- 1Department of Urology, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
- 3Department of Urology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Nephrolithiasis is one of the most common diseases in urology, characterized by notable incidence and recurrence rates, leading to significant morbidity and financial burden. Despite its prevalence, the precise mechanisms underlying stone formation remain incompletely understood, thus hindering significant advancements in kidney stone management over the past three decades. Investigating the pivotal biological molecules that govern stone formation has consistently been a challenging and high-priority task. A significant portion of mammalian genomes are transcribed into noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), which have the ability to modulate gene expression and disease progression. They are thus emerging as a novel target class for diagnostics and pharmaceutical exploration. In recent years, the role of ncRNAs in stone formation has attracted burgeoning attention. They have been found to influence stone formation by regulating ion transportation, oxidative stress injury, inflammation, osteoblastic transformation, autophagy, and pyroptosis. These findings contributes new perspectives on the pathogenesis of nephrolithiasis. To enhance our understanding of the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of nephrolithiasis-associated ncRNAs, we summarized the expression profiles, biological functions, and clinical significance of these ncRNAs in the current review.
Introduction
Nephrolithiasis is one of the most prevalent diseases in urology and often causes renal colic, urinary tract infections, and damage to renal function (Thongprayoon et al., 2020). It is estimated that 1%–15% of individuals may suffer from kidney stones during their lifetime (Romero et al., 2010). Global prevalence rates for nephrolithiasis vary from 1% to 20% (Skolarikos et al., 2022). In countries such as Sweden, Canada, and America, the prevalence is notably higher than 10% (Skolarikos et al., 2024). The prevalence of kidney stones is 6.4% in China and shows an increasing trend (Zeng et al., 2017). Despite significant advancements in surgical treatments for kidney stones, medical treatments and preventions have seen minimal changes over the past three decades. This is primarily due to unclear mechanisms underlying stone formation (Khan et al., 2021). The 10-year recurrence rate for kidney stones after surgical interventions is reported to be as high as 50%, resulting in a huge morbidity and financial burden (Khan et al., 2016). The cost of nephrolithiasis treatment in the USA was $2 billion in 2000 and is estimated to be $4.5 billion by 2030 (Antonelli et al., 2014). Thus, it is important to explore the pathogenesis of nephrolithiasis and provide a theoretical basis for its treatment and prevention.
Approximately 80% of kidney stones primarily consist of calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystals, intermixed with varying amounts of calcium phosphate (Khan et al., 2021). Hyperoxaluria and hypercalciuria stand as the most prevalent metabolic abnormalities among patients with nephrolithiasis (Letavernier and Daudon, 2018; Witting et al., 2021). They can trigger the precipitation of urinary crystals and increase the risk of stone formation. According to classical lithogenic theory, there are specific crystal-attachment sites within the renal collecting system, termed interstitial Randall’s plaque and intraluminal Randall’s plug (Khan et al., 2016). Early-formed tiny urinary crystals can adhere to these sites and aggregate, eventually growing into kidney stones. However, the pathogenesis of nephrolithiasis is not solely based on urine supersaturation, but also involves intricate interactions between lithogenic factors and cellular components (Khan et al., 2021). Biological responses induced by the lithogenic microenvironment, including oxidative stress, inflammation, osteogenic transformation, apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis, have a significant impact on the initiation and progression of kidney stones (Wang et al., 2021). Investigating key biological molecules which govern kidney stone formation remains a central focus and challenge.
While it has traditionally been assumed that genetic information is predominantly conveyed by proteins, recent findings indicate that the majority of mammalian genomes are transcribed into noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) (Mattick and Makunin, 2006). Based on biological functions, ncRNAs are broadly classified into housekeeping and regulatory RNAs. Housekeeping ncRNAs include ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), transfer RNAs (tRNAs), small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) (Hombach and Kretz, 2016). These ncRNAs are consistently expressed and contribute to essential cellular functions. Regulatory ncRNAs exhibit tissue- and disease-specific expression patterns. They can be roughly categorized into long ncRNAs (lncRNAs) with sizes greater than 200 nucleotides, and small ncRNAs less than 200 nucleotides, which include microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and piwi-associated RNAs (piRNAs) (Hombach and Kretz, 2016; Tomar et al., 2020). Functionally, ncRNAs can modulate gene expression and influence disease progression, therefore emerging as a novel class of targets for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions (Yang et al., 2021; Simonson and Das, 2015; Zhou et al., 2021).
An increasing number of studies have demonstrated that miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs are closely associated with stone formation, offering potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for nephrolithiasis. In the current review, we aimed to summarize the expression profiles, biological functions and mechanisms, and clinical significance of regulatory ncRNAs in kidney stone disease.
Biogenesis and functions of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs
MiRNAs are single-stranded molecules that are approximately 21–23 nucleotides in length (Lu and Rothenberg, 2018). In humans, the biogenesis of miRNAs involves sequential nuclear and cytoplasmic processing events. MiRNAs are first transcribed as long transcripts called pri-miRNAs in the nucleus (Lee et al., 2002). RNA pol II is thought to be responsible for pri-miRNA transcription. The nuclear cleavage of pri-miRNAs into pre-miRNAs is carried out by RNase III endonuclease Drosha and pasha (Hombach and Kretz, 2016). Then, pre-miRNAs are transported into the cytoplasm via the interaction between exportin-5 and Ran-GTP (Yi et al., 2003). The maturation of pre-miRNAs in the cytoplasm is carried out by RNase III endonuclease Dicer, which separates the loop structure and leaves imperfect double strands known as the miRNA: miRNA complex. Subsequently, double-stranded RNAs are incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) (Vishnoi et al., 2017). Within this complex, mature single-stranded miRNAs bind to the Argonaute protein and act as a guide to partially complementary regions located in the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs (Vishnoi et al., 2017). The subsequent binding of trinucleotide repeat containing adaptor 6 (TNRC6) proteins plays a pivotal role in the translational repression and degradation of target mRNAs (Hombach and Kretz, 2016). It is estimated that more than 60% of mRNAs contain miRNA target sites in their 3′-UTR. Furthermore, each miRNA is able to target several mRNAs, indicating a complex regulatory network between miRNAs and mRNAs (Sayed and Abdellatif, 2011). MiRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of many diseases (Shi et al., 2021; Azhar et al., 2022; Juchnicka and Kuzmicki, 2021; Ho et al., 2022). Their potential value in diagnosis and treatment has attracted much attention. MiRNA inhibitors and mimics targeting various pathways are currently under development and undergoing evaluation in many clinical trials (Thakral and Ghoshal, 2015; Gomez et al., 2015).
LncRNAs are RNA molecules longer than 200 nucleotides that lack the potential to code for proteins. Compared to messenger RNAs (mRNAs), lncRNAs contain fewer and longer exons and are less evolutionarily conserved (Statello et al., 2021). The transcription and processing mechanisms of most lncRNAs are similar to those of mRNAs. Briefly, they are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, capped by 7-methyl guanosine (m7G) at their 5′ends, polyadenylated at their 3′ends, and exported to the cytoplasm by nuclear RNA export factor 1 (NXF1) (Statello et al., 2021). While a considerable portion of lncRNAs is retained in the nucleus, the exact underlying mechanisms remain largely elusive. The molecular functions of lncRNAs can be classified into signaling, decoying, scaffolding, and guiding (Wang and Chang, 2011). As signals, lncRNAs can act as transcription factors to regulate the expression of downstream genes in signaling pathways. As decoys, lncRNAs can bind to transcription factors and other chromatin proteins to disable them. Additionally, lncRNAs can sequester microRNA (miRNAs), preventing them from interacting with their target mRNAs. In the role of guides, lncRNAs can recruit chromatin-modifying enzymes to target genes. As scaffolds, lncRNAs bring proteins together to form ribonucleoprotein complexes, such as ribosomes. Implicated as key regulators in numerous pathophysiological processes including the cell cycle, cell proliferation, metabolism, and differentiation (Zhang et al., 2022; Xue et al., 2022; Chen M. et al., 2022), lncRNAs exhibit significant potential in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases (Chen Y. et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2020; Hussen et al., 2022; Winkle et al., 2021; Hashemi et al., 2022).
As a novel type of ncRNA, circRNAs were first found in viroids in 1976 (Sanger et al., 1976) and were subsequently observed in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell lines in 1979 (Hsu and Coca-Prados, 1979). The most prominent feature of circRNAs is that they are covalently closed loops without 5′caps and 3′polyadenylated tails. This explains why circRNAs have a longer half-life and stronger exonuclease resistance than linear RNAs (Jeck and Sharpless, 2014). CircRNAs originate from the exons and/or introns of pre-mRNA transcripts by back splicing (Memczak et al., 2013). Circularization competes with canonical pre-mRNA splicing, with the production primarily governed by flanking intronic sequences (Ashwal-Fluss et al., 2014). CircRNAs were thought to lack open reading frames, leading to the assumption that they mainly functioned as miRNA sponges or RNA-protein complexes (Wilusz and Sharp, 2013; Kristensen et al., 2019). However, recent studies have identified that a small number of circRNAs can also be effectively translated into specific proteins (Xia et al., 2019; Pan et al., 2022). Owing to their remarkable stability, CircRNAs tend to accumulate in specific cell types. They show tissue-specific expression patterns and play crucial biological roles in various diseases, making them attractive potential candidates as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets (Zhou et al., 2019; Mehta et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2019). Currently, circRNAs have become the focus of novel therapeutic strategies and vaccine development. Figure 1 illustrates the common biogenesis process of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs.
