- School of Biosciences and Bioengineering (SBB), Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)- Mandi, Mandi, India
Introduction: Collagens, the most abundant proteins in mammals, play pivotal roles in maintaining tissue structure, functions, cell-to-cell communication, cellular migration, cellular behavior, and growth. Structures of collagens are highly complex due to the presence of dynamic post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as hydroxylations (on prolines and lysine residues) and O-glycosylation (on hydroxylysines) enzymatically catalyzed during biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Collagen PTMs are essential for maintaining structural stability, elasticity, and different functions of collagens. The most prevalent modification in fibrillar collagens is prolyl 4-hydroxylation catalyzed by collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases (C-P4Hs). Prolyl 4-hydroxylation on collagens plays a critical role in collagen biosynthesis, thermostability, and cell-collagen interactions. Collagens are large proteins. Different regions of collagen perform different functions, so the presence or absence of a PTM on a particular collagen site can affect its functioning. However, comprehensive site-specific identification of these PTMs on fibrillar collagen chains of mice skin has not been performed yet. Furthermore, the effects of prolyl 4-hydroxylase alpha 1 (P4HA1) and P4HA2 on 3-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, and O-glycosylation sites of fibrillar collagen chains have not yet been explored.
Methodology: This study presents a comprehensive PTM analysis of fibrillar collagen chains extracted from the skin of different mutants of C-P4Hs (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) and wild-type mice. In this study, proteomics-based comprehensive PTM site identification by MS2 level ions from raw mass spectrometry data was performed, and MS1-level quantification was performed for PTM occupancy percentage analysis.
Results and discussion: A total of 421 site-specific PTMs were identified on fibrillar collagen chains (COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1) extracted from wild-type mice skin. A total of 23 P4HA1-specific and seven P4HA2-specific 4-hydroxyproline sites on fibrillar collagen chains were identified. Moreover, it was found that the P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion can affect the 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages in mice skin. Interestingly, increased levels of lysyl 5-hydroxylation were detected upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and full deletion of P4ha2. These findings show that the effects of deletion of prolyl 4-hydroxylases are not limited to less 4-hydroxylation on some specific proline sites, but it can also modulate the prolyl 3-hydroxylation, lysyl 5-hydroxylation, and O-glycosylation occupancy percentages in the fibrillar collagen chains in a site-specific manner.
1 Introduction
Collagens are the most abundant component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagens provide an attachment surface to the cells in the body and maintain the structural stability and elasticity of all tissues (Gelse et al., 2003). Collagens play important roles in cellular functions, including cell-to-cell communication, cell migration, and cell growth by interaction with cell-surface receptors (integrins, discoidin domain receptor, glycoprotein VI, and FC gamma receptor) (Leitinger and Hohenester, 2007; Borza et al., 2018; Sarohi et al., 2022a; Farndale et al., 2023). Collagens are very dynamic in structure. Collagens are heavily decorated with PTMs during biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) prior to helix formation. PTMs are required for proper folding, stability, and functioning of the collagens (Takaluoma et al., 2007; Vranka et al., 2010; Pokidysheva et al., 2014; Terajima et al., 2014; Montgomery et al., 2018; Morello, 2018; Rappu et al., 2019; Tonelli et al., 2020).
Collagen PTMs are site-specifically catalyzed by collagen-modifying enzymes. Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases (C-P4Hs), that is, prolyl 4-hydroxylase alpha 1 (P4HA1), P4HA2, and P4HA3, catalyze 4-hydroxylation on prolines present in collagen chains. The 3-hydroxylation on proline is further catalyzed by prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 (P3H1), P3H2, and P3H3 in the collagen chains. The lysine sites present in the collagens can also be 5-hydroxylated. Lysyl hydroxylation in the collagen is catalyzed by lysyl hydroxylase 1 (LH1), LH2, and LH3 encoded by procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenases (Plods). Furthermore, 5-hydroxylysines in collagen chains can be O-glycosylated to galactosyl-hydroxylysine (G-HyK) and glucosylgalactosyl-hydroxylysine (GG-HyK). G-HyK on 5-hydroxylysines is catalyzed by procollagen galactosyltransferases (COLGALTs), and GG-HyK is primarily catalyzed by LH3. One of the most well-studied PTM in the fibrillar collagen chain is prolyl 4-hydroxylation (Weiss and Klein, 1969; Risteli and Kivirikko, 1974; Chu et al., 1997; Nishi et al., 2005; Sipila et al., 2018; Rappu et al., 2019). The role of prolyl 4-hydroxylases has been studied in thermal stability and in adverse ECM remodeling leading to pathophysiological complications, such as fibrosis and cancer progression (Vasta and Raines, 2018; Xiong et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2021).
The two most abundant C-P4H forms in mice skin are P4HA1 and P4HA2 (Salo et al., 2024). The P4HA1 enzyme is essential for the functioning of the mouse body, and complete deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1−/−) is embryonically lethal (Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022). However, mice with a partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−) are viable, and mice with partial (P4ha2+/−) or complete (P4ha2−/−) deletion of P4ha2 are also viable with no apparent phenotype (Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022). Interestingly, mice with a partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−) and partial deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2+/−) also survive. However, a comprehensive analysis of the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on collagen PTMs, including 3-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, and O-glycosylation, has not yet been explored. Moreover, comprehensive site-specific identification of collagen PTMs in fibrillar collagen chains has not been performed. In this study, PTM analysis was performed to study the effects of deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2 on site-specific modifications of fibrillar collagen chains (COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1) extracted from the wild-type and P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion mutant (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) mice. This study utilizes the publicly available raw mass spectrometry data #PXD008802 (Sipila et al., 2018) of mice skin fibrillar collagen extracted from wild-type mice and different deletion mutants of P4ha1 and P4ha2.
2 Methods
2.1 Mass spectrometry data resource
The publicly available proteomic dataset #PXD008802 submitted by Sipila et al. (2018) in ProteomeXchange was utilized in this study. This dataset contains raw mass spectrometry data (54 files) of fibrillar collagen extracted from the skin of prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant and wild-type mice. There are 12 raw mass spectrometry files present for the P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/− mice group, 14 raw files for P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, 10 raw files for P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, eight raw files for P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−, and 10 raw files for the wild-type mice group. All the biological replicates had a technical duplicate. This proteomic dataset acquisition was performed using a nanoflow HPLC system (Easy-nLC1000, Thermo Fisher Scientific) coupled with a Q-Exactive mass spectrometer from ThermoFisher, as described earlier (Sipila et al., 2018).
2.2 Proteomic data analysis
In this study, 54 raw mass spectrometry files from dataset #PXD008802 were analyzed. The MyriMatch (Tabb et al., 2007) search engine was utilized for proteomic database searches. A two-step MyriMatch database search strategy (general search followed by PTM-specific search) was employed for in-depth analysis of site-specific collagen PTM (hydroxylation of prolines and lysines and O-glycosylation of hydroxylysines) present on fibrillar collagen chains of mice skin.
2.2.1 General MyriMatch database search
First, a general MyriMatch (Tabb et al., 2007) database search was performed on the Mus musculus database downloaded from Uniprot.org (downloaded on 4-Dec-2021) containing 17,090 entries. In general search, the tolerance for precursors was set at ±10 ppm, and for fragment ions, it was allowed up to ±20 ppm. Fully tryptic peptides were considered for database search with missed cleavages allowed up to a maximum of two per peptide. Carbamidomethylation (+57.0236) on cysteine was used as static modification, and methionine oxidation (+15.994916) along with hydroxyproline (+15.994916) were used as dynamic modifications (Sarohi et al., 2022b). The maximum dynamic modifications per peptide were set to a maximum of four per peptide. After the completion of the MyriMatch general database search, the results were imported to IDPICKER (Ma et al., 2009) for parsimonious protein grouping and controlling FDR. The FDR was controlled at <1% at peptide-spectrum matches (PSMs), peptide, and protein group levels. Then, this FDR-controlled list of identified proteins was exported from IDPicker as subset fasta. This subset fasta was utilized for an in-depth collagen PTM-specific database search.
2.2.2 MyriMatch PTM-specific database search
In the PTM-specific subset fasta database search using MyriMatch, precursor and fragment ion mass tolerance was kept at 10 ppm and 20 ppm, respectively (Sarohi et al., 2022b). Carbamidomethylation (+57.0236) of cysteine was used as static modification, and oxidation (+15.994916) of methionine was used as dynamic modification. Oxidation (+15.994916) of proline was used as a dynamic modification for the detection of hydroxyprolines in the full-length collagen chains. Further motif-based following dynamic modifications were also included: 3 prolyl-hydroxylation (GP!P! 15.994916), lysyl hydroxylation (GXK! 15.994916), galactosyl-hydroxylysine (GXK! 178.047738), and glucosylgalactosyl-hydroxylysine (GXK! 340.100562) (Sarohi et al., 2022b). A maximum of 10 modifications were allowed per peptide. A maximum number of four missed cleavages per fully tryptic peptide was allowed. After completion of the MyriMatch PTM-specific database search, the result files were further grouped for PSM matches, peptide, and protein group identification using IDPicker with <1% FDR (for PSM, peptide, and protein IDs). Identification of 3-hydroxyprolines was only considered if a proline residue was found to be hydroxylated at the “X” position of a “-Xaa-HyP-Gly” motif in the collagen chains. Furthermore, IDPicker and pLabel (Wang et al., 2007) were used for the identification, manual inspection, analysis, and validation of peptide-spectrum matches (PSMs) for assigning site-specific PTMs on fibrillar collagen chains.
