
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med. , 18 February 2025
Sec. Clinical and Translational Cardiovascular Medicine
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1517323
Introduction: Sepsis, a life-threatening condition arising from an uncontrolled immune response to infection, can lead to organ dysfunction, with severe inflammation potentially causing multiple organ failures. Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction (SIMD) is a common and severe complication of sepsis, significantly increasing patient mortality. Understanding the pathogenesis of SIMD is crucial for improving treatment, and microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important regulators in this process.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Science Direct, and Embase databases up to September 2024. The search terms included [“miRNA” or “microRNA”] and [“Cardiac” or “Heart”] and [“Sepsis” or “Septic”], with the language limited to English. After initial filtering by the database search engine, Excel software was used to further screen references. Duplicate articles, those without abstracts or full texts, and review/meta-analyses or non-English articles were excluded. Finally, 106 relevant research articles were included for data extraction and analysis.
Results: The pathogenesis of SIMD is complex and involves mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and pyroptosis, dysregulation of myocardial calcium homeostasis, myocardial inhibitory factors, autonomic nervous regulation disorders, hemodynamic changes, and myocardial structural alterations. miRNAs play diverse roles in SIMD. They are involved in regulating the above-mentioned pathological processes.
Discussion: Although significant progress has been made in understanding the role of miRNAs in SIMD, there are still challenges. Some studies on the pathogenesis of SIMD have limitations such as small sample sizes and failure to account for confounding factors. Research on miRNAs also faces issues like inconsistent measurement techniques and unclear miRNA-target gene relationships. Moreover, the translation of miRNA-based research into clinical applications is hindered by problems related to miRNA stability, delivery mechanisms, off-target effects, and long-term safety. In conclusion, miRNAs play a significant role in the pathogenesis of SIMD and have potential as diagnostic biomarkers. Further research is needed to overcome existing challenges and fully exploit the potential of miRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of SIMD.
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition characterized by organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated response to infection. Severe inflammatory reactions can lead to multiple organ failures, significantly threatening human health (1–5). In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported that nearly 30 million people worldwide suffer from sepsis yearly, with a mortality rate of approximately 25%–30% (6). Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction (SIMD) is a common complication of severe sepsis, with about 50% of patients experiencing some degree of myocardial injury (7). When sepsis progresses to cardiac dysfunction, the patient mortality rate increases 3–4 times (8) to reach about 80% (9), seriously threatening the lives of patients. Although several studies have been conducted on SIMD, the pathogenesis of SIMD is complex and not yet fully understood, resulting in slow progress in its treatment and a lack of specific treatment plans. In addition, the high cost and consumption of medical resources significantly impact the quality of life of patients. Recent studies have shown that epigenetic modifications such as microRNAs (miRNAs) play a critical role in the progression (10), diagnosis, and treatment of SIMD and are considered a significant breakthrough in understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms of SIMD.
Epigenetic modifications refer to the genetic phenomenon of altering deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and chromatin structures through chemical changes that affect gene expression (11). Common epigenetic modifications include: (1) DNA methylation, changing the gene expression pattern by adding a methyl group to the DNA molecules; (2) Histone modifications that alter chromatin structure and density, such as acetylation, acylation, methylation, and ubiquitination; (3) Chromatin remodeling, including histone replacement, transfer, and rearrangement of histone; (4) Recognition and linking of histones and DNA, involving the regulation and mediation of histone and DNA binding, such as histone modification readers; and (5) Non-coding RNAs, including miRNAs and long non-coding RNAs. These epigenetic modifications interact with each other and collectively affect gene expression and cell fate. Epigenetic modifications are critical in many biological processes, such as development, cell differentiation, and disease occurrence. MiRNAs are a class of non-coding RNAs, 19–24 nucleotides in length, characterized by a “hairpin loop” structure. It is mainly involved in post-transcriptional regulation through specific binding to the 3'-Untranslated Region (3'-UTR) of the target gene. It has been reported (12) that miRNAs play a key role in maintaining physiological homeostasis, regulating growth and development, and disease progression. Many types of miRNAs regulate various pathophysiological processes in the body, especially inflammatory cardiovascular diseases, and may play an important role in SIMD. Studies have shown that miRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of SIMD, making them potential biomarkers for SIMD diagnosis and treatment. This review explores the role and mechanism of miRNAs in SIMD to clarify the potential value of miRNAs as a biomarker and diagnosis of SIMD. The review also provides a new direction for the application of miRNAs in diagnosing and treating SIMD.
We searched PubMed, Science Direct, and Embase databases for studies published from inception through September 2024. The search keywords employed were as follows: [“miRNA” or “microRNA”] and [“Cardiac” or “Heart”] and [“Sepsis” or “Septic”]. The search was as follows: ((((“miRNA”) OR (“microRNA”)) OR (“MicroRNAs"[Mesh])) AND (((“Heart”) OR (“Cardiac”)) OR (“Heart"[Mesh]))) AND (((“Sepsis”) OR (“Septic”)) OR (“ Sepsis” [Mesh])). The language was limited to English. The database search engine was used to perform the initial filtering, which identified 269 relevant articles.
Before reading the full text intensively, we used Excel software to select references that matched the topic. We excluded 46 duplicate articles, 47 without abstract or full text, and 70 review/meta-analyses or non-English articles. Finally, 106 full texts of research articles that met the inclusion criteria were included. A flow chart of the search process is shown in Figure 1.
In the mechanistic study of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis, the design data were extracted and classified using a pre-defined data extraction table, indicating the model type, miRNAs, target gene, function, and outcome measures (SIMD-related behavior and indicators of mechanism). Data were extracted by one author and reviewed by other authors. Due to the similarity of some studies, the table lists information from partially or fully representative and recently published studies to analyze the mechanisms involved in miRNAs in SIMD.
The pathogenesis of SIMD is complex. This review found that the pathogenesis of SIMD is related to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and pyroptosis, dysregulation of myocardial calcium homeostasis, myocardial inhibitory factors, disorders of autonomic nerve regulation, hemodynamics and myocardial structural changes (Figure 2).
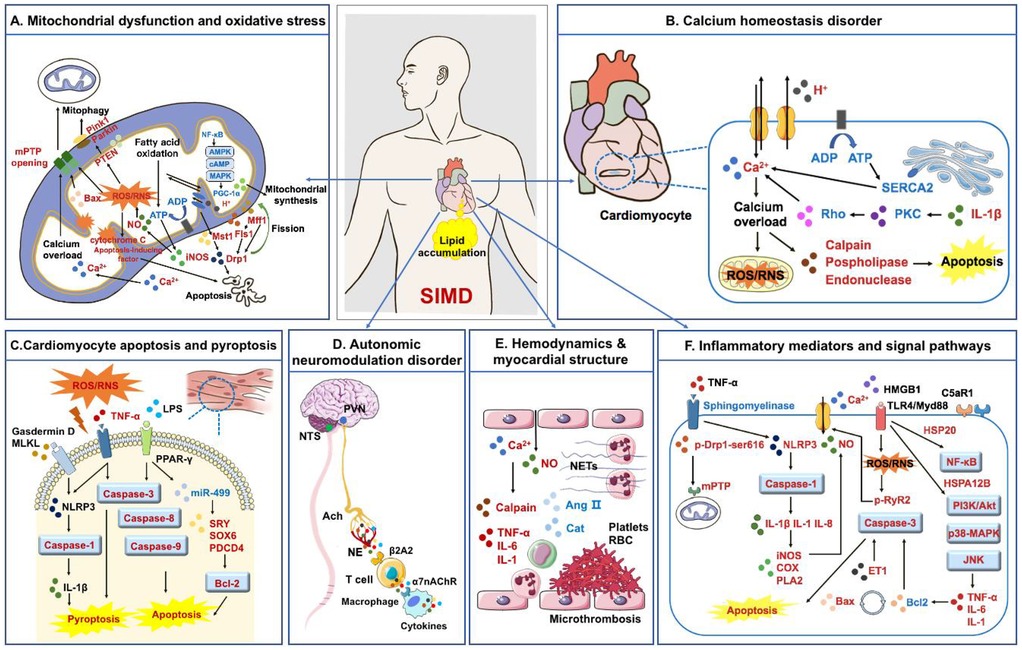
Figure 2. Pathogenesis of SIMD. (A) Mitochondrial fission and synthesis disorders, impaired mitochondrial autophagy function, and an imbalance between oxidative stress and antioxidants collectively contribute to SIMD; (B) calcium homeostasis imbalance is an important pathological process leading to oxidative stress and apoptosis of myocardial cells; (C) myocardial cell apoptosis and pyroptosis are direct factors leading to myocardial injury; (D) autonomic neuromodulation disorder is involved in the progression of SIMD; (E) hemodynamics and myocardial structural changes are specific manifestations of SIMD; (F) inflammatory cytokines and signaling pathways participate in various stages of SIMD formation. Factors in red are up-regulated in SIMD, while factors in blue are down-regulated in SIMD.
Mitochondrial fission and fusion are crucial for maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis and structural integrity. Mitochondrial fission is achieved through the coordinated action of various proteins and protein complexes, including the primary factors dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), mitochondrial fission 1 protein (Fis1), and mitochondrial fission factor (Mff) (13). Dynamin-related protein 1, a mitochondrial dynamin-related protein that can be assembled into circular oligomers through protein-protein interactions, is further recognized and located in the mitochondrial outer membrane and is involved in the contraction process of mitochondrial fission (14). Mitochondrial fission 1 protein, an outer mitochondrial membrane protein, is found at the mitochondrial constriction site and interacts with Drp1, forming a bidirectional cellular skeleton to facilitate mitochondrial fission contraction (15). Mitochondrial fission factor is a mitochondrial membrane protein that localizes to the mitochondrial constriction site and interacts with Drp1, promoting Drp1 aggregation and mitochondrial constriction. It has been observed that Mff can also form a complex with Fis1 to facilitate the first steps of mitochondrial fission (13). Mitofusins (Mfn1/2) and optic atrophy 1 (Opa1) are involved in mitochondrial inner membrane fusion that maintains normal mitochondrial morphology and promotes mitochondrial fission (15). Inflammation causes an imbalance in the mitochondrial fission and fusion of cardiomyocytes, reducing energy metabolism and cellular activity and leading to myocardial injury.
Studies have reported that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) can promote Drp1 expression in sepsis models by up-regulating Mammalian STE20-like kinase 1 (Mst1), activating mitochondrial fission, and enhancing mitochondria-related apoptotic signaling. Excessive mitochondrial division causes mitochondrial oxidative damage, decreases mitochondrial membrane potential, shifts mitochondrial pro-apoptotic factors to the cytoplasm/nuclei, impairs mitochondrial energy, and activates mitochondrial apoptosis, leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Simultaneously, excessive mitochondrial fission consumes most of the available actin, resulting in the disaggregation of the myocardial cytoskeleton, impairing myocardial cell contraction and reducing cardiac function (16, 17).
Mitochondrial synthesis in cardiomyocytes is mainly regulated by nuclear factors (18). Many transcription factors are activated in cardiomyocytes, promoting mitochondrial synthesis. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) is an important transcription factor that can promote mitochondrial synthesis and metabolism. Activation of PGC-1α can be achieved through several pathways, including cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling.
Cardiomyocytes can promote mitochondrial synthesis by increasing the rate of protein synthesis and transport, which are crucial for mitochondrial synthesis. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and the proteasome pathway are considered to be the major pathways for protein synthesis and transport. Reconstruction of the membrane structure is also necessary for mitochondrial synthesis, and cardiomyocytes can promote this process by increasing the reconstruction of mitochondrial inner membrane structure, including membrane expansion and fusion. Therefore, the main processes of mitochondrial synthesis in cardiomyocytes include transcriptional regulation, protein synthesis and transport, and membrane structure reconstruction. Sepsis can impair these processes, reduce the number and function of mitochondria in cardiomyocytes, and lead to myocardial injury. The expression of PGC-1α was significantly down-regulated in the heart tissue of septic mice, and mitochondrial biosynthesis was inhibited, leading to cardiac energy production disorders and affecting cardiac function (19, 20). The integrity of the mitochondrial membrane during the development of sepsis is damaged by the tyrosine signal transduction pathway, leading to myocardial mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, and reduced antioxidant defense (21).
Autophagy is a highly regulated cellular process through which cells degrade and recycle their own components, such as damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and other macromolecules. This process is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to various stressors, including nutrient deprivation, oxidative stress, and infection. Autophagy is mediated by the formation of autophagosomes, which engulf cellular debris, and their subsequent fusion with lysosomes, where the contents are broken down and recycled. The activation of autophagy plays a significant role in maintaining cell survival, regulating inflammation, and preventing the accumulation of toxic substances that may lead to cellular dysfunction.
Mitophagy is activated as a compensatory protective mechanism that can effectively remove damaged mitochondria, reduce damage to cardiomyocytes, and promote recovery of mitochondrial and cardiac function (22). Studies on mitophagy have shown that the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) Parkinson protein 2 (Parkin) pathway is involved in regulating mitophagy and attenuates cardiomyocyte injury, expression of inflammatory factors and cardiomyocyte injury factors (23). In sepsis, factors such as inflammation and oxidative stress cause damage to cardiac mitochondrial, activating the process of mitophagy. Mitochondrial damage leads to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells, activating the PINK1 and Parkin signaling pathways (18).
