
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 28 February 2025
Sec. Epigenomics and Epigenetics
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1443888
Background: Cellular senescence plays a key role in the development of cancer, but the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Recently, several recent studies have shown that RNA methylation is closely related to cancer cell aging. 8-Oxoguanine (o8G) is an important and widely distributed methylation modification whose role in cancer cell senescence is far from elucidated.
Methods: In this study, senescent cancer cell models (CaCO2 cells) were constructed by knocking down the ADAR1 gene. RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing was used to identify the o8G peaks on messenger RNA (mRNA) of normal CaCO2 cells and senescent CaCO2 cells, and the distribution characteristics of mRNA o8G modification were identified. Further bioinformatics analysis of the sequencing data was performed to preliminarily elucidate the potential function of the o8G-modified mRNA.
Results: There were significant differences in mRNA o8G modification distribution between normal and senescent CaCO2 cells. It is suggested that o8G modification may play a key role in inducing cancer cells or promoting cancer cell senescence. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis showed that the mRNAs modified by o8G were enriched in Cellular component organization or biogenesis, Focal adhesion, and RNA binding. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis showed that the genes modified by o8G are concentrated in Focal adhesion signaling pathway, Small cell lung cancer signaling pathway and Proteoglycans in cancer signaling pathway.
Conclusion: This study preliminarily revealed the different distribution patterns of o8G modification between normal CaCO2 cells and senescent CaCO2 cells. Our study established the link between o8G modification and cancer cell senescence, which provides a new insight into the mechanism of cancer cell senescence and a potential therapeutic target for subsequent cancer treatment.
Cellular senescence is a state of growth arrest induced by severe injury and stress, accompanied by a hypersecretory phenotype, morphological changes, and telomere dysfunction (Wang et al., 2022). Several inducing conditions, such as activated oncogenes, cytokines, reactive oxygen species, DNA damage, and nucleotide depletion, can trigger cellular senescence (Calcinotto et al., 2019; Chandrasekaran et al., 2017; Herranz and Gil, 2018; van Deursen, 2014). In cancer cells, senescence exhibits two distinct functions of anti-tumor and pro-tumor. For example, senescence can induce growth arrest in cancer cells, but it can also promote cancer progression through senescence-mediated tumorigenesis immune evasion (Schmitt et al., 2022).
Disorders of epigenetic regulation are an important feature of cellular senescence (López-Otín et al., 2013), and most of the epigenetic modifications are reversible relative to the genetic regulation represented by DNA sequences, suggesting that epigenetic regulation can be intervened to delay aging and treat aging-related diseases. Therefore, through the study of epigenetic changes in the aging process, we can better understand how to delay aging through external means. Epigenetic alterations play an important regulatory role in cellular senescence (Sen et al., 2016). However, most studies have focused on, for example, histone modifications (Baell et al., 2018) and DNA methylation (Xie et al., 2018). However, as an important epigenetic regulator, the role of RNA modification in the cellular senescence of cancer cells is still poorly understood, and only a few studies have explored the role of RNA modification in cancer cell senescence. METTL3 plays a key role in replicating senescence of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, and inhibition of METTL3 or targeted inhibition of CDKN2B methylation can effectively inhibit CRC senescence (Chen et al., 2024). In HeLa cells, METTL3/14 and ADAR1 synergistically increase the translation of p21 in response to oxidative stress, leading to cellular senescence (Li et al., 2017). In addition, there is a study that explores the role of m1 A in cellular senescence. Knockdown of Alkbh3 in NSCLC cells leads to senescence induction and cell cycle arrest, followed by increased expression of cell cycle arrest proteins p27 and p21 (Tasaki et al., 2011).
8-oxoguanine (o8G) RNA modification is a new RNA modification that has attracted extensive attention in the field of molecular biology and epitranscriptomics in recent years. This modification involves the guanine nucleotide in the RNA molecule being attacked by reactive oxygen species (ROS) under specific conditions, which in turn converts to o8G. While 8-oxoguanine (8-oxo-dG) in DNA has been extensively studied, o8G modifications in RNA are more common, as RNA is more susceptible to oxidative damage. This difference may be attributed to the single-stranded nature of RNA and its more dynamic distribution in cells (Hahm et al., 2022).
Recent studies have shown that o8G modification is not just a consequence of oxidative damage, it may also play a role in regulating gene expression. For example, it has been found that position-specific o8G modifications can occur in the seed region of miRNAs and modulate mRNA stability and translation through specific base pairing (Seok et al., 2020). Determining the distribution of o8G within the transcriptome can deepen our understanding of o8G.
Methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) is a commonly used technique for detecting o8G modifications. This method breaks down purified total RNA or mRNA into 100–150 nt RNA fragments; Subsequently, RNA fragments were co-incubated with o8G-modified antibodies, and the o8G-modified RNA fragments were enriched with antibodies for library construction and sequencing. Finally, the o8G-modified transcriptome region was obtained by comparison with the control library co-incubated with the o8G-modified antibody.
ADAR1 is an important regulator of aging, with knockdown of ADAR1 at the cellular level leading to cellular senescence, and overexpression of ADAR1 prevents senescence from occurring (Hao et al., 2022). In this study, we constructed an ADAR1-deficient colorectal cancer cell line to induce senescence in colorectal cancer cells. MeRIP-seq was performed on normal CaCO2 cells and senescent CaCO2 cells induced by ADR1 knockdown, and o8G-specific analysis and in-depth bioinformatics analysis were performed on o8G mRNA.
The results showed that there were significant differences in the number and distribution of o8G between the two groups. The number of o8G methylation peaks in normal CaCO2 cells was much higher than that in ADAR1 knockdown cells, and the distribution of o8G methylation peaks was significantly different, involving all chromosomes. Further bioinformatics analysis showed that the two groups of cells with different degrees of o8G methylation could cause significantly different changes in cell function. Our study preliminarily suggests an association between CRC and o8G modification in mRNA and predicts potential functional changes due to differences in o8G modification in mRNA. These results provide a solid foundation for further understanding the mechanism of cancer cell senescence from the perspective of o8G modification.
ADAR1 is an important regulator of aging, knockdown of ADAR1 can lead to cellular senescence, and overexpression of ADAR1 can prevent senescence from occurring. In the present study, we constructed ADAR1 deletion-induced senescence in colorectal cancer cells. The ADAR1 knockdown lentivirus construction system was obtained from Obio Company (Shanghai, China). CaCO2 cells were stably transfected with ADAR1 knockdown lentivirus (shADAR1) and a corresponding control (shNC) with an anti-puromycin plasmid. The stably transfected CaCO2 cell line was treated with puromycin (4 μg/mL) for 14 days for selection. The sequence of shRNA is GCCCACTGTTATCTTCACTTT.
In this study, we extracted total RNA using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, CA, United States) and reduced rRNA content using Ribo-Zero rRNA removal kit (Illumina, Inc., CA, United States). The quality of RNA was assessed using the OD260/OD280 ratio. When OD260/OD280 values are in the range of 1.8–2.1, RNA purity is considered to meet the standard, and RNA extracted from all samples in this study meets this standard. In this study, we extracted total RNA using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, CA, United States) and reduced rRNA content using Ribo-Zero rRNA removal kit (Illumina, Inc., CA, United States). The quality of RNA was assessed using the OD260/OD280 ratio. When OD260/OD280 values are in the range of 1.8–2.1, RNA purity is considered to meet the standard, and RNA extracted from all samples in this study meets this standard.
Methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) refers to the procedure previously reported in the literature (Lin et al., 2023). Three biological repeats of immunoprecipitation of o8G-containing RNA were performed under each condition and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) was removed from the sample using the GenSeq® rRNA Removal Kit (GenSeq, Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After the samples were qualified, o8G RIP kit from GenSeq was used for o8G-IP reaction. The process is described as follows: RNA is randomly fragmented into fragments of about 200 nt. Protein A/G magnetic beads and Anti-o8G antibody (QED Bioscience, Cat# 12501) were incubated at room temperature for 1 h to bind the antibodies to the magnetic beads. The RNA fragments were then incubated with an antibody bound with magnetic beads at 4°C for 4 h to bind the RNA to the antibody. After incubation, the RNA/antibody complex is cleaned several times. The captured RNA is then eluted from the complex and purified. RNA libraries of purified products were constructed using the GenSeq® Low Input Whole RNA Library Prep Kit (GenSeq, Inc.) kit, and quality control was performed using the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Finally, the library was sequenced by illumina 6000 with 2 × 150 bases in high throughput.
Raw reads (Raw Data) are generated after sequencing, image analysis, base recognition, and quality control on an Illumina novaseq 6000 sequenator. Start with the Q30 for quality control. Q30 > 80% indicates good sequencing quality. Then, use cutadapt software (v1.9.3) (Kechin et al., 2017) to remove the low-quality reads and obtain high-quality clean reads. The clean reads of all samples were matched to the reference genome using Hisat2 (Kim et al., 2015) software (v2.0.4). The MACS (Zhang et al., 2008) software was then used to identify the o8G-modified gene in each sample. Gene identification of differentially o8G modifications was performed using diffReps (Shen et al., 2013) software. Use your own program to screen for peaks located on the exon of the mRNA and annotate accordingly.
