- 1Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation, School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, China
- 2Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, Peking University, Beijing, China
The evolutionarily conserved Hedgehog (Hh) signaling plays a critical role in embryogenesis and adult tissue homeostasis. Aberrant Hh signaling often leads to various forms of developmental anomalies and cancer. Since altered microRNA (miRNA) expression is associated with developmental defects and tumorigenesis, it is not surprising that several miRNAs have been found to regulate Hh signaling. However, these miRNAs are mainly identified through small-scale in vivo screening or in vitro assays. As miRNAs preferentially reduce target gene expression via the 3′ untranslated region, we analyzed the effect of reduced expression of core components of the Hh signaling cascade on downstream signaling activity, and generated a transgenic Drosophila toolbox of in vivo miRNA sensors for core components of Hh signaling, including hh, patched (ptc), smoothened (smo), costal 2 (cos2), fused (fu), Suppressor of fused (Su(fu)), and cubitus interruptus (ci). With these tools in hand, we performed a genome-wide in vivo miRNA overexpression screen in the developing Drosophila wing imaginal disc. Of the twelve miRNAs identified, seven were not previously reported in the in vivo Hh regulatory network. Moreover, these miRNAs may act as general regulators of Hh signaling, as their overexpression disrupts Hh signaling-mediated cyst stem cell maintenance during spermatogenesis. To identify direct targets of these newly discovered miRNAs, we used the miRNA sensor toolbox to show that miR-10 and miR-958 directly target fu and smo, respectively, while the other five miRNAs act through yet-to-be-identified targets other than the seven core components of Hh signaling described above. Importantly, through loss-of-function analysis, we found that endogenous miR-10 and miR-958 target fu and smo, respectively, whereas deletion of the other five miRNAs leads to altered expression of Hh signaling components, suggesting that these seven newly discovered miRNAs regulate Hh signaling in vivo. Given the powerful effects of these miRNAs on Hh signaling, we believe that identifying their bona fide targets of the other five miRNAs will help reveal important new players in the Hh regulatory network.
Introduction
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is a highly conserved pathway that controls multiple developmental processes, including pattern formation, proliferation and differentiation within diverse tissues. Dysfunction of Hh signaling can lead to birth defects, such as holoprosencephaly and cyclopia, and is associated with multiple cancer types, including medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma (Lee et al., 2016; Pak and Segal, 2016; Jeng et al., 2020; Liu M. et al., 2021; Jiang, 2021; Sigafoos et al., 2021). As a classic model system, the Drosophila wing plays a seminal and pivotal role in the delineation of the Hh signaling cascade. In the developing wing imaginal disc, the primordium of the adult wing, the ligand Hh acts as a morphogen. It is expressed in posterior compartment cells and secreted into the anterior compartment, where it binds to the cell surface receptor Patched (Ptc) and releases the signal transducer Smoothened (Smo) from inhibition. Activated Smo is transported from the endosome to the plasma membrane, during which it is sequentially phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA) and casein kinase 1 (CK1), and then recruits the motor protein Costal2 (Cos2), Fused (Fu) kinase, and Suppressor of fused (Su(fu)) to form an activation complex. As a result, a cytoplasmic signaling complex containing Cos2, Fu, Su(fu), and transcription factor Cubitus interruptus (Ci) is disassociated. Full-length Ci (CiFL) becomes stable and enters the nucleus to activate the expression of downstream target genes, such as decapentaplegic (dpp), ptc, and collier (col) (Hartl and Scott, 2014; Liu M. et al., 2021; Jiang, 2021).
microRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous noncoding RNAs of approximately 22 nucleotides in length. They mediate post-transcriptional gene repression through sequence-specific pairing between the miRNA seed sequence at positions 2–7 and the corresponding complementary sequence located primarily in the 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) of the mRNA target, thereby inhibiting mRNA translation, promoting mRNA decay, or both (Bushati and Cohen, 2007; Bartel, 2018). miRNAs have been found to regulate Hh signaling during development and tumorigenesis. Several miRNAs, including miR-125b, miR-212, miR-324, and miR-326, are misregulated in human medulloblastoma and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and may target key Hh signaling components to promote tumor cell proliferation and invasion (Ferretti et al., 2008; Ma et al., 2014). Among them, miR-125b and miR-326 target SMO, and miR-324 and miR-212 target GLI1 (ortholog of ci) and PTCH1, respectively (Ferretti et al., 2008; Ma et al., 2014). Furthermore, miR-30c was reported to suppress mouse P19 cell differentiation by targeting Gli2 (Liu et al., 2016). In zebrafish, miR-214 targets Su(fu) and is required for precise specification of slow-muscle cell types (Flynt et al., 2007). In Drosophila, smo, cos2, and fu are targets of miR-12 and miR-283 (Friggi-Grelin et al., 2008). miR-7 and miR-14 negatively regulate Hh signaling by targeting interference hedgehog (ihog), a co-receptor of Hh ligand, and hh, respectively (Da Ros et al., 2013; Kim et al., 2014). In addition, two screens have been performed to identify miRNAs that regulate Hh signaling. The first screen was a small scale miRNA overexpression screen examining the role of 40 miRNAs in Drosophila wings and found that miR-5, miR-932, and miR-960 modulate Hh signaling by directly targeting smo, brother of ihog (boi), and smo, cos2 and fu, respectively (Wu et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2013a; Gao et al., 2013b). The second screen analyzed 132 miRNAs in cultured Drosophila S2R+ cells. Using in vitro miRNA sensors for core Hh pathway components as readouts, 43 miRNAs were identified as potential regulators of Hh signaling (Kim et al., 2014). However, these early screens were either poorly covered or not fully validated in vivo. For example, miR-5 and miR-960, which are known to regulate Hh signaling in wing discs, were not identified in the in vitro screen (Kim et al., 2014). miR-7 and miR-932 were reported in the in vivo screen to target ihog and boi, respectively (Gao et al., 2013b; Da Ros et al., 2013), but in vitro screening only found them to target cos2 and hh, respectively (Kim et al., 2014). Furthermore, miR-12 and miR-283 target multiple Hh pathway components in the developing wing, but were shown to regulate only a single target in the in vitro screen (Friggi-Grelin et al., 2008; Kim et al., 2014). These disagreements suggest that in vitro screening may not be sufficient to identify miRNAs that regulate Hh signaling in vivo. Therefore, a genome-wide in vivo screen is required to systematically assess the in vivo role of miRNAs in Hh signaling.
In this study, we performed a genome-wide miRNA overexpression screen in Drosophila wing discs to dissect the miRNA network regulating Hh signaling. By examining the effects of overexpressed miRNAs on Hh signaling activation, such as CiFL stabilization and col activation, five out of the seven miRNAs known to regulate Hh signaling in vivo were identified. Moreover, our screen added seven additional miRNAs, namely miR-10, miR-133, miR-190, miR-375, miR-927, miR-958, and miR-964, to the miRNA network regulating Hh signaling. These newly discovered miRNAs all regulate Hh signaling in a cell-autonomous manner, as revealed by FLIPout clonal analysis. Furthermore, these miRNAs can regulate Hh signaling in the Drosophila testis, suggesting that they may act as general regulators of Hh signaling. Using the in vivo miRNA sensor transgenic fly toolbox, we provided direct evidence that miR-10 and miR-958 target fu and smo, respectively. Consistently, deletion of miR-10 and miR-958 significantly increased the expression of fu and smo, respectively. We have not yet identified the direct targets of the remaining five miRNAs in the Hh pathway regulatory network. However, aberrant expression of Hh pathway components was observed in loss-of-function alleles of these five miRNAs, suggesting that these newly identified miRNAs are physiologically required to maintain Hh signaling homeostasis. Therefore, finding their targets may lead to the discovery of new players in the regulatory network of Hh signaling associated with development and Hh-related diseases.
Results
The Developing Drosophila Wing as an Ideal Model System for Dissecting the miRNA Network That Regulates Hh Signaling
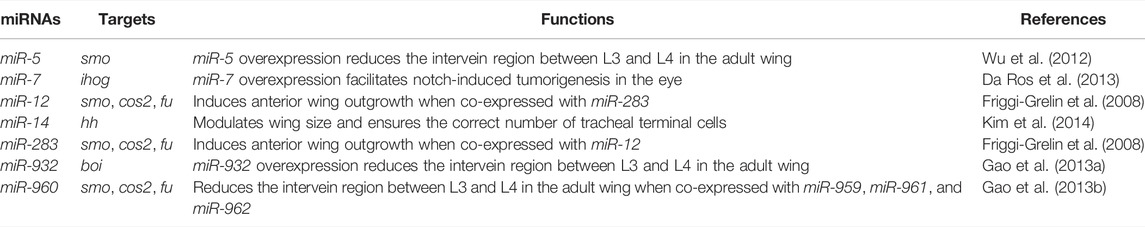
The adult Drosophila wing consists of five longitudinal veins that intersect with two transverse crossveins, extending distally to the wing margin. This stereotypical adult wing morphology is pre-patterned during larval development in a primordial tissue called the wing imaginal disc (Blair, 2007; Hartl and Scott, 2014). Hh glycoprotein, secreted from the posterior half of the wing disc, acts as a morphogen to control patterning and cell proliferation in the anterior half of the wing disc. Anterior cells abutting the anterior-posterior (A-P) boundary are sensitive to Hh signaling activity. Hh morphogen stabilizes CiFL protein to activate transcription of col/kn, which encodes a transcription factor required for patterning a region in the wing pouch corresponding to the area between longitudinal L3 and L4 veins in the adult wing blade (Blair, 2007; Hartl and Scott, 2014; Figure 1A). As the loss of ci or col expression in the wing disc results in a reduction in the space between the L3 and L4 veins (Vervoort et al., 1999), stabilization of CiFL and activation of col transcription are ideal indicators of Hh signaling activity, which can be easily determined by immunostaining with specific antibodies or through enhancer trap transgenic reporters. Monoclonal antibody 2A1 is commonly used to monitor CiFL stability (Motzny and Holmgren, 1995). Notably, in anterior cells immediately adjacent to the A-P boundary, stabilized CiFL is converted to the labile activated form of Ci (CiA). Consequently, the protein levels of 2A1-labeled CiFL are relatively low in these cells (Motzny and Holmgren, 1995; Aza-Blanc et al., 1997; Ohlmeyer and Kalderon, 1998). col transcription can be monitored by a polyclonal antibody specific for Col, or visualized in the activity of the kn-lacZ transgenic reporter, whose expression is controlled by the knMel701-1991 regulatory element (Hersh and Carroll, 2005).
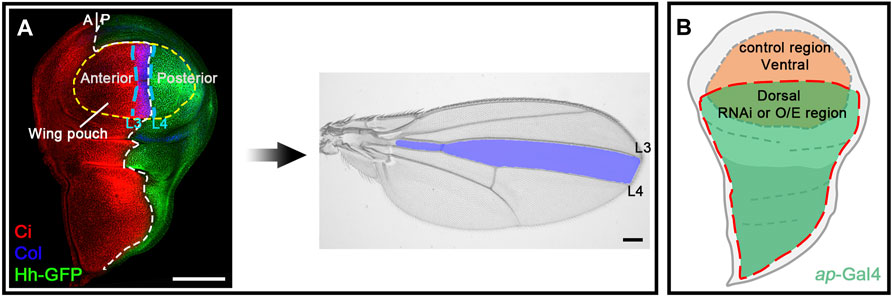
FIGURE 1. The developing Drosophila wing is an ideal model system for studying Hh signaling. (A) Shown are a wild-type third instar larval wing imaginal disc and an adult wing blade. Expression of Hh-GFP (green), Col (blue), and Ci (red) is shown. Hh protein is produced in the posterior compartment and diffuses into the anterior compartment to stabilize CiFL protein and activate col expression. The wing pouch (outlined by a yellow dashed circle) eventually metamorphose into the adult wing blade. The area between the longitudinal L3 and L4 veins of the adult wing is predetermined in the area between the two blue dashed lines in the larval wing disc, where Col is expressed. (B) A diagram showing ap-Gal4 expression area. Cells in the ventral compartment were used as an internal control. Scale bar, 100 μm.
Since miRNAs typically repress the expression of target genes, overexpressed miRNAs that directly target the Hh pathway may reduce the expression of genes encoding core Hh signaling components that contain miRNA-binding sites. As CiFL protein stabilization and col transcription are convenient and reliable readouts for Hh signaling activity, we reduced the expression of individual canonical Hh pathway components to analyze their effects on CiFL and Col for a comprehensive understanding of miRNA regulation in Hh signaling. Among the core components examined, Hh, Smo, and Ci are positive regulators, and Hh signaling activity is impaired when the genes encoding these positive regulators are mutated (Alexandre et al., 1996; van den Heuvel and Ingham, 1996; Strigini and Cohen, 1997; Vervoort et al., 1999). Consistently, when these genes were individually knocked down by apterous (ap)-Gal4-driven RNAi in dorsal compartment cells (Figure 1A and Figure 2A), we observed a significant reduction in the protein levels of CiFL and abrogation of Col expression (Figures 2B–B’’,D–D’’,H–H’’). Ptc and Cos2 negatively regulate Hh signaling by inhibiting the activation of Smo and promoting the degradation of Ci, respectively (Chen and Struhl, 1996; Sisson et al., 1997; Alcedo et al., 2000; Denef et al., 2000; Ingham et al., 2000; Zhu et al., 2003). Consistent with these studies, knockdown of ptc resulted in expansion of the labile CiA region as well as expansion and elevation of Col expression in dorsal compartment cells (Figures 2C–C’’). Likewise, reduction of cos2 expression by RNAi caused a marked increase in CiFL protein levels and an expansion of the Col-expression region (Figures 2E–E’’). The roles of Fu and Su(fu) in Hh signaling are more complex. On the one hand, Fu is required to transduce high levels of Hh signaling activity by converting CiFL to CiA (Ohlmeyer and Kalderon, 1998; Han et al., 2019). On the other hand, it also cooperates with Cos2 to promote the degradation of CiFL (Wang et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2005). In the wing discs of fu mutant flies, CiFL levels are elevated but, unexpectedly, Col expression is attenuated and labile CiA disappears (Alves et al., 1998). We observed similar results in dorsal compartment cells, where fu was knocked down by ap-Gal4-driven RNAi (Figures 2F–F’’). Su(fu) antagonizes the function of Fu, and reduced levels of CiFL are observed in Su(fu) mutants (Préat, 1992; Alves et al., 1998; Ohlmeyer and Kalderon, 1998). However, loss of Su(fu) does not result in ectopic activation of Hh signaling nor any apparent defects in adult wings (Préat et al., 1993). Consistent with previous studies, knockdown of Su(fu) in the dorsal compartment had no effects on Col expression, although decreased levels of CiFL protein were observed (Figures 2G–G’’).
