
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 28 February 2025
Sec. Molecular and Cellular Reproduction
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1562331
This article is part of the Research TopicRedox Regulation in Sperm and Oocyte from Gametogenesis to Fertilization for Reproductive HealthView all articles
Introduction: Microplastics and nanoplastics are prevalent environmental contaminants. Recent reports indicate that polystyrene nanoparticles may adversely impact male reproductive health. This study aims to examine the effects of polystyrene exposure on sperm metabolism and the development of pre-implantation embryos.
Methods: In this study, male C57BL/6 mice were orally gavage-administered polystyrene nanoplastics (60 nm, 20 mg/kg/day) for 35 days to assess their impact on male reproduction and early embryonic development. Experiments included testicular transcriptome analysis, sperm metabolomics, sperm motility and fertilization assays, embryonic ROS detection, and RNA sequencing of 2-cell embryos, revealing the adverse effects of polystyrene exposure on sperm metabolism and embryo development.
Results: The results revealed that oral gavage of polystyrene to male mice induced a pronounced immune-inflammatory response in testicular tissue, reduced sperm motility, and significantly lowered the fertilization rate. Notably, sperm from treated mice exhibited substantial metabolic disruptions, affecting key pathways, including glycerophospholipid biosynthesis and DNA repair. After fertilization, embryos at the 2-cell stage suffered damage in apoptotic and DNA repair pathways, subsequently impairing early embryo development.
Discussion: In conclusion, this study demonstrated that the oral gavage administration of polystyrene nanoplastics to male mice significantly affects male reproductive function, resulting in abnormalities in early embryonic development and alterations in associated gene expression profiles. These findings offer essential scientific insights for future research into sperm-mediated transgenerational effects and their impact on early embryonic development.
Microplastics (MP) and nanoplastics (NP) are pervasive and unavoidable in the environment (He and Yin, 2024). Microplastics are considered to be tiny plastic fragments with sizes ranging from 1 μm to 5 mm (Frias and Nash, 2019). In addition, microplastics can also degrade into smaller nanoscale particles with sizes ranging from 1–1,000 nm (Gagne, 2019). Among these, polystyrene microplastics and nanoparticles (PS-MNP) contribute significantly to environmental pollution (Camerano Spelta Rapini et al., 2024). Polystyrene (PS) is particularly prevalent in everyday products such as packaging materials, insulation, and consumer goods, presenting potential health risks (Geyer et al., 2017). The impact of environmental pollutants on reproductive health has become a growing concern (Dusza et al., 2023; Hu et al., 2024). Research on polystyrene’s effects on mammalian reproductive health has predominantly focused on gametogenesis, including oogenesis and spermatogenesis (Camerano Spelta Rapini et al., 2024; Tanveer et al., 2023).
Maternal exposure to polystyrene through drinking water during pregnancy can adversely affect both the placenta and fetus, leading to morphological abnormalities in skeletal muscle tissue. Moreover, exposure to high concentrations (10 mg/L) of polystyrene results in significant reductions in both absolute and relative fetal weight (Chen et al., 2023). Cross-generational toxicity studies have shown that maternal exposure to microplastics can cause premature death in rodent offspring. Survivors exhibit a range of disorders, including metabolic dysfunction, reproductive impairment, immune system abnormalities, and disruptions in neurodevelopment and cognition (He and Yin, 2024).
Spermatogenesis occurs within the seminiferous tubules of the testes, the seminiferous epithelium is composed of germ and sertoli cells. Spermatogonia differentiate into spermatocytes through mitosis, which then undergo meiosis to form round spermatids, ultimately maturing into sperm. This intricate process is regulated by endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine signals, and is influenced by various environmental and lifestyle factors (Gao et al., 2024; Makela et al., 2019; Saitou and Hayashi, 2021). Research has shown that male mice were oral gavage-administered polystyrene nanoparticles (25 nm, 50 nm, and 100 nm) for 56 days. Exposure to all three nanoparticle sizes resulted in reduced male fertility and potential infertility. These nanoparticles accumulated in the testes, inducing oxidative stress, altering the expression of genes associated with apoptosis and inflammation, and disrupting energy metabolism (Xu et al., 2023). Additionally, exposure to polystyrene microplastics led to developmental abnormalities in testicular tissue and decreased sperm count and motility in adult male mice. These effects may be attributed to the disruption of the Hippo pathway and abnormal cytokine secretion induced by polystyrene microplastics in the testes (Zhao et al., 2023). However, the impact of polystyrene exposure on sperm metabolite levels and its effects on early embryonic development and gene expression remain unclear.
In this study, male mice were exposed to polystyrene via oral gavage, resulting in an increased immune-inflammatory response in testicular tissue, alongside significant DNA damage in the testes. Notably, marked changes were observed in the metabolic profile of sperm from exposed mice, including alterations in metabolite levels related to glycerophospholipid biosynthesis and DNA damage repair. Furthermore, significant DNA damage was detected in sperm-derived early embryos, accompanied by disruptions in apoptosis and lipid metabolism at the 2-cell embryo stage. Overall, our findings suggest that polystyrene exposure in male mice leads to dysregulation of testicular gene expression and sperm metabolism, which in turn impacts lipid metabolism and oxidative stress pathways in early embryos, thereby reducing early embryo development. This study offers both theoretical and practical insights for future research into the mechanisms and biological effects of polystyrene.
In this study, 10- to 12-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were divided into two groups (n = 10 each group). The experimental group received daily oral gavage of polystyrene green fluorescent microspheres (60 nm, 20 mg/kg/day) for 35 days. The control group received an equal volume of ultrapure water (ddH2O). All experimental procedures and animal breeding protocols were conducted in accordance with the ethical guidelines for the use of experimental animals at Tongji University (TJBG14924101).
To perform superovulation in female mice, inject 5 IU of PMSG (San-Sheng, China) intraperitoneally into 8- to 10-week-old C57BL/6 female mice, followed by an injection of 6 IU of HCG (San-Sheng) 48 h later. Cumulus-oocyte complexes were collected from the oviducts 13–14 h after hCG injection. Next, place the cumulus-oocyte complexes in G-IVF to prepare for fertilization.
Male mice from both groups were euthanized by cervical dislocation. After euthanasia, the mice were placed in a dorsal position, and the epididymides were carefully removed using eye forceps. The epididymides and part of the vas deferens were dissected with scissors and placed in a dish. Using ophthalmic forceps, sperm were gently squeezed from the vas deferens, starting from the base and moving toward the head of the epididymis. An injection needle was used to puncture the epididymal head and extract the sperm. The sperm were then incubated in a G-IVF medium (Vitrolife, Sweden) for 20–30 min in a culture incubator.
