- The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou, Guangxi, China
Introduction: This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of dTRA for coronary angiography (CAG) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in comparison to cTRA.
Materials and methods: Four databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library) were searched from their inception to 13 April 2024 for studies comparing dTRA and cTRA in coronary diagnostic or interventional catheterization. The meta-analysis evaluated radial artery occlusion (RAO), procedure success, the success rate of catheter puncture, the success rate of a single attempt, hematoma occurrence, radial artery spasms, puncture site bleeding, puncture time, procedural time, the dosage of contrast medium, and hemostasis time.
Results: A total of 31 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Compared with cTRA, dTRA significantly reduced the incidence of RAO [odds ratio (OR) = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.34–0.50, P < 0.05], hematoma (OR = 0.67, 95% CI:0.56–0.80, P < 0.05), and shorter hemostasis time [weighted mean difference (WMD) = −0.43, 95% CI:−0.65 to −0.20, P < 0.05] but had a significantly lower procedure success rate (OR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.30–0.56, P < 0.05), a lower catheter puncture success rate (OR = 0.44, 95% CI: 0.27–0.71, P < 0.05), and a longer puncture time (WMD = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.44–0.75, P < 0.05). No significant differences were observed between dTRA and cTRA in terms of the success rate of a single attempt, radial artery spasms, puncture site bleeding, procedural time, and dosage of contrast medium.
Conclusions: Our results revealed that dTRA is a workable and safe method for cardiovascular interventional diagnostics and treatment. It significantly reduces the incidence of RAO and hematoma, as well as shortens hemostasis time following surgery.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42024596238, PROSPERO (CRD42024596238).
1 Introduction
Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains one of the leading causes of mortality, as reported by the World Health Organization (1). Coronary angiography (CAG) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are essential procedures for the diagnosis and treatment of CAD. These procedures can be performed using transradial, transbrachial, or transfemoral access. Just 12 years later, in 1989, Campeau reported the first 100 diagnostic CAGs using the radial approach, following the first successful femoral artery PCI in 1977 (2). The RIVAL study later verified the safety and high success rate of this approach, establishing it as the preferred referral technique for catheterization in compliance with the guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology (3).
Unfortunately, this procedure carries certain risks, including bleeding, hematoma, and pseudoaneurysm. In addition, prolonged bed relaxation following the procedure raises the risk of lower limb thrombosis and pulmonary embolism (4). Transradial artery access (TRA) is associated with fewer bleeding and vascular complications and significant safety advantages over transfemoral artery access (5). In 1993, Kiemeneij and Laarman, respectively, showed that TRA performed better than transfemoral access in a variety of areas, such as a lower risk of bleeding, a shorter length of hospital stay, early mobilization, reduced costs, and higher patient satisfaction; as a result, TRA has become the preferred approach for CAG (6–9). Despite its benefits, TRA also has certain drawbacks. These drawbacks include mild bleeding at the access site and radial artery occlusion (RAO) after the procedure. RAO, both early and late, which varies in frequency from 5% to 30% in various studies, is the most common complication (5, 10–12).
Babunashvili and Dundua recently developed dTRA, a retrograde method to unblock obstructed ipsilateral radial arteries (13). Its superiority over cTRA lies in providing enhanced comfort for both the patient and the operator throughout the process, and it can be performed without a palpable radial artery in an anatomical snuffbox (14). Moreover, it preserves antegrade blood flow via the superficial palmar arch in instances of RAO. Additional benefits include fewer complications at the puncture site, a shorter hospital stay, and the preservation of the radial artery for revascularization procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafts or the creation of AV-fistulas in patients with chronic kidney disease (15, 16) because these patients often exhibit more complex coronary artery disease and an elevated risk of periprocedural and postprocedural complications, including hemorrhage, thrombotic incidents, and contrast-induced acute kidney damage (17). Having said that, this method is not without its share of disadvantages, some of which include greater difficulty in needling, an increased risk of nerve irritation, and an inability to pass through bigger sheaths (16). Thus, the application of dTRA in interventional surgery for coronary heart disease remains debatable, necessitating more evidence of its safety and efficacy.
Thus, we conducted a meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of dTRA compared to cTRA for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
This meta-analysis adhered to the 2020 standards of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). The research was formally registered with PROSPERO, under registration number CRD42024596238. A comprehensive search was performed across four databases, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library, to collect relevant studies published until 13 April 2024. The search strategy adhered to the PICOS concept and utilized a combination of MeSH keywords and unconstrained textual phrases. The search method involved combining the terms “coronary disease,” “coronary angiography,” “percutaneous coronary intervention,” “radial artery,” “transradial,” “snuff box,” and “distal radial artery.” Supplementary Tables S1–S4 provide the details of the searched record across the four databases.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria are as follows: (1) patients aged >18 years with an indication for CAG or PCI; (2) patients in the intervention group received dTRA; (3) patients in the control group received cTRA; (4) studies reporting at least one of the following outcomes: RAO, procedure success, success rate of catheter puncture, success rate of a single attempt, hematoma incidence, radial artery spasms, puncture site bleeding, puncture time, procedural time, dosage of contrast medium, or hemostasis time; and (5) study design: randomized controlled trial (RCT), prospective study, or retrospective study.
The exclusion criteria are as follows: (1) studies that were of other types, such as case reports, protocols, letters, editorials, comments, reviews, and meta-analyses; (2) studies that were not relevant; (3) studies that did not compare dTRA vs. cTRA; (4) studies with duplicate patient cohorts; (5) studies where data cannot be extracted; and (6) studies that did not report relative outcomes.
2.3 Selection of studies
The literature selection procedure, which entailed eliminating duplicate items, was executed using EndNote (version 20; Clarivate Analytics). Two independent reviewers conducted the preliminary search. Duplicate entries were removed, and the titles and abstracts were evaluated for relevance. Each study was subsequently classified as either included or excluded. We addressed the issue by achieving a consensus. Should the parties fail to reach an agreement, a third reviewer acted as a mediator.
2.4 Data extraction
Data extraction was performed independently by two reviewers. The data collected comprised: (1) essential features of the included studies: author, nationality, year of publication, and research design; (2) baseline features of study participants: sample size, male-to-female ratio, age, prevalence of hypertension and diabetes, and smoking habit; (3) primary outcome: incidence of RAO; and (4) secondary outcomes: procedure success, success rate of catheter puncture, success rate of a single attempt, hematoma incidence, radial artery spasm, puncture site bleeding, puncture time, procedural time, dosage of contrast medium, and hemostasis time.
2.5 Quality assessment
Two independent reviewers assessed the quality of the included studies. We utilized the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) (18) to assess the quality of both retrospective and prospective studies in this analysis, covering eight domains: (1) representativeness of the exposed cohort; (2) selection of the non-exposed cohort; (3) ascertainment of exposure; (4) demonstration that the outcome of interest was not present at the start of the study; (5) comparability of cohorts based on study design or analysis; (6) assessment of the outcome; (7) adequacy of follow-up duration for outcomes to occur; and (8) adequacy of follow-up of cohorts. We evaluated the RCTs using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool, which encompasses seven domains: (1) random sequence generation; (2) allocation concealment; (3) participant and personnel blinding; (4) outcome assessment blinding; (5) incomplete outcome data; (6) selective reporting; and (7) other biases. We engaged in collaborative deliberation to resolve any inconsistencies in the contested findings.
