
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 21 February 2025
Sec. Cancer Cell Biology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1536320
Introduction: Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most malignant of the astrocytomas, primarily involving the cerebral hemispheres and cerebral cortex. It is one of the fatal refractory solid tumors with a 5-year survival rate of only 5% in adults. Cells in biological tissues are subjected to mechanical forces, including hydrostatic pressure, shear stress, compression and tension. Cells can convert mechanomechanical signals into biological or electrical signals, a process known as mechanical signaling. Piezo1 channels, members of the Piezo family of mechanosensitive ion channels, can be directly activated by mechanical stimuli alone, mediating mechanosensitive cation currents that activate subsequent signaling pathways. Studies have shown that Piezo1 is largely unexpressed in normal brain tissues but is expressed at high levels in glioblastoma and can significantly contribute to glioblastoma development and progression, but its role in the pathogenesis of glioblastoma remains unclear.
Methods: We reviewed the relevant literature and data in six major databases including PubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL, Scopus, Web of Science and TCGA. Finally, a total of 126 papers were selected for review and analysis (Search terms include: glioblastoma, piezo1, biomechanical, targeted therapy, mechanomechanical, extracellular matrix, radiation therapy and more). The role of piezo1 in the development of glioblastoma was summarized.
Results: Piezo1 affects several fundamental pathophysiological processes in glioblastoma, such as tissue sclerosis, angiogenesis, energy supply, and immune cell infiltration, and can be used as an indicator of malignancy and prognosis in patients with glioblastoma, as well as a therapeutic target to control tumor progression.
Discussion: The pathological mechanism of piezo1 in glioblastoma is very complex, and the aberrant expression of piezo1 plays a very important role in the development of glioblastoma. Specific mechanistic studies focusing on Piezo1 will help us understand the mechanobiology of glioblastoma and help us develop new therapeutic approaches for glioblastoma patients.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most malignant type of glioblastoma featuring fast proliferation, strong invasion, and poor prognosis (Peng et al., 2018). Patients with GBM usually show a variety of clinical manifestations that are caused by dysfunction of affected areas of the brain, such as lethargy, apathy, blindness, seizures, and language changes (McKinnon et al., 2021). Besides, it often grows in the brain parenchyma in an invasive manner (Lah et al., 2020).
Cells in biological tissues are subject to mechanical forces, including hydrostatic pressure, shear stress, compression, and tension (Humphrey et al., 2014). In biological systems, tissue stiffness varies considerably between organs and between healthy and diseased states of the same organ (Kai et al., 2016). In some regions, solid tumor tissue is harder than its untransformed counterpart, e.g., normal brain tissue is usually less than 100 Pa, whereas human low to high-grade glioblastomas (LGG and HGG) have progressively stiffer tissues ranging from 100 to 104 Pa. This is due to the uncontrolled proliferation of cells in confined spaces, vascular hyper-permeability, insufficient lymphatic drainage, and increased deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) protein deposition increases. Miroshnikova et al. used atomic force microscopy to quantify the hardness of non-tumor glial proliferation as well as glial cell tissue with different levels of malignant transformation in frozen human brain biopsies. The results showed that glial tissues have the lowest ECM hardness (Young’s modulus, E; 10–180 Pa), which increases progressively with the level of malignancy (50-1,400 Pa for LGGs and 70-13,500 Pa for GBM). NanoString nCounter gene expression analysis of prognostic predictor gene clusters from human GBM tissue biopsies (aggressiveness was categorized on a scale of 1–10, with 1 indicating the most aggressive) indicated that there was a significant correlation between ECM hardness and prognosis of glioblastomas, with higher hardness being associated with a worse prognosis (Miroshnikova et al., 2016). Chauvet et al. used intraoperative shear wave elastography to measure the elasticity of tumors and surrounding tissues in patients undergoing brain tumor resection. The study showed that the mean elasticity of meningiomas, low-grade gliomas, high-grade gliomas, and brain metastases was 33.1 ± 5.9 kPa (3.3 ± 0.6 m/s), 23.7 ± 4.9 kPa (2.8 ± 0.6 m/s), 11.4 ± 3.6 kPa (1.9 ± 0.6 m/s), and 16.7 ± 2.5 kPa (2.4 ± 0.4 m/s), respectively, demonstrating that the greater the tissue stiffness, the higher the malignancy., again demonstrating that the greater the tissue hardness, the higher the malignancy of the glioma (Chauvet et al., 2016). Increased tissue stiffness leads to tumor progression by modulating proliferation, invasion, apoptosis evasion, drug resistance, angiogenesis, metabolism, and growth-promoting signaling pathways (Northey et al., 2017; Oudin and Weaver, 2016).
Cells can convert mechanomechanical signals into biological or electrical signals, a process known as biomechanical signal transduction. Mechanical signal transduction pathways are often classified into three categories: cell membrane receptors and surface mechanosensitive ion channels, the cytoskeleton (stress fibers, microtubules, etc.), and the nucleoskeleton and cytoskeletal linker complexes (Chaudhuri et al., 2018). Mechanosensitive ion channels are protein pores embedded in the plasma membrane. When the channel is stimulated to open by a mechanical signal, ions enter the cell from the pore in the direction of the electrochemical gradient, without the need for energy from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis.
Piezo1 channels are a member of the Piezo family of mechanosensitive ion channels, the first mechanically gated cation channel family identified and established in mammals, which can be directly activated by mechanical stimuli alone to mediate mechanosensitive cationic currents (Coste et al., 2012). Piezo1 is mainly found in tissue cells that are sensitive to mechanical tension stimuli, such as the lung, bladder, and skin, and is involved in the development of various tumors (Coste et al., 2010). Studies have shown that Piezo1 is largely unexpressed in normal brain tissue, but is expressed at high levels within glioblastomas. However, their role in the pathogenesis of GBM remains unclear. This paper aims to summarise the role of Piezo1 in the development of GBM and the role of Piezo1 in the treatment of GBM and to discuss the role of Piezo1 inhibitors in the treatment of GBM.
The Piezo1 gene is located on human chromosome 16p24.3 and consists of 51 exons, 2547 amino acids and 3 transcripts (Yu and Liao, 2021). In plan view, it looks like a propeller blade or a tricuspid with an ion-penetrating pore in the middle and a cap c-terminal extracellular structural domain (CED) at the top. When viewed from the side, the Piezo1 channels distributed across the cell membrane interact with the lipid membranes surrounding the channels to form a dome-like structure (Guo and MacKinnon, 2017; Lin et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2022) and use the aforementioned trimeric structure to mediate mechanical force transfer via a lever principle mechanism (Wang et al., 2018; Thien et al., 2024). The central ion-conducting pore and the three peripheral propeller-like blades are two important regions for the function of Piezo1 as a mechanosensitive channel. Two transmembrane (TM) helices, called outer helix-inner helix (OH - IH) pairs, the C-terminal extracellular structural domain (CED) and the intracellular C-terminal structural domain (CTD) trimer form the transmembrane channel of Piezo1. The CED is located on top of the central ion pore and has been shown to regulate channel inactivation kinetics as well regulating cation specificity for the channels (Wu et al., 2017; Zhao and Zlokovic, 2020). The transmembrane portion of the channel is lined by hydrophobic amino acid residues of IH, which contract in the middle of the membrane to form the neck of the channel (Zhao et al., 2018). The channel has two transmembrane gates surrounded by an OH and two adjacent IHs. Below the transmembrane channel, cations enter the cytoplasm through two intracellular channels, a 10 Å-long constriction site, and three lateral channels closed by side bolts, triggering subsequent different signaling pathways (Saotome et al., 2018; Geng et al., 2020). (Figure 1).
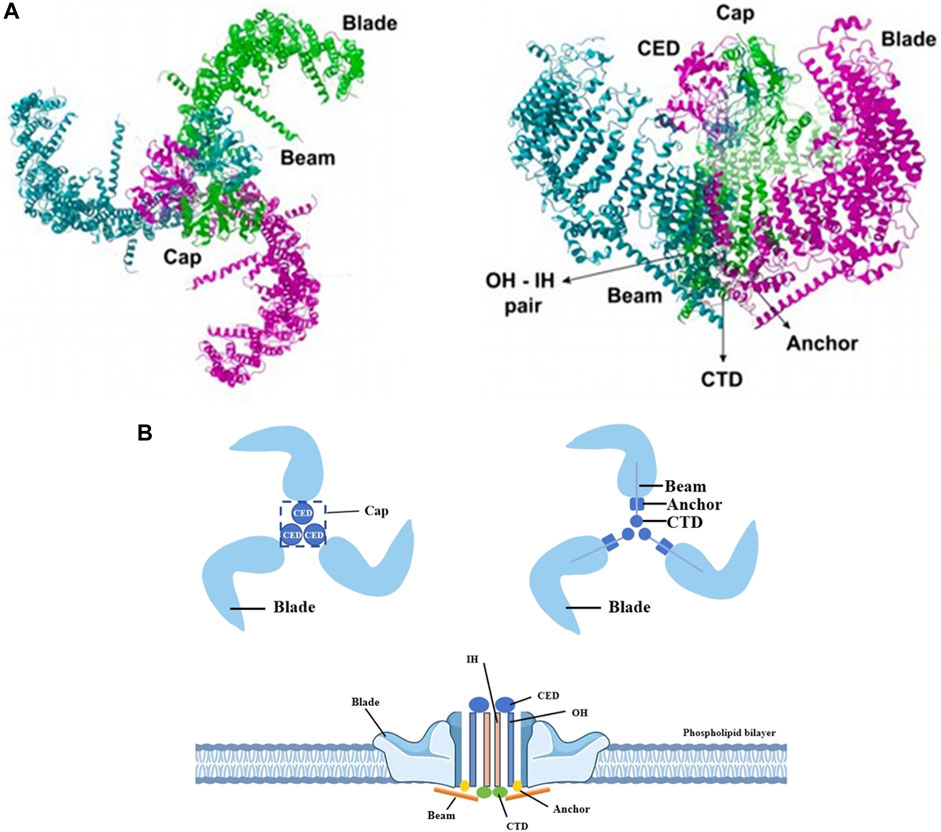
Figure 1. Different views of piezo1. (A) The Piezo1 protein exhibits a propeller-like three-bladed structure, with the 38 transmembrane helices of the three subunits coming together in the membrane plane to form a signature nanobowl-like structure. Adapted from (Thien et al., 2024). (B) Two transmembrane helices (OH - IH), the extracellular C-terminal structural domain (CED) and the intracellular C-terminal structural domain (CTD) trimer form the transmembrane channel of Piezo1. The CED, located between the OH and the IH, is the tip of the ion channel, and cations enter the channel through the open window (Cap) located directly above the membrane. The IH constricts in the middle of the membrane and forms the neck of the channel. When an external mechanical force stimulates the membrane, the stress causes the Piezo1 channel to change from a closed state to an open state, which induces Ca2+ influx into the interior of the cell and triggers different signaling pathways to follow.
The transmembrane pore is followed on the inner side of the cell by two ion-permeable pathways, including a 10-Å- long vertical constriction neck along the central axis and three lateral channels extending from the central pore through three lateral openings. It is now generally accepted that the lateral channels, rather than the vertical constriction necks, may serve as the primary intracellular cation conductance pathway. The fact that the outlets of the lateral channels and the central constriction neck are surrounded by negative and positive surface electrostatic potentials, respectively, further supports the structural suitability of the lateral channels for cation permeation.
One of the key issues for piezo1 channels is how to precisely determine and regulate their precise mechanical sensitivity and cation permeation properties. Each lateral channel has a lateral “plug”. This “plug” physically controls the on/off switching of the lateral ion channel, thus affecting both the ion permeation and the mechanical sensitivity of the piezo1. The lateral cation channels, the lateral plugs, the gating element and the central constrictor neck together form the “plug and latch” mechanism of piezo1, which coordinates the switching of the lateral channels using the plugs, which are connected to the central axis to form a lever-like mechanical transduction mechanism. The three lateral ion channels are equipped with three independently positioned lateral plugs that allow the piezo1 to move asymmetrically when external mechanical forces are applied asymmetrically to the force sensing vanes, and ultimately convert the conformational changes induced by peripheral vane tension into on/off switching of the ion channels inside the cell (Geng et al., 2020).
Piezo1 is embedded in lipid bilayers and is sensitive to local and global stresses in the bilayer. It is located in the endoplasmic reticulum, the cytoplasmic compartment, and the nuclear membrane close to the nucleus (Eisenhoffer et al., 2012; Gudipaty et al., 2017). Piezo1 enables cells to sense a variety of mechanical forces, including radial pressure, membrane stretch, compression, shear stress, matrix stiffness, ultrasound, and matrix pressure (Nourse and Pathak, 2017; Ridone et al., 2019). When a mechanical stimulus impinges on the cell membrane, the stress is distributed to all components including the bilayer, cytoskeleton (CSK), and extracellular matrix (ECM), which converge on the Piezo1 channel, inducing a change from a closed to an open state of the Piezo1 channel. The Piezo1 channel opens to allow Ca2+, K+, and Na+ plasma flow. Under mechanical stress, Piezo1 regulates a variety of functions such as protein synthesis, secretion, migration, proliferation, and apoptosis (Hong et al., 2023). Therefore, the main factors affecting Piezo1 gating include cell membrane tension and stiffness, cytoskeletal proteins, and other channels or proteins that interact with Piezo1.
Piezo1 channel protein is widely expressed in a variety of cells, including osteoblasts, immune cells, and cancer cells, among others. It is associated with a variety of mechanotransduction processes under different physiological and pathophysiological conditions. To emphasize the effectiveness of Piezo1 as a novel drug target for disease intervention, we summarize its physiological roles in different tissues (Table 1) and organs and its expression in different tumor tissues (Table 2).
