
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 24 December 2024
Sec. Cancer Cell Biology
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1436033
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the main histological subtype of lung cancer. For locally advanced and advanced NSCLC, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-targeted therapy has been the first choice for NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations. TKIs, as targeted drugs, inhibit kinase activity and autophosphorylation by competitively binding to the ATP binding site of the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain, which blocks the signal transduction mediated by EGFR and thus inhibits the proliferation of tumor cells. However, drug resistance to TKIs is inevitable. EGFR is also a highly glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase, and a wide range of crosstalk occurs between phosphorylation and glycosylation. Therefore, can the phosphorylation state be altered by glycosylation to improve drug resistance? In this review, we summarize phosphorylation, glycosylation and the crosstalk between these processes as well as the current research status and methods. We also summarize the autophosphorylation and glycosylation sites of the EGFR protein and their crosstalk. By exploring the relationship between EGFR glycosylation and autophosphorylation in targeted TKI therapy, we find that research on EGFR glycosylation is crucial for targeted NSCLC treatment and will become a research direction for identifying potential targets related to regulating TKI drug sensitivity.
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor with the highest morbidity and mortality of all cancers worldwide (Sung et al., 2021). NSCLC is the main histological subtype of lung cancer, accounting for more than 85% of all lung cancer cases (Wang et al., 2021). Lung cancer treatment includes traditional surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or a combination of these treatments; however, the survival rates and overall cure rates remain low (Herbst et al., 2018). In recent years, targeted EGFR-TKI therapy has been the first choice for patients with advanced NSCLC and EGFR mutations, which has improved the quality of life of these patients.
Mechanistically, in non-small cell lung cancer, mutations in EGFR lead to destabilization of the nonactive conformation of the EGFR protein and continuous activation of its kinase domain (Di Maio, 2023), which leads to continuous autophosphorylation of the C-terminal tyrosine site and results in tumorigenesis (Irmer et al., 2007; Reita et al., 2021). In contrast, TKIs inhibit kinase activity and autophosphorylation by competitively binding the ATP binding site of the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain and blocking EGFR-mediated signal transduction, thus inhibiting tumor cell proliferation (Pao and Chmielecki, 2010; Roskoski, 2014). However, drug resistance is inevitable (Cooper et al., 2022; Noronha et al., 2022).
In addition, EGFR is a highly glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase (Han et al., 2021; Xiao et al., 2023). Many studies have confirmed extensive crosstalk between glycosylation and phosphorylation (Patwardhan et al., 2021; Pienkowski et al., 2023). Therefore, the study of proteomic posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of EGFR can provide a basis for the discovery of potential glycosylation-related targets in EGFR-TKI therapy for NSCLC.
The central dogma of molecular biology is that genetic information in a biological system is transferred from DNA to RNA and then to protein. However, butterflies and caterpillars share the same genome but have different morphologies, which is attributed mainly to PTMs (Crick, 1970). After RNA is translated into a protein, a covalent chemical modification of specific amino acid residues occurs, which is called a protein PTM. PTMs are ubiquitous in organisms and contribute to almost all cellular activities, especially signal transduction. In some cases, PTMs can act as molecular switching valves to activate or inhibit signaling pathways and to change the life processes of proteins (Zecha et al., 2023). PTMs endow proteins with additional forms of expression, which increases the complexity of human life processes (Keenan et al., 2021; Geffen et al., 2023).
To date, nearly 500 types of protein PTMs have been reported (Keenan et al., 2021), including ubiquitination, methylation, acetylation, glycosylation, and phosphorylation (Zhu et al., 2021). Different PTMs not only affect protein folding and conformational stability but also play important roles in cell development and transformation and the cell signaling network (Thygesen et al., 2018) and serve as targets for the diagnosis and treatment of many types of tumors (Kuntz et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2018). Currently, the most studied and widely applied protein PTMs are phosphorylation and glycosylation, as these account for more than 50% of PTMs (Pagel et al., 2015). Each individual protein may contain multiple PTM sites, one of which can affect the removal or addition of another modification at the same proximal or distal location. This phenomenon is called PTM “crosstalk” (Vu et al., 2018; Cutler et al., 2021). For example, the crosstalk between phosphorylation and O-acetylglucosamine modification (O-GlcNAcylation) can be used as a nutrient/pressure sensor to regulate functions such as signal transduction, transcription and the cytoskeleton (Tang et al., 2023).
Phosphorylation, which is one of the most common PTMs of proteins, occurs on more than 30% of proteins in cells and is the most common, basic and important mechanism for regulating and controlling protein function (Cohen, 2002; Yadav et al., 2017). Phosphorylation is involved in the regulation of a variety of biological processes, and the overexpression of kinases and abnormalities in their regulatory mechanism can lead to the activation or imbalance of kinase signaling pathways, which is the basis of most cases of cancer development (Fujimoto et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). During phosphorylation, under kinase catalysis, the γ phosphate group of ATP is transferred to the side chain hydroxyl group of threonine (T), serine (S) or tyrosine (Y) to form a phosphate ester. This process is reversible; that is, the phosphorylated group can be hydrolyzed and removed by phosphatase, which results in dephosphorylation (Hu et al., 2023). Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation are common regulatory modes that regulate protein conformation, protein cell localization and interactions between signaling molecules, and these modes are involved in cellular activities such as cell proliferation, migration, differentiation and apoptosis. Both phosphorylation and dephosphorylation have broad functions in signaling pathway transduction, apoptosis, development and differentiation, and cancer mechanisms, among other processes (Wang et al., 2022).
Many biochemical studies have focused on the treatment of diseases, such as autoimmunity (Aso et al., 2023), inflammation (Tu et al., 2022), metabolism (Batista et al., 2020), and degenerative diseases (Zheng et al., 2020), by interfering with phosphorylation-based signal transduction. For example, researchers combined global proteomics and phosphoproteomics data and revealed that diabetes leads to β-cell failure through a GSK3-PDX1-dependent axis, which aids in identifying potential islet-related therapeutic targets for human type 2 diabetes (Sacco et al., 2019). Suhas Vasaikar et al. used phosphoproteomics to analyze colorectal cancer and adjacent tissues and reported that Rb phosphorylation is an oncogenic driver in colorectal cancer. Targeting Rb phosphorylation in colorectal cancer via CDK2 inhibition represents a unique opportunity (Vasaikar et al., 2019). Furthermore, some studies have revealed a significant accumulation of phosphorylated tau in GABAergic interneurons of the dentate gyrus in Alzheimer’s disease patients, which subsequently inhibits GABAergic transmission and disinhibits the neural circuitry within the neurogenic niche, thereby impairing adult hippocampal neurogenesis and leading to cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease (Zheng et al., 2020). Additionally, researchers have used quantitative phosphoproteomics to reveal that tyrosine phosphorylation at key sites in the phosphatase SHP2 is inhibited and reduced, leading to subsequent suppression of the RAS/MAPK pathway and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. By performing inverse correlation analysis on a published drug-induced P100 phosphoproteomics dataset, they predicted that the combination of the PI3K/MTOR inhibitor dactolisib with osimertinib could overcome resistance to EGFR TKIs (Zhang et al., 2021). Therefore, understanding and intervening in the role of protein phosphorylation in tumors has become an important direction in cancer research.
