- 1Department of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 2Department of Immunology, College of Basic Medical Science, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 3Molecular Medical Laboratory, College of Basic Medical Science, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Background: Systemic inflammation, immune and nutrition status are closely linked to the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease (CHD). Pan-immune-inflammation value (PIV) is a new method for evaluating systemic inflammation and immune status. Our objective is to explore the connection between PIV and CHD especially in elderly people, as well as the diagnostic value of PIV combined with controlling nutritional status (COUNT) score for CHD.
Methods: Participants eligible for the study were sourced from NHANES data from 1999 to 2018. Logistic regression models were employed to evaluate the link between PIV and CHD. Additionally, restricted cubic spline was utilized to explore the correlations. Subgroup analysis was adopted in order to ensure the credibility of the results. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used to explore the predictive value of PIV combined with COUNT score for CHD.
Results: 41,713 individuals qualified for analysis. The individuals with CHD had higher levels of PIV. In the logistic regression model, PIV was positively related to CHD [Q4 vs. Q1, OR = 1.23 (1.03–1.48, P < 0.001)]. Restricted cubic spline indicated a positive non-linear relationship (P for overall <0.001, P for non-linear = 0.009). However, restricted cubic spline shows that this positive correlation is only significant in the elderly population aged 60 and above. Subgroup analysis shows that the relationship between PIV and CHD is more significant in the elderly population (P < 0.001). The ROC curve shows that PIV has better diagnostic value for CHD than other common inflammatory indicators. Furthermore, the combination of PIV and COUNT score is superior to PIV or COUNT score.
Conclusions: A positive link between PIV and CHD, especially in the elderly. The combination of PIV and COUNT score has better diagnostic value for CHD.
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) rank as the foremost cause of mortality across the globe, representing approximately one-third of all annual fatalities (1, 2). Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the main type of CVDs and the leading cause of cardiovascular mortality in both men and women (3, 4). In addition, the incidence of CHD is increasing year by year with the intensification of population aging. The development of CHD can also cause serious adverse cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, malignant arrhythmia, etc. (5). Research shows that more than 20 million Americans suffer from CHD, which brings huge economic and medical burden to the country (6, 7).
The pathological basis of CHD is atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease driven by lipid. Chronic inflammation can induce endothelial cells to release adhesion molecules, promote smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, and exacerbate the infiltration of pro-inflammatory immune cells. These pathological processes can accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis (8, 9). The development of CHD is significantly influenced by inflammation and the immune response. These factors are intricately connected. Inflammation can promote immune response, leading to further inflammation in turn. Under the constant stimulation of immune response and inflammatory effect, atheromatous plaque can gradually increase, inducing plaque rupture and thrombosis, which ultimately leads to adverse cardiovascular events. Although many measures have been taken, the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis are still difficult. Therefore, further development of biomarkers for predicting the risk of disease occurrence and improving patient risk stratification is crucial for the general public.
Common indicators of blood routine include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, platelets, etc. Researchers have found that the combination of these indicators can better reflect the inflammatory state of the body and is closely related to the increased risk of diseases (10, 11). In addition, pan-immune inflammation value (PIV), a novel marker of inflammation, was developed for research, integrating four types of immune cells including neutrophils, monocytes, platelets, and lymphocytes. The definition of PIV is as follows: neutrophil count × platelet count × monocyte count/lymphocyte count (12). Due to its potential ability to comprehensively reveal the status of systemic immune and cancer-related inflammatory responses, PIV is considered a reliable predictor of clinical outcomes in patients with inflammatory diseases and cancer (13). - In contrast to other immune indices such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and systemic immune inflammation index(SII), PIV seems to have higher predictive value for diseases (14–16).
In addition, patients with CHD are often elderly and suffer from malnutrition (17, 18). There is also a close relationship between inflammation and malnutrition. The relationship between inflammation and malnutrition may be bidirectional. Inflammation is a driving factor for malnutrition, and malnutrition can exacerbate inflammation (19). The controlling nutritional status (COUNT) score is a classic evaluation of the body's nutritional status by taking into account the composition of lymphocytes, levels of total cholesterol, and albumin (20). It involves three aspects of protein reserves, calorie expenditure, and immune defense in the body. Furthermore, it can be used as an early screening tool for malnutrition in hospitalized patients and continuous monitoring of nutritional status during treatment (21). PIV is used to measure the level of inflammation in the body, while COUNT score is used to measure the nutritional status of the body. The difference between the two is significant. Therefore, we also want to further explore whether the combination of PIV and COUNT score has better predictive value for CHD.
PIV is associated with many diseases, including tumors, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and hypertension (22–24). Nonetheless, the correlation between PIV and CHD risk remains ambiguous. Consequently, the objective is to explore the link between PIV and CHD, as well as the diagnostic value of PIV combined with controlling nutritional status (COUNT) score for CHD.
