
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 10 March 2025
Sec. Heart Failure and Transplantation
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1531509
This article is part of the Research TopicOutcome-Oriented Approaches to Arrhythmia and Heart Failure TreatmentView all 6 articles
Introduction: The pathogenesis of human heart failure is diverse, and a large number of animal models have emerged to better understand the development of heart failure in humans. Among them, there are several methods of induction in mouse heart failure models, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The use of drug induced heart failure models has greatly facilitated basic research and reduced the disadvantages of time-consuming and labor-intensive surgical modeling.
Methods: In our experiments, we used a combination of isoprenaline (ISO) and phenylephrine (PE) for modeling; we aimed to evaluate whether it is superior to conventional drug-induced models, especially those induced by isoprenaline alone. The ISO and PE were administered for 2 weeks by subcutaneous implantation with a micro-osmolar pump, and the mice were monitored dynamically for cardiac ultrasound and blood pressure.
Results: RNA sequencing of myocardial tissues after execution of mice further clarified that hypertrophy, fibrosis genes, Sympathetic nervous system (SNS), and Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) pathways were upregulated.
Discussion: Therefore, we conclude that the ISO/PE-induced mouse heart failure model can activate both the SNS and RAAS, through the activation of both α-adrenergic receptor (α-AR) and β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR), which is more consistent with the development of human heart failure than the ISO-induced model and is expected to be a unique and representative heart failure modeling method.
Heart failure (HF) is the end-stage of many cardiovascular diseases, affecting the quality of life of 1%–2% of the global population, approximately 40 million people (1). The sympathetic nervous system (SNS), the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), and the natriuretic peptide system (NPS) were the three key roles in the development of heart failure (2). The natriuretic peptide system displays a protective role in the progression of heart failure through water/sodium drainage, vasodilation, and inhibition of aldosterone secretion (3). The SNS and RAAS were activated earlier during the development of heart failure, although in the short term they can play a compensatory role by enhancing myocardial contractility, promoting water and sodium retention, and constricting peripheral vasculature (4), long-term activation of both would lead to deterioration of heart function through cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis (5). For this reason, β-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), and aldosterone receptor antagonists have been used clinically to counteract the prolonged activation of both systems and can benefit patients with heart failure (4, 6, 7).
In the past, HF mouse model constructions include two types; the first type was drug-induced HF model such as isoprenaline, angiotensin II, doxorubicin, etc. (8–10); the second one was surgical modeling such as aortic arch constriction (TAC) and anterior descending coronary artery ligation (11, 12). The degree of TAC modeling narrowing is not easily controlled and requires high operator competence (13), anterior descending branch ligation is more widely used in the field of ischemia-reperfusion studies (14). Therefore, many basic researchers prefer to use drug-induced HF models due to their convenience and stability. Isoprenaline, a non-selective β-receptor agonist, acts mainly through activation of the sympathetic nervous system (15); previous studies found that the ISO-induced HF mouse model mainly shows the upregulation of cardiac fibrosis and inflammatory gene expression (16) due to the less activation of RAAS. Angiotensin II, on the other hand, mainly induced cardiac hypertrophy rather than cardiac fibrosis through activation of RAAS, has little effect on the sympathetic nervous system, and could not fully simulate human HF development (17). Doxorubicin-induced heart failure is mainly achieved by destroying cardiomyocytes, and the predominantly apoptotic changes are not consistent with the progression of heart failure in humans (18). Until now, no animal model of heart failure has been able to fully simulate the progression and development of human heart failure through both activations of RAAS and SNS.
In the development of HF, it is important to note that sympathetic nervous system activation can occur not only through β-adrenergic receptors (β-ARs) but also by agonizing α-adrenergic receptors (α-ARs) (19). There are 2 principal types of α-ARs, α1-AR, and α2-AR, α1-ARs are the classic postsynaptic α receptors and are widely expressed in vascular smooth muscle, which participates in blood pressure control (20). Recent studies have found that ISO promotes the progression of heart failure by inducing MD2 activation in cardiomyocytes via the β1-AR-cAMP-PKA-ROS signalling axis and inflammatory responses in macrophages via the β2-AR-cAMP-PKA-ROS axis.
The expression of the cardiac α1-AR changes during the course of heart failure. Normally, the percentage of α1-AR in the heart is about 10%, whereas in heart failure, its expression is upregulated to about 25%. This increase in expression is associated with the pathophysiological mechanisms of heart failure, and α1-AR plays important adaptive roles in heart failure, including enhancing myocardial contractility, modulating myocardial adaptive hypertrophy, preventing cell death, and protecting against ischaemic injury. Thus, α1-AR plays a complex role in the process of myocardial hypertrophy, both as part of adaptive remodelling of the heart and potentially contributing to the deterioration of cardiac function in long-term pathological states. Investigating the mechanism of action of α1-AR is important for understanding the pathophysiological process of cardiac hypertrophy and the development of therapeutic strategies. α1-AR activation of phospholipase C β1 at the nuclear membrane leading to myo-inositol [1,4,5]-triphosphate-dependent nuclear release of Ca2+ histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) and CAMKII-induced nuclear export are central mechanisms for the induction of heart failure (21). The activation of phospholipase C β1 at the nuclear membrane by α1-AR, leading to the release of Ca2+ histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) and CAMKII-induced nuclear export, is a central mechanism in the induction of heart failure (22). In our study, we co-administrated ISO and PE via minipump to chronic perfusion and induced a novel mouse HF model which could activate both β-ARs and α1-ARs (23) to mimic the stimulation of RAAS and SNS. Our experimental results demonstrated that the combined use of ISO and PE-induced mouse model could better simulate the developmental process of human HF through the activation of RAAS and SNS. In addition to an early onset of heart failure phenotype, ISO/PE group can better induce cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis; the upregulation of related genes was also more obvious than in the ISO-induced mouse model.
All animal care and experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Policy and Welfare Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of the University of Science and Technology of China (Approval File No. AF/SC-12-2/04.0). All animals received humane care according to NIH guidelines (Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals). The animals used for the experimental modeling were 6–8 weeks old wild-type C57BL/6JGpt male mice, purchased from Collective Pharmachem (Nanjing, China). The mice were raised in the animal house of Hefei University of Technology. The living environment of the mice was maintained at room temperature of 24 ± 1°C and humidity of 50%±10%; day and night hours were 12 h (light was provided from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m.); and they were fed and watered extensively.
Mice were acclimatized to feeding for one week and then subjected to micro-osmotic pump implantation modeling. The dosage of ISO (SIGMA, #BCCG5557) and PE (Tocris, #BP284) were both 30 mg/kg/d24. The average volume of the osmotic pump was 246.6 ul (alzet, #10135-05). The pump was dispensed one day before micro-osmotic pump implantation, placed in saline and stored overnight at 37°C protected from light; the mice were depilated using hair removal cream, prepared for the skin. Isoflurane was used to induce and maintain anesthesia, and the dorsal skin was incised, the skin and subcutaneous tissue were separated, incorporated into a micro-osmotic pump, and sutured. After implantation, the mice were placed on a heating pad and observed for 10 min to determine normal vital signs before being placed in the cage for further feeding. In this experiment, the mice were divided into three groups, the control group only had saline (0.9% NaCl solvent) in the osmotic pump, and the other two experimental groups had ISO and ISO/PE in the osmotic pump, respectively. According to previous reports in the literature, ISO-induced heart failure was modelled for 2 weeks. Therefore, the duration of modelling in this study was determined to be 2 weeks.
