
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 03 February 2025
Sec. Stem Cell Research
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1517369
This article is part of the Research TopicStem Cell Therapy for Hereditary Neuromuscular DiseasesView all articles
 Kamran Sheikhi1†
Kamran Sheikhi1† Salah Ghaderi2†
Salah Ghaderi2† Hassan Firouzi3
Hassan Firouzi3 Sarvenaz Rahimibarghani4
Sarvenaz Rahimibarghani4 Ehsan Shabani5
Ehsan Shabani5 Hamed Afkhami6,7,8*
Hamed Afkhami6,7,8* Aref Yarahmadi9*
Aref Yarahmadi9*Multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic autoimmune disorder of the central nervous system (CNS), is characterized by inflammation, demyelination, and neurodegeneration, leading to diverse clinical manifestations such as fatigue, sensory impairment, and cognitive dysfunction. Current pharmacological treatments primarily target immune modulation but fail to arrest disease progression or entirely reverse CNS damage. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy offers a promising alternative, leveraging its immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and regenerative capabilities. This review provides an in-depth analysis of MSC mechanisms of action, including immune system regulation, promotion of remyelination, and neuroregeneration. It examines preclinical studies and clinical trials evaluating the efficacy, safety, and limitations of MSC therapy in various MS phenotypes. Special attention is given to challenges such as delivery routes, dosing regimens, and integrating MSCs with conventional therapies. By highlighting advancements and ongoing challenges, this review underscores the potential of MSCs to revolutionize MS treatment, paving the way for personalized and combinatory therapeutic approaches.
The chronic autoimmune illness of the central nervous system (CNS), known as multiple sclerosis (MS), affects a sizable portion of the global population and has had a profound effect on public health globally (Kobelt et al., 2017; Sumowski et al., 2018; Bjornevik et al., 2022). This illness is typified by inflammation and myelin loss, which results in neurodegeneration. Clinical characteristics include exhaustion and mental/cognitive impairment, in addition to more unusual ones such as vision loss and sensorimotor complaints. It primarily affects female patients and younger people (Penesová et al., 2018). The illness is categorized into three clinical forms: primary progressive (PPMS), secondary progressive (SPMS), and relapsing-remitting (RRMS). Each type is distinguished by a different level of pathology, spanning acute/chronic inflammation and, or neurodegeneration (Stoiloudis et al., 2022). Numerous environmental, dietary, viral (such as the Epstein-Barr virus), genetic, and epigenetic factors may be causal in the onset and progression of MS. The pathophysiology and etiology of MS are complicated (Bjornevik et al., 2022; Ascherio, 2013; Miclea et al., 2020). The MS Atlas estimated in 2020 that one person with MS is diagnosed every 5 min throughout the world, with an average age of 32 years, adding to the 2.8 million people who already have the condition (Charabati et al., 2023). Its frequency varies by region, with Europe and North America having the highest rates (Thompson et al., 2018). Jean-Martin Charcot termed this condition sclérose en plaques in 1868, which was eventually shortened to MS. Charcot and colleagues (Charcot, 1868) discovered that pathological indicators of MS entail the identification of lesions in the regions of the CNS that involve both white and gray matter. These lesions exhibit different levels of demyelination, perivascular immune cell infiltration, reactive gliosis, and, or neurodegeneration. Subsequent research identified abnormalities of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and axonal transection as additional characteristics of these lesions (Schreiner et al., 2022; Mey et al., 2023). Up till now, several treatment strategies, including fingolimod (FTY720), natalizumab, glatiramer acetate, and interferon-β (IFN-β), have been proposed to regulate aberrant immune responses in MS patients. These medications primarily work by inhibiting immunological responses, which lowers the frequency of relapses and slows the advancement of neurologic impairment. Nevertheless, they have not achieved consistent success (Yousefi et al., 2019; Bejargafshe et al., 2019). According to reports, these therapies are unable to stop the deterioration of nerve tissue in patients with a severe type of MS (Bejargafshe et al., 2019).
Stem cell-based therapies, among the various available methods, hold significant potential to effectively reduce neuronal damage in both in vivo and in vitro models of neurological disorders (Abdallah et al., 2019). The use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for treating MS has demonstrated encouraging results (ArefNezhad et al., 2023; Zolfaghari Baghbadorani et al., 2023; González et al., 2022; Zhang Y. et al., 2023). Friedenstein and associates identified MSCs as multipotent stem cells in the late 1960s (Friedenstein et al., 1966). Kaplan first used the term “MSCs” in 1991 following his study on human bone marrow (BM) (Caplan, 1991). The capacity of engineered stem cells to multiply (self-renew) and differentiate is well-known. Mammalian tissues such as BM, adipose tissue (AT), dental pulp, amniotic fluid (AF), umbilical cord (UC), etc., are practically all known to contain MSCs. When organs and tissues are damaged, they are in charge of tissue regeneration and repair (Andrzejewska et al., 2019; Yu et al., 2014; Shi et al., 2018). By producing co-stimulatory molecules, they exhibit immunomodulatory features that enable them to control immunological responses and cytokine release (Jiang and Xu, 2020). MSCs are readily extracted from BM, AT, peripheral blood, the placenta, and the UC (Figure 1) (Caplan and Correa, 2011; Laroye et al., 2020). Afterward, they can be grown into a massive population in a culture medium to facilitate cell-based treatment (Planchon et al., 2018). Recently, stem cell-based therapy has given MS patients hope and is currently seen as the most popular noninvasive way to treat many disorders (Xiao et al., 2015).
The primary aim of this review is to investigate and evaluate the valuable capacity of MSCs in managing MS. This includes examining their immunomodulatory and regenerative capacities, discussing findings from preclinical and clinical studies, and identifying challenges such as optimal delivery methods and therapeutic integration. By leveraging the latest advancements in MSC-based research, this review seeks to provide a comprehensive perspective on their clinical applications, limitations, and future directions in MS therapy.
MS, a condition characterized by the breakdown of myelin and loss of axons, is the most frequently encountered non-traumatic debilitating ailment (Hauser et al., 2020). Sclerotic plaques and lesion development in the CNS and cerebrospinal cord are common characteristics of MS (Oh et al., 2018; Kurtzke, 1983). Through controlling synaptic architecture, neurogenesis, and oligodendrogenesis, the immune system plays a crucial role in the evolution of the nervous system. As a result, immune cells may play a part in the cause and development of MS (Rahmati et al., 2021; Sedaghat et al., 2019). Environmental, genetic, and hormonal variables have a significant role in the etiology of MS. Changes in the expression and functionality of immunological agents, including T-cell receptor (TCR), immunoglobulin (Ig), major histocompatibility complex (MHC), and cytokines, have been linked to an elevated risk of MS. According to current MS research, the BBB breach and the start of an autoimmune cascade trigger autoreactive T-cell migration to the CNS, which destroys the myelin sheath and results in sclerotic lesions and plaques. One of the leading causes of MS is the destruction of the myelin sheath, which is essential for axon survival and integration (Khan et al., 2024; Kuhlmann et al., 2023).
MS primarily presents in three distinct clinical courses. RRMS, the most common form of the disease, is characterized by exacerbations followed by complete or partial remissions, affecting 85%–90% of MS patients. After several years, approximately 50%–60% of these individuals progress to SPMS, marked by a gradual worsening of symptoms without remission. Approximately 15% of individuals are diagnosed with PPMS, a condition characterized by a gradual decline in neurological function, with or without episodes of exacerbation (Oliveira et al., 2020).
The primary effector cells involved in the demyelination and destruction of the CNS are T helper 1 (Th1) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells. Specific pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-17 (IL-17), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and IL-1, are produced by Th1 and Th17. Additionally, MS lesions contain CD8+ T lymphocytes, particularly in the vicinity of the blood vessels. Prior research has demonstrated that in MS patients, CD8+ T cells proliferate more than CD4+ T cells, which is mainly linked to axon damage (Khan et al., 2024; Dong et al., 2021; Dadfar et al., 2024). Other immune cells have significant involvement in the development of lesions and plaques in addition to T cells’ responsibilities in the pathogenesis of MS. More CNS antigens are exposed due to myelin being destroyed by Th1 cytokines, which activate macrophages. Although autoreactive T cells are the primary effector cells involved in the development of MS, there have been indications in some studies that autoreactive B cells also contribute significantly to the demyelination and axonal damage by presenting antigens, producing autoantibodies and secreting cytokines (Sedaghat, 2018). Autoantibodies are significant immune mediators present in MS plaques. Several reports suggest a potential correlation between immunoglobulin G (IgG) and the manifestation of symptoms related to MS. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that IgG, particularly IgG targeting myelin fundamental proteins (MBP) and proteolipid proteins (PLP), may be regarded as characteristic markers of the disease. However, their specific roles in the pathogenesis of MS have not been fully elucidated (Maroto-García, 2023; Amin and Hersh, 2023). Research has shown that the introduction of T-cell lines or clones targeting CND myelin antigens into genetically identical, naïve recipient mice has led to the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a suitable animal model for MS (Ben-Nun and Lando, 1983; Ben-Nun et al., 1981; Zamvil et al., 1985). Therefore, inflammation has been seen in MS due to damage to myelin along with axons and neurons, finally resulting in neurodegeneration. The primary means of diagnosis, in addition to clinical presentation, is the temporal and regional appearance of inflammatory lesions as shown by magnetic resonance imaging (Dadfar et al., 2024; Ananthavarathan et al., 2024).
MSCs are multipotent stromal cells that can undergo self-renewal and differentiate into various mesenchymal cell lineages (Dominici et al., 2006; Cesarz and Tamama, 2016; Afkhami et al., 2023; Mirshekar et al., 2023). They can also reduce excessive immune responses and hyperinflammatory processes by inducing the expression of Foxp3+ in CD4 T cells in a laboratory setting (English et al., 2009; Aliniay-Sharafshadehi et al., 2024). MSCs have various ways of regulating the immune system, such as promoting the production of regulatory T cells (Tregs) through direct interaction with T cells and releasing anti-inflammatory substances in a laboratory setting. These mechanisms enable MSCs to manage the development of autoimmune conditions like MS (Figure 1) (Yang et al., 2023; Andalib et al., 2023; Teymouri et al., 2024). When given the right triggers, MSCs can develop into various specialized cell types that originate from mesenchymal tissue, such as bone cells, muscle cells, ligament cells, cartilage cells, and tendon cells (Heldman et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2009; Fakouri et al., 2024). Various non-mesodermal cell lineages have been observed to undergo differentiation, including alveolar cells, hepatocytes, epithelial cells, astrocytes, mature neurons, and neural precursors. These findings indicate that MSCs may play a possible role in the inherent healing process of tissues (Liu et al., 2009; Weiss and Dahlke, 2019; Uccelli et al., 2008).
Previous studies have provided evidence that suggests these cells hold potential as viable treatment options for a range of neurological disorders, such as MS and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (Najafi et al., 2023; Vaheb, 2024). The immunomodulatory impacts of MSCs may be demonstrated through their direct engagement with immune cells or through the transmission of paracrine signals. Research has shown that MSCs can inhibit the differentiation of Th17 and Th1 cells. Research has indicated that MSCs expanded in a laboratory setting can hinder the growth of T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells, as well as impede the maturation and differentiation of dendritic cells (DCs) (Yang et al., 2023; Mei et al., 2024). In recent times, stem cell-based therapy has become a promising strategy for treating patients with MS. It is currently considered the most preferred and least intrusive treatment option for a range of medical conditions (Papaccio et al., 2017; Islam et al., 2023).
In RRMS, inflammation is dominant, driven by autoreactive T cells and a disrupted BBB. Several studies have demonstrated a reduction in relapse frequency and lesion formation in preclinical models of RRMS following MSC therapy (Vaheb, 2024; Gavasso et al., 2024). Applying MSCs in clinical research involving patients with RRMS has yielded promising results. The study observed a trend toward reduced levels of pathogenic inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cell subtypes, accompanied by a decrease in inflammation as indicated by MRI scans. Notably, there was also an increase in regulatory B cells (Llufriu et al., 2014a). In progressive forms of MS, such as PPMS and SPMS, the primary challenge lies in addressing neurodegeneration and promoting repair mechanisms. To treat PPMS and SPMS, MSC therapy has been investigated as a potential option for targeting various therapeutic targets (Gavasso et al., 2024; Ghareghani et al., 2024). The first placebo-controlled trial utilizing intrathecal administration of MSCs in patients with active progressive MS demonstrated a positive impact on disease outcomes. This included reduced neurofilament light chain levels (NfLs), stabilization or improvement of disability scores, and the achievement of status without evidence of disease activity (Roig-Carles et al., 2021; Colasanti et al., 2014). Despite showing signs of neuroprotection, MSC did not seem to influence humoral immunity to common antigens or peripheral T-cell subsets in the context of SPMS (Connick et al., 2012). This suggests that there may be significant differences in the mechanisms underlying the effects of MSCs in RRMS and progressive MS. It highlights the idea that, depending on the local environment, disease state, and phenotype, MSCs exhibit diverse immunomodulatory effects on various types of immune cells (Zhao, 2019).
MSCs have the potential to provide structural support to axons and improve the stability of neurons. Additionally, they are believed to possess antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties and can release trophic factors. Additionally, they have the potential to facilitate the generation of fresh neurons and glial cells, such as oligodendrocytes (ODCs) (Guimarães-Camboa et al., 2017; Song et al., 2018). In individuals with MS, MSC has the potential to augment the differentiation of neural cells, reduce neuronal cell death, and stimulate the formation of new blood vessels, ultimately contributing to the repair of the CNS (Gavasso et al., 2024). According to recent research, it has been determined that MSCs can enhance peripheral tolerance by suppressing the differentiation and function of DCs, consequently diminishing antigen presentation and impeding the expansion of self-reactive T cells (Zhuo et al., 2023). In addition, MSCs can produce hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which leads to an increase in tolerogenic DCs. Research has revealed that the administration of MSCs in combination with HGF results in a reduction of CNS inflammatory reactions and the infiltration of immune cells in mice with EAE. Consequently, MSCs derived from HGF demonstrate potential as a viable therapeutic approach for MS and other autoimmune disorders (Bai et al., 2012; Mansoor et al., 2019).
IL-6 and CD20 are key molecules intricately linked to the inflammasome and immune regulation, playing significant roles in the inflammatory cascade observed in MS (Margoni et al., 2022; Chmielewska and Szyndler, 2023). One of the most well-known pro-inflammatory cytokines is thought to be IL-6. More than 100 nations have approved using the neutralizing monoclonal antibody tocilizumab to treat autoimmune diseases by blocking IL-6 (Kishimoto, 2005; Tanaka, 2014). While circulating IL-6 levels are as low as 1–5 pg/mL under homeostatic settings, they may increase by over 1,000 times during inflammatory states, and in severe situations that result in sepsis, IL-6 levels as high as µg/mL have been seen (Waage et al., 1989). IL-6 is synthesized by myeloid cells in response to stimulation of Toll-like receptors, in conjunction with the cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α. This interaction initiates a feed-forward loop that significantly enhances the production of IL-6 in the context of inflammatory responses (Tanaka et al., 2014). IL-6 is a key mediator in the activation of the inflammasome, playing a significant role in chronic inflammation and tissue damage associated with MS. Elevated levels of IL-6 have been correlated with disease severity, underscoring its contribution to the persistence of neuroinflammation and the impairment of remyelination processes (Stampanoni Bassi et al., 2020; Vandebergh et al., 2022).
MSCs possess the ability to express and secrete various cytokines, including IL-6. However, they generally produce lower levels of IL-6 than immune cells such as T cells and macrophages. Under certain conditions, such as exposure to inflammatory stimuli or interaction with immune cells, MSCs can increase their production of IL-6 (Kerkis et al., 2024; Philipp et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2022). MSCs demonstrate potential in regulating IL-6 expression in the context of neuroinflammation. Both autocrine and paracrine signaling loops, along with feedback control from the immune system, contribute to the downregulation of IL-6 by MSCs (Hofer and Tuan, 2016; Lopez-Santalla et al., 2020; Molnar et al., 2022). The complex relationship between MSCs and endogenous IL-6 production depends on experimental conditions and cellular interactions (Dorronsoro et al., 2020). Gu et al. (2016) demonstrated that the release of endogenous IL-6 induced by MSCs led to an upregulation of IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) and phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3) levels in astrocytes subjected to oxygen and glucose deprivation. Notably, a significant increase in the ratio of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) to Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), critical downstream components of the STAT3 signaling pathway, was observed. This study elucidated the neuroprotective effects of MSC transplantation in a rat model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, suggesting that these effects are partially mediated by IL-6, which enhances the anti-apoptotic properties of damaged astrocytes through the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Through paracrine signaling and immunomodulatory mechanisms, MSCs have demonstrated their ability to inhibit the production of IL-6 by immune cells such as T cells and macrophages. However, MSC-derived IL-6 has also been shown to stimulate or modulate the activity of other immune cells, which in turn affects endogenous IL-6 levels (Song et al., 2020; Toh, 2017; Glenn and Whartenby, 2014). MSCs have anti-inflammatory properties that influence IL-6 levels in a variety of settings. They can also reduce IL-6 synthesis by inhibiting immune cell activation (Dabrowska et al., 2021; Saadh et al., 2023).