It has been reported that PINK1 can accumulate on the outer membrane of mitochondria and phosphorylate Parkin protein, activating Parkin and translocating it to the surface of damaged mitochondria. Parkin binds to multiple proteins on the outer membrane of mitochondria and induces the formation of a vesicular membrane structure in areas of mitochondrial outer membrane damage. The vesicular membrane can facilitate the fusion of mitochondria with lysosomes, ultimately forming an autophagosome. The autophagosome is a membrane structure that envelops and encloses mitochondria and eventually fuses with lysosomes for degradation. In sepsis, mitochondrial autophagy can reduce cardiomyocyte death. Studies have reported that further damage to mitochondrial autophagy function can lead to myocardial injury.
Under normal fatty acid oxidation conditions, 70% of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the myocardium is derived from fatty acid oxidation; the other part is derived from glucose oxidation (24). In the septic state, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and other inflammatory factors can down-regulate low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) expression in cardiomyocytes. At the same time, reducing LDLR and fatty acid transporter CD36 can inhibit lipid uptake in cardiomyocytes (24, 25). Sepsis inhibits intracellular fatty acid oxidation, ultimately reducing ATP production in cardiomyocytes and leading to myocardial dysfunction.
Mitochondrial oxidative stress occurs in the early stages of sepsis. When the body is infected, inflammatory cells (such as neutrophils and macrophages) can release some inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, which can further activate oxidative stress reactions and increase oxidative stress. At the same time, the hypoxic state and metabolic abnormalities during the infection process can also lead to increased mitochondrial free radical production. Oxidative stress can impair the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system and respiratory chain, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and disturbances in myocardial energy metabolism and calcium ion homeostasis imbalance. Oxidative stress can also cause the mitochondrial permeability transition, which releases proteins such as cytochrome C and apoptosis-inducing factors from the mitochondria, further inducing apoptosis of myocardial cells. In addition, oxidative stress can oxidatively damage mitochondrial DNA, down-regulating mitochondrial gene expression and synthesis of mitochondrial proteins, ultimately leading to functional and structural abnormalities of myocardial cells. Several studies have confirmed the oxidative-reductive imbalance in sepsis patients (26–30).
Tissue hypoxia inhibits the mitochondrial electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation, reduces ATP synthesis, and increases inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS) expression to produce a significant amount of nitric oxide (NO) (31). It has been reported that a considerable amount of NO can inhibit respiratory chain complexes, producing substantial ROS. Combining NO and superoxide can induce protein dysfunction, lipid peroxidation, and DNA damage. At the same time, NO competes for the oxygen binding site of cytochrome C oxidase, leading to dysfunction of the myocardial mitochondria electron transport chain, resulting in mitochondrial damage and myocardial cell energy failure (32). In addition, by reducing the response of myofibrils to calcium, NO can relax the vascular smooth muscle to alter the pre- and post-cardiac load and downregulate myocardial perfusion β receptor expression, altering adrenal hormone levels and affecting the redox function of mitochondria. Reactive oxygen species can also alter mitochondrial ultrastructure, damage mitochondrial biosynthesis, and affect mitochondrial function through oxidative modification of mitochondrial DNA and other macromolecules, promoting cell apoptosis and aggravating SIMD (33). Inhibition of cytochrome C oxidase disrupts the activity of the mitochondrial electron transport chain enzyme complex (34), so the cell cannot produce ATP through oxygenation, which eventually results in the production of substantial ROS and inhibits the oxidative phosphorylation process (35).
When mitochondrial dysfunction persists, damaged cardiomyocytes produce ROS, and ROS-mediated oxidative stress causes mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately leading to SIMD (36). When oxidative/antioxidant imbalance occurs, excessive ROS can also directly damage the membrane structure and organelles of cardiomyocytes, thereby increasing the cell membrane permeability, leading to cardiomyocyte dysfunction and even cell autolysis (37). Studies have reported that ROS/reactive nitrogen species (RNS) can cause lipid peroxidation, protein nitrification, and protein oxidation in endothelial cells, leading to abnormal adhesion of leukocytes and platelets and increasing capillary permeability. Endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) is upregulated in endothelial cells, which weakens endothelial cell-dependent vasodilation and aggravates microcirculatory disorders (38). Oxygen free radicals directly attack mitochondrial membrane proteins and nucleotides, disrupting the integrity of the mitochondrial membrane and the activity of biological enzymes, resulting in cell damage and death. Damage to the mitochondrial membrane can lead to oxidative phosphorylation disorders in the respiratory chain, impairing ATP generation and leading to disorders in energy metabolism (39). Functional proteins on the surface of mitochondria are involved in signal transduction, Ca2+ regulation and other processes to cause abnormal signal transduction and excitation-contraction coupling disorders in cardiomyocytes (40).
The production and release of a considerable amount of ROS and RNS lead to structural changes of structural proteins at the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP). The pathological opening of mPTP increases mitochondrial permeability and causes mitochondrial damage (41). Activation of downstream signaling pathways can lead to cardiomyocyte apoptosis and necrosis (42, 43). Opening of mPTP downregulates expression of the mitochondrial complex Ⅱ/V and significantly decreases ATP concentration in cardiomyocytes (44, 45), leading to mitochondrial dysfunction (46, 47). High expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax can cause mPTP to open. In contrast, the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 can inhibit the process. Regulation of Bax/Bcl-2 at mPTP opening alters mitochondrial membrane permeability, ultimately leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis (48).
When SIMD occurs, the myocardial autophagy mechanism gets activated to reduce its damage. Autophagy has a cytoprotective effect and can adapt to the pathological state of the myocardium (49). This dynamic process allows damaged cellular components, such as organelles and misfolded proteins, to be phagocytosed, packaged, and fused to lysosomes for degradation. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) can induce cardiomyocyte death by upregulating Drp1 expression and enhancing mitochondrial translocation, inhibiting the autophagy function of cardiomyocytes, and leading to irreversible damage that accelerates the development of SIMD (50). Inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress can activate the caspase-3 pathway and lead to apoptosis of cardiomyocyte (51, 52). Endotoxin can activate caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 of cardiomyocytes, which not only induces end-stage nuclear apoptosis, myofilament, and sarcomere disruption in the myocardium but also decreases the contractile response of ventricular myocytes to norepinephrine (53). While caspase-3 inhibitor application can improve endotoxin-induced myocardial systolic dysfunction (54), LPS can inhibit expression of miR-499, and increase expression of sex-determining region Y (SRY), SRY type HMG box (SOX6) and programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4). In addition, studies have reported that LPS activates the Bcl-2 family signaling pathway, resulting in increased expression of pro-apoptotic genes and decreased expression of anti-apoptotic genes. These results suggest that the miR-499-SOX6/PDCD4-Bcl2 signaling pathway is involved in the pathophysiology of SIMD (55).
Pyroptosis is distinct from apoptosis and cell necrosis. Both apoptosis and pyroptosis involve DNA breakage and destruction of the cell membrane, resulting in leakage of cell contents and complete cell death. The difference between the two is that the execution of apoptosis depends on the mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), which selectively leads to cell membrane oligomerization and plasma membrane translocation, resulting in a change in intracellular and extracellular osmotic pressure and cell rupture. However, pyroptosis depends on the Gasdermin D protein, which does not selectively destroy the cell membrane, but instead leads to the release of cell contents, cell flattening, and cell death (56, 57). The NLR Family Pyrin Domain-Containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome/caspase-1/IL-1β pathway may be involved to some extent in the occurrence of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (58). Treatment with an NLRP3 inhibitor in septic mice can significantly inhibit NLRP3-mediated inflammasome formation, caspase-1 activation, and IL-1β secretion and has been shown to be protective for the myocardium (59).
Cardiac dysfunction caused by a calcium imbalance in sepsis is related to the reduction in L-type calcium channels, inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump, abnormal ryanodine receptors, and decreased myofilaments sensitivity to calcium (60). In sepsis, microcirculation disorders associated with myocardial ischemia and hypoxia, on the one hand, directly affect the production of ATP, reduce the activity of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase 2 (SERCA2), accompanied by the decrease in phospholamban (PLB) phosphorylation, and lead to impaired function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the uptake of free calcium. On the other hand, dysfunction of the membrane pump, accumulation of intracellular acid metabolites, and increased Na+/H+ exchange can lead to the opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels in the cell membrane. A large amount of extracellular Ca2+ flows inwards. Exceeding the regulatory capacity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and calcium-binding protein results in intracellular calcium overload (61). When calcium overload occurs, a substantial amount of Ca2+ floods into cells and accumulates in mitochondria, resulting in dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory, an increase in oxygen free radicals, and lipid peroxidation damage in mitochondria and cardiomyocytes. At the same time, calpain, calcium-dependent phospholipase, calcium-dependent nucleotide endonuclease, and other digestive enzymes are activated, which can also lead to the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes (62).
It has been experimentally demonstrated that PLB mediates the transport of Ca2+ between the cytosol and the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Dephosphorylation of PLB can increase calcium pump activity and Ca2+ flux, promoting myocardial contraction. Phosphorylation of PLB can inhibit calcium pump activity and reduce the flow of Ca2+, thereby promoting myocardial relaxation (63). Excessive leakage of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and influx across the cell membrane can activate calmodulin-dependent proteins and lead to cardiomyocyte death (60).
Decreased sensitivity of cardiac myofilaments to Ca2+ prolongs myocardial contraction and ventricular density, thereby impairing the Frank-Starling effect of cardiomyocytes. The reduced calcium sensitivity may be due to the downregulation of protein kinase C (PKC) and Rho kinase expression by inflammatory factors, such as IL-1β (64). In turn, the increase in Ca2+ in immune cells of sepsis patients can promote the production of cytokines by LPS-induced monocytes/macrophages, exacerbate inflammatory responses and vascular leakage, and ultimately lead to impaired cardiac function (65).
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) can induce cardiomyocyte death by enhancing the phosphorylation level of Drp1-ser616 and mitochondrial translocation (50). In addition, TNF-α can activate sphingolipase on the surface of the cardiac membrane, inhibit Ca2+ transport in cardiomyocytes, stimulate NO production, activate proteolytic enzymes, degrade troponin and other important related proteins, and weaken cardiac systolic function (66). Activation of NLRP3 and other protein complexes results in increased release of IL-1 and IL-8, decreasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate expression in cardiomyocytes, inhibiting myocardial contractile function, and ultimately causing myocardial dysfunction (67). On the other hand, IL-1β induces transcription of NOS, cyclooxygenase, phospholipase A2, and other genes by activating the neurophospholipid pathway to cause cardiac dysfunction (68). High mobility group box-1 (HMGB1)-Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) interaction induces increased intracellular ROS levels, which enhance oxidative stress and phosphorylation of the type 2 ryanodine receptor (RyR2), resulting in Ca2+ leakage and attenuating cardiomyocyte contractility (69).
Several studies have reported that the C5a complement is involved in cardiac dysfunction in sepsis, and myocardial injury in vivo was prevented by blocking the C5a antibody. This finding demonstrates that reducing C5a receptor levels in cardiomyocytes from sepsis patients is beneficial for treatment (70). In addition, heat shock protein 72 (HSP72), heat shock protein 20 (HSP20), and heat shock protein A12B (HSPA12B) are beneficial in the management of myocardial injury in patients with sepsis. Heat shock protein 72 can reverse cardiac dysfunction in a sepsis model, and HSP20 can inhibit apoptosis by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation (44). Heat shock protein A12B can reduce leukocyte infiltration into the myocardium to improve cardiac dysfunction in sepsis by continuously activating phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3 K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling (71, 72). Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) promotes neutrophil and macrophage recruitment, endothelial cell adhesion, and blood flow blockage, resulting in myocardial injury. Meanwhile, MyD88 antagonistic mice improve cardiac function by reducing cytokine release, neutrophil infiltration, and apoptosis (73).
The main signaling pathways involved in SIMD include TLR4 nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), TLR4 c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), PI3K/AKT, and other signaling pathways. Activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) on monocytes and macrophages increases inflammatory cytokines, promoting immune response activation in the myocardium, thereby causing cardiomyocyte injury. Toll-like receptor signaling can be transmitted through different signaling pathways, such as NF-κB and MAPKs, to increase the production of inflammatory cytokines and interferon-induced genes. Its regulation may affect cardiac dysfunction in sepsis (74–78). Activation of the TLR4/JNK signaling pathway promotes increased production of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6 and then downregulates Bcl-2 expression, activates caspase-3 cleavage and activation, and promotes apoptosis (54, 79). Activation of p38-MAPK mediates LPS-induced myocardial systolic dysfunction and TNF-α release and indirectly induces IL-1 and IL-6 production, exacerbating cardiomyocyte injury (80). As a ligand, LPS directly activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by binding to the TLR4 receptor, and activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway can inhibit LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis (81). The PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in regulating inflammatory response during sepsis and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the internal environment of the body and regulating the immune response (82, 83).