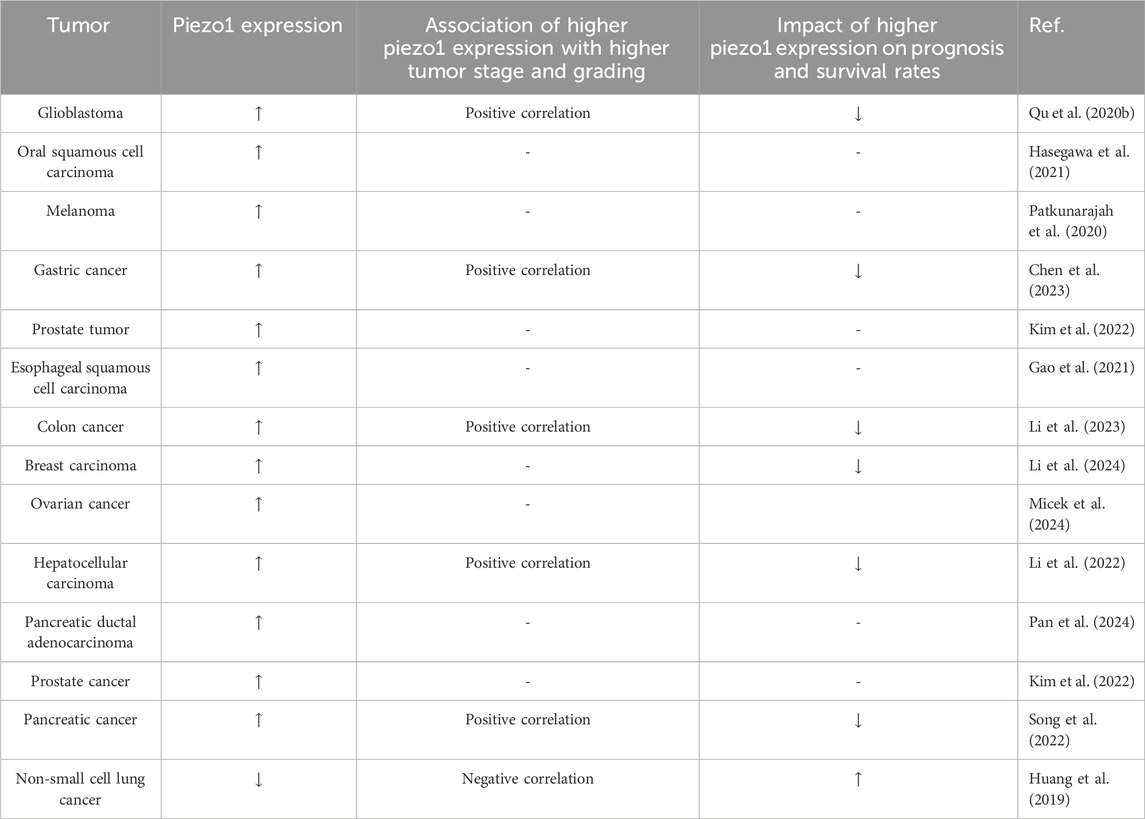
Table 2. Expression of piezo1 in different tumor tissues and its relationship with different tumor grades and prognosis.
Neurons and glial cells in the central nervous system exhibit significant mechanosensitivity and can sense mechanical stimuli from the surrounding environment and convert them into biochemical signals to regulate their function (Cox et al., 2016; Tortorella et al., 2022). Piezo1 is expressed in neuronal cells, microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neural stem cells, and is activated when neuronal cells are stimulated by external tensile forces, activated when neuronal cells are stimulated by external changes in stretch force, osmotic pressure, and matrix stiffness (Hong et al., 2023), and participates in cellular physiological activities in a variety of ways, such as increasing cytoplasmic Ca2+ signaling or initiating Ca2+ inward flow and affecting the levels of downstream Ca2+ signaling proteins involved in neuronal function, through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways (Liu et al., 2021).
It was demonstrated that all histological subtypes of gliomas, except oligodendrogliomas, showed Piezo1 overexpression compared to normal brain tissue and that the expression level of Piezo1 was positively correlated with World Health Organization (WHO) grade and histopathology (Chen et al., 2018). Piezo1 expression was more significantly upregulated in high-grade gliomas (WHO grade III and IV) than in low-grade gliomas (WHO grade II). Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation, CpG island methylation (G-CIMP) phenotype, and 1p/19q co-deletion are important molecular biomarkers in gliomas to guide prognosis and treatment. Piezo1 expression was significantly higher in the IDH1 wild-type group of gliomas than in the IDH1 mutant group and was elevated in the 1p/19q-non-co-deletion group. Gliomas with non-G-CIMP phenotypes had higher levels of Piezo1 expression compared to G-CIMP phenotypes. Grade II oligodendrogliomas with IDH1 mutation and 1p/19q co-deletion had the lowest level of Piezo1 protein expression. IDH mutation established a glioma hypermethylation phenotype, and the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) structural domains spanning the Piezo1 promoter and 8000 bp upstream of the Piezo1 transcriptional start site (TSS) were also hypermethylated in IDH mutant gliomas. The methylation status of these probes was negatively correlated with Piezo1 messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression. Thus more aggressive IDH wild-type gliomas are epigenetically more inclined to upregulate Piezo1 at the transcriptional level (Zhou et al., 2020).
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of multiple human glioblastoma datasets showed that patients with elevated Piezo1 expression had significantly worse overall survival (Figure 2). Multifactorial Cox regression analysis showed that Piezo1 overexpression was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival (OS) in glioblastoma patients (Qu et al., 2020b). These results suggest that Piezo1 can be used as a prognostic biomarker for glioblastoma patients in conjunction with molecular markers such as IDH wild-type, 1p/19q non-coding, and non-G-CIMP phenotypes.
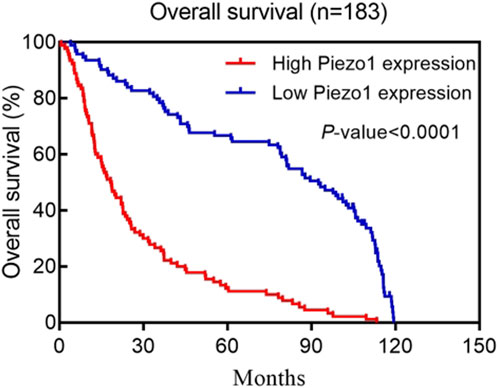
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier postoperative survival curve for patterns of patients with glioma and Piezo1 expression. Adapted from (Qu et al., 2020b).
Altered matrix stiffness in glioblastomas promotes elevated expression of piezo1 in glioblastomas, and Piezo1 is physically localized to the focal adhesions of glioblastoma cells, catalyzing the maturation and growth of focal adhesions through a force-dependent calcium signaling pathway. Piezo1 is one of the major ion channels conferring mechanosensitivity to GBM stem cells, and RNA of Piezo1 knockdown glioblastoma cell lines sequencing and dual-assay TCGA database analysis of Piezo1-related genes showed that Piezo1 is associated with activation of extracellular matrix (ECM), actin cytoskeleton remodeling and integrin adhesion signaling. In addition, Piezo1 expression transduces mechanical stimuli between glioblastoma cells, promoting tumorigenesis and progression (Hong et al., 2023). This finding could explain why the self-stiffening changes in glioblastomas are mainly caused by pressure gradients generated by the tumor itself rather than collagen deposition or cross-linking.
Piezo1 knockdown inhibited clonal growth of GBM cell lines. Tumor ball formation was blocked in GBM stem cells after Piezo1 knockdown. In vitro experiments, GBM cells were able to express Piezo1 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) in a doxycycline-dependent manner. Knockdown of Piezo1 expression by doxycycline-induced Piezo1 shRNA could be observed after treatment of glioblastoma model mice with doxycycline, which significantly suppressed GBM tumor growth and prolonged the survival time of the mice, suggesting that Piezo1 is critical for the maintenance and progression of glioblastomas once tumors form (Chen et al., 2018).
Regulated volume reduction (RVD) is an evolutionarily conserved process used by animal cells to restore normal volume when osmotic shock-induced swelling occurs. RVD plays an important role in a number of physiological processes, including the prevention of necrotic cell death induced by persistent cellular swelling, and is mediated primarily by the concerted activity of ion channels that mediate the passage of CI− and K+ ions (Miyazaki et al., 2007). Volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC), a heterodimeric protein that mediates swelling-activated CI− currents (ICl), has been identified during hypotonic cell swelling as the common and major channel responsible for CI− transport during RVD in almost all vertebrate cells. Tension-activated K+ channels, voltage-dependent K+ channels, and Ca2+-activated K+ (KCa) large-, medium-, and small-conductance channels (BK, IK, and SK, respectively) also play key roles in volume regulation in many cell types (Caramia et al., 2019).
In addition to CI− and K+ channels, nonselective Ca2+-permeable mechanosensitive channels (MSC) are also involved in cell volume regulation. During hypotonic cell swelling, MSCs sense changes in cell membrane tension and activate as a result. Their activation then triggers intracellular Ca2+ signaling, which in turn regulates various effectors. (Arniges et al., 2004).
In human glioblastoma cells, Piezo1 is the main component of MSCs activated by cell swelling in glioblastoma cells, and is also primarily responsible for mechanotransduction during glioblastoma cell volume regulation. Ca2+ signaling can be amplified by activation of the mechanism, which is activated by the influx of MSCs activated by hypertonic cell swelling to activate IK and BK channels and VRAC, which are essential for RVD development. The cascade mechanism of Piezo1 activation from Ca2+ influx to IK/BK channel activation, which ultimately regulates cell volume, is an important signaling pathway for Piezo1 regulation of glioblastoma cell spreading, migration, and death (Michelucci and Catacuzzeno, 2024).
In glioblastoma tissues, the infiltration of isolated tumor cells into the peritumoral parenchyma often culminates in tumor migration and invasion. This situation greatly limits the success of surgical resection. The invasion of GBM cells into the confined space of healthy brain parenchyma requires that they be able to sense the presence of external barriers and forces from the environment and adjust their size and shape accordingly to pass through. It has been shown that glioblastoma cells use piezo1 channels to sense mechanical stimuli from the tumor microenvironment and deform the cell membrane (stretching, indentation, invagination, etc.), inducing an increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ through, for example, activation of KCa channels and modulation of actin cytoskeletal polymerization, which allows for a change in the volume and shape of the cells required to invade healthy brain parenchyma.
KCa3.1 channels (also known as KCNN4, IK1 or SK4 channels) are moderately conductive calcium-activated potassium channels that regulate membrane potential and maintain calcium homeostasis. It has been shown to be involved in regulating GBM migration in response to C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL), serum and bradykinin in vitro. Studies have shown that the volume of invasive glioma cells is reduced by a maximum of 30%–35% compared to the volume of normal glial cells, which requires glioma cells to release all free unbound cytoplasmic water as well as K+ channels. Water permeably follows the release of ions through ion channels and cotransporter proteins, with a consequent change in cell volume. Inhibition of KCa3.1 channels retards cell invasion and migration (Watkins and Sontheimer, 2011).
Volume changes are critical in cell death, such as in apoptotic cell death, which is preceded by a contraction of cell volume called apoptotic volume decrease (AVD). In GBM cells, KCa channels are directly involved in AVD induced by the addition of astrocystin or TNF-α-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), which activate intrinsic or extrinsic pathways of apoptosis, respectively.
Ca2+ regulates glioblastoma maintenance, proliferation, migration, and cell cycle (Leclerc et al., 2016; Satir and Christensen, 2007). Most cancer cells obtain higher glucose utilization under aerobic conditions by producing ATP using glycolysis, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect (Vander Heiden et al., 2009). When intracellular glucose is deficient, free fatty acid oxidation replaces glucose for cellular energy and maintains intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and calcium homeostasis, Ca2+ is closely related to lipid metabolism (Li et al., 2018; Wires et al., 2017).
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is a non-invasive technique based on the combination of acoustic sensitizers and acoustic activation that disrupts the mitochondrial respiratory chain, leading to an increase in intracellular ROS levels and calcium overload, as well as inhibition of proliferation, invasion, and promotion of apoptosis in the biologically more aggressive grade IV glioblastomas (Chen et al., 2022). On the one hand, the mechanical force introduced by ultrasound activated the opening of the transient calcium channel Piezo1 on the membrane, maintained the open state of the Piezo1 channel by increasing the level of intracellular oxidative stress, prolonged the opening time of Piezo1, and increased the Ca2+ inward flow, which caused the cell to swell and activated the calcium overload pathway of the death mechanism. On the other hand, ROS generated by ultrasound-activated intracellular ultrasound sensitizers prolonged the opening time of Piezo1 and promoted Ca2+ entry into the cell to bind to lipid droplets to form complexes, thereby affecting lipid metabolism and preventing it from providing energy to glioblastoma cells, leading to cell death (Chen et al., 2022).
ROS generated by SDT activates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway (Chen et al., 2017), leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage, which sustains mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) channel activity and induces Ca2+ overload in the mitochondria, further aggravating the mitochondrial dysfunction, generating more ROS, and forming a vicious cycle that ends in death.
Peritumoral oedema is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis and recurrence of glioblastoma (Schoenegger et al., 2009). Peritumoral oedema can exacerbate neurological signs and clinical symptoms in glioblastoma patients, such as seizures, neurological deficits, and increased intracranial pressure, and can even lead to brain herniation. In addition, peritumoral oedema can affect tumor exposure during surgery and make surgical resection more difficult (Wang et al., 2011; Hou et al., 2013). A recent study reported a linear correlation between the expression level of Piezo1 and the severity of peritumoral oedema, with preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and corresponding Piezo1 immunohistochemical staining results in patients with different degrees of oedema. The higher the degree of oedema, the higher the Piezo1 expression (Qu et al., 2020a).
Peritumoral brain oedema (PTBE) includes vasogenic and cytotoxic oedema (Qu et al., 2020a; Liang et al., 2007). Vasogenic oedema is usually due to the degradation of tight junctions between endothelial cells (e.g., E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and b-catenin), which increases vascular permeability. Intravascular fluid then leaks out into the tissue space, further causing tissue oedema. The Piezo1 protein acts as a calcium channel to promote calcium ion influx into vascular endothelial cells, which in turn activates calcium-dependent calpain. Calpain further promotes the degradation of tight junctions between vascular endothelial cells and increases vascular permeability (Friedrich et al., 2019). High vascular permeability allows the extravasation of protein-rich fluid, leading to cerebral oedema. Extracellular cations enter neurons and glial cells through cation channels and accumulate intracellularly, while cation in-flow drives anion inflow, leading to increased intracellular osmotic pressure and entry of extracellular interstitial water molecules into the cells, resulting in cellular swelling and the formation of cytotoxic oedema occurs. Thus, inhibition of Piezo1 reduces clinical symptoms in glioblastoma patients and may be a therapeutic target for diseases involving blood-brain barrier collapse (Qu et al., 2020a).
The ROS-c-JunN-terminalkinase 1 (JNK1) and AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways are the main molecular mechanisms involved in glioblastoma cell survival, proliferation, motility, and differentiation, and the activation and activity of this signaling pathway is regulated by intracellular Ca2+ signaling (Mohamed et al., 2022; Park et al., 2008). Activation of cell cycle proteins D1 and cyclin-dependent kinases 4 (CDK4) and assembly of the cell cycle protein D1-CDK4 complex are essential for promoting the cell cycle transition from G1 to S phase. Highly expressed and aberrantly activated piezo1 in glioblastoma induces calcium inward flow. Large amounts of intracellular Ca2+ promote phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR, followed by activation of the cell cycle protein D1/CDK4 complex, which promotes cell survival, cell cycle progression, cell proliferation, and migration. In addition, since Akt stabilizes the mature cell cycle protein D1, piezo1-induced activation of Akt can promote the transition of tumor cells from G1 to S phase by activating the cell cycle protein D1. knockdown of Piezo1 may inactivate Akt, inhibit the activation of the cell cycle protein D1, and cause the cells to stagnate in the G1 phase (Han et al., 2019). Meanwhile, studies have shown that inhibition of Piezo1 further increases the expression of P-JNK1 (T183/Y185), promotes the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as c-Jun N-terminal kinase (cJUN), Bcl2-associated X (BAX), etc., inhibits tumor cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis of glioma cells (Liu et al., 2019).
