- 1Center for Computational and Integrative Biology, Rutgers, The State University of NJ, Camden, NJ, United States
- 2Department of Biology, Rutgers, The State University of NJ, Camden, NJ, United States
Focusing on selected model organisms to establish scientific communities and resources has greatly advanced our understanding of biological processes, including embryogenesis, and facilitated the translation of these data into developing human remedies. However, by restricting our research to a small number of model organisms, we risk overlooking the underlying mechanisms controlling animal diversity and speciation. Changes in cell signaling, protein compatibility, and genetic tinkering are often neglected due to the lack of molecular tools in non-traditional model organisms. The era of high-throughput genome sequencing, computational gene prediction, and emerging genome editing and imaging tools, offers an opportunity to explore novel mechanisms of organismal development and homeostasis. As we develop new model platforms, it is imperative to prioritize resources effectively. What criteria make an organism a “good” candidate for becoming a new model organism for exploring embryogenesis? The axis of the Drosophila embryo is set during eggshell patterning. Although species with a dorsal ridge exhibit dramatically different patterns of the dorsalization signal, epidermal growth factor receptor activation, compared to Drosophila melanogaster, the embryonic dorsal-ventral axis remains consistent. Despite the increasing number of sequenced fly species’ genomes, the experimental tools necessary to study these species are still lagging. Here, we emphasize the need to further develop genetic and molecular tools for studying nontraditional model organisms to understand complex processes like evolution of maternal contribution and correct embryonic body axis. We address current challenges in achieving these goals, such as genetic markers, selectable markers, and the efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genomic editing.
1 Introduction
The use of model organisms has been essential in unraveling complex mechanisms of biological functions. The similarity of biological functions across living organisms allows the scientific community to leverage the experimental advantages of model organisms for studying questions in many fields: cell division, transcriptional regulation and profiling, cell signaling, signaling integration, protein translation, tissue morphogenesis, organogenesis, and models for human diseases (Wangler et al., 2017; Bertile et al., 2023). The importance of these organisms was recognized by the Human Genome Project, the seminal scientific achievement of the 20th century. In addition to sequencing the entire haploid genome of humans, model organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, worms, flies, and mice were also sequenced (Lander et al., 2001; Hood and Rowen, 2013). This project opened the genomics era, prompting a shift from the traditional practice of testing one gene at a time to a high throughput quantitative study of all genes at organismal and single-cell levels. This transition was aided by using simple organisms such as C. elegans and Drosophila melanogaster, in addition to mice, as effective models for human diseases. Most research resources are still invested in a few model organisms that allow us to deeply investigate cellular components in the large puzzle of embryogenesis. However, some changes do not depend on a single modification, which requires the exploration of evolutionary changes in the native species. However, we still lack efficient molecular and genetic tools to study them.
2 Model organisms are useful and important tools for scientific research
Model organisms such as Neurospora, C. elegans, D. melanogaster, Arabidopsis, and Mus musculus, successfully established large communities to study metabolism, cell lineage and differentiation, signaling pathways and patterning, plant biology, and disease (Davis, 2004; Irion and Nusslein-Volhard, 2022; Jacob and Monod, 1961; Sinclair et al., 1998; Phifer-Rixey and Nachman, 2015; Victor Atoki et al., 2025). The fundamental similarities of basic processes across organisms permit the lateral transfer of information across distant organisms and consequently facilitates the translation of this knowledge to fight human pathologies. Traditional mutation screens generated thousands of mutant lines associated with various phenotypic groups (Nusslein-Volhard and Wieschaus, 1980; Schupbach and Wieschaus, 1986; Jorgensen and Mango, 2002; St Johnston, 2002; Mullins et al., 1994). Some of these mutations were in the same genes and others in genes that participate in the same process (i.e., axis formation, organogenesis, segmentation, etc.). These large-scale screens were bed-rock initiatives which created model-organism centered communities of scientists producing large bodies of work mechanistically connecting these phenotypes to genes.
3 Limitations of current model organisms
Model organisms have been essential to discovering a multitude of fundamental processes common in animals. For example, morphological and patterning changes can be simply explained by alteration in cis-regulatory modules. Examples include the fish egg-spot, digit number, wing spots, and limbs, to mention a few (Carroll, 2008; Carroll et al., 2008; Beldade and Brakefield, 2002; Santos et al., 2014; Lettice et al., 2008; Xu et al., 2020; Sagai et al., 2005). At the same time, evolution has tinkered with these mechanisms, adjusting species to exhibit unique functions. For example, the expression pattern of neuronal ectoderm (NEE) genes in flies’ embryos occupy the same ventral-lateral position across species. Reporter genes driven by the NEE enhancers successfully recapitulated the endogenous pattern in the corresponding native species. However, when the same reporters were expressed in D. melanogaster, they showed a large deviation from the ectoderm domain (Crocker et al., 2008). These findings display how co-evolving cellular environments maintain correct axis patterning, however, a single component, such as an enhancer, cannot fully account for the conserved domain across species.
The emergence of genome engineering tools, like CRISPR/Cas9, have reduced the need for substantial mutation screens in traditional model organisms (Bier et al., 2018; Biering et al., 2022; Kramer et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2017) and opened up a new avenue for more faithfully representing the cellular environments of species of interest. This allows the traditional approach of exploring one component at a time in a heterologous organism to be replaced by a new approach that allows us to explore the co-evolution of multiple components, some of them as yet unidentified (Cooper, 2024). Despite readily available genomes for many related species, both the computational methods and the genetic tools for conducting mechanistic studies outside of model organisms are limited (Tomoyasu and Halfon, 2020).
