
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 19 September 2024
Sec. Signaling
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1423665
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) serves as the underlying pathology for various spinal degenerative conditions and is a primary contributor to low back pain (LBP). Recent studies have revealed a strong correlation between IDD and biological processes such as Programmed Cell Death (PCD), cellular senescence, inflammation, cell proliferation, extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, and oxidative stress (OS). Of particular interest is the emerging evidence highlighting the significant involvement of the JNK signaling pathway in these fundamental biological processes of IDD. This paper explores the potential mechanisms through the JNK signaling pathway influences IDD in diverse ways. The objective of this article is to offer a fresh perspective and methodology for in-depth investigation into the pathogenesis of IDD by thoroughly examining the interplay between the JNK signaling pathway and IDD. Moreover, this paper summarizes the drugs and natural compounds that alleviate the progression of IDD by regulating the JNK signaling pathway. This paper aims to identify potential therapeutic targets and strategies for IDD treatment, providing valuable insights for clinical application.
Low back pain (LBP) is a significant global public health concern, causing physical discomfort and potential psychological issues like anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances (Ugwu and Pope, 2023; Rhon et al., 2024). LBP has now emerged as a leading cause of work-related absences, sick leave, and disability worldwide (Wu et al., 2021; Grolier et al., 2023), has become a heavy burden on public health and social economy (Hartvigsen et al., 2018). Approximately 40% of LBP cases are linked to IDD (Luoma et al., 2000). Various factors, including trauma, infection, genetic predisposition, obesity, smoking, aging, and mechanical stress, can trigger molecular, cellular, and tissue alterations in intervertebral discs (IVD), ultimately leading to IDD (Zhang et al., 2024; Silwal et al., 2023; Wang Y. et al., 2020). Recent research has focused on biological treatment options for IDD, such as gene therapy, growth factor therapy, platelet-rich plasma therapy, cell therapy, and tissue engineering implants (Bowles and Setton, 2017; Ekram et al., 2021; Wang S. Z. et al., 2015; Melrose, 2016). However, current treatment strategies primarily target pain relief or pain control rather than reversing IDD at a cellular or molecular level due to a limited understanding of its pathogenesis (Le Maitre et al., 2015; Adams et al., 2010). Therefore, thorough exploration of the disease’s pathogenic mechanisms is crucial for identifying new targets for early diagnosis and treatment of IDD, as well as for guiding effective treatment and rehabilitation efforts.
IVD is composed of highly hydrated gel-shaped nucleus pulposus (NP), annulus fibrosus (AF), and cartilage end plate (CEP) (Kos et al., 2019), playing an important role in maintaining the flexibility and stability of the spine (Sivan et al., 2014). When IDD occurs, there are significant changes in the tissue morphology of the IVD, characterized by the loss of proteoglycans and water in NPs, decreased IVD height, AF rupture, and destruction or calcification of the CEP (Kirnaz et al., 2022; Feng et al., 2017; Edelson and Nathan, 1988). From a cellular perspective, the type, quantity, and function of IVD cells are closely linked to their structural integrity and function. In a healthy IVD, the NP primarily contains notochordal and nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs), while the AF comprises AF cells, and the CEP comprises chondrocytes (Oichi et al., 2020). Notochordal cells disappear from the NP around the age of 10 years (Boos et al., 2002), and their absence is associated with IDD onset (Aguiar et al., 1999; Cappello et al., 2006). IDD may be initiated in early childhood (Yurube et al., 2023). As IDD progresses, the composition of tissue cells within the IVD significantly shifts. Normally, the inner layers of the AF and NP lack blood vessels and nerve tissue, relying on the microvasculature of the adjacent CEP and the surrounding AF for nutrient supply and waste removal (Roberts et al., 2006). However, endothelial cells undergo apoptosis, decreasing endplate microvascular density and impairing nutrient delivery and waste removal in the IVD during IDD (Xu et al., 2019). To compensate for this change, nerve fibers and microvasculature form and grow into the inner layer of the AF, even the NP tissue, forming the anatomical basis for discogenic LBP (Bogduk et al., 1981; Fields et al., 2014; Freemont et al., 2002a). Additionally, immune cells, such as M1 and M2c phenotype macrophages, T lymphocytes, and mast cells, have been detected in degenerative IVD tissues, playing important roles in developing or repairing IVD (Nakazawa et al., 2018; Gorth et al., 2018; Freemont et al., 2002b; Wiet et al., 2017). Notably, a subset of the locally remaining human NPCs generated by a degraded IVD is linked to the development of discogenic pain under specific conditions (Jiang et al., 2023). Although the cell density in the IVD increases during IDD, the number of aging and dead cells continues to rise, accumulating inappropriate metabolites in surviving cells during aging and degradation (Gruber and Hanley, 1998; Hastreiter et al., 2001) (Figure 1). These organizational structures and cell-type alterations are governed by intricate signal transduction networks and interactions with various effector molecules; however, the precise mechanisms remain unclear (Silwal et al., 2023; Vo et al., 2016). Previous studies have indicated that IDD is intricately connected to programmed cell death (PCD), cellular aging, inflammation, proliferation, extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, oxidative stress (OS), and DNA damage (Zhang et al., 2024; Silwal et al., 2023; Yurube et al., 2023; Cao et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023).
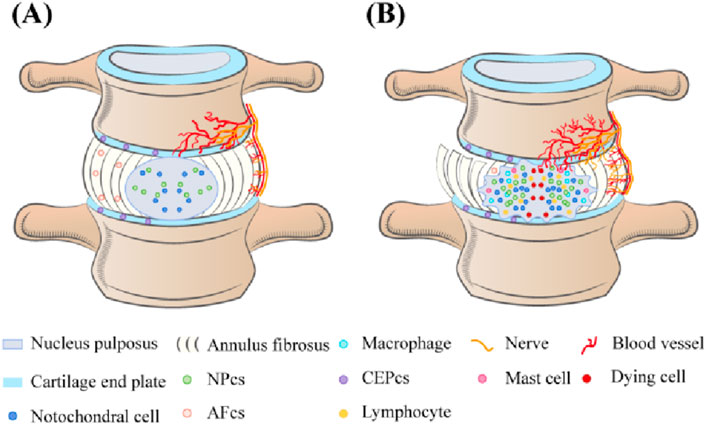
Figure 1. (A) In normal IVD, the cell types in NP are notochord cells and NPCs, in AE are AF cells, and in CEP are chondrocytes. Neurovessels exist only in the outer layers of the AF and CEP. (B) The number of senescent and dead cells in the degenerated IVD continued to increase, cell density increased, and macrophages, T lymphocytes, and mast cells appeared. The density of microvessels in the endplate decreases, and nerve fibers and microvessels form compensatory growth into the inner layer of AF and even NP tissue. Loss of proteoglycans and water in the NP, reduced IVD height, AF rupture, and destruction or calcification of the CEP.