After incubation, a small volume of sperm was collected from the upper layer with a pipette and transferred into an IVF culture dish containing cumulus-oocyte complexes. Once fertilization was complete, any remaining sperm were washed off the fertilized oocytes, and the fertilized egg were transferred into the G1-PLUS medium (Vitrolife, 10128) for further culture.
Remove the sperm from the tail of the mouse epididymis (Section 2.3). Place the sperm to be tested in a 35°C water bath for 10–15 min. Take 10 μL of sperm and transfer it to preheated CASA special glass slides and cover slides. Drop the sperm onto the glass slide, cover them with the cover slide, and let them stand for about 5 s for observation (n = 5 each group). Use the microscope equipped with CASA to locate sperm and observe them in real-time using computer.
To assess oxidative stress of sperm, DCFH-DA (Beyotime, S0033S) was diluted in the DPBS at a 1:1000 ratio, resulting in a final concentration of 10 µM. Incubate the upstream sperm in the solution for 20 min at 37°C. After incubation, the sperm were washed three times with DPBS and examined under a microscope (n = 3 each group).
Similarly, DCFH-DA was diluted in the G1-PLUS medium at a 1:1,000 ratio, resulting in a final concentration of 10 µM. The embryos were incubated in this solution for 20 min at 37°C to allow sufficient interaction between the probe and the embryos. After incubation, the embryos were washed three times with fresh culture medium droplets and examined under a microscope. Fluorescence signals from each embryo were quantified using ImageJ software, and statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired t-test. A p-value of < 0.0001 was considered statistically significant (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).
Fix 4-cell embryos with 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 1 h. Wash once with 0.5% BSA-PBS. Next, the embryos were permeabilized with 0.5% TritonX-100 and incubated at room temperature for 20 min. Prepare TUNEL staining solution using TdT enzyme (5 μL) and fluorescent labeling solution (45 μL). Wash twice with 0.5% BSA-PBS. Add 50 μL TUNEL detection solution and incubate at 37°C in the dark for 60 min. Wash twice with 0.5% BSA-PBS. Detect the fluorescence intensity of embryos under a fluorescence microscope.
Sperm acquisition involved sperm capacitation and in vitro fertilization (IVF). The upstream sperm were then washed 2 to 3 times with 0.5% BSA-PBS at 1,500 rpm for 5 min. Following this, the sperm pellet was dissolved in a 1:1 solution of acetonitrile and water, analyzed, and separated using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) with an ACQUITY UPLC BEH amide column. To ensure data reliability, quality control (QC) samples were introduced during the analysis. Further sample analysis was performed using quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QToFMS; Triple TOF 6600; AB Sciex GmbH) in both positive and negative ion modes of electrospray ionization (ESI). Metabolites were identified by comparing their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) accuracy (within 25 ppm) and MS/MS spectra to an internal database of established standards. Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) was performed using the R software package (Wang et al., 2024). Differential metabolites were identified based on a predictive variable importance (VIP) threshold >1, and the results were validated with an adjusted P-value <0.05. Metabolome enrichment analysis was carried out using MetaboAnalyst 6.0 software (Pang et al., 2024). The detection of untargeted metabolomics was performed by Applied Protein Technology Co. (Shanghai, China).
Testicular tissue cells were thoroughly dissolved in a Trizol solution. To this, 200 μL CHCl3 was added, followed by vortexing and standing for 5 min. The mixture was then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 15 min at room temperature. The supernatant was collected, and an equal volume of isopropanol was added. The mixture was placed at −20°C for 10 min and centrifuged again at 13,000 rpm for 15 min. After discarding the supernatant, the sample was washed twice with 75% ethanol, centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, and finally dissolved in ddH2O.
For the construction of RNA-seq library of testicular tissue, RNA was extracted from testicular tissue, and the concentration of RNA was detected by Qubit (n = 3 each group). Starting with an initial RNA quantity of 500 ng, the KAPA Stranded RNA-Seq Kits (Cat# 07962169001) were utilized to construct the RNA-seq library.
For the 2-cell embryos, the zona pellucida was digested using the PE enzyme, and approximately 10–20 single-cell blastomeres were used to construct each library. The polar body was removed, and the embryo was separated into individual blastomeres using an oral pipette. These blastomeres were washed 2–3 times with 0.5% BSA-PBS. Individual 2-cell blastomeres were then transferred into pre-cooled low-adsorption PCR tubes containing lysis buffer using the oral pipette, followed by gentle mixing and centrifugation. The detailed methodology for RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) library construction is available in previously published articles. For sequencing, the constructed library was run on the NovaSeq 6000 S4 platform using paired-end 150 bp sequencing.
Adapters were removed from the RNA-seq data, and low-quality reads were trimmed using Trim_Galore (version 0.6.4) with default parameters. The processed reads were mapped to the mm10 reference genome using hisat2 (version 2.2.1) (Kim et al., 2019). The expression levels of all RefSeq genes were quantified in fragments per kilobase million (FPKM) using StringTie (v1.3.1c) (Shumate et al., 2022). Gene read counts were calculated using FeatureCounts (version 2.0.0) (Liao et al., 2014), and differential expression analysis was performed with Deseq2 (version 1.26.0) (Love et al., 2014). Genes with an adjusted P-value < 0.05 and a fold change >1.5 were considered differentially expressed.
Functional annotation was performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) Bioinformatics Resource, version 6.8 (Huang da et al., 2009).
A total of 30–50 2-cell embryos derived from sperm exposed to polystyrene and ddH2O was used to obtain RNA by the phenol-chloroform extraction method. cDNA was synthesized using 5X All-in-One RT MasterMix (abm). Quantitative reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was performed using SYBR Premix ExTaq (Takara), and the signals were detected with the ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) was used as an endogenous control. RT-qPCR were plotted and analyzed using Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, United States).
RT-qPCR were plotted and analyzed using Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, United States). Unpaired t-test, ∗∗∗∗p-value < 0.0001, ∗p-value < 0.05. Details of the other statistical data involved in this paper, including the statistical testing methods used and the number of samples required for the statistics, can be found in the figure legends.
To investigate the effects of polystyrene nanoplsatics on the reproductive system of male mice, 10- to 12-week-old male mice were exposed to polystyrene via oral gavage at a dose of 20 mg/kg/day for 35 days, as illustrated in the schematic diagram (Figure 1A). Weekly body weight measurements were taken for male mice in both the polystyrene (PS) and ultrapure water (Control) groups. Although a slight decrease in body weight was observed in the PS group, this change was not statistically significant when compared to the Control group (Figure 1B). In addition, we conducted data analysis on the weight of testicular tissue and the ratio of testicular weight to body weight after 35 days of treatment, and found that there was no significant difference between the Control and the PS group (Supplementary Figure S1A). However, we found partial atrophy of seminiferous tubules in the testes of the PS group through H&E staining of the transverse section of testicular tissue, indicating that exposed to polystyrene may have an impact on the reproductive health of male mice (Supplementary Figure S1B).
