
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 25 July 2024
Sec. Stem Cell Research
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1419893
This article is a correction to:
Nitric Oxide Alleviated High Salt–Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy Independent of Blood Pressure in Rats
A Corrigendum on
Nitric oxide alleviated high salt-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy independent of blood pressure in rats
by Li Y, Wu X, Mao Y, Liu C, Wu Y, Tang J, Zhao K and Li P (2021). 9:646575. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646575
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5J as published. The wrong representative image of TUNEL-staining was used. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
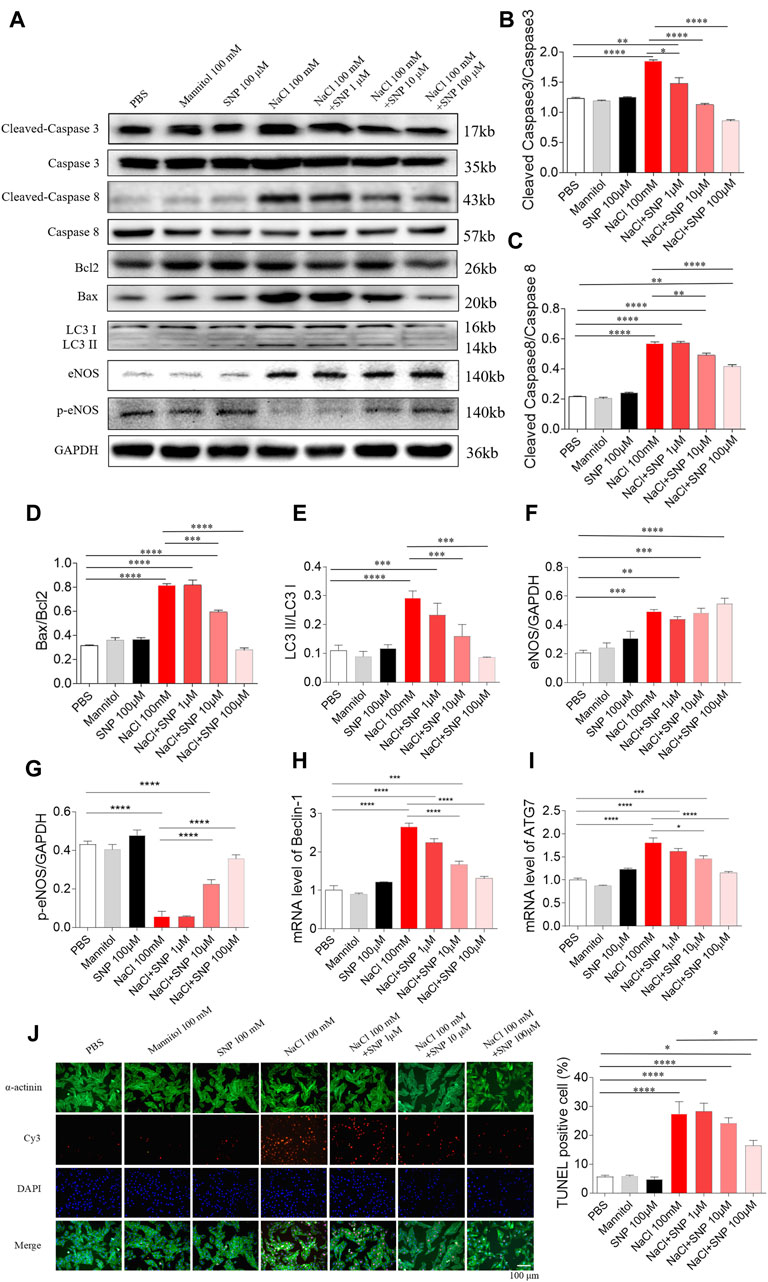
Figure 5. Effects of different doses of nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on NaCl-induced apoptosis and autophagy in H9C2 cells. (A–I), SNP attenuated the increases in the levels of cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 8/caspase 8, Bax/Bcl2, LC3 II/LC3 I, Beclin-1, and autophagy related 7 (ATG7), and enhanced the decrease of p-endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) induced by NaCl (100 mM) in H9C2 cells. (J) The increase of TUNEL-positive cell number was inhibited by high dose of SNP (100 µM), but not middle (10 µM) or low dose (1 µM) of SNP. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 7J as published. The wrong representative image of TUNEL-staining was used. The corrected Figure 7 and its caption appear below.