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), also known as stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK), is a key branch of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in mammalian cells (Cui et al., 2007). It plays a significant role in various physiological and pathological (Bogoyevitch and Kobe, 2006; Weston and Davis, 2007). Similar to other MAPK pathways, the JNK pathway is composed of MAP3K (TAK1, MEKK1/4, ASK1, and MLK2/3), MKK4, MKK7, and JNK1/2/3 (Kyriakis et al., 1994; Zeke et al., 2016). Various extracellular stimuli, such as stresses (ultraviolet (UV), mechanical stress, and protein synthesis inhibitors), cytokines [tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-beta (IL-1β)], growth factors, pathogens, hormones, and intracellular stressors (OS and DNA damage),extracellular-derived stress signals are introduced into the cell via the corresponding membrane receptors on the cell membrane and activate the JNK signaling pathway (Minden and Karin, 1997; Ichijo, 1999; Monaghan et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2020; Arthur and Ley, 2013; Hsu et al., 2010). Upon stimulation, MAP3K is activated, leading to the phosphorylation of MKK4 or MKK7. Ultimately, the dual phosphorylation functional region, Thr-Pro-Tyr, of JNK is double phosphorylated by MKK4 or MKK7, activating JNK (Bogoyevitch and Kobe, 2006; Zeke et al., 2016; Yan et al., 2024). This series of phosphorylation events forms a cascade reaction for signal amplification (Figure 2). In this process, MKK7 specifically activates JNK, while MKK4 can simultaneously activate both JNK1 and p38 (Haeusgen et al., 2011; Vander et al., 2005). JNK1/2/3 exhibits high sequence conservation throughout evolution (Gupta et al., 1996; Ait-Hamlat et al., 2020), with JNK1 and JNK2 broadly expressed, and JNK3 predominantly found in the brain, heart, testes, and pancreas (Kyriakis et al., 1994; Xie et al., 1998; Garg et al., 2021; Nakano et al., 2020; Vallerie and Hotamisligil, 2010). Activated JNK enters the nucleus and binds to transcription factors, such as ATF2, Elk-1, and c-Jun, phosphorylating their active regions to regulate specific gene expression (Kyriakis et al., 1994; Barr and Bogoyevitch, 2001). JNK can also phosphorylate non-nuclear proteins, such as mitochondrial BCL-2 family members (BCL-XL and BCL-2) (Kyriakis et al., 1994). Besides the core mechanisms mentioned above, the JNK signaling pathway interacts intricately with other pathways, including PI3K/Akt and NF-ĸB, to influence cell growth, survival, and metabolism (Li S. T. et al., 2018; Dong et al., 2022; Kriehuber et al., 2005). JNK activation and regulation are highly complex, with signal transduction dysfunction playing a crucial role in human diseases. Once the JNK pathway is activated, it will transmit signals by phosphorylating a series of substrates, thus affecting the biological processes of IVD cells such as survival, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Studies have indicated the close relationship between the JNK signaling pathway and processes like PCD, cell aging, inflammation, proliferation, ECM degradation, and OS (Sui et al., 2014; Papaconstantinou, 2019; Pinal et al., 2019; Du X. F. et al., 2023; Levada et al., 2018). Delving into the connection between the JNK signaling pathway and IDD is crucial for uncovering the pathological mechanisms of IDD and identifying new treatment methods and drug targets. This provides new perspectives for IDD treatment and a valuable reference for managing related diseases.
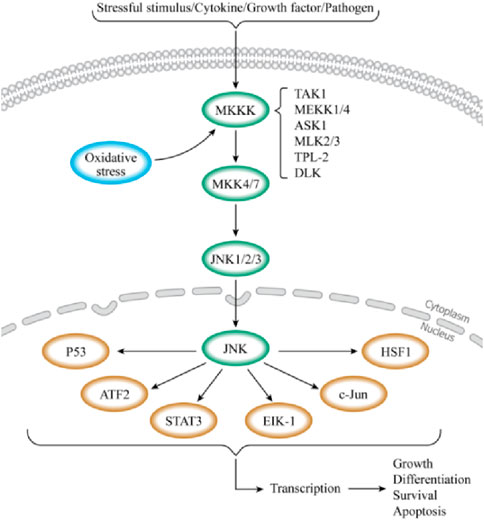
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the JNK signaling pathway. When cells are stimulated by external stimuli or when receptors on the cell membrane bind to ligands, the JNK signaling pathway is triggered. The activation of this pathway is a three-stage cascade that begins with protein signaling. MAP3Ks (TAK1, MEKK1/4, ASK1, and MLK2/3) are activated in this pathway, further phosphorylating MKK4 or MKK7. JNK is also activated upon phosphorylation by MKK4 or MKK7. Then, activated JNK enters the nucleus, binds to transcription factors such as ATF2, Elk-1, and c-Jun, and regulates the specific gene expression by phosphorylating the active regions of these transcription factors. This process regulates physiological processes, such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Extracellular factors, such as mechanical stress, inflammation, and infection, as well as intracellular factors, such as DNA damage, can trigger IDD and activate the JNK signaling pathway. Additionally, biological processes linked to JNK, such as cell death, aging, inflammation, proliferation, ECM breakdown, and OS, are well-documented contributors to IDD. Therefore, we have ample reason to believe a close and profound relationship exists between IDD and the JNK signaling pathway. This provides strong theoretical support and practical guidance to further investigate the association between the JNK signaling pathway and IDD (As is shown in Figure 3).

Figure 3. The activation of JNK signaling pathway resulting in changes of various factors in IVD and eventually disc degeneration.
Currently, PCD forms such as cell apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and PANoptosis have received extensive research attention (Liu et al., 2022). Numerous studies have confirmed that PCD plays a crucial role in the occurrence of IDD (Zhao et al., 2006). Although PANoptosis is a form of PCD, there is currently no literature indicating a direct relationship between it and IDD. However, a relationship between the JNK pathway, cell necroptosis, and pyroptosis has been revealed (Du J. et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2020). Moreover, cell necroptosis and pyroptosis can cause IDD (Khaleque et al., 2023; Luo et al., 2022). However, there is currently insufficient evidence to support whether the JNK pathway is involved in the specific mechanisms of necroptosis and pyroptosis in IDD. Therefore, the mechanism of action of the JNK pathway in necroptosis and pyroptosis in IDD remains unclear, and further research is needed.
Apoptosis is a key factor leading to a decreased number of cells in NP tissues, and this process plays an important role in degrading IVD (Ding et al., 2013). The JNK signaling pathway is closely linked to cell apoptosis, as confirmed by research (Farrell et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022). Recent studies have found that RASSF7 can negatively regulate apoptotic JNK signaling by inhibiting the activity of phosphorylated MKK7 (Takahashi et al., 2011). In human cadaver studies, the RASSF7 expression level was significantly higher in non-degenerative intervertebral disc tissues than in degenerative intervertebral disc tissues (Liu et al., 2015). This discovery suggests that there may be a direct or indirect association between the activation of the JNK signaling pathway and apoptosis of NPCs, and RASSF7 may serve as an inhibitor of the JNK signaling pathway, providing new ideas for treating IDD. Direct evidence suggests that the JNK pathway can mediate the occurrence of IVD via mechanisms such as infection and high osmotic stress. Researchers used animal models infected with Propionibacterium acnes to study and found that it induces apoptosis in NPCs via the Toll-like receptor 2/JNK pathway and mitochondrial-mediated cell death mechanism (Lin et al., 2018). Additionally, animal experiments have shown that signal-regulated kinase-1 facilitated the senescence and apoptosis of NP cells in promoting IDD progression via the JNK/p38 pathway (Zou et al., 2024). Bai et al. showed that by modulating the JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, Baicalin attenuates IL-1β-induced apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells (Bai et al., 2023). Moreover, the JNK signaling pathway is involved in IVD cell apoptosis caused by inflammation. Research has found that TNF-α binding to TNF receptors can activate JNK/ERK-MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in NPCs induces inflammation-induced cell apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2019). Meanwhile, rhTSG-6 can protect NPCs from IL-1β-induced apoptosis and ECM degradation by inhibiting the p38, JNK, and ERK pathways (Pei et al., 2020). The JNK signaling pathway also involves other molecular mechanisms linked to IVD cell apoptosis. For example, glycyrrhizin can inhibit the expression of high mobility group protein box1 (HMGB1) via the p38/p-JNK signaling pathway, thereby reducing inflammation and cell apoptosis in human NP (Liu et al., 2019). In summary, there is a close correlation between the JNK pathway and apoptosis in IVD cells. Excessive JNK activation in IVD cells is the main driving factor for IVD cell apoptosis, reduced ECM production, and IDD progression. Therefore, in-depth research on the mechanism of the JNK pathway in IDD is of great significance for revealing the pathological process of IDD and for developing new treatment strategies.
