
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 30 October 2023
Sec. Epigenomics and Epigenetics
Volume 11 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1264552
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is a series of malignant tumors with a high incidence globally. Although approaches for tumor diagnosis and therapy have advanced substantially, the mechanisms underlying the occurrence and progression of GI cancer are still unclear. Increasing evidence supports an important role for N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in many biological processes, including cancer-related processes via splicing, export, degradation, and translation of mRNAs. Under distinct cancer contexts, m6A regulators have different expression patterns and can regulate or be regulated by mRNAs and non-coding RNAs, especially long non-coding RNAs. The roles of m6A in cancer development have attracted increasing attention in epigenetics research. In this review, we synthesize progress in our understanding of m6A and its roles in GI cancer, especially esophageal, gastric, and colorectal cancers. Furthermore, we clarify the mechanism by which m6A contributes to GI cancer, providing a basis for the development of diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic targets.
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is a set of malignant tumors accounting for over 25% of cancer incidence annually, and the morbidity and mortality of esophageal, gastric, colon, rectal, liver, pancreatic, and gallbladder cancers rank high with an estimated 5 million new cases and 3,609,607 deaths in the global cancer statistics for 2020 (Sung et al., 2021). GI cancer poses a serious threat to human health with a large number of cases. Due to the growth of population, aging, and lifestyle changes, the burden of digestive system tumors worldwide especially in East Asia is increasing day by day, and the incidence of tumors is becoming younger. Despite advances in immunotherapy and molecular targeted therapy in addition to conventional surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, the early diagnosis and treatment of advanced GI tumors are still unsatisfactory owing to an incomplete understanding of the molecular mechanisms. Accordingly, it is necessary to further clarify the mechanisms underlying these digestive tract cancers.
m6A (N6-methyladenosine) modification has a significant regulatory role in many biological processes and diseases (Frye et al., 2018; Wei and He, 2021). Recent studies have demonstrated that m6A plays an important role in tumor progression and suppression, especially in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), glioblastoma (GBM), and breast cancer (Table 1). Vu et al. found that m6A could control the translation of PTEN, c-MYC, and BCL2, which are involved in the differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in AML (Vu et al., 2017). m6A modifications have also been linked to survival rate in GBM, in which interactions with long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been demonstrated (Zhang et al., 2017). In breast cancer, m6A can be negatively regulated by microRNAs (miRNAs) (Cai et al., 2018). In eukaryotic cells, m6A methylation of messenger RNA (mRNA) is the most pervasive chemical modification, ahead of N1-methyladenosine (m1A), 5-methylcytosine (m5C), and N7-methylguanosine (m7G); it was first discovered in the 1970s (Desrosiers et al., 1974; Roundtree et al., 2017). The deposition of m6A is nearly identical in nascent and mature mRNA and is generally distributed in the exons of 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) and stop codons (Ke et al., 2017; Shi et al., 2019) (Figure 1A). Recent studies have shown that some non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) also act as coding RNAs, participating in peptide translation (Zhou et al., 2021). m6A modification has been detected in both coding and non-coding RNAs, including miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circular RNAs (circRNAs). As a prevalent post-transcriptional modification, it has a great impact on the fate of RNAs by binding with “m6A writers” and “m6A erasers” as well as recruiting “m6A readers” (Zaccara et al., 2019; Yi et al., 2020). Dynamic m6A methylation is vital for both normal biological processes and aberrant regulation in diseases (Li et al., 2017a; Du et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2018; Visvanathan et al., 2018; Han et al., 2019a; Wang et al., 2019a; Jia et al., 2019; Jin et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020a; Zhang et al., 2020a; Wang et al., 2020b; Guo et al., 2020; Hanniford et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Wen et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021a; Huang et al., 2022) (Table 1).
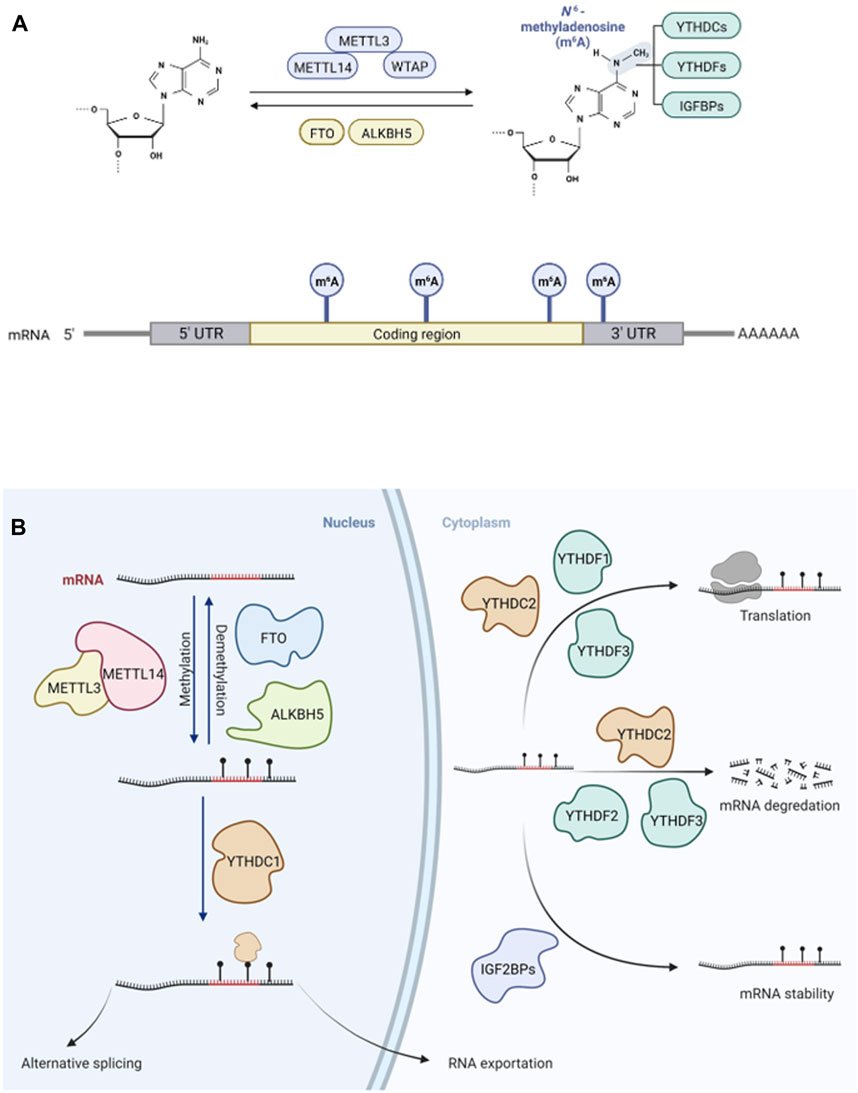
FIGURE 1. Dynamic and reversible m6A modification on mRNA in eukaryocytes. (A). The adenosine (A) can be methylated by m6A “writer”, a complex of METTL3, METTL14 and WTAP, becoming N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and m6A can be demethylated by m6A “erasers”, FTO and ALKBH5 reversibly. m6A can be recognized by m6A” readers”, influencing targeted mRNA fates. m6A is mostly deposited on exons of 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) and stop codons of mRNA. (B). The modification of m6A “writers”, “erasers” and “readers” can lead to aberrant regulations in cancers, such as RNA exportation, splicing, translation, degradation, and stability.
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3), Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14), Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP), and auxiliary proteins form a molecular complex including vir-like m6A methyltransferase associated (VIRMA), RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15 and RBM15B), Cbl proto-oncogene like 1 (CBLL1), and zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 13 (ZC3H13) (Wang et al., 2020c). These m6A methyltransferase can catalyze RNA methylation to insert a methyl substituent into the sixth N atom of adenosine in RNA. Using crystallization methods, it has been shown that METTL3 mainly has catalytic functions and METTL14 is a structural support factor; these loci function as m6A writers (Zeng et al., 2020). Another m6A methyltransferase, METTL16, could interact with mRNAs and small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) using S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as a methyl donor (Satterwhite and Mansfield, 2021). Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) and alkB homologue 5 (ALKBH5) are two common demethylases functioning as m6A erasers, reversibly removing m6A in nuclei (Jia et al., 2011; Zheng et al., 2013). FTO possesses multiple substrates including mRNA, tRNA, U RNAs, and RNAs transcribed from repetitive elements (Wei et al., 2018; Wei et al., 2022). m6A readers include YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3, YTHDC1, and YTHDC2, which belong to the YT521-B homology (YTH) domain family and function downstream of m6A methylation or demethylation by m6A writers (Zhao et al., 2017). Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BP) have functions similar to those of m6A readers (Deng et al., 2018), mediating mRNA stability and translation (Figure 1B). The functions of these m6A readers mainly include specific binding to the m6A methylation region, weakening homologous binding to RNA-binding proteins, and altering the RNA secondary structure to alter protein-RNA interactions.
m6A is tightly associated with the post-transcriptional modification of gene expression by its deposition on RNA transcripts, thereby impacting tumorigenesis. ncRNAs also regulate the expression of m6A regulators, influencing the characteristics of cancers. Nevertheless, the relationship between m6A modification and GI cancer, especially the modification of ncRNAs, has not been summarized systematically. Here, we review the effects of m6A methylation on mRNAs and ncRNAs as well as the effects of ncRNAs on m6A regulators in GI cancer to explore the role of m6A modification in GI cancer, its potential as a diagnostic/prognostic marker, and its implications for therapy. Furthermore, we describe the prognostic and therapeutic value of m6A regulators in GI cancer.
Recently, aberrant levels of m6A and abnormal expression levels of m6A regulators have been found in GI cancer. These changes are mediated by various signaling pathways. Nevertheless, m6A regulators could be deposited on various oncogenes, or tumor suppressor genes, and these two factors might have opposite effects on tumorigenesis. The mechanisms underlying m6A modification and downstream effects are still unclear and have not been summarized systematically. Herein, we summarize the relationship between m6A and its associated coding and non-coding RNAs in GI cancer, to present a detailed overview of the contribution of epigenetic modifications in GI tumors.
Methyltransferase, demethylase, and recognition factors play important roles in the molecular mechanisms of action of m6A RNA methylation, modulating mRNA stability, splicing, nuclear export, and translation (Table 2).
METTL3 is an m6A methyltransferase that has been studied extensively owing to its roles in various cancers. For example, METTL3 mediates carcinogenesis in GBM by influencing characteristics of mRNA, and its m6A modification has been studied in AML as much as in GBM (He et al., 2019a). METTL3 contributes substantially to GI cancer, and the impact of its dysregulation on targeted mRNAs leads to different outcomes.