Ultrasound and blood pressure monitoring were performed before and 3, 7, and 14 days after modeling, respectively. The mice were depilated with hair removal cream before ultrasound; ultrasound measurements were performed after isoflurane induction and maintenance anesthesia. During the image acquisition process, we closely monitored the heart rate and respiration of the mice, and adjusted the concentration of anesthetics as needed, while dopamine was given to maintain the heart rate within 400–500 bpm, and mimic heart failure and its movement during exercise condition. Ultrasound measurements were taken in both the transverse and longitudinal axes to dynamically observe changes in cardiac function, with left ventricular ejection fraction and ventricular wall thickness as the main indicators. Blood pressure measurements were performed in the animal room, and the systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rates were measured 5 min after adaptation. In the quiet state, we tested the blood pressure of mice in the awake state. We attached a sensor to the tail of the mouse and monitored the blood flow signal by inflating and deflating the caudal artery while simultaneously applying and releasing pressure to derive the blood pressure value. Ultrasound equipment was purchased from VINNO (VINNO, Suzhou, China), and the blood pressure instrument was purchased from Zongshi Technology Company (Zongshi, Beijing, China).
Heart tissues were excised from mice after execution, preserved in 4% paraformaldehyde, dehydrated in a dehydrator, embedded in paraffin, sectioned, and stained with HE and Masson. Masson staining was performed using Masson trichrome staining solution (Baso, #BA4079A) purchased from Baso, HE staining was performed using hematoxylin staining solution from biosharp, and eosin solution was eosin powder purchased from SenBeiJia, which was prepared ready to use.
Ventricular tissues were excised, added to Trizol, and placed in negative 80°C for freezing, tissue RNA was extracted, reverse transcribed, and subjected to RT-qPCR and experimental data were analyzed using LightCycler® 96 SW 1.1 software. The primer sequences used were shown in Table 1.
After the mice were executed, the ventricular muscle tissue was excised and frozen at –80°C. Lysis was added with protease inhibitors and phosphatase inhibitors for lysing the tissues to extract proteins. Protein concentration was determined by the Bradford assay (item 5000205, Bio-Rad, California, USA). Samples were separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and electrotransferred to a PVDF membrane. The membranes were then closed in 5% skimmed milk for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies were incubated at 4°C overnight. The membrane is then incubated with the appropriate HRP coupled secondary antibody for 1 h at room temperature. According to previous studies, the main members mediating cardiac remodeling are the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family (24). Therefore, our experiments focused on monitoring the phosphorylation levels of its main members, ERK, JNK, and P38, to assess their activation status. The internal reference used in the experiment is Vinculin (1:1,000, CST, #13901). Other antibodies used in the experiment include ERK1/2(1:1,000, CST, #4695), Phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204)(1:1,000, Proteintech, 80031-1-RR), JNK(1:10,000, Proteintech, 66210-1-Ig), Phospho-JNK(Try185)(1:2,000, Proteintech, 80024-1-RR), p38(1:1,000, CST. #8690), Phospho-p38 (Thr180/Tyr182)(1:1,000, CST, #4511). Secondary antibody using Goat-anti-Rabbit (1:10,000, LI-COR, 926-68071) or Goat-anti-Mouse (1:10,000, LI-COR, 926-32210) fluorescent secondary antibody. Stripes were imaged with the Odyssey® DLx imaging system (LI-COR Odyssey, DLx) in the 800 nm or 700 nm channel. Quantify the band density using ImageJ analysis software.
Tissues from the right and left ventricles of mice were excised after execution and placed in RNA seq preservation solution, and sent to Lianchuan Biotech (Hangzhou, China) for sequencing. The preservation solution used for sequencing was provided by the company, and the data were processed and mapped using the Unichuan BioCloud platform (OmicStudio) and Rstudio. At the same time, the sequencing results were further validated by enrichment analysis of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) using the platform database.
In this experiment, a mouse model was constructed using subcutaneous implantation of a micro-osmotic pump, divided into a control group, ISO group, and ISO/PE group; 6 mice in each group. The ISO-induced mouse model has been widely used, and the dosage of ISO and PE were taken as 30 mg/kg/day in this experiment with reference to the former approach of modeling (15). The experimental design is shown in Figure 1A. One week after the mice were acclimated to rearing, the anterior thoracic region was depilated and preoperative ultrasound monitoring was performed. Afterward, the back is depilated and the micro-osmosis pump is embedded under the skin. Isoflurane was used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia for both ultrasound and micro-osmotic pump implantation. To better compare the differences and effects between the ISO group and ISO/PE group, we gave cardiac ultrasound and blood pressure monitoring before and 3, 7, and 14 days after modeling, respectively. Cardiac ultrasound mainly monitors ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) and other cardiac function-related indicators.

Figure 1. Experimental design and a comparation among 3 groups in terms of systolic BP, heart rate and HW/TL. (A) Experimental design: mouse model was constructed using subcutaneous implantation of micro-osmotic pump, divided into control group, ISO (30 mg/kg/day) group and ISO/PE (30 mg/kg/day) group; 6 mice in each group. Cardiac ultrasound monitoring and blood pressure monitoring were performed before and 3, 7 and 14 days after surgery, respectively; mice were executed at 1 and 2 weeks, respectively, and the heart-to-tibial length (HW/TL) ratio was measured. (B) Systolic pressure and (C) heart rate both monitored by blood pressure monitors through the tail root. (D) HW/TL ratio was obtained by measuring heart weight and tibia length after execution of mice on days 0, 3, 7, and 14 of modeling. Individual data, mean ± SEM of n = 6 animals are shown. P values were determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05.
Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism 8. The results of data were presented uniformly using mean ± SEM, and an unpaired t-test was used for the comparison between two groups; one-way ANOVA was used for the comparison among three groups. GraphPad Prism 8 was used for graphing; Image J was used for staining and western blot quantitative analysis. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The survival rate of mice after the operation was 100%, no infection appeared, and the mobility, feeding condition, and mental status were comparable to the control group. Dynamic mouse tail-cuff blood pressure (BP) monitoring showed that ISO/PE group could effectively raise BP starting on the third day (detailed data shown in Figure 1B). At the early stage, we also found a significant up-regulation of heart rate in ISO and ISO/PE groups due to the activation of β1-AR. However, the effect on heart rate is not as pronounced as blood pressure at the end of the second week (ISO/PE: 670.33 ± 41.63 vs. ISO: 664 ± 35.51 vs. Con: 617 ± 40.37 bpm; P = 0.0647) (Figure 1C), due to the desensitization of β1-AR under long term ISO stimulation. Interestingly, we did not find a difference in terms of HW/TL ratio between the ISO and ISO/PE groups in the first week, instead, the ISO group displayed a slight rise compared to ISO/PE group. That result was the same as Pan and Matthias report [29]. With the development of HF, the HW/TL ratio was significantly higher in the ISO/PE group than the ISO group (ISO/PE: 11.4 ± 1.03 vs. ISO: 9.07 ± 1.31 vs. Con: 7.76 ± 0.53 mg/mm; P = 0.0020) (Figure 1D) at the end of the second week. Also, the decrease of ejection fraction and fraction shortening were more pronounced in the ISO/PE group compared to the ISO group at the end of the second week (EF: ISO/PE: 44.57 ± 5.35% vs. ISO: 45.2 ± 6.88 vs. Con:70.32 ± 5.57, P < 0.0001) (Figures 2B–E). The detailed data of ultrasound results are shown in Table 2. It was evident from the results that although both modeling methods were effective in inducing a decrease in cardiac function in mice 2 weeks after the modeling, the ISO/PE group displayed a pronounced HF phenotype compared to the ISO group.