Glycosylation is a key posttranslational modification of proteins and encompasses the glycosidic bonds produced by enzymes between sugars and other sugars, proteins or lipids (Moremen et al., 2012). N-glycosylation and O-glycosylation are the two most common types of protein glycosylation (Bennett et al., 2012). Oligosaccharides involved in N-glycosylation are connected to asparagine residues and have a conserved pentasaccharide core structure, whereas oligosaccharides involved in O-glycosylation are linked to serine or threonine residues and are catalyzed by different glycosyltransferases, one monosaccharide at a time (You et al., 2018). Sugar chains are diverse due to differences in monosaccharide composition, connections between monosaccharides, heterogeneity, branching structures, the presence of other substituents and connections to their aglycones (Savarino et al., 2023). Glycosylation plays important roles in transcriptional activity (Myers et al., 2016; Constable et al., 2017), epigenetic regulation (Wu et al., 2017), neuronal function (Yim et al., 2022), response to external stressors (Ma et al., 2021) and regulation of protein‒protein interactions (Tarbet et al., 2018). Many studies on human glycosylation defects and their associations with disease have shown that mammalian sugar chains contain a large amount of biological information (Hoffman et al., 2023). Identification of the biological function of each sugar chain and sugar chain-binding protein has made important contributions to the diagnosis and treatment of multiple diseases (Davighi et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2023).
Sialylation is an important type of cell glycosylation. The sialylated sugar chain structure plays an important role in cell recognition, adhesion and signal transmission. When glycosyltransferase expression changes, sialylation is related to the occurrence and development of cancer (Rossi et al., 2022). Serum CA199 is a tumor-related marker that is used clinically and is mainly detected in patients with pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer or cholangiocarcinoma. However, the expression of α2,3-sialylate type 1 (SLeA) is primarily detected for clinical diagnosis and monitoring of treatment response (Izquierdo-Sanchez et al., 2022).
Fucosylation, which involves synthesis by a series of fucosyltransferases, is an unextensible modification that is usually divided into terminal fucosylation and core fucosylation (Fujita et al., 2021). The final step of systemic lupus erythematosus antigen biosynthesis includes α1,3- or α1,4-fucosylation. An increase in core fucosylation is closely related to the occurrence of liver cancer (Loong et al., 2021). The core fucosylation of α-fetoprotein is a recognized biomarker for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma that helps distinguish between chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis (Sanda et al., 2021). In cancers, core fucosylation of EGFR is associated with increased dimerization and phosphorylation, which leads to an increase in EGFR-mediated signaling related to tumor cell growth and malignancy (Zhang et al., 2020; Ament et al., 2023).
The increased expression of the GlcNAc-N- sugar chain is due to the increased activity of GnT-V, which is encoded by the mannoside acetylglucosaminyltransferase 5 (MGAT5) gene. MGAT5 expression is regulated by the insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling pathway (Salvi et al., 2022). O-(ligated)-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc), which is involved in a unique glycosylation reaction, is usually transferred to the hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine residues of proteins (Fan et al., 2023). O-GlcNAc glycosylation is very sensitive to uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl glucosamine. Uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl glucosamine is the donor of O-GlcNAc glycosylation (Ruan et al., 2013) and the downstream metabolite of glucose; thus, O-GlcNAc glycosylation is often referred to as a cellular nutritional receptor (Bond and Hanover, 2013). Like protein phosphorylation, O-GlcNAc plays an important role in regulating cell signaling and energy production (Yang and Qian, 2017). Loss of O-GlcNAc glycosylation has been shown to lead to cell dysfunction and even cell death (O'Donnell et al., 2004), whereas O-GlcNAc dysfunction is associated with many diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes and other chronic diseases (Banerjee et al., 2016; Ma et al., 2017). The mucin-type O-glycosylation component GalNAc-type O-glycan, also known as mucin-O-glycan, is common in most transmembrane and secretory glycoproteins. Its abnormal expression is closely related to the development of malignant tumors (Berois et al., 2013). Furthermore, some studies have shown that the expression of GalNAc transferase, which initiates mucin O-glycosylation, also changes during the occurrence and development of cancer (Gornes et al., 2009).
Notch glycosylation is unique; the Notch signaling pathway is crucial for cell fate decisions, and its imbalance can lead to a variety of human diseases. Glycosylation of the extracellular domain of Notch has been shown to regulate its activity. Notch ligands bind to the receptor in the extracellular domain and activate it by inducing conformational changes in Notch, which exposes multiple cleavage sites. The cleavage of these sites leads to the release of the Notch intracellular domain, which shifts to the nucleus and controls the transcriptional activation of recombination signal binding protein inhibitors. The extracellular domain of Notch is modified by different types of carbohydrates, including N-glycans and O-polysaccharides (Moloney et al., 2000). Glycosylation-dependent Notch signal regulation controls development, maintains the “dryness” of tumor cells, and mediates cancer metastasis (Takeuchi and Haltiwanger, 2014).
Most protein PTMs occur on specific amino acids, and the density of coexisting PTMs on proteins is very high; that is, a single protein may contain multiple different PTMs, and thus, the first modification may affect the addition or removal of the next modification (Schwein and Woo, 2020) (Figure 1). Multiple PTMs can positively or negatively affect other behaviors, which is called crosstalk between PTMs (Gan and Fan, 2024). An example of early evidence for the existence of crosstalk is that shortly after Hart et al. discovered O-GlcNAc glycosylation in 1984, researchers noticed that O-GlcNAc glycosylation occurred at known phosphorylation sites (Torres and Hart, 1984). The most studied form of PTM crosstalk is crosstalk between phosphorylation and O-GlcNAc glycosylation because these processes predominantly involve serine and threonine residues. When more than 800 phosphorylation sites were inhibited, the phosphorylation at 280 sites decreased, and the glycosylation at 148 sites increased. In addition, a change in O-GlcNAc glycosylation after the inhibition of serine/threonine phosphatases was also observed (Wang et al., 2008). Other studies have shown that calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV (CaMKIV) is phosphorylated at multiple sites, including Thr200, and that CaMKIV undergoes O-GlcNAc glycosylation on at least five specific residues, including Ser137 and Ser189. The glycosylation of Ser137 leads to a slight increase in the phosphorylation of CaMKIV at Thr200, whereas the glycosylation of Ser189 leads to a substantial increase in phosphorylation at Thr200 (Dias et al., 2009). Consistent with these findings, the inhibition of GSK3β phosphorylation leads to an increase in O-GlcNAc glycosylation in COS7 cells (Wang et al., 2007). Currently, many cases of crosstalk between O-GlcNAc glycosylation and phosphorylation have been described, from which several individual modification sites have been identified, including Thr58 on c-Myc, which is modified by phosphorylation or O-GlcNAc glycosylation of the transcriptional activation domain (Kamemura et al., 2002), and the mouse estrogen receptor at Ser16, which regulates receptor activity (Chen et al., 2006).
