
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 03 January 2025
Sec. Stem Cell Research
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1498669
This article is part of the Research Topic Studying Rare Diseases Using induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)-based Model Systems View all 4 articles
The introduction of pluripotent stem cells into the field of disease modelling resulted in numerous opportunities to study and uncover disease mechanisms in a petri dish. This promising avenue has also been applied to model Marfan syndrome, a disease affecting multiple organ systems, including the skeletal and cardiovascular system. Marfan syndrome is caused by pathogenic variants in FBN1, the gene encoding for the extracellular matrix protein fibrillin-1 which ensembles into microfibrils. There is a poor genotype-phenotype correlation displayed by the diverse clinical manifestations of this disease in patients. Up to now, 52 different human pluripotent stem cells lines have been established and reported for Marfan syndrome. These stem cells have been employed to model aortopathy, skeletal abnormalities and cardiomyopathy in vitro. These models were able to recapitulate key features of the disease that are also observed in patients. The use of pluripotent stem cells will help to uncover disease mechanisms and to identify new therapeutic strategies in Marfan syndrome.
Marfan syndrome (OMIM: 154700) is a connective tissue disorder affecting multiple organ systems. Patients with Marfan syndrome display a wide range of clinical features with diverse clinical severity that could significantly add to morbidity and mortality. Skeletal features include long limbs, tall stature and arachnodactyly, scoliosis, pectus carinatum and pectus excavatum (Pyeritz, 2000). The most important cardiovascular manifestations include aortic root dilatation, which untreated can lead to aneurysm and dissection, and mitral valve prolapse (Groth et al., 2018). Other known but less prevalent cardiovascular problems are pulmonary artery dilatation, ventricular and atrial arrythmias and cardiomyopathy (Demolder et al., 2020; Isekame et al., 2016; Lazea et al., 2021). Besides the skeletal- and cardiovascular manifestations, the ocular system is affected with lens luxation (ectopia lentis) and myopia being the most important ophthalmological features (Kinori et al., 2017; Sharma et al., 2002). There is a great variability in the clinical expression of Marfan syndrome, ranging from mild to severely affected patients. Even within the members of the same family, carrying the same pathogenic variant, a wide range of clinical presentations have been described (Aalberts et al., 2010; Ergoren et al., 2019; Li et al., 2016). Both morbidity and mortality related to Marfan syndrome progresses with age.
Marfan syndrome is caused by pathogenic variants in the fibrillin 1 gene (FBN1). This gene is positioned at chromosome 15q21.1. Fibrillin-1 is a large glycoprotein of 350 kDa which assembles into microfibrils that are important in elastic tissues. Microfibrils are important for the structural integrity of the connective tissue and provide tensile strength (Sakai et al., 1986). Deposition of elastin on microfibrils occurs during development and thus explains the close association between these two proteins (Milewicz et al., 2021). Furthermore, microfibrils provide an important substrate for cell adhesion through interaction with integrins, more specifically integrins α5β1, integrin αVβ3 and integrin αVβ6 (Bax et al., 2003; Jovanovic et al., 2007). Besides structural mechanical support, microfibrils are involved in the control of cell signalling pathways and play an important role in bioavailability of growth factors by binding latent transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) binding proteins and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) (Sengle and Sakai, 2015).
To date more than 3,305 different variants have been described in FBN1 gene, in all 65 coding exons (ClinVar: FBN1, Landrum et al. (2014)). Approximately 25% of all the FBN1 pathogenic variants are de novo (Chiu et al., 2014). There are different types of pathogenic variants, of which missense variants are the most abundant. Most commonly these missense variants disrupt one of the calcium binding EGF-domains by substituting or inserting a cysteine residue or disrupting one of the amino acids of the calcium binding sequence ([D]-X-[D/N]-[E/H]-Xm-[D/N]-Xn-[Y/F]). These changes influence either the disulfide-bridge formation or calcium binding which are essential for correct fibrillin-1 domain conformation (Arnaud et al., 2021). Besides affecting the function, these modifications also leave the protein more vulnerable for proteolysis. Other types of pathogenic variants included nonsense, splice-site variants, and small in-frame or, frameshift insertions and deletions (Caspar et al., 2018; Stenson et al., 2003). Most of the described pathogenic variants in FBN1 are heterozygous, homozygous is very rare and are associated with a severe phenotype (Arnaud et al., 2017). Fibrillin-1 haploinsufficiency causes Marfan syndrome in approximately 10%–15% of patients (Arnaud et al., 2021). Some studies suggest that haploinsufficient variants such as nonsense or frameshift and variants deleting a cysteine residue are associated with more severe clinical features and involvement of the aorta (Arnaud et al., 2021; Takeda et al., 2018).
Genotype-phenotype associations are however challenging because of the large variation in clinical expression. The most consistent genotype-phenotype correlation has been the association of severe and often early-onset of Marfan syndrome with pathogenic variants in exon 25 to 33 (Arnaud et al., 2021; Stheneur et al., 2011). Sex effects impact the clinical manifestations in Marfan syndrome. Males are observed to have a more severe cardiovascular presentation, including increased incidence of aortic dissections irrespective of the type of pathogenic variant (Arnaud et al., 2021; Détaint et al., 2010). Skeletal features were more frequently observed in female (Arnaud et al., 2021). Ectopia lentis and mitral valve prolapse presented a similar incidence in both sexes (Arnaud et al., 2021; Détaint et al., 2010; Du et al., 2021).
Besides clinical research, Marfan syndrome mouse models have been undoubtedly the most important tool for advancing our knowledge of the underlying pathophysiology in Marfan syndrome so far, although other species, such as zebrafish are increasingly gaining importance (Yin et al., 2021). Advancements in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC) (Takahashi et al., 2007) could provide important human cell models for modelling the various clinical features of Marfan syndrome. Together with important knowledge gained from animal studies, hPSCs models could be applied, for instance in preclinical trials. Moreover, differences between animal models and humans, due to genetic- and physiologic differences form an important barrier for translating findings from the lab into the clinic. hPSCs have the potential to address these issues. The cellular models for Marfan syndrome can help to uncover disease mechanisms and aid in the drug discovery. Especially since hPSCs can phenocopy the human response to novel drugs, which might be different than the responses to drug observed in animals, highlighting the translational value of hPSCs. Also drug responses and toxicity could be evaluated in patient specific manner, allowing to identify important differences between individuals that can be translated into a more personalized clinical management. These insights could for instance be used as a tool for risk stratification and decision making in clinical management.
The hPSC technology provides a new tool for personalized medicine in Marfan syndrome. Using this technology, patient’s DNA with specific pathogenic variants in FBN1 could be studied on an individual level. hPSCs can be generated from a single donation of somatic cells by patients in the form of a blood-or urine sample or a tissue biopsy and can be differentiated to all the cells of the three germ layers, providing an unlimited resource to study. Numerous directed differentiation protocols have been established and optimized, including those to cardiomyocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells (Burridge et al., 2014; Lian et al., 2013). These patient-specific models can be interrogated extensively and compared to isogenic controls and hPSC models from other patients with Marfan syndrome carrying a different pathogenic variant. The contribution of the abnormal fibrillin-1 protein, as well as other elements that can contribute to the disease severity can be studied using these in vitro models.
In 2006, Yamanaka and Takahashi demonstrated for the first time that mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) could be reprogrammed to mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) (Takahashi and Yamanaka, 2006). They systematically screened 24 candidate genes, of which four factors, being Oct3/4, Sox2, c-Myc, and Klf4 were essential in the transduction process. One year later, in 2007, the group of Yamanaka was able to generate human iPSCs from human dermal fibroblasts (Takahashi et al., 2007) using the same four pluripotent factors that were previously successful in the transduction of MEFs. Pluripotency of cells is defined as the ability to give rise to all three germ layers, being endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm. However, iPSCs are not able to differentiate into epiblast cells, meaning that they are not able to fully recapitulate an embryo. Because of the pluripotent nature of iPSCs, cells of all lineages can be obtained, including cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells and neurons.
Before the generation of iPSC was established, embryonic stem cells (ESC) were employed. ESCs are derived from the inner cell mass of mammalian blastocysts. The first human ESC lines were derived and described in 1998 by Thomson and co-workers (Thomson et al., 1998). Similar to iPSCs, they have the ability to grow indefinitely in a pluripotent state and give rise to all cells of the three germ layers. Several commercially available human ESCs have been established, among which are H1, H7 and H9, which are available from WiCell as cell lines WA01, WA07 and WA09 respectively.