Materials and methods
Data source and sample selection
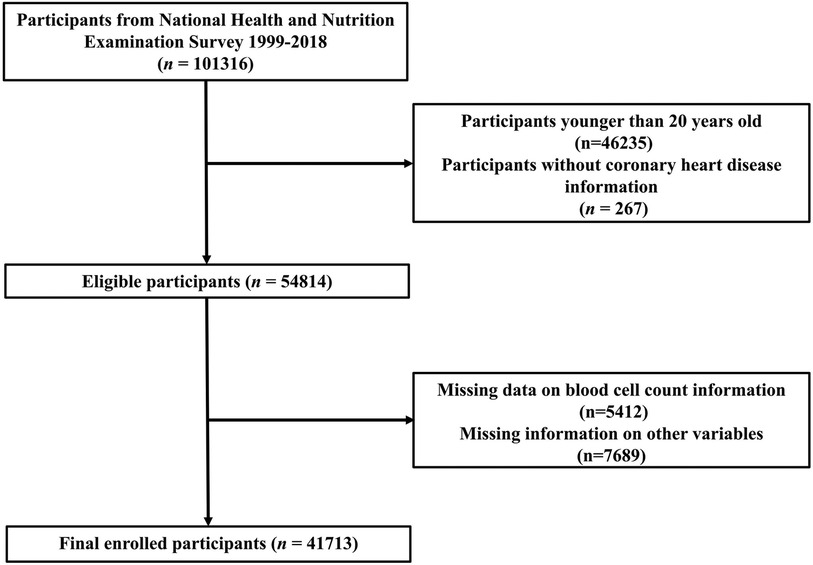
Data for this study were obtained from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database (https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/). We aim to include adults with complete information from the NHANES database from 1999 to 2018. Initially, a total of 101,316 participants were included in the database from 1999 to 2018. First, we excluded individuals under 20 years of age (n = 46,235) and those without CHD data (n = 267). The calculation of PIV and COUNT scores requires complete hematological examination results, and we further excluded indiiduals with missing incomplete blood cell information (n = 5,412). Due to the possible impact of missing covariates on the results, we also excluded participants who were missing data on various covariates (n = 7,689). As a result, the final sample for analysis included 41,713 participants. The details of the screening methodology are illustrated in Figure 1.
Calculation of inflammatory indicators and COUNT score
PIV is calculated by integrating four types of immune cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, platelets, and lymphocytes. The calculation formula for PIV, NLR, MLR and SII are as follows:
PIV = neutrophil count × platelet count × monocyte count/lymphocyte count (25). NLR = neutrophil count/lymphocyte count (26). MLR = monocyte count/lymphocyte count (27). SII = neutrophil count × platelet count/lymphocyte count. The CONUT score acts as a measure for assessing nutritional and immune status by taking into account the composition of lymphocytes, levels of total cholesterol, and albumin (28). The COUNT score is the sum of the scores corresponding to three indicators. The specific scoring criteria are shown in Supplementary Table S2.
Covariates
Based on previous research on CHD in NHANES, we also obtained other variables from the database, including age, sex, race, body mass index (BMI), education level, blood lipids, uric acid, glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). In addition, we also extracted smoking, drinking, hypertension and diabetes mellitus (DM).
Statistical analysis
Initially, the dataset was categorized into two distinct groups: the non-CHD group and the CHD group. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SEM (Standard Error of the Mean), while categorical variables were represented as proportions (95% CI), with P values <0.05 considered statistically significant. Second, we conducted weighted logistic regression analysis. This statistical method was employed to investigate the potential link between PIV and CHD. Two models were developed: Model I, and Model II. Model I was adjusted for age, gender, and race. Model II was adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, education attainment, total cholesterol(TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), smoking, alcohol consumption, uric acid, eGFR, hypertension and DM. Restrictive cubic spline is commonly used to model the relationship between continuous variables and dependent variables. Especially in regression analysis, it allows for capturing non-linear relationships and avoiding overfitting while maintaining smoothness. Nonlinear is closer to the essence of objective things and is one of the important methods for quantitatively studying and understanding complex problems. Restricted cubic spline was utilized to examine the link between PIV and CHD. NHANES data comes from representative populations in various parts of the United States, and weighted analysis can accurately reflect the characteristics of the overall population. In addition, some studies have indicated that outcomes from weighted analyses and unweighted analyses may occasionally differ. To verify our findings, we conducted unweighted logistic regression. Furthermore, subgroup analysis was carried out as well. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve is used to compare the superiority and inferiority of different inflammatory indicators in predicting CHD. Due to the close relationship between inflammation and malnutrition, we also investigated the predictive value of PIV combined with COUNT score for CHD.