2.2.3 MS1 level quantitation of the occupancy percentage of site-specific collagen PTMs using Skyline
The results files of the MyriMatch PTM-specific database search were parsed through Peptide Prophet (TPP pipeline module) (Pedrioli, 2010) for probability scoring between 0 and 1. Parsed MyriMatch results were used to build the spectral library in the Skyline (MacLean et al., 2010). The spectral library was utilized for the extraction of MS1 intensities of different unmodified and modified forms of collagen peptides from the raw mass spectrometry. For the occupancy percentage calculation, MS1 intensities of valid modified (with a particular modification site) peptides and respective unmodified peptides were extracted using Skyline.
2.3 Statistical analysis
A two-tailed Student’s test was applied for the statistical analysis of the occupancy percentage of site-specific PTMs. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant in all tests.
3 Results
Skin is one of the most collagen-rich tissues of the mouse. The high abundance of collagen in the skin provides the opportunity for in-depth collagen PTM analysis. In this study, site-specific identification of PTMs was performed on fibrillar collagen chains extracted from wild-type mice skin. Additionally, site-specific PTM quantitation was performed to assess the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on fibrillar collagen PTM networks.
3.1 Identification of site-specific collagen PTMs in fibrillar collagens extracted from wild-type mouse skin
In this study, site-specific collagen PTMs, that is, 4-hydroxyproline (4-HyP), 3-hydroxyproline (3-HyP), hydroxyproline (HyP), 5-hydroxylysine (HyK), galactosyl-hydroxylysine (G-HyK), and glucosylgalactosyl-hydroxylysine (GG-HyK) sites were identified on COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 chains extracted from the wild-type mice skin (Table 1). Hydroxyproline present on the Yaa position of the -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- motif was considered as 4-hydroxyproline. Hydroxyproline present on the Xaa position of the -Xaa-4HyP-Gly- motif was considered as 3-hydroxyproline. Sites where hydroxyproline is present on the Xaa position of the -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- motif and Yaa is not a proline/hydroxyproline were labeled as only “hydroxyproline” sites in this study. However, there is a high probability that these sites are also 4-hydroxyproline sites (Van Huizen et al., 2019). Hydroxylysine present on the Yaa position of -Xaa-Yaa-Gly was considered as 5-hydroxylysine (Perdivara et al., 2013). The O-glycosylation was identified based on the mass of monosaccharide (G-HyK) and disaccharide (GG-HyK) (Perdivara et al., 2013; Yamauchi et al., 2019; Sarohi et al., 2022b).
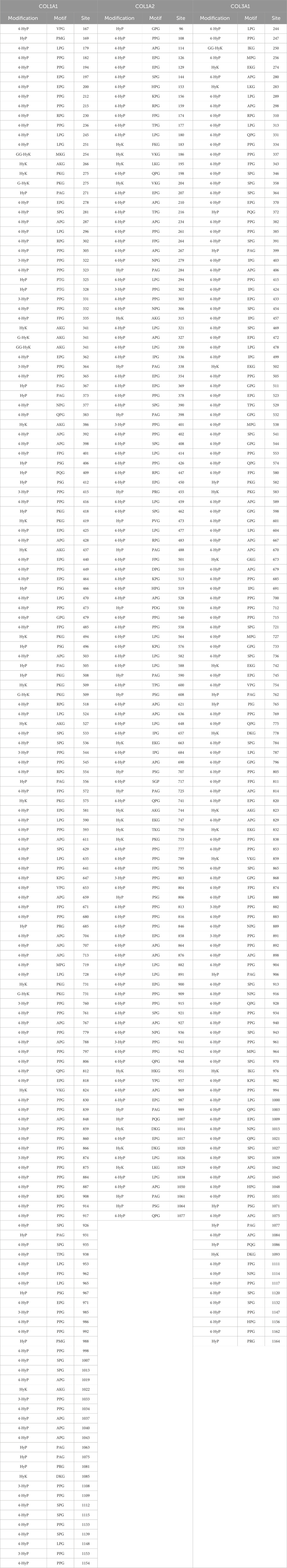
Table 1. Site-specific collagen PTMs identified on fibrillar collagen chains extracted from wild-type mouse skin. Collagen PTMs, that is, 4-hydroxyproline (4-HyP), 3-hydroxyproline (3-HyP), hydroxyproline (HyP), 5-hydroxylysine (HyK), galactosyl-hydroxylysine (G-HyK), and glucosylgalactosyl-hydroxylysine (GG-HyK), are listed under the “Modifications” column in the table. The -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- motif of collagen PTMs is represented under the “Motif” column, where a one-letter code for three amino acids (X position amino acid, Y position amino acid, and glycine) is written for every collagen PTM that was identified separately in COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 chains. Under the “Site” column, the specific site (number of that amino acid in the full-length protein) that is identified to have a specific PTM is written in Table 1.
On the wild-type mice skin COL1A1 chain, a total of 160 site-specific PTMs were detected. A total of 106 4-hydroxyproline sites, 12 3-hydroxyproline sites, 22 hydroxyproline sites, 14 5-hydroxylysine sites, four galactosyl-hydroxylysine sites, and two glucosylgalactosyl-hydroxylysine sites on COL1A1 were identified. On COL1A2 extracted from wild-type mice skin, a total of 124 PTM sites were identified in this analysis. A total of 89 4-hydroxyproline sites, four 3-hydroxyproline sites, 17 hydroxyproline sites, and 14 5-hydroxylysine sites were detected on COL1A2. In this analysis, no O-glycosylation site was detected on COL1A2 extracted from the skin of wild-type mice.
Except for these two chains of collagen I, site-specific PTMs on collagen III, which form a homotrimer of COL3A1 chains, were also identified. A total of 137 PTM sites on wild-type mice skin COL3A1 were identified. COL3A1 was found to have 112 4-hydroxyproline sites, two 3-hydroxyproline sites, 10 hydroxyproline sites, 12 5-hydroxylysine sites, and one glucosyl-galactosyl-hydroxylysine site. In this analysis, a total of 421 site-specific collagen PTMs were identified by MS2-level peptide-spectrum match-based validation on COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 chains extracted from wild-type mice skin. COL1A1 was found to be the most modified and COL1A2 to be the least modified among the three fibrillar collagen chains.
3.2 Mass spectrometry-based validation of the -Xaa-Pro-Gly- motif catalyzed by prolyl 4-hydroxylases
There are -Gly-Xaa-Yaa- repeats present in the helical region of collagen 1. During the proteomics analyses, proline present on the Yaa position of -Gly-Xaa-Yaa- or -Gly-Xaa-Yaa-Gly- motif was considered to be 4-hydroxylated. However, previous studies show that proline present in the -Xaa-Pro-Gly- motif is catalyzed by prolyl 4-hydroxylases C-P4Hs (Pihlajaniemi et al., 1991; Myllyharju and Kivirikko, 1999; Pekkala et al., 2003; Koski et al., 2009; Perdivara et al., 2013). In this regard, the MS analysis shows an interesting finding (Figure 1). This study shows that glycine before -Xaa-Pro- is not required for the catalysis of hydroxylation on proline by C-P4Hs (Figures 1A2, B2); rather, glycine is found after the -Xaa-Pro- position in all identified 4-hydroxyproline sites (Table 1). The presence of hydroxylation on COL1A1 P167 and COL1A2 P96 depicts that glycine is not required before -Xaa-Pro- (Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino acid) for motif recognition by C-P4Hs. The COL1A1 P167 does not fit in the “-Gly-Xaa-Yaa-” or “-Gly-Xaa-Yaa-Gly-” motifs because serine (S) and valine (V) are present on 165 and 166 sites, respectively (Figure 1A2). Glycine is not present on the COL1A1 165 site, but it is present on the 168 sites. This means that site COL1A1 P167 only fits in the “-Xaa-Yaa-Gly-” motif. Similarly, in the case of COL1A2 P96, serine is present before -Xaa-Pro- (Figure 1B2), and P96 fits only in the “-Xaa-Yaa-Gly-” motif. Moreover, every other proline modification site shown in Table 1 follows the -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- motif. Collagen contains -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- repeats in the helical region of collagen 1. Repetition of these -Xaa-Yaa-Gly motifs led to the confusion of considering either -Gly-Xaa-Yaa- or -Gly-Xaa-Yaa-Gly- to be the preferred motif of C-P4H activity. Previously, several groups have shown that -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- is the C-P4H-specific motif on collagen (Risteli and Kivirikko, 1974; Pihlajaniemi et al., 1991; Myllyharju and Kivirikko, 1999; Pekkala et al., 2003; Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022). This study provides proteomics-based evidence (Figure 1) for the “-Xaa-Yaa-Gly-” motif validation.
