
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 07 February 2025
Sec. Cardiovascular Biologics and Regenerative Medicine
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1533105
Cardiovascular diseases are the most lethal diseases worldwide, of which myocardial infarction is the leading cause of death. After myocardial infarction, in order to ensure normal blood supply to the heart, the remaining cardiomyocytes compensate for the loss of cardiomyocytes mainly by working at high capacity rather than by proliferating to produce new cardiomyocytes. This is partly due to the extremely limited ability of the adult heart to repair itself. A growing body of research suggests that the loss of cardiac regenerative capacity is closely related to metabolic shifts in energy sources. Currently, a large number of studies have focused on changes in metabolic levels before and after the proliferation window of cardiomyocytes, so it is crucial to search for relevant factors in metabolic pathways to regulate the cell cycle in cardiomyocyte progression. This paper presents a review of the role of myocardial energy metabolism in regenerative repair after cardiac injury. It aims to elucidate the effects of myocardial metabolic shifts on cardiomyocyte proliferation in adult mammals and to point out directions for cardiac regeneration research and clinical treatment of myocardial infarction.
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains a significant contributor to morbidity, but mortality has been significantly reduced in the last decades due to the introduction of thrombolytic therapy and acute vascular interventions (1). Despite the enormous global efforts in the prevention and treatment of MI, the situation faced remains critical, partly because adult mammalian cardiomyocytes are at the stage of terminal differentiation and have an extremely limited proliferative capacity. Cardiomyocytes die under the action of persistent cardiac ischemia and other injurious factors, and irreversible damage occurs to the heart, which is one of the important mechanisms causing MI (2). At this stage, the most important strategy for the treatment of MI is the rapid restoration of blood flow. Reperfusion therapies, such as coronary intervention, are an important means of treating MI in a timely and effective manner to minimize cardiac damage. However, when blood supply is restored, it triggers ischemia-reperfusion injury (I/R), which leads to a series of serious pathological sequelae and further aggravates cardiac damage (3). MI progresses to the final stage leading to the development of heart failure (HF), and heart transplantation is the most effective therapeutic strategy for patients with end-stage HF, but organ shortages are the main problem faced today. Currently, commonly used clinical agents include statins, receptor blockers, or angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, but the search for new therapeutic targets remains an important endeavor. Therefore, the search for novel preventive and curative measures for MI is of great significance in reducing cardiovascular disease mortality.
In contrast to the limited self-repair capacity of the adult heart, the heart of newly born mice has a strong regenerative capacity, and the proliferation of the newly formed cardiac tissue comes mainly from the proliferation of endogenous cardiomyocytes (4). When MI occurs in the adult heart, mature cardiomyocytes do not have the ability to divide and proliferate; instead, the surrounding healthy cells make up for the missing parts by proliferation. However, this is not enough to replace the dead cardiomyocytes, which will cause myocardial ischemia and hypoxia, and ultimately lead to myocardial degeneration, necrosis, fibrosis, etc (5). The decreased proliferative capacity of cardiomyocytes may be related to the loss of myocardial progenitor cells or the reduced proliferative potential of mature cardiomyocytes during cardiac development (6). Recently, several studies have aimed to repair the heart by inducing cardiomyocyte re-entry into the cell cycle and promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation after MI (7). Thus, stimulating the proliferation of terminally differentiated cardiomyocytes and promoting cardiac regeneration is a viable approach for post-MI therapy.
In recent years, researchers have found that the mammalian heart converts its major metabolic substrate from glucose to fatty acids shortly after birth. This corresponds to a change in metabolic mode from anaerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation. Importantly, this metabolic conversion occurs concurrently with the loss of cardiac regenerative capacity (8). Thus, the loss of cardiac regenerative capacity in adults is associated with a shift in energy metabolism. The metabolic shift from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation leads to a stagnation of the cell cycle in cardiomyocytes, resulting in the loss of cardiac regenerative capacity (8–10). In summary, it is crucial to understand the metabolic changes in the heart before and after the proliferative window in mammals. It is also important to promote the re-entry of mature cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle by inducing metabolic pathway-related factors. This can provide new research directions in the field of promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration.
In this paper, we briefly review the changes in mitochondrial energy metabolism during cardiac regeneration, focusing on the application of sugar metabolism, especially the glycolytic process, in regenerative repair after cardiac injury. We further summarize the strategies for cardiac regenerative repair after MI by targeting cardiomyocytes’ glucose metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, ketone body metabolism, and tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism, which provides insights into potential therapeutic approaches.
The heart is the top energy-consuming organ in the body, but its energy reserves are low. The energy to maintain normal pump function and basal metabolism in the adult heart is mainly derived from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis (11, 12). Glycolysis produces ATP without the involvement of oxygen, and compared with glucose, fatty acid oxidation consumes more oxygen to be utilized by the electron transport chain for oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation derives 40%–60% of its energy from fatty acid oxidation and glucose metabolism (13, 14), but these substrates have limited storage capacities. Therefore, the selection of suitable substrates for energy generation, as well as the maintenance of a dynamic network balance of energy metabolism, is crucial (15) (Figure 1).
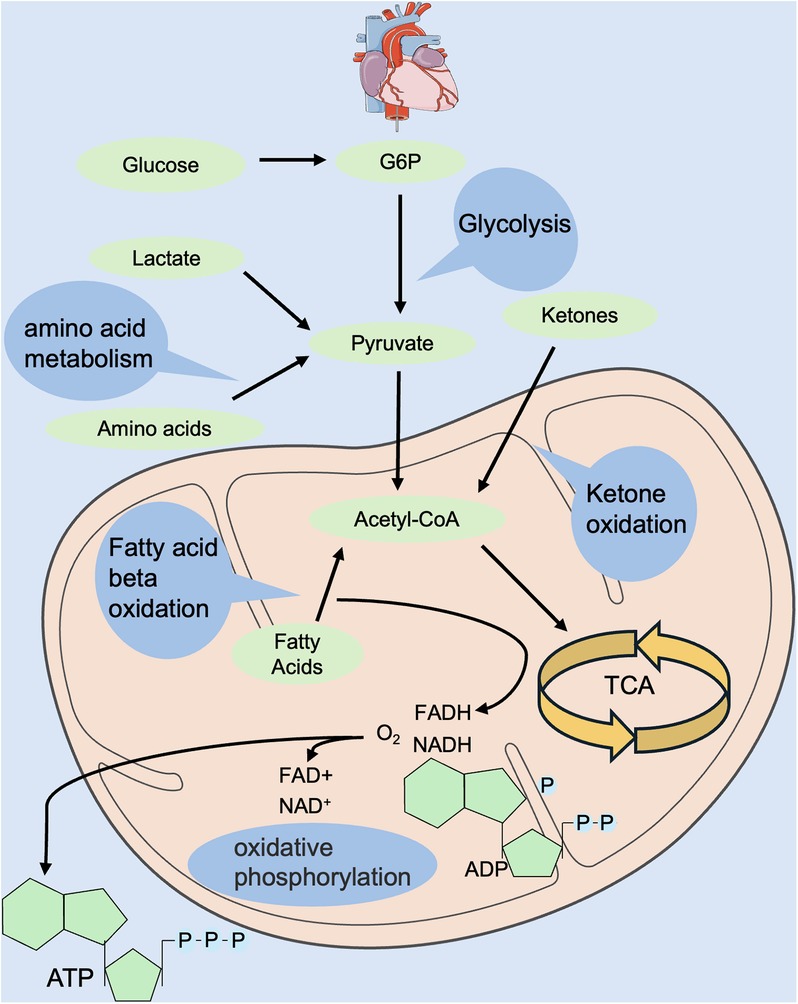
Figure 1. Regulation of energy metabolism in the normal heart. Energy metabolism includes glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, amino acid oxidation, ketone body oxidation, tricarboxylic acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, etc. Energy donors include glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, ketone bodies, etc. Hydrogen donors include NADH and FADH. FADH, flavin adenine dinucleotide; NADH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
During the mammalian embryonic period, the heart is in a low-oxygen environment and requires energy mainly from glycolysis and lactate metabolism and, to a lesser extent, from oxidative phosphorylation (16–18). Nearly half of the ATP required by the heart in neonatal suckling rats (P7) is supplied by glycolysis (16), whereas after P7, the utilization of glycolysis gradually decreases and is replaced by a significant increase in fatty acid oxidation to maintain the energy metabolism of the heart (16, 19). During the juvenile period, the energy source of the heart is mainly fatty acid oxidation, and the amount of ATP produced almost approaches that of the adult mammalian heart (20). In conclusion, oxygen levels at different developmental stages regulate changes in cardiac metabolic energy, which in turn affects cardiomyocyte metabolism and ultimately regulates cardiomyocyte proliferative capacity.
After cardiac injury, especially in the stage of HF, the metabolic processes of glucose and fatty acids in cardiomyocytes are disturbed. This disruption leads to alterations in the metabolic state of cardiomyocytes and remodeling of myocardial energy metabolism, which ultimately results in abnormalities in myocardial structure and function (21). On the one hand, during this process, substrate utilization is altered, and myocardial energy supply is converted from fatty acid oxidation to glycolysis, resulting in “embryonic re-evolution” of energy metabolism (22). On the other hand, mitochondrial structural abnormalities, reduced respiratory chain complex activity and ATP synthase activity, and impaired oxidative phosphorylation in HF lead to reduced energy production and cardiomyocyte damage (23–26).
In summary, energy metabolism in the healthy adult heart is highly flexible. Under normal conditions, the metabolic substrate is primarily fatty acid oxidation. When the heart is injured, it undergoes metabolic remodeling. This involves disturbances in glucose and fatty acid metabolism, as well as abnormalities in myocardial structure and function. In addition to a change in substrate, there is a shift from fatty acid oxidation to glycolysis, along with a series of changes in the metabolism of cardiomyocytes.
It was long believed that highly differentiated cardiomyocytes permanently exit the cell cycle until Porrello et al. (4) found that the neonatal suckling mouse heart has the potential to regenerate. In addition, a growing number of studies have shown that cardiomyocytes can be reintroduced into the cell cycle by stimulating them in adult mammals (27–29). Recently, metabolism-related factors have been recognized as key factors regulating cardiomyocyte cell cycle progression.