2.6 Statistical analysis
We conducted the study selection process, using EndNote (version 20; Clarivate Analytics) to eliminate duplicates. We utilized Review Manager 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK) to examine the outcomes of all included studies. We analyzed binary variables using odds ratios (ORs) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). We employed the weighted mean difference (WMD) with a 95% CI to analyze continuous variables. We transformed the medians and interquartile ranges of continuous data into means and standard deviations. We evaluated the statistical heterogeneity among the studies used in the analysis using the Cochrane Q-test and the I2 index. An I2 score greater than 50% signifies a considerable degree of heterogeneity. The random effects model was employed when substantial variability existed among the studies, whereas the fixed effects model was utilized in its absence. Statistical heterogeneity was evaluated using a conventional chi-square test and deemed significant at P < 0.05. We assessed the possibility of publication bias by a visual examination of the funnel plots.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
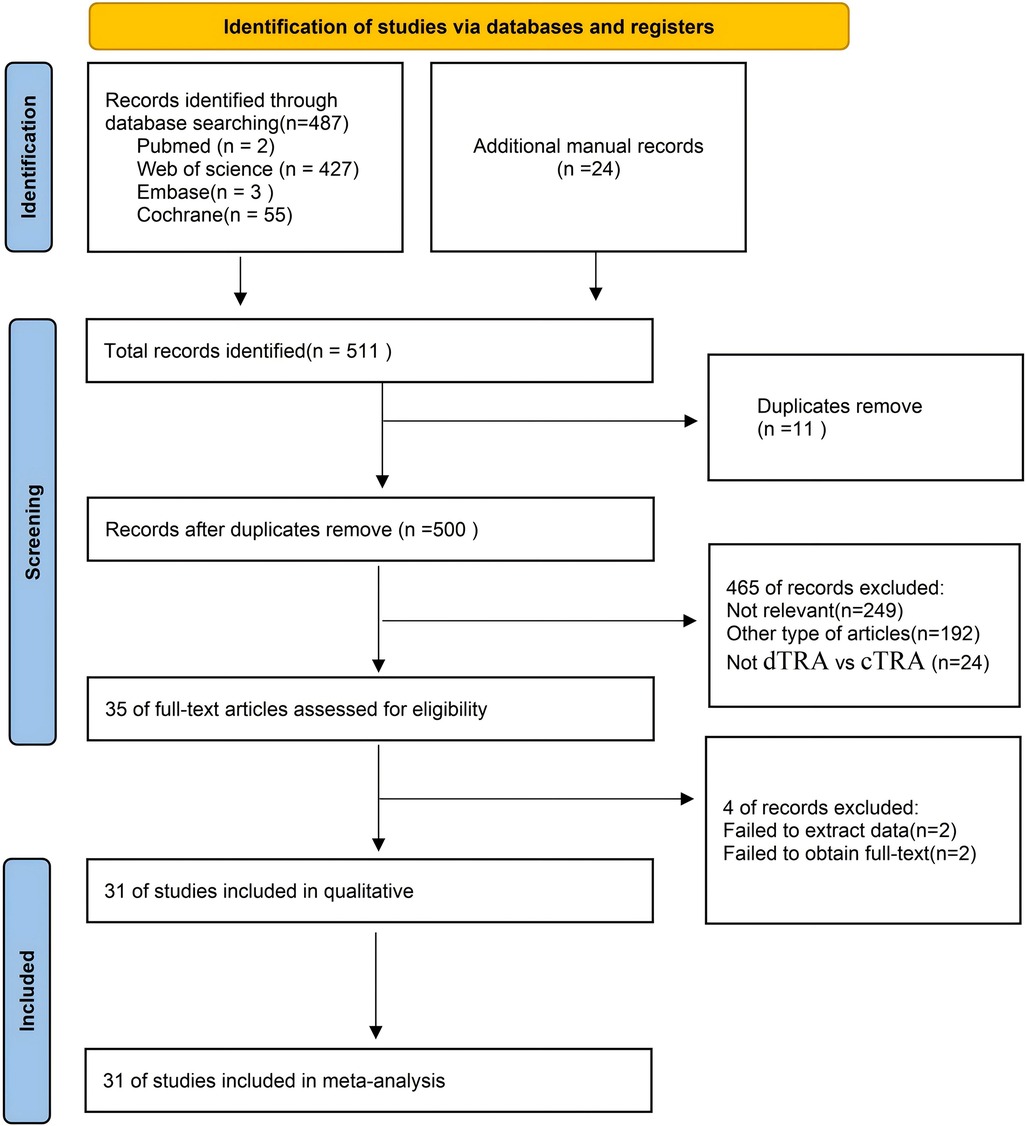
Figure 1 illustrates the process of literature selection and inclusion. We acquired a total of 487 publications from four databases and identified an additional 24 articles by examining the bibliographies of the aforementioned studies. We incorporated 31 articles (19–33) in the final meta-analysis, conforming to the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Figure 1 illustrates the process of choosing and incorporating the literature.
3.2 Study characteristics
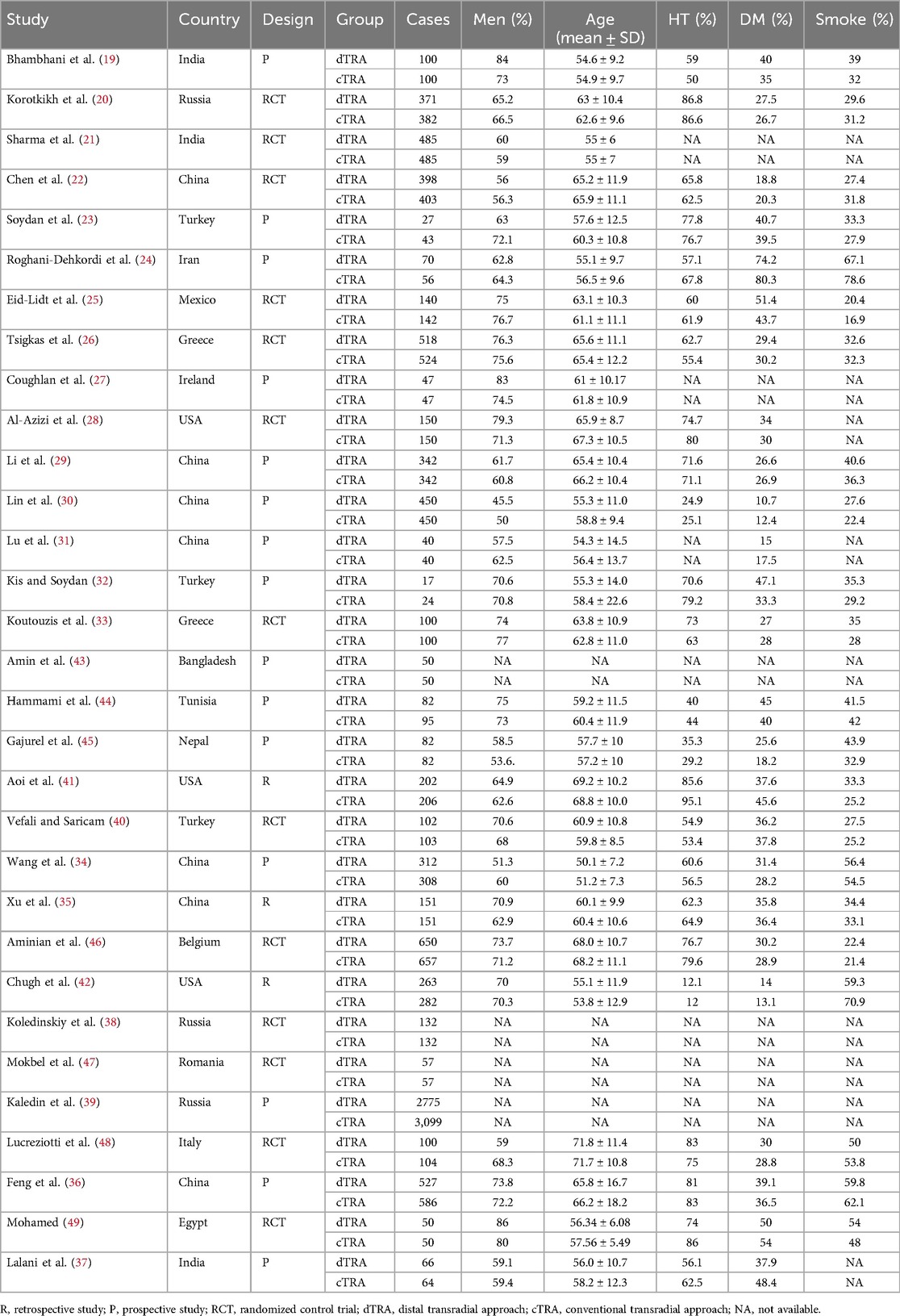
The meta-analysis comprised 31 studies, consisting of 13 RCTs, 15 prospective studies, and 3 retrospective studies. The meta-analysis comprised a total of 16,891 individuals, including 8,260 patients in the dTRA group and 8,631 patients in the TRA group. The included studies were conducted in several countries, including China (22, 29–31, 34–36), India (19, 21, 37), Russia (20, 38, 39), Turkey (23, 32, 40), Iran (24), Mexico (25), Greece (26, 33), Ireland (27), America (28, 41, 42), Bangladesh (43), Tunisia (44), Nepal (45), Belgium (46), Romania (47), Italy (48), and Egypt (49). Table 1 provides the characteristics of the included studies and patients.
