
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 18 July 2024
Sec. Molecular and Cellular Pathology
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1450040
This article is a correction to:
Characterizing the Neutrophilic Inflammation in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps
 Jian-Wen Ruan
Jian-Wen Ruan Jie-Fang Zhao
Jie-Fang Zhao Xue-Li Li
Xue-Li Li Bo Liao
Bo Liao Li Pan
Li Pan Ke-Zhang Zhu
Ke-Zhang Zhu Qi-Miao Feng
Qi-Miao Feng Jin-Xin Liu
Jin-Xin Liu Zi-E. Yu
Zi-E. Yu Jia Song
Jia Song Hai Wang*
Hai Wang* Zheng Liu*
Zheng Liu*A Corrigendum on
Characterizing the neutrophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
by Ruan J-W, Zhao J-F, Li X-L, Liao B, Pan L, Zhu K-Z, Feng Q-M, Liu J-X, Yu Z-E, Song J, Wang H and Liu Z (2021). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:793073. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.793073
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1B as published. (In the Neu-low NP panel in Figure 1B, an image from Neu-high NP group was mistakenly inserted). The corrected (Figure 1) and its caption appear below.
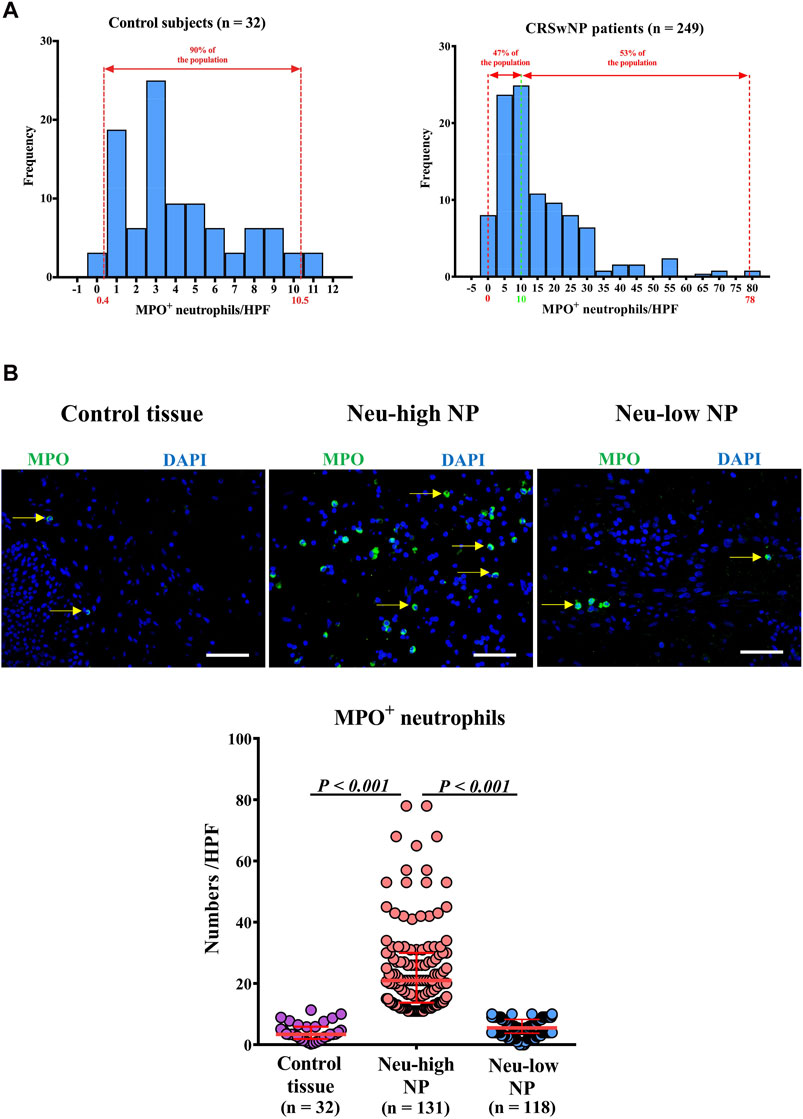
Figure 1. Distribution of tissue neutrophils in patients with CRSwNP. (A) Distribution of tissue neutrophils in control subjects (right panel) and CRSwNP patients (left panel). The red dotted lines represent 5th percentile (0.4) and 95th percentile (10.5) in the left panel. The red dotted lines represent minimum (0) and maximum (78.0), and the green dotted line represents the cut-off value (10) to define Neu-low and Neu-high NPs in the right panel. (B) Representative photomicrographs showing immunofluorescence staining of MPO positive cells and quantification of MPO positive cells. Original magnification ×400. Scale bar, 100 μm. Arrows denote representative positive cells. CRSwNP, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; NP, nasal polyp; Neu-high, neutrophil-high; Neu-low, neutrophil-low; MPO, myeloperoxidase; HPF, high-power field.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: apoptosis, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, granulocyte colonystimulating factor, neutrophil, inflammation
Citation: Ruan J-W, Zhao J-F, Li X-L, Liao B, Pan L, Zhu K-Z, Feng Q-M, Liu J-X, Yu Z-E, Song J, Wang H and Liu Z (2024) Corrigendum: Characterizing the neutrophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1450040. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1450040
Received: 16 June 2024; Accepted: 03 July 2024;
Published: 18 July 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Claus Bachert, University Hospital Münster, GermanyCopyright © 2024 Ruan, Zhao, Li, Liao, Pan, Zhu, Feng, Liu, Yu, Song, Wang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hai Wang, ODE0ODk5MDk2QHFxLmNvbQ==; Zheng Liu, emhlbmdsaXVlbnRAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.