
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 24 January 2025
Sec. Cancer Cell Biology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1485422
Exosomes, as key mediators of intercellular communication, have been increasingly recognized for their role in the oncogenic processes, particularly in facilitating drug resistance. This article delves into the emerging evidence linking exosomal lncRNAs to the modulation of drug resistance mechanisms in cancers such as ovarian, cervical, and endometrial cancer. It synthesizes current research findings on how these lncRNAs influence cancer cell survival, tumor microenvironment, and chemotherapy efficacy. Additionally, the review highlights potential therapeutic strategies targeting exosomal lncRNAs, proposing a new frontier in overcoming drug resistance. By mapping the interface of exosomal lncRNAs and drug resistance, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding that could pave the way for innovative treatments and improved patient outcomes in female reproductive system cancers.
Neoplasms affecting the female reproductive organs, such as ovarian, cervical, and endometrial types, constitute a substantial global health challenge due to their high incidence and associated mortality (Bertone et al., 2004). These malignancies are distinguished by distinct biological characteristics, causes, and treatment responses (Carninci et al., 2005). Despite the progress in medical research, the outlook for individuals with late-stage reproductive neoplasms remains unfavorable, primarily due to emerging drug resistance. Deciphering the underlying mechanisms of this resistance is crucial for improving treatment efficacy and extending patient survival (Li et al., 2019a).
Exosomes, small extracellular vesicles derived from endosomes, have emerged as key players in intercellular communication (Zhang et al., 2018). They carry a diverse range of molecular constituents, including proteins, lipids, DNA, mRNA, and various non-coding RNAs. In the field of oncology, exosomes contribute to numerous processes such as tumor progression, metastasis, immune response modulation, and the development of drug resistance (Lakhotia et al., 2020). The role of exosomes in the tumor milieu and their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic agents have become focal points in cancer research (O’Brien et al., 2020).
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), a class of non-coding RNAs that exceed 200 nucleotides in length and are not predominantly involved in protein synthesis, were initially perceived as transcriptional noise (Bertone et al., 2004; Carninci et al., 2005). However, they are now recognized for their critical roles in gene expression regulation at several levels, including chromatin reconfiguration, transcription, and post-transcriptional processing. In cancer research, lncRNAs are known to play essential roles in regulating oncogenic and tumor suppressive pathways (Li et al., 2019a; Zhang et al., 2018). The discovery of lncRNAs in exosomes has opened new avenues for understanding drug resistance in cancer. These exosomal lncRNAs, which can be transferred among cancer cells and other cells within the tumor microenvironment, influence drug sensitivity and resistance (Bertone et al., 2004; Carninci et al., 2005). The mechanisms by which exosomal lncRNAs contribute to drug resistance are multifaceted, involving the modulation of cell death, drug efflux, DNA repair processes, and interactions in the tumor microenvironment (Lakhotia et al., 2020).
A primary obstacle in treating cancers of the female reproductive system is the onset of resistance to established chemotherapy protocols. This resistance, which can be inherent or acquired, frequently results in treatment failure and cancer progression. Investigating exosomal lncRNAs presents a promising approach to comprehend and potentially counteract this resistance. These entities may act as indicators for predicting therapeutic response and as novel targets to increase the susceptibility of cancer cells to treatments. Recent investigations are beginning to decode the intricate connections between exosomal lncRNAs and mechanisms of drug resistance in cancers of the female reproductive system. Though still in early stages, this research offers significant potential for devising new therapeutic approaches. The future trajectory in this domain involves a thorough analysis of exosomal lncRNAs, understanding their biological roles, and assessing their clinical application.
Exosomes are a subpopulation of extracellular vesicles (EVs), nanoscale structures with a lipid bilayer membrane performing their biological functions mainly by transferring cargoes such as proteins, RNAs, DNAs, and lipids in an intercellular communication substrate (Figure 1). Based on their size, EVs are divided into four groups: exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic bodies, and oncosomes (O’Brien et al., 2020). In cancer biology, among EVs, exosomes play the most important regulatory role (Chang et al., 2021; De Los Santos et al., 2019; Fontana et al., 2021). The term exosome (different from exosome complex, which plays a role in RNA degradation) was first applied to vesicles of unknown origin released from cultured cells with 5′-nucleotidase activity (van Niel et al., 2018), and they were thought to contain cellular waste (Harding and Stahl, 1983; Pan and Johnstone, 1983). Exosomes usually differ in size between 40 and 150 nm, and their surface contains marker proteins such as tetraspanins (CD63, CD81, CD82, and CD9), flotillin, and MHC, depending on their origin cell (Zhang et al., 2018; Hao et al., 2022). Generally, exosome biogenesis occurs within the endosomal system. Several steps of this process are regulated by intracellular and extracellular signals. At the start, the invagination of the plasma membrane forms a primary endosome, and the maturation of it goes on with continuous buddying of intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) into the primary endosome space. The primary endosome containing ILVs is known as the primary multivesicular body (MVB) at this stage (De Los Santos et al., 2019; Bebelman et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2022a). Two pathways have been identified in the process of ILV generation. One way requires ESCRT, a cluster of five subunits (ESCRT-0, ESCRT-I, ESCRT-II, ESCRT-III, and Vps4), and the other one is referred to as ESCRT-independent. It has been observed that the ESCRT-dependent pathway can actually be considered as the main pathway. There are also some other pathways dependent on ceramide or tetraspanins, which fall under the ESCRT-independent category. For example, nSMase2 produces ceramide via hydrolysis of sphingomyelin located in the MVB membrane, thus, playing a role in endosomal maturation (Fu et al., 2019; Trajkovic et al., 2008). In this stage, exosome cargoes are loaded into the exosome, and then transmembrane proteins such as tetraspanins are added to the exosome membrane, which means endosomal sorting is completed (van Niel et al., 2011). After that, the MVB may be destroyed via the lysosomal pathway or is converted into a mature MVB for exosomal release, which happens with the help of cytoskeleton proteins such as actin and microtubules (De Los Santos et al., 2019; Mashouri et al., 2019). Finally, Rab GTPase proteins such as Rab27a and Rab27b, which control vesicular transport, enable MVB binding and exosome release into the extracellular space (Mathieu et al., 2019; Ostrowski et al., 2010). Also, Rab27a and Rab27b have been shown to regulate the trafficking of the pro-invasive matrix metalloproteinase MMP14 (Macpherson et al., 2014). This process is aided by the SNARE complex that is responsible for MVB and cell membrane fusion (Hessvik and Llorente, 2018).
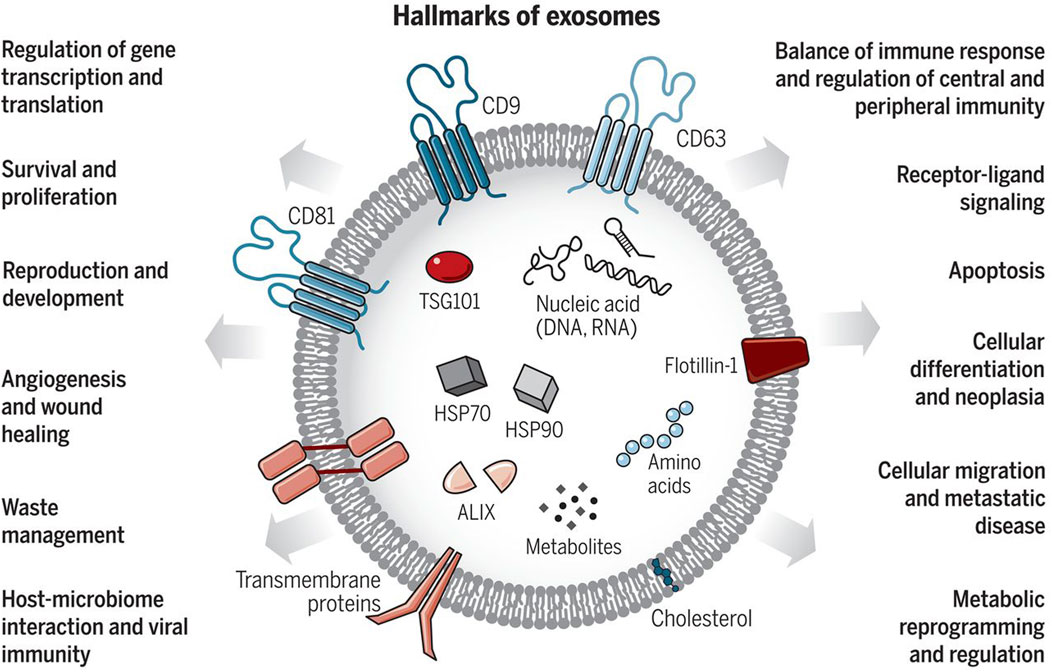
Figure 1. Exosomes: Sorting of Cellular Transport Network in Humans with Multifaceted Roles. Exosomes are tiny vesicles released by every cell type, encapsulating nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and metabolic products. Serving as conduits for both paracrine and autocrine cell communication, they play critical roles in both healthy and diseased states, influencing numerous cellular processes. Re-printed from Science (Chang et al., 2021).
Exosomes possess the ability to transport molecular cargos from a donor cell to a recipient cell; thus, they are considered a major piece of cell-cell communications (Hannafon and Ding, 2013). Dendritic cells, macrophages, cancer cells, and mesenchymal stem cells are only some of the cell types utilizing this mechanism as a means of local and systematic communication. Figure 2 describes the process of exosome biogenesis. As the cargos they carry to new cells are capable of exerting new biological changes, these exosomes can affect various mechanisms of cell biology in health and disease (Kalluri and LeBleu, 2020; Gurung et al., 2021). Table 1 outlines the crucial functions of exosomes in facilitating cell-cell communication, a fundamental process in both physiological and pathological contexts. After exosomes are released into the extracellular matrix (ECM), they proceed to their destination cell by taking one of the following pathways: autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, or endocrine (Hao et al., 2022). Uptake of exosomes is done depending on the cell they enter. Exosomes may bind directly to the surface receptors of a recipient cell through their surface ligands, such as glycans, lectins, integrins, or other cell adhesion molecules. This results in the activation of the downstream signaling pathway without internalization. In the second approach, exosome uptake is done through endocytosis, including clathrin-dependent endocytosis, clathrin-independent endocytosis, phagocytosis, or macropinocytosis. After exosomes enter recipient cells, endosomes containing them may be degraded within lysosomes, recycled through plasma membrane recombination, or released into target cells (Hessvik and Llorente, 2018; Gurung et al., 2021; Han et al., 2020; McKelvey et al., 2015).
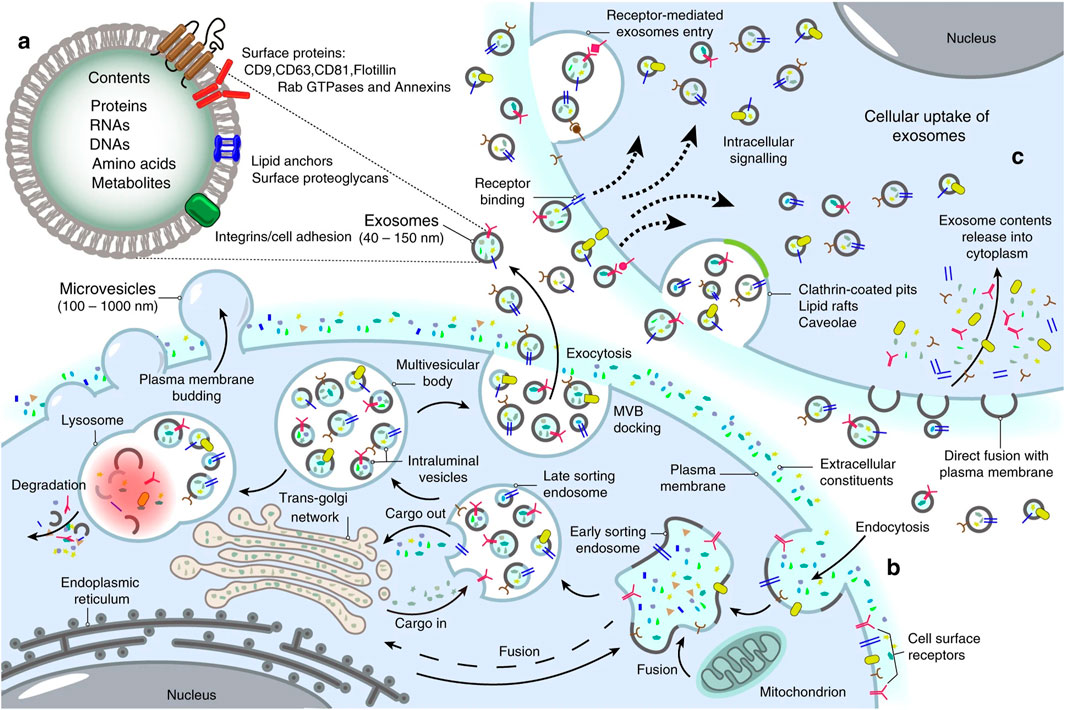
Figure 2. Landscape of exosome biogenesis. (A) Exosomes are composed of various proteins, nucleic acids, amino acids, and metabolites. Specific markers such as CD9, CD63, CD81, flotillin, and Annexins help identify them. (B) The process begins with the uptake of extracellular elements and cell surface proteins through endocytosis and invagination of the plasma membrane. This leads to the creation of early sorting endosomes (ESEs) through the merging of plasma membrane buds with components from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), trans-Golgi network (TGN), and mitochondria. ESEs evolve into late sorting endosomes (LSEs), where further invagination and cargo modification result in the production of intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) and the development of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Some MVBs merge with lysosomes for degradation of their contents, while others are transported to the cell surface, where they fuse with the plasma membrane. This fusion leads to the release of ILVs as exosomes outside the cell. (C) Exosomes can then enter other cells through various mechanisms, including direct fusion with the plasma membranes, receptor-mediated uptake, clathrin-coated pits, and lipid rafts. Re-printed from Springer Nature (De Los Santos et al., 2019).
Figure 3 describes the exosome and cargo recycling. Exosomes may partake in transferring various types of functional molecules such as lipids, proteins, and genetic material, and have been identified in different body fluids, including saliva, urine, breast milk, semen, blood, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (van Niel et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2016). These vesicles may play a different role based on their donor cell, their destination, or the cargos they carry. In addition, they can transfer bioactive molecules between cancer and other cells in the tumor microenvironment over near or long distances and are involved in cancer development by controlling processes such as immune system regulation, metastasis, angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), entry into quiescence (G0 phase), senescence, and drug resistance (Li, 2022; Soltész et al., 2021; Sundararajan et al., 2018; Tai et al., 2018). The fact that drug resistance can be induced in drug-sensitive cells through exosomes derived from exosome-resistant cells has been approved in several studies (Li and Nabet, 2019; Lobb et al., 2017; Mikamori et al., 2017; Takahashi et al., 2014a). Increasing the expression of multidrug resistance proteins, expelling chemotherapeutic drugs from cells, decreasing drug uptake, drug detoxification, and increasing DNA repair are some of the mechanisms through which exosomes increase drug resistance, all by releasing bioactive molecules in their target cells (Li, 2022; Sundararajan et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2020a; Li et al., 2020; Xie et al., 2019). Interestingly, some mediators of drug resistance, such as annexin 3 and RAB7, have been proven to participate in production of EVs in cancer cells. This means drug-resistant cells are eager to cause resistance in non-resistant cells (Guerra and Bucci, 2019; Xavier et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2012).
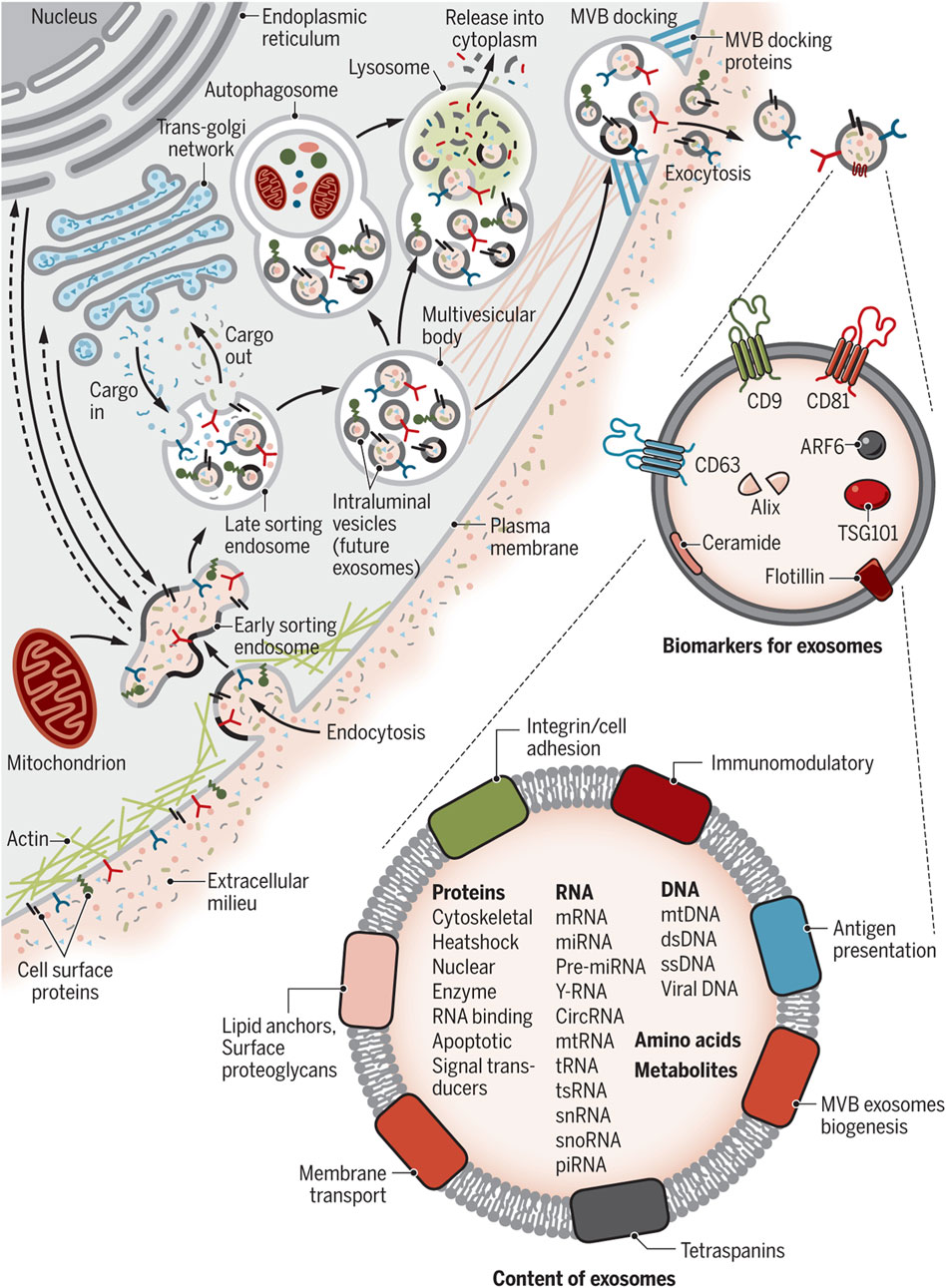
Figure 3. Exosome and cargo recycling. The process begins when various substances, including proteins, lipids, metabolites, and small molecules, enter cells through endocytosis or the inward folding of the cell membrane. This leads to the creation of early sorting endosomes (ESEs), either directly through budding or by merging with pre-existing ESEs formed from components of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), trans-Golgi network (TGN), and mitochondria. These ESEs can merge with the ER and TGN, suggesting a method for the endocytic materials to reach these organelles. ESEs, containing a mix of membrane and internal materials from various origins, evolve into late sorting endosomes (LSEs). A second folding within the LSE forms intraluminal vesicles (ILVs), altering the composition of what will become exosomes, including the entry of cytoplasmic elements into these vesicles. This process can distribute cell surface proteins across ILVs in a unique manner and lead to ILVs of different sizes and compositions. LSEs then develop into multivesicular bodies (MVBs) that contain these ILVs. MVBs may merge with autophagosomes for content degradation in lysosomes, or directly with lysosomes. Alternatively, MVBs can move to the cell surface, where they release exosomes through exocytosis, maintaining a similar membrane orientation. The creation of exosomes involves several proteins, such as Rab GTPases and ESCRT proteins, along with markers like CD9, CD81, CD63, and others. Exosomes are characterized by their content, which includes various proteins, RNAs, DNAs, amino acids, and metabolites, as well as surface proteins like tetraspanins and integrins. Re-printed from Science (Chang et al., 2021).