Results
The baseline characteristics of participants
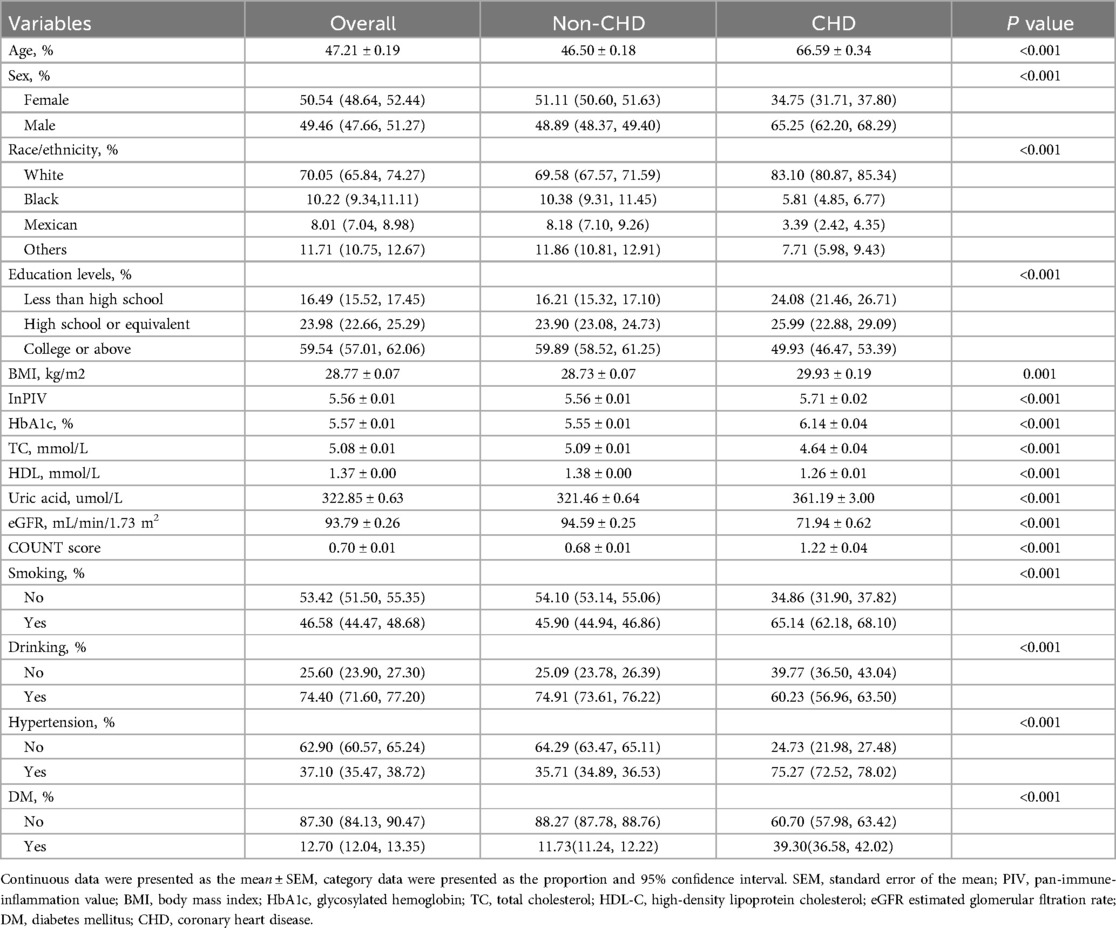
41,713 adults were screened for this study. Table 1 presents the clinical characteristics of all participants, encompassing a variety of clinical details. Firstly, we divided the patients into two groups: the CHD group and the non-CHD group. Table 1 illustrates that the participants in the CHD group were of an older age. In contrast, those in the non-CHD group displayed a lower prevalence of smoking (45.9%), diabetes mellitus (11.73%) and hypertension (35.71%). The incidence of obesity is higher in the CHD group, and the levels of uric acid and HbA1c are also higher. On the contrary, patients with CHD have lower HDL-C and are accompanied by a decline in renal function (P < 0.001).As expected, patients with CHD have higher COUNT scores (P < 0.001). This also indicates that patients with CHD are to some extent accompanied by malnutrition. It is worth noting that we also observed a significant statistical difference in lnPIV between the two groups (non-CHD vs. CHD: 5.56 ± 0.01 vs. 5.71 ± 0.02, P < 0.001***). Supplementary Table S1 presents clinical data based on PIV quartiles. The incidence of CHD gradually increased with the increase of PIV (P < 0.001). Compared with the highest PIV group, patients in the lowest PIV group had lowest CHD incidence. With the increase of PIV, the proportion of smoking, hypertension and diabetes gradually increases (P < 0.001). Furthermore, notable variations were also observed in terms of age, ethnicity, BMI, HbA1c, eGFR, HDL-C, TC, uric acid, alcohol consumption and educational attainment between the four groups (P < 0.001).
The link between PIV and CHD
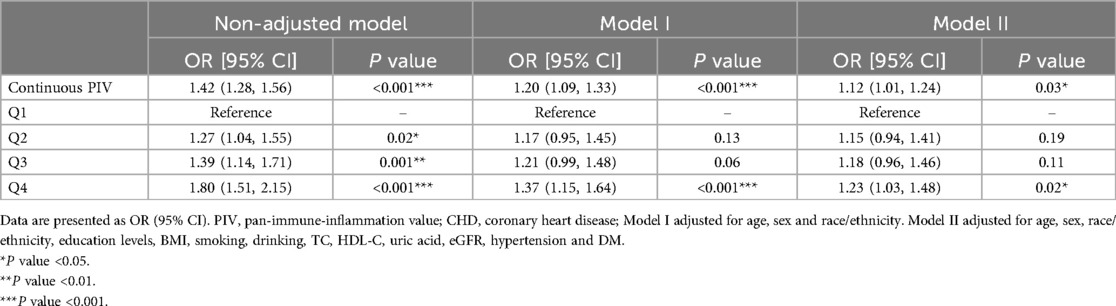
As a continuous variable, a positive correlation was showed between PIV and CHD, with an OR of 1.42 (95%CI: 1.28–1.56) in unadjusted logistic regression analysis (Table 2). After adjusting the confounding factors in Model II, this relationship still exists(OR = 1.12, 95%CI: 1.01–1.24). As a categorical variable, the highest quartile also showed a highest risk of CHD in Model II after adjusting the confounding factors (OR = 1.23, 95%CI: 1.03–1.48).
