
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 03 April 2025
Sec. General Cardiovascular Medicine
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1514564
This article is part of the Research TopicNovel Role and Mechanisms of Inflammation in Myocardial InfarctionView all articles
 Xiao Wang1*
Xiao Wang1* Tao Kong2*
Tao Kong2*
Background: In-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) refers to the occurrence of cardiac arrest in hospitalized patients requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation, with only about one-third of patients achieving return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Pan-immune-inflammation value (PIIV) is an indicator assessing the overall inflammatory status within the body, but the relationship between PIIV and ROSC remains unclear.
Objective: This study aims to analyze the occurrence of ROSC and its influencing factors, and investigate the predictive value of PIIV, in order to provide insights for clinical prevention and treatment.
Methods: Clinical data of IHCA patients admitted to our hospital were retrospectively collected. Patients were divided into the ROSC group and non-ROSC group based on whether spontaneous circulation was restored after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyze factors affecting ROSC, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was employed to calculate the area under the curve (AUC) to evaluate the predictive value of PIIV.
Results: 168 patients' clinical data were collected, including 62 patients with ROSC and 106 with non-ROSC. The results of multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, adrenaline dosage, blood lactate (Lac), and PIIV were independent influencing factors for ROSC in IHCA patients (P < 0.05). The ROC curve analysis revealed that the AUC of PIIV for predicting ROSC in IHCA patients was 0.805 (95% CI: 0.720–0.891), with an optimal cutoff value of 395.3, sensitivity of 83.33%, and specificity of 70.37%.
Conclusion: PIIV demonstrates valuable application in predicting ROSC in IHCA patients.
Cardiac arrest (CA), as a serious medical emergency, refers to the sudden cessation of the heart's pumping action, leading to ineffective blood circulation to various organs throughout the body, especially the brain. Symptoms of cardiac arrest include loss of consciousness, cessation of breathing, and absence of a pulse (1). In the Utstein Resuscitation Registry template, in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) is defined as the provision of chest compressions and/or defibrillation to hospitalized patients experiencing cardiac arrest (2). According to the American Heart Association's guidelines, the incidence of IHCA between 2008 and 2017 has increased to 292,600 cases annually, with at least 9–10 cases occurring per 1,000 hospitalized patients, posing a significant threat to patients' life and health during hospitalization (3). Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is one of the primary measures for resuscitating patients experiencing respiratory and cardiac arrest, involving such interventions as endotracheal intubation, chest compressions, defibrillation, aimed at restoring the patient's cardiac circulation autonomously to achieve the goal of resuscitation (4, 5). However, studies indicate that the success rate of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in China is much lower than in countries like the United States (6). Previous research has shown that only about one-third of patients achieve return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) following cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and some patients may experience poor neurological outcomes leading to resuscitation failure or long-term complications, resulting in adverse prognosis. Therefore, identifying potential indicators that can predict ROSC is critically important for improving patient outcomes (7, 8). While the specific reasons for ROSC remain unclear, the association between inflammation and ROSC has been extensively studied (9, 10). The pan-immune-inflammation value (PIIV), proposed by scholars such as Fuca from the University of Milan in Italy, is an indicator assessing the overall inflammatory status within the body. It combines various inflammatory markers to provide a comprehensive assessment of inflammation, including neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, and platelet counts, directly reflecting the dynamic balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes (11). Previous studies have demonstrated that PIIV is closely related to the overall mortality and prognosis of patients during hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction (12, 13). However, the relationship between PIIV and ROSC remains unclear. This study aims to analyze the occurrence of ROSC and its influencing factors, investigate the predictive value of PIIV, and provide insights for clinical prevention and treatment.
