
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 20 January 2025
Sec. Cancer Cell Biology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1521151
Renal cell carcinoma is a common type of cancer, with approximately 30% of patients potentially developing metastatic disease. Some patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma are found in advanced stages, so the 5-year survival rate for metastatic renal cell carcinoma is only 14%. Currently, there are several drugs available for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma, and their overall survival can be extended to nearly 5 years. However, the sensitivity and efficacy of the treatment are still unsatisfactory. New targets and drugs to improve patient prognosis are urgently needed, but these are closely linked to the molecular mechanisms of renal cell carcinoma metastasis. In this review, we present the definition and common molecular mechanisms of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and provide new insights on their potential link to targeted therapies, which may enlighten scientists to develop future targeted therapeutic agents to improve the prognosis of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a common cancer worldwide, with 81,610 new cases and 14,390 deaths expected in the United States in the year 2024 (Siegel et al., 2024). As for metastatic kidney cancer, the median overall survival of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) patients currently treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) is estimated to be approximately 50 months (Park et al., 2024). To date, mRCC remains one of the most challenging aspects of renal cancer treatment. Targeted therapy for metastatic tumors, as an emerging approach, holds broader application prospects and is crucial for improving patient outcomes. The foundation of targeted therapy lies in identifying new therapeutic targets. The mechanisms driving RCC metastasis are intricate and involve multiple pathways and molecules, as reported in the literature (Ganesh and Massagué, 2021). At the molecular level, related studies have shown that tumor metastasis depends on clonal selection, the potential of metastatic cells to dynamically transition to different states, and the ability to exploit the immune environment (Gerstberger et al., 2023). Up to now, a few reviews have focused on the molecular mechanisms of RCC progression, but no reviews have focused on the summary of mechanisms of RCC metastasis and linked them to targeted therapy particularly. In this review, we summarized the definition and common molecular mechanisms of renal cell carcinoma metastasis and proposed new insights into its potential connection with targeted therapies, which may enlighten future targeted therapy drug development for improving the outcome of mRCC patients.
Clear cell renal carcinoma (ccRCC) accounts for 70%–80% of all pathologic types of RCC, with other types of RCC including papillary, chromophobe, medullary, collecting duct, microphthalmia (MiT) family translocation, succinate dehydrogenase–deficient, hereditary leiomyomatosis and syndrome-associated, and unclassified RCC (Barata et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). The most common symptoms of kidney cancer are hematuria or microscopic hematuria, lateral dorsal or flank pain, and palpable abdominal mass. However, due to its retroperitoneal location, RCC can grow significantly without causing symptoms. In some cases, metastatic lesions are detected before the primary kidney tumor is identified through systemic examination and pathology (Petejova and Martinek, 2016; Singla et al., 2022). The initial diagnosis of RCC relies on imaging modalities, and enhanced CT and MRI provide strong evidence for the detection of malignant mass (Bahadoram et al., 2022). Liquid biopsy has made significant progress in RCC through the use of circulating tumor cells (CTCs), ctDNA/cfDNA, cfRNAs, exosomes, and tumor-derived metabolites or proteins, with advancements in next-generation sequencing (NGS), droplet digital PCR (ddPCR), and methylation analysis enhancing the accuracy and applicability of ctDNA/cfDNA. However, challenges remain, including low CTC levels, difficulty distinguishing ctRNAs from cfRNAs, complex miRNA regulatory networks, and insufficient standardization of biomarker analysis (Li M. et al., 2023). Imaging diagnostics for RCC have seen advancements with agents like 68Ga-DPI-4452 and 68Ga-FAPI-PET/CT showing high sensitivity and specificity for detecting ccRCC, alongside CD8 PET imaging for predicting responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Nonetheless, the long clearance time of high molecular weight tracers increases patient radiation burden, and small molecule tracers with rapid clearance are in need (Ali et al., 2024). While kidney biopsy is essential for histopathologic confirmation in certain cases, its use is controversial due to concerns about influencing treatment decisions, potential complications like bleeding and infection, and questions about accuracy and safety. Standard treatments like nephrectomy often provide the necessary histopathologic evidence (Bahadoram et al., 2022). Of all patients diagnosed with RCC, 20%–30% have metastasis at initial presentation, yet 20%–40% of patients with RCC still develop recurrence and metastasis after radical nephrectomy (Teishima et al., 2023; Vig et al., 2020).
For non-metastatic renal mass, the preferred treatment is surgical resection. For specific patients, a kidney-preserving partial nephrectomy prioritizing the achievement of negative surgical margins is recommended. Based on clinical indications, radical nephrectomy is indicated for patients with an increased oncologic risk as well as for patients scheduled for targeted therapy (Gray and Harris, 2019). In recent years, several agents have been developed to improve the prognosis of metastatic and recurrent RCC patients. These agents target the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) such as bevacizumab and its receptor (VEGFR) such as sunitinib, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) such as temsirolimus, immunocheckpoints programmed death-1 (PD-1) such as nivolumab and its ligand (PD-L1) such as atezolizumab, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) such as ipilimumab (Aurilio et al., 2019). Although advances have been made in some aspects of the diagnosis, screening, and treatment of RCC, the survival of patients with metastatic RCC remains unsatisfactory compared to other cancers (Ryalen et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2023a). In addition, drug resistance and side effects of drug therapy are shortcomings that cannot be ignored (Li X. et al., 2024). This means that more researches are still in need to discover new targets, optimize existing therapies, and ultimately improve the outcome and quality of life of mRCC patients.
Hematogenous metastasis is one of the most common modes of metastasis for kidney cancer, and other common modes of RCC metastasis include lymphatic metastasis and direct extension (Huang et al., 2017). The most common sites of metastasis for renal cell carcinoma are the renal vein and its branches, the inferior vena cava, lung, bone, liver, lymph nodes, adrenal gland, and brain (Liu et al., 2021; Matuszczak et al., 2023). In recent years, metastasis of renal cell carcinoma to the larynx, mandible, eyelids, small intestine, appendix, and penis has also been reported in the literature (Ahmed et al., 2023; Bellouki et al., 2023; Cho et al., 2024; Elmusa et al., 2022; Huang and Yu, 2023; Ushakova and Ravakhah, 2023). The TNM staging system of renal cell carcinoma is considered to be the criterion for evaluating the metastasis of RCC, which contains tumor (T), node (N), and metastasis (M) classification. Localized RCC (LRCC) stands for RCC staging T1-2N0M0, advanced RCC consists of the remaining stages, while metastatic renal cell carcinoma is defined as tumor invasion through the perirenal fascia and/or presence of distant metastasis (Chen et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). An interesting study showed that histological subtype, nuclear grade, and sarcomatoid differentiation are important predictors of metastasis in patients with RCC (Park, 2023). Besides, another retrospective cohort study showed that RCC WHO/ISUP grades are associated with metastasis, with the high-grade group (Grade 3–4) being more likely to metastasize than the low-grade group (Grade 1–2) (Fujita et al., 2022).
