- 1The Osteoporosis Clinical Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 2Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 3Division of Spine Surgery, The Quzhou Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Quzhou People’s Hospital, Quzhou, China
Introduction: The utilization of denosumab in treating osteoporosis highlights promising prospects for osteoporosis intervention guided by gene targets. While omics-based research into osteoporosis pathogenesis yields a plethora of potential gene targets for clinical transformation, identifying effective gene targets has posed challenges.
Methods: We first queried the omics data of osteoporosis clinical samples on PubMed, used International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC) to screen differentially expressed genes, and conducted preliminary functional verification of candidate genes in human Saos2 cells through osteogenic differentiation and mineralization experiments. We then selected the candidate genes with the most significant effects on osteogenic differentiation and further verified the osteogenic differentiation and mineralization functions in mouse 3T3-E1 and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC). Finally, we used RNA-seq to explore the regulation of osteogenesis by the target gene.
Results: We identified PPP2R2A, RRBP1, HSPB6, SLC22A15, ADAMTS4, ATP8B1, CTNNB1, ROBO1, and EFR3B, which may contribute to osteoporosis. ROBO1 was the most significant regulator of osteogenesis in both human and mouse osteoblast. The inhibitory effect of Robo1 knockdown on osteogenic differentiation may be related to the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways.
Conclusion: Our study provides several novel molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. ROBO1 is a potential target for osteoporosis intervention.
Introduction
Osteoporosis, prevalent among the elderly, is a chronic decondition characterized by reduced bone mass, increased fragility, and heightened susceptibility to fractures (Watts and Manson, 2017). This condition poses a significant threat to the health and longevity of the elderly population. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts are essential cellular components in the regulation of bone metabolism. When osteoclasts-mediated bone resorption exceeds osteoblast-mediated bone formation, the balance of bone remodeling is disturbed, ultimately leading to osteoporosis.
Advancements in omics technologies, including transcriptomics and proteomics, offer opportunities to discover novel molecular targets for osteoporosis. Jemtland et al. highlighted DKK1, SOST, SOX4, MMP13, and MEPE as differentially expressed genes based on RNA transcriptome studies of iliac bone samples from postmenopausal women (Jemtland et al., 2011). Notably, romosozumab, which targets the SOST gene, is now clinically utilized for osteoporosis treatment. However, the heterogeneity of cell types within bone tissue, including osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, vascular endothelial cells, neurons, and immune cells (Kular et al., 2012), presents challenges in omics data analysis for identifying genes that determine osteoporosis phenotype. This heterogeneity may lead to uncertainties regarding the cell origin of differentially expressed genes and can result in false negatives due to inconsistent expression changes of a single gene across various cells types, potentially overlooking critical genes. Additionally, many studies have identified key molecules associated with osteoporosis pathogenesis by isolating bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC), osteoblasts, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) for transcriptome or proteome analysis (Panach et al., 2020; Roforth et al., 2015; Choi et al., 2017; Song et al., 2017; Zhang L. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2016; Qiu et al., 2020; Jin et al., 2018; Zeng et al., 2016; Li et al., 2024). These omics approaches serve as valuable resources for identifying new targets for the regulation and intervention of osteoporosis.
While omics data provides a wealth information on of differentially expressed genes, confirming the role of each gene target in bone mass regulation often requires both in vivo and in vitro gene knockout studies. The IMPC plays a crucial role in this endeavor, undertaking phenotypic analyses of 20,000 mouse mutants and annotating their functions. This database offers vital support for investigating gene targets associated with human diseases (Groza et al., 2022). Leveraging the IMPC database alongside human disease-related gene expression data, a recent study successfully identified gene targets associated with osteoarthritis, potentially offering new avenues for osteoarthritis treatment (Butterfield et al., 2021). Moreover, Zhang et al. utilized the IMPC database to identify and validate genes involved in the body’s response to external environmental stimuli and biological clock regulation (Zhang T. et al., 2020). Based on the above application of IPMC in screening genetic factors that regulate human diseases and physiological activities, we would like to utilize this database to conduct a preliminary screening of genes associated with bone phenotypes identified in samples from osteoporosis patients.
This study integrates various osteoporosis-related omics datasets, juxtaposes differentially expressed genes/proteins across diverse cell types with genes exhibiting bone metabolism-related phenotypes in the IMPC database, and identified 9 genes including PPP2R2A, RRBP1, HSPB6, SLC22A15, ADAMTS4, ATP8B1, CTNNB1, ROBO1, and EFR3B, which may contribute to pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Through in vitro osteogenic differentiation, we further identified ROBO1 as a conserved regulator of osteogenesis in both human and mouse osteoblast cell lines. The inhibitory effect of osteogenesis may be related to the activation of inflammation in osteoblasts with downregulated of Robo1.
Results
Overview of osteoporosis-related omics research
We conducted a PubMed search for omics articles focusing on clinical samples of postmenopausal osteoporosis over the past 15 years. Articles with comprehensive data information were selected, and lists of differentially expressed genes or proteins were downloaded. The data were categorized according to the type of clinical sample. Currently, clinical samples are primarily divided into four categories: human bone tissue samples, human osteoblast samples, human BMSC samples, and human PBMC samples, among which osteoblasts and BMSCs are pertinent to osteogenesis. Whole bone tissue samples contain a variety of cell types (Table 1).
Enrichment analysis of bone phenotype-related gene pathways in the IMPC database
By querying abnormal bone mineral density, abnormal bone mineral content, and abnormal bone structure in the IMPC database, we obtained a list of 694 genes, along with their corresponding phenotypes and statistical P-values (Figure 1A). To elucidate the pathways associated with bone phenotypes, we conducted Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses on these 694 genes. GO pathway enrichment analysis revealed several enriched pathways across various biological aspects. In terms of biological processes, pathways such as regulation of sodium ion transport, excitatory postsynaptic potential, protein ubiquitination, neural projection, forward transcriptional regulation of RNA polymerase II, chemical synaptic transduction, and chromatin structure were enriched. Regarding cellular components, pathways such as endoplasmic reticulum, cell membrane, axon, nucleus, synapse, cell junction, and cytoplasm showed enrichment. Molecular functions enrichment included MAPK binding, transferase activity, protein binding, protein serine/threonine kinase binding, metal ion binding, nuclear receptor binding, histone methyltransferase (H3-K4), cysteine peptidase activity, and transcription factor binding (Figure 1B). KEGG pathway analysis reveals enrichment of mitophagy and lysosomes in Cellular Processes, while the AMPK signaling pathway, neuro-activating ligand receptor interaction, phospholipase D signaling pathway, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and Hippo signaling are enriched in Environmental Information Processing. Genetic Information Processing shows enrichment in ubiquitination-mediated protein degradation. Human Diseases exhibit enrichment in nicotine addiction, cancer proteoglycans, and Kaposi’s sarcoma-related viral infection. Metabolism enriched pathways include glycosaminoglycan degradation, fluctuating sugar and mannose metabolism, cysteine and methionine metabolism, and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis. Organismal Systems are enriched in Glutamatergic synapses, rhythm traction, auxin synthesis and secretion, cholinergic pathways and chemokine pathways (Figure 1C).