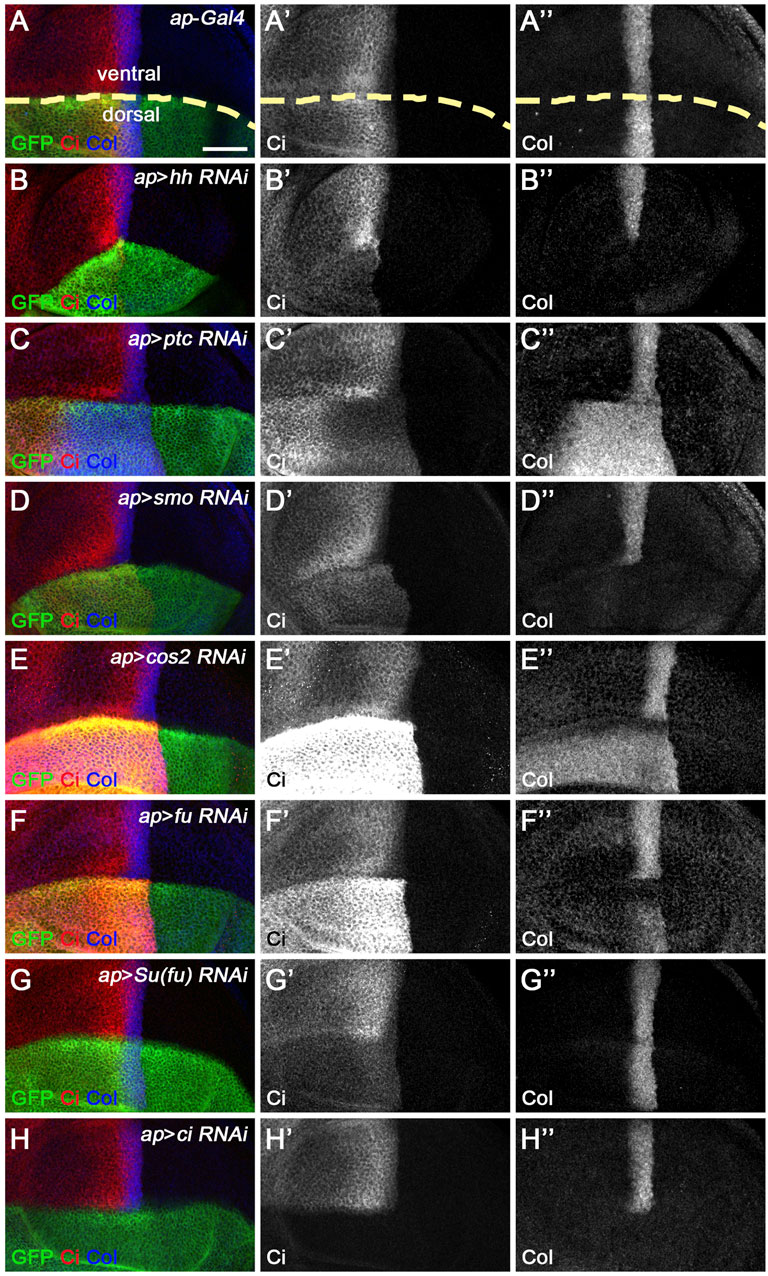
FIGURE 2. Knockdown of core Hh pathway components alters CiFL levels and Col expression. CiFL levels and Col expression were visualized by immunostaining in third instar larval wing discs of the indicated genotypes. GFP marks dsRNA-expressing cells in the dorsal compartment. (A–B’’,D–D’’,H–H’’) ap-Gal4-driven RNAi of the positive regulators of Hh signaling (i.e. hh, smo, and ci) resulted in significantly reduced levels of CiFL (B’,D’) and loss of Col expression (B”,D”,H”) in dorsal compartment cells. (C–C’’,E–E’’) Conversely, knockdown of ptc caused expansion of the labile CiA region (C’) and expansion and increase in Col expression (C”). Significant increases in CiFL levels (E’) and expanded Col expression (E”) were observed when cos2 was knocked down. (F–G’’) Decreased expression of fu resulted in elevated levels of CiFL (F’) and downregulation of Col (F”), whereas knockdown of Su(fu) led to significantly decreased levels of CiFL (G’) but had no effects on Col expression (G”). The dorsal-ventral boundary of the wing disc is marked with a yellow dashed line. Scale bar, 50 μm.
The Generation of an in vivo miRNA Sensor Toolbox for Core Hh Signaling Components
Since miRNAs primarily act by reducing target gene expression, a direct comparison of the impact of overproduced miRNAs with that of reduced expression of individual components of the Hh pathway will help identify specific Hh signaling components as potential miRNA targets. In addition, in vivo miRNA sensors containing 3′ UTRs of known Hh signaling players will provide clear evidence that candidate miRNAs function by directly targeting the corresponding core Hh pathway components (Brennecke et al., 2003). Previously, in vivo miRNA sensors for smo, cos2, and fu have been generated and used to identify these genes individually or in combination as direct targets of miR-5, miR-12, miR-283, or miR-960 (Friggi-Grelin et al., 2008; Wu et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2013a).
To extend the coverage of in vivo miRNA sensors to all known core components of the Hh pathway, we added four additional miRNA sensors for hh, ptc, Su(fu), and ci to assemble an in vivo miRNA sensor toolbox for Hh signaling. In these miRNA sensors, the expression of gfp reporter is controlled by the αTub84B promoter and the 3′ UTR derived from hh, ptc, smo, cos2, fu, Su(fu), or ci (Supplementary Figure S1A). Transgenic flies were generated through φC31 integrase-mediated site-directed integration. As expected, ubiquitous GFP expression was observed for all seven miRNA sensors in the wing disc (Supplementary Figures S1B–H’’). To demonstrate the effectiveness of these miRNA sensors, we used dpp-Gal4 to overexpress miR-14, miR-960, and miR-12, which are known to target hh, smo, and cos2 and fu, respectively, in anterior cells abutting the A-P boundary (Friggi-Grelin et al., 2008; Gao et al., 2013a; Kim et al., 2014). Consistent with previous reports, overexpression of miR-14 caused a mild but consistent downregulation of the miRNA sensor activity for hh (gfp: 3′UTRhh) (Supplementary Figures S2A–A’’). Increased miR-960 expression by ptc-Gal4 resulted in a significant decrease in gfp: 3′UTRsmo activity and Smo protein levels (Supplementary Figures S2B–B’’). miR-12 is known to directly target cos2 and fu. Consistently, increased miR-12 expression led to significantly decreased expression of gfp: 3′UTRcos2 and gfp: 3′UTRfu (Supplementary Figures S2C–D’’). Although the remaining three miRNA sensors for ptc, Su(fu), and ci were not examined because no miRNAs targeting these genes were reported, the above results suggest that the assembled in vivo miRNA sensor toolbox can be used to determine whether candidate miRNAs directly target core Hh pathway genes.
A Targeted Genome-Wide in vivo miRNA Overexpression Screen to Identify Novel miRNAs Regulating Hh Signaling
Using these two tools, we performed a genome-wide in vivo miRNA overexpression screen to systematically assess the regulation of Hh signaling by miRNAs. The Drosophila melanogaster genome contains 258 miRNA precursors, resulting in 469 mature miRNA sequences, most of which were determined by miRNA sequencing and bioinformatics prediction (Griffiths-Jones et al., 2008; Kozomara and Griffiths-Jones, 2011). In our screen, we analyzed more than 97% of miRNA precursors (149 out of 153) whose expression was confirmed by miRNA sequencing in vivo (Kozomara and Griffiths-Jones, 2014; Larkin et al., 2021). Of note, we did not include miR-283, miR-9369, miR-9388, and miR-10404 in the screen because no transgenic flies were available. Furthermore, our screen included 30 additional miRNAs whose expression in vivo had not been validated. Together, we screened 190 transgenic overexpression fly lines, covering a total of 179 miRNA precursors (hereafter referred to as miRNAs), to dissect their roles in Hh signaling (Supplementary Table S1). To unbiasedly assess the impact of individual miRNAs in Hh signaling, miRNA overexpression was confined to the dorsal half of the wing disc using the ap-Gal4 driver, whereas unaffected wild-type cells in the ventral half of the wing disc served as a perfect internal control for miRNA overexpression (Figure 1B).
In our screen, five of the seven miRNAs previously reported to regulate Hh signaling in vivo were shown to affect the expression of Ci and/or kn-lacZ (Figure 3). Among these miRNAs, miR-7, miR-14, and miR-932 negatively regulate Hh signaling by targeting ihog, hh, and boi, respectively (Table 1). Consistent with previous reports (Wu et al., 2012; Da Ros et al., 2013; Gao et al., 2013b; Kim et al., 2014), overexpression of miR-7 or miR-14 resulted in decreased levels of CiFL and downstream target col expression, compared with wild-type cells in the ventral half of the disc (Figures 3B–B’’,D–D’’). Likewise, increased miR-932 expression led to a modest increase in CiFL protein levels and a narrowing of the Col-expression domain (Figures 3E–E’’). As described previously, both miR-12 and miR-960 target multiple genes encoding components of the Hh signaling pathway, namely smo, cos2, and fu (Table 1). Overexpression of miR-12 induced elevated levels of CiFL, but not enough to alter the expression of the dpp-lacZ reporter (Friggi-Grelin et al., 2008). Consistently, we observed increased levels of CiFL and little change in kn-lacZ expression when miR-12 was overexpressed by the ap-Gal4 in the dorsal compartment (Figure 3C–C’’). Although the effect of overexpressed miR-960 on Ci protein stability and col expression was not examined in the previous study (Gao et al., 2013a), given that it shares the same targets as miR-12, we speculated that miR-960 may regulate Hh signaling in a similar manner to miR-12. Indeed, overexpression of miR-960 resulted in an obvious increase in CiFL levels, while kn-lacZ expression remained unchanged (Figures 3F–F”). These results demonstrate that our screen using the Drosophila wing disc as an in vivo model platform is robust and sensitive to identify Hh signaling-regulating miRNAs.
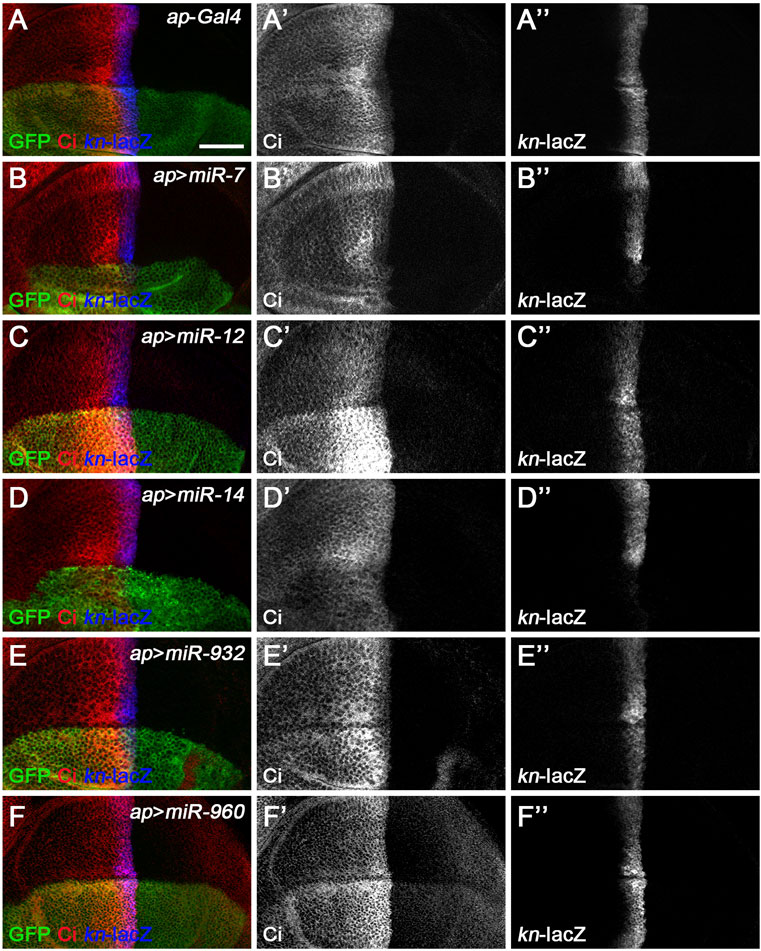
FIGURE 3. Overexpression of previously known Hh signaling-regulating miRNAs alters CiFL levels and kn-lacZ reporter activity. CiFL levels and kn-lacZ activity were monitored by immunostaining in third instar larval wing discs of the indicated genotypes. (A–B’’,D–D’’) ap-Gal4-driven overexpression of miR-7 or miR-14 resulted in decreased levels of CiFL (B’,D’) and loss of kn-lacZ expression (B”,D”) in the dorsal compartment. (C–C’’,F–F’’) Increased expression of miR-12 or miR-960 led to markedly elevated levels of CiFL (C’,F’), but little change in kn-lacZ activity (C”,F”). (E–E’’) A mild increase in CiFL levels (E’) and a weak downregulation of kn-lacZ activity (E”) were observed in GFP-positive cells overexpressing miR-932. Scale bar, 50 μm.