In the early stages of cardiac function impairment, β1 and β2 receptors in cardiomyocytes are downregulated and desensitized, while the β3 receptor content is significantly increased. The negative inotropic effect serves to protect the cardiomyocytes. The persistent increase in β3 receptor results in a continuous negative inotropic effect resulting in myocardial inhibition, which deteriorates cardiac function (84).
Persistently elevated levels of endothelin-1 are associated with myocardial dysfunction in sepsis (85). In the rat sepsis model, long-term exposure to endothelin precursors can cause decompensated hypertrophy of ventricular myocytes, leading to increased caspase-3 activity in cardiomyocytes and, ultimately, cardiomyocyte apoptosis (86, 87).
Hypotension and hypovolemia caused by bacterial toxins and cytokines in the septic state rapidly activate the myocardial renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which maintains tissue perfusion. However, excessive secretion of angiotensin Ⅱ (AngⅡ) inevitably causes myocardial injury (88).
During the SIMD process, endotoxin can inhibit the cardiac autonomic nerve conduction pathway, induce apoptosis of neuronal and glial cells, and trigger the depolarization current of the sinoatrial node controlled by the cholinergic nerve due to the increase of plasma cytokines, resulting in the loss of heart rate variability (89–91). High concentrations of catecholamines can also decrease heart rate variability and response to endogenous catecholamines. Loss of heart rate variability indicates a high probability of progression to multi-organ failure and a poor prognosis in sepsis (92).
When sepsis occurs, factors such as inflammatory mediators and abnormal distribution of intracellular and extracellular Ca2+ lead to endothelial dysfunction of the microcirculation vessels and increased capillary permeability, decreasing the volume of microcirculation vessels (93). Overproduction of NO, decreased reactivity of angiotensin Ⅱ, catecholamines, and other vasoconstrictor factors, and inhibition of signal transduction pathways mediate decreased vascular tone, resulting in systemic hypotension and microvascular response (94). Thrombin deposition leads to microthrombi, inflammatory cell migration, and leukocyte adhesion, which increase blood viscosity and lead to microcirculation disorders. The decrease in microcirculation vessel volume, vascular tone, and microcirculation disorder in sepsis leads to reduced myocardial perfusion, affecting the uptake and utilization of oxygen by cardiomyocytes, the systolic and diastolic functions of the heart to varying degrees and ultimately leading to SIMD. At the same time, the myocardial structure is damaged after sepsis, manifested as calcium overload, increased expression of calpain-1, and enzymatic degradation of actin and myosin, inducing myocardial injury and apoptosis and leading to SIMD (95).
At present, the pathogenesis of SIMD is mainly believed to be that after the occurrence of sepsis, the increase of inflammatory reaction and oxidative stress, the disorder of mitochondrial structure and function, and the increase of myocardial cell apoptosis will affect the normal function of the heart. In this process, miRNAs participate in the occurrence and development of SIMD in various ways. As shown in Figure 3, miRNAs are involved in the occurrence, progression, and treatment of SIMD through various mechanisms, including inflammation, mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, cardiomyocyte viability, apoptosis, necroptosis, cardiomyocyte ferroptosis, and myocardial fibrosis. In Figure 3, miRNAs in red font are upregulated in SIMD, indicating that these miRNAs have harmful effects in SIMD. For example, miR-155, miR-214, and miR-874 exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the development of SIMD. Conversely, miRNAs in blue font are downregulated in SIMD, and their upregulation is generally considered beneficial for improving SIMD. For instance, miR-150–5p, miR-193-3p, and miR-194-5p are downregulated in SIMD, and upregulating these miRNAs can suppress inflammation, thereby aiding in the improvement of SIMD.
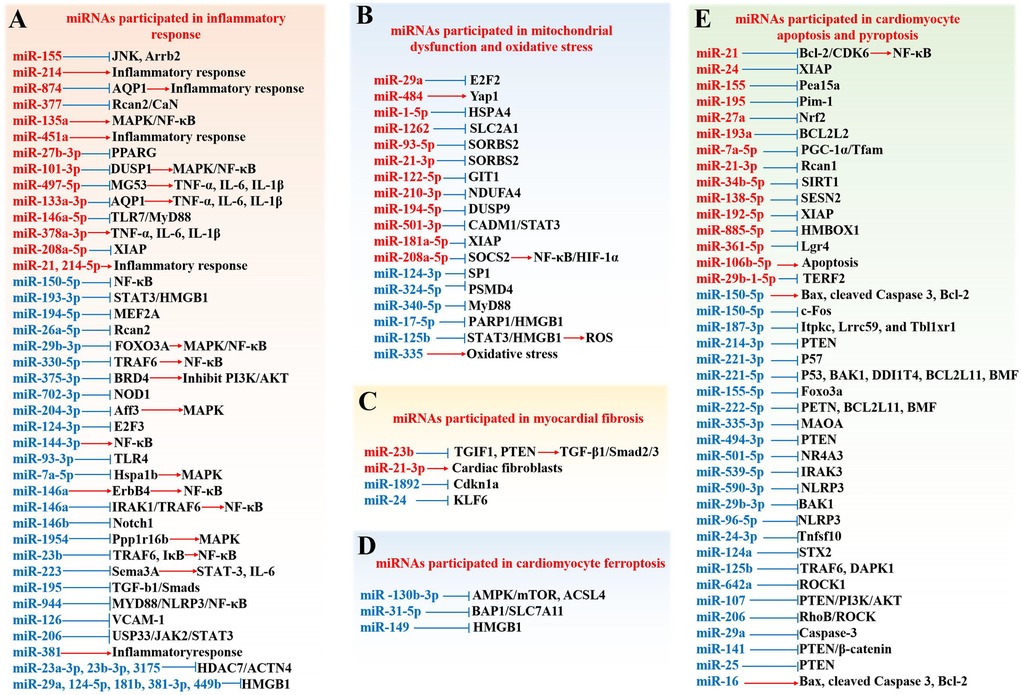
Figure 3. Role and mechanisms of miRNAs in SIMD. (A) miRNAs are involved in the inflammatory response; (B) miRNAs participate in mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress; (C) miRNAs are implicated in myocardial fibrosis (D) miRNAs are implicated in cardiomyocyte ferroptosis; E. miRNAs contribute to cardiomyocyte apoptosis and pyroptosis. Factors highlighted in red are up-regulated in SIMD, while those in blue are down-regulated.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that miRNAs regulate the inflammatory response in SIMD mainly through signaling pathways, including TLR4, MAPK, NF-κB, PI3 K/AKT, JNK, STAT3, and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)/Smads and the expression of inflammatory factors such as HMGB1, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β (Table 1). For instance, miR-93-3p can inhibit the TLR4 signaling pathway, protecting against LPS-induced cardiomyocyte inflammation and apoptosis (96). By targeting forkhead box transcription factor 3a (FOXO3A), miR-29b-3p can inhibit the activation of MAPKs and nuclear translocation of NF-κB to block LPS-activated NF-κB signaling, thereby reducing inflammatory injury (97). On the other hand, the overexpression of miR-101-3p/miR-135a can activate the MAPK/NF-κB pathway, inducing SIMD (98, 99). Furthermore, low expression of miRNAs such as miR-23a-3p (107), miR-23b (106), miR-330-5p (100), and others plays a role in the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby inducing SIMD. By targeting the Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4), miR-375-3p can activate the PI3 K/AKT pathway and alleviate SIMD in rats (108). Additionally, miR-155 can target JNK-related inflammatory signals and β-arrestin 2 (ARRB2)-mediated immunosuppression to attenuate cardiac insufficiency and improve survival in late-stage sepsis patients (109). MiR-193-3p (12) and miR-223 (110) can inhibit inflammation and relieve SIMD-related symptoms by targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway. Lastly, miR-195 can activate the TGF-β1/Smads pathway to promote cardiac remodeling and regulate the inflammatory response in septic rats (111).
These miRNAs, through their involvement in inflammation, not only contribute to the development of myocardial injury in sepsis but also play a crucial role in sepsis-induced lung injury, renal injury, intestinal damage, and brain injury. Research has shown that miR-144-3p and miR-146a-5p activate the Janus kinase (JAK)/transcription (STAT) signaling pathway (139) and promote dendritic cell activation and glycolysis (140) by targeting Caveolin-2 and autophagy-related 7 (ATG7), respectively, accelerating the occurrence of Sepsis-associated acute lung injury (SA-ALI). miR-21 (141, 142) and miR-223 (143) worsen SA-ALI by targeting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, miR-23a-3p targets the Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1)/STAT1/STAT3 signaling pathway to promote M1 polarization of macrophages (144), and miR-23b mainly targets zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) to induce vascular leakage and aggravate SA-ALI (145). MiR-21-3p promotes the progression of Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SA-AKI) by regulating the AKT/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)/forkhead box-1 (FOXO1) pathway [Lin, et al., (146)]. MiR-214-5p exacerbates SA-AKI by inhibiting the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R)/AMPK axis [Guo, et al., (147)]. MiR-214 targets KLF6 [Zhao, et al., (148)] or PTEN [Sang, et al., (149)] to regulate the AKT/mTOR pathway and participate in the pathological process of septic renal injury. Overexpression of MiR-133a-3p promotes apoptosis of septic intestinal epithelial cells by downregulating transgelin-2 (TAGLN2) (150). MiR-141 induces septic intestinal injury through the TLR4 pathway (151). Upregulation of miR-146b-5p inhibits cell proliferation and migration by targeting Cyclin D2 (Ccnd2) and plays a crucial role in the development of septic intestinal injury (152). MiR-25-5p alleviates LPS-induced inflammation, reactive oxygen species generation, and brain injury by negatively regulating the expression of TXNIP (153). Additionally, miR-146a-5p targets TLR7 to regulate innate immune responses in microglia/astrocytes and the intact brain (154).
Mitochondria are the only organelles responsible for generating ATP in body cells. Therefore, their normal function is very important for maintaining the normal pathophysiological functioning of cells, tissues and organs. Because of its continuous pumping action, the heart requires a large amount of ATP to maintain its normal contractile activity. Therefore, the mitochondria in cardiomyocytes must produce adequate energy in the form of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. In addition, mitochondria play an important role in maintaining proper cardiac function by regulating calcium homeostasis, ROS and related signal transduction in cardiomyocytes.
As shown in Table 2, miR-484 promotes mitochondrial fission by targeting Yes Associated Protein 1, thereby aggravating LPS-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation (155). MiR-324-5p can target proteasome 26S subunit non-ATPase 4 (PSMD4) and act on mitochondrial fission regulator 1 (Mtfr1) to change mitochondrial morphology and promote cardiomyocyte death (156). CircTLK1 can sponge miR-17-5p, activate the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1)/HMGB1 axis, and aggravate the oxidative damage of mitochondrial genome (mtDNA), resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in sepsis (157). Both miR-21-3p and miR-93-5p target SH3 domain-containing protein 2 (SORBS2), potentially causing mitochondrial ultrastructural damage and autophagy, leading to cardiac dysfunction in SIMD (158, 159). MiR-210-3p targets NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex 4 (NDUFA4) causing mitochondrial dysfunction and promoting the pathogenesis of SIMD (160). LPS can upregulate MiR-29a, further damaging mitochondrial function, reducing mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), generating ROS, and damaging cardiomyocytes (162). In sepsis, serum exosomes from patients with SIMD can target the transcription of glucose transporter GLUT1 (SLC2A1) in cardiomyocytes through miR-1262, inhibiting mitochondrial glycolysis rate and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis, ultimately aggravating myocardial injury (163). LPS upregulates miR-208a-5p in sepsis, which has been shown to activate the NF-κB/HIF-1α axis mediated by SOCS2, causing mitochondrial swelling and ultimately leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis (164). MiR-194-5p targets DUSP9 and is involved in oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, exacerbating sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (165). In addition, studies have shown that the lncRNA RMRP can regulate post-transcriptional function, inhibit mitochondrial damage, and attenuate cardiomyocyte apoptosis in SIMD by inhibiting miR-1-5p from targeting HSPA4 (161). lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 alleviates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by improving inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function through the inhibition of the miR-501-3p/CADM1/STAT3 axis (166).
Additionally, studies have shown that these miRNAs can regulate mitochondrial function and contribute to the progression of liver injury in sepsis. Upregulation of miR-155 exacerbates sepsis-induced liver damage by targeting nuclear factor E2-related factor (Nrf-2) and mediating oxidative stress-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction (167). In contrast, the inhibition of miR-155 attenuates sepsis-induced liver injury by enhancing the expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) and blocking the JAK/STAT pathway (168).