Complete sequencing of the human genome and developing technologies such as high-throughput next-generation sequencing have aided our understanding of coding and non-coding RNAs (Bertone et al., 2004; Carninci et al., 2005). About 75% of the human genome is transcribed into RNA, and of this amount of RNA, only 3% contains protein-coding mRNA (Yan and Bu, 2021). Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) can be classified into different types based on their transcript length, function, structure and position in the genome (Lakhotia et al., 2020). The ncRNAs that play an important role in regulating gene expression and have been studied in recent years include small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNA), and long ncRNAs (lncRNA) (Yan and Bu, 2021). According to a classification based on transcript size, ncRNAs are divided into two groups: small ncRNAs (less than 200 nt) and long ncRNAs (more than 200 nt) (Kashi et al., 2016; St Laurent et al., 2015). ciRNAs and lncRNAs are both composed of more than 200 nucleotides, and the difference lies in their structure. LncRNAs are generally linear molecules that can form complex seconary structures, such as stem-loops and hairpins, while circRNAs are characterized by a covalently closed loop, lacking 5′ and 3′ ends (Yan and Bu, 2021; Zampetaki et al., 2018). LncRNAs are mRNA-like transcripts longer than 200 nt with limited protein-coding potential (Gao et al., 2020; Sahu et al., 2015). Most of them are transcribed by the RNA polymerase II and have a polyadenylated 3′ end and a m7G-cap at their 5′ end (Statello et al., 2021). Unlike mRNA, lncRNAs usually lack an open reading frame, have fewer exons, and are also expressed at lower levels with more tissue-specific expression patterns. These types of ncRNAs have been under weaker pressure of natural selection during evolution, and many of them are specific to mammals (Li et al., 2019a; Zhang et al., 2018). LncRNAs are classified into different classes according to their location in the genome, sequence, length, morphology, structure, and functional properties. Based on their genomic position, there are six general groups: intergenic (between two protein-coding genes), intronic (in the intronic regions of the protein-coding gene), enhancer (eRNA; transcribed from the DNA sequence of the enhancer regions), sense (transcribed from the same strand and in the same direction as the neighboring protein-coding gene), antisense (transcribed from the opposite strand and in the opposite direction of the neighboring protein-coding gene), and bidirectional (1 Kb away from the promoter region of a protein-coding gene, and it is transcribed from the opposite strand) (Hermans-Beijnsberger et al., 2018; Blokhin et al., 2018; Sun and Kraus, 2015; Borkiewicz et al., 2021). Table 2 outlines the diverse roles and mechanisms through which long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in biological functions.
LncRNAs can be observed in a variety of intracellular components such as the nucleus or cytoplasm (Gudenas and Wang, 2018). LncRNAs are capable of modifying a landscape of cellular process, such as replication, pre/post transcription, and translation. They are able to regulate chromatin structure at various functional stages prior to transcription, which include histone methylation and acetylation, DNA methylation, and chromatin remodeling (Li et al., 2019a; Liu et al., 2022b). For example, the lncRNA HOTTIP binds to the WDR5-MLL complex and then, by targeting the ΄5HOXA locus, mediates activation of HOXA transcription through H3K4 methylation (Wang et al., 2011). In addition, lncPRESS1 plays an important role in regulating the cell differentiation process through its interaction with the deacetylase SIRT6 (Jain et al., 2016). Furthermore, lncRNAs can play the role of a cis-regulator or a trans-regulator, or they can interfere with imprinting in pre-transcriptional regulation (Sun and Kraus, 2015; Jarroux et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2021a; Yao et al., 2019; Kornienko et al., 2013). LncRNAs can also regulate gene expression by binding directly to transcription factors or the polymerase machinery or by interfering with polymerase-promoter bonds (He et al., 2019). For example, the lncRNA 7SK represses elongation by binding to the transcription factor PTEFβ and preventing its phosphorylation for elongation (Peterlin et al., 2012). The mechanisms of lncRNAs interfering with post-transcriptional regulation include regulation of mRNA alternative splicing, mRNA stability, protein stability, DNA regulation, regulation of protein localization, and acting as a sponge for miRNA (Li et al., 2019a; Statello et al., 2021; Pisignano and Ladomery, 2021; Karakas and Ozpolat, 2021; Zhou et al., 2019). For instance, the lncRNA TINCR interacts with the staufen1 (STAU1) protein to promote the stability and expression of differentiation-related mRNAs such as KRT80 (Kretz et al., 2013). Figure 4 provides examples of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and their mechanisms that contribute to cancer progression.
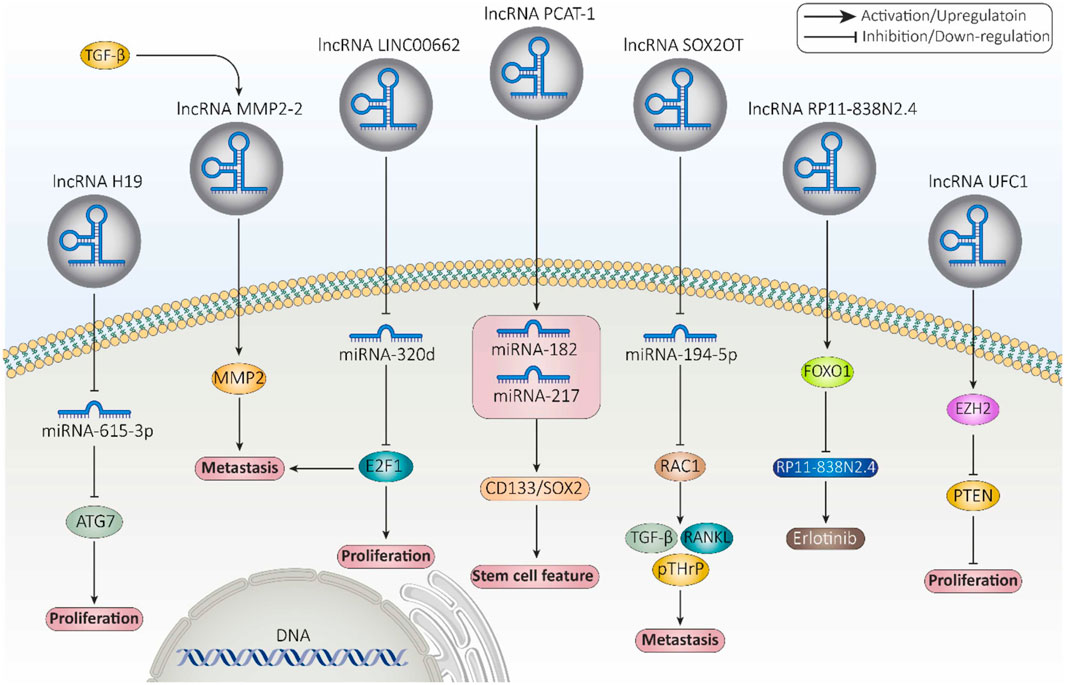
Figure 4. Examples of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and their mechanisms involved in cancer progression (Fontana et al., 2021).
Regarding the biological functions of lncRNAs and their significant contribution to both activation and inhibition of gene expression, lncRNAs have the potential to participate in various diseases such as cancer (Ahadi, 2021). According to multiple studies, dysregulation of lncRNAs may contribute to cancer initiation and development by affecting different biological processes and pathways such as proliferation, differentiation, metastasis, invasion, cell death, angiogenesis, cell cycle, and miRNA silencing (Ahadi, 2021; Smolarz et al., 2021). LncRNA SChLAP1 acts as an antagonist of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex in prostate cancer cells and contributes to metastasis and aggressiveness of cancer cells (Prensner et al., 2013). TFAP2A-AS1, which is associated with decreased expression in breast cancer, acts as a miRNA sponge for miR-933 and this way regulates Smad2 expression (Zhou et al., 2019). Among the lncRNAs related to various cancers are MALAT1, HOTAIR, LUCAT1, MRPS30-DT, and IFNG-AS1 (Taniue and Akimitsu, 2021; Xing et al., 2021; Hajjari and Salavaty, 2015; Shirani et al., 2024; Yaghoobi et al., 2018). Therefore, lncRNAs can be used in diagnosis and targeted therapy in cancer.
There is still no detailed understanding of how lncRNAs are packaged into exosomes. However, studies conducted have been suggesting that several proteins, including the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNP) family, such as hnRNPA2B1 (Chen et al., 2020a; Lei et al., 2018; Zheng et al., 2019) and hnRNPK (Gao et al., 2018) as well as human antigen R (HuR) (Deng et al., 2020) are some of the proteins that aid the sorting of lncRNAs into exosomes (Fabbiano et al., 2020). What is clear is that in almost every situation, RNAs are present as a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex in cells or exosomes. Thus, proteins with the ability of shaping a complex with RNAs are undoubtedly essential for the encapsulation of ncRNAs into exosomes (Zang et al., 2020).
One protein whose role in regulating lncRNAs has been proven is hnRNPA2B1 (Qiu et al., 2021). In bladder cancer (BC) cells, hnRNPA2B1 specifically binds to lncRNA LNMAT2 and is packed into exosomes. This was approved because hnRNPA2B1 knockdown had no effect on the expression levels of LNMAT2 in BC cells, but exosome levels of this lncRNA was evidently decreased (Chen et al., 2020a). LncRNA H19 in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) also forms a complex with hnRNPA2B1. The investigation by Lei et al. further proved that evaluated expression levels of hnRNPA2B1 promoted exosomal levels of H19 secreted by gefitinib-resistance cells of NSCLC (Lei et al., 2018). In another study conducted by Chen et al., lncARSR could bind to hnRNPA2B1 and be packaged into exosomes. hnRNPA2B1-lncARSR complex was seen in cytoplasm and exosomes rather than nucleus, which hnRNPA2B1 was initially identified. This observation proved that hnRNPA2B1 is specifically involved in the wrapping of lncARSR into the exosomes (Qu et al., 2016). Zheng et al. also indicated that in human breast cancer cells, hnRNPA2B1 is upregulated and has a correlation with the expression of exosomal lncRNA AGAP2AS1, and silencing hnRNPA2B1 resulted in downregulation of AGAP2AS1. Ultimately, it was proved that encapsulation of AGAP2AS1 into exosomes and its secretion outside breast cancer cells is done in an hnRNPA2B1-dependent manner (Zheng et al., 2019). Also, Gao et al. showcased the contribution of hnRNPK in the packaging of lncRNA 91H in colorectal cancer (CRC) which caused aggressive tumor relapse and metastasis (Gao et al., 2018). The study conducted by Liu et al. highlights the crucial role of exosomal long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), with a particular focus on LINC01133, in the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), an extremely aggressive and lethal form of cancer (Figure 5). It was found that LINC01133 is not just highly present in PDAC cases but also associated with more advanced cancer stages and lower survival rates in patients. The study explores how LINC01133 affects PDAC progression, showing that Periostin increases both exosome release and LINC01133 levels, which in turn activates several cancer-promoting processes such as cell growth, movement, invasion, and the transition from epithelial to mesenchymal states via the EGFR pathway and interaction with c-myc. Crucially, LINC01133 boosts the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through its interaction with EZH2, resulting in AXIN2 suppression and β-catenin activation via H3K27 trimethylation. These insights highlight the central role of exosomal LINC01133 in PDAC and propose that targeting LINC01133 could be an effective approach for treating this cancer (van Niel et al., 2018).
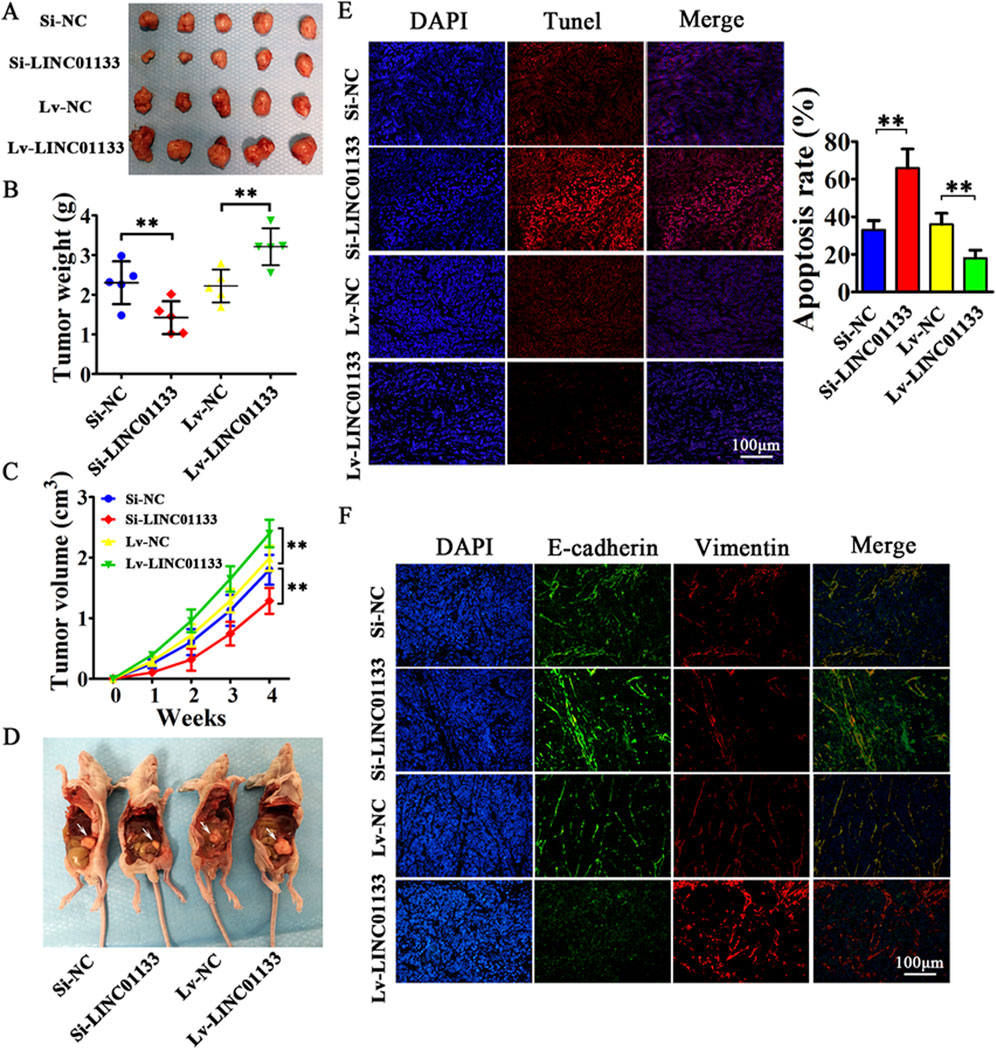
Figure 5. the results of an experiment where 4 million CFPAC-1 cells, treated with either Si-LINC01133, Si-NC, Lv-LINC01133, or Lv-NC, were injected into the right side of nude mice. (A) One month later, the mice were euthanized, and the tumor grafts were removed for analysis. (B) The findings showed that CFPAC-1 cells treated with Lv-LINC01133 resulted in heavier xenografts, while those treated with Si-LINC01133 led to lighter xenografts. (C) Additionally, CFPAC-1 cells exposed to Lv-LINC01133 demonstrated faster growth and larger tumor volumes compared to those treated with Si-LINC01133, which exhibited slower growth and smaller tumor volumes. (D) Furthermore, when 1 million CFPAC-1 cells treated with each of the substances were injected into the lower left abdomen quadrant, the spread within the abdominal cavity was assessed, with metastatic nodules identified by white arrowheads. (E) The study also found that LINC01133 significantly reduced apoptosis in the xenograft tumors of CFPAC-1 cells, as verified by TUNEL assay, with the apoptosis rate measured across five random fields in three repeated experiments. (F) Lastly, the expression levels of E-cadherin and Vimentin in the xenograft tumors were examined through immunofluorescence. Re-printed from Springer Nature (van Niel et al., 2018).
The type of a cell and its homeostatic state define the ncRNAs that load into an exosome with other cargos; however, not much is known about the exact mechanisms and factors that contribute to the selective sorting of lncRNAs into exosomes (Qiu et al., 2021). Nevertheless, some nucleotide sequences have been identified on RNAs that can determine how RNAs are chosen and then packed into exosomes (Groot and Lee, 2020; Hoek et al., 1998; Hwang et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2010b). Ahadi et al., investigated some exosomal lncRNAs secreted from four different prostate cancer cell lines (VCaP, LNCaP, DU145, PC3) and one normal prostate cell line. The aim was to determine if any specific RBP binding sites on lncRNAs could be found. They were able to identify 126 different six-base motifs that were particularly expressed in the four prostate cancer cell lines but not the healthy prostate cell line (Ahadi et al., 2016). Chen et al. found that there is a sequence of GGAG on the 1930-1960 nt region of LNMAT2 that binds with hnRNPA2B1 specifically. This sequence is located on a stem-loop structure and is recognized by hnRNPA2B1 (Chen et al., 2020a). In the case of exosomal lncRNA H19 originated from NSCLC, Lei et al. found the same special sequence of GGAG at the 5′ -end of the lncRNA which was the specific binding site of hnRNPA2B1 (Lei et al., 2018). Moreover, in RCC cells, lncARSR could bind to hnRNPA2B1 through its special motifs (GGAG/CCCU) at the 5′ terminal region (Qu et al., 2016).
A tumor microenvironment (TME) is a mixture of non-cancerous cells, blood vessels, secreted factors, and extracellular matrix (ECM), which collectively promote the growth of a tumor. From the beginning of the tumor growth, the cancer cells start to have interactions with their surrounding normal cells through secreting exosomes and will induce the transformation of their local environment to shape the desired TME that supports immunosuppression, cancer cell survival, local invasion, and metastatic dissemination (Chen et al., 2019a; Jin and Jin, 2020; Pathania and Challagundla, 2021). LncRNAs constitute a significant portion of this cell-cell communication between cancer cells and TME (Pathania and Challagundla, 2021). LncRNAs secreted from tumor cells can affect ECM, stromal cells, immune cells, endothelial cells, macrophages, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) (Chen et al., 2019a). One major event during tumor progression is the lack of oxygen supply or hypoxia. This situation leads to the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α pathway and eventually a great deal of lncRNAs are produced and secreted into TME that elevate cell survival (Masoud and Li, 2015; Takahashi et al., 2014b). For instance, in BC cell line 5637, lncRNA urothelial cancer-associated 1 (UCA1) is secreted during hypoxia condition and aids tumor promotion via epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Xue et al., 2017). In another study it was shown that CCAL (colorectal cancer-associated lncRNA) is transferred from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) to cancer cells via exosomes. Once inside the CRC cells, CCAL suppresses apoptosis, enhances chemoresistance, and activates the β-catenin pathway, both in vitro and in vivo (Deng et al., 2020). Furthermore, Liang et al., found that exosomes derived from CRC cells transport lncRNA RPPH1 into macrophages. This transfer promotes the polarization of macrophages into the M2 phenotype, which in turn facilitates metastasis and proliferation of CRC cells. Additionally, levels of exosomal RPPH1 in blood plasma were higher in treatment-naive CRC patients but decreased after tumor resection (Liang et al., 2019). Another study on CRC showed that the expression of lncRNA 91H in serum was closely associated with exosomes, both in vitro and in vivo. The association was likely to enhance tumor-cell migration and invasion during tumor development by altering HNRNPK expression. Also, CRC patients with high levels of lncRNA 91H expression had a higher risk of tumor recurrence and metastasis compared to patients with low lncRNA 91H expression (Gao et al., 2018). Moreover, Pan et al., found that the expression of ZFAS1 was elevated in tumor tissues, serum, and serum exosomes of GC patients, which was significantly correlated with lymphatic metastasis and the TNM stage of the disease (Pan et al., 2017).
Some other exosomal lncRNAs have been identified that can contribute to cell growth (Zhao et al., 2019a), proliferation (Zhao et al., 2019a; Xu et al., 2020a; Hu and Hu, 2019; Conigliaro et al., 2015), angiogenesis (Chen et al., 2020a; Conigliaro et al., 2015), migration (Chen et al., 2020a; Zhao et al., 2019a; Xu et al., 2020a; Hu and Hu, 2019; Chen et al., 2020b; Feng et al., 2019), invasion (Xu et al., 2020a; Chen et al., 2020b; Lu et al., 2020), metastasis (Chen et al., 2020a; Zhao et al., 2019a), drug resistance through activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in recipient cells (Deng et al., 2020), inhibition of apoptosis (Chen et al., 2020b; Yin et al., 2020; Song et al., 2020), and inhibition of inflammation (Song et al., 2020; Li et al., 2018a), all of which ultimately promotes tumor growth. Lastly, recent studies have pointed out the involvement of exosomal lncRNAs in autophagy. Tumor cells tend to upregulate autophagy in order to minimize environmental stress, protect themselves from chemotherapy, and maintain their fuel supply. Exosomal lncRNAs have been proven to play a significant role in inducing autophagy which leads to cell survival and proliferation (Pathania and Challagundla, 2021; Sun et al., 2013). For example, high lncRNA-CAF levels in normal stromal fibroblasts reinforce tumor proliferation, and are associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients (Ding et al., 2018). Table 3 details the specific roles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) contained within exosomes in the context of tumor microenvironment modulation.
Drug resistance has long been an issue in many cancer studies. Despite the efforts and successes in cancer treatment, anticancer drug resistance remains a major problem in the treatment of this disease and has a significant impact on the clinical outcome (Mondal and Meeran, 2021; Vasan et al., 2019). In general, there are two types of drug resistance: intrinsic, which exists before treatment starts, and acquired resistance. In acquired resistance, cancer cells that have already received the drugs can acquire resistance to the treatment at later stages, which is the most important cause of relapse and death in cancer patients (Wang et al., 2019a). Chemical resistance can be divided into two categories: single-drug resistance and multidrug resistance. In the case of single-drug resistance, the cancer cells are resistant to a specific drug. In contrast, multidrug resistance occurs when the cancer cells are resistant not only to the drugs currently being used, but also to other chemotherapeutic agents to which they have not previously been exposed (Gacche and Assaraf, 2018). MDR is one of the most important mechanisms in the development of drug resistance and is responsible for more than 90% of deaths in cancer patients receiving anticancer drugs. The major mechanisms in the development of MDR include overexpression of ABC transporters, defects in the apoptotic system, alterations in drug metabolism or drug targets, epigenetic changes, oncogene amplification, and increased DNA repair capacity (Bukowski et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2014; Vaidya et al., 2022).