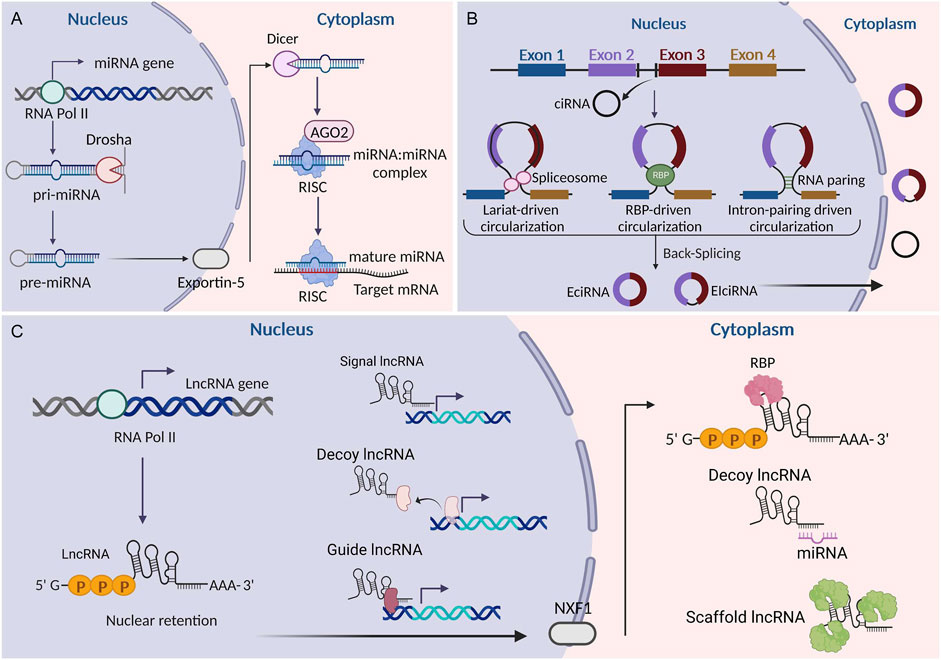
Figure 1. Biogenesis of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs. (A) Biogenesis of miRNAs. (B) Biogenesis of circRNAs. (C) Biogenesis of lncRNAs. LncRNAs can be classified into signaling, decoying, scaffolding, and guiding lncRNAs according to their functions. EciRNA, exonic circRNA; CiRNA, circular intronic RNA; EIciRNA, exon-intron circRNA; RBP, RNA binding protein; AGO2, argonaute 2; NXF1, nuclear RNA export factor 1; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
Integrated analysis of ncRNAs and mRNAs
Most ncRNAs do not code for proteins. Instead, they play important roles in mRNA regulation, chromatin organization, and other cellular processes. An integrated analysis of ncRNAs and mRNAs is a useful strategy for exploring the biological role of ncRNAs. Integrative data analysis involves pooling or combining two or more independent datasets into one, which is then statistically analyzed. Accordingly, integrated analysis of ncRNAs and mRNAs involves profiling the expression levels of both RNA types via high-throughput technologies (RNA sequencing or microarray analysis). It puts both types of RNAs together to gain a comprehensive understanding of gene expression regulation and its impact on cellular function and disease process (Kristensen et al., 2014). Common analyses include co-expression analysis, target prediction, functional enrichment analysis, and competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNA) network analysis (Zhang et al., 2019; Shvedova et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2023). These analyses reveal how ncRNAs regulate the expression of target mRNAs, modulate signaling pathways, and influence cellular processes. This information is essential and highly efficient for researchers in identifying intricate regulatory networks, novel biomarkers, and reliable therapeutic targets for various diseases.
ncRNA expression profiles in kidney stone disease
Identifying ncRNAs with abnormal expression is an important strategy in the study of nephrolithiasis. In recent years, the rapid development of high-throughput genomics, especially microarray and RNA-sequencing technologies, has shown great advantages for exploring stone-related differential ncRNAs (Figure 2). An overview of ncRNAs identified by RNA sequencing and microarrays in kidney stone disease is listed in Table 1.
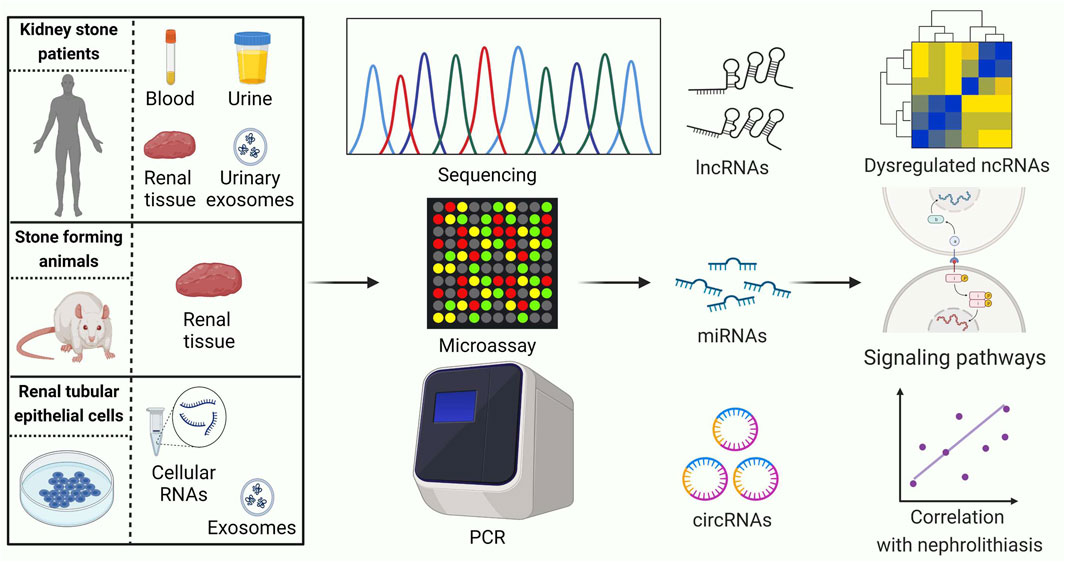
Figure 2. Current strategies for conducting ncRNA expression profiling studies related to kidney stones. PCR: polymerase chain reaction. LncRNAs, long noncoding RNAs; MiRNAs, microRNAs; CircRNAs, circular RNAs. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
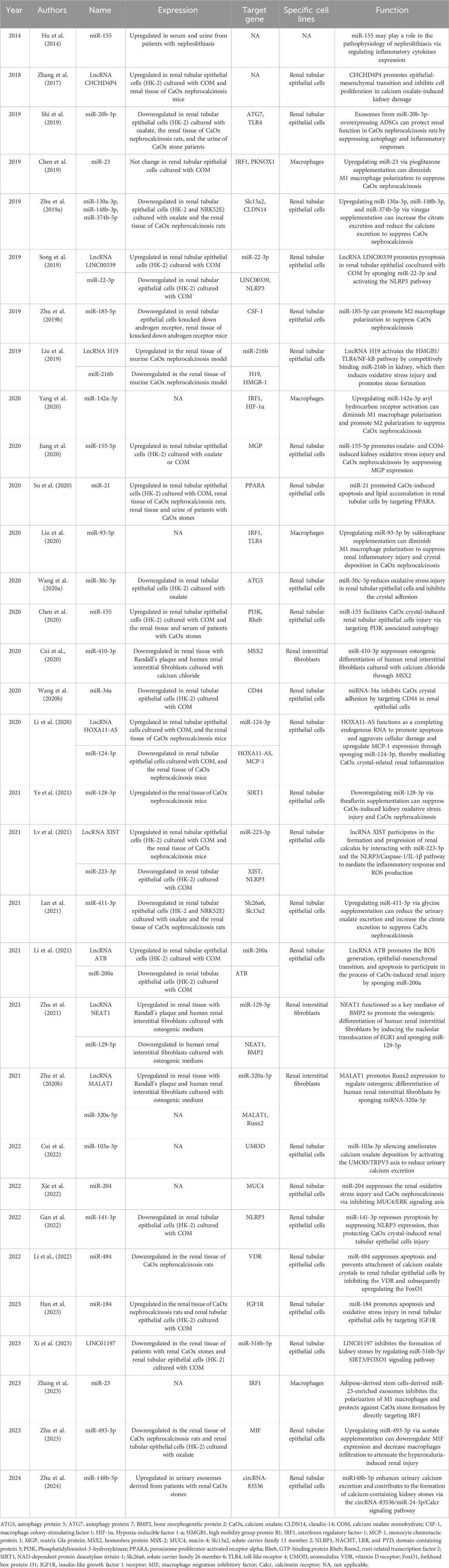
Numerous studies have profiled ncRNA expression in renal tissue using stone-forming animal models, with a predominant focus on miRNAs. We investigated renal miRNA profiles using a microarray in 12 paired genetic hypercalciuric stone-forming (GHS) rats and normal Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Ten miRNAs were found to be upregulated and nine were downregulated (>2-fold change, p < 0.05) in GHS rats (Lu et al., 2016). Liu et al. (2016) and Lan et al. (2017) have both conducted microarray experiments to explore the renal expression of miRNAs in CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats. Liu et al. (2016) identified 20 upregulated and eight downregulated miRNAs (>2-fold change, p < 0.05) in nephrocalcinosis rats. Lan et al. (2017) identified 38 mature miRNAs. Among them, eighteen miRNAs were upregulated, while 20 were downregulated (>2-fold change, p < 0.05) in the stone group. Cao et al. (2018) explored lncRNA and circRNA expression profiles in the kidneys from CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats. As a result, the expression of 1,440 lncRNAs and 145 circRNAs was found to be altered (>2-fold change, p < 0.05 and false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05). Additionally, Zhang et al. (2017) analyzed the lncRNA profiles in renal tissue from CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice and found that 154 lncRNAs were upregulated, while 222 lncRNAs were downregulated (>1.5-fold change, p < 0.05). Xu et al. also uploaded the renal miRNA-sequencing data from six paired normal C57BL/6J mice and CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice to the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (GSE186793).