Low-vertebrate animals, such as zebrafish, maintain a strong regenerative capacity of the heart in adulthood (30–32). In 2002, Poss et al. (30) utilized surgical removal of 20% of the heart of an adult zebrafish, and the full regeneration of the zebrafish heart was achieved 60 days after the surgery. Subsequently, a zebrafish cardiac cryoinjury model was established to simulate mammalian MI, and in the following two months, the fibrotic scar tissue was gradually eliminated by apoptosis and eventually replaced by newborn myocardium (33). To investigate whether the mechanism of cardiomyocyte regeneration after the specific killing of cardiomyocytes is the same as that after mechanical injury, a genetic cell-killing model was established in zebrafish. In this model, cardiomyocytes rapidly proliferated and completed regeneration in the following days (34). Similar to zebrafish, 1-day-old neonatal mice also achieve full regeneration after cardiac injury (4). However, in 7-day-old mice subjected to apicoectomy, there was no regenerating myocardium in the area of injury, and irreversible fibrosis occurred, with the heart losing its regenerative capacity (4). So what prevents the proliferation and regeneration of cardiomyocytes in mammals such as mice seven days after birth (Figure 2)?
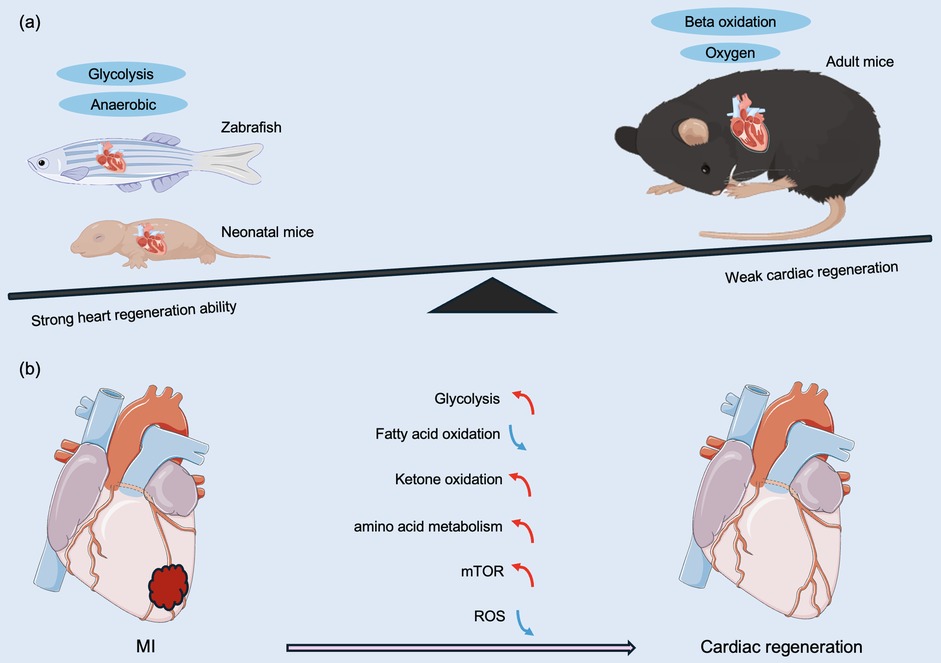
Figure 2. Different metabolic patterns before and after birth affect myocardial regeneration capacity. (a) Comparison of regenerative capacity and energy metabolism on regeneration of damaged hearts after MI in representative lower vertebrates, neonatal animals, and adult mammals. (b) Anaerobic glycolysis, ketone body oxidation, amino acid metabolism, and the mTOR pathway promote cardiac regeneration and improve regenerative capacity. Changes in cardiac metabolic state during neonatal mouse growth, fatty acid β-oxidation under aerobic conditions, and ROS lead to a decrease in myocardial regenerative capacity. MI, myocardial infarction; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; ROS, reactive oxygen species. The red line indicates activation, the blue line indicates inhibition, the green line indicates a decrease in level, and the purple line indicates an increase in level.
Adult zebrafish and mammals have been exposed to a hypoxic environment during embryonic life, and the heart has a strong regenerative capacity (35). In contrast, mammals are exposed to a hypoxic to a hyperoxic environment after birth, which corresponds to a marked difference in energy metabolism between the embryonic and adult heart. During embryonic development, cardiomyocytes use anaerobic glycolysis as the main source of energy, whereas adult cardiomyocytes primarily utilize oxygen-dependent mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation for energy supply (8, 36). In addition, mature cardiomyocytes derive more than 80% of their energy from fatty acid β-oxidation (37), and oxidative phosphorylation produces 18 times more ATP than cytoplasmic glycolysis (19). Although oxidative phosphorylation has a greater energetic advantage over glycolysis, it is accompanied by an increased accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in an increase in the DNA damage response pathway (DDR) pathway (38), which is one of the factors that induce cardiomyocytes to exit the cell cycle. Mitochondrial ROS are generated by the leakage of electrons from the mitochondrial respiratory chain and the reaction of these electrons with O2 (39, 40), which can cause oxidative damage to DNA, single- or double-strand breaks, and ultimately cell cycle arrest (41).
It has been shown that after birth in mammals, the expression of most of the enzymes associated with glycolysis decreases significantly after seven days of life, while most of the enzymes involved in the mitochondrial Krebs cycle are upregulated within the same timeframe (42). This is consistent with the pattern of the cell cycle in cardiomyocyte arrest. Thus, the postnatal shift in metabolic pattern from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation results in the inhibition of the cell cycle in cardiomyocyte progression.
The adult mouse heart renews approximately 5% of its cardiomyocytes annually, with the majority located in the subendocardial muscle (43–45). Furthermore, in the human heart, cardiomyocyte proliferative capacity is around 1% at age 20 and decreases to 0.4% at age 75 (46–48). In contrast, the neonatal mammalian heart has a potential regenerative capacity; however, this regenerative capacity is lost after the first week of life (4, 49), which is closely related to the metabolic shift from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation in cardiomyocytes after birth (8–10, 50, 51). This is because increased mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation activity promotes cardiomyocyte maturation while decreasing the proliferative capacity of cardiomyocytes (52).
Under pathological conditions such as MI or HF, cardiomyocytes revert from glucose as an energy source (53). This is mainly due to the fact that after cardiomyocyte ischemia, oxygen concentration decreases, and energy metabolism is forced to switch to glycolysis, resulting in the reentry of cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle and reactivation of cardiomyocyte proliferation in the injured heart (52, 54, 55).
Taken together, the metabolic pathway shift from anaerobic glycolysis in fetal life to oxidative phosphorylation in adulthood inhibits the proliferative capacity of mammalian cardiac cardiomyocytes.
In recent years, changes in the metabolic levels of the heart in pathological states have received increasing and widespread attention. The metabolic level of the heart is highly regulated, allowing for the ability to switch between available substrates. It is well known that fatty acids are the energy substrates with the lowest energy production efficiency (production of ATP/consumption of O2) (53). In contrast, glucose, an important fuel in the heart, is the most energy-efficient substrate for ATP production under anaerobic conditions via pyruvate conversion by glycolysis (53). In recent years, lactate metabolism, amino acid oxidation, and ketone body metabolism have also been recognized as potential sources of cardiac energy (56–60). In the following, we provide a brief overview of energy metabolism during cardiac regeneration (Figure 3).
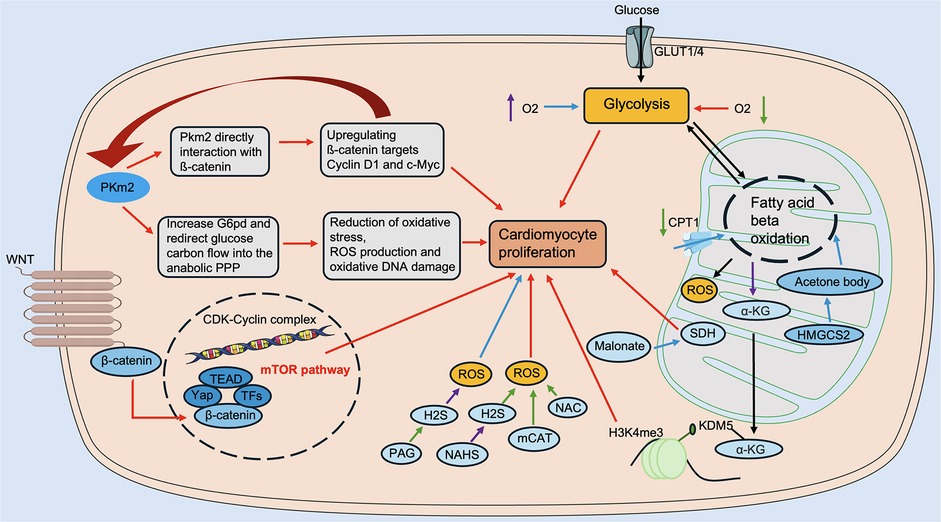
Figure 3. Regulation of energy metabolism in cardiac regeneration. Glucose metabolism includes Pkm2, Malonate, SDH, etc. Fatty acid metabolism includes CPT1, α-KG, KDM5, and others. Amino acid metabolism includes Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR, and others. Ketone body metabolism includes HMGCS2, etc. ROS modulators include NAHS, mCAT, NAC, PAG, etc. α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; HMGCS2, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2; KDM5, lysine demethylase 5; mCAT, mitochondrial peroxiredoxin; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; NAHS, sodium hydrosulfide hydrate; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; PAG, DL-Propargylglycine; Pkm2, pyruvate kinase muscle isoform 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase. The red line indicates activation, the blue line indicates inhibition, the green line indicates a decrease in level, and the purple line indicates an increase in level.
Glucose is an important energy substrate in the heart. A growing body of research now suggests a potential link between glucose metabolism and cardiomyocyte proliferation. Glucose is transported into cardiomyocytes via glucose transporter proteins (GLUT), of which GLUT1 is the predominant isoform in mammalian embryonic and neonatal hearts (61), which corresponds to the fact that glycolysis is embryonic and neonatal. Studies have shown that when GLUT1 is overexpressed, there is an increase in glucose uptake in cardiomyocytes and an increase in glycogen accumulation, and the metabolic pattern shifts to glycolysis, promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation (62). In addition, flow cytometry identified two distinct cell populations: a recombinant troponin t type (Tnnt)1high cell population and a relatively immature Tnnt2low cell population, in which the Tnnt2low cell population responds to high glucose uptake after cardiac injury and promotes mitosis in cardiomyocytes, thereby accelerating cardiac regeneration (62).
Key components of glycolysis play an integral role in cardiac regeneration. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) is an important enzyme in the regulation of glycolysis, and the expression level of PDK is significantly up-regulated in both zebrafish and mammalian injured hearts and regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation in the injured heart (54). Pyruvate kinase muscle isoform 2 (PKM2), a key enzyme in the final step of glycolysis, promotes cardiomyocyte cell division by regulating the cell cycle through the anabolic pathway and β-catenin and reducing oxidative stress injury. After MI, PKM2 induces cardiomyocyte cell cycle, increases angiogenesis, prolongs cardiomyocyte survival time, and reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress to prevent or reverse cardiac remodeling after MI (63). Therefore, targeting the cell cycle to promote cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration is an effective approach.