CD20, a surface marker predominantly expressed in B cells, is another molecule associated with the pathogenesis of MS. It plays a crucial role in B cell activation, antigen presentation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Margoni et al., 2022; de Sèze et al., 2023). In recent years, there has been a growing interest in CD20-targeting therapies, specifically anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies that facilitate B-cell depletion, including ocrelizumab, rituximab, and ofatumumab. The therapeutic scenario for treating MS patients has significantly expanded due to the remarkable effectiveness and favorable safety profile of these selective B-cell-depleting treatments (Hauser et al., 2020; Hauser et al., 2008; Montalban et al., 2017). MSCs can complement this approach by further modulating B cell activity, promoting regulatory B cells, and inhibiting the production of autoantibodies that exacerbate disease progression (Yordanova et al., 2024; Veh et al., 2024). The negative regulatory influence of MSCs on B lymphocytes may result from direct contact with B cells, leading to the release of various soluble cytokines that impact B cell function. This, in turn, prevents B cells from proliferating and reduces the generation of memory B cells and plasma cells, which decreases the number of B cells that secrete cytokines, chemokines, and antibodies (Hoorweg et al., 2015). MSC can enhance the synthesis of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) through the involvement of stem cell antigen 1/lymphocyte antigen 6AIE protein while simultaneously inhibiting the maturation of B lymphocytes. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted by MSCs plays a crucial role in suppressing B lymphocytes by downregulating or inhibiting IL-7 produced by stromal cells (Hoorweg et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2015). The application of MSCs in MS, particularly concerning IL-6 and CD20, highlights their dual role in targeting innate and adaptive immune responses.
The success of MSC therapy in MS is significantly influenced by the route of administration, dosing regimen, and infusion vehicle. Preclinical and clinical studies have primarily utilized intravenous (IV) and intrathecal (IT) routes. IV administration allows systemic delivery, while IT targets the CNS directly, potentially enhancing therapeutic efficacy (Table 1) (Cohen et al., 2018; Iacobaeus et al., 2019; Harris et al., 2016; Harris et al., 2018). Empirical investigations have demonstrated that the IV delivery of MSCs exhibits immunosuppressive properties and mitigates the symptoms of autoimmune disorders (Sato et al., 2009; Jiang et al., 2017). Studies have also shown that the transfer of MSC results in a notable improvement in the clinical results of MS in experimental models of EAE (Bazinet and Popradi, 2019; Alanazi et al., 2022). Recent clinical trials have investigated the effectiveness and safety of MSCs in treating MS. The tests have shown that MSCs, when administered intrathecally into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the spinal cord, can successfully migrate to brain lesions (Alanazi et al., 2022; de Witte et al., 2018; Uder et al., 2018). This intervention is expected to enhance the viability of brain cells by promoting their transformation into precursor cells for neurons and glial cells, thus mitigating the impairment of brain function. Consequently, this approach can potentially reduce the severity of the disease and enhance the overall wellbeing of individuals affected by MS (Von Wunster, 2018; Neal et al., 2018). Syngeneic MSC via IV administration in the EAE model induces tolerance in myelin ODC glycoprotein (MOG)-specific T cells. This leads to a reduction in immune cell infiltration into the CNS, an amelioration of clinical outcomes, and decreased myelin degradation (Freedman et al., 2010).
Dosing varies widely, from single infusions of 1 × 106 cells/kg to repeated doses administered monthly or biannually. Liu et al. (2019) administered umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) IV in Cynomolgus monkeys with EAE on days 74 and 84, using a dose of 1 × 106 cells/kg/mL, which significantly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-5 and IFN-γ while increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10. Similarly, MSCs derived from the whole spinal cord were injected into C57BL/6 mice via the tail vein at a dose of 5 × 105 cells 11 days post-immunization (dpi), resulting in reduced inflammation, improved BBB integrity and enhanced neurobehavioral outcomes (Liu Y. et al., 2020). In another study by Clark et al. (2019), placental MSC-derived extracellular vesicles (PMSC-EVs) were infused at doses of 1 × 107 and 1 × 1010 PMSC-EVs, showcasing the dose-dependent improvement of motor function scores in EAE-induced mice (Clark et al., 2019).
Moreover, the mode of infusion plays a vital role in the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs. Barati et al. (2019) administered BM-MSCs directly into the right lateral ventricle in a cuprizone-fed demyelination model of mice, emphasizing the localized enhancement of ODC populations and remyelination processes. Yan et al. (2018) demonstrated the importance of IT and IV routes for human embryonic stem cells (EMSCs) in Cynomolgus monkeys. IT injections showed superior outcomes in reducing brain abnormalities and demyelination compared to IV. Importantly, infusion vehicles such as saline or specialized buffers were crucial for cell viability and delivery efficiency, though specific details on vehicles were sparsely reported (Fernández-Santos et al., 2022). Collectively, these studies underscore the significance of optimizing the route, dose, and infusion medium to maximize the immunomodulatory and neuroprotective potential of MSC-based therapies in MS models.
ODCs function as the cells responsible for myelination within the CNS. They are derived from precursor cells of ODCs through intricately coordinated processes involving migration, differentiation, and proliferation (Moore et al., 2020; Zeisel et al., 2015; Bradl and Lassmann, 2010). ODCs play a crucial role in developing myelin in the CNS and are essential for the regenerating myelin after injury, including in the prevalent demyelinating disease MS (Franklin and Ffrench-Constant, 2017; Nave, 2010). The ODCs surrounding axons in the CNS have been crucial in improving the speed of nerve impulse conduction, maintaining the structural integrity of axons, and directly supplying metabolic support to lengthy axons (Thompson et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2016; Kassmann et al., 2007). The inability to form a myelin sheath, known as myelination, or the breakdown of the myelin sheath due to diseases or injuries, disrupts the efficient transmission of action potentials in the vertebrate nervous system, ultimately contributing to the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as MS (Vincze et al., 2011; Oudejans et al., 2021). MSCs significantly increased the amount and size of ODC processes; moreover, inhibition experiments demonstrated that the soluble factor Sonic hedgehog created by EMSCs, extracellular matrix molecule, and laminin gap junction protein connexin 43 were responsible for stimulating OPC differentiation because preventing the function of either of the three proteins resulted in significant retraction of processes and ODC detachment. The MSC culture system might be a model for enhancing ODC differentiation and maturation. MSCs could be a promising cell resource for treating neurological disorders related to ODC destruction and demyelination (Zhang et al., 2016; Aggarwal and Pittenger, 2005; Rivera et al., 2019; Manu et al., 2021).
MSCs are generally a group of cells that adhere to surfaces and can renew themselves and transform into various cell types, such as bone, fat, and cartilage cells. Furthermore, MSCs demonstrate significant promise in the modulation of the immune system and exhibit low immunogenicity. MSCs derived from various sources exhibit comparable characteristics. These cells hold promise for applications in regenerative medicine and contribute to maintaining tissue equilibrium (Li et al., 2019; Shang et al., 2021; Casado-Díaz et al., 2020; Nethi et al., 2023; Farokhi et al., 2024).
MSCs were observed to migrate to the injured brain, indicating their potential as a promising cell source for regenerating damaged organs, including the CNS (Li et al., 2002; Andrzejewska et al., 2021). Induction of EAE in mice enhanced brain thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and nitric oxide (NO), TNF-α, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) and decreased brain glutathione (GSH) content and IL-10, compared to the control group. MSC therapy reduced NO, TBRS, TNF-α, and MPO levels while increasing GSH and IL-10 range. This suggests that MSC therapy may be a practical approach for reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in the CNS (Mahfouz et al., 2017a; He et al., 2021).
Recently, Li et al. demonstrated that menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MB-MSCs)- and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) could ameliorate MS severity when transplanted at different phases of EAE by either IV or intraperitoneal (IP) route. They identified decreased Th1 and Th17 cell response, which, in turn, led to reduced severity of EAE disease. As a result, in MS-related inflammation, they concluded that MSCs could be used as allo-MSCs (Ling et al., 2022).
Furthermore, their minimal immunogenicity, related to a low expression of MHC-I and an absolute lack of MHC-II (Wang et al., 2019; Ankrum et al., 2014) and co-stimulatory molecules, allows them to elude immune surveillance (Han et al., 2019). In another study, MSCs were differentiated into neurotrophic factor-producing cells (NTFCs) in vitro to investigate the clinical usage of NTFCs for EAE symptoms. The NTFCs and MSCs were injected intracerebroventricularly (ICV) into EAE mice, resulting in delayed symptom onset and raised animal survival. MSCs and NTFCs were found to suppress mouse immune cells and protect brain cells from oxidative stress (Barhum et al., 2010). Moreover, systemic administration of MSCs enhanced the expression of neural progenitor markers, including nestin (NESTIN), paired box protein Pax-6 (PAX6), vimentin (VIMENTIN), and class III beta-tubulin (TUJ1), in the brains of treated MS rodent models. Analysis revealed that MSCs home the CNS produced an anti-inflammatory mediator, enhanced Treg cell numbers, and induced neuroprotection and myelination in treated models (Brown et al., 2021). Recent reports also demonstrated that co-administration of MSC and FTY720 could exert better therapeutic benefits compared to the administration of each of them. This combination therapy drastically decreased axonal loss and inflammatory CNS infiltrations. Accordingly, FTY720 may promote future immunomodulatory medication and cellular therapy combinations to enhance the advantages of progressive MS (Kassis et al., 2021).
Additional research has demonstrated that the inclusion of rapamycin in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BM-MSC) transplantation in EAE mice resulted in a notable decrease in demyelination and inflammation infiltration, an enhancement of immunomodulatory functions and a suppression of the advancement of neurological impairments when compared to BM-MSC transplantation alone and control groups. BM-MSC and rapamycin co-treatments had immunological effects that increased the production of the IL-4, IL10, and Th-2 cytokines and decreased CD8+ cytolytic activity, Ag-specific lymphocyte proliferation, and Th1-type cytokines (Togha et al., 2017; Xin et al., 2020; Ceccariglia et al., 2020). The use of rapamycin with BM-MSCs illustrates the potential of combining immunomodulatory therapies for more effective MS treatment.
Table 1 is an overview of studies investigating the effect of stem cells (especially MSCs) on various animal models of MS.
Empirical evidence indicates that MSCs derived from various sources and delivered using different techniques can reduce inflammatory cell infiltration and demyelination, resulting in symptom improvement and better clinical outcomes. Moreover, preconditioned or differentiated MSCs, as well as MSCs combined with other compounds, demonstrate greater therapeutic potential and provide enhanced protection in MS models compared to native MSCs (Gugliandolo et al., 2020; Kilian et al., 2010; Brown et al., 2019; Mahjoor et al., 2021; Mahjoor et al., 2023a). Recent reports have delivered proof that estradiol plays an essential role in controlling several MSC functions, including the synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and procedures of cell proliferation (Erwin et al., 2009; Mihai et al., 2019; Cho et al., 2021). Meanwhile, MSCs primed with 17β-estradiol (17-ED) exhibited enhanced therapeutic efficacy compared to naïve MSCs in EAE rat models. This was demonstrated by improved neuropathological changes, a reduced total clinical score, and a significant increase in body weight (Heidari barchi nezhad et al., 2018). Besides, tetramethylpyrazine treatment reduced apoptosis in UCMSCs and enhanced their proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, tetramethylpyrazine-UCMSC treatment significantly decreased clinical scores, demyelination, BBB disruption, and inflammation in experimental EAE mice (Zhang et al., 2020). Ling et al. also exhibited that IFN-γ-UC-MSCs transplantation considerably reduced clinical scores and body weight loss of EAE mice more evidently compared to naive UCMSCs. The intervention also reduced IL-17 levels in treated mice, conferring the patent anti-inflammatory role of IFN-γ-UCMSCs in vivo (Ling et al., 2022). Similarly, IFN-γ enhanced the secretion of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), a valuable biomolecule produced by MSCs to perform their immunosuppressive function. Meanwhile, it has been suggested that IFN-γ-UCMSCs systemic administration resulted in decreased levels of TNF-α in EAE mice. Likewise, IFN-β- adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) preserved and promoted the functional features in EAE mice primarily by reducing central and peripheral neuroinflammation (Zhou X. et al., 2020; Marin-Bañasco et al., 2017).
In conclusion, priming or preconditioning MSCs with various molecules, such as estradiol or IFN-γ, significantly enhances their therapeutic potential in MS models. These approaches contribute to more effective modulation of immune responses and inflammation, presenting a promising avenue for MSC-based therapies in MS treatment.
Genetic modification caused improved migration, adhesion, and survival, preconditioning change, and reduced premature senescence in MSCs. In the process of genetic modification, a newly created gene sequence is inserted into the vector to facilitate its entry into the MSCs. Once inside the MSC, it activates the expression of particular genes or causes them to be overexpressed. A gene switch may be used to modulate transgenic expression, or it may remain constant, resulting in the specific production of particular molecular proteins (Phillips and Tang, 2008; Ocansey et al., 2020; Lan et al., 2020). Different genetic engineering techniques have been used to improve the gene expression patterns of MSCs. These methods can be categorized as those using non-viral or viral vector methods. Replication-deficient viruses, which are commonly used as gene transfer agents, are preferred due to their effective DNA transfer capabilities. However, their clinical use is limited by the high cost of generating cell lines and the potential for immune responses (Park et al., 2015). In contrast, non-viral methods, which include physical or chemical processes, are less immunogenic and can be produced in large quantities. Physical methods for genetically modifying MSCs include nucleofection, sonoporation, and electroporation, while chemical techniques employ lipidic molecules, inorganic nanoparticles, and polymers (Damasceno et al., 2020).
Recent in vivo studies have demonstrated that MSCs genetically engineered to produce IL-4, a cytokine known for modulating the autoimmune inflammatory response, exhibited enhanced protective effects when transplanted during the early stages of the disease. Compared to unmodified MSCs, MSC-IL-4 significantly reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-6, leading to a decrease in disease severity (Payne et al., 2012). Rostami et al. also found that IL-23 receptor (RIL-23R) mRNA transfection significantly improved MSC features in the inflamed areas of EAE models and increased their ability to control the proliferation of T lymphocytes. MSCs-IL-23R also showed a more substantial therapeutic effect than MSCs during in vivo therapy in EAE mice, as documented with increased myelination and a decrease in the entrance of inflammatory mediators into the white matter (Rostami et al., 2022). Moreover, transfecting MSCs with P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) and sialyl Lewis X (SLeX) mRNA significantly enhanced MSC homing to inflamed areas in vivo. The overexpression of PSGL-1/SLeX increased the rolling and adhesion of cells on brain microvascular endothelial cells and contributed to the integrity of the BBB in EAE mice (Liao et al., 2016). In another study, CD4+ T cell proliferation isolated from EAE mice was significantly inhibited by MSCs modified to overexpress IL-10. Wang et al. also demonstrated that transplanting sphingosine kinase 1 (SPK1) gene-modified UC-MSCs (UCMSC-SPK1) significantly decreased the intensity of the neurological impairment in EAE mice models by reducing axonal loss, demyelination, and astrogliosis. Additionally, UCMSC-SPK1 transplantation upregulated the proportion of FoxP3+ (Treg) CD4+ CD25+ T cells and facilitated the development of NK cell responses in the EAE mice’s spleen (Wang et al., 2018). In another study, researchers used MSCs as a treatment plan and a vehicle to transfer fully processing 3.3-kDa vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) to the inflamed CNS and peripheral immune organs. Intraperitoneal injection of MSCs-VIP reduced neuroinflammation and demyelination and increased CNS neuronal integrity in part by inhibiting T-cell activation (Cobo et al., 2013).
In conclusion, genetic modification of MSCs offers a promising strategy to enhance their therapeutic efficacy in MS models. By modifying MSCs to produce specific cytokines or surface molecules, their migratory, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective properties are significantly improved, providing a potential avenue for more effective MS treatments (Rostami et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Moeinabadi-Bidgoli et al., 2023).