ncRNA profiles in kidney stone patients have also been studied. Liang et al. (2019) investigated the urinary lncRNA and microRNA profiles using microarray technology in five CaOx stone patients and six healthy controls. Nine miRNAs and 1,002 lncRNAs were found to be dysregulated (>1.5-fold change, p < 0.05) in patients with nephrolithiasis, including four upregulated and five downregulated miRNAs and 790 upregulated and 212 downregulated lncRNAs. Yang et al. (2022) isolated urinary exosomes from the first morning voids of three paired CaOx stone patients and healthy controls. Urinary exosomal miRNA profiles were detected by sequencing. In the stone group, fourteen downregulated miRNAs and 40 upregulated miRNAs (>2-fold change, p < 0.01) were identified. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis indicated that these dysregulated miRNAs were enriched in oxidative stress, focal adhesion, cell adhesion molecule binding, and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Similarly, Zhu et al. (2024) also detected the urinary exosomal miRNA profiles by sequencing in renal CaOx stone patients and found that 523 miRNAs were upregulated, while 296 miRNAs were downregulated (>2-fold change, p < 0.05). Cui et al. detected lncRNA profiles in human renal papillary tissues with Randall’s plaque (GSE117518).
In vitro studies are often conducted in human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2). Wang et al. (2014) investigated miRNA profiles by microarray technology in HK-2 cells cultured with calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM). Twenty-five miRNAs were found to be differentially expressed with more than a 1.5-fold change. Among them, 16 were upregulated and nine were downregulated. Another sequencing study identified nine upregulated lncRNAs and 16 downregulated lncRNAs (>2-fold change, FDR<0.05) in HK-2 cells cultured with COM (Wang et al., 2019). Guan et al. have uploaded the miRNA-sequencing data of exosomes from COM-treated HK-2 cells to the GEO database (GSE110509).
Biological functions and molecular mechanisms of ncRNAs in kidney stone disease
Ion transportation
In addition to hypercalciuria and hyperoxaluria, other metabolic abnormalities, such as hyperuricosuria, hypomagnesuria, and hypocitraturia, can also increase the risk of nephrolithiasis (Skolarikos et al., 2024). Ameliorating the abnormal ion concentration in urine is a feasible method to prevent kidney stone formation. Oxalate is transferred from renal epithelial cells to the lumen through solute carrier family 26 member 6 (Slc26a6), while urinary citrate is mainly reabsorbed in the proximal renal tubule via solute carrier family 13 member 2 (Slc13a2). Lan et al. (2021) discovered that miR-411-3p directly bound to the 3′-UTRs of both Slc26a6 and Slc13a2 mRNAs. Supplementation with glycine was found to upregulate miR-411-3p, leading to the inhibition of protein expression of Slc26a6 and Slc13a2 in renal tubular epithelial cells. This resulted in reduced urinary oxalate excretion and increased citrate excretion, ultimately leading to a decrease in renal CaOx crystal deposition. Zhu et al. (2019a) demonstrated that miR-130a-3p and miR-148b-3p could also target Slc13a2. Vinegar supplementation increased the expression of miR-130a-3p and miR-148b-3p in renal tubular epithelial cells. This led to the suppression of Slc13a2 expression and an enhancement in the concentration of urinary citric acid. Additionally, vinegar reduced urinary calcium excretion by stimulating miR-374b-5p gene transcription, thus suppressing the expression of Claudin-14, a potential treatment target for hypercalciuria. Zhu et al. (2024) further reported that miR-148b-5p could inhibit the expression of circRNA-83536, thereby reducing its suppression of miR-24-3p. MiR-24-3p could bind to the 3′-UTRs of the calcitonin receptor (Calcr), then leading to downregulation of its expression. This cascade of events ultimately results in the promotion of urinary calcium excretion and stone formation. In a study by Cui et al. (2022), miR-103a-3p was found to negatively regulate the expression of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 5 (TRPV5) by targeting uromodulin. Silencing miR-103a-3p could activate the expression of TRPV5 and promote the reabsorption of calcium ions by renal tubular epithelial cells. This lead to a reduction in urinary calcium excretion and crystal deposition in the kidneys of hyperoxaluria rats.
Oxidative stress injury
Stone formation is closely associated with an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the kidney (Khan, 2014). ROS generated during aerobic metabolism encompass diverse molecules such as superoxide anion, nitric oxide free radical, hydroxyl, hydrogen peroxide, and so on (Yang and Lian, 2020). In general, the production and clearance of cellular ROS are balanced to maintain physiological functions. However, under certain pathological circumstances, such as stimulation by calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystals or elevated concentrations of oxalate or calcium, the production of ROS escalates while clearance mechanisms become insufficient. This imbalance leads to oxidative stress injury and then promotes the adhesion of crystals to renal tubular epithelial cells (Chaiyarit and Thongboonkerd, 2020; Albert et al., 2020).
SIRT1 is an NAD-dependent protein deacetylase showing anti-inflammatory and antioxidative functions. Ye et al. (2021) found that miR-128-3p was upregulated in the kidneys of CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice and it suppressed the expression of SIRT1 by binding its 3′-UTR. Theaflavin supplementation could alleviate CaOx-induced renal oxidative stress injury by inhibiting miR-128-3p while upregulating SIRT1. In our previous study, we demonstrated that the expression of miR-155-5p was increased in HK-2 cells cocultured with COM and that miR-155-5p could directly target matrix Gla protein (MGP). Additionally, miR-155-5p antagonist significantly reduced renal crystal disposition and ROS generation in CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats (Jiang et al., 2020). Wang X. et al. (2020a) reported that the expression of miR-30c-5p expression was significantly downregulated in HK-2 cells treated with sodium oxalate. Overexpression of miR-30c-5p reversed apoptosis, crystal deposition, lactate dehydrogenase, malondialdehyde and ROS levels in the kidneys of CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice by targeting autophagy protein 5 (ATG5). In addition, another study has shown that supplementation with miR-204 agonists could reduce CaOx-induced oxidative stress injury in renal tubular epithelial cells, offering potential targets for preventing stone formation (Xie et al., 2022).
It has been reported that NACHT, LRR and PYD domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) plays a crucial role in inflammation. Lv et al. found that miR-223-3p bound to the 3′-UTR of both NLRP3 and lncRNA X inactive specific transcript (XIST). CaOx could upregulate the expression of XIST, which competitively bound to miR-223-3p, leading to the release of NLRP3 mRNA from miR-223-3p in renal tubular epithelial cells. These competing interactions between XIST/miRNA-223/NLRP3 ultimately exacerbated the production of ROS, inflammatory injury, and crystal deposition in the renal tissue of CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice (Lv et al., 2021). Similarly, studies regarding XIST sponging miRNAs to activate NLRP3 inflammasome in other diseases have also been reported (Ma et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2022). Evidence has shown that lncRNA H19 is involved in inflammatory regulation and induces tissue injury (Song et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2017). Genome-wide expression profile analysis of renal tissue with Randall’s plaques demonstrated that H19 expression was upregulated (Taguchi et al., 2017). Liu et al. (2019) found that miR-216b bound to the 3′-UTR of both H19 and high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1). H19 could activate the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway by competitively binding miR-216b in the kidney. This activation subsequently induced oxidative stress injury and promoted stone formation. Li et al. (2021) reported that the expression of lncRNA ATB was increased, while the expression of miR-200a was decreased in HK-2 cells after incubation with COM. Further investigation revealed that miR-200a directly bound to the 3′-UTR of lncRNA ATB, as confirmed by a dual-luciferase reporter experiment. ATB promoted ROS generation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and apoptosis to contribute to CaOx-induced renal injury by sponging miR-200a. It should be indicated that competing regulations between ATB and miR-200 family also played a role in the pathogenesis of carcinoma and neurotoxicity (Wang et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018; Zhu L. et al., 2020). Li et al. (2022) found that the expression of miR-484 was downregulated in the renal tissue of CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats. MiR-484 could upregulate the expression of forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) by targeting Vitamin D receptor (VDR), then suppressing apoptosis and oxidative stress injury in renal tubular epithelial cells. Han et al. (2023) reported that miR-184 was upregulated in both the renal tissue of CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats and renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) cultured with COM. This miRNA is capable of directly binding to the 3′-UTR of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R), subsequently promoting COM-induced oxidative stress injury and apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Inflammation
In recent years, increasing attention has been given to the role of the immune response in kidney stone formation (Deng et al., 2018). The lithogenic microenvironment can continuously stimulate renal tubular epithelial cells to secrete inflammatory factors. This results in an amplified inflammatory response that leads to renal tissue damage, promoting adhesion, aggregation, and growth of urine crystals. Moreover, macrophages are significantly increased in the kidneys of patients with CaOx nephrolithiasis, indicating their involvement in the immune regulation (Taguchi et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2022). Studies have shown that M1 macrophages secrete proinflammatory factors and promote kidney stone formation, whereas M2 macrophages secrete anti-inflammatory factors and play a role in inhibiting stone formation (Khan et al., 2021; Dominguez-Gutierrez et al., 2020).