Celastrol is a major active natural product extracted from the root bark of the traditional Chinese medicine Rehmannia glutinosa, which possesses a wide range of biological properties such as anti-tumor, immunosuppression, and weight loss (Liu et al., 2015; Hu et al., 2017b). Previous studies have shown that celastrol inhibits the growth of rat glioblastoma cells and human glioblastoma cells by inhibiting VEGFR expression, inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (Huang et al., 2008; Ge et al., 2010). Recent studies have shown that celastrol triggers apoptosis and autophagy by activating the ROS/JNK signaling pathway and blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, inducing G2/M phase block, and in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo experiments showed that celastrol increased the levels of cleaved Caspase-3, LC3B, and p-JNK, decreased the expression of p-AKT and mTOR, and inhibited the growth of tumors in a mouse glioblastoma in situ transplantation model. Naïve T cells are relatively quiescent until exposed to antigenic stimulation, they are metabolically quiescent and have low nutrient uptake, glycolytic rate and biosynthesis. Calcium store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) directs the proliferation of naïve T cells and adaptive immune responses by activating the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFA T) and the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway regulating the expression of glucose transporter proteins, glycolytic enzymes, and metabolic regulators (Vaeth et al., 2017). It was shown that both channels are regulated by intracellular Ca2+ signaling and were shown to be involved in the downstream mechanisms of Piezo1 (Liu et al., 2019).
Adhesion zones are hubs of cytoskeletal structures connecting the extracellular matrix to the intracellular skeleton, and they detect and transmit external mechanical forces. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a member of the adhesion zone proteins, is a key regulator of adhesion plaque dynamics and cytoskeletal remodeling, which exhibits high expression in a wide range of tumors and correlates with poor prognosis. FAK activation promotes tumor growth, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis through kinase-dependent (such as PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, P53 signaling pathway, RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway, YAP signaling pathway) and kinase-independent pathways (e.g., inhibition of T-cells, B-cells, and dendritic cells in the immune microenvironment. Promote myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF), and so on.) (Hu et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2011). Piezo1 interacts with FAK and signals to transcriptional co-activators through the pdz-binding motif (TAZ), leading to chromatin remodeling and changes in transcript levels (Hu et al., 2017a). Tumor tissue sclerosis provides a mechanistic microenvironment for the activation of Piezo1, which promotes adhesion plaque assembly and activates the β1-integrin-FAK signaling pathway, regulates cell proliferation and participates in extracellular matrix remodeling, which further regulates tissue stiffness and the stiffer environment further enhances Piezo1 expression, which increases mechanosensory and mechanotransduction capacities of tumor cells (Chen et al., 2018). Tumor cells thus form a feedback loop between Piezo1-dependent mechanosensing and abnormal tissue mechanics that interact and exacerbate disease. Integrin inhibitors (such as cilengitide or etanercept) have been tested in clinical trials. A randomized phase II trial demonstrated that cilengitide monotherapy was well tolerated and had modest anti-tumor activity against recurrent glioblastoma (Chen et al., 2018). However, a phase III trial demonstrated that cilengitide in combination with standard temozolomide radiotherapy did not have better efficacy than conventional treatment in glioblastoma, particularly in tumors with methylated O6 -methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoters, and the use of cilengitide as a subunit antagonist of the integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 is currently still controversial (Desgrosellier and Cheresh, 2010).
Yes-associated protein (YAP), an important co-transcription factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, plays an important role in mechanistic effects and the malignant proliferation and invasion of tumor cells. YAP/transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) is an effector of mechanistic signaling stimuli of matrix stiffness, stretch, and cell density. Mechanically relevant events such as altering mechanical stimuli inside and outside the cell, inoculating cells with different matrix stiffnesses, exposing cells to periodic stretching motions, and adjusting the degree of cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix can cause activation of YAP/TAZ in the nucleus (Zanconato et al., 2016). Abnormalities in YAP function have been closely associated with glioblastomagenesis, cellular proliferation, maintenance of tumor cell stemness, and invasive metastasis. Matrix stiffness can promote glioblastoma cell proliferation, EMT, and angiogenic mimicry formation through YAP, etc (Castellan et al., 2021). Piezo1 acts as a mechanosignal receptor, transmits extracellular matrix stiffness signals, and promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the nuclear expression and activity of YAP and subsequent TAZ activation. The study demonstrated that the piezo1 agonist Yoda1 significantly increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration in the cytoplasm of valvular mesenchymal stromal cells, whereas piezo1 knockdown reduced Ca2+ influx. Simultaneous immunofluorescence determination of YAP subcellular localization demonstrated that Yoda1 triggered YAP nuclear translocation, whereas piezo1 knockdown prevented cytoplasmic YAP from migrating to the nucleus. Using the calcium chelator1,2-bis (2-aminophenoxy)ethane-n,n,n0,n0-tetraacetic Acid Tetrakis (acetoxymethyl Ester) (BAPTA-AM) to reduce intracellular Ca2+ concentration, it was observed that BAPTA-AM eliminated Yoda1-induced intracellular Ca2+ accumulation and that BAPTA-AM inhibited Yoda1-induced YAP nuclear translocation, resulting in YAP being mostly localized in the cytoplasm. These results suggest that intracellular calcium accumulation is responsible for the YAP nuclear translocation induced by piezo1 (Zhong et al., 2023). Meanwhile, it was found that YAP was located downstream of β1-integrin-RhoA, which was an important effector of cellular response to matrix signals and mechanical stimuli (Zoi et al., 2022). Downregulation of the expression of Piezo1 had a significant effect on the β1-integrin/FAK pathway, and also significantly affected the nuclear localization and activity of YAP, suggesting that Piezo1 promotes the progression of glioblastoma invasion through the β1-integrin/FAK/YAP axis. invasion progression. It was shown that knockdown of the Piezo1 gene in glioblastomas using interfering shRNA lentiviral vectors resulted in a significant increase in the expression of the cellular epithelial marker E-cadherin, and a significant decrease in the expression of the mesenchymal markers waveform protein, SNAIL, and Slug. This suggests that the expression of Piezo1 regulates EMT, and maintains mesenchymal characteristics of glioblastoma cells. characteristics of glioblastoma cells (Figure 3).
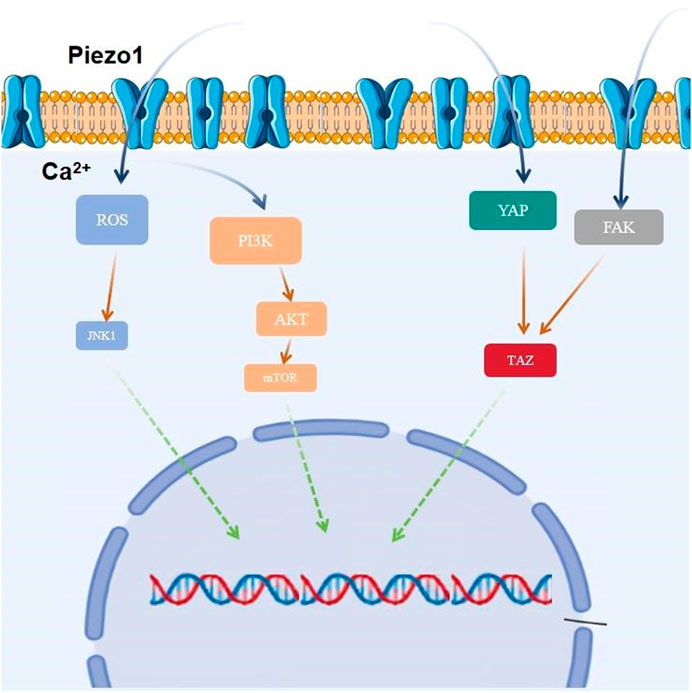
Figure 3. Piezo1 is involved in glioblastoma proliferation by regulating multiple signaling pathways.
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a diameter of 40–160 nm (average ∼100 nm) that mediate intercellular communication (Kalluri and LeBleu, 2020). Exosomes contain components such as proteins, lipids, DNA, mRNA, and non-coding RNAs, which play important roles in tumor angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance. Cyclic RNAs are a novel class of RNA transcripts produced by head-to-tail splicing of exons, which are produced and structured differently from mRNAs and therefore have unique cellular functions and potential biomedical applications (Memczak et al., 2013). Studies have shown that circular RNAs play an important regulatory role in glioblastoma. circZNF800 is a recently identified circular RNA that is highly expressed in glioblastoma stem cells. Studies have shown that glioblastoma stem cells secrete exosomes to enhance GBM cell proliferation and migration and inhibit apoptosis in glioblastoma. highly expressed circZNF800 regulates the expression of tumor-associated genes through the circRNA/PI3K/AKT axis and promotes glioblastoma progression (Zhang et al., 2024).
Micro RNAs (miRNAs) are small, highly conserved, small non-coding RNA molecules that control gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. It inhibits translation or promotes degradation of mRNAs by binding to complementary binding sites within the 3‘ untranslated region (3’UTR) of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs)(Bartel, 2004). miRNA-139 is located at 11q13.4 and exhibits anti-tumor and anti-metastatic activities in humans. It was shown that miR-139-5p was significantly reduced and negatively correlated with circZNF800 expression in GBM tissues compared with normal brain tissues. miR-139-5p inhibitor significantly promoted the expression of p-AKT protein, which further promoted the invasion of U251 and U87 cells and inhibited apoptosis of GBM cells, whereas the downregulation of circZNF800 eliminated this effect. Piezo1, a direct target of miR - 1395p, was regulated by circZNF800, and correlation analysis showed a positive correlation between the expression levels of circZNF800 and Piezo1 mRNA. In GBM cells, miR-139-5p significantly reduced the expression of Piezo1 mRNA. Whereas overexpression of circZNF800 significantly increased Piezo1 mRNA expression. CircZNF800 activated the Piezo1/AKT signaling pathway through phagocytosis of miR-139-5p and regulated proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of GBM cells (Zhang et al., 2024).
The extracellular matrix is the general scaffold that maintains the homeostasis of tissues and organs in vivo. It is also a key component of the cancer microenvironment that supports tumorigenesis. During tumor development and progression, a complex ECM network is established by fibrous or nonfibrous collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, glycoproteins, laminin, fibronectin, and other matrix proteins. The extracellular matrix not only provides nests for cancer cells and stromal cells, but also serves as a reservoir for growth factors and cytokines. In addition, the ECM interacts with stromal, parenchymal, precancerous or cancer cells to initiate different cell signaling cascades that stimulate cellular differentiation metastasis, autophagy, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell migration, invasion and metabolic reprogramming to promote cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and immune evasion. mechanical stimuli induced by both the ECM per se and by ECM sclerosis can activate cell membrane receptors and mechanosensors such as integrins, piezo1 and transient receptor potential ion channel subfamily V 4 (TRPV4), thereby modulating the malignant phenotype of tumor and stromal cells. In the glioblastoma tumor microenvironment, Piezo1 plays a particularly strong role in the ECM signaling pathway.
As a therapeutic target for glioblastomas, Piezo1 senses microenvironmental stiffness and converts mechanical stimuli into electrical and chemical signals that promote calcium influx. Elevated intracellular Ca2+ concentration catalyzes the assembly and maturation of focal adhesions and directly activates the integrin-focal adhesion pathway, which stimulates cell proliferation and regulates extracellular matrix remodeling, further increasing glioblastoma tissue stiffness in positive feedback. Enhanced stiffness between glioblastoma cells and the ECM microenvironment in turn regulates the activation of Piezo1.
Tumor cells and stromal cells can respond to mechanical signals induced by matrix sclerosis. ECM sclerosis typically induces mechanical perturbation of the lipid bilayer and activation of transient receptor potential (TRP) family channels and piezo1 channels, evolutionarily conserved ion channels that link ECM sclerosis-associated mechanical forces to cellular signaling pathways, particularly Ca2+ signaling in tumor and stromal cells. The cell surface receptor integrin is a mechanosignal transducer that can be activated by Piezo1 to promote cancer stem cells and drug resistance. Physical interactions between the extracellular structural domains of integrins and ECM proteins induce the assembly of cytoplasmic complexes consisting of scaffolding proteins (neuregulin, talin, stumpins, etc.), adhesion plaque kinase (FAK), Src, and PI3K/Akt, which orchestrate adhesion plaque and cytoskeletal assembly with stromal mechanical cues. The Rap1 GTPase also responds to the cytoplasmic signaling of integrins by stabilizing integrins and recruiting neuregulin to the adhesion plaque. Rap1 GTPase also responds to matrix sclerosis by stabilizing integrins and recruiting connexins to adhesion patches. In addition, Rho-associated coiled-coil kinases (ROCK) activation may be induced by ECM sclerosis, which then promotes integrin signaling, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation, and SNAIL stabilization. Integrins, integrin-linked kinase (ILK), SNAIL, and Src upregulate YAP expression and activation, thereby upregulating piezo1 expression.
Piezo1 senses the stiffness of the microenvironment and converts mechanical stimuli into electronic and chemical signals that promote calcium influx. Elevated intracellular Ca2+ concentrations catalyze the assembly and maturation of focal adhesions, and piezo1 activates the integrin-FAK pathway when the extracellular structural domains of integrins interact with ECM proteins such as collagen, laminin, and tendon proteins, whose cytoplasmic structural domains are complexed with scaffolding proteins, including ankyrin and stumpyrin, as well as kinases, such as adhesion patch kinase (FAK) and Src. Through integrin-taIin, talin-FAK interactions, multiple FAK molecules accumulate at the focal adhesion site, resulting in the activation of FAK by phosphorylation and its association with other signaling molecules. Upon activation of FAK, its phosphorylated Tyr397 binds to the Src family of kinases, causing the PAK/Src complex by forming the FAK/Src complex. Src complex and causes phosphorylation of Paxillin and clustered regularly interspaced shortpalindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated systems (Cas), which activate mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), a kinase downstream of the rat sarcoma (Ras) pathway, via the junction proteins cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinases (Crk) and growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2) to control lesion adhesion and cytoskeleton assembly, regulate extracellular matrix remodeling, and increase the stiffness of glioblastoma tissues. and activate integrin-dependent intracellular kinase signaling to regulate cell adhesion, motility, proliferation, survival and differentiation (Chen et al., 2018).
It was shown that GBM stem cells were cultured in polyacrylamide hydrogels at different stiffness levels (100-5,000 Pa) in the normal human brain, low-grade glioblastomas, and high-grade glioblastomas. The percentage of proliferatively active GBM stem cells and the total number of cells increased with increasing stiffness, while Piezo1 knockdown eliminated this stiffness-dependent tumor cell growth (Chen et al., 2018).