Notably, the common practice of using traditional model organisms to test functions of regulatory DNA or proteins from closely related species may conceal the actual interacting partners in the native species. Furthermore, testing functions in model organisms that are too evolutionary distant may lead to conclusions that do not automatically reflect their native function, but rather their function in the model organism. Phenotypes obtained through perturbation reflect the impact (sufficiency/necessity) of this mutation in the model organisms (Cooper, 2024).
As we work to explore developmental complexity and identify new mechanisms underlying species-specific traits, molecular tools should be expanded and adjusted for use in additional organisms. This broader approach will help to capture the scope of co-evolutionary processes across multiple levels (molecular, cellular, tissue, organismal, community). Additionally, deviation from focusing on a handful of traditional model organisms would facilitate the exploration of novel mechanisms in cell signaling, development, and homeostasis, helping us to better understand pathologies and find new strategies for curing diseases.
4 What makes an organism a good model?
Mendel’s research pioneered the field of genetics. His selection of peas as a model system was viewed unfavorably at the time and perceived as an isolated example. Yet, selecting a system that is easy to grow, has a short life cycle, produces many offspring by controlled crossing, and has discrete and easily identifiable true bred phenotypes made peas an excellent model organism for exploring the laws of inheritance (Stenseth et al., 2022). Similar rules apply for the discovery of the Lac-operon. A short generation time, a large number of progeny for finding rare mutations, no dependance on lactose for growth, and inducible genes, all made bacteria an excellent system to study the coordinated regulation of genes that participate in the same metabolic process (Jacob and Monod, 1961). Hence, the selection of a model system is essential once the research question is defined.
The successful path from model system to “true” model organism rests on building large and collaborative communities to develop robust and sophisticated resources, including molecular, genetic, and genomic tools, strategies for maintaining and sharing stocks, the creation and maintenance of databases, and the advancement of computational and bioinformatics tools (Irion and Nusslein-Volhard, 2022). A crucial first step in selecting new model organisms is leveraging the information and resources of an already established community. This can save time and effort, as genome engineering tools can be adapted to operate in related species with relatively modest adjustments. This approach opens new opportunities for exploring evolutionary tinkering in embryogenesis.
5 Focusing on Drosophila
Several productive communities have been working with a few model organisms. In this perspective, we focus on Drosophila, which has been central to breakthrough discoveries in developmental biology, cell signaling, neurobiology, computational modeling and bioinformatics, evolution, and genetics, to name a few (Victor Atoki et al., 2025). Research utilizing D. melanogaster embryos has cemented the connections between genomic and phenotypic change and provided countless translational insights into human diseases (Verheyen, 2022; Perrimon et al., 2016). From Morgan’s white-eyed phenotype (Morgan, 1910), through Muller’s X-ray mutation screens on the X chromosome (Muller, 1928), the large screens in Heidelberg (Nusslein-Volhard and Wieschaus, 1980; Schupbach and Wieschaus, 1986; Wieschaus and Nusslein-Volhard, 2016), the discovery of Hox genes (Lewis, 1978; McGinnis et al., 1984), the investigation of immune response (Hoffmann, 2007), and the elucidation of and circadian clock (Allada et al., 1998), Drosophila has been at the forefront of embryogenesis studies. These seminal discoveries have been recognized by the international community with numerous awards including six Nobel prizes (Mohr, 2018).
Most resources have been directed at D. melanogaster with some investment in other Drosophila species, including comparative genomics, evolution of cell signaling, patterning, morphologies, vision, behavior, and communication. However, the tremendous diversity among Drosophila species provides an unparalleled opportunity to study the nature of speciation in vivo, accounting for the complex co-evolving systems unique to each species. We argue that the lack of effective genome engineering tools prevents researchers in the Drosophila research community from fully leveraging this co-evolutionary wealth (Tomoyasu and Halfon, 2020). The combination of short life cycles, complex tissue organization with low genetic redundancy, sequenced genomes across multiple species, availability of species with novel patterning and morphologies, ease of quantitative imaging in both live and fixed samples, as well as advances in molecular and genome engineering tools, all make the Drosophila group an exciting “model clade” for exploring mechanisms underlying evolutionary changes (Kim et al., 2021; Brand and Perrimon, 1993; Niepielko et al., 2011; Niepielko et al., 2014; Kanca et al., 2022; Garcia et al., 2013). Hence, the conditions have ripened to systematically explore co-evolving circuits at both molecular and organismal levels.
6 A comprehensive example: EGFR signaling and embryo axis formation
The dorsal-ventral (DV) axis in Drosophila is established during oogenesis by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (Roth, 1993). Specifically, in egg chambers, the precursor of the mature egg, the TGF-alpha like ligand Gurken (GRK), localized around the oocyte nucleus, activates EGFR in the overlaying follicle cells after being secreted into the perivitelline space (Nilson and Schupbach, 1999). During DV axis formation, EGFR signaling represses pipe (pip), limiting it to the ventral domain (Sen et al., 1998; Cho et al., 2010; Moussian and Roth, 2005). The ventral restriction of Pip confines the cleavage of the Toll pathway ligand, Spätzle, to the ventral side of the Drosophila embryo, thereby setting domains along the DV axis. Through pip regulation, the DV axis is highly sensitive to changes in EGFR activation levels; reduced levels ventralize the embryo by increasing the pip domain dorsally, and elevated levels dorsalize the embryos by reducing pip expression (Roth, 1993; Schupbach and Roth, 1994).