The overexpression of centromere protein A (CENPA) would regulate the cell cycle and activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, resulting in ccRCC proliferation and metastasis (Wang et al., 2021). Moreover, Sun et al. found the Follistatin-like 3 (FSTL3) regulates the GSK-3β/β-catenin and BMP1/SMAD pathways, enabling RCC proliferation and metastasis (Sun et al., 2021). In addition, a lncRNA named SLERCC inhibits RCC progression and metastasis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and directly binding to UPF1. However, high DNMT3A expression recruits DNMT3A to the SLERCC promoter region, inducing aberrant hypermethylation and ultimately inhibiting SLERCC expression (Mao et al., 2022).
Mao and colleagues reported that ciRS-7 can act as a sponge for miR-139-3p, a microRNA that inhibits RCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. However, based on targeting TAGLN, ciRS-7 can activate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by regulating the miR-139-3p/TAGLN axis, thus assisting the proliferation and metastasis of RCC cells (Mao et al., 2021). Additionally, DEP domain containing 1 (DEPDC1) promotes glycolysis in RCC via the AKT/mTOR/HIF1α pathway, which in turn affects tumor metastasis and TKI resistance (Di et al., 2024). Another study found that tescalcin promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via the NHE1/pHi axis and AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway (Luo et al., 2019). Besides, AGK also promotes RCC metastasis through the PI3K/AKT pathway as mentioned above (Zhu et al., 2020). Moreover, centrosomal protein 55 (CEP55) could promote the upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of N-cadherin and ZEB1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, resulting in RCC epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), proliferation, and metastasis (Chen et al., 2019).
Researchers found that tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) activates the NF-κB pathway in RCC cells, leading to p65 binding at the Rictor promoter and ultimately promoting cancer metastasis (Sun et al., 2016). Further, metastasis-associated gene 1 (MTA1) is overexpressed in RCC and regulates the expression of MMP2/MMP9 as well as E-calmodulin through the NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to RCC migration and invasion (Lv et al., 2020). Moreover, sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) promotes the proliferation, migration, and EMT of RCC cells through activation of its receptor S1PR3, thereby accelerating RCC carcinogenesis and metastasis. This process involves the S1PR3/Gi/p38/Akt/p65/cyclin D1-CDK4 signaling pathway to regulate cell proliferation, and the S1PR3/Gi/q/ERK/p38/p65 signaling pathway to regulate cell migration (Yan et al., 2022). As mentioned, Tescalcin is also associated with NF-κB signaling pathway (Luo et al., 2019).
Metadherin (MTDH) activates SND1 to mediate ERK signaling and EMT, thereby promoting migration and metastasis (He et al., 2020). Additionally, MRCCAT1, a key lncRNA, inhibits NPR3 transcription by recruiting PRC2 to the NPR3 promoter region, therefore activating the p38-MAPK signaling pathway and promoting ccRCC metastasis (Li et al., 2017). Furthermore, ApoC1 could promote the activation of STAT3 and enhance the metastasis of ccRCC. Meanwhile, exosomes could transfer ApoC1 from the ccRCC cells to the vascular endothelial cells to promote tumor angiogenesis and metastasis via STAT3 pathway (Li et al., 2020).
Scientists have found that miR-148a-3p targets circUBAP2 in ccRCC, with its expression level negatively correlating with that of circUBAP2. The miR-148a-3p could reverse the inhibitory effect of circUBAP2 on ccRCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and it could also target FOXK2 to affect ccRCC proliferation and metastasis (Sun et al., 2020). Dong’s team has found that lncRNA ZFAS1 could promote ccRCC growth and metastasis through the miR-10a/SKA1 pathway (Dong et al., 2019). Similarly, miR-100 promotes autophagy and inhibits migration and invasion of RCC cells by targeting NOX4 and inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway (Liu et al., 2022). Besides, miR-139-3p would be inhibited by ciRS-7 to promote RCC metastasis (Mao et al., 2021).
Regarding lncRNAs, lncHILAR upregulates Jagged-1 and CXCR4 expression by acting as a ceRNA for miR-613/206/1-1-3p, thus activating the Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 signaling pathway and promoting RCC cell invasion and metastasis (Hu et al., 2021). Additionally, via binding to the promoter area of ERβ, lncRNA-SERB could regulate ERβ functions through transcriptional regulation of zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1), thus promoting vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation (Tang et al., 2024).
In addition, circSDHC could protect CDKN3 from miR-127-3p inhibition by competitively binding to miR-127-3p, which in turn activated the E2F1 pathway and promoted RCC proliferation and invasion (Cen et al., 2021).
Lu et al. reported that KLF2 deficiency impairs the transcriptional repression of GPX4, inhibiting ferroptosis and thereby promoting ccRCC cell migration and invasion (Lu et al., 2021). Also, c-Myb could transcriptionally activate miR-520h, which would target MAGI1. Then, MAGI1 could stabilize the PTEN/MAGI1/β-catenin complex to modulate β-catenin signaling pathway, mediating RCC metastasis (Wang W. et al., 2019). Besides, HIF-2 transcriptionally targeted the hypoxia response element on the Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) promoter, which promoted Plk1 expression in ccRCC, leading to ccRCC growth, metastasis, and drug resistance (Dufies et al., 2021). Moreover, YBX1 could promote SPP1 expression by interacting with G3BP1, which in turn activates the NF-κB signaling pathway, ultimately leading to increased invasion and metastasis of RCC (Wang Y. et al., 2019). Interestingly, N-acetyltransferase 10 (NAT10) promotes ankyrin repeat and zinc finger peptidyl tRNA hydrolase 1 (ANKZF1) expression through N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) modification, which in turn regulates YAP1 activity and activates the expression of pro-lymphangiogenic factors to promote lymphangiogenesis and tumor progression in ccRCC (Miao et al., 2024).