Restricted cubic spline
It was employed to investigate the curve relationship between InPIV and CHD. Our results uncover a non-linear positive link between InPIV and CHD (P for overall <0.001, P for non-linear = 0.009). At first, as InPIV rose, the incidence of CHD slowly increased. However, the incidence of CHD increased significantly when it exceeded a certain threshold (Figure 2). Interestingly, this positive correlation seems to be more pronounced in the elderly population (Figure 3A). This positive correlation has also been noted in both male and female participants (Figures 3B).
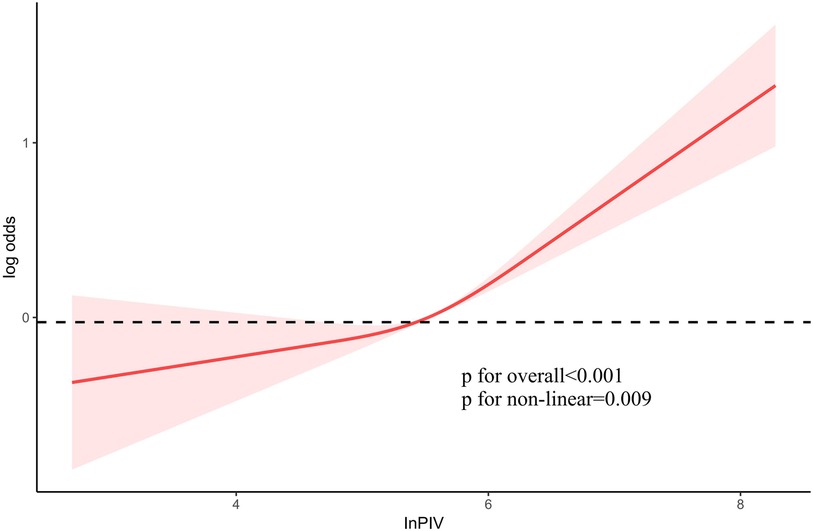
Figure 2. The link between PIV and the risk of CHD. PIV, pan-immune inflammation value; CHD, coronary heart disease.
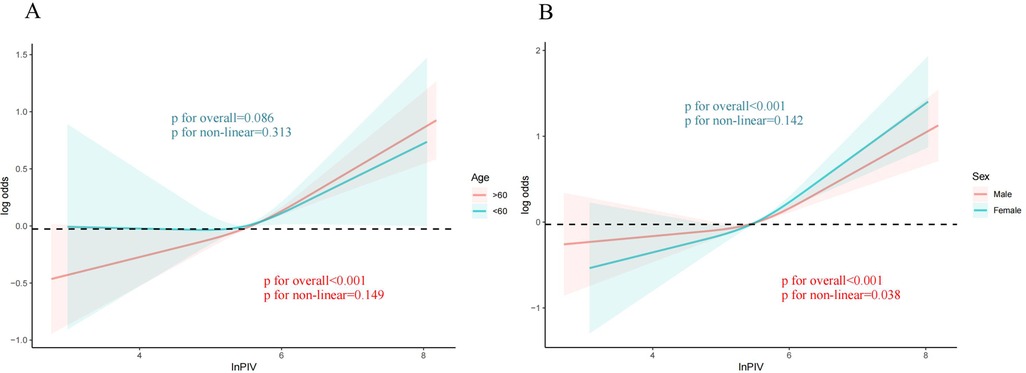
Figure 3. The link between PIV and CHD in different subgroups. (A) Age; The red curve represents the population over 60 years old and the green curve represents the population under 60 years old (B) Sex; The red curve represents males, and the green curve represents females. PIV, pan-immune inflammation value; CHD, coronary heart disease.
Sensitivity analysis
Studies have indicated that outcomes from weighted analyses and unweighted analyses may occasionally differ. Therefore, we employ unweighted approaches to confirm the reliability of our findings. As a continuous variable, a positive correlation was showed between PIV and CHD, with an OR of 1.12 (95%CI: 1.04–1.21) in Model II. Compared to the Q1 quartile of InPIV, the Q4 quartile exhibits the greatest risk of CHD (OR = 1.24, 95% CI: 1.06–1.45) in Model II (Table 3).