The level and duration of EGFR signaling on the dorsal side of the egg chamber, is dramatically different among Drosophila species during DV axis determination (Niepielko et al., 2014; Niepielko and Yakoby, 2014; Kagesawa et al., 2008). In D. melanogaster, EGFR activation is initially restricted to the dorsal midline of egg chamber (Figure 1A). This signal expands laterally a few hours later by activation of EGFR through Spitz (Figure 1B). EGFR activation leads to the formation of two dorsal appendage primordia on either side of the dorsal midline, marked by fasciclin III (FASIII) (Figures 1A’, B’), which give rise to the two embryonic respiratory structures, the dorsal appendages (Figure 1C). The mesoderm, marked by Twist (Twi), is restricted to ∼30% of the cells in the ventral domain of the embryo (Figure 1D).
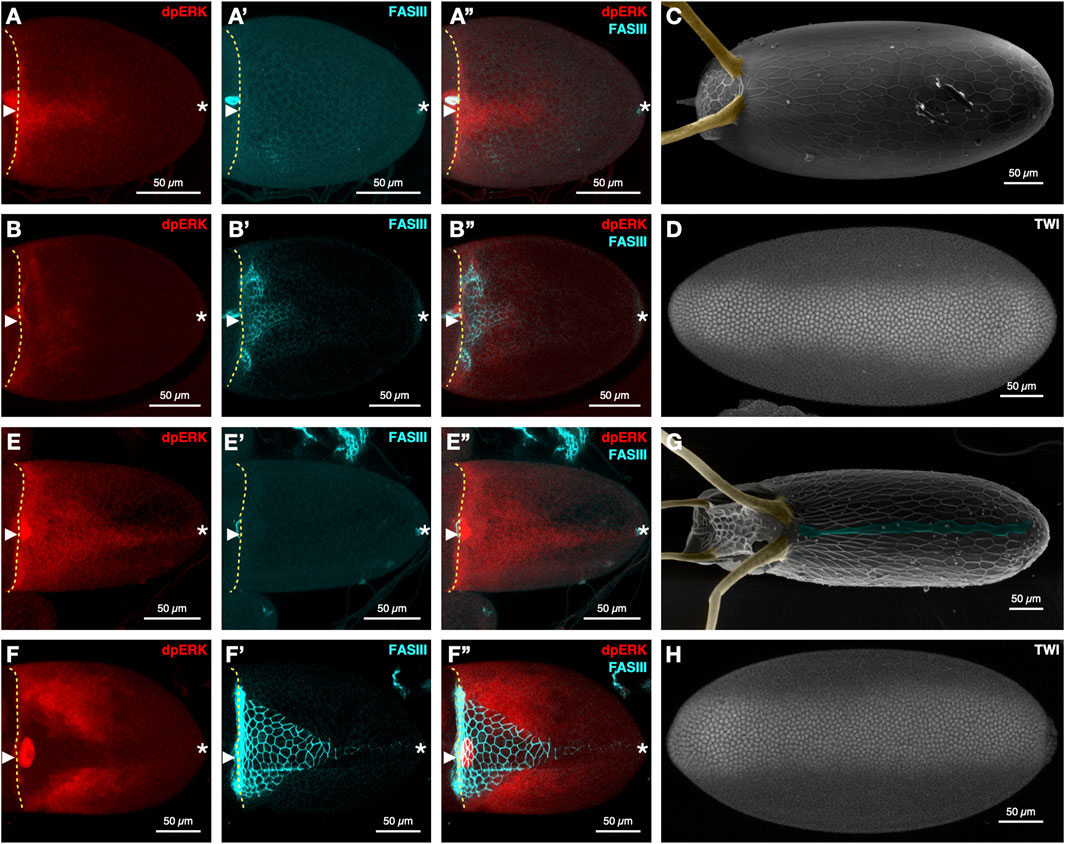
Figure 1. EGFR signaling and dorsal-ventral axis formation in D. melanogaster (A–D) and D. nasuta (E–H). Stage 10A (A-A”) and 10B (B-B″) egg chambers of D. melanogaster stained for EGFR signaling (dpERK), FasIII, and merged (n = 7 and n = 28, respectively). D. melanogaster (C) eggshell (n = 12), dorsal appendages (yellow), and (D) embryo stained for Twist (n = 5). Stage 10A (E-E″) and 10B (F-F″) egg chambers stained for dpERK, FASIII, and merged (n = 12 and n = 9, respectively). D. nasuta (G) Eggshells (n = 27). Dorsal appendages (yellow) and dorsal ridge (blue), and (H) embryo stained for Twist (n = 5). Immunohistochemistry, confocal imaging, and SEM imaging were performed as described before (Niepielko and Yakoby, 2014; Stevens et al., 2022) (anti-dpERK antibody, 1:100, Cell Signaling; anti-FASIII antibody, 1:100, DSHB 1D4). Rat anti-TWIST (1:1,000; gift from the Wieschaus lab) was used as in (He et al., 2014). Anterior to the left for all images, dorsal views for egg chambers and eggshells, ventral views for embryos. The yellow broken line denotes the anterior of the oocyte. Arrowhead denotes the dorsal midline. Asterisk denotes the posterior end.
In Drosophila species with a dorsal ridge - a lumen-like structure on the embryo casing (Niepielko and Yakoby, 2014) - the level, duration, and domains of EGFR activation differ considerably from the pattern observed in D. melanogaster. In D. nasuta, EGFR signaling levels are substantially elevated along the dorsal side of the egg chamber during early stage 10A (Figure 1E). The memory of this activation pattern is reflected in the extended expression of FASIII at stage 10B (compare D. melanogaster Figure 1B’ to D. nasuta Figure 1F’). Additionally, the lateral expansion of EGFR signaling at stage 10B is more extensive in D. nasuta than D. melanogaster (compare D. melanogaster Figure 1B to D. nasuta Figure 1F) and contributes to the formation of four dorsal appendages in the final eggshell (Figure 1G).
