- 1Department of Extracorporeal Circulation, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
- 2NHC Key Laboratory of Assisted Circulation and Vascular Diseases, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Introduction: Sepsis is a major cause of ICU admission and mortality in patients with infective endocarditis patients. This study aimed to explore the effect of intraoperative HA380 blood adsorption on surgical outcomes in infective endocarditis patients, given its ability to adsorb inflammatory factors.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of patients who underwent surgical treatment for infective endocarditis at our hospital. After propensity score matching, eligible patients were matched in a 1:1 ratio between HA380 users and non-users. The primary endpoint was the incidence of postoperative sepsis, while secondary outcomes included ICU stay, postoperative hospital stay, and the need for CRRT, IABP, and ECMO therapies. Laboratory results were compared at 24, 48, and 72 h postoperatively.
Results: A total of 148 patients were included in the analysis. After 1:1 matching, 39 pairs were further analyzed. There was no significant difference in the incidence of postoperative sepsis (20.5% vs. 15.4%, p = 0.724). However, HA380 patients had a significantly shorter postoperative hospital stay (21.2 vs. 28.1 days, p = 0.014), with no differences observed in the use of CRRT, IABP, or ECMO. Laboratory results showed that HA380 patients had significantly lower fibrinogen levels and a higher albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio.
Discussion: This study did not demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative sepsis with HA380 blood adsorption. Although the HA380 group had a shorter postoperative hospital stay, lower fibrinogen levels, and a higher albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio, the overall effectiveness of HA380 requires further investigation.
1 Background
The incidence of infective endocarditis varies by region, ranging from 2 to 10 cases per 100,000 individuals (1–3). Despite significant advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and perioperative management, the in-hospital mortality rate remains high, exceeding 20% (4–7). Surgical intervention is the primary approach for valve reconstruction in infective endocarditis, and in-hospital mortality is closely associated with sepsis-induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) (8, 9).Sepsis-related inflammatory factors are believed to trigger an excessive systemic inflammatory response (SIRS), which can lead to MODS (10). Therefore, reducing inflammatory factors through intraoperative blood adsorption is considered a promising strategy. While the HA380 adsorption filter has demonstrated efficacy in vitro (4, 11–14), its in vivo effectiveness remains a subject of debate. This study aims to evaluate the impact of HA380 blood adsorption on surgical outcomes in patients with infective endocarditis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patients
This single-center, retrospective observational study analyzed data from 148 patients with infective endocarditis who underwent cardiac surgery at our hospital between January 1, 2019, and March 1, 2022.
Inclusion criteria: Patients with acute infective endocarditis undergoing valve reconstruction surgery were included.
Exclusion criteria: (1) Inability to undergo valve reconstruction surgery. (2) Incomplete clinical information. (3) Postoperative pathological results indicating non-bacterial endocarditis, such as marantic endocarditis related to malignancy or Libman-Sacks endocarditis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (15).
2.2 Outcome
The primary outcome of this study was the incidence of postoperative sepsis, with sepsis diagnosed based on the third international consensus definition (16, 17). Sepsis is defined as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Patients with an increase in Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score of ≥2 and suspected or proven infection were considered to have sepsis.
Secondary outcomes included length of stay, postoperative hospital stay, use of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
2.3 Data collection
General clinical data of patients were collected, such as patient gender, age, medical history, preoperative laboratory test results. Intraoperative data included surgical approach, intraoperative transfusion and blood product usage, and cardiopulmonary bypass-related data (aortic cross-clamp time, hypothermic time). Postoperative data included the occurrence of sepsis, length of hospital stay, ICU stay, major postoperative complications, use of CRRT or ECMO, and postoperative continuous laboratory test results.
2.4 Use of HA380
The HA380 blood perfusion device was integrated with the cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) circuit for blood perfusion. Venous blood initially entered the reservoir and subsequently flowed into the oxygenator, driven by the pump. After oxygenation, the majority of oxygenated blood was directed into the arterial circulation for perfusion, with approximately 700 ml/min (14%–18%) undergoing blood filtration through the HA380 blood perfusion device. The filtered blood was then returned to the reservoir and mixed with venous blood. No additional equipment was required for this process.