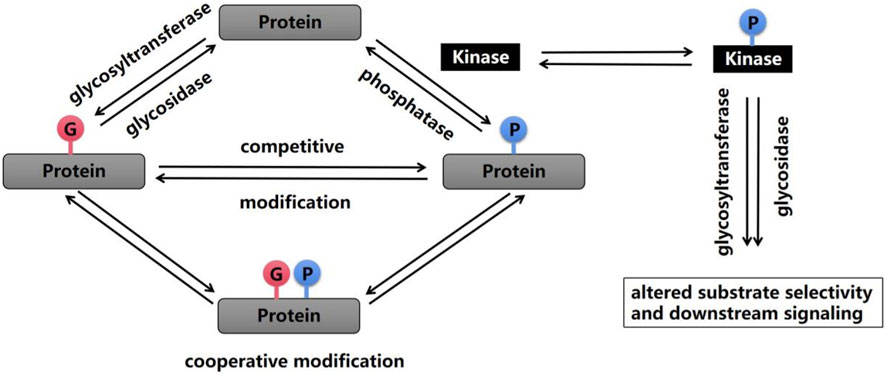
Figure 1. Phosphorylation and glycosylation are two important PTMs that are reversible by enzymatic action. A wide range of crosstalk between these two processes has been shown, and this crosstalk can occur on the same amino acid or at similar modification sites, which alters substrate selectivity and downstream signaling.
In recent years, targeted EGFR-TKI therapy has been the first choice for patients with advanced NSCLC and EGFR mutations; although the quality of life of patients has considerably improved with this treatment, drug resistance is inevitable. EGFR is currently an important target for targeted therapy of NSCLC; thus, the study of PTMs of EGFR can provide a basis for the discovery of potential glycosylation-related targets in EGFR-TKI therapy for NSCLC.
EGFR is a highly glycosylated tyrosine kinase type I transmembrane receptor of the ErbB family. Its total molecular weight is 170 kDa, and its protein sequence contains 1,186 amino acid residues, which constitute the N-terminal extracellular domain, transmembrane domain (TM), near-membrane domain (JM), tyrosine kinase domain (TK) and C-terminal domain (Chen et al., 2016; Amelia et al., 2022). EGFR binds to EGF and other ligands through the N-terminal extracellular domain to activate its conformation and dimerization; this binding also activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, which causes the protein to self-phosphorylate its C-terminal tyrosine site and then activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways, such as the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/AKT (PKB) and PLC γ pathways. This initiation includes a series of cellular physiological and pathological effects, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, tumor invasion and metastasis (Ferguson, 2008; Seshacharyulu et al., 2012). At present, many confirmed mutations in EGFR phosphorylation sites cause disease (Table 1).
EGFR is an important target protein for targeted therapy in cancer, especially non-small cell lung cancer. Abnormal changes, such as overexpression, enhanced activity and mutations of specific amino acid sites in the kinase domain, occur in a variety of tumor cells (Roskoski, 2014). Among non-small cell lung cancer patients, approximately 30%–40% of Asian patients have EGFR mutations (Herbst et al., 2008), approximately 90% of which are exon 19 deletion mutations (Del19) and exon 21 L858R mutations, accounting for 44%–51% and 38%–40% (Reita et al., 2021) of all mutations, respectively. The type of L858R EGFR mutant leads to destabilization of the nonactive conformation of EGFR so that it can spontaneously dimerize; this results in continuous activation of the kinase domain, which leads to continuous autophosphorylation of the C-terminal tyrosine site (Irmer et al., 2007; Reita et al., 2021). The type of Del19 EGFR mutant does not depend on dimerization (Jeonghee C et al., 2013).
With respect to the Del19 and L858R mutations, first-generation TKIs, such as gefitinib and erlotinib, can competitively bind to the ATP binding site of the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain, inhibit its kinase activity and autophosphorylation, and block EGFR-mediated signal transduction, thus inhibiting tumor cell proliferation (Pao and Chmielecki, 2010; Roskoski, 2014). However, most patients treated with first-generation TKI drug therapy develop mutations that cause acquired drug resistance, represented by EGFR T790M (exon 20) (49%–63%), after a progression-free survival period of approximately 10–14 months (Sequist et al., 2011; Tang and Lu, 2018). These mutations increase the affinity between EGFR and ATP while weakening the affinity of EGFR for TKIs, which leads to reactivation of the EGFR-mediated signal transduction pathway.
The third-generation TKI osimertinib is used mainly as a second-line therapy in patients with EGFR T790M mutations, but osimertinib can also be used as a first-line therapy in patients with Del19 and L858R mutations (Uchibori et al., 2018). However, the problem of acquired drug resistance will eventually occur. The representative types of mutations that cause drug resistance are T790M/C797S (during second-line therapy) and Del19/C797S and L858R/C797S (during first-line therapy). The mechanism of drug resistance is that C797 is a covalent binding site between osimertinib and EGFR, and a mutation at this site weakens the ability of osimertinib to bind to EGFR (Tang and Lu, 2018). To improve the targeted therapeutic effect of TKI drugs and prolong the progression-free survival time of patients, in addition to the development of a new generation of TKI drugs for drug-resistant mutations in EGFR, the exploration of a combination therapy strategy to increase the sensitivity of drug-resistant cell lines to TKI drugs is also considered a potentially effective approach (Yen et al., 2015).
As mentioned earlier, EGFR is a highly glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase, and the molecular weight of its glycosylated part (glycosylated chain) is approximately 40 kDa. At present, many glycosylation events at EGFR sites have been confirmed (Table 2). Moreover, EGFR consists of 11 typical N-glycosylation sites (NmurXMel Sstroke TMagre X is not proline), 4 atypical N-glycosylation sites (N-X-C) (Zhen et al., 2003; Takahashi et al., 2016) and a limited number of mucin-type O-glycosylation sites (Nguyen et al., 2009). These glycosylation sites are distributed mainly in the N-terminal extracellular domain of EGFR, as shown in Figure 2. In addition to the Asn337 site, which is a high-mannose-type sugar chain, the other glycosylation sites of EGFR are mainly sialylation- and (core) fucosylation-modified complex sugar chains, some of which also include isotypic branching structures and terminal fine structures, such as sLeX, sLeA, and LeY (Ferreira et al., 2018). The glycosylation characteristics of EGFR include glycosylation sites, the abundance distribution of glycosylation structures at each site (i.e., glycosylation microheterogeneity) and specific glycosylation types (e.g., sialylation and core fucosylation).