3.3 Quality assessment
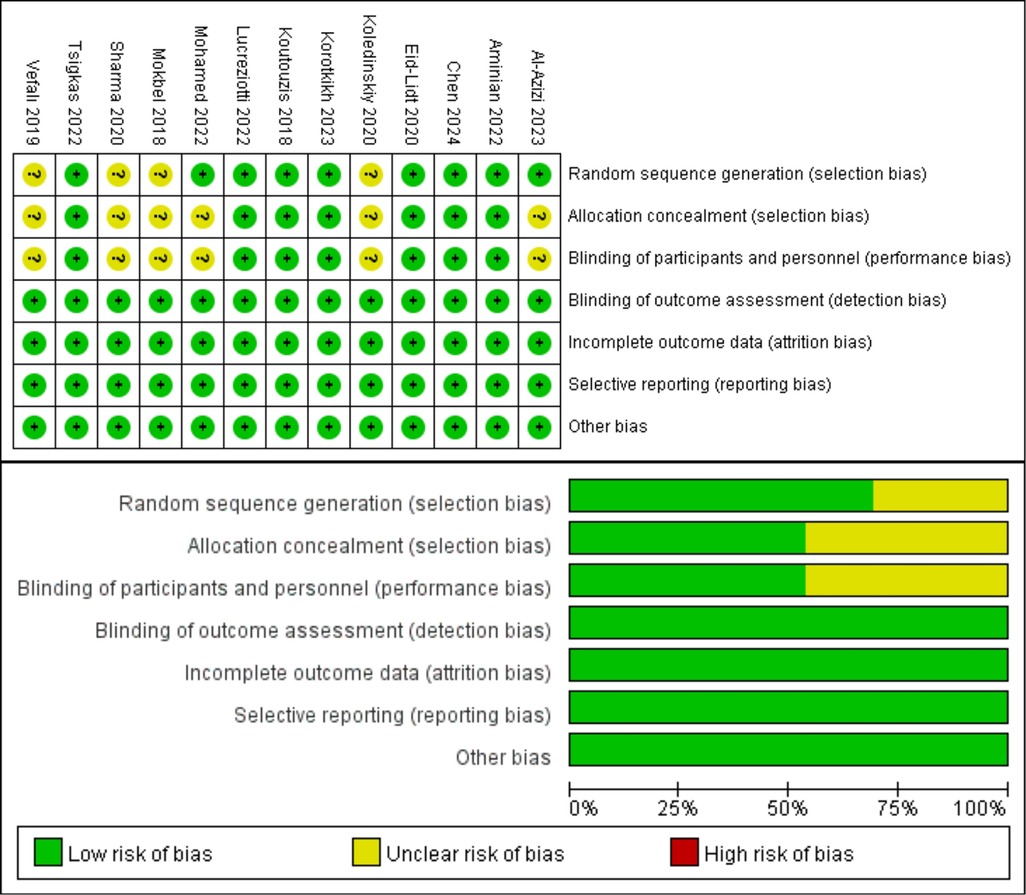
The NOS was used to evaluate the quality of the included prospective studies and retrospective studies. Among the 18 studies, 5 received a grade of 9, 8 received a rating of 8, and 5 received a rating of 7, indicating that all included studies were of good quality. Table 2 presents the specifics of the quality assessment by the NOS. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool was used to assess the quality of 13 RCTs. Seven trials utilized blinded individuals or treatments, 13 trials conducted blindfold outcome assessments, 13 trials provided comprehensive results, 13 trials did not selectively disclose data, and 13 trials exhibited no risk of additional biases. Figure 2 presents comprehensive information on the quality assessment of RCTs.
3.4 Clinical outcomes
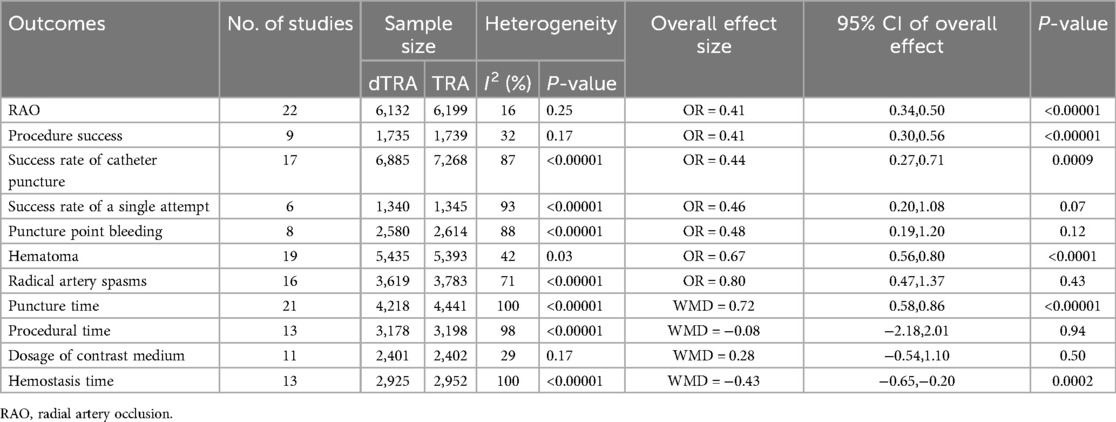
Table 3 summarizes the results of the meta-analysis for all clinical outcomes.