Interestingly, despite the expansion of dorsal EGFR signaling in D. nasuta and the expected change in DV axis, the mesoderm of the D. nasuta embryo still spans the same number of cells as in D. melanogaster (Figures 1F, 2A,B). Furthermore, in D. nasuta, the dorsal anterior activation of EGFR expands laterally, yet the anterior mesoderm domain unexpectedly trends to span more nuclei (Figures 1D,H; Figure 2). Given the sensitivity of the embryos’ DV axis to changes in EGFR signaling (Queenan et al., 1997), it is intriguing to explore how the mesoderm maintains a consistent ventral domain despite the differences in EGFR signaling.
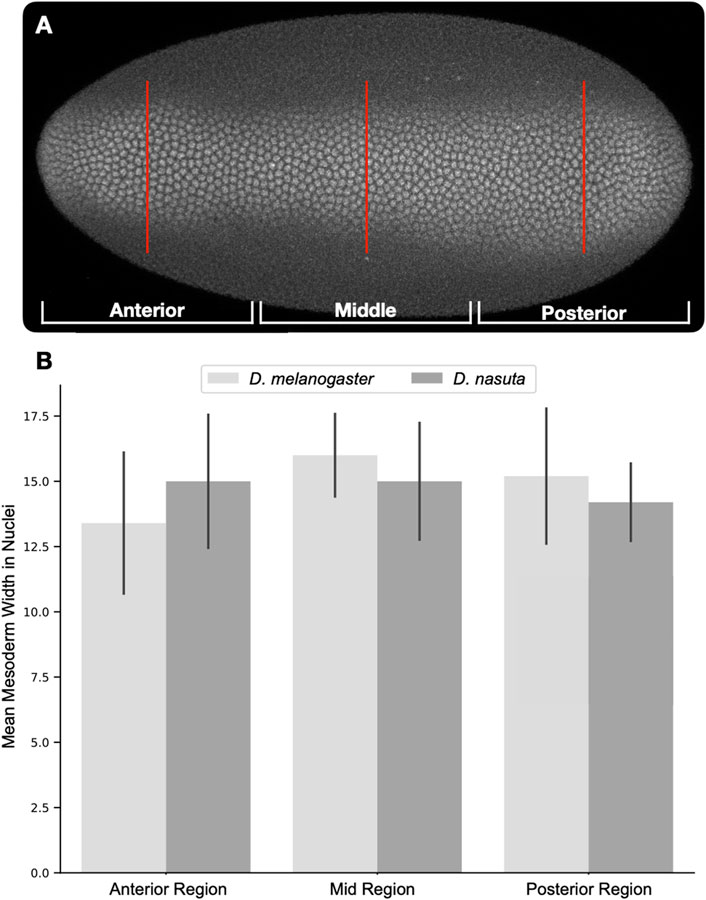
Figure 2. Quantification of mesoderm width using Twist positive nuclei. Dorsally oriented embryos were divided into thirds (anterior, middle, posterior). Twist positive nuclei were counted along a line in the center of each third [(A), red lines]. Nuclei counts were averaged for each region and compared across both species [(B), D. melanogaster n = 5, D. nasuta n = 5]. Comparison of nuclear counts at each region using the Student’s t-test revealed no significant differences.
7 What’s next? How do we explore diverse EGFR activation levels with constant DV axis?
To account for the spatial changes in EGFR signaling in these species, molecular and computational tools must be employed to explore directly co-evolving components of EGFR signaling and downstream targets.
7.1 Experimental tools to explore casual effects
The long history of D. melanogaster as a prominent model organism for genetic research has led to the development of an extraordinary array of molecular and genetic tools to unravel complex processes in biology. Some of the key innovations include the use of dominant, homozygous lethal mutations and balancer chromosomes to track genetic manipulations and prevent recombination, the implementation of targeted expression systems like UAS/Gal4 for functional perturbations, the cultivation white-eyed flies allowing for easy screening of transgenics and the optimization of gene insertion techniques like the phiC31 integrase vector system and genome editing techniques like CRISPR/Cas9 (Brand and Perrimon, 1993; Kanca et al., 2022; Stern et al., 2023; Gratz et al., 2014). For example, we can insert coding and non-coding sequences from other Drosophila species into the D. melanogaster genome to test their effects on signaling intensity or gene expression. Inserting grk from D. willistoni, a dorsal ridge species, into D. melanogaster not only rescued a grk null fly, but also generated a short dorsal ridge in a low percentage of the eggshells (Niepielko and Yakoby, 2014).
Importantly, the same grk in D. willistoni is necessary for the robust formation of dorsal ridge, however, the penetrance in D. melanogaster is very low, likely due to other components unique to D. willistoni (Niepielko and Yakoby, 2014). Similar experiments can be done with grk from D. nasuta and D. nebulosa, as well as other components related to EGFR signaling pathway, including downstream targets like rhomboid, spitz, sprouty, and kekkon controlling both positive and negative feedback loops of signaling (Zartman et al., 2009; Shilo, 2005). However, testing one component at a time in D. melanogaster is time consuming, costly, and does not always reflect the full function of the gene in the native species. August Krogh noted in his 1929 essay that for a given question, there is usually a particular animal model best suited to address that question (Garcia et al., 2013). The most suitable system for answering coevolutionary questions is not a single model organism. Answering these questions requires the development of a “model clade,” a group of closely related species accompanied by the genetic and molecular tools necessary for reciprocal editing to more accurately examine predicted functions in the relevant context.