Li et al. (2020) reported that lncRNA HOXA11-AS was upregulated in the renal tissue of CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice, while miR-124-3p was downregulated. It was observed that miR-124-3p had the ability to bind to the 3′-UTR of both monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) and HOXA11-AS. LncRNA HOXA11-AS acted as a competing endogenous RNA to promote apoptosis, aggravate cellular damage and upregulate MCP-1 expression by sponging miR-124-3p, thereby mediating CaOx crystal-related renal inflammation. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) can recruit macrophages and promote M2 polarization. Zhu et al. (2019b) found that androgen receptor upregulated miR-185-5p by binding to the androgen response element on its 5ʹ promoter in renal tubular epithelial cells. Dual luciferase reporter experiments showed that miR-185-5p bound to the 3′-UTR of CSF-1. Silencing the androgen receptor (AR) in renal tubular epithelial cells lead to upregulation of CSF-1 expression by downregulating miR-185-5p. This ultimately promoted macrophage recruitment and M2 polarization, which reduced renal crystal disposition in CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats.
The interferon regulatory factor (IRF) family is a class of important nuclear transcription factors that regulate the polarization of macrophages. The expression of IRF-1 is increased in the kidneys of mice with hyperoxaluria, and IRF-1 is considered to play a lithogenic role. Liu et al. (2020) found that nuclear factor erythroid 2-related 2 (Nrf2) exhibited positive transcriptional activation of miR-93-5p by binding to its promoter. MiR-93-5p could target IRF1 and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) mRNAs to inhibit their expression in macrophages. Sulforaphane, a pharmacological activator of Nrf2, could promote M2 macrophage polarization to suppress renal inflammation and crystal adhesion in CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice. Pioglitazone has also been reported to negatively regulate IRF1 expression by upregulating miR-23 in macrophages and then decreasing CaOx nephrocalcinosis (Chen et al., 2019). In another study by Yang et al. (2020), bioinformatics analysis and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays confirmed that the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in bone marrow-derived macrophages could bind the promoter to transcriptionally activate miR-142a-3p. This activation subsequently inhibited the expression of IRF1 and HIF-1α by directly targeting their 3′-UTRs. AhR activation could diminish M1 macrophage polarization and promote M2 polarization to suppress CaOx nephrocalcinosis via the miR-142a-IRF1/HIF-1α pathway. In addition, Zhang et al. (2023) reported that adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs)-derived miR-23-enriched exosomes could inhibit the polarization of M1 macrophages and protects against CaOx stone formation by directly targeting IRF1 in macrophages. Zhu et al. (2023) found that miR-493-3p bound to the 3′-UTR of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Acetate supplementation could enhance the H3K9 and H3K27 acetylation levels at the promoter region of miR-493-3p, subsequently upregulating miR-493-3p and downregulating MIF expression. This process decreased macrophage infiltration, therefore attenuating hyperoxaluria-induced renal injury.
Osteogenic transformation
Randall’s plaque is an ectopic calcification located in the renal papillary interstitium. Its main component is hydroxyapatite, which is similar to the bone matrix (Wiener et al., 2018). The plaque can gradually grow into the renal interstitium and eventually break through the urothelium and contact urine. Early-formed urinary crystals can adhere to the plaque and then form stones. Therefore, Randall’s plaque is considered to be the origin of kidney stones by many researchers (Daudon et al., 2015). It has been reported that osteogenic transformation of cells in the renal collecting system, including renal tubular epithelial cells and renal interstitial fibroblasts, plays a role in the formation of Randall’s plaque (Gambaro et al., 2004; Joshi et al., 2015; Jia et al., 2014).
Cui et al. (2020) identified a series of ncRNAs that regulated the osteogenic transformation of renal interstitial fibroblasts in a lithogenic microenvironment. They found that the expression of miR-410-3p was decreased in renal interstitial fibroblasts cultured with osteoblastic medium and in renal papillary tissue with Randall’s plaque. A binding relationship between homeobox protein MSX-2 (MSX2) and miR-410-3p was confirmed through dual-luciferase reporter gene analysis. miR-410-3p could target MSX-2 to inhibit the osteogenic transformation of renal interstitial fibroblasts. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) has been reported to be a classical phenotypic molecule during osteogenic transformation. It has been reported that lncRNA NEAT1 may act as a key activator of BMP2, thus promoting the osteogenic differentiation of renal interstitial fibroblasts. In the cytoplasm, NEAT1 sponges miR-129-5p to stabilize BMP2 mRNA. In the nucleus, NEAT1 induces the nucleolar translocation of early growth response protein 1 (EGR1), which then binds to the promotor of BMP2 and promotes its transcription (Zhu et al., 2021). The expression of LncRNA MALAT1 was also found to be increased in human renal papillary tissue with Randall’s plaque. miR-320a-5p could bind to the 3′-UTR of both MALAT1 and runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2). MALAT1 acted as a sponge of miR-320a-5p to promote Runx2 expression, thus upregulating the expression of osteogenesis-associated proteins in renal interstitial fibroblasts (Zhu Z. et al., 2020).
Other roles
Hu et al. (2014) compared the serum and urinary levels of miR-155 between 60 patients with nephrolithiasis and 50 healthy volunteers. They found that both serum and urinary levels of miR-155 were significantly higher in nephrolithiasis patients. They observed a positive correlation between plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and urinary miR-155 levels. Additionally, the urinary expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α showed an inverse correlation with urinary miR-155 levels. Chen et al. (2020) explored the exact role of miR-155 in stone formation. Similarly, they found that serum and renal levels of miR-155 were elevated in patients with CaOx stones. PI3K and Rheb were identified as downstream targets of miR-155. They ultimately showed that miR-155 facilitated CaOx crystal-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury through PI3K-mediated autophagy. Shi et al. (2019) reported that miR-20b-3p was decreased in the renal tissue of CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats and in the urine of CaOx stone patients. Treatment with miR-20b-3p-enriched exosomes protected renal function in CaOx nephrocalcinosis rats. In vitro experiments confirmed that miR-20b-3p-enriched exosomes could alleviate oxalate-induced autophagy and crystal adhesions in renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting autophagy protein 7 (ATG7) and TLR4. Gan et al. (2022) and Song et al. (2019) reported that CaOx crystals could suppress the expression of miR-22-3p and miR-141-3p in renal tubular epithelial cells, leading to the activation of NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. This, in turn, promoted cell injury and crystal adhesion. In addition, the lncRNA LINC00339 was upregulated in HK-2 cells treated with COM and could sponge miR-22-3p (Song et al., 2019). Su et al. (2020) reported that miR-21 was elevated in the renal tissue and urine of patients with CaOx stones. miR-21 promoted CaOx-induced apoptosis and lipid accumulation in renal tubular cells by targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARA). Wang B. et al. (2020b) demonstrated that miR-34a could inhibit the expression of the adhesion molecule CD44 to reduce COM adhesions to renal tubular epithelial cells. The expression of LncRNA CHCHD4P4 was upregulated in the renal tissue of CaOx nephrocalcinosis mice. This change promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition in CaOx-induced renal damage (Zhang et al., 2017). Xi et al. (2023) demonstrated that lncRNA LINC01197 played an inhibitory role in stone formation by sponging miR-516b-5p and subsequently activating the SIRT3/FOXO1 signaling pathway. An overview of dysregulated ncRNAs in kidney stone disease is shown in Table 2.
Conclusion
The role of ncRNAs in kidney stone disease has attracted much attention in recent years, offering novel perspectives to the pathogenesis of nephrolithiasis. NcRNAs can influence stone formation by regulating ion transportation, oxidative stress, inflammation, osteoblastic transformation, autophagy, and pyroptosis (Figure 3). Among the myriad dysregulated ncRNAs, we found that miR-155 was the focus of three different studies (Jiang et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2020). MiR-155 is encoded by the miR-155 host gene (mir155 hg), which produces miR-155-3p and miR-155-5p forms. MiR-155 is strongly implicated in inflammatory autoimmune diseases (Xu et al., 2022; Zingale et al., 2021; Maciak et al., 2021). Drugs targeting miR-155 have been designed to treat T cell cutaneous lymphoma and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in preclinical trials (Chakraborty et al., 2020). In terms of kidney stone disease, in vitro and animal studies suggest that miR-155 plays a lithogenic role by promoting CaOx-induced renal injury (Jiang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2020). The expression of miR-155 is upregulated not only in renal tubular epithelial cells cultured with CaOx but also in the renal tissue, serum, and urine from kidney stone patients (Jiang et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2020). Therefore, can miR-155 serve as a reliable diagnostic and therapeutic target for nephrolithiasis? Well-designed prospective studies with an adequate number of kidney stone patients are expected to answer this question.