Currently, most breast cancer therapies are based on targeted treatments, as this disease has considerable heterogeneity. ER+ (estrogen receptor) and PR+ (progesterone receptor) breast cancers belong to the subtype of hormone-dependent cancers (Kinnel et al., 2023). Approximately 70%–80% of all breast cancers are HR+, which can be effectively treated by endocrine therapy or anti-estrogen therapy by modulating ER or lowering estrogen levels. One of the main drugs in the treatment of HR + breast cancer is tamoxifen. This drug is a selective estrogen receptor modulator that blocks the effect of estrogen on ER-positive breast cancer cells. Hormone therapy for premenopausal women includes administration of tamoxifen alone or a combination of a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analog with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor (AI). Postmenopausal women are treated with aromatase inhibitors such as letrozole and exemestane or tamoxifen combined with SERDs (selective estrogen receptor degraders) like fulvestrant (Kay et al., 2021). Also, abemaciclib is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) that was recently approved for HR + advanced breast cancer in combination with endocrine therapy (Johnston et al., 2020). The role of tyrosine kinase receptors (activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway), transcription factors (activation of the C-MYC/HDAC5/SOX9 axis), cell cycle regulators (interaction of LEM4 with CDK 4/6 and Rb to accelerate the G1–S transition), and autophagy (activation of LAMP3) are among the mechanisms involved in tamoxifen resistance (Yao et al., 2020). 15%–20% of breast cancers have overexpression of the HER-2 gene and are more aggressive than HER-2 negative breast cancers (Le Du et al., 2021). Trastuzumab, a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody, has been one of the first drugs used in the treatment of HER-2+ breast cancer. First-line therapy for most patients consists of a mix of trastuzumab, pertuzumab (another monoclonal antibody), and taxanes (a class of chemotherapeutic agents), while trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) is the second-line therapy (Kay et al., 2021; Le Du et al., 2021; Martínez-Sáez and Prat, 2021). Several novel treatments such as tucatinib, lapatinib, neratinib, fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki (DS-8201a), and margetuximab-cmkb that have recently been approved are among the third-line treatment options (Martínez-Sáez and Prat, 2021). Despite medical advances in the treatment of this type of breast cancer, approximately 22%–25% of HER-2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients have congenital or acquired drug resistance, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality (Choong et al., 2020). Mechanisms of drug resistance in HER-2+ breast cancer include inadequate blockade of the HER-2 receptor, activation of downstream signaling pathways like PI3K and MAPK, inhibition of tumor suppressor genes, acquired HER-2 mutations, dysregulation of cell cycle regulators (high copy number of the CCND1 gene encoding cyclin D1), and non-cell autonomous mechanisms within the tumor microenvironment (Kay et al., 2021; Choong et al., 2020; Zhang, 2021). Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacks ER, PR, and HER-2 receptors. It accounts for 15%–20% of all breast cancers, and due to its heterogeneity and complexity, treatment strategies are usually unsuccessful (Merikhian et al., 2021; Marra et al., 2020). Currently, chemotherapy is the first line of treatment, and most patients become resistant to chemotherapeutic agents (Cosentino et al., 2021). Conventional chemotherapy used in TNBC treatment can be divided into two categories: neoadjuvant therapy and adjuvant therapy. Anthracycline–cyclophosphamide drugs (AC regimen) such as doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide and paclitaxel are used in neoadjuvant therapy, which can improve the efficacy of treatment when combined with cisplatin. Other neoadjuvant drugs include carboplatin, Abraxane, and bevacizumab (a monoclonal antibody that inhibits VEGF activation). Neoadjuvant therapy also utilizes anthracycline-taxane like doxorubicin, docetaxel, and cyclophosphamide. In cases of advanced or metastatic breast cancers where these drugs are ineffective, capecitabine may be given alone or in combination with docetaxel (Medina et al., 2020). Some mechanisms involved in TNBC chemoresistance are upregulation of ABC transporters (an important mechanism), presence of cancer stem cells (CSCs), hypoxia, and TP53 mutations (Marra et al., 2020).
Ovarian cancer treatment generally begins with surgical removal and is followed by chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Alatise et al., 2022). High-dose chemotherapy usually leads to drug resistance development in patients, and about 80% of patients experience a relapse after treatment and gradually become resistant to chemotherapeutic agents (Alatise et al., 2022; Brasseur et al., 2017). Platinum-based and taxane-based drugs, including cisplatin (DDP), are mainly used to treat ovarian cancer, and resistance to these drugs has caused many problems so far (Alatise et al., 2022; Cui, 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). In advanced cases, a combination of cisplatin with gemcitabine is recommended to increase the response to cisplatin treatment (Garrido et al., 2021).
Ovarian cancer (OC) is categorized into two main types: epithelial OC and non-epithelial OC. Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of all malignant ovarian tumors. EOC consists of several subtypes, including endometrioid, clear cell, serous carcinoma [low-grade serous carcinoma (LGSOC) and high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC)], undifferentiated, and mucinous. Among these, HGSOC is the most common subtype and is responsible for 75% of EOC cases (Lukanović et al., 2022; Gaona-Luviano et al., 2020; Shih et al., 2021). Recently, polyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerases (PARP) inhibitors (niraparib, cediranib, olaparib, and pembrolizumab) and anti-angiogenic options (trebananib, sorafenib, entrectinib) have been shown to be effective in the treatment of epithelial origin (EOC) (Garrido et al., 2021). The endometrioid and clear cell subtypes make up 20%–25% and 5%–10% of EOCs, respectively (Zhou et al., 2021c). In one study, a signaling pathway was discovered that can be targeted to increase the sensitivity of platinum-resistant ovarian endometrioid cancer cells to chemotherapy. The study revealed that using non-receptor tyrosine kinase Lymphocyte Cell-Specific Protein-Tyrosine Kinase inhibitors (LCKi) followed by co-treatment with cisplatin resulted in lower cell viability and increased cell death in laboratory tests. This effect was associated with increased DNA adduct formation and reduced tumor growth in vivo (Crean-Tate et al., 2021). Clear cell carcinoma (CCC) is one of the most common chemoresistant cancers. However, the precise mechanisms underlying drug resistance in this type of cancer are not fully understood. Studies have demonstrated that genes associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway are markedly elevated in cases of ovarian CCC that do not respond to chemotherapy. This suggests that the EMT pathway plays a crucial role in the development of chemotherapy resistance (Takahashi et al., 2023). Although 60%–80% of patients with HGSOC initially exhibit a positive response to treatment, most will eventually develop resistance to platinum-based therapies. Epigenetic modifications like DNA methylation, histone deacetylation, and microRNA expression have been linked to the development of chemoresistance in HGSOC. For instance, hypomethylation of MSX1 contributes to EMT by promoting cancer cell transition to a mesenchymal phenotype, resulting in chemoresistant HGSOC patients. These modifications could be targeted by epigenetic modulation therapies to overcome chemoresistance (Matthews et al., 2021).
Non-epithelial ovarian cancers (NEOC) are rare malignancies, accounting for approximately 10% of all ovarian cancer cases. This group mainly comprises germ cell tumors (GCT), sex cord-stromal tumors (SCST), and a few exceptionally rare tumor subtypes (Martínez-Sáez and Prat, 2021). GCTs and SCSTs represent 2%–5% and 2% of ovarian cancers, respectively. Cisplatin-based chemotherapy with surgery can effectively treat most GCTs. However, resistance to cisplatin (CDDP) can develop due to changes in the levels of critical factors such as p53, mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2), octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (Oct4), and cytoplasmic p21. Due to the lack of high-quality studies in this area, current practice guidelines recommend using chemotherapy regimens established for testicular germ cell tumors due to their similar origin (De Giorgi et al., 2019; Uccello et al., 2020). The current targeted therapy approaches being studied in clinical trials for GCTs and SCSTs include tyrosine kinase inhibitors, angiogenesis inhibition, immunotherapy, and endocrine therapy. However, there is still limited research on many aspects of non-epithelial ovarian tumors, especially their resistance to chemotherapy (Maoz et al., 2020).
Examples of chemotherapy resistance mechanisms in ovarian cancer include expression of anti-apoptotic proteins, overexpression of MAPK-activating death domain protein (MADD), disruption of major DNA repair pathways, increased efflux due to high expression of APC transporters, and the presence of a small subset of cancer stem cells (CSCs) (Alatise et al., 2022; Ortiz et al., 2022).
Cervical cancer has two main types: squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), accounting for about 75% of cases, and adenocarcinomas, responsible for approximately 25% of cervical cancers.
High-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, predominantly types 16 and 18, is considered a major factor in the development of most SCCs (Volkova et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023). Although, HPV-independent tumors are associated with both adenocarcinomas and squamous histologic subtypes (Fernandes et al., 2022). HPV-negative cervical cancers have a more aggressive course, which is clinically significant (Volkova et al., 2021). HPV oncoproteins like E6 and E7, which inactivate tumor suppressor genes p53 and Rb, further promote resistance by allowing cells to evade apoptosis (Xiong et al., 2022).
Surgery and radiotherapy are the main treatments of cervical cancer, and chemotherapy is often used if metastasis or tumor recurrence happens (Li et al., 2017). One of the main chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cervical cancer is cisplatin, which exerts its effects by attacking DNA and forming irreparable bonds with it (Mahapatra et al., 2022). Research has shown that the combination of platinum and paclitaxel has better efficacy in treatment response compared with cisplatin alone (Della Corte et al., 2020). In advanced cervical cancer, patients become resistant to these drugs, and cancer cells evade its anti-cancer effects; therefore, finding a solution to overcome the acquired resistance is of great importance (Mahapatra et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2016a). Acquired cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer therapy is due to decreased uptake of cisplatin (downregulation of the transmembrane protein CTR1), increased efflux (overexpression of MRP1), inactivation of the apoptotic pathway, inactivation of proteins containing thiol groups, and activation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Bhattacharjee et al., 2022).
Endometrial cancer is a common gynecological cancer that affects the uterus. According to Bokhman’s classification, it is divided into two types: estrogen-independent, which has a poorer outlook and is often diagnosed late, and estrogen-dependent endometrial cancers. Moreover, WHO classifies endometrial cancer into four types: endometrioid endometrial cancer (EEC), serous adenocarcinoma, clear cell adenocarcinoma and mixed endometrial cancer and uterine carcinosarcoma. EECs are generally estrogen-dependent tumors and are the most common type of endometrial cancer, accounting for more than 80% of cases (Yang et al., 2024). Treatment typically involves surgery, vaginal brachytherapy, external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) and in advanced cases, carboplatin, paclitaxel, adriamycin, and cisplatin may be administered (Saito et al., 2021). For hormone receptor-positive cancers, hormone therapies such as progestins, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, or aromatase inhibitors are used (Kailasam and Langstraat, 2022). Emerging treatments include immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab, particularly for cancers with microsatellite instability (MSI) or mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR), and targeted therapies such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors (Yang et al., 2024; Jeong et al., 2023; Venkata et al., 2022; Colombo et al., 2024). Resistance to treatment in endometrial cancer often occurs due to activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, especially in tumors with mutations in the PIK3CA gene or loss of PTEN function. These mutations promote cell survival and reduce the effectiveness of hormonal and chemotherapeutic treatments (Yang et al., 2024; Lee, 2021). Additionally, some endometrial cancers that initially respond to immunotherapy can develop resistance by upregulating immune evasion mechanisms, such as increased PD-L1 expression, while hormone therapy resistance is often linked to mutations in estrogen and progesterone receptors (Yang et al., 2024; Hao et al., 2024). Table 4 provides a list of various drugs and how they cause drug resistance in different types of cancers.
LncRNAs have emerged as significant players in the molecular landscape of various cancers, including gynecological cancers. Table 5, which focuses on clinical trials investigating the role of lncRNAs in cancers, provides an overview of the ongoing and completed studies aimed at understanding how these molecules influence cancer development, progression, and response to treatment.
Approximately 98% of the human genome is made up of ncRNAs. They were once believed to be transcriptional waste, but recent studies have proven this theory wrong. ncRNAs are in fact functional factors with the ability to regulate a great number of molecular processes (Wang et al., 2021b). It was discovered that certain lncRNAs are upregulated in cancer cells or patients, as well as in exosomes present in serum or other body fluids of patients. Further investigations proved that these exosomal lncRNAs could actually aid a number of cancer cell characteristics including drug resistance, as well as conferring these characteristics in new cells through exosomal transfer. This notion was proven when exosomal lncRNAs that showed correlation with other contributing factors in cancer drug resistance were targeted in a number of malignancies and resistant cells were resensitized to cancer drugs (De Los Santos et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021b; Guo et al., 2020c). For example, downregulation of lncRNA HOXA transcript at the distal tip (HOTTIP) made gastric cancer (GC) cells sensitive to cisplatin. In addition, HOTTIP were packaged into exosomes and transmitted to sensitive cells, which made them resistant to cisplatin (Wang et al., 2019b). High levels of SBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SBF2-AS1) were detected in exosomes secreted from glioblastomas (GBM) cells and were associated with poor response to temozolomide (TMZ). These exosomes were also able to transfer lncRNA SBF2-AS1 to chemoresponsive cells. Therefore, the previously sensitive cells would show resistance to TMZ (Zhang et al., 2019). In another study, urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 (UCA1) levels were much higher in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer (CRC) cells than that of sensitive cells. The same trend was noticed in progressive disease patients compared to partially or completely responsive patients. Moreover, exosomes from resistant cells could modulate UCA1 expression in recipient sensitive cells and disseminate resistance in them (Yang et al., 2018). Takahashi et al. also investigated the role of lincRNA-ROR (linc-ROR) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. After confirming upregulation of linc-ROR in sorafenib-resistant cells, cells were treated with small interfering RNA (siRNA) lincRNA-ROR-1. This resulted in increased early apoptosis and total apoptotic cells. It was concluded that linc-ROR contributed to apoptosis suppression and cell survival promotion by altering chemosensitivity (Takahashi et al., 2014c).
Integral transmission of genetic information is a direct consequence of faultless DNA replication and orderly progression of cell cycle (Brandmaier et al., 2017). Principally, cell cycle is a conserved process in organisms, from unicellular eukaryotes to complex metazoans (Asghar et al., 2015). This procedure takes place in accordance with cell signals that mark the right time of phase transition (G0/G1, S, G2, and M) (Otto and Sicinski, 2017). Errors in cell cycle and the resulting uncontrolled cell proliferation is one of the fundamental characteristics of cancer (Otto and Sicinski, 2017; Malumbres and Barbacid, 2009). Cell cycle in mammals is primarily regulated by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), their activators, and inhibitors. CDKs are a subfamily of regulatory enzymes that have a periodic activation and deactivation (Asghar et al., 2015; Malumbres and Barbacid, 2009; Ye et al., 2022). In cancer cells, the occurrence of genetic or epigenetic changes in the mentioned regulators leads to cell cycle disruption, which is followed by genetic instabilities such as increased DNA mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, and changes in the number of chromosomes (Malumbres and Barbacid, 2009). According to some studies, a number of exosome-derived lncRNAs have the ability to neutralize the effects of drugs that aim to repress cell proliferation and contribute to tumor progression (Ye et al., 2022).
One major mechanism of homeostasis that forms balance between cell survival and death, is apoptosis or programmed cell death. This process can be induced or inhibited by intracellular or extracellular signals through different pathways. During tumor progression, the balance between anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic regulators is disrupted, resulting in higher cancer cell survival (Dogan et al., 2022). Inducing apoptosis in cancer cells has been a very common approach in designing anticancer drugs, and exosomal lncRNAs seem to have developed mechanisms to interfere with drug functions. By suppressing apoptosis, lncRNAs cause drug resistance in a variety of malignancies (Takeiwa et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2019b).
Sufficient intracellular concentration is one of the main prerequisites for anticancer drugs to exert their cytotoxic effects. In response, cancer cells have strengthened a coping mechanism named drug efflux, which can be exerted through different paths. One example is the direct transfer of drugs outside the cell by exosomes (Dong et al., 2020; Xue et al., 2022). In 2003, Shedden et al. showed that breast cancer cells are capable of expelling doxorubicin outside the cell with the help of exosomes (Shedden et al., 2003). Another way is through upregulating drug efflux pumps (Dong et al., 2020). Overexpression of the ABC transporter family is one of the most known and studied causes of multidrug resistance. ABC transporter proteins can pump chemotherapy drugs out of the cancer cell against the concentration gradient in an ATP-dependent manner, thereby reducing intracellular accumulation of the drug and protecting the cancer cell from chemotherapeutic agents. So far, 48 ABC transporters have been identified. Among the most considerable ones are multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) (International Transporter Consortium et al., 2010). Drug efflux caused by increased number of ABC transporters is one of the criteria which lncRNAs can control and cause tumor recurrence (Pathania and Challagundla, 2021).
Autophagy is a regulatory self-destructive process that occurs in response to stress, such as organelle damage, the presence of abnormal proteins, hypoxia, nutrient deficiency, aging, cell death, or cancer in order to maintain homeostasis (Ariosa et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2018; Ueno et al., 2019). Currently, there are three known forms of autophagy, including macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-associated autophagy, which differ in accordance to the delivery methods of cargoes to lysosome for either degradation and recycling. The term “autophagy” usually refers to macroautophagy (Shan et al., 2021). Autophagy starts with formation of autophagosomes containing degraded components, then the autophagosome is combined with a lysosome to form an autolysosome. Finally, the internal materials are broken down and recycled (Du et al., 2021; Yun and Lee, 2018). Autophagy also plays an important role in tumor drug resistance (Chang and Zou, 2020; Li et al., 2019c). Autophagy takes two different approaches facing tumor cells. In the positive approach, autophagy causes cell death in cancer cells by suppressing apoptotic pathways. In the negative approach, on the other hand, it protects cancer cells from chemotherapy drugs. Hence, autophagy helps cancer cell survival in the time of hypoxia or metabolic stress and reduces the damages caused by antitumor drugs (Li et al., 2019c; Liu et al., 2020; New and Thomas, 2019; Sun et al., 2020). Several studies indicate the role of lncRNAs as autophagy regulators in cancer drug resistance (Bermúdez et al., 2019; Jin et al., 2020).
Epigenetic changes are common in tumorigenesis, and so far their role has been observed in many molecular mechanisms of cancer, such as resistance to apoptosis, DNA repair, increased drug efflux and drug detoxification (Adhikari et al., 2022). In the course of tumorigenesis, a complex network of signaling pathways are vulnerable to aberrant epigenetic changes (Toh et al., 2017). Many studies conducted in the area of drug resistance indicate the occurrence of epigenetic changes, and state that acquired drug resistance in cancer does not necessarily require a permanent genetic change (Adhikari et al., 2022; Sharma et al., 2010). Based on the studies, cancer cells apply their epigenetic modulations through methylation, acetylation or other modifications of histone and non-histone proteins (Adhikari et al., 2022).
Studies conducted in the field of cancer drug resistance have identified a number of key exosome-derived lncRNAs playing significant roles in this regard. Deng et al. investigated the role of lncRNA colorectal cancer-associated (CCAL) in CRC cells. Higher expression levels of CCAL were recorded in the tumor stroma compared to cancer cells. Exosomal CCAL was produced in CAFs and later transferred to CRC cells, where they caused apoptosis suppression and resistance to oxaliplatin. This action was done through direct interaction of CCAL with HuR, which activates the β-catenin pathway and confers chemoresistance (Deng et al., 2020). In another study done by Ren et al., lncRNA H19 secreted by CAFs was found to be promoting chemoresistance and stemness in CRC cells. H19 would act as a ceRNA for miR-141, which is responsible for inhibiting the stemness of cells. This whole situation would first activate the β-catenin pathway and second promote the stemness of the cells (Ren et al., 2018). In a 2018 study by Yang et al., high levels of lncRNA UCA1 were found in CRC patient’s serum. Further investigations showed that UCA1 plays a role in conferring resistance to cetuximab, and if transferred to sensitive cells by exosomes, has the ability to make them resistant to the drug (Yang et al., 2018).
lncRNA HOTTIP was found to be upregulated in GC cells resistant to cisplatin. In GC cells, miR-218 was proved to bind to HOTTIP in order to inhibit its actions. In response to that, HOTTIP would activate HMGA1, a target for miR-218. By modulating miR-218/HMGA1 axis, lncRNA HOTTIP could promote cisplatin resistance in GC cells (Wang et al., 2019b). Overexpression of lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in TMZ-resistant GBM cells and tissues was observed by Zhang et al. It was discovered that ZEB1, a transcription factor, binds to SBF2-AS1 promoter region and upregulates its expression. X-ray repair cross complementing 4 (XRCC4) is an enhancer of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) repair, and its function is limited by miR-151a-3p. In GBM cells, SBF2-AS1 acts as a ceRNA for miR-151a-3p. This eventually leads to poor response to TMZ treatment (Zhang et al., 2019).
In human HCC, the most common type of primary liver cancer, linc-ROR, a stress-responsive lncRNA, was remarkably upregulated and enriched within extracellular vesicles secreted from tumor cells. Among the liver cells, stem cells with CD133 surface markers were seen to exhibit higher rates of drug resistance. It was revealed that in CD133+ cells, transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) modulated the expression and secretion pattern of lincRNA-ROR in response to being treated with sorafenib or doxorubicin. linc-ROR was proved to participate in increasing drug resistance by modulating caspase-3/7 activity; thus contributing to a chemoresistant phenotype (Takahashi et al., 2014c).