In summary, glucose metabolism plays a critical role in cardiac regeneration. Although more research is needed to elucidate myocardial regeneration in greater detail, these findings provide hope that targeting one or more key components of glucose metabolism in the clinical setting may be one of the most effective strategies for cardiac regeneration and functional recovery.
During the embryonic period, cardiomyocytes are virtually not able to utilize fatty acids for energy production due to limited mitochondrial and fatty acid availability. After birth, the fetal heart rapidly switches to fatty acid β-oxidation (64, 65), a change that coincides with the point in time when cardiac regenerative capacity is lost. Thus, fatty acid metabolism is closely related to cardiomyocyte proliferation.
It has been shown that postnatal neonatal suckling rats consuming milk deficient in fatty acids prolonged the cardiomyocyte proliferation window (66). Thus, inhibition of fatty acid oxidation promoted myocardial proliferation and regeneration. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT), as a key enzyme in fatty acid oxidation, plays an essential role in regulating cardiomyocyte proliferation. The relative activity of CPT1 in cardiomyocyte mitochondria increases progressively after birth in mice (67), whereas the use of an inhibitor of CPT1 results in a decrease in fatty acid β-oxidation and enhances cardiomyocyte proliferation (68, 69). Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation through modulation of CPT1 isoforms results in the accumulation of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). This, in turn, activates the α-ketoglutarate-dependent lysine demethylase KDM5. The activated KDM5 then drives the demethylation of the mature H3K4me3 structural domain in cardiomyocytes. This process reduces their transcriptional levels and transitions the cardiomyocytes to a less mature state. Ultimately, this promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and ischemia-reperfusion regeneration of the heart after injury (51). Furthermore, the role of sphingolipid metabolism in cardiac regeneration was revealed, in which sphingosine kinase (SphK), a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism, plays a critical regulatory role (50). SphK1 inhibits cardiac regeneration by regulating the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts; on the contrary, SphK2 promotes the proliferation of cardiomyocytes by reversing the process of the mature cell cycle (50). It is noteworthy why SphK1 and SphK2 play diametrically opposed roles as isoenzymes. Possibly due to their different distribution locations, the specific mechanisms involved remain to be further explored.
In summary, inhibiting lipid metabolism and thus stimulating cardiomyocytes to re-enter the cell cycle may present a potential target for regenerative therapy after cardiac injury.
Protein synthesis is necessary for cardiomyocyte growth and maturation, and increased protein synthesis inevitably leads to increased amino acid metabolism. Amino acid oxidation is also a source of cardiac ATP, of which oxidation of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) produces only 2% of total cardiac ATP (57), but BCAAs play an important role in regulating cardiac regeneration.
BCAAs comprise three amino acids, including leucine, isoleucine, and valine, which play an integral role in the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway that regulates cardiac regeneration (53). Elevated expression of glutamine as a transporter of amino acids in zebrafish and neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes activates the amino acid-driven mTOR signaling pathway, which in turn promotes mitochondrial maturation and regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation (70). In addition, high concentrations of leucine and glutamate also activate mTOR signaling and promote myocardial regeneration (70).
The Wnt signaling pathway is an important signaling pathway that regulates cardiomyocyte differentiation and cardiac regeneration (71). A study showed that neonatal mouse hearts were prepared for initiation of mTOR signaling through amino acid and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. RNA sequencing showed that Wnt/β-catenin signaling was higher in neonatal mouse hearts than in adult mouse hearts, whereas downregulation of Wnt ligand and Wnt/β-catenin signaling was found in the apical portion of P7 mice. This trend persisted into the adult stage, which is consistent with the cell cycle in cardiomyocytes exiting pattern (70). Furthermore, in the TOR-initiated state, metabolism shifts to amino acid oxidation, and zebrafish and mammalian cardiomyocytes are regenerative (70).
Thus, the metabolic state of amino acids influences the progression of the cell cycle in cardiomyocytes. However, this area has not been well studied and needs to be further explored.
In recent years, by comparing data from the proteome and gene expression profiles of the mouse heart before and after birth, researchers have found that the activity of genes involved in ketone body metabolism changes significantly in the perinatal period. Compared with embryonic day 18.5, the expression level of a ketogenic rate-limiting enzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2), increased more than tenfold in P7 hearts, inducing a loss of cardiac regenerative capacity (72). At the same time, loss of HMGCS2 impairs postnatal cardiac development in mice, which can be rescued by lactation supplementation with ketone bodies. This is because ketone body defects inhibit lipid oxidation by inhibiting β-hydroxybutyrylation, which prevents the metabolic flow from acetyl-coenzyme A delivery to the ketone bodies (72), thereby echoing the previously discussed inhibition of cardiac proliferation and regeneration by fatty acid metabolism.
Increased ketone body metabolism is a key event in HF and pathological remodeling (73). Data from animal models and patients with HF suggest that ketone body oxidation is increased in the failing heart (74). In addition, endothelial cells of the heart are capable of oxidizing ketone bodies, which enhances cell proliferation, migration, and vascular sprouting (75). It has been shown that the beneficial effects of ketone body supplementation during cardiac hypertrophy are attributed to ketone body oxidation in cardiomyocytes and that ketone body oxidation enhances the respiratory efficiency of cardiomyocytes in failing hearts (75). The above studies suggest the importance of ketone body metabolism in the heart during pathologic cardiac remodeling.
In summary, ketone bodies inhibit cardiomyocyte proliferation after birth, possibly by regulating lipid metabolism in the neonatal heart. Ketone bodies are critical for mitochondrial maturation, the metabolic shift of mitochondria from anaerobic glycolysis to aerobic fatty acid β-oxidation, and the loss of cardiac regenerative capacity. Thus inducing a metabolic shift by inhibiting ketogenesis may promote cardiac regeneration.
The tricarboxylic acid cycle is the metabolic center of carbohydrate-lipid-amino acid binding and the final metabolic pathway for all three nutrients. The postnatal increase in mitochondrial DNA in mice leads to a significant increase in mitochondrial ROS (42), and ROS damage cellular proteins, lipids, and DNA and induce cell cycle arrest (41, 76–78). Therefore, it is crucial to elucidate the role of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in cardiac regeneration.
Studies have shown that the hearts of neonatal mice and adult zebrafish have low mitochondrial content and complexity and lack markers for DDR; however, these markers are significantly increased in mouse hearts in the first few days of life (42). Therefore, is it possible to promote cardiomyocyte proliferation by inhibiting mitochondrial oxidation to reduce ROS production and, consequently, energy metabolism? Overexpression of the ROS scavengers N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and mitochondrial peroxiredoxin (mCAT) in cardiomyocytes was able to reduce DDR and reverse cell cycle in cardiomyocytes progression (42). In cardiomyocytes, the transcription factor (paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2) Pitx2 promotes cardiac repair by recruiting yes-associated protein (YAP) to activate the antioxidant response to reduce ROS after cardiac injury (42). In addition, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) scavenges ROS and promotes the reentry of cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle, and Pei et al. inhibited myocardial proliferation and regeneration by using the inhibitor of H2S, DL-Propargylglycine (PAG), which promotes ROS deposition in cardiomyocytes (79). In contrast, inhibition of ROS accumulation by using sodium hydrosulfide hydrate (NaHS), a donor of H2S, promoted cardiomyocyte proliferation (79). The above results suggest that activating antioxidant responses after cardiac injury reduces ROS and thus promotes cardiac repair.
In cardiomyocytes, inhibition of key metabolites in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) cycle is also another strategy to inhibit energy metabolism. Bae et al. showed that malonate prolonged the proliferation window of cardiomyocytes in neonatal mice and reintroduced cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle in adult injured hearts by inhibiting succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (9). By analyzing metabolites from postnatal day 0.5 to day 7 in mice, α-KG was found to rank the highest among the reduced metabolites. Subsequent injection of α-KG prolonged the window of proliferation of cardiomyocytes during cardiac development and facilitated cardiac regeneration after MI by inducing cardiomyocyte proliferation (80).
Thus, the above study reveals a strategy to inhibit energy metabolism-mediated cardiac regeneration and points to a new direction for the treatment of cardiomyopathy.
Adult mammals have limited ability to regenerate their hearts after cardiac injury. However, adult zebrafish can regenerate effectively after heart injury, so it is crucial to reveal the molecular mechanisms that regulate cardiac proliferation and regeneration. Currently, more and more factors regulating cardiomyocyte proliferation have been reported, including cell cycle regulation, non-coding genes, and signaling pathways (Figure 4).
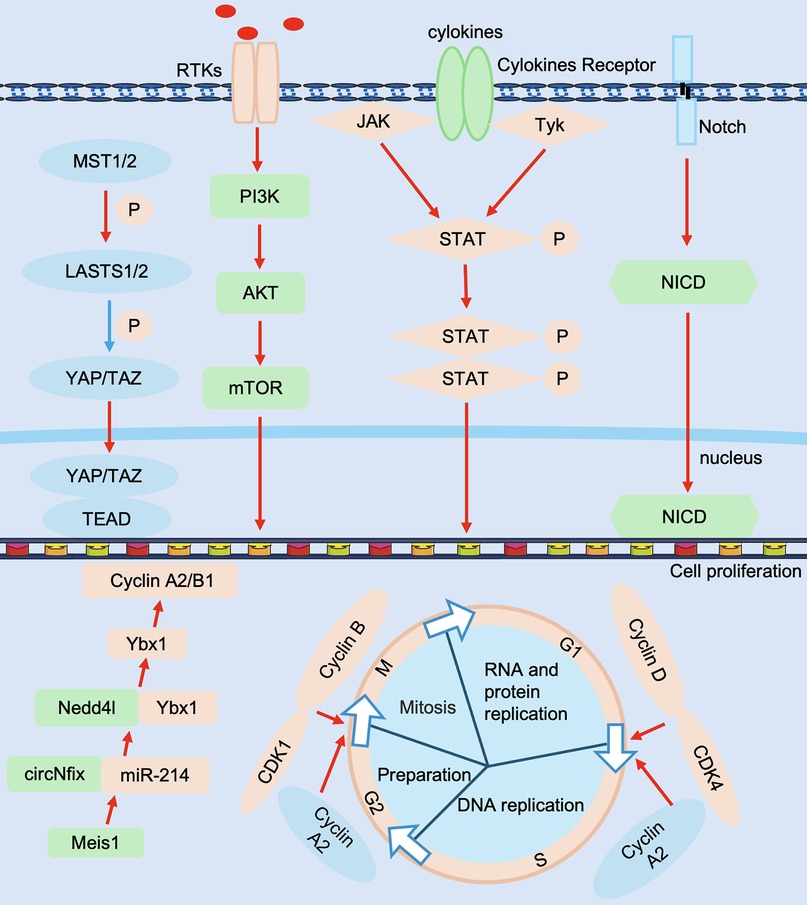
Figure 4. Molecular mechanisms in cardiac regeneration. Regulators include Cyclin D, CDK4, Cyclin B, CDK1, Cyclin A2, etc., non-coding RNAs include circNfix, miR-214, etc., signaling pathways include Hippo-YAP, Notch, PI3K-AkT and JAK/STAT, etc., and effectors include TEAD, NICD, etc. JAK/STAT, Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; PI3K-AkT, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt; TEAD, transcriptional enhanced associate domains. The red line represents activation and the blue line represents inhibition.