Autophagy is significantly enhanced in degenerative IVD cells than in normal IVD cells (Ye et al., 2013). Xu et al. (2015) found that inhibition of NF-κB and JNK pathways can enhance autophagy in NPCs of rat. Research has found that overexpression of islet amyloid polypeptide upregulates the phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR while downregulating the expression of phosphorylated p38 and JNK, as well as downregulating the gene expression such as Bcl-2, Beclin-1, and ATG5, increasing autophagy and reducing apoptosis in NPCs (Wu et al., 2017). Li Z. et al. (2021) revealed that compressive stress induces NPCs autophagy by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activating the JNK pathway. JNK pathway inhibition caused cell death and increased ROS generation, decreasing NP cell autophagy capacity. Additionally, Zhang Y. et al. (2023) conducted experiments on large-eared white female rabbits and discovered the tension load-induced cartilage endplate stem cell (CESC) degeneration model, inhibiting the expression of JNK and ERK can inhibit the phosphorylation of Raptor and mTOR in the mTOR signaling pathway, thereby increasing the autophagy level of CESC and alleviating its degradation. In Berberine’s research on preventing OS-induced cell apoptosis, the IRE1/JNK pathway induced endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent autophagy (Luo et al., 2019). This evidence indicates that the JNK pathway plays a complex and important regulatory role in autophagy in IVD cells.
Ferroptosis plays an important role in IDD (Wang et al., 2022). The JNK signaling pathway is crucial for ferroptosis-induced degenerative lesions (Sun et al., 2023). Lu et al. found that (Lu et al., 2021) Hinokitiol enhances the nuclear translocation of metal-regulated transcription factor 1 by inhibiting the JNK pathway, restoring the normal function of FPN, reducing intercellular iron overload under OS, protecting human NPCs from iron death, and improving the progression of IDD in vivo. This indicates that the JNK signaling pathway plays a role in the ferroptosis mechanism of IVD cells. However, further research is needed to elucidate its mechanism due to the limited research on the involvement of the JNK signaling pathway in the ferroptosis mechanism of IVD cells.
The hallmarks of IDD are ECM degradation, apoptosis, and inflammation (Cazzanelli and Wuertz-Kozak, 2020). Multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF and IL-1β. Increased IL-6 and IL-17 levels cause IVD tissue degeneration and pain induction (Risbud and Shapiro, 2014). Evidence suggests that the JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the increased expression of inflammatory factors in IVD. Specifically, IL-17A activates the JNK and P38-MAPK signaling pathways, increasing COX2 expression and PGE2 production in an activating protein-1 -dependent manner and mediating IVD inflammation (Li J. K. et al., 2016). Additionally, Visfatin upregulates IL-6 expression in NPCs by activating the JNK/ERK/p38-MAPK signaling pathway (Cui et al., 2021). IL-1β-induced inflammatory response and pain in IVD cells (Li W. et al., 2015). Tanshinone IIA regulates the expression of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1, p38, JNK, and NF-κB signaling pathway to effectively inhibit inflammatory response and pain in IVD cells. Additionally, studies have shown that piperine inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS) mediated JNK phosphorylation, and NF-κB activation significantly reduced IL-1β and TNF-α. The expression of various inflammatory factors, such as IL-6 and OS-related genes (Li Y. et al., 2015). The JNK signaling pathway also participates in the inflammatory process of IVD via other pathways. Sesamin and Carthamin yellow effectively inhibited NP cell matrix degradation and inflammation induced by LPS via the MAPK signaling pathway by inhibiting the JNK/P38/ERK phosphorylation (Chen et al., 2017; Li K et al., 2016). Acacetin enhances antioxidant protein expression, such as HO-1, NQO1, and SOD, by activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting phosphorylation of p38, JNK, and ERK1/2, thereby improving inflammation and matrix degradation in NPCs (Wang H. et al., 2020). JNK signaling pathways cross-interact with other signaling pathways, jointly participating in the inflammatory process in IDD. Animal experiments have shown that the JNK signaling pathway plays an important role in Wnt5a’s inhibition of inflammation, leading to IDD via the TNF-α/NF-κB Wnt5a negative feedback loop (Li Z. et al., 2018). Chen et al. (2021) found that Dehydroostus lactone can inhibit the activation of JNK/P38 mapk/ERK and NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway, and improve the aging of NPCs activated by the STING-TBK1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Besides, the JNK signaling pathway can exert their effect in the inflammatory response in IVD induced by pro-inflammatory macrophages. Inhibiting the JNK pathway can reduce metabolic and inflammatory gene expression induced by M1 polarized RAW264.7 cells (Ni et al., 2019). In summary, the JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in inflammatory factor expression and inflammatory processes in IVD. Comprehensively studying its potential therapeutic targets and implementing targeted interventions is an important direction for alleviating IDD and treating discogenic pain.
ECM degradation, an important criterion for IDD, has always been a hot research topic regarding its regulatory mechanism (Cazzanelli and Wuertz-Kozak, 2020). Specific stimuli or substances play a crucial role in ECM metabolism in IVD cells by regulating the JNK pathway activity. The JNK signaling pathway independently regulates ECM metabolism in IVD cells and interacts with other signaling pathways to regulate the metabolic balance of the ECM. Research has indicated that under hypoxic conditions, the JNK signaling pathway is involved in the ECM degradation of NPCs induced by serum deprivation by activating JNK1/2 (Wang et al., 2017). Additionally, Rhizoma drynariae total flavonoids were extracted from Drynaria fortunei J. Sm reduced the matrix metalloproteins expression by inhibiting the JNK/P38-MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and regulating the expression of aggregates and collagen types I, II, and III, thereby effectively inhibiting ECM degradation. This discovery reveals the potential of traditional Chinese medicine in treating ECM degradation by regulating the JNK signaling pathway (Zhao et al., 2021). The JNK signaling pathway can interact with other pathways to regulate ECM metabolism. For example, FAM20B regulates TGF-β. The JNK/P38-MAPK/ERK signaling pathway affects glycosaminoglycans synthesis, thereby regulating ECM metabolism and cell degeneration in AF cells (Saiyin et al., 2019). Additionally, platelet-driven growth factor-BB promotes ECM metabolism in NPCs by regulating the ERK, JNK, and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways while inhibiting pyroptosis and the production of pyroptosis products in NPCs (Zhang et al., 2022). The JNK signaling pathway also promotes an imbalance in extracellular matrix metabolism in NPCs by M2a macrophages (Li L. et al., 2021). Therefore, the JNK signaling pathway is crucial in regulating ECM metabolism.
Cellular senescence (CS) is a key factor in aging, and aging cells accumulate continuously with age (Roger et al., 2021). Aging has been proven to be the primary cause of IDD, and CS is an important mechanism for IDD occurrence (Silwal et al., 2023). During this process, the JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in CS (Papaconstantinou, 2019; Grootaert et al., 2021). Further research has indicated that the JNK signaling pathway plays an important role in the aging of IVD cells. Specifically, stress can activate the cascade response of the JNK signaling pathway, thereby participating in stress-induced premature aging of IVD cells (Patil et al., 2018; Maruyama et al., 2009). Additionally, studies have shown that activation of heat shock protein 70 can inhibit the JNK/c-Jun pathway and hinder apoptosis and aging of human NP stem cells induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (Zhang et al., 2021). However, the mechanism by which the JNK signaling pathway regulates intervertebral disc cell aging remains unclear due to relatively limited research. Therefore, more in-depth research is needed to explore this issue and to confirm whether the JNK signaling pathway may be a direct therapeutic target for reducing IVD cell aging. This will provide new ideas and directions for treating IDD and relieving discogenic pain.