This study is a retrospective investigation. Clinical data of IHCA patients admitted to our hospital from November 2022 to May 2024 were collected. Inclusion criteria comprised patients aged 18 years or older who experienced an IHCA during their hospital stay and subsequently received CPR, with documented initial cardiac rhythms—categorized as either shockable (ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia) or non-shockable (asystole or pulseless electrical activity)—thus including both types of cardiac arrest. Additionally, only patients with complete clinical information, including detailed resuscitation data, laboratory parameters, and outcome measures, were enrolled. Exclusion criteria consisted of patients who experienced out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, cases in which resuscitation was not initiated due to family refusal, patients with incomplete or missing key clinical data necessary for analysis, and instances where the initial cardiac rhythm was unclear or undocumented. Patients were categorized into ROSC group and non-ROSC group based on whether spontaneous circulation was restored after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The criteria for ROSC were as follows: restoration of spontaneous sinus or supraventricular rhythm with a systolic blood pressure ≥50 mmHg (1 mmHg = 0.133 kPa), with the aforementioned criteria sustained for at least 20 min. This study adheres to Helsinki Declaration and has been approved by our hospital's medical ethics committee. Informed consent of patients has been obtained for this study.
General information, diagnostic and treatment-related data, and resuscitation-related data of the patients were collected, including gender, age, smoking history, alcohol consumption history, past medical history, time of IHCA occurrence, season of occurrence, initial department visited, current department, cause of cardiac arrest, initial monitored rhythm (shockable rhythm, non-shockable rhythm), intubation status, defibrillation, duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, amount of epinephrine used. In addition, blood biochemistry parameters were collected at two time points: at admission and after the occurrence of cardiac arrest. These parameters include complete blood count, blood lactate (Lac), albumin, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and blood pH. The admission data served as the baseline inflammatory and biochemical profile, while the post-arrest measurements were also recorded.
In-hospital complete blood counts were obtained with an automated hematology analyzer to measure neutrophil count, platelet count, monocyte count, and lymphocyte count. PIIV was calculated as follows: PIIV = (neutrophil count × platelet count × monocyte count)/lymphocyte count (14). In this study, PIIV was measured at two time points: at admission (baseline PIIV) and after the occurrence of cardiac arrest. Unless explicitly noted as “PIIV at admission” (baseline PIIV), all PIIV measurements reported refer to samples obtained post-cardiac arrest.
Data analysis in this study was conducted with SPSS 27.0. Continuous data were presented as`X ± S, and between-group comparisons were performed using independent sample t-test. Categorical data were presented as frequencies or percentages, and comparisons were made with chi-square test. Factors influencing non-ROSC were analyzed using multivariate logistic regression analysis. Additionally, the predictive value of PIIV was assessed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to calculate the area under the curve (AUC). The significance level was set at α = 0.05.
174 clinical records of IHCA patients were collected, with 6 cases excluded due to incomplete data. Ultimately, 168 patients were included, comprising 62 patients with ROSC and 106 patients with non-ROSC. The flowchart of case selection is as shown in Figure 1.
In the non-ROSC group, there were 65 males and 41 females, with an age range of 59–79 years (mean age: 67.22 ± 9.54 years). In the ROSC group, there were 40 males and 22 females, with an age range of 55–76 years (mean age: 64.19 ± 10.45 years). There were no statistically significant differences in gender, age, smoking history, and other general data between the two groups (P > 0.05), as shown in Table 1.
In comparison to the ROSC group, the non-ROSC group had a significantly higher number of instances of initially monitored rhythms that were not shockable (P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in other diagnostic and treatment-related data such as IHCA occurrence time and season between the two groups (P > 0.05), as shown in Table 2.