2.5 Data analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software, and propensity score matching (PSM) analysis was conducted using the R language. The propensity score (PS) was derived from a multivariate logistic regression model that estimated the group affiliation (HA380 vs. non-HA380) based on variables such as gender, age, medical history, preoperative laboratory test results, and more. The nearest neighbor algorithm was employed for 1:1 PSM to minimize potential confounding effects and achieve covariate balance between the groups. Given the high mortality rate associated with infective endocarditis but its relatively low incidence, a caliper was not applied to maximize the use of patients who received HA380. To After matching, comparisons between groups were made using the paired t-test or rank sum test for continuous variables and the McNemar test for categorical variables. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.6 Ethics
This study was designed in accordance with the principles outlined in the the Helsinki Declaration and complied with the regulations set forth in the Law on Medical Research Involving Human Subjects and the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. The relevant document numbers was 45362023653.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
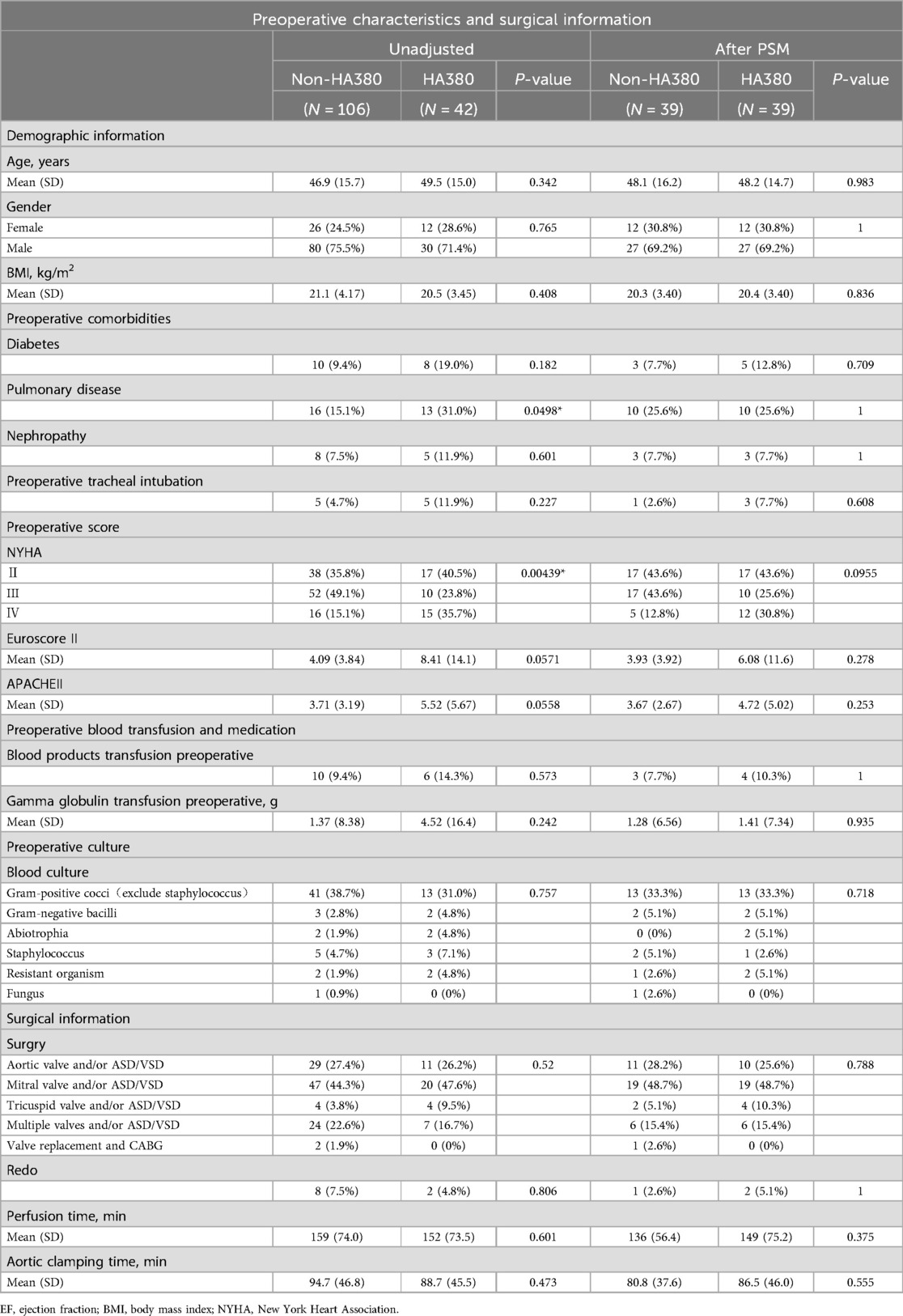