Furthermore, many signaling pathways such as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) family, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) family, and others are positively correlated with high expression of Piezo1 during the pathology of glioblastoma development. Various pathways such as the mitotic cell cycle, focal adhesion, ECM, and tumor cell response to mechanical stimuli were altered after the knockdown of Piezo1. In the CGGA and TCGA databases, Piezo1 expression was positively correlated with the genes TIMP1, MMP2, MMP9, MAPK13, MAPKAPK2, PIK3R6, PIK3CD, PLOD1, and AKT2, and was also positively correlated with the genes TIMP1, MMP2, MMP9, MAPK13, MAPKAPK2, PIK3R6, PIK3CD, PLOD1, and AKT2, as opposed to low-grade glioblastomas (WHO classification II and WHO classification III) in glioblastomas (WHO grade IV) had significantly higher expression of all ECM-related genes positively associated with Piezo1. Among these genes, TIMP1, MAPK13, MAPKAPK2, and MAPKAPK3 regulate cell proliferation, PLOD1, MMP14, ADAM9, and PLAU control ECM remodeling, MMP2, and MMP9 control tumor-associated tissue remodeling; PIK3CD is involved in immune response, AKT2 regulates tumorigenesis, FHL3 controls actin cytoskeleton, and TAZ regulates the mechanosensitive HIPPO signaling pathway (Figure 4). Taken together, these data suggest that Piezo1 not only delivers mechanical inputs to promote glioblastoma growth but also positively regulates the ECM and other mechanotransduction mechanisms in tumors (Zhou et al., 2020).
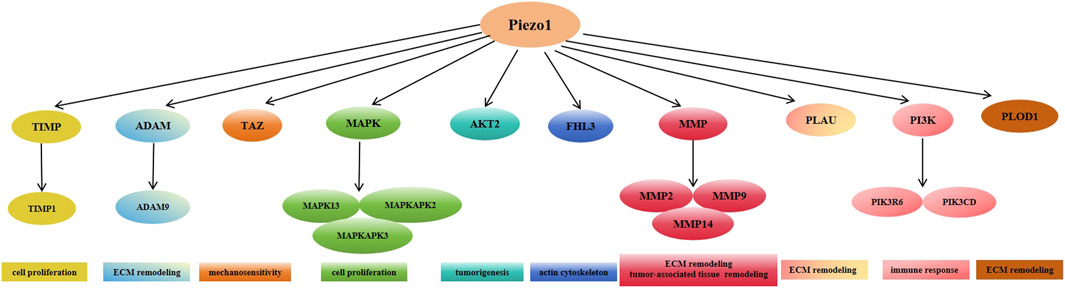
Figure 4. Expression of Piezo1 positively correlates with multiple genes mediating extracellular matrix remodeling in glioblastoma.
In healthy brain tissue, glioblastoma-associated microglia (GAM) are highly branched, and branched microglia usually exhibit properties of M1-type macrophages that secrete pro-inflammatory factors to destroy pathogens. When inflammation, infection, trauma, or other neurologic diseases occur in the brain, microglia transform to the M2-type macrophage form. The transformed microglia have enlarged cell bodies, shortened protrusions, amoeboid morphology and activated phagocytosis. (Gieryng et al., 2017). GAM is the predominant inflammatory cell in the tumor micro-environment (TME), which not only exerts an immunosuppressive function and induces immune tolerance, but also promotes tumor growth and metastasis (Lin et al., 2024). Additionally, studies have shown that the immunosuppressive phenotype of GAMs correlates with GBM grade, with higher grades showing greater prevalence of tolerant or protumor GAMs (De et al., 2016). Neovascularisation in malignant tumors is one of the features that distinguish them from benign tumors, and the results of both clinical and experimental studies support the production of angiogenic factors [e.g., VEGF] by GAM to stimulate angiogenesis in glioblastomas. Studies have shown that IL-6 released from GAM keeps the blood-brain barrier in glioblastoma patients highly permeable by activating the Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK/STAT3) pathway in endothelial cells and down-regulating the levels of intercellular junction proteins, which is responsible for the formation of vasogenic brain oedema (Couto et al., 2019). GAM-released IL-1β can also be used to stimulate the formation of vasculogenic brain oedema in glioblastoma cells by promoting glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 (GPD2) phosphorylation and glycolysis, thereby accelerating tumor proliferation and growth (Lu et al., 2020). In addition, microglia induce platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) expression in mouse glioblastoma models and tumor cells from human patients, and the expression of this receptor stimulates glioblastoma cell migration, thereby accelerating tumor progression (Sherafat et al., 2021; Wallmann et al., 2018). Piezo1-mediated increases in cytoplasmic Ca2+ are involved in the inhibition of microglia proliferation. Piezo1 opening promotes extracellular Ca2+ endocytosis and releases Ca2+ stored in the endoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm, creating a cytoplasmic Ca2+ peak that interferes with the homeostasis of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial Ca2+ communication and induces microglial dysfunction. Piezo1 is recruited to the endoplasmic reticulum via the R-Ras (which is most likely in an activated state), and then stimulates calcineurin signaling to maintain integrin activation, thereby enhancing cell adhesion. In vitro, microglia cultured on hardness-gradient hydrogels migrate to harder regions and are more responsive in these regions, suggesting that microglia may migrate towards and function in harder tumor tissue in vivo. Inhibition of Piezo1 expression modulates the affinity for integrins within microglia, thereby increasing the rate of cell migration (Hu et al., 2023). Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) migrate to the tumor site and accumulate in the central region of the GBM, exerting a predominantly immunosuppressive effect, whereas resident microglia have little or no immunosuppressive function. In grade II and III glioblastomas, microglia accounted for the majority of macrophages and lacked significant immunosuppressive activity (Miller and Hjelmeland, 2023). Activation of Piezo1 channel proteins by mechanical stimulation regulates macrophage functional differentiation, modulates dendritic cells (DC) responses triggers inflammation, and participates in T-cell activation, among many other ways, in immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment (Pinton et al., 2019).
Mechanical signaling has been identified as a potential trigger for inflammatory activation in microglia. Piezo1 has the ability to regulate microglial migration patterns and immune responses, and has been suggested to act as a mechanosensor for microglial cell lines. Piezo1 regulates the pro-inflammatory response of microglial cells upon activation by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a commonly used surrogate for bacterial infections, inducing a transient changes. In vitro and in vivo, deletion of the Piezo1 gene in microglia reduced LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokine production, whereas Yoda1 increased LPS-stimulated proinflammatory cytokine production in microglia. Similar to microglia, macrophages lacking the Piezo1 gene exhibited reduced inflammation under both resting and endotoxin-stimulated conditions, accompanied by decreased proinflammatory cytokine production. These alterations may be related to Piezo1-mediated Ca2+influx and crosstalk between cytoskeletal and integrin proteins and piezo1 (Hu et al., 2023). While at the same time, some studies have shown that LPS can lead to microglia activation via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), leading to activation of NF-κB signaling via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, which ultimately drives TNF-α and IL-6 expression and production. However Yoda1 inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB activation by activating piezo1-Ca2+ signaling. These results suggest that activation of piezo1 channels reduces LPS-induced microglia activation and proinflammatory cytokine production, and that NF-κB signaling may act as a major mediator of (Malko et al., 2023).
In addition to this, ROS generated by SDT stimulation interferes with mitochondrial oxidative respiration, allowing more Ca2+ to enter the mitochondria, leading to mitochondrial calcium overload and dysfunction. MCU inhibition due to mitochondrial dysfunction prevents mitochondrial calcium uptake and promotes M1 polarization (Tedesco et al., 2019). Early intervention of Ca2+ channels in combination with SDT increases the proportion of M1-type macrophages with pro-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects.
Piezo1, integrins, and YAP are also strongly associated with cancer immunity. High collagen density and piezo1 activation promote macrophage polarization and enhance their immunosuppressive phenotype, leading to a decrease in cytotoxic T cell numbers and proliferation and inducing the expansion of immunosuppressive myeloid cells. Studies have shown that deletion of piezo1 in T cells does not affect effector T cell function but increases immunosuppressive myeloid cell, suggesting that activation of piezo1 in T cells may enhance the immune response in autoimmune diseases. In addition, increased matrix stiffness impedes the ability of dendritic cells to elicit an immune response in vitro and inhibits dendritic cell migration, which is essential for activating T cells and eliciting an immune response. necessary for T cells and eliciting an immune response (Jiang et al., 2022).
Increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration plays a crucial role in angiogenesis and arterial remodeling (Moccia et al., 2014; Moccia et al., 2012). Growth factors and cytokines, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), angiopoietin, and stromal-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α), trigger potent Ca2+ signaling in vascular endothelial cells (Potenza et al., 2014; Moccia et al., 2003; Noren et al., 2016; Munaron and Fiorio Pla, 2000) recruiting large numbers of downstream Ca2+-dependent pro-angiogenic transcription factors. These transcription factors include but are not limited to the nuclear factor of activated t-cells (NFAT), nuclear factor κ b (NF-κB) and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) -response element binding protein (CREB) (Noren et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2016), myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and myosin 2 (Tsai et al., 2014), endothelial-type nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)(Berra-Romani et al., 2013; Charoensin et al., 2017), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 12 (ERK 1/2) and AKT (Lyubchenko et al., 2011). Subsequent studies have demonstrated that endothelial Ca2+ signaling may also drive tumor angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis. Piezo1 regulates glioblastoma angiogenesis by engaging the Ca2+-dependent proteins eNOS and calpain, which promote the migration, alignment, and rearrangement of vascular endothelial cells in the direction of blood flow (Zhou et al., 2020; Barnes et al., 2017).
Piezo1 is highly expressed and co-localized in extensively angiogenic GBM endothelial cells and promotes aberrant angiogenesis in glioblastoma through the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. Myosin 1b promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/myc/myosin 1b/piezo1 axis. myosin 1b can block the degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) (a marker of hypoxia) by inhibiting autophagosome-lysosome fusion to promote the expression of VEGF. myc is a transcription factor of myosin 1b, which is induced by VEGFA. Myc is a transcription factor of myosin 1b and plays a key role in VEGFA-induced myosin 1b expression. myosin 1b regulates the expression of Piezo1 and Ca2+ influx, and Piezo1 knockdown reverses VEGF-induced intracellular Ca2+ influx. Ca2+ influx induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (Lv et al., 2024).
Given that Piezo1 is expressed in a wide range of cells and is involved in a variety of physiopathological processes, targeting this mechanosensitive protein would constitute a novel strategy for treating certain pathological conditions. Many studies have investigated the ionotropic and mechanogating mechanisms of Piezo1 channels.
The amphiphilic peptide toxin GsMTx4 interferes with Piezo1 by modulating local membrane tension and does not act directly on Piezo1 itself (Suchyna, 2017). In unstressed membranes, GsMTx4 occupies a small region of the bilayer surface, stabilized by the positive charge of lysine residues. When pressure is applied to force the lipid to stretch, GsMTx4 sinks deeper into the membrane, forming a ‘regional reservoir’ to ‘clamp’ the tension applied to the outer layer. As a result, the efficiency of stimulus transport to the Piezo1 channel is disrupted, thereby inhibiting the Ca2+-mediated AKT/mTOR pathway, which plays a crucial role in tumor development (Gnanasambandam et al., 2017). Due to its specificity as a cationic mechanosensitive channel inhibitor, GsMTx4 has been widely used to study the physiological and pathological roles of Piezo1 channels. An increasing number of studies have begun to explore the potential of GsMTx4 as a new strategy for glioblastoma treatment (Chen et al., 2022).
Tetradecylamine-1-κ5n,2-κ5n,3-κ4n-di-μ-oxohexachlorotrisruthenium, also known as ruthenium red (RR), is a blocker of Piezo1-induced mechanosensitive currents, and has been widely used in biological studies as a non-selective inhibitor of calcium channels (Tapia and Velasco, 1997). RR inhibits the inward, but not the outward, mPiezo1 MA currents, suggesting the presence of a pore-blocking mechanism (Coste et al., 2012).
Gadolinium (Gd3+), a trivalent lanthanide, can inhibit Piezo1 by binding to intramembrane anionic phospholipids interfering with neighboring membrane lipids and does not block Piezo1 by directly blocking the channel pore (Ermakov Yu et al., 1998). Gd3+ efficiently binds to intramembrane anionic phospholipids such as phosphatidylserine, with a consequent increase in the membrane side pressure, which further stabilizes the Piezo1 channel towards the closed state (Ermakov et al., 2010).
Although ruthenium red and gadolinium exhibit inhibitory properties of piezo1, both are prone to off-targeting when acting as piezo1 inhibitors because they are non-specific blockers of many stretch-activated cation channels.
Amyloid (aβ) is a group of peptides that play a key role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Similar to GsMTx4, the amphiphilic nature of Aβ peptides suggests that they can modulate membrane structure. Aβ peptides can affect cellular mechanotransduction by inhibiting Piezo1 activity. Accumulation of Aβ peptides is closely associated with upregulation of Piezo1 in reactive astrocytes (Velasco-Estevez et al., 2018) and microglial cells (Jäntti et al., 2022).
Saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids Dietary fatty acids are important components of cell membranes and have a significant impact on their mechanical properties (e.g., bending stiffness and viscosity). Saturated margaric acid (n-heptadecanoic acid) stabilized the closed state of Piezo1 channels by increasing membrane order and binding stiffness in a concentration-dependent manner, inhibiting of Piezo1 channels (Romero et al., 2019). Several polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are also negative modulators of Piezo1, e.g., arachidonic acid (AA) or eicosapentaenoic acid, either by mediating a metastable coupling between the inner pore helix (IH) and c-terminal extracellular structural domains (CED) or by disrupting the regulation of Piezo1 by other membrane proteins (Thien et al., 2024).
Tubeimoside I is a triterpenoid saponin extracted from the Chinese herb Bolbostemmatis Rhizoma, whose sugar chain is linked by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid, forming a unique macrocyclic structure. Tubeimoside I had a significant inhibitory effect on Ca2+ responses in 293T cells overexpressing piezo1 by Yoda1. Tubeimoside I was also relatively selective for Pio 1 because it did not block Ca2+ currents induced by other mechanical actions. A negative correlation was shown between the concentration of Yoda1 and the inhibitory response of Tubeimoside I, and the two compounds may reversibly compete with each other for piezo1 in the Yoda1 binding site (Liu et al., 2020).
It was shown that TBMS1 inhibited viability and AKT phosphorylation in U251 cells. PI3K/AKT inhibitor lY294002 showed the same effect. Furthermore, the combination of TBMS1 and lY294002 enhanced these inhibitory effects (Cao et al., 2020).
The cell cycle control system is based on two major protein families, cell cycle proteins and cdKs. Normally, the expression levels of cell cycle proteins are dynamic, whereas cdKs act as catalytic subunits that stabilize the expression levels of cell cycle proteins. During the transition from G2 to M phase, cyclin B1 activates CDK1, leading to an increase in activated CDK1 (Arellano and Moreno, 1997). In glioblastoma cells, constitutive activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling cascade and reduced levels of p21 protein expression are common, leading to defective cell cycle progression (Yang et al., 2016). It has been shown that TBMS1 reduces cyclin B1, CDK1, and AKT phosphorylation levels and elevates the level of the cKd1 inhibitor p21, which inhibits DNA synthesis and induces G2/M phase block in glioblastoma cells by targeting the PI3K/AKT/p21 and p21/CDK1/cyclin B1 signaling cascades (Cao et al., 2020).