Oxidative stress refers to the imbalance between oxidation and antioxidation in the intracellular and extracellular environments. As a result, harmful molecules such as oxygen free radicals accumulate, causing oxidative damage. In sepsis patients, the level of oxidative stress is significantly increased due to various factors such as infection and inflammatory reactions. The effect of oxidative stress on cardiac function is multifaceted. First, oxidative stress can cause myocardial cell damage and apoptosis, ultimately leading to a decrease in normal myocardial contractile function and heart failure. Second, oxidative stress can lead to dysfunction of endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in the cardiovascular system, leading to impaired vascular contraction function and microcirculation disorder, reducing blood supply and oxygen delivery to the heart. Third, oxidative stress can activate inflammation and blood coagulation, exacerbating cardiac load and hypoxia, leading to serious consequences such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction. Therefore, oxidative stress plays an important role in sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction, and maintaining oxidant/antioxidant balance with antioxidant therapy may be an important strategy for preventing and treating SIMD (Table 3).
LPS-treated H9C2 cells inhibited the expression of miR-124-3p, upregulated specific protein 1 (SP1), and targeted histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4)/Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) to mediate oxidative stress, causing myocardial injury in septic rats (169). LPS can inhibit the expression of miR-125b, resulting in the upregulation of downstream target gene transcription 3 (STAT3) mRNA, which binds to the promoter of HMGB1, ultimately leading to the generation of ROS, which can cause autophagy and damage to the cardiomyocytes (170). In sepsis, miR-122-5p level is increased, which reduces the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px), leading to the generation of ROS and oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes. At the same time, the upregulation of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β coupled with the cleavage of caspase-3 leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis (173). Overexpression of miR-340-5p can reduce oxidative stress-induced injury in cardiomyocytes and improve cardiac dysfunction in sepsis by targeting MyD88 (171). Up-regulation of miR-335 can protect cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress and alleviate myocardial cell injury in sepsis (172). lncRNA SNHG1 shows a protective effect on cardomyocyes in sepsis by targeting miR-181a-5p/X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) axis. This activity inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, which enhances cardiomyocyte viability, and finally alleviates myocardial cell injury (174).
MiRNAs play a role in SIMD pathogenesis through affecting cardiomyocyte viability and regulating various pathways critical to cardiomyocyte survival, differentiation, and proliferation, and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis (Table 4). Studies have shown that in the rat model of SIMD, miR-21 (175), miR-106b-5p (176), miR-642a (177), and others may affect the viability of cardiomyocytes, suggesting their role in the pathological process of SIMD. MiR-141 loaded into exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can inhibit the expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), further enhance the activity of β-catenin, improve myocardial injury, and reduce inflammatory cell infiltration and apoptosis in septic mice (212). Overexpression of miR-539-5p can promote the survival and proliferation of LPS-treated H9c2 cells and inhibit apoptosis by targeting interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-3 (IRAK3) (179). MiR-221-3p, miR-221-5p, miR-155-5p, and miR-222-5p can promote the survival of cardiomyocytes by down-regulating three apoptosis-related proteins: brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated kinase 1 (BAK1), P53, and PTEN (181). Inhibition of miR-214-3p has been implicated involved in the pathogenesis of SIMD, whereas its overexpression can attenuate SIMD by inhibiting the expression of PTEN, inducing myocardial autophagy, and activating AKT/mTOR pathway (187). Downregulation of miR-16 (188), miR-150-5p (191, 192), miR-501-5p (193), and others promotes myocardial injury in sepsis by regulating apoptosis-related proteins such as Bax/Bcl-2 apoptosis family proteins and caspase-3. Upregulation of miR-21 (190), miR-24 (189), miR-7a-5p (196), and others has also been confirmed to promote apoptosis in septic cardiomyocytes. One study found that exosomes derived from sepsis patients’ blood can upregulate miR-885-5p in AC16 cells, downregulate homeobox containing 1 (HMBOX1) and increase IL-1β and IL-18, further promoting pyroptosis of AC16 cells (184). Similarly, the upregulation of miR-138-5p (185) and downregulation of miR-590-3p (186) can cause cardiomyocyte pyroptosis, leading to SIMD. MiR-96-5p targets NLRP3, leading to cardiomyocyte pyroptosis and exacerbating septic cardiomyopathy (211). Additionally, USF2 transcriptionally inhibits miR-206, activating the RhoB/ROCK pathway, which further promotes pyroptosis in septic cardiomyocytes (210).
Ferroptosis, on the other hand, is a form of regulated cell death that is distinct from apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy. It is characterized by the accumulation of lethal levels of lipid peroxides, particularly in the presence of iron, leading to cellular membrane damage and rupture. Ferroptosis is primarily driven by iron-dependent oxidative stress, where excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) oxidize polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes, resulting in lipid peroxidation. This process is tightly regulated by key enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), which normally protects cells from lipid peroxidation. When this defense mechanism is overwhelmed or inhibited, ferroptosis occurs. Unlike other forms of cell death, ferroptosis does not involve the classic apoptotic markers, but rather is marked by specific molecular pathways linked to iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation.
Ferroptosis has been reported in cardiac tissues of patients with sepsis, suggesting its potential role in myocardial injury in SIMD. Recent studies have shown that ferroptosis is involved in the development of SIMD. Resveratrol can upregulate miR-149, downregulate HMGB1, and inhibit ferroptosis pathway, thereby ameliorating LPS-induced endotoxemic cardiomyocyte injury (213). MiR-130b-3p mitigates septic cardiomyopathy by combating ferroptosis through the regulation of the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway and directly targeting ACSL4 (214). Additionally, miR-31-5p alleviates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by inhibiting the deubiquitination of SLC7A11 via targeting BAP1, thereby also counteracting ferroptosis (215).
MiRNAs also play an important role in SIMD by regulating myocardial fibrosis and ferroptosis pathway (Table 5). Studies have shown that LPS induces the upregulation of plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) in myocardial fibroblasts. In turn, PVT1 inhibits the expression of miR-24 and upregulates Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6), ultimately inducing the proliferation and migration of myocardial fibroblasts (219). MiR-21-3p is overexpressed in cardiac fibroblasts and transferred to cardiomyocytes to induce SIMD, which is associated with elevated N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide and cardiac troponin (216). MiR-23b-mediated TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling promotes the differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts by inhibiting TGF-beta induced factor homeobox 1 (TGIF1). MiR-23b also promotes the deposition of extracellular matrix by inhibiting AKT/N-Cadherin signal transduction via PTEN, leading to myocardial fibrosis (217).
At present, miRNAs are regarded as the most promising biomarkers for differentiating SIMD from other myocardial injuries, primarily due to their stable existence in the body's circulatory system. As a result, numerous researchers have endeavored to screen out miRNAs that exhibit specific changes in the serum of patients with SIMD (Table 6). Studies have demonstrated that miR—497, cardiac troponin—I antigen (cTnI), fatty acid binding protein 3 (FABP3), and glycogen phosphorylase BB (GPBB) are elevated in the plasma of children with SIMD. The combination of these clinical indicators holds high diagnostic value, which is of great significance for the early diagnosis and treatment of pediatric SIMD (220). Moreover, miR—132 and miR—223 are negatively correlated with the activities of heart—type isoenzyme (CK—MB), cTnI, TNF—α, and IL—6 in serum, indicating their combined clinical value for the early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of SIMD (221). Additionally, miR—499a—5p also shows good diagnostic and prognostic value for SIMD (222).
In comparison with other potential biomarkers for SIMD, miRNAs have their unique advantages. Traditional biomarkers like cTnI and CK—MB have relatively low sensitivity and specificity in the early stage of SIMD. In contrast, miRNAs can be detected at an earlier stage and show more specific changes, enabling more accurate diagnosis. When it comes to diagnostic/therapeutic approaches, current methods mainly rely on clinical symptoms and traditional biomarker detection for diagnosis and drug—based therapies for treatment. The use of miRNAs not only provides a new perspective for diagnosis but also holds the potential for targeted therapy, which may offer more effective treatment options in the future.
Furthermore, inhibition of miR—29c—3p expression in animal models can reduce cardiac dysfunction and inflammation caused by sepsis, indicating its potential as a reliable biomarker for the diagnosis of sepsis (223). Reducing the expression level of miR—328 can improve cardiac dysfunction and inflammation in patients with sepsis, suggesting its role as a diagnostic indicator of sepsis (224). MiR—495 and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score are good diagnostic indicators for patients with SIMD, and overexpression of miR—495 can reduce inflammation and cardiac dysfunction caused by sepsis (225). In addition, miRNAs such as miR—21—3p, miR—155, miR—135a, miR—494—3p, and miR—223 in sepsis patients and miR—223, miR—495, miR—125b, miR—146, miR—135a, miR—495, miR—214, and miR—29b—3p in sepsis mice were identified as useful diagnostic markers for SIMD (226).
Sepsis is a severe systemic inflammatory response that often results in cardiac dysfunction. Therefore, investigating the pathogenesis of SIMD, including the role of miRNAs in its development, has clinically significant value. MiRNAs have been found to play a critical role in regulating gene expression, protein synthesis, and cellular function, making their study essential for understanding the development and therapeutic targets of SIMD. In addition, as miRNAs have been shown to play a key role in signal transduction, understanding their regulatory function and biological characteristics can help develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies. By studying miRNAs expression profiles and regulatory mechanisms, new therapeutic targets can be identified, leading to the development of more precise treatment methods.
Although significant progress has been made in understanding the relationship between miRNAs and SIMD, there are still some unresolved issues. In terms of the pathogenesis of SIMD, some studies have a relatively small sample size, which may impact the reliability of the results and make it difficult to accurately reflect the overall situation. For example, when investigating the relationship between mitochondrial function and SIMD, some in vitro experiments may not fully simulate the complex in vivo physiological environment, leading to results that may deviate from actual conditions. Additionally, in the design of certain experiments, some studies have not adequately accounted for confounding factors, which significantly undermines the accuracy of their conclusions. Similarly, research on the involvement of miRNAs in SIMD also faces related limitations. There are differences in the techniques and methods used to measure miRNA expression levels across studies, which may result in inconsistencies in the findings. Moreover, some studies lack sufficient validation experiments when investigating miRNA target genes, making the relationship between miRNAs and their target genes unclear. For example, with regard to miR-132, different studies report varying effects on cardiac function. Our analysis suggests that these discrepancies may be due to differences in experimental models, the timing of measurements, or variations in the study populations. By analyzing these conflicting pieces of evidence, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the role of miRNAs in SIMD, providing valuable insights for future research.
Moreover, although miRNAs demonstrate immense potential as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for SIMD, several challenges remain in the translational process from basic research to clinical application, particularly in key areas such as stability, delivery mechanisms, off-target effects, and long-term safety. The stability of miRNAs in vivo is one of the critical factors affecting their clinical applicability. The presence of abundant ribonucleases in the blood can rapidly degrade miRNAs, resulting in a relatively short half-life in the circulatory system. For instance, some miRNAs may be degraded within hours in serum or plasma samples, making accurate detection and utilization of miRNAs difficult. Furthermore, individual variations in the internal environment, such as pH and enzyme activity, can influence the stability of miRNAs, thereby interfering with the consistency of miRNA-based diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic outcomes. Effective delivery of miRNAs represents another key challenge in clinical translation. As nucleic acid molecules, miRNAs have difficulty crossing cell membranes to reach target cells and exert their effects. Commonly used delivery methods include liposomes, viral vectors, and nanoparticles. While liposomes offer good biocompatibility, they suffer from low encapsulation efficiency and susceptibility to clearance by the reticuloendothelial system. Viral vectors, although highly efficient for transfection, may provoke immune responses, posing safety risks. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems face challenges such as complex preparation processes and unclear potential toxicity. For example, while certain nanoparticle-based delivery systems can effectively deliver miRNAs in animal experiments, they may cause unknown long-term toxicity in human applications due to nanoparticle accumulation in the body. MiRNAs typically exert their effects by complementary binding to target genes, but they may also bind to unintended target genes, leading to off-target effects. Such effects can trigger a series of adverse consequences, such as disrupting the physiological functions of normal cells and causing dysfunction in other organ systems. Taking miRNA-based treatment for SIMD as an example, if miRNAs off-target bind to genes unrelated to cardiac function, it could affect the normal expression of these genes, thereby adversely impacting organs such as the liver and kidneys. While bioinformatic predictions and experimental validation methods can reduce the risk of off-target effects to some extent, completely avoiding these effects remains an urgent challenge. Long-term safety of miRNA therapies is an important factor that must be considered in clinical applications. As miRNAs participate in various intracellular regulatory processes, prolonged modulation of miRNA expression could have unforeseen consequences on the body. For instance, sustained inhibition or overexpression of a particular miRNA might lead to metabolic disorders, immune dysfunction, and other issues. Currently, most studies on miRNA-based therapies are still in animal or early clinical trial stages, with a lack of long-term follow-up data to assess their prolonged impact on human health. This limits the widespread clinical application of miRNA therapies.