While the introduction of hPSCs propelled the field of in vitro research, hPSCs also displayed experimental variability that can be difficult to control. Therefore standardization in hPSC cultures and experiments is important to increase reproducibility. This challenge also attracted the attention of the industry, which developed several solutions, including pluripotency screening with for instance the PluriTest bioinformatics assay and trilineage differentiation potential using TaqMan hPSC Scorecard, both from ThermoFisher. Previously, teratoma assays were performed to determine spontaneous differentiation to all three germ layers when transplanting PSCs into an immunocompromised mice (Aoi, 2016). The novel techniques can now replace the ethically questionable teratoma assays to determine potency of pluripotent stem cells.
Other important quality controls to consider are genetic integrity and potential contamination of the cell culture. Genetic screening of PSCs is important because in vitro culture, especially in long term culture may induce genetic alterations (Assou et al., 2020; Närvä et al., 2010). Different options are available for the genetic screening, amongst which G-band karyotyping is most frequently employed, others are single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) or copy number variation (CNV) sequencing based (Jo et al., 2020). Biological contamination of bacteria, fungi or viruses are important to monitor. It is for instance recommended to routinely screen for mycoplasma. Lastly, it is good practice to establish the identity of hPSCs by short tandem repeat (STR) analysis. Since this STR profile is unique for every individual it could be used to track identity throughout experiments, for instance to compare somatic cells with reprogrammed hPSCs.
CRISPR/Cas technology facilities efficient gene editing of hPSCs. This advancement provides an important tool for in vitro modelling as isogenic controls can be generated. An isogenic control shares an identical genetic background and only differs in the presence or absence of the pathogenic variant. Other genetic elements, apart from the pathogenic variant, can influence the observed phenotype of the model and could be cancelled out using this isogenic approach. Alternatively, hPSCs generated from healthy individuals could function as a control. Here it could be considered to use an unaffected family member of the patient to have limited differences in genetic background. CRISPR/Cas technology could also be used to introduce different pathogenic variants in a healthy hPSC line, which allows to generate numerous hPSC lines for Marfan syndrome. This approach was used by Borsoi and co-workers to generate several hPSC lines (Borsoi et al., 2021a). The advantage of introducing a pathogenic variant in healthy donor hPSC line is that it does not require somatic cells of Marfan syndrome patients, and allows to model the effect of rare pathogenic variants, independently of the patient’s genetic background, more specifically. However, the absence of the patient’s specific genetic background might be actually necessary for full disease manifestation and the use of healthy donor hPSC line might fail to accurately phenocopy the pathogenic variant in vitro.
A comprehensive overview of the current established hPSC lines for Marfan syndrome is provided together with a brief description of their main findings and implications. The list provided here only includes stem cell lines that are registered in an online registry (either NIH stem cell registry or on the hPSC registry (hpscreg.eu) or published in peer-reviewed articles (Table 1). It is likely that more Marfan hPSC lines are already established but not yet shared with the scientific community.
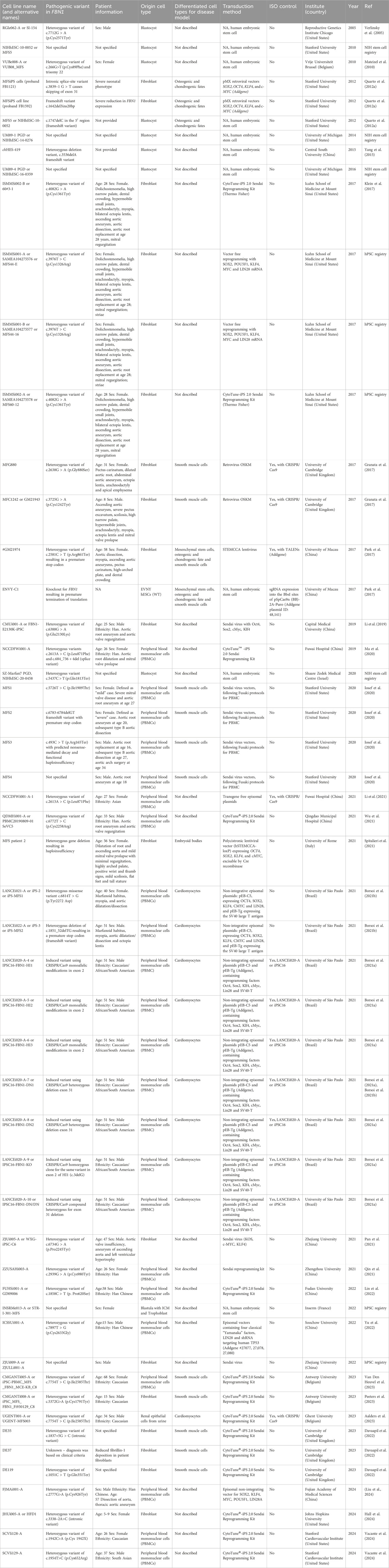
Table 1. A summary of all established human pluripotent stem cell lines for Marfan syndrome that are described in peer-reviewed articles, or deposited in online stem cell registries, being NIH stem cell registry and hPSC registry. For each line, the pathogenic variant and patient information is summarized, if available. Also, original cell source, cell types obtained by directed differentiations for disease model, method of reprogramming, availability of isogenic (ISO) control, the generator of the line and the year of publication or deposition. Abbreviations: NA (not available), United States (United States of America).
The increasing number of described Marfan hPSCs, especially using the reprogramming of somatic cells, provides an important source for modelling the disease in a dish. A special article type called Lab Resource was introduced by Elsevier’s journal Stem Cell Research which provides researchers the opportunity to publish newly established pluripotent stem cell lines derived from embryos or generated through somatic cell reprogramming in detail. Furthermore, the partnership between Elsevier and the hPSC registry (https://hpscreg.eu/) further boosted transparency, standardization, and availability of hPSC for disease modelling. Remarkably, Marfan hPSCs that were not registered in the hPSC registry oftentimes did not specify essential information on the line such as pathogenic variant, age, or sex (see Table 1).
It is apparent that an increasing number of hPSC lines have been established for Marfan syndrome, especially the last few year (Figure 1A). Possibly due to advances in the reprogramming of somatic cells to hPSCs with robust tools such as CytoTune®-iPS 2.0 Sendai Reprogramming Kit (Thermofisher Scientific). This has facilitated researchers with the opportunity of reprogramming, without the need of viral handling and modifying viral vectors. The use of embryonic derived stem cells has been regulated more strictly over the years due to ethical concerns, which are likely be replaced completely by iPSCs in the coming decade. In total 52 different hPSC lines for Marfan syndrome were identified. The distribution of countries shows that most hPSCs were generated in The United States of America (USA), being 18, closely followed by China (13) and Brazil (9) (Figure 1B). However, this only addresses the publicly shared hPSC lines, and thus potentially not accurately reflecting the real distribution. For instance, projects with NIH funding (United States funding body) pose strict regulations and require that data, including generated hPSCs are publicly available. Whereas other funding bodies might not have the requirement to share all data publicly, potentially leading to an underrepresentation of those countries in this current overview.
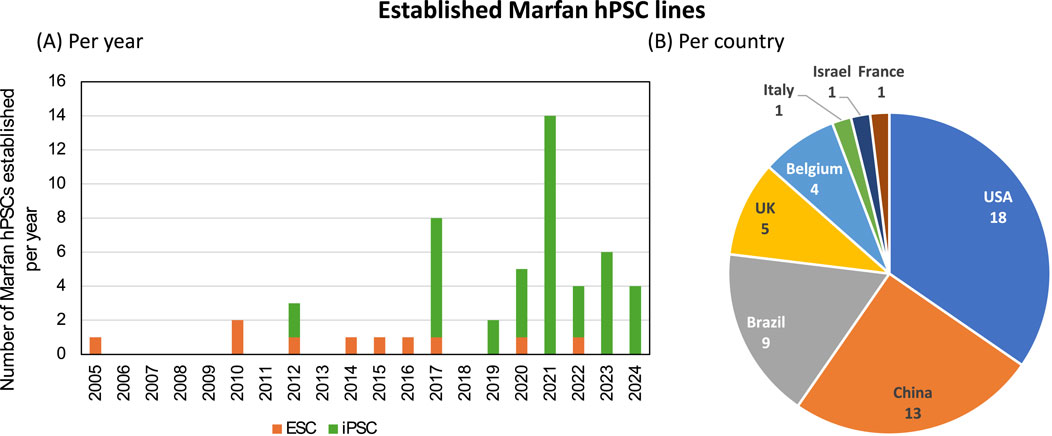
Figure 1. Established human pluripotent stem cell lines for Marfan syndrome. In total 52 human stem cell lines were identified in scientific literature or in online registries. (A) The distribution of generated stem cell lines, either human embryonic stem cells (ESC, orange) or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC, green) over the years. (B) Distribution of generated stem cell lines per country.