Xu et al. found that circPOLR2A forms a UBE3C/circPOLR2A/PEBP1 protein-RNA ternary complex with UBE3C and PEBP1 proteins, which enhances UBE3C-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of PEBP1 proteins, which activates the ERK via ERK1/2 phosphorylation signaling pathway, thereby promoting angiogenesis (Xu et al., 2022). Acylglycerol kinase (AGK) activates the GSK3β S9 phosphorylation site via the PI3K/AKT pathway, leading to GSK3β inactivation, β-catenin stabilization, and subsequent promotion of RCC growth and metastasis (Zhu et al., 2020).
EF-hand domain family member D1 (EFHD1) binds to MCU through its N-terminal domain, suppressing mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and thereby inactivating the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway (Meng et al., 2023). Similarly, leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) attenuates ccRCC metastasis by upregulating Hippo signaling pathway kinase activity, which inhibits YAP expression (Lei et al., 2018). Yin’s team found that HOOK1 could inhibit RCC proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, and sunitinib resistance via TNFSF13B/VEGF-A signaling. Moreover, meletin, an agonist of HOOK1, demonstrates greater antitumor efficacy when combined with sunitinib or nivolumab compared to its use as a monotherapy (Yin et al., 2023). Additionally, MUC15 inhibits RCC cell invasion and metastasis through PI3K/AKT signaling (Yue et al., 2020). Nuclear receptor coactivator 7 (NCOA7) inhibits the MAPK/ERK pathway, regulating EMT and apoptosis and thereby inhibiting ccRCC progression and metastasis (Guo et al., 2023). Similarly, SH3BGRL2 inhibits ccRCC proliferation and metastasis by activating the LATS1/2-YAP-TEAD1 signaling pathway, and TEAD1 promotes EMT through TWIST1 upregulation (Yin et al., 2020). Zhang et al. found that thymoquinone induces autophagy in RCC cells by activating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, which inhibits the EMT and metastasis of RCC cells (Zhang et al., 2018). Likewise, FOXC1 activates the AMPK signaling pathway and inhibits the mTOR signaling pathway by upregulating the expression of ABHD5 to inhibit the growth and metastasis of RCC cells (Li J. et al., 2024).
The cRAPGEF5 acts as a sponge of oncogenic miR-27a-3p, which targets the suppressor gene TXNIP, thus inhibiting RCC progression and metastasis (Chen et al., 2020). Additionally, melatonin reduces the DNA-binding activity of p65 and p52, thereby inhibiting MMP-9 transcriptionally and affecting its transcriptional activation and cell migration via Akt-mediated JNK1/2 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Besides, high MMP-9 expression correlates with a poorer RCC prognosis (Lin et al., 2016).
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 53 (USP53) prevents the inactivation of the NF-κB pathway by reducing ubiquitination of IκBα, thereby further inhibiting ccRCC proliferation and metastasis (Gui et al., 2021). Likewise, ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 (USP2) downregulates the NF-κB pathway, inhibiting EMT in clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis (Duan et al., 2022). Luo and colleagues discovered that the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) protein MFN2 inhibits ccRCC tumor growth and metastasis by binding to the small GTPase Rab21, facilitating interaction with endocytosed EGFR in ccRCC. This process promotes docking of endocytosed EGFR to mitochondria, where it is subsequently dephosphorylated by OMM-resident tyrosine-protein phosphatase receptor type J (PTPRJ), leading to inactivation of the EGFR signaling pathway and attenuation of EGFR oncogenic signaling (Luo et al., 2023). Besides, EFHD1 would also upregulate STARD13 to enhance YAP protein phosphorylation at Ser-127 to suppress cell migration and metastasis (Meng et al., 2023). Moreover, IL6 mediates crosstalk between normal fibroblasts and RCC cells, promoting cell migration via the STAT3 pathway. Conversely, GATA3 reduces STAT3 phosphorylation, inhibiting RCC cell migration (Shi et al., 2020) (Table 1).
Current major targeted therapies and potential drugs under investigation primarily focus on specific signaling pathways, including tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and mTOR inhibitors. Pazopanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, enhances the function of dendritic cells (DCs) by inhibiting the Erk/β-catenin pathway. This inhibition leads to the upregulation of maturation markers such as HLA-DR, CD40, and CCR7, reduces IL-10 production and endocytosis, and increases T-cell proliferation. Additionally, pazopanib downregulates PD-L1 expression. These effects collectively improve the antigen-presenting capability and immune-stimulating capacity of DCs, potentially augmenting the immune response in mRCC patients. Furthermore, pazopanib increases the population of circulating CD4+ T cells expressing CD137 (4-1BB), suggesting a potentially exploitable immunomodulatory effect that could be leveraged to improve responses when combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in tailored treatment protocols (Zizzari et al., 2018). Besides, mTOR inhibitors have been the first-line treatment for mRCC. However, since the mTOR signaling axis is activated in only a subset of RCC patients, clinical trials involving mTOR inhibitors are ongoing (Zheng et al., 2021). A recent clinical trial revealed that the on-treatment tumor growth rate was 1.7 times higher for apitolisib (a dual PI3K/mTORC1/2 inhibitor) compared to everolimus (an mTORC1 inhibitor). The estimated half-life for the loss of treatment effect was 16.1 weeks for everolimus and 7.72 weeks for apitolisib, indicating a faster tumor regrowth rate for patients treated with apitolisib, possibly due to rapid resistance development (Moein et al., 2024). Another study found that MC-4, a novel Akt/PKM2 inhibitor, can potentially overcome the limitations of existing mTOR inhibitors. Therefore, combining MC-4 with current treatments may represent a promising new strategy for treating patients with rapidly progressing advanced RCC (Son et al., 2018). An intriguing study found that PI3K-mutant patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models exhibit significant resistance to TKI treatment. However, these PDX models seem to be sensitive to mTOR inhibitor treatment. Thus, combination therapies that incorporate drugs with different mechanisms of action, such as pairing mTOR inhibitors with TKI, could offer greater benefits to patients. Combination therapy strategies simultaneously target multiple signaling pathways and address potential resistance issues arising from monotherapy, thereby enhancing overall treatment effectiveness (Wu et al., 2023b). Currently, no therapeutic approaches specifically target NF-κB signaling in mRCC. However, inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies that target this pathway have been studied in other diseases and may represent a promising therapeutic approach for mRCC (Guo et al., 2024).