In addition to the previously identified miRNAs, we discovered seven additional miRNAs, namely miR-10, miR-133, miR-190, miR-375, miR-927, miR-958, and miR-964, as novel regulators of Hh signaling. All of these newly discovered miRNAs have detectable expression in larval imaginal discs, with miR-964 being the most highly expressed miRNA, 8-fold higher than the other six miRNAs (Ruby et al., 2007). Furthermore, miR-964 was found to be specifically enriched in imaginal tissues (Ruby et al., 2007; Supplementary Table S2). When comparing our screen with previously reported miRNA screens, we found that miR-5, reported to target smo (Wu et al., 2012), was not identified in our screen, nor was it found in a miRNA screen conducted in vitro in S2R+ cells (Kim et al., 2014). Overexpression of miR-5 had no obvious effects on the expression of Smo, Ci, or kn-lacZ (Supplementary Figure S3). This observation was further validated in S2R+ cells, as increased miR-5 expression did not have any apparent effect on the activity of the miRNA sensor for smo (Kim et al., 2014). This inconsistency may be due to the different transgenic flies used for miRNA overexpression (Wu et al., 2012). We further noted that among the seven newly identified miRNAs, miR-10, miR-133, miR-927, and miR-964 appeared in our screen as well as in the in vitro screen with S2R+ cells, while the other three miRNAs, miR-190, miR-375, and miR-958, were only identified in our screen, suggesting that the in vitro screen in hemocyte-like S2R+ cells (Schneider, 1972) may not be sufficient to identify miRNAs that regulate Hh signaling in wing discs.
miR-10 Negatively Regulates Hh Signaling by Targeting fu
Based on their effects on CiFL stability and col target gene transcription in wing discs, we classified the newly discovered miRNAs into three categories. miR-10 belongs to the first category. Overexpression of miR-10 resulted in elevated levels of CiFL protein at the expense of labile CiA (Figure 4B’), an effect likely due to decreased Hh signaling activity at the highest level. In addition, decreased kn-lacZ reporter activity and Col protein levels by anti-Col antibody staining were detected (Figures 4B’’,D’’), confirming the effect of reducing the highest level of Hh signaling. These results were also observed in wing disc cells, where fu function was impaired in loss-of-function mutants (Alves et al., 1998) or by RNAi (Figures 2F–F”). Therefore, miR-10 could act through fu. We tested this hypothesis using the in vivo gfp: 3′UTRfu miRNA sensor transgenic flies. Overexpression of miR-10 by dpp-Gal4 along the A-P boundary resulted in a significant decrease in gfp: 3′UTRfu sensor activity (Figures 4G–G”), indicating that fu is one of the direct targets of miR-10. Bioinformatics analysis (http://www.targetscan.org/) further supported this conclusion by identifying two putative miR-10 binding sites in the 3′ UTR of fu (Figure 4F). To verify that miR-10 regulates Hh signaling through these two miRNA binding sites, we generated gfp: 3′UTRmutfu in which the miR-10 binding sites in the 3’ UTR of fu were mutated (Figure 4F). We found that increased miR-10 expression was no longer able to reduce gfp: 3′UTRmutfu sensor activity (Figures 4H–H”). As altered Smo phosphorylation and activity may lead to changes in the highest levels of Hh signaling activity, we tested whether miR-10 regulated Hh signaling by targeting other core Hh pathway genes. miR-10 was overexpressed along the A-P boundary in the wing disc of miRNA sensor flies for hh, ptc, smo, cos2, Su(fu), and ci, respectively. We found that miR-10 failed to reduce the activity of any miRNA sensor other than fu in our assembled miRNA sensor toolbox (Supplementary Figure S4). Taken together, miR-10 negatively regulates Hh signaling by specifically targeting fu.
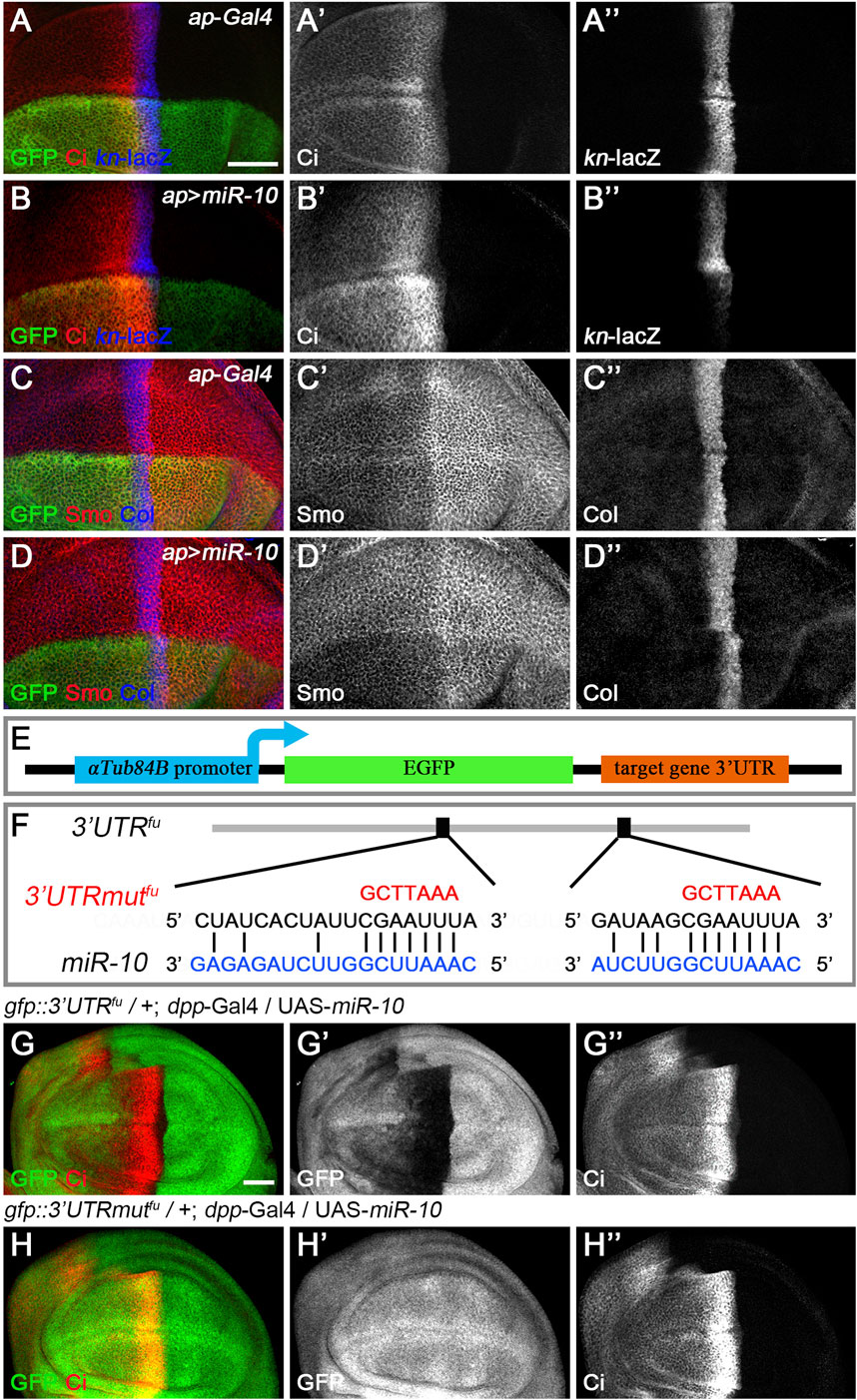
FIGURE 4. miR-10 negatively regulates Hh signaling by targeting fu. (A–B”) Overexpression of miR-10 by ap-Gal4 in the dorsal compartment of the wing disc resulted in an obvious increase in CiFL levels (B’) and a significant decrease in kn-lacZ activity (B”). Smo protein levels were significantly reduced in both anterior and posterior compartment cells (D’), and the expression region of Col was narrowed (D”). (E) Schematic showing the composition of a miRNA sensor containing the αTub84B promoter, the egfp coding sequence, and the 3′ UTR of individual core Hh pathway genes. (F) Two predicted miR-10 binding sites are present in the 3′ UTR of fu. Mutated binding sites are shown in red. (G–H”) GFP expression of gfp: 3′UTRfu and gfp: 3′UTRmutfu sensor lines in dpp-Gal4-driven miR-10 overexpression wing discs are shown. Increased miR-10 expression resulted in significantly reduced GFP expression (G′) and elevated CiFL levels (G”) along the A-P boundary in gfp: 3′UTRfu sensor wing discs. In contrast, overexpressed miR-10 did not affect GFP expression in gfp: 3′UTRmutfu sensor wing discs (H’), although CiFL was upregulated (H”). Scale bar, 50 μm.
miR-958 Acts as a Negative Regulator of Hh Signaling by Targeting smo
miR-133, miR-375, miR-927, and miR-958 belong to the second class of Hh signaling-regulating miRNAs, as overexpression of these miRNAs by ap-Gal4 in dorsal compartment cells all resulted in significantly reduced levels of CiFL, and kn-lacZ reporter activity and Col protein levels were completely lost (Figures 5A–A”,B”,C–C”,D”,E–E”,F”, Figure 6A–A’’,B’’). The above strongly reduced Hh signaling may be due to reduced expression of key positive regulators of Hh signaling, such as hh, smo, and ci. Since we did not have a working Hh antibody, we only examined the effect of overexpressing miRNAs on Smo and Ci levels. Overexpression of miR-958 in the dorsal compartment of the wing disc completely abolished Smo expression (Figure 6B’), whereas miR-133 had the opposite effect, resulting in a significant upregulation of Smo protein levels (Figure 5B’). In contrast to the homogeneous effects of miR-958 and miR-133 on Smo protein present in both anterior and posterior compartments, overexpressed miR-927 only increased Smo protein levels in anterior compartment cells; the posteriorly localized Smo remained unchanged (Figure 5F’). The effects of miR-375 overexpression were more complex. Since increased miR-375 activity perturbed wing disc formation, it was difficult to determine whether the reduction in Smo protein levels was directly caused by altered miR-375 expression (Figure 5D’). Thus, the differential effects of these four miRNAs on Smo protein levels, and sometimes even opposite effects observed for anteriorly and posteriorly localized Smo, suggest that they must regulate Hh signaling through distinct mechanisms.
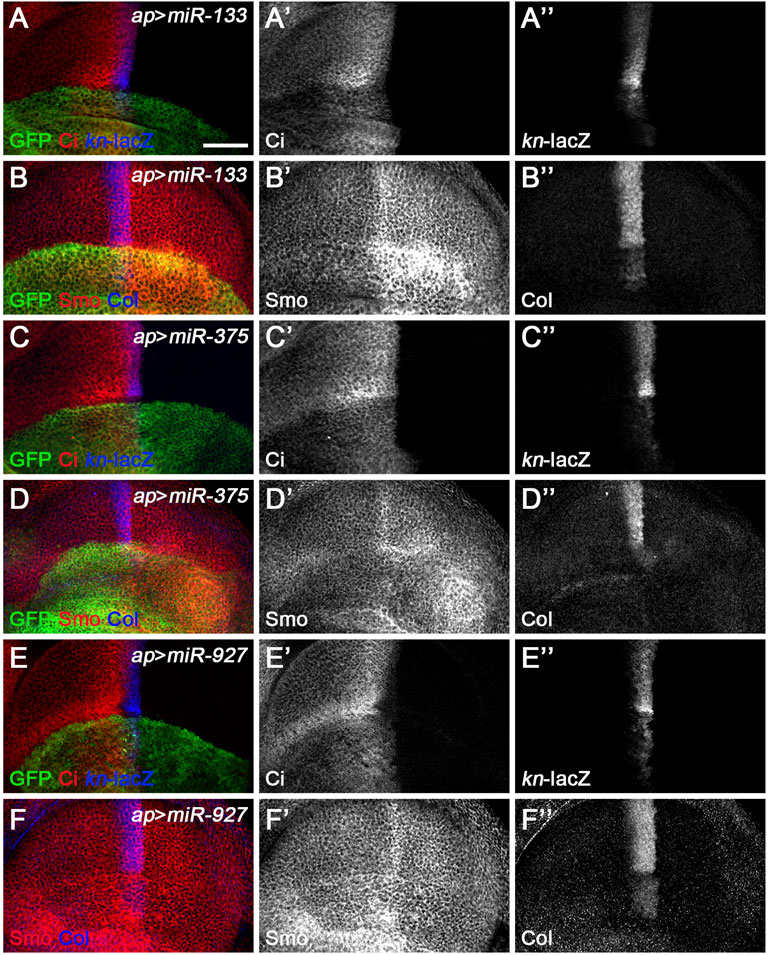
FIGURE 5. miR-133, miR-375, and miR-927 are negative regulators of Hh signaling. Smo, CiFL, and Col levels and kn-lacZ activity were visualized by immunostaining in wing discs overexpressing miR-133 (A–B”), miR-375 (C–D”), or miR-927 (E–F”). GFP marks the expression region of ap-Gal4. Although overexpression of miR-133, miR-375, and miR-927 all resulted in significant decrease in CiFL levels (A’,C’,E’), kn-lacZ activity (A”,C”,E”), and Col expression (B”,D”,F”), different effects on Smo expression were observed. Increased miR-133 expression led to a marked increase in Smo protein levels in the posterior compartment, whereas the increase in the anterior compartment was very mild (B’). It is difficult to determine the effect of miR-375 overexpression on Smo expression because the formation of the dorsal compartment of the wing disc was disrupted (D’). Overexpression of miR-927 resulted in mildly elevated Smo levels, especially in the anterior compartment (F’). Scale bar, 50 μm.