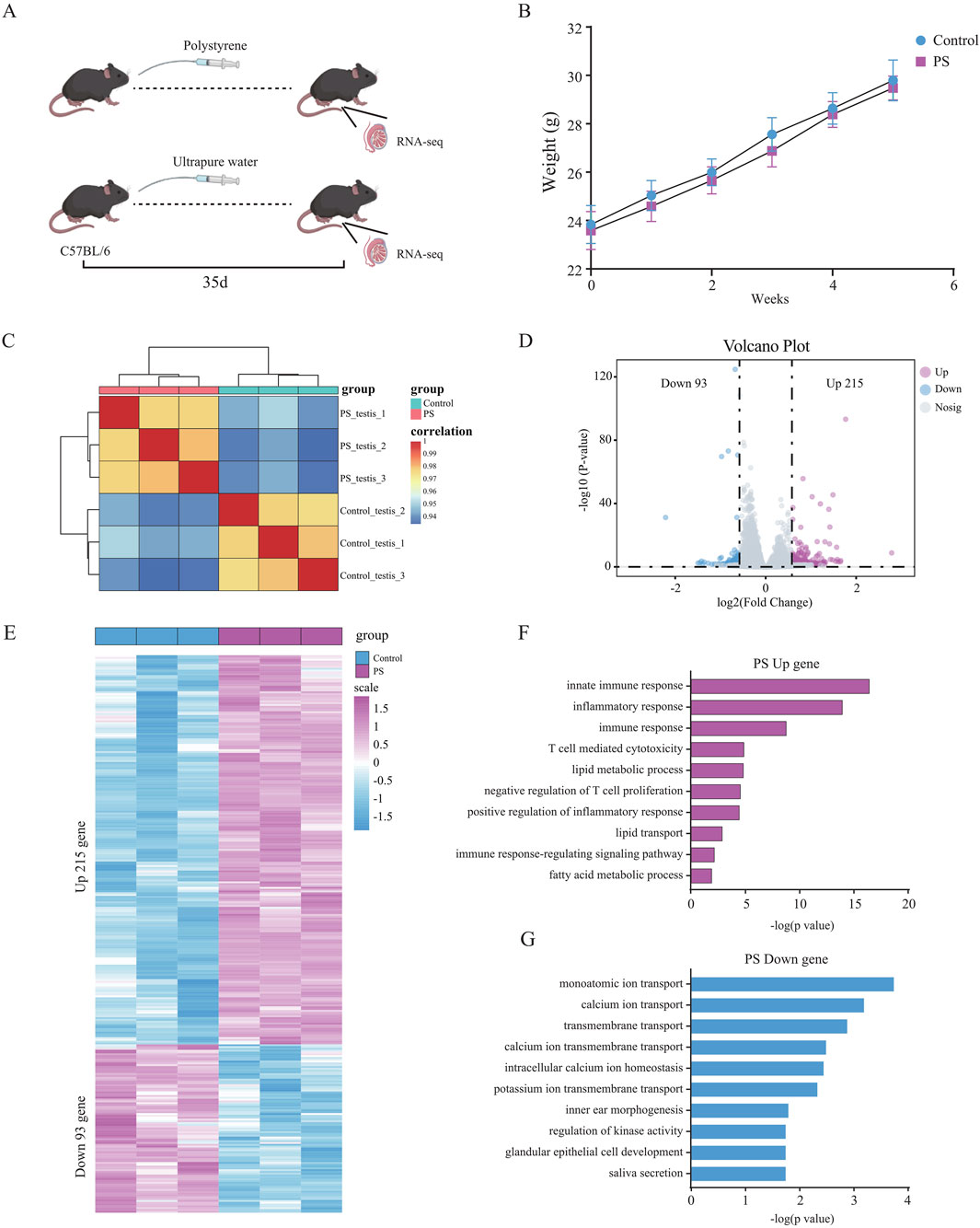
Figure 1. Differential gene expression and functional analysis of testicular tissue in male mice exposed to polystyrene (A). Schematic diagram of male mice exposed to ultrapure water (Control) and polystyrene (PS). (B) Body weight statistics of 10- to 12-week-old male C57BL/6 mice oral gavage with ultrapure water or polystyrene (n = 10 each group). (C) Correlation analysis of transcriptome data between the Control and PS groups. (D) Volcano plot analysis of differentially expressed genes between Control and PS groups. (E) Heatmap showing the expression of 308 differential genes in the Control and PS groups. (F, G) Gene ontology analysis of upregulated genes (log2 FC > 0.58 and p-value < 0.05) (F) and downregulated genes (log2 FC < −0.58 and p-value < 0.05) (G) in the Control and PS groups.
Subsequently, RNA-seq was performed on testicular tissue from both the PS and Control groups. The transcriptome data showed good reproducibility, confirming its suitability for downstream analyses (Figure 1C). A total of 308 differentially expressed genes were identified, with 215 genes upregulated and 93 genes downregulated in the testes of mice exposed to polystyrene (Figures 1D, E; Supplementary Table S1). Gene Ontology (GO) analysis revealed that the upregulated genes were predominantly associated with innate immune response, inflammatory response, T cell-mediated cytotoxicity, lipid metabolic processes, and negative regulation of T cell proliferation. Conversely, the downregulated genes were enriched in processes related to monoatomic ion transport, calcium ion transport, transmembrane transport, and calcium ion transmembrane transport, suggesting disruptions in testicular tissue function due to polystyrene exposure, particularly affecting immune and metabolic pathways (Figures 1F, G).
In summary, our findings indicate that exposure to polystyrene induces gene expression alterations in the testicular tissue of male mice, with significant impacts on biological functions such as immune inflammation and lipid metabolism.
To investigate the potential effects of polystyrene exposure on sperm metabolism, male mice were exposed to ultrapure water or polystyrene for 35 days (n = 10 per group). Five male mice were randomly selected from each group for untargeted metabolomics analysis of sperm. OPLS-DA analysis revealed significant discrimination between sperm from male mice exposed to ultrapure water and polystyrene, both in positive-ion (Figures 2A, B) and negative-ion (Figures 2C, D) modes. To prevent overfitting of the OPLS-DA model, permutation tests were performed.