Glycosylation has a fine regulatory effect on the biological function of EGFR through direct and indirect regulatory mechanisms (Ferreira et al., 2018). Among them, the indirect regulatory mechanism refers to the interaction between the GlcNAc terminus of the EGFR N-linked chain and ganglioside GM3, which inhibits signaling, whereas the interaction with GD3 enhances signaling (Milani et al., 2007; Liang et al., 2017). The direct regulatory mechanism means that glycosylation regulates the tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation state of the EGFR protein by affecting its conformation, whereas the indirect regulatory mechanism means that EGFR glycosylation affects the turnover, metabolism and signal transduction of EGFR through its interaction with galectins or gangliosides. Under direct regulatory mechanisms, glycosylation characteristics, such as sialylation, core fucosylation, sugar chain branching and terminal fine structure, all have important effects on the autophosphorylation state of EGFR. These effects are generally believed to be achieved in two ways (Matsumoto et al., 2008):
• Glycosylation can change the binding affinity of EGFR for its ligands, thus regulating its kinase activity and autophosphorylation state. Sialylation of α2-3 and α2-6, loss of core fucose, a bispecific branching structure and a fine sLeX terminal structure decrease the affinity between EGFR and its ligands and decrease the level of casein autophosphorylation (Gu et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2015). Among these modifications, sialylation can even specifically regulate the phosphorylation level of specific tyrosine residues (such as Y1173) and thus shows site-specific regulation (Yen et al., 2015).
• Glycosylation can directly affect the ability of EGFR to form dimers, thus regulating its tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation state in a ligand-independent manner (Fernandes et al., 2001). As previously mentioned, when EGFR contains specific site mutations (such as L858R), spontaneous dimerization occurs. Therefore, this process plays an important role in regulating kinase activity and autophosphorylation when EGFR is mutated. Studies have shown that the sugar chains at the Asn420 and Asn579 sites can inhibit the ligand-independent dimerization of EGFR and that the loss of sugar chains at the Asn579 site increases the conformational flexibility of EGFR, which leads to the dimerization of EGFR without ligand binding and increases its autophosphorylation level (Tsuda et al., 2000; Whitson et al., 2005).
A fine regulatory relationship between the glycosylation characteristics of EGFR and its autophosphorylation state has been described, and it is worth noting that the direct regulatory mechanism of glycosylation (especially through the second pathway) also has an important effect on drug sensitivity in TKI drug resistance, as shown in Figure 3. The deglycosylation, sialylation and core fucosylation of EGFR can affect its autophosphorylation state and the sensitivity of EGFR-TKI-resistant mutant cells (L858R/T790M and Del19/T790M) to gefitinib or erlotinib (Matsumoto et al., 2008; Ling et al., 2009; Park et al., 2012; Britain et al., 2018). Since the glycosylation of EGFR can affect the sensitivity of drug-resistant cells to TKIs by regulating the autophosphorylation state of EGFR and because the glycosylation characteristics of EGFR are regulated mainly by glycosyltransferases and glycosidases in the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum, glycosyltransferases or glycosidases have become potential effective targets for enhancing sensitivity to TKIs (Lopez Sambrooks et al., 2018).
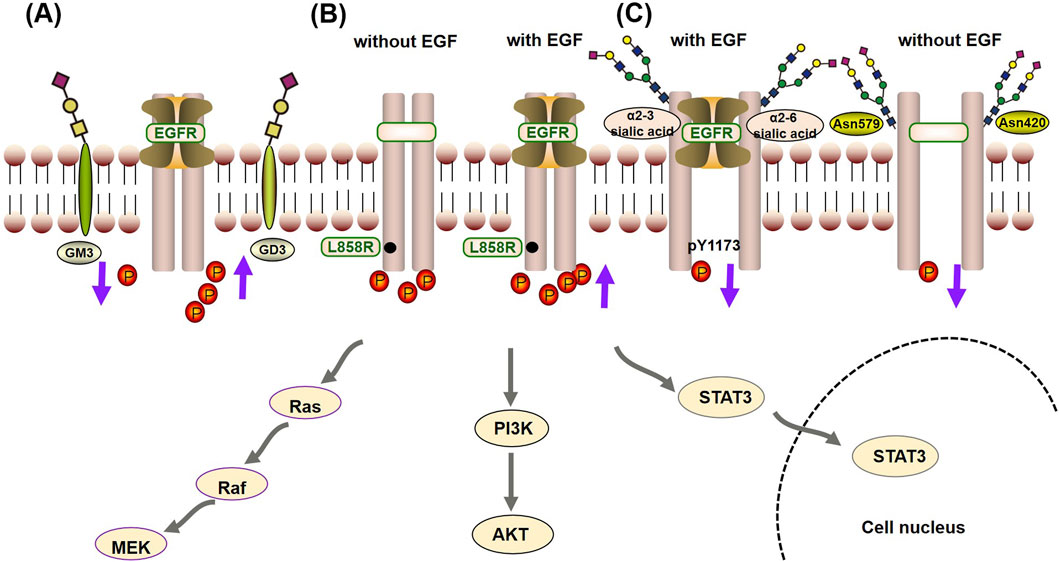
Figure 3. Crosstalk mechanism between glycosylation and autophosphorylation of EGFR: (A) The indirect regulatory mechanism, the interaction between the GlcNAc terminus of the EGFR N-linked chain and the ganglioside GM3, inhibits phosphorylation, thereby suppressing signal transduction. On the other hand, interaction with GD3 promotes phosphorylation, enhancing signaling. (B) When EGFR contains specific site mutations (such as L858R), it promotes its kinase activity and autophosphorylation state independently of EGF, but it is also enhanced by EGF. (C) In the direct regulatory mechanism, glycosylation can change the binding affinity of EGFR for its ligands (such as α2-3 and α2-6 sialic acid), reducing the occurrence of phosphorylation. Furthermore, sialylation can specifically inhibit the phosphorylation level of specific tyrosine residues (such as Y1173). At last, the sugar chains at the Asn420 and Asn579 sites can inhibit the ligand-independent dimerization of EGFR, reducing the autophosphorylation level.
Proteins are the executors of all cellular activities and embody biological functions. The existence of PTMs greatly increases the complexity of proteins. Studying the PTMs of proteins is crucial for understanding the mechanism of intracellular signal transduction, elucidating the physiological functions of life, and determining the pathogenic mechanism of related diseases. The study of PTMs can help us identify additional potential drug targets. In recent years, with the rapid development of proteomics technology based on biological mass spectrometry, especially for phosphorylation, the identification of PTM sites has tended to be saturated, and the study of PTMs has gradually shifted from qualitative to quantitative studies. Combined with this exquisite experimental design, the dynamic changes in PTMs over time and at different locations have been characterized, and finally, the dynamic changes in PTMs have been shown to be related to their biological function. With the further study of PTMs, crosstalk between PTMs has gradually become an urgent problem.
The primary premise of target discovery in EGFR-TKI therapy is to explore the key glycosylation characteristics related to TKI drug sensitivity. On this basis, the correlation between the key glycosylation characteristics and the autophosphorylation state of EGFR can be further established, which can lay a foundation for the systematic interpretation of the scientific principle by which EGFR glycosylation regulates the sensitivity of drug-resistant mutants to TKIs (Yen et al., 2015). Currently, the correlations between EGFR glycosylation characteristics and the autophosphorylation state of EGFR, as well as the effect of glycosylation on TKI drug sensitivity, are still largely limited to first-generation TKI drugs, and systematic studies on third-generation TKI drugs, such as osimertinib, are scarce. Therefore, further clinical sample analysis is needed to identify and verify the key differential glycosylation characteristics, establish correlations between those characteristics and the EGFR autophosphorylation state, identify therapeutic targets that affect the sensitivity of the third-generation TKI drug osimertinib, and provide key information on glycosylation characteristics.