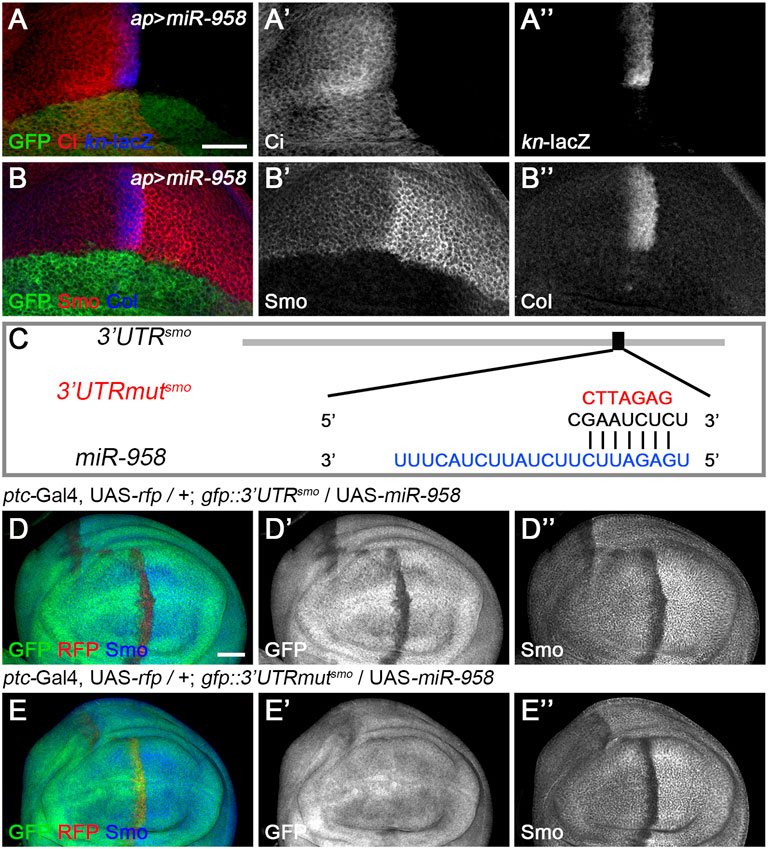
FIGURE 6. miR-958 targets smo to regulate Hh signaling (A–B”) ap-Gal4-driven overexpression of miR-958 in the dorsal compartment resulted in a marked reduction in CiFL levels (A’), abrogation of Smo expression (B’) and complete loss of kn-lacZ activity (A”) and Col expression (B”). (C) The predicted miR-958 binding site is present in the 3′ UTR of smo, and the mutated binding site is shown in red (D–E”) GFP expression in wing discs of gfp: 3′UTRsmo and gfp: 3′UTRmutsmo sensor lines is shown when miR-958 was overexpressed. ptc-Gal4-driven overexpression of miR-958 resulted in obviously reduced GFP (D’) and Smo expression (D”) along the A-P boundary in the gfp:3’UTRfu sensor wing disc. In contrast, increased miR-958 expression had no effects on GFP expression in the gfp: 3′UTRmutfu sensor wing disc (E’), although Smo protein levels were significantly reduced (E”). Scale bar, 50 μm.
Since miR-958 had the same effect on Smo expression in the anterior and posterior compartments, it may control Hh signaling at the level of smo or its direct regulators. We therefore used gfp: 3′UTRsmo sensor flies to test whether smo was a direct target of miR-958. As hypothesized, overexpression of miR-958 by ptc-Gal4 along the A-P boundary resulted in a significant reduction in gfp: 3′UTRsmo sensor activity (Figures 6D–D”) but not the gfp: 3′UTRmutsmo control sensor activity (Figures 6E–E”), confirming that smo is a direct target of miR-958. After examining the effects of miR-958 on the remaining miRNA sensor flies in our miRNA senor toolbox, we found that smo is the only target of miR-958 in the core components of the Hh signaling cascade (Supplementary Figure S5). For the other three miRNAs that indirectly control Smo protein levels, we found that miR-133 and miR-927 did not act on any of the seven sensors in the toolbox (Supplementary Figures S6, S8), while miR-375 overexpression slightly reduced GFP expression in the wing disc of gfp: 3′UTRfu sensor flies (Supplementary Figures S7E–E”). Given that no predicted binding sites for miR-375 was found in the 3′ UTR of fu, we speculated that it may regulate the activity of gfp: 3′UTRfu in an indirect manner. Moreover, we investigated the effect of reducing the expression of seven core components of Hh signaling on Smo protein levels in wing discs to examine whether miR-133, miR-375, and miR-927 regulate Smo through these core components of Hh signaling. When hh was knocked down by ap-Gal4-driven RNAi in the dorsal compartment, downregulation of Smo protein was observed both anteriorly and posteriorly (Figure 7B’). In contrast, reducing Ptc activity by RNAi resulted in elevated Smo levels only in anterior cells (Figure 7C’). As expected, ap-Gal4-driven RNAi of smo resulted in ablation of Smo protein (Figure 7D’). Although Smo forms distinct signaling complexes with Cos2, Fu, Su(fu), and Ci, knockdown of cos2 or Su(fu) had no effects on Smo (Figures 7E’,G’). In contrast, reduced fu expression resulted in Smo downregulation only in the posterior compartment (Figure 7F’). Surprisingly, we found that knocking down ci produced similar effects as ptc RNAi (Figure 7H’). However, the above-mentioned phenotypes are not the same as the effects caused by overexpression of miR-133, miR-375, or miR-927, so we believe that the other three miRNAs in the second category may act through targets other than the seven core components of the Hh signaling pathway.
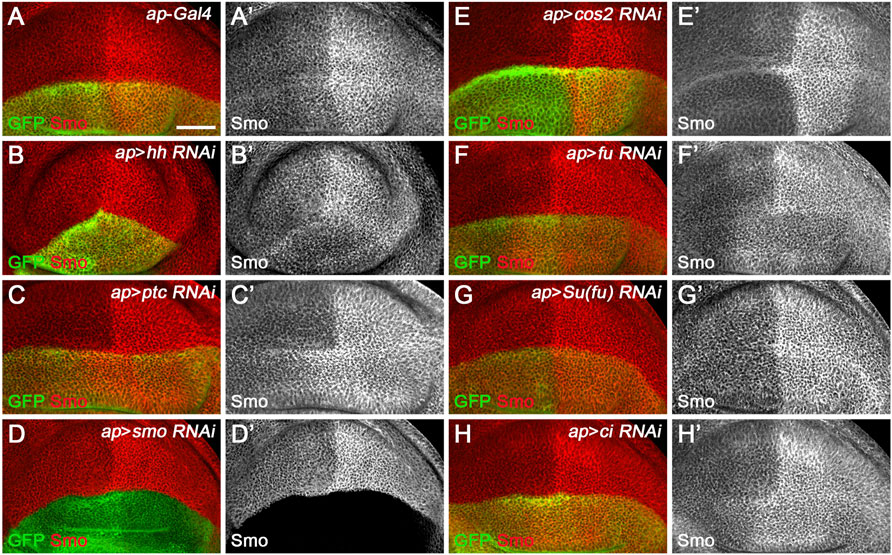
FIGURE 7. Effects of core Hh pathway gene knockdown on Smo protein levels. Smo expression in wing discs of the indicated genotypes is shown. (A–B’’) ap-Gal4-driven hh RNAi caused a slight decrease in Smo protein levels in both anterior and posterior compartment cells (B’). (C,C’,H,H’) Knockdown of either ptc or ci resulted in a similar increase in Smo protein levels in the cells of the anterior compartment adjacent to the A-P boundary (C’,H’). (D,D’) Knockdown of smo resulted in loss of Smo expression, as expected (D’). (E–G’) Reducing cos2 or Su(fu) expression had no apparent effects on Smo expression (E’,G’). In addition, knockdown of fu specifically reduced Smo protein levels in the posterior compartment (F’). Scale bar, 50 μm.
miR-190 and miR-964 Target Genes Other Than the Core Hh Pathway Components
A third class of newly discovered Hh signaling-regulating miRNA includes miR-190 and miR-964, since overexpression of either had similar effect, significantly reducing CiFL levels, while kn-lacZ expression was almost unchanged (Figures 8A–A”,C–C”). These phenotypes contrast directly with those observed for class I Hh signaling-regulating miRNA. In addition, their functions for Smo and Col proteins also differ significantly. Overexpression of miR-964 did not affect the expression of Col or Smo (Figures 8D–D”). This result is similar to loss-of-function Su(fu) in wing disc cells (Figure 2G’, Figure 7G’), making Su(fu) a potential target for miR-964. We tested this hypothesis using the gfp: 3′UTRSu(fu) miRNA sensor flies. However, overexpression of miR-964 did not alter GFP expression in the Su(fu) miRNA sensor fly wing disc (Supplementary Figures S9F–F”). This is also consistent with the lack of a miR-964 binding site in the 3′ UTR of Su(fu). Based on these observations, we propose that miR-964 negatively regulates Hh signaling and controls Su(fu) activity through unknown target genes.
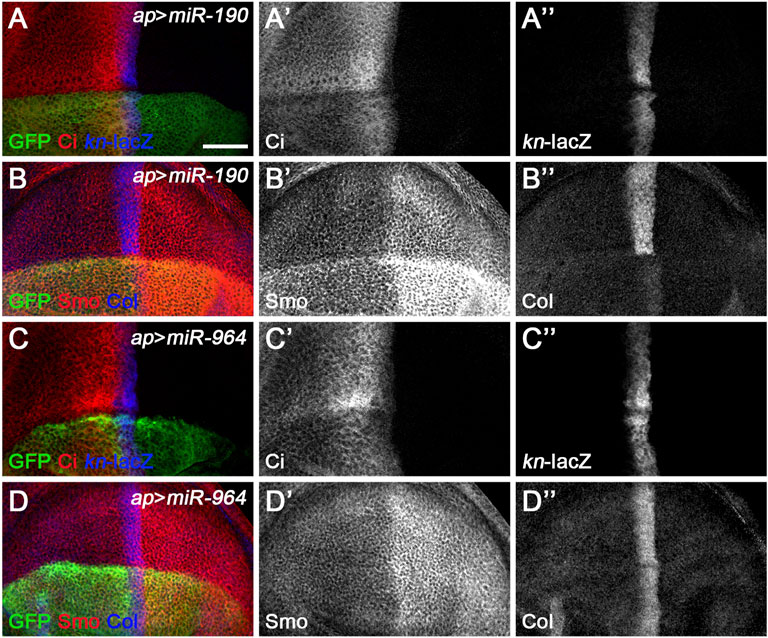
FIGURE 8. miR-190 and miR-964 act as negative regulators of Hh signaling. CiFL levels and expression of kn-lacZ, Smo, and Col in wing discs overexpressing either miR-190 (A–B”) or miR-964 (C–D”) were monitored by immunostaining. Overexpression of miR-190 or miR-964 led to obviously reduced levels of CiFL (A’,C’) and almost unchanged kn-lacZ activity (A”,C”). Increased miR-190 expression induced a significant increase in Smo protein levels in both anterior and posterior compartment cells (B’) and abrogation of Col expression (B”), whereas overexpressing miR-964 did not affect the expression of Smo and Col (D’,D”). Scale bar, 50 μm.
We noticed a clear difference between the effect of miR-190 overexpression on kn-lacZ activity and the effect on Col protein expression. While the ap-Gal4-induced increase in miR-190 activity in the dorsal compartment had no apparent effects on kn-lacZ expression (Figure 8A’’ and Supplementary Figure S10A”), Col protein levels were almost completely abolished compared with wild-type ventral cells (Figure 8B’’ and Supplementary Figure S10A’’’). The presence of six putative miR-190 binding sites in the 3′ UTR of col (Supplementary Figures S10B–E) suggests that col may be a target of miR-190 and that the large reduction in Col expression may be caused by the direct effect of miR-190 on col mRNA. If this is the case, it explains why the kn-lacZ expression has not changed. In addition, overexpressed miR-190 also resulted in a strong increase in Smo expression in both anterior and posterior cells (Figure 8B’), possibly due to the transcriptional upregulation of smo in miR-190-overexpressing cells. The effect of miR-190 overexpression on Hh signaling is distinct from the phenotype resulting from loss of any single core component of Hh signaling. Consistently, miR-190 overexpression did not alter GFP expression in any of the miRNA sensor toolbox flies (Supplementary Figure S11), implying that miR-190 can regulate Hh signaling at multiple steps through novel Hh signaling players.
Newly Discovered miRNAs Function in a Cell Autonomous Manner and May Regulate Hh Signaling During Spermatogenesis
The ap-Gal4 driver was used to efficiently induce miRNA overexpression in the dorsal compartment of the wing disc. However, in some cases, increased miRNA expression resulted in patterning defects that prevented us from clearly discerning their functions. This was the case for miR-375 (Figures 5D–D”). To overcome this deficiency, we used the FLIPout technique (Ito et al., 1997; Pignoni and Zipursky, 1997) to induce miR-375 overexpression in only a few wing epithelial cells and found that FLIPout clones had significantly reduced Smo protein in the anterior compartment of the wing disc (Figures 9D–D”). The inability of miR-375 to reduce Smo protein levels in posteriorly localized FLIPout clones suggests that miR-375 does not control smo transcription, but rather functions in a step after Hh activation. The above FLIPout analysis indicates that miR-375 regulates Hh signaling in a cell-autonomous manner. This also applies to the remaining six miRNAs (Figures 9A–C”,E–G”). However, one difference was noticed. Unlike ap-Gal4-induced miR-133 activity (Figure 5A’), Ci and Smo protein levels were selectively affected in miR-133 FLIPout wing disc clones (Figures 9B–B”). This inconsistency may be due to different timings used to induce miR-133 expression.