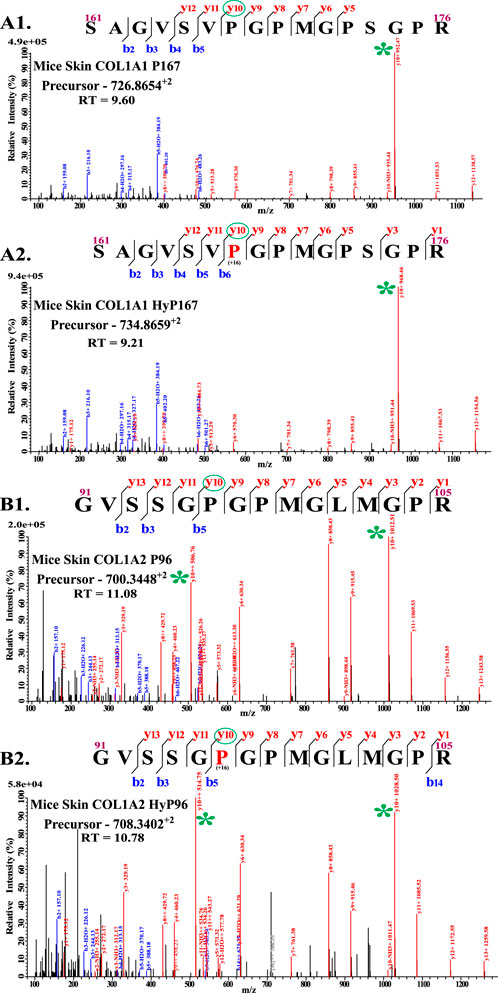
Figure 1. Validation of C-P4h specific motif (-Xaa-Pro-Gly-). (A1) shows the unmodified peptide from COL1A1 with residues numbered 161–176. (A2) shows the presence of hydroxyproline on P167 and the presence of hydroxyproline on the -Xaa-Pro-Gly- motif. Similarly, (B1) shows an unmodified peptide from COL1A2 (91–105), and (B2) shows the presence of hydroxyproline on P96 on the “Yaa” position of the -Xaa-Yaa-Gly- motif.
Table 1 shows that all 4-hydroxyproline sites have a -Xaa-Pro-Gly motif. Of 106 4-hydroxyproline sites on wild-type mice skin COL1A1, 17 4-hydroxyproline sites were detected on -Ala-Pro-Gly- motif, 10 4-hydroxyproline sites were detected on -Glu-Pro-Gly- motif, and seven 4-hydroxyproline sites are detected on -Phe-Pro-Gly- motif. In this analysis, the most common motif for 4-hydroxyproline is the -Pro-Pro-Gly- motif, and 35 4-hydroxyproline sites on this motif were identified. A total of 12 4-hydroxyproline sites on the -Leu-Pro-Gly- motif, five 4-hydroxyproline sites on the -Arg-Pro-Gly- motif, 11 4-hydroxyproline sites on the -Ser-Pro-Gly- motif, two 4-hydroxyproline sites on the -Gln-Pro-Gly- motif and -Val-Pro-Gly- motifs, and one site each on the -Gly-Pro-Gly- motif, -Lys-Pro-Gly-, -Met-Pro-Gly-, -Asn-Pro-Gly- motif, and -Thr-Pro-Gly- motif were detected. Similarly to wild-type COL1A1, 4-hydroxyproline sites were present in -Xaa-Pro-Gly- motifs in COL1A2 and COL3A1 chains.
3.3 Identification of site-specificity of C-P4Hs in fibrillar collagens
C-P4Hs modify proline residues present on the -Xaa-Pro-Gly- motif in collagens. However, collagen-modifying enzymes are known to have site-specificity (Morello et al., 2006; Pokidysheva et al., 2013; 2014; Hudson et al., 2015; Terajima et al., 2016; Tonelli et al., 2020; Ishikawa et al., 2022). In this study, 4-HyP occupancy percentage quantitation was performed to determine site-specificity of P4HA1 and P4HA2 enzymes on COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 extracted from skin of wild-type and C-P4Hs mutant (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) mice.
3.3.1 Identification of site-specificity of P4HA1 in fibrillar collagens
P4HA1 is the predominant C-P4H form in mice skin, constituting ∼83% of all C-P4Hs (Salo et al., 2024). P4HA1 is essential for the survival of a mouse. A complete deletion (P4ha1−/−) of P4ha1 is embryonically lethal in mice (Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022). P4HA1 null mice are not viable. This means that P4HA1 activity on collagen is highly important for the development of the mouse body. P4HA1 is a prolyl 4-hydroxylase enzyme; this means that some 4-hydroxyproline sites are pivotal for mouse development, and without 4-hydroxylation on these proline sites, mice cannot survive. Interestingly, P4ha1 ± mutant mice are viable. Prolyl 4-hydroxylation activity is still retained in mice upon partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−). Surprisingly, a total of 23 sites on mice skin COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 chains were found to be fully (≥99%) 4-hydroxylated in the wild type as well as in P4ha1 and P4ha2 mutants (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) (Table 2).
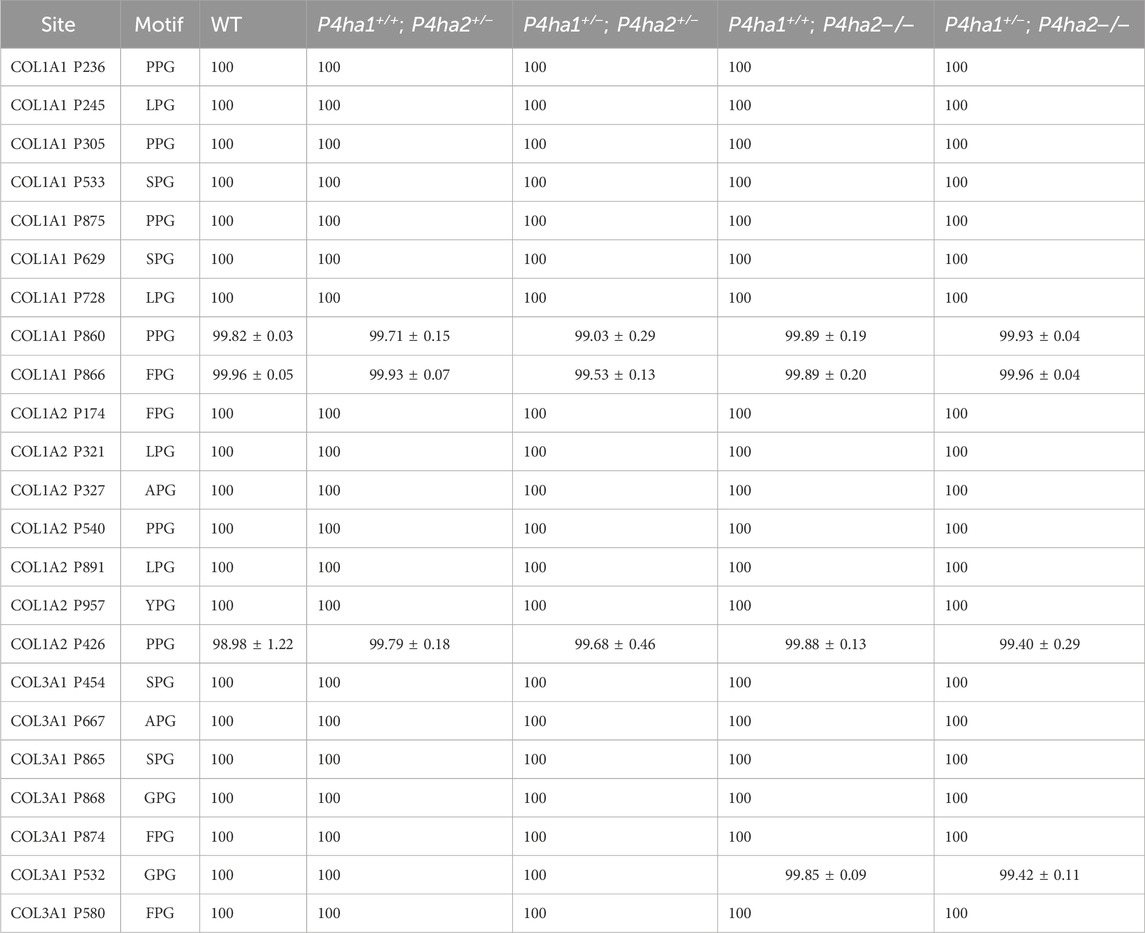
Table 2. P4HA1-specific 4-hydroxyproline sites with occupancy (%) in mouse skin fibrillar collagen chains.