The o8G peaks on the mRNA of the samples in each group were combined to obtain the o8G peaks of each group. Use the Bed Tool software to find the common peaks between the two groups. The 50 bp sequences on either side of the apex of the o8G peak were scanned using DRAME software (Bailey, 2011) to find meaningful motifs. The E value of the motif is calculated as the enriched P value multiplied by the number of candidate motif for the test, and the enriched P value is calculated using Fisher’s exact test to enrich the motif in the positive sequence. The lower the E value, the higher the confidence level. Methylation fold enrichment (FE) of each mRNA in the sample was collected and log2 converted. The log FE value is used for clustering in the heatmap. The mRNA region in which the o8G peak is located in each sample was calculated according to the published method and the results were plotted as a pie chart.
Functional analysis (http://www.geneontology.org) of differentially o8G-modified coding genes was performed using Gene Ontology (GO) to annotate and speculate on the function of these differentially methylated genes. Pathway analysis of differentially o8G-modified coding genes was performed using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) to annotate and speculate on the pathways in which they may be involved. In addition, we used the fold change in enrichment intensity of the two groups of samples in the MeRIP-seq experiment to sequence the signals of all coding genes. We chose FDR < 0.25 as the screening criteria. The technology roadmap is shown in Figure 1.
SAβ-Gal is a commonly used marker of cellular senescence. SA-β-Gal (Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase) is a β-galactosidase that exhibits increased activity during cellular senescence. By measuring the activity level of SA-β-Gal in cells, the degree of senescence of cells can be assessed. The results of SA-β-Gal showed that CaCO2 cells senescent compared with normal cells after knockdown of ADAR1, as shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
In this study, we found 1,835 clean o8G methylation peaks in CaCO2 cells and 592 clean o8G methylation peaks in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells. We mapped up to 1,279 CaCO2 annotation genes and 402 sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cellular annotation genes. Among them, 2,131 o8G modification peaks were found in CaCO2 cells and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells, corresponding to 1,478 o8G modification genes (Figures 2A,B). We further investigated the distribution of o8G peaks on chromosomes using Circos software and found that the number and distribution of o8G peaks on each chromosome of CaCO2 cells and senescent CaCO2 cells differed, with the most significant differences between chromosomes 1 and 11 (Figure 2C).
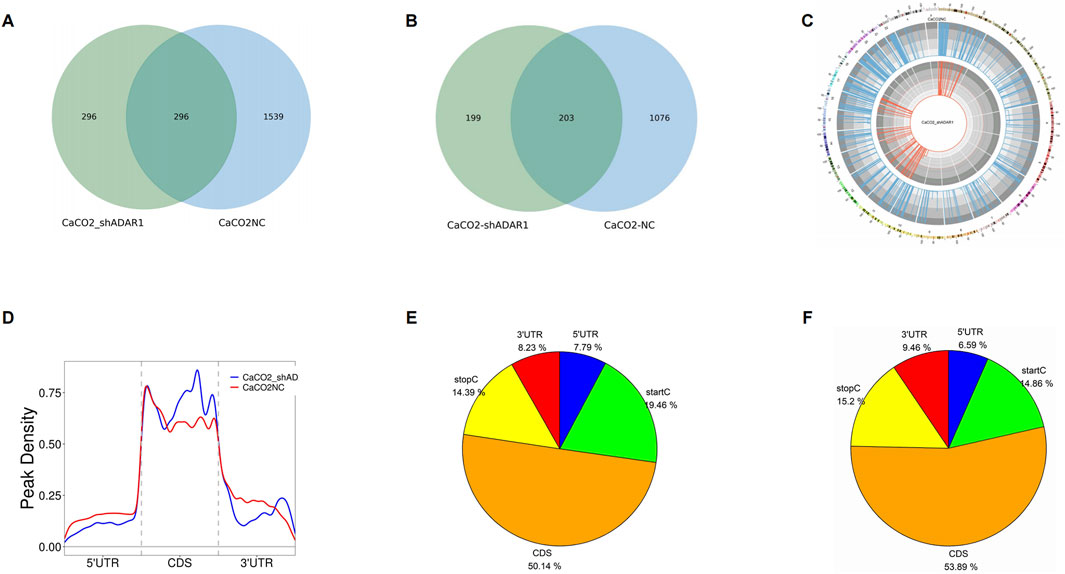
Figure 2. Characteristics of o8G peaks in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (A) Venn diagram of o8G peaks in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (B) Venn diagram of o8G genes in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (C) Visualization of o8G at the chromosome level in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (D) Accumulation of the region of average o8G peaks along all transcripts in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (E,F) Pie chart of the source of methylated mRNA in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell.