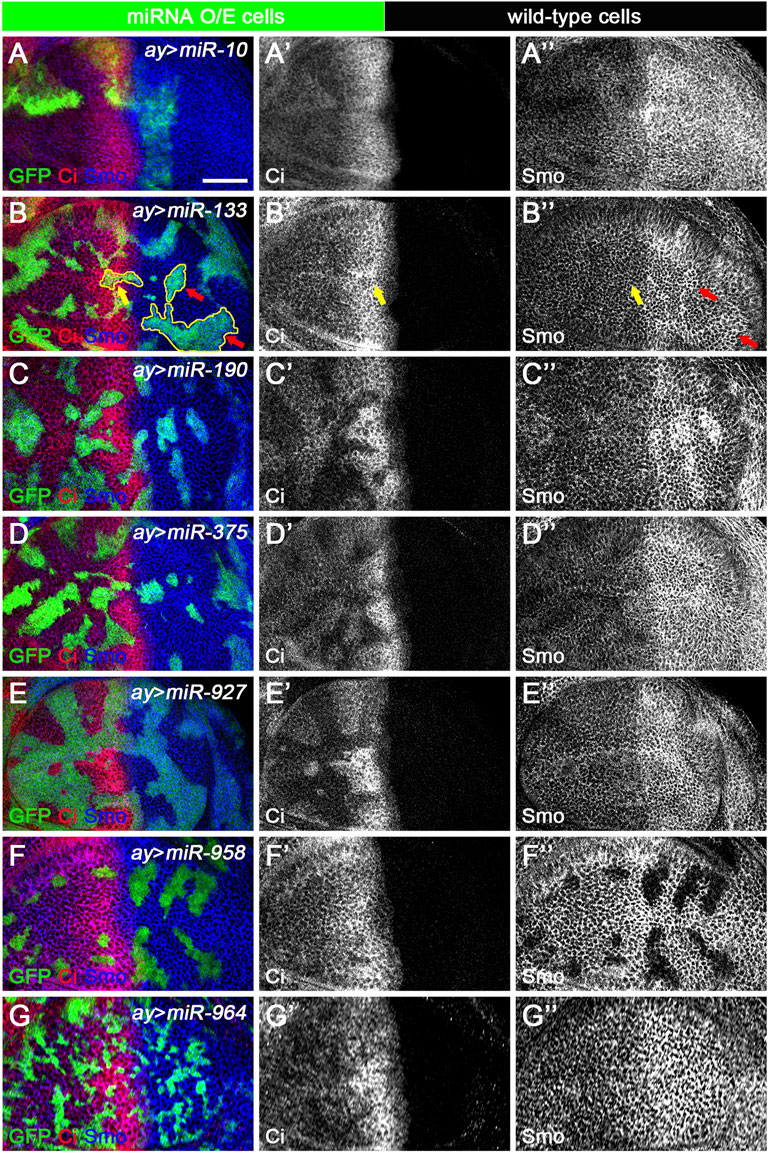
FIGURE 9. Newly discovered miRNAs regulate Hh signaling in a cell-autonomous manner. All miRNAs were overexpressed in GFP-marked clones in wing discs induced by the FLIPout technique. CiFL levels and Smo expression were visualized by immunostaining. (A–A’’) In miR-10 overexpressed cells, CiFL levels were slightly increased (A’), while Smo protein levels were reduced in clones located in the anterior compartment (A”). (B–B’’) CiFL levels were only decreased in miR-133-expressing clones adjacent to the A-P boundary (yellow arrow in B’), and Smo expression was increased in clones located in the posterior compartment (red arrows in B”), but not anterior compartment (yellow arrows in B”). (C–E’’,G–G’’) Overexpression of miR-190, miR-375, miR-927, and miR-964 all resulted in a significant decrease in CiFL levels (C’,D’,E’,G’). However, they had different effects on Smo expression. Overexpression of miR-190 led to increased Smo levels in anterior and posterior clones (C”), whereas increased expression of miR-375 resulted in decreased Smo levels, especially in anterior clones (D”). Overexpression of miR-927 or miR-964 had no apparent effects on Smo expression (E”,G”). (F–F’’) Increased expression of miR-958 led to a mild decrease in CiFL levels in clones located in the anterior compartment, whereas Smo expression was completely lost in clones located in both anterior and posterior compartments (F”). Scale bar, 50 μm.
Hh morphogens function in a cell-nonautonomous manner to regulate a range of developmental events beyond wing development (Guerrero and Kornberg, 2014). One of the systems that best illustrates Hh-mediated cell specification is Drosophila testis development. Hh is produced in niche cells in the apical tip of the testis and activates Hh signaling in adjacent cyst stem cells (CySCs) to maintain their self-renewal. As a result, CiFL and Smo proteins are found to be more stable around the niche (Michel et al., 2012; Amoyel et al., 2013). The transcription factor Traffic jam (Tj) marks CySCs and early cyst cells (Li et al., 2003). When Hh signaling activity is impaired, the number of Tj-positive cells is significantly reduced (Michel et al., 2012; Amoyel et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2013b). Conversely, hyperactivation of Hh signaling in somatic cells leads to massive overproduction of CySCs (Zhang et al., 2013b). We used the tj-Gal4 driver to specifically overexpress our newly discovered miRNAs in somatic cells and examined their effect on the number of Tj-positive cyst cells. Our results showed that overexpression of each miRNA, except miR-964, resulted in a 24%–48% reduction in the number of Tj-positive cells (Figure 10), suggesting that these miRNAs negatively regulate Hh signaling to maintain cyst cell homeostasis. We noted that induction of miR-964 activity in cyst cells had no effects, consistent with its regulation of Su(fu). Taken together, the above results suggest that the newly discovered miRNAs, when overexpressed in cyst cells, can regulate Hh signaling during spermatogenesis and may act as general negative regulators of Hh signaling.
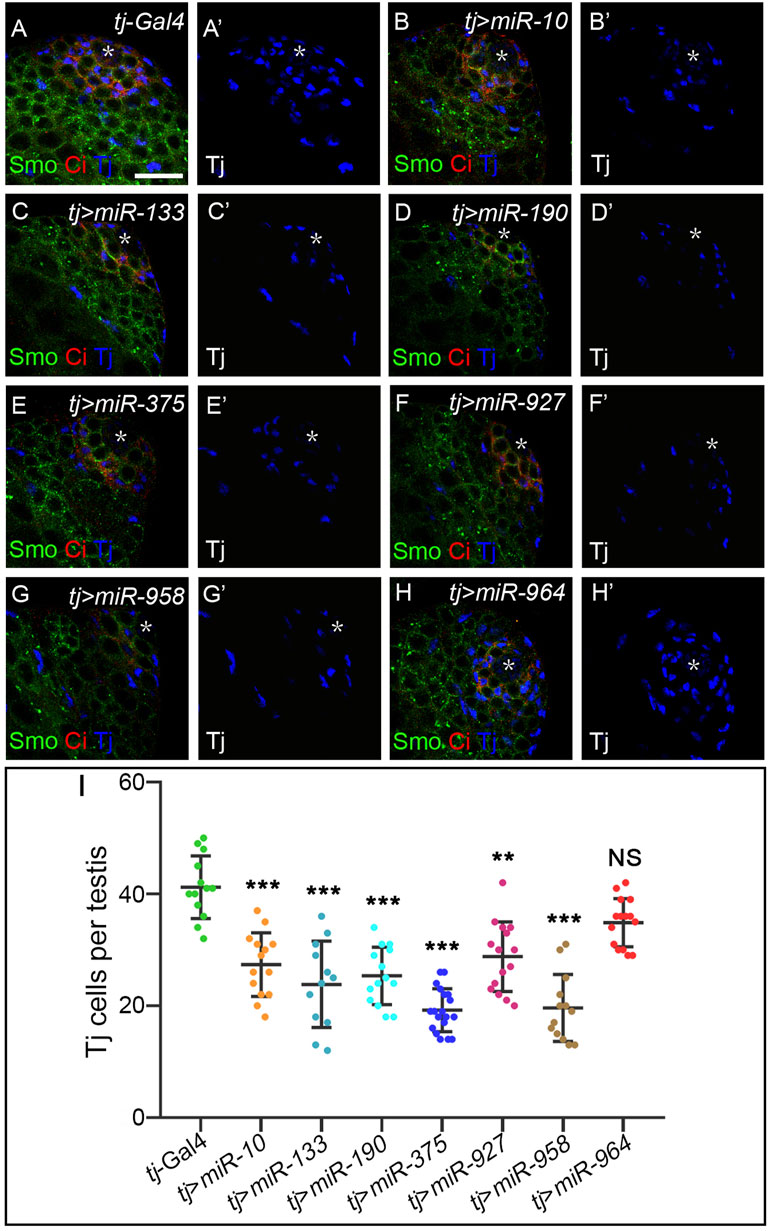
FIGURE 10. Newly discovered miRNAs, except miR-964, are involved in Hh signaling-controlled CySC maintenance during spermatogenesis. (A–H”) All newly discovered miRNAs were specifically overexpressed by tj-Gal4 in early cyst cells. CiFL levels and expression of Smo and Tj were monitored by immunostaining. Overexpression of miR-10, miR-133, miR-190, miR-375, miR-927, and miR-958, but not miR-964, obviously reduced the number of Tj-positive cells in the testis. (I) Shown is statistical analysis of the number of Tj-positive cells per testis. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (ntj-Gal4 = 13, ntj>miR−10 = 14, ntj>miR−133 = 12, ntj>miR−190 = 14, ntj>miR−375 = 19, ntj>miR−927 = 15, ntj>miR−958 = 13, ntj>miR−964 = 15). One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s tests was used. NS, not significant. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. Scale bar, 25 μm.
Loss-Of-Function Analysis of the Newly Discovered miRNAs
To better understand the endogenous functions of the newly discovered miRNAs, we obtained and analyzed knockout lines for all seven miRNAs (Chen et al., 2014). We found that miR-190KO was lethal at the third instar larval stage, while the remaining six miRNA mutants survived into adulthood. These features allowed us to study the effect of individual deletions of these miRNAs on the transcription of Hh signaling components (hh, ptc, smo, cos2, fu, Su(fu), ci, ihog, boi, dally, and dally-like (dlp)), and downstream targets (col and dpp) as well as CiFL, Col and Smo protein levels. Furthermore, the Hh signaling-related phenotypes of adult wing morphogenesis of these miRNA knockout mutants were also examined.
As expected, transcripts of fu and smo were significantly upregulated in miR-10KO and miR-958KO mutants, respectively (Figure 11A). Consistently, the activities of miRNA sensors for fu and smo were respectively enhanced in miR-10KO and miR-958KO wing discs (Figures 11B–E). Since overexpression of fu had no visible effects on adult wing morphology and Hh signaling activity (Claret et al., 2007), it is not surprising that CiFL, Smo and Col protein levels were not altered in miR-10KO mutant wing discs (Figures 12B–B”). In miR-10KO mutants, however, adult wings were significantly reduced in size (Figures 11G,N), likely due to the effect of additional miR-10 targets important for wing development.
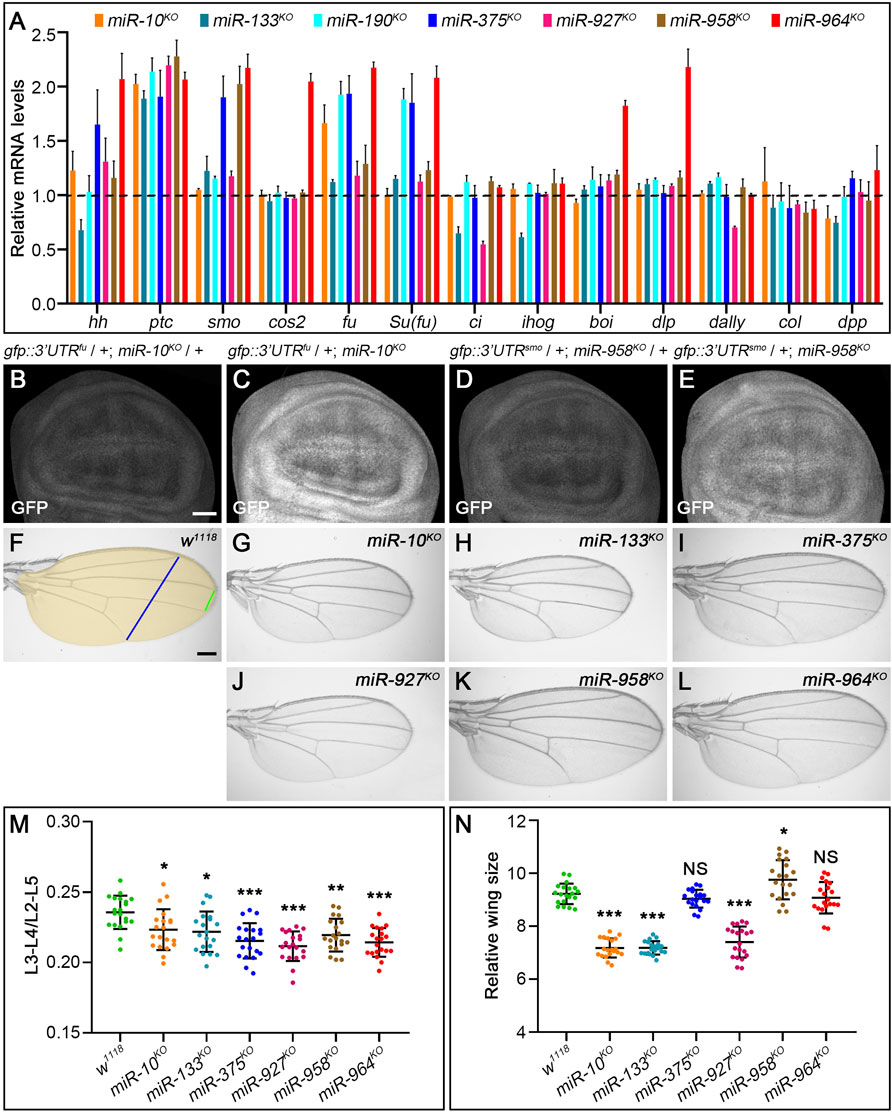
FIGURE 11. Loss-of-function analysis of the seven newly discovered miRNAs. (A) Quantification of mRNA expression of hh, ptc, smo, cos2, fu, Su(fu), ci, ihog, boi, dally, dlp, col, and dpp in seven miRNA knockout mutant larvae by qPCR. Bar plots represent relative mRNA levels of indicated genotypes (n = 3); error bars represent standard deviation (S.D.). (B–E) The GFP expression of the gfp: 3’UTRfu sensor was significantly increased in miR-10KO homozygotes (C) compared with miR-10KO heterozygotes (B). The same goes for the gfp:3’UTRsmo sensor in miR-958KO homozygotes (D,E). (F–L) Adult wings of the indicated genotypes are shown. The distance between L3-L4 veins (green line in F), the distance between L2-L5 veins (blue line in F), and the size of adult wings (yellow area in F) were measured, (M,N) Shown is statistical analysis of the ratio of L3-L4 distance to L2-L5 distance (M), and wing size (N) for the indicated genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 20). One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s tests was used. NS, not significant. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. Scale bar, (B–E), 50 μm; F-L, 100 μm.