From January 1, 2019, to March 1, 2022, a total of 148 patients with definitive infective endocarditis who underwent surgical therapy with cardiopulmonary bypass were included in our study. The cohort consisted of 110 males and 38 females, with a mean age of 48.2 years. Preoperative blood cultures were negative in 72 cases and positive in 76 cases. Among these patients, 106 did not receive HA380, while 42 received HA380. The period of HA380 use ranged from September 1, 2020 and March 1, 2022. After PSM, 78 patients were evenly distributed into the HA380 group and the non-HA380 group. The baseline characteristics of the patients are detailed in Table 1. The proportion of patients with preoperative lung disease was higher in the HA380 group compared to the non-HA380 group (31% vs. 15.1%, p = 0.049). The preoperative albumin level was lower in the HA380 group (34.5 vs. 36.2 g/L, p = 0.048). The difference in New York heart association (NYHA) functional class scores between the two groups was statistically significant (HA380 vs. non-HA380, NYHA II 35.8% vs. 40.5%; NYHA III 49.1% vs. 23.8%; NYHA IV 15.1% vs. 35.7%). No other clinical variables showed statistically significant differences. However, after PSM, none of the baseline differences remained statistically significant.
3.2 Endpoint events
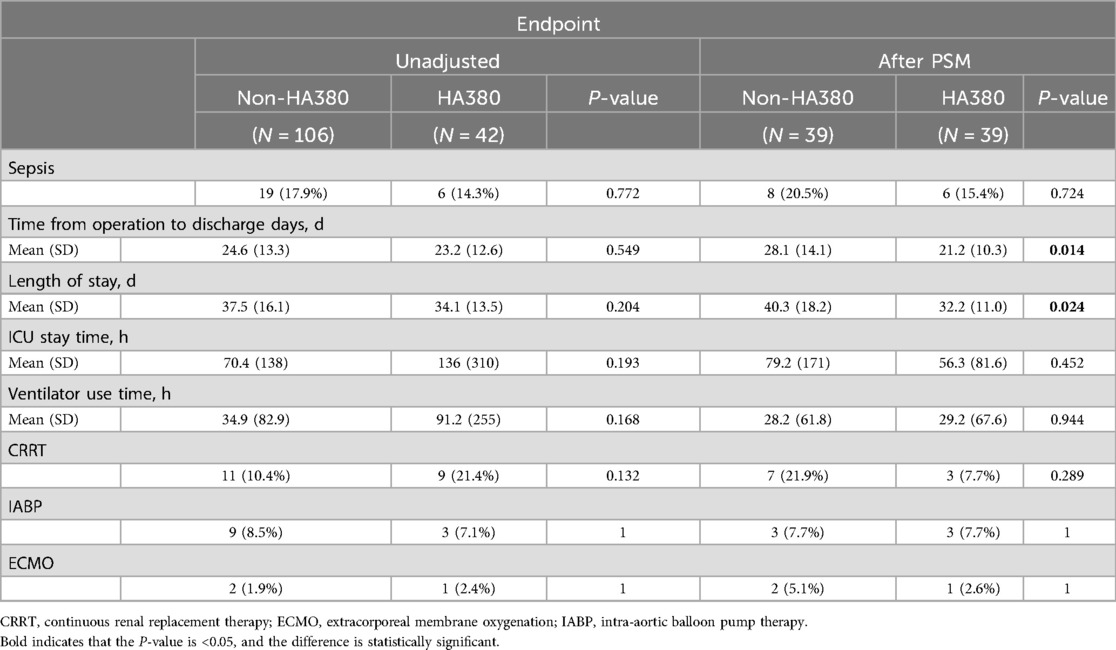
The summary of the endpoint events is presented in Table 2.
3.2.1 Primary outcome
Before PSM, the incidence of postoperative sepsis did not show a statistically significant difference (17.9% vs. 14.3%, p = 0.722). After PSM, no statistically significant difference was found between the HA380 group and the control group (15.4% vs. 20.5%, p = 0.724).