In summary, the pathogenesis of SIMD is complex, involving several factors, including mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and pyroptosis, dysregulation of myocardial calcium homeostasis, myocardial inhibitory factors, autonomic nervous regulation disorders, hemodynamic changes, and alterations in myocardial structure. MiRNAs play significant roles in the progression of SIMD by regulating mitochondrial function and oxidative stress levels, myocardial cell vitality, apoptosis and pyroptosis, inflammatory reactions, myocardial fibrosis, and myocardial cell ferroptosis. Certain miRNAs have strong potential for clinical applications as early indicators for the diagnosis of sepsis-related cardiac dysfunction. Furthermore, many of the miRNAs that target SIMD are also involved in the development and treatment of other sepsis-associated injuries in various organs, such as lung, kidney, intestines, liver and brain.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
ZL: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. NL: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition. YC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China No.2019YFC1712200-2019YFC1712204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No.82305370), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No.2022M721536).
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review, as well as MJEditor (https://www.mjeditor.com) for providing English editing services during the preparation of this manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Tracey KJ, Fong Y, Hesse DG, Manogue KR, Lee AT, Kuo GC, et al. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. (1987) 330(6149):662–4. doi: 10.1038/330662a0
2. Nathan C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature. (2002) 420(6917):846–52. doi: 10.1038/nature01320
3. Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat Med. (2003) 9(5):517–24. doi: 10.1038/nm0503-517
4. Ulloa L, Tracey KJ. The “cytokine profile": a code for sepsis. Trends Mol Med. (2005) 11(2):56–63. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.12.007
5. Ulloa L, Brunner M, Ramos L, Deitch EA. Scientific and clinical challenges in sepsis. Curr Pharm Des. (2009) 15(16):1918–35. doi: 10.2174/138161209788453248
6. Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 193(3):259–72. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC
7. Romero-Bermejo FJ, Ruiz-Bailen M, Gil-Cebrian J, Huertos-Ranchal MJ. Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Curr Cardiol Rev. (2011) 7(3):163–83. doi: 10.2174/157340311798220494
8. Merx MW, Weber C. Sepsis and the heart. Circulation. (2007) 116(7):793–802. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.678359
9. Flierl MA, Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Sarma JV, Ward PA. Molecular events in the cardiomyopathy of sepsis. Mol Med. (2008) 14(5-6):327–36. doi: 10.2119/2007-00130.Flierl
10. Wang Y, Xu M, Yue P, Zhang D, Tong J, Li Y. Novel insights into the potential mechanisms of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification on sepsis-induced cardiovascular dysfunction: an update summary on direct and indirect evidences. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:772921. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.772921
11. Tammen SA, Friso S, Choi SW. Epigenetics: the link between nature and nurture. Mol Aspects Med. (2013) 34(4):753–64. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.018
12. Pan J, Alexan B, Dennis D, Bettina C, Christoph L, Tang Y. microRNA-193-3p attenuates myocardial injury of mice with sepsis via STAT3/HMGB1 axis. J Transl Med. (2021) 19(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03022-x
13. Chang X, Li Y, Cai C, Wu F, He J, Zhang Y, et al. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as molecular targets in diabetic heart. Metab Clin Exp. (2022) 137:155313. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155313
14. Chang X, Li Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Guan X, Wu Q, et al. ß-tubulin contributes to tongyang huoxue decoction-induced protection against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury of sinoatrial node cells through SIRT1-mediated regulation of mitochondrial quality surveillance. Phytomedicine. (2023) 108:154502. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154502
15. Wang S, Zhu H, Li R, Mui D, Toan S, Chang X, et al. DNA-PKcs interacts with and phosphorylates Fis1 to induce mitochondrial fragmentation in tubular cells during acute kidney injury. Sci Signal. (2022) 15(725):eabh1121. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abh1121
16. Shang X, Li J, Yu R, Zhu P, Zhang Y, Xu J, et al. Sepsis-related myocardial injury is associated with Mst1 upregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction and the Drp1/F-actin signaling pathway. J Mol Histol. (2019) 50(2):91–103. doi: 10.1007/s10735-018-09809-5
17. Tan Y, Ouyang H, Xiao X, Zhong J, Dong M. Irisin ameliorates septic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting DRP1-related mitochondrial fission and normalizing the JNK-LATS2 signaling pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones. (2019) 24(3):595–608. doi: 10.1007/s12192-019-00992-2
18. Chang X, Toan S, Li R, Zhou H. Therapeutic strategies in ischemic cardiomyopathy: focus on mitochondrial quality surveillance. EBioMedicine. (2022) 84:104260. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104260
19. Schilling J, Lai L, Sambandam N, Dey CE, Leone TC, Kelly DP. Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory signaling reprograms cardiac energy metabolism by repressing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1 signaling. Circ Heart Fail. (2011) 4(4):474–82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.110.959833
20. Smeding L, Leong-Poi H, Hu P, Shan Y, Haitsma JJ, Horvath E, et al. Salutary effect of resveratrol on sepsis-induced myocardial depression. Crit Care Med. (2012) 40(6):1896–907. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31824e1370
21. Rademann P, Weidinger A, Drechsler S, Meszaros A, Zipperle J, Jafarmadar M, et al. Mitochondria-Targeted antioxidants SkQ1 and MitoTEMPO failed to exert a long-term beneficial effect in murine polymicrobial sepsis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:6412682. doi: 10.1155/2017/6412682
22. Piquereau J, Godin R, Deschênes S, Bessi VL, Mofarrahi M, Hussain SN, et al. Protective role of PARK2/parkin in sepsis-induced cardiac contractile and mitochondrial dysfunction. Autophagy. (2013) 9(11):1837–51. doi: 10.4161/auto.26502
23. Li J, Shi W, Zhang J, Ren L. To explore the protective mechanism of PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1)/parkin mitophagy-mediated extract of periplaneta Americana on lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:1383–91. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912980
24. Drosatos K, Lymperopoulos A, Kennel PJ, Pollak N, Schulze PC, Goldberg IJ. Pathophysiology of sepsis-related cardiac dysfunction: driven by inflammation, energy mismanagement, or both. Curr Heart Fail Rep. (2015) 12(2):130–40. doi: 10.1007/s11897-014-0247-z
25. Jia L, Takahashi M, Morimoto H, Takahashi S, Izawa A, Ise H, et al. Changes in cardiac lipid metabolism during sepsis: the essential role of very low-density lipoprotein receptors. Cardiovasc Res. (2006) 69(2):545–55. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.11.014
26. Takeda K, Shimada Y, Amano M, Sakai T, Okada T, Yoshiya I. Plasma lipid peroxides and alpha-tocopherol in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. (1984) 12(11):957–9. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198411000-00007
27. Goode HF, Cowley HC, Walker BE, Howdle PD, Webster NR. Decreased antioxidant status and increased lipid peroxidation in patients with septic shock and secondary organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med. (1995) 23(4):646–51. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199504000-00011
28. Cowley HC, Bacon PJ, Goode HF, Webster NR, Jones JG, Menon DK. Plasma antioxidant potential in severe sepsis: a comparison of survivors and nonsurvivors. Crit Care Med. (1996) 24(7):1179–83. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199607000-00019
29. Chuang CC, Shiesh SC, Chi CH, Tu YF, Hor LI, Shieh CC, et al. Serum total antioxidant capacity reflects severity of illness in patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care. (2006) 10(1):R36. doi: 10.1186/cc4826
30. Karapetsa M, Pitsika M, Goutzourelas N, Stagos D, Tousia Becker A, Zakynthinos E. Oxidative status in ICU patients with septic shock. Food Chem Toxicol. (2013) 61:106–11. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.03.026
31. van de Sandt AM, Windler R, Gödecke A, Ohlig J, Zander S, Reinartz M, et al. Endothelial NOS (NOS3) impairs myocardial function in developing sepsis. Basic Res Cardiol. (2013) 108(2):330. doi: 10.1007/s00395-013-0330-8
32. Lupp C, Baasner S, Ince C, Nocken F, Stover JF, Westphal M. Differentiated control of deranged nitric oxide metabolism: a therapeutic option in sepsis. Crit Care. (2013) 17(3):311. doi: 10.1186/cc12538
33. Tsolaki V, Makris D, Mantzarlis K, Zakynthinos E. Sepsis-Induced cardiomyopathy: oxidative implications in the initiation and resolution of the damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:7393525. doi: 10.1155/2017/7393525
34. Levy RJ, Deutschman CS. Cytochrome c oxidase dysfunction in sepsis. Crit Care Med. (2007) 35(9 Suppl):S468–75. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000278604.93569.27
35. Levy RJ, Vijayasarathy C, Raj NR, Avadhani NG, Deutschman CS. Competitive and noncompetitive inhibition of myocardial cytochrome C oxidase in sepsis. Shock. (2004) 21(2):110–4. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000108400.56565.ab
36. Galley HF. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis. Br J Anaesth. (2011) 107(1):57–64. doi: 10.1093/bja/aer093
37. Celes MR, Torres-Dueñas D, Malvestio LM, Blefari V, Campos EC, Ramos SG, et al. Disruption of sarcolemmal dystrophin and beta-dystroglycan may be a potential mechanism for myocardial dysfunction in severe sepsis. Lab Invest. (2010) 90(4):531–42. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.3
38. Huet O, Dupic L, Harrois A, Duranteau J. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction during sepsis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2011) 16(5):1986–95. doi: 10.2741/3835
39. Crouser ED. Mitochondrial dysfunction in septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Mitochondrion. (2004) 4(5-6):729–41. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2004.07.023
40. Giroir BP, Stromberg D. Myocardial depression versus myocardial destruction: integrating the multiple mechanisms of myocardial dysfunction during sepsis. Crit Care Med. (2000) 28(8):3111–2. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200008000-00088
41. Gonzalez AS, Elguero ME, Finocchietto P, Holod S, Romorini L, Miriuka SG, et al. Abnormal mitochondrial fusion-fission balance contributes to the progression of experimental sepsis. Free Radic Res. (2014) 48(7):769–83. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.906592
42. Xu Y, Ma HB, Fang YL, Zhang ZR, Shao J, Hong M, et al. Cisplatin-induced necroptosis in TNFα dependent and independent pathways. Cell Signal. (2017) 31:112–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.01.004
43. Li X, Chen M, Yang Z, Wang W, Lin H, Xu S. Selenoprotein S silencing triggers mouse hepatoma cells apoptosis and necrosis involving in intracellular calcium imbalance and ROS-mPTP-ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. (2018) 1862(10):2113–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.07.005
44. Chen HW, Hsu C, Lu TS, Wang SJ, Yang RC. Heat shock pretreatment prevents cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction during sepsis. Shock. (2003) 20(3):274–9. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200309000-00013
45. Bugger H, Abel ED. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. (2014) 57(4):660–71. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3171-6
46. Cimolai MC, Alvarez S, Bode C, Bugger H. Mitochondrial mechanisms in septic cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2015) 16(8):17763–78. doi: 10.3390/ijms160817763
47. Neri M, Riezzo I, Pomara C, Schiavone S, Turillazzi E. Oxidative-nitrosative stress and myocardial dysfunctions in sepsis: evidence from the literature and postmortem observations. Mediators Inflamm. (2016) 2016:3423450. doi: 10.1155/2016/3423450
48. Yao X, Carlson D, Sun Y, Ma L, Wolf SE, Minei JP, et al. Mitochondrial ROS induces cardiac inflammation via a pathway through mtDNA damage in a pneumonia-related sepsis model. PLoS One. (2015) 10(10):e0139416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139416
49. Mm WC, Long Y, Wang H, Mm WH, Zhang J, Cui N. Role of the mTOR signalling pathway in human sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Can J Cardiol. (2019) 35(7):875–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2019.03.022
50. Shen YL, Shi YZ, Chen GG, Wang LL, Zheng MZ, Jin HF, et al. TNF-α induces Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation during inflammatory cardiomyocyte injury. Int J Mol Med. (2018) 41(4):2317–27. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3385
51. Kumar A, Kumar A, Michael P, Brabant D, Parissenti AM, Ramana CV, et al. Human serum from patients with septic shock activates transcription factors STAT1, IRF1, and NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis in human cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280(52):42619–26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508416200
52. Neviere R, Hassoun SM, Decoster B, Bouazza Y, Montaigne D, Maréchal X, et al. Caspase-dependent protein phosphatase 2A activation contributes to endotoxin-induced cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction. Crit Care Med. (2010) 38(10):2031–6. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181eedafb
53. Gupta S, Lee CM, Wang JF, Parodo J, Jia SH, Hu J, et al. Heat-shock protein-90 prolongs septic neutrophil survival by protecting c-src kinase and caspase-8 from proteasomal degradation. J Leukoc Biol. (2018) 103(5):933–44. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4A0816-354R
54. Wang Y, Wang Y, Yang D, Yu X, Li H, Lv X, et al. β₁-adrenoceptor stimulation promotes LPS-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through activating PKA and enhancing CaMKII and IκBα phosphorylation. Crit Care. (2015) 19(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0820-1
55. Jia Z, Wang J, Shi Q, Liu S, Wang W, Tian Y, et al. SOX6 and PDCD4 enhance cardiomyocyte apoptosis through LPS-induced miR-499 inhibition. Apoptosis. (2016) 21(2):174–83. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1201-6
56. Chen X, He WT, Hu L, Li J, Fang Y, Wang X, et al. Pyroptosis is driven by non-selective gasdermin-D pore and its morphology is different from MLKL channel-mediated necroptosis. Cell Res. (2016) 26(9):1007–20. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.100
57. Zhang J, Yang Y, He W, Sun L. Necrosome core machinery: mLKL. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2016) 73(11-12):2153–63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2190-5