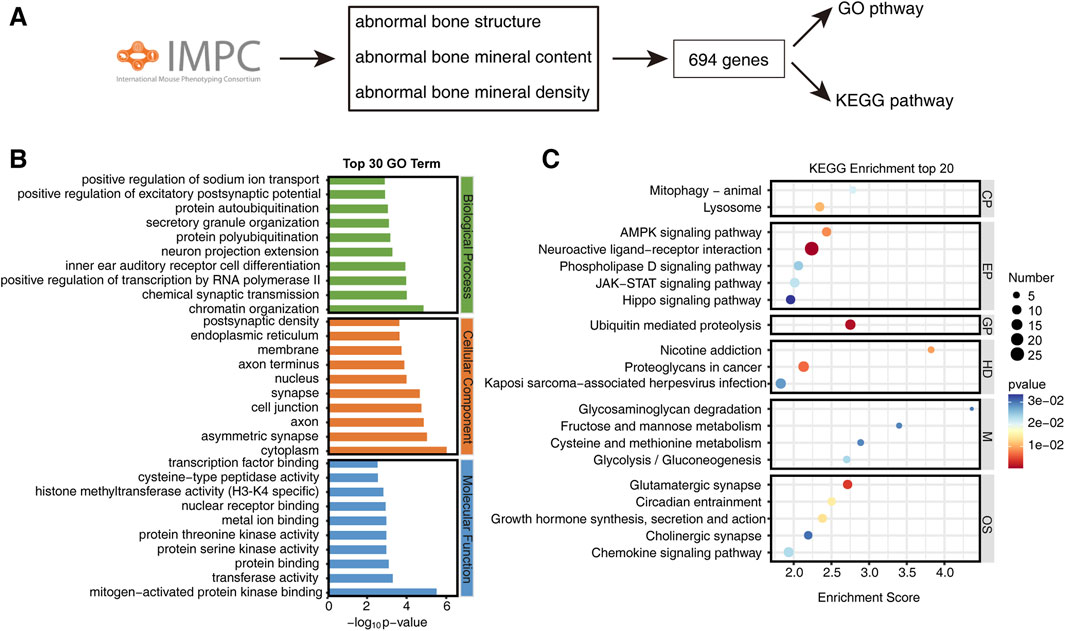
Figure 1. Enrichment of bone phenotype-related gene pathways in the IMPC database. (A) Roadmap for screening bone phenotype-related genes from IMPC. (B) Top 30 GO enriched pathways of bone phenotype-related genes. (C) Top 20 KEGG enriched pathways of bone phenotype-related genes. CP, Cellular processes; EP, Environmental information processing; GP, Genetic information processing; HD, Human diseases; M, Metabolism; OS, Organismal systems.
These findings suggest that bone metabolism diseases may involve a multitude of factors, including neural influences, transcriptional regulation, epigenetic modifications, ubiquitination, biological rhythms, autophagy, hormones, and more.
Combining omics data with IMPC data to screen target genes
We categorized omics data into four distinct categories: bone tissue, osteoblasts, BMSC and PBMC. By intersecting with the IMPC gene list, we identified 18 differentially expressed genes in bone tissues, 29 in osteoblasts, 6 in BMSC, and 4 in PBMC (Figures 2A–D). Additionally, we identified 9 candidate genes (PPP2R2A, RRBP1, HSPB6, SLC22A15, ADAMTS4, ATP8B1, CTNNB1, ROBO1, and EFR3B) by screening IMPC bone phenotypes with a significance threshold of P ≤ 1 × 10^-4 in at least one gender. Gene knockout, whether homozygous or heterozygous (with lethality in homozygotes), resulted in significant alterations in bone density, bone mineral content, or bone structure (Figures 2E–M).
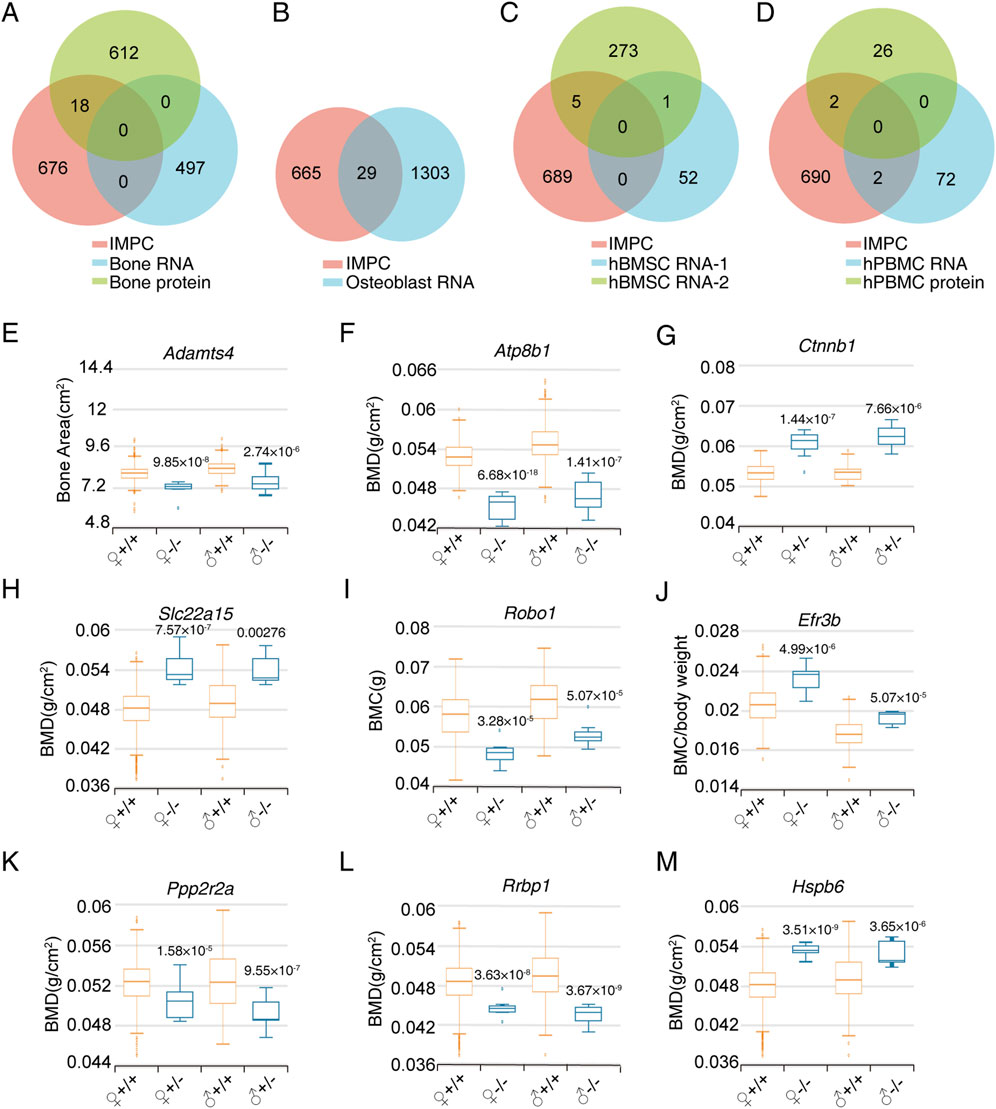
Figure 2. Screening of bone phenotype-related genes in specific cell types based on omics data. (A) Venn diagram of IMPC bone phenotype-related genes and differentially expressed genes in bone tissue proteome and RNA transcriptome. (B) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes between IMPC bone phenotype-related genes and osteoblast RNA transcriptome. (C) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes between IMPC bone phenotype-related genes and BMSC RNA transcriptome. (D) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes between IMPC bone phenotype-related genes and PBMC proteome and RNA transcriptome. (E–M) Bone phenotype statistical data of the final candidate genes through limited P value screening. The sample numbers for every group were as follows. ADAMTS4: 633, 7, 595, 8; ATP8B1: 352, 8, 369, 8; CTNNB1: 30, 10, 38, 12; SLC22A15: 2,241, 7, 2,192, 7; ROBO1: 324, 8, 321, 8; EFR3B: 470, 8, 488, 8; PPP2R2A: 418, 7, 410, 7; RRBP: 2,633, 7, 2,574, 8; HSPB6: 2,241, 8, 2,192, 8. Values represent the mean ± SD, the P-values are represented in the figure.