However, drug insensitivity is also tricky from molecular apects. A study found that the O-GlcNAcylation of RIPK1 at Ser331, Ser440, and Ser669 regulates its ubiquitination, thereby reducing the formation of the RIPK1/FADD/Caspase-8 complex. This alteration promotes NF-κB activation, ultimately inhibiting sunitinib-induced RIPK-dependent apoptosis in RCC (Zeng et al., 2024). Conversely, another intriguing study found that SEC14L3 not only emerges as a potential therapeutic target but also uncovers an SEC14L3/RPS3/NF-κB positive feedback loop that can inhibit ccRCC progression and sunitinib resistance. Modulating SEC14L3 expression to activate this feedback loop could offer new therapeutic strategies for ccRCC treatment (Jiang et al., 2024). Besides, ZZDHHC2 mediates AGK’s S-palmitoylation, promoting its translocation to the plasma membrane and activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in ccRCC, thereby modulating sunitinib sensitivity. This indicates that targeting ZDHHC2 could enhance the antitumor efficacy of sunitinib in ccRCC (Sun et al., 2023). Moreover, circPTEN suppresses ccRCC progression and resistance to mTOR inhibitors by enhancing PTEN expression through reduced methylation of the PTEN promoter and decreasing GLUT1 expression by lowering its m6A methylation (Zhan et al., 2023). Overall, these molecular mechanisms provide promising therapeutic avenues for enhancing sunitinib sensitivity and overcoming resistance in RCC, although they also carry the risk of drug insensitivity. Rational utilization of these mechanisms and molecules will contribute to the clinical translation of these fundamental discoveries.
While the overall 5-year survival rate for renal cell carcinoma is approximately 76%, this rate plummets to 14% for patients with mRCC (Aldin et al., 2023). To date, over 800 clinical trials on advanced RCC have been registered on https://clinicaltrials.gov/, with the majority focusing on single-agent or multi-agent targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Nevertheless, while drug treatments—primarily targeted therapies and immunotherapies, administered as single agents or in combination—can extend patient overall survival (OS) in advanced kidney cancer, significant improvements in treatment efficacy remain necessary (Semenescu et al., 2023).
The molecular mechanisms underlying renal cell carcinoma metastasis are complex, diverse, and interconnected, with various pathways intersecting. Mutations in upstream genes associated with metastasis are relatively rare and exhibit high variability. In addition, the regulation of non-coding RNAs, the regulation of transcription factors, and protein modifications can be drivers of metastasis as well. However, certain downstream pathways, including the Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT, and NF-κB signaling pathways, share common features. These pathways regulate the cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy, angiogenesis, and EMT, contributing to rapid tumor proliferation and metastasis (Ma et al., 2023; Mabeta and Steenkamp, 2022; Mirzaei et al., 2022; Wang, 2021) (Figure 1).
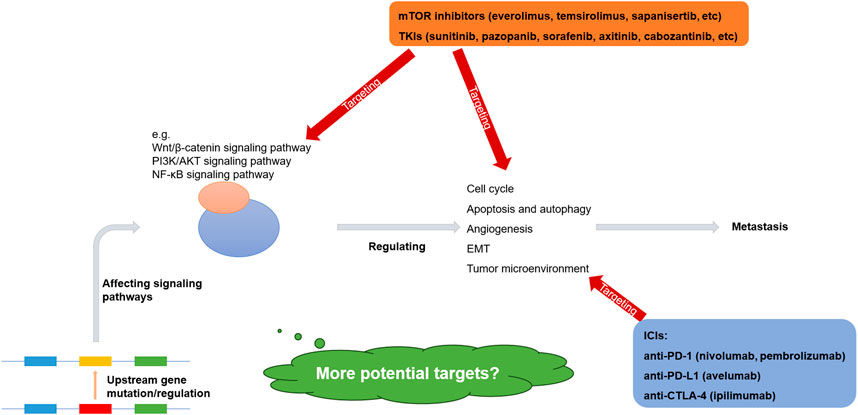
Figure 1. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (Wu et al., 2023b; Sharma et al., 2021; Motzer et al., 2021; Choueiri et al., 2023; Grimm et al., 2024).
However, current research into the metastatic mechanisms of renal cancer predominantly focuses on RCC cells, with limited studies addressing the tumor microenvironment (TME) where these cells reside. Non-immune cells in the extracellular matrix are inextricably linked to the invasion and migration of cancer cells (Oxburgh, 2022). Immune cells within the TME differentiate and undergo functional changes as tumors progress, suppressing or depleting local tumor immunity and thereby fostering an environment conducive to renal cancer cell metastasis (Mei et al., 2024). A notable study reported that tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) from VHL-deficient tumors displayed increased in vivo glucose uptake, enhanced phagocytic activity, and heightened inflammatory gene expression. Conversely, lymphocytes from Vhl-KO tumors exhibited decreased activation and reduced responsiveness to anti-programmed cell death 1 (anti-PD-1) therapy in vivo (Wolf et al., 2024).
Newly identified therapeutic targets offer hope for treating mRCC. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing revealed ceruloplasmin (CP) and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 6 (PCSK6) as promising ccRCC markers with potential diagnostic and prognostic significance (Wu et al., 2023c). Another study utilized a large sample size and multi-omics techniques to identify UCHL1 expression as one of the potential biomarkers for high-grade tumors with BAP1 mutations, genomic instability, or increased tumor hypermethylation, potentially influencing clinical and therapeutic management (Li Y. et al., 2023).
Future treatment modalities for metastatic renal cell carcinoma hold significant promise. Multi-drug combination therapies have already demonstrated improved patient outcomes compared to monotherapy, suggesting that integrating multiple targeted drugs or combining them with immunotherapy could be a promising direction for future development (Semenescu et al., 2023). Furthermore, genomics and proteomics analyses can predict patient sensitivity or resistance to specific drugs, while the presence or absence of certain biomarkers can guide personalized treatment choices, enabling more precise and individualized care plans (Elias et al., 2021). Moreover, continued in-depth investigation into the shared downstream pathways among different signaling pathways, regulatory mechanisms of gene expression, and cellular interactions within the TME of metastatic renal cell carcinoma could uncover additional therapeutic targets. Additionally, factors within the TME—such as inflammatory responses, hypoxic conditions, metabolic reprogramming, and mechanical stresses—further promote tumor metastasis. These interactions and environmental pressures contribute to genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity, highlighting the need for therapeutic targets that address these components. Importantly, given the relatively poor prognosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma, developing reliable biomarkers to predict therapeutic response and monitor disease progression is crucial for guiding clinical decision-making. For example, co-deletions involving VHL alongside one or more of the three genes—PBRM1, BAP1, and SETD2—encoding proteins involved in chromatin modification and remodeling, are common and serve as significant co-drivers of tumorigenesis (Walton et al., 2023).