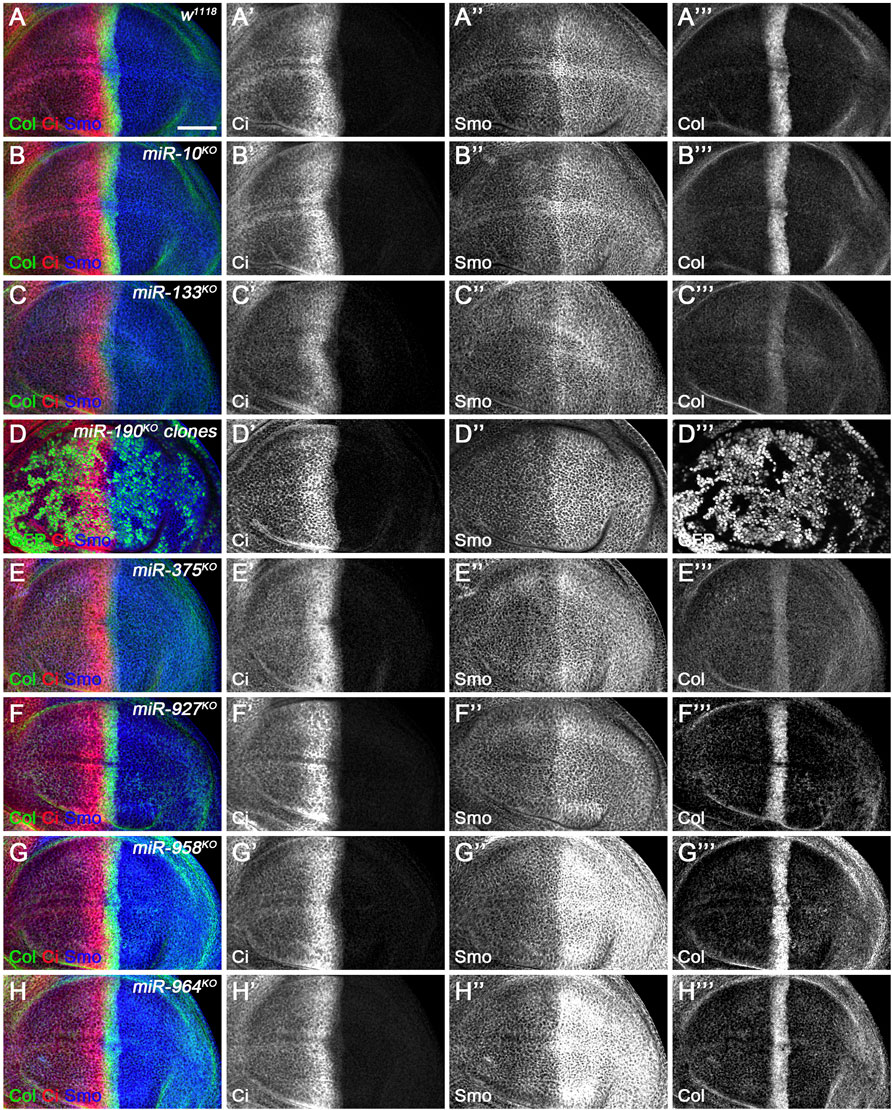
FIGURE 12. CiFL and Smo levels and Col expression in loss-of-function mutants of newly discovered miRNAs. CiFL and Smo protein levels and Col expression were visualized by immunostaining in third instar larval wing discs of the indicated genotypes. Loss of miR-10 or miR-927 had no apparent effects on CiFL and Smo levels and Col expression (B–B’’’, F–F’’’). CiFL levels and Col expression were significantly reduced in miR-133KO mutants (C’,C’’’), while Smo levels remained unchanged (C”). CiFL and Smo levels were unaffected in miR-190KO clones negatively marked by GFP (D–D’’’). Col expression was significantly decreased in miR-375KO mutants (E’’’), whereas CiFL and Smo levels were unchanged (E’,E”). Deletion of miR-958 or miR-964 significantly elevated Smo levels in the posterior compartment (G”,H”), but hardly changed CiFL levels and Col expression (G’,G’’’,H’,H’’’). Scale bar, 50 μm.
The upregulation of smo transcripts in the miR-958KO mutant was confirmed at the protein level, as obviously increased Smo protein levels were observed in the posterior compartment of the wing disc (Figure 12G’’). In contrast, anteriorly localized Smo was only slightly upregulated (Figure 12G’’). This differential effect of miR-958KO on Smo protein can be attributed to post-translational regulation of Smo protein stability in anterior wing disc cells (Denef et al., 2000). Previously studies have shown that overexpression of wild-type Smo is not sufficient to induce a distinct gain-of-function Hh signaling phenotype (Hooper, 2003; Zhu et al., 2003). Thus, only the Iroquois (Iro) expression domain, the Hh target representing low-level Hh activity, is expanded, but not the medium-to-high Hh signaling targets Dpp, Ptc, and Col (Hooper, 2003). Consistent with these reports, the adult wing size of miR-958KO mutant flies increased only slightly (Figures 11K,N), while the levels of CiFL and Col in the wing disc remained unchanged (Figures 12G’,G’’’). In addition to miR-958, significantly elevated Smo were observed in the posterior compartment of miR-964KO wing discs (Figure 12H’’). Unlike miR-958, the mRNA levels of hh, smo, cos2, fu, Su(fu), boi, and dlp were all increased in miR-964KO larvae (Figure 11A).
For the remaining four newly discovered miRNAs, we found reduced adult wing size in miR-133KO and miR-927KO flies (Figures 11H,J,N). This phenotype is very consistent with marked reductions in CiFL stability and Col expression (Figures 12C’,C’’’) and reduced ci and hh transcription in miR-133KO mutants (Figure 11A). Likewise, decreased expression of ci and dally was observed in miR-927KO larvae (Figure 11A). While fu and Su(fu) expression was increased in miR-190KO and miR-375KO mutant larvae (Figure 11A), Smo and CiFL levels were not changed in miR-190KO clones (Figures 12D–D’’’). Additional effects were observed in miR-375KO flies, including decreased Col protein levels (Figure 12E’’’) and hh and smo expression (Figure 11A). Interestingly, ptc expression was increased in all miRNA knockout mutant larvae (Figure 11A), which could partly explain the slight but consistent decrease in the distance between L3-L4 longitudinal veins in adult wing blades (Figure 11M).
Take together, we provide genetic and molecular evidence that endogenous miR-10 and miR-958 paly a role in Hh signaling, directly targeting fu and smo, respectively. We further demonstrate that the loss of the remaining five newly discovered miRNAs results in dysregulated gene expression associated with Hh signaling, suggesting that these miRNAs are required for the maintenance of Hh signaling homeostasis in development.
Discussion
In this study, we systemically assessed the impact of 179 miRNAs on Hh signaling through an in vivo miRNA overexpression screen in Drosophila and identified seven miRNAs as novel negative regulators of Hh signaling. We further demonstrated that two of these miRNAs, miR-10 and miR-958, target fu and smo, respectively, while the other five miRNAs control Hh signaling through targets other than core Hh pathway components. Importantly, loss-of-function analysis indicated that these seven newly discovered miRNAs also regulate Hh signaling in vivo.
Prior to our in vivo genome-wide screen, another comprehensive miRNA overexpression screen was performed in cultured S2R+ cells (Kim et al., 2014). Both screens identified the same set of Hh signaling-regulating miRNAs, including miR-7, miR-10, miR-12, miR-14, miR-133, miR-927, miR-932, and miR-964. Furthermore, we discovered two other miRNAs, miR-190 and miR-375, that target as yet unidentified novel Hh signaling regulators in addition to the canonical Hh signaling components. It is not surprising that miR-190 and miR-375 were not found in the in vitro screen, as the screen was mainly based on changes in the activity of miRNA sensors for known regulators of Hh signaling (Kim et al., 2014). It is also possible that these in vitro miRNA sensors expressed in S2R+ cells may not be sensitive enough as it did not respond to the smo-targeting miR-958 that emerged from our screen. Furthermore, the activity of the in vitro sensors tested in S2R+ cells may not reflect Hh regulation as faithfully as in wing epithelial cells. miR-927 and miR-964 have been reported to target the 3’ UTR of ci in S2R+ cells (Kim et al., 2014). When overexpressed, these two miRNAs had no effects on GFP expression in the ci miRNA sensor flies. miR-133, another positive result from our in vivo screen, was thought to target CK1α and GSK3 (Kim et al., 2014), which encode two negative regulators of Hh signaling (Price and Kalderon, 2002; Su et al., 2011). However, increased miR-133 expression in wing discs did not upregulate Hh signaling, but significantly decreased Hh signaling by reducing Ci and Col protein levels, strongly suggesting that CK1α and GSK3 are not direct targets of miR-133 in vivo.
Among seven novel miRNAs involved in Hh signaling in vivo, we found that miR-10 and miR-958 target fu and smo, respectively, while the direct targets of the other five miRNAs, miR-133, miR-190, miR-375, miR-927, and miR-964, have not been identified from the Hh signaling regulatory network. Nevertheless, direct targets of some of these miRNAs have been reported experimentally in Drosophila, and they play important roles in processes other than Hh signaling. For example, miR-133 targets the phosphodiesterase encoding Pde1c to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition in wing discs (Jung et al., 2021). fga is a direct target of miR-190 and inhibits the HIF-dependent hypoxia response (De Lella Ezcurra et al., 2016). miR-927 controls larval growth through its target Kr-h1 (He Q. et al., 2020), while miR-964 targets Drs to inhibit Toll signaling in response to bacterial infection (Li et al., 2017). Among these validated targets, Pde1c may be involved in Hh signaling regulation, as the phosphodiesterase family protein PDE4D is known to enhance Hh signaling activity by inhibiting PKA in human medulloblastoma cells (Ge et al., 2015). Other targets did not show modulating Hh signaling. Further experiments are required to determine their potential role in Hh signaling.
It should be noted that the validated targets of miR-10 and miR-958 in our study, fu and smo, as well as the targets of the other five miRNAs mentioned above, are listed in the miRNA target prediction database TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/). For the five miRNAs whose bona fide targets for Hh signaling have not yet been identified, further analysis of the predicted target set for each miRNA in TargetScan may expand the miRNA network that regulates Hh signaling. Synaptobrevin (Syb), another predicted target of miR-133, is required for basal cytoneme formation. Hh gradient and signaling activity are impaired when Syb is knocked down by RNAi (Chen et al., 2017). tout-velu (ttv) is a predicted target gene of miR-190. It encodes a glycosyltransferase that positively regulates Hh signaling through its role in the biosynthesis of heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), which are required for Hh morphogen propagation. In ttv mutant clones, both CiFL levels and expression of downstream targets of Hh signaling, such as ptc, are reduced (Bellaiche et al., 1998; Bornemann et al., 2004). As CiFL levels and Col expression were significantly decreased in miR-190-overexpressing cells (Figures 8A’,B” and Figure 9C’), miR-190 could regulate Hh signaling by targeting ttv. In addition, brother of tout-velu (botv), another glycosyltransferase-encoding gene required for the spread of the Hh morphogen (Han et al., 2004; Takei et al., 2004), is a predicted target of miR-375. Similar to ttv, Hh signaling is significantly impaired in botv mutant clones, resembling the miR-375 overexpression phenotype. Therefore, botv may be a potential target of miR-375 to regulate Hh signaling. Interestingly, no predicted target genes of miR-927 and miR-964 were reported to play a role in Hh signaling, suggesting that these two miRNAs may regulate Hh signaling by targeting novel players in the Hh regulatory network.
In addition to the TargetScan database, a recent study provided a new set of binding sites for the top 59 CLIP-enriched miRNAs by assigning miRNA seed matches on PAR-CLIP and HITS-CLIP of Argonaute-1 (AGO1) (Wessels et al., 2019). According to this study, miR-190 has 323 predicted targets (Supplementary Table S3), of which seven genes are involved in Hh signaling, namely crooked neck (crn), Multi drug resistance 49 (Mdr49), brother of odd with entrails limited (bowl), Cullin1 (Cul1), Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), G protein-coupled receptor kinase 1 (Gprk1), and Gprk2 (Ou et al., 2002; Kent et al., 2006; Benítez et al., 2009; Cheng et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2013a; Liu et al., 2014; Deshpande et al., 2016). Among them, Crn, Mdr49, and Bowl are positive regulators of Hh signaling. Given the negative role of miR-190 in Hh signaling, it may regulate Hh signaling by targeting these three candidate genes.