Further analysis of the source of the o8G methylation peak revealed that the distribution of the o8G modification covered all regions of the mRNA but was enriched in the coding sequence region (CDS) (Figures 2D–F). However, the o8G peak in CaCO2 cells and the o8G peak in senescent CaCO2 cells exhibit different patterns. The number of o8G peaks in the start codon (start C) of normal CaCO2 cells (CaCO2: 19.46% vs. sh-ADAR1 CaCO2: 14.86%) and the o8G peaks in the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) (CaCO2: 7.79% vs. sh-ADAR1 CaCO2: 6.59%) was higher than that of senescent cancer cells.
The number of o8G peaks in CDS region of normal CaCO2 cells (CaCO2: 50.14%, vs. sh-ADAR1 CaCO2: 53.89%) and the number of o8G peaks in stop codon (stop C) (CaCO2: 14.39% vs. sh-ADAR1 CaCO2) were decreased compared with senescent cancer cells. In the meantime, the number of o8G peaks in 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) of normal CaCO2 cells (CaCO2: 8.23% vs. sh-ADAR1 CaCO2: 9.46%) were also decreased compared with senescent cancer cells.
The results showed that GCWGCWGC was the most common and most confident methylation site motif in CaCO2 cells (p = 1.6e-017), while AGGAGWW is the most common and most confident methylation site motif in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells (p = 1.8e-016) (Figure 3A). We performed methylation heat mapping and cluster analysis on the total data. The results of cluster analysis showed that there were significant differences in expression among the groups, and the expression was consistent within the groups. These differences are due to a decrease in the level of o8G modification due to aging (Figure 3B). In addition, we identified 142 upregulated o8G methylation peaks and 1,574 downregulated o8G methylation peaks of senescent CaCO2 compared to normal CaCO2 cells using DiffReps software (Figure 3C).
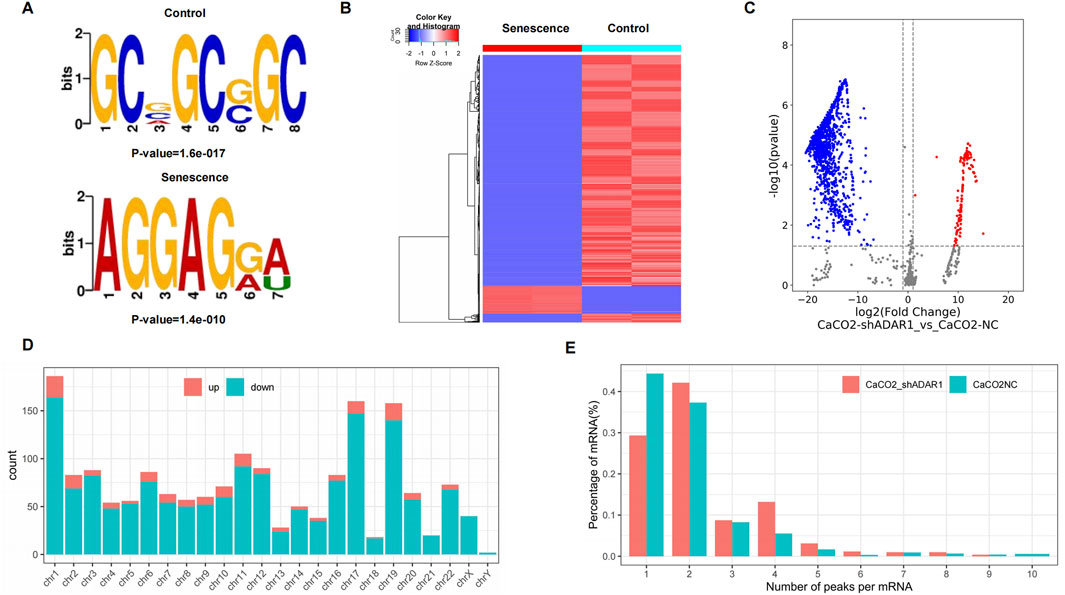
Figure 3. Characteristics of altered o8G peaks in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (A) The sequence motif of o8G sites in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (B) Cluster analysis of methylation in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell. (C) Volcano plots showing the significantly differential o8G peaks. (D) The distributions of altered o8G peaks in human chromosomes. (E) The number of o8G peaks in CaCO2 cell and sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell on each mRNA. Most mRNAs have only one methylation peak.
We have listed the top 10 mRNAs with the largest fold change in Tables 1, 2. Dysregulated o8G methylation peaks are distributed on all chromosomes, especially on chromosome 1 (Figure 3D). In addition, to determine the number of o8G peaks on each mRNA, we calculated the methylation peak and the mRNA corresponding to the methylation peak. The results showed that most of the mRNAs at the methylation site in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells had only one methylation peak (29.8%), while CaCO2 cells had a higher proportion of methylation peaks (44.6%). At the same time, the number of mRNAs with three or more methylation peaks on 1 mRNA in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells was higher than in CaCO2 cells (p < 0.05) (Figure 3E).