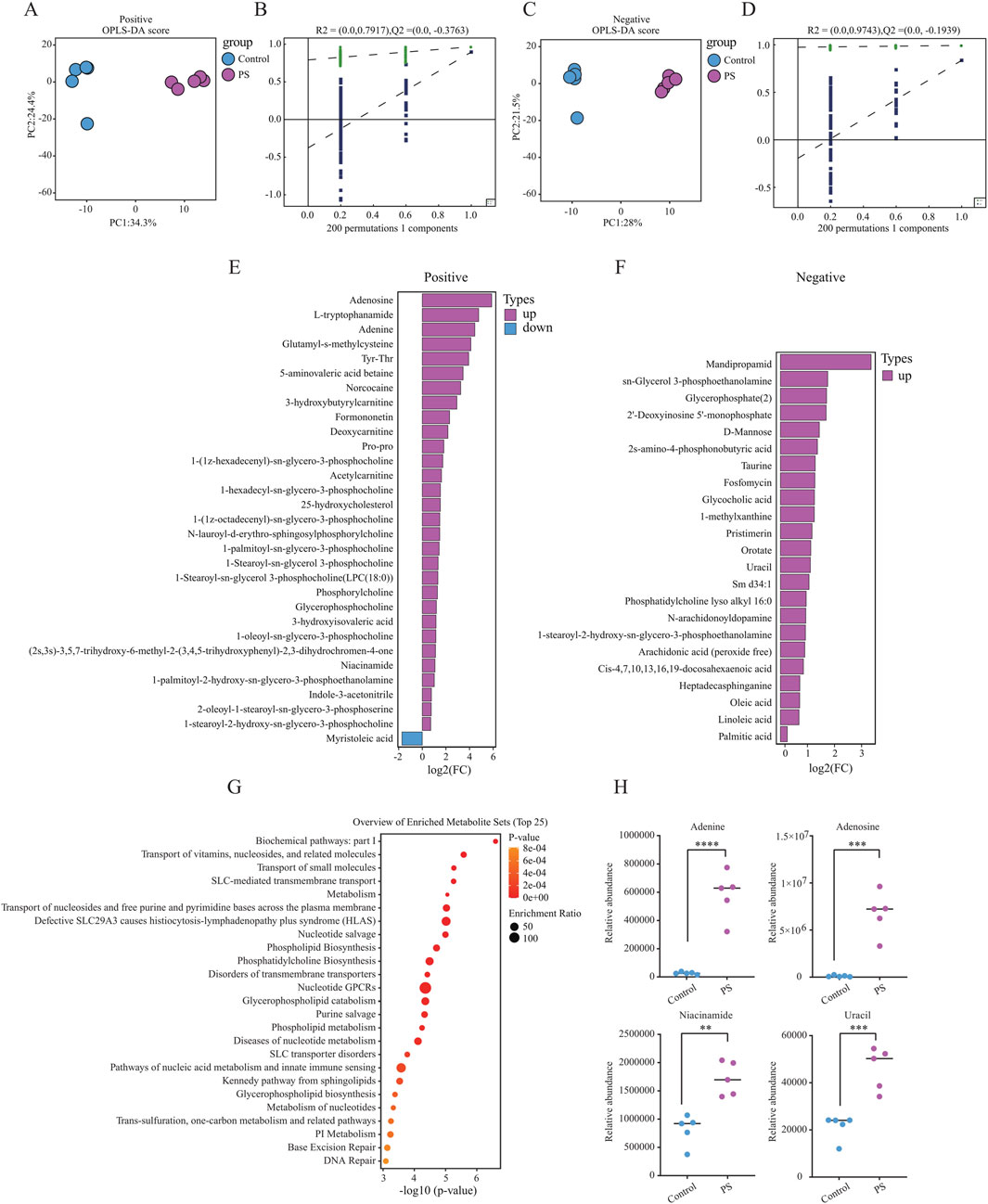
Figure 2. Untargeted metabolomics analysis in male mice between the Control and PS groups (A, B). OPLS-DA model displaying sperm metabolites in male mice exposed to ultrapure water (Control, n = 5) and polystyrene (PS, n = 5) in positive-ion mode (A). OPLS-DA model validation by permutation test (B). (C, D) OPLS-DA model displaying sperm metabolites in male mice exposed to ultrapure water (Control, n = 5) and polystyrene (PS, n = 5) in negative-ion mode (C). OPLS-DA model validation by permutation test (D). (E) Bar plot showing the differentially expressed metabolites in the positive-ion mode group. (F) Bar plot showing the differentially expressed metabolites in the negative-ion mode group. (G) Enrichment pathway analysis of KEGG for differential metabolites between the Control and PS groups. (H) Levels of differential metabolites in DNA damage-related metabolic pathways observed in both the Control and PS groups (Unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01).
In the analysis of differential metabolites in positive-ion mode, 31 significant metabolites were identified, with 30 upregulated and 1 downregulated in the sperm from polystyrene-exposed mice. In the negative-ion mode, 23 differential metabolites were detected, all of which were upregulated in the sperm of mice exposed to polystyrene (Figures 2E, F; Supplementary Table S2). KEGG pathway analysis of the differential metabolites revealed enrichment in metabolic pathways related to the transport of vitamins, nucleosides, and related molecules, glycerophospholipid catabolism, nucleic acid metabolism, innate immune sensing, base excision repair, and DNA repair (Figure 2G). Additionally, metabolites associated with DNA damage, such as adenine, adenosine, niacinamide, and uracil, were identified in both the Control and PS groups (Figure 2H).
In summary, significant differences were observed in the metabolic profiles of sperm exposed to polystyrene. These metabolic alterations in sperm may influence early embryonic development and disrupt gene expression in pre-implantation embryos.
Polystyrene exposure in male mice disrupts testicular gene expression and sperm metabolism, prompting further examination of its impact on sperm quality, including the detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS), motility and fertilization capacity. Computer-assisted sperm analysis (CASA) revealed a significant decrease in sperm motility, aligning with prior studies on the effects of microplastics on male reproduction (Contino et al., 2023; Hu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). We found that male mice exposed to polystyrene had increased ROS levels in sperm, which may lead to oxidative stress in the sperm (Supplementary Figures S2A, B). Meanwhile, progressive motility of sperm from polystyrene-exposed mice decreased by over 20%, while the proportion of static sperm increased markedly (Figure 3A). Fertilization capacity was assessed through IVF using sperm and oocytes from 8-10-week-old female C57BL/6 mice, revealing a significant reduction in the fertilizing ability of polystyrene-exposed sperm (Figure 3B). Furthermore, when fertilized eggs were cultured to the blastocyst stage, the blastocyst formation rate in the polystyrene-exposed group was also significantly reduced (Figures 3C, D).