Apoptotic signaling pathways are divided into death receptor (exogenous) pathways and mitochondrial (intrinsic) pathways (Creagh, 2014). The Bcl-2 family, which includes anti-apoptotic components such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl, as well as pro-apoptotic components such as Bax, Bak, and Bad, is involved in the regulation of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mitochondria-dependent signaling occurs through the cleavage of caspase-9, which subsequently activates downstream caspase-3, leading to the cleavage of various key cellular substrates, including ParP, thereby inducing apoptosis (Palmer et al., 2011). Previous studies have shown that TBMS1 prevents glioblastoma progression by triggering apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT-mediated Bcl-2 signaling pathway via TBMS1. In vitro experiments showed that after 24 h of TBMS1 action, U251 cells showed chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation, and formation of apoptotic vesicles.
Overall, TBMS1 exhibited inhibition of cell growth, promotion of apoptosis, and induction of cell cycle arrest by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT-mediated signaling pathway in glioblastoma cells. This provides a theoretical basis for in vivo studies using TBMS1 as a potential cancer therapeutic compound (Cao et al., 2020). (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Tubeimoside I is currently the most rapidly studied Piezo1 inhibitor in the field of glioblastoma treatment. Compared to other inhibitors, Tubeimoside I has the advantages of stability, specificity, and high humoral solubility.
Although a variety of piezo1 inhibitors have been shown to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and promote apoptosis, most of the piezo1 inhibitors are non-specific inhibitors of piezo1 and have strong off-target properties. However, most of the piezo1 inhibitors are non-specific inhibitors of piezo1, with strong off-target properties, and most of the piezo1 inhibitors, except Tubeimoside I and GsMTx4, are unable to pass the blood-brain barrier, and they cannot act directly on glioblastoma tumor tissues, so their therapeutic application value is limited. At the same time, some inhibitors such as Dooku1 have poor solubility in body fluids, which seriously affects their activity in vivo.
Studies have shown that it is feasible to treat glioblastoma with autologous T cells. However, the off-target effect due to the tumor microenvironment, tumor heterogeneity, and loss of antigenicity of glioblastoma makes accurate killing of glioblastoma difficult (Bagley et al., 2018). We can try to achieve controlled, non-invasive, and precise immunotherapy for glioblastomas by expressing Piezo1 on T cells and then locally stimulating glioblastomas using ultrasound or drugs targeting Piezo1, which activates Piezo1 and induces the activation of nuclear factor of t-cells (NFAT), which in turn drives the expression properties of the target genes (Pan et al., 2018).
Ultrasound and its associated energy can be delivered safely and non-invasively with high spatial and temporal resolution to small volumes of tissue deep within the body (Song et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023). Indeed, high-frequency ultrasound (HFU) can be focused for mechanical stimulation of individual cells in subcellular regions smaller than 10 μm. Due to the large difference in acoustic impedance between the surrounding medium and the air inside the bubble, microbubbles can further amplify the effects of low-frequency ultrasound stimulation with the ability to penetrate cells physically coupled to the microbubbles over long distances. The ultrasound power was stabilized in a range between 22.1 and 31.6 V to generate sufficient ultrasound to mechanically stimulate the cells without causing damage to the target cells.
Ultrasound can be used to stimulate Piezo1 (Qiu et al., 2019) and subsequent calcium inward flow using microbubble coupling to activate the calcium-sensitive phosphatase calmodulin phosphatase, which dephosphorylates the nuclear factor of activated t-cells (NFAT), and then this transcription factor translocates to the nucleus to activate the NFAT response element (RE) to drive the expression of the designed target gene. Microbubbles mechanically coupled to Piezo1 can be used to amplify low-frequency 2 MHz ultrasonic mechanical waves over a centimeter distance. The microbubbles are coated with streptavidin and coupled to a biotinylated Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide, which binds to the integrin and connects to Piezo1 via the cytoskeleton and membrane tension to promote calcium influx into the cell upon ultrasound stimulation at 2 MHz. Jurkat T cells and monocytes implanted with microbubbles showed a significant increase in anti-CD19 CAR-encoding mRNA and expression in response to ultrasound stimulation. After co-incubation of the sonication-induced CAR-expressing Jurkat cells with target tumor cells expressing CD19 antigen for 24 h, the surface marker CD69, which reflects t-cell activation, was significantly upregulated in the Jurkat cells, indicating that sonication-induced CAR is produced in Jurkat T cells and mediates binding to target tumor cell antigens, thereby exerting a tumor cell killing effect (Pan et al., 2018). (Figure 6).
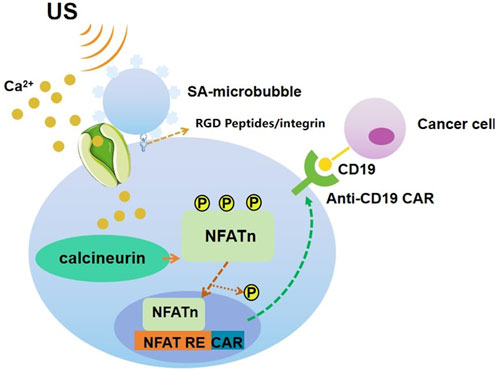
Figure 6. Schematic drawing of ultrasound-induced cell activation and gene expression. Microbubbles can be coupled to the surface of a cell, where mechanosensitive Piezo1 channels are expressed. Upon exposure to ultrasound waves, the mechanical stimulation can activate the Piezo1 ion channels. The subsequent calcium entry triggers the downstream pathways, including calcineurin activation, NFAT dephosphorylation, and translocation into the nucleus. The nucleus-translocated NFAT can bind to upstream response elements to initiate gene expression through one-stage or two-stage genetic transducing modules.
The system is highly modular, as shown by the multiple designs of genetic circuits with various base levels and activation potentials, thus allowing for continuous evolution and optimization for multiple types of cancer and pre-cancer diseases, and will bring the full power of remote control of gene and cellular activation to the scientific and clinical communities, thus allowing precise control of therapies in space and time, and ushering in a new era of life sciences and medical technologies.
Dendritic cells (DCs) are specialized antigen-presenting cells that play a crucial role in initiating immune responses to cancer immunotherapy through various activation pathways. Cell packets (BPs) are soft disk-shaped particles that modulate the phenotype of macrophages in vivo. The backpacks are prepared from biodegradable polymers using microcontact printing, and each backpack contains a cell adhesion layer, a poly (lactic-hydroxyglycolic acid) (PLGA) layer, a poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) layer and a second PLGA layer. Studies have shown that the “backpacks” can evade phagocytosis by macrophages, which enhances the stability of the drug in vivo (Shields et al., 2020). BPs represent an alternative approach for targeted delivery of immune activators and immune cells, providing prolonged immune modulation and enhanced therapeutic effects. Empty BPs act as modulators of DC immune function by activating cell-surface piezo1. Upon binding to DCs, BPs open piezo1 mechanoionic channels by binding to DCs, induce Ca2+ inward currents, activate local FAK and intracellular cytoskeletal remodeling to increase cellular stiffness, participate in the PI3K/Akt/mTOR cascade signaling to enhance IRF3 phosphorylation, and promote type I interferon production, and this activation leads to the initiation of the innate immunity-associated PI3K/Akt/mTOR/type I interferon signaling pathway. Radiation therapy combined with DC-BP (BPs that bind to DC cells) had a significant activating effect on the expression of mature dendritic cells, migrating dendritic cells, and lectin receptor-associated DCs, inducing a potent anti-tumor effect. Meanwhile, radiation therapy combined with DC-BP also significantly activated cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTLs) in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMCs), and activated T cells exhibited enhanced reactivity, leading to increased production of cytokines such as interferon gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which exhibited potent systemic antitumor effects. This approach holds great promise for synergistic radioimmunotherapy in cancer treatment, providing a multimodal therapeutic platform with great potential. The DC-BP vaccine combined with radiotherapy has been shown to significantly promote tumor shrinkage and to have the same killing effect on distant tumors in bladder cancer.
In the future, it could be tried to improve the local control rate and prolong the survival of glioblastoma patients who undergo surgical treatment with standard post-surgical adjuvant concurrent radiotherapy (total dose of 60Gy for more than 6 weeks with daily temozolomide, followed by 6 cycles of temozolomide maintenance therapy) with activation of piezo1 by the DC-BP vaccine, offering new possibilities for glioblastoma treatment (Yu et al., 2024).
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene is a tyrosine kinase receptor located on chromosome 7p11-p13, participating in key signaling pathways responsible for the cell cycle, growth, proliferation, migration, and survival of tumor cells. Mutations or overexpression are closely related to the development of more aggressive malignant phenotypes, leading to treatment resistance and poor clinical outcomes. After binding to endogenous ligands, EGFR forms homodimers or heterodimers, thereby activating the intracellular tyrosine kinase (TK) domain and causing phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues. Under the operation of phosphorylated tyrosine, downstream PI3K/Akt, Ras/Raf/MAPK, JAK/STAT, and other pathways are activated. These pathways are closely related to the proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis of gliomas, ultimately leading to the malignant biological behavior of gliomas. Currently, pan-targeted anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting EGFR mainly act on the extracellular domain of EGFR, blocking intracellular signaling pathways such as MAPK and PI3K in tumor cells to control tumor growth, which is the direction of anti-EGFR treatment for gliomas. However, most of the current results are still in phase II clinical trials, and there is no reliable phase III clinical data to prove their effectiveness (Westphal et al., 2015; Lombardi et al., 2019).
Piezo1 activates EGFR through a typical epidermal growth factor (EGF) activation alternative pathway. During the steady-state cell turnover process, EGF activates EGFR signaling through tyrosine autophosphorylation, receptor internalization, and cytoplasmic extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK) activation. Piezo1-dependent EGFR signaling (such as ERK activation and activator protein 1 (AP-1)induction) requires EGFR internalization through clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) rather than its kinase activity or Y1173 autophosphorylation, indicating that the internalization of the epidermal growth factor receptor is the key to piezo1 activation-induced AP-1. Internalized EGFR has a pro-survival function in kinase-independent cancer cells and is not affected by current tyrosine kinase-targeted therapy. The combination of Piezo1 inhibitors and TKI drugs provides a new direction for future targeted therapy of glioblastoma (Pardo-Pastor and Rosenblatt, 2023).
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), a member of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha family, induces apoptosis in cancer cells through death receptor activation (Lincoln et al., 2018; Fulda and Debatin, 2005). This ligand is expressed on the surface of activated natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, DC, and T cells and plays a role in the innate immune response (Ralff and El-Deiry, 2018; Shepard and Badley, 2009). TRAIL has been found to trigger apoptosis in many tumor cell types by binding to death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4/5)(Lee et al., 2014). This binding leads to trimerization of the receptor, which then binds intracellularly to the Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and caspase-8 to form the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). TRAIL is of particular interest in cancer therapy because of its ability to induce apoptosis in tumor cells without harming normal cells. However, xenograft animal studies have also shown that the use of TRAIL alone to treat the primary tumor itself is rarely successful. In addition, approximately 50% of tumor cell lines tested exhibit some degree of TRAIL resistance, and glioblastomas are particularly resistant to TRAIL. Therefore, for TRAIL to be a viable treatment, cancer cells must be sensitized to TRAIL (Lincoln et al., 2018; Fulda and Debatin, 2005).
One way in which TRAIL sensitization occurs is through the fluid shear stress (FSS) experienced by circulating tumor cells (CTCs) during circulation. Activation of the mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 via the agonist Yoda1 induces TRAIL sensitization under static conditions, and in vivo, Yoda1 significantly increased apoptosis in prostate, breast, and colon cancer cell lines compared to TRAIL alone (Hope et al., 2019). It was demonstrated that the combination of Yoda1 and TRAIL resulted in decreased GBM cell viability and increased late-stage apoptosis. The combination of FSS + TRAIL treatment resulted in a significant decrease in U87 and LN18 cell viability. These findings further demonstrated the efficacy of promoting TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through Piezo1 activation.
Combined treatment with Yoda1 and TRAIL increased mitochondrial depolarisation in GBM cells. Piezo1 has been shown to sensitize PC3 prostate cancer cells to TRAIL via the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, where Ca2+ activates calpain via Piezo1, subsequently amplifying death-inducing signals in the TRAIL-mediated apoptotic pathway (Knoblauch et al., 2023). These pro-apoptotic proteases induce pore formation in the mitochondrial membrane, which leads to mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Ultimately, MOMP leads to the release of apoptotic proteins through the mitochondrial pore, resulting in multiple cell death pathways (Hope et al., 2019; Chipuk et al., 2006).
Bax is a component of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway that triggers MOMP, and Bax channel blockers (BCBs) reduce mitochondrial depolarisation in GBM cells. Calpeptin, a calpain inhibitor, is an important component of the Piezo1 pathway. Yoda1 and TRAIL treatment inhibits calpain leading to a significant reduction in mitochondrial depolarisation.
Temozolomide (TMZ) is the standard chemotherapy used for the treatment of GBM.U87 cells are sensitive to TMZ, whereas LN18 cells are resistant to the drug. Studies have shown that LN18 cells are more sensitive to Yoda1 + TRAIL treatment than to TMZ treatment. U87 cells with low levels of Piezo1 expression responded comparably to both treatments. The sensitivity of these GBM cells to Yoda1 + TRAIL treatment suggests that the therapy may be successful in targeting tumors that are particularly resistant to current standard treatments. Thus Yoda1 + TRAIL combination therapy is expected to be a potential GBM treatment (Knoblauch et al., 2023).
Studies have shown that the abnormal activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signaling pathway induced by EGFR promotes the proliferation of glioma cells and is related to MGMT promoter methylation or expression, subsequently enhancing glioma drug resistance, and the efficacy of chemotherapy drugs such as TMZ is weakened due to drug resistance. This is the main obstacle in the treatment of GBM. Studies have shown that TBMS1 can reduce the expression of EGFR in MGMT + cell lines by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signaling pathway. The combination of TBMS1 and TMZ strongly induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells, accompanied by the formation of strong DSB, γH2AX foci, and an increase in PARP cleavage, and reduces the expression of MGMT in TMZ-resistant GBM cells, thereby reducing DNA damage repair and synthetic functions and restoring the sensitivity of MGMT + cells to TMZ. This study provides a theoretical basis for the combined application of TMZ and TBMS1 as a potential chemotherapy for MGMT + GBM patients (Tang et al., 2022).