7.2 Challenges in manipulating other Drosophila species
CRISPR/Cas9 was used successfully to disrupt genes in other Drosophila species (Baker et al., 2024; Lamb et al., 2020; Sottolano et al., 2022), however, unlike its use in D. melanogaster, achieving homology directed repair (HDR) in non-model Drosophilids has been mostly unsuccessful with one exception (Stern et al., 2023). Additionally, the lack of balancer chromosomes and dominant genetic markers makes it difficult to follow and maintain edits to the genome. Most D. melanogaster transgenic flies rely on complementation of the white gene mutation, or the use of fluorescent eye markers to track successful integration of transgenes in a white-eyed fly (Bellen and Yamamoto, 2015). Despite this common practice, the disruption of the white gene affects courtship behavior and mating success in D. melanogaster (Xiao et al., 2017). Although white-eyed stocks have been established in other Drosophila species (Holtzman et al., 2010), in D. nebulosa, white-eyed males do not attempt to mate at all, preventing the effective use of white-eyed flies and fluorescent eye markers in this species (Sottolano et al., 2022). Likewise, mutations in the Of-white gene of the Milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus were lethal (Reding and Pick, 2020).
Genome manipulations in D. melanogaster were not always simple and have undergone a series of optimizations. Incorporating Cas9 and phiC31 integrase under the control of germ line promoters greatly improved transgenesis efficiency in this species (Bischof et al., 2007; Kondo and Ueda, 2013). This same strategy has been used in a variety of non-model insects to improve gene editing outcomes (Li et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2017). Several labs have recently published methods for increasing HDR efficiency in D. melanogaster, including the use of short homology arms and the pJAT plasmid platform (Kanca et al., 2022; Stern et al., 2023). Incorporating a species-specific native nos promoter to drive cas9 in the germline, together with the more efficient CRISPR strategies may expedite successful HDR in a variety of non-model Drosophila species. Options for maintaining the inheritance of edited loci are also emerging. A suite of transgenic tools developed by the Stern lab was used to generate a balancer chromosome for D. simulans (Stern, 2022). It may be possible to replicate this success in other non-model Drosophilids to stabilize transgenic constructs by preventing recombination.
Another recent innovation is the use of antibiotic resistance genes as selectable markers in flies (Matinyan et al., 2021), which eliminates the need to screen for visible selection markers and reliance on white-eyed fly strains. Growing transgenic flies on antibiotic treated food may permit the maintenance of deleterious edits across multiple generations without the use of balancer chromosomes. Additionally, titration of antibiotic concentrations could facilitate the selection of offspring homozygous for edits without the use of additional markers to follow the edited and unedited chromosomes through sequences of crosses. Another more traditional option is to identify non-vision related mutations on the X chromosome (like the white gene). The Drosophila wing has two cross-veins regulated by crossveinless-2 (cv-2). Mutations in cv-2 lead to the loss of the two cross veins on the wing, a simple visual phenotype (Conley et al., 2000). The cv-2 cDNA (4329bp) is of similar size to the commonly used mini-white cassette (4136bp) in transformation vectors.
7.3 Computational tools to predict co-evolution
Beyond the ability to perturb known genes in a signaling pathway and their known targets in new model systems, we can also leverage computational predictions of co-evolving domains in interacting proteins to further refine our exploration of co-evolving systems. The sequenced genomes of flies like D. nasuta and D. nebulosa provide a good starting point for exploring how evolution along the EGFR signaling pathway can both maintain stasis for critical functions like mesoderm specification while also permitting the emergence of new forms like the dorsal ridge, a downstream target of elevated EGFR signaling (Niepielko et al., 2014; Niepielko and Yakoby, 2014). Phylogenetic comparative methods like iBIS2 (protein-protein co-evolution, (Oteri et al., 2022)) and PhyloACC (convergent evolution in regulatory elements, (Hu et al., 2019)) can highlight significant areas of convergence and divergence linked to selected phenotypic outcomes like the dorsal ridge.
One hurdle in implementing this approach is the lack of comprehensive collections of phenotype data, particularly data that identifies instances of phenotypic convergence, to match our growing library of high-quality genomes. Once implemented, labeling strategies like immunohistochemistry and Single Molecule Fluorescent in situ Hybridization can provide complimentary insights by revealing cross-species changes in gene expression patterns, protein localization, and signaling intensity. These methods can provide valuable spatiotemporal markers to further support the insights from phylogenies. Although these methods are still correlative, the generated predictions can be prioritized and validated in the new gene editing platforms, thus accounting for the overall evolutionary changes that occurred during speciation.
8 Concluding remarks
The triangle of a biological question, experimental tools to address the question, and computational tools to analyze the data have come to a full circle in the post-genomics era. High-quality genome sequences of many species, beyond the traditional model organisms, are available (Kim et al., 2021). Additionally, predictive computational tools to identify co-evolving domain are also accessible (Oteri et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2019). Therefore, the groundwork is in place to tackle the next challenge: understanding speciation in native species. To accomplish that, computational tools will need to be supplemented with species’ traits (e.g., morphology, pattern, function, etc.) to narrow down the list of predicted co-evolving domains. Moreover, adjusting genome engineering tools to enable HDR, together with robust and inexpensive selection of transgenic organisms will allow the scientific community to explore complex, heterogenous systems within their native context. We argue that branching out from established communities, like that of Drosophila, is the most efficient path forward.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
HLS: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Research in the Yakoby Lab is supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (2R15GM101597-02 to NY) and by the National Science Foundation (IOS-1926802 to NY).