Many studies have demonstrated that METTL3 could affect the stabilization of mRNA. For example, METTL3 promotes the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) through the stabilization of NOTCH1 and EGR1 mRNA, followed by activation of Notch and EGR1/Snail signaling pathways (Li et al., 2021a; Han et al., 2021). The activation of METTL3 transcription promotes the m6A methylation of Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor (HDGF) mRNA, and subsequent binding to IGF2BP3, an m6A reader, leading to increased stability of HDGF mRNA in GC (Wang et al., 2020d). Yue et al. reported that in GC, METTL3 targets zinc finger MYM-type containing 1 (ZMYM1), increasing its expression, and thereby influencing the process of EMT (Yue et al., 2019). The mRNA levels of the basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor 2 (BATF2) decrease in response to increased METTL3 in GC, resulting in a decrease in the stability of BATF2 mRNA (Xie et al., 2020). In addition to the elevated level of METTL3 in GC, the locus is correlated with lung/lymph node metastasis, due to its stabilizing of Pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 1 (PBX1), an oncogene (Liu et al., 2022a). Zhu et al. found that METTL3 could lead to stabilization of CCNE1 mRNA by binding to its 3′-UTR and methylating it, promoting CRC (Zhu et al., 2020a). Similarly, some studies have shown that cancer-related oncogene can be modified by METTL3 to enhance their mRNA stability in CRC (Liu et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2022). Furthermore, METTL3 is involved in stabilizing the mRNA of HK2 and SLC2A1 (GLUT1), and degrading the mRNA of APC; all these effects are associated with the glycolysis and proliferation of tumor cells (Shen et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021a). A recent study has shown that knockdown of METTL3 could prevent the degradation of CRB3 mRNA in CRC, mediating the activation of the Hippo signaling pathway (Yang et al., 2021a). Li et al. also reported that increased METTL3 expression in CRC is associated with metastasis; furthermore, METTL3 can reduce the degradation of the downstream factor SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 (SOX2), by methylating coding sequence regions by an IGF2BP2-dependent mechanism, in which K homology domains of IGF2BPs are responsible for tumorigenesis (Huang et al., 2018; Li et al., 2019). Accordingly, METTL3 is a candidate target for the treatment of CRC and other cancers.
In addition to stabilization, METTL3 could influence translation. Altered METTL3 is important for GC development; however, the regulatory processes downstream of m6A factors are still unclear. METTL3 is upregulated, increasing the translation of the oncogene MYC in GC and promoting proliferation (Yang et al., 2020a). METTL3 and YTHDF1 positively regulate the translation of Sphingosine kinase (SPHK), leading to the migration and invasion of GC (Huo et al., 2021). However, given that METTL3 could facilitate cancer progression through an anchoring effect in a non-m6A modification manner, there are still unknown mechanisms in the METTL3 regulatory role in GI carcinogenesis. This suggests that METTL3 may promote the translation of certain epigenetic factors in the cytoplasm in a m6A-independent manner.
As a homolog of METTL3, METTL14 is also aberrantly expressed in tumorigenesis. METTL14 acts as an anti-oncogene in CRC, abolishing SOX4 mRNA stability and facilitating SOX4 mRNA degradation in a YTHDF2-dependent manner, preventing metastasis in CRC (Chen et al., 2020a). Moreover, arrestin domain-containing 4 (ARRDC4), another target of METTL14, could be degraded via m6A modification by METTL14 and YTHDF2, resulting in low expression of the EMT regulator ZEB1 (Wang et al., 2021b). The association between colorectal anti-cancer gene KLF4 and metastasis is inhibited by reduced METLL14, which promotes KLF4 mRNA degradation in a IGF2BP2-dependent manner in CRC (Wang et al., 2021c). The role of METTL14 in tumor development is not limited to its effect on mRNA stability; it also affects ncRNAs such as circRNAs. This is detailed in the following section.
Similar to METTL3 and METTL14, another m6A methyltransferase, METTL16, has been found to be involved in the processing of pre-mRNA by interacting with the methylation of U6 snRNA, where it can bind to the 5′ splice sites of pre-mRNA (Warda et al., 2017). The downregulation of another methyltransferase, METTL16, inhibits the proliferation of GC cells by suppressing the GC cell cycle in G1/S phase and decreasing cyclin D1 mRNA stability (Wang et al., 2021d). As the most studied m6A regulators, “writers” can be viewed as novel targets for facilitating the treatment of GI cancer.
FTO catalyzes the oxidative demethylation of m6A-modified nuclear RNA (Jia et al., 2011). A recent study has revealed that FTO acts as an oncogene, demethylating the mRNA of the Homeobox gene HOXB13, which augments the expression of HOXB13 in GC (Guo et al., 2021a). Other studies have suggested that the upregulation of FTO in GC, especially in cases with liver metastasis, promotes the degradation of caveolin-1 mRNA by reducing m6A deposition, impeding mitochondrial fission and inducing GC metastasis (Zhou et al., 2022). Nevertheless, the level of FTO was downregulated in the peripheral blood of patients with GC (Ge et al., 2020), contrary to its expression pattern in GC tissues. A clinical trial has revealed that FTO can demethylate MYC mRNA, sustaining its stability in GC cells and mediating proliferation, migration, and invasion of GC (Yang et al., 2021b). However, METTL3 and FTO have opposite functions in GC; still, their effects on MYC expression have been shown to be similar. The upregulation of FTO could also regulate MYC expression in CRC via the miR-96/AMPKα2/FTO/m6A/MYC axis (Yue et al., 2020). Subsequently, Zhang et al. reported that FTO facilitates CRC proliferation by targeting the MAF1/c-MYC axis, which can be inhibited by glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) (Zhang et al., 2021b).
ALKBH5 functions in esophageal cancer cells (ESCC), and its overexpression results in the inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion by arresting cells in the G1 phase (Xiao et al., 2021); however, demethylated mRNA of ALKBH5 and related signaling pathways in ESCC are unclear. The demethylation of ZNF333 by ALKBH5 leads to a reduction in the degradation of ZNF333 mRNA, and this is dependent on YTHDF2 recognition, and hyperactivation of NF-κB to induce gastric intestinal metaplasia (IM) (Yue et al., 2021a). In vitro and in vivo assays revealed that the downregulation of ALKBH5 can increase the expression level of PKMYT1 by maintaining its stability with the assistance of IGF2BP3 via the demethylation of PKMYT1 in GC (Hu et al., 2022). Considering that m6A modification is a reversible process, “erasers” play an important role in carcinogenesis and tumor progression.
Most readers of m6A mediate the fates of RNA following modification by m6A writers. In processes related to tumorigenesis, m6A readers may lead to aberrant changes in targeted RNAs via variation in m6A readers themselves or misinterpretation of m6A writers. For example, YTHDC2, the first studied m6A reader, can recognize m6A sites on YAP mRNA, enhancing its translation (rather than influencing its mRNA level) and promoting proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of GC (Yuan et al., 2022). ALKBH5 levels can also increase due to the upregulation of YAP, forming a positive feedback loop. YTHDF1 acts as an oncogene, promoting GC progression and metastasis by recognizing frizzled 7 (FZD7) mRNA based on m6A via the activation of the Wnt/FZD7/β-catenin pathway (Pi et al., 2021). It has recently been demonstrated that YTHDF1 is highly expressed in CRC and enhances the translation of its target, ARHGEF2, via RhoA signaling (Wang et al., 2022a).
IGF2BP1/2/3 proteins are newly identified m6A readers able to recognize m6A modifications and promote stability (Huang et al., 2018). Elevated IGF2BP2 has been detected in CRC, and its function has been found to be the same as that of YTHDC2 in GC, i.e., it promotes the stability and translation of YAP by recognizing its mRNA, activating ErbB2 and leading to a malignant phenotype in CRC cells (Cui et al., 2021a). Compared with the levels in normal colon tissues, IGF2BP3 levels are elevated in CRC (Yang et al., 2020b). Knockdown of IGF2BP3 results in decreased efficacy of reading the m6A sites of the mRNAs of the cell cycle protein Cyclin D1 (CCND1) and Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), impairing their mRNA stability, inhibiting proliferation, and repressing angiogenesis (Yang et al., 2020b). Recently, studies of m6A readers have not been limited to their downregulated targets, but also include their up-regulatory mechanisms. The functions of m6A readers need further specific explorations to be applied in GI cancer intervention.
Some studies have focused on the upstream regulatory mechanism of m6A regulators in GI cancer, and have found that some coding RNAs can influence the level of m6A. METTL3 has been confirmed to be a downstream target of specific signaling pathways, and to play a critical role in EMT progression, by elevating m6A levels (Song and Zhou, 2021) (Table 2). As it functions in breast cancer, hepatitis B X-interacting protein (HBXIP) could positively regulate METTL3 levels in GC cells, where METTL3 could interact with the oncogene MYC to increase m6A deposition, promoting proliferation, invasion, and metastasis (Yang et al., 2020a). Chen proposed a more complex mechanism of m6A regulation in CRC involving gut microbiota, in which Fusobacterium nucleatum facilitates metastasis by downregulating METTL3 via the inhibition of the HIPPO signaling pathway, activation of YAP signaling pathways, and elevation of the expression of the oncogene KIF26B due to reduced YTHDF2-dependent degradation (Chen et al., 2022a; You et al., 2022). These results indicate that the up-regulatory factors of m6A modification need further exploration to understand what influences the m6A methylation.
Increasing evidence suggests that ncRNAs are involved in biological processes and disease development. They function by regulating gene expression but lack protein-coding capacity. ncRNAs can be divided into small ncRNAs and long ncRNAs using a threshold length of 200 nucleotides (Beermann et al., 2016). As ncRNAs are related to carcinogenesis, the m6A-mediated regulation of gene expression and interactions with related ncRNAs contribute to pathological processes (Chen et al., 2020b). For example, the m6A eraser ALKBH5 is colocated with the lncRNA NEAT1 in the nuclei of GC cells, leading to the demethylation of NEAT1, thereby influencing invasion and metastasis (Zhang et al., 2019a) (Table 3).
Recently, the deregulation of m6A factors has been found to play a key role in the occurrence of esophageal cancer (EC). Genetic mutation of m6A regulators has been demonstrated to be associated with ESCC patients’ prognosis (Guo et al., 2021b; Zhao et al., 2021). ESCC-associated m6A eraser FTO assists in promoting cell-cycle progression and proliferation by decreasing the m6A level of the LINC00022 transcripts, upregulating the expression of LINC00022 (Cui et al., 2021b). Similar regulatory function is also observed in the relationship between m6A reader HNRNPA2B1and miR-17-92 in ESCC (Li et al., 2021b). MALAT1-m6A recognition by YTHDC1 has been implicated in the metastasis of EC as demonstrated in vitro and in vivo (Wang et al., 2021e). As for mechanism, one study has shown that ALKBH5 can demethylate pri-miR-194-2, decreasing the level of miR-194-2, which functions as inhibitor in ESCC (Chen et al., 2021a). Current studies mostly address the phenotypic regulation of tumors by m6A factors, but specific modification mechanisms also require further study.