58. Zhang B, Liu Y, Sui YB, Cai HQ, Liu WX, Zhu M, et al. Cortistatin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts during sepsis. J Card Fail. (2015) 21(5):426–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2015.01.002
59. Zhang W, Xu X, Kao R, Mele T, Kvietys P, Martin CM, et al. Cardiac fibroblasts contribute to myocardial dysfunction in mice with sepsis: the role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. PLoS One. (2014) 9(9):e107639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107639
60. Hobai IA, Edgecomb J, LaBarge K, Colucci WS. Dysregulation of intracellular calcium transporters in animal models of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Shock. (2015) 43(1):3–15. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000261
61. Rudiger A, Singer M. Mechanisms of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. (2007) 35(6):1599–608. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000266683.64081.02
62. Smith MA, Schnellmann RG. Calpains, mitochondria, and apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 96(1):32–7. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs163
63. Durand A, Duburcq T, Dekeyser T, Neviere R, Howsam M, Favory R, et al. Involvement of mitochondrial disorders in septic cardiomyopathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:4076348. doi: 10.1155/2017/4076348
64. Liang JL, Yang GM, Li T, Liu LM. Effects of interleukin-1β on vascular reactivity after lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock in rabbits and its relationship with PKC and rho kinase. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2013) 62(1):84–9. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182927ea4
65. Collage RD, Howell GM, Zhang X, Stripay JL, Lee JS, Angus DC, et al. Calcium supplementation during sepsis exacerbates organ failure and mortality via calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase signaling. Crit Care Med. (2013) 41(11):e352–60. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31828cf436
66. Kurt AN, Aygun AD, Godekmerdan A, Kurt A, Dogan Y, Yilmaz E. Serum IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha levels in early diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. (2007) 2007:31397. doi: 10.1155/2007/31397
67. Zhang W, Tao A, Lan T, Cepinskas G, Kao R, Martin CM, et al. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-3 improves myocardial function in mice with sepsis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cardiac fibroblasts. Basic Res Cardiol. (2017) 112(2):16. doi: 10.1007/s00395-017-0603-8
68. Finkel MS, Oddis CV, Jacob TD, Watkins SC, Hattler BG, Simmons RL. Negative inotropic effects of cytokines on the heart mediated by nitric oxide. Science. (1992) 257(5068):387–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1631560
69. Zhang C, Mo M, Ding W, Liu W, Yan D, Deng J, et al. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) impaired cardiac excitation-contraction coupling by enhancing the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) ca(2+) leak through TLR4-ROS signaling in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 74:260–73. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.06.003
70. Niederbichler AD, Hoesel LM, Westfall MV, Gao H, Ipaktchi KR, Sun L, et al. An essential role for complement C5a in the pathogenesis of septic cardiac dysfunction. J Exp Med. (2006) 203(1):53–61. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051207
71. Wang X, Zingarelli B, O'Connor M, Zhang P, Adeyemo A, Kranias EG, et al. Overexpression of Hsp20 prevents endotoxin-induced myocardial dysfunction and apoptosis via inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2009) 47(3):382–90. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.05.016
72. Zhou H, Qian J, Li C, Li J, Zhang X, Ding Z, et al. Attenuation of cardiac dysfunction by HSPA12B in endotoxin-induced sepsis in mice through a PI3K-dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc Res. (2011) 89(1):109–18. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq268
73. Ouyang MZ, Zhou D, Zhu Y, Zhang M, Li L. The inhibition of MyD88 and TRIF signaling serve equivalent roles in attenuating myocardial deterioration due to acute severe inflammation. Int J Mol Med. (2018) 41(1):399–408. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3239
74. Hoebe K, Jiang Z, Georgel P, Tabeta K, Janssen E, Du X, et al. TLR signaling pathways: opportunities for activation and blockade in pursuit of therapy. Curr Pharm Des. (2006) 12(32):4123–34. doi: 10.2174/138161206778743466
75. Feng Y, Zou L, Chen C, Li D, Chao W. Role of cardiac- and myeloid-MyD88 signaling in endotoxin shock: a study with tissue-specific deletion models. Anesthesiology. (2014) 121(6):1258–69. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000398
76. Zhang M, Zou L, Feng Y, Chen YJ, Zhou Q, Ichinose F, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is essential to preserving cardiac function and survival in low-grade polymicrobial sepsis. Anesthesiology. (2014) 121(6):1270–80. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000337
77. Echem C, Bomfim GF, Ceravolo GS, Oliveira MA, Santos-Eichler RA, Bechara LR, et al. Anti-toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) therapy diminishes cardiac remodeling regardless of changes in blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Int J Cardiol. (2015) 187:243–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.03.190
78. Zhang J, Zhao P, Quan N, Wang L, Chen X, Cates C, et al. The endotoxemia cardiac dysfunction is attenuated by AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway regulating autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 492(3):520–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.034
79. Haudek SB, Taffet GE, Schneider MD, Mann DL. TNF provokes cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac remodeling through activation of multiple cell death pathways. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117(9):2692–701. doi: 10.1172/JCI29134
80. Wang M, Sankula R, Tsai BM, Meldrum KK, Turrentine M, March KL, et al. P38 MAPK mediates myocardial proinflammatory cytokine production and endotoxin-induced contractile suppression. Shock. (2004) 21(2):170–4. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000110623.20647.aa
81. Peairs A, Dai R, Gan L, Shimp S, Rylander MN, Li L, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates inflammation in MRL/lpr mouse mesangial cells. Cell Mol Immunol. (2010) 7(2):123–32. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.1
82. Chiou YS, Huang Q, Ho CT, Wang YJ, Pan MH. Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 94:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.02.010
83. Li M, Ye J, Zhao G, Hong G, Hu X, Cao K, et al. Gas6 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α expression and apoptosis in H9C2 cells through NF-κB and MAPK inhibition via the axl/PI3K/akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 44(3):982–94. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4275
84. Moniotte S, Belge C, Sekkali B, Massion PB, Rozec B, Dessy C, et al. Sepsis is associated with an upregulation of functional beta3 adrenoceptors in the myocardium. Eur J Heart Fail. (2007) 9(12):1163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.10.006
85. Chopra M, Sharma AC. Distinct cardiodynamic and molecular characteristics during early and late stages of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Life Sci. (2007) 81(4):306–16. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.05.021
86. Smeding L, Plötz FB, Groeneveld AB, Kneyber MC. Structural changes of the heart during severe sepsis or septic shock. Shock. (2012) 37(5):449–56. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31824c3238
87. Kong W, Kang K, Gao Y, Liu H, Meng X, Yang S, et al. Dexmedetomidine alleviates LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in mice. Am J Transl Res. (2017) 9(11):5040–7.29218102
88. Zink W, Kaess M, Hofer S, Plachky J, Zausig YA, Sinner B, et al. Alterations in intracellular Ca2+-homeostasis of skeletal muscle fibers during sepsis. Crit Care Med. (2008) 36(5):1559–63. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318170aa97
89. Sharshar T, Gray F, de la Grandmaison GL, Hopkinson NS, Ross E, Dorandeu A, et al. Apoptosis of neurons in cardiovascular autonomic centres triggered by inducible nitric oxide synthase after death from septic shock. Lancet. (2003) 362(9398):1799–805. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14899-4
90. Zorn-Pauly K, Pelzmann B, Lang P, Mächler H, Schmidt H, Ebelt H, et al. Endotoxin impairs the human pacemaker current if. Shock. (2007) 28(6):655–61. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e31812386bf
91. Gholami M, Mazaheri P, Mohamadi A, Dehpour T, Safari F, Hajizadeh S, et al. Endotoxemia is associated with partial uncoupling of cardiac pacemaker from cholinergic neural control in rats. Shock. (2012) 37(2):219–27. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318240b4be
92. Sharshar T, Annane D, de la Grandmaison GL, Brouland JP, Hopkinson NS, Françoise G. The neuropathology of septic shock. Brain Pathol. (2004) 14(1):21–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00494.x
93. Hawiger J, Veach RA, Zienkiewicz J. New paradigms in sepsis: from prevention to protection of failing microcirculation. J Thromb Haemost. (2015) 13(10):1743–56. doi: 10.1111/jth.13061
94. Levy B, Collin S, Sennoun N, Ducrocq N, Kimmoun A, Asfar P, et al. Vascular hyporesponsiveness to vasopressors in septic shock: from bench to bedside. Intensive Care Med. (2010) 36(12):2019–29. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-2045-8
95. Celes MR, Malvestio LM, Suadicani SO, Prado CM, Figueiredo MJ, Campos EC, et al. Disruption of calcium homeostasis in cardiomyocytes underlies cardiac structural and functional changes in severe sepsis. PLoS One. (2013) 8(7):e68809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068809
96. Tang B, Xuan L, Tang M, Wang H, Zhou J, Liu J, et al. miR-93-3p alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes by inhibiting toll-like receptor 4. Pathol Res Pract. (2018) 214(10):1686–93. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.08.024
97. Li Z, Yi N, Chen R, Meng Y, Wang Y, Liu H, et al. miR-29b-3p protects cardiomyocytes against endotoxin-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through targeting FOXO3A. Cell Signal. (2020) 74:109716. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109716
98. Xin Y, Tang L, Chen J, Chen D, Wen W, Han F. Inhibition of miR-101-3p protects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB pathway activation via the upregulation of DUSP1. Int J Mol Med. (2021) 47(3):20. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4853
99. Zheng G, Pan M, Jin W, Jin G, Huang Y. MicroRNA-135a is up-regulated and aggravates myocardial depression in sepsis via regulating p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2017) 45:6–12. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.029
100. Xing PC, An P, Hu GY, Wang DL, Zhou MJ. LncRNA MIAT promotes inflammation and oxidative stress in sepsis-induced cardiac injury by targeting miR-330-5p/TRAF6/NF-κB axis. Biochem Genet. (2020) 58(5):783–800. doi: 10.1007/s10528-020-09976-9
101. Xie J, Zhang L, Fan X, Dong X, Zhang Z, Fan W. MicroRNA-146a improves sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulating the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 18(1):779–85. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7657
102. An R, Feng J, Xi C, Xu J, Sun L. miR-146a attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by suppressing IRAK1 and TRAF6 via targeting ErbB4 expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:7163057. doi: 10.1155/2018/7163057
103. Gao M, Wang X, Zhang X, Ha T, Ma H, Liu L, et al. Attenuation of cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis by MicroRNA-146a is mediated via targeting of IRAK1 and TRAF6 expression. J Immunol. (2015) 195(2):672–82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403155
104. Wei JL, Wu CJ, Chen JJ, Shang FT, Guo SG, Zhang XC, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes the progression of sepsis-induced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-144-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24(2):851–61. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202001_20069
105. Wei S, Liu Q. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 modulates sepsis-induced cardiac inflammation through the miR-150-5p/NF-κB axis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2019) 12(9):3311–9.31934174
106. Cao C, Zhang Y, Chai Y, Wang L, Yin C, Shou S, et al. Attenuation of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulation of MicroRNA-23b is mediated through targeting of MyD88-mediated NF-κB activation. Inflammation. (2019) 42(3):973–86. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-00958-7
107. Luo Q, Ma H, Guo E, Yu L, Jia L, Zhang B, et al. MicroRNAs promote the progression of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy and neurovascular dysfunction through upregulation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway-associated HDAC7/ACTN4. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:909828. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.909828
108. Hong X, Wang J, Li S, Zhao Z, Feng Z. MicroRNA-375-3p in endothelial progenitor cells-derived extracellular vesicles relieves myocardial injury in septic rats via BRD4-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 96:107740. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107740
109. Zhou Y, Song Y, Shaikh Z, Li H, Zhang H, Caudle Y, et al. MicroRNA-155 attenuates late sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through JNK and β-arrestin 2. Oncotarget. (2017) 8(29):47317–29. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17636
110. Wang X, Huang W, Yang Y, Wang Y, Peng T, Chang J, et al. Loss of duplexmiR-223 (5p and 3p) aggravates myocardial depression and mortality in polymicrobial sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2014) 1842(5):701–11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.01.012
111. Zheng P, Feng X, Deng Q, Guo R, Li W. Study on the efficacy of nanoantibiotics in rats with sepsis based on MicroRNA-195 and TGF-β1/smads signaling pathway. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. (2021) 21(2):1357–64. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2021.18646
112. Luo YY, Yang ZQ, Lin XF, Zhao FL, Tu HT, Wang LJ, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA PVT1 attenuated macrophage M1 polarization and relieved sepsis induced myocardial injury via miR-29a/HMGB1 axis. Cytokine. (2021) 143:155509. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155509
113. Nong R, Qin C, Lin Q, Lu Y, Li J. Down-regulated HDAC1 and up-regulated microRNA-124-5p recover myocardial damage of septic mice. Bioengineered. (2022) 13(3):7168–80. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2034583