Interestingly, neither the occupancy percentages of these specific 4-HyP sites nor the partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−) decreased upon the complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−). These findings hint that P4HA2 does not catalyze 4-hydroxylation on these 23 sites (Table 2). On the other hand, P4HA3 constitutes only ∼2% of C-P4Hs in wild-type mice skin (Salo et al., 2024). Because P4HA1 is the most abundant (∼83% abundance) C-P4H isoform in the skin, even after partial deletion, it is likely to be present in higher amounts than P4HA2 and P4HA3. This indicates that even after partial deletion of gene P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−), the P4HA1 enzyme retains the ability to fully catalyze the 4-hydroxylation on these 23 proline sites. These sites have specificity for P4HA1 in mice skin, as the 4-HyP occupancy percentages on these sites are not affected by the absence/reduced abundance of other C-P4Hs (Table 2).
3.3.2 Identification of site-specificity of P4HA2 in fibrillar collagens
P4HA2 is the second-most abundant isoform of the C-P4H family, and it constitutes ∼15% of all C-P4Hs in mice skin. Interestingly, this study reveals P4HA2-specific 4-HyP sites that are not compensated by predominant P4HA1 in the absence of P4HA2 in mice skin. Interestingly, this study shows that partial deletion (P4ha2+/−) and complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−) differently affect the 4-hydroxyproline level in seven fibrillar collagen sites (Figure 2). In this analysis, seven 4-HyP sites of mice skin COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 chains were found to have more than 95% occupancy in wild type, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± mice. In mice with a single allele deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2+/−), the 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on these seven sites (Table 3; Figure 3) were similar to wild-type mice. However, the 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on these seven sites were significantly decreased (Figure 3; Table 3) in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/− and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−). These findings indicate that P4HA2 is required to fully modify these sites, and other C-P4Hs were not able to sufficiently modify these seven sites site up to the level of the wild-type mice group upon complete deletion (Figures 2–4; Table 3).
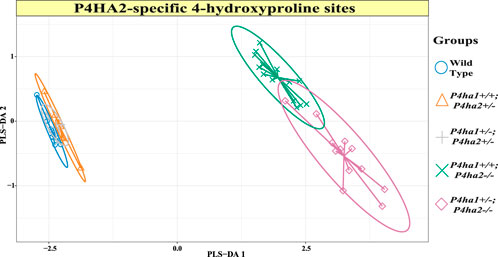
Figure 2. Expression of 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on P4HA2-specific sites. The sPLS-DA plot of seven P4HA2-specific 4-hydroxyproline site occupancy percentages shows that the 4-hydroxyproline expression is almost similar in wild-type, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± mice. However, the expression of occupancy percentages of these seven 4-hydroxyproline sites is different in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−).
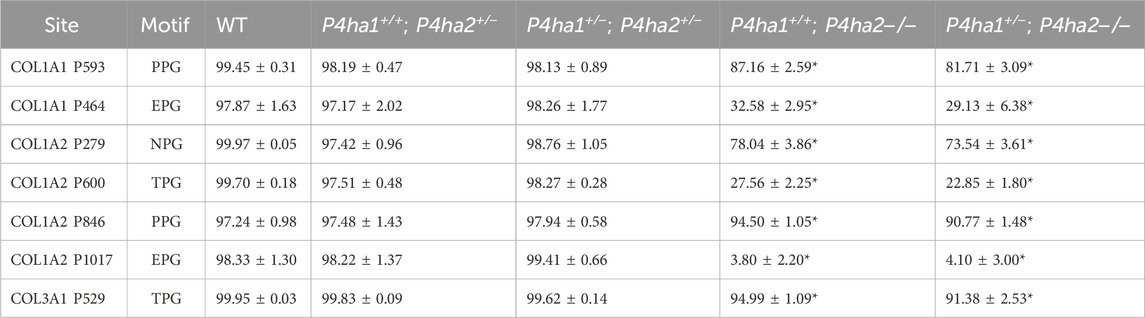
Table 3. P4HA2-specific 4-hydroxyproline sites with occupancy (%) in mouse skin. In the table, (*) represents a p-value <0.05 calculated using Student’s t-test, conducted on wild-type and prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant mice.
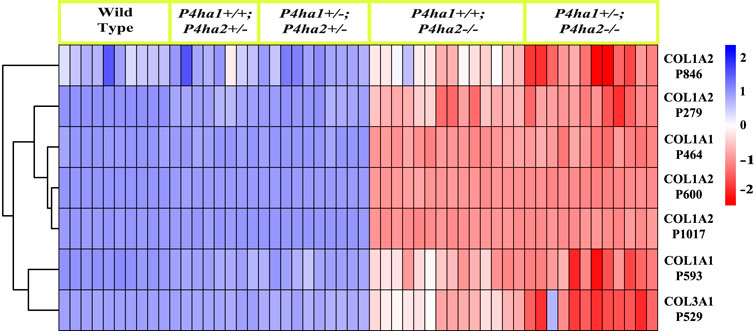
Figure 3. Occupancy percentages of P4HA2-specific 4-HyP sites. The heatmap shows that the 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on seven fibrillar collagen sites are almost similar in wild-type, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± mice, but occupancy is significantly decreased in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−).
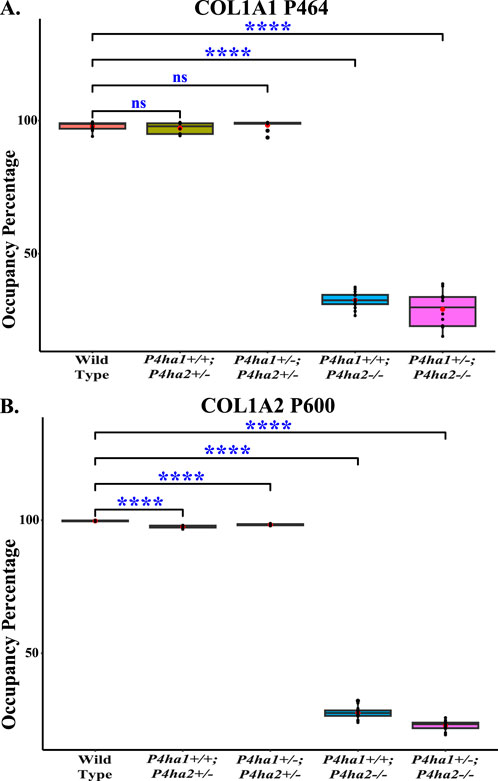
Figure 4. Occupancy percentages of COL1A1 P464 and COL1A2 P600. On the P4HA2-specific sites P464 (A) and P600 (B), the 4-hydroxyproline occupancy is almost similar in wild-type, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± mice, but occupancy is significantly decreased in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−). In the figure, (ns) represents a p-value >0.05, and (****) represents a p-value <0.0001. The p-value is calculated using the Student’s t-test, conducted on wild-type and respective prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant mice.
3.4 Analysis of the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on other site-specific PTMs of mouse skin collagen I
In order to delineate the effect of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on collagen PTMs other than 4-hydroxyproline, the site-specific quantitation of 3-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, and O-glycosylation sites was performed on COL1A1 and COL1A2 chains extracted from the skin of wild-type mice and C-P4H mutant (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) mice.
3.4.1 Analysis of the effect of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on the site-specific 3-hydroxylation on mouse skin collagen I
The effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on the occupancy percentages of prolyl 3-hydroxylation sites on COL1A1 and COL1A2 were analyzed in this study. P3H1 is a prominent prolyl 3-hydroxylase. P3H1 catalyzes the site-specific prolyl 3-hydroxylation on collagen I (COL1A1 and COL1A2) chains (Cabral et al., 2007; Vranka et al., 2010; Pokidysheva et al., 2013). In COL1A1, 3-HyP sites, that is, P1153 (it is site P986 in cleaved COL1A1) and P874 (P707), are reported to be 3-hydroxylated by P3H1 (Pokidysheva et al., 2013) and in COL1A2, P803 (P707) is modified by P3H1 in mice bone (Pokidysheva et al., 2013). In this study, quantitation of 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentage on these three classical 3-HyP sites of collagen 1 was performed. On site COL1A1 P1153, a 94.65% occupancy percentage was detected in wild-type mice skin, which is in accordance with the previous findings by Pokidysheva et al. (2013). Additionally, on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803, respectively, 5.7% and 13.55% occupancy percentages were detected in wild-type mice skin. However, these COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites were not previously detected in mice skin by Pokidysheva et al. (2013).
Interestingly, this study reveals that partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−) and complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−) significantly increases the 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites compared to wild-type mice (Figure 5; Table 4). On the COL1A1 P1153 site, a significant decrease in 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentage in P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± mice was detected compared to wild-type mice (Figure 5; Table 4). However, the 3-HyP occupancy of P1153 was significantly increased in complete P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−) deleted mutant mice similar to COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites (Figure 5; Table 4). This indicates that complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−) enhances the prolyl 3-hydroxylation on specific sites on collagen 1.
