
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. , 05 January 2023
Sec. Cell Death and Survival
Volume 10 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.1118466
This article is part of the Research Topic Spatiotemporal Regulation of Central Nervous System Disorders: Molecular Mechanisms and Emerging Techniques View all 8 articles
This article is a correction to:
Electrochemically induced in vitro focal hypoxia in human neurons
A Corrigendum on
Electrochemically induced in vitro focal hypoxia in human neurons
by Wong JJY, Varga BV, Káradóttir RT and Hall EAH (2022). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10:968341. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.968341
In the published article, there was an error in Table 2 as published. This was due to a formatting error during publication causing rows to become misplaced in the final printed copy and subscript information to be lost.
The corrected Table 2 and its caption Experimental design appear below.
In the published article, there was an error in Table 3 as published. This was due to a formatting error during publication causing rows to become misplaced in the final printed copy.
The corrected Table 3 and its caption pH and H2O2 concentration under eLOS oxygen scavenging appear below.
Error in Table carried over to the index figure.
In the published article, there was an error in Index figure as published. This arose as a carry-over of the error in the formatting of the table that the publishers used as index figure A corrected index figure appears below corresponding to Figure 10 in the manuscript.
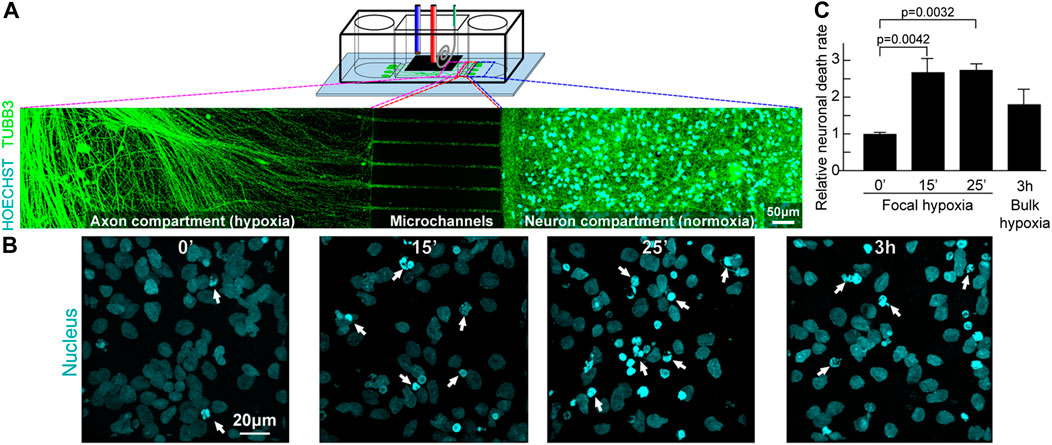
FIGURE 10. Focal hypoxia in a human cortical neuron microchannel model. (A) Schematic presentation of the microchannel model. Representative confocal tile image of neurons growing across the microchannels. Cyan: cell nucleus; green: axons. (B) Representative confocal image of cell nucleus (cyan) at the end chambers and axons in the central chamber after hypoxic insults. (C) Quantitative analysis of cells with chromatin condensation (n = 4).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: hypoxia, electrochemistry, microfluidic, human cortical neural progenitor, cortical neuron, axon, small vessel disease, lacunar infarct
Citation: Wong JJY, Varga BV, Káradóttir RT and Hall EAH (2023) Corrigendum: Electrochemically induced in vitro focal hypoxia in human neurons. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10:1118466. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1118466
Received: 07 December 2022; Accepted: 08 December 2022;
Published: 05 January 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Wong, Varga, Káradóttir and Hall. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Elizabeth A. H. Hall, ZWFoMTZAY2FtLmFjLnVr
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.