In conclusion, although significant progress has been made in targeted therapies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma, many challenges still exist. Future studies will require a deeper understanding of the biological process of this disease, which will contribute to the development of more effective treatments to improve patient survival and quality of life.
XL: Writing–original draft. WX: Writing–review and editing. ZX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Our study was supported by the Key Research and Development Plan in China (Grant No. 2017YFB1303100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82202911, 82300786), Shenzhen Medical Research Fund (Grant No. B2302054), and Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation Projects (Grant No. 2023AFB210 and 2024AFB640) and Wuhan Talent Plan Funds (Grant No. 02.05.22030029).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahmed, S. S., Barik, S. K., Adhya, A. K., Das, D. K., Parida, A. V., Mukherjee, P., et al. (2023). Metastatic renal cell carcinoma masquerading as a laryngeal tumor: a case report. Cureus 15 (5), e39229. doi:10.7759/cureus.39229
Aldin, A., Besiroglu, B., Adams, A., Monsef, I., Piechotta, V., Tomlinson, E., et al. (2023). First-line therapy for adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 5 (5), Cd013798. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013798.pub2
Ali, M., Eid, M., Saliby, R. M., Choi, S., McKay, R. R., Siva, S., et al. (2024). Emerging novel functional imaging and immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma and current treatment sequencing strategies after immunotherapy. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 44 (3), e438658. doi:10.1200/EDBK_438658
Aurilio, G., Piva, F., Santoni, M., Cimadamore, A., Sorgentoni, G., Lopez-Beltran, A., et al. (2019). The role of obesity in renal cell carcinoma patients: clinical-pathological implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (22), 5683. doi:10.3390/ijms20225683
Bahadoram, S., Davoodi, M., Hassanzadeh, S., Bahadoram, M., Barahman, M., and Mafakher, L. (2022). Renal cell carcinoma: an overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. G. Ital. Nefrol. 39 (3).
Barata, P., Gulati, S., Elliott, A., Hammers, H. J., Burgess, E., Gartrell, B. A., et al. (2024). Renal cell carcinoma histologic subtypes exhibit distinct transcriptional profiles. J. Clin. Invest 134 (11), e178915. doi:10.1172/JCI178915
Bellouki, O., Ibrahimi, A., Soufiani, I., Boualaoui, I., El Sayegh, H., and Nouini, Y. (2023). Blepharoptosis revealing a metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a rare case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 112, 108910. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108910
Cen, J., Liang, Y., Huang, Y., Pan, Y., Shu, G., Zheng, Z., et al. (2021). Circular RNA circSDHC serves as a sponge for miR-127-3p to promote the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via the CDKN3/E2F1 axis. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 19. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01314-w
Chen, H., Zhu, D., Zheng, Z., Cai, Y., Chen, Z., and Xie, W. (2019). CEP55 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell carcinoma through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 21 (7), 939–949. doi:10.1007/s12094-018-02012-8
Chen, J., Cao, N., Li, S., and Wang, Y. (2021). Identification of a risk stratification model to predict overall survival and surgical benefit in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with distant metastasis. Front. Oncol. 11, 630842. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.630842
Chen, Q., Liu, T., Bao, Y., Zhao, T., Wang, J., Wang, H., et al. (2020). CircRNA cRAPGEF5 inhibits the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via the miR-27a-3p/TXNIP pathway. Cancer Lett. 469, 68–77. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.017
Cho, D. Y., Kim, H. J., and Kim, J. Y. (2024). Renal cell carcinoma metastasis to the penis: a case report and literature review. Med. Kaunas. 60 (4), 554. doi:10.3390/medicina60040554
Choueiri, T. K., Powles, T., Albiges, L., Burotto, M., Szczylik, C., Zurawski, B., et al. (2023). Cabozantinib plus nivolumab and ipilimumab in renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 388 (19), 1767–1778. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2212851
Di, S. C., Chen, W. J., Yang, W., Zhang, X. M., Dong, K. Q., Tian, Y. J., et al. (2024). DEPDC1 as a metabolic target regulates glycolysis in renal cell carcinoma through AKT/mTOR/HIF1α pathway. Cell Death Dis. 15 (7), 533. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06913-1
Dong, D., Mu, Z., Wei, N., Sun, M., Wang, W., Xin, N., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via targeting miR-10a/SKA1 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 111, 917–925. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.143
Duan, J., Jin, M., Yang, D., Shi, J., Gao, J., Guo, D., et al. (2022). Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis by downregulating the NF-κB pathway. Bioengineered 13 (2), 4455–4467. doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2033403
Dufies, M., Verbiest, A., Cooley, L. S., Ndiaye, P. D., He, X., Nottet, N., et al. (2021). Plk1, upregulated by HIF-2, mediates metastasis and drug resistance of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Commun. Biol. 4 (1), 166. doi:10.1038/s42003-021-01653-w
Elias, R., Tcheuyap, V. T., Kaushik, A. K., Singla, N., Gao, M., Reig Torras, O., et al. (2021). A renal cell carcinoma tumorgraft platform to advance precision medicine. Cell Rep. 37 (8), 110055. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110055
Elmusa, E., Raza, M. W., Hamza, A., Khokhar, H. T., and Butt, M. (2022). Metastatic jejunal renal cell carcinoma intussusception presenting as melena. Cureus 14 (12), e32554. doi:10.7759/cureus.32554
Fujita, K., Kimura, G., Tsuzuki, T., Kato, T., Banno, E., Kazama, A., et al. (2022). The association of tumor immune microenvironment of the primary lesion with time to metastasis in patients with renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective analysis. Cancers (Basel) 14 (21), 5258. doi:10.3390/cancers14215258
Ganesh, K., and Massagué, J. (2021). Targeting metastatic cancer. Nat. Med. 27 (1), 34–44. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01195-4
Gerstberger, S., Jiang, Q., and Ganesh, K. (2023). Metastasis. Cell 186 (8), 1564–1579. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.003
Gray, R. E., and Harris, G. T. (2019). Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 99 (3), 179–184.