The normal physiological function of IVD tissue is established based on healthy cell proliferation and tissue repair ability (Bhujel et al., 2022). The close relationship between the JNK signaling pathway and cell proliferation has attracted attention during this process (Wang JX et al., 2023). Previous research has shown that the JNK signaling pathway plays an important regulatory role in IVD cell proliferation, and its abnormal activation may inhibit IVD cell proliferation, thereby accelerating IDD development. Dimozi et al. (2015) confirmed this by finding that the p38-MAPK, ERK, and JNK signaling pathways are involved in H2O2-induced G1 cell cycle delay and reduced cell proliferation in NPCs. Additionally, TNF-α, an important inflammatory factor, is NF-κB. The JNK and p38-MAPK pathways regulate the proliferation of NPCs (Wang X. H. et al., 2015). The JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in regulating IVD cell proliferation, providing new perspectives and ideas to understand the pathogenesis of IDD at the molecular level.
ROS and OS are closely related to the occurrence of IDD (Feng et al., 2017). Excessive ROS generation triggers the OS response of IVD cells (Suzuki et al., 2015). The JNK signaling pathway is involved in ROS accumulation in IVD cells during this process. In the rat tailbone IDD model, andrographolide upregulated the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), p-Nrf2, p-p38, p-Erk1/2, and p-JNK, activating the MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and effectively inhibiting static mechanical pressure-induced apoptosis and ROS accumulation in NPC (Zhang C. et al., 2023). Additionally, the JNK signaling pathway plays an important role in the OS response of IVD cells. Research has shown that the JNK/P-38/ERK signaling pathway is involved in mediating the inhibitory effect of amobarbital and N-acetylcysteine on OS in NPCs (Seol et al., 2021). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells rapidly promote mitophagy via the JNK signaling pathway in the early stages of IDD OS. However, they reduce mitophagy and increase apoptosis in the later stages, demonstrating their complex regulatory mechanisms in response to OS (Fan et al., 2019). Although there is currently relatively limited research on the JNK signaling pathway in OS in IVD cells, it can be concluded that the JNK signaling pathway plays an irreplaceable role in the OS mechanism in IVD cells.
The JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of IDD and simultaneously participates in multiple regulatory processes. Tang et al. (2018) found that Honoriol inhibits the XNIP/NLRP3/caspase-1/interleukin-1 signaling axis by effectively blocking the activation of NF-kB and JNK, thereby mitigating H2O2-induced apoptosis, OS, and inflammatory responses in NPCs. Similarly, Chen et al. (2020) found that quinazoline dephosphorylates key signaling molecules, such as IKKβ, IκBα, and NFs, such as p65, ERK, JNK, and p38, thereby inhibiting IL-1β-induced OS and inflammation via the NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathway, promoting cell proliferation, and preventing NP cell degeneration. Since IL-1β can activate p38 MAPK, c-Jun, and NF-κB signaling pathways, leading to IVD degeneration, inhibiting the IL-1β signaling pathway is crucial in preventing IDD progression (Daniels et al., 2017). Wang et al. conducted Network pharmacological analysis and revealed that the active compound Kaempferol in Eucommia ulmoides significantly reduces IL-1β levels and promotes phosphorylation of p38, JNK, and ERK1/2, thereby protecting NPCs from IL-1β-induced damage via multiple mechanisms (Wang X. et al., 2023). Furthermore, the JNK signaling pathway regulates IDD via various pathways. Reports indicate that high-temperature requirement A1 regulates ADAMTS expression in human NPCs via the JNK pathway, thereby contributing to IDD development (Li et al., 2019). Syndecan-4 also influences NP cell function and IDD progression by activating the JNK and p53 signaling pathways (Ge et al., 2020). Leptin upregulates catabolic gene expression in rat NPCs by modulating the JNK/P38-MAPK/ERK and JAK2/STAT3 pathways (Miao and Zhang, 2015). Hu et al. (2018) found that TGF-β stimulates the expression of chondroitin polymerizing factor and sulfated glycosaminoglycan in NPCs via various signaling pathways, including Smad3, RhoA/ROCK1, JNK, p38, and ERK1/2. This highlights the potential therapeutic role of TGF-β in IDD.
From the foregoing, it can be inferred that in the process of IDD, apoptosis, OS, inflammation, and ECM degradation may occurr at the same time; And apoptosis and cell aging may occurr at the same time. However, whether these processes occur in parallel or simultaneously when IDD is present, is not supported by evidence and further research is needed to confirm.
As summarized above, the JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the pathological process of IDD. Research on drugs and natural compounds that alleviate the progression of IDD by regulating the JNK signaling pathway is of great significance. However, according to literature searches, there are currently very limited reports on how drugs and natural compounds influence the progression of IDD through the regulation of the JNK pathway. Only 19 drugs or natural compounds that can regulate the JNK pathway to affect the progression of IDD have been identified in published literature (Regulation mechanism of the JNK pathway and research conclusions are shown in Table 1). Therefore, there is broad potential and significant room for exploration in the treatment of IDD with drugs and natural compounds targeting the JNK signaling pathway. We should enhance the development and research of clinical drugs targeting the JNK pathway and build evidence-based support based on big data to further promote its application and development in the field of IDD treatment.
This study provides an overview of the pathogenic mechanism of IDD and discusses the current research status of the role of the JNK signaling pathway in IDD. The JNK signaling pathway regulates IDD by influencing various cellular mechanisms such as PCD, cell aging, inflammation, proliferation, ECM degradation, and OS. Furthermore, upstream and downstream signaling molecules of the JNK pathway can impact physiological processes like intervertebral disc PCD, inflammation, and ECM degradation by modulating the JNK pathway. However, there is limited literature on the involvement of cell aging, OS, and ferroptosis in JNK and IDD, and further research is needed to explore the relationship between IVD cell pyroptosis, necroptosis, pan-apoptosis, and the JNK signaling pathway in IDD. The JNK pathway interacts with multiple cellular mechanisms in IDD and can crosstalk with other signaling pathways, presenting a challenge in achieving precise targeted treatment of IDD without disrupting the normal IVD cell function. This study discusses various drugs and natural compounds that regulate IDD via the JNK signaling pathway. However, specific regulatory targets and mechanisms of the JNK pathway in IDD remain unclear. This study encourages researchers to further investigate the JNK signaling pathway in IDD to gain a better understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of IDD, but related research is scarce, and mostly non-clinical. Therefore, there is no clear evidence that the above-mentioned drugs or natural compounds can be applied in humans, and their effectiveness and safety remain to be studied. This will enhance the development of targeted therapies for IDD, using JNK as a therapeutic target, leading to more effective treatment strategies and innovative approaches.
GL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LG: Writing–review and editing, Visualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. YW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XX: Writing–review and editing, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. XG: Writing–review and editing, Validation, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. XW: Writing–review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization.
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study was funded by the Research topics in traditional Chinese medicine, Heilongjiang Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023 China (ZHY2023-131).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adams, M. A., Stefanakis, M., and Dolan, P. (2010). Healing of a painful intervertebral disc should not be confused with reversing disc degeneration: implications for physical therapies for discogenic back pain. Clin. Biomech. (Bristol, Avon) 25 (10), 961–971. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2010.07.016
Aguiar, D. J., Johnson, S. L., and Oegema, T. R. (1999). Notochordal cells interact with nucleus pulposus cells: regulation of proteoglycan synthesis. Exp. Cell Res. 246 (1), 129–137. doi:10.1006/excr.1998.4287
Ait-Hamlat, A., Zea, D. J., Labeeuw, A., Polit, L., Richard, H., and Laine, E. (2020). Transcripts' evolutionary history and structural dynamics give mechanistic insights into the functional diversity of the JNK family. J. Mol. Biol. 432 (7), 2121–2140. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.032
Arthur, J. S. C., and Ley, S. C. (2013). Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13 (9), 679–692. doi:10.1038/nri3495
Bai, X., Yao, M., Zhu, X., Lian, Y., and Zhang, M. (2023). Baicalin suppresses interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and extracellular matrix degradation in human nucleus pulposus cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 45 (4), 433–442. doi:10.1080/08923973.2023.2165942
Barr, R. K., and Bogoyevitch, M. A. (2001). The c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase family of mitogen-activated protein kinases (JNK MAPKs). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 33 (11), 1047–1063. doi:10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00093-0
Bhujel, B., Shin, H. E., Choi, D. J., and Han, I. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and intervertebral disc regeneration: review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (13), 7306. doi:10.3390/ijms23137306
Bogduk, N., Tynan, W., and Wilson, A. S. (1981). The nerve supply to the human lumbar intervertebral discs. J. Anat. 132 (Pt 1), 39–56.