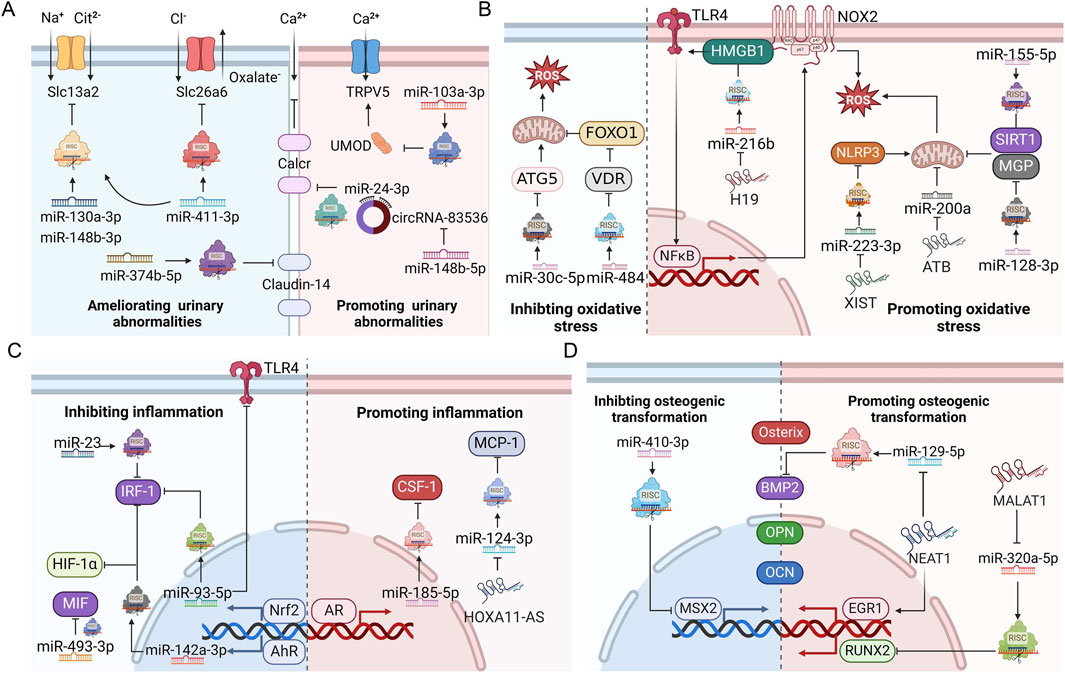
Figure 3. ncRNAs regulate ion transportation, oxidative stress injury, inflammation, and osteogenic transformation during stone formation. (A) Roles of ncRNAs in urinary ion transportation. (B) Roles of ncRNAs in oxidative stress. (C) Roles of ncRNAs in inflammation. (D) Roles of ncRNAs in osteogenic transformation. AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; AR, androgen receptor; BMP2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; CSF-1, macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1; EGR1, early growth response protein 1; HIF-1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α; HMGB1, high mobility group protein B1; IRF1, interferon regulatory factor-1; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1; MGP, matrix Gla protein; MSX2, homeobox protein MSX-2; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR and PYD domain-containing protein 3; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related 2; OCN, osteocalcin; OPN, osteopontin; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; SIRT1, NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1; Slc13a2, solute carrier family 13 member 2; Slc26a6, solute carrier family 26 member 6; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; ATG5, autophagy protein 5; TRPV5, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 5; UMOD, uromodulin; VDR, vitamin D receptor; FoxO1, forkhead box protein O1; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; Calcr, calcitonin receptor. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
Perspectives
Developing diagnostic and therapeutic methods related to ncRNAs holds great promise for precision medicine and personalized healthcare. Commonly employed strategies include identifying differential ncRNAs for early detection and monitoring of diseases, synthetizing antisense oligonucleotides to specifically inhibit the function of ncRNAs, developing effective delivery systems to enhance the bioavailability of ncRNAs, constructing small molecules to target specific ncRNA-protein interactions or ncRNA secondary structures, and using CRISPR-Cas9 system to precisely edit the genomic sequences encoding ncRNAs (Nemeth et al., 2024; Winkle et al., 2021; Matsui and Corey, 2017; Chen B. et al., 2022). These methods make the clinical application of ncRNA-based diagnosis and therapeutics in urolithiasis possible.
It is important to acknowledge that the majority of existing findings concerning nephrolithiasis-related ncRNAs come from cell and animal experiments, with limited studies conducted in patient populations. Although some studies have identified differential ncRNAs between kidney stone patients and healthy populations, the sample size is often small, and the diagnostic or therapeutic value of these ncRNAs has not been further confirmed using follow-up data. Moreover, the reported ncRNAs lack specificity, as they have also been implicated in other diseases. The stability of ncRNAs associated with nephrolithiasis has also not been thoroughly discussed either. These limitations currently hinder the application of ncRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of kidney stone disease. It is anticipated that with future advances in research, ncRNAs can be used as reliable biomarkers or therapeutic targets in kidney stone disease.
Author contributions
QW: Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZY: Writing–original draft. XC: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. YY: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. KJ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82160147), the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Project (QKHJC-ZK [2022] YB258), the Foundation of Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital Post-Doctoral Workstation ([2019]5626), and Subsidy funding for the 2021 National Natural Science Foundation of China (GPPH-NSFC-2021-9).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Albert, A., Paul, E., Rajakumar, S., and Saso, L. (2020). Oxidative stress and endoplasmic stress in calcium oxalate stone disease: the chicken or the egg? Free Radic. Res. 54, 244–253. doi:10.1080/10715762.2020.1751835
Antonelli, J. A., Maalouf, N. M., Pearle, M. S., and Lotan, Y. (2014). Use of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to calculate the impact of obesity and diabetes on cost and prevalence of urolithiasis in 2030. Eur. Urol. 66, 724–729. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.06.036
Ashwal-Fluss, R., Meyer, M., Pamudurti, N. R., Ivanov, A., Bartok, O., Hanan, M., et al. (2014). circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 56, 55–66. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019
Azhar, A., Khan, W. H., Al-Hosaini, K., and Kamal, M. A. (2022). miRNAs in SARS-CoV-2 infection: an update. Curr. Drug Metab. 23, 283–298. doi:10.2174/1389200223666220321102824
Cao, Y., Gao, X., Yang, Y., Ye, Z., Wang, E., and Dong, Z. (2018). Changing expression profiles of long non-coding RNAs, mRNAs and circular RNAs in ethylene glycol-induced kidney calculi rats. BMC Genomics 19, 660. doi:10.1186/s12864-018-5052-8
Chaiyarit, S., and Thongboonkerd, V. (2020). Mitochondrial dysfunction and kidney stone disease. Front. Physiol. 11, 566506. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.566506
Chakraborty, C., Sharma, A. R., Sharma, G., and Lee, S. S. (2020). Therapeutic advances of miRNAs: a preclinical and clinical update. J. Adv. Res. 28, 127–138. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2020.08.012
Chen, B., Dragomir, M. P., Yang, C., Li, Q., Horst, D., and Calin, G. A. (2022c). Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7, 121. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00975-3
Chen, M., Zhang, C., Liu, W., Du, X., Liu, X., and Xing, B. (2022a). Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through orchestrating aspartate metabolic reprogramming. Mol. Ther. 30, 2354–2369. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.02.020
Chen, X., Zhang, X. B., Li, D. J., Qi, G. N., Dai, Y. Q., Gu, J., et al. (2020). miR-155 facilitates calcium oxalate crystal-induced HK-2 cell injury via targeting PI3K associated autophagy. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 115, 104450. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104450
Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Lu, J., Liu, Z., Zhao, S., Zhang, M., et al. (2022b). Characteristics of prognostic programmed cell death-related long noncoding RNAs associated with immune infiltration and therapeutic responses to colon cancer. Front. Immunol. 13, 828243. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.828243
Chen, Z., Yuan, P., Sun, X., Tang, K., Liu, H., Han, S., et al. (2019). Pioglitazone decreased renal calcium oxalate crystal formation by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via the PPAR-γ-miR-23 axis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 317, F137–f151. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00047.2019
Cui, Y., Zeng, F., Zhu, Z., Huang, F., Chen, J., He, C., et al. (2020). Suppression of osteogenic-like differentiation in human renal interstitial fibroblasts by miRNA-410-3p through MSX2. Transl. Androl. Urol. 9, 2082–2093. doi:10.21037/tau-20-607
Cui, Z., Li, Y., Liu, G., and Jiang, Y. (2022). miR-103a-3p silencing ameliorates calcium oxalate deposition in rat kidney by activating the UMOD/TRPV5 axis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2602717. doi:10.1155/2022/2602717
Daudon, M., Bazin, D., and Letavernier, E. (2015). Randall's plaque as the origin of calcium oxalate kidney stones. Urolithiasis 43 (1), 5–11. doi:10.1007/s00240-014-0703-y
Deng, Y. L., Liu, Y. L., Tao, Z. W., and Wang, X. (2018). The role of cell-crystal reaction mediated inflammation in the formation of intrarenal calcium oxalate crystals. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 56, 733–736. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2018.10.004
Dominguez-Gutierrez, P. R., Kwenda, E. P., Khan, S. R., and Canales, B. K. (2020). Immunotherapy for stone disease. Curr. Opin. Urol. 30, 183–189. doi:10.1097/MOU.0000000000000729
Gambaro, G., D'Angelo, A., Fabris, A., Tosetto, E., Anglani, F., and Lupo, A. (2004). Crystals, Randall's plaques and renal stones: do bone and atherosclerosis teach us something? J. Nephrol. 17, 774–777.