To understand the biological function of differentially o8G-modified mRNA in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells and CaCO2 cells, we performed GO analysis. For genes that are upregulated in o8G methylation in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells, GO analysis showed that these genes are enriched in Cellular component organization or biogenesis (GO terminology: BP), Focal adhesion (GO term: CC), and RNA binding (GO term: MF) (Figures 4A–C). As for genes downregulated by o8G modification in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells, GO analysis showed that these genes were mainly enriched in cellular metabolic process (GO term: BP), intracellular anatomical structure (GO term: CC), and protein binding (GO term: MF) (Figures 4D–F).
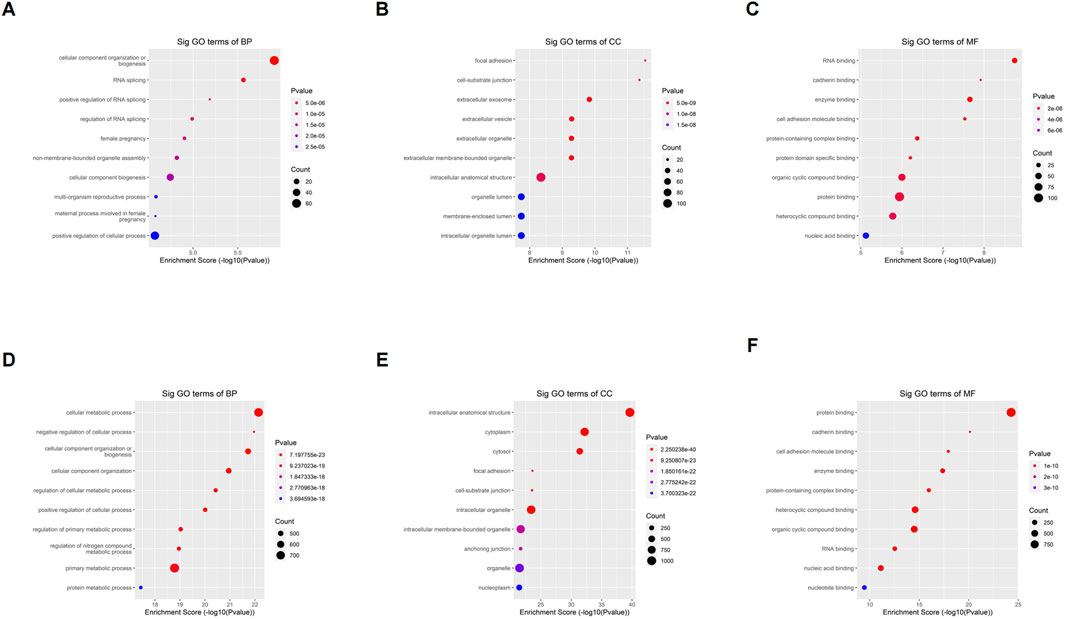
Figure 4. Gene ontology analyses of CaCO2 and shADAR1-CaCO2 cell. (A) Biological processes, (B) cellular components, and (C) molecular functions of genes annotated by upregulated o8G peaks in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell group. (D) Biological processes, (E) cellular components, and (F) molecular functions of genes annotated by downregulated o8G peaks in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell group. The top ten most significant terms are shown for each analysis.
To elucidate the biological function of differentially o8G-modified mRNAs in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells and CaCO2 cells, we performed KEGG pathway analysis on differentially o8G-modified mRNAs. KEGG pathway analysis showed that the mRNA upregulated by o8G modification in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cells was enriched in Focal adhesion signaling pathway, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton signaling pathway and Small cell lung cancer signaling pathway (Figures 5A,B). mRNA downregulated by o8G was enriched in the Salmonella infection signaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer signaling pathway and Adherens junction signaling pathway (Figures 5C,D).