Bevacizumab is a recombinant humanized immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody that can bind to VEGF-A, inhibit its binding to VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2), and subsequently inhibit the biological effects of VEGF, including affecting vascular permeability, proliferation, and the migration and survival of endothelial cells. The anti-angiogenic therapy represented by Bevacizumab normalizes tumor vessels, leading to excessive pruning of endothelial cells and perivascular cells, reduced vascular tortuosity, and decreased interstitial pressure, thereby improving oxygenation and delivering chemotherapy to tumor cells, amplifying the anti-tumor effect of chemotherapy. Meanwhile, Bevacizumab can bind to VEGF, preventing VEGF from binding to its receptors on the surface of endothelial cells, thereby pruning vessels, regulating vascular permeability, reducing brain edema caused by brain necrosis, and treating brain necrosis (Nayak et al., 2021). Piezo1 inhibitors can block VEGF activation caused by piezo1. In the future, they can be tried in combination with bevacizumab to reduce abnormal glioblastoma vessels and inhibit tumor progression.
In addition to this, the piezo1 agonist Yoda1 + TRAIL can successfully kill glioblastoma cells that are particularly resistant to current standard therapies by activating piezo1, providing a new idea for the treatment of glioblastoma resistant to temozolomide.
Piezo1 is the first mechanosensitive cation channel protein identified and plays an important role in the development of a wide range of tumors. Glioblastoma, one of the most common and malignant brain tumors in adults, exhibits Piezo1 overexpression. Several studies have demonstrated that Piezo1 affects several underlying pathophysiological processes such as tissue hardening, angiogenesis, energy supply, and immune cell infiltration in glioblastoma, and can be used as an indicator of malignancy and prognostic assessment of glioblastoma patients, as well as a therapeutic target for controlling tumor progression (Figure 7). Specific mechanistic studies centered on Piezo1 will contribute to our understanding of the mechanistic biology of glioblastoma and help us develop new therapeutic approaches for glioblastoma patients.
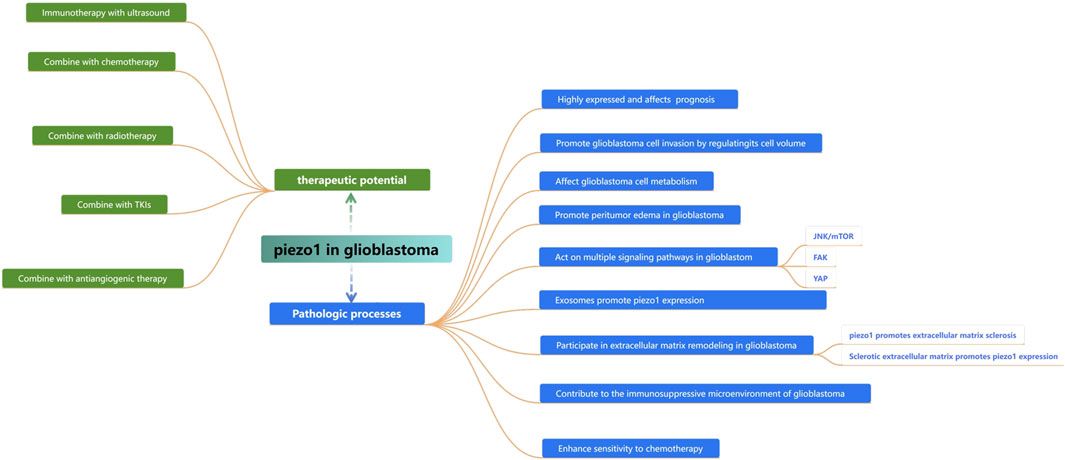
Figure 7. Summarizing the role of piezo1 in the proliferation, invasion, and progression of glioblastoma and its therapeutic potential.
WF: Writing–original draft. XH: Writing–review and editing. LD: Writing–review and editing. JW: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. WH: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Beijing Medical Award Foundation (Grant number YXJL-2021-0476-0473).
In memory of Mrs Hongyan Li for her unwaving support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Amado, N. G., Nosyreva, E. D., Thompson, D., Egeland, T. J., Ogujiofor, O. W., Yang, M., et al. (2024). PIEZO1 loss-of-function compound heterozygous mutations in the rare congenital human disorder Prune Belly Syndrome. Nat. Commun. 15, 339. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-44594-0
Arellano, M., and Moreno, S. (1997). Regulation of CDK/cyclin complexes during the cell cycle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 29, 559–573. doi:10.1016/s1357-2725(96)00178-1
Arniges, M., VáZQUEZ, E., FernáNDEZ-FernáNDEZ, J. M., and Valverde, M. A. (2004). Swelling-activated Ca2+ entry via TRPV4 channel is defective in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 54062–54068. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409708200
Bagley, S. J., Desai, A. S., Linette, G. P., June, C. H., and O'Rourke, D. M. (2018). CAR T-cell therapy for glioblastoma: recent clinical advances and future challenges. Neuro Oncol. 20, 1429–1438. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noy032
Barnes, J. M., Przybyla, L., and Weaver, V. M. (2017). Tissue mechanics regulate brain development, homeostasis and disease. J. Cell. Sci. 130, 71–82. doi:10.1242/jcs.191742
Bartel, D. P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116, 281–297. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5
Berra-Romani, R., Avelino-Cruz, J. E., Raqeeb, A., Della Corte, A., Cinelli, M., Montagnani, S., et al. (2013). Ca2⁺-dependent nitric oxide release in the injured endothelium of excised rat aorta: a promising mechanism applying in vascular prosthetic devices in aging patients. BMC Surg. 13 (Suppl. 2), S40. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-13-S2-S40
Cao, L. J., Xie, H. T., Chu, Z. X., Ma, Y., Wang, M. M., and Shi, Z. (2020). Tubeimoside-1 induces apoptosis in human glioma U251 cells by suppressing PI3K/Akt-mediated signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 22, 1527–1535. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11224
Caramia, M., Sforna, L., Franciolini, F., and Catacuzzeno, L. (2019). The volume-regulated anion channel in glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel) 11. doi:10.3390/cancers11030307
Castellan, M., Guarnieri, A., Fujimura, A., Zanconato, F., Battilana, G., Panciera, T., et al. (2021). Single-cell analyses reveal YAP/TAZ as regulators of stemness and cell plasticity in Glioblastoma. Nat. Cancer 2, 174–188. doi:10.1038/s43018-020-00150-z
Charoensin, S., Eroglu, E., Opelt, M., Bischof, H., Madreiter-Sokolowski, C. T., Kirsch, A., et al. (2017). Intact mitochondrial Ca(2+) uniport is essential for agonist-induced activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 102, 248–259. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.049
Chaudhuri, P. K., Low, B. C., and Lim, C. T. (2018). Mechanobiology of tumor growth. Chem. Rev. 118, 6499–6515. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00042
Chauvet, D., Imbault, M., Capelle, L., Demene, C., Mossad, M., Karachi, C., et al. (2016). In vivo measurement of brain tumor elasticity using intraoperative shear wave elastography. Ultraschall Med. 37, 584–590. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1399152
Chen, B., Liu, X., Yu, P., Xie, F., Kwan, J. S. H., Chan, W. N., et al. (2023). H. pylori-induced NF-κB-PIEZO1-YAP1-CTGF axis drives gastric cancer progression and cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated tumour microenvironment remodelling. Clin. Transl. Med. 13, e1481. doi:10.1002/ctm2.1481
Chen, F., Zhu, L., Cai, L., Zhang, J., Zeng, X., Li, J., et al. (2016). A stromal interaction molecule 1 variant up-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by strengthening nucleoplasmic Ca2+ signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863, 617–629. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.01.007
Chen, L., Cong, D., Li, Y., Wang, D., Li, Q., and Hu, S. (2017). Combination of sonodynamic with temozolomide inhibits C6 glioma migration and promotes mitochondrial pathway apoptosis via suppressing NHE-1 expression. Ultrason. Sonochem 39, 654–661. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.05.013
Chen, L., Yan, Y., Kong, F., Wang, J., Zeng, J., Fang, Z., et al. (2022). Contribution of oxidative stress induced by sonodynamic therapy to the calcium homeostasis imbalance enhances macrophage infiltration in glioma cells. Cancers (Basel) 14. doi:10.3390/cancers14082036
Chen, X., Wanggou, S., Bodalia, A., Zhu, M., Dong, W., Fan, J. J., et al. (2018). A feedforward mechanism mediated by mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 and tissue mechanics promotes glioma aggression. Neuron 100, 799–815. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.046
Chipuk, J. E., Bouchier-Hayes, L., and Green, D. R. (2006). Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario. Cell. Death Differ. 13, 1396–1402. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401963
Choi, D., Park, E., Yu, R. P., Cooper, M. N., Cho, I. T., Choi, J., et al. (2022). Piezo1-Regulated mechanotransduction controls flow-activated lymphatic expansion. Circ. Res. 131, e2–e21. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.320565
Coste, B., Mathur, J., Schmidt, M., Earley, T. J., Ranade, S., Petrus, M. J., et al. (2010). Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science 330, 55–60. doi:10.1126/science.1193270
Coste, B., Xiao, B., Santos, J. S., Syeda, R., Grandl, J., Spencer, K. S., et al. (2012). Piezo proteins are pore-forming subunits of mechanically activated channels. Nature 483, 176–181. doi:10.1038/nature10812
Couto, M., Coelho-Santos, V., Santos, L., Fontes-Ribeiro, C., Silva, A. P., and Gomes, C. M. F. (2019). The interplay between glioblastoma and microglia cells leads to endothelial cell monolayer dysfunction via the interleukin-6-induced JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 19750–19760. doi:10.1002/jcp.28575
Cox, C. D., Bae, C., Ziegler, L., Hartley, S., Nikolova-Krstevski, V., Rohde, P. R., et al. (2016). Removal of the mechanoprotective influence of the cytoskeleton reveals PIEZO1 is gated by bilayer tension. Nat. Commun. 7, 10366. doi:10.1038/ncomms10366
Creagh, E. M. (2014). Caspase crosstalk: integration of apoptotic and innate immune signalling pathways. Trends Immunol. 35, 631–640. doi:10.1016/j.it.2014.10.004
De, I., Steffen, M. D., Clark, P. A., Patros, C. J., Sokn, E., Bishop, S. M., et al. (2016). CSF1 overexpression promotes high-grade glioma formation without impacting the polarization status of glioma-associated microglia and macrophages. Cancer Res. 76, 2552–2560. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2386
Desgrosellier, J. S., and Cheresh, D. A. (2010). Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 9–22. doi:10.1038/nrc2748
Eisenhoffer, G. T., Loftus, P. D., Yoshigi, M., Otsuna, H., Chien, C. B., Morcos, P. A., et al. (2012). Crowding induces live cell extrusion to maintain homeostatic cell numbers in epithelia. Nature 484, 546–549. doi:10.1038/nature10999
Ermakov, Y. A., Kamaraju, K., Sengupta, K., and Sukharev, S. (2010). Gadolinium ions block mechanosensitive channels by altering the packing and lateral pressure of anionic lipids. Biophys. J. 98, 1018–1027. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2009.11.044
Ermakov Yu, A., Averbakh, A. Z., Arbuzova, A. B., and Sukharev, S. I. (1998). Lipid and cell membranes in the presence of gadolinium and other ions with high affinity to lipids. 2. A dipole component of the boundary potential on membranes with different surface charge. Membr. Cell. Biol. 12, 411–426.