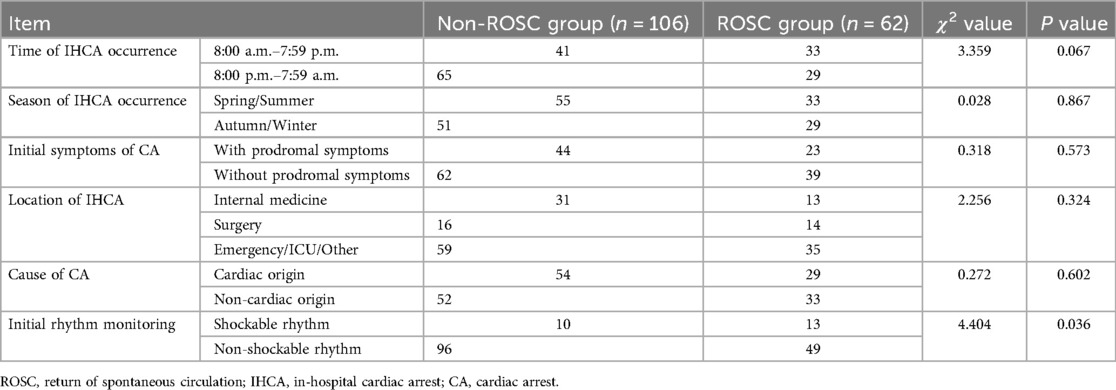
Table 2. Comparison of diagnostic and treatment-related data between non-ROSC group and ROSC group (cases).
In comparison to the ROSC group, the non-ROSC group had significantly more cases with defibrillation, CPR duration >30 min, administration of epinephrine, and epinephrine usage >5 mg, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the number of cases with endotracheal intubation between the two groups (P > 0.05), as shown in Table 3.
Compared to the ROSC group, the non-ROSC group exhibited significantly higher levels of Lac, NT-ProBNP, and PIIV, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in such parameters as albumin, blood glucose, and PIIV at admission between the two groups (P > 0.05), as shown in Table 4.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed with variables showing statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) in the univariate analysis as independent variables and the occurrence of ROSC in IHCA patients as the dependent variable. The results indicate that the duration of CPR, epinephrine dosage, lactate levels (Lac), and PIIV are independent influencing factors for ROSC in IHCA patients (P < 0.05), as shown in Table 5.
The ROC curve analysis results indicated that the Area Under the Curve (AUC) for PIIV in predicting ROSC in IHCA patients was 0.805 (95% CI: 0.720–0.891). The optimal cutoff value was 395.3, with a sensitivity of 83.33% and specificity of 70.37%, as shown in Figure 2.
In this study, a total of 168 IHCA patients who underwent CPR were included, with 62 cases achieving ROSC, accounting for 36.90%. This proportion is slightly higher than the data reported in the Swedish CPR registry at 35.6% (15). This difference may be attributed to the relatively better overall health status of the patients included in this study. Additionally, the study period for patient inclusion in this research ranged from November 2022 to May 2024, whereas the Swedish study was conducted in 2020. CPR outcomes typically evolve over time with advancements in technology and improvements in treatment methods, such as enhanced CPR techniques, drug utilization, and equipment, which may contribute to an increased ROSC rate. Numerous studies have demonstrated that by predicting the likelihood of ROSC early on, medical teams can better adjust treatment strategies and allocate resources, thereby enhancing patients' chances of recovery and overall prognosis. Simultaneously, by predicting the likelihood of ROSC, healthcare personnel can exercise caution when intervening with low-prognosis patients, avoiding excessive treatments for patients with unclear benefits. This approach helps reduce unnecessary medical interventions and their associated burdens (16, 17).