Positive cell cycle regulators such as cyclin, cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK), and proto-oncogenes are highly expressed in mouse embryonic and neonatal hearts, whereas their expression tends to decrease in adult mouse hearts. In contrast, negative cell cycle regulators such as cell cycle protein-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) are highly expressed in adult mouse hearts and downregulated in embryonic and neonatal mouse hearts (81). Currently, promoting the reentry of endogenous cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle by modulating cell cycle factors may provide new targets or ideas for cardiac regenerative medicine.
Mammalian cell cycle activity is an important factor influencing the proliferative capacity of postnatal cardiomyocytes. Recently, researchers have focused their attention on two major protein families that regulate the cell cycle. For cell cycle proteins to play a role in regulating the cell cycle, they must bind to CDK in order to have kinase activity that phosphorylates cell cycle-associated proteins, thus playing a key role in cell cycle regulation. Thus, Cyclin D, a cell cycle protein in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, drives the G1/S phase transition by binding to CDK4. It has been shown that sustained expression of cyclin D2 drives cardiomyocyte proliferation, induces DNA synthesis, and reduces infarct size (82). Cyclin B, a cell cycle protein in the G2 phase of the cell cycle, regulates the entry and exit of cells into and out of the M phase of the cell cycle by binding to CDK1. Overexpression of the cyclin B1-CDC2 complex stimulates cell division in adult mouse cardiomyocytes, and deficiency of the cyclin B1-CDC2 complex results in adult mouse cardiomyocytes remaining in the G2/M phase and inhibits cardiomyocyte proliferation (83). Cyclin A2 promotes the transition of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase as well as from the G2 phase to the M phase. Overexpression of cyclin A2 in adult porcine hearts improved cardiac function and induced DNA synthesis and cardiomyocyte mitosis in ischemically injured mice (84). The above studies suggest that positive cell cycle proteins such as Cyclin D, Cyclin B, and Cyclin A may be potential targets for stimulating cardiomyocyte proliferation after injury.
In addition, CKI binding to CDK can inactivate the cyclin-CDK complex, thereby negatively regulating cell cycle activity and inhibiting cardiomyocyte proliferation. Recently, it has been shown that adult mouse cardiomyocytes contain a large number of CDK inhibitors, which negatively regulate the cell cycle activity of adult mouse cardiomyocytes and, therefore, inhibit the proliferation and division of cardiomyocytes (85, 86). Multiple studies have shown that CIP/KIP family members (p21, p27, and p57) are present in mature cardiomyocytes and regulate CDKs to shut down the cell cycle (87). p21 and p27 knockout mice fail to exit the cell cycle in cardiomyocytes in the G1 phase and undergo DNA replication after birth (88, 89). Mechanistically, p21/p27 binds to cyclin A/cyclin E-CDK after birth in mice and promotes cell exit from the cell cycle (88). In addition, the CDK inhibitor p27 interacts with p57 to allow cell cycle exit and differentiation to occur (90, 91). These results suggest that members of the CIP/KIP family play an important role in cell cycle exit in postnatal cardiomyocytes.
Recently, investigators found that in vivo overexpression of a combination of viral-mediated cell cycle regulators (CDK1/CCNB/CDK4/CCND) stimulated the proliferation of adult mouse, rat, or human cardiomyocytes. Moreover, replacing CDK1/CCNB with Wee1 inhibitors and transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) inhibitors further facilitated the entry of cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle reduced scarring after cardiac injury area, and improved cardiac function (92). Our group's study revealed that ABRO1A (93) and TMEM11 (94) negatively regulate the cardiomyocyte cell cycle through post-translational modifications and inhibit cardiomyocyte cell cycle proliferation and cardiac regeneration. Therefore, influencing cardiomyocyte proliferation and thus promoting cardiac regeneration by modulating cell cycle regulators during cardiac growth and development is expected to be one of the future therapeutic strategies for cardiac repair.
In recent years, more and more researchers have found that non-coding RNAs regulate the cell cycle in cardiomyocytes, which in turn regulate cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration. The following summarizes non-coding RNAs in cardiac regeneration, including microRNAs, circRNAs and lncRNAs.
microRNAs (miRs) are small non-coding RNAs that are important for suppressing gene expression and maintaining homeostasis of cardiomyocyte proliferation. A high-throughput functional screen revealed that miR-590 and miR-199a promoted the re-entry of cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle in neonatal and adult mice and facilitated cardiomyocyte proliferation and recovery of cardiac function after MI (95). It has been shown that the expression level of miR-34a is progressively upregulated after birth. Overexpression of miR-34a in the hearts of neonatal mice with MI inhibits cardiomyocyte proliferation and subsequent recovery of cardiac function. In contrast, remodeling after MI was significantly ameliorated by nucleic acid-based antimiR-34a treatment in the hearts of adult mice after MI (96). Furthermore, miR-17-92, miR302-367, and miR-294 positively regulate cardiomyocyte proliferation (97, 98), whereas miR-15 and miR-128 negatively regulate cardiomyocyte cell cycle progression (46, 99). Taken together, these studies suggest that targeting miRNAs is a promising therapeutic strategy for inducing cardiac repair processes.
circRNAs are a class of noncoding RNAs with covalent closed-loop structures. circNfix, which is predominantly expressed in cardiomyocytes, is driven by the transcription factor Meis1. It interacts with miR-214 to prompt the interaction of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4L with Y-box binding protein 1 (Ybx1), thereby inducing the ubiquitination and degradation of Ybx1. This degradation down-regulates the downstream target genes of Ybx1, Cyclin A2, and Cyclin B1, which in turn regulates cell cycle progression and thus inhibits cardiomyocyte proliferation (100). circSamd4 and circMdc1 play a role in positively and negatively regulating cardiomyocyte proliferation by localizing in the mitochondria and regulating ROS and DDR, respectively (101, 102).
After birth, lncRNA CRRL (103), lncRNA CAREL (104), lncRNA NPPA-AS1 (105), and lncRNA AZIN2-sv (106), whose expression was elevated in the heart, inhibited cardiomyocyte proliferation, whereas lncRNA ECRAR (107), lncRNA Sirt1 antisense (108), and lncRNA Snhg1 (109), whose expression is reduced in the heart, promote cardiomyocyte proliferation and regeneration. lncRNAs regulate cardiomyocyte proliferation mainly in two ways. On the one hand, it plays a role in regulating the cell cycle in cardiomyocytes through the lncRNA/miRNA/mRNA axis (103, 104, 106, 110). On the other hand, lncRNAs regulate cardiomyocyte proliferation by interacting with mRNAs and proteins to mediate chromatin remodeling and DNA repair (105, 107–109, 111).
Our research team demonstrated that lncRNA CPR recruits DNA methyltransferase 3α (Dnmt3a) to the promoter region of the Mcm3 gene, promoting methylation modification of DNA, inhibits Mcm3 expression and DNA replication induced by it, and thus inhibits cardiomyocyte proliferation (112). In summary, targeting non-coding RNA is a promising therapeutic strategy to induce cardiac regeneration.
The Hippo-YAP signaling pathway is a widely studied pathway for cardiac regeneration. When the Hippo pathway is activated, its kinases MST1/2 and LATS1/2 phosphorylate the nuclear transcription factor YAP. This phosphorylation prevents YAP from entering the nucleus to activate the transcription of target genes, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation. On the contrary, when the Hippo pathway is inhibited or YAP is activated, YAP enters the nucleus and binds to other transcription factors, promoting the expression of genes related to the cell cycle and proliferation (113). The downstream effector of Hippo, YAP/Transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ), is required for postnatal cardiomyocyte proliferation, and deletion of YAP/TAZ in the mouse heart results in myocardial hypoplasia and lethality due to reduced cardiomyocyte proliferation (113). In contrast, postnatal overexpression of YAP increases cardiomyocyte proliferation (113, 114).
Wnt/β-Catenin signaling is one of the major signaling pathways regulating cardiac development and regenerative processes. The role of the Wnt pathway on myocardial proliferation is more complex, and interventions at different stages of development while targeting different parts of the pathway may yield different results. At mouse embryonic day 13.5, proliferatively active cardiomyocytes highly expressed β-catenin, and myocardial-specific knockdown of β-catenin reduced the number of proliferating cardiomyocytes. This effect was associated with changes in the level of Cyclin D2, a target gene of β-catenin (115). In addition, YAP, another key molecule in the regulation of myocardial proliferation, forms a complex with β-catenin that synergistically enhances β-catenin activity and promotes myocardial proliferation during development (116). In adult mouse cardiomyocytes, activation/elevation of β-catenin promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and post-MI myocardial repair (63, 117).
Over the past two decades, there have also been many reports on the regulatory role of a Notch signaling pathway (Notch), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt (PI3K-AkT), and Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathways in cardiomyocyte proliferation. Activation of the Notch signaling pathway, a highly conserved signaling pathway in the heart, is critical for cardiomyocyte proliferation at birth and for cardiac development (118). The Notch signaling pathway promotes myocardial proliferation in neonatal individuals, and this effect is markedly attenuated in an adult mouse MI model. This phenomenon is associated with the modification of histone methylation in Notch target genes in adult cardiomyocytes, which are unable to respond to Notch signaling (119). PI3K-AKT is an intracellular signaling pathway and one of the drivers of the cell cycle. Studies on the heart have shown that activation of PI3K-AKT signaling leads to increased mitosis and higher cardiomyocyte numbers in both suckling mice and adult cardiomyocytes (120). The JAK/STAT signaling pathway is one of the signaling pathways that play a crucial role in cardiac regeneration. In zebrafish, inhibition of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway resulted in decreased cardiomyocyte proliferation and increased scar formation after myocardial injury (121). In mice, recovery from myocarditis injury is achieved by the re-entry of pre-existing cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle to proliferate through STAT3 (122).
Energy metabolism plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiac function, and its disorders are often closely associated with the onset and progression of various cardiac diseases. An in-depth study of changes in energy metabolism and related therapies in cardiovascular diseases is important for understanding disease mechanisms and finding effective treatments (Table 1).
Glycolysis is closely related to cardiac function, especially in pathological states such as MI and HF. Studies have shown that the heart increases glycolysis in ischemic states to compensate for energy deficits, although this compensatory mechanism may not be sufficient to maintain normal cardiac function. In patients with HF, increased glycolysis is often accompanied by decreased mitochondrial function, leading to reduced cardiac efficiency (135). Numerous studies have found that trimetazidine (TMZ) has significant anti-ischemic efficacy in chronic stable angina pectoris (136, 137). Its mechanism of action is mainly through the regulation of glycolysis-related enzymes - adenylate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which in turn promotes the process of glycolysis, enabling the energy supply of cardiomyocytes to increase, thereby exerting the anti-ischemic protective effect on the heart (123).