Friedrich, E. E., Hong, Z., Xiong, S., Zhong, M., Di, A., Rehman, J., et al. (2019). Endothelial cell Piezo1 mediates pressure-induced lung vascular hyperpermeability via disruption of adherens junctions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 12980–12985. doi:10.1073/pnas.1902165116
Fulda, S., and Debatin, K. M. (2005). HDAC inhibitors: double edge sword for TRAIL cancer therapy? Cancer Biol. Ther. 4, 1113–1115. doi:10.4161/cbt.4.10.2100
Gao, L., Ji, Y., Wang, L., He, M., Yang, X., Qiu, Y., et al. (2021). Suppression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development by mechanosensitive protein Piezo1 downregulation. ACS Omega 6, 10196–10206. doi:10.1021/acsomega.1c00505
Geng, J., Liu, W., Zhou, H., Zhang, T., Wang, L., Zhang, M., et al. (2020). A plug-and-latch mechanism for gating the mechanosensitive piezo channel. Neuron 106, 438–451. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2020.02.010
Ge, P., Ji, X., Ding, Y., Wang, X., Fu, S., Meng, F., et al. (2010). Celastrol causes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in rat glioma cells. Neurol. Res. 32, 94–100. doi:10.1179/016164109X12518779082273
Gieryng, A., Pszczolkowska, D., Walentynowicz, K. A., Rajan, W. D., and Kaminska, B. (2017). Immune microenvironment of gliomas. Lab. Investig. 97, 498–518. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2017.19
Gnanasambandam, R., Ghatak, C., Yasmann, A., Nishizawa, K., Sachs, F., Ladokhin, A. S., et al. (2017). GsMTx4: mechanism of inhibiting mechanosensitive ion channels. Biophys. J. 112, 31–45. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.013
Guan, H., Wang, W., Jiang, Z., Zhang, B., Ye, Z., Zheng, J., et al. (2024). Magnetic aggregation-induced bone-targeting nanocarrier with effects of Piezo1 activation and osteogenic-angiogenic coupling for osteoporotic bone repair. Adv. Mater 36, e2312081. doi:10.1002/adma.202312081
Gudipaty, S. A., Lindblom, J., Loftus, P. D., Redd, M. J., Edes, K., Davey, C. F., et al. (2017). Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1. Nature 543, 118–121. doi:10.1038/nature21407
Guo, Y. R., and Mackinnon, R. (2017). Structure-based membrane dome mechanism for Piezo mechanosensitivity. Elife 6. doi:10.7554/eLife.33660
Han, Y., Liu, C., Zhang, D., Men, H., Huo, L., Geng, Q., et al. (2019). Mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 promotes prostate cancer development through the activation of the Akt/mTOR pathway and acceleration of cell cycle. Int. J. Oncol. 55, 629–644. doi:10.3892/ijo.2019.4839
Hasegawa, K., Fujii, S., Matsumoto, S., Tajiri, Y., Kikuchi, A., and Kiyoshima, T. (2021). YAP signaling induces PIEZO1 to promote oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation. J. Pathol. 253, 80–93. doi:10.1002/path.5553
Hong, R., Yang, D., Jing, Y., Chen, S., Tian, H., and Yang, Y. (2023). PIEZO1-Related physiological and pathological processes in CNS: focus on the gliomas. Cancers (Basel) 15. doi:10.3390/cancers15030883
Hope, J. M., Lopez-Cavestany, M., Wang, W., Reinhart-King, C. A., and King, M. R. (2019). Activation of Piezo1 sensitizes cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through mitochondrial outer membrane permeability. Cell. Death Dis. 10, 837. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2063-6
Hou, J., Kshettry, V. R., Selman, W. R., and Bambakidis, N. C. (2013). Peritumoral brain edema in intracranial meningiomas: the emergence of vascular endothelial growth factor-directed therapy. Neurosurg. Focus 35, E2. doi:10.3171/2013.8.FOCUS13301
Hu, H. H., Wang, S. Q., Shang, H. L., Lv, H. F., Chen, B. B., Gao, S. G., et al. (2024). Roles and inhibitors of FAK in cancer: current advances and future directions. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1274209. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1274209
Hu, J. K., Du, W., Shelton, S. J., Oldham, M. C., Dipersio, C. M., and Klein, O. D. (2017a). An FAK-YAP-mTOR signaling Axis regulates stem cell-based tissue renewal in mice. Cell. Stem Cell. 21, 91–106. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2017.03.023
Huang, Y., Zhou, Y., Fan, Y., and Zhou, D. (2008). Celastrol inhibits the growth of human glioma xenografts in nude mice through suppressing VEGFR expression. Cancer Lett. 264, 101–106. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.01.043
Huang, Z., Sun, Z., Zhang, X., Niu, K., Wang, Y., Zheng, J., et al. (2019). Loss of stretch-activated channels, PIEZOs, accelerates non-small cell lung cancer progression and cell migration. Biosci. Rep. 39. doi:10.1042/BSR20181679
Hu, J., Chen, Q., Zhu, H., Hou, L., Liu, W., Yang, Q., et al. (2023). Microglial Piezo1 senses Aβ fibril stiffness to restrict Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 111, 15–29.e8. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.021
Hu, M., Luo, Q., Alitongbieke, G., Chong, S., Xu, C., Xie, L., et al. (2017b). Celastrol-induced Nur77 interaction with TRAF2 alleviates inflammation by promoting mitochondrial ubiquitination and autophagy. Mol. Cell. 66, 141–153. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2017.03.008
Humphrey, J. D., Dufresne, E. R., and Schwartz, M. A. (2014). Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 802–812. doi:10.1038/nrm3896
JäNTTI, H., Sitnikova, V., Ishchenko, Y., Shakirzyanova, A., Giudice, L., Ugidos, I. F., et al. (2022). Microglial amyloid beta clearance is driven by PIEZO1 channels. J. Neuroinflammation 19, 147. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02486-y
Jiang, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Luo, T., and Hua, H. (2022). Targeting extracellular matrix stiffness and mechanotransducers to improve cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 15, 34. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01252-0
Kai, F., Laklai, H., and Weaver, V. M. (2016). Force matters: biomechanical regulation of cell invasion and migration in disease. Trends Cell. Biol. 26, 486–497. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2016.03.007
Kalluri, R., and Lebleu, V. S. (2020). The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367. doi:10.1126/science.aau6977
Kim, O. H., Choi, Y. W., Park, J. H., Hong, S. A., Hong, M., Chang, I. H., et al. (2022). Fluid shear stress facilitates prostate cancer metastasis through Piezo1-Src-YAP axis. Life Sci. 308, 120936. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120936
Kim, S. H., Turnbull, J., and Guimond, S. (2011). Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J. Endocrinol. 209, 139–151. doi:10.1530/JOE-10-0377
Knoblauch, S. V., Desai, S. H., Dombroski, J. A., Sarna, N. S., Hope, J. M., and King, M. R. (2023). Chemical activation and mechanical sensitization of Piezo1 enhance TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. ACS Omega 8, 16975–16986. doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c00705
Lah, T. T., Novak, M., and Breznik, B. (2020). Brain malignancies: glioblastoma and brain metastases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 60, 262–273. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.10.010
Leclerc, C., Haeich, J., Aulestia, F. J., Kilhoffer, M. C., Miller, A. L., NéANT, I., et al. (2016). Calcium signaling orchestrates glioblastoma development: facts and conjunctures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863, 1447–1459. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.01.018
Lee, D. H., Kim, D. W., Jung, C. H., Lee, Y. J., and Park, D. (2014). Gingerol sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptotic cell death of glioblastoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 279, 253–265. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2014.06.030
Li, X. X., Wang, Z. J., Zheng, Y., Guan, Y. F., Yang, P. B., Chen, X., et al. (2018). Nuclear receptor Nur77 facilitates melanoma cell survival under metabolic stress by protecting fatty acid oxidation. Mol. Cell. 69, 480–492. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.001
Liang, D., Bhatta, S., Gerzanich, V., and Simard, J. M. (2007). Cytotoxic edema: mechanisms of pathological cell swelling. Neurosurg. Focus 22, E2. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.22.5.3
Li, B., Chen, Z., Zhang, Z., Liu, H., Han, D., Yang, H., et al. (2024). Zuogui pill disrupt the malignant cycle in breast cancer bone metastasis through the Piezo1-Notch-1-GPX4 pathway and active molecules fishing. Phytomedicine 123, 155257. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155257
Li, J., Hou, B., Tumova, S., Muraki, K., Bruns, A., Ludlow, M. J., et al. (2014). Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature 515, 279–282. doi:10.1038/nature13701
Li, M., Zhang, X., Wang, M., Wang, Y., Qian, J., Xing, X., et al. (2022). Activation of Piezo1 contributes to matrix stiffness-induced angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Commun. (Lond) 42, 1162–1184. doi:10.1002/cac2.12364
Lin, Y. C., Guo, Y. R., Miyagi, A., Levring, J., Mackinnon, R., and Scheuring, S. (2019). Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature 573, 230–234. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2
Lincoln, F. A., Imig, D., Boccellato, C., Juric, V., Noonan, J., Kontermann, R. E., et al. (2018). Sensitization of glioblastoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by IAP- and Bcl-2 antagonism. Cell. Death Dis. 9, 1112. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1160-2
Lin, H., Liu, C., Hu, A., Zhang, D., Yang, H., and Mao, Y. (2024). Understanding the immunosuppressive microenvironment of glioma: mechanistic insights and clinical perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 17, 31. doi:10.1186/s13045-024-01544-7
Li, R., Wang, D., Li, H., Lei, X., Liao, W., and Liu, X. Y. (2023). Identification of Piezo1 as a potential target for therapy of colon cancer stem-like cells. Discov. Oncol. 14, 95. doi:10.1007/s12672-023-00712-4
Liu, H., Bian, W., Yang, D., Yang, M., and Luo, H. (2021). Inhibiting the Piezo1 channel protects microglia from acute hyperglycaemia damage through the JNK1 and mTOR signalling pathways. Life Sci. 264, 118667. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118667
Liu, J., Lee, J., Salazar Hernandez, M. A., Mazitschek, R., and Ozcan, U. (2015). Treatment of obesity with celastrol. Cell. 161, 999–1011. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.011
Liu, S., Pan, X., Cheng, W., Deng, B., He, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2020). Tubeimoside I antagonizes yoda1-evoked Piezo1 channel activation. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 768. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00768
Liu, X., Zhao, P., Wang, X., Wang, L., Zhu, Y., Song, Y., et al. (2019). Celastrol mediates autophagy and apoptosis via the ROS/JNK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in glioma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38, 184. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1173-4
Lombardi, G., De Salvo, G. L., Brandes, A. A., Eoli, M., Rudà, R., Faedi, M., et al. (2019). Regorafenib compared with lomustine in patients with relapsed glioblastoma (REGOMA): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20, 110–119. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30675-2
Lu, J., Xu, Z., Duan, H., Ji, H., Zhen, Z., Li, B., et al. (2020). Tumor-associated macrophage interleukin-β promotes glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activation, glycolysis and tumorigenesis in glioma cells. Cancer Sci. 111, 1979–1990. doi:10.1111/cas.14408
Lv, W., Yang, F., Ge, Z., Xin, L., Zhang, L., Zhai, Y., et al. (2024). Aberrant overexpression of myosin 1b in glioblastoma promotes angiogenesis via VEGF-myc-myosin 1b-Piezo1 axis. J. Biol. Chem. 300, 107807. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107807
Lyubchenko, T., Woodward, H., Veo, K. D., Burns, N., Nijmeh, H., Liubchenko, G. A., et al. (2011). P2Y1 and P2Y13 purinergic receptors mediate Ca2+ signaling and proliferative responses in pulmonary artery vasa vasorum endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 300, C266–C275. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00237.2010
Malko, P., Jia, X., Wood, I., and Jiang, L. H. (2023). Piezo1 channel-mediated Ca(2+) signaling inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of the NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway and generation of TNF-α and IL-6 in microglial cells. Glia 71, 848–865. doi:10.1002/glia.24311
Mckinnon, C., Nandhabalan, M., Murray, S. A., and Plaha, P. (2021). Glioblastoma: clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management. Bmj 374, n1560. doi:10.1136/bmj.n1560
Memczak, S., Jens, M., Elefsinioti, A., Torti, F., Krueger, J., Rybak, A., et al. (2013). Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495, 333–338. doi:10.1038/nature11928
Micek, H. M., Yang, N., Dutta, M., Rosenstock, L., Ma, Y., Hielsberg, C., et al. (2024). The role of Piezo1 mechanotransduction in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: insights from an in vitro model of collective detachment. Sci. Adv. 10, eadl4463. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adl4463
Michelucci, A., and Catacuzzeno, L. (2024). Piezo1, the new actor in cell volume regulation. Pflugers Arch. 476, 1023–1039. doi:10.1007/s00424-024-02951-y
Miller, C. R., and Hjelmeland, A. B. (2023). Breaking the feed forward inflammatory cytokine loop in the tumor microenvironment of PDGFB-driven glioblastomas. J. Clin. Investig. 133. doi:10.1172/JCI175127
Miroshnikova, Y. A., Mouw, J. K., Barnes, J. M., Pickup, M. W., Lakins, J. N., Kim, Y., et al. (2016). Tissue mechanics promote IDH1-dependent HIF1α-tenascin C feedback to regulate glioblastoma aggression. Nat. Cell. Biol. 18, 1336–1345. doi:10.1038/ncb3429
Miyazaki, H., Shiozaki, A., Niisato, N., and Marunaka, Y. (2007). Physiological significance of hypotonicity-induced regulatory volume decrease: reduction in intracellular Cl-concentration acting as an intracellular signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 292, F1411–F1417. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00244.2006
Moccia, F., Berra-Romani, R., and Tanzi, F. (2012). Update on vascular endothelial Ca(2+) signalling: a tale of ion channels, pumps and transporters. World J. Biol. Chem. 3, 127–158. doi:10.4331/wjbc.v3.i7.127
Moccia, F., Berra-Romani, R., Tritto, S., Signorelli, S., Taglietti, V., and Tanzi, F. (2003). Epidermal growth factor induces intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in microvascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 194, 139–150. doi:10.1002/jcp.10198
Moccia, F., Tanzi, F., and Munaron, L. (2014). Endothelial remodelling and intracellular calcium machinery. Curr. Mol. Med. 14, 457–480. doi:10.2174/1566524013666131118113410
Mohamed, E., Kumar, A., Zhang, Y., Wang, A. S., Chen, K., Lim, Y., et al. (2022). PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway activity in IDH-mutant diffuse glioma and clinical implications. Neuro Oncol. 24, 1471–1481. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noac064
Munaron, L., and Fiorio Pla, A. (2000). Calcium influx induced by activation of tyrosine kinase receptors in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 185, 454–463. doi:10.1002/1097-4652(200012)185:3<454::AID-JCP17>3.0.CO;2-A
Nayak, L., Molinaro, A. M., Peters, K., Clarke, J. L., Jordan, J. T., De Groot, J., et al. (2021). Randomized phase II and biomarker study of pembrolizumab plus bevacizumab versus pembrolizumab alone for patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 27, 1048–1057. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2500
Noren, D. P., Chou, W. H., Lee, S. H., Qutub, A. A., Warmflash, A., Wagner, D. S., et al. (2016). Endothelial cells decode VEGF-mediated Ca2+ signaling patterns to produce distinct functional responses. Sci. Signal 9, ra20. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aad3188
Northey, J. J., Przybyla, L., and Weaver, V. M. (2017). Tissue force programs cell fate and tumor aggression. Cancer Discov. 7, 1224–1237. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0733
Nourse, J. L., and Pathak, M. M. (2017). How cells channel their stress: interplay between Piezo1 and the cytoskeleton. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 71, 3–12. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.06.018
Oudin, M. J., and Weaver, V. M. (2016). Physical and chemical gradients in the tumor microenvironment regulate tumor cell invasion, migration, and metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 81, 189–205. doi:10.1101/sqb.2016.81.030817
Palmer, C. S., Osellame, L. D., Stojanovski, D., and Ryan, M. T. (2011). The regulation of mitochondrial morphology: intricate mechanisms and dynamic machinery. Cell. Signal 23, 1534–1545. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.05.021
Pan, H., Zhang, X., Zhu, S., Zhu, B., Wu, D., Yan, J., et al. (2024). Piezo1 mediates glycolysis-boosted pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma chemoresistance within a biomimetic three-dimensional matrix stiffness. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 10, 7632–7646. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c01319
Pan, Y., Yoon, S., Sun, J., Huang, Z., Lee, C., Allen, M., et al. (2018). Mechanogenetics for the remote and noninvasive control of cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, 992–997. doi:10.1073/pnas.1714900115
Pardo-Pastor, C., and Rosenblatt, J. (2023). Piezo1 activates noncanonical EGFR endocytosis and signaling. Sci. Adv. 9, eadi1328. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adi1328
Park, M. A., Yacoub, A., Sarkar, D., Emdad, L., Rahmani, M., Spiegel, S., et al. (2008). PERK-dependent regulation of MDA-7/IL-24-induced autophagy in primary human glioma cells. Autophagy 4, 513–515. doi:10.4161/auto.5725