YM: Writing–original draft. FZ: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. JiL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. JuL: Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YL: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Amelia, T., Kartasasmita, R., Ohwada, T., and Tjahjono, D. (2022). Structural insight and development of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Molecules 27 (3), 819. doi:10.3390/molecules27030819
Ament, C. E., Steinmann, S., Evert, K., Pes, G. M., Ribback, S., Gigante, I., et al. (2023). Aberrant fucosylation sustains the NOTCH and EGFR/NF-κB pathways and has a prognostic value in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 78 (6), 1742–1754. doi:10.1097/hep.0000000000000322
Aso, K., Kono, M., Kanda, M., Kudo, Y., Sakiyama, K., Hisada, R., et al. (2023). Itaconate ameliorates autoimmunity by modulating T cell imbalance via metabolic and epigenetic reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 984. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36594-x
Banerjee, P. S., Lagerlof, O., and Hart, G. W. (2016). Roles of O-GlcNAc in chronic diseases of aging. Mol. Aspects Med. 51, 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2016.05.005
Batista, T. M., Jayavelu, A. K., Wewer Albrechtsen, N. J., Iovino, S., Lebastchi, J., Pan, H., et al. (2020). A cell-autonomous signature of dysregulated protein phosphorylation underlies muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 32 (5), 844–859. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.007
Bennett, E., Mandel, U., Clausen, H., Gerken, T., Fritz, T., and Tabak, L. (2012). Control of mucin-type O-glycosylation: a classification of the polypeptide GalNAc-transferase gene family. Glycobiology 22 (6), 736–756. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwr182
Berois, N., Gattolliat, C. H., Barrios, E., Capandeguy, L., Douc-Rasy, S., Valteau-Couanet, D., et al. (2013). GALNT9 gene expression is a prognostic marker in neuroblastoma patients. Clin. Chem. 59 (1), 225–233. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2012.192328
Bond, M. R., and Hanover, J. A. (2013). O-GlcNAc cycling: a link between metabolism and chronic disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 33, 205–229. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161240
Brewer, M., Choi, S., Alvarado, D., Moravcevic, K., Pozzi, A., Lemmon, M., et al. (2009). The juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor functions as an activation domain. Mol. Cell 34, 641–651. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.04.034
Britain, C., Holdbrooks, A., Anderson, J., Willey, C., and Bellis, S. J. J. o.o.r. (2018). Sialylation of EGFR by the ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes EGFR activation and resistance to gefitinib-mediated cell death. J. Ovarian Res. 11 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s13048-018-0385-0
Chen, J., Zeng, F., Forrester, S., Eguchi, S., Zhang, M., and Harris, R. (2016). Expression and function of the epidermal growth factor receptor in physiology and disease. Physiol. Rev. 96 (3), 1025–1069. doi:10.1152/physrev.00030.2015
Chen, R., Jiang, X., Sun, D., Han, G., Wang, F., Ye, M., et al. (2009). Glycoproteomics analysis of human liver tissue by combination of multiple enzyme digestion and hydrazide chemistry. J. proteome Res. 8 (2), 651–661. doi:10.1021/pr8008012
Chen, Y. X., Du, J. T., Zhou, L. X., Liu, X. H., Zhao, Y. F., Nakanishi, H., et al. (2006). Alternative O-GlcNAcylation/O-phosphorylation of Ser16 induce different conformational disturbances to the N terminus of murine estrogen receptor beta. Chem. and Biol. 13 (9), 937–944. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.06.017
Cohen, P. (2002). The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 4 (5), E127–E130. doi:10.1038/ncb0502-e127
Constable, S., Lim, J. M., Vaidyanathan, K., and Wells, L. (2017). O-GlcNAc transferase regulates transcriptional activity of human Oct4. Glycobiology 27 (10), 927–937. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwx055
Cooper, A., Sequist, L., and Lin, J. (2022). Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 19 (8), 499–514. doi:10.1038/s41571-022-00639-9
Crick, F. (1970). Central dogma of molecular biology. Nature 227 (5258), 561–563. doi:10.1038/227561a0
Cutler, J., Perner, F., and Armstrong, S. (2021). Histone PTM crosstalk stimulates Dot1 methyltransferase activity. Trends Biochem. Sci. 46 (7), 522–524. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2021.04.001
Davighi, M., Matassini, C., Goti, A., Ferraroni, M., Angeli, A., Supuran, C., et al. (2023). Mono- and three-tailed sugar and iminosugar decorated benzenesulfonamide carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 21 (21), 4491–4503. doi:10.1039/d3ob00529a
Dias, W. B., Cheung, W. D., Wang, Z. H., and Hart, G. W. (2009). Regulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV by O-GlcNAc modification. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (32), 21327–21337. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.007310
Di Maio, M. (2023). Osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 389 (14), 1341–1342. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2309385
Fan, J., Guo, F., Mo, R., Chen, L. Y., Mo, J. W., Lu, C. L., et al. (2023). O-GlcNAc transferase in astrocytes modulates depression-related stress susceptibility through glutamatergic synaptic transmission. J. Clin. Invest 133 (7), e160016. doi:10.1172/jci160016
Ferguson, K. (2008). Structure-based view of epidermal growth factor receptor regulation. Annu. Rev. biophysics 37, 353–373. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.125829
Ferguson, K., Berger, M., Mendrola, J., Cho, H., Leahy, D., and Lemmon, M. (2003). EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol. cell 11 (2), 507–517. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00047-9
Fernandes, H., Cohen, S., and Bishayee, S. (2001). Glycosylation-induced conformational modification positively regulates receptor-receptor association: a study with an aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII/DeltaEGFR) expressed in cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (7), 5375–5383. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005599200
Ferreira, I., Pucci, M., Venturi, G., Malagolini, N., Chiricolo, M., and Dall'Olio, F. J. I. j.o.m.s. (2018). Glycosylation as a main regulator of growth and death factor receptors signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (2), 580. doi:10.3390/ijms19020580
Fujimoto, M., Takii, R., Matsumoto, M., Okada, M., Nakayama, K. I., Nakato, R., et al. (2022). HSF1 phosphorylation establishes an active chromatin state via the TRRAP-TIP60 complex and promotes tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 4355. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-32034-4
Fujita, K., Hatano, K., Hashimoto, M., Tomiyama, E., Miyoshi, E., Nonomura, N., et al. (2021). Fucosylation in urological cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (24), 13333. doi:10.3390/ijms222413333
Gan, Q., and Fan, C. (2024). Orthogonal translation for site-specific installation of post-translational modifications. Chem. Rev. 124 (5), 2805–2838. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00850
Garrett, T., McKern, N., Lou, M., Elleman, T., Adams, T., Lovrecz, G., et al. (2002). Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell 110, 763–773. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00940-6