3.4.1 RAO
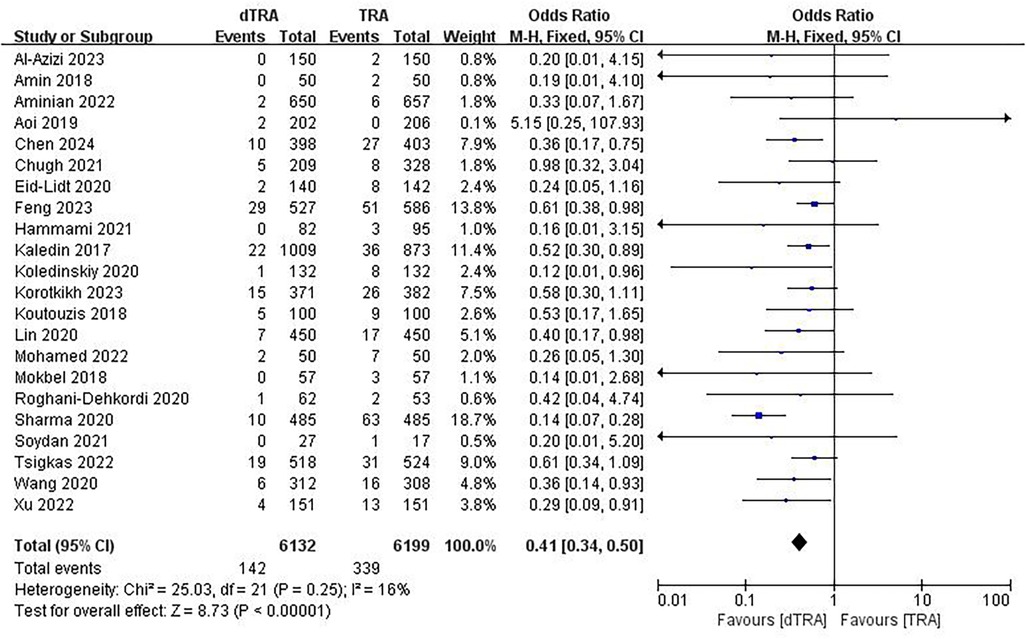
A total of 22 studies (20–26, 28, 30, 33, 34, 41, 43, 44) documented RAO. The aggregated findings indicated that dTRA reduced the occurrence of RAO compared to cTRA (OR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.34, 0.50, P < 0.00001, I2 = 16%) (Figure 3). A subgroup analysis of RAO in terms of time evaluation was performed. The subgroup analysis indicated that dTRA markedly reduced the occurrence of RAO during hospitalization (OR = 0.36, 95% CI: 0.25, 0.52, P < 0.00001, I2 = 0%) (Supplementary Figure S1) or RAO after 30 days (OR = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.37, 0.72, P < 0.00001, I2 = 15%) (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.4.2 Success rate of catheter puncture
A total of 17 studies (19, 22, 26, 29–31, 34–37, 39–41, 45, 46, 48, 49) reported on the success rate of catheter puncture. The results showed a significant difference between the two groups, with dTRA exhibiting a lower success rate of catheter puncture compared to cTRA (OR = 0.44, 95% CI: 0.27, 0.71, P = 0.0009, I2 = 87%) (Supplementary Figure S3).
3.4.3 Success rate of a single attempt
Six studies (21, 22, 25, 33, 35, 37) documented the success rate of a single attempt. No statistically significant difference was noted between the two groups in terms of the success rate of a single attempt (OR = 0.46, 95% CI: 0.20, 1.08, P = 0.07, I2 = 93%) (Supplementary Figure S4).
3.4.4 Puncture point bleeding
Eight studies (20, 22, 28–30, 32, 41, 46) reported on puncture point bleeding. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of puncture point bleeding (OR = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.19, 1.20, P = 0.12, I2 = 88%) (Supplementary Figure S5).
3.4.5 Procedure success
Nine studies (19, 21, 22, 24, 29, 35, 44, 47, 49) reported on procedure success. The aggregate findings indicated that dTRA exhibited a markedly reduced procedural success compared to cTRA (OR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.30, 0.56, P < 0.00001, I2 = 32%) (Supplementary Figure S6).
3.4.6 Hematoma
A total of 19 studies (20–22, 25, 26, 28–30, 32, 33, 34, 36, 38, 39, 41, 43, 45, 48, 49) reported on the incidence of hematoma. The difference between dTRA and cTRA was statistically significant, with dTRA exhibiting a notably reduced incidence of hematoma compared to cTRA (OR = 0.67, 95% CI: 0.56, 0.80, P < 0.0001, I2 = 42%) (Supplementary Figure S7).
3.4.7 Radial artery spasm
A total of 16 studies (20, 21, 25, 26, 32–35, 40–42, 44–46) reported on radial artery spasms. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of radial artery spasms (OR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.47, 1.37, P = 0.43, I2 = 71%) (Supplementary Figure S8).
3.4.8 Puncture time (min)
A total of 21 studies (19, 20, 22, 24–26, 29, 30, 33, 35–38, 40–45, 48, 49) reported on puncture time. The pooled results revealed that dTRA had a significantly longer puncture time than cTRA (MD = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.58, 0.86, P < 0.00001, I2 = 100%) (Supplementary Figure S9).
3.4.9 Procedural time (min)
A total of 13 studies (19, 20, 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 33, 34, 35, 46, 48, 49) reported on procedural time. The two groups did not show a statistically significant difference in procedural time (MD = −0.08, 95% CI: −2.18, 2.01, P = 0.94, I2 = 98%) (Supplementary Figure S10).
3.4.10 Dosage of contrast medium (ml)
A total of 11 studies (22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 33, 35, 40, 46, 48, 49) reported on the dosage of contrast medium. The two groups did not show a statistically significant difference in contrast medium dosage (MD = 0.28, 95% CI: −0.54, 1.10, P = 0.50, I2 = 29%) (Supplementary Figure S11).
3.4.11 Hemostasis time (h)
A total of 13 studies (26–30, 33, 35, 38, 40, 41, 46, 48, 49) reported on hemostasis time. The pooled results showed that dTRA exhibited a significantly shorter hemostasis time than cTRA (MD = −0.43, 95% CI: −0.65,−0.20, P = 0.0002, I2 = 100%) (Supplementary Figure S12).
3.5 Subgroup analysis regarding patients with ACS
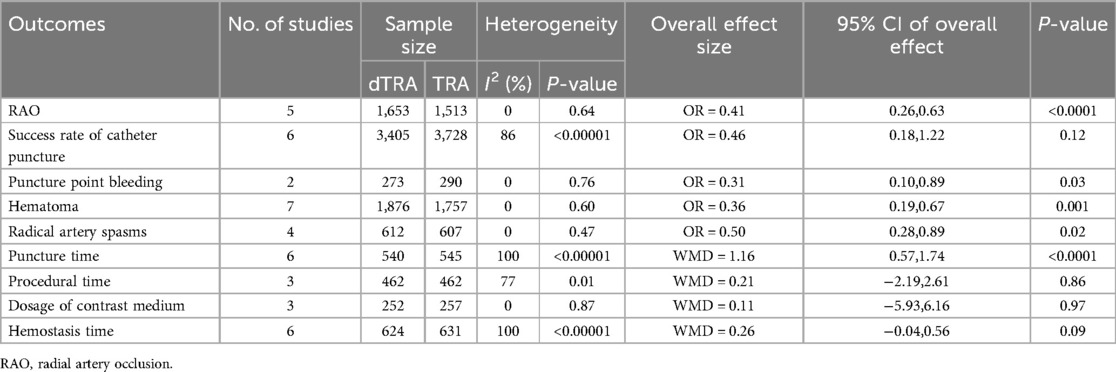
A subgroup analysis focusing on patients with ACS was performed (Table 4, Supplementary Figure S13–S21). The results showed that compared with cTRA, dTRA significantly reduced the incidence of RAO, puncture point bleeding, hematoma, and radical artery spasms but had significantly longer puncture time. There was no significant difference in the success rate of catheter puncture, procedural time, dosage of contrast medium, and hemostasis time.