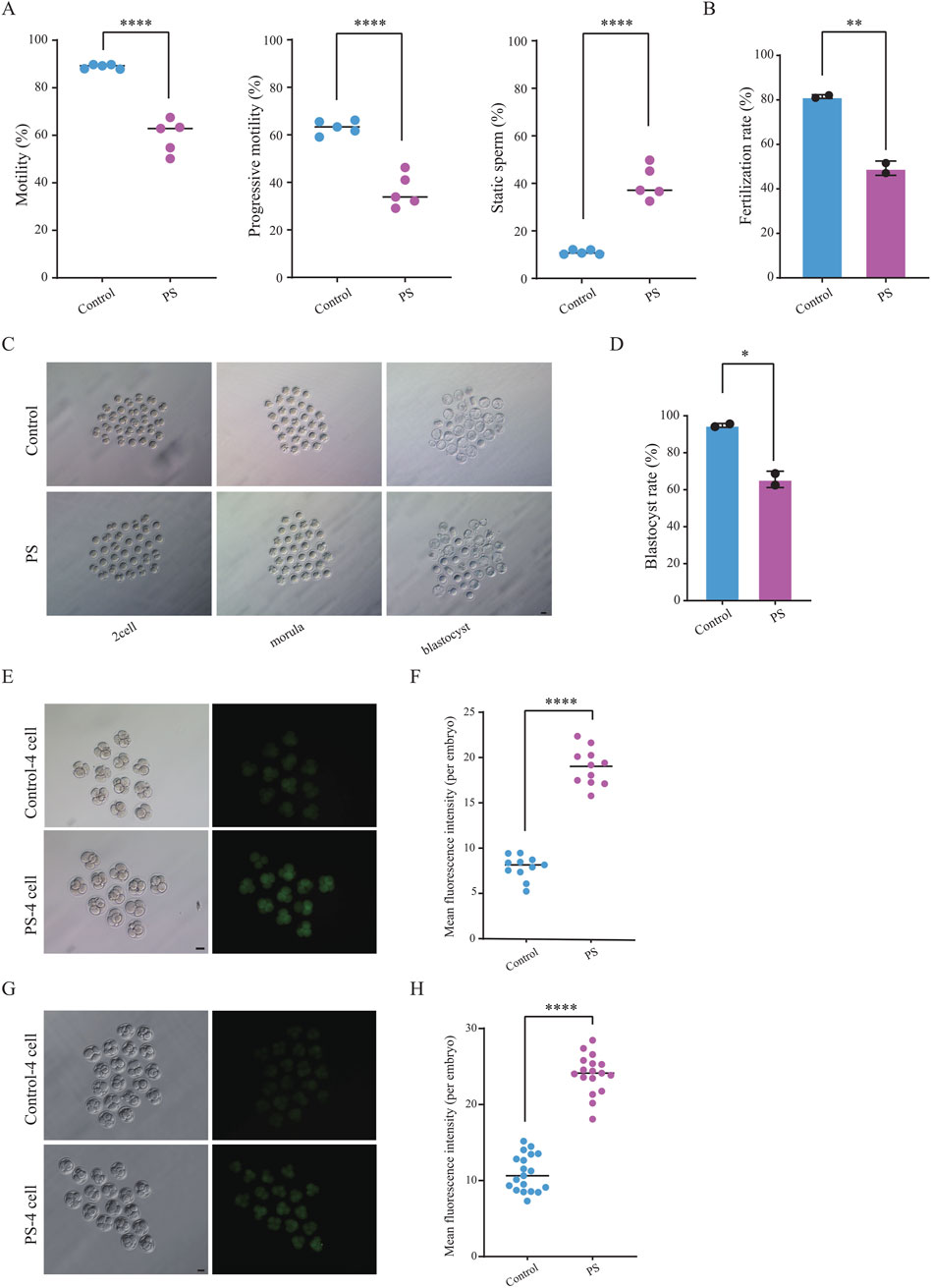
Figure 3. Detection of sperm motility and embryonic reactive oxygen species (ROS) in male mice exposed to polystyrene (A). Total motility, progressive motility, and proportion of static sperm in male mice from the Control and PS groups (Unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001). (B) Bar plot showing sperm fertilization capacity testing for the Control and PS groups (Unpaired t-test, **P < 0.01). (C) Representative images of pre-implantation development in the Control and PS groups (scale bar = 50 µm). (D) Bar plot showing the blastocyst ratio in the Control and PS groups (Unpaired t-test, *p-value < 0.05). (E, F) Bright-field and ROS fluorescent images of four-cell embryos (n = 11 in each group) (E). ROS fluorescence intensity quantified using ImageJ software (F) (scale bar = 50 μm; Unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001). (G-H). TUNEL staining during the four-cell stage (n = 19 in Control group and n = 17 in PS group) (G). Fluorescence intensity quantified using ImageJ software (H) (scale bar = 50 μm; Unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001).
Disruption of metabolic pathways related to DNA damage repair was identified in sperm from polystyrene-exposed mice through untargeted metabolomics. To further investigate potential oxidative DNA damage, ROS levels were measured in 4-cell embryos (Figure 3E). The results revealed an increased ROS fluorescence signal intensity in sperm-derived 4-cell embryos exposed to polystyrene (Figure 3F). In addition, we also performed TUNEL staining on 4-cell embryos and found that the fluorescence signal intensity was higher in the exposed group, indicating the presence of significant apoptosis and DNA damage in the embryos (Figures 3G, H).
Overall, polystyrene exposure in male mice impaired sperm motility and fertilization capacity, while also hindering pre-implantation embryo development and elevating oxidative damage. These results suggest that polystyrene exposure in male mice can adversely affect early embryo development via sperm-mediated pathways.
Polystyrene exposure in male mice not only disrupted pre-implantation embryo development but also led to an increase in ROS in the embryos, potentially contributing to oxidative stress and DNA damage. To further explore this, Smart-seq2 sequencing was performed on sperm-derived late-stage 2-cell embryos from the polystyrene and Control groups (Figure 4A). Correlation analysis demonstrated high biological replication in the 2-cell RNA-seq data (Figure 4B). A total of 426 differentially expressed genes were identified, with 213 upregulated in the sperm-derived 2-cell transcriptome of polystyrene-exposed male mice (Figures 4C, D; Supplementary Table S3). Gene ontology analysis revealed that the upregulated genes were enriched in processes such as methylation, chromatin remodeling, protein ubiquitination, innate immune response, apoptosis and androgen metabolism. Conversely, downregulated genes were associated with stem cell population maintenance, embryonic development, positive regulation of nuclear protein export, lipopolysaccharide response, and negative regulation of epithelial apoptosis (Figures 4E, F). RT-qPCR further confirmed significant gene expression disturbances in 2-cell embryos derived from sperm exposed to polystyrene. Notably, genes involved in apoptosis (Akap1 and Rps3), androgen metabolism (Tiparp), stem cell maintenance (Smarca2 and Dpf2), and embryonic development (Csk1b) exhibited altered expression (Figure 4G; Supplementary Table S4).