3.2.2 Secondary outcomes
Before PSM, there were no significant differences in time from operation to discharge (24.6 vs. 23.2 days, p = 0.549), length of stay (37.5 vs. 34.1 days, p = 0.204), ICU stay time (70.4 vs. 136 h, p = 0.193) and Ventilator use time (34.9 vs. 91.2 h, p = 0.168). Additionally, there were no differences in the use of CRRT (10.4% vs. 21.4%, p = 0.132), IABP (8.5% vs. 7.1%, p = 1.0) or ECMO (1.9% vs. 2.4%, p = 1.0) therapy between the two groups. After PSM, Time from operation to discharge was shorter in the HA380 group (21.2 vs. 28.1, p = 0.014), as well as length of stay (32.2 vs. 40.3, p = 0.024). There were no differences in ICU stay time (79.2 vs. 56.3 h, p = 0.452) and ventilator use time (28.2 vs. 29.2 h, p = 0.994), CRRT (21.9% vs. 7.7%, p = 0.289), IABP (7.7% vs. 7.7%, p = 1.0) or ECMO (5.1% vs. 2.6%, p = 1) therapy between the two groups.
3.3 SOFA scores and postoperative laboratory results
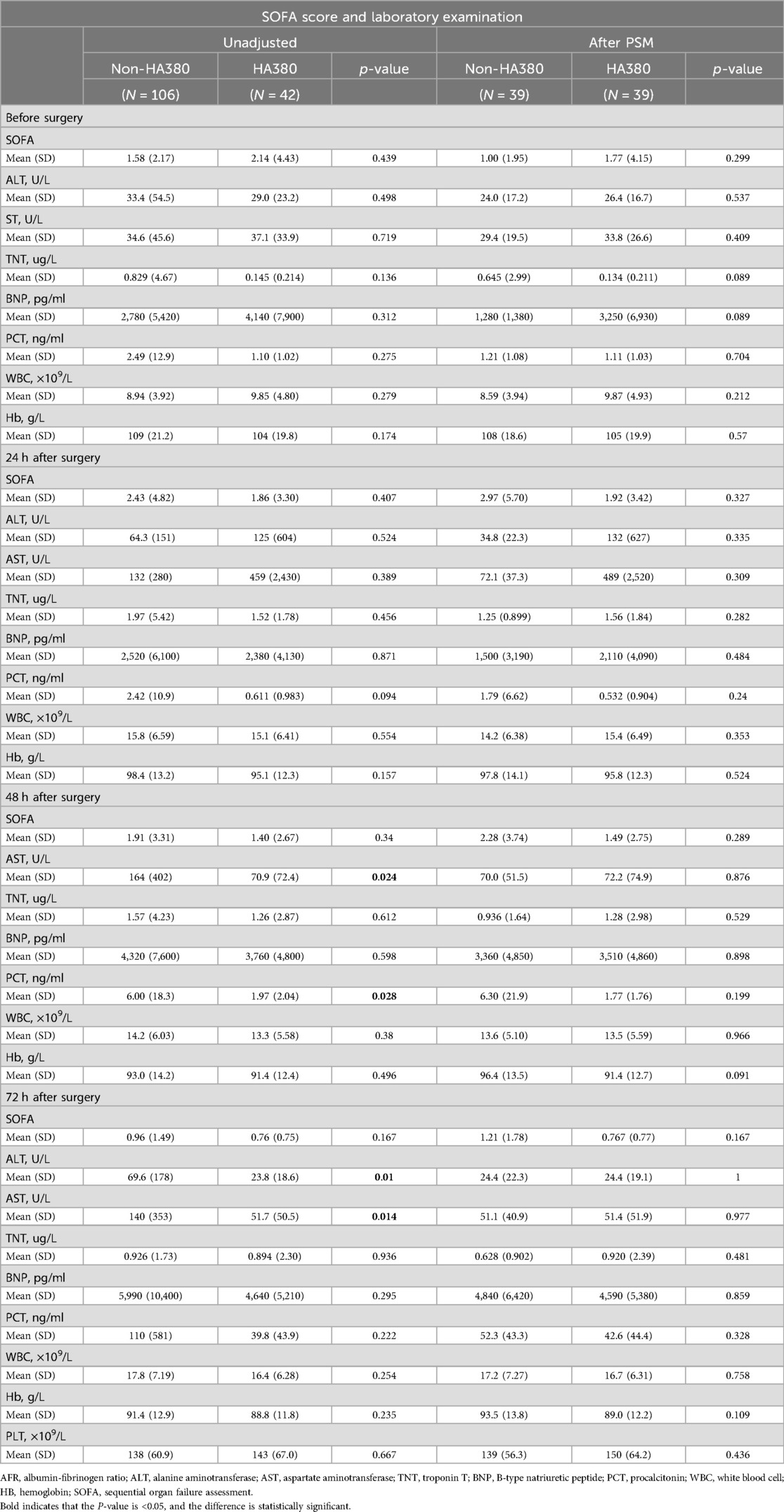
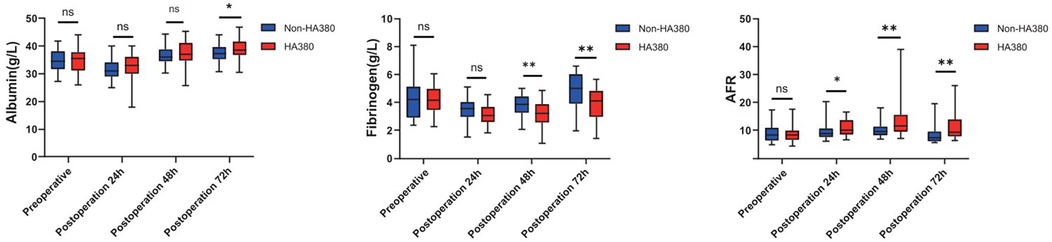
We collected relevant SOFA scores and postoperative laboratory results of the patients, as shown in Table 3. The difference in postoperative SOFA scores between the two groups was not statistically significant (24 h: 2.97 vs. 1.92, p = 0.327; 48 h: 2.28 vs. 1.49, p = 0.289; 72 h 1.21 vs. 0.767, p = 0.167). In the HA380 group, fibrinogen levels were significantly lower than in the non-HA380 group (24 h: 3.15 vs. 3.51, p = 0.053; 48 h: 3.14 vs. 3.82, p = 0.002; 72 h: 3.94 vs. 4.80, p = 0.006). Conversely, the albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio (AFR) was significantly higher in the HA380 group compared to the non-HA380 group (24 h: 10.9 vs. 9.53, p = 0.038; 48 h: 13.4 vs. 10.0, p = 0.005; 72 h: 11.1 vs. 8.57, p = 0.009) (Figure 1). The differences in other laboratory results were not statistically significant.
4 Discussion