Since miRNAs contribute to many gene regulatory networks and diverse signaling pathways, it is not surprising that they play important roles in multisteps of cancer development, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, and angiogenesis (Lee and Dutta, 2009; Bartel, 2018; He B. et al., 2020). In our screen, four newly discovered miRNAs are conserved from Drosophila to humans and have been implicated in the development of various cancers. However, the targets of some of these miRNAs are only found in certain types of cancer. For example, miR-10 regulates the oncogene USF2 in myeloid leukaemia (Agirre et al., 2008; Jongen-Lavrencic et al., 2008), BDNF in cervical cancer (Zhai et al., 2017), and Tiam1 in gastric cancer (Liu F. et al., 2021). Likewise, miR-190 acts through multiple targets and exerts its tumor suppressor effect in various cancer types, including breast, colon and prostate cancer, glioma, and hepatocellular carcinoma (Yu and Cao, 2019). However, the targets of miR-10 in intestinal neoplasia (Stadthagen et al., 2013) and miR-190 in cervical and rectal cancer remain unknown (Yu and Cao, 2019). As for miR-133 and miR-375, two other conserved miRNAs, their potential underlying regulatory mechanisms in their respective cancers and their true targets of action remain unclear and require further study (Bandrés et al., 2006; Arvidsson et al., 2018). Given that uncontrolled Hh signaling is associated with more than 20% of all forms of cancer (Jeng et al., 2020; Sigafoos et al., 2021), the miRNAs identified in our screen as negative regulators of Hh signaling, most likely control cancer progression through its targeting in the Hh regulatory network. Identifying the bona fide targets of these conserved miRNAs in Hh signaling, especially in Drosophila with robust genetics, will greatly aid in the discovery of new therapeutic targets in cancer therapy.
Materials and Methods
Fly Genetics
The transgenic miRNA-overexpression and miRNA-knockout fly strains used in this study are listed in Supplementary Table S1. All fly crosses were maintained at 25°C except those listed in Supplementary Table S4. w1118, ap-Gal4 (bl-3041), dpp-Gal4, ptc-Gal4, UAS-ptc RNAi (bl-28795), and UAS-ci RNAi (bl-28984) were obtained from the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center. UAS-cos2 RNAi (KK#108914), UAS-fu RNAi (GD#27662), and UAS-smo RNAi (GD#9542) were obtained from the Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center. UAS-hh RNAi (TH201500473.S) and UAS-Su(fu) RNAi (THU3468) were obtained from the TsingHua Fly Center. tj-Gal4 was a gift of Zhaohui Wang. hs-flp122; Act5C > yw > Gal4, UAS-gfp was a gift of Haiyun Song. The phenotypes induced by Hh pathway gene knockdown or miRNA overexpression in this study were fully penetrant.
Immunofluorescence Staining
Wing disc immunofluorescence staining was performed using standard procedures (Su et al., 2011). Testes were immunostained using the described protocol (Inaba et al., 2015). Briefly, adult testes on day 3 post-eclosion were dissected in PBS and fixed in 4% formaldehyde in PBS for 30 min. After permeabilization in 0.3% PBST (PBS + 0.3% Triton X-100) for 1 h the testes were incubated with primary antibody in 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBST overnight at 4°C. Then, the samples were washed three times in PBST for 20 min each and incubated with secondary antibody in 3% BSA in PBST for 3 h at room temperature. The following primary antibodies were used: mouse anti β-galactosidase [1:200; 40-1A; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB)], rat anti-Ci (1:20; 2A1; DSHB), mouse anti-Smo (1:20; 20C6; DSHB), and guinea-pig anti-Tj (1:5000; a gift of Dorothea Godt) (Gunawan et al., 2013). Alexa Fluor-conjugated secondary antibodies generated in goat (1:400; Invitrogen) were used.
Antibody Production
A rabbit polyclonal antibody against Col was generated in this study. The full-length Col protein fused with GST was purified and injected into rabbits for immunization, and the sera were further affinity purified to obtain the final antibody (Abclonal Biotech.). This antibody was used for immunostaining at 1:4000.
Generation of the in vivo miRNA Sensors
For φC31 integrase-mediated site-directed integration, the attB sequence was introduced into pCaSpeR-tub-egfp (a gift of Xinhua Lin) (Brennecke et al., 2003). The 3′ UTRs of hh, ptc, smo, cos2, fu, Su(fu), and ci were amplified from genomic DNA using the primers listed in Supplementary Table S5, and then cloned into the pCaSpeR-tub-egfp-attB plasmid. All miRNA sensor constructs were integrated to the attP40 site by φC31 integrase. For the convenience of the cross scheme, miRNA sensor lines for smo integrated to the attP2 site were also generated. To generate miRNA-binding sites mutated sensors for fu and smo, site-directed mutagenesis was performed using a PCR-based approach with primers listed in Supplementary Table S5.
RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from second or third instar larvae using Eastep Super Total RNA Extraction Kit (LS1040; Promega). Reverse transcription was performed with Eastep RT Master Mix Kit (LS 2050; Promega). cDNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR in a 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) using 2x Universal SYBR Green Fast qPCR Mix (RM21203; ABclonal). Relative fold changes of hh, ptc, smo, cos2, fu, Su(fu), ci, ihog, boi, dally, dlp, col, and dpp transcripts were calculated using the comparative CT method. Samples from three independent experiments were prepared and run in duplicate. Primers used for qPCR are listed in Supplementary Table S6.
Quantification and Statistical Analysis
The number of Tj-positive somatic cells in each testis, the ratio of the distance between the L3-L4 longitudinal veins to the distance between L2-L5, and the size in each adult wing of different genotypes were quantified and statistically analyzed using Graphpad Prism 8. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used. Standard errors of mean were represented. NS, not significant. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
TH, ML, and AZ designed the study, TH, YF, and YW performed experiments and data analyses, TH, ML, and AZ wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2021YFA0805800 to AZ and ML), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31830058 and 31725019 to AZ and 32170716 to ML), Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, and Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation (to AZ).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dorothea Godt, Xinhua Lin, Haiyun Song, Zhaohui Wang, Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, FlyORF, TsingHua Fly Center, and Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center for plasmids, antibodies, and fly stocks.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2022.866491/full#supplementary-material
References
Agirre, X., Jiménez-Velasco, A., San José-Enériz, E., Garate, L., Bandrés, E., Cordeu, L., et al. (2008). Down-regulation of Hsa-miR-10a in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia CD34+ Cells Increases USF2-Mediated Cell Growth. Mol. Cancer Res. 6, 1830–1840. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-08-0167
Alcedo, J., Zou, Y., and Noll, M. (2000). Posttranscriptional Regulation of Smoothened Is Part of a Self-Correcting Mechanism in the Hedgehog Signaling System. Mol. Cell 6, 457–465. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00044-7
Alexandre, C., Jacinto, A., and Ingham, P. W. (1996). Transcriptional Activation of Hedgehog Target Genes in Drosophila Is Mediated Directly by the Cubitus Interruptus Protein, a Member of the GLI Family of Zinc finger DNA-Binding Proteins. Genes Dev. 10, 2003–2013. doi:10.1101/gad.10.16.2003
Alves, G., Limbourg-Bouchon, B., Tricoire, H., Brissard-Zahraoui, J., Lamour-Isnard, C., and Busson, D. (1998). Modulation of Hedgehog Target Gene Expression by the Fused Serine-Threonine Kinase in Wing Imaginal Discs. Mech. Dev. 78, 17–31. doi:10.1016/s0925-4773(98)00130-0
Amoyel, M., Sanny, J., Burel, M., and Bach, E. A. (2013). Hedgehog Is Required for CySC Self-Renewal but Does Not Contribute to the GSC Niche in the Drosophila Testis. Development 140, 56–65. doi:10.1242/dev.086413
Arvidsson, Y., Rehammar, A., Bergström, A., Andersson, E., Altiparmak, G., Swärd, C., et al. (2018). miRNA Profiling of Small Intestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors Defines Novel Molecular Subtypes and Identifies miR-375 as a Biomarker of Patient Survival. Mod. Pathol. 31, 1302–1317. doi:10.1038/s41379-018-0010-1
Aza-Blanc, P., Ramírez-Weber, F.-A., Laget, M.-P., Schwartz, C., and Kornberg, T. B. (1997). Proteolysis that Is Inhibited by Hedgehog Targets Cubitus Interruptus Protein to the Nucleus and Converts it to a Repressor. Cell 89, 1043–1053. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80292-5
Bandrés, E., Cubedo, E., Agirre, X., Malumbres, R., Zárate, R., Ramirez, N., et al. (2006). Identification by Real-Time PCR of 13 Mature microRNAs Differentially Expressed in Colorectal Cancer and Non-tumoral Tissues. Mol. Cancer 5, 29. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-5-29
Bellaiche, Y., The, I., and Perrimon, N. (1998). tout-velu is a Drosophila Homologue of the Putative Tumour Suppressor EXT-1 and Is Needed for Hh Diffusion. Nature 394, 85–88. doi:10.1038/27932
Benítez, E., Bray, S. J., Rodriguez, I., and Guerrero, I. (2009). Lines Is Required for normal Operation of Wingless, Hedgehog and Notch Pathways during Wing Development. Development 136, 1211–1221. doi:10.1242/dev.021428
Blair, S. S. (2007). Wing Vein Patterning in Drosophila and the Analysis of Intercellular Signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 293–319. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123606
Bornemann, D. J., Duncan, J. E., Staatz, W., Selleck, S., and Warrior, R. (2004). Abrogation of Heparan Sulfate Synthesis in Drosophila Disrupts the Wingless, Hedgehog and Decapentaplegic Signaling Pathways. Development 131, 1927–1938. doi:10.1242/dev.01061
Brennecke, J., Hipfner, D. R., Stark, A., Russell, R. B., and Cohen, S. M. (2003). bantam Encodes a Developmentally Regulated microRNA that Controls Cell Proliferation and Regulates the Proapoptotic Gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113, 25–36. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00231-9
Bushati, N., and Cohen, S. M. (2007). microRNA Functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 175–205. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123406
Chen, W., Huang, H., Hatori, R., and Kornberg, T. B. (2017). Essential Basal Cytonemes Take up Hedgehog in the Drosophila Wing Imaginal Disc. Development 144, 3134–3144. doi:10.1242/dev.149856
Chen, Y.-W., Song, S., Weng, R., Verma, P., Kugler, J.-M., Buescher, M., et al. (2014). Systematic Study of Drosophila microRNA Functions Using a Collection of Targeted Knockout Mutations. Dev. Cell 31, 784–800. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2014.11.029
Chen, Y., and Struhl, G. (1996). Dual Roles for Patched in Sequestering and Transducing Hedgehog. Cell 87, 553–563. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81374-4
Cheng, S., Maier, D., Neubueser, D., and Hipfner, D. R. (2010). Regulation of Smoothened by Drosophila G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases. Dev. Biol. 337, 99–109. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.10.014
Claret, S., Sanial, M., and Plessis, A. (2007). Evidence for a Novel Feedback Loop in the Hedgehog Pathway Involving Smoothened and Fused. Curr. Biol. 17, 1326–1333. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.059
Da Ros, V. G., Gutierrez-Perez, I., Ferres-Marco, D., and Dominguez, M. (2013). Dampening the Signals Transduced through Hedgehog via microRNA miR-7 Facilitates Notch-Induced Tumourigenesis. PLoS Biol. 11, e1001554. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001554
De Lella Ezcurra, A. L., Bertolin, A. P., Kim, K., Katz, M. J., Gándara, L., Misra, T., et al. (2016). miR-190 Enhances HIF-dependent Responses to Hypoxia in Drosophila by Inhibiting the Prolyl-4-Hydroxylase Fatiga. PLoS Genet. 12, e1006073. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1006073
Denef, N., Neubüser, D., Perez, L., and Cohen, S. M. (2000). Hedgehog Induces Opposite Changes in Turnover and Subcellular Localization of Patched and Smoothened. Cell 102, 521–531. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00056-8
Deshpande, G., Manry, D., Jourjine, N., Mogila, V., Mozes, H., Bialistoky, T., et al. (2016). Functioning of an ABC Transporter, Mdr49, in Hh Signaling and Germ Cell Migration. Development 143, 2111–2120. doi:10.1242/dev.133587
Ferretti, E., De Smaele, E., Miele, E., Laneve, P., Po, A., Pelloni, M., et al. (2008). Concerted microRNA Control of Hedgehog Signalling in Cerebellar Neuronal Progenitor and Tumour Cells. EMBO J. 27, 2616–2627. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.172
Flynt, A. S., Li, N., Thatcher, E. J., Solnica-Krezel, L., and Patton, J. G. (2007). Zebrafish miR-214 Modulates Hedgehog Signaling to Specify Muscle Cell Fate. Nat. Genet. 39, 259–263. doi:10.1038/ng1953
Friggi-Grelin, F., Lavenant-Staccini, L., and Therond, P. (2008). Control of Antagonistic Components of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway by microRNAs in Drosophila. Genetics 179, 429–439. doi:10.1534/genetics.107.083733
Gao, L., Hou, X., Wu, L., Zhang, F., Zhang, Q., Ye, X., et al. (2013a). Drosophila miR-960 Negatively Regulates Hedgehog Signaling by Suppressing smoothened, costal-2 and fused. Cell Signal. 25, 1301–1309. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.023
Gao, L., Wu, L., Hou, X., Zhang, Q., Zhang, F., Ye, X., et al. (2013b). Drosophila miR-932 Modulates Hedgehog Signaling by Targeting its Co-receptor brother of ihog. Dev. Biol. 377, 166–176. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.02.002
Ge, X., Milenkovic, L., Suyama, K., Hartl, T., Purzner, T., Winans, A., et al. (2015). Phosphodiesterase 4D Acts Downstream of Neuropilin to Control Hedgehog Signal Transduction and the Growth of Medulloblastoma. eLife 4, e07068. doi:10.7554/eLife.07068