Bogoyevitch, M. A., and Kobe, B. (2006). Uses for JNK: the many and varied substrates of the c-Jun N-terminal kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70 (4), 1061–1095. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00025-06
Boos, N., Weissbach, S., Rohrbach, H., Weiler, C., Spratt, K. F., and Nerlich, A. G. (2002). Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27 (23), 2631–2644. doi:10.1097/00007632-200212010-00002
Bowles, R. D., and Setton, L. A. (2017). Biomaterials for intervertebral disc regeneration and repair. Biomaterials 129, 54–67. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.03.013
Cao, G., Yang, S., Cao, J., Tan, Z., Wu, L., Dong, F., et al. (2022). The role of oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2166817. doi:10.1155/2022/2166817
Cappello, R., Bird, J. L., Pfeiffer, D., Bayliss, M. T., and Dudhia, J. (2006). Notochordal cell produce and assemble extracellular matrix in a distinct manner, which may be responsible for the maintenance of healthy nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31 (8), 873–882. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000209302.00820.fd
Cazzanelli, P., and Wuertz-Kozak, K. (2020). MicroRNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration, apoptosis, inflammation, and mechanobiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (10), 3601. doi:10.3390/ijms21103601
Chen, B., Wang, H. T., Yu, B., Zhang, J. D., and Feng, Y. (2017). Carthamin yellow inhibits matrix degradation and inflammation induced by LPS in the intervertebral disc via suppression of MAPK pathway activation. Exp. Ther. Med. 14 (2), 1614–1620. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4645
Chen, Z., Song, J., Xie, L., Xu, G., Zheng, C., Xia, X., et al. (2023). N6-methyladenosine hypomethylation of circGPATCH2L regulates DNA damage and apoptosis through TRIM28 in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 30 (8), 1957–1972. doi:10.1038/s41418-023-01190-5
Chen, Z., Yang, X., Zhou, Y., Liang, Z., Chen, C., Han, C., et al. (2021). Dehydrocostus lactone attenuates the senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of STING-TBK1/NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 641098. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.641098
Chen, Z.-B., Yu, Y.-B., Wa, Q.-B., Zhou, J.-W., He, M., and Cen, Y. (2020). The role of quinazoline in ameliorating intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting oxidative stress and anti-inflammation via NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24 (4), 2077–2086. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202002_20387
Cui, H., Du, X., Liu, C., Chen, S., Cui, H., Liu, H., et al. (2021). Visfatin promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by inducing IL-6 expression through the ERK/JNK/p38 signalling pathways. Adipocyte 10 (1), 201–215. doi:10.1080/21623945.2021.1910155
Cui, J., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y. Q., and Xu, Z. H. (2007). JNK pathway: diseases and therapeutic potential. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 28 (5), 601–608. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00579.x
Daniels, J., Binch, A. A., and Le Maitre, C. L. (2017). Inhibiting IL-1 signaling pathways to inhibit catabolic processes in disc degeneration. J. Orthop. Res. 35 (1), 74–85. doi:10.1002/jor.23363
Dimozi, A., Mavrogonatou, E., Sklirou, A., and Kletsas, D. (2015). Oxidative stress inhibits the proliferation, induces premature senescence and promotes a catabolic phenotype in human nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells. Eur. Cell Mater 30, 89–102. doi:10.22203/ecm.v030a07
Ding, F., Shao, Z. W., and Xiong, L. M. (2013). Cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis 18 (7), 777–785. doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0839-1
Dong, Y., Zheng, Y., Zhu, L., Li, T., Guan, Y., Zhao, S., et al. (2022). Hua-tan-sheng-jing decoction treats obesity with oligoasthenozoospermia by up-regulating the PI3K-AKT and down-regulating the JNK MAPK signaling pathways: at the crossroad of obesity and oligoasthenozoospermia. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 896434. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.896434
Du, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, J., Huo, S., Li, B., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Necroptosis and NLPR3 inflammasome activation mediated by ROS/JNK pathway participate in AlCl3-induced kidney damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 178, 113915. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2023.113915
Du, X. F., Huang, K., Chen, X. Y., Huang, C. H., Cao, H. Y., Wang, G. J., et al. (2023). Gremlin-1 promotes IL-1β-stimulated chondrocyte inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation via activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 37 (9), e23404. doi:10.1002/jbt.23404
Edelson, J. G., and Nathan, H. (1988). Stages in the natural history of the vertebral end-plates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 13 (1), 21–26. doi:10.1097/00007632-198801000-00006
Ekram, S., Khalid, S., Salim, A., and Khan, I. (2021). Regulating the fate of stem cells for regenerating the intervertebral disc degeneration. World J. Stem Cells 13 (12), 1881–1904. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1881
Fan, P., Yu, X. Y., Xie, X. H., Chen, C. H., Zhang, P., Yang, C., et al. (2019). Mitophagy is a protective response against oxidative damage in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 229, 36–45. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.027
Farrell, L., Puig-Barbe, A., Haque, M. I., Amcheslavsky, A., Yu, M., Bergmann, A., et al. (2022). Actin remodeling mediates ROS production and JNK activation to drive apoptosis-induced proliferation. PLoS Genet. 18 (12), e1010533. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1010533
Feng, C., Yang, M., Lan, M., Liu, C., Zhang, Y., Huang, B., et al. (2017). ROS: crucial intermediators in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 5601593. doi:10.1155/2017/5601593
Fields, A. J., Liebenberg, E. C., and Lotz, J. C. (2014). Innervation of pathologies in the lumbar vertebral end plate and intervertebral disc. Spine J. 14 (3), 513–521. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.06.075
Freemont, A. J., Jeziorska, M., Hoyland, J. A., Rooney, P., and Kumar, S. (2002b). Mast cells in the pathogenesis of chronic back pain: a hypothesis. J. Pathol. 197 (3), 281–285. doi:10.1002/path.1107
Freemont, A. J., Watkins, A., Le Maitre, C., Baird, P., Jeziorska, M., Knight, M. T., et al. (2002a). Nerve growth factor expression and innervation of the painful intervertebral disc. J. Pathol. 197 (3), 286–292. doi:10.1002/path.1108
Garg, R., Kumariya, S., Katekar, R., Verma, S., Goand, U. K., and Gayen, J. R. (2021). JNK signaling pathway in metabolic disorders: an emerging therapeutic target. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 901, 174079. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174079
Ge, J., Cheng, X., Yuan, C., Qian, J., Wu, C., Cao, C., et al. (2020). Syndecan-4 is a novel therapeutic target for intervertebral disc degeneration via suppressing JNK/p53 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 16 (5), 766–776. doi:10.7150/ijbs.40189
Gorth, D. J., Shapiro, I. M., and Risbud, M. V. (2018). Transgenic mice overexpressing human TNF-α experience early onset spontaneous intervertebral disc herniation in the absence of overt degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 10 (1), 7. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1246-x
Grolier, M., Lanhers, C., Lefevre-Colau, M. M., Pereira, B., and Coudeyre, E. (2023). Return-to-work self-efficacy questionnaires are relevant for people with chronic non-specific low back pain. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 66 (3), 101716. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2022.101716