Several exosome-derived lncRNAs have been identified to play crucial roles in conferring drug resistance through various mechanisms such as modulating cell cycle, apoptosis, drug efflux, autophagy, and epigenetic changes. The following sections will discuss specific case studies that illustrate how exosomal lncRNAs influence drug resistance in breast, ovarian, and cervical cancers. These studies provide insights into the molecular pathways and potential therapeutic targets that could be leveraged to overcome drug resistance in these malignancies.
In a study conducted by Zhou et al., increased expression of lncRNA NEAT1 was observed in serum EVs of a group of breast cancer patients. The EVs were about 40–100 nm in diameter (Zhou et al., 2021d), which corresponds to the approximate diameter range of exosomes (Hao et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2016). Two breast cancer cell lines were treated with extracted EVs of the patients. The EVs were absorbed by the cell lines. Further research revealed that lncRNA NEAT1 binds to miR-141-3p, and causes KLF12 overexpression (Zhou et al., 2021d). KLF12 is a transcription factor and its overexpression has been confirmed in a number of cancers (Zhou et al., 2021d; Yang et al., 2022). Elevated expression of lncRNA NEAT1 was associated with increased proliferation, invasion, and migration, as well as resistance to cisplatin, paclitaxel, and 5-FU. Also, treating the cell lines with NEAT1 siRNA, resensitized them to the drugs, prevented colony formation, induced apoptosis, and reduced MDR1 expression (Zhou et al., 2021d). Tang et al. found that high expression of lncRNA HOTAIR-containing exosomes in serum extracted from breast tumor tissues was associated with poor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. It was also shown that overexpressed lncRNA HOTAIR is responsible for resistance to tamoxifen hormone therapy. To date, no information has been reported about how lncRNA HOTAIR exerts its involvement in breast cancer chemoresistance (Tang et al., 2019a). However, one study confirmed that lncRNA HOTAIR induces tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer patients through enhancing ER signaling (Xue et al., 2016). Xu et al. confirmed that the expression of lncRNA UCA1 in a tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell line was 20-fold higher than a sensitive cell line. Further testing showed that exosomes secreted by resistant cells can induce resistance to tamoxifen, resulting in increased cell survival and repressed apoptosis in sensitive cells. Moreover, knockdown of exosomal lncRNA UCA1 reversed the acquired resistance (Xu et al., 2016).
In a survey done by Chen et al., exosome-derived lncRNA HISLA released by TAMs in the tumor microenvironment was found to increase glycolysis in recipient breast cancer cells, which protected them from apoptosis. LncRNA HISLA binds to PHD2, which is responsible for hydroxylation of HIF-1α, then aerobic glycolysis is induced. That causes resistance to apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Interestingly, increased aerobic glycolysis results in lactate secretion into the tumor microenvironment. Lactate then increases HISLA expression via the ERK-ELK1 signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2019b). LncRNA H19 showed overexpression in doxorubicin-resistant cell lines and their secreted exosomes in a survey conducted by Wang et al. Silencing H19 caused a decline in colony forming ability and increased doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Further, exosomes extracted from resistant cells led to a higher IC50 of doxorubicin in sensitive cells along with apoptosis inhibition and enhanced colony formation. Also, doxorubicin-resistant patients were found to have elevated serum levels of exosomal H19, which can be used as a biomarker (Wang et al., 2020). In another study lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 showed upregulation in two breast cancer cell lines with acquired trastuzumab resistance. Zheng et al. observed that knockdown of AGAP2-AS1 resensitized the cell lines to trastuzumab, indicating its involvement in the acquired resistance. The knockdown led to DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. Further results confirmed that AGAP2-AS1 is packaged into exosomes by hnRNPA2B1 and this way transfers trastuzumab resistance to sensitive breast cancer cells (Zheng et al., 2019). In a 2021 study, exosomal lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 was able to modulate autophagy through Autophagy related 10 (ATG10), which made breast cancer cells resistant to trastuzumab. AGAP2-AS1 binds to ELAV-like RNA binding protein 1 (ELAVL1/HuR), then the complex interlocks with the ATG10 promoter region and activates ATG10 transcription by causing epigenetic changes at H3K27ac (acetylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 protein subunit) and H3K4me3 (Tri-methylation of histone H3 lysine 4). ATG10 is an autophagic E2-like enzyme that aids autophagosome formation and its overexpression has been observed in cancers like colorectal and lung (Qian et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2016; Jo et al., 2012). It was also confirmed that targeting AGAP2-AS1 by Antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), reverses drug resistance (Qian et al., 2021).
Li et al. observed that lncRNA UCA1 was able to make ovarian cancer cells resistant to cisplatin. Silencing UCA1 inhibited proliferation and increased apoptosis induced by cisplatin. On the contrary, overexpression of UCA1 in sensitive cell lines inhibited cisplatin-induced apoptosis and increased tumor growth. LncRNA UCA1 targets miR-143, which is responsible for inhibiting the expression of a transcription factor called Fos-like antigen 2/FRA-2 (FOSL2). This makes ovarian cancer cells resistant to cisplatin (Li et al., 2019d; Wan et al., 2021).
Lou et al. confirmed the involvement of lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 in triggering drug resistance in cervical cancer. LncRNA HNF1A-AS1 was upregulated in a cisplatin-resistant cell line compared to the sensitive one, and silencing it resulted in inhibited cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. Further investigation indicated that lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 acts as a ceRNA for miR-34b and inhibits its activity which is followed by Tuftelin 1 (TUFT1) upregulation (Luo et al., 2019). Overexpressed TUFT1 has been observed in a number of malignancies including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), breast cancer, thyroid carcinoma, and osteosarcoma (Lin et al., 2021). Table 6 illustrates the role of exosomal lncRNAs in the development of drug resistance in breast, ovarian, and cervical cancers.
Knowing that the expression of lncRNAs undergoes significant changes during tumorigenesis, and based on studies on lncRNAs involvement in carcinogenesis, the application of lncRNAs for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes seems necessary. LncRNAs can accumulate in exosomes and are present in different body fluids, tissues and cells (Hao et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2021). In addition, exosomes are known as the third carriage after circulating tumor DNAs (ctDNAs) and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in liquid biopsy and can be used as non-invasive biomarkers for cancer treatment (Zhang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021a). The presence of some exosomal lncRNAs is an indication of tumor stage, treatment outcome (Lee et al., 2019), metastasis (Gao et al., 2018), tumor recurrence, or drug resistance (Zhang et al., 2021), and based on these results, it may be possible to plan a more fitting treatment for the affected person.
The emergence of immunotherapy, especially immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has become a revolution in cancer treatment. ICIs target immune receptors such as programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and enhance anticancer properties (Jacob et al., 2023). Exosomal lncRNAs have the ability to modulate the interaction between immune ligand and receptor, thereby bypassing the immune response of immune cells in different types of cancer (Zhang et al., 2022). The exosomal lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 secreted by colorectal cancer (CRC) cells inhibits ubiquitination of PD-L1 on CD8+ T cells by regulating the miR-30a-5p/USP22 pathway and escapes the immune response (Xian et al., 2021). Another study revealed that secretion of exosomes containing PCED1B-AS1 lncRNA from HCC in the co-culture of HCC cell line and human T cells can enhance the expression of PD-Ls via sponging hsa-mir-194-5p (Fan et al., 2021). According to studies, targeting exosomal lncRNAs involved in the regulation of immune checkpoints with siRNAs may be a potential therapeutic approach to reduce tumor progression (Zhang et al., 2022). For example, knockdown of the exosomal lncRNA PCAT6 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using siRNA can suppress M2 polarization via the miR-326/KLF1 axis and extend tumor growth (Chen et al., 2022).
As mentioned previously, exosomal long non-coding RNAs have the potential to serve as valuable diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic biomarkers (Zhang et al., 2021; Da et al., 2021).
LY et al. found that exosomal lncRNA UEGC1 is highly expressed in patients with early-stage gastric cancer (EGC) compared with healthy individuals and has the potential to be as a sensitive noninvasive biomarker for EGC diagnosis (Lin et al., 2018). In another investigation, exosomal CRNDE-h was shown to be upregulated in the serum of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and derived from tumor cells. Based on the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve at a cut-off value of 0.020, the AUC reached a value of 0.892, with corresponding sensitivity and specificity rates of 70.3% and 94.4%, respectively, for the diagnosis of CRC (Liu et al., 2016b). According to one study, patients with early-stage NSCLC had significantly lower expression of growth arrest-specific transcript 5 lncRNA in the exosome (Exo-GAS5) compared with the control group. In terms of ROC curve analysis, Exo-GAS5 may have the potential to discriminate against individuals with stage I NSCLC and have an AUC value of 0.822 (Li et al., 2019e). RP11-85G21.1 (lnc85) is a novel exosomal lncRNA that was significantly elevated in HCC patients regardless of their alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) status and might be a potential diagnostic marker for HCC. RP11-85G21.1 was also shown to enhance HCC proliferation and migration via modulation of miR-324-5p (Huang et al., 2020). Plasma-derived exosomal SOX2-OT exhibited substantially increased expression levels in patients diagnosed with LSCC. This study suggests that SOX2-OT as a detecting biomarker can significantly differentiate LSCC patients from non-LSCC patients with an AUC of 0.864 in ROC analysis as a detecting biomarker (Teng et al., 2019). The study conducted by Abbastabar et al. demonstrated a significant upregulation of exosomal PVT-1, ANRIL, and PCAT-1 in urine samples from patients with bladder cancer (BC) compared with the control group. These findings suggest that these biomarkers hold potential as valuable diagnostic indicators for bladder cancer (Abbastabar et al., 2020).
The independent prognostic factor of EOC was identified through a multivariate Cox regression model, which demonstrated that serum exosomal hypoxia-inducible factor (aHIF) level played a significant role. EOC patients were found to have elevated levels of exosomal aHIF in serum, and there was a positive correlation between the expression of serum exosomal aHIF and the aHIF lncRNA levels in EOC tissues. Furthermore, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that EOC patients who had elevated expression of exosomal aHIF in serum experienced a significantly worse overall survival outcome (Tang et al., 2019b). According to another study, serum exosomal myocardial infarction associated transcript (MIAT) levels were remarkably upregulated in patients diagnosed with gastric cancer (GC) in comparison to individuals with gastric adenoma and healthy controls. The overall survival rate of GC patients with high expression of exosomal lncRNA aHIF in serum was lower, and MIAT was identified as an effective diagnostic and prognostic marker of GC (Xu et al., 2020b). The findings of another study revealed a correlation between the level of exosomal ATB and both tumor stage and portal vein thrombosis. Moreover, patients with elevated levels of circulating exosomal lncRNA-activated by tumor growth factor-beta (TGF-β) (lncRNA-ATB) exhibited notably reduced overall survival and progression-free survival rates (Lee et al., 2019). In addition, other exosomal lncRNAs such as CRNDE-h (Liu et al., 2016b), SPINT1-AS1 (Li et al., 2018b) and lncRNA 91H (Gao et al., 2018) in CRC, RP5-977B1 in NSCL (Min et al., 2022), and MALAT1 (Qiu et al., 2018) in OC have been identified as potential prognostic biomarkers.
Chen et al. demonstrated in their study that exosomal lncRNA lymph node metastasis-associated transcript 2 (LNMAT2), plays a significant role in promoting tube formation and migration of human lymphatic endothelial cells, as well as enhancing tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node (LN) metastasis in bladder cancer (BCa). The results suggested that LNMAT may be a treatment biomarker for LN metastasis in BCa (Chen et al., 2020a). Another investigation showed that exosomal H19 promoted resistance to erlotinib in NSCLC through the regulation of miR-615-3p/ATG7 axis which may offer a prospective diagnosis and treatment marker for NSCLC patients (Pan and Zhou, 2020). Furthermore, exosomal lncRNA HOTAIR, UCA1 and H19 in drug-resistant breast cancer and exosomal lncRNA UCA1 in drug-resistant ovarian cancer seem to be promising diagnostic biomarkers and molecular targets to reduce drug resistance (Tang et al., 2019a; Xu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2020; Li et al., 2019d).
Since exosomes are great nanoparticles for carrying cargoes such as ncRNAs, proteins, lipids, and other biological compounds, they can be used to carry lncRNAs capable of reversing drug resistance (Li et al., 2016) or anti-lncRNAs to knock down lncRNAs that cause drug resistance (Guo et al., 2020c; Wang et al., 2018). Applying various physical and chemical techniques, including electroporation, ultrasound, and liposome-mediated membrane fusion, can be utilized to acquire gene-enriched exosomes. Engineered exosomes can be modified to target specific tissues or organs, allowing for real-time monitoring of their pharmacokinetics and potentially improving therapeutic outcomes. This offers promising prospects for enhancing the efficacy of exosomal lncRNAs in clinical application (Yuan and Huang, 2021). Another approach could be using locked nucleic acids (LNAs), antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), Small interfering RNA (siRNAs), CRISPR/Cas9 system, and some small designed molecules to disrupt exosomal lncRNAs responsible for anticancer drug resistance (Qu et al., 2016; Ye et al., 2022; Yousefi et al., 2020; Deocesano-Pereira et al., 2019). For instance, exosomal lncRNA lncARSR was upregulated in Sunitinib-Resistant RCC Cells, which acts as an oncogene and promotes sunitinib resistance through targeting miR-34/miR-44 to activate AXL and c-MET expression in RCC cells. It was also shown that utilization of locked nucleic acids (LNAs) that specifically target lncARSR might resensitize RCC cells to sunitinib (Qu et al., 2016). In a study that aimed to knockout MEG3 in Hs578T cells, the CRISPR/Cas9 system was performed. MEG3 deletion promoted cell proliferation, and cell growth (Deocesano-Pereira et al., 2019). Additionally, the regulation of lncRNAs can be achieved using specific small molecules. Hao et al. designed and identified a curcumin analogue called Comp34 which was able to suppress NUDT3-AS4 and consequently reduced the TNBC development. This compound effectively inhibited breast cancer by suppressing the lncRNA NUDT3-AS4 that acts as a sponge for miR-99s and increases the AKT1/mTOR pathway (Hao et al., 2020).
Another strategy could be purifying blood from the exosomes containing lncRNAs involved in drug resistance (Kalluri, 2016). An example of this approach is the new system developed by Aethlon Medical called Aethlon ADAPTTM, which is capable of rapid absorption and selective retention of target particles smaller than 200 nm from the entire circulatory system. This technology is based on the interactions between serum components and an affinity matrix which contains substrates such as monoclonal antibodies and lectins in order to absorb tumor-derived exosomes and other oncological agents (Marleau et al., 2012). Moreover, prevention of exosomal lncRNA uptake by sensitive cells may be another solution (Xie et al., 2019; Marleau et al., 2012). Enhancing the effectiveness of therapy and impeding the progression of cancer can be achieved by developing drugs that hinder the transfer of exosomal lncRNAs from drug-resistant cells to drug-sensitive cells (Zhang et al., 2021). Undoubtedly, developing such therapeutic mechanisms requires more concentrated studies. The Combination of antitumor drugs and targeting involved exosomal lncRNAs can improve therapy outcomes and prevent tumor recurrence. Applications of exosomal lncRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive system cancers is summarized in Figure 6.
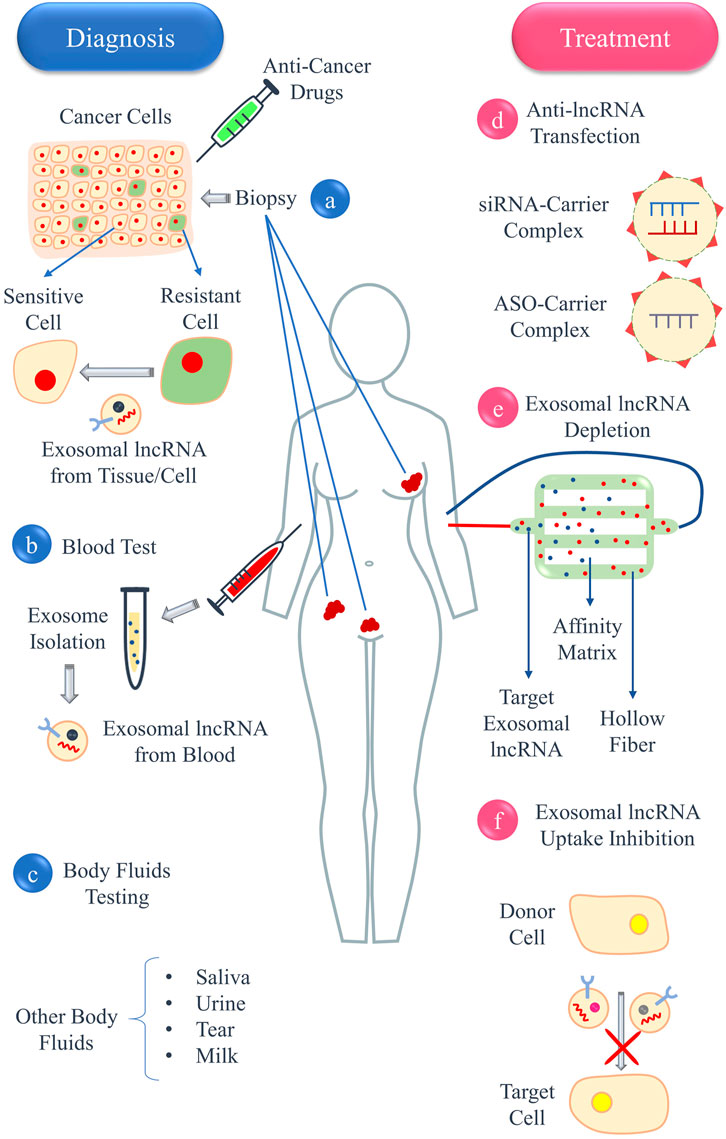
Figure 6. Application of exosomal lncRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive system cancers. Exosomal lncRNAs can be present in (A) tissue biopsy of cancer cells, (B) blood, or (C) other body fluids, such as saliva, urine, tears, and milk. Treatment methods include (D) using anti-lncRNAs, such as siRNAs or ASOs, against exosomal lncRNAs responsible for drug resistance, (E) depleting blood from exosomes containing lncRNAs involved in drug resistance using a system called ADAPT, and (F) inhibiting the uptake of exosomal lncRNAs by drug-sensitive cells.
Exosomal lncRNAs have plenty to offer when it comes to diagnostic methods, due to the fact that they exist in most body fluids and are secreted from almost every living cell. Nevertheless, there are still some potential circumscriptions in their clinical application as tumor markers (Hosseini et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2021). For example, exosome isolation methods are still far from being perfect. They can be extremely costly, difficult, and time-consuming, in addition to not being effective and sharp enough to provide reliable analytical results (Hosseini et al., 2022). One major problem in isolating exosomes is the contamination caused by ribonucleoprotein complexes, lipoproteins, and other contaminating molecules, and if the RNA levels are low, biological contamination can effortlessly interfere with the isolation process and create false results. Ultracentrifugation is probably the most prominent method for exosome isolation providing the highest purity (Hosseini et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2020b; Makler and Asghar, 2020; Wu et al., 2020). Another significant step in studying exosomal lncRNAs is the identification and quantification of exosomes (Hosseini et al., 2022; Makler and Asghar, 2020). To precisely separate tumor signals from normal cell signals is a serious challenge. This problem is worsened when the liquid biopsy is done from plasma. A great volume of platelet-derived RNAs are present in plasma that can meddle with the results. Thus, employing tumor-specific surface markers to differentiate tumor-derived exosomes is of great importance (Yu et al., 2021; Brinkman et al., 2020). A few methods are being used at the moment in this regard. Flow cytometry, for example, is able to detect and classify exosomes by species and in great numbers. However, it requires expensive equipment, and the results it presents are not consistent. In enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA), specific antibodies against tumor markers are used. This allows ELISA to obtain tumor-derived exosomes in a more specific manner. Although this method seems very promising, in exosome identification with ELISA the samples are very prone to be contaminated with biological waste or other biomolecules. Another approach to identify exosomes is nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), whose limitations are its expensive equipment and time-consuming process (Hosseini et al., 2022; Makler and Asghar, 2020). The next technical challenge would be RNA extraction. Eldh et al. conducted a research to examine which RNA extraction method is best suited for lncRNAs. Seven different methods were investigated. The quality of lncRNAs were pretty high in all seven methods, but total RNA yield, size of RNA molecules, and purity of RNA varied in accordance to the method (Eldh et al., 2012). These results imply that choosing the appropriate method for extracting lncRNAs should be directed towards the aims of a research (Tellez-Gabriel and Heymann, 2019). At last, when it comes to detection of exosomal lncRNAs, the methods being used are mostly next-generation sequencing (NGS), lncRNA microarray, or RT-qPCR. New methods like dPCR have also been practiced, but highest levels of accuracy are yet to be achieved. NGS and lncRNA microarray are both considered expensive methods and they require big storage spaces for the data they generate; therefore, although there is room for improvement, RT-qPCR remains as the most common practice in lncRNA detection (Wu et al., 2020; Tellez-Gabriel and Heymann, 2019).