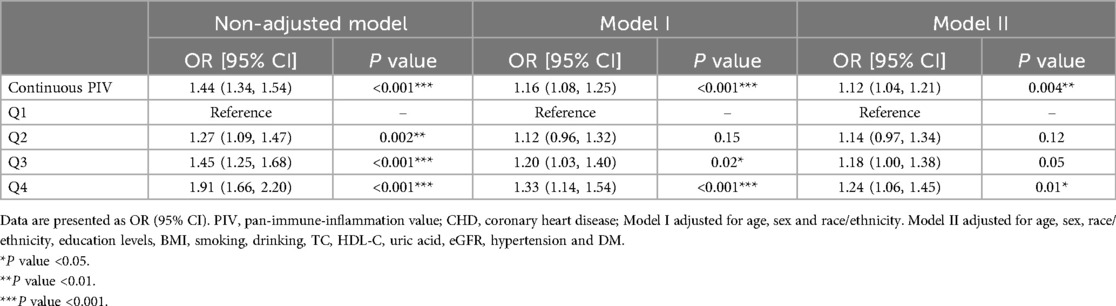
Table 3. Unweighted logistic regression analysis on the correlation between PIV and CHD in sensitivity analysis.
Subgroups analysis
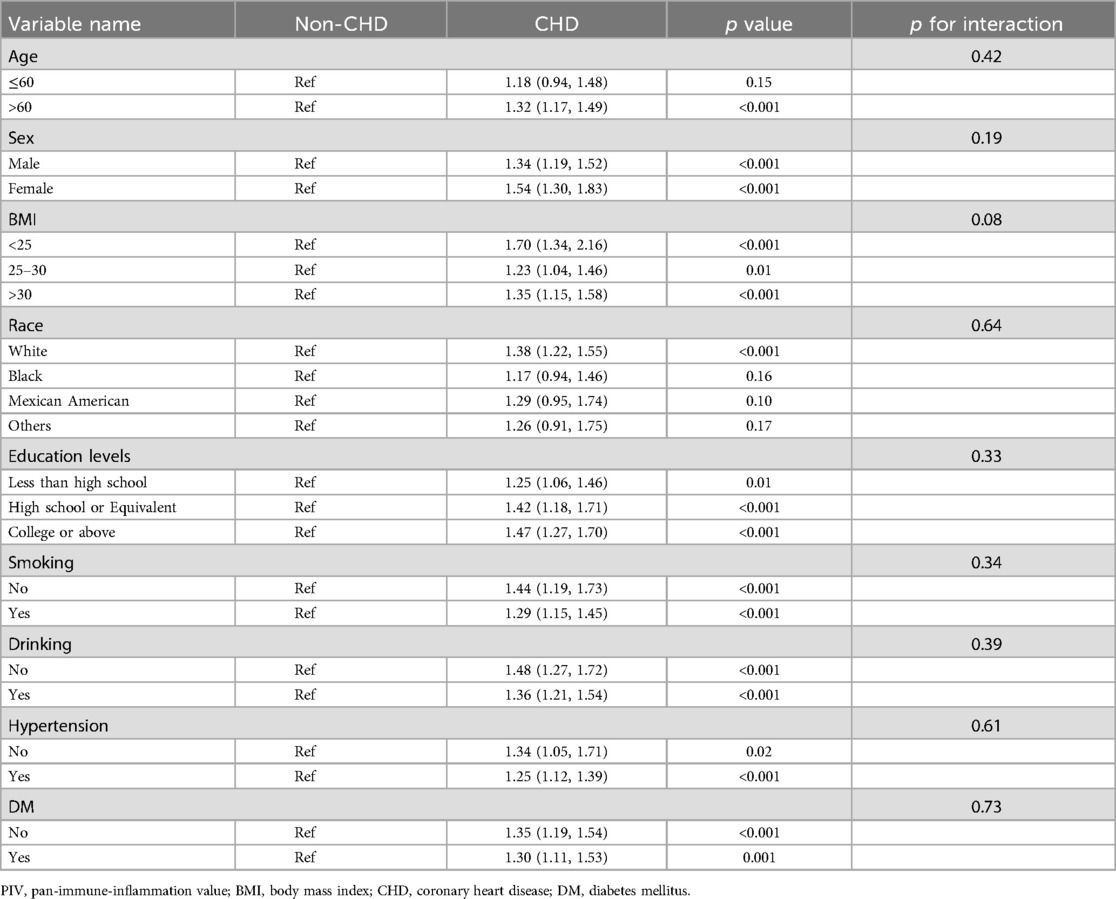
To further elucidate the link between PIV and CHD, subgroup analysis was utilized to investigate the potential link between PIV and CHD in different subgroups based on age, sex, BMI, race, education levels, smoking, drinking, hypertension and DM. However, there were no notable differences found in the impact of PIV on CHD within the other subgroups. Interestingly, this relationship is particularly significant in elderly patients aged 60 and above (Table 4).
ROC curve analysis
ROC curve analysis shows that PIV has better predictive value for CHD than NLR, MLR and SII (PIV vs. NLR vs. MLR vs. SII: 0.665 vs. 0.613 vs. 0.569 vs. 0.525). The ROC curve cut-off value of PIV is 324. The sensitivity is 57.47% and the specificity is 67.81%. Due to the close correlation between inflammation and malnutrition, ROC curve analysis also found that PIV combined with COUNT score has greater predictive value for CHD (PIV + COUNT vs. PIV vs. COUNT: 0.678 vs. 0.665 vs. 0.639) (Figure 4).