Acknowledgments
Research in the Yakoby Lab is supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (2R15GM101597-02 to NY) and by the National Science Foundation (IOS-1926802 to NY).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Allada, R., White, N. E., So, W. V., Hall, J. C., and Rosbash, M. (1998). A mutant Drosophila homolog of mammalian Clock disrupts circadian rhythms and transcription of period and timeless. Cell 93 (5), 791–804. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81440-3
Baker, C. A., Guan, X. J., Choi, M., and Murthy, M. (2024). The role of fruitless in specifying courtship behaviors across divergent Drosophila species. Sci. Adv. 10 (11), adk1273. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adk1273
Beldade, P., and Brakefield, P. M. (2002). The genetics and evo-devo of butterfly wing patterns. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3 (6), 442–452. doi:10.1038/nrg818
Bellen, H. J., and Yamamoto, S. (2015). Morgan’s legacy: fruit flies and the functional annotation of conserved genes. Cell 163 (1), 12–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.009
Bertile, F., Matallana-Surget, S., Tholey, A., Cristobal, S., and Armengaud, J. (2023). Diversifying the concept of model organisms in the age of -omics. Commun. Biol. 6 (1), 1062. doi:10.1038/s42003-023-05458-x
Bier, E., Harrison, M. M., O’Connor-Giles, K. M., and Wildonger, J. (2018). Advances in engineering the fly genome with the CRISPR-cas system. Genetics 208 (1), 1–18. doi:10.1534/genetics.117.1113
Biering, S. B., Sarnik, S. A., Wang, E., Zengel, J. R., Leist, S. R., Schafer, A., et al. (2022). Genome-wide bidirectional CRISPR screens identify mucins as host factors modulating SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Genet. 54 (8), 1078–1089. doi:10.1038/s41588-022-01131-x
Bischof, J., Maeda, R. K., Hediger, M., Karch, F., and Basler, K. (2007). An optimized transgenesis system for Drosophila using germ-line-specific phiC31 integrases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104 (9), 3312–3317. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611511104
Brand, A. H., and Perrimon, N. (1993). Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118 (2), 401–415. doi:10.1242/dev.118.2.401
Carroll, S. B. (2008). Evo-devo and an expanding evolutionary synthesis: a genetic theory of morphological evolution. Cell 134 (1), 25–36. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.030
Carroll, S. B., Prud'homme, B., and Gompel, N. (2008). Regulating evolution. Sci. Am. 298 (5), 60–67. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0508-60
Cho, Y. S., Stevens, L. M., and Stein, D. (2010). Pipe-dependent ventral processing of Easter by Snake is the defining step in Drosophila embryo DV axis formation. Curr. Biol. 20 (12), 1133–1137. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2010.04.056
Conley, C. A., Silburn, R., Singer, M. A., Ralston, A., Rohwer-Nutter, D., Olson, D. J., et al. (2000). Crossveinless 2 contains cysteine-rich domains and is required for high levels of BMP-like activity during the formation of the cross veins in Drosophila. Development 127 (18), 3947–3959. doi:10.1242/dev.127.18.3947
Cooper, K. L. (2024). The case against simplistic genetic explanations of evolution. Development 151 (20), dev203077. doi:10.1242/dev.203077
Crocker, J., Tamori, Y., and Erives, A. (2008). Evolution acts on enhancer organization to fine-tune gradient threshold readouts. PLoS Biol. 6 (11), e263. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060263
Garcia, H. G., Tikhonov, M., Lin, A., and Gregor, T. (2013). Quantitative imaging of transcription in living Drosophila embryos links polymerase activity to patterning. Curr. Biol. 23 (21), 2140–2145. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.08.054
Gratz, S. J., Ukken, F. P., Rubinstein, C. D., Thiede, G., Donohue, L. K., Cummings, A. M., et al. (2014). Highly specific and efficient CRISPR/Cas9-catalyzed homology-directed repair in Drosophila. Genetics 196 (4), 961–971. doi:10.1534/genetics.113.160713
He, B., Doubrovinski, K., Polyakov, O., and Wieschaus, E. (2014). Apical constriction drives tissue-scale hydrodynamic flow to mediate cell elongation. Nature 508 (7496), 392–396. doi:10.1038/nature13070
Hoffmann, J. (2007). Antifungal defense in Drosophila. Nat. Immunol. 8 (6), 543–545. doi:10.1038/ni0607-543
Holtzman, S., Miller, D., Eisman, R., Kuwayama, H., Niimi, T., and Kaufman, T. (2010). Transgenic tools for members of the genus Drosophila with sequenced genomes. Fly. (Austin). 4 (4), 349–362. doi:10.4161/fly.4.4.13304
Hood, L., and Rowen, L. (2013). The Human Genome Project: big science transforms biology and medicine. Genome Med. 5 (9), 79. doi:10.1186/gm483
Hu, Z., Sackton, T. B., Edwards, S. V., and Liu, J. S. (2019). Bayesian detection of convergent rate changes of conserved noncoding elements on phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 36 (5), 1086–1100. doi:10.1093/molbev/msz049
Irion, U., and Nusslein-Volhard, C. (2022). Developmental genetics with model organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119 (30), e2122148119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2122148119
Jacob, F., and Monod, J. (1961). Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 3, 318–356. doi:10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7
Jorgensen, E. M., and Mango, S. E. (2002). The art and design of genetic screens: caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3 (5), 356–369. doi:10.1038/nrg794
Kagesawa, T., Nakamura, Y., Nishikawa, M., Akiyama, Y., Kajiwara, M., and Matsuno, K. (2008). Distinct activation patterns of EGF receptor signaling in the homoplastic evolution of eggshell morphology in genus Drosophila. Mech. Dev. 125 (11–12), 1020–1032. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2008.08.001