The study of lncRNAs have gained much interest through recent years, and while it appears to be a fairly promising approach in personalized medicine, there is still a lot to investigate and achieve in this field. Identifying pivotal lncRNAs by searching liquid biopsies or tissues from more patients and discovering their underlying mechanisms, the true nature of interactions between donor cells and recipient cells and how to minimize their undesirable communications, why some certain lncRNAs are chosen to enter exosomes and transfer to other cells, and how exosomes and their biological content affect each other are just a few of the perspectives that are yet to be fully comprehended (Yuan and Huang, 2021). For example, an interesting connection between expression levels of lncRNAs and the amount of exosomes a cell releases has been detected in some studies. In a 2019 study, Yang et al. observed that exosome secretion from HCC cells are elevated in response to lncRNA HOTAIR upregulation (Yang et al., 2019), and some other studies have demonstrated the opposite of this relationship (Li et al., 2021b; Xing et al., 2020). The heterogeneity of exosomes is another intriguing subject to explore. Tumors can secrete a variety of exosome subtypes. Identifying and categorizing these subtypes like how blood cells are classified, and understanding how lncRNAs are loaded into each subtype of exosomes can be a big step in using exosome-derived lncRNAs as a mean of personalized tumor therapy (Hosseini et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2020b; Wu et al., 2020).
Aside from further understanding the molecular aspects of exosomal lncRNAs, the techniques and equipment used in this regard hold great importance. One important factor to consider when studying and using exosomes and its content as biomarkers is the methods that are used to purify exosomes. It has been observed that exosomal lncRNAs obtained from different cells and patients vary in biological and functional aspects. Accordingly, it seems reasonable that methods used to isolate exosomes and their cargos should be performed with precision and under uniform for them to have clinical application. The study in this field is still in its beginning and to better understand and compare the results, it is important that the methods are standardized so no problem is caused during the normalization of results (Yuan and Huang, 2021; Xiao et al., 2020b). To choose the optimum method, the problem being addressed in a research should be considered. For instance, when an exosomal lncRNA is investigated as a biomarker to diagnose a disease and its relationship with the disease has already been proven and clear, the purity of exosomes is not as important. However, when it comes to determining the relationship between an exosomal lncRNA and other biological molecules, molecular pathways, or diseases, it is important to prevent any false result and inaccuracy; thus, applying a separation method that provides samples with the highest levels of purity seems like a wise approach (Wu et al., 2020). That being said, it is clear that exosomal lncRNA utility in personalized medicine is still in its infancy. Thus, for it to achieve real clinical application, a long track of investigations and innovative approaches is ahead.
Several studies on lncRNAs support the fact that they have regulatory functions in numerous molecular processes. These molecules are widely detected in different tissues, cells, and body fluids. Since lncRNAs can be transferred from 1 cell to another through exosomes, they can exert their regulatory actions in new areas. Exosomal lncRNAs by being involved in various biological processes such as migration, invasion, proliferation, and drug resistance can modulate the progression of cancer. The mechanisms of drug resistance in reproductive cancers, including breast, ovarian, and cervical cancers, were found to be highly influenced by the regulatory actions of exosome-derived lncRNAs. Hence, a comprehensive understanding of the intricate mechanisms involved in the cancer microenvironment, such as exosomal lncRNAs, which are the focus of this study, is crucial for the effective treatment of these cancers. According to several investigations exosomal lncRNAs show promise as potential diagnostic, prognostic, and treatment biomarkers for predicting drug resistance and monitoring drug efficacy. By elucidating the mechanisms underlying drug resistance through exosomal lncRNAs and related research, as well as discussing treatment strategies and associated challenges, this study provides a broad perspective for designing future studies in the field of targeted cancer treatment and potential drug development. Given that we possess little knowledge concerning exosomal lncRNAs, the need for more fundamental research and improvement in methods used in this field seems evident. It is necessary to fully understand and identify key exosome-derived lncRNAs and uncover the exact mechanisms affected by them. Achieving this data is a major step in using and targeting lncRNAs clinically. For example, if lncRNAs are to be used for diagnosis purposes, the identification of universal lncRNA biomarkers should be earnestly pursued. Same exosomal lncRNAs have been released and identified in different malignancies. This can cause challenges in the process of using lncRNAs as specific biomarkers or their clinical application. Undoubtedly, further comparative studies with large sample sizes are required to solve these problems (Xiao et al., 2020b; Kang et al., 2022). As for the techniques and equipment that are currently available, although a lot of them showcase precision and efficiency, a sound method is yet to be introduced (Wu et al., 2020). High accuracy, low cost, simple procedure, and time efficiency are some of the factors that should be taken into account for developing new methods (Hosseini et al., 2022). The need for more methods applicable for isolation, identification and classification of exosomes, RNA extraction, and analysis of exosomal lncRNAs with high-throughput has never been greater (Wu et al., 2020). Bearing in mind that the study of exosomal lncRNAs is in its early days and there is a lot to be discovered about them, this field of study should be paid more attention and effort.
NS: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NA: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MaC: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. MoC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences (IR.SKUMS.REC.1403.001).
We would like to thank Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences’ Office of Research, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences and Novin Genome (NG) Lab, Shahrekord branch, Research and Development Center for Biotechnology in southwest Iran for their kind cooperation.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbastabar, M., Sarfi, M., Golestani, A., Karimi, A., Pourmand, G., and Khalili, E. (2020). Tumor-derived urinary exosomal long non-coding RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer. Excli J. 19, 301–310. doi:10.17179/excli2019-1683
Adhikari, S., Bhattacharya, A., Adhikary, S., Singh, V., Gadad, S. S., Roy, S., et al. (2022). The paradigm of drug resistance in cancer: an epigenetic perspective. Biosci. Rep. 42 (4). doi:10.1042/BSR20211812
Ahadi, A. (2021). Functional roles of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of cancer. Genes Dis. 8 (4), 424–437. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2020.04.009
Ahadi, A., Brennan, S., Kennedy, P. J., Hutvagner, G., and Tran, N. (2016). Long non-coding RNAs harboring miRNA seed regions are enriched in prostate cancer exosomes. Sci. Rep. 6, 24922. doi:10.1038/srep24922
Alatise, K. L., Gardner, S., and Alexander-Bryant, A. (2022). Mechanisms of drug resistance in ovarian cancer and associated gene targets. Cancers (Basel) 14 (24), 6246. doi:10.3390/cancers14246246
An, H., Elvers, K. T., Gillespie, J. A., Jones, K., Atack, J. R., Grubisha, O., et al. (2022). A toolkit for the identification of NEAT1_2/paraspeckle modulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (20), e119. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac771
Andergassen, D., Muckenhuber, M., Bammer, P. C., Kulinski, T. M., Theussl, H. C., Shimizu, T., et al. (2019). The Airn lncRNA does not require any DNA elements within its locus to silence distant imprinted genes. PLoS Genet. 15 (7), e1008268. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008268
Andres, J., Smith, L. C., Murray, A., Jin, Y., Businaro, R., and Laskin, J. D. (2020). Role of extracellular vesicles in cell-cell communication and inflammation following exposure to pulmonary toxicants. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 51, 12–18. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019
Ariosa, A. R., Lahiri, V., Lei, Y., Yang, Y., Yin, Z., Zhang, Z., et al. (2021). A perspective on the role of autophagy in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1867 (12), 166262. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166262
Asghar, U., Witkiewicz, A. K., Turner, N. C., and Knudsen, E. S. (2015). The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 14 (2), 130–146. doi:10.1038/nrd4504
Askarian-Amiri, M. E., Crawford, J., French, J. D., Smart, C. E., Smith, M. A., Clark, M. B., et al. (2011). SNORD-host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer. Rna 17 (5), 878–891. doi:10.1261/rna.2528811
Barnes, P. J. (2008). Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8 (3), 183–192. doi:10.1038/nri2254
Bebelman, M. P., Smit, M. J., Pegtel, D. M., and Baglio, S. R. (2018). Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 188, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.013
Bentzinger, C. F., Wang, Y. X., and Rudnicki, M. A. (2012). Building muscle: molecular regulation of myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4 (2), a008342. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008342
Bermúdez, M., Aguilar-Medina, M., Lizárraga-Verdugo, E., Avendaño-Félix, M., Silva-Benítez, E., López-Camarillo, C., et al. (2019). LncRNAs as regulators of autophagy and drug resistance in colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 9, 1008. doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.01008
Bertone, P., Stolc, V., Royce, T. E., Rozowsky, J. S., Urban, A. E., Zhu, X., et al. (2004). Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science 306 (5705), 2242–2246. doi:10.1126/science.1103388
Bhattacharjee, R., Dey, T., Kumar, L., Kar, S., Sarkar, R., Ghorai, M., et al. (2022). Cellular landscaping of cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 153, 113345. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113345
Blokhin, I., Khorkova, O., Hsiao, J., and Wahlestedt, C. (2018). Developments in lncRNA drug discovery: where are we heading? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 13 (9), 837–849. doi:10.1080/17460441.2018.1501024
Borkiewicz, L., Kalafut, J., Dudziak, K., Przybyszewska-Podstawka, A., and Telejko, I. (2021). Decoding LncRNAs. Cancers (Basel) 13 (11), 2643. doi:10.3390/cancers13112643
Brandmaier, A., Hou, S. Q., and Shen, W. H. (2017). Cell cycle control by PTEN. J. Mol. Biol. 429 (15), 2265–2277. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2017.06.004
Brasseur, K., Gévry, N., and Asselin, E. (2017). Chemoresistance and targeted therapies in ovarian and endometrial cancers. Oncotarget 8 (3), 4008–4042. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14021
Brinkman, K., Meyer, L., Bickel, A., Enderle, D., Berking, C., Skog, J., et al. (2020). Extracellular vesicles from plasma have higher tumour RNA fraction than platelets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 9 (1), 1741176. doi:10.1080/20013078.2020.1741176
Bukowski, K., Kciuk, M., and Kontek, R. (2020). Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (9), 3233. doi:10.3390/ijms21093233
Cajigas, I., Chakraborty, A., Lynam, M., Swyter, K. R., Bastidas, M., Collens, L., et al. (2021). Sox2-Evf2 lncRNA-mediated mechanisms of chromosome topological control in developing forebrain. Development 148 (6), dev197202. doi:10.1242/dev.197202
Cajigas, I., Chakraborty, A., Swyter, K. R., Luo, H., Bastidas, M., Nigro, M., et al. (2018). The Evf2 ultraconserved enhancer lncRNA functionally and spatially organizes megabase distant genes in the developing forebrain. Mol. Cell 71 (6), 956–972.e9. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.024
Carninci, P., Kasukawa, T., Katayama, S., Gough, J., Frith, M. C., Maeda, N., et al. (2005). The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 309 (5740), 1559–1563. doi:10.1126/science.1112014
Castellano, J. J., Marrades, R. M., Molins, L., Viñolas, N., Moises, J., Canals, J., et al. (2020). Extracellular vesicle lincRNA-p21 expression in tumor-draining pulmonary vein defines prognosis in NSCLC and modulates endothelial cell behavior. Cancers (Basel) 12 (3), 734. doi:10.3390/cancers12030734
Chang, H., and Zou, Z. (2020). Targeting autophagy to overcome drug resistance: further developments. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13 (1), 159. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-01000-2
Chang, W. H., Cerione, R. A., and Antonyak, M. A. (2021). Extracellular vesicles and their roles in cancer progression. Methods Mol. Biol. 2174, 143–170. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0759-6_10
Chen, C., Luo, Y., He, W., Zhao, Y., Kong, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2020a). Exosomal long noncoding RNA LNMAT2 promotes lymphatic metastasis in bladder cancer. J. Clin. Invest 130 (1), 404–421. doi:10.1172/JCI130892
Chen, D., Lu, T., Tan, J., Li, H., Wang, Q., and Wei, L. (2019a). Long non-coding RNAs as communicators and mediators between the tumor microenvironment and cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 9, 739. doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.00739
Chen, F., Chen, J., Yang, L., Liu, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019b). Extracellular vesicle-packaged HIF-1α-stabilizing lncRNA from tumour-associated macrophages regulates aerobic glycolysis of breast cancer cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 21 (4), 498–510. doi:10.1038/s41556-019-0299-0
Chen, S. Y., Wang, Y., Telen, M. J., and Chi, J. T. (2008). The genomic analysis of erythrocyte microRNA expression in sickle cell diseases. PLoS One 3 (6), e2360. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002360
Chen, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, Q., Liu, B., Cheng, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020c). Exosomal long non-coding RNA HOTTIP increases resistance of colorectal cancer cells to mitomycin via impairing MiR-214-mediated degradation of KPNA3. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 582723. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.582723
Chen, Y., Ding, H., Wei, M., Zha, W., Guan, S., Liu, N., et al. (2020b). MSC-secreted exosomal H19 promotes trophoblast cell invasion and migration by downregulating let-7b and upregulating FOXO1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 19, 1237–1249. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.031
Chen, Y., Hong, C., Qu, J., Chen, J., and Qin, Z. (2022). Knockdown of lncRNA PCAT6 suppresses the growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting macrophages M2 polarization via miR-326/KLF1 axis. Bioengineered 13 (5), 12834–12846. doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2076388
Chen, Y., Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Yang, J., Yuan, Y., and Wu, W. (2024). Exosomal lncRNA SNHG12 promotes angiogenesis and breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer 31 (4), 607–620. doi:10.1007/s12282-024-01574-6
Choong, G. M., Cullen, G. D., and O'Sullivan, C. C. (2020). Evolving standards of care and new challenges in the management of HER2-positive breast cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 70 (5), 355–374. doi:10.3322/caac.21634
Colombo, I., Karakasis, K., Suku, S., and Oza, A. M. (2023). Chasing immune checkpoint inhibitors in ovarian cancer: novel combinations and biomarker discovery. Cancers (Basel) 15 (12), 3220. doi:10.3390/cancers15123220
Colombo, N., Caruso, G., and Jalving, M. (2024). Immune checkpoint inhibitors in endometrial cancer: a cinderella story. Ann. Oncol. 35 (8), 686–688. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2024.06.008
Conigliaro, A., Costa, V., Lo Dico, A., Saieva, L., Buccheri, S., Dieli, F., et al. (2015). CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 14, 155. doi:10.1186/s12943-015-0426-x
Cosentino, G., Plantamura, I., Tagliabue, E., Iorio, M. V., and Cataldo, A. (2021). Breast cancer drug resistance: overcoming the challenge by capitalizing on MicroRNA and tumor microenvironment interplay. Cancers (Basel) 13 (15), 3691. doi:10.3390/cancers13153691
Crean-Tate, K. K., Braley, C., Dey, G., Esakov, E., Saygin, C., Trestan, A., et al. (2021). Pretreatment with LCK inhibitors chemosensitizes cisplatin-resistant endometrioid ovarian tumors. J. Ovarian Res. 14 (1), 55. doi:10.1186/s13048-021-00797-x
Cui, S. (2022). METTL3-mediated m6A modification of lnc RNA RHPN1-AS1 enhances cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by activating PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 36 (12), e24761. doi:10.1002/jcla.24761
Da, M., Jiang, H., Xie, Y., Jin, W., and Han, S. (2021). The biological roles of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancers. Onco Targets Ther. 14, 271–287. doi:10.2147/OTT.S281175
De Giorgi, U., Casadei, C., Bergamini, A., Attademo, L., Cormio, G., Lorusso, D., et al. (2019). Therapeutic challenges for cisplatin-resistant ovarian germ cell tumors. Cancers (Basel) 11 (10), 1584. doi:10.3390/cancers11101584
Della Corte, L., Barra, F., Foreste, V., Giampaolino, P., Evangelisti, G., Ferrero, S., et al. (2020). Advances in paclitaxel combinations for treating cervical cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 21 (6), 663–677. doi:10.1080/14656566.2020.1724284
De Los Santos, M. C., Dragomir, M. P., and Calin, G. A. (2019). The role of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer drug resistance. Cancer Drug Resist 2 (4), 1178–1192. doi:10.20517/cdr.2019.74
Deng, X., Ruan, H., Zhang, X., Xu, X., Zhu, Y., Peng, H., et al. (2020). Long noncoding RNA CCAL transferred from fibroblasts by exosomes promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 146 (6), 1700–1716. doi:10.1002/ijc.32608
Deocesano-Pereira, C., Machado, R. A. C., De Jesus-Ferreira, H. C., Marchini, T., Pereira, T. F., Carreira, A. C. O., et al. (2019). Functional impact of the long non-coding RNA MEG3 deletion by CRISPR/Cas9 in the human triple negative metastatic Hs578T cancer cell line. Oncol. Lett. 18 (6), 5941–5951. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10969
Devaux, Y., Zangrando, J., Schroen, B., Creemers, E. E., Pedrazzini, T., Chang, C. P., et al. (2015). Long noncoding RNAs in cardiac development and ageing. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 12 (7), 415–425. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2015.55
Dimitrova, N., Zamudio, J. R., Jong, R. M., Soukup, D., Resnick, R., Sarma, K., et al. (2014). LincRNA-p21 activates p21 in cis to promote Polycomb target gene expression and to enforce the G1/S checkpoint. Mol. Cell 54 (5), 777–790. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.04.025
Ding, L., Ren, J., Zhang, D., Li, Y., Huang, X., Hu, Q., et al. (2018). A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis 39 (3), 397–406. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgy006
Dogan, E., Kara, H. G., Kosova, B., and Cetintas, V. B. (2022). “Targeting apoptosis to overcome chemotherapy resistance,” in Metastasis. Editor C. M. Sergi (Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications).