Verification of siRNA knockdown efficiency
Since the current drugs for the treatment of osteoporosis mainly target osteoclasts, there are relatively few genetic intervention targets for osteoblasts. This study excluded EFR3B, which was screened out from the omics data of PBMCs capable of differentiating into osteoclasts, and focused solely on verifying the functions of the remaining 8 genes in osteogenesis. We developed three small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting each of the 8 candidate genes. In Saos-2 cells, the knockdown efficiency for PPP2R2A, RRBP1, HSPB6, SLC22A15, ADAMTS4, ATP8B1, CTNNB1, and ROBO1 siRNA exceeded 70% (Figure 3). These results indicate the successful screening of siRNA for the candidate genes, paving the way for further research.
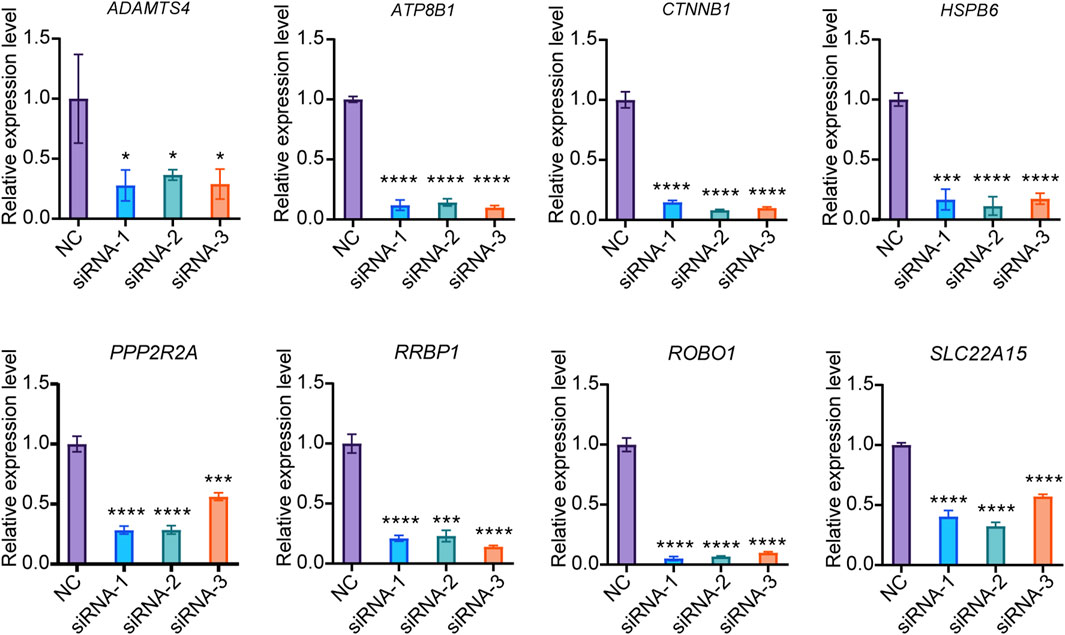
Figure 3. Knockdown efficiency of siRNA. The expression of target genes in Saos-2 cells were detected by qPCR (N = 3). Values represent the mean ± SD. *: P < 0.05, ***: P < 0.001, ****: P < 0.0001.
Effect of gene knockdown on osteogenic differentiation of Saos-2
To investigate the regulatory role of candidate genes in osteogenic differentiation, we induced osteogenic differentiation in Saos-2 cells following siRNA transfection. We evaluated the expression levels of osteogenic differentiation markers, ALP and RUNX2 on the 6th days of differentiation. Our experimental findings reveal that the knockdown of ATP8B increases ALP expression, whereas the knockdown of CTNNB, HSPB6, ROBO1, and RRBP1 decreases ALP expression. Additionally, the knockdown of PPP2R2A and ROBO1 inhibits the expression of RUNX2 (Figures 4A, B).