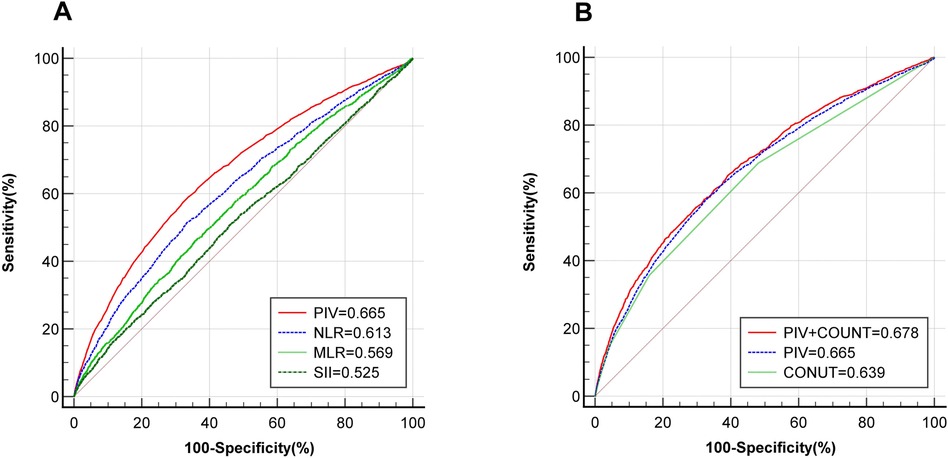
Figure 4. ROC curve reveals the diagnostic value of PIV for CHD. (A) Comparison of the predictive value of PIV(red), NLR(blue), MLR(light green) and SII(deep green) for CHD; (B) The predictive value of PIV(blue), COUNT score(light green) and PIV combined with COUNT score(red) for CHD. ROC, receiver operator characteristic; PIV, pan-immune inflammation value; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; MLR, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; SII, systemic immune inflammation index; COUNT, controlling nutritional status; CHD, coronary heart disease.
Discussion
This research demonstrates that a positive relationship existed between PIV and CHD, especially in elderly people. The predictive value of PIV for CHD is superior to NLR, MLR and SII. The combination of PIV and COUNT score has better predictive value for CHD.
Chronic inflammation is vital in the development of atherosclerosis. In the early stage of atherosclerosis, neutrophils can induce endothelial dysfunction, promote the formation of foam cells and inflammatory response. In addition, neutrophils also participate in plaque vascular injury, necrotic nucleus formation, and thinning of fibrous caps, promoting unstable plaque rupture and activating platelets, leading to secondary thrombosis (29, 30). In addition, the chemotaxis, adhesion and migration of monocytes are also involved in the regulation of atherosclerosis inflammation (31). platelets can combine with a variety of cells and factors, participate in cascade inflammatory reaction, and promote the formation of atherosclerosis (32). Lymphocytes participate in the immune regulation of atherosclerosis, and maintain the balance between proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses (33). The interaction of these cells may promote the progression of atherosclerosis.
In recent years, researchers have developed various inflammatory indices, including NLR and MLR, which are associated with prognosis in various diseases. In addition, the relationship between these indicators and CHD is constantly being confirmed (34, 35). Recently, some scholars found that PIV integrates four types of blood cell counts, which can better reflect the inflammatory and immune condition, and has shown good value in various diseases. Furthermore, studies have found that PIV is associated with slow coronary flow and adverse cardiovascular events (36, 37). Similarly, our findings indicate that higher levels of PIV are linked to a greater risk of CHD, and this relationship is superior to other inflammatory markers. In clinical practice, PIV integrates four types of blood cells, which can better reflect systemic inflammation. Therefore, it has good evaluation value for patients’ disease status as a novel inflammatory marker, especially in CHD. In addition, several studies have discovered that patients with CHD are often older and mostly suffer from malnutrition. The COUNT score is commonly used for predicting the prognosis of inflammatory diseases or chronic wasting diseases, with good predictive performance and convenient use (38, 39). There is an inseparable relationship between malnutrition and inflammation. Inflammation can induce malnutrition, which in turn exacerbates inflammation (40). Our study also suggests that PIV combined with COUNT score has better predictive value for CHD. Our findings may provide help for the management of CHD.
It is noteworthy that the positive link between elderly people was significant. Aging is a chronic inflammatory process, and chronic inflammation can further exacerbate aging in turn. Therefore, It is relatively easy to grasp that inflammation may play a more important role in elderly patients. Additionally, malnutrition prevalence is elevated among older adults, and we also found that PIV combined with COUNT score has greater predictive value for CHD.
This study provides important references for the management of CHD patients. The NHANES database, which is extensive and international, offers robust support for the risk assessment of CHD. Compared with other common clinical inflammatory indices, PIV can comprehensively reflect the systemic inflammatory status, which provides better help for the health of Americans. However, our research also has some limitations. First, we cannot determine the causal relationship. Second, we have not monitored the dynamic changes in hematological indices. Third, the results of this study are mainly applicable to the American population. In addition, the diagnostic criteria for CHD is based on a history of CHD. Furthermore, CHD is also classified into stable angina and acute coronary syndrome according to severity in clinical practice. We did not explore the correlation between PIV and the severity of CHD in this study. Finally, there might still be other confounding elements that could affect the results, including medication use, dietary habits, and physical activity. In the future, we will further explore the relationship between PIV and CHD by combining clinical cases.