Dong, H., Yang, C., Chen, X., Sun, H., He, X., and Wang, W. (2023). Breast cancer-derived exosomal lncRNA SNHG14 induces normal fibroblast activation to cancer-associated fibroblasts via the EBF1/FAM171A1 axis. Breast Cancer 30 (6), 1028–1040. doi:10.1007/s12282-023-01496-9
Dong, X., Bai, X., Ni, J., Zhang, H., Duan, W., Graham, P., et al. (2020). Exosomes and breast cancer drug resistance. Cell Death Dis. 11 (11), 987. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03189-z
Du, W., Xu, A., Huang, Y., Cao, J., Zhu, H., Yang, B., et al. (2021). The role of autophagy in targeted therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Autophagy 17 (10), 2665–2679. doi:10.1080/15548627.2020.1822628
Eldh, M., Lötvall, J., Malmhäll, C., and Ekström, K. (2012). Importance of RNA isolation methods for analysis of exosomal RNA: evaluation of different methods. Mol. Immunol. 50 (4), 278–286. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2012.02.001
Fabbiano, F., Corsi, J., Gurrieri, E., Trevisan, C., Notarangelo, M., and D'Agostino, V. G. (2020). RNA packaging into extracellular vesicles: an orchestra of RNA-binding proteins? J. Extracell. Vesicles 10 (2), e12043. doi:10.1002/jev2.12043
Fan, F., Chen, K., Lu, X., Liu, C., and Wu, B. (2021). Dual targeting of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by PCED1B-AS1 via sponging hsa-miR-194-5p induces immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 15 (2), 444–458. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10101-6
Fan, Y., Li, Z., and He, Y. (2022). Exosomes in the pathogenesis, progression, and treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioengineering (Basel) 9 (3), 99. doi:10.3390/bioengineering9030099
Feki, A., Jefford, C. E., Berardi, P., Wu, J. Y., Cartier, L., Krause, K. H., et al. (2005). BARD1 induces apoptosis by catalysing phosphorylation of p53 by DNA-damage response kinase. Oncogene 24 (23), 3726–3736. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208491
Feng, T., Zhang, P., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Tong, J., Dai, H., et al. (2019). High throughput sequencing identifies breast cancer-secreted exosomal LncRNAs initiating pulmonary pre-metastatic niche formation. Gene 710, 258–264. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2019.06.004
Fernandes, A., Viveros-Carreño, D., Hoegl, J., Ávila, M., and Pareja, R. (2022). Human papillomavirus-independent cervical cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 32 (1), 1–7. doi:10.1136/ijgc-2021-003014
Fontana, F., Carollo, E., Melling, G. E., and Carter, D. R. F. (2021). Extracellular vesicles: emerging modulators of cancer drug resistance. Cancers (Basel) 13 (4), 749. doi:10.3390/cancers13040749
Fu, M., Gu, J., Jiang, P., Qian, H., Xu, W., and Zhang, X. (2019). Exosomes in gastric cancer: roles, mechanisms, and applications. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 41. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1001-7
Gacche, R. N., and Assaraf, Y. G. (2018). Redundant angiogenic signaling and tumor drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat 36, 47–76. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2018.01.002
Gangadaran, P., Madhyastha, H., Madhyastha, R., Rajendran, R. L., Nakajima, Y., Watanabe, N., et al. (2023). The emerging role of exosomes in innate immunity, diagnosis and therapy. Front. Immunol. 13, 1085057. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1085057
Gao, B., Wang, L., Wen, T., Xie, X., Rui, X., and Chen, Q. (2024). Colon cancer-derived exosomal LncRNA-XIST promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by regulating PDGFRA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (21), 11433. doi:10.3390/ijms252111433
Gao, N., Li, Y., Li, J., Gao, Z., Yang, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2020). Long non-coding RNAs: the regulatory mechanisms, research strategies, and future directions in cancers. Front. Oncol. 10, 598817. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.598817
Gao, T., Liu, X., He, B., Nie, Z., Zhu, C., Zhang, P., et al. (2018). Exosomal lncRNA 91H is associated with poor development in colorectal cancer by modifying HNRNPK expression. Cancer Cell Int. 18, 11. doi:10.1186/s12935-018-0506-2
Gaona-Luviano, P., Medina-Gaona, L. A., and Magaña-Pérez, K. (2020). Epidemiology of ovarian cancer. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 9 (4), 47. doi:10.21037/cco-20-34
Garrido, M. P., Fredes, A. N., Lobos-González, L., Valenzuela-Valderrama, M., Vera, D. B., and Romero, C. (2021). Current treatments and new possible complementary therapies for epithelial ovarian cancer. Biomedicines 10 (1), 77. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10010077
Gibbons, H. R., Shaginurova, G., Kim, L. C., Chapman, N., Spurlock, C. F., and Aune, T. M. (2018). Divergent lncRNA GATA3-AS1 regulates GATA3 transcription in T-helper 2 cells. Front. Immunol. 9, 2512. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02512
Gong, T., Liu, Y. T., and Fan, J. (2024). Exosomal mediators in sepsis and inflammatory organ injury: unraveling the role of exosomes in intercellular crosstalk and organ dysfunction. Military Med. Res. 24 (2024). doi:10.1186/s40779-024-00527-6
Groot, M., and Lee, H. (2020). Sorting mechanisms for MicroRNAs into extracellular vesicles and their associated diseases. Cells 9 (4), 1044. doi:10.3390/cells9041044
Gudenas, B. L., and Wang, L. (2018). Prediction of LncRNA subcellular localization with deep learning from sequence features. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 16385. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-34708-w
Guerra, F., and Bucci, C. (2019). Role of the RAB7 protein in tumor progression and cisplatin chemoresistance. Cancers (Basel) 11 (8), 1096. doi:10.3390/cancers11081096
Guo, C., Liu, J., Zhou, Q., Song, J., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., et al. (2020c). Exosomal noncoding RNAs and tumor drug resistance. Cancer Res. 80 (20), 4307–4313. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0032
Guo, Q. R., Wang, H., Yan, Y. d., Liu, Y., Su, C. Y., Chen, H. B., et al. (2020a). The role of exosomal microRNA in cancer drug resistance. Front. Oncol. 10, 472. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00472
Guo, Z., Wang, X., Yang, Y., Chen, W., Zhang, K., Teng, B., et al. (2020b). Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes angiogenesis via miR-96-5p/AMOTL2 in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 22, 179–195. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.021
Gurung, S., Perocheau, D., Touramanidou, L., and Baruteau, J. (2021). The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal 19 (1), 47. doi:10.1186/s12964-021-00730-1
Hajjari, M., and Salavaty, A. (2015). HOTAIR: an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Cancer Biol. Med. 12 (1), 1–9. doi:10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2015.0006
Hamanishi, J., Mandai, M., Ikeda, T., Minami, M., Kawaguchi, A., Murayama, T., et al. (2015). Safety and antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 antibody, nivolumab, in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 33 (34), 4015–4022. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.62.3397
Han, S., Qi, Y., Luo, Y., Chen, X., and Liang, H. (2020). Exosomal long non-coding RNA: interaction between cancer cells and non-cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 10, 617837. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.617837
Hannafon, B. N., and Ding, W. Q. (2013). Intercellular communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14 (7), 14240–14269. doi:10.3390/ijms140714240
Hao, M., Xiao, L., and Liu, Y. (2024). METTL3-induced FGD5-AS1 contributes to the tumorigenesis and PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint to enhance the resistance to paclitaxel of endometrial carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 28 (5), e17971. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17971
Hao, Q., Wang, P., Dutta, P., Chung, S., Li, Q., Wang, K., et al. (2020). Comp34 displays potent preclinical antitumor efficacy in triple-negative breast cancer via inhibition of NUDT3-AS4, a novel oncogenic long noncoding RNA. Cell Death Dis. 11 (12), 1052. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03235-w
Hao, Q., Wu, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, P., and Vadgama, J. V. (2022). Tumor-derived exosomes in tumor-induced immune suppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (3), 1461. doi:10.3390/ijms23031461
Harding, C., and Stahl, P. (1983). Transferrin recycling in reticulocytes: pH and iron are important determinants of ligand binding and processing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 113 (2), 650–658. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(83)91776-x
Hatchell, E. C., Colley, S. M., Beveridge, D. J., Epis, M. R., Stuart, L. M., Giles, K. M., et al. (2006). SLIRP, a small SRA binding protein, is a nuclear receptor corepressor. Mol. Cell 22 (5), 657–668. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.024
Hazrati, A., Soudi, S., Malekpour, K., Mahmoudi, M., Rahimi, A., Hashemi, S. M., et al. (2022). Immune cells-derived exosomes function as a double-edged sword: role in disease progression and their therapeutic applications. Biomark Res. 10 (1), 30. doi:10.1186/s40364-022-00374-4
He, R. Z., Luo, D. X., and Mo, Y. Y. (2019). Emerging roles of lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Genes Dis. 6 (1), 6–15. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2019.01.003
Hermans-Beijnsberger, S., van Bilsen, M., and Schroen, B. (2018). Long non-coding RNAs in the failing heart and vasculature. Noncoding RNA Res. 3 (3), 118–130. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2018.04.002
Hessvik, N. P., and Llorente, A. (2018). Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 75 (2), 193–208. doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2595-9
Hirose, T., Virnicchi, G., Tanigawa, A., Naganuma, T., Li, R., Kimura, H., et al. (2014). NEAT1 long noncoding RNA regulates transcription via protein sequestration within subnuclear bodies. Mol. Biol. Cell 25 (1), 169–183. doi:10.1091/mbc.E13-09-0558
Hoek, K. S., Kidd, G. J., Carson, J. H., and Smith, R. (1998). hnRNP A2 selectively binds the cytoplasmic transport sequence of myelin basic protein mRNA. Biochemistry 37 (19), 7021–7029. doi:10.1021/bi9800247
Hohn, J., Tan, W., Carver, A., Barrett, H., and Carver, W. (2021). Roles of exosomes in cardiac fibroblast activation and fibrosis. Cells 10 (11), 2933. doi:10.3390/cells10112933
Hosseini, K., Ranjbar, M., Pirpour Tazehkand, A., Asgharian, P., Montazersaheb, S., Tarhriz, V., et al. (2022). Evaluation of exosomal non-coding RNAs in cancer using high-throughput sequencing. J. Transl. Med. 20 (1), 30. doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03231-y
Hu, T., and Hu, J. (2019). Melanoma-derived exosomes induce reprogramming fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts via Gm26809 delivery. Cell Cycle 18 (22), 3085–3094. doi:10.1080/15384101.2019.1669380
Huang, F., Wang, B. R., and Wang, Y. G. (2018). Role of autophagy in tumorigenesis, metastasis, targeted therapy and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 24 (41), 4643–4651. doi:10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4643
Huang, X., Sun, L., Wen, S., Deng, D., Wan, F., He, X., et al. (2020). RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes revealed novel functional long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 111 (9), 3338–3349. doi:10.1111/cas.14516
Huarte, M., Guttman, M., Feldser, D., Garber, M., Koziol, M. J., Kenzelmann-Broz, D., et al. (2010). A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 142 (3), 409–419. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.040
Huber, H. J., and Holvoet, P. (2015). Exosomes: emerging roles in communication between blood cells and vascular tissues during atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 26 (5), 412–419. doi:10.1097/MOL.0000000000000214
Hwang, H. W., Wentzel, E. A., and Mendell, J. T. (2007). A hexanucleotide element directs microRNA nuclear import. Science 315 (5808), 97–100. doi:10.1126/science.1136235
International Transporter Consortium; Giacomini, K. M., Huang, S. M., Tweedie, D. J., Benet, L. Z., Brouwer, K. L., et al. (2010). Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9 (3), 215–236. doi:10.1038/nrd3028
Irminger-Finger, I., and Jefford, C. E. (2006). Is there more to BARD1 than BRCA1? Nat. Rev. Cancer 6 (5), 382–391. doi:10.1038/nrc1878
Jacob, S. L., Huppert, L. A., and Rugo, H. S. (2023). Role of immunotherapy in breast cancer. JCO Oncol. Pract. 19 (4), 167–179. doi:10.1200/OP.22.00483
Jain, A. K., Xi, Y., McCarthy, R., Allton, K., Akdemir, K. C., Patel, L. R., et al. (2016). LncPRESS1 is a p53-regulated LncRNA that safeguards pluripotency by disrupting SIRT6-mediated de-acetylation of histone H3K56. Mol. Cell 64 (5), 967–981. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.10.039
Jarroux, J., Morillon, A., and Pinskaya, M. (2017). History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1008, 1–46. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-5203-3_1
Jeong, Y. G., Katuwal, N. B., Kang, M. S., Ghosh, M., Hong, S. D., Park, S. M., et al. (2023). Combined PI3K inhibitor and eribulin enhances anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of paclitaxel-resistant, PIK3CA-mutated endometrial cancer. Cancers (Basel) 15 (19), 4887. doi:10.3390/cancers15194887
Jin, C., Yuan, M., and Bu, H. (2022). Antiangiogenic strategies in epithelial ovarian cancer: mechanism, resistance, and combination therapy. J. Oncol. 2022, 4880355. doi:10.1155/2022/4880355
Jin, K. T., Lu, Z. B., Lv, J. Q., and Zhang, J. G. (2020). The role of long non-coding RNAs in mediating chemoresistance by modulating autophagy in cancer. RNA Biol. 17 (12), 1727–1740. doi:10.1080/15476286.2020.1737787
Jin, M.-Z., and Jin, W.-L. (2020). The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 5 (1), 166. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00280-x
Jo, Y. K., Kim, S. C., Park, I. J., Park, S. J., Jin, D. H., Hong, S. W., et al. (2012). Increased expression of ATG10 in colorectal cancer is associated with lymphovascular invasion and lymph node metastasis. PLoS One 7 (12), e52705. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052705
Johnston, S. R. D., Harbeck, N., Hegg, R., Toi, M., Martin, M., Shao, Z. M., et al. (2020). Abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy for the adjuvant treatment of HR+, HER2-node-positive, high-risk, early breast cancer (monarchE). J. Clin. Oncol. 38 (34), 3987–3998. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.02514
Jordan, V. C. (2003). Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2 (3), 205–213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
Kailasam, A., and Langstraat, C. (2022). Contemporary use of hormonal therapy in endometrial cancer: a literature review. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 23 (12), 1818–1828. doi:10.1007/s11864-022-01031-6
Kalluri, R. (2016). The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J. Clin. Invest 126 (4), 1208–1215. doi:10.1172/JCI81135
Kalluri, R., and LeBleu, V. S. (2020). The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367 (6478), eaau6977. doi:10.1126/science.aau6977
Kang, F., Jiang, F., Ouyang, L., Wu, S., Fu, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Potential biological roles of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in gastrointestinal cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 886191. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.886191
Karakas, D., and Ozpolat, B. (2021). The role of LncRNAs in translation. Noncoding RNA 7 (1), 16. doi:10.3390/ncrna7010016
Kashi, K., Henderson, L., Bonetti, A., and Carninci, P. (2016). Discovery and functional analysis of lncRNAs: methodologies to investigate an uncharacterized transcriptome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1859 (1), 3–15. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.10.010
Kato, G. J., Piel, F. B., Reid, C. D., Gaston, M. H., Ohene-Frempong, K., Krishnamurti, L., et al. (2018). Sickle cell disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 4, 18010. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2018.10
Kato, T., Miyaki, S., Ishitobi, H., Nakamura, Y., Nakasa, T., Lotz, M. K., et al. (2014). Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 16 (4), R163. doi:10.1186/ar4679
Katsumata, N., Yasuda, M., Takahashi, F., Isonishi, S., Jobo, T., Aoki, D., et al. (2009). Dose-dense paclitaxel once a week in combination with carboplatin every 3 weeks for advanced ovarian cancer: a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 374 (9698), 1331–1338. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61157-0
Kay, C., Martínez-Pérez, C., Meehan, J., Gray, M., Webber, V., Dixon, J. M., et al. (2021). Current trends in the treatment of HR+/HER2+ breast cancer. Future Oncol. 17 (13), 1665–1681. doi:10.2217/fon-2020-0504
Kelland, L. (2007). The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7 (8), 573–584. doi:10.1038/nrc2167
Keshavarz, F., Mokhtari, M. J., and Poursadeghfard, M. (2024). Increased level of GATA3-AS1 long non-coding RNA is correlated with the upregulation of GATA3 and IL-4 genes in multiple sclerosis patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 51 (1), 874. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-09818-6
Khawar, I. A., Kim, J. H., and Kuh, H. J. (2015). Improving drug delivery to solid tumors: priming the tumor microenvironment. J. Control Release 201, 78–89. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.018
Kinnel, B., Singh, S. K., Oprea-Ilies, G., and Singh, R. (2023). Targeted therapy and mechanisms of drug resistance in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 15 (4), 1320. doi:10.3390/cancers15041320
Klattenhoff, C. A., Scheuermann, J. C., Surface, L. E., Bradley, R. K., Fields, P. A., Steinhauser, M. L., et al. (2013). Braveheart, a long noncoding RNA required for cardiovascular lineage commitment. Cell 152 (3), 570–583. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.003
Kong, W., Zhang, L., Chen, Y., Yu, Z., and Zhao, Z. (2022). Cancer cell-derived exosomal LINC00313 induces M2 macrophage differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 24 (12), 2395–2408. doi:10.1007/s12094-022-02907-7
Konstantinopoulos, P. A., and Matulonis, U. A. (2018). Targeting DNA damage response and repair as a therapeutic strategy for ovarian cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 32 (6), 997–1010. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.07.006
Kornienko, A. E., Guenzl, P. M., Barlow, D. P., and Pauler, F. M. (2013). Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol. 11, 59. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-11-59
Kretz, M., Siprashvili, Z., Chu, C., Webster, D. E., Zehnder, A., Qu, K., et al. (2013). Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding RNA TINCR. Nature 493 (7431), 231–235. doi:10.1038/nature11661
Lai, R. C., Yeo, R. W. Y., Tan, K. H., and Lim, S. K. (2013). Exosomes for drug delivery - a novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell. Biotechnol. Adv. 31 (5), 543–551. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.08.008
Lakhotia, S. C., Mallick, B., and Roy, J. (2020). “Non-coding RNAs: ever-expanding diversity of types and functions,” in RNA-based regulation in human health and disease (Academic Press), 5–57.
Le Du, F., Diéras, V., and Curigliano, G. (2021). The role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of HER2+ metastatic breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 154, 175–189. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2021.06.026
Lee, S.-y. (2021). Tailored therapy based on molecular characteristics in endometrial cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2021 (1), 2068023. doi:10.1155/2021/2068023
Lee, Y. R., Kim, G., Tak, W. Y., Jang, S. Y., Kweon, Y. O., Park, J. G., et al. (2019). Circulating exosomal noncoding RNAs as prognostic biomarkers in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 144 (6), 1444–1452. doi:10.1002/ijc.31931
Lei, L. M., Lin, X., Xu, F., Shan, S. K., Guo, B., Li, F. X., et al. (2021). Exosomes and obesity-related insulin resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 651996. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.651996
Lei, Y., Guo, W., Chen, B., Chen, L., Gong, J., and Li, W. (2018). Tumor-released lncRNA H19 promotes gefitinib resistance via packaging into exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 40 (6), 3438–3446. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6762
Li, C., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, T., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018b). Increased expression of antisense lncRNA SPINT1-AS1 predicts a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer and is negatively correlated with its sense transcript. Onco Targets Ther. 11, 3969–3978. doi:10.2147/OTT.S163883
Li, C., Lv, Y., Shao, C., Chen, C., Zhang, T., Wei, Y., et al. (2019e). Tumor-derived exosomal lncRNA GAS5 as a biomarker for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer diagnosis. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (11), 20721–20727. doi:10.1002/jcp.28678
Li, D., Liu, J., Guo, B., Liang, C., Dang, L., Lu, C., et al. (2016). Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat. Commun. 7, 10872. doi:10.1038/ncomms10872
Li, I., and Nabet, B. Y. (2019). Exosomes in the tumor microenvironment as mediators of cancer therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 32. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0975-5
Li, J., Gao, N., Gao, Z., Liu, W., Pang, B., Dong, X., et al. (2021a). The emerging role of exosomes in cancer chemoresistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 737962. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.737962
Li, J., Zhang, Q., and Jiao, H. (2021b). LncRNA NRON promotes M2 macrophage polarization and alleviates atrial fibrosis through suppressing exosomal miR-23a derived from atrial myocytes. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 120 (7), 1512–1519. doi:10.1016/j.jfma.2020.11.004
Li, J. H., Wang, M., Zhang, R., Gao, W. L., Meng, S. H., Ma, X. L., et al. (2017). E2F1-directed activation of nc886 mediates drug resistance in cervical cancer cells via regulation of major vault protein. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 10 (9), 9233–9242.