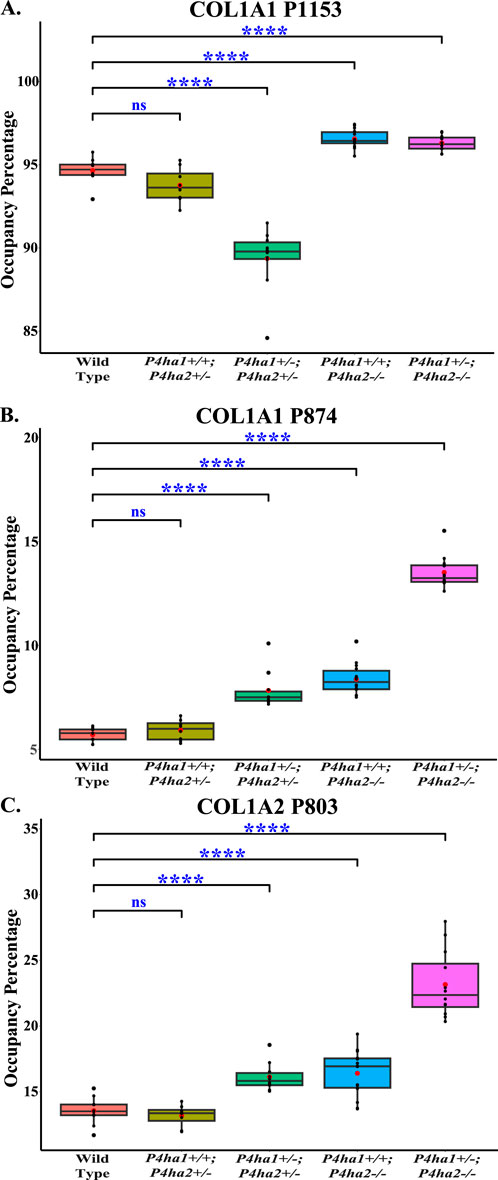
Figure 5. Altered occupancy percentages of P3H1-specific 3-hydroxyproline sites of collagen I upon P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion. (A) The 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentage on COL1A1 P1153 (P986) is decreased compared to wild type upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2 but is increased upon complete deletion of P4ha2. On the other hand, 3-hydroxyproline occupancy on (B) COL1A1 P874 (COL1A1 P707) and (C) COL1A1 P803 (P707) is elevated compared to wild-type mice upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and/or complete deletion of P4ha2. In the figure, (ns) represents a p-value >0.05, and (****) represents a p-value <0.0001. The p-value is calculated using the Student’s t-test, conducted on wild-type and respective prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant mice.
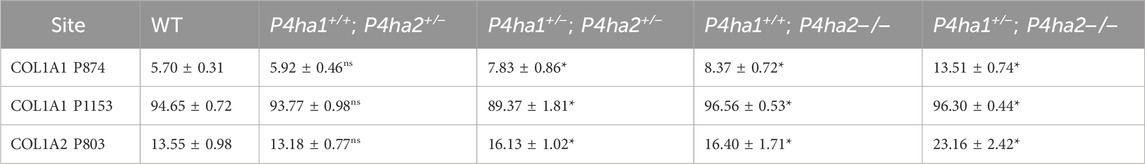
Table 4. Quantitation of 3-hydroxyproline occupancy (%) on P3H1-specific sites in collagen I. In the table, (*) represents a p-value <0.05 calculated using Student’s t-test, conducted on wild-type and respective prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant mice.
3.4.2 Analysis of the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on site-specific lysyl 5-hydroxylation on mouse skin collagen I
In collagens, lysines are also heavily modified. Lysine sites are vital for collagen cross-linking in the extracellular matrix. In this study, quantitation of the occupancy percentages of hydroxylysine and O-glycosylation on helical collagen cross-linking lysine sites and helical collagen non-cross-linking lysine sites was performed. It was found that COL1A1 N-terminal helical cross-linking site K254 (generally known as K87) was fully (∼99%) (Table 5) modified with glucosylgalactosyl-hydroxylysine (GG-HyK) in wild-type mice and in C-P4H mutant (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) mice. Interestingly, it was detected that partial deletion of P4ha1 and complete deletion of P4ha2 significantly increased the hydroxylysine level in COL1A2 N-terminal helical cross-linking site K183 (Figure 6; Table 5). Similarly, an elevation in hydroxylysine occupancy percentage in non-cross-linking COL1A1 K731 and COL1A2 K315 sites was also detected. Moreover, the occupancy percentages of COL1A1 K731 galactosyl-hydroxylysine (G-HyK) were found to be elevated upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and complete deletion of P4ha2 (Table 5). These findings indicate that prolyl 4-hydroxylases play a crucial role in the hydroxylation of helical cross-linking lysine sites and helical non-cross-linking lysine sites in collagen 1 (Figure 6; Table 5).
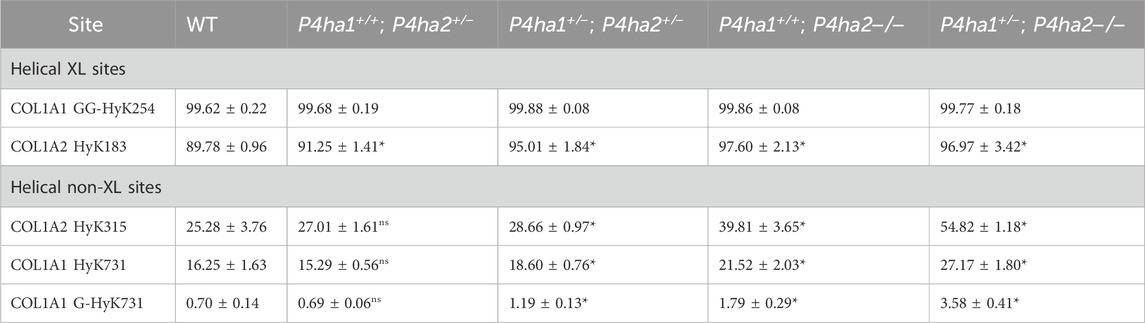
Table 5. Occupancy (%) levels of lysyl hydroxylation and O-glycosylation on collagen I helical cross-linking and non-cross-linking sites. In the table, (*) represents a p-value <0.05, and (ns) represents a p-value>0.05 calculated using Student’s t-test, conducted on wild-type and respective prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant mice.
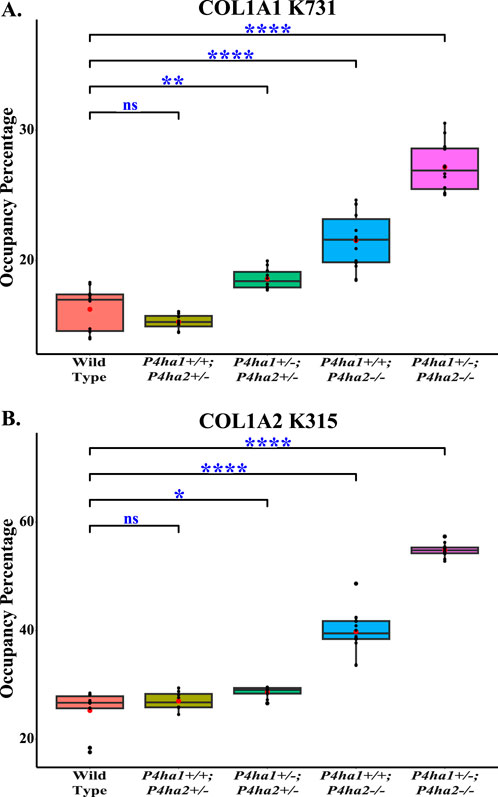
Figure 6. Altered occupancy percentages of two non-cross-linking helical hydroxylysine sites upon deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2. Occupancy percentages of collagen I helical cross-linking sites in wild-type and C-P4h mutant mice. 5-hydroxylysine occupancy percentages on COL1A1 K731 (A) and COL1A2 K315 (B) are increased upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and/or complete deletion of P4ha2. In the figure, (ns) represents a p-value >0.05, (*) represents a p-value <0.05, (**) represents a p-value <0.01, and (****) represents a p-value <0.0001. The p-value is calculated using Student’s t-test, conducted on wild-type and respective prolyl 4-hydroxylase mutant mice.
4 Discussion
In wild-type mice skin, P4HA1 is the most abundant isoform among all three C-P4Hs. P4HA1 constitutes ∼83% and P4HA2 constitutes ∼15% of total C-P4Hs in wild-type mice skin (Salo et al., 2024). P4HA1 has 5-fold more abundance than the second most abundant C-P4H isoform, that is, P4HA2. Complete deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1−/−) is embryonically lethal in mice (Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022). However, mice with a partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−) are viable. This means that the P4HA1 enzyme encoded by only one allele (P4ha1+/−) can also catalyze the modifications of specific collagen sites that are important for mouse survival. On the other hand, mice with a partial (P4ha2+/−) or complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−) are viable and do not have any visible phenotype (Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022). This fact makes it interesting to decode the contribution of P4HA2 in mice skin collagen networks.