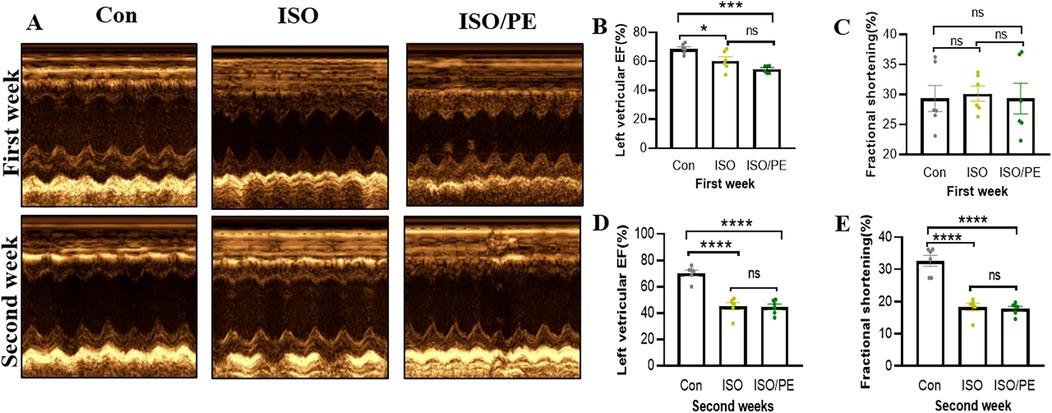
Figure 2. Echocardiographic evaluation of left ventricle EF and FS. (A) Echocardiography analysis of cardiac function in control (NaCl), isoprenaline (ISO) and isoprenaline/phenylephrine (ISO/PE) treated mice. Showing ultrasound results after 1 week and 2 weeks of dosing. (B–E) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and short-axis fractional shortening (% FS) results, statistical analysis was performed at 1 week and 2 weeks after drug administration as monitoring points. Individual data, mean ± SEM of n = 6 animals are shown. P values were determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
The SNS and RAAS are two interdependent systems. β1-adrenergic receptor stimulation of the adrenal glands induces renin secretion and hence leads to the production of the vasoconstrictor Ang-II, while in turn, Ang-II stimulates sympathetic nerve ends enhancing the release of catecholamines (25). In addition, ISO is promoting vasodilatation and a reduction in blood pressure via β2-AR activation on smooth muscle cells (26), while PE acts as an α1-AR agonist and hence a vasoconstrictor. We, therefore, hypothesized that the stabilization in BP is based on RAAS activation and hence increased Ang-II levels.
To analyze the impact of Ang-II on BP, mice receiving catecholamines stimulation were additionally treated with the ATR1 receptor antagonist losartan for 7 days. Blood pressure measurement after 24 h performed by tail-cuff confirmed that BP is stabilizing in the ISO and ISO/PE control groups, although with a significant delay in the ISO group. The average of level blood pressure was attenuated in losartan-treated animals (Figure 3A). Moreover, during this early stage of catecholamine exposure, losartan almost completely abolished hypertrophic growth (Figure 3B). The transcriptional regulation was more prominent affected in the ISO/PE group leading to a significant reduction in the expression of ANP, Periostin, and IL-6 (Figures 3D–F). Taken together, our data confirmed that RAAS has a major impact on the outcome of co-ISO/PE stimulation.
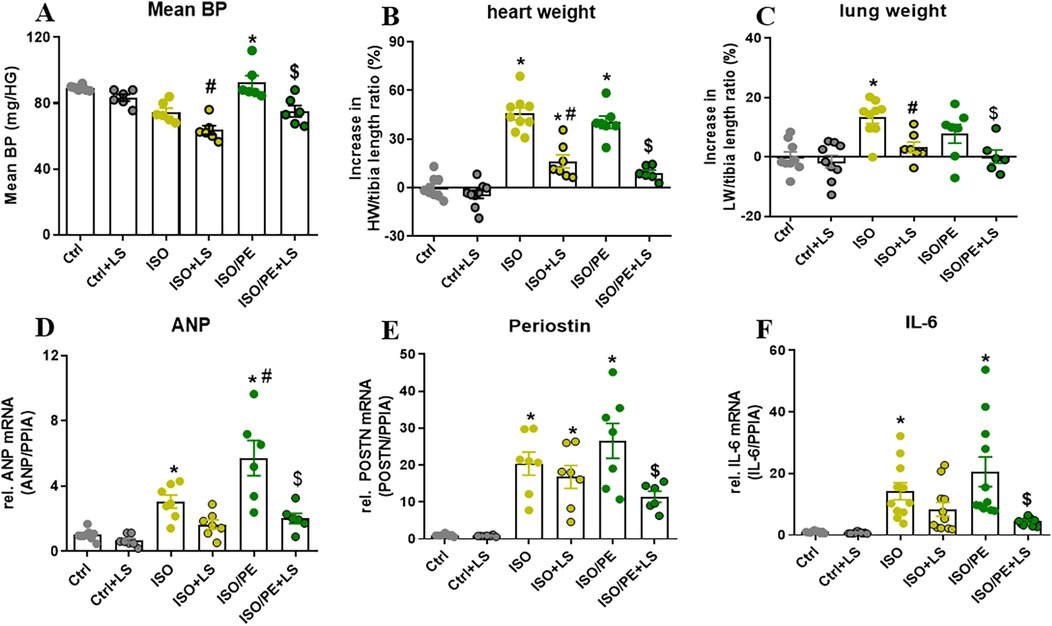
Figure 3. Contribution of RAAS activation in ISO/PE induced hypertrophic growth. (A) Mean BP measured by tail-cuff 24 h after minipump implantation and 48 h our losartan was added to the drinking water. (B) Percent increase in heart weight/tibia length (HW/TL) ratios renormalized to naCl. (C) Percent increase in lung weight/tibia length (LW/TL) ratios renormalized to NaCl. (D–F) Gene regulation (qPCR, whole heart tissue) in mice subjected to chronic perfusion of either ISO or ISO/PE (30 mg/kg/day). Values are shown as mean ± SEM; one-way-ANOVA, plus Sidak post-test, *p < 0.05 vs. respective controls, #p < 0.05 vs. ISO, $p < 0.05 vs. ISO/PE.