M6A modification can mediate GC development by controlling the process and fate of ncRNAs, including their maturation, stability, and transportation. For example, the overexpression of METTL3 facilitates the maturation of pri-miR-17-92, which targets AKT/mTOR pathway, promoting GC growth and peritoneal metastasis (Sun et al., 2020). The lncRNA THAP7-AS1 is a downstream target of METTL3 and its effects are dependent on IGF2BP1, whose stability is maintained and expression is increased, exerting carcinogenic effects in GC (Liu et al., 2022b). METTL14, a writer of m6A, and METTL3 have opposite regulatory effects in GC. The depletion of METTL14 facilitates the growth of GC and abolishes m6A on circORC5, augmenting its expression by sponging miR-30c-2-3p (Fan et al., 2022) (Figure 2A).
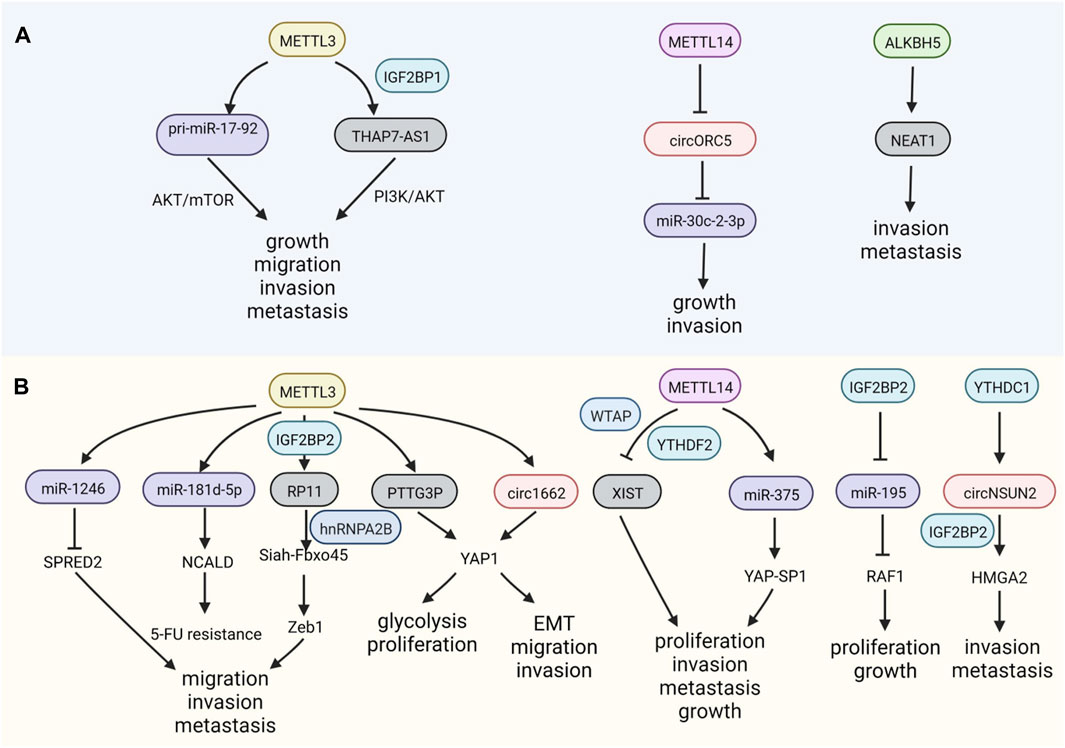
FIGURE 2. m6A modifications on non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in GI cancers. (A) m6A regulators have positive or negative functions on ncRNAs in gastric cancer (GC). (B) m6A modulates the expression of ncRNAs, influencing colorectal cancer (CRC).
The upregulation of METTL3, an m6A writer, is also critical for the migration and invasion of CRC via its effects on miR-1246, whose downstream targets include the anti-oncogene SPRED2, which functions through the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway (Peng et al., 2019). In addition to the malignant characteristics of CRC, METTL3 can also regulate chemotherapeutic resistance by processing miR-181d-5p via DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8 (DGCR8) (Pan et al., 2022). The invasion and metastasis of CRC can also be modulated by the lncRNA RP11 methylation mediated by METTL3, and the formation of the RP11/hnRNP2B1/mRNA complex leads to the upregulation of the EMT-related factor Zeb1 (Wu et al., 2019). METTL3 helps stabilize the lncRNA PTTG3P, which is recognized by IGF2BP2, thereby promoting CRC (Zheng et al., 2021). In addition to miRNAs and lncRNAs modified by m6A, recent studies have also focused on the m6A methylation of circRNAs. Interestingly, binding to circ1662 flanking reverse repeats, METTTL3 upregulates circ1662, facilitating YAP1 nuclear transportation, which inhibits the EMT-related gene SMAD3 and promotes migration and invasion in CRC (Chen et al., 2021b).
The lncRNA X inactivate-specific transcript (XIST) is methylated by METTL3, WTAP, RBM15, and RBM15B, and is recognized by YTHDC1, inactivating gene transcription on the X chromosome (Patil et al., 2016). The knockdown of METTL14 contributes to the progression of CRC via the recognition of YTHDF2, which modifies XIST, which is related to tumorigenesis in CRC by reducing its degradation (Patil et al., 2016; Yang et al., 2020c), similar to the function of METTL14 in GC.
YTH domain-containing protein 1 (YTHDC1) is bound to RNA in nuclei, where it impacts RNA splicing. Dependent on the m6A reader YTHDC1, circNSUN2 could be exported to the cytoplasm to combine with another reader, IGF2BP2; the resulting complex promotes the stability of high mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) mRNA, facilitating the metastasis of CRC (Chen et al., 2019a). Elevated IGF2BP2 expression maintains the stability of RAF1 mRNA by reversing miR-195-mediated degradation, promoting CRC (Ye et al., 2016). Similarly, YTHDF2 can inhibit circ_0003215 expression by degrading its RNA, leading to metabolic reprogramming of CRC cells (Chen et al., 2022b). These reports reveal that several special m6A regulators are responsible for ncRNA processing in GI cancer (Figure 2B).
ncRNAs have both positive and negative regulatory roles in m6A modification in GI cancer (Table 4). For example, miR-186 has been validated to suppress the expression of HNRNPC, a little-studied m6A regulator, facilitating migration and invasion in ESCC, whose regulatory mechanism still remains unclear (Li et al., 2021b). Furthermore, the repression of miR455-3p can increase the m6A modification of Heat shock transcription factor (HSF1) mRNA by competing with METTL3 to promote CRC (Song et al., 2020). Another miRNA, miR-96, contributes substantially to CRC development by inhibiting FTO, elevating m6A modification (Yue et al., 2020). The lncRNA LINC00470 is highly upregulated in GC in a manner dependent on the m6A binding proteins METTL3 and YTHDF2, exerting structural effects on PTEN mRNA, leading to its instability and degradation and promoting GC (Yan et al., 2020). The lincRNA NRON is overexpressed in GC, recruiting the m6A eraser ALKBH5 and decreasing the decay of Nanog transcripts by reducing m6A levels on Nanog mRNA (Wang et al., 2021f). MiR-1269b suppresses GC migration and invasion by targeting METTL3 (Kang et al., 2021). The lncRNA BLACAT2 promotes GC development via miR-193b-5p/METTL3 by obstructing apoptosis (Hu et al., 2021). Similarly, the lncRNA LINC000240 acting as a sponge facilitates the malignant phenotype of GC via the miR-338-5p/METTL3 axis (Wang et al., 2021b). In colon cancer, suppression of the lncRNA HOTAIR was found to downregulate the expression of IGF2BP2; HOTAIR can inhibit EMT, proliferation, cell cycle, metastasis, and invasion and facilitate cell apoptosis (Wu et al., 2018). Therefore, ncRNAs are important for m6A modulation because they control the expression of m6A.
As the most widely known m6A writer, METTL3 is upregulated in distinct cancer types. In GC, SEC62, a gene involved in carcinogenesis, is methylated by METTL3 (Liu et al., 2021), recruiting the m6A reader IGF2BP2 and stabilizing SEC62 mRNA; however, this carcinogenic effect can be attenuated by miR-4429 (He et al., 2019b). MiR-338-5p is downregulated by embryonic ectoderm development protein (EED) and then reduces METTL3 inhibition and increases the translation of CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), inducing proliferation and invasion in GC (Zhang et al., 2021c). Gao et al. reported that the lncRNA LINC02253 stabilizes KRT18 mRNA by recruiting METTL3, without affecting its expression, thus promoting GC proliferation and metastasis (Gao et al., 2022). In addition, IGF2BP3 plays a significant role in GC propagation and metastasis, and its effects are facilitated by miR-34a silencing (Zhou et al., 2017). CircRNAs are a well-studied group of ncRNAs with a covalently closed structure; they function as sponges, assimilating miRNAs and proteins, and have a vital role in the development of many diseases. A recent study has clarified the function of circRPMS1 in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma (EBVaGC) and suggested that via the interaction with Sam68, circRPMS1 activates METTL3 (Zhang et al., 2022) (Figure 3A).