Although TMZ has some efficacy in the treatment of heart disease, long-term use of trimetazidine may lead to drug resistance, affecting the effectiveness of treatment (138). In the future, the specific mechanism of action of trimetazidine in myocardial energy metabolism can be investigated by optimizing the dosage and regimen, further research, and exploring its interaction with other metabolic pathways. It is expected to further improve cardiac function and effectively prevent the progression of cardiomyopathy.
Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation in early HF is part of cardiac metabolic remodeling, but this inhibition progressively leads to mitochondrial dysfunction, which ultimately manifests itself in severe energy metabolism disturbances in advanced HF (53, 139). In addition, Pgrmc1 functions as a healthy metabolic regulator in the heart. Individuals with low cardiac Pgrmc1 expression may be more susceptible to mitochondrial damage and the progression to HF. Induction of Pgrmc1 expression increases the basal cardiac energy capacity and reduces cardiac lipid accumulation. This is achieved by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial respiration, which can significantly increase ATP production capacity. This enhancement is crucial for targeted therapies aimed at treating cardiomyopathies (125).
L-carnitine plays a crucial role in cardiac energy metabolism by promoting beta-oxidation of fatty acids, balanced cardiac energy metabolism, regulating coenzyme A levels, reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, and protecting cardiomyocytes from damage. L-carnitine has a wide range of applications in heart diseases such as HF, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and arrhythmia (126). Future studies will further reveal the mechanism of action of leucovorin and energy metabolism, optimize its clinical application, and provide more opportunities for the treatment of cardiac diseases. Metformin, a widely used insulin sensitizer in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), not only excels in glycemic control but also has a significant positive impact on cardiovascular health. Its use in patients with HF has been shown to be safe and effective in reducing HF morbidity and mortality. The mechanism of action of this drug is mainly through the activation of AMPK, which in turn regulates lipid and glucose metabolism processes, thus optimizing the energy metabolism of the myocardium (140). Specifically, activation of AMPK promotes translocation of GLUT4 to cardiomyocyte membranes and accelerates insulin-dependent glucose uptake (141). In addition, metformin promotes mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids by enhancing the expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1, reducing apoptosis in cardiomyocytes, and decreasing the formation of myocardial mid- and late-phase glycosylation end products (AGEs) (128).
In summary, although Pgrmc1, L-carnitine, and metformin have potential applications in the treatment of heart disease, there are individual differences in the response of different patients to these treatments, resulting in the possibility that some patients may not derive the expected effectiveness from them (142–144). Future improvements can be made through the implementation of personalized treatment protocols, the conduct of multi-center clinical trials, and the application of cutting-edge technologies, among other multi-dimensional improvement measures. These are expected to significantly enhance the effectiveness and safety of the application of these drugs in clinical practice, thus bringing more treatment options and hope to patients with cardiomyopathy.
Abnormalities in amino acid metabolism are closely associated with the development of several cardiac diseases. Studies have shown that patients with HF have significant changes in amino acid levels, especially in the oxidative capacity of branched-chain amino acids, leading to impaired cardiac energy metabolism (145). In addition, interactions between the gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism have been suggested to play an important role in the progression of heart disease. Amino acids metabolized by gut microbes may affect heart health by modulating cardiac function and inflammatory responses (146). Rapamycin and its analogs exert inhibitory effects on cardiomyocyte apoptosis and promote cardiomyocyte autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway (147). This mechanism is closely related to amino acid metabolism. In pathological conditions such as MI, rapamycin is effective in limiting the death of cardiomyocytes and thus reducing the extent of infarction. At the same time, they can also attenuate the hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes and provide relief to the process of cardiac remodeling (129). Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have emerged as important agents in the treatment of HF and have been shown to be effective in reducing the rate of HF hospitalization and the risk of cardiovascular death (148). SGLT2i induces degradation of abnormal branched-chain amino acids in failing myocardium as an alternative source of myocardial fuel to optimize cardiac energy supply (130).
In conclusion, both rapamycin and SGLT2i have limitations in the treatment of heart disease, and rapamycin is immunosuppressive and may increase the risk of infection with long-term use (149). SGLT2i may increase the risk of urinary tract infections (150). In the future, it can be used in combination with other drugs, such as anti-inflammatory drugs. This is not only expected to reduce the risk of infection but also to further enhance the therapeutic effect on cardiomyopathy. Thus, it would provide a safer and more effective treatment option for cardiomyopathy patients.
Ketone bodies, consisting of β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone, are metabolic byproducts known as energy substrates during fasting. In recent years, studies have shown the potential of promoting the utilization of ketone bodies as a means of preventing the progression of HF (151). In patients with HF, blood concentrations of ketone bodies increase, as does the utilization of ketone bodies within the myocardium (57, 152–154). The addition of ketone bodies has been reported to inhibit cardiac utilization of glucose in HF and increase the efficiency of energy production (155). In addition, β-hydroxybutyrate in ketone bodies inhibits the activation of NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammatory vesicles and exerts cardioprotective effects through its anti-inflammatory properties (131). SGLT2i induces a shift in the heart's primary energy source from fat to ketone bodies and promotes ketone body oxidation, a shift that not only has intrinsic anti-inflammatory and anti-remodeling effects but also provides a more efficient source of energy (132).
Beta-hydroxybutyric acid is a ketone body, and when it accumulates in the body in excess, disorders of ketone body metabolism can lead to fatal consequences such as ketoacidosis (156). Therefore, treating the disease while maintaining ketone homeostasis is also a direction that needs to be explored in future research.
In cardiac metabolism, the TCA cycle is of particular importance. The heart is a high-energy-consuming organ that relies on efficient energy-generating pathways to maintain its contractile function. Studies have shown that the heart adjusts the activity of the TCA cycle to meet its energy requirements in different physiological and pathological states. In the case of HF, the heart enhances the utilization of ketone bodies and may compensate for the energy deficit by increasing the activity of the TCA cycle (57). In addition, intermediates of the TCA cycle, such as α-KG and succinate, are involved in regulating cardiac cell growth and survival and influencing cardiac remodeling processes (80). Itaconic acid plays an important role during ischemia as an inhibitor of SDH. It effectively reduces the abnormal accumulation of succinate during ischemia by inhibiting SDH activity (133). This reduction in ischemic succinate accumulation has a significant positive effect on ameliorating cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury (134).
Itaconic acid is a bypass metabolite of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and its accumulation in cells can regulate the body's immune activity through various pathways (157). However, these complex regulatory mechanisms may exhibit different effects in different cardiac pathological states, and the current understanding of their specific mechanisms of action is not sufficiently deep, which limits the wide application of itaconic acid in cardiac therapy. The specific mechanism of action of itaconic acid in different cardiac pathological states can be further investigated in the future. Through high-throughput screening and gene editing technologies, the signaling pathways and targets of itaconic acid in cells can be revealed, providing a theoretical basis for the development of more effective cardiac therapeutic strategies.
Ischemic heart disease causes 13% of global deaths in men and up to 14% in women (158). HF occurs with an inadequate supply of cardiac energy and places a tremendous burden on the heart, which further leads to a decrease in mitochondrial oxidative capacity, an increase in glycolysis associated with glucose oxidation, and a decrease in fatty acid oxidation. The first step in cardiac regeneration is to promote the re-entry of pre-existing cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle for cell division and proliferation. In this review, we summarize the current state of research on the metabolic regulation of myocardial regeneration (Table 2), including the regulation of glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism for cardiac regeneration. Based on this, altering the relevant components of the metabolic pathway to reintroduce cardiomyocytes into the cell cycle and promote cardiomyocyte proliferation, which in turn enhances cardiac regeneration, is an effective therapy for the treatment of MI. The application of energy metabolism in cardiovascular disease is summarized at the end of the article (Table 1), which elucidates the relationship between energy metabolism and disease and provides a strong rationale for the transformation of energy metabolism and regenerative therapy for MI.
However, further research is needed to find solutions to questions such as, what mechanisms regulate shifts between metabolism? By what mechanisms do metabolic shifts promote cardiomyocyte regeneration after a metabolic shift? Secondly, given the potential of drugs to modulate cardiac metabolism, the development of new drugs to precisely target specific metabolic pathways will be an important research topic. Furthermore, are there other metabolic pathways involved in the regulation of cardiac regeneration in addition to the five major metabolisms discussed in this review?
Therefore, in the future, in-depth translational research can be carried out regarding the mutual transformation between myocardial energy metabolism, which can provide new targets for future clinical translation. Furthermore, it is of great significance to further explore the relationship between the myocardial regeneration mechanism and myocardial energy metabolism transformation. Myocardial regeneration is one of the key topics in regenerative medicine. The findings of the review on the inter-transformation of energy metabolism to promote cell regeneration are not only applicable to cardiac regeneration but also provide a useful reference for regeneration studies of other tissues and organs, such as nerve regeneration and liver regeneration. This has broad disciplinary implications and is of great importance for the development of the entire field of regenerative medicine. All in all, we are optimistic that human cardiac regeneration is likely to make great progress.