To observe the degree of cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, we executed the mice at one week and two weeks after modeling and took heart tissue for paraffin-embedded sectioning. Then we performed HE as well as Masson staining of cardiac tissues, and the results showed that both ISO and ISO/PE groups could effectively induce ventricular hypertrophy and fibrosis (Figures 4A,B). Quantification results also showed that the fibrotic phenotype of the ISO/PE group was superior to that of the ISO group. As shown in Figure 4C, after one week of dosing, a definite fibrosis phenotype was observed in the ISO/PE group, with the percentage of fibrosis area up to 12.23 ± 3.76%. At this time, the fibrotic phenotype of the ISO group was not yet obvious, and the collagen percentage was 5.66 ± 2.07%. Two weeks after micro-osmotic pump implantation, the fibrosis of the ISO/PE group was more obvious and the percentage of collagen was higher than ISO group (ISO/PE: 37.27 ± 16.32% vs. ISO: 13.39 ± 8.56% vs. Con:0.64 ± 1.14%, P < 0.0001) (Figure 4D). This was further validated by the results of the subsequent RT-qPCR (Figure 5). There was a clear upregulation of fibrosis-related genes such as Col1a1 and Postn in the ISO/PE group. AS for Col1a1, ISO/PE group has more than a 2-fold elevation compared to the control group and a 1.5-fold increase compared to the ISO group (P = 0.0405). Postn appeared more clearly upregulated in the ISO/PE group, with more than a 12-fold increase compared to the control group; also more than a 3-fold increase compared to the ISO group (P < 0.0001) (Figure 5A). In addition, the hypertrophy gene Myh7 was also more obviously up-regulated in the ISO/PE group (more than a 3-fold increase compare to the control group and more than a 4-fold increase compare to the ISO group) (P < 0.0001) (Figure 5B). The heart failure marker gene Nppb was also more significantly overexpressed in ISO/PE group (more than a 3-fold increase compare to the control group and more than a 2-fold increase compare to the ISO group) (P = 0.0008) (Figure 5C). However, we also found that the upregulation of the inflammation-related gene IL-6 was significantly higher in the ISO group than in the ISO/PE group (more than a 3-fold increase compared to the control group and has onefold increase compared to the ISO/PE group) (P < 0.0001) (Figure 5D). Taken together, our experimental data further demonstrate that the co-administrated ISO and PE-induced mouse model displayed a higher hypertrophic gene expression and collagen deposition.
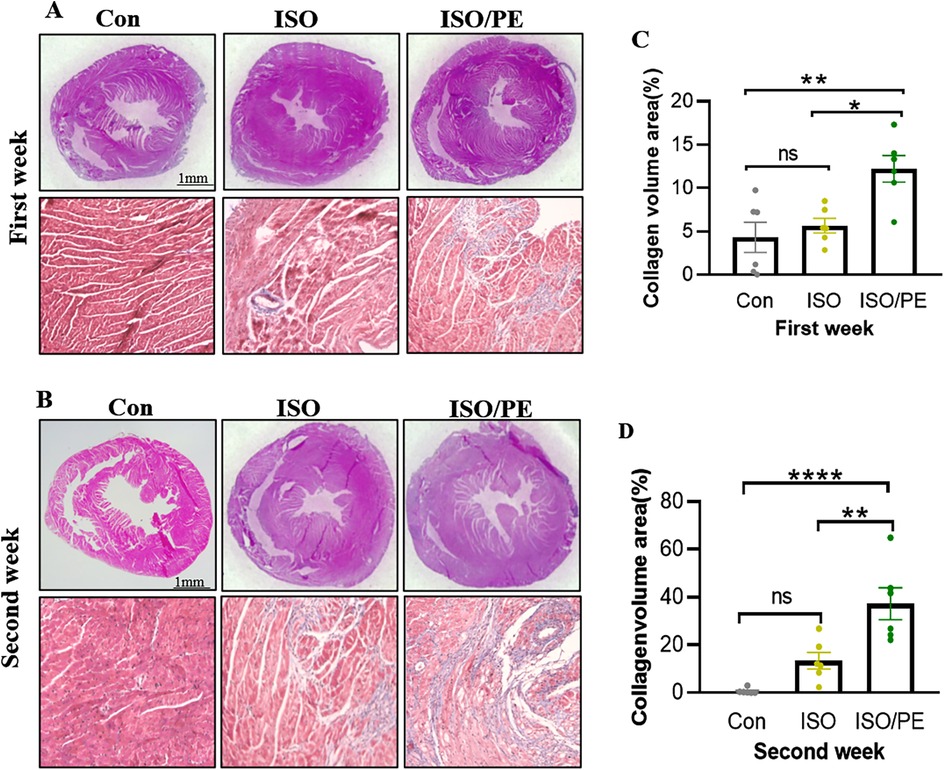
Figure 4. Cardiac hypertrophy growth and collagen deposition. (A,B) The mice were drug-molded at 1 and 2 weeks (n = 6 in each group), and the hearts were harvested for paraffin-embedded sections and stained with HE and Masson. (C,D) Using Image J to quantify the degree of fibrosis in the Masson stain, the ISO/PE group exhibited a significant fibrotic phenotype. Data are presented in the form of mean ± SEM. P values were determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.
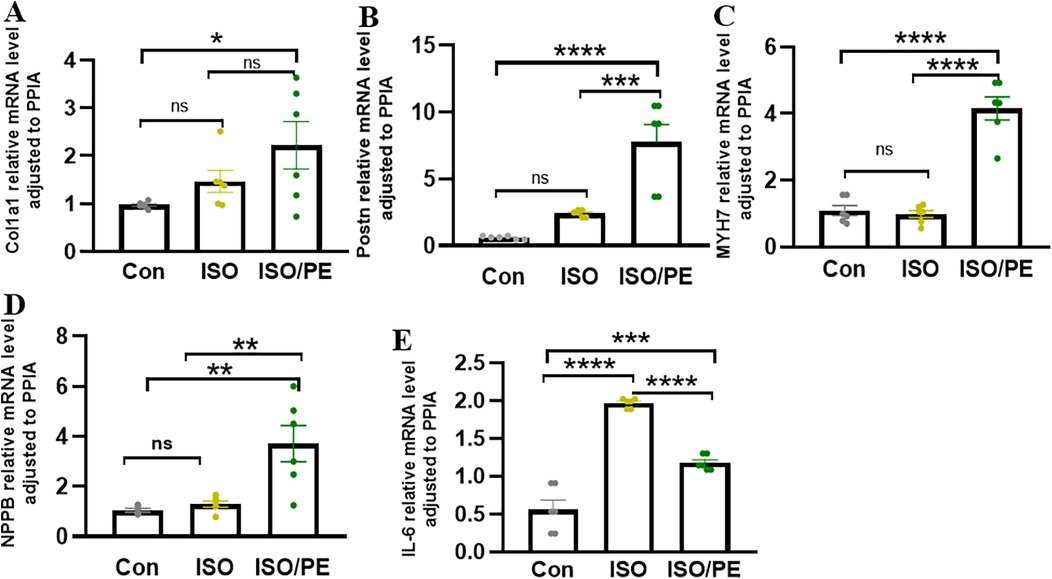
Figure 5. HF associated genes were significantly upregulated in the ISO/PE group. (A,B) Two-week post-modeling cardiac tissues were subjected to qPCR (n = 6 in each group). Fibrosis-related genes Postn and Col1a1; (C,D) hypertrophy-related gene Myh7 and heart failure marker gene Nppb were clearly upregulated in the ISO/PE group compared with the ISO and control groups. (E) The expression of the inflammation-related gene IL-6 tended to be more significantly upregulated in the ISO group. Data are presented in the form of mean ± SEM. P values were determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway plays a key role in the functional regulation of eukaryotic cells (27). The MAPK pathway is involved in cellular inflammatory responses, cell survival, stress responses, and tumor growth (28), and includes three major executive proteins: extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 (29). Previous studies have confirmed that the upregulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation played a key role in cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis (30). And as early as 2014, it was shown that α1-ARs can contribute to the development of cardiac hypertrophy through ERK1/2 (31). Thus, we detected the phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2 and other members of MAPKs. We found that phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was upregulated in the ISO/PE group one week after modeling, a 1.4-fold increase compared to the control group (Figure 6A) and a 1.6-fold increase compared to the ISO group (P < 0.0001). Two weeks later, the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was still significantly upregulated in ISO/PE group, 1.3-fold increase compare to the control group and 1.4-fold increase compared to the ISO group (P = 0.0061) (Figure 6B). At the same time, we found that the phosphorylation levels of two other important members of the MAPKs family, JNK and p38, did not show significant differences between the three groups (Figure 6). Thus, our results further confirmed that activation of ERK1/2 under α1-ARs (32) was the main reason for the hypertrophic growth.