Grootaert, M. O. J., Finigan, A., Figg, N. L., Uryga, A. K., and Bennett, M. R. (2021). SIRT6 protects smooth muscle cells from senescence and reduces atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 128 (4), 474–491. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318353
Gruber, H. E., and Hanley, E. N. (1998). Analysis of aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Comparison of surgical specimens with normal controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23 (7), 751–757. doi:10.1097/00007632-199804010-00001
Gupta, S., Barrett, T., Whitmarsh, A. J., Cavanagh, J., Sluss, H. K., Dérijard, B., et al. (1996). Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors. EMBO J. 15 (11), 2760–2770. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00636.x
Haeusgen, W., Herdegen, T., and Waetzig, V. (2011). The bottleneck of JNK signaling: molecular and functional characteristics of MKK4 and MKK7. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 90 (6-7), 536–544. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.11.008
Hartvigsen, J., Hancock, M. J., Kongsted, A., Louw, Q., Ferreira, M. L., Genevay, S., et al. (2018). What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet 391 (10137), 2356–2367. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30480-X
Hastreiter, D., Ozuna, R. M., and Spector, M. (2001). Regional variations in certain cellular characteristics in human lumbar intervertebral discs, including the presence of alpha-smooth muscle actin. J. Orthop. Res. 19 (4), 597–604. doi:10.1016/S0736-0266(00)00069-3
Hsu, H. J., Lee, C. F., Locke, A., Vanderzyl, S. Q., and Kaunas, R. (2010). Stretch-induced stress fiber remodeling and the activations of JNK and ERK depend on mechanical strain rate, but not FAK. PLoS One 5 (8), e12470. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012470
Hu, B., Xu, C., Cao, P., Tian, Y., Zhang, Y., Shi, C., et al. (2018). TGF-Β stimulates expression of chondroitin polymerizing factor in nucleus pulposus cells through the Smad3, RhoA/ROCK1, and MAPK signaling pathways. J. Cell Biochem. 119 (1), 566–579. doi:10.1002/jcb.26215
Ichijo, H. (1999). From receptors to stress-activated MAP kinases. Oncogene 18 (45), 6087–6093. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203129
Jiang, W., Glaeser, J. D., Kaneda, G., Sheyn, J., Wechsler, J. T., Stephan, S., et al. (2023). Intervertebral disc human nucleus pulposus cells associated with back pain trigger neurite outgrowth in vitro and pain behaviors in rats. Sci. Transl. Med. 15 (725), eadg7020. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.adg7020
Khaleque, M. A., Kim, J. H., Hwang, B. J., Kang, J. K., Quan, M., and Kim, Y. Y. (2023). Role of necroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (20), 15292. doi:10.3390/ijms242015292
Kirnaz, S., Capadona, C., Wong, T., Goldberg, J. L., Medary, B., Sommer, F., et al. (2022). Fundamentals of intervertebral disc degeneration. World Neurosurg. 157, 264–273. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2021.09.066
Kos, N., Gradisnik, L., and Velnar, T. (2019). A brief review of the degenerative intervertebral disc disease. Med. Arch. 73 (6), 421–424. doi:10.5455/medarh.2019.73.421-424
Kriehuber, E., Bauer, W., Charbonnier, A. S., Winter, D., Amatschek, S., Tamandl, D., et al. (2005). Balance between NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activity controls dendritic cell life and death. Blood 106 (1), 175–183. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-08-3072
Kyriakis, J. M., Banerjee, P., Nikolakaki, E., Dai, T., Rubie, E. A., Ahmad, M. F., et al. (1994). The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature 369 (6476), 156–160. doi:10.1038/369156a0
Le Maitre, C. L., Binch, A. L., Thorpe, A. A., and Hughes, S. P. (2015). Degeneration of the intervertebral disc with new approaches for treating low back pain. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 59 (1), 47–61.
Levada, K., Guldiken, N., Zhang, X., Vella, G., Mo, F. R., James, L. P., et al. (2018). Hsp72 protects against liver injury via attenuation of hepatocellular death, oxidative stress, and JNK signaling. J. Hepatol. 68 (5), 996–1005. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2018.01.003
Li, D., Wu, Y., Wu, Y., Ni, C., Jiang, P., Li, J., et al. (2019). HtrA1 upregulates the expression of ADAMTS-5 in HNPCs via the ERK/NF-κB/JNK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (8), 5114–5121.
Li, J. K., Nie, L., Zhao, Y. P., Zhang, Y. Q., Wang, X., Wang, S. S., et al. (2016). IL-17 mediates inflammatory reactions via p38/c-Fos and JNK/c-Jun activation in an AP-1-dependent manner in human nucleus pulposus cells. J. Transl. Med. 14, 77. doi:10.1186/s12967-016-0833-9
Li, K., Li, Y., Ma, Z., and Zhao, J. (2015). Crocin exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-catabolic effects on rat intervertebral discs by suppressing the activation of JNK. Int. J. Mol. Med. 36 (5), 1291–1299. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2015.2359
Li, K., Li, Y., Xu, B., Mao, L., and Zhao, J. (2016). Sesamin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and extracellular matrix catabolism in rat intervertebral disc. Connect. Tissue Res. 57 (5), 347–359. doi:10.1080/03008207.2016.1182998
Li, L., Wei, K., Ding, Y., Ahati, P., Xu, H., Fang, H., et al. (2021). M2a macrophage-secreted CHI3L1 promotes extracellular matrix metabolic imbalances via activation of IL-13rα2/MAPK pathway in rat intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Immunol. 12, 666361. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.666361
Li, S. T., Dai, Q., Zhang, S. X., Liu, Y. J., Yu, Q. Q., Tan, F., et al. (2018). Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-κB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 39 (8), 1294–1304. doi:10.1038/aps.2017.143
Li, W., Zhang, Y., Xing, C., and Zhang, M. (2015). Tanshinone IIA represses inflammatory response and reduces radiculopathic pain by inhibiting IRAK-1 and NF-κB/p38/JNK signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 28 (1), 382–389. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2015.06.032
Li, Y., Li, K., Hu, Y., Xu, B., and Zhao, J. (2015). Piperine mediates LPS induced inflammatory and catabolic effects in rat intervertebral disc. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8 (6), 6203–6213.
Li, Z., Wang, J., Deng, X., Huang, D., Shao, Z., and Ma, K. (2021). Compression stress induces nucleus pulposus cell autophagy by inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and activation of the JNK pathway. Connect. Tissue Res. 62 (3), 337–349. doi:10.1080/03008207.2020.1736578
Li, Z., Zhang, K., Li, X., Pan, H., Li, S., Chen, F., et al. (2018). Wnt5a suppresses inflammation-driven intervertebral disc degeneration via a TNF-α/NF-κB-Wnt5a negative-feedback loop. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 26 (7), 966–977. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2018.04.002
Lin, Y., Jiao, Y., Yuan, Y., Zhou, Z., Zheng, Y., Xiao, J., et al. (2018). Propionibacterium acnes induces intervertebral disc degeneration by promoting nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via the TLR2/JNK/mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 7 (1), 1. doi:10.1038/s41426-017-0002-0
Liu, J., Hong, M., Li, Y., Chen, D., Wu, Y., and Hu, Y. (2022). Programmed cell death tunes tumor immunity. Front. Immunol. 13, 847345. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.847345
Liu, X., Zhuang, J., Wang, D., Lv, L., Zhu, F., Yao, A., et al. (2019). Glycyrrhizin suppresses inflammation and cell apoptosis by inhibition of HMGB1 via p38/p-JUK signaling pathway in attenuating intervertebral disc degeneration. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (8), 5105–5113.
Liu, Z., Yao, X., Jiang, W., Li, W., Zhu, S., Liao, C., et al. (2020). Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J. Neuroinflammation 17 (1), 90. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-01751-2
Liu, Z. H., Huo, J. L., Wu, Z. G., Sun, Z., Bai, F., Samartzis, D., et al. (2015). RASSF7 expression and its regulatory roles on apoptosis in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8 (12), 16097–16103.