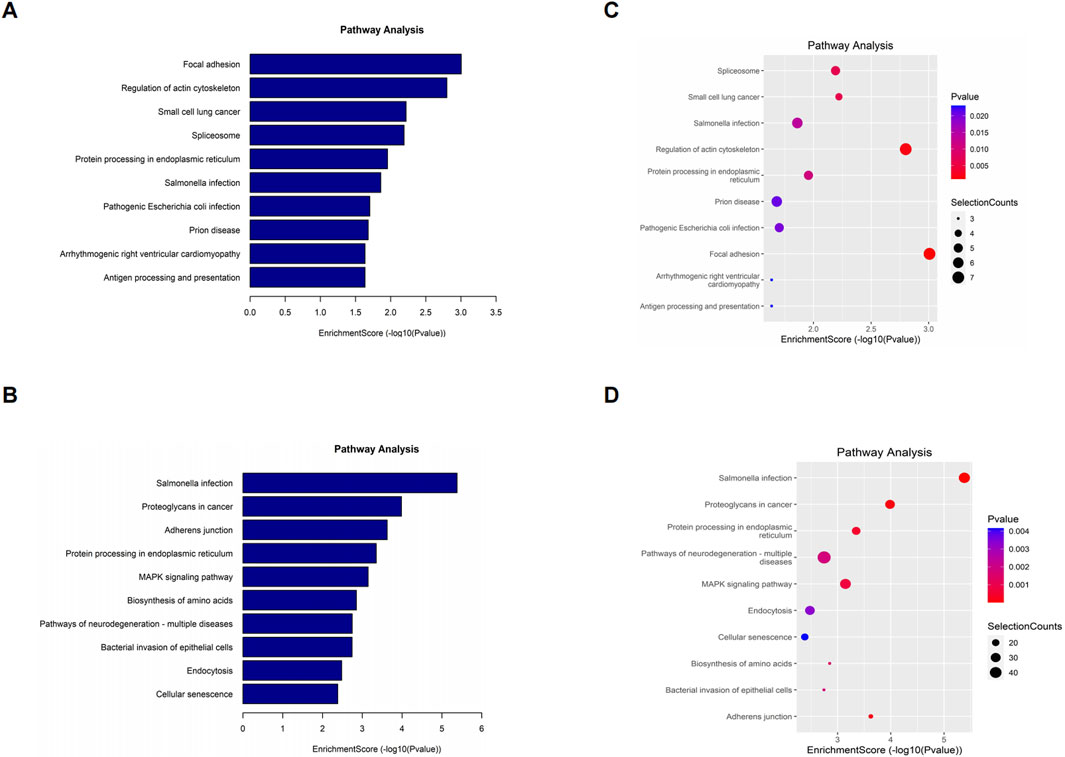
Figure 5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis of differentially methylated genes in CaCO2 and shADAR1-CaCO2 cell. (A,B) Pathway analysis of up-methylated genes in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell group. (C,D) Pathway analysis of down-methylated genes in sh-ADAR1 CaCO2 cell group. The top ten most significant terms are shown for each analysis.
As an especially important post-transcriptional modification, RNA modification has been shown to be closely related to cell senescence and the occurrence and progression of cancer (Zhou et al., 2024; Cavinato et al., 2021), but there are few studies on RNA modification and cancer cell senescence. The o8G modification is an RNA modification produced by the attack of guanine in mRNA by reactive oxygen species in mammalian cells, which can pair with adenine and induce guanine-thymine (G > T) mutations, which is a modification in pathophysiology that causes disease phenotype through reactive oxygen species oxidation. o8G modifications in RNA can cause problems with abnormal quality and translation fidelity (Hahm et al., 2022). Due to the ability of o8G·A to base pair, o8G alters the structural and functional RNA-RNA interactions, enabling post-transcriptional regulation to be redirected (Seok et al., 2020). Recent studies have shown that tRF-1-AspGTC has o8G (5o8G) modification on the 5th G in its seed region, so that 5o8G tRF-1-AspGTC can retarget new downstream genes WNT5A and CASP (Zhang et al., 2024). At present, the mechanism of oxidative modification of o8G RNA, as a new class of RNA modification, is far from elucidated (Eom et al., 2023). In this study, we explored the potential role of o8G modification in senescent cancer cells.
First, our study showed that knockdown of ADAR1 can effectively induce senescence in CRC cells, and knockdown of ADAR1 increases SA-β-gal activity. Next, we used MeRIP-seq to sequence the relevant samples and characterize the o8G modification profile of mRNA in CaCO2 cells and senescent CaCO2 cells using bioinformatics methods. A total of 2,131 o8G modification peaks were found in CaCO2 cells and senescent CaCO2 cells, corresponding to 1,478 o8G modification genes. A total of 1,835 o8G methylation peaks were found in CaCO2 cells and 592 o8G methylation peaks were found in senescent CaCO2 cells. The number of mRNA o8G methylation peaks in CaCO2 cells were significantly higher than that in senescent CaCO2 cells. The results of cluster analysis showed that the degree of methylation could clearly distinguish CaCO2 cells from senescent CaCO2 cells, which further confirmed the potential relationship between o8G and senescent cancer cells. The o8G peaks were distributed in all regions of mRNA, and the CDS region had the highest proportion. The o8G peaks is also found on all chromosomes, mainly on chromosome 1, chromosome 17 and chromosome 19.
We annotated 1,279 genes with altered o8G methylation in CaCO2 cells and 402 genes with altered o8G methylation in senescent CaCO2 cells. The peak value of mRNA o8G modification in CaCO2 cells was significantly higher than that in senescent CaCO2 cells. In senescent CaCO2 cells and normal CaCO2 cells, the peaks of o8G modification on some mRNAs, such as LIF, CAPN2, and HOXB9, can be as high as million-fold.
