
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 07 April 2025
Sec. Cell Death and Survival
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1546582
This article is a correction to:
Mitochondrial-Derived Vesicles Protect Cardiomyocytes Against Hypoxic Damage
 Binghu Li
Binghu Li Hongliang Zhao
Hongliang Zhao Yue Wu
Yue Wu Yu Zhu
Yu Zhu Jie Zhang
Jie Zhang Guangming Yang
Guangming Yang Qingguang Yan
Qingguang Yan Junxia Li
Junxia Li Tao Li*
Tao Li* Liangming Liu*
Liangming Liu*A Corrigendum on
Mitochondrial-derived vesicles protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxic damage
by Li B, Zhao H, Wu Y, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Yang G, Yan Q, Li J, Li T and Liu L (2020). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8:214. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00214
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6 as published. There was an error in pasting the figure of DAPI of the ischemia group in Figure 6B. The corrected Figure 6 and its caption “Effect of exogenous MDVs on myocardial injury in general ischemic animals. (A) Transmission electron microscopy images of the heart tissues from the general ischemic rats. (B and C) TUNEL staining of the cardiac tissues (n = 3); P values were estimated by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; * P < 0.05 versus control, # P < 0.05 versus ischemia. (D–F) Statistical histogram of TnT, LDH, and CK-MB levels in each group (n = 6 per group); P values were estimated by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; * P < 0.05 versus control.” appear below.
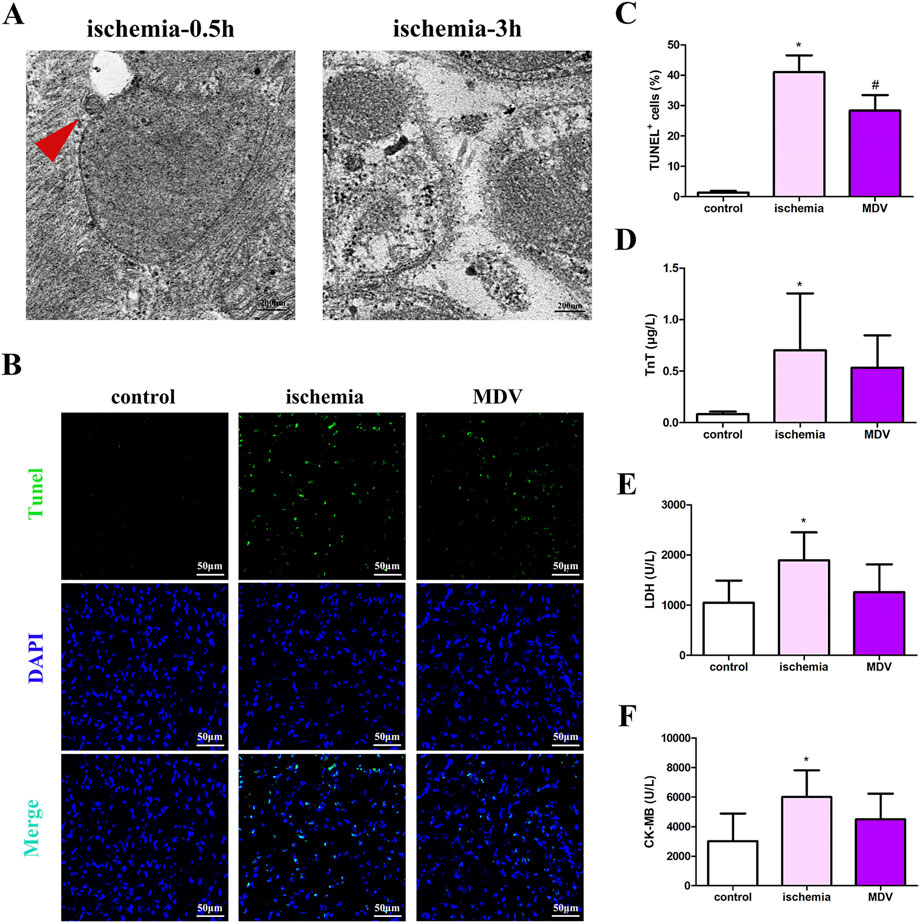
Figure 6. Effect of exogenous MDVs on myocardial injury in general ischemic animals. (A) Transmission electron microscopy images of the heart tissues from the general ischemic rats. (B, C) TUNEL staining of the cardiac tissues (n = 3); P values were estimated by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; * P < 0.05 versus control, # P < 0.05 versus ischemia. (D–F) Statistical histogram of TnT, LDH, and CK-MB levels in each group (n = 6 per group); P values were estimated by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; * P < 0.05 versus control.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: mitochondrial-derived vesicles, myocardial ischemia, mitochondrial, hypoxia, apoptosis
Citation: Li B, Zhao H, Wu Y, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Yang G, Yan Q, Li J, Li T and Liu L (2025) Corrigendum: Mitochondrial-derived vesicles protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxic damage. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1546582. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1546582
Received: 17 December 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 07 April 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Jochen H. M. Prehn, Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland, IrelandCopyright © 2025 Li, Zhao, Wu, Zhu, Zhang, Yang, Yan, Li, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Li, bHQyMDAxMzJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Liangming Liu, bGlhbmdtaW5nbGl1QHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.