Conclusion
A positive relationship was observed between PIV and CHD, especially in the elderly. The combination of PIV and COUNT score has better diagnostic value for CHD.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/.
Ethics statement
The data is accessible to the public (found in the NHANES database), therefore there is no need for an ethical approval statement or informed consent for the study.
Author contributions
RM: Writing – original draft. JR: Data curation, Writing – original draft. XC: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. YD: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Dalian Medical University Interdisciplinary Research Cooperation Project Team Funding (JCHZ2023010).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1538643/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; CHD, coronary heart disease; COUNT, controlling nutritional status; PIV, pan-immune inflammation value; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; MLR, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; SII, systemic immune inflammation index; COUNT, controlling nutritional status; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; BMI, body mass index; EGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; DM, diabetes mellitus; SEM, standard error of the mean; C, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ROC, receiver operator characteristic.
References
1. Timmis A, Aboyans V, Vardas P, Townsend N, Torbica A, Kavousi M, et al. European society of cardiology: the 2023 atlas of cardiovascular disease statistics. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45(38):4019–62. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae466
2. Mensah GA, Myers T, Schmelzer R Jr, Spaeth S, Roth GA, Fuster V. Turning data into action: the JACC global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risks interactive tool and resources. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2024) 83(24):2610–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.05.007
3. Montone RA, Camilli M, Calvieri C, Magnani G, Bonanni A, Bhatt DL, et al. Exposome in ischaemic heart disease: beyond traditional risk factors. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45(6):419–38. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae001
4. GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403(10440):2100–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2
5. Wang Y, Huang B, Sun M, Yu B, Ping L. Type D personality as a risk factor for 3-year cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease and their spouse: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2024):zwae377. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae377
6. Zhu Y, Llamosas-Falcón L, Kerr WC, Rehm J, Probst C. Behavioral risk factors and socioeconomic inequalities in ischemic heart disease mortality in the United States: a causal mediation analysis using record linkage data. PLoS Med. (2024) 21(9):e1004455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004455
7. Kazi DS, Elkind MSV, Deutsch A, Dowd WN, Heidenreich P, Khavjou O, et al. Forecasting the economic burden of cardiovascular disease and stroke in the United States through 2050: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2024) 150(4):e89–e101. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001258
8. Shoaran M, Maffia P. Tackling inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2024) 21(7):442. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01007-z
9. Ridker PM. The time to initiate anti-inflammatory therapy for patients with chronic coronary atherosclerosis has arrived. Circulation. (2023) 148(14):1071–3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.066510
10. Wu H, Cao T, Ji T, Luo Y, Huang J, Ma K. Predictive value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the prognosis and risk of death for adult sepsis patients: a meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1336456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1336456
11. Vakhshoori M, Nemati S, Sabouhi S, Shakarami M, Yavari B, Emami SA, et al. Prognostic impact of monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio in coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. (2023) 51(10):3000605231204469. doi: 10.1177/03000605231204469
12. Fucà G, Guarini V, Antoniotti C, Morano F, Moretto R, Corallo S, et al. The pan-immune-inflammation value is a new prognostic biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from a pooled-analysis of the valentino and TRIBE first-line trials. Br J Cancer. (2020) 123(3):403–9. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0894-7
13. Jin C, Li X, Luo Y, Zhang C, Zuo D. Associations between pan-immune-inflammation value and abdominal aortic calcification: a cross-sectional study. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1370516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1370516
14. Gambichler T, Hessam S, Cramer P, Abu Rached N, Bechara FG. Complete blood collection-based systemic inflammation biomarkers for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2022) 36(9):1593–6. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18175
15. Murat B, Murat S, Ozgeyik M, Bilgin M. Comparison of pan-immune-inflammation value with other inflammation markers of long-term survival after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur J Clin Invest. (2023) 53(1):e13872. doi: 10.1111/eci.13872
16. Ning X, Wu C, Song B, Wang HM, Jin HZ. Evaluation of hematological inflammatory parameters in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis. Int J Dermatol. (2024) 63(12):1713–9. doi: 10.1111/ijd.17230
17. Park JY, Bu SY. The ability of the geriatric nutritional risk index to predict the risk of heart diseases in Korean adults: a Korean genome and epidemiology study cohort. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1276073. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1276073
18. Özkan C, Dolu AK, Çelik MC, Demirtaş B, Karayiğit O. Evaluating the prognostic nutritional index for predicting the clinical relevance of angiographically intermediate coronary lesions. Anatol J Cardiol. (2024) 29(1):19–25. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4407
19. Simonenko SY, Bogdanova DA, Kuldyushev NA. Emerging roles of vitamin B(12) in aging and inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(9):5044. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095044