Grimm, M. O., Oya, M., Choueiri, T. K., Motzer, R. J., Schmidinger, M., Quinn, D. I., et al. (2024). Impact of prior cytoreductive nephrectomy on efficacy in patients with synchronous metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with avelumab plus axitinib or sunitinib: post hoc analysis from the JAVELIN renal 101 phase 3 trial. Eur. Urol. 85 (1), 8–12. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2023.09.016
Gui, D., Dong, Z., Peng, W., Jiang, W., Huang, G., Liu, G., et al. (2021). Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 53 inhibits the occurrence and development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through NF-κB pathway inactivation. Cancer Med. 10 (11), 3674–3688. doi:10.1002/cam4.3911
Guo, J., Ke, S., Chen, Q., Zhou, J., Guo, J., and Qiu, T. (2023). NCOA7 regulates growth and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (14), 11584. doi:10.3390/ijms241411584
Guo, Q., Jin, Y., Chen, X., Ye, X., Shen, X., Lin, M., et al. (2024). NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9 (1), 53. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9
He, A., He, S., Huang, C., Chen, Z., Wu, Y., Gong, Y., et al. (2020). MTDH promotes metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by activating SND1-mediated ERK signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Aging (Albany NY) 12 (2), 1465–1487. doi:10.18632/aging.102694
Hu, G., Ma, J., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Liu, H., Huang, Y., et al. (2021). Hypoxia-induced lncHILAR promotes renal cancer metastasis via ceRNA for the miR-613/206/1-1-3p/Jagged-1/Notch/CXCR4 signaling pathway. Mol. Ther. 29 (10), 2979–2994. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.05.020
Huang, Q., Sun, Y., Ma, X., Gao, Y., Li, X., Niu, Y., et al. (2017). Androgen receptor increases hematogenous metastasis yet decreases lymphatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 8 (1), 918. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00701-6
Huang, X. F., and Yu, Z. L. (2023). Clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the mandible: a unique case report and literature review. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 26 (4), 265–270. doi:10.3290/j.cjdr.b4784061
Jiang, Z., Yang, G., Wang, G., Wan, J., Zhang, Y., Song, W., et al. (2024). SEC14L3 knockdown inhibited clear cell renal cell carcinoma proliferation, metastasis and sunitinib resistance through an SEC14L3/RPS3/NFκB positive feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43 (1), 288. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03206-5
Lei, C., Lv, S., Wang, H., Liu, C., Zhai, Q., Wang, S., et al. (2018). Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor suppresses the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through negative regulation of the yes-associated protein. DNA Cell Biol. 37 (8), 659–669. doi:10.1089/dna.2017.4102
Li, J., Chen, S., Xiao, J., Ji, J., Huang, C., and Shu, G. (2024b). FOXC1 transcriptionally suppresses ABHD5 to inhibit the progression of renal cell carcinoma through AMPK/mTOR pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 40 (1), 62. doi:10.1007/s10565-024-09899-w
Li, J. K., Chen, C., Liu, J. Y., Shi, J. Z., Liu, S. P., Liu, B., et al. (2017). Long noncoding RNA MRCCAT1 promotes metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via inhibiting NPR3 and activating p38-MAPK signaling. Mol. Cancer 16 (1), 111. doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0681-0
Li, M., Li, L., Zheng, J., Li, Z., Li, S., Wang, K., et al. (2023a). Liquid biopsy at the frontier in renal cell carcinoma: recent analysis of techniques and clinical application. Mol. Cancer 22 (1), 37. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01745-7
Li, X., Xiao, W., Yang, H., and Zhang, X. (2024a). Exosome in renal cell carcinoma progression and implications for targeted therapy. Front. Oncol. 14, 1458616. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1458616
Li, Y., Lih, T. M., Dhanasekaran, S. M., Mannan, R., Chen, L., Cieslik, M., et al. (2023b). Histopathologic and proteogenomic heterogeneity reveals features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness. Cancer Cell 41 (1), 139–163.e17. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2022.12.001
Li, Y. L., Wu, L. W., Zeng, L. H., Zhang, Z. Y., Wang, W., Zhang, C., et al. (2020). ApoC1 promotes the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activation of STAT3. Oncogene 39 (39), 6203–6217. doi:10.1038/s41388-020-01428-3
Lin, Y. W., Lee, L. M., Lee, W. J., Chu, C. Y., Tan, P., Yang, Y. C., et al. (2016). Melatonin inhibits MMP-9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by suppressing Akt-MAPKs pathway and NF-κB DNA-binding activity. J. Pineal Res. 60 (3), 277–290. doi:10.1111/jpi.12308
Liu, X., Zhong, L., Li, P., and Zhao, P. (2022). MicroRNA-100 enhances autophagy and suppresses migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells via disruption of NOX4-dependent mTOR pathway. Clin. Transl. Sci. 15 (2), 567–575. doi:10.1111/cts.12798
Liu, Z., Zhang, Q., Zhao, X., Zhu, G., Tang, S., Hong, P., et al. (2021). Inferior vena cava interruption in renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: surgical strategy and perioperative results. BMC Surg. 21 (1), 402. doi:10.1186/s12893-021-01400-2
Lu, Y., Qin, H., Jiang, B., Lu, W., Hao, J., Cao, W., et al. (2021). KLF2 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion by regulating ferroptosis through GPX4 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 522, 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.09.014
Luo, A. J., Tan, J., He, L. Y., Jiang, X. Z., Jiang, Z. Q., Zeng, Q., et al. (2019). Suppression of Tescalcin inhibits growth and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma via downregulating NHE1 and NF-kB signaling. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 107, 110–117. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.12.004
Luo, L., Wei, D., Pan, Y., Wang, Q. X., Feng, J. X., Yu, B., et al. (2023). MFN2 suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by modulating mitochondria-dependent dephosphorylation of EGFR. Cancer Commun. (Lond). 43 (7), 808–833. doi:10.1002/cac2.12428
Lv, C., Huang, Y., Lei, Q., Liu, Z., Shen, S., and Si, W. (2020). Elevated MTA1 induced the migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma through the NF-κB pathway. BMC Urol. 20 (1), 160. doi:10.1186/s12894-020-00731-1
Ma, Q., Yu, J., Zhang, X., Wu, X., and Deng, G. (2023). Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway-a versatile player in apoptosis and autophagy. Biochimie 211, 57–67. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2023.03.001
Mabeta, P., and Steenkamp, V. (2022). The VEGF/VEGFR Axis revisited: implications for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (24), 15585. doi:10.3390/ijms232415585
Mao, W., Wang, K., Xu, B., Zhang, H., Sun, S., Hu, Q., et al. (2021). ciRS-7 is a prognostic biomarker and potential gene therapy target for renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 142. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01443-2