3.6 Subgroup analysis regarding only RCTs
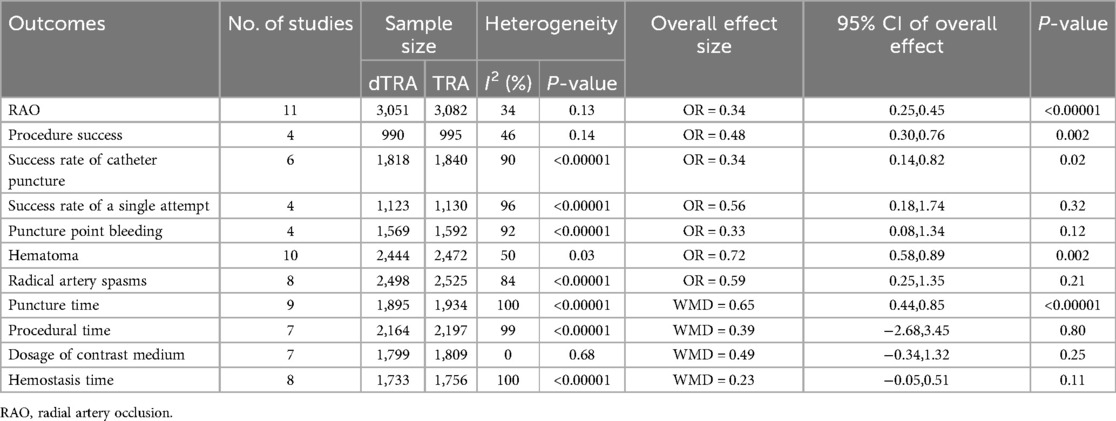
A RCT subgroup analysis was performed (Table 5, Supplementary Figure S22–S32). Compared with cTRA, dTRA significantly reduced the incidence of RAO, hematoma, and hemostasis. However, dTRA had a significantly lower procedure success rate, a lower success rate of catheter puncture, and a longer puncture time. There was no significant difference between the two approaches in terms of success rate of a single attempt, radial artery spasm, hemostasis time, puncture site bleeding, procedural time, or dosage of contrast medium.
3.7 Publication bias
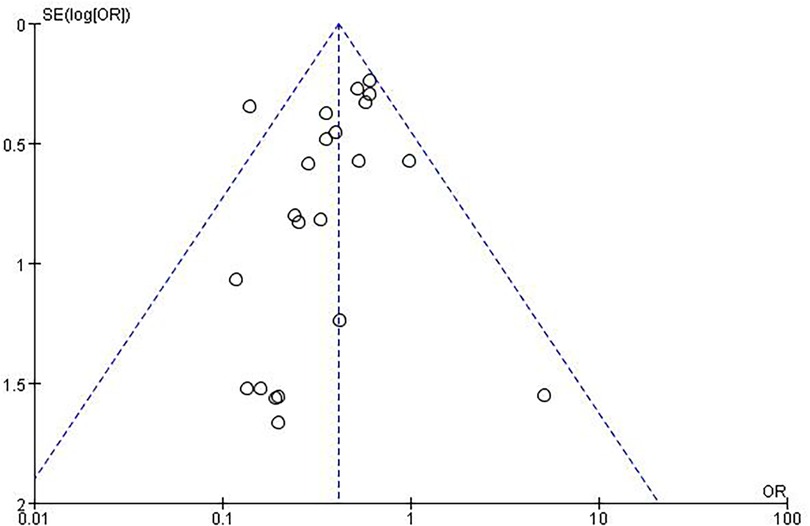
An evaluation of publication bias related to RAO was conducted using a funnel plot (Figure 4). The bilaterally symmetric funnel plot of the RAO did not reveal any significant evidence of publication bias.
4 Discussion
As TRA has a lower risk of consequences than transfemoral access, including death in patients presenting with acute coronary syndromes, it is presently the preferred access method for coronary operations (50, 51). However, TRA is not a panacea—RAO remains the “Achilles’ heel” of this method. In addition, because the hand has two sets of blood vessels coming from the palmar arch, RAO rarely shows up in the real world. However, RAO prevents the radial artery form being used for future invasive treatments or coronary artery bypass grafting. Estimates of how often it happens remain uncertain because the rates depend a lot on patient characteristics, procedural factors, anticoagulation protocols, and hemostasis techniques (52). DTRA through the anatomic snuffbox has emerged as a new method for CAG and PCI in the last few years (10). Meanwhile, several investigations have shown that recanalizing radial artery stenosis or occlusion via dTRA is both safe and practical (53–55). Moreover, no studies have reported that dTRA is associated with a higher radiation dose (56). The reduced size of the distal radial artery heightens the difficulty of puncture (55). Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of dTRA vs. cTRA for coronary diagnostic or interventional catheterization.
Our results indicated that dTRA substantially decreases the incidence of RAO compared to cTRA. Thrombosis is a significant contributor to the development of RAO, with its pathogenesis and etiology involving abnormalities in blood flow (stasis), vascular endothelial damage, and hypercoagulability (57). The smaller diameter of the radial artery, the lower amount of nitric oxide released during puncture, endothelial damage, and reduced blood flow due to sheaths and catheters, along with the increase in intimal hyperplasia and intima-media thickness due to constant intubation, contribute to the higher likelihood of RAO with cTRA (58, 59). Among these factors, endothelial damage is the most significant cause of RAO. The repeated introduction and withdrawal of catheters can easily damage the arterial intima, leading to RAO (60). While most RAO cases are asymptomatic, the condition makes it harder to use for catheterizations and as a conduit in people who need coronary artery bypass grafting or radial arteriovenous fistula formation in people with kidney dysfunction. As a result, RAO prevention and management are critical. Preinterventional visualization of the radial artery in both limbs with Doppler ultrasonography is recommended to evaluate the characteristics of the radial artery. It is particularly beneficial for selecting an artery with a larger diameter and determining the size and depth of the artery. Consequently, arterial cannulation is facilitated, diminishing the need for multiple puncture attempts. This imaging modality can assist in determining the suitable sheath size to decrease the sheath-to-artery mismatch, reducing the incidence of RAO (61). In addition, anticoagulants can also effectively prevent and treat thrombosis, thus averting the beginning of RAO (62), including novel oral anticoagulants (63). Furthermore, the lack of blood flow during hemostasis dramatically also increases the probability of RAO, as flow interruption at this stage is a key predictor of such occlusion (64). Studies have shown that interventions like patent hemostasis (65), nitroglycerin administration through the sheath before its removal (66), and ipsilateral ulnar artery compression during radial artery hemostasis (67) can reduce the incidence of postcatheterization RAO (68). In this context, dTRA may help preserve the potency of forearm radial artery during hemostatic compression or obstruction at the puncture site. Maintaining blood flow in the distal radial access is crucial to preventing proximal thrombus formation and keeping the forearm radial artery open after TRA (21). This is made easier by the collateralization of blood vessels. In the context of forearm radial artery obstruction, dTRA is preferable to cTRA.
Compared to cTRA, dTRA decreases the incidence of hematoma, as shown in this current meta-analysis. Hematoma formation is likely caused by poor compression positioning, dual antiplatelet therapy, heparin use, advanced age, delicate skin, and multiple puncture attempts. A standardized technique for compression duration and a specialized compression device may help reduce the incidence of possible bleeding issues (69, 70). Our findings indicate that dTRA can reduce hemostasis time compared to cTRA; this may suggest a decreased occurrence of hematoma in dTRA, attributable to the anatomical structure of the distal radial artery, which has a smaller diameter and is situated over a bony basis formed by the scaphoid and trapezium carpal bones (26).
Our results indicated that dTRA has a lower procedural success rate and effective catheter puncture rate compared to cTRA, which necessitates a longer puncture time. Multiple variables may contribute to their occurrence: (1) the radial artery in the AS is narrower than that at the wrist (71), complicating puncture or sheath insertion following a successful puncture; (2) the distal radial artery frequently displays tortuosity, which can readily result in the unsuccessful insertion of the guidewire and sheath into the radial artery; and (3) dTRA is a novel approach for CAG and PCI, and many operators lack expertise in puncture management and must surmount the learning curve (29). The standard ultrasound-guided approach and enhanced proficiency in the puncture technique may elevate the success rate over time and reduce the risk of puncture-induced vasospasm (44). Lee et al. (69) discovered that the puncture duration progressively stabilized after roughly 150 distal radial artery punctures. A multicenter study indicated that after treating 150 patients, the learning curve achieved an optimal average of two puncture attempts, each lasting under 30 s (72). Deora et al. indicated that, after a specific learning curve (minimum of 50 successful punctures), operational time could be further reduced with further expertise, particularly in assessing the arterial entry via the distal radial artery (73). Therefore, the learning curve varies among different operators, depending on their skills in radial artery access puncture. Mori et al. found that ultrasound-guided dTRA for CAG or PCI exhibited a reduced failure rate compared to traditional dTRA (74). Two meta-analyses (75, 76) compared ultrasound-guided puncture with a palpation-based blind puncture for traditional radial artery access, indicating that ultrasound-guided puncture yields a greater first-pass success rate, reduced puncture time, and decreased hematoma development. Furthermore, although the success rate of catheter puncture for dTRA is lower than that for cTRA (2.89% lower), the success rate remains notably high (91.93% vs. 94.82%). Based on the lower complication rate of dTRA, predominantly with a lower incidence of RAO, we preferentially recommend dTRA for interventional surgeries in coronary heart disease. The cTRA procedure may serve as an alternative in cases where dTRA is unsuccessful.