Kanca, O., Zirin, J., Hu, Y., Tepe, B., Dutta, D., Lin, W. W., et al. (2022). An expanded toolkit for Drosophila gene tagging using synthesized homology donor constructs for CRISPR-mediated homologous recombination. Elife 11, e76077. doi:10.7554/eLife.76077
Kim, B. Y., Wang, J. R., Miller, D. E., Barmina, O., Delaney, E., Thompson, A., et al. (2021). Highly contiguous assemblies of 101 drosophilid genomes. Elife 10, e66405. doi:10.7554/eLife.66405
Kondo, S., and Ueda, R. (2013). Highly improved gene targeting by germline-specific Cas9 expression in Drosophila. Genetics 195 (3), 715–721. doi:10.1534/genetics.113.156737
Kramer, N. J., Haney, M. S., Morgens, D. W., Jovicic, A., Couthouis, J., Li, A., et al. (2018). CRISPR-Cas9 screens in human cells and primary neurons identify modifiers of C9ORF72 dipeptide-repeat-protein toxicity. Nat. Genet. 50 (4), 603–612. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0070-7
Lamb, A. M., Wang, Z., Simmer, P., Chung, H., and Wittkopp, P. J. (2020). Ebony affects pigmentation divergence and cuticular hydrocarbons in Drosophila americana and D. novamexicana. Front. Ecol. Evol. 8, 184. doi:10.3389/fevo.2020.00184
Lander, E. S., Linton, L. M., Birren, B., Nusbaum, C., Zody, M. C., Baldwin, J., et al. (2001). Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409 (6822), 860–921. doi:10.1038/35057062
Lettice, L. A., Hill, A. E., Devenney, P. S., and Hill, R. E. (2008). Point mutations in a distant sonic hedgehog cis-regulator generate a variable regulatory output responsible for preaxial polydactyly. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17 (7), 978–985. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm370
Lewis, E. B. (1978). A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature 276 (5688), 565–570. doi:10.1038/276565a0
Li, M., Bui, M., Yang, T., Bowman, C. S., White, B. J., and Akbari, O. S. (2017). Germline Cas9 expression yields highly efficient genome engineering in a major worldwide disease vector, Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (49), E10540-–E10549. doi:10.1073/pnas.1711538114
Matinyan, N., Karkhanis, M. S., Gonzalez, Y., Jain, A., Saltzman, A., Malovannaya, A., et al. (2021). Multiplexed drug-based selection and counterselection genetic manipulations in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 36 (11), 109700. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109700
McGinnis, W., Levine, M. S., Hafen, E., Kuroiwa, A., and Gehring, W. J. (1984). A conserved DNA sequence in homoeotic genes of the Drosophila Antennapedia and bithorax complexes. Nature 308 (5958), 428–433. doi:10.1038/308428a0
Mohr, S. E. (2018). First in fly: Drosophila research and biological discovery. 1 Stephanie Elizabeth Mohr Harvard University Press, 258 p.
Morgan, T. H. (1910). Sex limited inheritance in Drosophila. Science 32 (812), 120–122. doi:10.1126/science.32.812.120
Moussian, B., and Roth, S. (2005). Dorsoventral axis formation in the Drosophila embryo--shaping and transducing a morphogen gradient. Curr. Biol. 15 (21), R887–R899. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.10.026
Muller, H. J. (1928). The production of mutations by X-rays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 14 (9), 714–726. doi:10.1073/pnas.14.9.714
Mullins, M. C., Hammerschmidt, M., Haffter, P., and Nusslein-Volhard, C. (1994). Large-scale mutagenesis in the zebrafish: in search of genes controlling development in a vertebrate. Curr. Biol. 4 (3), 189–202. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00048-8
Niepielko, M. G., Hernaiz-Hernandez, Y., and Yakoby, N. (2011). BMP signaling dynamics in the follicle cells of multiple Drosophila species. Dev. Biol. 354 (1), 151–159. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.03.005
Niepielko, M. G., Marmion, R. A., Kim, K., Luor, D., Ray, C., and Yakoby, N. (2014). Chorion patterning: a window into gene regulation and Drosophila species’ relatedness. Mol. Biol. Evol. 31 (1), 154–164. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst186
Niepielko, M. G., and Yakoby, N. (2014). Evolutionary changes in TGFα distribution underlie morphological diversity in eggshells from Drosophila species. Development 141 (24), 4710–4715. doi:10.1242/dev.111898
Nilson, L. A., and Schupbach, T. (1999). EGF receptor signaling in Drosophila oogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 44, 203–243. doi:10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60471-8
Nusslein-Volhard, C., and Wieschaus, E. (1980). Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287 (5785), 795–801. doi:10.1038/287795a0
Oteri, F., Sarti, E., Nadalin, F., and Carbone, A. (2022). iBIS2Analyzer: a web server for a phylogeny-driven coevolution analysis of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (W1), W412–W419. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac481
Perrimon, N., Bonini, N. M., and Dhillon, P. (2016). Fruit flies on the front line: the translational impact of Drosophila. Dis. Model Mech. 9 (3), 229–231. doi:10.1242/dmm.024810
Phifer-Rixey, M., and Nachman, M. W. (2015). Insights into mammalian biology from the wild house mouse Mus musculus. Elife 4, e05959. doi:10.7554/eLife.05959
Queenan, A. M., Ghabrial, A., and Schupbach, T. (1997). Ectopic activation of torpedo/Egfr, a Drosophila receptor tyrosine kinase, dorsalizes both the eggshell and the embryo. Development 124 (19), 3871–3880. doi:10.1242/dev.124.19.3871
Reding, K., and Pick, L. (2020). High-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis of the white gene in the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus. Genetics 215 (4), 1027–1037. doi:10.1534/genetics.120.303269
