinda, R., Molloy, T. J., et al. (2021). miR-10a as a therapeutic target and predictive biomarker for MDM2 inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 35, 1933–1948. doi:10.1038/s41375-020-01095-z
Touqan, N., Diggle, C. P., Verghese, E. T., Perry, S., Horgan, K., Merchant, W., et al. (2013). An observational study on the expression levels of MDM2 and MDMX proteins, and associated effects on P53 in a series of human liposarcomas. BMC Clin. Pathol. 13 (1), 32. doi:10.1186/1472-6890-13-32
Trino, S., Lamorte, D., Caivano, A., Laurenzana, I., Tagliaferri, D., Falco, G., et al. (2018). MicroRNAs as new biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis, and as potential therapeutic targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (2), 460. doi:10.3390/ijms19020460
Vousden, K. H., and Lane, D. P. (2007). p53 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 275–283. doi:10.1038/nrm2147
Wade, M., Li, Y.-C., and Wahl, G. M. (2013). MDM2, MDMX and p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13 (2), 83–96. doi:10.1038/nrc3430
Wallace, J. A., and Connell, R. M. O. (2017). MicroRNAs and acute myeloid leukemia: therapeutic implications and emerging concepts. Blood 130 (11), 1290–1301. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-697698
Wang, J., Zhou, H., Tu, X., He, Y., Liu, Q., Liu, Q., et al. (2019). Prediction of competing endogenous RNA coexpression network as prognostic markers in AML. Aging (Albany NY) 11 (10), 3333–3347. doi:10.18632/aging.101985
Wang, X., Wang, J., and Jiang, X. (2011). MdmX protein is essential for Mdm2 protein-mediated p53 polyubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (27), 23725–23734. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.213868
Wang, Y., Guo, X., Wang, L., Xing, L., Zhang, X., and Ren, J. (2022). miR-342-3p inhibits acute myeloid leukemia progression by targeting SOX12. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 1275141. doi:10.1155/2022/1275141
Warde-farley, D., Donaldson, S. L., Comes, O., Zuberi, K., Badrawi, R., Chao, P., et al. (2010). The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 214–220. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq537
Wu, J., Xiao, Y., Sun, J., Sun, H., Chen, H., Zhu, Y., et al. (2020). A single-cell survey of cellular hierarchy in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13 (1), 128. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00941-y
Wu, Y., Lai, H., Huang, T., Chen, Y., Ye, R., Chang, P., et al. (2021). Aberrantly reduced expression of miR-342-5p contributes to CCND1-associated chronic myeloid leukemia progression and imatinib resistance. Cell Death Dis. 12 (10), 908. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04209-2
Xin, X., Xu, Z., Wei, J., and Zhang, Y. (2022). MiR-376a-3p increases cell apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting MT1X. Cancer Biol. Ther. 23 (1), 234–242. doi:10.1080/15384047.2022.2054243
Zhao, L., and Zhang, Y. (2015). miR-342-3p affects hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation via regulating nF-κB pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 457 (3), 370–377. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.119
Zhao, Y., Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., Kong, D., Qin, F., Sun, J., et al. (2015). Identification of potential therapeutic target genes, key miRNAs and mechanisms in acute myeloid leukemia based on bioinformatics analysis. Med. Oncol. 32, 152. doi:10.1007/s12032-015-0572-4
Zhao, Z., Zuber, J., Diaz-flores, E., Lintault, L., Kogan, S. C., Shannon, K., et al. (2010). p53 loss promotes acute myeloid leukemia by enabling aberrant self-renewal. Genes Dev. 24, 1389–1402. doi:10.1101/gad.1940710
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia, biomarkers, bioinformatics, non-coding RNAs, miRNA
Citation: Misir S, Ozer Yaman S, Hepokur C, Akidan O, Aliyazicioglu Y, Enguita FJ and Al Zoubi MS (2024) Identification of miR-342-5p/MDM4/p53 network in acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Cell Death 3:1503241. doi: 10.3389/fceld.2024.1503241
Received: 28 September 2024; Accepted: 31 October 2024;
Published: 14 November 2024.
Edited by:
Lissinda Hester Du Plessis, North-West University, South AfricaReviewed by:
Zesong Yang, First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, ChinaShivangi Srivastava, Bristol Myers Squibb, United States
Copyright © 2024 Misir, Ozer Yaman, Hepokur, Akidan, Aliyazicioglu, Enguita and Al Zoubi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sema Misir, c21pc2lyQGN1bWh1cml5ZXQuZWR1LnRy
 Sema Misir
Sema Misir Serap Ozer Yaman2,3
Serap Ozer Yaman2,3 Ceylan Hepokur
Ceylan Hepokur Osman Akidan
Osman Akidan Yuksel Aliyazicioglu
Yuksel Aliyazicioglu Francisco J. Enguita
Francisco J. Enguita Mazhar Salim Al Zoubi
Mazhar Salim Al Zoubi