A subgroup analysis focusing on patients with ACS was performed in our study. Compared with cTRA, dTRA significantly reduced the incidence of RAO, puncture site bleeding, hematoma, and radical artery spasms but had a significantly longer puncture time (WMD = 1.16 min). Notably, there was no significant difference between the two groups in the total procedural time. In the acute environment, every minute is critical, particularly for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, and dTRA necessitates additional time for effective arterial access. Apostolos et al. have discussed the use of dTRA in patients with acute coronary syndrome (77). dTRA has been linked to expedited hemostasis, quicker patient mobilization, and a reduction in local sequelae, including substantial hematomas or compartment syndrome. Considering these factors, the prior delays from dTRA should not impede its initial application in patients with acute coronary syndrome. In addition, Desora et al. indicated that, after a specific learning curve, operational time can be further minimized with further expertise, particularly in assessing the arterial entry via the distal radial artery (73).
Although previous meta-analyses (50, 78–80) have compared dTRA and cTRA, the number of articles included in these meta-analyses was relatively low due to insufficient search strategies or shorter study durations. To our knowledge, this updated meta-analysis includes the largest number of studies comparing the outcomes of dTRA vs. cTRA for cardiovascular interventional diagnosis and/or treatment. To manage confounding variables, we performed subgroup analyses focusing on patients with ACS or RCTs. This may result in a more trustworthy judgment. The findings of our meta-analysis provided valuable perspectives on the clinical selection of interventional surgical techniques, which enhance clinical practice and research in the area of cardiovascular interventional diagnosis and/or treatment. However, we acknowledge the possible shortcomings of our study. First, a large number of the studies were not randomized controlled trials, which resulted in a relatively poor quality of evidence and credibility. Second, we could not manage confounding variables, including varying inclusion criteria, population disparities, and the level of experience of surgeons, which may lead to heterogeneity among the trials and introduce bias. Consequently, more clinical outcomes reported by prospective randomized controlled studies are essential to further validate the benefits of dTRA.
In conclusion, our results demonstrated that dTRA is a feasible and safe approach for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention. Compared with cTRA, dTRA significantly reduces postoperative complications, particularly the occurrence of RAO, and expedites the period to hemostasis.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
QY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. CL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YQ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HZ: Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. MQ: Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. YZ: Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SZ: Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. WL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. JL: Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Appropriate Healthcare Technology Development and Promotion Project of Guangxi Health Commission (S2022142), the Appropriate Healthcare Technology Development and Promotion Project of Guangxi Health Commission (S2020007), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi Health Commission (Z20211087).
Acknowledgments
Everyone who contributed significantly to this study has been listed.
Conflict of interest
The authors assert that the study was performed without any commercial or financial affiliations that may be seen as a possible conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1530995/full#supplementary-material
References
1. GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403(10440):2100–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2
2. Campeau L. Percutaneous radial artery approach for coronary angiography. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. (1989) 16(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/ccd.1810160103
3. Jolly SS, Yusuf S, Cairns J, Niemela K, Xavier D, Widimsky P, et al. Radial versus femoral access for coronary angiography and intervention in patients with acute coronary syndromes (RIVAL): a randomised, parallel group, multicentre trial. Lancet. (2011) 377(9775):1409–20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60404-2
4. Feldman DN, Swaminathan RV, Kaltenbach LA, Baklanov DV, Kim LK, Wong SC, et al. Adoption of radial access and comparison of outcomes to femoral access in percutaneous coronary intervention: an updated report from the national cardiovascular data registry (2007–2012). Circulation. (2013) 127(23):2295–306. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000536
5. Aldoori JS, Mohammed AI. Transradial approach for coronary angiography and percutaneos coronary intervention: personal experience. Egypt Heart J. (2019) 71(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s43044-019-0006-2
6. Liu P, Gao XL, Li BF, Ding XZ, Wang ZH, Dang YP, et al. Radial versus femoral artery access for percutaneous coronary angiography and intervention: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in Chinese population. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2015) 8(10):17151–66.26770309
7. Kiemeneij F, Laarman GJ. Percutaneous transradial artery approach for coronary stent implantation. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. (1993) 30(2):173–8. doi: 10.1002/ccd.1810300220
8. Brener MI, Bush A, Miller JM, Hasan RK. Influence of radial versus femoral access site on coronary angiography and intervention outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2017) 90(7):1093–104. doi: 10.1002/ccd.27043
9. Caputo RP, Tremmel JA, Rao S, Gilchrist IC, Pyne C, Pancholy S, et al. Transradial arterial access for coronary and peripheral procedures: executive summary by the transradial committee of the SCAI. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2011) 78(6):823–39. doi: 10.1002/ccd.23052
10. Kiemeneij F. Left distal transradial access in the anatomical snuffbox for coronary angiography (ldTRA) and interventions (ldTRI). EuroIntervention. (2017) 13(7):851–7. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-17-00079
11. Sinha SK, Jha MJ, Mishra V, Thakur R, Goel A, Kumar A, et al. Radial artery occlusion—incidence, predictors and long-term outcome after TRAnsradial catheterization: clinico-Doppler ultrasound-based study (RAIL-TRAC study). Acta Cardiol. (2017) 72(3):318–27. doi: 10.1080/00015385.2017.1305158
12. Kanei Y, Kwan T, Nakra NC, Liou M, Huang Y, Vales LL, et al. Transradial cardiac catheterization: a review of access site complications. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2011) 78(6):840–6. doi: 10.1002/ccd.22978
13. Babunashvili A, Dundua D. Recanalization and reuse of early occluded radial artery within 6 days after previous transradial diagnostic procedure. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2011) 77(4):530–6. doi: 10.1002/ccd.22846
14. Apostolos A, Papanikolaou A, Papageorgiou A, Moulias A, Vasilagkos G, Pappelis K, et al. Distal radial artery palpability and successful arterial access for coronary angiography: a post-hoc analysis from two randomized trials. J Vasc Access. (2024) 0:1–8. doi: 10.1177/11297298241296570
15. Hadjivassiliou A, Cardarelli-Leite L, Jalal S, Chung J, Liu D, Ho S, et al. Left distal transradial access (ldTRA): a comparative assessment of conventional and distal radial artery size. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. (2020) 43(6):850–7. doi: 10.1007/s00270-020-02485-7
16. Roh JH, Lee JH. Distal radial approach through the anatomical snuff box for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention. Korean Circ J. (2018) 48(12):1131–4. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0293
17. Guedeney P, Sorrentino S, Vogel B, Baber U, Claessen BE, Mehran R. Assessing and minimizing the risk of percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. (2018) 16(11):825–35. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2018.1526082
18. Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses (2021). Available at: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (Accessed April 05, 2024).