Gan, X. G., Wang, Z. H., and Xu, H. T. (2022). Mechanism of miRNA-141-3p in calcium oxalate-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury via NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 47, 300–308. doi:10.1159/000521795
Gomez, I. G., MacKenna, D. A., Johnson, B. G., Kaimal, V., Roach, A. M., Ren, S., et al. (2015). Anti-microRNA-21 oligonucleotides prevent Alport nephropathy progression by stimulating metabolic pathways. J. Clin. Invest. 125, 141–156. doi:10.1172/JCI75852
Han, M., Zhang, D., Ji, J., Zhang, J., and Qin, M. (2023). Downregulating miR-184 relieves calcium oxalate crystal-mediated renal cell damage via activating the Rap1 signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 15, 14749–14763. doi:10.18632/aging.205286
Hashemi, M., Moosavi, M. S., Abed, H. M., Dehghani, M., Aalipour, M., Heydari, E. A., et al. (2022). Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 in human cancer: from proliferation and metastasis to therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 184, 106418. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106418
Ho, P. T. B., Clark, I. M., and Le, L. T. T. (2022). MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7167. doi:10.3390/ijms23137167
Hombach, S., and Kretz, M. (2016). Non-coding RNAs: classification, biology and functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 937, 3–17. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-42059-2_1
Hsu, M. T., and Coca-Prados, M. (1979). Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 280, 339–340. doi:10.1038/280339a0
Hu, Y. Y., Dong, W. D., Xu, Y. F., Yao, X. D., Peng, B., Liu, M., et al. (2014). Elevated levels of miR-155 in blood and urine from patients with nephrolithiasis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 295651. doi:10.1155/2014/295651
Hussen, B. M., Nicknafs, F., Hidayat, H. J., Sayad, A., Ghafouri-Fard, S., and Taheri, M. (2022). A diagnostic panel for acquired immune-mediated polyneuropathies based on the expression of lncRNAs. Front. Immunol. 12, 643615. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.643615
Jeck, W. R., and Sharpless, N. E. (2014). Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 453–461. doi:10.1038/nbt.2890
Jia, Z., Wang, S., Tang, J., He, D., Cui, L., Liu, Z., et al. (2014). Does crystal deposition in genetic hypercalciuric rat kidney tissue share similarities with bone formation? Urology 83 (509), e507–e514. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2013.11.004
Jiang, K., Hu, J., Luo, G., Song, D., Zhang, P., Zhu, J., et al. (2020). miR-155-5p promotes oxalate- and calcium-induced kidney oxidative stress injury by suppressing MGP expression. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 5863617. doi:10.1155/2020/5863617
Joshi, S., Clapp, W. L., Wang, W., and Khan, S. R. (2015). Osteogenic changes in kidneys of hyperoxaluric rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1852, 2000–2012. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.06.020
Juchnicka, I., and Kuzmicki, M. (2021). Influence of MiRNAs in gestational diabetes mellitus development. Ginekol. Pol. 92, 579–582. doi:10.5603/GP.a2021.0121
Khan, S. R. (2014). Reactive oxygen species, inflammation and calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 3, 256–276. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2014.06.04
Khan, S. R., Canales, B. K., and Dominguez-Gutierrez, P. R. (2021). Randall's plaque and calcium oxalate stone formation: role for immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 17, 417–433. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-00392-1
Khan, S. R., Pearle, M. S., Robertson, W. G., Gambaro, G., Canales, B. K., Doizi, S., et al. (2016). Kidney stones. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2, 16008. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.8
Kristensen, L. S., Andersen, M. S., Stagsted, L. V. W., Ebbesen, K. K., Hansen, T. B., and Kjems, J. (2019). The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 20, 675–691. doi:10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7
Kristensen, V. N., Lingjærde, O. C., Russnes, H. G., Vollan, H. K., Frigessi, A., and Børresen-Dale, A. L. (2014). Principles and methods of integrative genomic analyses in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 299–313. doi:10.1038/nrc3721
Kumar, P., Yang, Z., Lever, J. M., Chávez, M. D., Fatima, H., Crossman, D. K., et al. (2022). Hydroxyproline stimulates inflammation and reprograms macrophage signaling in a rat kidney stone model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1868, 166442. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166442
Lan, C., Chen, D., Liang, X., Huang, J., Zeng, T., Duan, X., et al. (2017). Integrative analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis rat model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 8306736. doi:10.1155/2017/8306736
Lan, Y., Zhu, W., Duan, X., Deng, T., Li, S., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Glycine suppresses kidney calcium oxalate crystal depositions via regulating urinary excretions of oxalate and citrate. J. Cell Physiol. 236, 6824–6835. doi:10.1002/jcp.30370
Lee, Y., Jeon, K., Lee, J. T., Kim, S., and Kim, V. N. (2002). MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. Embo J. 21, 4663–4670. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf476
Letavernier, E., and Daudon, M. (2018). Vitamin D, hypercalciuria and kidney stones. Nutrients 10, 366. doi:10.3390/nu10030366
Li, F., Li, H., and Huo, W. (2022). Inhibitory role of microRNA-484 in kidney stone formation by repressing calcium oxalate crystallization via a VDR/FoxO1 regulator axis. Urolithiasis. 50, 665–678. doi:10.1007/s00240-022-01359-6
Li, R. H., Chen, M., Liu, J., Shao, C. C., Guo, C. P., Wei, X. L., et al. (2018). Long noncoding RNA ATB promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by upregulating the miR-200c/Twist1 axe and predicts poor prognosis in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9, 1171. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1210-9
Li, Y., Ding, T., Hu, H., Zhao, T., Zhu, C., Ding, J., et al. (2021). LncRNA-ATB participates in the regulation of calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal injury by sponging the miR-200 family. Mol. Med. 27, 143. doi:10.1186/s10020-021-00403-2
Li, Y., Yan, G., Zhang, J., Chen, W., Ding, T., Yin, Y., et al. (2020). LncRNA HOXA11-AS regulates calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal inflammation via miR-124-3p/MCP-1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24, 238–249. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14706
Liang, X., Lai, Y., Wu, W., Chen, D., Zhong, F., Huang, J., et al. (2019). LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA expression variation profile in the urine of calcium oxalate stone patients. BMC Med. Genomics 12, 57. doi:10.1186/s12920-019-0502-y
Liu, H., Yang, X., Tang, K., Ye, T., Duan, C., Lv, P., et al. (2020). Sulforaphane elicts dual therapeutic effects on renal inflammatory injury and crystal deposition in calcium oxalate nephrocalcinosis. Theranostics 10, 7319–7334. doi:10.7150/thno.44054
Liu, H., Ye, T., Yang, X., Liu, J., Jiang, K., Lu, H., et al. (2019). H19 promote calcium oxalate nephrocalcinosis-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury via a ceRNA pathway. EBioMedicine 50, 366–378. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.059
Liu, X., Song, W., Zhang, X., Long, F., Yin, J., He, X., et al. (2021). Downregulating LncRNA XIST attenuated contrast-induced nephropathy injury via regulating miR-133a-3p/ NLRP3 axis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 52, 440–453. doi:10.1007/s11239-020-02369-0
Liu, Z., Jiang, H., Yang, J., Wang, T., Ding, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2016). Analysis of altered microRNA expression profiles in the kidney tissues of ethylene glycol-induced hyperoxaluric rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 14, 4650–4658. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5833
Lu, T. X., and Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 141, 1202–1207. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Lu, Y., Qin, B., Hu, H., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., et al. (2016). Integrative microRNA-gene expression network analysis in genetic hypercalciuric stone-forming rat kidney. PeerJ 4, e1884. doi:10.7717/peerj.1884
Lv, P., Liu, H., Ye, T., Yang, X., Duan, C., Yao, X., et al. (2021). XIST Inhibition attenuates calcium oxalate nephrocalcinosis-induced renal inflammation and oxidative injury via the miR-223/NLRP3 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 1676152. doi:10.1155/2021/1676152
Ma, M., Pei, Y., Wang, X., Feng, J., Zhang, Y., and Gao, M. Q. (2019). LncRNA XIST mediates bovine mammary epithelial cell inflammatory response via NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Cell Prolif. 52, e12525. doi:10.1111/cpr.12525
Maciak, K., Dziedzic, A., Miller, E., and Saluk-Bijak, J. (2021). MiR-155 as an important regulator of multiple sclerosis pathogenesis. A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4332. doi:10.3390/ijms22094332
Matsui, M., and Corey, D. R. (2017). Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 16, 167–179. doi:10.1038/nrd.2016.117
Mattick, J. S., and Makunin, I. V. (2006). Non-coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15 (1), R17–R29. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl046
Mehta, S. L., Dempsey, R. J., and Vemuganti, R. (2020). Role of circular RNAs in brain development and CNS diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. 186, 101746. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101746
Memczak, S., Jens, M., Elefsinioti, A., Torti, F., Krueger, J., Rybak, A., et al. (2013). Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495, 333–338. doi:10.1038/nature11928
Nemeth, K., Bayraktar, R., Ferracin, M., and Calin, G. A. (2024). Non-coding RNAs in disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 25, 211–232. doi:10.1038/s41576-023-00662-1
Pan, Z., Zheng, J., Zhang, J., Lin, J., Lai, J., Lyu, Z., et al. (2022). A novel protein encoded by exosomal circATG4B induces oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer by promoting autophagy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 9, e2204513. doi:10.1002/advs.202204513
Romero, V., Akpinar, H., and Assimos, D. G. (2010). Kidney stones: a global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev. Urol. 12, e86–e96. doi:10.3909/riu0459
Sanger, H. L., Klotz, G., Riesner, D., Gross, H. J., and Kleinschmidt, A. K. (1976). Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 73, 3852–3856. doi:10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852
Sayed, D., and Abdellatif, M. (2011). MicroRNAs in development and disease. Physiol. Rev. 91, 827–887. doi:10.1152/physrev.00006.2010
Shi, J., Duan, J., Gong, H., Pang, Y., Wang, L., and Yan, Y. (2019). Exosomes from miR-20b-3p-overexpressing stromal cells ameliorate calcium oxalate deposition in rat kidney. J. Cell Mol. Med. 23, 7268–7278. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14555
Shi, Y., Liu, Z., Lin, Q., Luo, Q., Cen, Y., Li, J., et al. (2021). MiRNAs and cancer: key link in diagnosis and therapy. Genes (Basel) 12, 1289. doi:10.3390/genes12081289
Shvedova, A. A., Yanamala, N., Kisin, E. R., Khailullin, T. O., Birch, M. E., and Fatkhutdinova, L. M. (2016). Integrated analysis of dysregulated ncRNA and mRNA expression profiles in humans exposed to carbon nanotubes. PLoS One 11, e0150628. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150628
Simonson, B., and Das, S. (2015). MicroRNA therapeutics: the next magic bullet? Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 15, 467–474. doi:10.2174/1389557515666150324123208
Skolarikos, A., Jung, H., Neisius, A., Petřík, A., Somani, B., Tailly, T., et al. (2024). EAU guidelines on urolithiasis 2024. Eur. Assoc. Urology. Available at: http://uroweb.org/guideline/urolithiasis/.