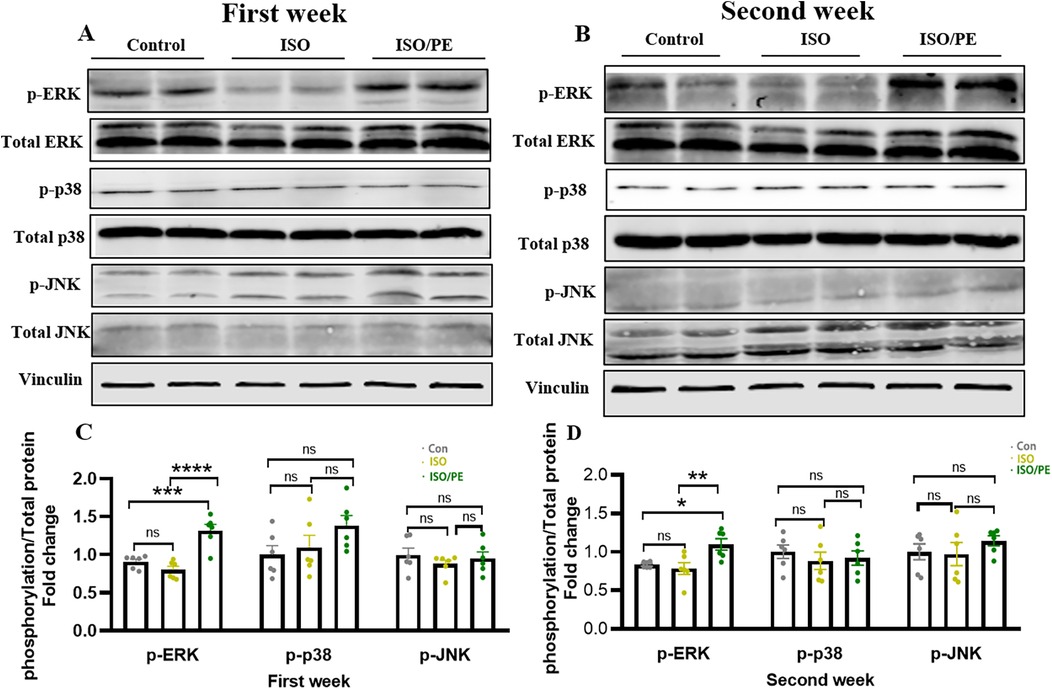
Figure 6. ISO/PE group showed α 1-activation induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2. (A–D) The phosphorylation and total protein levels of ERK, JNK and p38, the major protein components of the MAPKs family, were measured after lysis of the tissues using lysis solutions with protease inhibitors and phosphatase inhibitors in the 1-week and 2-week modeling groups (n = 6 in each group), respectively. Vinculin was used as an internal reference. Data are presented in the form of mean ± SEM. P values were determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
To investigate the gene expression in different treatment groups, we performed RNA sequencing on the left ventricular tissues of mice. The difference genes between the two comparisons of the groups were represented by Venn diagrams. Compared with the control group, the ISO group had 129 up-regulated genes and 39 down-regulated genes, while the ISO/PE group had 894 up-regulated genes and 504 down-regulated genes compared to the control group, both of which were much higher than the ISO group. The ISO/PE group also showed a significant change in gene expression compared to the ISO group, with 660 up-regulated genes and 463 down-regulated genes (Figures 7A,B). Compared with the control group, the heart failure marker genes Nppa and Nppb; fibrosis-related gene Postn, and hypertrophy-related gene Myh7 were upregulated in the ISO/PE group (Figure 7C). Compared with the ISO group, the heart failure marker genes NPPa and NPPb; fibrosis-related gene Postn and hypertrophy-related gene Myh7 also showed clear upregulation in the ISO/PE group (Figure 7D).
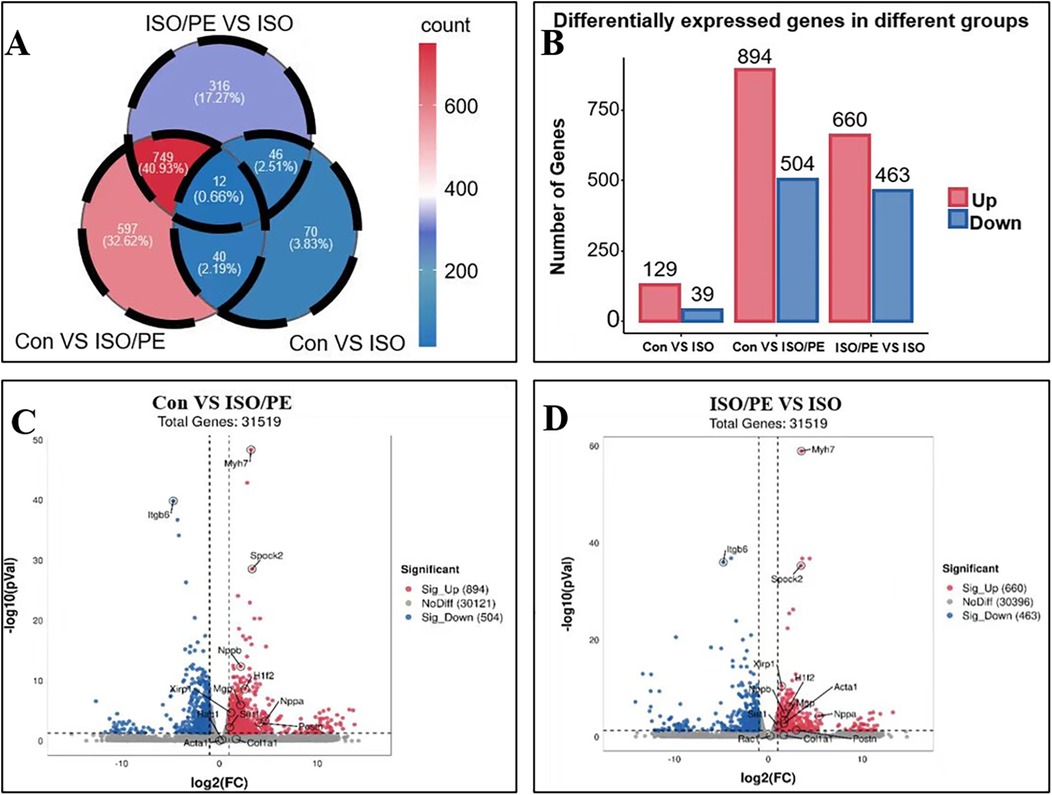
Figure 7. Gene expression changes were more significant in the ISO/PE group. (A,B) Myocardial tissues from the control, ISO and ISO/PE groups were sequenced for transcriptomic sequencing (n = 3 in Control group, n = 4 in ISO group, n = 3 in ISO/PE group); a two-by-two comparison between the three groups showed that the ISO/PE group showed the most significant up-regulation and down-regulation of gene expression compared with the control group, followed by the inter-group comparison between the ISO/PE and ISO groups, followed by the difference between the ISO and control groups. (C,D) Compared to the control and ISO groups, the hypertrophy gene Myh7 and the heart failure marker gene Nppb were clearly upregulated in the ISO/PE group.