MSCs possess a secretome that comprises both a soluble and a vesicular fraction. The soluble fraction contains numerous neurotrophic growth factors, chemokines, and cytokines, including IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL-10), glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), VEGF, fibroblast growth factor (FGF), HGF, nerve growth factor (NGF), and insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 (IGF-1 and IGF-2). The vesicular fraction contains extracellular vesicles (EVs) of various sizes, including exosomes (Pinho et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2019; Mahjoor et al., 2023b). Through T-cell inhibition and macrophage regulation, studies have shown that the secretome of MSCs lowers inflammation. This leads to decreased pro-inflammatory cytokine production and better results in mouse MS models (Zappia et al., 2005; Shimojima et al., 2016). It has also been demonstrated that the MSC secretome promotes ODC development, which improves remyelination and improves the functional state of mice induced with EAE (Bai et al., 2012). According to recent studies, EVs play a crucial role in the therapeutic benefits of MSCs and their secretome (Kråkenes et al., 2024).
Recent studies have shown that exosomes originating from MSCs are significantly involved in the physiological activities of MSCs and may potentially yield more beneficial therapeutic outcomes compared to the original MSCs. Exosomes are a heterogeneous class of bilayer lipid membrane vesicles with a nano-sized diameter released by various cells consisting of adult MSCs. Initially, they are formed by endosomal membrane intraparticles to generate multivesicular bodies. Respecting molecular reports, exosomes produced by MSCs include a variety of molecular components, including lipids, proteins, RNA, and DNA profiles (Kråkenes et al., 2024; Kang et al., 2020; Zhou B. et al., 2020; Li, 2020; Ha et al., 2020; Liang et al., 2020; Shen et al., 2021; Gurung et al., 2021; Tan et al., 2024). MSCs-derived exosomes surrounded by a lipid membrane, as we discussed previously, keep their contents and permit them to migrate in tissues and targeted cells. They can participate in the pleiotropic functions of their parent cells, which include improving tissue regeneration. Currently, seven methods are available for effective exosome isolation, including differential centrifugation, ultrafiltration, flushing separation, mass spectrometry (MS), antibody affinity capture, precipitation, and microfluidic separation (Tang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2018; Gao et al., 2022). Ultracentrifugation is frequently used to isolate exosomes. This method is not appropriate for isolating uncontaminated exosomes. Besides, immunoaffinity chromatography is a valuable method for obtaining pure exosomes. However, it is possible to approach this procedure by loading a small sample (Maqsood et al., 2020; Guan et al., 2020). The Tetraspanin family, which includes several proteins including CD9, CD63, and CD81, and some heat-shock proteins like Hsp90, Hsp70, and Hsp60, is abundant in the membrane. They act as markers and remain on the surface of the exosome. Importantly, exosomes produced by MSCs from younger or older hosts displayed various miRNA expression patterns (Fang et al., 2019).
Exosome biosynthesis begins with endosomal maturation, which entails specific changes to the endosomal membrane (Cunha e Rocha et al., 2024). Throughout this phase, the invagination process generates intraluminal vesicles (ILVs), leading to the formation of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). These MVBs can be transported to the plasma membrane for exocytosis, releasing ILVs as exosomes into the extracellular environment, or they can be directed to lysosomes for degradation. The specific mechanisms that determine whether exosomes evade degradation remain unclear. The three primary steps in exosome biosynthesis are cargo sorting, MVB transport and fusion with the plasma membrane, and MVB production (Cunha e Rocha et al., 2024; Kalluri et al., 2020).
It has strongly been evidenced that MSCs-derived exosome shows several merits such as neuroprotective effects, inherent stem cell source features, and BBB-crossing potential. However, exosomes may be effective drug delivery systems for neurodegenerative disorders therapy. They hinder local and systemic inflammation and have excellent biocompatibility, minimal immunogenicity, and low toxicity (Hosseini Shamili et al., 2019; Kyurkchiev et al., 2014). Recently, Fathollahi et al. administered MSC-derived exosomes to EAE mice via the intranasal (IN) route. The results demonstrated a considerable decrease in clinical scores associated with increases in immunomodulatory reactions, such as an increase in the percentage of CD25+ Foxp3+ Tregs and TGF-β levels (Fathollahi et al., 2021). In another study, placenta-derived MSCs (PMSCs)-exosome improved motor function in treated EAE mice more efficiently than PMSCs therapy. PMSC-exosome also decreased the damage of DNA in oligodendroglia and enhanced myelination in the treated mice’s spinal cord by stimulating endogenous ODC progenitor cells to develop into mature myelinating ODCs. Thereby, PMSC-derived EVs provide a practical option for cellular-based treatments for MS, as shown in the mice model of the disease (Clark et al., 2019). Jafarinia and his coworkers also studied and compared the effects of hADSC and hADSC-exosome on EAE in mice. Based on the results, the myelin ODC glycoprotein-induced splenocyte proliferation and the highest mean clinical score in hADSC and hADSC-exosome-treated animals were considerably lower than in control mice. The inflammation level and demyelination rates were also decreased following the administration of both hADSC-exosome and parental hADSC (Jafarinia et al., 2020). A recent study also showed that BM-MSCs cross the BBB and target neural cells. They could significantly enhance the numbers of newly generated ODCs and the level of MBP; moreover, BM-MSCs-exosome decreased neuroinflammation by enhancing the macrophage M2/M1 ratio and suppressing inflammatory TLR2/IRAK1/NFκB pathway (Zhang et al., 2022; Son et al., 2006; Ullah et al., 2015).
As the primary immune cells in the central nervous system, microglia are essential to the pathophysiology of MS because they promote both neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Microglia in MS adopt a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype in response to CNS damage and inflammation, releasing cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (Liu et al., 2023; Zhang X. et al., 2023). MSC-derived exosomes contain therapeutic molecules that show promise in regulating microglial activation. Research has demonstrated that MSC exosomes can induce the polarization of microglia from the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to the anti-inflammatory M2 state. This transition is characterized by a decrease in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and an increase in the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as TGF-β and IL-10 (Liu W. et al., 2020). Furthermore, the phagocytic function of microglia is essential for removing myelin debris and apoptotic cells, which hinders remyelination. In MS, successful remyelination and neuronal survival rely on this process of elimination (Kråkenes et al., 2024). Specific miRNAs transported by MSC exosomes play a crucial role in regulating microglial polarization. Exosomes derived from hypoxic BM-MSCs have been shown to overexpress miR-216a-5p, which can reverse the release of inflammatory factors by microglia, including TNF-α, IL-6, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (Liu W. et al., 2020). Furthermore, research has demonstrated that miR-146a-5p and miR-125a reduce pro-inflammatory microglial activity following CNS damage. By inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/PI3K/AKT inflammatory cascade, MSC exosomes modify the inflammatory phenotype of microglia, shifting it towards an anti-inflammatory state (Liu W. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). Exosomes were administered intravenously as a single dose following spinal cord injury (SCI) in a mouse model to demonstrate this effect. Consequently, the mice that received exosomes exhibited significantly better performance compared to the control group (Liu W. et al., 2020).
In summary, MSC-derived exosomes represent a promising therapeutic avenue for MS and other neurodegenerative disorders. They offer multifaceted benefits through their immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and regenerative properties, thereby paving the way for innovative and targeted treatment strategies.
Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions are commonly managed with immunosuppressive medications, although their efficacy may vary among a diverse patient cohort. Consistent use of drugs may exacerbate adverse reactions, while prolonged suppression of the immune system heightens susceptibility to infections over time (Jung and Kim, 2022; Wigerblad and Kaplan, 2023). Recent studies have shown that MSCs are significantly involved in immune system regulation and tissue regeneration, suggesting their potential as a therapeutic approach for autoimmune conditions (Ding et al., 2015; Lv et al., 2014). Numerous recent clinical trials have been carried out using MSCs to manage MS. In the second phase of a randomized clinical trial, five patients with RRMS received MSC treatment for 6 months, leading to decreased brain MRI lesions (Llufriu et al., 2014b). Recently, Meng et al. (Meng et al., 2018) found that the systemic delivery of allogeneic UC-MSCs resulted in amelioration of the clinical manifestations in patients with MS. UC-MSCs therapy also reduced and Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) and the frequency of foci, as determined with MRI. The most frequently reported adverse outcomes included elevated body temperature, head pain, and lightheadedness of feelings. The intervention also decreased levels of IL-2, CD86, HLADRB1, and CTLA-4 in peripheral blood (Meng et al., 2018). Other open-label prospective clinical trials (phase I/IIa) also revealed the clinical potentials of BM-MSCs in MS patients. Treatment reduced EDSS without altering lesion volume. Early-stage lesion reduction correlated with increased VEGF, IL-6, and IL-8 levels (Dahbour et al., 2017). Another study on 24 patients with active-progressive MS exhibited that the reduction in EDSS has an intimate association with increased FoxP3+CD4+CD25+ cells and decreased lymphocyte proliferation (Petrou et al., 2021a). Additional double-masked phase II clinical trials that were randomized and evaluated the effects of intrathecal (IT) or IV transplantation of MSC yielded comparable findings. The levels of NF-L CSF were notably reduced 6 months following the administration of MSC-IT treatment. Nine out of fifteen patients in the MSC-IT group experienced a reduction of more than 50% in their NF-L levels, as opposed to 33% in the MSC-IV group and 6.6% in the control group (Petrou et al., 2022). Llufriu et al. (2014b) found a non-significant decrease in the occurrence of Th1 (CD4+ IFN-γ+) cells in the bloodstream of patients who received autologous BMMSCs therapy. Of course, individuals who received MSC treatment demonstrated a reduced average total count of gadolinium-enhancing lesions (GEL). Finally, a shift from Th1 to Th2 immunity in hUCMSC-treated MS has been supported, according to reports (Li et al., 2014). On the other hand, Fernández et al. (2018) discovered that the IV administration of AT-MSCs did not lead to a statistically significant improvement in clinical outcome measures. These metrics encompassed the frequency of relapses, the EDSS score, the non-normalized cerebral volume on MRI scans, or the number of active lesions observed in gadolinium-enhanced T1 scans (Fernández et al., 2018). Yamout et al. (2010) administered autologous BM-derived MSCs via injection to nine with SPMS and one patient with RRMS. They documented improved clinical results in their patients following 3 months to 1 year. In this phase 2a clinical study, 10 individuals diagnosed with SPMS were administered MSCs intravascularly over 6 months. Following this intervention, the investigators examined to assess the impact of MSCs on the processes of remyelination and neuroprotection (Yamout et al., 2010). In a clinical study involving 15 patients with RRMS who had not responded to traditional disease-modifying therapies (DMTs), MSCs demonstrated systemic benefits for the immune system. The percentage of activated myeloid DCs and lymphocytes decreased while the number of regulatory T cells increased. Notably, these MSC-induced effects persisted in vitro, as immune cells from treated individuals demonstrated a reduction in lymphocyte proliferation. The effectiveness of MSC treatment was clinically supported by a reduction in the mean EDSS scores and the absence of new MRI lesions at the six-month follow-up (Karussis et al., 2010). Furthermore, in their 2007 study, M. Bonab and colleagues (MOHY et al., 2007) investigated the progression of the disease following the IT administration of MSC to 10 MS patients. Consequently, it has been observed that the advancement of the disease has progressively decelerated in 50% of the subjects being investigated (MOHY et al., 2007). Table 2 summarizes studies on the clinical application of stem cell therapy for MS and related adverse effects, along with observed results in patients.
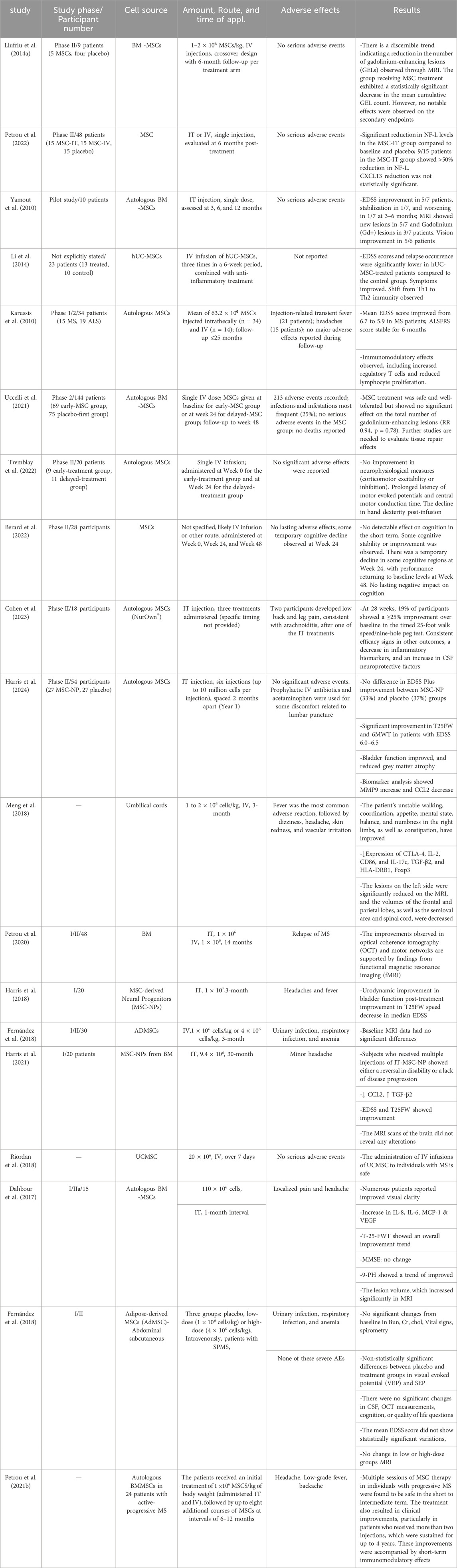
Table 2. Therapeutic applications of MSCs and their utilization in clinical trials for the treatment of MS.
There are presently specific disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) available to stop the accumulation of structural brain damage associated with MS and its adverse effects on MS patients (Filippi et al., 2022; Wiendl et al., 2021). The advent of more effective DMTs during the past several years has significantly changed the landscape of MS treatment (Comi et al., 2017; Giovannoni et al., 2020; Goldschmidt and McGinley, 2021). Currently, available DMTs are categorized based on their efficacy into two primary classifications: high-efficacy (HE) DMTs and moderate-efficacy (ME) DMTs. The HE DMTs include natalizumab, fingolimod, ozanimod, siponimod, alemtuzumab, cladribine, ocrelizumab, and ofatumumab. In contrast, the ME DMTs comprise glatiramer acetate, interferon-beta (IFN-β), teriflunomide, and dimethyl fumarate (Comi et al., 2017; Giovannoni et al., 2020; Simpson-Yap et al., 2021). Additionally, high-dose methylprednisolone is frequently used to manage acute relapses by suppressing inflammation (Sormani et al., 2021; Travers et al., 2022). Subcutaneous IFN-β1b, the first MS DMT ever created, was authorized by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 to treat progressive relapsing MS (PRMS) (Bayas and Gold, 2003).
DMTs have demonstrated effectiveness in managing MS; however, they are associated with several limitations. These limitations include heterogeneous responses among patients, the potential for long-term toxicity, and an incomplete capacity to halt disease progression, particularly in the later stages of the condition (Langer-Gould et al., 2023). In contrast, cell-based therapies, particularly those utilizing MSCs, have garnered attention due to their anti-apoptotic properties, paracrine signaling capabilities, and multidirectional differentiation potential. These characteristics have prompted their investigation in translational research and clinical trials aimed at addressing prevalent diseases, including neurological disorders that affect CNS structures, such as stroke, Huntington’s disease (HD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), MS, and SCI (Andrzejewska et al., 2021).
• Synergistic effects: DMTs reduce systemic inflammation and immune activation, potentially creating an environment that fosters MSC-mediated repair and neuroprotection. For example, the immunomodulatory effects of IFN-β or natalizumab may enhance the anti-inflammatory cytokines secreted by MSCs (Dadfar et al., 2024; Gharibi et al., 2015; Emamnejad et al., 2019).
• Broad therapeutic coverage: While DMTs primarily target immune dysregulation, MSCs directly address neurodegeneration and promote remyelination, thereby tackling different aspects of the disease’s pathophysiology (Orrù et al., 2024; Karussis et al., 2008).
• Enhanced Efficacy: Combining cell therapy and DMTs may reduce relapse rates more effectively than either treatment alone. More importantly, this combination may also accelerate recovery from damage (Peterson et al., 2022).