Li, Q. (2022). Role of exosomes in cellular communication between tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment. Oncol. Lett. 24 (1), 240. doi:10.3892/ol.2022.13360
Li, R. B., Yang, X. H., Zhang, J. D., and Cui, W. (2023). GAS6-AS1, a long noncoding RNA, functions as a key candidate gene in atrial fibrillation related stroke determined by ceRNA network analysis and WGCNA. BMC Med. Genomics 16 (1), 51. doi:10.1186/s12920-023-01478-y
Li, S., Yi, M., Dong, B., Jiao, Y., Luo, S., and Wu, K. (2020). The roles of exosomes in cancer drug resistance and its therapeutic application. Clin. Transl. Med. 10 (8), e257. doi:10.1002/ctm2.257
Li, W., Zhai, L., Wang, H., Liu, C., Zhang, J., Chen, W., et al. (2016). Downregulation of LncRNA GAS5 causes trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget 7 (19), 27778–27786. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8413
Li, X., Lei, Y., and Wu, M. (2018a). Regulation of macrophage activation and polarization by HCC-derived exosomal lncRNA TUC339. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (10), 2958. doi:10.3390/ijms19102958
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Li, Y., Yang, L., Ma, Y., Peng, X., et al. (2019c). Autophagy: a novel mechanism of chemoresistance in cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 119, 109415. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109415
Li, Z., et al. (2019a). The role of long noncoding RNAs in gene expression regulation. Gene Expr. Profiling Cancer, 1–17. doi:10.5772/intechopen.81773
Li, Z., Niu, H., Qin, Q., Yang, S., Wang, Q., Yu, C., et al. (2019d). lncRNA UCA1 mediates resistance to cisplatin by regulating the miR-143/FOSL2-signaling pathway in ovarian cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 17, 92–101. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.007
Li, Z., Qin, X., Bian, W., Li, Y., Shan, B., Yao, Z., et al. (2019b). Exosomal lncRNA ZFAS1 regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis via microRNA-124/STAT3 axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 477. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1473-8
Liang, Z. X., Liu, H. S., Wang, F. W., Xiong, L., Zhou, C., Hu, T., et al. (2019). LncRNA RPPH1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by interacting with TUBB3 and by promoting exosomes-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Death Dis. 10 (11), 829. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2077-0
Lin, H., Zeng, W., Lei, Y., Chen, D., and Nie, Z. (2021). Tuftelin 1 (TUFT1) promotes the proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 27, 640936. doi:10.3389/pore.2021.640936
Lin, L. Y., Yang, L., Zeng, Q., Wang, L., Chen, M. L., Zhao, Z. H., et al. (2018). Tumor-originated exosomal lncUEGC1 as a circulating biomarker for early-stage gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 17 (1), 84. doi:10.1186/s12943-018-0834-9
Liu, C., Zhang, M., Yan, X., Ni, Y., Gong, Y., Wang, C., et al. (2023). Single-cell dissection of cellular and molecular features underlying human cervical squamous cell carcinoma initiation and progression. Sci. Adv. 9 (4), eadd8977. doi:10.1126/sciadv.add8977
Liu, F., Peng, W., Chen, J., Xu, Z., Jiang, R., Shao, Q., et al. (2021). Exosomes derived from alveolar epithelial cells promote alveolar macrophage activation mediated by mir-92a-3p in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11, 646546. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.646546
Liu, H., Wang, H., Li, C., Zhang, T., Meng, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2016a). Spheres from cervical cancer cells display stemness and cancer drug resistance. Oncol. Lett. 12 (3), 2184–2188. doi:10.3892/ol.2016.4893
Liu, J. L., Liu, Y. S., Zheng, M. J., and He, H. Y. (2022b). The management of bone defect using long non-coding RNA as a potential biomarker for regulating the osteogenic differentiation process. Mol. Biol. Rep. 49 (3), 2443–2453. doi:10.1007/s11033-021-07013-5
Liu, K., Gao, X., Kang, B., Liu, Y., Wang, D., and Wang, Y. (2022a). The role of tumor stem cell exosomes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Front. Oncol. 12, 836548. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.836548
Liu, L., Yan, L., Liao, N., Wu, W. Q., and Shi, J. L. (2020). A review of ULK1-mediated autophagy in drug resistance of cancer. Cancers (Basel) 12 (2), 352. doi:10.3390/cancers12020352
Liu, S. L., Sun, P., Li, Y., Liu, S. S., and Lu, Y. (2019). Exosomes as critical mediators of cell-to-cell communication in cancer pathogenesis and their potential clinical application. Transl. Cancer Res. 8 (1), 298–311. doi:10.21037/tcr.2019.01.03
Liu, T., Zhang, X., Gao, S., Jing, F., Yang, Y., Du, L., et al. (2016b). Exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a novel serum-based biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 7 (51), 85551–85563. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.13465
Lobb, R. J., van Amerongen, R., Wiegmans, A., Ham, S., Larsen, J. E., and Möller, A. (2017). Exosomes derived from mesenchymal non-small cell lung cancer cells promote chemoresistance. Int. J. Cancer 141 (3), 614–620. doi:10.1002/ijc.30752
Lord, C. J., and Ashworth, A. (2017). PARP inhibitors: synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science 355 (6330), 1152–1158. doi:10.1126/science.aam7344
Lu, L., Huang, J., Mo, J., Da, X., Li, Q., Fan, M., et al. (2022). Exosomal lncRNA TUG1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes liver cancer cell migration, invasion, and glycolysis by regulating the miR-524-5p/SIX1 axis. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 27 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s11658-022-00309-9
Lu, Y., Chen, L., Li, L., and Cao, Y. (2020). Exosomes derived from brain metastatic breast cancer cells destroy the blood-brain barrier by carrying lncRNA GS1-600G8.5. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 7461727. doi:10.1155/2020/7461727
Lukanović, D., Kobal, B., and Černe, K. (2022). Ovarian cancer: treatment and resistance to pharmacotherapy. Reprod. Med. 3 (2), 127–140. doi:10.3390/reprodmed3020011
Luo, X., Wei, J., Yang, F. L., Pang, X. X., Shi, F., Wei, Y. X., et al. (2019). Exosomal lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 affects cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer cells through regulating microRNA-34b/TUFT1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 19, 323. doi:10.1186/s12935-019-1042-4
Luo, J., Pu, Q., and Wu, X. (2024). Recent advances of exosomes derived from skeletal muscle and crosstalk with other tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (20), 10877. doi:10.3390/ijms252010877
Ma, L., Bajic, V. B., and Zhang, Z. (2013). On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10 (6), 925–933. doi:10.4161/rna.24604
Macpherson, I. R., Rainero, E., Mitchell, L. E., van den Berghe, P. V. E., Speirs, C., Dozynkiewicz, M. A., et al. (2014). CLIC3 controls recycling of late endosomal MT1-MMP and dictates invasion and metastasis in breast cancer. J. Cell Sci. 127 (Pt 18), 3893–3901. doi:10.1242/jcs.135947
Mahapatra, E., Sengupta, D., Kumar, R., Dehury, B., Das, S., Roy, M., et al. (2022). Phenethylisothiocyanate potentiates platinum therapy by reversing cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 803114. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.803114
Magnani, L., Frige, G., Gadaleta, R. M., Corleone, G., Fabris, S., Kempe, M. H., et al. (2017). Acquired CYP19A1 amplification is an early specific mechanism of aromatase inhibitor resistance in ERα metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 49 (3), 444–450. doi:10.1038/ng.3773
Makker, V., Taylor, M. H., Aghajanian, C., Oaknin, A., Mier, J., Cohn, A. L., et al. (2020). Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced endometrial cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 38 (26), 2981–2992. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.02627
Makler, A., and Asghar, W. (2020). Exosomal biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and patient monitoring. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn 20 (4), 387–400. doi:10.1080/14737159.2020.1731308
Malumbres, M., and Barbacid, M. (2009). Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9 (3), 153–166. doi:10.1038/nrc2602
Manzoor, T., Farooq, N., Sharma, A., Shiekh, P. A., Hassan, A., Dar, L. A., et al. (2024). Exosomes in nanomedicine: a promising cell-free therapeutic intervention in burn wounds. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15 (1), 355. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03970-3
Maoz, A., Matsuo, K., Ciccone, M. A., Matsuzaki, S., Klar, M., Roman, L. D., et al. (2020). Molecular pathways and targeted therapies for malignant ovarian germ cell tumors and sex cord-stromal tumors: a contemporary review. Cancers (Basel) 12 (6), 1398. doi:10.3390/cancers12061398
Marleau, A. M., Chen, C. S., Joyce, J. A., and Tullis, R. H. (2012). Exosome removal as a therapeutic adjuvant in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 10, 134. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-10-134
Marra, A., Trapani, D., Viale, G., Criscitiello, C., and Curigliano, G. (2020). Practical classification of triple-negative breast cancer: intratumoral heterogeneity, mechanisms of drug resistance, and novel therapies. NPJ Breast Cancer 6, 54. doi:10.1038/s41523-020-00197-2
Martínez-Sáez, O., and Prat, A. (2021). Current and future management of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. JCO Oncol. Pract. 17 (10), 594–604. doi:10.1200/OP.21.00172
Mashouri, L., Yousefi, H., Aref, A. R., Ahadi, A. M., Molaei, F., and Alahari, S. K. (2019). Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 75. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0991-5
Masoud, G. N., and Li, W. (2015). HIF-1α pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 5 (5), 378–389. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.007
Mathieu, M., Martin-Jaular, L., Lavieu, G., and Théry, C. (2019). Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 21 (1), 9–17. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0250-9
Matthews, B. G., Bowden, N. A., and Wong-Brown, M. W. (2021). Epigenetic mechanisms and therapeutic targets in chemoresistant high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13 (23), 5993. doi:10.3390/cancers13235993
McGuire, W. P., and Markman, M. (2003). Primary ovarian cancer chemotherapy: current standards of care. Br. J. Cancer 89 (Suppl. 3), S3–S8. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601494
McKelvey, K. J., Powell, K. L., Ashton, A. W., Morris, J. M., and McCracken, S. A. (2015). Exosomes: mechanisms of uptake. J. Circ. Biomark. 4, 7. doi:10.5772/61186
Medina, M. A., Oza, G., Sharma, A., Arriaga, L. G., Hernández Hernández, J. M., Rotello, V. M., et al. (2020). Triple-negative breast cancer: a review of conventional and advanced therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17 (6), 2078. doi:10.3390/ijerph17062078
Mei, R., Qin, W., Zheng, Y., Wan, Z., and Liu, L. (2022). Role of adipose tissue derived exosomes in metabolic disease. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 873865. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.873865
Merikhian, P., Eisavand, M. R., and Farahmand, L. (2021). Triple-negative breast cancer: understanding Wnt signaling in drug resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 21 (1), 419. doi:10.1186/s12935-021-02107-3
Mikamori, M., Yamada, D., Eguchi, H., Hasegawa, S., Kishimoto, T., Tomimaru, Y., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-155 controls exosome synthesis and promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 7, 42339. doi:10.1038/srep42339
Miller, W. R. (2003). Aromatase inhibitors: mechanism of action and role in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 30 (4 Suppl. 14), 3–11. doi:10.1016/s0093-7754(03)00302-6
Mills, J. N., Rutkovsky, A. C., and Giordano, A. (2018). Mechanisms of resistance in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer: overcoming resistance to tamoxifen/aromatase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 41, 59–65. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2018.04.009
Min, L., Zhu, T., Lv, B., An, T., Zhang, Q., Shang, Y., et al. (2022). Exosomal LncRNA RP5-977B1 as a novel minimally invasive biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 27 (6), 1013–1024. doi:10.1007/s10147-022-02129-5
Mirza, M. R., Monk, B. J., Herrstedt, J., Oza, A. M., Mahner, S., Redondo, A., et al. (2016). Niraparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 375 (22), 2154–2164. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1611310
Mohammad, F., Mondal, T., Guseva, N., Pandey, G. K., and Kanduri, C. (2010). Kcnq1ot1 noncoding RNA mediates transcriptional gene silencing by interacting with Dnmt1. Development 137 (15), 2493–2499. doi:10.1242/dev.048181
Mondal, P., and Meeran, S. M. (2021). microRNAs in cancer chemoresistance: the sword and the shield. Noncoding RNA Res. 6 (4), 200–210. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2021.12.001
Montecalvo, A., Shufesky, W. J., Stolz, D. B., Sullivan, M. G., Wang, Z., Divito, S. J., et al. (2008). Exosomes as a short-range mechanism to spread alloantigen between dendritic cells during T cell allorecognition. J. Immunol. 180 (5), 3081–3090. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.3081
Nagano, T., Mitchell, J. A., Sanz, L. A., Pauler, F. M., Ferguson-Smith, A. C., Feil, R., et al. (2008). The Air noncoding RNA epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to chromatin. Science 322 (5908), 1717–1720. doi:10.1126/science.1163802
Naganuma, T., Nakagawa, S., Tanigawa, A., Sasaki, Y. F., Goshima, N., and Hirose, T. (2012). Alternative 3'-end processing of long noncoding RNA initiates construction of nuclear paraspeckles. Embo J. 31 (20), 4020–4034. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.251
New, J., and Thomas, S. M. (2019). Autophagy-dependent secretion: mechanism, factors secreted, and disease implications. Autophagy 15 (10), 1682–1693. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1596479
Nurden, A. T. (2011). Platelets, inflammation and tissue regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 105 (Suppl. 1), S13–S33. doi:10.1160/THS10-11-0720
O'Brien, K., Breyne, K., Ughetto, S., Laurent, L. C., and Breakefield, X. O. (2020). RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21 (10), 585–606. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-0251-y
Ortiz, M., Wabel, E., Mitchell, K., and Horibata, S. (2022). Mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Drug Resist 5 (2), 304–316. doi:10.20517/cdr.2021.147
Osborne, C. K., and Schiff, R. (2011). Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 62, 233–247. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-070909-182917
Ostrowski, M., Carmo, N. B., Krumeich, S., Fanget, I., Raposo, G., Savina, A., et al. (2010). Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 12 (1), 19–13. doi:10.1038/ncb2000
Otto, T., and Sicinski, P. (2017). Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17 (2), 93–115. doi:10.1038/nrc.2016.138
Pan, B. T., and Johnstone, R. M. (1983). Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 33 (3), 967–978. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90040-5
Pan, L., Liang, W., Fu, M., Huang, Z. H., Li, X., Zhang, W., et al. (2017). Exosomes-mediated transfer of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes gastric cancer progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 143 (6), 991–1004. doi:10.1007/s00432-017-2361-2
Pan, R., and Zhou, H. (2020). Exosomal transfer of lncRNA H19 promotes erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via miR-615-3p/ATG7 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 4283–4297. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S241095
Panda, S. S., Sahoo, R. K., Patra, S. K., Biswal, S., and Biswal, B. K. (2024). Molecular insights to therapeutic in cancer: role of exosomes in tumor microenvironment, metastatic progression and drug resistance. Drug Discover. Today, 104061.
Pandey, R. R., Mondal, T., Mohammad, F., Enroth, S., Redrup, L., Komorowski, J., et al. (2008). Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol. Cell 32 (2), 232–246. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.022
Pathania, A. S., and Challagundla, K. B. (2021). Exosomal long non-coding RNAs: emerging players in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 23, 1371–1383. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.039
Peterlin, B. M., Brogie, J. E., and Price, D. H. (2012). 7SK snRNA: a noncoding RNA that plays a major role in regulating eukaryotic transcription. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 3 (1), 92–103. doi:10.1002/wrna.106
Phinney, D. G., and Pittenger, M. F. (2017). Concise review: MSC-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem Cells 35 (4), 851–858. doi:10.1002/stem.2575
Pisignano, G., and Ladomery, M. (2021). Post-transcriptional regulation through long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Noncoding RNA 7 (2), 29. doi:10.3390/ncrna7020029
Porcu, C., Dobrowolny, G., and Scicchitano, B. M. (2024). Exploring the role of extracellular vesicles in skeletal muscle regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (11), 5811.
Prasai, A., Jay, J. W., Jupiter, D., Wolf, S. E., and El Ayadi, A. (2022). Role of exosomes in dermal wound healing: a systematic review. J. Invest. Dermatol. 142 (3 Pt A), 662–678. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2021.07.167
Prensner, J. R., Iyer, M. K., Sahu, A., Asangani, I. A., Cao, Q., Patel, L., et al. (2013). The long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 promotes aggressive prostate cancer and antagonizes the SWI/SNF complex. Nat. Genet. 45 (11), 1392–1398. doi:10.1038/ng.2771
Pujade-Lauraine, E., Banerjee, S., and Pignata, S. (2019). Management of platinum-resistant, relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer and new drug perspectives. J. Clin. Oncol. 37 (27), 2437–2448. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00194
Qian, X., Qu, H., Zhang, F., Peng, S., Dou, D., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Exosomal long noncoding RNA AGAP2-AS1 regulates trastuzumab resistance via inducing autophagy in breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 11 (5), 1962–1981.
Qiu, J. J., Lin, X. J., Tang, X. Y., Zheng, T. T., Lin, Y. Y., and Hua, K. Q. (2018). Exosomal metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 promotes angiogenesis and predicts poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 14 (14), 1960–1973. doi:10.7150/ijbs.28048
Qiu, Y., Zhang, Z., and Wu, M. (2021). Insights into exosomal non-coding RNAs sorting mechanism and clinical application. Front. Oncol. 11, 664904. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.664904
Qu, L., Ding, J., Chen, C., Wu, Z. J., Liu, B., Gao, Y., et al. (2016). Exosome-transmitted lncARSR promotes sunitinib resistance in renal cancer by acting as a competing endogenous RNA. Cancer Cell 29 (5), 653–668. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.004
Reiss, A. B., Ahmed, S., Johnson, M., Saeedullah, U., and De Leon, J. (2023). Exosomes in cardiovascular disease: from mechanism to therapeutic target. Metabolites 13 (4), 479. doi:10.3390/metabo13040479
Ren, J., Ding, L., Zhang, D., Shi, G., Xu, Q., Shen, S., et al. (2018). Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 8 (14), 3932–3948. doi:10.7150/thno.25541
Sahu, A., Singhal, U., and Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2015). Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: from function to translation. Trends Cancer 1 (2), 93–109. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2015.08.010
Saito, A., Yoshida, H., Nishikawa, T., and Yonemori, K. (2021). Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 targeted therapy in endometrial cancer: clinical and pathological perspectives. World J. Clin. Oncol. 12 (10), 868–881. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i10.868
Santoro, A., Angelico, G., Inzani, F., Arciuolo, D., d'Amati, A., Addante, F., et al. (2024). The emerging and challenging role of PD-L1 in patients with gynecological cancers: an updating review with clinico-pathological considerations. Gynecol. Oncol. 184, 57–66. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2024.01.032
Santoro, F., Mayer, D., Klement, R. M., Warczok, K. E., Stukalov, A., Barlow, D. P., et al. (2013). Imprinted Igf2r silencing depends on continuous Airn lncRNA expression and is not restricted to a developmental window. Development 140 (6), 1184–1195. doi:10.1242/dev.088849
Shan, C., Chen, X., Cai, H., Hao, X., Li, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). The emerging roles of autophagy-related MicroRNAs in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17 (1), 134–150. doi:10.7150/ijbs.50773
Sharma, S. V., Lee, D. Y., Li, B., Quinlan, M. P., Takahashi, F., Maheswaran, S., et al. (2010). A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 141 (1), 69–80. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.027
Shedden, K., Xie, X. T., Chandaroy, P., Chang, Y. T., and Rosania, G. R. (2003). Expulsion of small molecules in vesicles shed by cancer cells: association with gene expression and chemosensitivity profiles. Cancer Res. 63 (15), 4331–4337.
Shih, I. M., Wang, Y., and Wang, T. L. (2021). The origin of ovarian cancer species and precancerous landscape. Am. J. Pathol. 191 (1), 26–39. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.09.006
Shirani, N., Mahdi-Esferizi, R., Eshraghi Samani, R., Tahmasebian, S., and Yaghoobi, H. (2024). In silico identification and in vitro evaluation of MRPS30-DT lncRNA and MRPS30 gene expression in breast cancer. Cancer Rep (Hoboken) 7 (6), e2114. doi:10.1002/cnr2.2114
Smolarz, B., Zadrożna-Nowak, A., and Romanowicz, H. (2021). Pharmacogenetics of drug-resistant epilepsy (review of literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (16), 11696. doi:10.3390/ijms222111696
Soltész, B., Buglyó, G., Németh, N., Szilágyi, M., Pös, O., Szemes, T., et al. (2021). The role of exosomes in cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (1), 8. doi:10.3390/ijms23010008
Song, Y., Ren, X., and Feng, C. (2020). SNHG9, delivered by adipocyte-derived exosomes, alleviates inflammation and apoptosis of endothelial cells through suppressing TRADD expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 872, 172977. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172977
Statello, L., Guo, C. J., Chen, L. L., and Huarte, M. (2021). Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22 (2), 96–118. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00315-9
St Laurent, G., Wahlestedt, C., and Kapranov, P. (2015). The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet. 31 (5), 239–251. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2015.03.007
Sun, J., Jia, H., Bao, X., Wu, Y., Zhu, T., Li, R., et al. (2021a). Tumor exosome promotes Th17 cell differentiation by transmitting the lncRNA CRNDE-h in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12 (1), 123. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03376-y
Sun, K., Deng, W., Zhang, S., Cai, N., Jiao, S., Song, J., et al. (2013). Paradoxical roles of autophagy in different stages of tumorigenesis: protector for normal or cancer cells. Cell Biosci. 3 (1), 35. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-3-35
Sun, M., and Kraus, W. L. (2015). From discovery to function: the expanding roles of long noncoding RNAs in physiology and disease. Endocr. Rev. 36 (1), 25–64. doi:10.1210/er.2014-1034
Sun, W., Li, J., Zhou, L., Han, J., Liu, R., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). The c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 regulatory axis regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 10 (5), 1981–1996. doi:10.7150/thno.37621
Sun, Y., Hao, G., Zhuang, M., Lv, H., Liu, C., and Su, K. (2022). MEG3 LncRNA from exosomes released from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances cisplatin chemoresistance in SCLC via a MiR-15a-5p/CCNE1 Axis. Yonsei Med. J. 63 (3), 229–240. doi:10.3349/ymj.2022.63.3.229
Sun, Z., Sun, D., Feng, Y., Zhang, B., Sun, P., Zhou, B., et al. (2021b). Exosomal linc-ROR mediates crosstalk between cancer cells and adipocytes to promote tumor growth in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 26, 253–268. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2021.06.001
Sundararajan, V., Sarkar, F. H., and Ramasamy, T. S. (2018). Correction to: the versatile role of exosomes in cancer progression: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cell Oncol. (Dordr) 41 (4), 463. doi:10.1007/s13402-018-0396-2
Tai, Y. L., Chen, K. C., Hsieh, J. T., and Shen, T. L. (2018). Exosomes in cancer development and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 109 (8), 2364–2374. doi:10.1111/cas.13697
Takahashi, K., Yan, I. K., Haga, H., and Patel, T. (2014b). Modulation of hypoxia-signaling pathways by extracellular linc-RoR. J. Cell Sci. 127 (Pt 7), 1585–1594. doi:10.1242/jcs.141069
Takahashi, K., Yan, I. K., Kogure, T., Haga, H., and Patel, T. (2014c). Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of long non-coding RNA ROR modulates chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular cancer. FEBS Open Bio 4, 458–467. doi:10.1016/j.fob.2014.04.007
Takahashi, K., Yan, I. K., Wood, J., Haga, H., and Patel, T. (2014a). Involvement of extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) in tumor cell responses to chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Res. 12 (10), 1377–1387. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0636