Geffen, Y., Anand, S., Akiyama, Y., Yaron, T., Song, Y., Johnson, J., et al. (2023). Pan-cancer analysis of post-translational modifications reveals shared patterns of protein regulation. Cell 186 (18), 3945–3967.e26. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.013
Gornes, J., Marcos, N. T., Berois, N., Osinaga, E., Magalhaes, A., Pinto-de-Sousa, J., et al. (2009). Expression of UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-6 in gastric mucosa, intestinal metaplasia, and gastric carcinoma. J. Histochem. and Cytochem. 57 (1), 79–86. doi:10.1369/jhc.2008.952283
Gu, J., Zhao, Y., Isaji, T., Shibukawa, Y., Ihara, H., Takahashi, M., et al. (2004). Beta1,4-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase III down-regulates neurite outgrowth induced by costimulation of epidermal growth factor and integrins through the Ras/ERK signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Glycobiology 14 (2), 177–186. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwh016
Han, C., Chen, X., Lan, A., Hsu, Y., Wu, P., Hung, P., et al. (2021). N-glycosylated GPNMB ligand independently activates mutated EGFR signaling and promotes metastasis in NSCLC. Cancer Sci. 112 (5), 1911–1923. doi:10.1111/cas.14872
Herbst, R., Heymach, J., and Lippman, S. (2008). Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 359 (13), 1367–1380. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0802714
Herbst, R. S., Morgensztern, D., and Boshoff, C. (2018). The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553 (7689), 446–454. doi:10.1038/nature25183
Hoffman, E., Song, Y., Zhang, F., Asarian, L., Downs, I., Young, B., et al. (2023). Regional and disease-specific glycosaminoglycan composition and function in decellularized human lung extracellular matrix. Acta Biomater. 168, 388–399. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.06.043
Hu, Z., Chen, P. H., Li, W., Douglas, T., Hines, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Targeted dephosphorylation of tau by phosphorylation targeting chimeras (PhosTACs) as a therapeutic modality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 4045–4055. doi:10.1021/jacs.2c11706
Irmer, D., Funk, J., and Blaukat, A. (2007). EGFR kinase domain mutations - functional impact and relevance for lung cancer therapy. Oncogene 26 (39), 5693–5701. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210383
Izquierdo-Sanchez, L., Lamarca, A., La Casta, A., Buettner, S., Utpatel, K., Klümpen, H. J., et al. (2022). Cholangiocarcinoma landscape in Europe: diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic insights from the ENSCCA Registry. J. Hepatol. 76 (5), 1109–1121. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.010
Jeonghee, C., Liang, C., Naveen, S., Takafumi, O., Kimio, Y., Joshua, M. F., et al. (2013). Cetuximab response of lung cancer-derived EGF receptor mutants is associated with asymmetric dimerization. Cancer Res. 73 (22), 6770–6779. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1145
Jura, N., Endres, N., Engel, K., Deindl, S., Das, R., Lamers, M., et al. (2009). Mechanism for activation of the EGF receptor catalytic domain by the juxtamembrane segment. Cell 137, 1293–1307. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.025
Kamemura, K., Hayes, B. K., Comer, F. I., and Hart, G. W. (2002). Dynamic interplay between O-glycosylation and O-phosphorylation of nucleocytoplasmic proteins - alternative glycosylation/phosphorylation of Thr-58, a known mutational hot spot of c-Myc in lymphomas, is regulated by mitogens. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (21), 19229–19235. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201729200
Keenan, E. K., Zachman, D. K., and Hirschey, M. D. (2021). Discovering the landscape of protein modifications. Mol. Cell 81 (9), 1868–1878. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.015
Kuntz, E. M., Baquero, P., Michie, A. M., Dunn, K., Tardito, S., Holyoake, T. L., et al. (2017). Targeting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation eradicates therapy-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Nat. Med. 23(10), 1234. 1240. doi:10.1038/nm.4399
Li, J., Zhan, H., Ren, Y., Feng, M., Wang, Q., Jiao, Q., et al. (2023). Sirtuin 4 activates autophagy and inhibits tumorigenesis by upregulating the p53 signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 30 (2), 313–326. doi:10.1038/s41418-022-01063-3
Liang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, I., Chen, Y., Li, L., Lin, C., et al. (2017). Interaction of glycosphingolipids GD3 and GD2 with growth factor receptors maintains breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Oncotarget 8 (29), 47454–47473. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17665
Liang, Y., Zhang, H., Tian, L., Shi, C., Zheng, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Gut microbiota and metabolic profile as affected by Maillard reaction products derived from bighead carp meat hydrolysates with galactose and galacto-oligosaccharides during in vitro pig fecal fermentation. Food Chem. 398, 133905. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133905
Ling, Y., Li, T., Perez-Soler, R., and Haigentz, M. J. C. c.pharmacology (2009). Activation of ER stress and inhibition of EGFR N-glycosylation by tunicamycin enhances susceptibility of human non-small cell lung cancer cells to erlotinib. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 64 (3), 539–548. doi:10.1007/s00280-008-0902-8
Liu, Y., Yen, H., Chen, C., Chen, C., Cheng, P., Juan, Y., et al. (2011). Sialylation and fucosylation of epidermal growth factor receptor suppress its dimerization and activation in lung cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (28), 11332–11337. doi:10.1073/pnas.1107385108
Loong, J. H., Wong, T. L., Tong, M., Sharma, R., Zhou, L., Ng, K. Y., et al. (2021). Glucose deprivation-induced aberrant FUT1-mediated fucosylation drives cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Invest 131 (11), e143377. doi:10.1172/jci143377
Lopez Sambrooks, C., Baro, M., Quijano, A., Narayan, A., Cui, W., Greninger, P., et al. (2018). Oligosaccharyltransferase inhibition overcomes therapeutic resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 78 (17), 5094–5106. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-0505
Lu, C., MI, L., Grey, M., Zhu, J., Graef, E., Yokoyama, S., et al. (2010). Structural evidence for loose linkage between ligand binding and kinase activation in the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol. Cell Biol. 30, 5432–5443. doi:10.1128/mcb.00742-10
Ma, Q., Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., Yu, S., Huang, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Post-translational modifications in oral bacteria and their functional impact. Front. Microbiol. 12, 784923. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.784923
Ma, X. F., Li, H., He, Y. T., and Hao, J. W. (2017). The emerging link between O-GlcNAcylation and neurological disorders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 74 (20), 3667–3686. doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2542-9
Matsumoto, K., Yokote, H., Arao, T., Maegawa, M., Tanaka, K., Fujita, Y., et al. (2008). N-Glycan fucosylation of epidermal growth factor receptor modulates receptor activity and sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Sci. 99 (8), 1611–1617. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00847.x
Milani, S., Sottocornola, E., Zava, S., Berselli, P., Berra, B., and Colombo, I. (2007). Ganglioside GM(3) is stably associated to tyrosine-phosphorylated ErbB2/EGFR receptor complexes and EGFR monomers, but not to ErbB2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1771 (7), 873–878. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.04.008