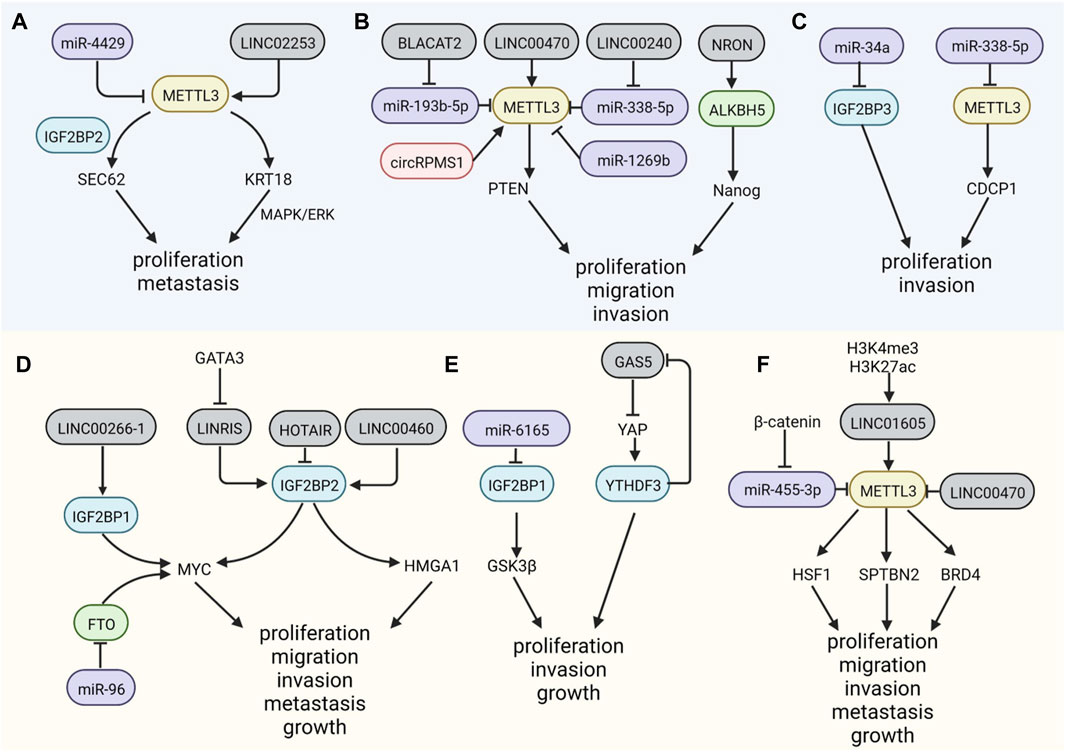
FIGURE 3. Non-coding RNAs participate in the regulation of m6A factors. (A–C). MicroRNAs, lincRNAs and circRNA can modulate the expression level of m6A regulators mediating the development of GC. (D–F). NcRNAs also modify the methyl group m6A regulators in CRC.
In CRC, METTL3 could interact with LINC1605 in the cytoplasm, regulating the translation of downstream factors and inducing malignant characteristics (Yue et al., 2021b). The expression of m6A reader YTHDF2 is inhibited by miR-6165, by binding to the 3′UTR of YTHDF2 mRNA, leading to stabilization of m6A transcripts of GSK3β, downstream of YTHDF2, and inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin/Cyclin D1 pathway, suppressing CRC carcinogenesis (Li et al., 2021d). Large intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are found to be modified by m6A, and most common motifs are GG/A(m6A)CH, different from the motifs in mRNAs (Xiao et al., 2019); m6A could be regulated by lincRNAs. IGF2BP2s, functioning as m6A readers, are highly blocked by the downregulation of LINRIS, a kind of lincRNA, via the ubiquitination-autophagy pathway, destroying its stability and the autophagy-lysosome pathway and assisting its degradation in CRC (Wang et al., 2019b). Long intergenic non-coding RNA 460 (LINC00460) is a novel non-coding RNA; its overexpression is associated with the progression of CRC. LINC00460 can increase the m6A modification of high mobility group A1 (HMGA1) mRNA by binding to IGF2BP2s and ATP-dependent RNA helicase A (DHX9), which enhances the stability of HMGA1 (Hou et al., 2021). Another lncRNA, GAS5, impedes the progression of CRC via the phosphorylation and degradation of YAP by the negative regulation of the m6A reader YTHDF3 (Ni et al., 2019). Some lncRNAs have the ability to encode proteins involved in m6A regulation. A peptide encoded by LINC00266-1, called “RNA binding regulatory peptide” (RBRP), can interact with IGF2BP1 and the complex targets c-Myc to facilitate its stability, promoting CRC (Zhu et al., 2020b). In vitro and in vivo assays have shown that circLPAR1 in exosomes can sponge RNA-binding proteins (RBP) elF3h, reducing their binding to METTL3 in CRC cells, resulting in decreased translation of BRD4 mRNA and the suppression of CRC (Zheng et al., 2022) (Figure 3B). Overall, the evidence of the ncRNAs regulatory function on m6A, by coding or binding with m6A regulators, provides novel targets. The pathways involved in this relationship, such as cancer metabolism, remain limited, and related ncRNAs might be regulators that inhibit malignant phenotype in GI cancer.
The identification of m6A-associated protein-coding genes in pan-cancer analyses has provided novel candidate targets for clinical diagnosis and treatment (Shen et al., 2021). Recent evidence suggests that m6A-associated ncRNAs could be used to construct prediction models for prognosis in GI cancer (Wang et al., 2022b; Xu et al., 2022). Due to dynamic and reversible changes in m6A regulators during cancer development, m6A methylation could serve as a prognostic biomarker to guide therapeutic schemes for numerous cancer types (Ji G et al., 2020; Jin et al., 2021). The main enzyme of m6A modification, METTL3, could facilitate tumor progression by depositing m6A modification on key transcripts. Furthermore, tumor progression may be independent of the catalytic activity of METTL3, but be related to recruitment of eukaryotic translation initiation factors into the translation initiation complex. METTL3 is upregulated in both GC and CRC, and the elevation in METTL3 is a prognostic factor for poor overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) (Li et al., 2019; Yue et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020d). Furthermore, METTL3 and IGF2BP3 have been reported to be independent factors for ESCC prognosis (Guo et al., 2021b). In addition, low level of METTL14 is related to a poor prognosis in GC and CRC patients, and to the opposite in ESCC patients (Chen et al., 2020b; Xu et al., 2020; Fan et al., 2022). It can be seen that METTL14 plays a suppressive role in GI cancer by targeting key downstream molecules. The m6A erasers FTO and ALKBH5 are also associated with a worse OS (Liu et al., 2022a; Zhou et al., 2022), which could modulate the metabolism of cancer cells and facilitate immune escape. Similarly, the upregulation of the m6A reader IGF2BP3 has been identified as a new biomarker of many cancers; for instance, the co-expression of IGF2BP3 and the lncRNA DDRMR is a diagnostic and prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (Gu et al., 2021a). IGF2BP3 has been demonstrated to promote cancer progression by being stabilized by ncRNAs and stabilizing mRNA of downstream genes. The upregulation of IGF2BP3 in GC could be a prognostic biomarker associated with an advanced stage (Zhou et al., 2017). The upregulation of IGF2BP3 is associated with poor OS and an advanced stage of colon cancer, suggesting that IGF2BP3 can serve as a prognostic biomarker (Yang et al., 2020b).
The targets of m6A regulators could also have prognostic value. For instance, levels of m6A vary among the mRNAs of cancer-related genes, such as MORC2 and PARM1, and might predict CRC prognosis (Zhang et al., 2021d). The above findings are all based on comparisons of tumor tissues and normal tissues; however, a recent study has revealed that m6A in the peripheral blood is an effective marker for assessing prognosis in patients with GC after surgery (Ge et al., 2020), providing a novel direction for the diagnosis and treatment of GI cancer.
m6A methylation contributes to clinical treatment approaches. Since m6A regulators can be affected by several small molecules and drugs, they may provide a basis for the development of potent therapeutic targets and tumor hallmarks (Nombela et al., 2021).
Increasing evidence has demonstrated that m6A modification has critical functions in tumor-related immune processes, providing novel therapeutic targets based on the modulation of immune responses. m6A participates in the inhibition of innate immunity targeting circRNAs, which are suppressed by YTHDF2 in the cytoplasm (Chen et al., 2019b). m6A mediates not only innate immune responses but also adaptive responses (Paramasivam and Vijayashree Priyadharsini, 2020). For instance, YTHDF1 can lead to immune escape by binding to the mRNAs of lysosomal cathepsins, facilitating translation and suppressing cross-presentation of dendritic cells (DCs) (Han et al., 2019b). Increased transcription of CD40, CD80, and the TL4 signaling adapter Tirap is modified by METTL3 in DCs, leading to T cell stimulation (Wang et al., 2019c). T cell homeostasis has been shown to be maintained by the regulation of m6A targets such as IL-7, STAT5, and SOCS (Li et al., 2017b). Song et al. explained the restriction of natural killer cells in anti-tumor immunity, which enhances cancer development via the reduction of SHP-2 m6A modification by decreased METTL3 (Song et al., 2021), indicating that m6A has an important role in homeostasis and the infiltration of NK cells. In addition, m6A methylation can regulate the immune response in GC by interferon modulation (Zhang et al., 2019b).
In addition to its involvement in the regulation of immune cells, m6A also activates other key cells that are crucial in cancer immunity. It has been observed that m6A modification is correlated with the tumor microenvironment (TME), due to its modulation of hypoxia, metabolic dysregulation, immune escape, and chronic inflammation (Gu et al., 2021b; Li et al., 2022a), where T-cell transport varies significantly, forming different patterns of infiltration in GC and providing a novel system for evaluating prognosis and guiding immunotherapy (Zhang et al., 2020b). Immune cell infiltration and T-cell associated immune responses are restrained when WTAP is upregulated in GC (Li et al., 2020). Similarly, Bai et al. have reported that the upregulation of YTHDF1 in GC limits the induction of dendritic cell recruitment and infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, repressing anti-tumor immunity (Bai et al., 2022). METTL14 is downregulated in macrophages of CRC, promoting tumor progression; this reveals a potential relationship between these cells and the infiltration of surrounding CD8+ T cells in the TME. Accordingly, METTL14 might be a new target of CRC immunotherapy (Dong et al., 2021). We can manipulate m6A modification of immune cells for improving immunotherapy outcomes in GI cancer patients. A research team has utilized nanoparticle-encapsulated YTHDF1-siRNA to enhance anti-tumor immunity in CD34 humanised CRC mouse model (Bao et al., 2023). Another study demonstrates that depletion of METTL3 or METTL14 could increase the sensitivity of anti-PD-1 therapy by supporting the function of cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells (Wang et al., 2020e). These studies collectively illustrate the potential link between m6A regulators and the efficacy of immunotherapy in GI cancer, and suggest new therapeutic targets.
The levels of m6A regulators could be used to predict immune features of the TME (Gu et al., 2021b). Based on a principal component analysis, an m6A score associated with the TME phenotype was established and showed predictive value for the anti-PD-1/L1-based immunotherapy response in GC (Zhang et al., 2020b). In colon cancer, an m6Sig scoring system for quantifying the levels of m6A, influenced by m6A phenotype-related genes, is correlated with immune infiltration and immune responses (Chong et al., 2021). In addition, a reduction of METTL3 in macrophages inhibits the efficacy of Programmed Cell Death (PD-1) blockade therapy (Yin et al., 2021). However, Wang et al. recently found that in pMMR-MSI-L CRC tumors with low mutational burdens, the depletion of METTL3 or loss of METTL14 stimulates the secretion of CXCL9 and CXCL10 and induces METTL3/14-related STAT1 and IRF1 mRNA stability by YTHDF2, improving the response to anti-PD-1 therapy (Wang et al., 2020e). These two contradictory effects of METTL3 on anti-PD-1 treatment might be attributed to differences among cancer types, as well as distinct regulatory mechanisms.