In this study, the duration of CPR, epinephrine dosage, and Lac were identified as independent influencing factors for ROSC in IHCA patients, aligning closely with findings from previous research (18). The optimal duration of CPR remains a topic of debate in the international arena. High-quality uninterrupted chest compressions significantly impact the success rate of ROSC following CPR. However, if CPR is prolonged beyond the body's tolerance, it can lead to hypoxia, ischemia-reperfusion injury in vital organs such as the heart, brain, and lungs, resulting in irreversible damage that affects the success rate of ROSC (19). A study by Coppler indicated that the type of brain injury is associated with the duration of CPR, where the duration serves as a surrogate marker for the severity of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Longer CPR durations correlate with lower survival rates (20). Research by Okubo and colleagues, based on extensive multicenter in-hospital cardiac arrest registry data, highlighted a gradual decline in survival rates and favorable functional outcomes with prolonged CPR durations. Beyond 39 min of CPR, survival rates dropped to below 1%, and at 32 min of CPR, the probability of favorable functional outcomes also fell below 1%. This suggests that while CPR can be effective within a certain timeframe, the likelihood of successful recovery significantly diminishes after a specific duration (21). The optimal duration of CPR for successful outcomes remains unclear, underscoring the necessity for large-scale research to comprehend the impact of CPR duration on survival rates.
Numerous studies have indicated that the use of epinephrine can increase the rate of ROSC, with epinephrine being recommended as the preferred rescue medication for CPR by many guidelines (22, 23). However, continuous use of more than 5 mg of epinephrine may increase cardiac oxygen consumption. While it can elevate blood pressure and perfusion in the early stages of resuscitation, excessive use under hypoxic conditions may lead to damage to myocardial cells, especially in cases of cardiac hypoxia, resulting in post-resuscitation cardiac dysfunction (24). Some studies suggest that excessive use of epinephrine may be associated with poorer functional outcomes. While it may increase the occurrence of ROSC, it could potentially have adverse effects on survival quality and functional outcomes post-recovery (25). CPR guidelines typically recommend a dose of 1 mg (1:10,000 dilution) of epinephrine per administration, with repeat doses every 3–5 min if circulation has not been restored. The total dose used should be within an appropriate range. This highlights the need in clinical practice to balance the potential benefits and risks of using epinephrine, adjusting medication strategies based on the patient's specific condition (26). Lactic acid is a metabolic byproduct of hypoxia and poor tissue perfusion. During cardiac arrest, the cessation of cardiac pumping leads to severe systemic tissue hypoxia, particularly affecting oxygen supply to vital organs such as the brain and heart, resulting in elevated lactate levels. High lactate levels reflect the extent of tissue hypoxia and metabolic disruption, thus correlating with the severity of cardiac arrest and the difficulty of resuscitation (27). Research by Li et al. highlighted that high lactate levels are an independent risk factor for mortality in patients undergoing CPR. Elevated lactate levels typically indicate severe tissue hypoxia and difficulty in circulatory restoration, thereby reducing the likelihood of ROSC (28).
Cardiac arrest and the resuscitation process can trigger significant systemic inflammatory responses. This inflammation includes elevated markers such as cytokines, interleukins, CRP, and other indicators. Previous studies have indicated that post-cardiac arrest, tissue hypoxia, and reperfusion injury can lead to local and systemic inflammatory responses (29). A high pan-immune inflammation index signifies elevated levels of inflammation in the body, which may exacerbate tissue damage, impact the effectiveness of cardiac recovery and rehabilitation, and reduce the success rate of ROSC. Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells in the circulatory system and can reflect the body's systemic or local inflammatory state. They regulate the inflammatory microenvironment by releasing cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, thereby promoting the body's inflammatory response. Platelets are closely related to various inflammatory processes as they secrete and express many pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cell molecules after activation through Toll-like receptors binding with pathogens, playing a role in antigen presentation. Lymphocytes play various roles in the inflammatory response through mechanisms such as regulating immune responses, directly killing infected cells, producing antibodies, and secreting cytokines. Their role is crucial for effectively clearing pathogens and maintaining immune balance, but improper or excessive inflammatory responses may also lead to tissue damage and disease progression (30).