To better understand the functions and action pathways of the above differentially expressed genes, we used KEGG gene enrichment analysis to predict them. Many of the differential genes are components of the RAAS and MAPKs pathways (Figure 8A). The genes upregulated by additional PE supplementary could be clustered into four groups: myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism (Figure 8B). In addition to hypertrophy and fibrosis genes, which are also upregulated by conventional modeling methods, the modeling approach used in this experiment can also clearly upregulate genes related to oxidative stress and lipid metabolism pathways, which is of great value in studying the complex factors affecting the development of heart failure.
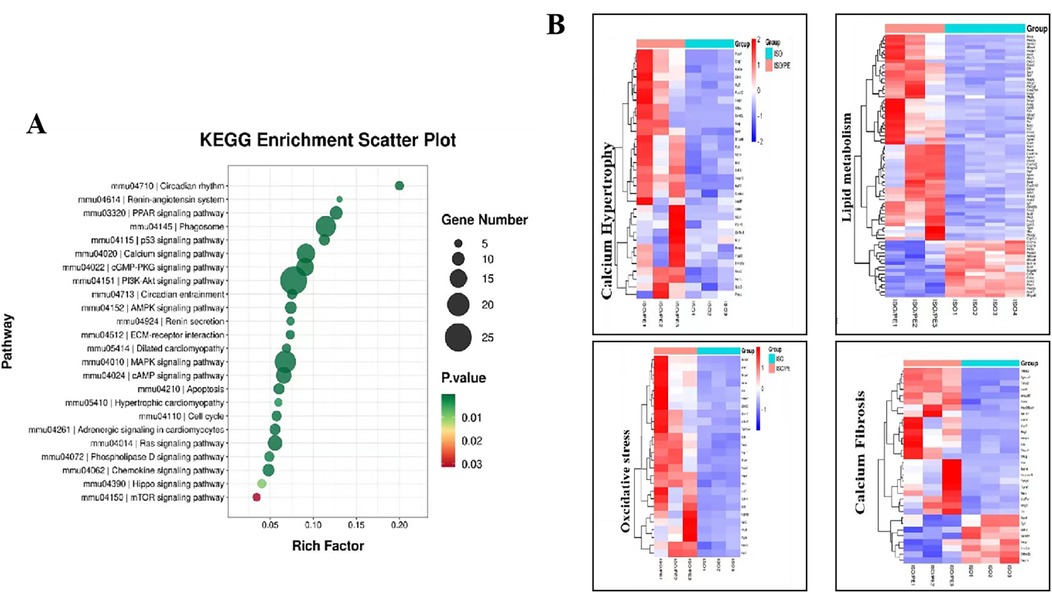
Figure 8. KEGG terms identified by pathway enrichment analysis of the indicated subgroups. (A) KEGG gene enrichment analysis of the differential genes among the control, ISO and ISO/PE groups revealed that the differential genes were heavily enriched in RAAS, AMPKs and other pathways. (B) Gene list taken from the indicated GO terms summarized as myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis, oxidative stress and lipid metabolism.
In this study, we constructed a novel mouse heart failure model by the combination use of ISO/PE. Our modeling approach has clear advantages over traditional drug-induced heart failure models. Morphologically, we confirmed the better and faster induction of heart failure in the ISO/PE group by gross indicators, which were confirmed by cardiac ultrasound monitoring and the ratio of HW/TL. At the histological and molecular levels, we confirmed by HE and Masson staining that the ISO/PE group could better induce cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis; these results were further validated by qPCR and seq-data, respectively. At the same time, the seq-results showed that the expression of genes related to oxidative stress and fatty acid metabolism could also be upregulated. In addition to the well-known activation of SNS, ISO/PE is also effective in activating RAAS, which has been verified through losartan-blocking Ang-II receptors.
Heart failure has a complex pathogenesis and a high morbidity and mortality rate (33). The SNS, RAAS, and natriuretic peptide system play a key regulatory role in the development of heart failure. Among them, the activation of SNS and RAAS played a facilitating role in the progression of heart failure, and the two systems can influence each other (34). The natriuretic peptide system consists of three bioactive peptides, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain (or B-type) are expressed in the heart, both will be elevated in heart failure (35). In the early stages of heart failure, the natriuretic peptide system can play a protective role in maintaining cardiac function by activating the SNS and RAAS, but long-term activation of the RAAS and SNS will lead to a steady decline in cardiac function (36). Hyperactivation of the sympathetic system and RAAS have a crucial effect on cardiac remodeling, and this effect is achieved through a combination activation of α-ARs and β-ARs (37). Therefore, the simultaneous activation of α-AR and β-AR can undoubtedly better simulate the development of heart failure. Previously used ISO-induced heart failure mouse models were mainly achieved through the activation of β-ARs, more prominently by upregulation of inflammatory gene expression (38). By adding the α1-AR agonist PE, our experimental results showed effective activation of the SNS and RAAS. As expected, the final experimental results confirm that ISO/PE modeling is indeed better than conventional ISO modeling.
Activation of α1-AR by various agonists induces a hypertrophic response characterised by immediate activation of early genes (c-Fos, c-Jun) and reactivation of “fetal” genes [c-myc, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), α-skeletal actin and β-myosin heavy chain] (22). Similarly, animals develop cardiac hypertrophy after prolonged infusion of low-dose NE or PE. β-ARs have been reported in relation to HF inflammation. Previous studies have shown that β-ARs are involved in the inflammatory response of cardiomyocytes and immune cells (39). The sympathetic nervous system is considered to be an important regulator of the inflammatory response. xiao et al. demonstrated that β1-AR mediated ISO-induced activation of inflammatory vesicles and inflammatory responses in cardiomyocytes. The activation of β-ARs resulted in elevated levels of cAMP in the myocardium (21). cAMP is a known mediator of anti-inflammatory responses, and cAMP-dependent signalling has been pharmacologically used to treat inflammatory diseases. cAMP can act as a positive regulator of a variety of inflammatory genes. In ISO-induced HF, cardiac overexpression of phosphodiesterase 4B, a cAMP-hydrolysing protein, attenuates the β-AR response and maladaptive remodelling, suggesting a pathogenic role for cAMP in sympathoexcitation-associated HF (40).