Mao, W., Wang, K., Zhang, W., Chen, S., Xie, J., Zheng, Z., et al. (2022). Transfection with Plasmid-Encoding lncRNA-SLERCC nanoparticle-mediated delivery suppressed tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 41 (1), 252. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02467-2
Matuszczak, M., Kiljańczyk, A., and Salagierski, M. (2023). Surgical approach in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a literature review. Cancers (Basel) 15 (6), 1804. doi:10.3390/cancers15061804
Mei, S., Alchahin, A. M., Tsea, I., Kfoury, Y., Hirz, T., Jeffries, N. E., et al. (2024). Single-cell analysis of immune and stroma cell remodeling in clear cell renal cell carcinoma primary tumors and bone metastatic lesions. Genome Med. 16 (1), 1. doi:10.1186/s13073-023-01272-6
Meng, K., Hu, Y., Wang, D., Li, Y., Shi, F., Lu, J., et al. (2023). EFHD1, a novel mitochondrial regulator of tumor metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 114 (5), 2029–2040. doi:10.1111/cas.15749
Miao, D., Shi, J., Lv, Q., Tan, D., Zhao, C., Xiong, Z., et al. (2024). NAT10-mediated ac(4)C-modified ANKZF1 promotes tumor progression and lymphangiogenesis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma by attenuating YWHAE-driven cytoplasmic retention of YAP1. Cancer Commun. (Lond). 44 (3), 361–383. doi:10.1002/cac2.12523
Mirzaei, S., Saghari, S., Bassiri, F., Raesi, R., Zarrabi, A., Hushmandi, K., et al. (2022). NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: a focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Physiol. 237 (7), 2770–2795. doi:10.1002/jcp.30759
Moein, A., Jin, J. Y., Wright, M. R., and Wong, H. (2024). Quantitative assessment of drug efficacy and emergence of resistance in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma using a longitudinal exposure-tumor growth inhibition model: apitolisib (dual PI3K/mTORC1/2 inhibitor) versus everolimus (mTORC1 inhibitor). J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64 (9), 1101–1111. doi:10.1002/jcph.2444
Motzer, R., Alekseev, B., Rha, S. Y., Porta, C., Eto, M., Powles, T., et al. (2021). Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or everolimus for advanced renal cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 384 (14), 1289–1300. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035716
Oxburgh, L. (2022). The extracellular matrix environment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 14 (17), 4072. doi:10.3390/cancers14174072
Park, C. L., Moria, F. A., Ghosh, S., Wood, L., Bjarnason, G. A., Bhindi, B., et al. (2024). Impact of timing of immunotherapy and cytoreductive nephrectomy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: real-world Data on survival outcomes from the CKCis database. Curr. Oncol. 31 (8), 4704–4712. doi:10.3390/curroncol31080351
Park, H. K. (2023). The metastasis pattern of renal cell carcinoma is influenced by histologic subtype, grade, and sarcomatoid differentiation. Med. Kaunas. 59 (10), 1845. doi:10.3390/medicina59101845
Petejova, N., and Martinek, A. (2016). Renal cell carcinoma: review of etiology, pathophysiology and risk factors. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech Repub. 160 (2), 183–194. doi:10.5507/bp.2015.050
Ryalen, P. C., Møller, B., Laache, C. H., Stensrud, M. J., and Røysland, K. (2023). Prognosis of cancer survivors: estimation based on differential equations. Biostatistics 24 (2), 345–357. doi:10.1093/biostatistics/kxab009
Semenescu, L. E., Kamel, A., Ciubotaru, V., Baez-Rodriguez, S. M., Furtos, M., Costachi, A., et al. (2023). An overview of systemic targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma, with a focus on metastatic renal cell carcinoma and brain metastases. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45 (9), 7680–7704. doi:10.3390/cimb45090485
Sharma, R., Kadife, E., Myers, M., Kannourakis, G., Prithviraj, P., and Ahmed, N. (2021). Determinants of resistance to VEGF-TKI and immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 186. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-01961-3
Shi, Q., Xu, R., Song, G., Lu, H., Xue, D., He, X., et al. (2020). GATA3 suppresses human fibroblasts-induced metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via an anti-IL6/STAT3 mechanism. Cancer Gene Ther. 27 (9), 726–738. doi:10.1038/s41417-019-0146-2
Siegel, R. L., Giaquinto, A. N., and Jemal, A. (2024). Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74 (1), 12–49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
Singla, A., Sharma, U., Makkar, A., Masood, P. F., Goel, H. K., Sood, R., et al. (2022). Rare metastatic sites of renal cell carcinoma: a case series. Pan Afr. Med. J. 42, 26. doi:10.11604/pamj.2022.42.26.33578
Son, J. Y., Yoon, S., Tae, I. H., Park, Y. J., De, U., Jeon, Y., et al. (2018). Novel therapeutic roles of MC-4 in combination with everolimus against advanced renal cell carcinoma by dual targeting of Akt/pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme M2 and mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 pathways. Cancer Med. 7 (10), 5083–5095. doi:10.1002/cam4.1748
Sun, B., Chen, L., Fu, H., Guo, L., Guo, H., and Zhang, N. (2016). Upregulation of RICTOR gene transcription by the proinflammatory cytokines through NF-κB pathway contributes to the metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37 (4), 4457–4466. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4296-z
Sun, F., Sun, P., Yang, X., Hu, L., Gao, J., and Tian, T. (2021). Inhibition of FSTL3 abates the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 13 (18), 22528–22543. doi:10.18632/aging.203564
Sun, J., Yin, A., Zhang, W., Lv, J., Liang, Y., Li, H., et al. (2020). CircUBAP2 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via targeting miR-148a-3p/FOXK2 pathway. Cell Transpl. 29, 963689720925751. doi:10.1177/0963689720925751
Sun, Y., Zhu, L., Liu, P., Zhang, H., Guo, F., and Jin, X. (2023). ZDHHC2-Mediated AGK palmitoylation activates AKT-mTOR signaling to reduce sunitinib sensitivity in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 83 (12), 2034–2051. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3105
Tang, S., Chen, F., Zhang, J., Chang, F., Lv, Z., Li, K., et al. (2024). LncRNA-SERB promotes vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and tumor metastasis in renal cell carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 300 (5), 107297. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107297
Teishima, J., Murata, D., Yukihiro, K., Sekino, Y., Inoue, S., Hayashi, T., et al. (2023). Significance of timing of therapeutic line on effectiveness of nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Curr. Urol. 17 (1), 52–57. doi:10.1097/CU9.0000000000000105
Ushakova, O., and Ravakhah, K. (2023). Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma presenting as acute appendicitis. Cureus 15 (8), e44155. doi:10.7759/cureus.44155