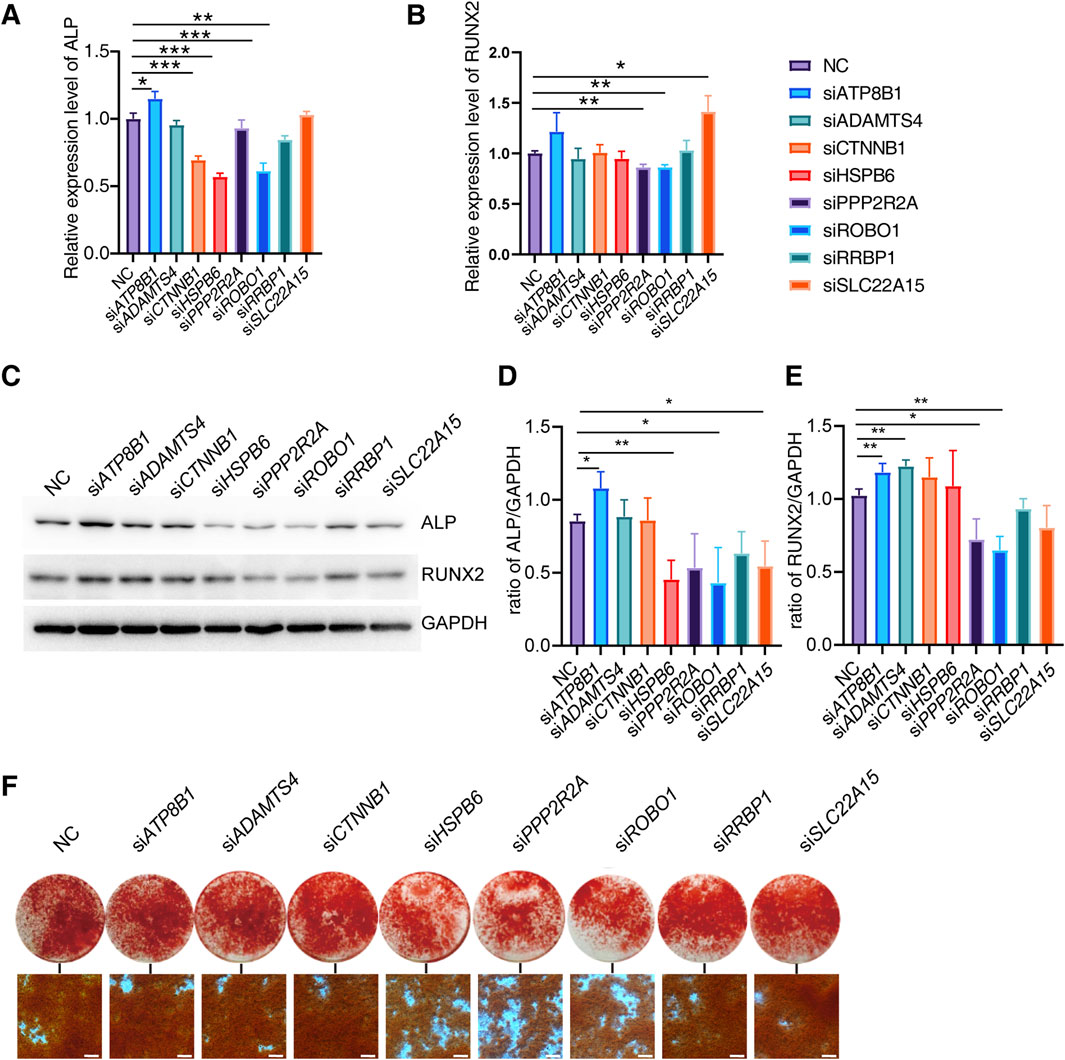
Figure 4. Effect of candidate genes on osteogenic differentiation. (A, B) Relative expression of ALP, RUNX2 mRNA in Saos-2 on days 6 of differentiation after candidate gene knockdown (N = 3). (C–E) Protein expression and quantification of ALP and RUNX2 in Saos-2 on day 6 of differentiation (N = 3). (F) Alizarin red staining of Saos-2 on day 14 of osteogenic differentiation (Scale bar: 200 μm). Values represent the mean ± SD. *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, ****: P < 0.0001.
We further examined the expression of ALP and RUNX2 proteins on the 6th day of differentiation. Our results indicate that the knockdown of ATP8B significantly increases the expression of both ALP and RUNX2 proteins. Conversely, the knockdown of PPP2R2A, ROBO1, RRBP1, and SLC22A15 significantly inhibits the expression of ALP and RUNX2 proteins, while HSPB6 alone suppresses the expression of ALP (Figures 4C–E).
To further investigate the impact of candidate genes on mineralization, we knocked down specific genes in Saos-2 cells and conducted osteogenic differentiation. Additionally, we performed Alizarin red staining on the 14th day of differentiation. We found that the knockdown of HSP60, PPP2R2A, and ROBO1 genes significantly inhibited Saos-2 mineralization (Figure 4F).
These findings suggest that different genes may have varying effects on osteogenic differentiation at both the transcriptional and translational levels, and their regulation of ALP and RUNX2 may exhibit certain distinctions. Through knockdown experiments, we effectively confirmed the role of specific genes in regulating osteogenic differentiation. Concurrently, we observed discrepancies between the outcomes of gene knockdown and the phenotypic manifestations in knockout mice. This suggests the potential role of these genes in osteoclast functionality as well.
Robo1 knockdown inhibits 3T3-E1 osteogenic differentiation
Compared to other candidate genes, the knockdown of ROBO1 significantly inhibits the osteogenic differentiation at both the RNA and protein levels, and it reduces mineralization in Saos-2 cells. Therefore, we further investigated the role of Robo1 in mouse osteoblast precursor cells 3T3-E1.
Similarly, we employed siRNA to knock down the Robo1 gene in 3T3-E1 cells and confirmed its knockdown effect at the protein level (Figures 5A, B). The siRNA-1 significantly downregulated the ROBO1 expression (P = 0.0177). Subsequently, we selected siRNA-1 to transfect 3T3-E1, and detected the expression of ALP and RUNX2 on the 6th day of osteogenic differentiation. The results indicated that Robo1 knockdown could significantly inhibit the expression of ALP (P = 0.0322) and RUNX2 (P = 0.0499) (Figures 5C–E). Moreover, we knocked down Robo1 in 3T3-E1 cells and BMSCs respectively, and performed Alizarin red staining on the 21st day of differentiation. The results showed that the knockdown of Robo1 significantly inhibits the mineralization function of osteoblasts (Figures 5F, G).
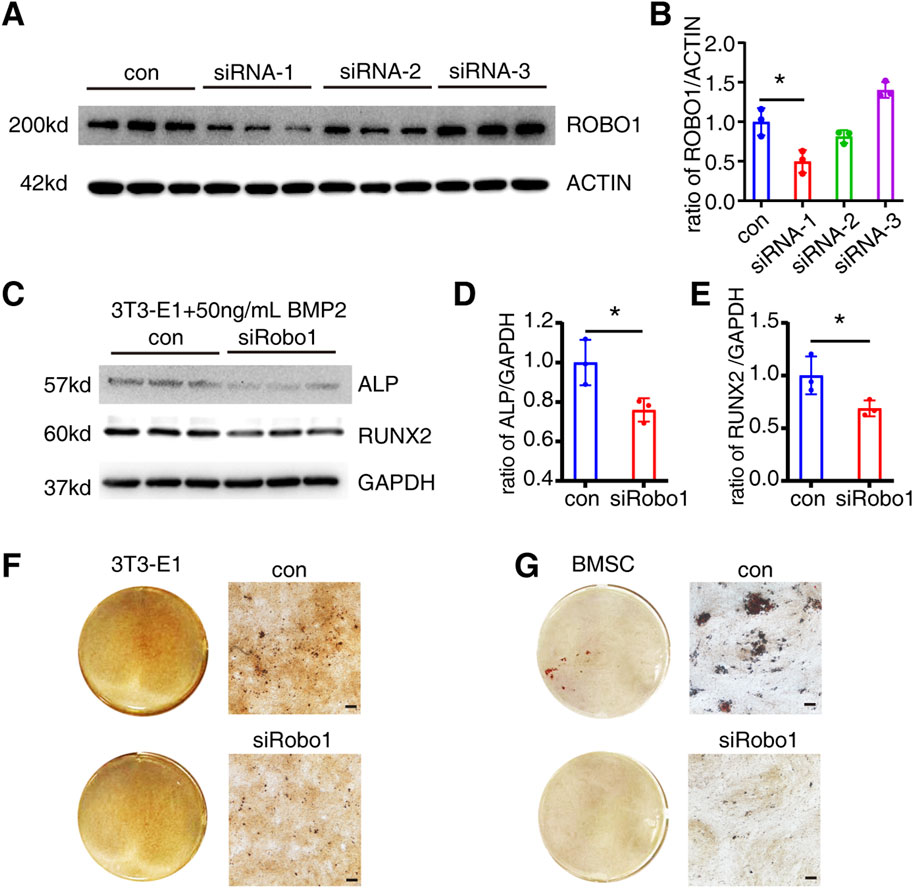
Figure 5. Robo1 knockdown inhibits osteogenic differentiation of 3T3-E1. (A, B) Protein expression and quantification of ROBO1 expression after siRNA transfection 3T3-E1 (N = 3). (C–E) Protein expression and quantification of ALP and RUNX2 in 3T3-E1 on day 6 of differentiation (N = 3). (F) Alizarin red staining of 3T3-E1. (G) Alizarin red staining of BMSC (Scale bar: 100 μm). Values represent the mean ± SD.*: P < 0.05.