Resistance to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and molecular targeted therapy is an urgent problem. Given that the microenvironment around the solid tumor is complex, radiotherapy resistance is associated with multiple characteristics, such as DNA damage, reduced apoptosis, arrested cell cycle, and dysfunctional mitochondria in GI cancer cells. Based on (5-fluorouracil) 5-FU, chemotherapy regimens for GI cancer display the limitation due to drug resistance, which causes relapse after standard chemotherapeutic courses. Although patients’ specificity is considered by immunotherapy strategy like anti–PD-1/PD-L1 immune-checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment, mutation patterns such as mismatch-repair- proficient (pMMR) and microsatellite-stable (MSS) of CRC lead to not respond to immunotherapy. Several mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance have been reported, such as multi-drug resistant genes, epigenetic changes, DNA damage repair, and cancer stem cells (Holohan et al., 2013). In addition to applications for the exploration of novel immunotherapy drugs, m6A plays an important role in therapy resistance (Zhuang et al., 2023). m6A mediates therapy resistance by regulating the drug transportation, autophagy, DNA damage repair, and TME remodeling (Lin et al., 2022). As mentioned above, METTL3 is highly expressed in GC via the METTL3/miR-17-92 pathway and is related to an elevated sensitivity to everolimus (Sun et al., 2020). However, Li et al. reported that METTL3 is elevated in CD133+ GC stem cells and the recruitment of YTHDF1 to the 3′UTR of PRAP1 mRNA stabilizes PRAP1, mediating oxaliplatin resistance (Li et al., 2022b). Additionally, m6A methylation of human Polycomb 3 (CBX8) increases chemoresistance in colon cancer by maintaining the stability of CBX8 mRNA (Zhang et al., 2019c).There is evidence suggesting that chemotherapeutic resistance in CRC relies on METTL3-mediated Sec62 expression (Liu et al., 2021). METTL3 is also upregulated in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in patients with CRC with oxaliplatin resistance and downregulates TRAF5, inhibiting necroptosis (Lan et al., 2021), similar to its role in GC. In subsequent work, Pan et al. explored the mechanism by which m6A contributes to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) resistance and found that exosomal miR-181d-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) is promoted by METTL3 in CRC cells, inhibiting neurocalcin δ (NCALD) and mediating resistance to 5-FU (Pan et al., 2022). These data indicate that METTL3 mediates different drug resistance mechanisms for different chemotherapy regimens in GC, providing a new target for individualized treatment and overcoming drug resistance. Furthermore, Chen et al. found that increased YTHDF1 can improve cisplatin resistance in colon cancer by increasing glutaminase (GLS) translation (Chen et al., 2021c).
In addition to chemotherapy resistance, m6A is involved in resistance to molecular targeted therapy. In resistant leukemia cells treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, the overexpression of FTO elevates mRNA stability and promotes tumor cell survival, providing a target for inhibition of drug resistance (Yan et al., 2018). Resistance to cetuximab, which targets epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), is related to the upregulation of pleckstrin homology-like domain, family B, member 2 (PHLDB2), whose mRNA might be methylated by METTL14 (Luo et al., 2022). These results suggest that the abnormal expression of m6A regulators mediates drug resistance or that various treatments alter their expression patterns and thus result in resistance. Given that most m6A regulators tend to enhance the resistance of GI cancer, selective small-molecule inhibitors of these regulators, which combines other therapies such as chemotherapy, might be applied in the clinic.
As a major focus of recent research, m6A is involved in various aspects of cancer biology, including development and cancer-related metabolism. The feasibility of high-throughput sequencing and other detection techniques has improved our understanding of the critical functions of m6A modification in controlling cancer cell phenotypes and gene expression, particularly by the post-transcriptional regulation of mRNAs and ncRNAs. In this review, we comprehensively summarized recent progress on the mechanisms of m6A regulation in GI cancer from the perspectives of related coding and non-coding RNAs and the potential impact of m6A on the efficiency of GI cancer therapy. From the existing researches, we have found that m6A regulates tumor growth and progression, and we can predict that m6A regulators can be associated with prognosis of GI cancer patients, which provides a new idea for future GI cancer diagnosis and therapy. Previous studies have revealed that ncRNAs are involved in cancer development, including tumor proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and carcinogenesis, and are mutually regulated (Yi et al., 2020). However, further research related to the specific regulatory mechanism underlying the effects of m6A, such as its direct function on RNAs, is still in a preliminary stage in GI and other cancers. Relationships between m6A factors and their targeted RNAs provide a novel direction for clinical diagnosis and treatment. However, the vast majority of published studies explore the m6A regulatory factors as tumor prognostic markers and reflect the value of the treatment effect. Meanwhile, almost no studies address ncRNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker. This might be due to the abnormal expression of these molecules, which can be detected in a wide variety of cancers; in addition, the regulatory mechanism in each cancer is still in the exploratory stage. Additionally, it is unclear whether the risk factors of GI cancer, such as infection of Hp, diabetes, and aging leading to carcinogenesis are due to the change of the m6A level. As a result, its specificity as an early diagnostic marker is insufficient. Furthermore, future studies of m6A regulation should focus on systematically combining concrete protein, RNA modification, and signaling pathway data. The effect of small molecular specific inhibitors of m6A are still observed in mouse models, and has not been reported clinically. Exploring effective inhibitors targeting m6A regulators and combining them with the existing drugs will provide a new window for GI cancer treatment.
MW: Writing–original draft. ZL: Writing–review and editing. XF: Writing–review and editing. XC: Writing–review and editing. YH: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Project of Jilin Province (Grant No. 20210101337JC,20220402071GH).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Bai, X., Wong, C. C., Pan, Y., Chen, H., Liu, W., Zhai, J., et al. (2022). Loss of YTHDF1 in gastric tumors restores sensitivity to antitumor immunity by recruiting mature dendritic cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 10 (2), e003663. doi:10.1136/jitc-2021-003663
Bao, Y., Zhai, J., Chen, H., Wong, C. C., Liang, C., Ding, Y., et al. (2023). Targeting m6A reader YTHDF1 augments antitumour immunity and boosts anti-PD-1 efficacy in colorectal cancer. Gut 72 (8), 1497–1509. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328845
Beermann, J., Piccoli, M. T., Viereck, J., and Thum, T. (2016). Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: background, mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol. Rev. 96 (4), 1297–1325. doi:10.1152/physrev.00041.2015
Cai, X., Wang, X., Cao, C., Gao, Y., Zhang, S., Yang, Z., et al. (2018). HBXIP-elevated methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. 415, 11–19. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.018
Chen, B., Hong, Y., Gui, R., Zheng, H., Tian, S., Zhai, X., et al. (2022b). N6-methyladenosine modification of circ_0003215 suppresses the pentose phosphate pathway and malignancy of colorectal cancer through the miR-663b/DLG4/G6PD axis. Cell. Death Dis. 13 (9), 804. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05245-2
Chen, C., Yuan, W., Zhou, Q., Shao, B., Guo, Y., Wang, W., et al. (2021b). N6-methyladenosine-induced circ1662 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by accelerating YAP1 nuclear localization. Theranostics 11 (9), 4298–4315. doi:10.7150/thno.51342
Chen, M., Wei, L., Law, C. T., Tsang, F. H., Shen, J., Cheng, C. L., et al. (2018). RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology 67 (6), 2254–2270. doi:10.1002/hep.29683
Chen, P., Li, S., Zhang, K., Zhao, R., Cui, J., Zhou, W., et al. (2021a). N6-methyladenosine demethylase ALKBH5 suppresses malignancy of esophageal cancer by regulating microRNA biogenesis and RAI1 expression. Oncogene 40 (37), 5600–5612. doi:10.1038/s41388-021-01966-4
Chen, P., Liu, X. Q., Lin, X., Gao, L. Y., Zhang, S., and Huang, X. (2021c). Targeting YTHDF1 effectively re-sensitizes cisplatin-resistant colon cancer cells by modulating GLS-mediated glutamine metabolism. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 20, 228–239. doi:10.1016/j.omto.2021.01.001
Chen, R. X., Chen, X., Xia, L. P., Zhang, J. X., Pan, Z. Z., Ma, X. D., et al. (2019a). N6-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 4695. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12651-2
Chen, S., Zhang, L., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Sun, M., Wang, L., et al. (2022a). Fusobacterium nucleatum reduces METTL3-mediated m6A modification and contributes to colorectal cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 1248. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28913-5
Chen, X., Xu, M., Xu, X., Zeng, K., Liu, X., Pan, B., et al. (2020a). METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SOX4 mRNA inhibits tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 106. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01220-7
Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Shu, Y., He, J., and Gao, W. (2020b). Interaction between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 94. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01207-4
Chen, Y. G., Chen, R., Ahmad, S., Verma, R., Kasturi, S. P., Amaya, L., et al. (2019b). N6-Methyladenosine modification controls circular RNA immunity. Mol. Cell. 76 (1), 96–109. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.016
Chong, W., Shang, L., Liu, J., Fang, Z., Du, F., Wu, H., et al. (2021). m6A regulator-based methylation modification patterns characterized by distinct tumor microenvironment immune profiles in colon cancer. Theranostics 11 (5), 2201–2217. doi:10.7150/thno.52717
Cui, J., Tian, J., Wang, W., He, T., Li, X., Gu, C., et al. (2021a). IGF2BP2 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer through a YAP-dependent mechanism. Cancer Sci. 112 (10), 4087–4099. doi:10.1111/cas.15083
Cui, Y., Zhang, C., Ma, S., Li, Z., Wang, W., Li, Y., et al. (2021b). RNA m6A demethylase FTO-mediated epigenetic up-regulation of LINC00022 promotes tumorigenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 294. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02096-1