CPB may induce a sudden release of inflammatory cytokines. Theoretically, the application of HA380 could facilitate the adsorption of inflammatory mediators, thereby contributing to improved postoperative outcomes (14, 18). However, in our study, no statistically significant difference in the incidence of sepsis was observed between the HA380 and non-HA380 groups. Additionally, compared to the non-HA380 group, the HA380 group exhibited shorter postoperative hospital stay, shorter total hospital stay, lower fibrinogen level and a higher AFR.
Wang et al. found that although the serum IL-6 levels increased more rapidly in the control group than in the HA380 group after surgery, the incidence of postoperative acute kidney injury(AKI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS) was lower in the HA380 group. However, the incidence of other postoperative complications, including ventilation time, ICU stay, hospital stay, and in-hospital mortality were not significantly different between the two groups (14). While in a 2022 study, patients in the HA380 group had significantly lower IL-6 levels, required less vasopressin, had shorter mechanical ventilation duration, and had shorter ICU stays. The authors concluded that HA380 was effective in reducing SIRS and promoting postoperative recovery (19). In studies of blood adsorption using other perfusion devices, several studies have reported no differences in the incidence of sepsis, ICU length of stay, ventilator treatment, and 30-day mortality rate following blood adsorption. Haidari et al. indicated that the sepsis-related mortality rate was lower in patients who underwent blood adsorption (34% vs. 43%, p = 0.041), while there were no differences in the incidence of sepsis or in-hospital mortality (11, 20, 21). Our study failed to demonstrate that the use of HA380 could reduce the incidence of postoperative sepsis. Despite shorter hospital stays, there were no differences in incidence of sepsis, ICU length of stay, ventilator use, CRRT, IABP or ECMO.