Lu, S., Song, Y., Luo, R., Li, S., Li, G., Wang, K., et al. (2021). Ferroportin-dependent iron homeostasis protects against oxidative stress-induced nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 6670497. doi:10.1155/2021/6670497
Luo, J., Yang, Y., Wang, X., Chang, X., and Fu, S. (2022). Role of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration and its therapeutic implications. Biomolecules 12 (12), 1804. doi:10.3390/biom12121804
Luo, R., Liao, Z., Song, Y., Yin, H., Zhan, S., Li, G., et al. (2019). Berberine ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by modulating ER stress and autophagy in human nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 228, 85–97. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.064
Luoma, K., Riihimäki, H., Luukkonen, R., Raininko, R., Viikari-Juntura, E., and Lamminen, A. (2000). Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25 (4), 487–492. doi:10.1097/00007632-200002150-00016
Maruyama, J., Naguro, I., Takeda, K., and Ichijo, H. (2009). Stress-activated MAP kinase cascades in cellular senescence. Curr. Med. Chem. 16 (10), 1229–1235. doi:10.2174/092986709787846613
Melrose, J. (2016). Strategies in regenerative medicine for intervertebral disc repair using mesenchymal stem cells and bioscaffolds. Regen. Med. 11 (7), 705–724. doi:10.2217/rme-2016-0069
Miao, D., and Zhang, L. (2015). Leptin modulates the expression of catabolic genes in rat nucleus pulposus cells through the mitogen-activated protein kinase and Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 12 (2), 1761–1768. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.3646
Minden, A., and Karin, M. (1997). Regulation and function of the JNK subgroup of MAP kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1333 (2), F85–F104. doi:10.1016/s0304-419x(97)00018-8
Monaghan, D., O'Connell, E., Cruickshank, F. L., O'Sullivan, B., Giles, F. J., Hulme, A. N., et al. (2014). Inhibition of protein synthesis and JNK activation are not required for cell death induced by anisomycin and anisomycin analogues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 443 (2), 761–767. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.041
Nakano, R., Nakayama, T., and Sugiya, H. (2020). Biological properties of JNK3 and its function in neurons, astrocytes, pancreatic β-cells and cardiovascular cells. Cells 9 (8), 1802. doi:10.3390/cells9081802
Nakazawa, K. R., Walter, B. A., Laudier, D. M., Krishnamoorthy, D., Mosley, G. E., Spiller, K. L., et al. (2018). Accumulation and localization of macrophage phenotypes with human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 18 (2), 343–356. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2017.09.018
Ni, L., Zheng, Y., Gong, T., Xiu, C., Li, K., Saijilafu, L. B., et al. (2019). Proinflammatory macrophages promote degenerative phenotypes in rat nucleus pulpous cells partly through ERK and JNK signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (5), 5362–5371. doi:10.1002/jcp.27507
Oichi, T., Taniguchi, Y., Oshima, Y., Tanaka, S., and Saito, T. (2020). Pathomechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine 3 (1), e1076. doi:10.1002/jsp2.1076
Papaconstantinou, J. (2019). The role of signaling pathways of inflammation and oxidative stress in development of senescence and aging phenotypes in cardiovascular disease. Cells 8 (11), 1383. doi:10.3390/cells8111383
Patil, P., Niedernhofer, L. J., Robbins, P. D., Lee, J., Sowa, G., and Vo, N. (2018). Cellular senescence in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Curr. Mol. Biol. Rep. 4 (4), 180–190. doi:10.1007/s40610-018-0108-8
Pei, S., Ying, J., Zhang, Y., Su, L., Cheng, S., and Ruan, D. (2020). RhTSG-6 inhibits IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix degradation and apoptosis by suppressing the p38, and JNK pathways in nucleus pulposus cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 58 (3), 227–234. doi:10.5603/FHC.a2020.0019
Pinal, N., Calleja, M., and Morata, G. (2019). Pro-apoptotic and pro-proliferation functions of the JNK pathway of Drosophila: roles in cell competition, tumorigenesis and regeneration. Open Biol. 9 (3), 180256. doi:10.1098/rsob.180256
Rhon, D. I., George, S. Z., Greenlee, T. A., Farrokhi, S., and Lentz, T. A. (2024). General and pain-associated psychological distress phenotypes among patients with low back pain in the military health system. Arthritis Care Res. Hob. 76, 943–952. doi:10.1002/acr.25315
Risbud, V., and Shapiro, I. M. (2014). Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 10 (1), 44–56. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2013.160
Roberts, S., Evans, H., Trivedi, J., and Menage, J. (2006). Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 88 (Suppl. 2), 10–14. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00019
Roger, L., Tomas, F., and Gire, V. (2021). Mechanisms and regulation of cellular senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (23), 13173. doi:10.3390/ijms222313173
Saiyin, W., Li, L., Zhang, H., Lu, Y., and Qin, C. (2019). Inactivation of FAM20B causes cell fate changes in annulus fibrosus of mouse intervertebral disc and disc defects via the alterations of TGF-β and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1865 (12), 165555. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165555
Seol, D., Coleman, M. C., Martin, J. A., Song, I., Jaidev, L. R., Salem, A. K., et al. (2021). Targeting oxidative stress with amobarbital to prevent intervertebral disc degeneration: Part I. in vitro and ex vivo studies. Spine J. 21 (6), 1021–1030. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2021.02.008
Silwal, P., Nguyen-Thai, A. M., Mohammad, H. A., Wang, Y., Robbins, P. D., Lee, J. Y., et al. (2023). Cellular senescence in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic opportunities. Biomolecules 13 (4), 686. doi:10.3390/biom13040686
Sivan, S. S., Hayes, A. J., Wachtel, E., Caterson, B., Merkher, Y., Maroudas, A., et al. (2014). Biochemical composition and turnover of the extracellular matrix of the normal and degenerate intervertebral disc. Eur. Spine J. 23 (Suppl. 3), S344–S353. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2767-8
Sui, X., Kong, N., Ye, L., Han, W., Zhou, J., Zhang, Q., et al. (2014). p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett. 344 (2), 174–179. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.019
Sun, K., Hou, L., Guo, Z., Wang, G., Guo, J., Xu, J., et al. (2023). JNK-JUN-NCOA4 axis contributes to chondrocyte ferroptosis and aggravates osteoarthritis via ferritinophagy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 200, 87–101. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.008
Suzuki, S., Fujita, N., Hosogane, N., Watanabe, K., Ishii, K., Toyama, Y., et al. (2015). Excessive reactive oxygen species are therapeutic targets for intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res. Ther. 17, 316. doi:10.1186/s13075-015-0834-8
Takahashi, S., Ebihara, A., Kajiho, H., Kontani, K., Nishina, H., and Katada, T. (2011). RASSF7 negatively regulates pro-apoptotic JNK signaling by inhibiting the activity of phosphorylated-MKK7. Cell Death Differ. 18 (4), 645–655. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.137
Tang, P., Gu, J. M., Xie, Z. A., Gu, Y., Jie, Z. W., Huang, K. M., et al. (2018). Honokiol alleviates the degeneration of intervertebral disc via suppressing the activation of TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 120, 368–379. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.04.008
Tu, J., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Wu, X., Song, Y., Kang, L., et al. (2017). Simvastatin inhibits IL-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation by suppressing the NF-kB and MAPK pathways in nucleus pulposus cells. Inflammation 40 (3), 725–734. doi:10.1007/s10753-017-0516-6
Ugwu, C. I., and Pope, D. (2023). Quantifying the association between psychological distress and low back pain in urban Europe: a secondary analysis of a large cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 13 (2), e047103. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047103
Vallerie, S. N., and Hotamisligil, G. S. (2010). The role of JNK proteins in metabolism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2 (60), 60rv5. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001007
Vander, G. D. J., Kocherginsky, M., Hickson, J. A., Stadler, W. M., Lin, A., and Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W. (2005). Suppression of metastatic colonization by the context-dependent activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase kinases JNKK1/MKK4 and MKK7. Cancer Res. 65 (23), 10984–10991. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2382
Vo, N. V., Hartman, R. A., Patil, P. R., Risbud, M. V., Kletsas, D., Iatridis, J. C., et al. (2016). Molecular mechanisms of biological aging in intervertebral discs. J. Orthop. Res. 34 (8), 1289–1306. doi:10.1002/jor.23195