Regulation of osteogenic differentiation by Robo1 linked to inflammatory pathways
To further explore the mechanism by which Robo1 regulates osteogenic differentiation, we knocked down Robo1 in 3T3 cells, extracted RNA, and performed RNA sequencing (RNA-seq).
The results of the PCA analysis indicated significant differences between the samples in the Robo1 knockdown group and the control group (Figure 6A). By performing differential expression analysis we identified 47 genes that were upregulated and 58 genes that were downregulated following Robo1 knockdown (Figure 6B). By performing GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis on these 105 differential genes, we found that acute inflammatory response, response to interleukin-1, IL-17 signaling pathway and other inflammation-related pathways were most significantly enriched (Figures 6C, D). Furthermore, the pro-inflammatory factor IL-6 was significantly upregulated after Robo1 knockdown (Supplementary Table 2). Through GSEA analysis, we found that the top five pathways include complement and coagulation cascades, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, herpes simplex virus 1 infection, HlF-1 signaling pathway, and NF-κB signaling pathway, and most of the genes in these pathways were upregulated.
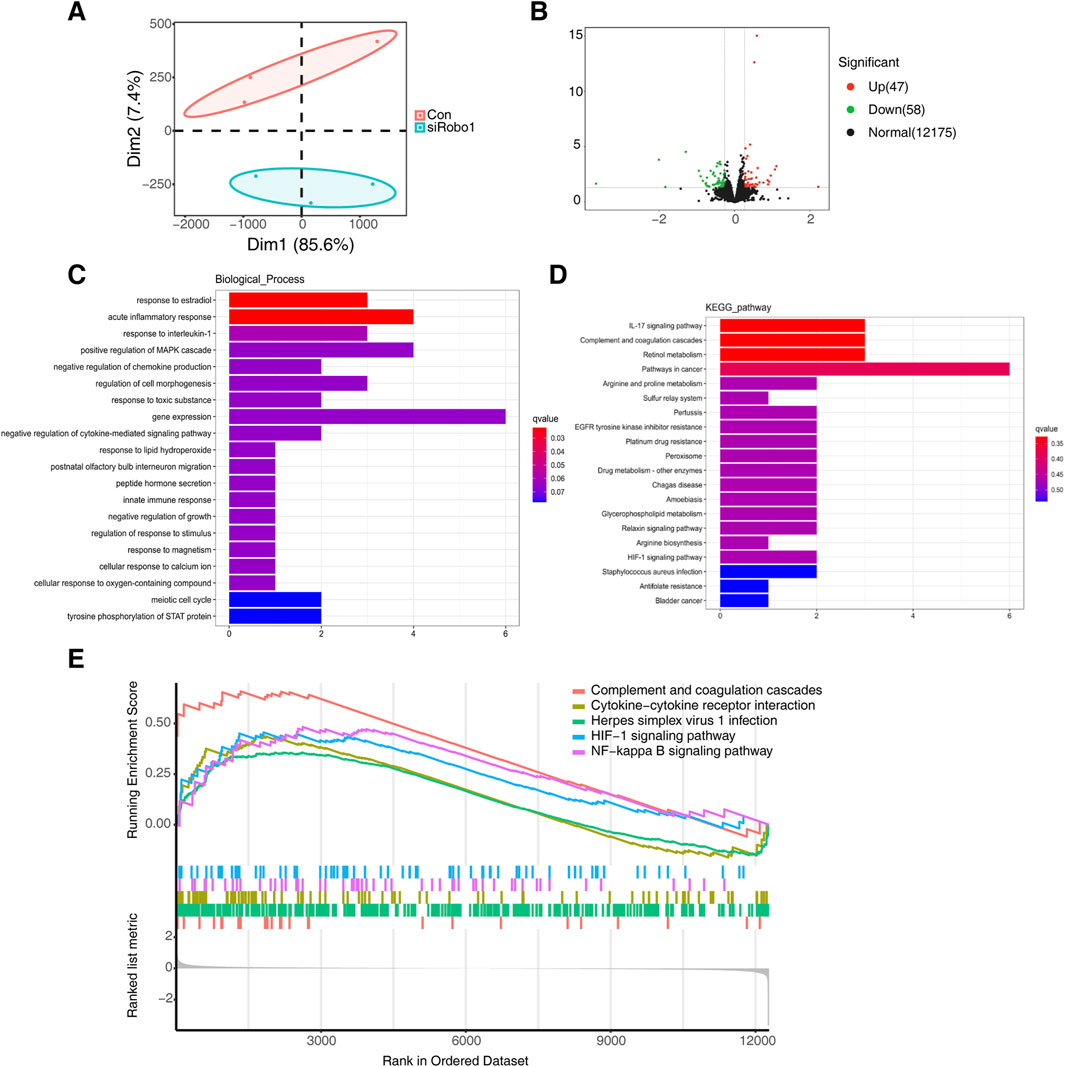
Figure 6. Robo1 regulates inflammatory pathways in 3T3-E1. (A) PCA analysis of control and Robo1 knocked down samples (N = 3). (B) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes. (C) GO enrichment of differentially expressed genes. (D) KEGG enrichment of differentially expressed genes. (E) GSEA analysis of control and Robo1 knocked down samples.
The above results indicate that the knockdown of Robo1 may activate inflammation-related pathways in osteoblasts, thereby inhibiting osteogenic differentiation and mineralization.
Discussion
Clinical translation of osteoporosis intervention based on gene targets
At present, Denosumab, an FDA-approved monoclonal antibody targeting RANKL, has demonstrated effectiveness in long-term clinical treatment of osteoporosis without increasing the risk of cancer, infection, cardiovascular diseases, delayed fracture healing, or hypocalcemia (Bone et al., 2017). Notably, denosumab has been associated with certain side effects in specific populations undergoing anti-osteoporosis treatment, such as inducing hypocalcemia syndrome in patients with cancers and chronic kidney disease (Gouldthorpe et al., 2020; Gopaul et al., 2021), increasing infection risks in patients with chronic kidney disease (Al Adhoubi and Al Salmi, 2021), and elevating the risk of spontaneous vertebral fractures after drug withdrawal (Lamy et al., 2019).
Osteocytes, derived from osteoblasts, constitute the predominant cell type within bone tissue. They play a pivotal role in regulating bone metabolism through the secretion of cytokines and their ability to sense external mechanical stresses (Schaffler et al., 2014; Bonewald and Johnson, 2008). Among the cytokines secreted by osteocytes are DKK1, sclerostin (SOST), RANKL and OPG. Research indicates that knockout of Dkk1 and Sost can lead to increased bone mass (Yee et al., 2018; Witcher et al., 2018; Colditz et al., 2018), highlighting the potential therapeutic significance of targeting these genes in osteoporosis treatment. Omosozumab, a monoclonal antibody against SOST, has received approval and is now utilized in clinical management of osteoporosis. Studies have demonstrated that Romosozumab can promote bone formation, suppress bone resorption, enhance trabecular bone microstructure, and reduce the risk of clinical fractures (Chavassieux et al., 2019; Cosman et al., 2016).