In the 1980s and 1990s, the MAPKs family, as members of the protein kinase family, received attention from researchers for their involvement in cell cycle regulation and transduction of various signaling pathways (41). ERK, as the first recognized member of the mammalian MAPKs family, mainly includes two types of ERK1 and ERK2, with 85% similarity, and both are widely expressed in various types of cells, including cardiomyocytes (42). The effective induction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation by α1-AR agonism has been demonstrated in previous cellular experiments, which is also consistent with our experimental results (43). Previous studies also found that the ERK/MAPK pathway is closely associated with myocardial hypertrophy and fibrotic phenotype (44), which is also consistent with our experimental results. In addition, blocking the ERK signaling pathway can effectively inhibit collagen deposition and apoptosis (45), so the ERK/MAPKs pathway is likely to be a major mediator of heart failure through cardiac remodeling. However, in the development of heart failure, not only the structural changes of the myocardial cells but also the functional changes of the myocardium itself play a crucial role in the process of heart failure, the most prominent of these is the change in energy metabolism (46).
The heart, being a high-energy consumption organ, normally uses fatty acids (especially long-chain fatty acids) as the main energy substrate (47). However, during the heart failure phase, the energy supply ratio of fatty acids decreases, accompanied by significant changes in other energy substrates (46). In 2021, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor drugs were included in heart failure prevention and treatment guidelines (44). So it has become indisputable that alterations in metabolism during the heart failure phase can serve as an intervention target. Oxidative stress refers to a state of imbalance in the production and processing of reactive oxygen species, which plays a key role in the development of heart failure (48). Since oxidative phosphorylation of mitochondria is the main source of cellular reactive oxygen species, changes in mitochondrial ROS production brought about by alterations in energy metabolism and subsequent changes in mitochondrial function also contribute significantly to the development of heart failure (49). Our study presents a novel approach to heart failure induction in mice, which not only upregulates hypertrophy and fibrosis-related genes but also shows clear upregulation of oxidative stress and lipid metabolism pathways. Since the development of heart failure is mediated by a combination of factors, the modeling approach proposed in this study appears to be more consistent with the real-world progression of heart failure.
As a drug-induced heart failure model, our modeling approach not only has the advantage of saving time and effort in traditional drug-induced models but also can activate both SNS and RAAS, which can better simulate the development of heart failure compared to traditional mouse models. Although this modeling approach takes into account the relative complexity of heart failure progression mechanisms, it also has some disadvantages. First, the mice used in this experiment were all males and there were only 6 mice in each group, so the number was relatively small. Second, although we confirmed that the ISO/PE group could activate SNS and RAAS well, the degree of activation of RAAS was not measured. Although this study confirms that the use of ISO/PE is effective in activating multiple pro-heart failure factors, the exact mechanism has not been elucidated. Despite the above shortcomings, it still has good prospects for future basic research as a new method for induction of heart failure models.
Currently available modeling methods have their own merits and drawbacks, and different research directions require different animal models to meet the research needs. In this experiment, the traditional modeling method can be improved to better simulate the development of heart failure, which is a good modeling solution. Our modeling approach has very clear advantages over conventional modeling. First, it is more reproducible than TAC and anterior descending coronary artery ligation. Second, our approach is faster and more stable than ISO group. More certainly, it is more compatible with the human heart failure process than doxorubicin dosing. In addition, it also activates the RAAS besides the SNS, which more closely resembles the pathological features of the heart failure state than the angiotensin-induced heart failure model alone.
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA1000310.
The animal study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the First Hospital Affiliated to the University of Science and Technology of China (Anhui Provincial Hospital). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
HS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ML: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Writing – review & editing. BT: Writing – review & editing. HH: Writing – review & editing. L-KM: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2208085MH197) awarded to JP, we also acknowledge the funding from National Nature Science Foundation of China (82170263) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFA0804904) awarded to L-KM.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1531509/full#supplementary-material
2. D’Elia E, Iacovoni A, Vaduganathan M, Lorini FL, Perlini S, Senni M. Neprilysin inhibition in heart failure: mechanisms and substrates beyond modulating natriuretic peptides. Eur J Heart Fail. (2017) 19:710–17. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.799
3. Nishikimi T, Maeda N, Matsuoka H. The role of natriuretic peptides in cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res. (2006) 69:318–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.10.001
4. Hartupee J, Mann DL. Neurohormonal activation in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14:30–8. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.163
5. Ferrari R, Ceconi C, Curello S, Visioli O. The neuroendocrine and sympathetic nervous system in congestive heart failure. Eur Heart J. (1998) 19(Suppl F):F45–51.9651735
6. Iaccarino G, Tomhave ED, Lefkowitz RJ, Koch WJ. Reciprocal in vivo regulation of myocardial G protein-coupled receptor kinase expression by beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation and blockade. Circulation. (1998) 98:1783–9. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.98.17.1783
7. Pontremoli R, Borghi C, Perrone Filardi P. Renal protection in chronic heart failure: focus on sacubitril/valsartan. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. (2021) 7:445–52. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvab030
8. Bacmeister L, Schwarzl M, Warnke S, Stoffers B, Blankenberg S, Westermann D, et al. Inflammation and fibrosis in murine models of heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol. (2019) 114:19. doi: 10.1007/s00395-019-0722-5
9. Tang X, Wang P, Zhang R, Watanabe I, Chang E, Vinayachandran V, et al. KLF2 regulates neutrophil activation and thrombosis in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure progression. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:2–3. doi: 10.1172/JCI147191
10. Li H, Zhang M, Wang Y, Gong K, Yan T, Wang D, et al. Daidzein alleviates doxorubicin-induced heart failure via the SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway. Food Funct. (2022) 13:9576–88. doi: 10.1039/D2FO00772J
11. Huo JL, Jiao L, An Q, Chen X, Qi Y, Wei B, et al. Myofibroblast deficiency of LSD1 alleviates TAC-induced heart failure. Circ Res. (2021) 129:400–13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318149
12. Wang P, Xu S, Xu J, Xin Y, Lu Y, Zhang H, et al. Elevated MCU expression by CaMKIIδB limits pathological cardiac remodeling. Circulation. (2022) 145:1067–83. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055841
13. Bosch L, de Haan JJ, Bastemeijer M, van der, Burg J, van der, Worp E, Wesseling M, et al. The transverse aortic constriction heart failure animal model: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail Rev. (2021) 26:1515–24. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-09960-w
14. Cheng Y, Cheng L, Gao X, Chen S, Wu P, Wang C, et al. Covalent modification of Keap1 at Cys77 and Cys434 by pubescenoside a suppresses oxidative stress-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Theranostics. (2021) 11:861–77. doi: 10.7150/thno.48436
15. Chang SC, Ren S, Rau CD, Wang JJ. Isoproterenol-induced heart failure mouse model using osmotic pump implantation. Methods Mol Biol. (2018) 1816:207–20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8597-5_16