Wang, H., Jiang, Z., Pang, Z., Zhou, T., and Gu, Y. (2020). Acacetin alleviates inflammation and matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 4801–4813. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S274812
Wang, J., Pan, H., Li, X., Zhang, K., Li, Z., Wang, H., et al. (2017). Hypoxia suppresses serum deprivation-induced degradation of the nucleus pulposus cell extracellular matrix through the JNK and NF-κB pathways. J. Orthop. Res. 35 (9), 2059–2066. doi:10.1002/jor.23486
Wang, J. X., Cao, B., Ma, N., Wu, K. Y., Chen, W. B., Wu, W., et al. (2023). Collectin-11 promotes cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. JCI Insight 8 (5), e159452. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.159452
Wang, S. Z., Chang, Q., Lu, J., and Wang, C. (2015). Growth factors and platelet-rich plasma: promising biological strategies for early intervertebral disc degeneration. Int. Orthop. 39 (5), 927–934. doi:10.1007/s00264-014-2664-8
Wang, W., Jing, X., Du, T., Ren, J., Liu, X., Chen, F., et al. (2022). Iron overload promotes intervertebral disc degeneration via inducing oxidative stress and ferroptosis in endplate chondrocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 190, 234–246. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.018
Wang, X., Tan, Y., Liu, F., Wang, J., Liu, F., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023). Pharmacological network analysis of the functions and mechanism of kaempferol from Du Zhong in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). J. Orthop. Transl. 39, 135–146. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2023.01.002
Wang, X. H., Hong, X., Zhu, L., Wang, Y. T., Bao, J. P., Liu, L., et al. (2015). Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes the proliferation of human nucleus pulposus cells via nuclear factor-κB, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 240 (4), 411–417. doi:10.1177/1535370214554533
Wang, Y., Che, M., Xin, J., Zheng, Z., Li, J., and Zhang, S. (2020). The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 131, 110660. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110660
Weston, C. R., and Davis, R. J. (2007). The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19 (2), 142–149. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2007.02.001
Wiet, M. G., Piscioneri, A., Khan, S. N., Ballinger, M. N., Hoyland, J. A., and Purmessur, D. (2017). Mast Cell-Intervertebral disc cell interactions regulate inflammation, catabolism and angiogenesis in Discogenic Back Pain. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 12492. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12666-z
Wu, C. C., Peterson, A., Zinshteyn, B., Regot, S., and Green, R. (2020). Ribosome collisions trigger general stress responses to regulate cell fate. Cell 182 (2), 404–416. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.006
Wu, D., Wong, P., Guo, C., Tam, L. S., and Gu, J. (2021). Pattern and trend of five major musculoskeletal disorders in China from 1990 to 2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMC Med. 19 (1), 34. doi:10.1186/s12916-021-01905-w
Wu, X., Song, Y., Liu, W., Wang, K., Gao, Y., Li, S., et al. (2017). IAPP modulates cellular autophagy, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix metabolism in human intervertebral disc cells. Cell Death Discov. 3, 16107. doi:10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.107
Xie, X., Gu, Y., Fox, T., Coll, J. T., Fleming, M. A., Markland, W., et al. (1998). Crystal structure of JNK3: a kinase implicated in neuronal apoptosis. Structure 6 (8), 983–991. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00100-2
Xu, H. M., Hu, F., Wang, X. Y., and Tong, S. L. (2019). Relationship between apoptosis of endplate microvasculature and degeneration of the intervertebral disk. World Neurosurg. 125, e392–e397. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.085
Xu, K., Chen, W., Wang, X., Peng, Y., Liang, A., Huang, D., et al. (2015). Autophagy attenuates the catabolic effect during inflammatory conditions in nucleus pulposus cells, as sustained by NF-κB and JNK inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Med. 36 (3), 661–668. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2015.2280
Yan, H., He, L., Lv, D., Yang, J., and Yuan, Z. (2024). The role of the dysregulated JNK signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of human diseases and its potential therapeutic strategies: a comprehensive review. Biomolecules 14 (2), 243. doi:10.3390/biom14020243
Ye, W., Zhu, W., Xu, K., Liang, A., Peng, Y., Huang, D., et al. (2013). Increased macroautophagy in the pathological process of intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. Connect. Tissue Res. 54 (1), 22–28. doi:10.3109/03008207.2012.715702
Yurube, T., Takeoka, Y., Kanda, Y., Kuroda, R., and Kakutani, K. (2023). Intervertebral disc cell fate during aging and degeneration: apoptosis, senescence, and autophagy. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 14, 100210. doi:10.1016/j.xnsj.2023.100210
Zeke, A., Misheva, M., Reményi, A., and Bogoyevitch, M. A. (2016). JNK signaling: regulation and functions based on complex protein-protein partnerships. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 80 (3), 793–835. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00043-14
Zhang, C., Lu, Z., Lyu, C., Zhang, S., and Wang, D. (2023). Andrographolide inhibits static mechanical pressure-induced intervertebral disc degeneration via the MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 17, 535–550. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S392535
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Liu, H., Li, Z., Chen, F., Wang, H., et al. (2019). TNF-α enhances apoptosis by promoting chop expression in nucleus pulposus cells: role of the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. J. Orthop. Res. 37 (3), 697–705. doi:10.1002/jor.24204
Zhang, S., Liu, W., Wang, P., Hu, B., Lv, X., Chen, S., et al. (2021). Activation of HSP70 impedes tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced apoptosis and senescence of human nucleus pulposus stem cells via inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 476 (5), 1979–1994. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04052-1
Zhang, W., Gong, Y., Zheng, X., Qiu, J., Jiang, T., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Platelet-derived growth factor-BB inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration via suppressing pyroptosis and activating the MAPK signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 799130. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.799130
Zhang, X., Zhang, Z., Zou, X., Wang, Y., Qi, J., Han, S., et al. (2024). Unraveling the mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration: an exploration of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1324561. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1324561
Zhang Y, Y., Liu, C., Li, Y., and Xu, H. (2023). Mechanism of the mitogen-activated protein kinases/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in the process of cartilage endplate stem cell degeneration induced by tension load. Glob. Spine J. 13 (8), 2396–2408. doi:10.1177/21925682221085226
Zhao, C. Q., Jiang, L. S., and Dai, L. Y. (2006). Programmed cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis 11 (12), 2079–2088. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-0290-7
Zhao, K., Chen, M., Liu, T., Zhang, P., Wang, S., Liu, X., et al. (2021). Rhizoma drynariae total flavonoids inhibit the inflammatory response and matrix degeneration via MAPK pathway in a rat degenerative cervical intervertebral disc model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 138, 111466. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111466
Zhou, J., Yao, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Zheng, T., Lu, Y., et al. (2022). JNK-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of EGR-1 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Apoptosis 27 (3-4), 246–260. doi:10.1007/s10495-022-01714-3
Keywords: intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD), JNK path, programmed cell death (PCD), cellular senescence (CS), cell proliferation, inflammation, extracellar matrix (ECM) degradation, oxidative stress (OS)
Citation: Liu G, Gao L, Wang Y, Xie X, Gao X and Wu X (2024) The JNK signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1423665. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1423665
Received: 26 April 2024; Accepted: 09 September 2024;
Published: 19 September 2024.
Edited by:
Weimin Gao, Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI), United StatesReviewed by:
Jiawei Li, Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Liu, Gao, Wang, Xie, Gao and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xingjie Wu, MjM5OTA2MTNAcXEuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.