The number of start codons and o8G modifications of 5′ UTR in CaCO2 cells was higher than that in senescent cancer cells. In the CDS region, the number of stop codons and o8G modifications of 3′ UTR was relatively lower than that of senescent cancer cells. The first codon for mRNA translation is called the start codon, and AUG is the most common start codon, which encodes the amino acid methionine (Met) in eukaryotes and formyl methionine (fMet) in prokaryotes. During protein synthesis, the tRNA recognizes the start codon AUG with the help of some initiation factors and initiates the translation of the mRNA. Considering that the stop codon also has o8G modification, it is reasonable to suspect that o8G modification plays an important regulatory role in mRNA translation. Further research is needed on how specific o8G modification sites regulate the translation of specific mRNAs. 3′ UTR plays a key role in post-transcriptional regulation, influencing gene expression and mRNA stability, localization, and the occurrence of post-transcriptional modifications. Depending on the properties of the 3′ UTR, o8G modification of the 3′ UTR may affect the binding of non-coding RNAs or RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) to mRNA, thereby regulating mRNA translation and stability.
We used the traditional method of predicting other RNA modifications, such as the m5C motif, to predict the possible motif of o8G modification, due to the lack of relevant studies on o8G, the o8G modification motif on the mRNA is still inconclusive, which depends on more sequencing to reveal the characteristics of the motif.
We found that differentially o8G-modified transcripts were enriched in a variety of important cell biology processes, such as Cellular component organization or biogenesis, Focal adhesion, and RNA binding, suggest that o8G modification may be involved in these biological processes regulating cancer cell base aging. Through KEGG analysis, we found that differentially o8G methylated mRNA was enriched in some key cancer-related pathways, such as Small cell lung cancer signaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer signaling pathway. It also proves from another aspect that o8G modification is closely related to the development of cancer.
In conclusion, our study shows that when cancer cells undergo senescence, their o8G modification spectrum changes significantly, and the changes are reflected in two aspects, one is the change in the number of modifications, and the other is the change in the distribution of modifications. We also performed further bioinformatics analysis of mRNA with changes in o8G modification and GO and KEGG analyses preliminarily revealed the potential direction of o8G modification on the regulation of senescent cancer cells. In follow-up studies, further in-depth analysis of the specific regulatory mechanism of o8G modification on cancer cell aging is expected to provide innovative ideas for the treatment of cancer.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, GSE284992.
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
JH: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing–original draft. YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing–original draft. YZ: Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. LW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by TCM science and technology project of Shandong Province (2020Q076).
We thank the Cloud-Seq Biotech Ltd. Co. (Shanghai, China) for the MeRIP-Seq service.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2025.1443888/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 | β-Gal showed that CaCO2 cells senescent compared with normal cells after knockdown of ADAR1.
o8G, 8-oxoguanine; m5C, 5-methylcytosine; GO, Gene ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP, biological processes; MF, molecular functions; CC, cellular components; IP, immunoprecipitation.
Baell, J. B., Leaver, D. J., Hermans, S. J., Kelly, G. L., Brennan, M. S., Downer, N. L., et al. (2018). Inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases KAT6A/B induce senescence and arrest tumour growth. Nature 560, 253–257. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0387-5
Bailey, T. L. (2011). DREME: motif discovery in transcription factor ChIP-seq data. Bioinformatics 27, 1653–1659. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr261
Calcinotto, A., Kohli, J., Zagato, E., Pellegrini, L., Demaria, M., and Alimonti, A. (2019). Cellular senescence: aging, cancer, and injury. Physiol. Rev. 99, 1047–1078. doi:10.1152/physrev.00020.2018
Cavinato, M., Madreiter-Sokolowski, C. T., Büttner, S., Schosserer, M., Zwerschke, W., Wedel, S., et al. (2021). Targeting cellular senescence based on interorganelle communication, multilevel proteostasis, and metabolic control. FEBS J. 288, 3834–3854. doi:10.1111/febs.15631
Chandrasekaran, A., Idelchik, M., and Melendez, J. A. (2017). Redox control of senescence and age-related disease. Redox Biol. 11, 91–102. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2016.11.005