Song, Y., Liu, C., Liu, X., Trottier, J., Beaudoin, M., Zhang, L., et al. (2017). H19 promotes cholestatic liver fibrosis by preventing ZEB1-mediated inhibition of epithelial cell adhesion molecule. Hepatology 66, 1183–1196. doi:10.1002/hep.29209
Song, Z., Zhang, Y., Gong, B., Xu, H., Hao, Z., and Liang, C. (2019). Long noncoding RNA LINC00339 promotes renal tubular epithelial pyroptosis by regulating the miR-22-3p/NLRP3 axis in calcium oxalate-induced kidney stone. J. Cell Biochem. 120, 10452–10462. doi:10.1002/jcb.28330
Statello, L., Guo, C. J., Chen, L. L., and Huarte, M. (2021). Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 96–118. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00315-9
Su, B., Han, H., Ji, C., Hu, W., Yao, J., Yang, J., et al. (2020). MiR-21 promotes calcium oxalate-induced renal tubular cell injury by targeting PPARA. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 319, F202–f214. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00132.2020
Taguchi, K., Hamamoto, S., Okada, A., Unno, R., Kamisawa, H., Naiki, T., et al. (2017). Genome-Wide gene expression profiling of Randall's Plaques in calcium oxalate stone formers. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 333–347. doi:10.1681/ASN.2015111271
Taguchi, K., Okada, A., Unno, R., Hamamoto, S., and Yasui, T. (2021). Macrophage function in calcium oxalate kidney stone formation: a systematic review of literature. Front. Immunol. 12, 673690. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.673690
Thakral, S., and Ghoshal, K. (2015). miR-122 is a unique molecule with great potential in diagnosis, prognosis of liver disease, and therapy both as miRNA mimic and antimir. Curr. Gene Ther. 15, 142–150. doi:10.2174/1566523214666141224095610
Thongprayoon, C., Krambeck, A. E., and Rule, A. D. (2020). Determining the true burden of kidney stone disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 16, 736–746. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-0320-7
Tomar, D., Yadav, A. S., Kumar, D., Bhadauriya, G., and Kundu, G. C. (2020). Non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 1863, 194378. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.04.005
Vishnoi, A., and Rani, S. (2017). “MiRNA biogenesis and regulation of diseases: an overview,” MicroRNA profiling. Methods in molecular biology, Editor S. Rani (New York, NY: Humana Press), 1509, 1–10. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-6524-3_1
Wang, B., He, G., Xu, G., Wen, J., and Yu, X. (2020b). miRNA-34a inhibits cell adhesion by targeting CD44 in human renal epithelial cells: implications for renal stone disease. Urolithiasis 48, 109–116. doi:10.1007/s00240-019-01155-9
Wang, B., Wu, B., Liu, J., Yao, W., Xia, D., Li, L., et al. (2014). Analysis of altered microRNA expression profiles in proximal renal tubular cells in response to calcium oxalate monohydrate crystal adhesion: implications for kidney stone disease. PLoS One 9, e101306. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101306
Wang, J., Cao, B., Han, D., Sun, M., and Feng, J. (2017). Long non-coding RNA H19 induces cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via activation of autophagy. Aging Dis. 8, 71–84. doi:10.14336/AD.2016.0530
Wang, J., Zhou, T., Wang, T., and Wang, B. (2018). Suppression of lncRNA-ATB prevents amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells via regulating miR-200/ZNF217 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 108, 707–715. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.155
Wang, K. C., and Chang, H. Y. (2011). Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 43, 904–914. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018
Wang, Q., Long, Z., Zhu, F., Li, H., Xiang, Z., Liang, H., et al. (2023). Integrated analysis of lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA in the proliferative phase of liver regeneration in mice with liver fibrosis. BMC Genomics 24, 417. doi:10.1186/s12864-023-09478-z
Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Han, S., Chen, H., Chen, C., Ji, L., et al. (2020a). Overexpression of miR-30c-5p reduces cellular cytotoxicity and inhibits the formation of kidney stones through ATG5. Int. J. Mol. Med. 45, 375–384. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4440
Wang, Z., Zhang, J. W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S. P., Hu, Q. Y., and Liang, H. (2019). Analyses of long non-coding RNA and mRNA profiling using RNA sequencing in calcium oxalate monohydrate-stimulated renal tubular epithelial cells. Urolithiasis 47, 225–234. doi:10.1007/s00240-018-1065-7
Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Deng, Q., and Liang, H. (2021). Recent advances on the mechanisms of kidney stone formation (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 48, 149. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2021.4982
Wiener, S. V., Ho, S. P., and Stoller, M. L. (2018). Beginnings of nephrolithiasis: insights into the past, present and future of Randall's plaque formation research. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 27, 236–242. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000414
Wilusz, J. E., and Sharp, P. A. (2013). Molecular biology. A circuitous route to noncoding RNA. Science 340, 440–441. doi:10.1126/science.1238522
Winkle, M., El-Daly, S. M., Fabbri, M., and Calin, G. A. (2021). Noncoding RNA therapeutics-challenges and potential solutions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20, 629–651. doi:10.1038/s41573-021-00219-z
Witting, C., Langman, C. B., Assimos, D., Baum, M. A., Kausz, A., Milliner, D., et al. (2021). Pathophysiology and treatment of enteric hyperoxaluria. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 487–495. doi:10.2215/CJN.08000520
Xi, J., Chen, Y., Jing, J., Qi, W., and Zhang, Y. (2023). LncRNA LINC01197 inhibited the formation of calcium oxalate-induced kidney stones by regulating miR-516b-5p/SIRT3/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 392, 553–563. doi:10.1007/s00441-022-03734-6
Xia, X., Li, X., Li, F., Wu, X., Zhang, M., Zhou, H., et al. (2019). A novel tumor suppressor protein encoded by circular AKT3 RNA inhibits glioblastoma tumorigenicity by competing with active phosphoinositide-dependent Kinase-1. Mol. Cancer 18, 131. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1056-5
Xie, Z., Chen, J., and Chen, Z. (2022). MicroRNA-204 attenuates oxidative stress damage of renal tubular epithelial cells in calcium oxalate kidney-stone formation via MUC4-mediated ERK signaling pathway. Urolithiasis 50, 1–10. doi:10.1007/s00240-021-01286-y
Xu, W. D., Feng, S. Y., and Huang, A. F. (2022). Role of miR-155 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review. Inflamm. Res. 71, 1501–1517. doi:10.1007/s00011-022-01643-6
Xue, S., Zheng, B., Cao, S., Ding, J. C., Hu, G. S., Liu, W., et al. (2022). Long non-coding RNA LINC00680 functions as a ceRNA to promote esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-423-5p/PAK6 axis. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 69. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01539-3
Yang, S., and Lian, G. (2020). ROS and diseases: role in metabolism and energy supply. Mol. Cell Biochem. 467, 1–12. doi:10.1007/s11010-019-03667-9
Yang, X., Liu, H., Ye, T., Duan, C., Lv, P., Wu, X., et al. (2020). AhR activation attenuates calcium oxalate nephrocalcinosis by diminishing M1 macrophage polarization and promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Theranostics 10, 12011–12025. doi:10.7150/thno.51144
Yang, X., Ye, T., Liu, H., Lv, P., Duan, C., Wu, X., et al. (2021). Expression profiles, biological functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in bladder cancer. Mol. Cancer 20, 4. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01300-8
Yang, Y., Wang, Q., Xun, Y., Li, C., and Wang, S. (2022). The preliminary exploration of what role miRNAs derived from urinary exosomes play in kidney stone formation. Urology 166, 104–110. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2022.05.019