The potential translational value of new osteoporosis regulatory targets screened out in this study
In this study, omics data served as a valuable resource for identifying candidate genes, while the IPMC database facilitated the verification of gene functions. Through in vitro experiments focusing on osteoblast differentiation, we successfully identified PPP2R2A, RRBP1, HSPB6, SLC22A15, ADAMTS4, ATP8B1, CTNNB1, and ROBO1 as potential candidates. These genes exhibit differential expression in patients with osteoporosis. Additionally, the data from gene knockout mouse models in the IMPC database reveal significant alterations in bone phenotypes.
Since the omics data for candidate genes screening was derived from human samples, we hope to first verify the functions of these genes in human osteoblast cell lines, among which Saos-2 is one of the commonly used human cells for studying osteoblast differentiation with more efficiency in forming mineralized nodules than BMSCs or 3T3-E1. The knockdown of ATP8B1 was found to enhance osteogenic differentiation. Notably, ATP8B1 knockout mice exhibited a significant decrease in bone mineral density (BMD), possibly indicating a greater influence of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption relative to osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Mechanistically, the regulation of osteoclast differentiation by ATP8B1 may involve the inflammatory response and macrophage efferocytosis (Yang et al., 2022). In addition, knockdown of PPP2R2A and ROBO1 can significantly inhibit osteogenic differentiation, which is consistent with the phenotype of decreased bone density in gene knockout mice, indicating that PPP2R2A and ROBO1 can affect bone mass changes by regulating osteogenic differentiation. BMD data revealed that ROBO1 knockout heterozygous mice exhibited a higher degree of bone loss compared to PPP2R2A knockout heterozygous mice. Consequently, ROBO1 emerge as a promising candidate for translational research in osteoporosis intervention based on osteoblast-mediated bone formation.
The bone homeostasis is regulated in the bone microenvironment within the basic multicellular unit (BMU), which contain osteoclasts and osteoblasts together with osteocytes, bone lining cells, osteal macrophages, and vascular endothelial cells (Kular et al., 2012). Several studies have shown that Robo1 may be involved in the regulation of various cells. In bone tissue, Robo1 is expressed in vascular endothelial cells, and knocking down Robo1 in bone marrow endothelial cells can inhibit the promotion of SLIT3 on their cell migration and tube formation (Xu et al., 2018). SLIT2-mediated pro-angiogenesis is also dependent on Robo1 (Li et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2018). In macrophages, SLIT2/ROBO1 signaling can regulate the cytoskeleton and prevent macropinocytosis and NF-κB activation (Bhosle et al., 2020), suggesting that downregulation of Robo1 in macrophages can increase inflammatory responses. In excitatory neurons, expression of Robo1 decrease with aging, indicating that Robo1 may be involved in the regulation of neuron senescence (Zhang et al., 2022). Although Robo1 is rarely expressed in osteoclasts (Xu et al., 2018), bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) Robo1 knockdown inhibits SLIT2-mediated osteoclast differentiation, suggesting that Robo1 may be directly involved in the regulation of osteoclast differentiation (Park et al., 2019). In vitro studies have found that Robo1 knockdown can promote osteoclast differentiation, but has no effect on osteoblast migration (Kim et al., 2018). Thus, the role of Robo1 in regulating osteogenic differentiation and osteoblast function remains unclear. It has been reported that Robo2 can regulate the osteogenic differentiation of 3T3-E1 by modulating autophagy (Yuan et al., 2023), suggesting that Robo1 may also be involved in the regulation of osteogenic differentiation through a similar pathway.
In vivo studies have demonstrated that Robo1−/− mice exhibit a significantly reduced trabecular bone mass, trabecular thickness, and trabecular number and a higher trabecular separation than their wild-type (WT) littermates. The bone formation rate was lower, and the bone resorption parameters were higher in Robo1−/− mice than in WT (Xu et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2018). Although Robo1 may affect bone homeostasis in various ways, the construction of osteoblast-specific Robo1 knockout mice can provide in vivo evidence that Robo1 affects bone mass by regulating osteogenesis mediated by osteoblasts.
ROBO1 and inflammatory response
This study used RNA-seq to preliminarily explore the potential mechanism of Robo1 regulating osteoblasts. The results suggested that inflammatory-related signaling pathways were activated after Robo1 knockdown. We found that the proinflammatory factor IL6 was significantly upregulated after Robo1 knockdown, and many studies have shown that IL6 can inhibit osteogenic differentiation (Kaneshiro et al., 2014; Peruzzi et al., 2012), indicating that the weakening of osteogenic differentiation caused by Robo1 knockdown may be related to the increased expression of IL6. Previous studies have shown that reactive oxygen species (ROS) can inhibit osteoblast differentiation and activity by inducing inflammatory response (Marques-Carvalho et al., 2023; Iantomasi et al., 2023). Our results showed that the peroxisome pathway was enriched in the KEGG analysis, and the HIF-1 signaling pathway was enriched in the GSEA analysis, suggesting that the activation of redox-related signaling pathways may be related to the inflammatory response of osteoblasts.
Summary
Through the results of omics sequencing of clinical samples and screening of IMPC, this study successfully screened ROBO1 as a key molecule regulating osteoporosis, and ROBO1 downregulation may promotes osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. Our study provides several novel molecular targets involved in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Further research on these molecular targets is expected to provide a new approach for the clinical intervention and treatment of osteoporosis, such as developing agonists, inhibitors or antibodies against gene targets.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Saos-2, 3T3-E1, BMSC were obtained from Procell Biological Company and cultured in a 37°C incubator containing 5% CO2. Saos-2 was cultured using McCoy’s 5A medium containing 15% FBS and 1% P/S. 3T3-E1 and BMSC were cultured using αMEM medium containing 10% FBS and 1% P/S.
siRNA transfection and qPCR
Use DEPC water to dissolve siRNA (Shenggong) to a final concentration of 10 nM. Use Lipofectamine RNAiMAX for RNA transfection according to the instructions. Change the medium within 24 h of transfection. After continuing to culture for 48 h, use an RNA extraction kit (Yeason) to extract cellular RNA.
The RNA concentration was determined by a NanoDrop (Thermo), and the cDNA was synthesized using a NovoScript Plus All-in-one 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (Novoprotein). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using NovoStart SYBR qPCR SuperMix plus (Novoprotein) with StepOne Plus (Applied Biosystems). The relative levels of target genes were normalized to Gapdh. Primer information for Q-PCR is included in the Supplementary Table 1.
Osteogenic differentiation
Add 10 mM β-Glycerophosphate disodium salt hydrate (Abmole), 50 ug/ml VC (Abmole) and 10 nM dexamethasone (MCE) to the growth medium to prepare an osteogenic differentiation medium. When the cells grew to 80% confluence, siRNA transfection was performed. The differentiation medium was replaced the next day and the medium was changed every 2 days.