The PIIV integrates these indicators and can comprehensively reflect the body's inflammatory status. A high inflammatory state is typically associated with poorer ROSC outcomes because inflammation can cause further damage to the heart and other vital organs. Research by Liu et al. indicated that compared to the systemic immune inflammation index (SII), PIIV has good predictive value for the prognosis of acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing coronary artery revascularization (31). A meta-analysis study demonstrated that PIIV can predict overall survival and progression-free survival in breast cancer patients (32). The results of this study confirm the value of PIIV in predicting ROSC in IHCA patients, suggesting that PIIV is a more reliable predictor for ROSC. PIIV as an independent influencing factor for ROSC in IHCA patients is because it comprehensively reflects the systemic inflammatory response post-cardiac arrest, which significantly impacts cardiac resuscitation and patient prognosis. A high level of inflammation usually indicates poorer tissue recovery and prognosis, thus serving as an effective predictor for ROSC. In addition to PIIV, other inflammatory markers like the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) have been investigated in various clinical contexts. SII, which is calculated as (platelet count × neutrophil count) divided by lymphocyte count, has been widely recognized as a predictor of outcomes in several patient populations. Compared to SII, PIIV incorporates monocyte count into its calculation, potentially offering a more comprehensive assessment of the systemic inflammatory response. Our findings suggest that PIIV is a robust predictor of ROSC in IHCA patients, and its prognostic performance may be enhanced by this additional parameter. However, direct comparisons between PIIV and SII in the context of IHCA are still limited. Future studies should aim to directly compare these indices in order to clarify their respective roles and to determine whether the inclusion of monocyte count in PIIV confers any significant advantage over SII in predicting clinical outcomes following cardiac arrest (33, 34).
One important limitation of our study is the variability in clinical protocols across different hospital departments. In our retrospective analysis, resuscitation procedures, medication usage, and post-resuscitation care were not standardized across all departments. For instance, some departments may have adopted more aggressive resuscitation strategies or had greater access to advanced life support resources, while others followed more conservative protocols due to resource constraints or differences in staff training. This heterogeneity could have influenced the observed outcomes, including ROSC rates, and may confound the relationship between inflammatory markers such as PIIV and ROSC. Additionally, our study included only those IHCA patients who underwent resuscitation attempts. As a result, the findings are applicable solely to the subset of patients deemed eligible for and who received resuscitation, and this selection bias may affect the overall characteristics and outcomes reported. Future studies should aim to standardize clinical protocols across departments or incorporate departmental variables into multivariate regression models, as well as include a broader patient population, to reduce these biases and improve the generalizability of the results. Furthermore, the retrospective design of our study inherently limits causal inference and may introduce additional selection biases. We also acknowledge that key variables—such as patient comorbidities, variability in resuscitation quality, and post-resuscitation care—were not comprehensively analyzed, which could influence the observed outcomes. Moreover, as resuscitation measures and medications continue to evolve, it is imperative to include additional factors influencing ROSC in future multivariate regression analyses.
In conclusion, PIIV has significant practical value for predicting ROSC in IHCA patients. It not only reflects the inflammatory and immune challenges faced by patients during resuscitation but also provides clinicians with a quantifiable tool to better manage resuscitation strategies, assess prognosis, and optimize patient care. By considering PIIV comprehensively, physicians can make more effective clinical decisions, enhancing the survival and recovery quality of in-hospital cardiac arrest patients.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital (2024051). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TK: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Project (No. LHGJ20230143).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Penketh J, Nolan JP. In-hospital cardiac arrest: the state of the art. Crit Care. (2022) 26(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04247-y
2. Andersen LW, Holmberg MJ, Berg KM, Donnino MW, Granfeldt A. In-hospital cardiac arrest: a review. J Am Med Assoc. (2019) 321(12):1200–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.1696