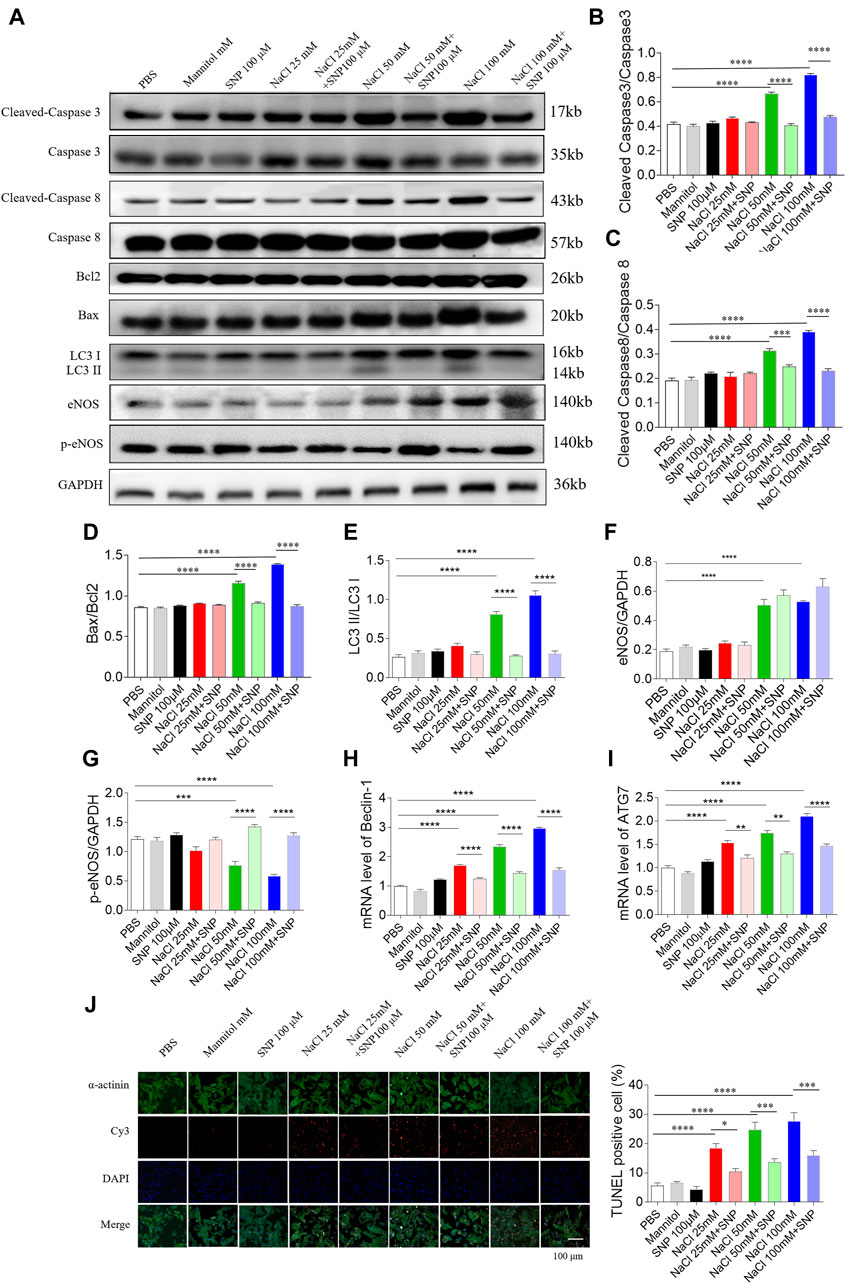
Figure 7. Effects of nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on apoptosis and autophagy induced by three doses of sodium chloride (NaCl) in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCM). SNP (100 µM) attenuated the increases in the levels of cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3 (A, B), cleaved-caspase 8/caspase 8 (A, C), Bax/Bcl2 (A, D), LC3 II/LC3 I (A,E), Beclin-1 (H), and autophagy related 7 (ATG7) (I), and enhanced the decrease of p-endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) induced by NaCl (50 or 100 mM) in NRCM (F, G). The increases of TUNEL-positive cell numbers induced by three doses of NaCl in the NRCM were attenuated by SNP (100 µM) treatment (J). The results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: high-salt diet, cardiomyocytes, apoptosis, autophagy, nitric oxide, sodium nitroprusside
Citation: Li Y, Wu X, Mao Y, Liu C, Wu Y, Tang J, Zhao K and Li P (2024) Corrigendum: Nitric oxide alleviated high salt-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy independent of blood pressure in rats. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:1419893. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1419893
Received: 19 April 2024; Accepted: 15 July 2024;
Published: 25 July 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Valerie Kouskoff, The University of Manchester, United KingdomCopyright © 2024 Li, Wu, Mao, Liu, Wu, Tang, Zhao and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peng Li, bGlwZW5nMTk4NkAxNjMuY29t; Kun Zhao, MTIyNzYyMTM3NEBxcS5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.