20. Raposeiras Roubín S, Abu Assi E, Cespón Fernandez M, Barreiro Pardal C, Lizancos Castro A, Parada JA, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of malnutrition in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76(7):828–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.058
21. Soler-Espejo E, Zazo-Luengo BÁ, Rivera-Caravaca JM, López-Gávez R, Esteve-Pastor MA, Lip GYH, et al. Poor clinical outcomes associated to multimorbidity, frailty and malnutrition in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Nutr Health Aging. (2025) 29(1):100430. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100430
22. Guven DC, Sahin TK, Erul E, Kilickap S, Gambichler T, Aksoy S. The association between the pan-immune-inflammation value and cancer prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel. (2022) 14(11):2675. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112675
23. Qiu S, Jiang Q, Li Y. The association between pan-immune-inflammation value and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: data from NHANES 1999–2018. Front Physiol. (2024) 15:1440264. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1440264
24. Wu B, Zhang C, Lin S, Zhang Y, Ding S, Song W. The relationship between the pan-immune-inflammation value and long-term prognoses in patients with hypertension: national health and nutrition examination study, 1999–2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1099427. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1099427
25. Kuang T, Qiu Z, Wang K, Zhang L, Dong K, Wang W. Pan-immune inflammation value as a prognostic biomarker for cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1326083. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1326083
26. Barbui T, Carobbio A, Ghirardi A, Fenili F, Finazzi MC, Castelli M, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator of mortality in polycythemia vera: insights from a prospective cohort analysis. Blood Cancer J. (2024) 14(1):195. doi: 10.1038/s41408-024-01176-7
27. Zhao H, Li M, Wu D, Chen S, Zhu C, Lan Y, et al. Physical activity modifies the risk of incident cardiac conduction disorders upon inflammation: a population-based cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13(16):e034754. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.034754
28. Zhang S, Li S, Gao L, Zhao Q, Yang T, Zeng Q, et al. Effects of malnutrition on disease severity and adverse outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: a retrospective cohort study. Respir Res. (2024) 25(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02925-9
29. Soehnlein O, Döring Y. Beyond association: high neutrophil counts are a causal risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(47):4965–7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad711
30. Herrero-Cervera A, Soehnlein O, Kenne E. Neutrophils in chronic inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19(2):177–91. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00832-3
31. Dong Z, Hou L, Luo W, Pan LH, Li X, Tan HP, et al. Myocardial infarction drives trained immunity of monocytes, accelerating atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45(9):669–84. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad787
32. Gawaz M, Geisler T, Borst O. Current concepts and novel targets for antiplatelet therapy. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20(9):583–99. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00854-6
33. Khan A, Ley K. Immunotherapy for atherosclerosis by targeting proinflammatory T cells. Cell Res. (2024) 34(7):467–8. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-00955-y
34. Gosav EM, Tanase DM, Buliga-Finis ON, Rezuș II, Morariu PC, Floria M, et al. The prognostic role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocytes ratio in the most frequent cardiovascular diseases: an update. Life (Basel). (2024) 14(8):985. doi: 10.3390/life14080985
35. Ma M, Liu Y, Wang L, Yang R, Li Z, Gao S, et al. Relationship between monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio as well as other leukocyte-derived ratios and carotid plaques in patients with coronary heart disease: a RCSCD-TCM study. J Inflamm Res. (2022) 15:5141–56. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S375759
36. Yang L, Guo J, Chen M, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang J. Pan-immune-inflammatory value is superior to other inflammatory indicators in predicting inpatient major adverse cardiovascular events and severe coronary artery stenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention in STEMI patients. Rev Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 25(8):294. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2508294
37. Akkaya S, Cakmak U. Association between pan-immune-inflammation value and coronary slow flow phenomenon in patients with angiographically normal coronary arteries. Int J Cardiol. (2024) 398:131631. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.131631
38. Li D, Sun J, Qi C, Fu X, Gao F. Predicting severity of inpatient acute cholangitis: combined neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and prognostic nutritional index. BMC Gastroenterol. (2024) 24(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03560-w
39. Rossi AP, Scalfi L, Abete P, Bellelli G, Bo M, Cherubini A, et al. Controlling nutritional status score and geriatric nutritional risk index as a predictor of mortality and hospitalization risk in hospitalized older adults. Nutrition. (2025) 131:112627. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2024.112627
Keywords: coronary heart disease, NHANES, pan-immune-inflammation value, controlling nutritional status score, elderly people
Citation: Ma R, Ren J, Chen X, Li X, Zhao Y and Ding Y (2025) Association between pan-immune-inflammation value and coronary heart disease in elderly population: a cross-sectional study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1538643. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1538643
Received: 3 December 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 10 February 2025.
Edited by:
Li-Da Wu, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xintian Cai, People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, ChinaYuhao Xie, St. John’s University, United States
Changjun Luo, Liuzhou Liutie Central Hospital, China
Copyright: © 2025 Ma, Ren, Chen, Li, Zhao and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Zhao, emhhb3lpbmcyMDAwMTEwNUAxMjYuY29t; Yanchun Ding, eWFuY2h1bmRpbmcwODgwQDE2My5jb20=
 Ruicong Ma
Ruicong Ma Jinyi Ren2
Jinyi Ren2 Xia Li
Xia Li Yanchun Ding
Yanchun Ding