Deng, X., Su, R., Weng, H., Huang, H., Li, Z., and Chen, J. (2018). RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in cancers: current status and perspectives. Cell. Res. 28 (5), 507–517. doi:10.1038/s41422-018-0034-6
Desrosiers, R., Friderici, K., and Rottman, F. (1974). Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 71 (10), 3971–3975. doi:10.1073/pnas.71.10.3971
Dong, L., Chen, C., Zhang, Y., Guo, P., Wang, Z., Li, J., et al. (2021). The loss of RNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase Mettl14 in tumor-associated macrophages promotes CD8 + T cell dysfunction and tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 39 (7), 945–957.e10. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.016
Du, M., Zhang, Y., Mao, Y., Mou, J., Zhao, J., Xue, Q., et al. (2017). MiR-33a suppresses proliferation of NSCLC cells via targeting METTL3 mRNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 482 (4), 582–589. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.077
Fan, H. N., Chen, Z. Y., Chen, X. Y., Chen, M., Yi, Y. C., Zhu, J. S., et al. (2022). METTL14-mediated m6A modification of circORC5 suppresses gastric cancer progression by regulating miR-30c-2-3p/AKT1S1 axis. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 51. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01521-z
Frye, M., Harada, B. T., Behm, M., and He, C. (2018). RNA modifications modulate gene expression during development. Science 361 (6409), 1346–1349. doi:10.1126/science.aau1646
Gao, Z., Long, Y., Wu, Y., Pu, Y., and Xue, F. (2022). LncRNA LINC02253 activates KRT18/MAPK/ERK pathway by mediating N6-methyladenosine modification of KRT18 mRNA in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 43 (5), 419–429. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgac018
Ge, L., Zhang, N., Chen, Z., Song, J., Wu, Y., Li, Z., et al. (2020). Level of N6-methyladenosine in peripheral blood RNA: a novel predictive biomarker for gastric cancer. Clin. Chem. 66 (2), 342–351. doi:10.1093/clinchem/hvz004
Gu, Y., Niu, S., Wang, Y., Duan, L., Pan, Y., Tong, Z., et al. (2021a). DMDRMR-mediated regulation of m(6)a-modified CDK4 by m(6)A reader IGF2BP3 drives ccRCC progression. Cancer Res. 81 (4), 923–934. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1619
Gu, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, J., Fang, Y., Pan, Y., Shu, Y., et al. (2021b). The evolving landscape of N6-methyladenosine modification in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 29 (5), 1703–1715. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.04.009
Guo, C., Chu, H., Gong, Z., Zhang, B., Li, C., Chen, J., et al. (2021a). HOXB13 promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via IGF-1R upregulation and subsequent activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Life Sci. 278, 119522. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119522
Guo, W., Tan, F., Huai, Q., Wang, Z., Shao, F., Zhang, G., et al. (2021b). Comprehensive analysis of PD-L1 expression, immune infiltrates, and m6A RNA methylation regulators in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 12, 669750. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.669750
Guo, X., Li, K., Jiang, W., Hu, Y., Xiao, W., Huang, Y., et al. (2020). RNA demethylase ALKBH5 prevents pancreatic cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of PER1 in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 91. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01158-w
Han, D., Liu, J., Chen, C., Dong, L., Liu, Y., Chang, R., et al. (2019b). Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m6A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature 566 (7743), 270–274. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0916-x
Han, H., Yang, C., Zhang, S., Cheng, M., Guo, S., Zhu, Y., et al. (2021). METTL3-mediated m6A mRNA modification promotes esophageal cancer initiation and progression via Notch signaling pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 26, 333–346. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2021.07.007
Han, J., Wang, J. Z., Yang, X., Yu, H., Zhou, R., Lu, H. C., et al. (2019a). METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 110. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1036-9
Hanniford, D., Ulloa-Morales, A., Karz, A., Berzoti-Coelho, M. G., Moubarak, R. S., Sánchez-Sendra, B., et al. (2020). Epigenetic silencing of CDR1as drives IGF2BP3-mediated melanoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Cell. 37 (1), 55–70. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2019.12.007
He, H., Wu, W., Sun, Z., and Chai, L. (2019b). MiR-4429 prevented gastric cancer progression through targeting METTL3 to inhibit m6A-caused stabilization of SEC62. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 517 (4), 581–587. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.058
He, L. E., Li, H. Y., Wu, A. Q., Peng, Y. L., Shu, G., and Yin, G. (2019a). Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 176. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1109-9
Holohan, C., Van Schaeybroeck, S., Longley, D. B., and Johnston, P. G. (2013). Cancer drug resistance an evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13 (10), 714–726. doi:10.1038/nrc3599
Hou, P., Meng, S., Li, M., Lin, T., Chu, S., Li, Z., et al. (2021). LINC00460/DHX9/IGF2BP2 complex promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by mediating HMGA1 mRNA stability depending on m6A modification. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 52. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-01857-2
Hu, H., Kong, Q., Huang, X. X., Zhang, H. R., Hu, K. F., Jing, Y., et al. (2021). Longnon-coding RNA BLACAT2 promotes gastric cancer progression via the miR-193b-5p/METTL3 pathway. J. Cancer 12 (11), 3209–3221. doi:10.7150/jca.50403
Hu, Y., Gong, C., Li, Z., Liu, J., Chen, Y., Huang, Y., et al. (2022). Demethylase ALKBH5 suppresses invasion of gastric cancer via PKMYT1 m6A modification. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 34. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01522-y
Huang, H., Weng, H., Sun, W., Qin, X., Shi, H., Wu, H., et al. (2018). Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat. Cell. Biol. 20 (3), 285–295. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z
Huang, J., Sun, W., Wang, Z., Lv, C., Zhang, T., Zhang, D., et al. (2022). FTO suppresses glycolysis and growth of papillary thyroid cancer via decreasing stability of APOE mRNA in an N6-methyladenosine-dependent manner. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 41 (1), 42. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02254-z
Huo, F. C., Zhu, Z. M., Zhu, W. T., Du, Q. Y., Liang, J., and Mou, J. (2021). METTL3-mediated m6A methylation of SPHK2 promotes gastric cancer progression by targeting KLF2. Oncogene 40 (16), 2968–2981. doi:10.1038/s41388-021-01753-1
Jia, G., Fu, Y., Zhao, X., Dai, Q., Zheng, G., Yang, Y., et al. (2011). N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7 (12), 885–887. doi:10.1038/nchembio.687
Jia, R., Chai, P., Wang, S., Sun, B., Xu, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2019). m6A modification suppresses ocular melanoma through modulating HINT2 mRNA translation. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 161. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1088-x
Ji G, H. C., He, S., Gong, Y., Song, G., Li, X., Zhou, L., et al. (2020). Comprehensive analysis of m6A regulators prognostic value in prostate cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 12 (14), 14863–14884. doi:10.18632/aging.103549
Jin, D., Guo, J., Wu, Y., Du, J., Yang, L., Wang, X., et al. (2019). m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce NSCLC drug resistance and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 12 (1), 135. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0830-6
Jin, Y., Wang, Z., He, D., Zhu, Y., Hu, X., Gong, L., et al. (2021). Analysis of m6A-related signatures in the tumor immune microenvironment and identification of clinical prognostic regulators in adrenocortical carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 12, 637933. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.637933
Kang, J., Huang, X., Dong, W., Zhu, X., Li, M., and Cui, N. (2021). MicroRNA-1269b inhibits gastric cancer development through regulating methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3). Bioengineered 12 (1), 1150–1160. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1909951
Ke, S., Saito, Y., Fak, J. J., Vågbø, C. B., Geula, S., Hanna, J. H., et al. (2017). m6A mRNA modifications are deposited in nascent pre-mRNA and are not required for splicing but do specify cytoplasmic turnover. Genes. Dev. 31 (10), 990–1006. doi:10.1101/gad.301036.117
Lan, H., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Wang, X., Guan, Z., Du, J., et al. (2021). Tumor-associated macrophages promote oxaliplatin resistance via METTL3-mediated m6A of TRAF5 and necroptosis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Pharm. 18 (3), 1026–1037. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00961
Li, H., Su, Q., Li, B., Lan, L., Wang, C., Li, W., et al. (2020). High expression of WTAP leads to poor prognosis of gastric cancer by influencing tumour-associated T lymphocyte infiltration. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24 (8), 4452–4465. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15104
Li, H., Wang, C., Lan, L., Yan, L., Li, W., Evans, I., et al. (2022b). METTL3 promotes oxaliplatin resistance of gastric cancer CD133+ stem cells by promoting PARP1 mRNA stability. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79 (3), 135. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04129-0
Li, H., Zhang, N., Jiao, X., Wang, C., Sun, W., He, Y., et al. (2021d). Downregulation of microRNA-6125 promotes colorectal cancer growth through YTHDF2-dependent recognition of N6-methyladenosine-modified GSK3β. Clin. Transl. Med. 11 (10), e602. doi:10.1002/ctm2.602
Li, H. B., Tong, J., Zhu, S., Batista, P. J., Duffy, E. E., Zhao, J., et al. (2017b). m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways. Nature 548 (7667), 338–342. doi:10.1038/nature23450
Li, K., Chen, J., Lou, X., Li, Y., Qian, B., Xu, D., et al. (2021b). HNRNPA2B1 affects the prognosis of esophageal cancer by regulating the miR-17-92 cluster. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9, 658642. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.658642
Li, L., Xie, R., and Wei, Q. (2021a). Network analysis of miRNA targeting m6A-related genes in patients with esophageal cancer. PeerJ 9, e11893. doi:10.7717/peerj.11893
Li, T., Hu, P. S., Zuo, Z., Lin, J. F., Li, X., Wu, Q. N., et al. (2019). METTL3 facilitates tumor progression via an m6A-IGF2BP2-dependent mechanism in colorectal carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 112. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1038-7
Li, X., Ma, S., Deng, Y., Yi, P., and Yu, J. (2022a). Targeting the RNA m6A modification for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 76. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01558-0
Li, Z., Weng, H., Su, R., Weng, X., Zuo, Z., Li, C., et al. (2017a). FTO plays an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a N(6)-methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell. 31 (1), 127–141. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.11.017