Different in vitro models derived from hPSCs with different pathogenic FBN1 variants have been established to study various aspects of the multi-organ affecting disease that is Marfan syndrome (Table 2; Figure 2A). The different pathogenic variants in FBN1 used in hPSC derived in vitro models can have different effects, including structural, mechanosensing and biochemical effects (Figure 2B). In case of cardiac disease modelling pathogenic variants in FBN1 can result in impaired cardiac function or arrythmia but the pathogenic variants can also impact heart function indirectly through altered hemodynamic load.
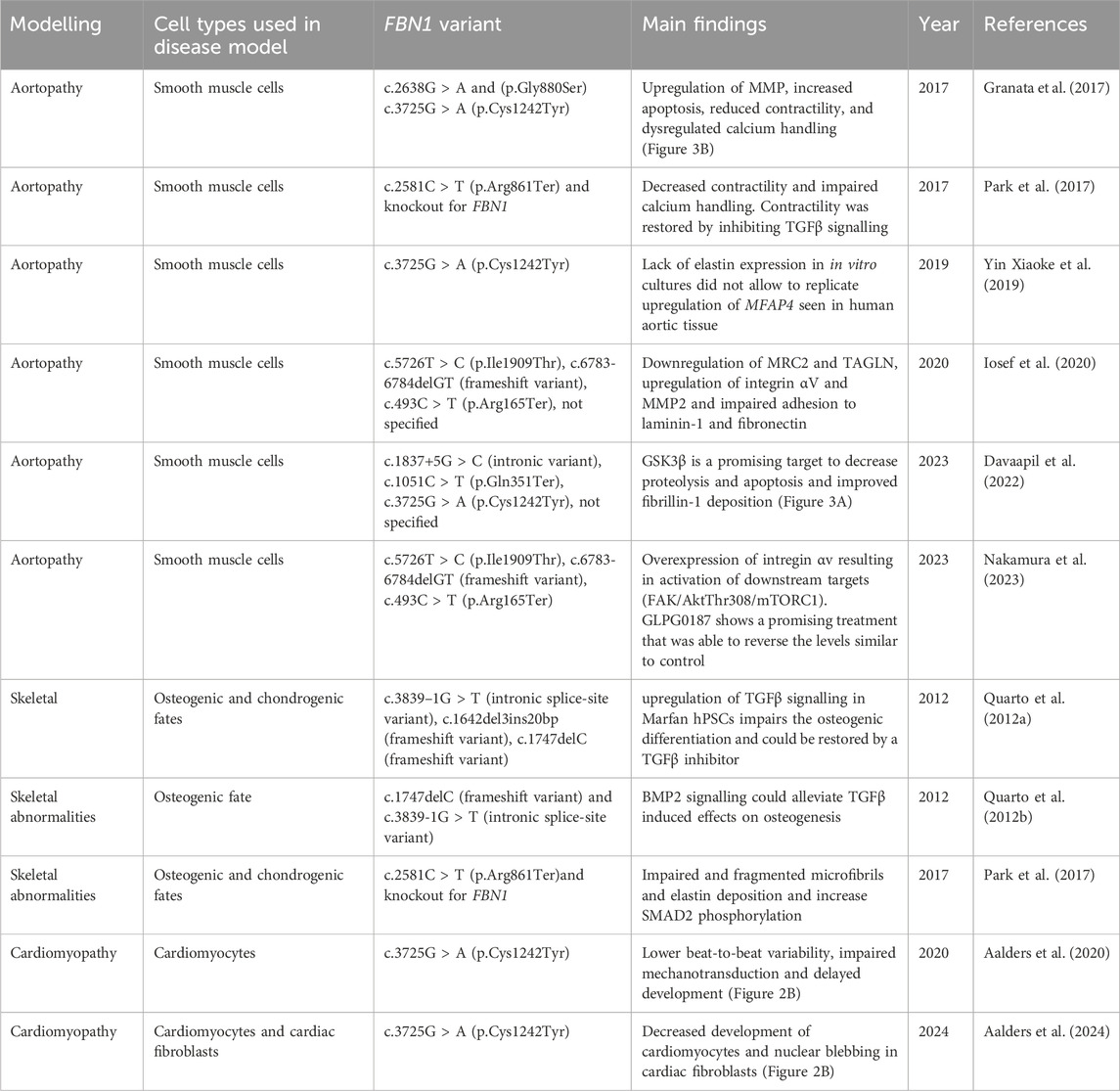
Table 2. Summary of in vitro cellular models for Marfan syndrome established with pluripotent stem cells to model various aspects of the disease, including aortopathy, skeletal phenotype and Marfan-related cardiomyopathy.
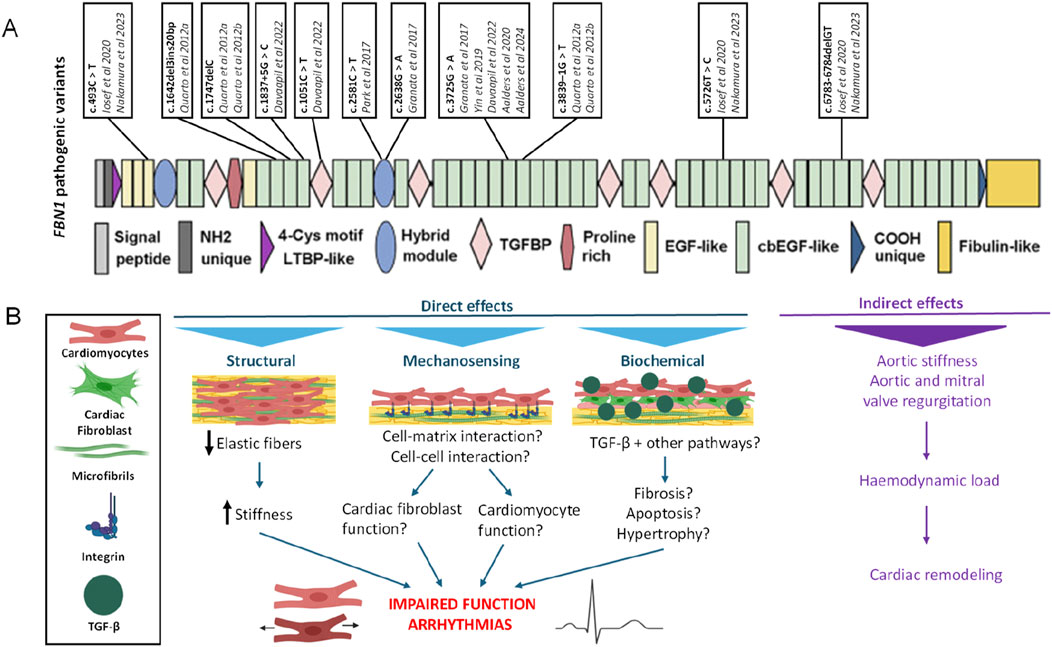
Figure 2. (A) Different pathogenic variants in FBN1 used for the modelling of Marfan syndrome in vitro. (B) Primary functions of fibrillin-1. FBN1 variants can have various effects which are illustrated in the context of heart function. Indirectly, by altering aortic characteristics which imposes abnormal haemodynamic loads on the heart. Or, directly, via structural, mechanosensing or biochemical pathways. For instance, by impaired elastin fibres, increased stiffness or disrupted interactions between cell and matrix or upregulation of TGFβ signalling. These direct and indirect effects on cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts could impair heart function and could induce arrhythmias. LTBP: latent TGFβ binding protein, EGF domain: epidermal growth factor-like domain, cbEGF domain: calcium binding epidermal growth factor-like domain.
In 2017, the Sinha group developed the first in vitro model for Marfan aortopathy (Granata et al., 2017). One of the major cell types involved in the aorta are the vascular smooth muscle cells. Depending on the location of the aorta (root, ascending, descending) the smooth muscle cells are different from another distinct mesodermal lineage. The smooth muscle cells in the descending aorta originate from paraxial mesoderm, the ascending aorta from the neural crest and the aortic root from the lateral plate mesoderm (Majesky, 2007). The different origins were reproduced by three distinct differentiation protocols used to derive smooth muscle cells from the three distinct regions of the aorta (Granata et al., 2017). The smooth muscle cells derived from the neural crest were best able to phenocopy the ascending aorta in Marfan patients and showed irregular fibrillin-1 deposition.