JR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Writing – review & editing. TW: Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – review & editing. KW: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82370291); Qingdao Science and Technology Benefiting the People Demonstration Project (24-1-8-smjk-7-nsh); Major Basic Research Projects in Shandong Province (ZR2024ZD46); Taishan Scholar Distinguished Expert and Guiding Fund of Government's Science and Technology (YDZX2021004).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2021) 143:e254–743. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
2. Blue L, Kranker K, Markovitz AR, Powell RE, Williams MV, Pu J, et al. Effects of the million hearts model on myocardial infarctions, strokes, and medicare spending: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2023) 330:1437–47. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.19597
3. Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a neglected therapeutic target. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:92–100. doi: 10.1172/JCI62874
4. Porrello ER, Mahmoud AI, Simpson E, Hill JA, Richardson JA, Olson EN, et al. Transient regenerative potential of the neonatal mouse heart. Science. (2011) 331:1078–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1200708
5. Frangogiannis NG. Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction. Compr Physiol. (2015) 5:1841–75. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150006
6. Sano T, Ishigami S, Ito T, Sano S. Stem cell therapy in heart disease: limitations and future possibilities. Acta Med Okayama. (2020) 74:185–90. doi: 10.18926/AMO/59948
7. Zhu F, Meng Q, Yu Y, Shao L, Shen Z. Adult cardiomyocyte proliferation: a new insight for myocardial infarction therapy. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2021) 14:457–66. doi: 10.1007/s12265-020-10067-8
8. Chen X, Wu H, Liu Y, Liu L, Houser SR, Wang WE. Metabolic reprogramming: a byproduct or a driver of cardiomyocyte proliferation? Circulation. (2024) 149:1598–610. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065880
9. Bae J, Salamon RJ, Brandt EB, Paltzer WG, Zhang Z, Britt EC, et al. Malonate promotes adult cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration. Circulation. (2021) 143:1973–86. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.049952
10. Du J, Zheng L, Gao P, Yang H, Yang WJ, Guo F, et al. A small-molecule cocktail promotes mammalian cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. (2022) 29:545–58.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.03.009
11. Saddik M, Lopaschuk GD. Myocardial triglyceride turnover and contribution to energy substrate utilization in isolated working rat hearts. J Biol Chem. (1991) 266:8162–70. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)92956-X
12. Wisneski JA, Stanley WC, Neese RA, Gertz EW. Effects of acute hyperglycemia on myocardial glycolytic activity in humans. J Clin Invest. (1990) 85:1648–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI114616
13. Karwi QG, Uddin GM, Ho KL, Lopaschuk GD. Loss of metabolic flexibility in the failing heart. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2018) 5:68. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00068
14. Neubauer S. The failing heart–an engine out of fuel. N Engl J Med. (2007) 356:1140–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra063052
15. Tuomainen T, Tavi P. The role of cardiac energy metabolism in cardiac hypertrophy and failure. Exp Cell Res. (2017) 360:12–8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.052
16. Lopaschuk GD, Spafford MA, Marsh DR. Glycolysis is predominant source of myocardial ATP production immediately after birth. Am J Physiol. (1991) 261:H1698–705. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.6.H1698
17. Werner JC, Sicard RE. Lactate metabolism of isolated, perfused fetal, and newborn pig hearts. Pediatr Res. (1987) 22:552–6. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198711000-00016
18. Bartelds B, Gratama JW, Knoester H, Takens J, Smid GB, Aarnoudse JG, et al. Perinatal changes in myocardial supply and flux of fatty acids, carbohydrates, and ketone bodies in lambs. Am J Physiol. (1998) 274:H1962–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1998.274.6.H1962
19. Lopaschuk GD, Spafford MA. Energy substrate utilization by isolated working hearts from newborn rabbits. Am J Physiol. (1990) 258:H1274–80. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.5.H1274
20. Itoi T, Lopaschuk GD. The contribution of glycolysis, glucose oxidation, lactate oxidation, and fatty acid oxidation to ATP production in isolated biventricular working hearts from 2-week-old rabbits. Pediatr Res. (1993) 34:735–41. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199312000-00008
21. van Bilsen M, Smeets PJ, Gilde AJ, van der Vusse GJ. Metabolic remodelling of the failing heart: the cardiac burn-out syndrome? Cardiovasc Res. (2004) 61:218–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.014
22. Osorio JC, Stanley WC, Linke A, Castellari M, Diep QN, Panchal AR, et al. Impaired myocardial fatty acid oxidation and reduced protein expression of retinoid X receptor-alpha in pacing-induced heart failure. Circulation. (2002) 106:606–12. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000023531.22727.c1
23. Brown DA, Perry JB, Allen ME, Sabbah HN, Stauffer BL, Shaikh SR, et al. Expert consensus document: mitochondrial function as a therapeutic target in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14:238–50. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.203
24. Marin-Garcia J, Goldenthal MJ, Moe GW. Abnormal cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in pacing-induced cardiac failure. Cardiovasc Res. (2001) 52:103–10. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00368-6
25. Casademont J, Miro O. Electron transport chain defects in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. (2002) 7:131–9. doi: 10.1023/A:1015372407647
26. Cadenas S. Mitochondrial uncoupling, ROS generation and cardioprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. (2018) 1859:940–50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.05.019
27. Bergmann O, Zdunek S, Felker A, Salehpour M, Alkass K, Bernard S, et al. Dynamics of cell generation and turnover in the human heart. Cell. (2015) 161:1566–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.026
28. Senyo SE, Steinhauser ML, Pizzimenti CL, Yang VK, Cai L, Wang M, et al. Mammalian heart renewal by pre-existing cardiomyocytes. Nature. (2013) 493:433–6. doi: 10.1038/nature11682
29. Malliaras K, Zhang Y, Seinfeld J, Galang G, Tseliou E, Cheng K, et al. Cardiomyocyte proliferation and progenitor cell recruitment underlie therapeutic regeneration after myocardial infarction in the adult mouse heart. EMBO Mol Med. (2013) 5:191–209. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201737
30. Poss KD, Wilson LG, Keating MT. Heart regeneration in zebrafish. Science. (2002) 298:2188–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1077857
31. Stewart KMR, Walker SL, Baker AH, Riley PR, Brittan M. Hooked on heart regeneration: the zebrafish guide to recovery. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118:1667–79. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab214
32. Jopling C, Sleep E, Raya M, Marti M, Raya A, Izpisua Belmonte JC. Zebrafish heart regeneration occurs by cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation. Nature. (2010) 464:606–9. doi: 10.1038/nature08899
33. Chablais F, Veit J, Rainer G, Jazwinska A. The zebrafish heart regenerates after cryoinjury-induced myocardial infarction. BMC Dev Biol. (2011) 11:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-11-21
34. Wang J, Panakova D, Kikuchi K, Holdway JE, Gemberling M, Burris JS, et al. The regenerative capacity of zebrafish reverses cardiac failure caused by genetic cardiomyocyte depletion. Development. (2011) 138:3421–30. doi: 10.1242/dev.068601
35. Jopling C, Sune G, Faucherre A, Fabregat C, Izpisua Belmonte JC. Hypoxia induces myocardial regeneration in zebrafish. Circulation. (2012) 126:3017–27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.107888
36. Lopaschuk GD, Jaswal JS. Energy metabolic phenotype of the cardiomyocyte during development, differentiation, and postnatal maturation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2010) 56:130–40. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181e74a14
37. Lopaschuk GD, Belke DD, Gamble J, Itoi T, Schonekess BO. Regulation of fatty acid oxidation in the mammalian heart in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1994) 1213:263–76. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)00082-4
38. Girard J, Ferre P, Pegorier JP, Duee PH. Adaptations of glucose and fatty acid metabolism during perinatal period and suckling-weaning transition. Physiol Rev. (1992) 72:507–62. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.2.507
39. Koopman WJ, Nijtmans LG, Dieteren CE, Roestenberg P, Valsecchi F, Smeitink JA, et al. Mammalian mitochondrial complex I: biogenesis, regulation, and reactive oxygen species generation. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2010) 12:1431–70. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2743
40. Osman A, Halling C, Crume M, Al Tabosh H, Odackal N, Ball MK. Meconium aspiration syndrome: a comprehensive review. J Perinatol. (2023) 43:1211–21. doi: 10.1038/s41372-023-01708-2
41. Marnett LJ, Riggins JN, West JD. Endogenous generation of reactive oxidants and electrophiles and their reactions with DNA and protein. J Clin Invest. (2003) 111:583–93. doi: 10.1172/JCI200318022
42. Puente BN, Kimura W, Muralidhar SA, Moon J, Amatruda JF, Phelps KL, et al. The oxygen-rich postnatal environment induces cardiomyocyte cell-cycle arrest through DNA damage response. Cell. (2014) 157:565–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.032
43. Lam NT, Sadek HA. Neonatal heart regeneration: comprehensive literature review. Circulation. (2018) 138:412–23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033648
44. Nadal-Ginard B. Generation of new cardiomyocytes in the adult heart: prospects of myocardial regeneration as an alternative to cardiac transplantation. Rev Esp Cardiol. (2001) 54:543–50. doi: 10.1016/S0300-8932(01)76354-3
45. Flink IL. Cell cycle reentry of ventricular and atrial cardiomyocytes and cells within the epicardium following amputation of the ventricular apex in the axolotl, amblystoma mexicanum: confocal microscopic immunofluorescent image analysis of bromodeoxyuridine-labeled nuclei. Anat Embryol (Berl). (2002) 205:235–44. doi: 10.1007/s00429-002-0249-6
46. Porrello ER, Mahmoud AI, Simpson E, Johnson BA, Grinsfelder D, Canseco D, et al. Regulation of neonatal and adult mammalian heart regeneration by the miR-15 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:187–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208863110
47. Zhu W, Zhang E, Zhao M, Chong Z, Fan C, Tang Y, et al. Regenerative potential of neonatal porcine hearts. Circulation. (2018) 138:2809–16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034886
48. Elhelaly WM, Cardoso AC, Pereira AHM, Elnawasany A, Ebrahimi S, Nakada Y, et al. C-Kit cells do not significantly contribute to cardiomyogenesis during neonatal heart regeneration. Circulation. (2019) 139:559–61. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.033150
49. Cardoso AC, Pereira AHM, Sadek HA. Mechanisms of neonatal heart regeneration. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2020) 22:33. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-01282-5
50. Ji X, Chen Z, Wang Q, Li B, Wei Y, Li Y, et al. Sphingolipid metabolism controls mammalian heart regeneration. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:839–56.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.01.017
51. Li X, Wu F, Gunther S, Looso M, Kuenne C, Zhang T, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation enables heart regeneration in adult mice. Nature. (2023) 622:619–26. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06585-5
52. Mills RJ, Titmarsh DM, Koenig X, Parker BL, Ryall JG, Quaife-Ryan GA, et al. Functional screening in human cardiac organoids reveals a metabolic mechanism for cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2017) 114:E8372–E81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703109114
53. Lopaschuk GD, Karwi QG, Tian R, Wende AR, Abel ED. Cardiac energy metabolism in heart failure. Circ Res. (2021) 128:1487–513. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318241
54. Fukuda R, Marin-Juez R, El-Sammak H, Beisaw A, Ramadass R, Kuenne C, et al. Stimulation of glycolysis promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation after injury in adult zebrafish. EMBO Rep. (2020) 21:e49752. doi: 10.15252/embr.201949752
55. Nakada Y, Canseco DC, Thet S, Abdisalaam S, Asaithamby A, Santos CX, et al. Hypoxia induces heart regeneration in adult mice. Nature. (2017) 541:222–7. doi: 10.1038/nature20173
56. van Hall G. Lactate kinetics in human tissues at rest and during exercise. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2010) 199:499–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02122.x