Roth, S. (1993). Mechanisms of dorsal-ventral axis determination in Drosophila embryos revealed by cytoplasmic transplantations. Development 117 (4), 1385–1396. doi:10.1242/dev.117.4.1385
Sagai, T., Hosoya, M., Mizushina, Y., Tamura, M., and Shiroishi, T. (2005). Elimination of a long-range cis-regulatory module causes complete loss of limb-specific Shh expression and truncation of the mouse limb. Development 132 (4), 797–803. doi:10.1242/dev.01613
Santos, M. E., Braasch, I., Boileau, N., Meyer, B. S., Sauteur, L., Bohne, A., et al. (2014). The evolution of cichlid fish egg-spots is linked with a cis-regulatory change. Nat. Commun. 5, 5149. doi:10.1038/ncomms6149
Schupbach, T., and Roth, S. (1994). Dorsoventral patterning in Drosophila oogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 4 (4), 502–507. doi:10.1016/0959-437x(94)90064-a
Schupbach, T., and Wieschaus, E. (1986). Maternal-effect mutations altering the anterior-posterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Rouxs Arch. Dev. Biol. 195 (5), 302–317. doi:10.1007/BF00376063
Sen, J., Goltz, J. S., Stevens, L., and Stein, D. (1998). Spatially restricted expression of pipe in the Drosophila egg chamber defines embryonic dorsal-ventral polarity. Cell 95 (4), 471–481. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81615-3
Shilo, B. Z. (2005). Regulating the dynamics of EGF receptor signaling in space and time. Development 132 (18), 4017–4027. doi:10.1242/dev.02006
Sinclair, D., Mills, K., and Guarente, L. (1998). Aging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 52, 533–560. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.52.1.533
Sottolano, C. J., Revaitis, N. T., Geneva, A. J., and Yakoby, N. (2022). Nebulous without white: annotated long-read genome assembly and CRISPR/Cas9 genome engineering in Drosophila nebulosa. G3 (Bethesda) 12 (11), jkac231. doi:10.1093/g3journal/jkac231
Stenseth, N. C., Andersson, L., and Hoekstra, H. E. (2022). Gregor Johann Mendel and the development of modern evolutionary biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119 (30), e2201327119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2201327119
Stern, D. L. (2022). Transgenic tools for targeted chromosome rearrangements allow construction of balancer chromosomes in non-melanogaster Drosophila species. G3 (Bethesda). 12 (4), jkac030. doi:10.1093/g3journal/jkac030
Stern, L. D., Kim, E., and Behrman, L. E. (2023). The Janelia Atalanta plasmids provide a simple and efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology directed repair platform for Drosophila. bioRxiv. 545412. doi:10.1101/2023.06.17.545412
Stevens, C. A., Stott, H. L., Desai, S. V., and Yakoby, N. (2022). Shared cis-regulatory modules control expression of the tandem paralogs midline and H15 in the follicular epithelium. Development 149 (22), dev201016. doi:10.1242/dev.201016
St Johnston, D. (2002). The art and design of genetic screens: Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3 (3), 176–188. doi:10.1038/nrg751
Sun, D., Guo, Z., Liu, Y., and Zhang, Y. (2017). Progress and prospects of CRISPR/cas systems in insects and other arthropods. Front. Physiol. 8, 608. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00608
Tomoyasu, Y., and Halfon, M. S. (2020). How to study enhancers in non-traditional insect models. J. Exp. Biol. 223 (Pt Suppl. 1), jeb212241. doi:10.1242/jeb.212241
Verheyen, E. M. (2022). The power of Drosophila in modeling human disease mechanisms. Dis. Model Mech. 15 (3), dmm049549. doi:10.1242/dmm.049549
Victor Atoki, A., Aja, P. M., Shinkafi, T. S., Ondari, E. N., Adeniyi, A. I., Fasogbon, I. V., et al. (2025). Exploring the versatility of Drosophila melanogaster as a model organism in biomedical research: a comprehensive review. Fly. (Austin). 19 (1), 2420453. doi:10.1080/19336934.2024.2420453
Wangler, M. F., Yamamoto, S., Chao, H. T., Posey, J. E., Westerfield, M., Postlethwait, J., et al. (2017). Model organisms facilitate rare disease diagnosis and therapeutic research. Genetics 207 (1), 9–27. doi:10.1534/genetics.117.203067
Wieschaus, E., and Nusslein-Volhard, C. (2016). The Heidelberg screen for pattern mutants of Drosophila: a personal account. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 32, 1–46. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-113015-023138
Xiao, C., Qiu, S., and Robertson, R. M. (2017). The white gene controls copulation success in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 7712. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-08155-y
Xu, C., Yang, X., Zhou, H., Li, Y., Xing, C., Zhou, T., et al. (2020). A novel ZRS variant causes preaxial polydactyly type I by increased sonic hedgehog expression in the developing limb bud. Genet. Med. 22 (1), 189–198. doi:10.1038/s41436-019-0626-7
Xu, X. S., Gantz, V. M., Siomava, N., and Bier, E. (2017). CRISPR/Cas9 and active genetics-based trans-species replacement of the endogenous Drosophila kni-L2 CRM reveals unexpected complexity. Elife 6, e30281. doi:10.7554/eLife.30281
Keywords: CRISPR/cas9, Drosophila, model clade, EGFR signaling, axis formation
Citation: Stott HL and Yakoby N (2025) Diversity of Drosophila egg patterning: The missing tools to explore embryonic axis formation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1569318. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1569318
Received: 31 January 2025; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 21 March 2025.
Edited by:
Aimin Liu, The Pennsylvania State University (PSU), United StatesReviewed by:
Gregory T Reeves, Texas A and M University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Stott and Yakoby. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nir Yakoby, yakoby@camden.rutgers.edu
 Helen L. Stott1
Helen L. Stott1