The development of novel DMTs has advanced significantly in recent years, particularly over the past decade. However, much work remains to be done before a broader range of alternatives becomes available to MS patients with varying clinical presentations. Only a few treatments have been thoroughly researched for more severe and active forms of MS, such as SPMS and PPMS. Consequently, many patients continue to experience substantial disease progression despite current DMT therapies. Additionally, there is a considerable risk of adverse effects associated with existing DMTs, including infusion reactions, infections, liver toxicity, and cardiovascular complications (McGinley et al., 2021). These medications, particularly natalizumab and fingolimod, have the potential to cause progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), a disease associated with a high fatality rate (Sriwastava et al., 2021). In addition, many DMTs are incredibly costly. The lifetime direct medical expenses for a patient with MS are estimated to be $4.8 million, making it the second most expensive chronic medical condition after heart failure. Furthermore, DMTs remain the single most significant contributor to these costs. In 2020, the median annual cost of available DMTs was $91,835, with several therapies exceeding this amount. Therefore, to reduce costs, it is crucial to keep looking at less expensive options for efficacy potential and to keep diversifying therapies (Hartung, 2021).
Understanding how DMTs influence the homing, engraftment, and therapeutic efficacy of MSCs remains an area of ongoing research. For instance, fingolimod alters lymphocyte trafficking, which might interact with MSC migration dynamics (Kassis et al., 2021; Wiendl et al., 2021; Yazdi et al., 2018). Clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of such combinations will be critical for developing protocols that maximize patient outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
An essential component of MSC therapy involves monitoring the therapeutic outcomes and identifying potential complications through follow-up and evolutionary biomarkers. These biomarkers provide crucial insights into the dynamics of MSC behavior, their interaction with the host environment, and the overall therapeutic efficacy (Ghareghani et al., 2024; Iacobaeus et al., 2019; Granchi et al., 2019). MSCs exert immunomodulatory effects, which can be tracked using biomarkers such as IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, IL-16, and TGF-β, and reductions in pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α. The normalization of these markers indicates the anti-inflammatory efficacy of MSCs, particularly in diseases like MS, where inflammation is a hallmark (Petrou et al., 2022; Li et al., 2014). Neurofilament proteins (NF), which are released into the CSF following axonal injury in the central nervous system, serve as reliable indicators of axonal damage and neuronal death. Among these, the neurofilament light chains (NF-L) are the most extensively studied subtype (Cairns et al., 2004). Since NF are essential parts of the neuron’s cytoskeleton, any neurological condition that damages neurons or axons may result in elevated CSF levels of these proteins. The CSF of patients with MS consistently contains elevated levels of NF-L, indicating that NF-L may function as a biomarker for MS disease activity, including subclinical activity, as well as for the responsiveness to various MS therapies. Additionally, studies have demonstrated that increased blood levels of NF-L in the early stages of MS may predict future increases in MS lesions and brain atrophy (Williams et al., 2021; Chitnis et al., 2018; Novakova et al., 2017; Håkansson et al., 2017). The most potent B-cell chemoattractant, the CXCR5 ligand CXCL13, is present in both active lesions of MS and the CSF of MS patients. Elevated levels of CXCL13 have been shown to predict the progression from clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) to MS. Furthermore, research indicates that CXCL13 is associated with disease exacerbations and a poorer prognosis in MS (Khademi et al., 2011). MSC-mediated healing processes can be identified by tissue regeneration markers such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), VEGF, and fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Particularly in the context of MS, these indicators are valuable for assessing the recovery of vascular and neuronal structures in the central nervous system (Gavasso et al., 2024; Hofer and Tuan, 2016; Farooq et al., 2021).
Biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and systemic metabolic markers, such as changes in glucose and lipid profiles, provide insights into broader systemic responses to MSC administration (Yang et al., 2018; Weiss et al., 2021).
A class of micromolecules with potential as biomarkers for MS is microRNAs, which are small non-coding RNAs that regulate post-transcriptional gene expression (Raphael et al., 2015).
Research on specific metabolic pathways associated with the pathophysiology of MS provides an additional approach to identifying biomarkers. For example, studies have shown that the kynurenine pathway, the primary mechanism for tryptophan degradation, regulates immune activity. Evidence suggests that during relapses, the CSF of MS patients exhibits elevated levels of the neuroprotective metabolite kynurenine acid (Lim et al., 2010).
By integrating these biomarkers into the clinical evaluation framework, it becomes possible to optimize the therapeutic potential of MSCs while minimizing adverse effects.
In recent years, there has been a significant focus on stem cell therapy. MSC therapy in translational medicine has considerable expectations. However, various aspects of MSC treatment need to be well-defined. Given the variety of methods explored, the full extent of the potential impacts of MSC therapy remains uncertain (Lukomska et al., 2019). Moreover, due to their possible application in autologous transplantation, MSCs have gained significant clinical interest. Numerous clinical trials involving MSCs have been conducted, with many more currently under investigation. As the clinical use of MSCs continues to expand, particularly in the context of both autologous and allogeneic transplantation, long-term monitoring of patients is essential to assess the safety and efficacy of MSC therapy. According to recent studies, thousands of patients have received culture-expanded allogeneic or autologous MSCs to treat various diseases (Squillaro et al., 2016; Shandil et al., 2022). MSC treatment has proven highly effective in most cases; however, long-term monitoring remains crucial to assess the potential hazards associated with MSC transplantation. Numerous in vitro and in vivo investigations provided evidence for MSC differentiation into specific cell types (Nowakowski et al., 2016). While most in vivo studies have confirmed the safety of MSC therapy and demonstrated promising results, the therapeutic benefits of MSC-based treatments remain limited. Furthermore, there are potential risks associated with using MSCs in specific cellular niches that should be carefully evaluated in long-term follow-up studies (Lukomska et al., 2019).
Although MSC therapy holds significance in treating MS and other diseases, it is essential to acknowledge the potential adverse effects associated with its administration. One of the most notable challenges is the method of administration. The route of administration significantly influences the therapeutic outcome, and it has been shown that different routes can lead to varying levels of efficacy and safety (Mansoor et al., 2019; Lukomska et al., 2019). The approach to administering MSCs is greatly determined by the specific therapeutic objectives. For instance, IV administration, one of the most common routes, has been associated with limited success in MS models. Studies indicate that MSCs administered IV are often trapped in the lungs and liver, and their presence in the inflammatory lesions of the CNS is minimal. This inefficiency in homing to the target tissue is primarily due to the BBB, which prevents the passage of MSCs into the brain, thus limiting their therapeutic effects in MS patients (Abramowski et al., 2016; Cerri et al., 2015). Moreover, MSCs derived from BM have shown poor therapeutic efficacy when administered systemically. They fail to reach the damaged neurons, and in some cases, they are cleared from the system within a month post-administration (Neirinckx et al., 2021). The use of local administration techniques is restricted due to the associated risks of direct tissue injection or intraventricular infusion aimed at enhancing MSC homing. While local injections have the potential to deliver drugs precisely where they are needed, they also carry the risk of varying degrees of local inflammation, infection, or tissue damage at the injection site. The dosage and frequency of MSC therapy directly influence both safety and effectiveness. Excessive administration of MSCs may lead to abnormal tissue growth due to overuse, immune reactions or tumor formation resulting from improper dosing. It is crucial to understand how the doses are spatiotemporally related and to determine the optimal total number of doses to minimize cumulative adverse effects over time (Caplan et al., 2019; Galipeau and Sensébé, 2018; Kabat et al., 2020; Afkhami et al., 2024). Regarding broader systemic effects, adverse reactions can vary from transient symptoms, such as nausea, fever, and headache, to more serious complications. Several studies have documented these adverse effects, including the occurrence of transient symptoms like vomiting, nausea, and impaired visual acuity in 4.3% of individuals receiving MSC infusion for steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (Table 3) (Dotoli et al., 2017). These side effects underscore the importance of monitoring patients during and after MSC treatment, especially when high doses or repeated infusions are involved.
Lastly, the quality of the MSC product and its source play an essential role in determining safety outcomes. The donor’s age appears to be the most critical parameter to consider. MSCs derived from older donors or patients with comorbidities may exhibit compromised functionality, affecting their therapeutic potential and increasing the risk of adverse reactions. This challenge is especially relevant in autologous transplantation, where geriatric patients may struggle to obtain a sufficient number of viable MSCs for treatment (Dufrane, 2017; Liu et al., 2017; Kokai et al., 2017; Pachón-Peña et al., 2016).
In summary, while MSCs present a novel and promising approach to treating MS, it is crucial to recognize the potential adverse effects and complications that may arise from their application.
MSC therapy has demonstrated significant potential as an innovative approach for managing MS, addressing both the immunological and neurodegenerative aspects of the disease. MSCs exhibit robust immunomodulatory properties, promote remyelination, and support neuroregeneration, making them a promising candidate for comprehensive MS therapy. Preclinical and clinical studies have shown encouraging results, particularly in reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression. However, limitations such as optimal dosing, delivery methods, and long-term safety concerns remain critical challenges. Despite these challenges, MSC therapy represents a transformative step forward in personalized medicine for MS, offering hope for improved quality of life for patients. Future research should address the remaining challenges associated with MSC therapy, such as optimizing delivery routes and dosing regimens to enhance therapeutic efficacy and reduce potential adverse effects.
KS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing–original draft. SG: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing–original draft. HF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing–review and editing. SR: Writing–review and editing, Investigation, Conceptualization. ES: Writing–review and editing, Investigation, Conceptualization. HA: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AY: Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdallah, A. N., Shamaa, A. A., and El-Tookhy, O. S. (2019). Evaluation of treatment of experimentally induced canine model of multiple sclerosis using laser activated non-expanded adipose derived stem cells. Res. veterinary Sci. 125, 71–81. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.05.016
Abramowski, P., Krasemann, S., Ernst, T., Lange, C., Ittrich, H., Schweizer, M., et al. (2016). Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells do not ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and are not detectable in the central nervous system of transplanted mice. Stem Cells Dev. 25 (15), 1134–1148. doi:10.1089/scd.2016.0020
Afkhami, H., Mahmoudvand, G., Fakouri, A., Shadab, A., Mahjoor, M., and Komeili Movahhed, T. (2023). New insights in application of mesenchymal stem cells therapy in tumor microenvironment: pros and cons. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1255697. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1255697
Afkhami, H., Yarahmadi, A., Bostani, S., Yarian, N., Haddad, M. S., Lesani, S. S., et al. (2024). Converging frontiers in cancer treatment: the role of nanomaterials, mesenchymal stem cells, and microbial agents—challenges and limitations. Discov. Oncol. 15 (1), 818. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01590-0
Aggarwal, S., and Pittenger, M. F. (2005). Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood 105 (4), 1815–1822. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-04-1559
Alanazi, A., Alassiri, M., Jawdat, D., and Almalik, Y. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell therapy: a review of clinical trials for multiple sclerosis. Regen. Ther. 21, 201–209. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2022.07.003
Aliniay-Sharafshadehi, S., Yousefi, M. H., Ghodratie, M., Kashfi, M., Afkhami, H., and Ghoreyshiamiri, S. M. (2024). Exploring the therapeutic potential of different sources of mesenchymal stem cells: a novel approach to combat burn wound infections. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1495011. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2024.1495011
Amin, M., and Hersh, C. M. J. N. d.m. (2023). Updates and advances in multiple sclerosis neurotherapeutics. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 13 (1), 47–70. doi:10.2217/nmt-2021-0058
Ananthavarathan, P., Sahi, N., and Chard, D. T. (2024). An update on the role of magnetic resonance imaging in predicting and monitoring multiple sclerosis progression. Expert Rev. Neurother. 24 (2), 201–216. doi:10.1080/14737175.2024.2304116
Andalib, E., Kashfi, M., Mahmoudvand, G., Rezaei, E., Mahjoor, M., Torki, A., et al. (2023). Application of hypoxia-mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of anaerobic bacterial wound infection: wound healing and infection recovery. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1251956. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1251956
Andrzejewska, A., Dabrowska, S., Lukomska, B., and Janowski, M. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells for neurological disorders. Adv. Sci. 8 (7), 2002944. doi:10.1002/advs.202002944
Andrzejewska, A., Lukomska, B., and Janowski, M. (2019). Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: from roots to boost. Stem cells 37 (7), 855–864. doi:10.1002/stem.3016
Ankrum, J. A., Ong, J. F., and Karp, J. M. (2014). Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 32 (3), 252–260. doi:10.1038/nbt.2816
ArefNezhad, R., and Motedayyen, H. (2023). Therapeutic features of mesenchymal stem cells and human amniotic epithelial cells in multiple sclerosis.