To evoke a phenotype in their Marfan aortopathy model the researchers made use of stretching, which could be compared to cyclic stretching of the aorta under physiological condition (Granata et al., 2017). The model revealed upregulation of TGFβ pathway, both canonical and noncanonical that results in upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), increased apoptosis, increased matrix degradation, reduced muscle contractility and disturbed calcium handling. Three different drug treatments were evaluated in the model, being TGFβ inhibitor, losartan and doxycycline. Losartan was most effective in reducing extracellular matrix degradation and could partially rescue the diminished cell proliferation in Marfan smooth muscle cells. They also found important downstream targets, being phosphorylation of Smad, Erk, KLF4 and p38. Based on their findings they proposed disease mechanism that regulates behaviour of smooth cells in Marfan aortopathy (Figure 3). Posing cyclic stetch on the Marfan smooth muscle cells resulted in increased p38 activation, which could be resulting from integrin β1 activity, implicating a role for impaired mechanosignaling in Marfan syndrome. Employing CRISPR/Cas9 technology allowed the researchers to correct the pathogenic variant that resulted in restored TGFβ, fibrillin-1 and MMP levels. Thus, providing evidence of the role for the pathogenic variant.
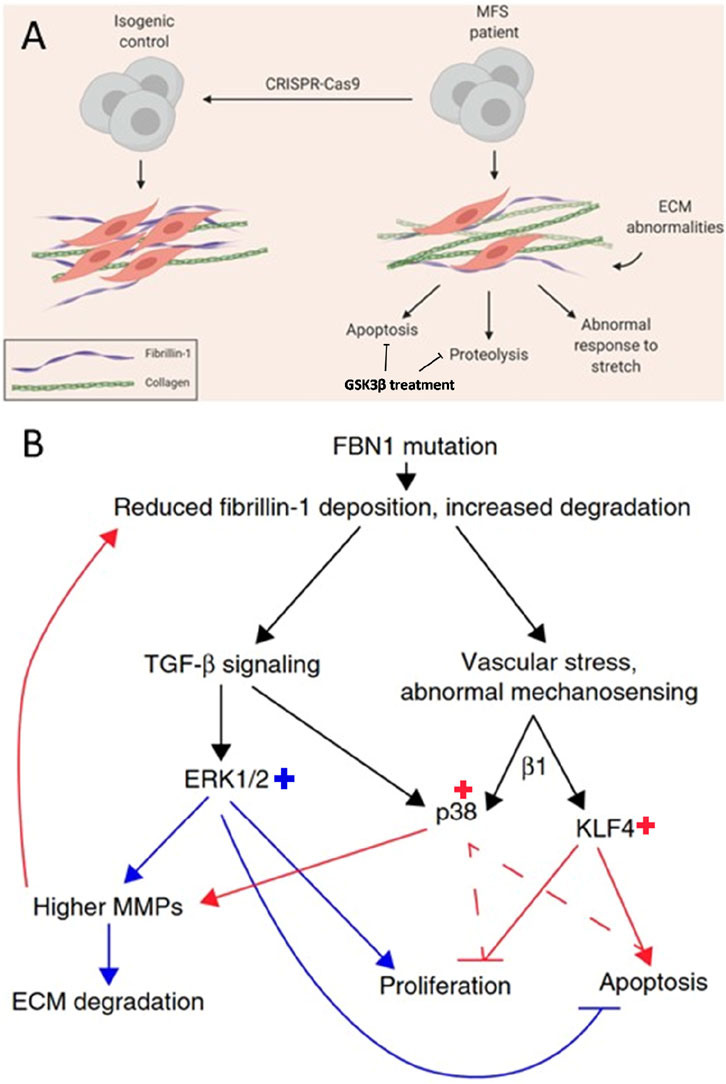
Figure 3. Schematic of an in vitro disease model for Marfan aortopathy based on pathogenic variants in FBN1 (c.2638G > A and c.3725G > A) used in two different studies. (A) Comparing Marfan iPSC-derived vascular smooth muscle cells, with the isogenic control reveals abnormalities in the extracellular matrix (ECM), increased levels of apoptosis, proteolysis, and an abnormal response to stretching. GSK3β treatment could be promising to decrease proteolytic and apoptotic effects. Adapted from (Davaapil et al., 2020). (B) The proposed mechanism for abnormal behaviour of vascular smooth muscle cells in Marfan aortopathy through abnormal mechanosensing effects in smooth muscle cells (red arrows) and abnormal TGFβ signalling (blue arrows) resulting in increased ERK1/2, p38 and KLF4. Adapted from (Granata et al., 2017).
Another study found upregulated MFAP4 (microfibril-associated glycoprotein 4) gene expression upon TGFβ exposure in smooth muscle cells form aortic tissue of human and mouse (Yin Xiaoke et al., 2019). This glycoprotein MFAP4 is involved in elastic fibre assembly. These findings were also studied using a Marfan hiPSC line with a c.3725G > A FBN1 pathogenic variant which was differentiated to neural crest derived vascular smooth muscle cells. Gene expression was evaluated for smooth muscle cells in stretched and unstretched condition. Expression of FBN1 was higher in Marfan smooth muscle cells compared to control irrespective of the stretching condition (Yin Xiaoke et al., 2019). No differences in gene expression of MFAP4 between hPSC derived Marfan and control smooth muscle cells could be detected and stretching did not attenuated expression of MFAP4. The authors observed only very little elastin expression in the in vitro cultures. However, some cultures that displayed detectable levels of elastin expression also showed increased MFAP4 expression. The authors reason that increase in MFAP4 is a disease mechanism resulting from abnormal elastin formation in Marfan syndrome, instead of a direct result of altered FBN1 expression.
Park and co-workers established hPSC lines with a pathogenic variant in FBN1 (c.2581C > T) and a knockout for FBN1 for differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to study osteogenesis and vascular smooth muscle cells to model Marfan aortopathy (Park et al., 2017). In their approach they generated an iPSC line with the variant in FBN1 and established an isogenic control by correcting the variant using TALENs, which they termed a ‘gain-of-function’ control line. In addition, FBN1 was knocked out in wild-type hESCs to produce a ‘loss-of-function’ line. The cellular model for Marfan syndrome revealed changes in microfibril formation, confirming the pathogenic role of FBN1 variants. Smooth muscle cells are involved in regulating blood pressures and flow by their contractility. Marfan vascular smooth muscle cells revealed decreased sensitivity to carbachol (which increases IP3 levels and cause IP3 mediated calcium release in smooth muscle cells) as showed by decreased contractility and impaired calcium handling. Interestingly, contractility could be restored when inhibiting TGFβ signalling with SB431542. This implies that impaired contractility mainly results from dysregulated TGFβ signalling. Decreased influx of Ca2+ was correlated with reduced contractility observed in Marfan smooth muscle cells. Also, Marfan vascular smooth muscle cells displayed distinct gene expression compared to control lines. Smooth muscle cells derived from the Marfan hPSC line displayed a distinct transcriptome compared to the smooth muscle cells derived from the corrected hPSC line. The downregulated genes in Marfan smooth muscle cells included genes involved in cell adhesion such as collagens, the upregulated genes were associated with inflammatory responses.
In 2020, a research group from Stanford University, used hiPSCs (c.5726T > C, c.6783-6784delGT, c.493 C > T) with the aim to uncover genotype-phenotype correlations in aortopathy (Iosef et al., 2020). In their approach they used quantitative proteomics on a set of different hiPSCs derived smooth muscle cell populations, representing the range of genotypes observed in Marfan syndrome. The intended goal was to establish a model for risk stratification and clinical decision making, for example the timing of prophylactic surgery. A proteomic profile shows the final downstream product of gene transcription and provides insight into cellular function. The vascular smooth muscle cells in the aorta originate from distinct mesoderm linages, in this study smooth muscle cells from the aortic root and the ascending aorta were derived from lateral mesoderm and neural crest, respectively. The protein composition was quantified using mass spectrometry for in total four Marfan hiPSCs derived smooth muscle cells. Specific Marfan related protein expressions were discovered that also associate with lineage origin of the vascular smooth muscle cells. For instance, in Marfan MRC2 (mannose receptor C type 2) and TAGLN (transgelin) expression was reduced in lateral mesoderm derived smooth muscle cells compared to neural crest derived smooth muscle cells, while wild-type smooth muscle cells did not display lineage differences. MRC2 is a cell surface receptor that causes internalization and degradation of collagen, the authors hypothesized that it could also contribute to aberrant trafficking of extracellular matrix components. The decreased expression of MRC2 was also confirmed in Marfan patient derived smooth muscle cells, however downregulation of MRC2 was observed in both the aortic root and the ascending aorta. Decreased TAGLN expression suggest impaired contractility for Marfan smooth muscle cells derived from lateral mesoderm, recapitulating the smooth muscle cells at the location of the aortic root. The most upregulated proteins in Marfan lateral mesoderm derived smooth muscle cells were integrin αV and MMP2. In human derived aortic tissue integrin αV upregulation was also only observed in aortic root Marfan smooth muscle cells, thus phenocopied by the in vitro model. Altered integrin αV could point to reduced adhesion of the Marfan smooth muscle cells in the aortic root, as the upregulation might be a compensatory mechanism. Interestingly, Marfan smooth muscle cells displayed impaired adhesion to laminin-1 and fibronectin, both ligands for integrin αV, which could be caused by dysregulated cytoskeleton dynamics.