Lin, H., Wang, Y., Wang, P., Long, F., and Wang, T. (2022). Mutual regulation between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and circular RNAs in cancer: impacts on therapeutic resistance. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 148. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01620-x
Liu, H. T., Zou, Y. X., Zhu, W. J., Sen, L., Zhang, G. H., Ma, R. R., et al. (2022b). lncRNA THAP7-AS1, transcriptionally activated by SP1 and post-transcriptionally stabilized by METTL3-mediated m6A modification, exerts oncogenic properties by improving CUL4B entry into the nucleus. Cell. Death Differ. 29 (3), 627–641. doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00879-9
Liu, L., Wang, J., Sun, G., Wu, Q., Ma, J., Zhang, X., et al. (2019). m6A mRNA methylation regulates CTNNB1 to promote the proliferation of hepatoblastoma. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 188. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1119-7
Liu, T., Wei, Q., Jin, J., Luo, Q., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2020). The m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via augmenting EIF3C translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (7), 3816–3831. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa048
Liu, X. F., Su, K. Q., Sun, X. Y., Jiang, Y., Wang, L. J., Hu, C. Y., et al. (2021). Sec62 promotes stemness and chemoresistance of human colorectal cancer through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 132. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-01934-6
Liu, Y., Zhai, E., Chen, J., Qian, Y., Zhao, R., Ma, Y., et al. (2022a). m6A-mediated regulation of PBX1-GCH1 axis promotes gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by elevating tetrahydrobiopterin levels. Cancer Commun. (Lond) 42 (4), 327–344. doi:10.1002/cac2.12281
Luo, M., Huang, Z., Yang, X., Chen, Y., Jiang, J., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). PHLDB2 mediates cetuximab resistance via interacting with EGFR in latent metastasis of colorectal cancer. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13 (4), 1223–1242. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.12.011
Ma, J. Z., Yang, F., Zhou, C. C., Liu, F., Yuan, J. H., Wang, F., et al. (2017). METTL14 suppresses the metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating N6 -methyladenosine-dependent primary MicroRNA processing. Hepatology 65 (2), 529–543. doi:10.1002/hep.28885
Ni, W., Yao, S., Zhou, Y., Liu, Y., Huang, P., Zhou, A., et al. (2019). Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by interacting with and triggering YAP phosphorylation and degradation and is negatively regulated by the m(6)A reader YTHDF3. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 143. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1079-y
Nombela, P., Miguel-Lopez, B., and Blanco, S. (2021). The role of m6A, m5C and Psi RNA modifications in cancer: novel therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 18. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01263-w
Pan, S., Deng, Y., Fu, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., and Qin, X. (2022). N6methyladenosine upregulates miR181d5p in exosomes derived from cancerassociated fibroblasts to inhibit 5FU sensitivity by targeting NCALD in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 60 (2), 14. doi:10.3892/ijo.2022.5304
Paramasivam, A., and Vijayashree Priyadharsini, J. (2020). Novel insights into m6A modification in circular RNA and implications for immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 17 (6), 668–669. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0387-x
Patil, D. P., Chen, C. K., Pickering, B. F., Chow, A., Jackson, C., Guttman, M., et al. (2016). m6A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 537 (7620), 369–373. doi:10.1038/nature19342
Peng, W., Li, J., Chen, R., Gu, Q., Yang, P., Qian, W., et al. (2019). Upregulated METTL3 promotes metastasis of colorectal Cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 393. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1408-4
Pi, J., Wang, W., Ji, M., Wang, X., Wei, X., Jin, J., et al. (2021). YTHDF1 promotes gastric carcinogenesis by controlling translation of FZD7. Cancer Res. 81 (10), 2651–2665. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0066
Roundtree, I. A., Evans, M. E., Pan, T., and He, C. (2017). Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell. 169 (7), 1187–1200. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.045
Satterwhite, E. R., and Mansfield, K. D. (2021). RNA methyltransferase METTL16: targets and function. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA, e1681. doi:10.1002/wrna.1681
Shen, C., Xuan, B., Yan, T., Ma, Y., Xu, P., Tian, X., et al. (2020). m6A-dependent glycolysis enhances colorectal cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 72. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01190-w
Shen, S., Zhang, R., Jiang, Y., Li, Y., Lin, L., Liu, Z., et al. (2021). Comprehensive analyses of m6A regulators and interactive coding and non-coding RNAs across 32 cancer types. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 67. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01362-2
Shi, H., Wei, J., and He, C. (2019). Where, when, and how: context-dependent functions of RNA methylation writers, readers, and erasers. Mol. Cell. 74 (4), 640–650. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.025
Song, C., and Zhou, C. (2021). HOXA10 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote gastric cancer metastasis partly via modulation of TGFB2/Smad/METTL3 signaling axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 62. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-01859-0
Song, H., Song, J., Cheng, M., Zheng, M., Wang, T., Tian, S., et al. (2021). METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation promotes the anti-tumour immunity of natural killer cells. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 5522. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25803-0
Song, P., Feng, L., Li, J., Dai, D., Zhu, L., Wang, C., et al. (2020). β-catenin represses miR455-3p to stimulate m6A modification of HSF1 mRNA and promote its translation in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 129. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01244-z
Sun, Y., Li, S., Yu, W., Zhao, Z., Gao, J., Chen, C., et al. (2020). N6-methyladenosine-dependent pri-miR-17-92. maturation suppresses PTEN/TMEM127 and promotes sensitivity to everolimus in gastric cancer. Cell. Death Dis. 11 (10), 836. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03049-w
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Visvanathan, A., Patil, V., Arora, A., Hegde, A. S., Arivazhagan, A., Santosh, V., et al. (2018). Essential role of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in glioma stem-like cells maintenance and radioresistance. Oncogene 37 (4), 522–533. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.351
Vu, L. P., Pickering, B. F., Cheng, Y., Zaccara, S., Nguyen, D., Minuesa, G., et al. (2017). The N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat. Med. 23 (11), 1369–1376. doi:10.1038/nm.4416
Wang, G., Zhang, Z., and Xia, C. (2021g). Long non-coding RNA LINC00240 promotes gastric cancer progression via modulating miR-338-5p/METTL3 axis. Bioengineered 12 (2), 9678–9691. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1983276
Wang, H., Hu, X., Huang, M., Liu, J., Gu, Y., Ma, L., et al. (2019c). Mettl3-mediated mRNA m6A methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 1898. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09903-6
Wang, H., Wei, W., Zhang, Z. Y., Liu, Y., Shi, B., Zhong, W., et al. (2021b). TCF4 and HuR mediated-METTL14 suppresses dissemination of colorectal cancer via N6-methyladenosine-dependent silencing of ARRDC4. Cell. Death Dis. 13 (1), 3. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04459-0
Wang, J. M., Li, X., Yang, P., Geng, W. B., and Wang, X. Y. (2022b). Identification of a novel m6A-related lncRNA pair signature for predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 22 (1), 76. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02159-3
Wang, L., Hui, H., Agrawal, K., Kang, Y., Li, N., Tang, R., et al. (2020e). m6A RNA methyltransferases METTL3/14 regulate immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. EMBO J. 39 (20), e104514. doi:10.15252/embj.2020104514
Wang, M., Liu, J., Zhao, Y., He, R., Xu, X., Guo, X., et al. (2020a). Upregulation of METTL14 mediates the elevation of PERP mRNA N6 adenosine methylation promoting the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 130. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01249-8
Wang, Q., Chen, C., Ding, Q. Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z. D., Chen, J. J., et al. (2020d). METTL3-mediated m6A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut 69 (7), 1193–1205. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319639
Wang, Q., Guo, X., Li, L., Gao, Z., Su, X., Ji, M., et al. (2020b). N6-methyladenosine METTL3 promotes cervical cancer tumorigenesis and Warburg effect through YTHDF1/HK2 modification. Cell. Death Dis. 11 (10), 911. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03071-y
Wang, S., Gan, M., Chen, C., Zhang, Y., Kong, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2021c). Methyl CpG binding protein 2 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating N6-methyladenosine methylation through methyltransferase-like 14. Cancer Sci. 112 (8), 3243–3254. doi:10.1111/cas.15011
Wang, S., Gao, S., Zeng, Y., Zhu, L., Mo, Y., Wong, C. C., et al. (2022a). N6-Methyladenosine reader YTHDF1 promotes ARHGEF2 translation and RhoA signaling in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 162 (4), 1183–1196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.269
Wang, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhu, C., Wang, C., Yu, F., et al. (2021f). Long non-coding RNA NRON promotes tumor proliferation by regulating ALKBH5 and Nanog in gastric cancer. J. Cancer 12 (22), 6861–6872. doi:10.7150/jca.60737
Wang, T., Kong, S., Tao, M., and Ju, S. (2020c). The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in Cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 88. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01204-7
Wang, W., Shao, F., Yang, X., Wang, J., Zhu, R., Yang, Y., et al. (2021a). METTL3 promotes tumour development by decreasing APC expression mediated by APC mRNA N6-methyladenosine-dependent YTHDF binding. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 3803. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23501-5
Wang, X., Liu, C., Zhang, S., Yan, H., Zhang, L., Jiang, A., et al. (2021e). N6-methyladenosine modification of MALAT1 promotes metastasis via reshaping nuclear speckles. Dev. Cell. 56 (5), 702–715.e8. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2021.01.015
Wang, X., Zhang, J., and Wang, Y. (2019a). Long noncoding RNA GAS5-AS1 suppresses growth and metastasis of cervical cancer by increasing GAS5 stability. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (8), 4909–4921.