Western blot
The cells were washed with PBS for once before adding RIPA. The cells were lysed on ice for 30 min and the lysate was collected. After centrifuging at 4°C and 13,000 rpm for 10 min, supernatant was collected. BCA method was used to determine the protein concentration. After SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, the protein was transferred to a PVDF membrane, then blocked with 5% milk. Membranes were incubated with primary antibodies (ALP: Affinity DF6225 1:1,000, RUNX2: proteintech 20700-1-AP 1:1,000, GAPDH: proteintech 60004-1-Ig 1:3,000, ACTIN: proteintech 23660-1-AP 1:3,000) overnight at 4°C. After washed three times with TBST, membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (proteintech SA00001-1 1:10,000, proteintech SA00001-2 1:10,000) at room temperature for 1 h. Membranes were then visualized with chemiluminescence imager (Tannon). Use ImageJ software for protein quantification.
Alizarin red staining
On the 14th day of Saos-2 differentiation, and the 20th day of 3T3-E1 and BMSC differentiation, the osteogenic mineralization level was detected using the Alizarin red staining kit. Wash the cells once with PBS, fix the cells with 4% PFA at room temperature for 20 min, and then wash the cells three times with PBS. Add an appropriate amount of Alizarin red S staining solution to evenly cover the cells, and stain at room temperature for 30 min. Wash thoroughly with distilled water, and then take pictures under a microscope.
RNA seq and enrichment analysis
RNA-seq was performed on an MGI platform at the Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Differential expression analysis of two groups was performed using the DESeq2 R package (1.26.0). The screening criteria for this project were: Fold Change ≥ 1.2 and P value < 0.05. We used KOBAS (Mao et al., 2005) software to test the statistical enrichment of differential expression genes in KEGG pathways. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was implemented by the GOseq R packages based Wallenius non-central hyper-geometric distribution (Young et al., 2010), which can adjust for gene length bias in DEGs. The GSEA analysis in this project uses the gene sets of KEGG pathways and GO BP, CC, and MF branches as the gene sets of interest, and uses the log2FC of each differential group as the score of the background gene set to analyze the enrichment of the gene set of interest.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-tests using GraphPad Prism 8. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001).
Data availability statement
The data presented in this study are deposited in the NCBI BioProject repository, accession number PRJNA1124862.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
XZ: Project administration, Writing–original draft. YW: Writing–review and editing, Data curation, Project administration. MZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. QW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. RZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. KZ: Data curation, Validation, Writing–review and editing. QZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing–review and editing. YX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFC2501702), Natural Science Foundation of China (82372455) to Youjia Xu, Quzhou Science and Technology Research Project (2023K107) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (ZCLQ24H0701) to Qiaocheng Zhai.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2024.1450215/full#supplementary-material
References
Al Adhoubi, N. K., and Al Salmi, I. (2021). Safety of denosumab in patients with chronic kidney disease. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 32 (5), 1235–1242. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.344742
Bhosle, V. K., Mukherjee, T., Huang, Y. W., Patel, S., Pang, B. W. F., Liu, G. Y., et al. (2020). SLIT2/ROBO1-signaling inhibits macropinocytosis by opposing cortical cytoskeletal remodeling. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 4112. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17651-1
Bone, H. G., Wagman, R. B., Brandi, M. L., Brown, J. P., Chapurlat, R., Cummings, S. R., et al. (2017). 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5 (7), 513–523. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30138-9
Bonewald, L. F., and Johnson, M. L. (2008). Osteocytes, mechanosensing and Wnt signaling. Bone 42 (4), 606–615. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2007.12.224
Butterfield, N. C., Curry, K. F., Steinberg, J., Dewhurst, H., Komla-Ebri, D., Mannan, N. S., et al. (2021). Accelerating functional gene discovery in osteoarthritis. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 467. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20761-5
Chavassieux, P., Chapurlat, R., Portero-Muzy, N., Roux, J. P., Garcia, P., Brown, J. P., et al. (2019). Bone-forming and antiresorptive effects of romosozumab in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: bone histomorphometry and microcomputed tomography analysis after 2 and 12 Months of treatment. J. Bone Min. Res. 34 (9), 1597–1608. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3735
Choi, Y. J., Song, I., Jin, Y., Jin, H. S., Ji, H. M., Jeong, S. Y., et al. (2017). Transcriptional profiling of human femoral mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis and its association with adipogenesis. Gene 632, 7–15. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2017.08.015
Colditz, J., Thiele, S., Baschant, U., Niehrs, C., Bonewald, L. F., Hofbauer, L. C., et al. (2018). Postnatal skeletal deletion of dickkopf-1 increases bone formation and bone volume in male and female mice, despite increased sclerostin expression. J. Bone Min. Res. 33 (9), 1698–1707. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3463
Cosman, F., Crittenden, D. B., Adachi, J. D., Binkley, N., Czerwinski, E., Ferrari, S., et al. (2016). Romosozumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 375 (16), 1532–1543. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1607948
Gopaul, A., Kanagalingam, T., Thain, J., Khan, T., Cowan, A., Sultan, N., et al. (2021). Denosumab in chronic kidney disease: a narrative review of treatment efficacy and safety. Arch. Osteoporos. 16 (1), 116. doi:10.1007/s11657-021-00971-0
Gouldthorpe, C., Quinton, R., and Wakefield, D. (2020). Denosumab-induced hypocalcaemia in metastatic gastric cancer. BMJ Support Palliat. Care–2020-002548. doi:10.1136/bmjspcare-2020-002548
Groza, T., Gomez, F. L., Mashhadi, H. H., Munoz-Fuentes, V., Gunes, O., Wilson, R., et al. (2022). The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium: comprehensive knockout phenotyping underpinning the study of human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D1038–D1045. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac972
Iantomasi, T., Romagnoli, C., Palmini, G., Donati, S., Falsetti, I., Miglietta, F., et al. (2023). Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis: molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (4), 3772. doi:10.3390/ijms24043772
Jemtland, R., Holden, M., Reppe, S., Olstad, O. K., Reinholt, F. P., Gautvik, V. T., et al. (2011). Molecular disease map of bone characterizing the postmenopausal osteoporosis phenotype. J. Bone Min. Res. 26 (8), 1793–1801. doi:10.1002/jbmr.396
Jin, D., Wu, X., Yu, H., Jiang, L., Zhou, P., Yao, X., et al. (2018). Systematic analysis of lncRNAs, mRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 10 (5), 1498–1510.