3. Lavonas EJ, Akpunonu PD, Arens AM, Babu KM, Cao D, Hoffman RS, et al. 2023 American heart association focused update on the management of patients with cardiac arrest or life-threatening toxicity due to poisoning: an update to the American heart association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. (2023) 148(16):e149–84. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001161
4. Morgan RW, Kirschen MP, Kilbaugh TJ, Sutton RM, Topjian AA. Pediatric in-hospital cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the United States: a review. JAMA Pediatr. (2021) 175(3):293–302. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5039
5. Cimpoesu D, Corlade-Andrei M, Popa TO, Grigorasi G, Bouros C, Rotaru L, et al. Cardiac arrest in special circumstances-recent advances in resuscitation. Am J Ther. (2019) 26(2):e276–83. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000927
6. Bai Z, Wang L, Yu B, Xing D, Su J, Qin H. The success rate of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and its correlated factors in patients with emergency prehospital cardiac arrest. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. (2023) 2:1–10. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2202516
7. Latif RK, Clifford SP, Byrne KR, Maggard B, Chowhan Y, Saleem J, et al. Hyperoxia after return of spontaneous circulation in cardiac arrest patients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. (2022) 36(5):1419–28. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2021.03.007
8. Vallentin MF, Granfeldt A, Meilandt C, Povlsen AL, Sindberg B, Holmberg MJ, et al. Effect of intravenous or intraosseous calcium vs saline on return of spontaneous circulation in adults with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Med Assoc. (2021) 326(22):2268–76. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.20929
9. Taha Sert E, Kokulu K, Mutlu H, Gül M, Uslu Y. Performance of the systemic immune-inflammation index in predicting survival to discharge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resusc Plus. (2023) 14:100382. doi: 10.1016/j.resplu.2023.100382
10. Zelniker TA, Kaya Z, Gamerdinger E, Spaich S, Stiepak J, Giannitsis E, et al. Relationship between markers of inflammation and hemodynamic stress and death in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):9954. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88474-3
11. Okyar Baş A, Güner M, Ceylan S, Hafızoğlu M, Şahiner Z, Doğu BB, et al. Pan-immune inflammation value; a novel biomarker reflecting inflammation associated with frailty. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2023) 35(8):1641–9. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02457-0
12. Murat B, Murat S, Ozgeyik M, Bilgin M. Comparison of pan-immune-inflammation value with other inflammation markers of long-term survival after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur J Clin Invest. (2023) 53(1):e13872. doi: 10.1111/eci.13872
13. Ko TS, Mavroudis CD, Morgan RW, Baker WB, Marquez AM, Boorady TW, et al. Non-invasive diffuse optical neuromonitoring during cardiopulmonary resuscitation predicts return of spontaneous circulation. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):3828. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83270-5
14. Lin F, Zhang LP, Xie SY, Huang HY, Chen XY, Jiang TC, et al. Pan-immune-inflammation value: a new prognostic index in operative breast cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:830138. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.830138
15. Jerkeman M, Sultanian P, Lundgren P, Nielsen N, Helleryd E, Dworeck C, et al. Trends in survival after cardiac arrest: a Swedish nationwide study over 30 years. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43(46):4817–29. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac414
16. Wang JJ, Zhou Q, Huang ZH, Han Y, Qin CZ, Chen ZQ, et al. Establishment of a prediction model for prehospital return of spontaneous circulation in out-of-hospital patients with cardiac arrest. World J Cardiol. (2023) 15(10):508–17. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i10.508
17. Benhamed A, Canon V, Mercier E, Heidet M, Gossiome A, Savary D, et al. Prehospital predictors for return of spontaneous circulation in traumatic cardiac arrest. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. (2022) 92(3):553–60. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000003474
18. Hannen LEM, Toprak B, Weimann J, Mahmoodi B, Fluschnik N, Schrage B, et al. Clinical characteristics, causes and predictors of outcomes in patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest: results from the SURVIVE-ARREST study. Clin Res Cardiol. (2023) 112(2):258–69. doi: 10.1007/s00392-022-02084-1
19. Yang J, Dong GJ, Wang HW, Zhao X, Wang FJ, Zhang J, et al. Influence of microcirculatory dysfunction on myocardial injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Biomed Environ Sci. (2022) 35(4):334–44. doi: 10.3967/bes2022.044