Ascherio, A. (2013). Environmental factors in multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 13 (Suppl. 2), 3–9. doi:10.1586/14737175.2013.865866
Bai, L., Lennon, D. P., Caplan, A. I., DeChant, A., Hecker, J., Kranso, J., et al. (2012). Hepatocyte growth factor mediates mesenchymal stem cell–induced recovery in multiple sclerosis models. Nat. Neurosci. 15 (6), 862–870. doi:10.1038/nn.3109
Barati, S., Kashani, I. R., Tahmasebi, F., Mehrabi, S., and Joghataei, M. T. (2019). Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on glial cells population in cuprizone induced demyelination model. Neuropeptides 75, 75–84. doi:10.1016/j.npep.2019.04.001
Barhum, Y., Gai-Castro, S., Bahat-Stromza, M., Barzilay, R., Melamed, E., and Offen, D. (2010). Intracerebroventricular transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells induced to secrete neurotrophic factors attenuates clinical symptoms in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 41 (1), 129–137. doi:10.1007/s12031-009-9302-8
Barkat, M. A. (2020). The potential therapeutic effect of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on cuprizone model of multiple sclerosis in the mice. Egypt. J. Histology 43 (1), 122–143. doi:10.21608/ejh.2019.13731.1129
Bayas, A., and Gold, R. (2003). Lessons from 10 years of interferon beta-1b (Betaferon/Betaseron) treatment. J. Neurol. 250, iv3–iv8. doi:10.1007/s00415-003-1402-8
Bazinet, A., and Popradi, G. (2019). A general practitioner’s guide to hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Curr. Oncol. 26 (3), 187–191. doi:10.3747/co.26.5033
Bejargafshe, M. J., Hedayati, M., Zahabiasli, S., Tahmasbpour, E., Rahmanzadeh, S., and Nejad-Moghaddam, A. (2019). Safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for treatment of neural damage in patients with multiple sclerosis. Stem Cell Investig. 6, 44. doi:10.21037/sci.2019.10.06
Ben-Nun, A., and Lando, Z. (1983). Detection of autoimmune cells proliferating to myelin basic protein and selection of T cell lines that mediate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J. Immunol. 130 (3), 1205–1209. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.130.3.1205
Ben-Nun, A., Wekerle, H., and Cohen, I. R. (1981). The rapid isolation of clonable antigen-specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 11 (3), 195–199. doi:10.1002/eji.1830110307
Berard, J. A., Freedman, M. S., Marrie, R. A., Marriott, J. J., Atkins, H. L., Szwajcer, D., et al. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell therapy and cognition in MS: preliminary findings from a phase II clinical trial. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 61, 103779. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2022.103779
Bjornevik, K., Cortese, M., Healy, B. C., Kuhle, J., Mina, M. J., Leng, Y., et al. (2022). Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 375 (6578), 296–301. doi:10.1126/science.abj8222
Bradl, M., and Lassmann, H. (2010). Oligodendrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta neuropathol. 119, 37–53. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0601-5
Brown, C., McKee, C., Bakshi, S., Walker, K., Hakman, E., Halassy, S., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells: cell therapy and regeneration potential. J. tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 13 (9), 1738–1755. doi:10.1002/term.2914
Brown, C., McKee, C., Halassy, S., Kojan, S., Feinstein, D. L., and Chaudhry, G. R. (2021). Neural stem cells derived from primitive mesenchymal stem cells reversed disease symptoms and promoted neurogenesis in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12 (1), 499. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02563-8
Cairns, N. J., Lee, V. M. Y., and Trojanowski, J. Q. (2004). The cytoskeleton in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Pathol. 204 (4), 438–449. doi:10.1002/path.1650
Caplan, A. I. (1991). Mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Res. 9 (5), 641–650. doi:10.1002/jor.1100090504
Caplan, A. I., and Correa, D. (2011). The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell stem cell 9 (1), 11–15. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.008
Caplan, H., Olson, S. D., Kumar, A., George, M., Prabhakara, K. S., Wenzel, P., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell therapeutic delivery: translational challenges to clinical application. Front. Immunol. 10, 1645. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01645
Casado-Díaz, A., Quesada-Gómez, J. M., and Dorado, G. (2020). Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in regenerative medicine: applications in skin wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 146. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.00146
Ceccariglia, S., Cargnoni, A., Silini, A. R., and Parolini, O. (2020). Autophagy: a potential key contributor to the therapeutic action of mesenchymal stem cells. Autophagy 16 (1), 28–37. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1630223
Cerri, S., Greco, R., Levandis, G., Ghezzi, C., Mangione, A. S., Fuzzati-Armentero, M. T., et al. (2015). Intracarotid infusion of mesenchymal stem cells in an animal model of Parkinson's disease, focusing on cell distribution and neuroprotective and behavioral effects. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 4 (9), 1073–1085. doi:10.5966/sctm.2015-0023
Cesarz, Z., and Tamama, K. (2016). Spheroid culture of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells Int. 2016, 9176357. doi:10.1155/2016/9176357
Charabati, M., Wheeler, M. A., Weiner, H. L., and Quintana, F. J. (2023). Multiple sclerosis: neuroimmune crosstalk and therapeutic targeting. Cell 186 (7), 1309–1327. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.008
Chen, G., Yue, A., Ruan, Z., Yin, Y., Wang, R., Ren, Y., et al. (2014). Monitoring the biology stability of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells during long-term culture in serum-free medium. Cell tissue Bank. 15 (4), 513–521. doi:10.1007/s10561-014-9420-6
Chitnis, T., Gonzalez, C., Healy, B. C., Saxena, S., Rosso, M., Barro, C., et al. (2018). Neurofilament light chain serum levels correlate with 10-year MRI outcomes in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 5 (12), 1478–1491. doi:10.1002/acn3.638
Chmielewska, N., and Szyndler, J. (2023). Targeting CD20 in multiple sclerosis—review of current treatment strategies. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 57 (3), 235–242. doi:10.5603/PJNNS.a2023.0022
Cho, J., Kim, T. H., Seok, J., Jun, J. H., Park, H., Kweon, M., et al. (2021). Vascular remodeling by placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells restores ovarian function in ovariectomized rat model via the VEGF pathway. Lab. Investig. 101 (3), 304–317. doi:10.1038/s41374-020-00513-1
Clark, K., Zhang, S., Barthe, S., Kumar, P., Pivetti, C., Kreutzberg, N., et al. (2019). Placental mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote myelin regeneration in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Cells 8 (12), 1497. doi:10.3390/cells8121497
Cobo, M., Anderson, P., Benabdellah, K., Toscano, M. G., Muñoz, P., García-Pérez, A., et al. (2013). Mesenchymal stem cells expressing vasoactive intestinal peptide ameliorate symptoms in a model of chronic multiple sclerosis. Cell Transpl. 22 (5), 839–854. doi:10.3727/096368912X657404
Cohen, J. A., Imrey, P. B., Planchon, S. M., Bermel, R. A., Fisher, E., Fox, R. J., et al. (2018). Pilot trial of intravenous autologous culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 24 (4), 501–511. doi:10.1177/1352458517703802
Cohen, J. A., Lublin, F. D., Lock, C., Pelletier, D., Chitnis, T., Mehra, M., et al. (2023). Evaluation of neurotrophic factor secreting mesenchymal stem cells in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 29 (1), 92–106. doi:10.1177/13524585221122156
Colasanti, A., Guo, Q., Muhlert, N., Giannetti, P., Onega, M., Newbould, R. D., et al. (2014). In vivo assessment of brain white matter inflammation in multiple sclerosis with 18F-PBR111 PET. J. Nucl. Med. 55 (7), 1112–1118. doi:10.2967/jnumed.113.135129
Comi, G., Radaelli, M., and Sørensen, P. (2017). Evolving concepts in the treatment of relapsing multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 389 (10076), 1347–1356. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32388-1
Connick, P., Kolappan, M., Crawley, C., Webber, D. J., Patani, R., Michell, A. W., et al. (2012). Autologous mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: an open-label phase 2a proof-of-concept study. Lancet. Neurol. 11 (2), 150–156. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70305-2
Cunha e Rocha, K., Ying, W., and Olefsky, J. M. (2024). Exosome-mediated impact on systemic metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 86 (1), 225–253. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-042222-024535
Dabrowska, S., Andrzejewska, A., Janowski, M., and Lukomska, B. (2021). Immunomodulatory and regenerative effects of mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles: therapeutic outlook for inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Front. Immunol. 11, 591065. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.591065
Dadfar, S., Yazdanpanah, E., Pazoki, A., Nemati, M. H., Eslami, M., Haghmorad, D., et al. (2024). The role of mesenchymal stem cells in modulating adaptive immune responses in multiple sclerosis. Cells 13 (18), 1556. doi:10.3390/cells13181556
Dahbour, S., Jamali, F., Alhattab, D., Al-Radaideh, A., Ababneh, O., Al-Ryalat, N., et al. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cells and conditioned media in the treatment of multiple sclerosis patients: clinical, ophthalmological and radiological assessments of safety and efficacy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 23 (11), 866–874. doi:10.1111/cns.12759
Dai, R., Wang, Z., Samanipour, R., Koo, K. I., and Kim, K. (2016). Adipose-derived stem cells for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Stem cells Int. 2016, 6737345. doi:10.1155/2016/6737345
Damasceno, P. K. F., de Santana, T. A., Santos, G. C., Orge, I. D., Silva, D. N., Albuquerque, J. F., et al. (2020). Genetic engineering as a strategy to improve the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 737. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.00737
Darlington, P. J., Boivin, M.-N., and Bar-Or, A. (2011). Harnessing the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 11 (9), 1295–1303. doi:10.1586/ern.11.113
de Sèze, J., Maillart, E., Gueguen, A., Laplaud, D. A., Michel, L., Thouvenot, E., et al. (2023). Anti-CD20 therapies in multiple sclerosis: from pathology to the clinic. Front. Immunol. 14, 1004795. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1004795
de Witte, S. F., Luk, F., Sierra Parraga, J. M., Gargesha, M., Merino, A., Korevaar, S. S., et al. (2018). Immunomodulation by therapeutic mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) is triggered through phagocytosis of MSC by monocytic cells. stem cells 36 (4), 602–615. doi:10.1002/stem.2779
Ding, D.-C., Chang, Y. H., Shyu, W. C., and Lin, S. Z. (2015). Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 24 (3), 339–347. doi:10.3727/096368915X686841
Ding, Y., Yang, H., Feng, J. B., Qiu, Y., Li, D. S., and Zeng, Y. (2013). Human umbilical cord-derived MSC culture: the replacement of animal sera with human cord blood plasma. Vitro Cell. and Dev. Biology-Animal 49, 771–777. doi:10.1007/s11626-013-9663-8
Dominici, M., Le Blanc, K., Mueller, I., Slaper-Cortenbach, I., Marini, F., Krause, D., et al. (2006). Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8 (4), 315–317. doi:10.1080/14653240600855905
Dong, H., Li, G., Shang, C., Yin, H., Luo, Y., Meng, H., et al. (2018). Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) transplantations for cerebral palsy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 10 (3), 901–906.
Dong, Y., D'Mello, C., Pinsky, W., Lozinski, B. M., Kaushik, D. K., Ghorbani, S., et al. (2021). Oxidized phosphatidylcholines found in multiple sclerosis lesions mediate neurodegeneration and are neutralized by microglia. Nat. Neurosci. 24 (4), 489–503. doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00801-z
Dorronsoro, A., Lang, V., Ferrin, I., Fernández-Rueda, J., Zabaleta, L., Pérez-Ruiz, E., et al. (2020). Intracellular role of IL-6 in mesenchymal stromal cell immunosuppression and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 21853. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78864-4
Dotoli, G., De Santis, G. C., Orellana, M. D., de Lima Prata, K., Caruso, S. R., Fernandes, T. R., et al. (2017). Mesenchymal stromal cell infusion to treat steroid-refractory acute GvHD III/IV after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone marrow Transplant. 52 (6), 859–862. doi:10.1038/bmt.2017.35
Dufrane, D. (2017). Impact of age on human adipose stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Cell Transpl. 26 (9), 1496–1504. doi:10.1177/0963689717721203
Emamnejad, R., Sahraian, M., Shakiba, Y., Salehi, Z., Masoomi, A., Imani, D., et al. (2019). Circulating mesenchymal stem cells, stromal derived factor (SDF)-1 and IP-10 levels increased in clinically active multiple sclerosis patients but not in clinically stable patients treated with beta interferon. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 35, 233–238. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2019.08.013
English, K., Ryan, J. M., Tobin, L., Murphy, M. J., Barry, F. P., and Mahon, B. P. (2009). Cell contact, prostaglandin E2 and transforming growth factor beta 1 play non-redundant roles in human mesenchymal stem cell induction of CD4+ CD25Highforkhead box P3+ regulatory T cells. Clin. and Exp. Immunol. 156 (1), 149–160. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03874.x
Erwin, G. S., Crisostomo, P. R., Wang, Y., Wang, M., Markel, T. A., Guzman, M., et al. (2009). Estradiol-treated mesenchymal stem cells improve myocardial recovery after ischemia. J. Surg. Res. 152 (2), 319–324. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2008.02.006
Fakouri, A., Razavi, Z. S., Mohammed, A. T., Hussein, A. H. A., Afkhami, H., and Hooshiar, M. H. (2024). Applications of mesenchymal stem cell-exosome components in wound infection healing: new insights. Burns and Trauma 12, tkae021. doi:10.1093/burnst/tkae021
Fang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhou, J., and Cao, K. (2019). Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a novel pathway for tissues repair. Cell Tissue Bank. 20 (2), 153–161. doi:10.1007/s10561-019-09761-y
Farokhi, S., Razavi, Z. S., Mavaei, M., Shadab, A., Afkhami, H., and Sardarabadi, H. (2024). New perspectives on arteriosclerosis treatment using nanoparticles and mesenchymal stem cells. Discov. Appl. Sci. 6 (8), 411–440. doi:10.1007/s42452-024-06113-8
Farooq, M., Khan, A. W., Kim, M. S., and Choi, S. (2021). The role of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling in tissue repair and regeneration. Cells 10 (11), 3242. doi:10.3390/cells10113242
Fathollahi, A., Hashemi, S. M., Haji Molla Hoseini, M., Tavakoli, S., Farahani, E., and Yeganeh, F. (2021). Intranasal administration of small extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorated the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 90, 107207. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107207
Fernández, O., Izquierdo, G., Fernández, V., Leyva, L., Reyes, V., Guerrero, M., et al. (2018). Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AdMSC) for the treatment of secondary-progressive multiple sclerosis: a triple blinded, placebo controlled, randomized phase I/II safety and feasibility study. PLoS One 13 (5), e0195891. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0195891
Fernández-Santos, M. E., Garcia-Arranz, M., Andreu, E. J., García-Hernández, A. M., López-Parra, M., Villarón, E., et al. (2022). Optimization of mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) manufacturing processes for a better therapeutic outcome. Front. Immunol. 13, 918565. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.918565
Filippi, M., Amato, M. P., Centonze, D., Gallo, P., Gasperini, C., Inglese, M., et al. (2022). Early use of high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies makes the difference in people with multiple sclerosis: an expert opinion. J. Neurol. 269 (10), 5382–5394. doi:10.1007/s00415-022-11193-w
Franklin, R. J., and Ffrench-Constant, C. (2017). Regenerating CNS myelin—from mechanisms to experimental medicines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18 (12), 753–769. doi:10.1038/nrn.2017.136
Freedman, M. S., Bar-Or, A., Atkins, H. L., Karussis, D., Frassoni, F., Lazarus, H., et al. (2010). The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation as a treatment for multiple sclerosis: consensus report of the International MSCT Study Group. Multiple Scler. J. 16 (4), 503–510. doi:10.1177/1352458509359727
Friedenstein, A., Piatetzky-Shapiro, I., and Petrakova, K. (1966). Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. Development 16 (3), 381–390. doi:10.1242/dev.16.3.381
Galipeau, J., and Sensébé, L. J. C. s.c. (2018). Mesenchymal stromal cells: clinical challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 22 (6), 824–833. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.004
Gao, M., Cai, J., Zitkovsky, H. S., Chen, B., and Guo, L. (2022). Comparison of yield, purity, and functional properties of large-volume exosome isolation using ultrafiltration and polymer-based precipitation. Plastic Reconstr. Surg. 149 (3), 638–649. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000008830
Gavasso, S., Kråkenes, T., Olsen, H., Evjenth, E. C., Ytterdal, M., Haugsøen, J. B., et al. (2024). The therapeutic mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells in MS—a review focusing on neuroprotective properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (3), 1365. doi:10.3390/ijms25031365
Ghareghani, M., Arneaud, A., and Rivest, S. (2024). The evolution of mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitor therapy for Multiple Sclerosis: from concept to clinic. Front. Cell Neurosci. 18, 1428652. doi:10.3389/fncel.2024.1428652
Gharibi, T., Ahmadi, M., Seyfizadeh, N., Jadidi-Niaragh, F., and Yousefi, M. (2015). Immunomodulatory characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells and their role in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Cell. Immunol. 293 (2), 113–121. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.01.002
Giovannoni, G., Lang, S., Wolff, R., Duffy, S., Hyde, R., Kinter, E., et al. (2020). A systematic review and mixed treatment comparison of pharmaceutical interventions for multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Ther. 9, 359–374. doi:10.1007/s40120-020-00212-5
Glenn, J. D., and Whartenby, K. A. J. W. j.o.s.c. (2014). Mesenchymal stem cells: emerging mechanisms of immunomodulation and therapy. World J. Stem Cells 6 (5), 526–539. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