In this study, the effects of partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−), partial (P4ha2+/−), and complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−) on 4-hydroxyproline sites were evaluated in detail to delineate the site-specificity of P4HA1 and P4HA2 enzymes. Surprisingly, 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on 23 sites were found to be around 100% (≥99%) in wild-type as well as mutant mice with partial P4ha1 deletion, partial P4ha2 deletion and complete P4ha2 deletion (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) (Table 2). The occupancy percentages of 4-hydroxylation on these proline sites did not decrease upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2. Moreover, 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on these 23 sites did not decrease even upon complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha2−/−). Because P4HA1 has the highest (∼83%) abundance among C-P4Hs in wild-type mice skin (Sipila et al., 2018; Tolonen et al., 2022; Salo et al., 2024), it is plausible that the P4HA1 enzyme encoded by only one allele P4ha1 (+/−) retains its prolyl 4-hydroxylation catalytic activity and can fully (∼100%) modify these 23 sites (Table 2). Except for these 23 sites, 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on COL1A1 P230 (GRPGER), COL1A1 P671 (GFPGER), COL1A1 P719 (GMPGER), and COL1A2 P159 (GRPGER) were also found to be ∼100%, as previously detected by Sipila et al. (2018). Full occupancy of 4-hydroxyproline on these 27 sites indicates that these sites have a high significance in collagen triple helix formation, triple helix stability, and function of fibrillar collagens.
This study also identified P4HA2-specific sites in fibrillar collagen chains. The 4-hydroxyproline occupancy percentages on seven sites (Table 3) were found to be >95% in wild-type, P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± mice. However, the occupancy percentages on these seven sites were significantly decreased in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/− and P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−). Among these seven sites, three sites (COL1A1 P464, COL1A2 P600, and COL1A2 P1017) were found to have only <35% occupancy percentages in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 compared to >95% occupancy percentages detected in wild-type and partial P4ha1/P4ha2 deleted mice (Figures 3, 4; Table 3). The decreased occupancy percentages on these seven sites in the absence of P4HA2 indicate that these sites have specificity for P4HA2, and these sites cannot be sufficiently (>95%) modified by P4HA1 and P4HA3 enzymes. These P4HA2-specific sites have >95% 4-hydroxylation occupancy in wild type, so these sites might have some role in collagen biosynthesis and collagen interactions with extracellular proteins and cell-surface receptors.
Recently, Salo et al. (2024) reported that the complete deletion of P4ha2 reduces the melting temperature of collagen and also affects collagen fibril assembly in the ECM. However, high levels of P4HA2 are associated with poor prognosis and progression of metastasis in many tissues of the human body (Aggarwal et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2022). Interestingly, it has even been reported that inhibition/absence of P4HA2 attenuates the metastasis progression and reduces the deposition of collagen in ECM (Lin et al., 2021; Shang et al., 2022). This indicates that although the basal levels of P4HA2 are required for proper collagen folding and collagen fibril assembly, elevated levels of P4HA2 can facilitate the progression of pathophysiological complications where collagen excessively gets deposited in the ECM. Therefore, P4HA2 can be a potential therapeutic target to inhibit excessive collagen deposition in ECM.
This study reports that the deletion of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases P4ha1 and P4ha2 alters the site-specific 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentage in mice skin (Figure 5; Table 4). The elevated levels of 3-hydroxyproline occupancy were detected on COL1A1 P874, COL1A1 P1153, and COL1A2 P803 sites in mice skin upon complete deletion of P4ha2 (Figure 5; Table 4). These 3-hydroxyprolines are reported to have specificity for the P3H1 enzyme in mice bone collagen 1 (Pokidysheva et al., 2013). Elevation of 3-hydroxylation on these sites hints toward the altered activity of prolyl 3-hydroxylases (P3H1, P3H2, P3H3) upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and complete deletion of P4ha2. These findings show that there is a strong association of P4HA1 and P4HA2 with prolyl 3-hydroxylation activity. However, there is complexity in the connection of P4HA1 and P4HA2 with prolyl 3-hydroxylase activity on these three proline sites. The 3-hydroxylation on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 was not changed upon partial deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2+/−) compared to wild-type (Figure 5; Table 4). This is the first study to identify COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites in the mice skin. These sites are popularly known as A3 sites in COL1A1 and COL1A2. The 3-hydroxylation on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 was elevated upon the partial deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2 (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−), and 3-hydroxylation was also increased in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/−, and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−) compared to the wild-type mice. Among all genotypes, mice with a partial deletion of P4ha1 and complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−) have the highest levels of 3-hydroxyproline occupancy on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites. This means that partial deletion of P4ha2 cannot alter the 3-hydroxylation activity on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites in mice skin, but partial deletion of P4ha1 or complete deletion of P4ha2 can elevate the 3-hydroxylation occupancy on these two sites.
On the other hand, P4ha1 deletion and P4ha2 deletion have different effects on the 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentage on the COL1A1 P1153 site. This P1153 site, popularly known as the A1 site, is associated with osteogenesis imperfecta. This site has been reported to have specificity for P3H1 in mice tendon, bone, and skin tissues (Pokidysheva et al., 2013). This analysis found that the 3-hydroxylation occupancy percentage on the COL1A1 P1153 site was decreased (∼4% compared to wild-type) upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2 (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−) (Figure 5; Table 4). However, 3-hydroxylation on this site was elevated (∼2% compared to wild-type) in P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/− mice, and a similar increase was detected in P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/− mice (Table 4). Partial deletion of P4ha1 has a different effect on P1153 than it has on COL1A1 P874 and COL1A2 P803 sites. Partial deletion of P4ha1 with partial deletion P4ha2 (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2+/−) results in decreased 3-hydroxyproline occupancy percentage on the P1153 site (Figure 5). This indicates that partial deletion of P4ha1 can decrease the 3-hydroxylation level on COL1A1 P1153. However, complete deletion of P4ha2 can elevate the 3-hydroxylation on P1153 compared to the wild-type. The different effects of P4ha1 deletion and P4ha2 deletion hint toward different modes of interaction of P4HA1 and P4HA2 with prolyl 3-hydroxylases.
This study highlights that the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion are not limited to the proline modifications. This study shows that lysine modifications are also affected by P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion. Despite having enzymatic activities of 4-hydroxylation on proline sites, deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2 can affect the lysine modifications as well. This analysis shows elevated levels of 5-hydroxylysine occupancy on collagen 1 helical cross-linking lysine site (COL1A2 K183) as well as helical non-cross-linking lysine sites (COL1A1 K731 and COL1A2 K315) in mice with a partial deletion of P4ha1 (P4ha1+/−; P4ha2 ± and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−) and mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 (P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/− and P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/−) compared to the wild-type mice (Figure 6; Table 5). The occupancy percentage of helical non-cross-linking site COL1A2 K315 was increased more than twofold in P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/− mice compared to the wild-type. Similarly, the levels of occupancy percentages of 5-hydroxylation and O-glycosylation (galactosyl-hydroxylysine) on the COL1A1 K731 site were also increased upon partial deletion of P4ha1 and complete deletion of P4ha2. This study reveals that partial deletion of P4ha1 and complete deletion of P4ha2 can elevate the 5-hydroxylysine and O-glycosylation occupancy percentages on helical cross-linking and non-cross-linking lysine sites. These findings indicate that P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion can modulate lysyl 5-hydroxylation activity in collagen 1. Modulation in 5-hydroxylysine occupancy on helical cross-linking sites upon P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion can also have effects on collagen cross-linking.
It has been reported that P4ha1+/−; P4ha2−/− mice have chondrodysplasia and defects in ECM in multiple tissues, while P4ha1+/+; P4ha2−/− have minor defects in ECM (Aro et al., 2015; Tolonen et al., 2022; Salo et al., 2024). This study also highlights modulation in modification level on collagen cross-linking sites, which can affect the collagen assembly in the ECM. Collagen cross-linking analysis on P4ha1/P4ha2 deleted or overexpressed mice can delineate the exact effects of P4ha2 on collagen cross-linking.
This study shows a comprehensive analysis of the effects of partial deletion of P4ha1 and partial or complete deletion of P4ha2 on different types of PTMs of mouse skin fibrillar collagen chains. A total of 421 site-specific collagen PTMs are identified in wild-type mice skin fibrillar collagen I (COL1A1 and COL1A2) and collagen III (COL3A1) (Table 1). This study also hints toward the crosstalk between prolyl 4-hydroxylases, prolyl 3-hydroxylation, lysyl 5-hydroxylation, and O-glycosylation in COL1A1 and COL1A2 of mice skin. Deletion of P4ha1 and P4ha2 affects the whole collagen PTM networks in mice skin. Some 4-hydroxyproline sites are underhydroxylated in the absence of P4ha1 and P4ha2, while some 3-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, and O-glycosylation sites are overmodified in mice skin collagen I (Figure 7). Prolyl 3-hydroxylases, lysyl hydroxylases, and the alpha subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylases have similarities in the C-terminal dioxygenase domain (Vranka et al., 2004; Pokidysheva et al., 2013). These enzymes also have similar requirements (2-oxoglutarate) for their catalytic activity.