A recent publication from the Sinha group highlights the powerful potential of hPSCs in high-throughput screening and the drug discovery process (Davaapil et al., 2022). The researchers differentiated neural crest derived vascular smooth muscle cells from hiPSCs. Taking advantage of the highly proteolytic characteristics of the Marfan smooth muscle cells, one of the major features that is phenocopied in this cellular model, they established a platform for high throughput screening of compounds (Davaapil et al., 2022). The activity of MMPs, causing proteolysis, was monitored by a fluorescence-quenched gelatine substrate. Upon cleaving by MMP activity a fluorescent signal is released which can be detected by a plate reader. In total 1,022 compounds have been evaluated in a collaboration with AstraZeneca. Interestingly, GSK3β was put forward as an interesting target to alleviate the highly proteolytic effect of the Marfan smooth muscle cells, also confirmed by decreased MMP expression upon GSK3β inhibition. Other hallmarks of Marfan smooth muscle cells were increased apoptosis, decreased proliferation and impaired fibrillin-1 deposition based on the previous model of the Sinha group (Granata et al., 2017). Besides the positive effect on decreasing proteolysis, inhibition of GSK3β resulted in decreased apoptosis and improved fibrillin-1 deposition, however it did not increase proliferation of Marfan smooth muscle cells (Davaapil et al., 2022).
Another effort using hPSC derived smooth muscle cells to uncover disease mechanisms in Marfan aortopathy revealed an important role for integrin αv (Nakamura et al., 2023). Moreover, hPSC derived Marfan smooth muscle cells derived from second heart field shows overexpression of intregin αv in comparison to derivation of the neural crest of healthy hPSC derived smooth muscle cells from the second heart field. The overexpression resulted in activation of downstream targets including FAK, AktThr308 and mTORC1. The hPSC derived Marfan smooth muscle cells from the second heart field had increased proliferation rates and migration. Interestingly by using GLPG0187, an integrin antagonist, the authors were able to reverse the activity of these downstream targets in hPSC derived Marfan smooth muscle cells from the second heart field to control levels. GLPG0187 was also effective in Fbn1C1039G/+ mice and resulted in reduced aneurysm growth and elastin fragmentation. The findings of this study demonstrate an important role for integrin αv in the functional behaviour of smooth muscle cells and provides a potential treatment strategy in Marfan syndrome patients with GLPG0187.
The Longaker group published in 2012 the first in vitro skeletogenic model for Marfan syndrome derived from hPSCs (Quarto et al., 2012a). Their models reveal that upregulation of TGFβ signalling in Marfan hPSCs impairs the osteogenic differentiation. This coincided with increased phosphorylated Smad2, an important downstream target of TGFβ and upregulated gene expression of PAI-1 and COL1A1. The differentiation towards osteoblasts could be restored by application of a TGFβ inhibitor. Reversely, osteogenic differentiation could be blocked in wild-type hPSCs by treatment of TGFβ (10 ng/mL). Interestingly, differentiation towards chondrocytes is not affected by upregulated TGFβ signalling in Marfan. But in case of wild-type hPSCs, TGFβ treatment was necessary to efficiently differentiate to chondrocytes. Applying a TGFβ inhibitor in Marfan syndrome hPSCs could block chondrogenesis. These results combined reveals an important role for TGFβ signalling in phenotype determination. Importantly, the authors found that their models from both hESCs and hiPSC display identical phenotypes. This highlights the relevancy of hiPSCs for in vitro disease modelling. The authors also hypothesize that the disease mechanism of tall stature in Marfan syndrome caused by skeletal overgrowth is regulated by TGFβ signalling.
The Longaker group progressed their skeletogenic model for Marfan syndrome and discovered that BMP2 signalling could alleviate TGFβ induced effects on osteogenesis (Quarto et al., 2012b). Increased TGFβ signalling caused the cells to decrease endogenous BMP signalling. The authors revealed an increased proliferation rate for Marfan hPSCs compared to wild-type hPSCs which they attribute to increased TGFβ. Interestingly, the increased proliferation rate was normalized to wild-type hPSCs when a TGFβ inhibitor was used. Phosphorylated Smad1/5 was reduced in Marfan hPSCs compared to control, indicating declined BMP signalling. Treatment of Marfan hPSCs with TGFβ inhibitor resulted in increased phosphorylation of Smad1/5, to similar levels as wild-type but decreased Smad2 phosphorylation. Exogenous addition of BMP resulted in increased phosphorylation of Smad1/5 and allows efficient osteogenic differentiation of Marfan hPSCs. This study highlights the importance of both TGFβ and BMP signalling in the osteogenic differentiation that play important roles in the skeletal phenotype observed in patients with Marfan syndrome.
In the study of Park and co-workers with the gain- and loss-of-function cell lines also the osteogenic differentiation capacity was investigated (Park et al., 2017). Mesenchymal stem cells derived from Marfan hPSCs showed a 3-4-fold lower fibrillin-1 expression compared to the corrected ‘gain-of-function’ hPSC derived mesenchymal stem cells as established by Western blot. The difference could be explained by nonsense-mediated decay due to the pathogenic variants thus representing haploinsufficiency for fibrillin-1. This results in impaired and fragmented microfibrils and elastin deposition. Furthermore, an increase in phosphorylated SMAD2 was observed for Marfan mesenchymal stem cells which is an important downstream target of TGFβ signalling. Upregulation of TGFβ is a hallmark of Marfan syndrome which results from compromised matrix structure, TGFβ causes extracellular matrix degradation, further enhancing TGFβ signalling. Interestingly, in the TALENs corrected hPSC derived mesenchymal stem cells only limited phosphorylated SMAD2 was observed, thus repair of the pathogenic variant in FBN1 also normalized TGFβ signalling. Upregulated TGFβ signalling results in reduced osteogenesis in Marfan mesenchymal stem cells, phenocopy the observed phenotype in patients with Marfan syndrome in this cellular model. In the corrected ‘gain-of-function’ model the researchers observed an equivalent osteogenesis potential compared to wild-type, thus a rescue effect.
Intrinsic cardiomyopathy is also attributed to Marfan syndrome. In 2020, the first in vitro model to study the disease mechanisms for Marfan-related cardiomyopathy was established (Aalders et al., 2020) which revealed several functional abnormalities including reduced contraction, increased stiffness and decreased heart rate variability which are depicted in Figure 4. The model was generated by differentiating hiPSCs from Marfan and its isogenic control to cardiomyocytes in a 2D mono-culture. These hiPSCs have been previously used for modelling of Marfan aortopathy by the Sinha group (Granata et al., 2017).
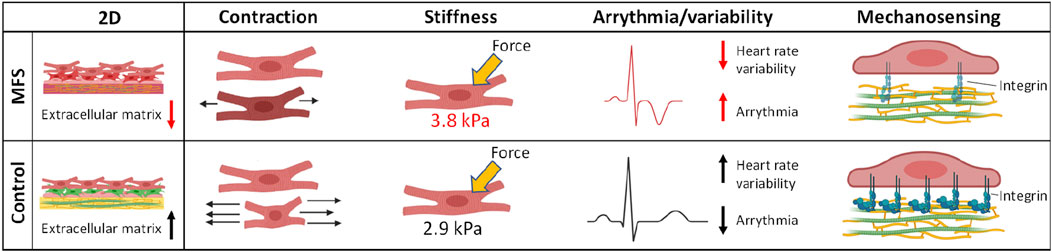
Figure 4. Functional abnormalities observed in the first in vitro model for Marfan-related cardiomyopathy using human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes. These abnormalities included impaired extracellular matrix, decreased contraction amplitude, increased stiffness of cardiomyocytes and decreased heart rate variability (Aalders et al., 2020).