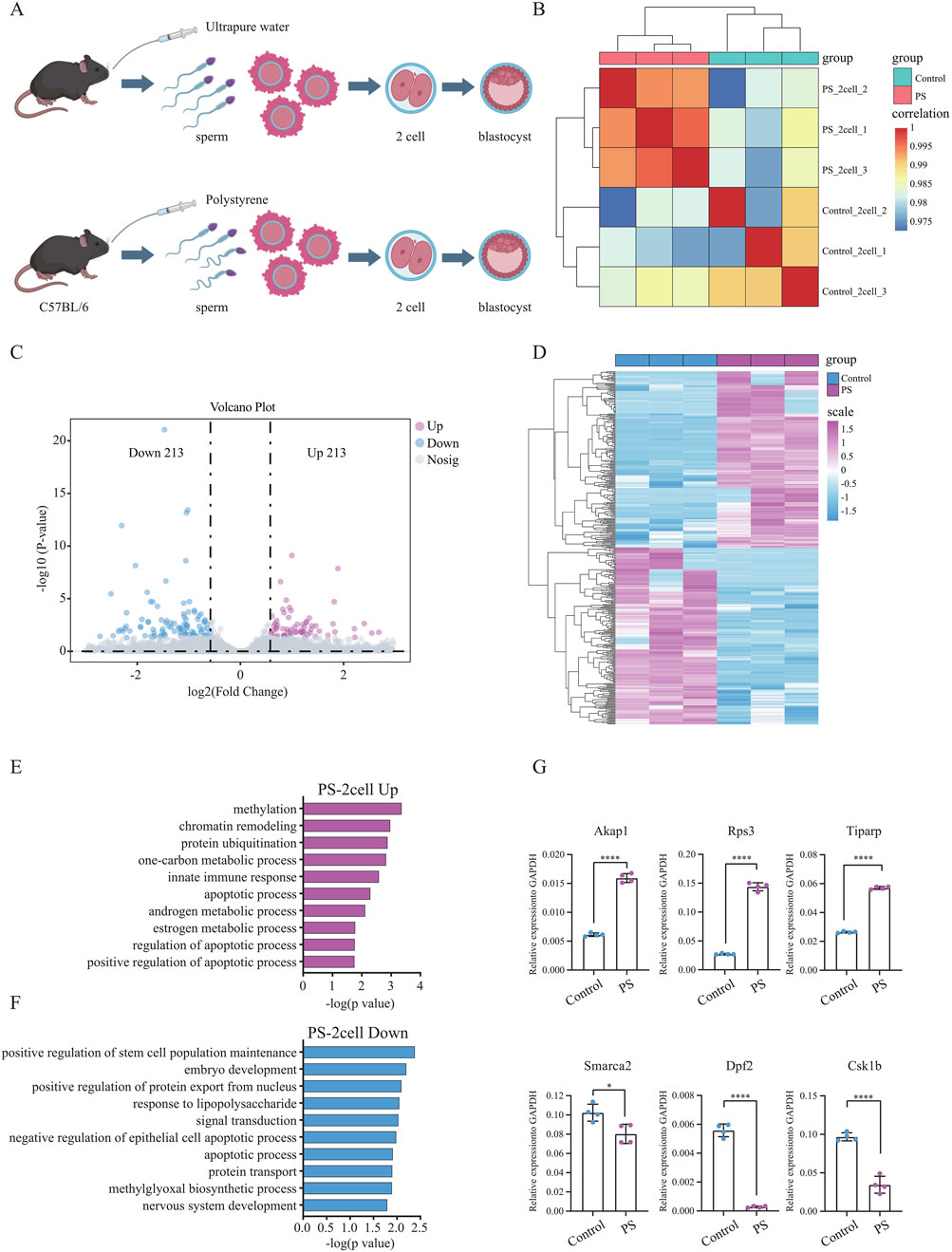
Figure 4. Differential gene expression and functional analysis of sperm-derived 2-cell embryos in male mice exposed to polystyrene (A). Schematic diagram of sperm-derived embryos in male mice exposed to ultrapure water (Control) and polystyrene (PS). (B) Correlation analysis of transcriptome data from 2-cell embryos between the Control and PS groups. (C) Volcano plot analysis of differentially expressed genes between the Control and PS groups in 2-cell embryos. (D) Heatmap showing the expression of 426 differential genes in 2-cell embryos from the Control and PS groups. (E, F) Gene ontology analysis of upregulated genes (log2 FC > 0.58 and p-value < 0.05) (E) and downregulated genes (log2 FC < −0.58 and p-value < 0.05) (F) in 2-cell embryos from the Control and PS groups. (G) RT-qPCR results for Akap1, Rps3, Tiparp, Smarca2, Dpf2, and Csk1b in 2-cell embryos from the Control and PS groups. (Unpaired t-test, ****p-value < 0.0001; *p-value < 0.05).
In summary, the expression of genes in sperm-derived early embryos from male mice exposed to polystyrene was significantly disturbed, which may contribute to reduced pre-implantation embryo development. These findings provide important insights for understanding how polystyrene exposure affects the transition from sperm to embryo.
Recent studies have increasingly highlighted the impact of microplastics, such as polystyrene, on living organisms. Exposure to polystyrene, in particular, has been shown to adversely affect the reproductive health of offspring (Xu K. et al., 2024; Xue et al., 2024). In male mice, polystyrene exposure leads to significant reductions in sperm count and motility, alongside a marked increase in sperm deformity rate (Wen et al., 2023; Xie et al., 2020). Previous research indicates that exposure to microplastics decreases the activity of key testicular metabolic enzymes, including succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and reduces serum testosterone levels (Zhu et al., 2014). However, the effects of polystyrene exposure on sperm metabolism remain poorly understood. Notably, significant metabolic disruptions were observed in the sperm of polystyrene-exposed male mice, particularly in pathways related to glycerophospholipid metabolism, nucleic acid metabolism, innate immune sensing and DNA damage repair.