Wang, X. K., Zhang, Y. W., Wang, C. M., Li, B., Zhang, T. Z., Zhou, W. J., et al. (2021d). METTL16 promotes cell proliferation by up-regulating cyclin D1 expression in gastric cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 25 (14), 6602–6617. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16664
Wang, Y., Lu, J. H., Wu, Q. N., Jin, Y., Wang, D. S., Chen, Y. X., et al. (2019b). LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 174. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1105-0
Warda, A. S., Kretschmer, J., Hackert, P., Lenz, C., Urlaub, H., Hobartner, C., et al. (2017). Human METTL16 is a N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 18 (11), 2004–2014. doi:10.15252/embr.201744940
Wei, J., and He, C. (2021). Chromatin and transcriptional regulation by reversible RNA methylation. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 70, 109–115. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2020.11.005
Wei, J., Liu, F., Lu, Z., Fei, Q., Ai, Y., He, P. C., et al. (2018). Differential m6A, m6Am, and m1A demethylation mediated by FTO in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. Mol. Cell. 71 (6), 973–985. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.011
Wei, J., Yu, X., Yang, L., Liu, X., Gao, B., Huang, B., et al. (2022). FTO mediates LINE1 m6A demethylation and chromatin regulation in mESCs and mouse development. Science 376 (6596), 968–973. doi:10.1126/science.abe9582
Wen, S., Wei, Y., Zen, C., Xiong, W., Niu, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes bone metastasis of prostate cancer through N6-methyladenosine. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 171. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01293-4
Wu, X. L., Lu, R. Y., Wang, L. K., Wang, Y. Y., Dai, Y. J., Wang, C. Y., et al. (2018). Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR silencing inhibits invasion and proliferation of human colon cancer LoVo cells via regulating IGF2BP2. J. Cell. Biochem. 120, 1221–1231. doi:10.1002/jcb.27079
Wu, Y., Yang, X., Chen, Z., Tian, L., Jiang, G., Chen, F., et al. (2019). m6A-induced lncRNA RP11 triggers the dissemination of colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of Zeb1. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 87. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1014-2
Xiao, D., Fang, T. X., Lei, Y., Xiao, S. J., Xia, J. W., Lin, T. Y., et al. (2021). m6A demethylase ALKBH5 suppression contributes to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. Aging 13 (17), 21497–21512. doi:10.18632/aging.203490
Xiao, S., Cao, S., Huang, Q., Xia, L., Deng, M., Yang, M., et al. (2019). The RNA N6-methyladenosine modification landscape of human fetal tissues. Nat. Cell. Biol. 21 (5), 651–661. doi:10.1038/s41556-019-0315-4
Xie, J. W., Huang, X. B., Chen, Q. Y., Ma, Y. B., Zhao, Y. J., Liu, L. C., et al. (2020). m6A modification-mediated BATF2 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer through inhibition of ERK signaling. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 114. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01223-4
Xu, L. C., Pan, J. X., and Pan, H. D. (2020). Construction and validation of an m6A RNA methylation regulators-based prognostic signature for esophageal cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 5385–5394. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S254870
Xu, S., Chen, W., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Xia, R., Shen, J., et al. (2022). N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs identified as potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival of Asian gastric cancer patients. BMC Cancer 22 (1), 721. doi:10.1186/s12885-022-09801-z
Yan, F., Al-Kali, A., Zhang, Z., Liu, J., Pang, J., Zhao, N., et al. (2018). A dynamic N6-methyladenosine methylome regulates intrinsic and acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cell. Res. 28 (11), 1062–1076. doi:10.1038/s41422-018-0097-4
Yan, J., Huang, X., Zhang, X., Chen, Z., Ye, C., Xiang, W., et al. (2020). LncRNA LINC00470 promotes the degradation of PTEN mRNA to facilitate malignant behavior in gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 521 (4), 887–893. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.016
Yang, X., Zhang, S., He, C., Xue, P., Zhang, L., He, Z., et al. (2020c). METTL14 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating oncogenic long non-coding RNA XIST. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 46. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-1146-4
Yang, Z., Jiang, X., Li, D., and Jiang, X. (2020a). HBXIP promotes gastric cancer via METTL3-mediated MYC mRNA m6A modification. Aging (Albany NY) 12 (24), 24967–24982. doi:10.18632/aging.103767
Yang, Z., Jiang, X., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Z., Xing, W., Liu, Y., et al. (2021b). HDAC3-dependent transcriptional repression of FOXA2 regulates FTO/m6A/MYC signaling to contribute to the development of gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 28 (1-2), 141–155. doi:10.1038/s41417-020-0193-8
Yang, Z., Li, J., Feng, G., Gao, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-145 modulates N6-methyladenosine levels by targeting the 3'-untranslated mRNA region of the N6-methyladenosine binding YTH domain family 2 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 292 (9), 3614–3623. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.749689
Yang, Z., Quan, Y., Chen, Y., Huang, Y., Huang, R., Yu, W., et al. (2021a). Knockdown of RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 represses Warburg effect in colorectal cancer via regulating HIF-1α. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6 (1), 89. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00473-y
Yang, Z., Wang, T., Wu, D., Min, Z., Tan, J., and Yu, B. (2020b). RNA N6-methyladenosine reader IGF2BP3 regulates cell cycle and angiogenesis in colon cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 39 (1), 203. doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01714-8
Ye, S., Song, W., Xu, X., Zhao, X., and Yang, L. (2016). IGF2BP2 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and survival through interfering with RAF-1 degradation by miR-195. FEBS Lett. 590 (11), 1641–1650. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.12205
Yi, Y. C., Chen, X. Y., Zhang, J., and Zhu, J. S. (2020). Novel insights into the interplay between m6A modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 121. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01233-2
Yin, H., Zhang, X., Yang, P., Zhang, X., Peng, Y., Li, D., et al. (2021). RNA m6A methylation orchestrates cancer growth and metastasis via macrophage reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 1394. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21514-8
You, A., Tian, W., Yuan, H., Gu, L., Zhou, J., and Deng, D. (2022). TTC22 promotes m6A-mediated WTAP expression and colon cancer metastasis in an RPL4 binding-dependent pattern. Oncogene 41 (32), 3925–3938. doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02402-x
Yu, T., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Chen, W., Liu, Z., Zhu, L., et al. (2022). METTL3 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by stabilizing PLAU mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 614, 9–16. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.04.141
Yuan, W., Chen, S., Li, B., Han, X., Meng, B., Zou, Y., et al. (2022). The N6-methyladenosine reader protein YTHDC2 promotes gastric cancer progression via enhancing YAP mRNA translation. Transl. Oncol. 16, 101308. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101308
Yue, B., Cui, R., Zheng, R., Jin, W., Song, C., Bao, T., et al. (2021a). Essential role of ALKBH5-mediated RNA demethylation modification in bile acid-induced gastric intestinal metaplasia. Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 26, 458–472. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2021.08.019
Yue, B., Song, C., Yang, L., Cui, R., Cheng, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019). METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 142. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1065-4
Yue, C., Chen, J., Li, Z., Li, L., Chen, J., and Guo, Y. (2020). microRNA-96 promotes occurrence and progression of colorectal cancer via regulation of the AMPKα2-FTO-m6A/MYC axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 39 (1), 240. doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01731-7
Yue, M., Liu, T., Yan, G., Luo, X., and Wang, L. (2021b). LINC01605, regulated by the EP300-SMYD2 complex, potentiates the binding between METTL3 and SPTBN2 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell. Int. 21 (1), 504. doi:10.1186/s12935-021-02180-8
Zaccara, S., Ries, R. J., and Jaffrey, S. R. (2019). Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (10), 608–624. doi:10.1038/s41580-019-0168-5
Zeng, C., Huang, W., Li, Y., and Weng, H. (2020). Roles of METTL3 in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13 (1), 117. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00951-w
Zhang, B., Wu, Q., Li, B., Wang, D., Wang, L., and Zhou, Y. L. (2020b). m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 53. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01170-0
Zhang, C., Huang, S., Zhuang, H., Ruan, S., Zhou, Z., Huang, K., et al. (2020a). YTHDF2 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4 expression via m6A RNA methylation. Oncogene 39 (23), 4507–4518. doi:10.1038/s41388-020-1303-7
Zhang, C., Zhang, M., Ge, S., Huang, W., Lin, X., Gao, J., et al. (2019b). Reduced m6A modification predicts malignant phenotypes and augmented Wnt/PI3K-Akt signaling in gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 8 (10), 4766–4781. doi:10.1002/cam4.2360
Zhang, F., Yan, Y., Cao, X., Zhang, J., Li, Y., and Guo, C. (2021c). Methylation of microRNA-338-5p by EED promotes METTL3-mediated translation of oncogene CDCP1 in gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 13 (8), 12224–12238. doi:10.18632/aging.103822
Zhang, J., Guo, S., Piao, H., Wang, Y., Wu, Y., Meng, X., et al. (2019a). ALKBH5 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by decreasing methylation of the lncRNA NEAT1. J. Physiology Biochem. 75 (3), 379–389. doi:10.1007/s13105-019-00690-8
Zhang, J. Y., Du, Y., Gong, L. P., Shao, Y. T., Pan, L. J., Feng, Z. Y., et al. (2022). ebv-circRPMS1 promotes the progression of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma via Sam68-dependent activation of METTL3. Cancer Lett. 535, 215646. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215646
Zhang, L., Wan, Y., Zhang, Z., Jiang, Y., Gu, Z., Ma, X., et al. (2021a). IGF2BP1 overexpression stabilizes PEG10 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner and promotes endometrial cancer progression. Theranostics 11 (3), 1100–1114. doi:10.7150/thno.49345
Zhang, S., Zhao, B. S., Zhou, A., Lin, K., Zheng, S., Lu, Z., et al. (2017). m6A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 31 (4), 591–606. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.013
Zhang, Y., Kang, M., Zhang, B., Meng, F., Song, J., Kaneko, H., et al. (2019c). m6A modification-mediated CBX8 induction regulates stemness and chemosensitivity of colon cancer via upregulation of LGR5. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 185. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1116-x
Zhang, Z., Gao, Q., and Wang, S. (2021b). Kinase GSK3β functions as a suppressor in colorectal carcinoma through the FTO-mediated MZF1/c-Myc axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 25 (5), 2655–2665. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16291
Zhang, Z., Wang, Q., Zhang, M., Zhang, W., Zhao, L., Yang, C., et al. (2021d). Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome-wide m6A methylome in colorectal cancer by MeRIP sequencing. Epigenetics 16 (4), 425–435. doi:10.1080/15592294.2020.1805684
Zhao, B. S., Roundtree, I. A., and He, C. (2017). Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (1), 31–42. doi:10.1038/nrm.2016.132
Zhao, H., Xu, Y., Xie, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, M., Li, S., et al. (2021). m6A Regulators is differently expressed and correlated with immune response of esophageal cancer. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9, 650023. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.650023
Zheng, G., Dahl, J. A., Niu, Y., Fedorcsak, P., Huang, C. M., Li, C. J., et al. (2013). ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol. Cell. 49 (1), 18–29. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.015
Zheng, R., Zhang, K., Tan, S., Gao, F., Zhang, Y., Xu, W., et al. (2022). Exosomal circLPAR1 functions in colorectal cancer diagnosis and tumorigenesis through suppressing BRD4 via METTL3-eIF3h interaction. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 49. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01471-y
Zheng, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Xie, L., Ge, J., Yu, G., et al. (2021). N6-Methyladenosine modification of PTTG3P contributes to colorectal cancer proliferation via YAP1. Front. Oncol. 11, 669731. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.669731
Zhou, B., Yang, H., Yang, C., Bao, Y. L., Yang, S. M., Liu, J., et al. (2021). Translation of noncoding RNAs and cancer. Cancer Lett. 497, 89–99. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.002
Zhou, Y., Huang, T., Siu, H. L., Wong, C. C., Dong, Y., Wu, F., et al. (2017). IGF2BP3 functions as a potential oncogene and is a crucial target of miR-34a in gastric carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 16 (1), 77. doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0647-2
Zhou, Y., Wang, Q., Deng, H., Xu, B., Zhou, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2022). N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via m6A modification of caveolin-1 and metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Cell. Death Dis. 13 (1), 72. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04503-7
Zhu, H., Gan, X., Jiang, X., Diao, S., Wu, H., and Hu, J. (2019). ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 163. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1159-2
Zhu, S., Wang, J. Z., Chen, D., He, Y. T., Meng, N., Chen, M., et al. (2020b). An oncopeptide regulates m6A recognition by the m6A reader IGF2BP1 and tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 1685. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15403-9
Zhu, W., Si, Y., Xu, J., Lin, Y., Wang, J. Z., Cao, M., et al. (2020a). Methyltransferase like 3 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by stabilizing CCNE1 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24 (6), 3521–3533. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15042
Keywords: m6A, mRNA, lncRNA, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer
Citation: Wang M, Liu Z, Fang X, Cong X and Hu Y (2023) The emerging role of m6A modification of non-coding RNA in gastrointestinal cancers: a comprehensive review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11:1264552. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1264552
Received: 21 July 2023; Accepted: 16 October 2023;
Published: 30 October 2023.
Edited by:
Maurizio Fanciulli, Hospital Physiotherapy Institutes (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Tianyun Long, University of California, San Diego, United StatesCopyright © 2023 Wang, Liu, Fang, Cong and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xianling Cong, Y29uZ3hsQGpsdS5lZHUuY24=; Yue Hu, eXVlaHVAamx1LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.