Goldschmidt, C., and McGinley, M. P. J. (2021). Advances in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Clin. 39 (1), 21–33. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2020.09.002
González, L. M., Ospina, L. N., Sperling, L. E., Chaparro, O., and Cucarián, J. D. (2022). Therapeutic effects of physical exercise and the mesenchymal stem cell secretome by modulating neuroinflammatory response in multiple sclerosis. Curr. Stem Cell Res. and Ther. 17 (7), 621–632. doi:10.2174/1574888X16666211209155333
Gramlich, O. W., Brown, A. J., Godwin, C. R., Chimenti, M. S., Boland, L. K., Ankrum, J. A., et al. (2020). Systemic mesenchymal stem cell treatment mitigates structural and functional retinal ganglion cell degeneration in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 9 (8), 16. doi:10.1167/tvst.9.8.16
Granchi, D., Ciapetti, G., Gómez-Barrena, E., Rojewski, M., Rosset, P., Layrolle, P., et al. (2019). Biomarkers of bone healing induced by a regenerative approach based on expanded bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy 21 (8), 870–885. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.06.002
Gu, Y., He, M., Zhou, X., Liu, J., Hou, N., Bin, T., et al. (2016). Endogenous IL-6 of mesenchymal stem cell improves behavioral outcome of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage neonatal rats by supressing apoptosis in astrocyte. Sci. Rep. 6 (1), 18587. doi:10.1038/srep18587
Guan, S., Yu, H., Yan, G., Gao, M., Sun, W., and Zhang, X. (2020). Characterization of urinary exosomes purified with size exclusion chromatography and ultracentrifugation. J. proteome Res. 19 (6), 2217–2225. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00693
Gugliandolo, A., Bramanti, P., and Mazzon, E. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis: recent evidence from pre-clinical to clinical studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (22), 8662. doi:10.3390/ijms21228662
Guimarães-Camboa, N., Cattaneo, P., Sun, Y., Moore-Morris, T., Gu, Y., Dalton, N. D., et al. (2017). Pericytes of multiple organs do not behave as mesenchymal stem cells in vivo. Cell stem cell 20 (3), 345–359.e5. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2016.12.006
Gurung, S., Perocheau, D., Touramanidou, L., and Baruteau, J. (2021). The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 19 (1), 47. doi:10.1186/s12964-021-00730-1
Ha, D. H., Kim, H. K., Lee, J., Kwon, H. H., Park, G. H., Yang, S. H., et al. (2020). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes for immunomodulatory therapeutics and skin regeneration. Cells 9 (5), 1157. doi:10.3390/cells9051157
Haghmorad, D., Khaleghian, A., Eslami, M., Sadeghnejad, A., Tarahomi, M., and Yousefi, B. (2023). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via modifying expression patterns of miRNAs. Mol. Biol. Rep. 50 (12), 9971–9984. doi:10.1007/s11033-023-08843-1
Håkansson, I., Tisell, A., Cassel, P., Blennow, K., Zetterberg, H., Lundberg, P., et al. (2017). Neurofilament light chain in cerebrospinal fluid and prediction of disease activity in clinically isolated syndrome and relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 24 (5), 703–712. doi:10.1111/ene.13274
Han, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Chang, F., and Ding, J. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine. Cells 8 (8), 886. doi:10.3390/cells8080886
Harris, V. K., Stark, J., Vyshkina, T., Blackshear, L., Joo, G., Stefanova, V., et al. (2018). Phase I trial of intrathecal mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors in progressive multiple sclerosis. EBioMedicine 29, 23–30. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.02.002
Harris, V. K., Stark, J., Williams, A., Roche, M., Malin, M., Kumar, A., et al. (2024). Efficacy of intrathecal mesenchymal stem cell-neural progenitor therapy in progressive MS: results from a phase II, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15 (1), 151. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03765-6
Harris, V. K., Stark, J. W., Yang, S., Zanker, S., Tuddenham, J., and Sadiq, S. A. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors in progressive MS: two-year follow-up of a phase I study. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm 8 (1), e928. doi:10.1212/NXI.0000000000000928
Harris, V. K., Vyshkina, T., and Sadiq, S. A. J. C. (2016). Clinical safety of intrathecal administration of mesenchymal stromal cell–derived neural progenitors in multiple sclerosis. Cytotherapy 18 (12), 1476–1482. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.08.007
Hartung, D. M. (2021). Health economics of disease-modifying therapy for multiple sclerosis in the United States. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 14, 1756286420987031. doi:10.1177/1756286420987031
Hauser, S. L., Bar-Or, A., Cohen, J. A., Comi, G., Correale, J., Coyle, P. K., et al. (2020). Ofatumumab versus teriflunomide in multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 383 (6), 546–557. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1917246
Hauser, S. L., Waubant, E., Arnold, D. L., Vollmer, T., Antel, J., Fox, R. J., et al. (2008). B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 358 (7), 676–688. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0706383
He, J., Liu, J., Huang, Y., Tang, X., Xiao, H., and Hu, Z. (2021). Oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy: potential targets of mesenchymal stem cells-based therapies in ischemic stroke. Front. Neurosci. 15, 641157. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.641157
Heidari barchi nezhad, R., Asadi, F., Mirzaei, M. R., and Abtahi Froushani, S. M. (2018). Comparison of the effects of 17β-estradiol treated and untreated mesenchymal stem cells on ameliorating animal model of multiple sclerosis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 21 (9), 936–942. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2018.29438.7115
Heldman, A. W., DiFede, D. L., Fishman, J. E., Zambrano, J. P., Trachtenberg, B. H., Karantalis, V., et al. (2014). Transendocardial mesenchymal stem cells and mononuclear bone marrow cells for ischemic cardiomyopathy: the TAC-HFT randomized trial. Jama 311 (1), 62–73. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282909
Herberts, C. A., Kwa, M. S., and Hermsen, H. P. (2011). Risk factors in the development of stem cell therapy. J. Transl. Med. 9, 29–14. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-29
Hofer, H. R., and Tuan, R. S. (2016). Secreted trophic factors of mesenchymal stem cells support neurovascular and musculoskeletal therapies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 7 (1), 1–14. doi:10.1186/s13287-016-0394-0
Hoorweg, K., Narang, P., Li, Z., Thuery, A., Papazian, N., Withers, D. R., et al. (2015). A stromal cell niche for human and mouse type 3 innate lymphoid cells. J. Immunol. 195 (9), 4257–4263. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1402584
Hosseini Shamili, F., Alibolandi, M., Rafatpanah, H., Abnous, K., Mahmoudi, M., Kalantari, M., et al. (2019). Immunomodulatory properties of MSC-derived exosomes armed with high affinity aptamer toward mylein as a platform for reducing multiple sclerosis clinical score. J. Control. Release 299, 149–164. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.02.032
Huang, P., Zhang, C., Delawary, M., Korchak, J. A., Suda, K., and Zubair, A. C. (2022). Development and evaluation of IL-6 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Dev. Eval. IL-6 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) 16 (3), 244–253. doi:10.1002/term.3274
Huang, X.-P., Sun, Z., Miyagi, Y., McDonald Kinkaid, H., Zhang, L., Weisel, R. D., et al. (2010). Differentiation of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells induces immunogenicity and limits their long-term benefits for myocardial repair. Circulation 122 (23), 2419–2429. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.955971
Iacobaeus, E., Kadri, N., Lefsihane, K., Boberg, E., Gavin, C., Törnqvist Andrén, A., et al. (2019). Short and long term clinical and immunologic follow up after bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in progressive multiple sclerosis—a phase I study. J. Clin. Med. 8 (12), 2102. doi:10.3390/jcm8122102
Islam, M. A., Alam, S. S., Kundu, S., Ahmed, S., Sultana, S., Patar, A., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 12 (19), 6311. doi:10.3390/jcm12196311
Jafarinia, M., Alsahebfosoul, F., Salehi, H., Eskandari, N., Azimzadeh, M., Mahmoodi, M., et al. (2020). Therapeutic effects of extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Cell. Physiol. 235 (11), 8779–8790. doi:10.1002/jcp.29721
Jiang, H., Zhang, Y., Tian, K., Wang, B., and Han, S. (2017). Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through transplantation of placental derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 41837. doi:10.1038/srep41837
Jiang, W., and Xu, J. (2020). Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 53 (1), e12712. doi:10.1111/cpr.12712
Jung, S. M., and Kim, W.-U. (2022). Targeted immunotherapy for autoimmune disease. Immune Netw. 22 (1), e9. doi:10.4110/in.2022.22.e9
Kabat, M., Bobkov, I., Kumar, S., and Grumet, M. (2020). Trends in mesenchymal stem cell clinical trials 2004-2018: is efficacy optimal in a narrow dose range? Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9 (1), 17–27. doi:10.1002/sctm.19-0202
Kalluri, R., and LeBleu, V. S. J. S. (2020). The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367(6478): p. eaau6977, doi:10.1126/science.aau6977
Kang, I. S., Suh, J., Lee, M. N., Lee, C., Jin, J., Lee, C., et al. (2020). Characterization of human cardiac mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles comparing with human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. BMB Rep. 53 (2), 118–123. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2020.53.2.235
Karussis, D., Karageorgiou, C., Vaknin-Dembinsky, A., Gowda-Kurkalli, B., Gomori, J. M., Kassis, I., et al. (2010). Safety and immunological effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Archives neurology 67 (10), 1187–1194. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2010.248
Karussis, D., Kassis, I., Kurkalli, B. G. S., and Slavin, S. (2008). Immunomodulation and neuroprotection with mesenchymal bone marrow stem cells (MSCs): a proposed treatment for multiple sclerosis and other neuroimmunological/neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 265 (1-2), 131–135. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2007.05.005
Kashani, I. R., Hedayatpour, A., Pasbakhsh, P., Kafami, L., Atlasi, N., Pirhajati Mahabadi, V., et al. (2012). 17β-Estradiol enhances the efficacy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on remyelination in mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Acta Medica Iran. 50 (12), 789–797.
Kassis, I., Ben-Zwi, M., Petrou, P., Halimi, M., and Karussis, D. (2021). Synergistic neuroprotective effects of Fingolimod and mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunol. Lett. 233, 11–19. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2021.03.003
Kassmann, C. M., Lappe-Siefke, C., Baes, M., Brügger, B., Mildner, A., Werner, H. B., et al. (2007). Axonal loss and neuroinflammation caused by peroxisome-deficient oligodendrocytes. Nat. Genet. 39 (8), 969–976. doi:10.1038/ng2070
Kerkis, I., da Silva, Á. P., and Araldi, R. P. (2024). The impact of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and mesenchymal stem cell-derived IL-6 on neurological conditions. Front. Immunol. 15, 1400533. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1400533
Khademi, M., Kockum, I., Andersson, M. L., Iacobaeus, E., Brundin, L., Sellebjerg, F., et al. (2011). Cerebrospinal fluid CXCL13 in multiple sclerosis: a suggestive prognostic marker for the disease course. Mult. Scler. 17 (3), 335–343. doi:10.1177/1352458510389102
Khan, Z., Mehan, S., Gupta, G. D., and Narula, A. S. (2024). Immune system dysregulation in the progression of multiple sclerosis: molecular insights and therapeutic implications. Neuroscience. 548, 9, 26. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.04.004
Kilian, K. A., Bugarija, B., Lahn, B. T., and Mrksich, M. (2010). Geometric cues for directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107 (11), 4872–4877. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903269107
Kim, J.-H., Jo, C. H., Kim, H. R., and Hwang, Y. i. (2018). Comparison of immunological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from the periodontal ligament, umbilical cord, and adipose tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2018/8429042
Kishimoto, T. J. A. R. I. (2005). Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine—40 years in immunology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23 (1), 1–21. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115806
Kobelt, G., Thompson, A., Berg, J., Gannedahl, M., and Eriksson, J.MSCOI Study Groupet al. (2017). New insights into the burden and costs of multiple sclerosis in Europe. Multiple Scler. J. 23 (8), 1123–1136. doi:10.1177/1352458517694432
Kokai, L. E., Traktuev, D. O., Zhang, L., Merfeld-Clauss, S., DiBernardo, G., Lu, H., et al. (2017). Adipose stem cell function maintained with age: an intra-subject study of long-term cryopreserved cells. Aesthet. Surg. J. 37 (4), 454–463. doi:10.1093/asj/sjw197
Kråkenes, T., Sandvik, C. E., Ytterdal, M., Gavasso, S., Evjenth, E. C., Bø, L., et al. (2024). The therapeutic potential of exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (19), 10292. doi:10.3390/ijms251910292
Kuhlmann, T., Moccia, M., Coetzee, T., Cohen, J. A., Correale, J., Graves, J., et al. (2023). Multiple sclerosis progression: time for a new mechanism-driven framework. Lancet. Neurol. 22 (1), 78–88. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00289-7
Kumar, P., Kandoi, S., Misra, R., S, V., K, R., and Verma, R. S. (2019). The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: a new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 46, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.04.002
Kurtzke, J. F. (1983). Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33 (11), 1444–1452. doi:10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444
Kyurkchiev, D., Bochev, I., Ivanova-Todorova, E., Mourdjeva, M., Oreshkova, T., Belemezova, K., et al. (2014). Secretion of immunoregulatory cytokines by mesenchymal stem cells. World J. stem cells 6 (5), 552–570. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.552
Lan, Q., Xia, S., Wang, Q., Xu, W., Huang, H., Jiang, S., et al. (2020). Development of oncolytic virotherapy: from genetic modification to combination therapy. Front. Med. 14, 160–184. doi:10.1007/s11684-020-0750-4
Langer-Gould, A. M., Smith, J. B., Gonzales, E. G., Piehl, F., and Li, B. H. (2023). Multiple sclerosis, disease-modifying therapies, and infections. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 10 (6), e200164. doi:10.1212/NXI.0000000000200164
Laroye, C., Gibot, S., Huselstein, C., and Bensoussan, D. (2020). Mesenchymal stromal cells for sepsis and septic shock: lessons for treatment of COVID-19. Stem cells Transl. Med. 9 (12), 1488–1494. doi:10.1002/sctm.20-0239
Laso-García, F., Ramos-Cejudo, J., Carrillo-Salinas, F. J., Otero-Ortega, L., Feliú, A., Gómez-de Frutos, M., et al. (2018). Therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells in a model of progressive multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 13 (9), e0202590. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0202590
Li, J. F., Zhang, D. J., Geng, T., Chen, L., Huang, H., Yin, H. L., et al. (2014). The potential of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a novel cellular therapy for multiple sclerosis. Cell Transpl. 23 (Suppl. 1), S113–S122. doi:10.3727/096368914X685005
Li, M., Jiang, Y., Hou, Q., Zhao, Y., Zhong, L., and Fu, X. (2022). Potential pre-activation strategies for improving therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells: current status and future prospects. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (1), 146. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-02822-2
Li, X. (2020). The significance of exosomes in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 19, 1–11. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1085-0
Li, X., Liu, L., Yang, J., Yu, Y., Chai, J., Wang, L., et al. (2016). Exosome derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell mediates MiR-181c attenuating burn-induced excessive inflammation. EBioMedicine 8, 72–82. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.030
Li, Y., Chen, J., Chen, X. G., Wang, L., Gautam, S. C., Xu, Y. X., et al. (2002). Human marrow stromal cell therapy for stroke in rat: neurotrophins and functional recovery. Neurology 59 (4), 514–523. doi:10.1212/wnl.59.4.514
Li, Z., Hu, X., and Zhong, J. F. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics, function, and application. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 8106818. doi:10.1155/2019/8106818
Liang, Y., Xu, X., Li, X., Xiong, J., Li, B., Duan, L., et al. (2020). Chondrocyte-targeted microRNA delivery by engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces 12 (33), 36938–36947. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c10458
Liao, W., Pham, V., Liu, L., Riazifar, M., Pone, E. J., Zhang, S. X., et al. (2016). Mesenchymal stem cells engineered to express selectin ligands and IL-10 exert enhanced therapeutic efficacy in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biomaterials 77, 87–97. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.005
Lim, C. K., Brew, B. J., Sundaram, G., and Guillemin, G. J. (2010). Understanding the roles of the kynurenine pathway in multiple sclerosis progression. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 3, 157–167. doi:10.4137/ijtr.s4294
Ling, X., Wang, T., Han, C., Wang, P., Liu, X., Zheng, C., et al. (2022). IFN-γ-Primed hUCMSCs significantly reduced inflammation via the foxp3/ROR-γt/STAT3 signaling pathway in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 13, 835345. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.835345
Liu, M., Lei, H., Dong, P., Fu, X., Yang, Z., Yang, Y., et al. (2017). Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from the elderly exhibit decreased migration and differentiation abilities with senescent properties. Cell Transpl. 26 (9), 1505–1519. doi:10.1177/0963689717721221
Liu, R., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Zhou, M., Sun, Y., Su, D., et al. (2015). Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells inhibited T follicular helper cell generation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 5 (1), 12777. doi:10.1038/srep12777
Liu, S., Wang, J., Han, R., Meng, M., Wang, W., Zhao, Y., et al. (2019). Therapeutic effect of transplanted umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in a cynomolgus monkey model of multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (4), 2516–2531.