Kaneshiro, S., Ebina, K., Shi, K., Higuchi, C., Hirao, M., Okamoto, M., et al. (2014). IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J. Bone Min. Metab. 32 (4), 378–392. doi:10.1007/s00774-013-0514-1
Kim, B. J., Lee, Y. S., Lee, S. Y., Baek, W. Y., Choi, Y. J., Moon, S. A., et al. (2018). Osteoclast-secreted SLIT3 coordinates bone resorption and formation. J. Clin. Invest 128 (4), 1429–1441. doi:10.1172/JCI91086
Kular, J., Tickner, J., Chim, S. M., and Xu, J. (2012). An overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular level. Clin. Biochem. 45 (12), 863–873. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.03.021
Lamy, O., Stoll, D., Aubry-Rozier, B., and Rodriguez, E. G. (2019). Stopping denosumab. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 17 (1), 8–15. doi:10.1007/s11914-019-00502-4
Li, S., Huang, L., Sun, Y., Bai, Y., Yang, F., Yu, W., et al. (2015). Slit2 promotes angiogenic activity via the robo1-VEGFR2-ERK1/2 pathway in both in vivo and in vitro studies. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 56 (9), 5210–5217. doi:10.1167/iovs-14-16184
Li, G., Wang, A., Tang, W., Fu, W., Tian, Q., Jian, J., et al. (2024). Progranulin deficiency associates with postmenopausal osteoporosis via increasing ubiquitination of estrogen receptor α. Genes & Dis. 101221, 101221. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101221
Liu, J., Hou, W., Guan, T., Tang, L., Zhu, X., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Slit2/Robo1 signaling is involved in angiogenesis of glomerular endothelial cells exposed to a diabetic-like environment. Angiogenesis 21 (2), 237–249. doi:10.1007/s10456-017-9592-3
Mao, X., Cai, T., Olyarchuk, J. G., and Wei, L. (2005). Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 21 (19), 3787–3793. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430
Marques-Carvalho, A., Kim, H. N., and Almeida, M. (2023). The role of reactive oxygen species in bone cell physiology and pathophysiology. Bone Rep. 19, 101664. doi:10.1016/j.bonr.2023.101664
Panach, L., Pertusa, C., Martinez-Rojas, B., Acebron, A., Mifsut, D., Tarin, J. J., et al. (2020). Comparative transcriptome analysis identifies CARM1 and DNMT3A as genes associated with osteoporosis. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 16298. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-72870-2
Park, S. J., Lee, J. Y., Lee, S. H., Koh, J. M., and Kim, B. J. (2019). SLIT2 inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by suppression of Cdc42 activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 514 (3), 868–874. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.046
Peruzzi, B., Cappariello, A., Del Fattore, A., Rucci, N., De Benedetti, F., and Teti, A. (2012). c-Src and IL-6 inhibit osteoblast differentiation and integrate IGFBP5 signalling. Nat. Commun. 3, 630. doi:10.1038/ncomms1651
Qiu, C., Yu, F., Su, K., Zhao, Q., Zhang, L., Xu, C., et al. (2020). Multi-omics data integration for identifying osteoporosis biomarkers and their biological interaction and causal mechanisms. iScience 23 (2), 100847. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.100847
Roforth, M. M., Farr, J. N., Fujita, K., McCready, L. K., Atkinson, E. J., Therneau, T. M., et al. (2015). Global transcriptional profiling using RNA sequencing and DNA methylation patterns in highly enriched mesenchymal cells from young versus elderly women. Bone 76, 49–57. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2015.03.017
Schaffler, M. B., Cheung, W. Y., Majeska, R., and Kennedy, O. (2014). Osteocytes: master orchestrators of bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 94 (1), 5–24. doi:10.1007/s00223-013-9790-y
Song, I., Choi, Y. J., Jin, Y., Kim, J. W., Koh, J. T., Ji, H. M., et al. (2017). STRA6 as a possible candidate gene for pathogenesis of osteoporosis from RNAseq analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 16 (4), 4075–4081. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7072
Watts, N. B., and Manson, J. E. (2017). Osteoporosis and fracture risk evaluation and management: shared decision making in clinical practice. JAMA 317 (3), 253–254. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19087
Witcher, P. C., Miner, S. E., Horan, D. J., Bullock, W. A., Lim, K. E., Kang, K. S., et al. (2018). Sclerostin neutralization unleashes the osteoanabolic effects of Dkk1 inhibition. JCI Insight 3 (11), e98673. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.98673
Xu, R., Yallowitz, A., Qin, A., Wu, Z., Shin, D. Y., Kim, J. M., et al. (2018). Targeting skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat. Med. 24 (6), 823–833. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0020-z
Yang, W. J., Cao, R. C., Xiao, W., Zhang, X. L., Xu, H., Wang, M., et al. (2022). Acinar ATP8b1/LPC pathway promotes macrophage efferocytosis and clearance of inflammation during chronic pancreatitis development. Cell Death Dis. 13 (10), 893. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05322-6
Yee, C. S., Manilay, J. O., Chang, J. C., Hum, N. R., Murugesh, D. K., Bajwa, J., et al. (2018). Conditional deletion of Sost in MSC-derived lineages identifies specific cell-type contributions to bone mass and B-cell development. J. Bone Min. Res. 33 (10), 1748–1759. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3467
Young, M. D., Wakefield, M. J., Smyth, G. K., and Oshlack, A. (2010). Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 11 (2), R14. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Yuan, N., Wang, X., and He, M. (2023). Robo2 promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization through autophagy and is activated by parathyroid hormone induction. Ann. Anat. 248, 152070. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2023.152070
Zeng, Y., Zhang, L., Zhu, W., Xu, C., He, H., Zhou, Y., et al. (2016). Quantitative proteomics and integrative network analysis identified novel genes and pathways related to osteoporosis. J. Proteomics 142, 45–52. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2016.04.044
Zhang, L., Liu, Y. Z., Zeng, Y., Zhu, W., Zhao, Y. C., Zhang, J. G., et al. (2016). Network-based proteomic analysis for postmenopausal osteoporosis in Caucasian females. Proteomics 16 (1), 12–28. doi:10.1002/pmic.201500005
Zhang, Y., Amaral, M. L., Zhu, C., Grieco, S. F., Hou, X., Lin, L., et al. (2022). Single-cell epigenome analysis reveals age-associated decay of heterochromatin domains in excitatory neurons in the mouse brain. Cell Res. 32 (11), 1008–1021. doi:10.1038/s41422-022-00719-6
Zhang, L., Peng, T. L., Wang, L., Meng, X. H., Zhu, W., Zeng, Y., et al. (2020). Network-based transcriptome-wide expression study for postmenopausal osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 105 (8), 2678–2691. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa319
Keywords: osteoporosis, IMPC, ROBO1, osteogenesis, inflammation
Citation: Zhang X, Wang Y, Zheng M, Wei Q, Zhang R, Zhu K, Zhai Q and Xu Y (2024) IMPC-based screening revealed that ROBO1 can regulate osteoporosis by inhibiting osteogenic differentiation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1450215. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1450215
Received: 10 July 2024; Accepted: 26 September 2024;
Published: 08 October 2024.
Edited by:
Jiake Xu, University of Western Australia, AustraliaReviewed by:
Jin Xu, Shandong Provincial Hospital, ChinaLingli Zhang, Shanghai University of Sport, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Wang, Zheng, Wei, Zhang, Zhu, Zhai and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiaocheng Zhai, emhhaXFpYW9jaGVuZ0B3bXUuZWR1LmNu; Youjia Xu, eHV5b3VqaWFAc3VkYS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiangzheng Zhang1†
Xiangzheng Zhang1† Yike Wang
Yike Wang Qiaocheng Zhai
Qiaocheng Zhai