Takahashi, N., Hatakeyama, K., Nagashima, T., Ohshima, K., Urakami, K., Yamaguchi, K., et al. (2023). Characterization of rare histological subtypes of ovarian cancer based on molecular profiling. Cancer Med. 12 (1), 387–395. doi:10.1002/cam4.4927
Takeiwa, T., Ikeda, K., Mitobe, Y., Horie-Inoue, K., and Inoue, S. (2020). Long noncoding RNAs involved in the endocrine therapy resistance of breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 12 (6), 1424. doi:10.3390/cancers12061424
Tan, H., Zhang, S., Zhang, J., Zhu, L., Chen, Y., Yang, H., et al. (2020). Long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: new emerging biological functions and therapeutic implications. Theranostics 10 (19), 8880–8902. doi:10.7150/thno.47548
Tang, H., Zhu, D., Li, W., Zhang, G., Zhang, H., and Peng, Q. (2024). Exosomal AFAP1-AS1 promotes the growth, metastasis, and glycolysis of pituitary adenoma by inhibiting HuR degradation. Mol. Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04387-y
Tang, S., Zheng, K., Tang, Y., Li, Z., Zou, T., and Liu, D. (2019a). Overexpression of serum exosomal HOTAIR is correlated with poor survival and poor response to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J. Biosci. 44 (2), 37. doi:10.1007/s12038-019-9861-y
Tang, X., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Lin, X., Zheng, T., Liu, X., et al. (2019b). Circulating serum exosomal aHIF is a novel prognostic predictor for epithelial ovarian cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 12, 7699–7711. doi:10.2147/OTT.S220533
Taniue, K., and Akimitsu, N. (2021). The functions and unique features of LncRNAs in cancer development and tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (2), 632. doi:10.3390/ijms22020632
Tellez-Gabriel, M., and Heymann, D. (2019). Exosomal lncRNAs: the newest promising liquid biopsy. Cancer Drug Resist 2 (4), 1002–1017. doi:10.20517/cdr.2019.69
Teng, Y., Kang, H., and Chu, Y. (2019). Identification of an exosomal long noncoding RNA SOX2-OT in plasma as a promising biomarker for lung squamous cell carcinoma. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 23 (4), 235–240. doi:10.1089/gtmb.2018.0103
Toh, T. B., Lim, J. J., and Chow, E. K. (2017). Epigenetics in cancer stem cells. Mol. Cancer 16 (1), 29. doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0596-9
Trajkovic, K., Hsu, C., Chiantia, S., Rajendran, L., Wenzel, D., Wieland, F., et al. (2008). Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319 (5867), 1244–1247. doi:10.1126/science.1153124
Tripathi, V., Ellis, J. D., Shen, Z., Song, D. Y., Pan, Q., Watt, A. T., et al. (2010). The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 39 (6), 925–938. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.011
Uccello, M., Boussios, S., Samartzis, E. P., and Moschetta, M. (2020). Systemic anti-cancer treatment in malignant ovarian germ cell tumours (MOGCTs): current management and promising approaches. Ann. Transl. Med. 8 (24), 1713. doi:10.21037/atm.2020.04.15
Ueno, T., Masuda, N., Kamigaki, S., Morimoto, T., Saji, S., Imoto, S., et al. (2019). Differential involvement of autophagy and apoptosis in response to chemoendocrine and endocrine therapy in breast cancer: JBCRG-07TR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (4), 984. doi:10.3390/ijms20040984
Vaidya, F. U., Sufiyan Chhipa, A., Mishra, V., Gupta, V. K., Rawat, S. G., Kumar, A., et al. (2022). Molecular and cellular paradigms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Cancer Rep. Hob. 5 (12), e1291. doi:10.1002/cnr2.1291
van Niel, G., Charrin, S., Simoes, S., Romao, M., Rochin, L., Saftig, P., et al. (2011). The tetraspanin CD63 regulates ESCRT-independent and -dependent endosomal sorting during melanogenesis. Dev. Cell 21 (4), 708–721. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.019
van Niel, G., D'Angelo, G., and Raposo, G. (2018). Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19 (4), 213–228. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.125
van Zyl, B., Tang, D., and Bowden, N. A. (2018). Biomarkers of platinum resistance in ovarian cancer: what can we use to improve treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 25 (5), R303–r318. doi:10.1530/ERC-17-0336
Vasan, N., Baselga, J., and Hyman, D. M. (2019). A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 575 (7782), 299–309. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1730-1
Venkata, P. P., Chen, Y., Alejo, S., He, Y., Palacios, B. E., Loeffel, I., et al. (2022). KDM1A inhibition augments the efficacy of rapamycin for the treatment of endometrial cancer. Cancer Lett. 524, 219–231. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.019
Volkova, L. V., Pashov, A. I., and Omelchuk, N. N. (2021). Cervical carcinoma: oncobiology and biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (22), 12571. doi:10.3390/ijms222212571
Walker, C. A., Spirtos, A. N., and Miller, D. S. (2023). Pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib combination therapy for advanced endometrial carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 23 (4), 361–368. doi:10.1080/14737140.2023.2194634
Wan, G., Hu, X., Liu, Y., Han, C., Sood, A. K., Calin, G. A., et al. (2013). A novel non-coding RNA lncRNA-JADE connects DNA damage signalling to histone H4 acetylation. Embo J. 32 (21), 2833–2847. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.221
Wan, X., Guan, S., Hou, Y., Qin, Y., Zeng, H., Yang, L., et al. (2021). FOSL2 promotes VEGF-independent angiogenesis by transcriptionnally activating Wnt5a in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts. Theranostics 11 (10), 4975–4991. doi:10.7150/thno.55074
Wang, G., Chen, H. W., Oktay, Y., Zhang, J., Allen, E. L., Smith, G. M., et al. (2010b). PNPASE regulates RNA import into mitochondria. Cell 142 (3), 456–467. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.035
Wang, J., Liu, X., Wu, H., Ni, P., Gu, Z., Qiao, Y., et al. (2010a). CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (16), 5366–5383. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq285
Wang, J., Lv, B., Su, Y., Wang, X., Bu, J., and Yao, L. (2019b). Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA HOTTIP promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells by regulating HMGA1/miR-218 Axis. Onco Targets Ther. 12, 11325–11338. doi:10.2147/OTT.S231846
Wang, J., Ma, W., and Liu, Y. (2017). Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes bladder cancer cells proliferation but inhibits apoptosis via regulation of ZIC2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark. 20 (4), 425–434. doi:10.3233/CBM-170188
Wang, J., Wang, N., Zheng, Z., Che, Y., Suzuki, M., Kano, S., et al. (2022). Exosomal lncRNA HOTAIR induce macrophages to M2 polarization via PI3K/p-AKT/AKT pathway and promote EMT and metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 22 (1), 1208. doi:10.1186/s12885-022-10210-5
Wang, J., Zheng, Y., and Zhao, M. (2016). Exosome-based cancer therapy: implication for targeting cancer stem cells. Front. Pharmacol. 7, 533. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00533
Wang, K. C., Yang, Y. W., Liu, B., Sanyal, A., Corces-Zimmerman, R., Chen, Y., et al. (2011). A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature 472 (7341), 120–124. doi:10.1038/nature09819
Wang, T., Li, J., Yang, L., Wu, M., and Ma, Q. (2021a). The role of long non-coding RNAs in human imprinting disorders: prospective therapeutic targets. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 730014. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.730014
Wang, X., Jian, Q., Zhang, Z., Gu, J., and Wang, Y. (2024a). Effect of tumor-derived extracellular vesicle-shuttled lncRNA MALAT1 on proliferation, invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by regulating macrophage M2 polarization via the POSTN/Hippo/YAP axis. Transl. Oncol. 49, 102076. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102076
Wang, X., Pei, X., Guo, G., Qian, X., Dou, D., Zhang, Z., et al. (2020). Exosome-mediated transfer of long noncoding RNA H19 induces doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 235 (10), 6896–6904. doi:10.1002/jcp.29585
Wang, X., Zhang, H., and Chen, X. (2019a). Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist 2 (2), 141–160. doi:10.20517/cdr.2019.10
Wang, Y., Liu, Q., and Wang, F. (2021b). Potential roles of exosome non-coding RNAs in cancer chemoresistance (Review). Oncol. Rep. 45 (2), 439–447. doi:10.3892/or.2020.7887
Wang, Y. H., Ji, J., Wang, B. C., Chen, H., Yang, Z. H., Wang, K., et al. (2018). Tumor-derived exosomal long noncoding RNAs as promising diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 46 (2), 532–545. doi:10.1159/000488620
Wang, Y., Xu, F., Zhong, J. Y., Lin, X., Shan, S. K., Guo, B., et al. (2020). Exosomes as mediators of cell-to-cell communication in thyroid disease. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 4378345. doi:10.1155/2020/4378345
Wang, Z., Luo, J., Huang, H., Wang, L., Lv, T., Wang, Z., et al. (2024b). NAT10-mediated upregulation of GAS5 facilitates immune cell infiltration in non-small cell lung cancer via the MYBBP1A-p53/IRF1/type I interferon signaling axis. Cell Death Discov. 10 (1), 240. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-01997-2
Weaver, B. A. (2014). How Taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 25 (18), 2677–2681. doi:10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0916
Whiteside, T. L. (2016). Tumor-derived exosomes and their role in cancer progression. Adv. Clin. Chem. 74, 103–141. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2015.12.005
Wu, Y., Wang, Y., Wei, M., Han, X., Xu, T., and Cui, M. (2020). Advances in the study of exosomal lncRNAs in tumors and the selection of research methods. Biomed. Pharmacother. 123, 109716. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109716
Xavier, C. P. R., Caires, H. R., Barbosa, M. A. G., Bergantim, R., Guimarães, J. E., and Vasconcelos, M. H. (2020). The role of extracellular vesicles in the hallmarks of cancer and drug resistance. Cells 9 (5), 1141. doi:10.3390/cells9051141
Xian, D., Niu, L., Zeng, J., and Wang, L. (2021). LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 secreted by tumor cell-derived exosomes mediates immune escape in colorectal cancer by regulating PD-L1 ubiquitination via MiR-30a-5p/USP22. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 653808. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.653808
Xiao, Y., Xiao, T., Ou, W., Wu, Z., Wu, J., Tang, J., et al. (2020a). LncRNA SNHG16 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in human cancers. Biomark. Res. 8, 41. doi:10.1186/s40364-020-00221-4
Xiao, Y., Zhong, J., Zhong, B., Huang, J., Jiang, L., Jiang, Y., et al. (2020b). Exosomes as potential sources of biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 476, 13–22. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.01.033
Xie, K., Liang, C., Li, Q., Yan, C., Wang, C., Gu, Y., et al. (2016). Role of ATG10 expression quantitative trait loci in non-small cell lung cancer survival. Int. J. Cancer 139 (7), 1564–1573. doi:10.1002/ijc.30205
Xie, Y., Dang, W., Zhang, S., Yue, W., Yang, L., Zhai, X., et al. (2019). The role of exosomal noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 37. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0984-4
Xing, C., Sun, S. G., Yue, Z. Q., and Bai, F. (2021). Role of lncRNA LUCAT1 in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 134, 111158. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111158
Xing, L., Tang, X., Wu, K., Huang, X., Yi, Y., and Huan, J. (2020). LncRNA HAND2-AS1 suppressed the growth of triple negative breast cancer via reducing secretion of MSCs derived exosomal miR-106a-5p. Aging (Albany NY) 13 (1), 424–436. doi:10.18632/aging.202148
Xiong, Y., Wang, Y., Ou, H., and Zhou, Y. (2022). HPV E7 oncogene expression impairs Rb function and confers CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in cervical cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 40, e17504. doi:10.1200/jco.2022.40.16_suppl.e17504
Xu, C. G., Yang, M. F., Ren, Y. Q., Wu, C. H., and Wang, L. Q. (2016). Exosomes mediated transfer of lncRNA UCA1 results in increased tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 20 (20), 4362–4368.
Xu, H., Zhou, J., Tang, J., Min, X., Yi, T., Zhao, J., et al. (2020b). Identification of serum exosomal lncRNA MIAT as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 34 (8), e23323. doi:10.1002/jcla.23323
Xu, J., Xiao, Y., Liu, B., Pan, S., Liu, Q., Shan, Y., et al. (2020a). Exosomal MALAT1 sponges miR-26a/26b to promote the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer via FUT4 enhanced fucosylation and PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 39 (1), 54. doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01562-6
Xue, D., Han, J., Liang, Z., Jia, L., Liu, Y., Tuo, H., et al. (2022). Current perspectives on the unique roles of exosomes in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 9, 99–112. doi:10.2147/JHC.S351038
Xue, M., Chen, W., Xiang, A., Wang, R., Chen, H., Pan, J., et al. (2017). Hypoxic exosomes facilitate bladder tumor growth and development through transferring long non-coding RNA-UCA1. Mol. Cancer 16 (1), 143. doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0714-8
Xue, X., Yang, Y. A., Zhang, A., Fong, K. W., Kim, J., Song, B., et al. (2016). LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 35 (21), 2746–2755. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.340
Yaghoobi, H., Azizi, H., Oskooei, V. K., Taheri, M., and Ghafouri-Fard, S. (2018). Assessment of expression of interferon γ (IFN-G) gene and its antisense (IFNG-AS1) in breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 16 (1), 211. doi:10.1186/s12957-018-1508-1
Yan, H., and Bu, P. (2021). Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. 65 (4), 625–639. doi:10.1042/EBC20200032
Yang, J., Liu, Z., Liu, B., and Sun, L. (2022). Silencing of circCYP51A1 represses cell progression and glycolysis by regulating miR-490-3p/KLF12 axis in osteosarcoma under hypoxia. J. Bone Oncol. 37, 100455. doi:10.1016/j.jbo.2022.100455
Yang, J. X., Xie, P., Li, Y. S., Wen, T., and Yang, X. C. (2020). Osteoclast-derived miR-23a-5p-containing exosomes inhibit osteogenic differentiation by regulating Runx2. Cell Signal 70, 109504. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109504
Yang, L., Peng, X., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Ma, Y., Wu, C., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes exosome secretion by regulating RAB35 and SNAP23 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 78. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0990-6
Yang, X., Yi, C., Luo, N., and Gong, C. (2014). Nanomedicine to overcome cancer multidrug resistance. Curr. Drug Metab. 15 (6), 632–649. doi:10.2174/1389200215666140926154443
Yang, X., Geng, B., Yan, J., Lin, L., Zhao, X., Xiao, H., et al. (2023). The role of exosomes in regulation and application of vascular homeostasis and vascular grafts. Smart Mater. Med. 4, 538–551.
Yang, Y., Wu, S. F., and Bao, W. (2024). Molecular subtypes of endometrial cancer: implications for adjuvant treatment strategies. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 164 (2), 436–459. doi:10.1002/ijgo.14969
Yang, Y. N., Zhang, R., Du, J. W., Yuan, H. H., Li, Y. J., Wei, X. L., et al. (2018). Predictive role of UCA1-containing exosomes in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 18, 164. doi:10.1186/s12935-018-0660-6
Yao, J., Deng, K., Huang, J., Zeng, R., and Zuo, J. (2020). Progress in the understanding of the mechanism of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 592912. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.592912
Yao, R. W., Wang, Y., and Chen, L. L. (2019). Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 21 (5), 542–551. doi:10.1038/s41556-019-0311-8
Ye, P., Feng, L., Shi, S., and Dong, C. (2022). The mechanisms of lncRNA-mediated multidrug resistance and the clinical application prospects of lncRNAs in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 14 (9), 2101. doi:10.3390/cancers14092101
Yin, J., Yan, X., Yao, X., Zhang, Y., Shan, Y., Mao, N., et al. (2012). Secretion of annexin A3 from ovarian cancer cells and its association with platinum resistance in ovarian cancer patients. J. Cell Mol. Med. 16 (2), 337–348. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01316.x
Yin, Z., Zhou, Y., Ma, T., Chen, S., Shi, N., Zou, Y., et al. (2020). Down-regulated lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in M2 macrophage-derived exosomes elevates miR-122-5p to restrict XIAP, thereby limiting pancreatic cancer development. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24 (9), 5028–5038. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15125
You, L. N., Tai, Q. W., Xu, L., Hao, Y., Guo, W. J., Zhang, Q., et al. (2021). Exosomal LINC00161 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis via regulating miR-590-3p/ROCK axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 28 (6), 719–736. doi:10.1038/s41417-020-00269-2
Yousefi, H., Maheronnaghsh, M., Molaei, F., Mashouri, L., Reza Aref, A., Momeny, M., et al. (2020). Long noncoding RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: classification, and mechanisms in breast cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Oncogene 39 (5), 953–974. doi:10.1038/s41388-019-1040-y
Yu, W., Hurley, J., Roberts, D., Chakrabortty, S. K., Enderle, D., Noerholm, M., et al. (2021). Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 32 (4), 466–477. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.074
Yuan, P., Ding, L., Chen, H., Wang, Y., Li, C., Zhao, S., et al. (2021). Neural stem cell-derived exosomes regulate neural stem cell differentiation through miR-9-hes1 Axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 601600. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.601600
Yuan, Z., and Huang, W. (2021). New developments in exosomal lncRNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 8, 709169. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.709169
Yun, C. W., and Lee, S. H. (2018). The roles of autophagy in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (11), 3466. doi:10.3390/ijms19113466
Zamarin, D., and Jazaeri, A. A. (2016). Leveraging immunotherapy for the treatment of gynecologic cancers in the era of precision medicine. Gynecol. Oncol. 141 (1), 86–94. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.12.030
Zampetaki, A., Albrecht, A., and Steinhofel, K. (2018). Long non-coding RNA structure and function: is there a link? Front. Physiol. 9, 1201. doi:10.3389/fphys.2018.01201
Zang, J., Lu, D., and Xu, A. (2020). The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J. Neurosci. Res. 98 (1), 87–97. doi:10.1002/jnr.24356
Zhang, L., Peng, D., Sood, A. K., Dang, C. V., and Zhong, X. (2018). Shedding light on the dark cancer genomes: long noncoding RNAs as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 17 (9), 1816–1823. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0124
Zhang, M., Viennois, E., Prasad, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, Z., et al. (2016). Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: a novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials 101, 321–340. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.06.018
Zhang, W., Wang, Q., Yang, Y., Zhou, S., Zhang, P., and Feng, T. (2021). The role of exosomal lncRNAs in cancer biology and clinical management. Exp. Mol. Med. 53 (11), 1669–1673. doi:10.1038/s12276-021-00699-4
Zhang, W., Yan, Y., Peng, J., Thakur, A., Bai, N., Yang, K., et al. (2022). Decoding roles of exosomal lncRNAs in tumor-immune regulation and therapeutic potential. Cancers (Basel) 15 (1), 286. doi:10.3390/cancers15010286
Zhang, X., Hong, S., Yang, J., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Peng, J., et al. (2023). Purvalanol A induces apoptosis and reverses cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Anticancer Drugs 34 (1), 29–43. doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000001339
Zhang, Y. (2021). The root cause of drug resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer and the therapeutic approaches to overcoming the resistance. Pharmacol. Ther. 218, 107677. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107677
Zhang, Z., Yin, J., Lu, C., Wei, Y., Zeng, A., and You, Y. (2019). Exosomal transfer of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 enhances chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 166. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1139-6
Zhao, W., Qin, P., Zhang, D., Cui, X., Gao, J., Yu, Z., et al. (2019a). Long non-coding RNA PVT1 encapsulated in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by stabilizing ERG and sponging miR-183-5p. Aging (Albany NY) 11 (21), 9581–9596. doi:10.18632/aging.102406
Zhao, W., Shan, B., He, D., Cheng, Y., Li, B., Zhang, C., et al. (2019b). Recent progress in characterizing long noncoding RNAs in cancer drug resistance. J. Cancer 10 (26), 6693–6702. doi:10.7150/jca.30877
Zheng, Z., Chen, M., Xing, P., Yan, X., and Xie, B. (2019). Increased expression of exosomal AGAP2-AS1 (AGAP2 antisense RNA 1) in breast cancer cells inhibits trastuzumab-induced cell cytotoxicity. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 2211–2220. doi:10.12659/MSM.915419
Zhong, L., Wang, J., Wang, P., Liu, X., Liu, P., Cheng, X., et al. (2015). Neural stem cell-derived exosomes and regeneration: cell-free therapeutic strategies for traumatic brain injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14 (1), 198. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03409-1
Zhou, B., Guo, H., and Tang, J. (2019). Long non-coding RNA tfap2a-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in breast cancer via miR-933/SMAD2. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 1242–1253. doi:10.12659/MSM.912421
Zhou, D., Gu, J., Wang, Y., Wu, H., Cheng, W., Wang, Q., et al. (2021d). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 transported by extracellular vesicles contributes to breast cancer development by sponging microRNA-141-3p and regulating KLF12. Cell Biosci. 11 (1), 68. doi:10.1186/s13578-021-00556-x
Zhou, D., Xia, Z., Xie, M., Gao, Y., Yu, Q., and He, B. (2021b). Exosomal long non-coding RNA SOX2 overlapping transcript enhances the resistance to EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer cell line H1975. Hum. Cell 34 (5), 1478–1489. doi:10.1007/s13577-021-00572-6
Zhou, H., Liu, W., Zhou, Y., Hong, Z., Ni, J., Zhang, X., et al. (2021a). Therapeutic inhibition of GAS6-AS1/YBX1/MYC axis suppresses cell propagation and disease progression of acute myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 353. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02145-9
Zhou, L., Yao, L., Dai, L., Zhu, H., Ye, X., Wang, S., et al. (2021c). Ovarian endometrioid carcinoma and clear cell carcinoma: a 21-year retrospective study. J. Ovarian Res. 14 (1), 63. doi:10.1186/s13048-021-00804-1
Zhou, M., He, X., Mei, C., and Ou, C. (2023). Exosome derived from tumor-associated macrophages: biogenesis, functions, and therapeutic implications in human cancers. Biomark Res. 11 (1), 100. doi:10.1186/s40364-023-00538-w
Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Guo, Y., Hu, L., Xiao, Z., Liu, X., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by targeting miR-497-5p/PIM1 axis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 23 (11), 7395–7405. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14601
Zou, J., Peng, H., and Liu, Y. (2021). The roles of exosomes in immunoregulation and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Front. Immunol. 12, 757674. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.757674
Zsiros, E., Lynam, S., Attwood, K. M., Wang, C., Chilakapati, S., Gomez, E. C., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab in combination with bevacizumab and oral metronomic cyclophosphamide in the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer: a phase 2 nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 7 (1), 78–85. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.5945
Keywords: exosomes, long non-coding RNAs, drug resistance, female reproductive system cancers, tumor microenvironment, chemotherapy efficacy, targeted therapies
Citation: Shirani N, Abdi N, Chehelgerdi M, Yaghoobi H and Chehelgerdi M (2025) Investigating the role of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in drug resistance within female reproductive system cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1485422. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1485422
Received: 23 August 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 24 January 2025.
Edited by:
Jaime Villegas, Andres Bello University, ChileReviewed by:
Udayan Bhattacharya, NewYork-Presbyterian, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Shirani, Abdi, Chehelgerdi, Yaghoobi and Chehelgerdi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hajar Yaghoobi, aGFqYXIueWFnaG9vYmk2NEBnbWFpbC5jb20=, aC55YWdob29iaUBza3Vtcy5hYy5pcg==; Mohammad Chehelgerdi, Y2hlaGVsZ2VyZGkxOTkyQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Nooshafarin Shirani, orcid.org/0009-0008-8898-4011, Neda Abdi, orcid.org/0009-0001-9112-3780, Matin Chehelgerdi, orcid.org/0009-0006-6747-3293, Hajar Yaghoobi, orcid.org/0000-0002-5362-2669, Mohammad Chehelgerdi, orcid.org/0000-0002-3483-9424
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
§These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.