Patkunarajah, A., Stear, J. H., Moroni, M., Schroeter, L., Blaszkiewicz, J., Tearle, J. L., et al. (2020). TMEM87a/Elkin1, a component of a novel mechanoelectrical transduction pathway, modulates melanoma adhesion and migration. Elife 9. doi:10.7554/eLife.53308
Peng, Z., Liu, C., and Wu, M. (2018). New insights into long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol. Cancer 17, 61. doi:10.1186/s12943-018-0812-2
Pinton, L., Masetto, E., Vettore, M., Solito, S., Magri, S., D'Andolfi, M., et al. (2019). The immune suppressive microenvironment of human gliomas depends on the accumulation of bone marrow-derived macrophages in the center of the lesion. J. Immunother. Cancer 7, 58. doi:10.1186/s40425-019-0536-x
Potenza, D. M., Guerra, G., Avanzato, D., Poletto, V., Pareek, S., Guido, D., et al. (2014). Hydrogen sulphide triggers VEGF-induced intracellular Ca2⁺ signals in human endothelial cells but not in their immature progenitors. Cell. Calcium 56, 225–234. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2014.07.010
Qiu, Z., Guo, J., Kala, S., Zhu, J., Xian, Q., Qiu, W., et al. (2019). The mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 significantly mediates in vitro ultrasonic stimulation of neurons. iScience 21, 448–457. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2019.10.037
Qu, S., Hu, T., Qiu, O., Su, Y., Gu, J., and Xia, Z. (2020a). Effect of Piezo1 overexpression on peritumoral brain edema in glioblastomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 41, 1423–1429. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A6638
Qu, S., Li, S., and Hu, Z. (2020b). Upregulation of Piezo1 is a novel prognostic indicator in glioma patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 3527–3536. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S251776
Ralff, M. D., and El-Deiry, W. S. (2018). TRAIL pathway targeting therapeutics. Expert Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 3, 197–204. doi:10.1080/23808993.2018.1476062
Ridone, P., Vassalli, M., and Martinac, B. (2019). Piezo1 mechanosensitive channels: what are they and why are they important. Biophys. Rev. 11, 795–805. doi:10.1007/s12551-019-00584-5
Romero, L. O., Massey, A. E., Mata-Daboin, A. D., Sierra-Valdez, F. J., Chauhan, S. C., Cordero-Morales, J. F., et al. (2019). Dietary fatty acids fine-tune Piezo1 mechanical response. Nat. Commun. 10, 1200. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09055-7
Saotome, K., Murthy, S. E., Kefauver, J. M., Whitwam, T., Patapoutian, A., and Ward, A. B. (2018). Structure of the mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1. Nature 554, 481–486. doi:10.1038/nature25453
Satir, P., and Christensen, S. T. (2007). Overview of structure and function of mammalian cilia. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69, 377–400. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.69.040705.141236
Schoenegger, K., Oberndorfer, S., Wuschitz, B., Struhal, W., Hainfellner, J., Prayer, D., et al. (2009). Peritumoral edema on MRI at initial diagnosis: an independent prognostic factor for glioblastoma? Eur. J. Neurol. 16, 874–878. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02613.x
Shepard, B. D., and Badley, A. D. (2009). The biology of TRAIL and the role of TRAIL-based therapeutics in infectious diseases. Antiinfect Agents Med. Chem. 8, 87–101. doi:10.2174/187152109787846060
Sherafat, A., Pfeiffer, F., Reiss, A. M., Wood, W. M., and Nishiyama, A. (2021). Microglial neuropilin-1 promotes oligodendrocyte expansion during development and remyelination by trans-activating platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Nat. Commun. 12, 2265. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22532-2
Shields, C. W. T., Evans, M. A., Wang, L. L., Baugh, N., Iyer, S., Wu, D., et al. (2020). Cellular backpacks for macrophage immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz6579. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaz6579
Song, Y., Chen, J., Zhang, C., Xin, L., Li, Q., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 induces cell apoptosis in pancreatic cancer by ultrasound with microbubbles. iScience 25, 103733. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.103733
Suchyna, T. M. (2017). Piezo channels and GsMTx4: two milestones in our understanding of excitatory mechanosensitive channels and their role in pathology. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 130, 244–253. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.07.011
Sun, M., Mao, S., Wu, C., Zhao, X., Guo, C., Hu, J., et al. (2024). Piezo1-Mediated neurogenic inflammatory cascade exacerbates ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Circulation 149, 1516–1533. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065390
Tang, Q., Cao, H., Tong, N., Liu, Y., Wang, W., Zou, Y., et al. (2022). Tubeimoside-I sensitizes temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cells to chemotherapy by reducing MGMT expression and suppressing EGFR induced PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB-mediated signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 99, 154016. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154016
Tapia, R., and Velasco, I. (1997). Ruthenium red as a tool to study calcium channels, neuronal death and the function of neural pathways. Neurochem. Int. 30, 137–147. doi:10.1016/s0197-0186(96)00056-3
Tedesco, S., Scattolini, V., Albiero, M., Bortolozzi, M., Avogaro, A., Cignarella, A., et al. (2019). Mitochondrial calcium uptake is instrumental to alternative macrophage polarization and phagocytic activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20. doi:10.3390/ijms20194966
Thien, N. D., Hai-Nam, N., Anh, D. T., and Baecker, D. (2024). Piezo1 and its inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 273, 116502. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116502
Tortorella, I., Argentati, C., Emiliani, C., Morena, F., and Martino, S. (2022). Biochemical pathways of cellular mechanosensing/mechanotransduction and their role in neurodegenerative diseases pathogenesis. Cells 11. doi:10.3390/cells11193093
Tsai, F. C., Seki, A., Yang, H. W., Hayer, A., Carrasco, S., Malmersjö, S., et al. (2014). A polarized Ca2+, diacylglycerol and STIM1 signalling system regulates directed cell migration. Nat. Cell. Biol. 16, 133–144. doi:10.1038/ncb2906
Vaeth, M., Maus, M., Klein-Hessling, S., Freinkman, E., Yang, J., Eckstein, M., et al. (2017). Store-operated Ca(2+) entry controls clonal expansion of T cells through metabolic reprogramming. Immunity 47, 664–679. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.09.003
Vander Heiden, M. G., Cantley, L. C., and Thompson, C. B. (2009). Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324, 1029–1033. doi:10.1126/science.1160809
Velasco-Estevez, M., Mampay, M., Boutin, H., Chaney, A., Warn, P., Sharp, A., et al. (2018). Infection augments expression of mechanosensing Piezo1 channels in amyloid plaque-reactive astrocytes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 10, 332. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2018.00332
Wallmann, T., Zhang, X. M., Wallerius, M., Bolin, S., Joly, A. L., Sobocki, C., et al. (2018). Microglia induce PDGFRB expression in glioma cells to enhance their migratory capacity. iScience 9, 71–83. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2018.10.011
Wang, P., Ni, R. Y., Chen, M. N., Mou, K. J., Mao, Q., and Liu, Y. H. (2011). Expression of aquaporin-4 in human supratentorial meningiomas with peritumoral brain edema and correlation of VEGF with edema formation. Genet. Mol. Res. 10, 2165–2171. doi:10.4238/vol10-3gmr1212
Wang, Y., Chi, S., Guo, H., Li, G., Wang, L., Zhao, Q., et al. (2018). A lever-like transduction pathway for long-distance chemical- and mechano-gating of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nat. Commun. 9, 1300. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03570-9
Watkins, S., and Sontheimer, H. (2011). Hydrodynamic cellular volume changes enable glioma cell invasion. J. Neurosci. 31, 17250–17259. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3938-11.2011
Westphal, M., Heese, O., Steinbach, J. P., Schnell, O., Schackert, G., Mehdorn, M., et al. (2015). A randomised, open label phase III trial with nimotuzumab, an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody in the treatment of newly diagnosed adult glioblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer 51, 522–532. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2014.12.019
Wires, E. S., Trychta, K. A., BäCK, S., Sulima, A., Rice, K. C., and Harvey, B. K. (2017). High fat diet disrupts endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis in the rat liver. J. Hepatol. 67, 1009–1017. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.05.023
Wu, J., Young, M., Lewis, A. H., Martfeld, A. N., Kalmeta, B., and Grandl, J. (2017). Inactivation of mechanically activated Piezo1 ion channels is determined by the C-terminal extracellular domain and the inner pore helix. Cell. Rep. 21, 2357–2366. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.120
Yang, R., Yi, L., Dong, Z., Ouyang, Q., Zhou, J., Pang, Y., et al. (2016). Tigecycline inhibits glioma growth by regulating miRNA-199b-5p-HES1-AKT pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 15, 421–429. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0709
Yang, X., Lin, C., Chen, X., Li, S., Li, X., and Xiao, B. (2022). Structure deformation and curvature sensing of PIEZO1 in lipid membranes. Nature 604, 377–383. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04574-8
Yu, J. L., and Liao, H. Y. (2021). Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 (Piezo1) in human cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 140, 111692. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111692
Yu, H., Liu, Z., Guo, H., Hu, X., Wang, Y., Cheng, X., et al. (2024). Mechanoimmune-Driven backpack sustains dendritic cell maturation for synergistic tumor radiotherapy. ACS Nano 18, 23741–23756. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c08701
Zanconato, F., Cordenonsi, M., and Piccolo, S. (2016). YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell. 29, 783–803. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.005
Zhang, D., Lin, W., Jiang, S., Deng, P., Liu, L., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Lepr-expressing PDLSCs contribute to periodontal homeostasis and respond to mechanical force by Piezo1. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10, e2303291. doi:10.1002/advs.202303291
Zhang, N., Wu, P., Mu, M., Niu, C., and Hu, S. (2024). Exosomal circZNF800 derived from glioma stem-like cells regulates glioblastoma tumorigenicity via the PIEZO1/akt Axis. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 6556–6571. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04002-0
Zhao, Q., Zhou, H., Chi, S., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Geng, J., et al. (2018). Structure and mechanogating mechanism of the Piezo1 channel. Nature 554, 487–492. doi:10.1038/nature25743
Zhao, Z., and Zlokovic, B. V. (2020). Endothelial tip cell finds its way with Piezo1. Neuron 108, 5–7. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2020.09.011
Zhong, G., Su, S., Li, J., Zhao, H., Hu, D., Chen, J., et al. (2023). Activation of Piezo1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of aortic valve interstitial cell through YAP-dependent glutaminolysis. Sci. Adv. 9, eadg0478. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adg0478
Zhou, W., Liu, X., Van Wijnbergen, J. W. M., Yuan, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, C., et al. (2020). Identification of PIEZO1 as a potential prognostic marker in gliomas. Sci. Rep. 10, 16121. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-72886-8
Zhu, J., Xian, Q., Hou, X., Wong, K. F., Zhu, T., Chen, Z., et al. (2023). The mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 contributes to ultrasound neuromodulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120, e2300291120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2300291120
Zhu, L., Luo, Y., Chen, T., Chen, F., Wang, T., and Hu, Q. (2008). Ca2+ oscillation frequency regulates agonist-stimulated gene expression in vascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Sci. 121, 2511–2518. doi:10.1242/jcs.031997
Zhu, S., Stanslowsky, N., FernáNDEZ-Trillo, J., Mamo, T. M., Yu, P., Kalmbach, N., et al. (2021). Generation of hiPSC-derived low threshold mechanoreceptors containing axonal termini resembling bulbous sensory nerve endings and expressing Piezo1 and Piezo2. Stem Cell. Res. 56, 102535. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102535
Zoi, I., Gargalionis, A. N., Papavassiliou, K. A., Nasiri-Ansari, N., Piperi, C., Basdra, E. K., et al. (2022). Polycystic-1 and hydrostatic pressure are implicated in glioblastoma pathogenesis in vitro. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 26, 1699–1709. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17212
GBM glioblastoma
LGG and HGG low to high-grade glioblastomas
ECM extracellular matrix
ATP adenosine triphosphate
CED c-terminal extracellular structural domain
TM transmembrane
OH - IH outer helix-inner helix
CTD c-terminal structural domain
THUs transmembrane helical units
CSK cytoskeleton
EMT epithelial-mesenchymal transition
VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
VEGFR2 vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
WHO World Health Organization
IDH isocitrate dehydrogenase
G-CIMP CpG island methylation
DNA deoxyribonucleic acid
TSS transcriptional start site
mRNA messenger ribonucleic acid
OS overall survival
shRNA short hairpin RNA
ROS reactive oxygen species
SDT sonodynamic therapy
MCU mitochondrial calcium uniporter
MRI magnetic resonance imaging
PTBE peritumoral brain oedema
SOCE store-manipulated calcium endocytosis
NFAHFUT nuclear factor of activated T cells
FAK focal adhesion kinase
YAP yes-associated protein
TAZ transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif
miRNAs micro RNAs
EVs extracellular vesicles
3’UTR 3‘ untranslated region
MMP matrix metalloproteinase
TIMP tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases
MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase
PI3K phosphoinositide 3 kinase
GAM glioblastoma-associated microglia
TME tumor micro-environment
GPD2 glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2
PDGFR platelet-derived growth factor receptor
JAK/STAT3 the Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
BMDM bone marrow-derived macrophages
RE response element
EGF epidermal growth factor
bFGF basic fibroblast growth factor
IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1
SDF-1α stromal-derived factor-1α
NF-κB nuclear factor κ b
cAMP cyclic adenosine monophosphate
CREB -response element binding protein
MLCK myosin light chain kinase
eNOS endothelial-type nitric oxide synthase
ERK 1/2 extracellular signal-regulated kinase 12
TRAIL tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
NK natural killer
DR4/5 death receptors 4 and 5
FADD fas-associated death domain
DISC death-inducing signaling complex
FSS fluid shear stress
CTCs circulating tumor cells
MOMP membrane permeabilization
BCBs Bax channel blockers
TMZ temozolomide
RR ruthenium red
Gd3+ Gadolinium
aβ Amyloid
PUFAs polyunsaturated fatty acids
AA arachidonic acid
RVD regulated volume reduction
VRAC volume-regulated anion channel
ICl swelling-activated CI − currents
KCa Ca2+-activated K+
MSC mechanosensitive channels
BK, IK, and SK Ca2+-activated K+ large-, medium-, and small-conductance channels
JNK1 c-JunN-terminalkinase 1
mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin
CDK4 cyclin-dependent kinases 4
cJUN c-Jun N-terminal kinase
BAX Bcl2-associated X
BAPTA-AM 1,2-bis (2-aminophenoxy)ethane-n,n,n0,n0-tetraacetic Acid Tetrakis (acetoxymethyl Ester)
TRPV4 transient receptor potential ion channel subfamily V 4
TRP transient receptor potential
ROCK Rho-associated coiled-coil kinases
Treg immunosuppressive regulatory T
RGD biotinylated Arg-Gly-Asp
HFU high-frequency ultrasound
DCs dendritic cells
BPs cell packets
CTLs cytotoxic T lymphocyte
PBMCs peripheral blood mononuclear cell
IFN -γinterferon gamma
TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α
IL-6 interleukin-6
CXCL C-X-C motif chemokine ligand
AVD apoptotic volume decrease
MDSC myeloid-derived suppressor cells
TAM tumor-associated macrophages
CAF cancer-associated fibroblasts
CRISPR clustered regularly interspaced shortpalindromic repeats
Cas -associated systems
MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase
Ras rat sarcoma
Crk cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinases
Grb2 growth factor receptor-bound protein 2
LPS lipopolysaccharide
HIF-1α hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
PLGA poly (lactic-hydroxyglycolic acid)
PVA poly (vinyl alcohol)
DC-BP BPs that bind to DC cells
EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor
TK tyrosine kinase
TKIs tyrosine kinase inhibitors
EGF epidermal growth factor
ERK extracellular regulated protein kinases
AP-1 activator protein 1
CME clathrin-mediated endocytosis
MGMT O6 -methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
IgG1 immunoglobulin G1
Keywords: glioblastoma, piezo1, biomechanical, targeted therapy, mechanomechanical
Citation: Fu W, Hou X, Ding L, Wei J and Hou W (2025) Piezo1-related physiological and pathological processes in glioblastoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1536320. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1536320
Received: 28 November 2024; Accepted: 30 January 2025;
Published: 21 February 2025.
Edited by:
Brian D. Adams, Brain Institute of America, United StatesReviewed by:
Maria Velasco-Estevez, Spanish National Cancer Research Center, SpainCopyright © 2025 Fu, Hou, Ding, Wei and Hou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Hou, aG91d2VpQGpsdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.