Liu, W., Rong, Y., Wang, J., Zhou, Z., Ge, X., Ji, C., et al. (2020b). Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J. Neuroinflammation 17, 47–22. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-1726-7
Liu, Y., Du, B., Wang, Y., Yang, G. Y., and Bi, X. (2020a). Mesenchymal stem cells attenuated blood-brain barrier disruption via downregulation of aquaporin-4 expression in EAE mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 57 (9), 3891–3901. doi:10.1007/s12035-020-01998-z
Liu, Y.-Y., Li, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, Y., Yuan, R., Yang, M. M., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes regulate microglia phenotypes: a promising treatment for acute central nervous system injury. Neural Regen. Res. 18 (8), 1657–1665. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.363819
Liu, Z. J., Zhuge, Y., and Velazquez, O. C. (2009). Trafficking and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 106 (6), 984–991. doi:10.1002/jcb.22091
Llufriu, S., Sepúlveda, M., Blanco, Y., Marín, P., Moreno, B., Berenguer, J., et al. (2014a). Randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis. PloS one 9 (12), e113936. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113936
Llufriu, S., Sepúlveda, M., Blanco, Y., Marín, P., Moreno, B., Berenguer, J., et al. (2014b). Randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 9 (12), e113936. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113936
Lopez-Santalla, M., Fernandez-Perez, R., and Garin, M. I. J. C. (2020). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells for rheumatoid arthritis treatment: an update on clinical applications. Cells 9 (8), 1852. doi:10.3390/cells9081852
Lukomska, B., Stanaszek, L., Zuba-Surma, E., Legosz, P., Sarzynska, S., and Drela, K. (2019). Challenges and controversies in human mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 9628536. doi:10.1155/2019/9628536
Lv, F.-J., Tuan, R. S., Cheung, K. M. C., and Leung, V. Y. L. (2014). Concise review: the surface markers and identity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells 32 (6), 1408–1419. doi:10.1002/stem.1681
Mahfouz, M. M., Abdelsalam, R. M., Masoud, M. A., Mansour, H. A., Ahmed-Farid, O. A., and kenawy, S. A. (2017a). The neuroprotective effect of mesenchymal stem cells on an experimentally induced model for multiple sclerosis in mice. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 31 (9), e21936. doi:10.1002/jbt.21936
Mahfouz, M. M., Abdelsalam, R. M., Masoud, M. A., Mansour, H. A., Ahmed-Farid, O. A., and Kenawy, S. A. (2017b). The neuroprotective effect of mesenchymal stem cells on an experimentally induced model for multiple sclerosis in mice. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 31 (9), e21936. doi:10.1002/jbt.21936
Mahjoor, M., Afkhami, H., Mollaei, M., Nasr, A., Shahriary, S., and Khorrami, S. (2021). MicroRNA-30c delivered by bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells induced apoptosis and diminished cell invasion in U-251 glioblastoma cell line. Life Sci. 279, 119643. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119643
Mahjoor, M., Afkhami, H., Najafi, M., Nasr, A., and Khorrami, S. (2023a). The role of microRNA-30c in targeting interleukin 6, as an inflammatory cytokine, in the mesenchymal stem cell: a therapeutic approach in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 149 (7), 3149–3160. doi:10.1007/s00432-022-04123-w
Mahjoor, M., Fakouri, A., Farokhi, S., Nazari, H., Afkhami, H., and Heidari, F. (2023b). Regenerative potential of mesenchymal stromal cells in wound healing: unveiling the influence of normoxic and hypoxic environments. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1245872. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1245872
Mansoor, S. R., Zabihi, E., and Ghasemi-Kasman, M. (2019). The potential use of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Life Sci. 235, 116830. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116830
Manu, M. S., Hohjoh, H., and Yamamura, T. (2021). Extracellular vesicles as pro-and anti-inflammatory mediators, biomarkers and potential therapeutic agents in multiple sclerosis. Aging Dis. 12 (6), 1451–1461. doi:10.14336/AD.2021.0513
Maqsood, M., Kang, M., Wu, X., Chen, J., Teng, L., and Qiu, L. (2020). Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 256, 118002. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118002
Margoni, M., Preziosa, P., Filippi, M., and Rocca, M. A. (2022). Anti-CD20 therapies for multiple sclerosis: current status and future perspectives. J. Neurol. 269 (3), 1316–1334. doi:10.1007/s00415-021-10744-x
Marin-Bañasco, C., Benabdellah, K., Melero-Jerez, C., Oliver, B., Pinto-Medel, M. J., Hurtado-Guerrero, I., et al. (2017). Gene therapy with mesenchymal stem cells expressing IFN-ß ameliorates neuroinflammation in experimental models of multiple sclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 174 (3), 238–253. doi:10.1111/bph.13674
Maroto-García, J., Martínez-Escribano, A., Delgado-Gil, V., Mañez, M., Mugueta, C., Varo, N., García de la Torre, Á., and Ruiz-Galdón, M. (2023). Biochemical biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 548:117471. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2023.117471
Mazini, L., Rochette, L., Amine, M., and Malka, G. (2019). Regenerative capacity of adipose derived stem cells (ADSCs), comparison with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (10), 2523. doi:10.3390/ijms20102523
McGinley, M. P., Goldschmidt, C. H., and Rae-Grant, A. D. J. J. (2021). Diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis: a review. JAMA 325(8). 765–779. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26858
Mei, R., Wan, Z., Yang, C., Shen, X., Wang, R., Zhang, H., et al. (2024). Advances and clinical challenges of mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Front. Immunol. 15, 1421854. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421854
Meng, M., Liu, Y., Wang, W., Wei, C., Liu, F., Du, Z., et al. (2018). Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 10 (1), 212–223.
Mey, G. M., Mahajan, K. R., and DeSilva, T. M. (2023). Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. WIREs Mech. Dis. 15 (1), e1583. doi:10.1002/wsbm.1583
Miclea, A., Bagnoud, M., Chan, A., and Hoepner, R. (2020). A brief review of the effects of vitamin D on multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 11, 781. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00781
Mihai, M. C., Popa, M. A., Suica, V. I., Antohe, F., Jackson, E. K., Simionescu, M., et al. (2019). Mechanism of 17β-estradiol stimulated integration of human mesenchymal stem cells in heart tissue. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 133, 115–124. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.06.007
Mirshekar, M., Afkhami, H., Razavi, S., Masjedian Jazi, F., Darban-Sarokhalil, D., Ohadi, E., et al. (2023). Potential antibacterial activity and healing effect of topical administration of bone marrow and adipose mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in collagen-fibrin hydrogel scaffold on full-thickness burn wound infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Burns 49 (8), 1944–1957. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2023.01.005
Moeinabadi-Bidgoli, K., Mazloomnejad, R., Beheshti Maal, A., Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H., Kazem Arki, M., Hossein-Khannazer, N., et al. (2023). Genetic modification and preconditioning strategies to enhance functionality of mesenchymal stromal cells: a clinical perspective. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 23 (6), 461–478. doi:10.1080/14712598.2023.2205017
Mohy, A. B. M., Yazdanbakhsh, S., Lotfi, J., Alimoghaddom, K., Talebian, F., Hooshmand, F., et al. (2007). Does mesenchymal stem cell therapy help multiple sclerosis patients? Report of a pilot study. Iran. J. Immunol. 4, 50–57.
Molnar, V., Pavelić, E., Vrdoljak, K., Čemerin, M., Klarić, E., Matišić, V., et al. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell mechanisms of action and clinical effects in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Genes (Basel). 13 (6), 949. doi:10.3390/genes13060949
Montalban, X., Hauser, S. L., Kappos, L., Arnold, D. L., Bar-Or, A., Comi, G., et al. (2017). Ocrelizumab versus placebo in primary progressive multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 376 (3), 209–220. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1606468
Moore, S., Meschkat, M., Ruhwedel, T., Trevisiol, A., Tzvetanova, I. D., Battefeld, A., et al. (2020). A role of oligodendrocytes in information processing. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 5497. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19152-7
Musiał-Wysocka, A., Kot, M., and Majka, M. (2019). The pros and cons of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies. Cell Transplant. 28 (7), 801–812. doi:10.1177/0963689719837897
Najafi, S., Najafi, P., Kaffash Farkhad, N., Hosseini Torshizi, G., Assaran Darban, R., Boroumand, A. R., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients: a comprehensive review of disease information and future perspectives. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 26 (8), 872–881. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2023.66364.14572
Nasri, F., Mohtasebi, M. S., Hashemi, E., Zarrabi, M., Gholijani, N., and Sarvestani, E. K. (2018). Therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells-derived neural progenitors in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. J. Stem Cells 11 (1), 68–77. doi:10.15283/ijsc17052
Nave, K.-A. (2010). Myelination and support of axonal integrity by glia. Nature 468 (7321), 244–252. doi:10.1038/nature09614
Neal, E. G., Liska, M. G., Lippert, T., Lin, R., Gonzalez, M., Russo, E., et al. (2018). An update on intracerebral stem cell grafts. Expert Rev. Neurother. 18 (7), 557–572. doi:10.1080/14737175.2018.1491309
Neirinckx, V., Agirman, G., Coste, C., Marquet, A., Dion, V., Rogister, B., et al. (2021). Correction to: adult bone marrow mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells are chemoattractive and accelerate motor recovery in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12 (1), 509. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02534-z
Nethi, S. K., Li, X., Bhatnagar, S., and Prabha, S. (2023). Enhancing anticancer efficacy of chemotherapeutics using targeting ligand-functionalized synthetic antigen receptor-mesenchymal stem cells. Pharmaceutics 15 (6), 1742. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15061742
Novakova, L., Zetterberg, H., Sundström, P., Axelsson, M., Khademi, M., Gunnarsson, M., et al. (2017). Monitoring disease activity in multiple sclerosis using serum neurofilament light protein. Neurology 89(22), 2230–2237. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000004683
Nowakowski, A., Drela, K., Rozycka, J., Janowski, M., and Lukomska, B. (2016). Engineered mesenchymal stem cells as an anti-cancer trojan Horse. Stem Cells Dev. 25 (20), 1513–1531. doi:10.1089/scd.2016.0120
Ocansey, D. K. W., Pei, B., Yan, Y., Qian, H., Zhang, X., Xu, W., et al. (2020). Improved therapeutics of modified mesenchymal stem cells: an update. J. Transl. Med. 18 (1), 42. doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02234-x
Oh, J., Vidal-Jordana, A., and Montalban, X. (2018). Multiple sclerosis: clinical aspects. Curr. Opin. neurology 31 (6), 752–759. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000622
Oliveira, A. G., Gonçalves, M., Ferreira, H., and M Neves, N. (2020). Growing evidence supporting the use of mesenchymal stem cell therapies in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 38, 101860. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2019.101860
Orrù, V., Serra, V., Marongiu, M., Lai, S., Lodde, V., Zoledziewska, M., et al. (2024). Implications of disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis on immune cells and response to COVID-19 vaccination. Front. Immunol. 15, 1416464. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1416464
Oudejans, E., Luchicchi, A., Strijbis, E. M. M., Geurts, J. J. G., and van Dam, A. M. (2021). Is MS affecting the CNS only? Lessons from clinic to myelin pathophysiology. Neurology-Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation 8 (1), e914. doi:10.1212/NXI.0000000000000914
Pachón-Peña, G., Serena, C., Ejarque, M., Petriz, J., Duran, X., Oliva-Olivera, W., et al. (2016). Obesity determines the immunophenotypic profile and functional characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 5 (4), 464–475. doi:10.5966/sctm.2015-0161
Papaccio, F., Paino, F., Regad, T., Papaccio, G., Desiderio, V., and Tirino, V. (2017). Concise review: cancer cells, cancer stem cells, and mesenchymal stem cells: influence in cancer development. Stem cells Transl. Med. 6 (12), 2115–2125. doi:10.1002/sctm.17-0138
Park, J. S., Suryaprakash, S., Lao, Y. H., and Leong, K. W. (2015). Engineering mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine and drug delivery. Methods 84, 3–16. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.03.002
Payne, N. L., Dantanarayana, A., Sun, G., Moussa, L., Caine, S., McDonald, C., et al. (2012). Early intervention with gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin-4 enhances anti-inflammatory responses and functional recovery in experimental autoimmune demyelination. Cell Adh Migr. 6 (3), 179–189. doi:10.4161/cam.20341
Penesová, A., Dean, Z., Kollár, B., Havranová, A., Imrich, R., Vlček, M., et al. (2018). Nutritional intervention as an essential part of multiple sclerosis treatment? Physiological research. Physiol. Res. 67 (4), 521–533. doi:10.33549/physiolres.933694
Perussolo, M. C., Mogharbel, B. F., Saçaki, C. S., Rosa, N. N. d., Irioda, A. C., Oliveira, N. B. d., et al. (2024). Cellular therapy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis as an adjuvant treatment to translate for multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (13), 6996. doi:10.3390/ijms25136996
Peterson, S., Jalil, A., Beard, K., Kakara, M., and Sriwastava, S. (2022). Updates on efficacy and safety outcomes of new and emerging disease modifying therapies and stem cell therapy for Multiple Sclerosis: a review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 68, 104125. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2022.104125
Petrou, P., Kassis, I., Ginzberg, A., Halimi, M., Yaghmour, N., Abramsky, O., et al. (2021a). Long-term clinical and immunological effects of repeated mesenchymal stem cell injections in patients with progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 12, 639315. doi:10.3389/fneur.2021.639315
Petrou, P., Kassis, I., Ginzberg, A., Halimi, M., Yaghmour, N., Abramsky, O., et al. (2021b). Long-term clinical and immunological effects of repeated mesenchymal stem cell injections in patients with progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurology 12, 639315. doi:10.3389/fneur.2021.639315
Petrou, P., Kassis, I., Ginzberg, A., Hallimi, M., and Karussis, D. (2022). Effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in progressive multiple sclerosis. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 11 (1), 55–58. doi:10.1093/stcltm/szab017
Petrou, P., Kassis, I., Levin, N., Paul, F., Backner, Y., Benoliel, T., et al. (2020). Beneficial effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain 143 (12), 3574–3588. doi:10.1093/brain/awaa333
Philipp, D., Suhr, L., Wahlers, T., Choi, Y. H., and Paunel-Görgülü, A. (2018) Preconditioning of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells highly strengthens their potential to promote IL-6-dependent M2b polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9, 1–17. doi:10.1186/s13287-018-1039-2
Phillips, M. I., and Tang, Y. L. (2008). Genetic modification of stem cells for transplantation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60 (2), 160–172. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2007.08.035
Pinheiro, L. L., de Lima, A. R., Martins, D. M., de Oliveira, E. H. C., Souza, M. P. C., de Carvalho Miranda, C. M. F., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells in dogs with demyelinating leukoencephalitis as an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Heliyon 5 (6), e01857. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01857
Pinho, A. G., Cibrão, J. R., Silva, N. A., Monteiro, S., and Salgado, A. J. (2020). Cell secretome: basic insights and therapeutic opportunities for CNS disorders. Pharm. (Basel). 13 (2), 31. doi:10.3390/ph13020031
Planchon, S. M., Lingas, K. T., Reese Koç, J., Hooper, B. M., Maitra, B., Fox, R. M., et al. (2018). Feasibility of mesenchymal stem cell culture expansion for a phase I clinical trial in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Scler. Journal–Experimental, Transl. Clin. 4 (1), 2055217318765288. doi:10.1177/2055217318765288
Quirici, N., Soligo, D., Bossolasco, P., Servida, F., Lumini, C., and Deliliers, G. L. (2002). Isolation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by anti-nerve growth factor receptor antibodies. Exp. Hematol. 30 (7), 783–791. doi:10.1016/s0301-472x(02)00812-3
Rahmati, M., Ghannadian, S. M., Kasiri, N., Ahmadi, L., Motedayyen, H., Shaygannejad, V., et al. (2021). Modulation of Th17 proliferation and IL-17A gene expression by acetylated form of apigenin in patients with multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Investig. 50 (2-3), 216–229. doi:10.1080/08820139.2020.1726381
Raphael, I., Webb, J., Stuve, O., Haskins, W., and Forsthuber, T. (2015). Body fluid biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: how far we have come and how they could affect the clinic now and in the future. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 11 (1), 69–91. doi:10.1586/1744666X.2015.991315
Riordan, N. H., Morales, I., Fernández, G., Allen, N., Fearnot, N. E., Leckrone, M. E., et al. (2018). Clinical feasibility of umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. J. Transl. Med. 16 (1), 57. doi:10.1186/s12967-018-1433-7
Rivera, F. J., de la Fuente, A. G., Zhao, C., Silva, M. E., Gonzalez, G. A., Wodnar, R., et al. (2019). Aging restricts the ability of mesenchymal stem cells to promote the generation of oligodendrocytes during remyelination. Glia 67 (8), 1510–1525. doi:10.1002/glia.23624
Roig-Carles, D., Willms, E., Fontijn, R. D., Martinez-Pacheco, S., Mäger, I., de Vries, H. E., et al. (2021). Endothelial-derived extracellular vesicles induce cerebrovascular dysfunction in inflammation. Pharmaceutics 13 (9), 1525. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13091525
Røsland, G. V., Svendsen, A., Torsvik, A., Sobala, E., McCormack, E., Immervoll, H., et al. (2009). Long-term cultures of bone marrow–derived human mesenchymal stem cells frequently undergo spontaneous malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 69 (13), 5331–5339. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4630
Rostami, M., Haidari, K., Amini, H., and Shahbazi, M. (2022). Genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cell therapy against murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol. Neurobiol. 59 (6), 3449–3457. doi:10.1007/s12035-022-02774-x
Saadh, M. J., Mikhailova, M. V., Rasoolzadegan, S., Falaki, M., Akhavanfar, R., Gonzáles, J. L. A., et al. (2023). Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs)-based cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) therapy. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28 (1), 47. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01008-7
Sadeghnejad, A., Pazoki, A., Yazdanpanah, E., Esmaeili, S. A., Yousefi, B., Sadighi-Moghaddam, B., et al. (2024). Exploring the role of mesenchymal stem cells in modulating immune responses via Treg and Th2 cell activation: insights from mouse model of multiple sclerosis. APMIS 132(11), 888–899. doi:10.1111/apm.13456
Sato, T., Vries, R. G., Snippert, H. J., van de Wetering, M., Barker, N., Stange, D. E., et al. (2009). Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 459 (7244), 262–265. doi:10.1038/nature07935
Schreiner, T. G., Romanescu, C., and Popescu, B. O. J. B. (2022). The blood–brain barrier—a key player in multiple sclerosis disease mechanisms. Biomolecules 12 (4), 538. doi:10.3390/biom12040538
Sedaghat, N. (2018). Effect of fingolimod on the frequency of regulatory T cells in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Immun. Res. 5, 1032. doi:10.26420/jimmunres.2018.1032
Sedaghat, N., Motedayyen, H., Alsahebfosoul, F., Etemadifar, M., Ostadi, V., Kianpour, F., et al. (2019). Increased expression of lymphocyte activation gene-3 by regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis patients with fingolimod treatment. Turkish J. Immunol. 7 (1). doi:10.25002/tji.2019.1035
Shandil, R. K., Dhup, S., and Narayanan, S. J. S. c.i. (2022). Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in preclinical models of autoimmune diseases. Stem Cells Int. 2022 (1), 6379161. doi:10.1155/2022/6379161
Shang, F., Yu, Y., Liu, S., Ming, L., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Z., et al. (2021). Advancing application of mesenchymal stem cell-based bone tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 6 (3), 666–683. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.08.014
Shen, Z., Huang, W., Liu, J., Tian, J., Wang, S., and Rui, K. (2021). Effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 12, 749192. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.749192
Shi, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Q., Liu, K., Hou, J., Shao, C., et al. (2018). Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 14 (8), 493–507. doi:10.1038/s41581-018-0023-5
Shimojima, C., Takeuchi, H., Jin, S., Parajuli, B., Hattori, H., Suzumura, A., et al. (2016). Conditioned medium from the stem cells of human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 196 (10), 4164–4171. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1501457
Simpson-Yap, S., De Brouwer, E., Kalincik, T., Rijke, N., Hillert, J. A., Walton, C., et al. (2021). Associations of disease-modifying therapies with COVID-19 severity in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 97(19), e1870–e1885. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000012753
Son, B. R., Marquez-Curtis, L. A., Kucia, M., Wysoczynski, M., Turner, A. R., Ratajczak, J., et al. (2006). Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-1-CXCR4 and hepatocyte growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloproteinases. Stem cells 24 (5), 1254–1264. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0271
Song, C.-G., Zhang, Y. Z., Wu, H. N., Cao, X. L., Guo, C. J., Li, Y. Q., et al. (2018). Stem cells: a promising candidate to treat neurological disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 13 (7), 1294–1304. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.235085
Song, N., Scholtemeijer, M., and Shah, K. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 41 (9), 653–664. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2020.06.009
Sormani, M. P., De Rossi, N., Schiavetti, I., Carmisciano, L., Cordioli, C., Moiola, L., et al. (2021). Disease-modifying therapies and coronavirus disease 2019 severity in multiple sclerosis. Ann. neurology 89 (4), 780–789. doi:10.1002/ana.26028
Squillaro, T., Peluso, G., and Galderisi, U. (2016). Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: an update. Cell Transpl. 25 (5), 829–848. doi:10.3727/096368915X689622
Sriwastava, S., Kataria, S., Srivastava, S., Kazemlou, S., Gao, S., Wen, S., et al. (2021). Disease-modifying therapies and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neuroimmunol. 360, 577721. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2021.577721
Stampanoni Bassi, M., Iezzi, E., Drulovic, J., Pekmezovic, T., Gilio, L., Furlan, R., et al. (2020). IL-6 in the cerebrospinal fluid signals disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Front. Cell Neurosci. 14, 120. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.00120
Stoiloudis, P., Kesidou, E., Bakirtzis, C., Sintila, S. A., Konstantinidou, N., Boziki, M., et al. (2022). The role of diet and interventions on multiple sclerosis: a review. Nutrients 14 (6), 1150. doi:10.3390/nu14061150
Sumowski, J. F., Benedict, R., Enzinger, C., Filippi, M., Geurts, J. J., Hamalainen, P., et al. (2018). Cognition in multiple sclerosis: state of the field and priorities for the future. Neurology 90 (6), 278–288. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000004977
Tan, F., Li, X., Wang, Z., Li, J., Shahzad, K., and Zheng, J. (2024). Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9 (1), 17. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01704-0
Tanaka, T. (2014). “A new era for the treatment of inflammatory autoimmune diseases by interleukin-6 blockade strategy,” in Seminars in immunology (Elsevier).