Vig, S. V. L., Zan, E., and Kang, S. K. (2020). Imaging for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Clin. North Am. 47 (3), 281–291. doi:10.1016/j.ucl.2020.04.005
Walton, J., Lawson, K., Prinos, P., Finelli, A., Arrowsmith, C., and Ailles, L. (2023). PBRM1, SETD2 and BAP1 - the trinity of 3p in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 20 (2), 96–115. doi:10.1038/s41585-022-00659-1
Wang, Q., Xu, J., Xiong, Z., Xu, T., Liu, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). CENPA promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Transl. Med. 19 (1), 417. doi:10.1186/s12967-021-03087-8
Wang, W., Yang, Y., Chen, X., Shao, S., Hu, S., and Zhang, T. (2019a). MAGI1 mediates tumor metastasis through c-Myb/miR-520h/MAGI1 signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Apoptosis 24 (11-12), 837–848. doi:10.1007/s10495-019-01562-8
Wang, Y., Su, J., Wang, Y., Fu, D., Ideozu, J. E., Geng, H., et al. (2019b). The interaction of YBX1 with G3BP1 promotes renal cell carcinoma cell metastasis via YBX1/G3BP1-SPP1- NF-κB signaling axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 386. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1347-0
Wang, Y., Suarez, E. R., Kastrunes, G., de Campos, N. S. P., Abbas, R., Pivetta, R. S., et al. (2024). Evolution of cell therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 23 (1), 8. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01911-x
Wang, Z. (2021). Regulation of cell cycle progression by growth factor-induced cell signaling. Cells 10 (12), 3327. doi:10.3390/cells10123327
Wolf, M. M., Madden, M. Z., Arner, E. N., Bader, J. E., Ye, X., Vlach, L., et al. (2024). VHL loss reprograms the immune landscape to promote an inflammatory myeloid microenvironment in renal tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Invest 134 (8), e173934. doi:10.1172/JCI173934
Wu, Y., Chen, S., Yang, X., Sato, K., Lal, P., Wang, Y., et al. (2023b). Combining the tyrosine kinase inhibitor cabozantinib and the mTORC1/2 inhibitor sapanisertib blocks ERK pathway activity and suppresses tumor growth in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 83 (24), 4161–4178. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0604
Wu, Y., Terekhanova, N. V., Caravan, W., Naser, A., Deen, N., Lal, P., et al. (2023c). Epigenetic and transcriptomic characterization reveals progression markers and essential pathways in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 1681. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37211-7
Wu, Y., Zhang, S., Chen, C., and Pang, J. (2023a). Dysregulation and implications of N6-methyladenosine modification in renal cell carcinoma. Curr. Urol. 17 (1), 45–51. doi:10.1097/CU9.0000000000000135
Xu, Z., Chen, S., Liu, R., Chen, H., Xu, B., Xu, W., et al. (2022). Circular RNA circPOLR2A promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by facilitating the UBE3C-induced ubiquitination of PEBP1 and, thereby, activating the ERK signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 146. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01607-8
Yan, Y., Bao, G., Pei, J., Cao, Y., Zhang, C., Zhao, P., et al. (2022). NF-κB and EGFR participate in S1PR3-mediated human renal cell carcinomas progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1868 (7), 166401. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166401
Yin, L., Li, W., Chen, X., Wang, R., Zhang, T., Meng, J., et al. (2023). HOOK1 inhibits the progression of renal cell carcinoma via TGF-β and TNFSF13B/VEGF-A Axis. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10 (17), e2206955. doi:10.1002/advs.202206955
Yin, L., Li, W., Xu, A., Shi, H., Wang, K., Yang, H., et al. (2020). SH3BGRL2 inhibits growth and metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activating hippo/TEAD1-Twist1 pathway. EBioMedicine 51, 102596. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.12.005
Yue, Y., Hui, K., Wu, S., Zhang, M., Que, T., Gu, Y., et al. (2020). MUC15 inhibits cancer metastasis via PI3K/AKT signaling in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 11 (5), 336. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2518-9
Zeng, X., Chen, Z., Zhu, Y., Liu, L., Zhang, Z., Xiao, Y., et al. (2024). O-GlcNAcylation regulation of RIPK1-dependent apoptosis dictates sensitivity to sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Drug Resist Updat 77, 101150. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2024.101150
Zhan, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, R., Chen, Q., Teng, F., Huang, Y., et al. (2023). CircPTEN suppresses human clear cell renal carcinoma progression and resistance to mTOR inhibitors by targeting epigenetic modification. Drug Resist Updat 71, 101003. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2023.101003
Zhang, J., Li, X., Lin, J., Liu, Z., Tian, Y., and Wang, Q. (2022). Modified cancer TNM classification for localized renal cell carcinoma based on the prognostic analysis of 3748 cases from a single center. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 100 (1), 5–11. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2021-0291
Zhang, Y., Fan, Y., Huang, S., Wang, G., Han, R., Lei, F., et al. (2018). Thymoquinone inhibits the metastasis of renal cell cancer cells by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 109 (12), 3865–3873. doi:10.1111/cas.13808
Zheng, J. Q., Lin, C. H., Lee, H. H., Wang, W. K., Tong, Y. S., Lee, K. Y., et al. (2021). Lactotransferrin downregulation serves as a potential predictor for the therapeutic effectiveness of mTOR inhibitors in the metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma without PTEN mutation. Biomedicines 9 (12), 1896. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9121896
Zhu, Q., Zhong, A. L., Hu, H., Zhao, J. J., Weng, D. S., Tang, Y., et al. (2020). Acylglycerol kinase promotes tumour growth and metastasis via activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signalling pathway in renal cell carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13 (1), 2. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0840-4
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma, metastasis, metastatic renal cell carcinoma, molecular mechanisms, targeted therapy
Citation: Li X, Xiong W, Xiong Z and Zhang X (2025) Molecular mechanisms of renal cell carcinoma metastasis and potential targets for therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1521151. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1521151
Received: 04 November 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 20 January 2025.
Edited by:
Qinong Ye, Beijing Institute of Biotechnology, ChinaReviewed by:
Alexander Zaslavsky, University of Michigan, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Li, Xiong, Xiong and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyong Xiong, dGp4aW9uZ3poaXlvbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Xiaoping Zhang, eHpoYW5nQGh1c3QuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.