114. Gao H, Ma H, Gao M, Chen A, Zha S, Yan J. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 aggravates myocardial depression in mice with sepsis via the microRNA-449b/HMGB1 axis and the NF-κB signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. (2021) 41(4):BSR20201738. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201738
115. Ling L, Zhi L, Wang H, Deng Y, Gu C. MicroRNA-181b inhibits inflammatory response and reduces myocardial injury in sepsis by downregulating HMGB1. Inflammation. (2021) 44(4):1263–73. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01411-w
116. Liu J, Yang Y, Lu R, Liu Q, Hong S, Zhang Z, et al. MicroRNA-381-3p signatures as a diagnostic marker in patients with sepsis and modulates sepsis-steered cardiac damage and inflammation by binding HMGB1. Bioengineered. (2021) 12(2):11936–46. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2006967
117. Wang Q, Liu K, Jin C. Clinical value of microRNA-378a-3p in sepsis and its role in sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Bioengineered. (2021) 12(1):8496–504. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1985339
118. Chu Y, Wang X, Yu N, Li Y, Kan J. Long non-coding RNA FGD5-AS1/microRNA-133a-3p upregulates aquaporin 1 to decrease the inflammatory response in LPS-induced sepsis. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 24(5):784. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12424
119. Liu C, Yang Y, Liang G, Zhang A, Xu F. MiR-702-3p inhibits the inflammatory injury in septic H9c2 cells by regulating NOD1. Transpl Immunol. (2022) 70:101493. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2021.101493
120. Li J, Jiang R, Hou Y, Lin A. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes prevent sepsis-induced myocardial injury by a CircRTN4/miR-497-5p/MG53 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2022) 618:133–40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.05.094
121. Wang S, Yang Y, Suen A, Zhu J, Williams B, Hu J, et al. Role of extracellular microRNA-146a-5p in host innate immunity and bacterial sepsis. iScience. (2021) 24(12):103441. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103441
122. Fang Y, Hu J, Wang Z, Zong H, Zhang L, Zhang R, et al. LncRNA H19 functions as an aquaporin 1 competitive endogenous RNA to regulate microRNA-874 expression in LPS sepsis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 105:1183–91. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.007
123. Wang X, Yu Y. MiR-146b protect against sepsis induced mice myocardial injury through inhibition of Notch1. J Mol Histol. (2018) 49(4):411–7. doi: 10.1007/s10735-018-9781-4
124. Ge C, Liu J, Dong S. miRNA-214 protects sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Shock. (2018) 50(1):112–8. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000978
125. Wang H, Cui W, Qiao L, Hu G. Overexpression of miR-451a in sepsis and septic shock patients is involved in the regulation of sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction and inflammation. Genet Mol Biol. (2020) 43(4):e20200009. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-gmb-2020-0009
126. Luo Y, Xu H, Yang Z, Lin X, Zhao F, Huang Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 silencing elevates microRNA-26a-5p to ameliorate myocardial injury in sepsis by reducing regulator of calcineurin 2. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2022) 715:109047. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.109047
127. Zhang C, Li J, Li H, Wang G, Wang Q, Zhang X, et al. lncRNA MIR155HG accelerates the progression of sepsis via upregulating MEF2A by sponging miR-194-5p. DNA Cell Biol. (2021) 40(6):811–20. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0038
128. Xie J, Li H, Li S, Li J, Li Y. Molecular mechanism of sevoflurane preconditioning based on whole-transcriptome sequencing of lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction in mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2022) 79(6):846–57. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001259
129. Zhao H, Wang Y, Zhu X. Chrysophanol exerts a protective effect against sepsis-induced acute myocardial injury through modulating the microRNA-27b-3p/peroxisomal proliferating-activated receptor gamma axis. Bioengineered. (2022) 13(5):12673–90. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2063560
130. Li C, Hou D, Huang Y, Liu Y, Li Y, Wang C. Corylin alleviated sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via attenuating inflammation through downregulation of microRNA-214-5p. Toxicol Res (Camb). (2024) 13(3):tfae081. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae081
131. Chen Y, Chen S, Zhang J, Hu X, Li N, Liu Z, et al. Electroacupuncture pre-treatment exerts a protective effect on LPS-induced cardiomyopathy in mice through the delivery of miR-381 via exosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870(5):167208. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167208
132. Peng J, Li S, Han M, Gao F, Qiao L, Tian Y. SNHG1/miR-21 axis mediates the cardioprotective role of aloin in sepsis through modulating cardiac cell viability and inflammatory responses. J Clin Lab Anal. (2023) 37(21-22):e24985. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24985
133. Wang S, Wang G, Dong L, Liu X, Pan W, Han J, et al. The overexpression of miR-377 aggravates sepsis-induced myocardial hypertrophy by binding to Rcan2 and mediating CaN activity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:6659183. doi: 10.1155/2022/6659183
134. Lv W, Liu H, Wang X, Hao R. CIRC_0003907 modulates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via enhancing MYD88/NLRP3/NF-κB axis BY sponging MIR-944. Shock. (2024) 61(5):705–11. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002271
135. Xu LJ, Yang Y, Yuan LF, Liu H, Xu NP, Yang Y, et al. SP1-stimulated miR-208a-5p aggravates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via targeting XIAP. Exp Cell Res. (2024) 435(1):113905. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113905
136. Wang YE, Chen J, Yang H, He J, Varier KM, Chen Y, et al. Polysialic acid driving cardiovascular targeting co-delivery 1,8-cineole and miR-126 to synergistically alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute cardiovascular injury. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 280(Pt 3):135970. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135970
137. Dong W, Chen J, Wang Y, Weng J, Du X, Fang X, et al. miR-206 alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury in cardiomyocytes via directly targeting USP33 to inhibit the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. (2024) 479(4):929–40. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04754-8
138. Chen W, Gao G, Yan M, Yu M, Shi K, Yang P. Long noncoding RNA MAPKAPK5-AS1 promoted lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in the myocardium by sponging microRNA-124-3p/E2F3. Mol Med. (2021) 27(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00385-1
139. Xu R, Shao Z, Cao Q. MicroRNA-144-3p enhances LPS induced septic acute lung injury in mice through downregulating caveolin-2. Immunol Lett. (2021) 231:18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.12.015
140. Yu J, Xue J, Liu C, Zhang A, Qin L, Liu J, et al. MiR-146a-5p accelerates sepsis through dendritic cell activation and glycolysis via targeting ATG7. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2022) 36(10):e23151. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23151
141. Zhu WD, Xu J, Zhang M, Zhu TM, Zhang YH, Sun K. MicroRNA-21 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting nuclear factor-κB. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 16(6):4616–22. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6789
142. Jiang WY, Ren J, Zhang XH, Lu ZL, Feng HJ, Yao XL, et al. Circc3p1 attenuated pro-inflammatory cytokine production and cell apoptosis in acute lung injury induced by sepsis through modulating miR-21. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24(19):11221–9. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15685
143. Ma X, Tian D, Lv W, Gao B, Ma Z, Zheng X. Anti-inflammatory effects of microRNA-223 on sepsis-induced lung injury in rats by targeting the toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 22(3):964. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10396
144. Jiang T, Sun L, Zhu J, Li N, Gu H, Zhang Y, et al. MicroRNA-23a-3p promotes macrophage M1 polarization and aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating PLK1/STAT1/STAT3 signalling. Int J Exp Pathol. (2022) 103(5):198–207. doi: 10.1111/iep.12445
145. Zheng D, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Kuang L, Zhu Y, Wu Y, et al. Endothelial microvesicles induce pulmonary vascular leakage and lung injury during sepsis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:643. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00643
146. Lin Z, Liu Z, Wang X, Qiu C, Zheng S. MiR-21-3p plays a crucial role in metabolism alteration of renal tubular epithelial cells during sepsis associated acute kidney injury via AKT/CDK2-FOXO1 pathway. Biomed Res Int. (2019) 2019:2821731. doi: 10.1155/2019/2821731
147. Guo C, Ye FX, Jian YH, Liu CH, Tu ZH, Yang DP. MicroRNA-214-5p aggravates sepsis-related acute kidney injury in mice. Drug Dev Res. (2022) 83(2):339–50. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21863
148. Zhao H, Chen B, Li Z, Wang B, Li L. Long noncoding RNA DANCR suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced septic acute kidney injury by regulating miR-214 in HK-2 cells. Med Sci Monit. (2020) 26:e921822. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921822
149. Sang Z, Dong S, Zhang P, Wei Y. Mir-214 ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via PTEN/AKT/mTOR-regulated autophagy. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 24(4):683. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12322
150. Tian X, Li L, Fu G, Wang J, He Q, Zhang C, et al. miR-133a-3p regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells by modulating the expression of TAGLN2. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 22(2):824. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10256
151. Qian WH, Liu YY, Li X, Pan Y. MicroRNA-141 ameliorates alcoholic hepatitis-induced intestinal injury and intestinal endotoxemia partially via a TLR4-dependent mechanism. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 44(2):569–81. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4221
152. Tong L, Tang C, Cai C, Guan X. Upregulation of the microRNA rno-miR-146b-5p may be involved in the development of intestinal injury through inhibition of kruppel-like factor 4 in intestinal sepsis. Bioengineered. (2020) 11(1):1334–49. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1851476
153. Wang J, Ye Z, Chen Y, Qiao X, Jin Y. MicroRNA-25-5p negatively regulates TXNIP expression and relieves inflammatory responses of brain induced by lipopolysaccharide. Sci Rep. (2022) 12(1):17915. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21169-5
154. Zou L, He J, Gu L, Shahror RA, Li Y, Cao T, et al. Brain innate immune response via miRNA-TLR7 sensing in polymicrobial sepsis. Brain Behav Immun. (2022) 100:10–24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.11.007
155. Xu M, Li XY, Song L, Tao C, Fang J, Tao L. miR-484 targeting of Yap1-induced LPS-inhibited proliferation, and promoted apoptosis and inflammation in cardiomyocyte. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. (2021) 85(2):378–85. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbaa009
156. Li J, Wu X, Li C, Sun G, Ding P, Li Y, et al. Identification and validation of immune-related biomarker gene and construction of ceRNA networks in septic cardiomyopathy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:912492. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.912492
157. Qiu Y, Yu Y, Qin XM, Jiang T, Tan YF, Ouyang WX, et al. CircTLK1 modulates sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via enhancing PARP1/HMGB1 axis-mediated mitochondrial DNA damage by sponging miR-17-5p. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25(17):8244–60. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16738
158. Wang H, Bei Y, Shen S, Huang P, Shi J, Zhang J, et al. miR-21-3p controls sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2016) 94:43–53. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.03.014
159. Shan B, Li JY, Liu YJ, Tang XB, Zhou Z, Luo LX. LncRNA H19 inhibits the progression of sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulation of the miR-93-5p/SORBS2 axis. Inflammation. (2021) 44(1):344–57. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01340-8
160. Chen D, Hou Y, Cai X. MiR-210-3p enhances cardiomyocyte apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction by targeting the NDUFA4 gene in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Int Heart J. (2021) 62(3):636–46. doi: 10.1536/ihj.20-512
161. Han Y, Cai Y, Lai X, Wang Z, Wei S, Tan K, et al. lncRNA RMRP prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the miR-1-5p/hsp70 axis in LPS-induced sepsis mice. Inflammation. (2020) 43(2):605–18. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01141-8
162. Pei X, Wu Y, Yu H, Li Y, Zhou X, Lei Y, et al. Protective role of lncRNA TTN-AS1 in sepsis-induced myocardial injury via miR-29a/E2F2 axis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2022) 36(3):399–412. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07244-5
163. Sun F, Geng H, Sun Y, Feng W, Tian T, Ye L, et al. Exosomes derived from the blood of patients with sepsis regulate apoptosis and aerobic glycolysis in human myocardial cells via the hsa-miR-1262/SLC2A1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. (2022) 25(4):119. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12635
164. Ouyang H, Tan Y, Li Q, Xia F, Xiao X, Zheng S, et al. MicroRNA-208-5p regulates myocardial injury of sepsis mice via targeting SOCS2-mediated NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 81:106204. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106204
165. Wang J, Wei T, Zhang W, Chu Y, Zhang D, Zhang M, et al. Inhibition of miR-194-5p avoids DUSP9 downregulation thus limiting sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):20313. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71166-z
166. Nie X, Deng W, Zhou H, Wang Z. Long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by improving inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function through mediating the miR-501-3p/CADM1/STAT3 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 128:111500. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111500
167. Yang ZB, Chen WW, Chen HP, Cai SX, Lin JD, Qiu LZ. MiR-155 aggravated septic liver injury by oxidative stress-mediated ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction via targeting nrf-2. Exp Mol Pathol. (2018) 105(3):387–94. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.09.003
168. Lv X, Zhang Y, Cui Y, Ren Y, Li R, Rong Q. Inhibition of microRNA-155 relieves sepsis-induced liver injury through inactivating the JAK/STAT pathway. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 12(4):6013–8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4188
169. Wu M, Huang Z, Huang W, Lin M, Liu W, Liu K, et al. microRNA-124-3p attenuates myocardial injury in sepsis via modulating SP1/HDAC4/HIF-1α axis. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00763-y