Moloney, D. J., Shair, L. H., Lu, F. M., Xia, J., Locke, R., Matta, K. L., et al. (2000). Mammalian Notch1 is modified with two unusual forms of O-linked glycosylation found on epidermal growth factor-like modules. J. Biol. Chem. 275(13), 9604–9611. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.13.9604
Moremen, K. W., Tiemeyer, M., and Nairn, A. V. (2012). Vertebrate protein glycosylation: diversity, synthesis and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13 (7), 448–462. doi:10.1038/nrm3383
Mozzi, A., Forcella, M., Riva, A., Difrancesco, C., Molinari, F., Martin, V., et al. (2015). NEU3 activity enhances EGFR activation without affecting EGFR expression and acts on its sialylation levels. Glycobiology 25 (8), 855–868. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwv026
Myers, S. A., Peddada, S., Chatterjee, N., Friedrich, T., Tomodo, K., Krings, G., et al. (2016). SOX2 O-GlcNAcylation alters its protein-protein interactions and genomic occupancy to modulate gene expression in pluripotent cells. Elife 5, e10647. doi:10.7554/eLife.10647
Nguyen, K., Kobayashi, S., and Costa, D. (2009). Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin. Lung Cancer 10 (4), 281–289. doi:10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039
Noronha, A., Belugali Nataraj, N., Lee, J., Zhitomirsky, B., Oren, Y., Oster, S., et al. (2022). AXL and error-prone DNA replication confer drug resistance and offer strategies to treat EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 12 (11), 2666–2683. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-22-0111
O'Donnell, N., Zachara, N. E., Hart, G. W., and Marth, J. D. (2004). Ogt-dependent X-chromosome-linked protein glycosylation is a requisite modification in somatic cell function and embryo viability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (4), 1680–1690. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.4.1680-1690.2004
Ogiso, H., Ishitani, R., Nureki, O., Fukai, S., Yamanaka, M., Kim, J., et al. (2002). Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell 110, 775–787. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00963-7
Pagel, O., Loroch, S., Sickmann, A., and Zahedi, R. (2015). Current strategies and findings in clinically relevant post-translational modification-specific proteomics. Expert Rev. proteomics 12 (3), 235–253. doi:10.1586/14789450.2015.1042867
Pao, W., and Chmielecki, J. (2010). Rational, biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10 (11), 760–774. doi:10.1038/nrc2947
Park, J., Yi, J., Jin, Y., Lee, Y., Lee, J., Lee, Y., et al. (2012). Sialylation of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates receptor activity and chemosensitivity to gefitinib in colon cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 83 (7), 849–857. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.007
Patwardhan, A., Cheng, N., and Trejo, J. (2021). Post-Translational modifications of G protein-coupled receptors control cellular signaling dynamics in space and time. Pharmacol. Rev. 73 (1), 120–151. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.120.000082
Pienkowski, T., Kowalczyk, T., Cysewski, D., Kretowski, A., and Ciborowski, M. (2023). Glioma and post-translational modifications: a complex relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1878 (6), 189009. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189009
Reita, D., Pabst, L., Pencreach, E., Guérin, E., Dano, L., Rimelen, V., et al. (2021). Molecular mechanism of EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: application to biological diagnostic and monitoring. Cancers (Basel) 13 (19), 4926. doi:10.3390/cancers13194926
Roskoski, R. (2014). The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 79, 34–74. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002
Rossi, M., Altea-Manzano, P., Demicco, M., Doglioni, G., Bornes, L., Fukano, M., et al. (2022). PHGDH heterogeneity potentiates cancer cell dissemination and metastasis. Nature 605 (7911), 747–753. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04758-2
Ruan, H. B., Singh, J. P., Li, M. D., Wu, J., and Yang, X. Y. (2013). Cracking the O-GlcNAc code in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metabolism 24 (6), 301–309. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2013.02.002
Sacco, F., Seeling, A., Humphrey, S. J., Krahmer, N., Volta, F., Reggio, A., et al. (2019). Phosphoproteomics reveals the GSK3-PDX1 axis as a key pathogenic signaling node in diabetic islets. Cell Metab 29 (6), 1422–1432. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.02.012
Salvi, R., Kumar, C., Brahmbhatt, K., Subedi, R., Idicula-Thomas, S., Madan, T., et al. (2022). N-linked glycosylation in Chinese hamster ovary cells is critical for insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (23), 14952. doi:10.3390/ijms232314952
Sanda, M., Ahn, J., Kozlik, P., and Goldman, R. (2021). Analysis of site and structure specific core fucosylation in liver cirrhosis using exoglycosidase-assisted data-independent LC-MS/MS. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 23273. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-02838-3
Sato, C., Kim, J., Abe, Y., Saito, K., Yokoyama, S., and Kohda, D. (2000). Characterization of the N-oligosaccharides attached to the atypical Asn-X-Cys sequence of recombinant human epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biochem. 127, 65–72. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022585
Savarino, P., Demeyer, M., Decroo, C., Colson, E., and Gerbaux, P. (2023). Mass spectrometry analysis of saponins. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 42 (3), 954–983. doi:10.1002/mas.21728
Schwein, P., and Woo, C. (2020). The O-GlcNAc modification on kinases. Chem. Biol. 15 (3), 602–617. doi:10.1021/acschembio.9b01015
Sequist, L., Waltman, B., Dias-Santagata, D., Digumarthy, S., Turke, A., Fidias, P., et al. (2011). Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 3 (75), 75ra26. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002003
Seshacharyulu, P., Ponnusamy, M., Haridas, D., Jain, M., Ganti, A., and Batra, S. (2012). Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 16 (1), 15–31. doi:10.1517/14728222.2011.648617
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Takahashi, M., Hasegawa, Y., Gao, C., Kuroki, Y., and Taniguchi, N. (2016). N-glycans of growth factor receptors: their role in receptor function and disease implications. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 130 (20), 1781–1792. doi:10.1042/cs20160273
Takeuchi, H., and Haltiwanger, R. (2014). Significance of glycosylation in Notch signaling. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 453 (2), 235–242. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.115
Tang, J., Long, G., Hu, K., Xiao, D., Liu, S., Xiao, L., et al. (2023). Targeting USP8 inhibits O-GlcNAcylation of SLC7A11 to promote ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via stabilization of OGT. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10, e2302953. doi:10.1002/advs.202302953
Tang, Z., and Lu, J. (2018). Osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. 420, 242–246. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.02.004
Tarbet, H. J., Toleman, C. A., and Boyce, M. (2018). A sweet embrace: control of protein-protein interactions by O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine. Biochemistry 57 (1), 13–21. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00871
Thygesen, C., Boll, I., Finsen, B., Modzel, M., and Larsen, M. R. (2018). Characterizing disease-associated changes in post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry. Expert Rev. Proteomics 15 (3), 245–258. doi:10.1080/14789450.2018.1433036