Chen, Z., Zhou, J., Wu, Y., Chen, F., Li, J., Tao, L., et al. (2024). METTL3 promotes cellular senescence of colorectal cancer via modulation of CDKN2B transcription and mRNA stability. Oncogene 43, 976–991. doi:10.1038/s41388-024-02956-y
Eom, S., Peak, J., Park, J., Ahn, S. H., Cho, Y. K., Jeong, Y., et al. (2023). Widespread 8-oxoguanine modifications of miRNA seeds differentially regulate redox-dependent cancer development. Nat. Cell Biol. 25, 1369–1383. doi:10.1038/s41556-023-01209-6
Hahm, J. Y., Park, J., Jang, E. S., and Chi, S. W. (2022). 8-oxoguanine: from oxidative damage to epigenetic and epitranscriptional modification. Exp. Mol. Med. 54, 1626–1642. doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00822-z
Hao, X., Shiromoto, Y., Sakurai, M., Towers, M., Zhang, Q., Wu, S., et al. (2022). ADAR1 downregulation by autophagy drives senescence independently of RNA editing by enhancing p16(INK4a) levels. Nat. Cell Biol. 24, 1202–1210. doi:10.1038/s41556-022-00959-z
Herranz, N., and Gil, J. (2018). Mechanisms and functions of cellular senescence. J. Clin. Invest. 128, 1238–1246. doi:10.1172/jci95148
Kechin, A., Boyarskikh, U., Kel, A., and Filipenko, M. (2017). cutPrimers: a new tool for accurate cutting of primers from reads of targeted next generation sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 24, 1138–1143. doi:10.1089/cmb.2017.0096
Kim, D., Langmead, B., and Salzberg, S. L. (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–360. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3317
Li, Q., Li, X., Tang, H., Jiang, B., Dou, Y., Gorospe, M., et al. (2017). NSUN2-Mediated m5C methylation and METTL3/METTL14-mediated m6A methylation cooperatively enhance p21 translation. J. Cell. Biochem. 118, 2587–2598. doi:10.1002/jcb.25957
Lin, Y., Zhao, Z., Nie, W., Huang, M., Cai, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). Overview of distinct 5-methylcytosine profiles of messenger RNA in normal and knock-down NSUN2 colorectal cancer cells. Front. Genet. 14, 1121063. doi:10.3389/fgene.2023.1121063
López-Otín, C., Blasco, M. A., Partridge, L., Serrano, M., and Kroemer, G. (2013). The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153, 1194–1217. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
Schmitt, C. A., Wang, B., and Demaria, M. (2022). Senescence and cancer – role and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 19, 619–636. doi:10.1038/s41571-022-00668-4
Sen, P., Shah, P. P., Nativio, R., and Berger, S. L. (2016). Epigenetic mechanisms of longevity and aging. Cell 166, 822–839. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.050
Seok, H., Lee, H., Lee, S., Ahn, S. H., Lee, H. S., Kim, G. W. D., et al. (2020). Position-specific oxidation of miR-1 encodes cardiac hypertrophy. Nature 584, 279–285. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2586-0
Shen, L., Shao, N. Y., Liu, X., Maze, I., Feng, J., and Nestler, E. J. (2013). diffReps: detecting differential chromatin modification sites from ChIP-seq data with biological replicates. PLoS One 8, e65598. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065598
Tasaki, M., Shimada, K., Kimura, H., Tsujikawa, K., and Konishi, N. (2011). ALKBH3, a human AlkB homologue, contributes to cell survival in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 104, 700–706. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6606012
van Deursen, J. M. (2014). The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 509, 439–446. doi:10.1038/nature13193
Wang, L., Lankhorst, L., and Bernards, R. (2022). Exploiting senescence for the treatment of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 22, 340–355. doi:10.1038/s41568-022-00450-9
Xie, W., Kagiampakis, I., Pan, L., Zhang, Y. W., Murphy, L., Tao, Y., et al. (2018). DNA methylation patterns separate senescence from transformation potential and indicate cancer risk. Cancer Cell 33, 309–321. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2018.01.008
Zhang, J., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Jia, Z., He, M., et al. (2024). o(8)G site-specifically modified tRF-1-AspGTC: a novel therapeutic target and biomarker for pulmonary hypertension. Circulation Res. 135, 76–92. doi:10.1161/circresaha.124.324421
Zhang, Y., Liu, T., Meyer, C. A., Eeckhoute, J., Johnson, D. S., Bernstein, B. E., et al. (2008). Model-based analysis of ChIP-seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 9, R137. doi:10.1186/gb-2008-9-9-r137
Keywords: 8-oxoguanine, senescence, RNA methylation, MeRIP-seq, cancer cell
Citation: Huang J, Lin Y, Zhao Y and Wei L (2025) Overview of distinct 8-oxoguanine profiles of messenger RNA in normal and senescent cancer cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1443888. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1443888
Received: 04 June 2024; Accepted: 30 January 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Ann-Kristin Östlund Farrants, Stockholm University, SwedenReviewed by:
Eliza Wyszko, Polish Academy of Sciences, PolandCopyright © 2025 Huang, Lin, Zhao and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lingbo Wei, dzgzNzc2MDI4QDEyNi5jb20=; Yu Lin, MTM1ODAzMTE3MjZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.