Unlike female mice, the effects of polystyrene exposure on the offspring of male mice remain relatively underexplored (Chen J. et al., 2024; Chen X. et al., 2024; Dou et al., 2024). Polystyrene microplastics disrupt maternal-fetal immune balance and induce reproductive toxicity in pregnant mice (Hu et al., 2021). Exposure to polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs) during pregnancy can impair endometrial decidualization in the parental generation, alter pregnancy outcomes, and compromise endometrial decidualization in the offspring. Notably, the levels of alkyl-phosphatidylcholine, vinylphosphatidylcholine, and vinylphosphatidylethanolamine in the liver and plasma of male offspring exposed to polystyrene were significantly elevated. Lipid metabolism disruption also displays dose-dependent, gender-specific and tissue-specific patterns (Deng et al., 2022).
Glycerophospholipids possess potent antioxidant properties, capable of neutralizing free radicals, slowing cellular aging and enhancing immune function (Gomes et al., 2016; Mata-Campuzano et al., 2015). In this study, untargeted metabolomics analysis was employed, with a particular focus on the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway. In the following research, we will conduct targeted metabolism experiments for further investigation. Previous research indicates that both phospholipid synthesis and DNA damage repair are intricately linked to cell cycle progression, however, their potential interactions warrant further investigation (Mingyao et al., 2024; Ovejero et al., 2022).
Exposure to polystyrene significantly impacts early embryonic development and gene expression in male mouse sperm, which is essential for understanding the transgenerational effects of polystyrene. Our findings indicate that polystyrene exposure in male mice elevates ROS levels in embryos, overwhelming the cellular antioxidant system and inducing oxidative stress (Schieber and Chandel, 2014; Xu X. et al., 2024). Additionally, reduced pre-implantation embryo development in male mice exposed to polystyrene suggests biological disruptions, such as DNA damage in the embryos. It remains unclear whether polystyrene exposure also induces epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation and histone modifications in sperm, which may further alter epigenetic profiles in embryos and disrupt gene expression (Dou et al., 2024; Malinowska et al., 2024).
This study provides an untargeted metabolomics analysis of sperm from male mice exposed to polystyrene, examining its impact on sperm metabolic profiles and investigating its influence on pre-implantation embryo development and gene expression. These findings offer new insights for future research on the effects of polystyrene exposure on offspring. However, this study also has certain limitations, when studying the effects of exposure to polystyrene on male reproductive health, especially the effects of sperm on early embryos, we should also pay attention to the fact that sperm maturation in the epididymis also requires a certain amount of time, rather than just considering the exposure of a 35 days spermatogenic cycle. Next, we will conduct controls at different time periods, such as 20, 40 and 60 days, to study the effects of polystyrene on male reproductive health. In addition, we need more precise research methods to explore how specific genetic or epigenetic changes in sperm caused by exposure to polystyrene affect offspring development.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
The animal study was approved by the Tongji University Experimental Animal Ethics Committee (TJBG14924101). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
YL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. FH: Writing–review and editing. HL: Writing–review and editing. WL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82271632).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2025.1562331/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 | Detection of testicular weight and body weight of male mice exposed to polystyrene. (A) Detection of testicular weight and the ratio of testis weight to body weight in Control and PS groups of male mice (n = 5 per group). (Unpair t-test, ns represents non-significant). (B) H&E staining of the transverse section of testicular tissue in Control and PS groups of male mice (n = 3 per group).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2 | Intracellular ROS in mouse sperm analysed by fluorescence microscopy using the DCFH-DA probe in different treatment groups. (A) Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in sperm of Control group mice (n = 3). (B) Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in sperm of PS group mice (n = 3).
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE S1 | Differential gene sets in the testicular tissue of male mice exposed to polystyrene and ultrapure water.
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE S2 | Differential metabolites in the sperm of male mice exposed to polystyrene and ultrapure water.
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE S3 | Differential gene sets in sperm-derived 2-cell embryos exposed to polystyrene and ultrapure water.
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE S4 | Sequences of RT-qPCR primers.
Camerano Spelta Rapini, C., Di Berardino, C., Peserico, A., Capacchietti, G., and Barboni, B. (2024). Can mammalian reproductive health withstand massive exposure to polystyrene micro- and nanoplastic derivatives? A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (22), 12166. doi:10.3390/ijms252212166
Chen, G., Xiong, S., Jing, Q., van Gestel, C. A. M., van Straalen, N. M., Roelofs, D., et al. (2023). Maternal exposure to polystyrene nanoparticles retarded fetal growth and triggered metabolic disorders of placenta and fetus in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 854, 158666. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158666
Chen, J., Yan, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Wei, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2024). Maternal exposure to nanopolystyrene induces neurotoxicity in offspring through P53-mediated ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in the rat hippocampus. J. Nanobiotechnology 22 (1), 651. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02911-9
Chen, X., Huang, S., Wang, L., Liu, K., and Wu, H. (2024). Maternal exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces sex-specific cardiotoxicity in offspring mice. Heliyon 10 (20), e39139. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39139
Contino, M., Ferruggia, G., Indelicato, S., Pecoraro, R., Scalisi, E. M., Salvaggio, A., et al. (2023). Polystyrene nanoplastics in aquatic microenvironments affect sperm metabolism and fertilization of Mytilus galloprovincialis (lamark, 1819). Toxics 11 (11), 924. doi:10.3390/toxics11110924
Deng, Y., Chen, H., Huang, Y., Wang, Q., Chen, W., and Chen, D. (2022). Polystyrene microplastics affect the reproductive performance of male mice and lipid homeostasis in their offspring. Environ. Sci. and Technol. Lett. 9 (9), 752–757. doi:10.1021/acs.estlett.2c00262
Dou, Y., Zhang, M., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., Feng, L., Hu, J., et al. (2024). Lactating exposure to microplastics at the dose of infants ingested during artificial feeding induced reproductive toxicity in female mice and their offspring. Sci. Total Environ. 949, 174972. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174972
Dusza, H. M., van Boxel, J., van Duursen, M. B. M., Forsberg, M. M., Legler, J., and Vahakangas, K. H. (2023). Experimental human placental models for studying uptake, transport and toxicity of micro- and nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 860, 160403. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160403
Frias, J., and Nash, R. (2019). Microplastics: finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 138, 145–147. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.022
Gagne, F. (2019). Detection of polystyrene nanoplastics in biological tissues with a fluorescent molecular rotor probe. J. Xenobiot. 9 (1), 8147. doi:10.4081/xeno.2019.8147