More recently, this in vitro model for Marfan-related cardiomyopathy was advanced by a 3D co-culture of hiPSC derived cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts, named cardiospheres (Aalders et al., 2024). Observations made in this model may point to novel disease features that still need to be confirmed in human cardiac tissues. The Marfan cardiomyocytes showed decreased binucleation and decreased sarcomere length, which could be preserved as markers of development (Figure 5). Most intriguing was the high frequency of nuclear blebbing observed in the Marfan cardiac fibroblasts which correlated with increased stiffness of the nuclear area in these cells. Combined, these results suggest abnormal early development of cardiomyocytes but also an important role for cardiac fibroblasts in the disease mechanism of Marfan-related cardiomyopathy.
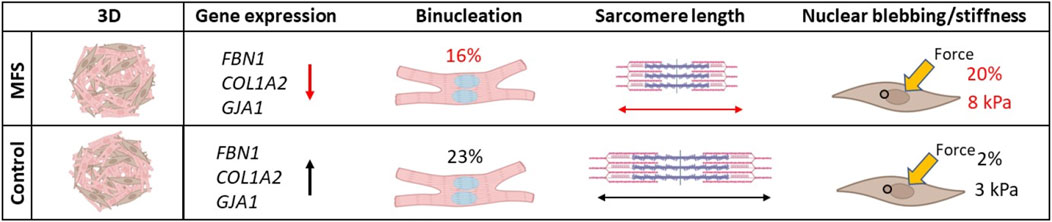
Figure 5. Novel disease mechanisms in Marfan-related cardiomyopathy uncovered by a 3D co-culture model with human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts shows a high percentage of nuclear blebbing in Marfan cardiac fibroblasts. Decreased binucleation and sarcomere length point to decreased development of cardiomyocytes as another disease mechanism at play in Marfan-related cardiomyopathy (Aalders et al., 2024).
To uncover abnormalities in structural conformations in Marfan, microgravity was used to evoke a potential phenotype (Spitalieri et al., 2021). Embryoid body (EB) formation mimics early differentiation similar to that in embryonic tissue. The use of microgravity allows to maintain pluripotency in EBs. Microfibrils, composed of fibrillin-1, can relay physical cues from their environment. The aim of this study from Spitalieri en co-workers was to uncover if impaired fibrillin-1 in Marfan syndrome is involved in dysregulated mechanosignalling. The researchers showed that 7 day old wild-type EBs displayed increased stemness in response to microgravity stimulation. The Marfan hiPSC was derived from a patient with a deletion of the complete FBN1 gene. The response was different for Marfan EBs, they showed reduced adaptation to microgravity. The authors hypothesized that the Marfan EBs have a deficient structure due to impaired fibrillin-1. Under normal gravity condition, that is 1 g, EB formation from Marfan hiPSCs showed macroscopic irregularities in shape, while wild-type EBs maintained round-shape in the first 2 days. Exposing the EBs to microgravity resulted in increased size and introduced more irregularities in the shape for both Marfan and control. Microgravity exposure resulted in significantly decreased gene expression for αSMA, NCAM and AFP that represent mesodermal, ectodermal and endodermal marker respectively compared to normal gravity for both Marfan and wild-type. These results indicate that microgravity can delay differentiation, however, to a lesser extent in Marfan EBs, as revealed by earlier upregulation of differentiation markers compared to wild-type. The authors also analysed gene expression related to the extracellular matrix. In wild-type EBs under microgravity condition E-cadherin, fibulin-1, COL12A1, COL8A2 and fibrillin-1 were upregulated at day 7 compared to normal gravity, while downregulated at day 14 and 22. Interestingly, only E-cadherin and COL12A1 were upregulated in Marfan EBs under microgravity conditions at day 7, reflecting the pathological effect of disrupted FBN1. Remarkably, while FBN1 expression is significantly lower at day 7 in Marfan EBs under microgravity compared to normal gravity, a significant increase in FBN1 expression was observed at day 22. The authors demonstrated that interrogating an in vitro model with microgravity could pronounce abnormalities and provides in interesting platform to study matrix diseases such as Marfan syndrome.
To date, only 11 hPSC models have been established, of which the majority of the models are employed for Marfan aortopathy (6 models), 3 models have been used to phenocopy skeletal features associated with Marfan syndrome, and 2 studies that describe in vitro models for Marfan-related cardiomyopathy (Table 2). These models provide promising insights in the disease mechanisms underlying Marfan syndrome.
The group of Sinha nicely demonstrated the use of hPSCs in screening for novel drug targets (Davaapil et al., 2022). In their study they first identified hallmark features for phenotypes observed in Marfan aortopathy using smooth muscle cells. These hallmark features in their model were increased apoptosis, decreased proliferation and enhanced proteolysis (Granata et al., 2017). In order to facilitate high-throughput screening, an easy and fast read-out method is preferred. Here they made use of the proteolytic activity of MMPs which degrades the extracellular matrix. By fluorescently labelling the provided matrix that is quenched upon degradation enables a suitable read-out.
An alternative approach for high throughput screening is to use a protein that is released in the culture medium as a biomarker. A fluorescently labelled antibody can be employed to quantify the amount of the specific biomarker and is compatible with high throughput. A potential biomarker could be elevated levels of MMPs (Granata et al., 2017), which have been described to result in extracellular matrix degradation in patients as an early marker of Marfan aortopathy. Taking advantage of a specific MMP biomarker will help to decide whether a novel compound is beneficial in the treatment of Marfan aortopathy.
The rapidly advancing field of in vitro disease modelling using hiPSC derived cells has opened the avenue for personalized medicine. Generating iPSCs from somatic cells to recreate individual specific cells facilitates high throughput screening platforms. Reducing costs and increasing throughput will enable future studies to use larger numbers of iPSCs, which allows to include a broader patient population. These advances allow to decipher the effects of different pathogenic variants in FBN1 and other extracellular matrix variants that cause cardiomyopathy and uncover the disease mechanisms. This increase in fundamental knowledge will ultimately allow to discover novel drug targets that can be addressed to treat patients with Marfan syndrome.
Not all clinical features are yet modelled using hPSCs, for instance ectopia lentis which is associated with high morbidity in patients with Marfan syndrome. Modelling ectopia lentis in vitro will likely require more advanced models. Also, aortopathy and cardiomyopathy modelling would benefit from more complex model systems where for instance hemodynamic stress and fluid sheer stress can be imposed on the cellular model. In the last decade, the field of hiPSCs emerged and in vitro modelling have made tremendous advancements. There awaits an optimistic and promising feature of human stem cell models for Marfan syndrome that we now only have seen the beginning of.