57. Murashige D, Jang C, Neinast M, Edwards JJ, Cowan A, Hyman MC, et al. Comprehensive quantification of fuel use by the failing and nonfailing human heart. Science. (2020) 370:364–8. doi: 10.1126/science.abc8861
58. Fillmore N, Wagg CS, Zhang L, Fukushima A, Lopaschuk GD. Cardiac branched-chain amino acid oxidation is reduced during insulin resistance in the heart. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 315:E1046–E52. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00097.2018
59. Karwi QG, Biswas D, Pulinilkunnil T, Lopaschuk GD. Myocardial ketones metabolism in heart failure. J Card Fail. (2020) 26:998–1005. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.04.005
60. Cotter DG, Schugar RC, Crawford PA. Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2013) 304:H1060–76. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00646.2012
61. Wang C, Hu SM. Developmental regulation in the expression of rat heart glucose transporters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (1991) 177:1095–100. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(91)90651-M
62. Fajardo VM, Feng I, Chen BY, Perez-Ramirez CA, Shi B, Clark P, et al. GLUT1 overexpression enhances glucose metabolism and promotes neonatal heart regeneration. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:8669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88159-x
63. Magadum A, Singh N, Kurian AA, Munir I, Mehmood T, Brown K, et al. Pkm2 regulates cardiomyocyte cell cycle and promotes cardiac regeneration. Circulation. (2020) 141:1249–65. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.043067
64. Onay-Besikci A. Regulation of cardiac energy metabolism in newborn. Mol Cell Biochem. (2006) 287:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11010-006-9123-9
65. Iruretagoyena JI, Davis W, Bird C, Olsen J, Radue R, Teo Broman A, et al. Metabolic gene profile in early human fetal heart development. Mol Hum Reprod. (2014) 20:690–700. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gau026
66. Cardoso AC, Lam NT, Savla JJ, Nakada Y, Pereira AHM, Elnwasany A, et al. Mitochondrial substrate utilization regulates cardiomyocyte cell cycle progression. Nat Metab. (2020) 2:167–78. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-0169-x
67. Brown NF, Weis BC, Husti JE, Foster DW, McGarry JD. Mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase I isoform switching in the developing rat heart. J Biol Chem. (1995) 270:8952–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8952
68. Cao T, Liccardo D, LaCanna R, Zhang X, Lu R, Finck BN, et al. Fatty acid oxidation promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation rate but does not change cardiomyocyte number in infant mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2019) 7:42. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00042
69. Wang W, Zhang L, Battiprolu PK, Fukushima A, Nguyen K, Milner K, et al. Malonyl CoA decarboxylase inhibition improves cardiac function post-myocardial infarction. JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2019) 4:385–400. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.02.003
70. Miklas JW, Levy S, Hofsteen P, Mex DI, Clark E, Muster J, et al. Amino acid primed mTOR activity is essential for heart regeneration. iScience. (2022) 25:103574. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103574
71. Li D, Sun J, Zhong TP. Wnt signaling in heart development and regeneration. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2022) 24:1425–38. doi: 10.1007/s11886-022-01756-8
72. Chong D, Gu Y, Zhang T, Xu Y, Bu D, Chen Z, et al. Neonatal ketone body elevation regulates postnatal heart development by promoting cardiomyocyte mitochondrial maturation and metabolic reprogramming. Cell Discov. (2022) 8:106. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00447-6
73. Abdul Kadir A, Clarke K, Evans RD. Cardiac ketone body metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2020) 1866:165739. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165739
74. Trum M, Wagner S, Maier LS, Mustroph J. CaMKII and GLUT1 in heart failure and the role of gliflozins. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2020) 1866:165729. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165729
75. Weis EM, Puchalska P, Nelson AB, Taylor J, Moll I, Hasan SS, et al. Ketone body oxidation increases cardiac endothelial cell proliferation. EMBO Mol Med. (2022) 14:e14753. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114753
76. Moos PJ, Edes K, Fitzpatrick FA. Inactivation of wild-type p53 tumor suppressor by electrophilic prostaglandins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2000) 97:9215–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.160241897
77. Elhelaly WM, Lam NT, Hamza M, Xia S, Sadek HA. Redox regulation of heart regeneration: an evolutionary tradeoff. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2016) 4:137. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00137
78. Hoeijmakers JH. DNA damage, aging, and cancer. N Engl J Med. (2009) 361:1475–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0804615
79. Pei J, Wang F, Pei S, Bai R, Cong X, Nie Y, et al. Hydrogen sulfide promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration via ROS scavenging. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:1412696. doi: 10.1155/2020/1412696
80. Shi Y, Tian M, Zhao X, Tang L, Wang F, Wu H, et al. alpha-ketoglutarate promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration after myocardial infarction. Nat Cardiovasc Res. (2024) 3:1083–97. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00531-y
81. Yester JW, Kuhn B. Mechanisms of cardiomyocyte proliferation and differentiation in development and regeneration. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2017) 19:13. doi: 10.1007/s11886-017-0826-1
82. Pasumarthi KB, Nakajima H, Nakajima HO, Soonpaa MH, Field LJ. Targeted expression of cyclin D2 results in cardiomyocyte DNA synthesis and infarct regression in transgenic mice. Circ Res. (2005) 96:110–8. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000152326.91223.4F
83. Bicknell KA, Coxon CH, Brooks G. Forced expression of the cyclin B1-CDC2 complex induces proliferation in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem J. (2004) 382:411–6. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031481
84. Chaudhry HW, Dashoush NH, Tang H, Zhang L, Wang X, Wu EX, et al. Cyclin A2 mediates cardiomyocyte mitosis in the postmitotic myocardium. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:35858–66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404975200
85. Tane S, Okayama H, Ikenishi A, Amemiya Y, Nakayama KI, Takeuchi T. Two inhibitory systems and CKIs regulate cell cycle exit of mammalian cardiomyocytes after birth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 466:147–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.08.102
86. Mahiny D, Hauck L, Premsingh B, Grothe D, Billia F. Cdk1 deficiency extends the postnatal window of cardiomyocyte proliferation and restores cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(19):10824. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910824
87. Ikenishi A, Okayama H, Iwamoto N, Yoshitome S, Tane S, Nakamura K, et al. Cell cycle regulation in mouse heart during embryonic and postnatal stages. Dev Growth Differ. (2012) 54:731–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2012.01373.x
88. Tane S, Ikenishi A, Okayama H, Iwamoto N, Nakayama KI, Takeuchi T. CDK inhibitors, p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1), participate in cell cycle exit of mammalian cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2014) 443:1105–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.109
89. Montero L, Okraine YV, Orlowski J, Matzkin S, Scarponi I, Miranda MV, et al. Conserved cysteine-switches for redox sensing operate in the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(CIP/KIP) protein family. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 224:494–505. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.09.013
90. Zhang P, Wong C, DePinho RA, Harper JW, Elledge SJ. Cooperation between the cdk inhibitors p27(KIP1) and p57(KIP2) in the control of tissue growth and development. Genes Dev. (1998) 12:3162–7. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.20.3162
91. Razavipour SF, Harikumar KB, Slingerland JM. P27 as a transcriptional regulator: new roles in development and cancer. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:3451–8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3663
92. Mohamed TMA, Ang YS, Radzinsky E, Zhou P, Huang Y, Elfenbein A, et al. Regulation of cell cycle to stimulate adult cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration. Cell. (2018) 173:104–16.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.014
93. Wang T, Zhou LY, Li XM, Liu F, Liang L, Chen XZ, et al. ABRO1 arrests cardiomyocyte proliferation and myocardial repair by suppressing PSPH. Mol Ther. (2023) 31:847–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.011
94. Chen XZ, Li XM, Xu SJ, Hu S, Wang T, Li RF, et al. TMEM11 regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair via METTL1-mediated m(7)G methylation of ATF5 mRNA. Cell Death Differ. (2023) 30:1786–98. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01179-0
95. Eulalio A, Mano M, Dal Ferro M, Zentilin L, Sinagra G, Zacchigna S, et al. Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature. (2012) 492:376–81. doi: 10.1038/nature11739
96. Yang Y, Cheng HW, Qiu Y, Dupee D, Noonan M, Lin YD, et al. MicroRNA-34a plays a key role in cardiac repair and regeneration following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. (2015) 117:450–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.305962
97. Chen J, Huang ZP, Seok HY, Ding J, Kataoka M, Zhang Z, et al.. mir-17-92 cluster is required for and sufficient to induce cardiomyocyte proliferation in postnatal and adult hearts. Circ Res. (2013) 112:1557–66. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300658
98. Borden A, Kurian J, Nickoloff E, Yang Y, Troupes CD, Ibetti J, et al. Transient introduction of miR-294 in the heart promotes cardiomyocyte cell cycle reentry after injury. Circ Res. (2019) 125:14–25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314223
99. Huang W, Feng Y, Liang J, Yu H, Wang C, Wang B, et al. Loss of microRNA-128 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:700. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03019-z
100. Huang S, Li X, Zheng H, Si X, Li B, Wei G, et al. Loss of super-enhancer-regulated circRNA nfix induces cardiac regeneration after myocardial infarction in adult mice. Circulation. (2019) 139:2857–76. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038361
101. Zheng H, Huang S, Wei G, Sun Y, Li C, Si X, et al. CircRNA Samd4 induces cardiac repair after myocardial infarction by blocking mitochondria-derived ROS output. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:3477–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.06.016
102. Ma W, Wang X, Sun H, Xu B, Song R, Tian Y, et al. Oxidant stress-sensitive circRNA Mdc1 controls cardiomyocyte chromosome stability and cell cycle re-entry during heart regeneration. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 184:106422. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106422
103. Chen G, Li H, Li X, Li B, Zhong L, Huang S, et al. Loss of long non-coding RNA CRRL promotes cardiomyocyte regeneration and improves cardiac repair by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2018) 122:152–64. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.08.013
104. Cai B, Ma W, Ding F, Zhang L, Huang Q, Wang X, et al. The long noncoding RNA CAREL controls cardiac regeneration. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 72:534–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.04.085
105. Fu W, Ren H, Shou J, Liao Q, Li L, Shi Y, et al. Loss of NPPA-AS1 promotes heart regeneration by stabilizing SFPQ-NONO heteromer-induced DNA repair. Basic Res Cardiol. (2022) 117:10. doi: 10.1007/s00395-022-00921-y
106. Li X, He X, Wang H, Li M, Huang S, Chen G, et al. Loss of AZIN2 splice variant facilitates endogenous cardiac regeneration. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114:1642–55. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy075
107. Chen Y, Li X, Li B, Wang H, Li M, Huang S, et al. Long non-coding RNA ECRAR triggers post-natal myocardial regeneration by activating ERK1/2 signaling. Mol Ther. (2019) 27:29–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.10.021
108. Li B, Hu Y, Li X, Jin G, Chen X, Chen G, et al. Sirt1 antisense long noncoding RNA promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation by enhancing the stability of Sirt1. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7:e009700. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009700
109. Li M, Zheng H, Han Y, Chen Y, Li B, Chen G, et al. LncRNA Snhg1-driven self-reinforcing regulatory network promoted cardiac regeneration and repair after myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2021) 11:9397–414. doi: 10.7150/thno.57037