20. Coppler PJ, Elmer J, Doshi AA, Guyette FX, Okubo M, Ratay C, et al. Duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and phenotype of post-cardiac arrest brain injury. Resuscitation. (2023) 188:109823. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2023.109823
21. Okubo M, Komukai S, Andersen LW, Berg RA, Kurz MC, Morrison LJ, et al. Duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and outcomes for adults with in-hospital cardiac arrest: retrospective cohort study. Br Med J. (2024) 384:e076019. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076019
22. Lv JH, Wang D, Zhang MN, Bai ZH, Sun JL, Shi Y, et al. The related factors for the recovery and maintenance time of sinus rhythm in hospitalized patients with cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a single-center retrospective case-control study. Medicine. (2019) 98(5):e14303. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014303
23. Butt W. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, epinephrine, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: finding the right balance. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2023) 24(11):975–8. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000003355
24. Kucher NM, Marquez AM, Guerguerian AM, Moga MA, Vargas-Gutierrez M, Todd M, et al. Epinephrine dosing use during extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation: single-center retrospective cohort. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2023) 24(11):e531–9. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000003323
25. Bougouin W, Slimani K, Renaudier M, Binois Y, Paul M, Dumas F, et al. Epinephrine versus norepinephrine in cardiac arrest patients with post-resuscitation shock. Intensive Care Med. (2022) 48(3):300–10. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06608-7
26. Fernando SM, Mathew R, Sadeghirad B, Rochwerg B, Hibbert B, Munshi L, et al. Epinephrine in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a network meta-analysis and subgroup analyses of shockable and nonshockable rhythms. Chest. (2023) 164(2):381–93. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.01.033
27. Sugimoto M, Takayama W, Inoue A, Hifumi T, Sakamoto T, Kuroda Y, et al. Impact of lactate clearance on clinical and neurological outcomes of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest treated with extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a secondary data analysis. Crit Care Med. (2024) 52(7):e341–50. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000006245
28. Li Z, Gao J, Wang J, Xie H, Guan Y, Zhuang X, et al. Mortality risk factors in patients receiving ECPR after cardiac arrest: development and validation of a clinical prognostic prediction model. Am J Emerg Med. (2024) 76:111–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2023.11.048
29. Feng J, Wang L, Yang X, Chen Q, Cheng X. Pretreatment pan-immune-inflammation value (PIV) in predicting therapeutic response and clinical outcomes of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2024) 31(1):272–83. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-14430-2
30. Su Z, Tang J, He Y, Zeng WH, Yu Q, Cao XL, et al. Pan-immune-inflammation value as a novel prognostic biomarker in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. (2024) 27(6):252. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14385
31. Liu Y, Liu J, Liu L, Cao S, Jin T, Chen L, et al. Association of systemic inflammatory response index and pan-immune-inflammation-value with long-term adverse cardiovascular events in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients after primary percutaneous coronary intervention. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:3437–54. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S421491
32. Cheng HW, Wang T, Yu GC, Xie LY, Shi B. Prognostic role of the systemic immune-inflammation index and pan-immune inflammation value for outcomes of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 28(1):180–90. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202401_34903
33. Hu B, Yang XR, Xu Y, Sun YF, Sun C, Guo W, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20(23):6212–22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442
Keywords: in-hospital cardiac arrest, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, return of spontaneous circulation, pan-immune-inflammation value, influencing factors
Citation: Wang X and Kong T (2025) Influencing factors and predictive indicators of return of spontaneous circulation in in-hospital cardiac arrest. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1514564. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1514564
Received: 21 October 2024; Accepted: 18 March 2025;
Published: 3 April 2025.
Edited by:
Haibo Liu, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Anna Valerianova, General University Hospital in Prague, CzechiaCopyright: © 2025 Wang and Kong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao Wang, d3h4d3MwOTkzQDE2My5jb20=; Tao Kong, YmVzdGtvbmd0YW9AMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.