16. Gao Y, Liang X, Tian Z, Ma Y, Sun C. Betalain exerts cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory effects against the experimental model of heart failure. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2021) 40:S16–28. doi: 10.1177/09603271211027933
17. Wang M, Luo W, Yu T, Liang S, Sun J, Zhang Y, et al. Corynoline protects ang II-induced hypertensive heart failure by increasing PPARα and inhibiting NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 150:113075. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113075
18. Qi W, Boliang W, Xiaoxi T, Guoqiang F, Jianbo X, Gang W. Cardamonin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by restraining oxidative stress and inflammation associated with Nrf2 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 122:109547. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109547
19. Triposkiadis F, Karayannis G, Giamouzis G, Skoularigis J, Louridas G, Butler J. The sympathetic nervous system in heart failure physiology, pathophysiology, and clinical implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2009) 54:1747–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.05.015
20. Perez DM. Current developments on the role of α(1)-adrenergic receptors in cognition, cardioprotection, and metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:652152. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.652152
21. Qian JF, Liang SQ, Wang QY, Xu JC, Luo W, Huang WJ, et al. Isoproterenol induces MD2 activation by β-AR-cAMP-PKA-ROS signalling axis in cardiomyocytes and macrophages drives inflammatory heart failure. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2024) 45:531–44. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01179-3
22. Zhang J, Simpson PC, Jensen BC. Cardiac α1A-adrenergic receptors: emerging protective roles in cardiovascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2021) 320:H725–33. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00621.2020
23. Xu C, Liu S, Qian D, Liu A, Liu C, Chen Y, et al. Preventive intramuscular phenylephrine in elective cesarean section under spinal anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Surg. (2019) 62:5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.12.014
24. Yang N, Zou C, Luo W, Xu D, Wang M, Wang Y, et al. Sclareol attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling and inflammation via inhibiting MAPK signaling. Phytother Res. (2023) 37:578–91. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7635
25. van Zwieten PA, de Jonge A. Interaction between the adrenergic and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-systems. Postgrad Med J. (1986) 62(Suppl 1):23–7.3534860
26. Garovic VD, Joyner MJ, Dietz NM, Boerwinkle E, Turner ST. Beta(2)-adrenergic receptor polymorphism and nitric oxide-dependent forearm blood flow responses to isoproterenol in humans. J Physiol. (2003) 546:583–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.031138
27. Hepworth EMW, Hinton SD. Pseudophosphatases as regulators of MAPK signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:1–3. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212595
28. Chen C, Nelson LJ, Ávila MA, Cubero FJ. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and cholangiocarcinoma: the missing link. Cells. (2019) 8:1–5. doi: 10.3390/cells8101172
29. Min L, He B, Hui L. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Semin Cancer Biol. (2011) 21:10–20. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.10.011
30. Mutlak M, Schlesinger-Laufer M, Haas T, Shofti R, Ballan N, Lewis YE, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation preserves cardiac function in pressure overload induced hypertrophy. Int J Cardiol. (2018) 270:204–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.05.068
31. Ogata T, Naito D, Nakanishi N, Hayashi YK, Taniguchi T, Miyagawa K, et al. MURC/Cavin-4 facilitates recruitment of ERK to caveolae and concentric cardiac hypertrophy induced by α1-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:3811–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315359111
32. Wallert M, McCoy A, Voog J, Rastedt D, Taves-Patterson J, Korpi-Steiner N, et al. α1 -adrenergic receptor-induced cytoskeletal organization and cell motility in CCL39 fibroblasts requires phospholipase D1. J Cell Biochem. (2011) 112:3025–34. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23227
33. Snipelisky D, Chaudhry SP, Stewart GC. The many faces of heart failure. Card Electrophysiol Clin. (2019) 11:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2018.11.001
34. Abassi Z, Khoury EE, Karram T, Aronson D. Edema formation in congestive heart failure and the underlying mechanisms. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:933215. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.933215
35. Nakagawa Y, Nishikimi T, Kuwahara K. Atrial and brain natriuretic peptides: hormones secreted from the heart. Peptides. (2019) 111:18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.05.012
36. Fu S, Chang Z, Luo L, Deng J. Therapeutic progress and knowledge basis on the natriuretic peptide system in heart failure. Curr Top Med Chem. (2019) 19:1850–66. doi: 10.2174/1568026619666190826163536
37. Dewenter M, Pan J, Knödler L, Tzschöckel N, Henrich J, Cordero J, Dobreva G, et al. Chronic isoprenaline/phenylephrine vs. exclusive isoprenaline stimulation in mice: critical contribution of alpha(1)-adrenoceptors to early cardiac stress responses. Basic Res Cardiol. (2022) 117:15. doi: 10.1007/s00395-022-00920-z
38. Naseroleslami M, Aboutaleb N, Mokhtari B. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells labeled by iron oxide nanoparticles exert cardioprotective effects against isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial damage by targeting inflammatory MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Drug Deliv Transl Res. (2021) 11:242–54. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00788-3
39. Adzika GK, Machuki JO, Shang W, Hou H, Ma T, Wu L, et al. Pathological cardiac hypertrophy: the synergy of adenylyl cyclases inhibition in cardiac and immune cells during chronic catecholamine stress. J Mol Med (Berl). (2019) 97:897–907. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01790-0
40. Karam S, Margaria JP, Bourcier A, Mika D, Varin A, Bedioune I, et al. Cardiac overexpression of PDE4B blunts β-adrenergic response and maladaptive remodeling in heart failure. Circulation. (2020) 142:161–74. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042573
41. Courchesne WE, Kunisawa R, Thorner J. A putative protein kinase overcomes pheromone-induced arrest of cell cycling in S. cerevisiae. Cell. (1989) 58:1107–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90509-6
42. Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, et al. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev. (2001) 22:153–83. doi: 10.1210/edrv.22.2.0428
43. Perez-Aso M, Segura V, Montó F, Barettino D, Noguera MA, Milligan G, et al. The three α1-adrenoceptor subtypes show different spatio-temporal mechanisms of internalization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2013) 1833:2322–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.013
44. McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:3599–726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368
45. Zhang X, Yan C, Zheng M. Sacubitril-valsartan ameliorates heart failure by inhibiting cardiac remodeling potentially via MAPK/ERK signaling. Ann Clin Lab Sci. (2022) 52:391–938.35777797
46. Lopaschuk GD, Karwi QG, Tian R, Wende AR, Abel ED. Cardiac energy metabolism in heart failure. Circ Res. (2021) 128:1487–513. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318241
47. Murashige D, Jang C, Neinast M, Edwards JJ, Cowan A, Hyman MC, et al. Comprehensive quantification of fuel use by the failing and nonfailing human heart. Science. (2020) 370:364–68. doi: 10.1126/science.abc8861
48. van der Pol A, van Gilst WH, Voors AA, van der Meer P. Treating oxidative stress in heart failure: past, present and future. Eur J Heart Fail. (2019) 21:425–35. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1320
Keywords: heart failure, drug modelling, mouse model, SNS, RAAS
Citation: Su H, Liu M, Wang S, Tian B, Hu H, Ma L-K and Pan J (2025) Co-administration of isoprenaline and phenylephrine induced a new HFrEF mouse model through activation of both SNS and RAAS. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1531509. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1531509
Received: 20 November 2024; Accepted: 3 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Concetta Pastore, University of Siena, ItalyReviewed by:
Xu Chen, University of Mississippi Medical Center, United StatesCopyright: © 2025 Su, Liu, Wang, Tian, Hu, Ma and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianyuan Pan, ZXlwYW5qaWFueXVhbkBzaW5hLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.