Gao, Y., Wang, Z., Long, Y., Yang, L., Jiang, Y., Ding, D., et al. (2024). Unveiling the roles of Sertoli cells lineage differentiation in reproductive development and disorders: a review. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 15, 1357594. doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1357594
Geyer, R., Jambeck, J. R., and Law, K. L. (2017). Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 3 (7), e1700782. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Gomes, P. J., Goncalves da Silva, A. M., Ribeiro, P. A., Oliveira, O. N., and Raposo, M. (2016). Radiation damage on Langmuir monolayers of the anionic 1.2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phospho-rac-(1-glycerol)] (sodium salt)(DPPG) phospholipid at the air-DNA solution interface. Mater Sci. Eng. C Mater Biol. Appl. 58, 576–579. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.09.017
He, Y., and Yin, R. (2024). The reproductive and transgenerational toxicity of microplastics and nanoplastics: a threat to mammalian fertility in both sexes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 44 (1), 66–85. doi:10.1002/jat.4510
Hu, J., Qin, X., Zhang, J., Zhu, Y., Zeng, W., Lin, Y., et al. (2021). Polystyrene microplastics disturb maternal-fetal immune balance and cause reproductive toxicity in pregnant mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 106, 42–50. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.10.002
Hu, Y., Shen, M., Wang, C., Huang, Q., Li, R., Dorj, G., et al. (2024). A meta-analysis-based adverse outcome pathway for the male reproductive toxicity induced by microplastics and nanoplastics in mammals. J. Hazard Mater 465, 133375. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.133375
Huang da, W., Sherman, B. T., and Lempicki, R. A. (2009). Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 4 (1), 44–57. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Kim, D., Paggi, J. M., Park, C., Bennett, C., and Salzberg, S. L. (2019). Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 37 (8), 907–915. doi:10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Liao, Y., Smyth, G. K., and Shi, W. (2014). featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30 (7), 923–930. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656
Love, M. I., Huber, W., and Anders, S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15 (12), 550. doi:10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Makela, J. A., Koskenniemi, J. J., Virtanen, H. E., and Toppari, J. (2019). Testis development. Endocr. Rev. 40 (4), 857–905. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00140
Malinowska, K., Tarhonska, K., Foksinski, M., Sicinska, P., Jablonska, E., Reszka, E., et al. (2024). Impact of short-term exposure to non-functionalized polystyrene nanoparticles on DNA methylation and gene expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (23), 12786. doi:10.3390/ijms252312786
Mata-Campuzano, M., Alvarez-Rodriguez, M., Alvarez, M., Tamayo-Canul, J., Anel, L., de Paz, P., et al. (2015). Post-thawing quality and incubation resilience of cryopreserved ram spermatozoa are affected by antioxidant supplementation and choice of extender. Theriogenology 83 (4), 520–528. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.10.018
Mingyao, E., Zhang, Z., Ji, P., Liu, Q., Qi, H., Hou, T., et al. (2024). A novel mechanism of major ginsenosides from Panax ginseng against multiple organ aging in middle-aged mice: phosphatidylcholine-myo-inositol metabolism based on metabolomic analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 719, 150027. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150027
Ovejero, S., Soulet, C., Kumanski, S., and Moriel-Carretero, M. (2022). Coordination between phospholipid pools and DNA damage sensing. Biol. Cell 114 (8), 211–219. doi:10.1111/boc.202200007
Pang, Z., Lu, Y., Zhou, G., Hui, F., Xu, L., Viau, C., et al. (2024). MetaboAnalyst 6.0: towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 52 (W1), W398–W406. doi:10.1093/nar/gkae253
Saitou, M., and Hayashi, K. (2021). Mammalian in vitro gametogenesis. Science 374 (6563), eaaz6830. doi:10.1126/science.aaz6830
Schieber, M., and Chandel, N. S. (2014). ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 24 (10), R453–R462. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Shumate, A., Wong, B., Pertea, G., and Pertea, M. (2022). Improved transcriptome assembly using a hybrid of long and short reads with StringTie. PLoS Comput. Biol. 18 (6), e1009730. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009730
Tanveer, M., Mansha, N., Nimra, A., Khawar, M. B., Afzal, A., Afzal, H., et al. (2023). Microplastics: unraveling the signaling pathways involved in reproductive health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 30 (42), 95077–95085. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29273-3
Wang, Q., Chi, F., Liu, Y., Chang, Q., Chen, S., Kong, P., et al. (2024). Polyethylene microplastic exposure adversely affects oocyte quality in human and mouse. Environ. Int. 195, 109236. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2024.109236
Wen, S., Chen, Y., Tang, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, S., You, T., et al. (2023). Male reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: study on the endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 172, 113577. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2022.113577
Xie, X., Deng, T., Duan, J., Xie, J., Yuan, J., and Chen, M. (2020). Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 190, 110133. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110133
Xu, K., Wang, Y., Gao, X., Wei, Z., Han, Q., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Polystyrene microplastics and di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate co-exposure: implications for female reproductive health. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol 22, 100471. doi:10.1016/j.ese.2024.100471
Xu, W., Yuan, Y., Tian, Y., Cheng, C., Chen, Y., Zeng, L., et al. (2023). Oral exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics reduced male fertility and even caused male infertility by inducing testicular and sperm toxicities in mice. J. Hazard Mater 454, 131470. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131470
Xu, X., Wang, Z., Lv, L., Liu, C., Wang, L., Sun, Y. N., et al. (2024). Molecular regulation of DNA damage and repair in female infertility: a systematic review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 22 (1), 103. doi:10.1186/s12958-024-01273-z
Xue, Y., Cheng, X., Ma, Z. Q., Wang, H. P., Zhou, C., Li, J., et al. (2024). Polystyrene nanoplastics induce apoptosis, autophagy, and steroidogenesis disruption in granulosa cells to reduce oocyte quality and fertility by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway in female mice. J. Nanobiotechnology 22 (1), 460. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02735-7
Zhang, C., Zhang, G., Sun, K., Ren, J., Zhou, J., Liu, X., et al. (2024). Association of mixed exposure to microplastics with sperm dysfunction: a multi-site study in China. EBioMedicine 108, 105369. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105369
Zhao, T., Shen, L., Ye, X., Bai, G., Liao, C., Chen, Z., et al. (2023). Prenatal and postnatal exposure to polystyrene microplastics induces testis developmental disorder and affects male fertility in mice. J. Hazard Mater 445, 130544. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130544
Keywords: polystyrene, immune-inflammatory response, sperm motility, metabolic disruptions, DNA repair, embryonic development
Citation: Liu Y, Hao F, Liang H, Liu W and Guo Y (2025) Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics impairs sperm metabolism and pre-implantation embryo development in mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1562331. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1562331
Received: 17 January 2025; Accepted: 12 February 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Fa Ren, Shandong Second Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Massimo Venditti, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Liu, Hao, Liang, Liu and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenqiang Liu, bGl1d2VucWlhbmdAdG9uZ2ppLmVkdS5jbg==; Yi Guo, Z3lfZ3VveWlAdG9uZ2ppLmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.