19. Bhambhani A, Pandey S, Nadamani AN, Tyagi K. An observational comparison of distal radial and traditional radial approaches for coronary angiography. J Saudi Heart Assoc. (2020) 32(1):17–24. doi: 10.37616/2212-5043.1004
20. Korotkikh A, Babunashvili A, Kaledin A, Akhramovich R, Derkach V, Portnov R, et al. Distal radiation access as an alternative to conventional radial access for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary interventions (according to TENDERA trial). Curr Probl Cardiol. (2023) 48(4):101546. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101546
21. Sharma AK, Razi MM, Prakash N, Sharma A, Sarraf S, Sinha S, et al. A comparative assessment of dorsal radial artery access versus classical radial artery access for percutaneous coronary angiography—a randomized control trial (DORA trial). Indian Heart J. (2020) 72(5):435–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2020.06.002
22. Chen T, Li L, Li F, Lu W, Shi G, Li W, et al. Comparison of long-term radial artery occlusion via distal vs. Conventional transradial access (CONDITION): a randomized controlled trial. BMC Med. (2024) 22(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03281-7
23. Soydan E, Kis M, Akin M. Evaluation of radial artery endothelial functions in transradial coronary angiography according to different radial access sites. Anatol J Cardiol. (2021) 25(1):42–8. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2020.59085
24. Roghani-Dehkordi F, Riazi A, Shafie D, Khosravi A, Sadeghi M, Vakhshoori M, et al. Trans-snuff box approach as a new access site for coronary angiography and angioplasty versus trans-radial approach in terms of feasibility, safety, and complications. ARYA Atheroscler. (2020) 16(6):263–8. doi: 10.22122/arya.v16i6.2018
25. Eid-Lidt G, Rivera Rodriguez A, Jimenez Castellanos J, Farjat Pasos JI, Estrada Lopez KE, Gaspar J. Distal radial artery approach to prevent radial artery occlusion trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2021) 14(4):378–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2020.10.013
26. Tsigkas G, Papageorgiou A, Moulias A, Kalogeropoulos AP, Papageorgopoulou C, Apostolos A, et al. Distal or traditional transradial access site for coronary procedures: a single-center, randomized study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2022) 15(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2021.09.037
27. Coughlan JJ, Zebrauskaite A, Arnous S, Kiernan TJ. Left distal trans-radial access facilitates earlier discharge post-coronary angiography. J Interv Cardiol. (2018) 31(6):964–8. doi: 10.1111/joic.12559
28. Al-Azizi K, Moubarak G, Dib C, Sayfo S, Szerlip M, Thomas S, et al. Distal versus proximal radial artery access for cardiac catheterization: 30-day outcomes of the DIPRA study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2023) 12(21):e030774. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.030774
29. Li F, Shi GW, Yu XL, Song RX, Xiao JQ, Huang HM, et al. Safety and efficacy of coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention via distal transradial artery access in the anatomical snuffbox: a single-centre prospective cohort study using a propensity score method. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2022) 22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02518-8
30. Lin Y, Sun X, Chen R, Liu H, Pang X, Chen J, et al. Feasibility and safety of the distal transradial artery for coronary diagnostic or interventional catheterization. J Interv Cardiol. (2020) 2020:4794838. doi: 10.1155/2020/4794838
31. Lu H, Wu D, Chen X. Comparison of distal transradial access in anatomic snuffbox versus transradial access for coronary angiography. Heart Surg Forum. (2020) 23(4):E407–10. doi: 10.1532/hsf.3041
32. Kis M, Soydan E. Preservation of radial vasomotor functions through the anatomic snuffbox: a prospective comparison with other radial accesses during coronary angiography. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. (2020) 30(11):1121–5. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2020.11.1121
33. Koutouzis M, Kontopodis E, Tassopoulos A, Tsiafoutis I, Katsanou K, Rigatou A, et al. Distal versus traditional radial approach for coronary angiography. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. (2019) 20(8):678–80. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2018.09.018
34. Wang H, Peng WJ, Liu YH, Ma GQ, Wang D, Su B, et al. A comparison of the clinical effects and safety between the distal radial artery and the classic radial artery approaches in percutaneous coronary intervention. Ann Palliat Med. (2020) 9(5):2568–74. doi: 10.21037/apm-19-479
35. Xu Y, Niu H, Yu Y, Yang L, Wang H, Zhang B, et al. The technical features of the diagnosis or treatment of coronary artery disease through the distal radial artery approach at the anatomical snuffbox compared with the conventional radial artery approach. J Cardiothorac Surg. (2022) 17(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s13019-022-01979-4
36. Feng C, Zong B, Liu Y, Chen M, Li S, Xu D, et al. Comparison of distal transradial approach versus conventional transradial approach for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention: a prospective observational study. Heliyon. (2023) 9(6):e17150. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17150
37. Lalani K, Devasia T, Paramasivam G. Can distal radial access replace conventional radial access for coronary catheterization? A study comparing puncture time, attempts, patient and operator comfort. Anatol J Cardiol. (2024) 28(9):454–60. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4363
38. Koledinskiy AG, Mikheeva YUV, Ogurtsov PP, Kurtasov DS, Vyazova NL. Hospital results of endovascular treatment of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) through distal radial access. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41(Suppl_2):ehaa946.2498. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/ehaa946.2498
39. Kaledin A, Kochanov I, Podmetin P, Seletsky S, Ardeev V. Distal radial artery in endovascular interventions. (2017).
40. Vefali V, Saricam E. The comparison of traditional radial access and novel distal radial access for cardiac catheterization. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. (2020) 21(4):496–500. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2019.07.001
41. Aoi S, Htun WW, Freeo S, Lee S, Kyaw H, Alfaro V, et al. Distal transradial artery access in the anatomical snuffbox for coronary angiography as an alternative access site for faster hemostasis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2019) 94(5):651–7. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28155
42. Chugh Y, Kanaparthy NS, Piplani S, Chugh S, Shroff A, Vidovich M, et al. Comparison of distal radial access versus standard transradial access in patients with smaller diameter radial arteries (the distal radial versus transradial access in small transradial Arteries Study: D.A.T.A—S.T.A.R study). Indian Heart J. (2021) 73(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2020.11.002
43. Amin MR, Singha CK, Banerjee SK, Hoque H, Mahabub SMEE, Hoque M, et al. Comparison of distal transradial in the anatomical snuffbox versus conventional transradial access for coronary angiography and intervention-an experience in 100 cases. University Heart J. (2018) 13(2):40–5. doi: 10.3329/uhj.v13i2.37657
44. Hammami R, Zouari F, Ben Abdessalem MA, Sassi A, Ellouze T, Bahloul A, et al. Distal radial approach versus conventional radial approach: a comparative study of feasibility and safety. Libyan J Med. (2021) 16(1):1830600. doi: 10.1080/19932820.2020.1830600
45. Gajurel RM, Sahi R, Shrestha H, Thapa S, Khanal R. Initial experience on anatomical snuff box approach for coronary angiogram & percutaneous coronary intervention in a tertiary care center Nepal. World J Cardiovasc Dis. (2018) 08(12):578–87. doi: 10.4236/wjcd.2018.812057
46. Aminian A, Sgueglia GA, Wiemer M, Kefer J, Gasparini GL, Ruzsa Z, et al. Distal versus conventional radial access for coronary angiography and intervention: the DISCO RADIAL trial. JACC Cardiovascular Interventions. (2022) 15(12):1191–201. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2022.04.032
47. Mokbel M, Sinescu C, Florescu N. P4398Snuff-box versus distal forearm for trans-radial access: performance and radial patency. Eur Heart J. (2018) 39(suppl_1):ehy563.P4398. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy563.P4398
48. Lucreziotti S, Persampieri S, Gentile D, Barbieri L, Salerno-Uriarte D, Valli F, et al. Access-site hematoma in distal and conventional transradial access: a randomized trial. Minerva Cardiol Angiol. (2022) 70(2):129–37. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5683.21.05483-9
49. Sanhoury MI, Sobhy MA, Saddaka MA, Nassar MA, Elwany MN. Distal radial approach between theory and clinical practice. Time to go distal!. Egypt Heart J. (2022) 74(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s43044-022-00243-3