JA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. LM: Writing–review and editing. JvH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by Special Research Fund of Ghent University (BOF19/24 J/139) and support of FWO (G000224N). This publication is based upon work from CorEuStem - CA20140, supported by COST (European Cooperation in Science and Technology).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aalberts, J. J., Schuurman, A. G., Pals, G., Hamel, B. J., Bosman, G., Hilhorst-Hofstee, Y., et al. (2010). Recurrent and founder mutations in The Netherlands: extensive clinical variability in Marfan syndrome patients with a single novel recurrent fibrillin-1 missense mutation. Heart J. 18, 85–89. doi:10.1007/bf03091743
Aalders, J., Léger, L., Demolder, A., Muiño Mosquera, L., Coucke, P., Menten, B., et al. (2023). Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cell line UGENTi001-A from a patient with Marfan syndrome carrying a heterozygous c.7754T > C variant in FBN1 and the isogenic control UGENT001-A-1 using CRISPR/Cas9 editing. Stem Cell Res. 67, 103036. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2023.103036
Aalders, J., Léger, L., Van der Meeren, L., Sinha, S., Skirtach, A. G., De Backer, J., et al. (2024). Three-dimensional co-culturing of stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts reveals a role for both cell types in Marfan-related cardiomyopathy. Matrix Biol. 126, 14–24. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2024.01.003
Aalders, J., Léger, L., Van der Meeren, L., Van den Vreken, N., Skirtach, A. G., Sinha, S., et al. (2020). Effects of fibrillin mutations on the behavior of heart muscle cells in Marfan syndrome. Sci. Rep. 10, 16756. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73802-w
Aoi, T. (2016). 10th anniversary of iPS cells: the challenges that lie ahead. J. Biochem. 160, 121–129. doi:10.1093/jb/mvw044
Arnaud, P., Hanna, N., Aubart, M., Leheup, B., Dupuis-Girod, S., Naudion, S., et al. (2017). Homozygous and compound heterozygous mutations in the FBN1 gene: unexpected findings in molecular diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 54, 100–103. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103996
Arnaud, P., Milleron, O., Hanna, N., Ropers, J., Ould Ouali, N., Affoune, A., et al. (2021). Clinical relevance of genotype-phenotype correlations beyond vascular events in a cohort study of 1500 Marfan syndrome patients with FBN1 pathogenic variants. Genet. Med. 23, 1296–1304. doi:10.1038/s41436-021-01132-x
Assou, S., Girault, N., Plinet, M., Bouckenheimer, J., Sansac, C., Combe, M., et al. (2020). Recurrent genetic abnormalities in human pluripotent stem cells: definition and routine detection in culture supernatant by targeted droplet digital PCR. Stem Cell Rep. 14, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.12.004
Bax, D. V., Bernard, S. E., Lomas, A., Morgan, A., Humphries, J., Shuttleworth, C. A., et al. (2003). Cell adhesion to fibrillin-1 molecules and microfibrils is mediated by alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 34605–34616. doi:10.1074/jbc.M303159200
Borsoi, J., Farinha-Arcieri, L. E., Morato-Marques, M., Delgado Sarafian, R., Pinheiro, M., and Veiga Pereira, L. (2021a). Generation of genetically modified human induced pluripotent stem cell lines harboring haploin sufficient or dominant negative variants in the FBN1 gene. Stem Cell Res. 54, 102434. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102434
Borsoi, J., Morato-Marques, M., de Araújo Tofoli, F., Assis Pereira, L., Farinha-Arcieri, L. E., Delgado Sarafian, R., et al. (2021b). Generation of two human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) lines derived from unrelated Marfan Syndrome patients. Stem Cell Res. 54, 102407. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102407
Burridge, P. W., Matsa, E., Shukla, P., Lin, Z. C., Churko, J. M., Ebert, A. D., et al. (2014). Chemically defined generation of human cardiomyocytes. Nat. Methods 11, 855–860. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2999
Caspar, S. M., Dubacher, N., Kopps, A. M., Meienberg, J., Henggeler, C., and Matyas, G. (2018). Clinical sequencing: from raw data to diagnosis with lifetime value. Clin. Genet. 93, 508–519. doi:10.1111/cge.13190
Chiu, H. H., Wu, M. H., Chen, H. C., Kao, F. Y., and Huang, S. K. (2014). Epidemiological profile of Marfan syndrome in a general population: a national database study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 89, 34–42. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.08.022
Davaapil, H., McNamara, M., Granata, A., Macrae, R. G. C., Hirano, M., Fitzek, M., et al. (2022). A phenotypic screen of Marfan syndrome iPSC-derived vascular smooth muscle cells uncovers GSK3β as a new target. Stem Cell Rep. 18, 555–569. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.12.014
Davaapil, H., Shetty, D. K., and Sinha, S. (2020). Aortic “Disease-in-a-Dish”: mechanistic insights and drug development using iPSC-based disease modeling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 550504. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.550504
Demolder, A., von Kodolitsch, Y., Muiño-Mosquera, L., and De Backer, J. (2020). Myocardial function, heart failure and arrhythmia in marfan syndrome: a systematic literature review. Diagnostics 10, 751. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10100751
Détaint, D., Faivre, L., Collod-Beroud, G., Child, A. H., Loeys, B. L., Binquet, C., et al. (2010). Cardiovascular manifestations in men and women carrying a FBN1 mutation. Eur. Heart J. 31, 2223–2229. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq258
Du, Q., Zhang, D., Zhuang, Y., Xia, Q., Wen, T., and Jia, H. (2021). The molecular genetics of marfan syndrome. Int. J. Med. Sci. 18, 2752–2766. doi:10.7150/ijms.60685
Ergoren, M. C., Turkgenc, B., Teralı, K., Rodoplu, O., Verstraeten, A., Van Laer, L., et al. (2019). Identification and characterization of a novel FBN1 gene variant in an extended family with variable clinical phenotype of Marfan syndrome. Connect. Tissue Res. 60, 146–154. doi:10.1080/03008207.2018.1472589
Granata, A., Serrano, F., Bernard, W. G., McNamara, M., Low, L., Sastry, P., et al. (2017). An iPSC-derived vascular model of Marfan syndrome identifies key mediators of smooth muscle cell death. Nat. Genet. 49, 97–109. doi:10.1038/ng.3723
Groth, K. A., Stochholm, K., Hove, H., Andersen, N. H., and Gravholt, C. H. (2018). Causes of mortality in the marfan syndrome (from a nationwide register study). Am. J. Cardiol. 122, 1231–1235. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.06.034
Hall, F. D., Miller, C. N., Gerecht, S., and Boheler, K. R. (2024). Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line, JHUi005-A, from a Marfan Syndrome patient harboring a pathogenic c.3338-2A > C intronic splicing variant. Stem Cell Res. 79, 103475. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2024.103475
Iosef, C., Pedroza, A. J., Cui, J. Z., Dalal, A. R., Arakawa, M., Tashima, Y., et al. (2020). Quantitative proteomics reveal lineage-specific protein profiles in iPSC-derived Marfan syndrome smooth muscle cells. Sci. Rep. 10, 20392. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77274-w
Isekame, Y., Gati, S., Aragon-Martin, J. A., Bastiaenen, R., Kondapally Seshasai, S. R., and Child, A. (2016). Cardiovascular management of adults with marfan syndrome. Eur. Cardiol. 11, 102–110. doi:10.15420/ecr/2016:19:2
Jo, H. Y., Han, H. W., Jung, I., Ju, J. H., Park, S. J., Moon, S., et al. (2020). Development of genetic quality tests for good manufacturing practice-compliant induced pluripotent stem cells and their derivatives. Sci. Rep. 10, 3939. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-60466-9
Jovanovic, J., Takagi, J., Choulier, L., Abrescia, N. G., Stuart, D. I., van der Merwe, P. A., et al. (2007). alphaVbeta6 is a novel receptor for human fibrillin-1. Comparative studies of molecular determinants underlying integrin-rgd affinity and specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 6743–6751. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607008200
Kinori, M., Wehrli, S., Kassem, I. S., Azar, N. F., Maumenee, I. H., and Mets, M. B. (2017). Biometry characteristics in adults and children with marfan syndrome: from the marfan eye consortium of chicago. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 177, 144–149. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2017.02.022
Klein, S., Dvornik, J. L., Yarrabothula, A. R., and Schaniel, C. (2017). A Marfan syndrome human induced pluripotent stem cell line with a heterozygous FBN1 c.4082G > A mutation, ISMMSi002-B, for disease modeling. Stem Cell Res. 23, 73–76. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2017.06.016
Landrum, M. J., Lee, J. M., Riley, G. R., Jang, W., Rubinstein, W. S., Church, D. M., et al. (2014). ClinVar: public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D980–D985. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1113
Lazea, C., Bucerzan, S., Crisan, M., Al-Khzouz, C., Miclea, D., Şufană, C., et al. (2021). Cardiovascular manifestations in Marfan syndrome. Med. Pharm. Rep. 94, S25–s27. doi:10.15386/mpr-2223
Li, T., Ma, B., Yang, H., Zhu, G., Shu, C., Luo, M., et al. (2021). Generation of a CRISPR/Cas9-corrected-hiPSC (NCCDFWi001-A-1) from a Marfan syndrome patient hiPSC with a heterozygous c.2613A > C variant in the fibrillin 1 (FBN1) gene. Stem Cell Res. 56, 102543. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102543
Li, X., Dong, T., Li, Y., Wu, F., and Lan, F. (2019). Generation of a human iPSC line from a patient with Marfan syndrome caused by mutation in FBN1. Stem Cell Res. 36, 101414. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2019.101414