Torres, C. R., and Hart, G. W. (1984). Topography and polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes. Evidence for O-linked GlcNAc. J. Biol. Chem. 259 (5), 3308–3317. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(17)43295-9
Tsuda, T., Ikeda, Y., and Taniguchi, N. (2000). The Asn-420-linked sugar chain in human epidermal growth factor receptor suppresses ligand-independent spontaneous oligomerization. Possible role of a specific sugar chain in controllable receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (29), 21988–21994. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003400200
Tu, H., Xiong, W., Zhang, J., Zhao, X., and Lin, X. (2022). Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates RIPK1 activity to limit cell death and inflammation. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 6603. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34080-4
Uchibori, K., Inase, N., Nishio, M., Fujita, N., and Katayama, R. J. J. o.t.o.o.p.o.t.I. A. f.t.S. o.L. C. (2018). Identification of mutation accumulation as resistance mechanism emerging in first-line osimertinib treatment. J thorac oncol. J. Thorac. Oncol. 13 (7), 915–925. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2018.04.005
Vasaikar, S., Huang, C., Wang, X., Petyuk, V. A., Savage, S. R., Wen, B., et al. (2019). Proteogenomic analysis of human colon cancer reveals new therapeutic opportunities. Cell 177 (4), 1035–1049.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.030
Vu, L. D., Gevaert, K., and De Smet, I. (2018). Protein Language: post-translational modifications talking to each other. Trends Plant Sci. 23 (12), 1068–1080. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2018.09.004
Wang, M., Herbst, R., and Boshoff, C. (2021). Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 27 (8), 1345–1356. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01450-2
Wang, Y., Fukuda, T., Isaji, T., Lu, J., Im, S., Hang, Q., et al. (2015). Loss of α1,6-fucosyltransferase inhibits chemical-induced hepatocellular carcinoma and tumorigenesis by down-regulating several cell signaling pathways. FASEB J. 29 (8), 3217–3227. doi:10.1096/fj.15-270710
Wang, Z., Gucek, M., and Hart, G. W. (2008). Cross-talk between GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in response to globally elevated O-GlcNAc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105 (37), 13793–13798. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806216105
Wang, Z., Li, M., Jiang, H., Luo, S., Shao, F., Xia, Y., et al. (2022). Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 functions as a protein phosphatase to dephosphorylate histone H3 and suppresses PPARα-regulated gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 24 (11), 1655–1665. doi:10.1038/s41556-022-01009-4
Wang, Z., Pandey, A., and Hart, G. W. (2007). Dynamic interplay between O-linked N-acetylglucosaminylation and glycogen synthase kinase-3-dependent phosphorylation. Mol. Cell Proteomics 6 (8), 1365–1379. doi:10.1074/mcp.M600453-MCP200
Whitson, K., Whitson, S., Red-Brewer, M., McCoy, A., Vitali, A., Walker, F., et al. (2005). Functional effects of glycosylation at Asn-579 of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry 44 (45), 14920–14931. doi:10.1021/bi050751j
Wu, D. L., Cai, Y., and Jin, J. G. (2017). Potential coordination role between O-GlcNAcylation and epigenetics. Protein and Cell 8 (10), 713–723. doi:10.1007/s13238-017-0416-4
Wu, S., Kim, J., Hancock, W., and Karger, B. (2005). Extended Range Proteomic Analysis (ERPA): a new and sensitive LC-MS platform for high sequence coverage of complex proteins with extensive post-translational modifications-comprehensive analysis of beta-casein and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). J. Proteome Res. 4, 1155–1170. doi:10.1021/pr050113n
Xiao, Z., Xu, H., Strosberg, J., Lu, R., Zhu, X., Deng, S., et al. (2023). EGFR is a potential therapeutic target for highly glycosylated and aggressive pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Int. J. Cancer 153 (1), 164–172. doi:10.1002/ijc.34499
Yadav, L., Tamene, F., Goos, H., van Drogen, A., Katainen, R., Aebersold, R., et al. (2017). Systematic analysis of human protein phosphatase interactions and dynamics. Cell Syst. 4(4), 430. 444. doi:10.1016/j.cels.2017.02.011
Yang, G. L., Hu, Y. W., Sun, S. S., Ouyang, C. Z., Yang, W. M., Wang, Q., et al. (2018). Comprehensive glycoproteomic analysis of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Anal. Chem. 90 (24), 14294–14302. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03520
Yang, X. Y., and Qian, K. V. (2017). Protein O-GlcNAcylation: emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 18 (7), 452–465. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.22
Yen, H., Liu, Y., Chen, N., Tsai, C., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2015). Effect of sialylation on EGFR phosphorylation and resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 (22), 6955–6960. doi:10.1073/pnas.1507329112
Yim, A., Smith, C., and Brown, A. M. (2022). Osteopontin/secreted phosphoprotein-1 harnesses glial-immune-and neuronal cell ligand-receptor interactions to sense and regulate acute and chronic neuroinflammation. Immunol. Rev. 311 (1), 224–233. doi:10.1111/imr.13081
You, X., Qin, H., and Ye, M. (2018). Recent advances in methods for the analysis of protein o-glycosylation at proteome level. J. Sep. Sci. 41 (1), 248–261. doi:10.1002/jssc.201700834
Zecha, J., Bayer, F. P., Wiechmann, S., Woortman, J., Berner, N., Müller, J., et al. (2023). Decrypting drug actions and protein modifications by dose- and time-resolved proteomics. Science 380 (6640), 93–101. doi:10.1126/science.ade3925
Zhang, L., Gao, Y., Zhang, X., Guo, M., Yang, J., Cui, H., et al. (2020). TSTA3 facilitates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through regulating fucosylation of LAMP2 and ERBB2. Theranostics 10 (24), 11339–11358. doi:10.7150/thno.48225
Zhang, X., Maity, T., Ross, K., Qi, Y., Cultraro, C., Bahta, M., et al. (2021). Alterations in the global proteome and phosphoproteome in third generation EGFR TKI resistance reveal drug targets to circumvent resistance. Cancer Res. 81 (11), 3051–3066. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-2435
Zhen, Y., Caprioli, R., and Staros, J. (2003). Characterization of glycosylation sites of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry 42, 5478–5492. doi:10.1021/bi027101p
Zheng, J., Li, H. L., Tian, N., Liu, F., Wang, L., Yin, Y. L., et al. (2020). Interneuron accumulation of phosphorylated tau impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis by suppressing GABAergic transmission. Cell Stem Cell 26(3), 462. 466. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.01.021
Keywords: EGFR-TKI resistance, phosphorylation, autophosphorylation, glycosylation, crosstalk, NSCLC
Citation: Ma Y, Zhang F, Li J, Li J and Li Y (2024) Diverse perspectives on proteomic posttranslational modifications to address EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1436033. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1436033
Received: 21 May 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 24 December 2024.
Edited by:
Brajendra Tripathi, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United StatesReviewed by:
Yoshiki Murakumo, Kitasato University, JapanCopyright © 2024 Ma, Zhang, Li, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Li, MjM2NDA2MDI0QHFxLmNvbQ==; Yanhua Li, bTE3NzA5ODcwMDU3XzFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.