50. Isath A, Elson D, Kayani W, Wang Z, Sharma S, Naidu SS, et al. A meta-analysis of traditional radial access and distal radial access in transradial access for percutaneous coronary procedures. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. (2023) 46:21–6. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2022.09.006
51. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM, Bischoff JM, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI guideline for coronary artery revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. (2022) 145(3):e18–114. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001038
52. Tsigkas G, Apostolos A, Davlouros P. Less is more, but not always: distal transradial access for radial artery occlusion prevention. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2022) 15(12):1202–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2022.05.001
53. Sheikh AR, Abdelaal E, Sastry S, Karim S, Zeb M. Novel distal left radial artery access in anatomical snuffbox for recanalization of proximal radial artery total occlusion and percutaneous coronary intervention through left internal mammary artery. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. (2018) 11(7):e006579. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.006579
54. Alkhawam H, Windish S, Abo-Salem E. Distal radial artery access among cases with radial artery occlusion for primary percutaneous intervention. Future Cardiol. (2019) 15(3):169–73. doi: 10.2217/fca-2018-0057
55. Li F, Shi GW, Zhang BF, Yu XL, Huang HM, Xiao JQ, et al. Recanalization of the occluded radial artery via distal transradial access in the anatomic snuffbox. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2021) 21(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-01890-1
56. Apostolos A, Vasilagkos G, Tsigkas G. Could radiation exposure be the Achilles’ heel of distal transradial artery access? Indian Heart J. (2022) 74(4):338–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2022.06.006
57. Roy S, Kabach M, Patel DB, Guzman LA, Jovin IS. Radial artery access complications: prevention, diagnosis and management. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. (2022) 40:163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2021.12.007
58. Zwaan EM, IJsselmuiden AJ, van Rosmalen J, van Geuns RM, Amoroso G, Moerman E, et al. Rationale and design of the ARCUS: effects of trAnsRadial perCUtaneouS coronary intervention on upper extremity function. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2016) 88(7):1036–43. doi: 10.1002/ccd.26525
59. Kotowycz MA, Dzavik V. Radial artery patency after transradial catheterization. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 5(1):127–33. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.111.965871
60. Sadaka MA, Etman W, Ahmed W, Kandil S, Eltahan S. Incidence and predictors of radial artery occlusion after transradial coronary catheterization. Egypt Heart J. (2019) 71(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s43044-019-0008-0
61. Tsigkas G, Papanikolaou A, Apostolos A, Kramvis A, Timpilis F, Latta A, et al. Preventing and managing radial artery occlusion following transradial procedures: strategies and considerations. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. (2023) 10(7):283. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10070283
62. Liang D, Lin Q, Zhu Q, Zhou X, Fang Y, Wang L, et al. Short-term postoperative use of rivaroxaban to prevent radial artery occlusion after transradial coronary procedure: the RESTORE randomized trial. Circ: Cardiovasc Interventions. (2022) 15(4):e011555. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.121.011555
63. Bates SM, Weitz JI. New anticoagulants: beyond heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin. Br J Pharmacol. (2005) 144(8):1017–28. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706153
64. Pancholy SB, Patel TM. Effect of duration of hemostatic compression on radial artery occlusion after transradial access. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 79(1):78–81. doi: 10.1002/ccd.22963
65. Pancholy S, Coppola J, Patel T, Roke-Thomas M. Prevention of radial artery occlusion-patent hemostasis evaluation trial (PROPHET study): a randomized comparison of traditional versus patency documented hemostasis after transradial catheterization. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2008) 72(3):335–40. doi: 10.1002/ccd.21639
66. Dharma S, Kedev S, Patel T, Kiemeneij F, Gilchrist IC. A novel approach to reduce radial artery occlusion after transradial catheterization: postprocedural/prehemostasis intra-arterial nitroglycerin. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2015) 85(5):818–25. doi: 10.1002/ccd.25661
67. Pancholy SB, Bernat I, Bertrand OF, Patel TM. Prevention of radial artery occlusion after transradial catheterization: the PROPHET-II randomized trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2016) 9(19):1992–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2016.07.020
68. Avdikos G, Karatasakis A, Tsoumeleas A, Lazaris E, Ziakas A, Koutouzis M. Radial artery occlusion after transradial coronary catheterization. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. (2017) 7(3):305–16. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2017.03.14
69. Lee JW, Park SW, Son JW, Ahn SG, Lee SH. Real-world experience of the left distal transradial approach for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention: a prospective observational study (LeDRA). EuroIntervention. (2018) 14(9):e995–1003. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-18-00635
70. Cai G, Huang H, Li F, Shi G, Yu X, Yu L. Distal transradial access: a review of the feasibility and safety in cardiovascular angiography and intervention. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2020) 20(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01625-8
71. Sgueglia GA, Di Giorgio A, Gaspardone A, Babunashvili A. Anatomic basis and physiological rationale of distal radial artery access for percutaneous coronary and endovascular procedures. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2018) 11(20):2113–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2018.04.045
72. Achim A, Kákonyi K, Jambrik Z, Nagy F, Tóth J, Sasi V, et al. Distal radial artery access for coronary and peripheral procedures: a multicenter experience. J Clin Med. (2021) 10(24):5974. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245974
73. Deora S, Agrawal D, Choudhary R, Kaushik A, Patel TM. Anatomical snuff box approach for percutaneous coronary interventions—current status. Indian Heart J. (2021) 73(5):539–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2021.08.007
74. Mori S, Hirano K, Yamawaki M, Kobayashi N, Sakamoto Y, Tsutsumi M, et al. A comparative analysis between ultrasound-guided and conventional distal transradial access for coronary angiography and intervention. J Interv Cardiol. (2020) 2020:7342732. doi: 10.1155/2020/7342732
75. Moussa Pacha H, Alahdab F, Al-Khadra Y, Idris A, Rabbat F, Darmoch F, et al. Ultrasound-guided versus palpation-guided radial artery catheterization in adult population: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am Heart J. (2018) 204:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2018.06.007
76. Tang L, Wang F, Li Y, Zhao L, Xi H, Guo Z, et al. Ultrasound guidance for radial artery catheterization: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. (2014) 9(11):e111527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111527
77. Apostolos A, Vasilagkos G, Tsigkas G. Distal transradial access in acute coronary syndromes: should we give the first try? JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2023) 16(2):238–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2022.12.003
78. Cao J, Cai H, Liu W, Zhu H, Cao G. Safety and effectiveness of coronary angiography or intervention through the distal radial access: a meta-analysis. J Interv Cardiol. (2021) 2021:4371744. doi: 10.1155/2021/4371744
79. Rigatelli G, Zuin M, Daggubati R, Vassilev D, Zuliani G, Nguyen T, et al. Distal snuffbox versus conventional radial artery access: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Access. (2022) 23(4):653–9. doi: 10.1177/11297298211005256
Keywords: coronary artery disease, coronary angiography, percutaneous coronary intervention, transradial access, radial artery occlusion, distal transradial access, meta-analysis
Citation: Yang Q, Wei X, Wu J, Li C, Qin Y, Zeng H, Qin M, Zou Y, Zhang S, Liang W and Li J (2025) Efficacy and safety of distal transradial access for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1530995. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1530995
Received: 19 November 2024; Accepted: 25 February 2025;
Published: 18 March 2025.
Edited by:
Aravinda Thiagalingam, Westmead Hospital, AustraliaReviewed by:
Anastasios Apostolos, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceLijian Gao, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China
Copyright: © 2025 Yang, Wei, Wu, Li, Qin, Zeng, Qin, Zou, Zhang, Liang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Li, MjAyMTAyNzAxMDc5QHN0ZG1haWwuZ3h1c3QuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
 Qinyan Yang†
Qinyan Yang† Weiming Liang
Weiming Liang Jie Li
Jie Li