Li, Y., Xu, J., Chen, M., Du, B., Li, Q., Xing, Q., et al. (2016). A FBN1 mutation association with different phenotypes of Marfan syndrome in a Chinese family. Clin. chimica acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem. 460, 102–106. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2016.06.031
Lian, X., Zhang, J., Azarin, S. M., Zhu, K., Hazeltine, L. B., Bao, X., et al. (2013). Directed cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling under fully defined conditions. Nat. Protoc. 8, 162–175. doi:10.1038/nprot.2012.150
Lin, A., Kang, X., Xu, Y., Feng, X., Zhang, S., Zhao, H., et al. (2022). Human induced pluripotent stem cells derived from a patient with a mutation of FBN1c.1858C > T (p. Pro620Ser). Stem Cell Res. 61, 102759. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2022.102759
Liu, R., Weng, G., Zheng, F., Chen, J., Wang, K., Han, J., et al. (2024). Generation of an integration-free induced pluripotent stem cell line, FJMAi001-A, from a Marfan syndrome patient with a heterozygous mutation c.2777G > A (p.Cys926Tyr) in FBN1. Stem Cell Res. 81, 103591. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2024.103591
Ma, B., Luo, M., Yang, H., Li, T., Liu, W., Xu, F., et al. (2020). Generation of a human induced pluripotent stem cell line (NCCDFWi001-A) from a Marfan syndrome patient carrying two FBN1 variants (c.2613A > C and c.684_736 + 4del). Stem Cell Res. 42, 101690. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2019.101690
Majesky, M. W. (2007). Developmental basis of vascular smooth muscle diversity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27, 1248–1258. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.107.141069
Mateizel, I., Spits, C., De Rycke, M., Liebaers, I., and Sermon, K. (2010). Derivation, culture, and characterization of VUB hESC lines. Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 46, 300–308. doi:10.1007/s11626-010-9284-4
Milewicz, D. M., Braverman, A. C., De Backer, J., Morris, S. A., Boileau, C., Maumenee, I. H., et al. (2021). Marfan syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 7, 64. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00298-7
Nakamura, K., Dalal, A. R., Yokoyama, N., Pedroza, A. J., Kusadokoro, S., Mitchel, O., et al. (2023). Lineage-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived smooth muscle cell modeling predicts integrin alpha-V antagonism reduces aortic root aneurysm formation in marfan syndrome mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 43, 1134–1153. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.122.318448
Närvä, E., Autio, R., Rahkonen, N., Kong, L., Harrison, N., Kitsberg, D., et al. (2010). High-resolution DNA analysis of human embryonic stem cell lines reveals culture-induced copy number changes and loss of heterozygosity. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 371–377. doi:10.1038/nbt.1615
Pan, Z., Wang, H., Wang, H., Liu, Y., and Liang, P. (2021). Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line from a patient carrying FBN1/c.6734 G > A mutation. Stem Cell Res. 55, 102459. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102459
Park, J. W., Yan, L., Stoddard, C., Wang, X., Yue, Z., Crandall, L., et al. (2017). Recapitulating and correcting marfan syndrome in a cellular model. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 13, 588–603. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19517
Peeters, S., Fedoryshchenko, I., Rabaut, L., Verstraeten, A., and Loeys, B. L. (2023). Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line of a Marfan syndrome patient with a pathogenic FBN1 c.5372G > A (p.Cys1791Tyr) variant. Stem Cell Res. 68, 103050. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2023.103050
Pyeritz, R. E. (2000). The Marfan syndrome. Annu. Rev. Med. 51, 481–510. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.51.1.481
Qin, Z., Sun, L., Sun, X., Gao, X., and Su, H. (2021). Reprogramming of a human induced pluripotent stem cell line from a Marfan syndrome patient harboring a heterozygous mutation of c.2939G > A in FBN1 gene. Stem Cell Res. 51, 102163. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102163
Quarto, N., Leonard, B., Li, S., Marchand, M., Anderson, E., Behr, B., et al. (2012a). Skeletogenic phenotype of human Marfan embryonic stem cells faithfully phenocopied by patient-specific induced-pluripotent stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 215–220. doi:10.1073/pnas.1113442109
Quarto, N., Li, S., Renda, A., and Longaker, M. T. (2012b). Exogenous activation of BMP-2 signaling overcomes TGFβ-mediated inhibition of osteogenesis in Marfan embryonic stem cells and Marfan patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 30, 2709–2719. doi:10.1002/stem.1250
Sakai, L. Y., Keene, D. R., and Engvall, E. (1986). Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J. Cell Biol. 103, 2499–2509. doi:10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499
Sengle, G., and Sakai, L. Y. (2015). The fibrillin microfibril scaffold: a niche for growth factors and mechanosensation? Matrix Biol. 47, 3–12. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2015.05.002
Sharma, T., Gopal, L., Shanmugam, M. P., Bhende, P. S., Agrawal, R., Shetty, N. S., et al. (2002). Retinal detachment in Marfan syndrome: clinical characteristics and surgical outcome. Retina 22, 423–428. doi:10.1097/00006982-200208000-00005
Spitalieri, P., Marini, M., Scioli, M. G., Murdocca, M., Longo, G., Orlandi, A., et al. (2021). Effects of simulated microgravity on wild type and marfan hiPSCs-derived embryoid bodies. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 14, 613–626. doi:10.1007/s12195-021-00680-1
Stenson, P. D., Ball, E. V., Mort, M., Phillips, A. D., Shiel, J. A., Thomas, N. S., et al. (2003). Human gene mutation database (HGMD): 2003 update. Hum. Mutat. 21, 577–581. doi:10.1002/humu.10212
Stheneur, C., Faivre, L., Collod-Béroud, G., Gautier, E., Binquet, C., Bonithon-Kopp, C., et al. (2011). Prognosis factors in probands with an FBN1 mutation diagnosed before the age of 1 year. Pediatr. Res. 69, 265–270. doi:10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182097219
Takahashi, K., Tanabe, K., Ohnuki, M., Narita, M., Ichisaka, T., Tomoda, K., et al. (2007). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131, 861–872. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019
Takahashi, K., and Yamanaka, S. (2006). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024
Takeda, N., Inuzuka, R., Maemura, S., Morita, H., Nawata, K., Fujita, D., et al. (2018). Impact of pathogenic FBN1 variant types on the progression of aortic disease in patients with marfan syndrome. Circ. Genom Precis. Med. 11, e002058. doi:10.1161/circgen.117.002058
Thomson, J. A., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., Shapiro, S. S., Waknitz, M. A., Swiergiel, J. J., Marshall, V. S., et al. (1998). Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147. doi:10.1126/science.282.5391.1145
Vacante, F., Venkateshappa, R., Htet, M., Yan, C., and Wu, J. C. (2024). Generation of Marfan syndrome-specific induced pluripotent stem cells harboring FBN1 mutations. Stem Cell Res. 80, 103518. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2024.103518
Van Den Heuvel, L. J. F., Peeters, S., Meester, J. A. N., Perik, M., Coucke, P., and Loeys, B. L. (2023). A generated induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line (CMGANTi005-A) of a Marfan syndrome patient with an FBN1 c.7754T > C (p.Ile2585Thr) variation. Stem Cell Res. 67, 103032. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2023.103032
Verlinsky, Y., Strelchenko, N., Kukharenko, V., Rechitsky, S., Verlinsky, O., Galat, V., et al. (2005). Human embryonic stem cell lines with genetic disorders. Reprod. Biomed. Online 10, 105–110. doi:10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60810-3
Wu, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, L., and Yu, J. (2021). Generation of a human iPSC line QDMHi001-A from a patient with Marfan syndrome carrying a heterozygous c.6772 T > C variant in FBN1. Stem Cell Res. 54, 102390. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2021.102390
Yang, Q., Zhou, X., Zhou, H., Li, L., Du, J., Lu, G., et al. (2015). Human embryonic stem cells derived from abnormal blastocyst donated by Marfan syndrome patient. Stem Cell Res. 15, 640–642. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2015.10.012
Yin, X., Hao, J., and Yao, Y. (2021). CRISPR/Cas9 in zebrafish: an attractive model for FBN1 genetic defects in humans. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 9, e1775. doi:10.1002/mgg3.1775
Yin Xiaoke, X., Wanga, S., Fellows, A. L., Barallobre-Barreiro, J., Lu, R., Davaapil, H., et al. (2019). Glycoproteomic analysis of the aortic extracellular matrix in marfan patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 39, 1859–1873. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312175
Keywords: human pluripotent stem cells, Marfan syndrome, disease modelling, in vitro, aortopathy, cardiomyopathy
Citation: Aalders J, Muiño Mosquera L and van Hengel J (2025) Human stem cell models for Marfan syndrome: a brief overview of the rising star in disease modelling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1498669. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1498669
Received: 19 September 2024; Accepted: 04 December 2024;
Published: 03 January 2025.
Edited by:
Erkan Kiris, Middle East Technical University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Ramachandran Prakasam, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Aalders, Muiño Mosquera and van Hengel. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jolanda van Hengel, am9sYW5kYS52YW5oZW5nZWxAdWdlbnQuYmU=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.