170. Yu Y, Ou-Yang WX, Zhang H, Jiang T, Tang L, Tan YF, et al. MiR-125b enhances autophagic flux to improve septic cardiomyopathy via targeting STAT3/HMGB1. Exp Cell Res. (2021) 409(2):112842. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112842
171. Zhang C, Zeng L, Cai G, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Zhan H, et al. miR-340-5p alleviates oxidative stress injury by targeting MyD88 in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:2939279. doi: 10.1155/2022/2939279
172. Long X, Huang Y, He J, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Wei Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-335 exerts protective effects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 24(5):806. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12446
173. Song W, Zhang T, Yang N, Zhang T, Wen R, Liu C. Inhibition of micro RNA miR-122-5p prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis via targeting GIT1. Bioengineered. (2021) 12(1):1902–15. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1926201
174. Luo S, Huang X, Liu S, Zhang L, Cai X, Chen B. Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 alleviates sepsis-associated myocardial injury by modulating the miR-181a-5p/XIAP axis in vitro. Ann Clin Lab Sci. (2021) 51(2):231–40.33941563
175. Zhang J, Liu Y, Liu L. Hyperoside prevents sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction through regulating cardiomyocyte viability and inflammation via inhibiting miR-21. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 138:111524. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111524
176. Liu Y, Liu L, Zhang J. Protective role of matrine in sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction through regulating the lncRNA PTENP1/miR-106b-5p axis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 134:111112. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111112
177. Wang J, Xin S, Yang R, Jiang J, Qiao Y. Knockdown of lncRNA LUCAT1 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-642a. Mamm Genome. (2021) 32(6):457–65. doi: 10.1007/s00335-021-09890-4
178. Song B, Wang XX, Yang HY, Kong LT, Sun HY. MiR-141 attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by targeting DAPK1. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2021) 40(12_suppl):S137–137S149. doi: 10.1177/09603271211033768
179. Hu X, Miao H. MiR-539-5p inhibits the inflammatory injury in septic H9c2 cells by regulating IRAK3. Mol Biol Rep. (2022) 49(1):121–30. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06849-1
180. Zhang L, Li B, Li W, Jiang J, Chen W, Yang H, et al. miR-107 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by targeting PTEN and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cells Tissues Organs. (2023) 212(6):523–34. doi: 10.1159/000525476
181. Cao Y, Wang Y, Xiao L, Xu JY, Liu Y, Jiang R, et al. Endothelial-derived exosomes induced by lipopolysaccharide alleviate rat cardiomyocytes injury and apoptosis. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13(3):1432–44.33841668
182. Song YX, Ou YM, Zhou JY. Gracillin inhibits apoptosis and inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to alleviate cardiac injury in mice via improving miR-29a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 523(3):580–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.129
183. Xue WL, Bai X, Zhang L. rhTNFR:fc increases Nrf2 expression via miR-27a mediation to protect myocardium against sepsis injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 464(3):855–61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.051
184. Tu GW, Ma JF, Li JK, Su Y, Luo JC, Hao GW, et al. Exosome-derived from sepsis Patients’ blood promoted pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes by regulating miR-885-5p/HMBOX1. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:774193. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.774193
185. An L, Yang T, Zhong Y, Yin Y, Li W, Gao H. Molecular pathways in sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis: novel finding on long non-coding RNA ZFAS1/miR-138-5p/SESN2 axis. Immunol Lett. (2021) 238:47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2021.07.003
186. Liu JJ, Li Y, Yang MS, Chen R, Cen CQ. SP1-induced ZFAS1 aggravates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via miR-590-3p/NLRP3-mediated autophagy and pyroptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2020) 695:108611. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108611
187. Sang Z, Zhang P, Wei Y, Dong S. miR-214-3p attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by inhibiting autophagy through PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:1409038. doi: 10.1155/2020/1409038
188. Wang Y, Zhang Y. LncRNA CAIF suppresses LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes through regulating miR-16 demethylation. Immun Inflamm Dis. (2021) 9(4):1468–78. doi: 10.1002/iid3.498
189. Chen T, Zhu C, Ye C. LncRNA CYTOR attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating miR-24/XIAP. Cell Biochem Funct. (2020) 38(7):976–85. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3524
190. Li Y, Sun G, Wang L. MiR-21 participates in LPS-induced myocardial injury by targeting bcl-2 and CDK6. Inflamm Res. (2022) 71(2):205–14. doi: 10.1007/s00011-021-01535-1
191. Zhu XG, Zhang TN, Wen R, Liu CF. Overexpression of miR-150-5p alleviates apoptosis in sepsis-induced myocardial depression. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:3023186. doi: 10.1155/2020/3023186
192. Wang X, Li XL, Qin LJ. The lncRNA XIST/miR-150-5p/c-fos axis regulates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via TXNIP-modulated pyroptosis. Lab Invest. (2021) 101(9):1118–29. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00607-4
193. Gao L, Zhai Z, Shi Q, Yan J, Zhou L, Wu Y, et al. MiR-501-5p alleviates cardiac dysfunction in septic patients through targeting NR4A3 to prevent its binding with bcl-2. Cell Cycle. (2022) 21(9):961–71. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2035618
194. Ma H, Wang X, Ha T, Gao M, Liu L, Wang R, et al. MicroRNA-125b prevents cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis by targeting TRAF6-mediated nuclear factor κB activation and p53-mediated apoptotic signaling. J Infect Dis. (2016) 214(11):1773–83. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw449
195. Xiao H, Fu Q, Min L. CircRNAPTK2 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis in septic mice by competitively binding to miR-29b-3p with BAK1. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2022) 183(5):552–65. doi: 10.1159/000520671
196. Liang D, Jin Y, Lin M, Xia X, Chen X, Huang A. Down-regulation of Xist and mir-7a-5p improves LPS-induced myocardial injury. Int J Med Sci. (2020) 17(16):2570–7. doi: 10.7150/ijms.45408
197. Chen DD, Wang HW, Cai XJ. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via target miR-34b-5p/SIRT1. Innate Immun. (2021) 27(5):377–87. doi: 10.1177/17534259211034221
198. Zhang Z, Lv M, Wang X, Zhao Z, Jiang D, Wang L. LncRNA LUADT1 sponges miR-195 to prevent cardiac endothelial cell apoptosis in sepsis. Mol Med. (2020) 26(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00228-5
199. Sun X, Liu Y, Wang J, Zhang M, Wang M. Cardioprotection of M2 macrophages-derived exosomal microRNA-24-3p/Tnfsf10 axis against myocardial injury after sepsis. Mol Immunol. (2022) 141:309–17. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.11.003
200. Wang H, Bei Y, Huang P, Zhou Q, Shi J, Sun Q, et al. Inhibition of miR-155 protects against LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis in mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2016) 5(10):e374. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2016.80
201. Sun F, Yuan W, Wu H, Chen G, Sun Y, Yuan L, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating miR-192-5p/XIAP axis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2020) 245(7):620–30. doi: 10.1177/1535370220908041
202. Wu P, Kong L, Li J. MicroRNA-494-3p protects rat cardiomyocytes against septic shock via PTEN. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 17(3):1706–16. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7116
203. Yao Y, Sun F, Lei M. miR-25 inhibits sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targetting PTEN. Biosci Rep. (2018) 38(2):BSR20171511. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171511
204. Diao X, Sun S. PMicroRNA-124a regulates LPS-induced septic cardiac dysfunction by targeting STX2. Biotechnol Lett. (2017) 39(9):1335–42. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2368-4
205. Ektesabi AM, Mori K, Tsoporis JN, Vaswani CM, Gupta S, Walsh C, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells increase cardiac miR-187-3p expression in a polymicrobial animal model of sepsis. Shock. (2021) 56(1):133–41. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001701
206. Liang L, Liu S, Wu Q, Chen R, Jiang S, Yang Z. m6A-mediated upregulation of miRNA-193a aggravates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammatory response in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy via the METTL3 miRNA-193a/BCL2L2 pathway. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 430(1):113712. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113712
207. Jiang Y, Xu J, Zeng H, Lin Z, Yi Q, Guo J, et al. miR-29b-1-5p exacerbates myocardial injury induced by sepsis in a mouse model by targeting TERF2. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2024) 56(4):607–20. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024020
208. Gong M, Tao L, Li X. MicroRNA-21-3p/Rcan1 signaling axis affects apoptosis of cardiomyocytes of sepsis rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. (2023) 42(3):217–27. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2022066
209. Li D, Le J, Ye J, Fan Z. MiR-361-5p inhibits the wnt axis via targeting Lgr4 and promotes sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Ann Clin Lab Sci. (2022) 52(6):927–37.36564072
210. Dong W, Liao R, Weng J, Du X, Chen J, Fang X, et al. USF2 Activates RhoB/ROCK pathway by transcriptional inhibition of miR-206 to promote pyroptosis in septic cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. (2024) 479(5):1093–108. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04781-5
211. Gong X, Li Y, He Y, Zhou F. USP7-SOX9-miR-96-5p-NLRP3 Network regulates myocardial injury and cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in sepsis. Hum Gene Ther. (2022) 33(19-20):1073–90. doi: 10.1089/hum.2022.078
212. Pei Y, Xie S, Li J, Jia B. Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-141 targets PTEN and activates β-catenin to alleviate myocardial injury in septic mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2021) 43(5):584–93. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2021.1955920
213. Wang X, Simayi A, Fu J, Zhao X, Xu G. Resveratrol mediates the miR-149/HMGB1 axis and regulates the ferroptosis pathway to protect myocardium in endotoxemia mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 323(1):E21–21E32. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00227.2021
214. Qi Z, Liu R, Ju H, Huang M, Li Z, Li W, et al. microRNA-130b-3p attenuates septic cardiomyopathy by regulating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathways and directly targeting ACSL4 against ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19(13):4223–41. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.82287
215. Liu Y, Hu N, Ai B, Xia H, Li W. MiR-31-5p alleviates septic cardiomyopathy by targeting BAP1 to inhibit SLC7A11 deubiquitination and ferroptosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2024) 24(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03954-4
216. Zhang TN, Yang N, Goodwin JE, Mahrer K, Li D, Xia J, et al. Characterization of circular RNA and microRNA profiles in septic myocardial depression: a lipopolysaccharide-induced rat septic shock model. Inflammation. (2019) 42(6):1990–2002. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01060-8
217. Zhang H, Caudle Y, Shaikh A, Yao B, Yin D. Inhibition of microRNA-23b prevents polymicrobial sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by modulating TGIF1 and PTEN. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 103:869–78. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.092
218. Gong CW, Yuan MM, Qiu BQ, Wang LJ, Zou HX, Hu T, et al. Identification and validation of ferroptosis-related biomarkers in septic cardiomyopathy via bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet. (2022) 13:827559. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.827559
219. Dai Q, Hong Y, Li J. PVT1 knockdown inhibited the biological behavior of LPS-induced cardiac fibroblasts by regulating miR-24. Genes Genomics. (2021) 43(9):1003–9. doi: 10.1007/s13258-021-01104-0
220. Huang C, Xiao S, Xia Z, Cheng Y, Li Y, Tang W, et al. The diagnostic value of plasma miRNA-497, cTnI, FABP3 and GPBB in pediatric sepsis complicated with myocardial injury. Ther Clin Risk Manag. (2021) 17:563–70. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S309800
221. Li Y, Lu B, Yu M, Zhai J, Yao Y, Chai Y. Diagnostic value and significance of serum miR-132 combined with miR-223 for sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 22(6):1396. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10832
222. Yang C, Wen K. Predictive value and regulatory mechanism of serum miR-499a-5p on myocardial dysfunction in sepsis. J Cardiothorac Surg. (2021) 16(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01679-5
223. Zhang B, Yu L, Sheng Y. Clinical value and role of microRNA-29c-3p in sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Eur J Med Res. (2021) 26(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00566-y
224. Sun B, Luan C, Guo L, Zhang B, Liu Y. Low expression of microRNA-328 can predict sepsis and alleviate sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and inflammatory response. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2020) 53(8):e9501. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20209501
225. Guo H, Tang L, Xu J, Lin C, Ling X, Lu C, et al. MicroRNA-495 serves as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with sepsis and regulates sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Eur J Med Res. (2019) 24(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0396-3
Keywords: microRNAs, sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction, progression, diagnosis, mechanisms
Citation: Liu Z, Li F, Li N, Chen Y and Chen Z (2025) MicroRNAs as regulators of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: pathogenesis and diagnostic potential. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1517323. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1517323
Received: 5 November 2024; Accepted: 29 January 2025;
Published: 18 February 2025.
Edited by:
Carmine Izzo, University of Salerno, ItalyReviewed by:
Zhengwu Sun, Dalian Municipal Central Hospital, ChinaCopyright: © 2025 Liu, Li, Li, Chen and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Chen, Y2hlbnlvbmd0Y21AMTYzLmNvbQ==; Zelin Chen, Y2hlbnplbGluMzI4QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.