Tanaka, T., Narazaki, M., and Kishimoto, T. (2014). IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 6 (10), a016295. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016295
Tang, Y., Zhou, Y., and Li, H.-J. (2021). Advances in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a review. Stem Cell Res. and Ther. 12 (1), 71. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02138-7
Tatsumi, K., Ohashi, K., Matsubara, Y., Kohori, A., Ohno, T., Kakidachi, H., et al. (2013). Tissue factor triggers procoagulation in transplanted mesenchymal stem cells leading to thromboembolism. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 431 (2), 203–209. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.134
Teymouri, S., Yousefi, M. H., Heidari, S., Farokhi, S., Afkhami, H., and Kashfi, M. (2024). Beyond antibiotics: mesenchymal stem cells and bacteriophages-new approaches to combat bacterial resistance in wound infections. Mol. Biol. Rep. 52 (1), 64. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-10163-x
Thompson, A. J., Banwell, B. L., Barkhof, F., Carroll, W. M., Coetzee, T., Comi, G., et al. (2018). Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 17 (2), 162–173. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30470-2
Togha, M., Jahanshahi, M., Alizadeh, L., Jahromi, S. R., Vakilzadeh, G., Alipour, B., et al. (2017). Rapamycin augments immunomodulatory properties of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol. Neurobiol. 54 (4), 2445–2457. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-9840-3
Toh, W. S. (2017). “MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: implications for osteoarthritis treatment,” in Seminars in cell and developmental biology (Elsevier).
Travers, B. S., Tsang, B. K., and Barton, J. L. J. A. j.o.g.p. (2022). Multiple sclerosis: diagnosis, disease-modifying therapy and prognosis. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 51 (4), 199–206. doi:10.31128/AJGP-07-21-6103
Tremblay, F., Ansari, Y., Remaud, A., and Freedman, M. S. (2022). Neurophysiological outcomes following mesenchymal stem cell therapy in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 136, 69–81. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2022.01.125
Uccelli, A., Laroni, A., Ali, R., Battaglia, M. A., Blinkenberg, M., Brundin, L., et al. (2021). Safety, tolerability, and activity of mesenchymal stem cells versus placebo in multiple sclerosis (MESEMS): a phase 2, randomised, double-blind crossover trial. Lancet. Neurol. 20 (11), 917–929. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00301-X
Uccelli, A., Laroni, A., and Freedman, M. S. (2011). Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Lancet Neurology 10 (7), 649–656. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70121-1
Uccelli, A., Moretta, L., and Pistoia, V. (2008). Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8 (9), 726–736. doi:10.1038/nri2395
Uder, C., Brückner, S., Winkler, S., Tautenhahn, H. M., and Christ, B. (2018). Mammalian MSC from selected species: features and applications. Cytom. Part A 93 (1), 32–49. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.23239
Ullah, I., Subbarao, R. B., and Rho, G. J. (2015). Human mesenchymal stem cells-current trends and future prospective. Biosci. Rep. 35 (2), e00191. doi:10.1042/BSR20150025
Vaheb, S. (2024). Neurological efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) therapy in people with multiple sclerosis (pwMS): an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.105681
Vandebergh, M., Becelaere, S., Dubois, B., and Goris, A. (2022). Body mass index, interleukin-6 signaling and multiple sclerosis: a mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 13, 834644. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.834644
Veh, J., Ludwig, C., Schrezenmeier, H., and Jahrsdörfer, B. (2024). Regulatory B cells—immunopathological and prognostic potential in humans. Cells 13 (4), 357. doi:10.3390/cells13040357
Vincze, O., Oláh, J., Zádori, D., Klivényi, P., Vécsei, L., and Ovádi, J. (2011). A new myelin protein, TPPP/p25, reduced in demyelinated lesions is enriched in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 409 (1), 137–141. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.130
Von Wunster, B. (2018). Advising patients seeking stem cell interventions for multiple sclerosis. BMJ Group, 472–476.
Waage, A., Brandtzaeg, P., Halstensen, A., Kierulf, P., and Espevik, T. (1989). The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J. Exp. Med. 169 (1), 333–338. doi:10.1084/jem.169.1.333
Wang, Y., Tian, M., Wang, F., Heng, B. C., Zhou, J., Cai, Z., et al. (2019). Understanding the immunological mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells in allogeneic transplantation: from the aspect of major histocompatibility complex class I. Stem Cells Dev. 28 (17), 1141–1150. doi:10.1089/scd.2018.0256
Wang, Y. L., Xue, P., Xu, C. Y., Wang, Z., Liu, X. S., Hua, L. L., et al. (2018). SPK1-transfected UCMSC has better therapeutic activity than UCMSC in the treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model of Multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 1756. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-19703-5
Weiss, A. R. R., and Dahlke, M. H. (2019). Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): mechanisms of action of living, apoptotic, and dead MSCs. Front. Immunol. 10, 1191. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01191
Weiss, D. J., Segal, K., Casaburi, R., Hayes, J., and Tashkin, D. (2021). Effect of mesenchymal stromal cell infusions on lung function in COPD patients with high CRP levels. Respir. Res. 22 (1), 142. doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01734-8
Wiendl, H., Gold, R., Berger, T., Derfuss, T., Linker, R., Mäurer, M., et al. (2021). Multiple Sclerosis Therapy Consensus Group (MSTCG): position statement on disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis (white paper). Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 14, 17562864211039648. doi:10.1177/17562864211039648
Wigerblad, G., and Kaplan, M. J. (2023). Neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 23 (5), 274–288. doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00787-0
Williams, T., Zetterberg, H., and Chataway, J. (2021). Neurofilaments in progressive multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. J. Neurol. 268, 3212–3222. doi:10.1007/s00415-020-09917-x
Xiao, J., Yang, R., Biswas, S., Qin, X., Zhang, M., and Deng, W. (2015). Mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells as therapies for multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 (5), 9283–9302. doi:10.3390/ijms16059283
Xin, Y., Gao, J., Hu, R., Li, H., Li, Q., Han, F., et al. (2020). Changes of immune parameters of T lymphocytes and macrophages in EAE mice after BM-MSCs transplantation. Immunol. Lett. 225, 66–73. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2020.05.005
Yamout, B., Hourani, R., Salti, H., Barada, W., El-Hajj, T., Al-Kutoubi, A., et al. (2010). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple sclerosis: a pilot study. J. Neuroimmunol. 227 (1-2), 185–189. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.07.013
Yan, L., Jiang, B., Niu, Y., Wang, H., Li, E., Yan, Y., et al. (2018). Intrathecal delivery of human ESC-derived mesenchymal stem cell spheres promotes recovery of a primate multiple sclerosis model. Cell Death Discov. 4 (1), 28. doi:10.1038/s41420-018-0091-0
Yang, G., Fan, X., Liu, Y., Jie, P., Mazhar, M., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 19 (5), 1214–1231. doi:10.1007/s12015-023-10539-9
Yang, Y., He, X., Zhao, R., Guo, W., Zhu, M., Xing, W., et al. (2018). Serum IFN-γ levels predict the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active rheumatoid arthritis. J. Transl. Med. 16, 165–169. doi:10.1186/s12967-018-1541-4
Yazdi, A., Mokhtarzadeh Khanghahi, A., Baharvand, H., and Javan, M. (2018). Fingolimod enhances oligodendrocyte differentiation of transplanted human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 17 (4), 1444–1457. doi:10.22037/ijpr.2018.2310
Yordanova, A., Ivanova, M., Tumangelova-Yuzeir, K., Angelov, A., Kyurkchiev, S., Belemezova, K., et al. (2024). Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome: a potential regulator of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (23), 12515. doi:10.3390/ijms252312515
Yousefi, F., Lavi Arab, F., Saeidi, K., Amiri, H., and Mahmoudi, M. (2019). Various strategies to improve efficacy of stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis: focus on mesenchymal stem cells and neuroprotection. J. Neuroimmunol. 328, 20–34. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.11.015
Yu, B., Zhang, X., and Li, X. (2014). Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15 (3), 4142–4157. doi:10.3390/ijms15034142
Zamvil, S., Nelson, P., Trotter, J., Mitchell, D., Knobler, R., Fritz, R., et al. (1985). T-cell clones specific for myelin basic protein induce chronic relapsing paralysis and demyelination. Nature 317 (6035), 355–358. doi:10.1038/317355a0
Zappia, E., Casazza, S., Pedemonte, E., Benvenuto, F., Bonanni, I., Gerdoni, E., et al. (2005). Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis inducing T-cell anergy. Blood 106(5), 1755–1761. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-04-1496
Zeisel, A., Muñoz-Manchado, A. B., Codeluppi, S., Lönnerberg, P., La Manno, G., Juréus, A., et al. (2015). Brain structure. Cell types in the mouse cortex and hippocampus revealed by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 347 (6226), 1138–1142. doi:10.1126/science.aaa1934
Zhang, B., Yeo, R. W. Y., Lai, R. C., Sim, E. W. K., Chin, K. C., and Lim, S. K. (2018). Mesenchymal stromal cell exosome–enhanced regulatory T-cell production through an antigen-presenting cell–mediated pathway. Cytotherapy 20 (5), 687–696. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.02.372
Zhang, J., Buller, B. A., Zhang, Z. G., Zhang, Y., Lu, M., Rosene, D. L., et al. (2022). Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells promote remyelination and reduce neuroinflammation in the demyelinating central nervous system. Exp. Neurol. 347, 113895. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113895
Zhang, L., Wang, X., Lu, X., Ma, Y., Xin, X., Xu, X., et al. (2020). Tetramethylpyrazine enhanced the therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11 (1), 186. doi:10.1186/s13287-020-01700-z
Zhang, X., Chen, F., Sun, M., Wu, N., Liu, B., Yi, X., et al. (2023b). Microglia in the context of multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 14, 1157287. doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1157287
Zhang, Y., Gu, J., Wang, X., Li, L., Fu, L., Wang, D., et al. (2023a). Opportunities and challenges: mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Neurosci. 133 (9), 1031–1044. doi:10.1080/00207454.2022.2042690
Zhang, Z., Li, Z., Deng, W., He, Q., Wang, Q., Shi, W., et al. (2016). Ectoderm mesenchymal stem cells promote differentiation and maturation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 480 (4), 727–733. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.115
Zhang, Z., Zou, X., Zhang, R., Xie, Y., Feng, Z., Li, F., et al. (2021). Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-146a-5p reduces microglial-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of the IRAK1/TRAF6 signaling pathway after ischemic stroke. Aging 13(2), 3060–3079. doi:10.18632/aging.202466
Zhao, W. (2019). Contact or noncontact cocultures of articular chondrocytes with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: cell proliferation and differentiation. CJTER 23(1), 24.
Zhou, B., Xu, K., Zheng, X., Chen, T., Wang, J., Song, Y., et al. (2020b). Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 5 (1), 144. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00258-9
Zhou, X., Liu, X., Liu, L., Han, C., Xie, Z., Liu, X., et al. (2020a). Transplantation of IFN-γ primed hUCMSCs significantly improved outcomes of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in a mouse model. Neurochem. Res. 45 (7), 1510–1517. doi:10.1007/s11064-020-03009-y
Zhuo, Y., Li, X., He, Z., and Lu, M. (2023). Pathological mechanisms of neuroimmune response and multitarget disease-modifying therapies of mesenchymal stem cells in Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14 (1), 80. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03280-0
Keywords: multiple sclerosis (MS), mesenchymal stem cell (MSC), immunomodulation, autoimmune disease (AD), cell therapy
Citation: Sheikhi K, Ghaderi S, Firouzi H, Rahimibarghani S, Shabani E, Afkhami H and Yarahmadi A (2025) Recent advances in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for multiple sclerosis: clinical applications and challenges. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1517369. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1517369
Received: 25 October 2024; Accepted: 09 January 2025;
Published: 03 February 2025.
Edited by:
Katsumasa Goto, Toyohashi Sozo University, JapanReviewed by:
Ulises Gomez-Pinedo, Health Research Institute of Hospital Clínico San Carlos, SpainCopyright © 2025 Sheikhi, Ghaderi, Firouzi, Rahimibarghani, Shabani, Afkhami and Yarahmadi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hamed Afkhami, aGFtZWRhZmtoYW1pNzBAZ21haWwuY29t; Aref Yarahmadi, YXJlZi55YXJhaG1hZGkyNkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.