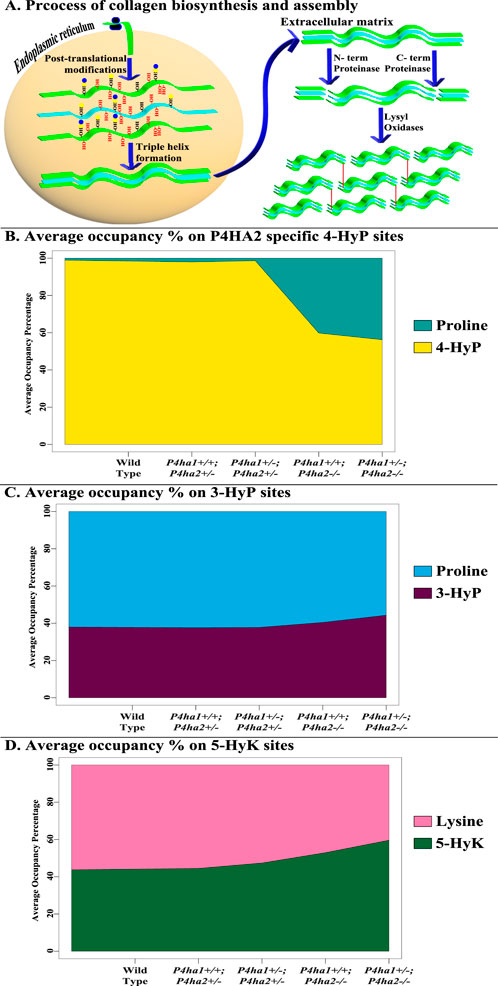
Figure 7. Occurrence of collagen PTMs during biosynthesis and deposition in the ECM. (A) shows the biosynthesis and deposition of collagen in the ECM. Newly translated collagen chains enter the endoplasmic reticulum and are heavily modified post-translationally in a site-specific manner by collagen-modifying enzymes. Modified collagen chains form a triple helix, which is transported to the ECM. In the ECM, N- and C-terminal proteinases cleave the pro-peptides of the collagen triple helix. Then, cross-linking and formation of collagen fiber assembly are induced by the activity of lysyl-oxidases. (B–D) show the effects of C-P4H deletion on different collagen PTMs. The average of 4-hydroxyproline (4-HyP) occupancy percentages of seven P4HA2-specific sites (Table 3) in wild-type and C-P4H mutant mice is shown in Figure 7B. It was found that average 4-HyP occupancy percentage decreased in mice with a complete deletion of P4ha2 compared to partial P4ha1- or P4ha2-deleted and wild-type mice. Interestingly, the average occupancy percentage of three 3-hydroxyproline sites (Table 4) and three 5-hydroxylysine sites (Table 5) was increased (Figures 7C, D) in complete P4ha2-deleted mice compared to wild-type and partial P4ha1- or P4ha2-deleted mice.
Interestingly, a study on P3h1 gene knockout has shown that complete deletion of P3h1 leads to altered lysine modification levels in mice (Pokidysheva et al., 2013). Prolyl 3-hydroxylation is catalyzed by a complex of P3H1, CRTAP, and cyclophilin B. Disruption of this complex by completely deleting cyclophilin B also results in site-specific modulation of lysine modifications (Terajima et al., 2016), indicating that the activities of different collagen-modifying enzymes are somehow interlinked. Three possible reasons for the over-modification of 3-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, and O-glycosylation sites in absence of C-P4Hs are: (i) there is direct/indirect crosstalk between different collagen-modifying enzymes, (ii) complete deletion of P4HA2 induces compensative effect on other collagen-modifying enzymes, and (iii) C-P4Hs, along with their catalytic activity, also act as chaperones to facilitate collagen folding and other collagen modify enzymes show compensatory effects in absence of C-P4Hs to modify and fold collagens. This study opens a plethora of opportunities to explore the significance of cooperation between different collagen-modifying enzymes in biosynthesis and the functioning of collagen chains.
5 Limitations
This study shows the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on site-specific PTMs. However, the effects of deletion of P4HA3 were not studied. The mRNA level expression of C-P4Hs is referred to, but the protein level expressions of C-P4Hs (P4HA1, P4HA2, and P4HA3) in the wild-type and mutant mice skin were not available in this study.
6 Future perspectives
This study highlights the crosstalk between different collagen-modifying enzymes and different site-specific collagen PTMs. This crosstalk can be further explored to better understand collagen biosynthesis in wild-type tissues and to therapeutically regulate collagen biosynthesis during fibrosis and cancer progression.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
VS: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, validation, visualization, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges Prof. Jyrki Heino and Dr. Pekka Rappu for publicly sharing the raw mass spectrometry dataset (PXD008802) (Sipila et al., 2018) on the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE partner repository.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2025.1527839/full#supplementary-material
References
Aggarwal, V., Sahoo, S., Donnenberg, V. S., Chakraborty, P., Jolly, M. K., and Sant, S. (2022). P4HA2: a link between tumor-intrinsic hypoxia, partial EMT and collective migration. Adv. cancer Biol. - metastasis 5, 100057. doi:10.1016/J.ADCANC.2022.100057
Aro, E., Salo, A. M., Khatri, R., Finnilä, M., Miinalainen, I., Sormunen, R., et al. (2015). Severe extracellular matrix abnormalities and chondrodysplasia in mice lacking collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase isoenzyme II in combination with a reduced amount of isoenzyme I. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 16964–16978. doi:10.1074/JBC.M115.662635
Borza, C. M., Pozzi, A., and Plosa, E. J. (2018). Discoidin domain receptor 2, a potential therapeutic target in lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 59, 277–278. doi:10.1165/RCMB.2018-0161ED
Cabral, W. A., Chang, W., Barnes, A. M., Weis, M., Scott, M. A., Leikin, S., et al. (2007). Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 deficiency causes a recessive metabolic bone disorder resembling lethal/severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Genet. 39, 359–365. doi:10.1038/NG1968
Chu, Q., Evans, B. T., and Zeece, M. G. (1997). Quantitative separation of 4-hydroxyproline from skeletal muscle collagen by micellar electrokinetic capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 692, 293–301. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00007-8
Farndale, R., Sonnenberg, A., DiPersio, C. M., Eble, J. A., Heino, J., and Gullberg, D. (2023). What does it take to be a collagen receptor? Matrix Biol. 115, 128–132. doi:10.1016/J.MATBIO.2022.12.004
Gelse, K., Pöschl, E., and Aigner, T. (2003). Collagens - structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 55, 1531–1546. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2003.08.002
Hudson, D. M., Joeng, K. S., Werther, R., Rajagopal, A., Weis, M., Lee, B. H., et al. (2015). Post-translationally abnormal collagens of prolyl 3-hydroxylase-2 null mice offer a pathobiological mechanism for the high myopia linked to human LEPREL1 mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 8613–8622. doi:10.1074/JBC.M114.634915
Ishikawa, Y., Taga, Y., Coste, T., Tufa, S. F., Keene, D. R., Mizuno, K., et al. (2022). Lysyl hydroxylase 3 mediated post-translational modifications are required for proper biosynthesis of collagen α1α1α2(IV). J. Biol. Chem. 298, 102713. doi:10.1016/J.JBC.2022.102713
Koski, M. K., Hieta, R., Hirsilä, M., Rönkä, A., Myllyharju, J., and Wierenga, R. K. (2009). The crystal structure of an algal prolyl 4-hydroxylase complexed with a proline-rich peptide reveals a novel buried tripeptide binding motif. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 25290–25301. doi:10.1074/JBC.M109.014050
Leitinger, B., and Hohenester, E. (2007). Mammalian collagen receptors. Matrix Biol. 26, 146–155. doi:10.1016/J.MATBIO.2006.10.007
Li, M., Wang, Q., Zheng, Q., Wu, L., Zhao, B., and Wu, Y. (2021). Prognostic and diagnostic roles of prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit α members in breast cancer. Biomark. Med. 15, 1085–1095. doi:10.2217/BMM-2020-0323
Lin, J., Jiang, L., Wang, X., Wei, W., Song, C., Cui, Y., et al. (2021). P4HA2 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and glioma malignancy through the collagen-dependent PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Oncol. 2021, 1406853. doi:10.1155/2021/1406853
Lu, X. H., Sang, D., Zhang, Y. R., and Yuan, Q. (2022). High expression of prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-2 in lung adenocarcinoma indicates poor prognosis. Clin. (Sao Paulo) 77, 100123. doi:10.1016/J.CLINSP.2022.100123
Ma, Z. Q., Dasari, S., Chambers, M. C., Litton, M. D., Sobecki, S. M., Zimmerman, L. J., et al. (2009). IDPicker 2.0: improved protein assembly with high discrimination peptide identification filtering. J. Proteome Res. 8, 3872–3881. doi:10.1021/PR900360J
MacLean, B., Tomazela, D. M., Shulman, N., Chambers, M., Finney, G. L., Frewen, B., et al. (2010). Skyline: an open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinformatics 26, 966–968. doi:10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTQ054
Montgomery, N. T., Zientek, K. D., Pokidysheva, E. N., and Bächinger, H. P. (2018). Post-translational modification of type IV collagen with 3-hydroxyproline affects its interactions with glycoprotein VI and nidogens 1 and 2. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 5987–5999. doi:10.1074/JBC.RA117.000406
Morello, R. (2018). Osteogenesis imperfecta and therapeutics. Matrix Biol. 71 (72), 294–312. doi:10.1016/J.MATBIO.2018.03.010
Morello, R., Bertin, T. K., Chen, Y., Hicks, J., Tonachini, L., Monticone, M., et al. (2006). CRTAP is required for prolyl 3- hydroxylation and mutations cause recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Cell 127, 291–304. doi:10.1016/J.CELL.2006.08.039