110. Wang J, Chen X, Shen D, Ge D, Chen J, Pei J, et al. A long noncoding RNA NR_045363 controls cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2019) 127:105–14. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.12.005
111. Rigaud VOC, Hoy RC, Kurian J, Zarka C, Behanan M, Brosious I, et al. RNA-binding protein LIN28a regulates new myocyte formation in the heart through long noncoding RNA-H19. Circulation. (2023) 147:324–37. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059346
112. Ponnusamy M, Liu F, Zhang YH, Li RB, Zhai M, Liu F, et al. Long noncoding RNA CPR (cardiomyocyte proliferation regulator) regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair. Circulation. (2019) 139:2668–84. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035832
113. Xin M, Kim Y, Sutherland LB, Murakami M, Qi X, McAnally J, et al. Hippo pathway effector yap promotes cardiac regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:13839–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313192110
114. Torrini C, Cubero RJ, Dirkx E, Braga L, Ali H, Prosdocimo G, et al. Common regulatory pathways mediate activity of MicroRNAs inducing cardiomyocyte proliferation. Cell Rep. (2019) 27:2759–71.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.005
115. Ye B, Hou N, Xiao L, Xu Y, Boyer J, Xu H, et al. APC controls asymmetric wnt/beta-catenin signaling and cardiomyocyte proliferation gradient in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2015) 89:287–96. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.10.018
116. Heallen T, Zhang M, Wang J, Bonilla-Claudio M, Klysik E, Johnson RL, et al. Hippo pathway inhibits wnt signaling to restrain cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart size. Science. (2011) 332:458–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1199010
117. Fan Y, Ho BX, Pang JKS, Pek NMQ, Hor JH, Ng SY, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin-mediated signaling re-activates proliferation of matured cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2018) 9:338. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1086-8
118. Bray SJ. Notch signalling in context. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2016) 17:722–35. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.94
119. Felician G, Collesi C, Lusic M, Martinelli V, Ferro MD, Zentilin L, et al. Epigenetic modification at notch responsive promoters blunts efficacy of inducing notch pathway reactivation after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. (2014) 115:636–49. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.304517
120. Beigi F, Schmeckpeper J, Pow-Anpongkul P, Payne JA, Zhang L, Zhang Z, et al. C3orf58, a novel paracrine protein, stimulates cardiomyocyte cell-cycle progression through the PI3K-AKT-CDK7 pathway. Circ Res. (2013) 113:372–80. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301075
121. Fang Y, Gupta V, Karra R, Holdway JE, Kikuchi K, Poss KD. Translational profiling of cardiomyocytes identifies an early Jak1/Stat3 injury response required for zebrafish heart regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:13416–21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309810110
122. Miyawaki A, Obana M, Mitsuhara Y, Orimoto A, Nakayasu Y, Yamashita T, et al. Adult murine cardiomyocytes exhibit regenerative activity with cell cycle reentry through STAT3 in the healing process of myocarditis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1407. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01426-8
123. Farzaei MH, Ramezani-Aliakbari F, Ramezani-Aliakbari M, Zarei M, Komaki A, Shahidi S, et al. Regulatory effects of trimetazidine in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2023) 396:1633–46. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02469-7
124. Wu S, Chang G, Gao L, Jiang D, Wang L, Li G, et al. Trimetazidine protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy. J Mol Med (Berl). (2018) 96:791–806. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1664-3
125. Lee SR, Mukae M, Jeong KJ, Park SH, Shin HJ, Kim SW, et al. PGRMC1 ablation protects from energy-starved heart failure by promoting fatty acid/pyruvate oxidation. Cells. (2023) 12(5):752. doi: 10.3390/cells12050752
126. Wang ZY, Liu YY, Liu GH, Lu HB, Mao CY. l-carnitine and heart disease. Life Sci. (2018) 194:88–97. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.015
127. Iliceto S, Scrutinio D, Bruzzi P, D'Ambrosio G, Boni L, Di Biase M, et al. Effects of L-carnitine administration on left ventricular remodeling after acute anterior myocardial infarction: the L-carnitine ecocardiografia digitalizzata infarto miocardico (CEDIM) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. (1995) 26:380–7. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)80010-E
128. Nesti L, Natali A. Metformin effects on the heart and the cardiovascular system: a review of experimental and clinical data. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2017) 27:657–69. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2017.04.009
129. Volkers M, Konstandin MH, Doroudgar S, Toko H, Quijada P, Din S, et al. Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 protects the heart from ischemic damage. Circulation. (2013) 128:2132–44. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003638
130. Kappel BA, Lehrke M, Schutt K, Artati A, Adamski J, Lebherz C, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on the metabolic signature of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. (2017) 136:969–72. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029166
131. Deng Y, Xie M, Li Q, Xu X, Ou W, Zhang Y, et al. Targeting mitochondria-inflammation circuit by beta-hydroxybutyrate mitigates HFpEF. Circ Res. (2021) 128:232–45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317933
132. Saucedo-Orozco H, Voorrips SN, Yurista SR, de Boer RA, Westenbrink BD. SGLT2 inhibitors and ketone metabolism in heart failure. J Lipid Atheroscler. (2022) 11:1–19. doi: 10.12997/jla.2022.11.1.1
133. Lei I, Huang W, Noly PE, Naik S, Ghali M, Liu L, et al. Metabolic reprogramming by immune-responsive gene 1 up-regulation improves donor heart preservation and function. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15:eade3782. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ade3782
134. Chouchani ET, Pell VR, Gaude E, Aksentijevic D, Sundier SY, Robb EL, et al. Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature. (2014) 515:431–5. doi: 10.1038/nature13909
135. Sun Q, Karwi QG, Wong N, Lopaschuk GD. Advances in myocardial energy metabolism: metabolic remodelling in heart failure and beyond. Cardiovasc Res. (2024) 120:1996–2016. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae231
136. Dalla-Volta S, Maraglino G, Della-Valentina P, Viena P, Desideri A. Comparison of trimetazidine with nifedipine in effort angina: a double-blind, crossover study. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (1990) 4(Suppl 4):853–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00051292
137. Lu C, Dabrowski P, Fragasso G, Chierchia SL. Effects of trimetazidine on ischemic left ventricular dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. (1998) 82:898–901. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(98)00500-1
138. McCarthy CP, Mullins KV, Kerins DM. The role of trimetazidine in cardiovascular disease: beyond an anti-anginal agent. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. (2016) 2:266–72. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvv051
139. Gallo G, Rubattu S, Volpe M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in heart failure: from pathophysiological mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(5):2667. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052667
140. Dziubak A, Wojcicka G, Wojtak A, Beltowski J. Metabolic effects of metformin in the failing heart. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19(10):2869. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102869
141. Young ME, McNulty P, Taegtmeyer H. Adaptation and maladaptation of the heart in diabetes: part II: potential mechanisms. Circulation. (2002) 105:1861–70. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000012467.61045.87
142. McGuire MR, Espenshade PJ. PGRMC1: an enigmatic heme-binding protein. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 241:108326. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108326
143. Zhao JV, Burgess S, Fan B, Schooling CM. L-carnitine, a friend or foe for cardiovascular disease? A Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. (2022) 20:272. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02477-z
144. Sharrack N, Knott KD, Gulsin GS, Kotecha T, Brown LAE, Yeo JL, et al. Metformin associates with higher myocardial perfusion reserve and survival in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:27280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77280-2
145. Karwi QG, Lopaschuk GD. Branched-Chain amino acid metabolism in the failing heart. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2023) 37:413–20. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07320-4
146. Tang WHW. Dysregulated amino acid metabolism in heart failure: role of gut microbiome. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2023) 26:195–200. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000897
147. Gao G, Chen W, Yan M, Liu J, Luo H, Wang C, et al. Rapamycin regulates the balance between cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy in chronic heart failure by inhibiting mTOR signaling. Int J Mol Med. (2020) 45:195–209. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4407
148. Pandey AK, Bhatt DL, Pandey A, Marx N, Cosentino F, Pandey A, et al. Mechanisms of benefits of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:3640–51. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad389
149. Parlakpinar H, Gunata M. Transplantation and immunosuppression: a review of novel transplant-related immunosuppressant drugs. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2021) 43:651–65. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2021.1966033
150. Tentolouris A, Vlachakis P, Tzeravini E, Eleftheriadou I, Tentolouris N. SGLT2 inhibitors: a review of their antidiabetic and cardioprotective effects. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16(16):2965. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16162965
151. Uchihashi M, Hoshino A, Okawa Y, Ariyoshi M, Kaimoto S, Tateishi S, et al. Cardiac-specific Bdh1 overexpression ameliorates oxidative stress and cardiac remodeling in pressure overload-induced heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. (2017) 10(12):e004417. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004417
152. Bedi KC Jr, Snyder NW, Brandimarto J, Aziz M, Mesaros C, Worth AJ, et al. Evidence for intramyocardial disruption of lipid metabolism and increased myocardial ketone utilization in advanced human heart failure. Circulation. (2016) 133:706–16.doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.017545
153. Vallon V, Verma S. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney and cardiovascular function. Annu Rev Physiol. (2021) 83:503–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-095920
154. Aubert G, Martin OJ, Horton JL, Lai L, Vega RB, Leone TC, et al. The failing heart relies on ketone bodies as a fuel. Circulation. (2016) 133:698–705. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.017355
155. Horton JL, Davidson MT, Kurishima C, Vega RB, Powers JC, Matsuura TR, et al. The failing heart utilizes 3-hydroxybutyrate as a metabolic stress defense. JCI Insight. (2019) 4(4):e124079. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.124079
156. Matsuura TR, Puchalska P, Crawford PA, Kelly DP. Ketones and the heart: metabolic principles and therapeutic implications. Circ Res. (2023) 132:882–98. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321872
157. Shi X, Zhou H, Wei J, Mo W, Li Q, Lv X. The signaling pathways and therapeutic potential of itaconate to alleviate inflammation and oxidative stress in inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. (2022) 58:102553. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102553
158. McEvoy JW, McCarthy CP, Bruno RM, Brouwers S, Canavan MD, Ceconi C, et al. 2024 ESC guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45:3912–4018. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae178
Keywords: myocardial infarction, cardiomyocyte proliferation, cardiac regeneration, energy metabolism, cell cycle
Citation: Ren J, Chen X, Wang T, Liu C and Wang K (2025) Regenerative therapies for myocardial infarction: exploring the critical role of energy metabolism in achieving cardiac repair. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1533105. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1533105
Received: 23 November 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 7 February 2025.
Edited by:
Kay-Dietrich Wagner, University of Nice Sophia Antipolis, FranceReviewed by:
Akiyuki Nishimura, National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS), JapanCopyright: © 2025 Ren, Chen, Wang, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cuiyun Liu, Y2F0aHljeWxpdUBhbGl5dW4uY29t; Kun Wang, d2FuZ2s2OTZAcWR1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.