Yang, Z., Qu, C. B., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W. F., Wang, D. D., Gao, C. C., et al. (2019). Dysregulation of p53-RBM25-mediated circAMOTL1L biogenesis contributes to prostate cancer progression through the circAMOTL1L-miR-193a-5p-Pcdha pathway. Oncogene 38, 2516–2532. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0602-8
Ye, T., Yang, X., Liu, H., Lv, P., Lu, H., Jiang, K., et al. (2021). Theaflavin protects against oxalate calcium-induced kidney oxidative stress injury via upregulation of SIRT1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 1050–1060. doi:10.7150/ijbs.57160
Yi, R., Qin, Y., Macara, I. G., and Cullen, B. R. (2003). Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 17, 3011–3016. doi:10.1101/gad.1158803
Yu, Y., Zhang, W., Li, A., Chen, Y., Ou, Q., He, Z., et al. (2020). Association of long noncoding RNA biomarkers with clinical immune subtype and prediction of immunotherapy response in patients with cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 3, e202149. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.2149
Zeng, G., Mai, Z., Xia, S., Wang, Z., Zhang, K., Wang, L., et al. (2017). Prevalence of kidney stones in China: an ultrasonography based cross-sectional study. BJU Int. 120, 109–116. doi:10.1111/bju.13828
Zhang, C., Yuan, J., Hu, H., Chen, W., Liu, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2017). Long non-coding RNA CHCHD4P4 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inhibits cell proliferation in calcium oxalate-induced kidney damage. Braz J. Med. Biol. Res. 51, e6536. doi:10.1590/1414-431X20176536
Zhang, P., Wu, W., Chen, Q., and Chen, M. (2019). Non-Coding RNAs and their integrated networks. J. Integr. Bioinform 16, 20190027. doi:10.1515/jib-2019-0027
Zhang, Y., Luo, M., Cui, X., O'Connell, D., and Yang, Y. (2022). Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes ferroptosis by modulating the miR-362-3p/MIOX axis as a ceRNA. Cell Death Differ. 29, 1850–1863. doi:10.1038/s41418-022-00970-9
Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, M., Wenjie, C., Yi, S., Luwei, X., et al. (2023). Exosomes from miR-23 overexpressing stromal cells suppress M1 macrophage and inhibit calcium oxalate deposition in hyperoxaluria rat model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2023, 2883623. doi:10.1155/2023/2883623
Zhao, X., Sun, J., Yuan, Y., Lin, S., Lin, J., and Mei, X. (2022). Zinc promotes microglial autophagy through NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation via XIST/miR-374a-5p axis in spinal cord injury. Neurochem. Res. 47, 372–381. doi:10.1007/s11064-021-03441-8
Zhou, Y., Sun, W., Qin, Z., Guo, S., Kang, Y., Zeng, S., et al. (2021). LncRNA regulation: new frontiers in epigenetic solutions to drug chemoresistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 189, 114228. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114228
Zhou, Z., Sun, B., Huang, S., and Zhao, L. (2019). Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis. 10, 503. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1744-5
Zhu, L., Jiang, S., Yu, S., Liu, X., Pu, S., Xie, P., et al. (2020a). Increased SIX-1 expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by regulating lncATB-miR-200s-ZEB1 axis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24, 5290–5303. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15185
Zhu, W., Liu, Y., Lan, Y., Li, X., Luo, L., Duan, X., et al. (2019a). Dietary vinegar prevents kidney stone recurrence via epigenetic regulations. EBioMedicine 45, 231–250. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.004
Zhu, W., Wu, C., Zhou, Z., Zhang, G., Luo, L., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Acetate attenuates hyperoxaluria-induced kidney injury by inhibiting macrophage infiltration via the miR-493-3p/MIF axis. Commun. Biol. 6, 270. doi:10.1038/s42003-023-04649-w
Zhu, W., Zhao, Z., Chou, F., Zuo, L., Liu, T., Yeh, S., et al. (2019b). Loss of the androgen receptor suppresses intrarenal calcium oxalate crystals deposition via altering macrophage recruitment/M2 polarization with change of the miR-185-5p/CSF-1 signals. Cell Death Dis. 10, 275. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1358-y
Zhu, W., Zhou, Z., Wu, C., Huang, Z., Zhao, R., Wang, X., et al. (2024). miR-148b-5p regulates hypercalciuria and calcium-containing nephrolithiasis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 81, 369. doi:10.1007/s00018-024-05408-8
Zhu, Z., Huang, F., Xia, W., Zeng, H., Gao, M., Li, Y., et al. (2020b). Osteogenic differentiation of renal interstitial fibroblasts promoted by lncRNA MALAT1 may partially contribute to Randall's Plaque formation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 596363. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.596363
Zhu, Z., Zhang, X., Jiang, Y., Ruan, S., Huang, F., Zeng, H., et al. (2021). NEAT1 functions as a key mediator of BMP2 to promote osteogenic differentiation of renal interstitial fibroblasts. Epigenomics 13, 1171–1186. doi:10.2217/epi-2021-0212
Zingale, V. D., Gugliandolo, A., and Mazzon, E. (2021). MiR-155: an important regulator of neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 90. doi:10.3390/ijms23010090
Glossary
ADSCs mesenchymal adipose-derived stromal cells
AGO2 argonaute 2
AhR aryl hydrocarbon receptor
AR androgen receptor
ATG5 autophagy protein 5
ATG7 autophagy protein 7
BMP2 bone morphogenetic protein 2
Calcr calcitonin receptor
CaOx calcium oxalate
CircRNA circular RNA
CiRNA circular intronic RNA
CLDN14 claudin-14
COM calcium oxalate monohydrate
CRP c-reactive protein
CSF-1 macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1
EciRNA exonic circRNA
EGR1 early growth response protein 1
EIciRNA exon-intron circRNA
FoxO1 forkhead box protein O1
GEO Gene Expression Omnibus database
GHS rats genetic hypercalciuric stone-forming rats
GO Gene Ontology
HIF-1α Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α
HMGB1 high mobility group protein B1
IGF1R insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
IL-1β interleukin-1β
IL-6 interleukin-6
IRF1 interferon regulatory factor-1
KEGG Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
LncRNA long noncoding RNA
m7G 7-methyl guanosine
MCP-1 monocyte chemotactic protein 1
MGP matrix Gla protein
MIF macrophage migration inhibitory factor
MiRNA microRNA
MSX2 homeobox protein MSX-2
MUC4 mucin-4
ncRNA noncoding RNA
NLRP3 NACHT, LRR and PYD domain-containing protein 3
Nrf2 nuclear factor erythroid 2-related 2
NXF1 nuclear RNA export factor 1
OCN osteocalcin
OPN osteopontin
PCR polymerase chain reaction
PI3K Phosphatidylinositol-3-hydroxykinase
piRNA piwi-associated RNA
PKNOX1 homeobox protein PKNOX1
PPARA peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
RBP RNA binding protein
Rheb GTP-binding protein Rheb
RISC RNA-induced silencing complex
ROS reactive oxygen species
rRNA ribosomal RNA
Runx2 runt-related transcription factor 2
SD rats Sprague-Dawley rats
SIRT1 NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1
Slc13a2 solute carrier family 13 member 2
Slc26a6 solute carrier family 26 member 6
snoRNA small nucleolar RNA
snRNA small nuclear RNA
TLR4 toll-like receptor 4
TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α
TNRC6 trinucleotide repeat containing adaptor 6
tRNA transfer RNA
TRPV5 transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 5
UMOD uromodulin
UTR untranslated region
VDR vitamin D receptor
Keywords: ncRNAs, nephrolithiasis, calcium oxalate, biomarkers, therapeutic targets
Citation: Wang Q, Yang Z, Chen X, Yang Y and Jiang K (2024) Noncoding RNA, friend or foe for nephrolithiasis?. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1457319. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1457319
Received: 01 July 2024; Accepted: 08 November 2024;
Published: 20 November 2024.
Edited by:
Hongbing Liu, Tulane University, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Wang, Yang, Chen, Yang and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanyuan Yang, MjkyMTg1NDI1MUBxcS5jb20=; Kehua Jiang, amlhbmdrZWh1YUBnejUwNTUuY29t
 Qing Wang
Qing Wang Zhenlu Yang
Zhenlu Yang Xiaolong Chen
Xiaolong Chen Yuanyuan Yang
Yuanyuan Yang Kehua Jiang
Kehua Jiang