Myllyharju, J., and Kivirikko, K. I. (1999). Identification of a novel proline-rich peptide-binding domain in prolyl 4-hydroxylase. EMBO J. 18, 306–312. doi:10.1093/EMBOJ/18.2.306
Nishi, Y., Uchiyama, S., Doi, M., Nishiuchi, Y., Nakazawa, T., Ohkubo, T., et al. (2005). Different effects of 4-hydroxyproline and 4-fluoroproline on the stability of collagen triple helix. Biochemistry 44, 6034–6042. doi:10.1021/bi047887m
Pedrioli, P. G. A. (2010). Trans-proteomic pipeline: a pipeline for proteomic analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 604, 213–238. doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-444-9_15
Pekkala, M., Hieta, R., Kursula, P., Kivirikko, K. I., Wierenga, R. K., and Myllyharju, J. (2003). Crystallization of the proline-rich-peptide binding domain of human type I collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 59, 940–942. doi:10.1107/S0907444903005420
Perdivara, I., Yamauchi, M., and Tomer, K. B. (2013). Molecular characterization of collagen hydroxylysine O-glycosylation by mass spectrometry: current status. Aust. J. Chem. 66, 760–769. doi:10.1071/CH13174
Pihlajaniemi, T., Myllylä, R., and Kivirikko, K. I. (1991). Prolyl 4-hydroxylase and its role in collagen synthesis. J. Hepatol. 13 (Suppl. 3), S2–S7. doi:10.1016/0168-8278(91)90002-S
Pokidysheva, E., Boudko, S., Vranka, J., Zientek, K., Maddox, K., Moser, M., et al. (2014). Biological role of prolyl 3-hydroxylation in type IV collagen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111, 161–166. doi:10.1073/pnas.1307597111
Pokidysheva, E., Zientek, K. D., Ishikawa, Y., Mizuno, K., Vranka, J. A., Montgomery, N. T., et al. (2013). Posttranslational modifications in type I collagen from different tissues extracted from wild type and prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 null mice. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 24742–24752. doi:10.1074/JBC.M113.464156
Rappu, P., Salo, A. M., Myllyharju, J., and Heino, J. (2019). Role of prolyl hydroxylation in the molecular interactions of collagens. Essays Biochem. 63, 325–335. doi:10.1042/EBC20180053
Risteli, J., and Kivirikko, K. I. (1974). Activities of prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl hydroxylase, collagen galactosyltransferase and collagen glucosyltransferase in the liver of rats with hepatic injury. Biochem. J. 144, 115–122. doi:10.1042/BJ1440115
Salo, A. M., Rappu, P., Koski, M. K., Karjalainen, E., Izzi, V., Drushinin, K., et al. (2024). Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase isoenzymes I and II have sequence specificity towards different X-Pro-Gly triplets. Matrix Biol. 125, 73–87. doi:10.1016/J.MATBIO.2023.12.001
Sarohi, V., Chakraborty, S., and Basak, T. (2022a). Exploring the cardiac ECM during fibrosis: a new era with next-gen proteomics. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9, 1030226. doi:10.3389/FMOLB.2022.1030226
Sarohi, V., Srivastava, S., and Basak, T. (2022b). Comprehensive mapping and dynamics of site-specific prolyl-hydroxylation, lysyl-hydroxylation and lysyl O-glycosylation of collagens deposited in ECM during zebrafish heart regeneration. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9, 554. doi:10.3389/FMOLB.2022.892763/BIBTEX
Shang, L., Jiang, W., Zhang, J., and Wu, W. (2022). P4HA2 promotes occurrence and progression of liver cancer by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Nan Fang. Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 42, 665–672. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.05.06
Shi, R., Gao, S., Zhang, J., Xu, J., Graham, L. M., Yang, X., et al. (2021). Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases modify tumor progression. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 53, 805–814. doi:10.1093/ABBS/GMAB065
Sipila, K. H., Drushinin, K., Rappu, P., Jokinen, J., Salminen, T. A., Salo, A. M., et al. (2018). Proline hydroxylation in collagen supports integrin binding by two distinct mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 7645–7658. doi:10.1074/JBC.RA118.002200
Tabb, D. L., Fernando, C. G., and Chambers, M. C. (2007). MyriMatch: highly accurate tandem mass spectral peptide identification by multivariate hypergeometric analysis. J. Proteome Res. 6, 654–661. doi:10.1021/PR0604054
Takaluoma, K., Hyry, M., Lantto, J., Sormunen, R., Bank, R. A., Kivirikko, K. I., et al. (2007). Tissue-specific changes in the hydroxylysine content and cross-links of collagens and alterations in fibril morphology in lysyl hydroxylase 1 knock-out mice. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 6588–6596. doi:10.1074/JBC.M608830200
Terajima, M., Perdivara, I., Sricholpech, M., Deguchi, Y., Pleshko, N., Tomer, K. B., et al. (2014). Glycosylation and cross-linking in bone type I collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 22636–22647. doi:10.1074/JBC.M113.528513
Terajima, M., Taga, Y., Chen, Y., Cabral, W. A., Hou-Fu, G., Srisawasdi, S., et al. (2016). Cyclophilin-B modulates collagen cross-linking by differentially affecting lysine hydroxylation in the helical and telopeptidyl domains of tendon type I collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 9501–9512. doi:10.1074/JBC.M115.699470
Tolonen, J. P., Salo, A. M., Finnilä, M., Aro, E., Karjalainen, E., Ronkainen, V. P., et al. (2022). Reduced bone mass in collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase P4ha1 +/-; P4ha2 -/- compound mutant mice. JBMR Plus 6, e10630. doi:10.1002/JBM4.10630
Tonelli, F., Cotti, S., Leoni, L., Besio, R., Gioia, R., Marchese, L., et al. (2020). Crtap and p3h1 knock out zebrafish support defective collagen chaperoning as the cause of their osteogenesis imperfecta phenotype. Matrix Biol. 90, 40–60. doi:10.1016/J.MATBIO.2020.03.004
Van Huizen, N. A., Burgers, P. C., Saintmont, F., Brocorens, P., Gerbaux, P., Stingl, C., et al. (2019). Identification of 4-hydroxyproline at the Xaa position in collagen by mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 18, 2045–2051. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00930
Vasta, J. D., and Raines, R. T. (2018). Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase as a therapeutic target. J. Med. Chem. 61, 10403–10411. doi:10.1021/ACS.JMEDCHEM.8B00822
Vranka, J. A., Pokidysheva, E., Hayashi, L., Zientek, K., Mizuno, K., Ishikawa, Y., et al. (2010). Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 null mice display abnormalities in fibrillar collagen-rich tissues such as tendons, skin, and bones. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 17253–17262. doi:10.1074/JBC.M110.102228
Vranka, J. A., Sakai, L. Y., and Bächinger, H. P. (2004). Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1, enzyme characterization and identification of a novel family of enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 23615–23621. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312807200
Wang, L. H., Li, D. Q., Fu, Y., Wang, H. P., Zhang, J. F., Yuan, Z. F., et al. (2007). pFind 2.0: a software package for peptide and protein identification via tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21, 2985–2991. doi:10.1002/RCM.3173
Weiss, P. H., and Klein, L. (1969). The quantitative relationship of urinary peptide hydroxyproline excretion to collagen degradation. J. Clin. Invest 48, 1–10. doi:10.1172/JCI105957
Xiong, G., Stewart, R. L., Chen, J., Gao, T., Scott, T. L., Samayoa, L. M., et al. (2018). Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase 1 is essential for HIF-1α stabilization and TNBC chemoresistance. Nat. Commun. 9, 4456. doi:10.1038/S41467-018-06893-9
Keywords: collagen PTMs, prolyl 4-hydroxylation, prolyl 3-hydroxylation, lysyl 5-hydroxylation, O-glycosylation
Citation: Sarohi V (2025) Comprehensive analysis of the effects of P4ha1 and P4ha2 deletion on post-translational modifications of fibrillar collagens in mouse skin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1527839. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1527839
Received: 13 November 2024; Accepted: 22 January 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Lynda Bourebaba, Wroclaw University of Environmental and Life Sciences, PolandReviewed by:
Kartick Patra, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIH), United StatesLouisa Bechohra, University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene, Algeria
Copyright © 2025 Sarohi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vivek Sarohi, dml2ZWtzYXJvaGlAZ21haWwuY29t
†ORCID: Vivek Sarohi, orcid.org/0000-0003-4229-1945
 Vivek Sarohi
Vivek Sarohi