Griffiths-Jones, S., Saini, H. K., van Dongen, S., and Enright, A. J. (2008). miRBase: Tools for microRNA Genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D154–D158. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm952
Guerrero, I., and Kornberg, T. B. (2014). Hedgehog and its Circuitous Journey from Producing to Target Cells. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 33, 52–62. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.06.016
Gunawan, F., Arandjelovic, M., and Godt, D. (2013). The Maf Factor Traffic Jam Both Enables and Inhibits Collective Cell Migration in Drosophila Oogenesis. Development 140, 2808–2817. doi:10.1242/dev.089896
Han, C., Belenkaya, T. Y., Khodoun, M., Tauchi, M., Lin, X., and Lin, X. (2004). Distinct and Collaborative Roles of Drosophila EXT Family Proteins in Morphogen Signalling and Gradient Formation. Development 131, 1563–1575. doi:10.1242/dev.01051
Han, Y., Wang, B., Cho, Y. S., Zhu, J., Wu, J., Chen, Y., et al. (2019). Phosphorylation of Ci/Gli by Fused Family Kinases Promotes Hedgehog Signaling. Dev. Cell 50, 610–626. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2019.06.008
Hartl, T. A., and Scott, M. P. (2014). Wing Tips: the Wing Disc as a Platform for Studying Hedgehog Signaling. Methods 68, 199–206. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.02.002
He, B., Zhao, Z., Cai, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhang, P., Shi, S., et al. (2020). miRNA-Based Biomarkers, Therapies, and Resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 16, 2628–2647. doi:10.7150/ijbs.47203
He, Q., Zhang, Y., and Dong, W. (2020). MicroRNA miR-927 Targets the Juvenile Hormone Primary Response Gene Krüppel Homolog1 to Control Drosophila Developmental Growth. Insect Mol. Biol. 29, 545–554. doi:10.1111/imb.12662
Hersh, B. M., and Carroll, S. B. (2005). Direct Regulation of knot Gene Expression by Ultrabithorax and the Evolution of Cis-Regulatory Elements in Drosophila. Development 132, 1567–1577. doi:10.1242/dev.01737
Hooper, J. E. (2003). Smoothened Translates Hedgehog Levels into Distinct Responses. Development 130, 3951–3963. doi:10.1242/dev.00594
Inaba, M., Buszczak, M., and Yamashita, Y. M. (2015). Nanotubes Mediate Niche-Stem-Cell Signalling in the Drosophila Testis. Nature 523, 329–332. doi:10.1038/nature14602
Ingham, P. W., Nystedt, S., Nakano, Y., Brown, W., Stark, D., van den Heuvel, M., et al. (2000). Patched Represses the Hedgehog Signalling Pathway by Promoting Modification of the Smoothened Protein. Curr. Biol. 10, 1315–1318. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00755-7
Ito, K., Awano, W., Suzuki, K., Hiromi, Y., and Yamamoto, D. (1997). The Drosophila Mushroom Body Is a Quadruple Structure of Clonal Units Each of Which Contains a Virtually Identical Set of Neurones and Glial Cells. Development 124, 761–771. doi:10.1242/dev.124.4.761
Jeng, K.-S., Chang, C.-F., and Lin, S.-S. (2020). Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Organogenesis, Tumors, and Tumor Microenvironments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 758. doi:10.3390/ijms21030758
Jiang, J. (2021). Hedgehog Signaling Mechanism and Role in Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. S1044-579X, 00104–00108. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.04.003
Jongen-Lavrencic, M., Sun, S. M., Dijkstra, M. K., Valk, P. J. M., and Löwenberg, B. (2008). microRNA Expression Profiling in Relation to the Genetic Heterogeneity of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 111, 5078–5085. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-01-133355
Jung, J. E., Lee, J. Y., Park, H. R., Kang, J. W., Kim, Y. H., and Lee, J. H. (2021). microRNA-133 Targets Phosphodiesterase 1C in Drosophila and Human Oral Cancer Cells to Regulate Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Cancer 12, 5296–5309. doi:10.7150/jca.56138
Kent, D., Bush, E. W., and Hooper, J. E. (2006). Roadkill Attenuates Hedgehog Responses through Degradation of Cubitus Interruptus. Development 133, 2001–2010. doi:10.1242/dev.02370
Kim, K., Vinayagam, A., and Perrimon, N. (2014). A Rapid Genome-wide microRNA Screen Identifies miR-14 as a Modulator of Hedgehog Signaling. Cell Rep. 7, 2066–2077. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.025
Kozomara, A., and Griffiths-Jones, S. (2014). miRBase: Annotating High Confidence microRNAs Using Deep Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D68–D73. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1181
Kozomara, A., and Griffiths-Jones, S. (2011). miRBase: Integrating microRNA Annotation and Deep-Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, D152–D157. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1027
Larkin, A., Marygold, S. J., Antonazzo, G., Attrill, H., dos Santos, G., Garapati, P. V., et al. (2021). FlyBase: Updates to the Drosophila melanogaster Knowledge Base. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D899–D907. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa1026
Lee, R. T. H., Zhao, Z., and Ingham, P. W. (2016). Hedgehog Signalling. Development 143, 367–372. doi:10.1242/dev.120154
Lee, Y. S., and Dutta, A. (2009). microRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 4, 199–227. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092222
Li, M. A., Alls, J. D., Avancini, R. M., Koo, K., and Godt, D. (2003). The Large Maf Factor Traffic Jam Controls Gonad Morphogenesis in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 994–1000. doi:10.1038/ncb1058
Li, S., Xu, J., Sun, L., Li, R., Jin, P., and Ma, F. (2017). Drosophila miR-964 Modulates Toll Signaling Pathway in Response to Bacterial Infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 77, 252–258. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2017.08.008
Liu, C., Zhou, Z., Yao, X., Chen, P., Sun, M., Su, M., et al. (2014). Hedgehog Signaling Downregulates Suppressor of Fused through the HIB/SPOP-Crn axis in Drosophila. Cell Res. 24, 595–609. doi:10.1038/cr.2014.29
Liu, F., An, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, N., Chen, B., Li, Z., et al. (2021). miR-10b-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis in Gastric Cancer Xenograft Mice Model through Down-Regulating Tiam1. Exp. Cell Res. 407, 112810. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112810
Liu, M., Su, Y., Peng, J., and Zhu, A. J. (2021). Protein Modifications in Hedgehog Signaling. Bioessays 43, 2100153. doi:10.1002/bies.202100153
Liu, X., Li, M., Peng, Y., Hu, X., Xu, J., Zhu, S., et al. (2016). miR-30c Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis and Differentiation via the Shh Signaling Pathway in P19 Cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 48, e248. doi:10.1038/emm.2016.57
Ma, C., Nong, K., Wu, B., Dong, B., Bai, Y., Zhu, H., et al. (2014). miR-212 Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion by Targeting the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Receptor Patched-1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 33, 54. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-33-54
Michel, M., Kupinski, A. P., Raabe, I., and Bökel, C. (2012). Hh Signalling Is Essential for Somatic Stem Cell Maintenance in the Drosophila Testis Niche. Development 139, 2663–2669. doi:10.1242/dev.075242
Motzny, C. K., and Holmgren, R. (1995). The Drosophila Cubitus Interruptus Protein and its Role in the Wingless and Hedgehog Signal Transduction Pathways. Mech. Development 52, 137–150. doi:10.1016/0925-4773(95)00397-j
Ohlmeyer, J. T., and Kalderon, D. (1998). Hedgehog Stimulates Maturation of Cubitus Interruptus into a Labile Transcriptional Activator. Nature 396, 749–753. doi:10.1038/25533
Ou, C.-Y., Lin, Y.-F., Chen, Y.-J., and Chien, C.-T. (2002). Distinct Protein Degradation Mechanisms Mediated by Cul1 and Cul3 Controlling Ci Stability in Drosophila Eye Development. Genes Dev. 16, 2403–2414. doi:10.1101/gad.1011402
Pak, E., and Segal, R. A. (2016). Hedgehog Signal Transduction: Key Players, Oncogenic Drivers, and Cancer Therapy. Dev. Cell 38, 333–344. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.026
Pignoni, F., and Zipursky, S. L. (1997). Induction of Drosophila Eye Development by Decapentaplegic. Development 124, 271–278. doi:10.1242/dev.124.2.271
Préat, T. (1992). Characterization of Suppressor Of fused, a Complete Suppressor of the Fused Segment Polarity Gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 132, 725–736. doi:10.1093/genetics/132.3.725
Préat, T., Thérond, P., Limbourg-Bouchon, B., Pham, A., Tricoire, H., Busson, D., et al. (1993). Segmental Polarity in Drosophila melanogaster: Genetic Dissection of fused in a Suppressor Of fused Background Reveals Interaction with costal-2. Genetics 135, 1047–1062. doi:10.1093/genetics/135.4.1047
Price, M. A., and Kalderon, D. (2002). Proteolysis of the Hedgehog Signaling Effector Cubitus Interruptus Requires Phosphorylation by Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 and Casein Kinase 1. Cell 108, 823–835. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00664-5
Ruby, J. G., Stark, A., Johnston, W. K., Kellis, M., Bartel, D. P., and Lai, E. C. (2007). Evolution, Biogenesis, Expression, and Target Predictions of a Substantially Expanded Set of Drosophila microRNAs. Genome Res. 17, 1850–1864. doi:10.1101/gr.6597907
Schneider, I. (1972). Cell Lines Derived from Late Embryonic Stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 27, 353–365. doi:10.1242/dev.27.2.353
Sigafoos, A. N., Paradise, B. D., and Fernandez-Zapico, M. E. (2021). Hedgehog/GLI Signaling Pathway: Transduction, Regulation, and Implications for Disease. Cancers 13, 3410. doi:10.3390/cancers13143410
Sisson, J. C., Ho, K. S., Suyama, K., and Scott, M. P. (1997). Costal2, a Novel Kinesin-Related Protein in the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell 90, 235–245. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80332-3
Stadthagen, G., Tehler, D., Høyland-Kroghsbo, N. M., Wen, J., Krogh, A., Jensen, K. T., et al. (2013). Loss of miR-10a Activates Lpo and Collaborates with Activated Wnt Signaling in Inducing Intestinal Neoplasia in Female Mice. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003913. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003913
Strigini, M., and Cohen, S. M. (1997). A Hedgehog Activity Gradient Contributes to AP Axial Patterning of the Drosophila wing. Development 124, 4697–4705. doi:10.1242/dev.124.22.4697
Su, Y., Ospina, J. K., Zhang, J., Michelson, A. P., Schoen, A. M., and Zhu, A. J. (2011). Sequential Phosphorylation of Smoothened Transduces Graded Hedgehog Signaling. Sci. Signal. 4, ra43. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2001747
Takei, Y., Ozawa, Y., Sato, M., Watanabe, A., and Tabata, T. (2004). Three Drosophila EXT Genes Shape Morphogen Gradients through Synthesis of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans. Development 131, 73–82. doi:10.1242/dev.00913
van den Heuvel, M., and Ingham, P. W. (1996). smoothened Encodes a Receptor-like Serpentine Protein Required for Hedgehog Signalling. Nature 382, 547–551. doi:10.1038/382547a0
Vervoort, M., Crozatier, M., Valle, D., and Vincent, A. (1999). The COE Transcription Factor Collier Is a Mediator of Short-Range Hedgehog-Induced Patterning of the Drosophila Wing. Curr. Biol. 9, 632–639. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80285-1
Wang, G., Amanai, K., Wang, B., and Jiang, J. (2000). Interactions with Costal2 and Suppressor of Fused Regulate Nuclear Translocation and Activity of Cubitus Interruptus. Genes Dev. 14, 2893–2905. doi:10.1101/gad.843900
Wessels, H.-H., Lebedeva, S., Hirsekorn, A., Wurmus, R., Akalin, A., Mukherjee, N., et al. (2019). Global Identification of Functional microRNA-mRNA Interactions in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 10, 1626. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09586-z
Wu, L.-F., Gao, X.-M., Zhang, Q.-H., Li, S., Yang, Y.-F., and Lin, X.-H. (2012). Drosophila miR-5 Suppresses Hedgehog Signaling by Directly Targeting Smoothened. FEBS Lett. 586, 4052–4060. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.10.008
Yu, Y., and Cao, X.-C. (2019). miR-190-5p in Human Diseases. Cancer Cell Int. 19, 257. doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0984-x
Zhai, L., Li, Y., Lan, X., and Ai, L. (2017). microRNA-10a-5p Suppresses Cancer Proliferation and Division in Human Cervical Cancer by Targeting BDNF. Exp. Ther. Med. 14, 6147–6151. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.5312
Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., Tong, C., Wang, G., Wang, B., Jia, J., et al. (2005). Hedgehog-regulated Costal2-Kinase Complexes Control Phosphorylation and Proteolytic Processing of Cubitus Interruptus. Dev. Cell 8, 267–278. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.001
Zhang, Z., Feng, J., Pan, C., Lv, X., Wu, W., Zhou, Z., et al. (2013a). Atrophin-Rpd3 Complex Represses Hedgehog Signaling by Acting as a Corepressor of CiR. J. Cell Biol. 203, 575–583. doi:10.1083/jcb.201306012
Zhang, Z., Lv, X., Jiang, J., Zhang, L., and Zhao, Y. (2013b). Dual Roles of Hh Signaling in the Regulation of Somatic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Germline Stem Cell Maintenance in Drosophila Testis. Cell Res. 23, 573–576. doi:10.1038/cr.2013.29
Keywords: Drosophila wing, hedgehog signaling, in vivo miRNA sensor toolbox, miR-10, miR-958
Citation: He T, Fan Y, Wang Y, Liu M and Zhu AJ (2022) Dissection of the microRNA Network Regulating Hedgehog Signaling in Drosophila. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10:866491. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.866491
Received: 31 January 2022; Accepted: 08 April 2022;
Published: 28 April 2022.
Edited by:
Steven Cheng, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Robert Holmgren, Northwestern University, United StatesJin Jiang, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, United States
Pascal Therond, CNRS UMR7277 Institut de Biologie Valrose, France
Copyright © 2022 He, Fan, Wang, Liu and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Liu, bGl1bWluMDJAcGt1LmVkdS5jbg==; Alan Jian Zhu, emh1YUBwa3UuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Tao He
Tao He Yu Fan
Yu Fan Yao Wang
Yao Wang Min Liu
Min Liu Alan Jian Zhu
Alan Jian Zhu