Blood adsorption effectively lowers fibrinogen levels, as evidenced by a significant reduction observed at the end of the procedure (22).Studies have linked lower fibrinogen levels in sepsis patients to higher mortality rates (23, 24), with thresholds below 1.6 g/L or 2.0 g/L showing a stronger correlation (25, 26). In the early stages of sepsis, fibrinogen levels rise, exacerbating inflammation (27, 28), while albumin levels typically decrease (29), reflecting the complex interplay of inflammation. As a novel biomarker, AFR has shown utility in various conditions, including cancer and autoimmune diseases (30–32). While cytokine adsorption has the potential to regulate immune responses, its clinical advantages remain poorly defined. Our research indicated significant reductions in fibrinogen levels and increases in AFR in the HA380 group; however, these findings did not translate into improved clinical outcomes. Consequently, the clinical significance of these results requires further investigation in the future.
Some reports suggest that propensity score matching (PSM) can reduce or even eliminate the impact of selection bias in both prospective and retrospective studies (33, 34). In this retrospective study, PSM was employed to match baseline characteristics, including demographic data, preoperative complications, medications, laboratory tests, and surgical details, aiming to reduce differences in disease severity and physical condition between groups. However, the matching for patients using HA380 was not strictly adjusted for confounding factors. Despite PSM's partial adjustment, the impact of unknown confounders persists. Additionally, the study did not collect or analyze more cytokines, such as interleukins and interferons, nor did it observe their specific changes.
Our study has several limitations. First, as a single-center retrospective study, it is limited by a relatively small sample size and inherent internal biases. Second, although PSM analysis was employed to balance baseline data, further multicenter, large-sample prospective clinical studies are required to validate our conclusions. Additionally, more detailed designs for laboratory tests should be implemented, such as collecting simultaneous data on inflammatory factors in patients, to better elucidate the specific effects and mechanisms of HA380.
5 Conclusion
The use of HA380 in surgical interventions for infective endocarditis did not result in a decreased incidence of postoperative sepsis. Although the HA380 group showed a shorter postoperative hospital stay, shorter total hospital stay, lower fibrinogen level, and a higher AFR, its overall effectiveness still requires further validation.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SH: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SY: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QK: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Beijing Huikang Charity Foundation (BHCF20220705).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
IE, infective endocarditis.; IABP, intra-aortic balloon pump therapy; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; GCP: good clinical practice; AFR, albumin-fibrinogen ratio.
References
1. Olmos C, Vilacosta I, Fernández-Pérez C, Bernal JL, Ferrera C, García-Arribas D, et al. The evolving nature of infective endocarditis in Spain: a population-based study (2003 to 2014). J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 70(22):2795–804. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.10.005
2. Malakan Rad E, Momtazmanesh S, Saeedi Moghaddam S, Rezaei N, Rezaei N, Jamshidi H, et al. Infective endocarditis in north Africa and the Middle East, 1990‒2019: updates from the global burden of disease study 2019. Arch Iran Med. (2024) 27(5):229–38. doi: 10.34172/aim.2024.34
3. Che D, Hu J, Zhu J, Lyu J, Zhang X. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting in-hospital mortality in ICU patients with infective endocarditis. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2024) 24(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02482-7
4. Kalisnik JM, Leiler S, Mamdooh H, Zibert J, Bertsch T, Vogt FA, et al. Single-centre retrospective evaluation of intraoperative hemoadsorption in left-sided acute infective endocarditis. J Clin Med. (2022) 11(14):3594. doi: 10.3390/jcm11143954
5. Cordeiro J, Raposo LM, Godoy PH. Mortality profile of deaths related to infective endocarditis in Brazil and regions: a population-based analysis of death records. Trop Med Infect Dis. (2024) 9(12):291. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9120291
6. Rajani R, Klein JL. Infective endocarditis: a contemporary update. Clin Med (Lond). (2020) 20(1):31–5. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.cme.20.1.1
7. Cresti A, Baratta P, De Sensi F, Aloia E, Sposato B, Limbruno U. Clinical features and mortality rate of infective endocarditis in intensive care unit: a large-scale study and literature review. Anatol J Cardiol. (2024) 28(1):44–54. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2023.3463
8. Mirabel M, Sonneville R, Hajage D, Novy E, Tubach F, Vignon P, et al. Long-term outcomes and cardiac surgery in critically ill patients with infective endocarditis. Eur Heart J. (2014) 35(18):1195–204. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht303
9. Kumar A, Anstey C, Tesar P, Shekar K. Risk factors for mortality in patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery for infective endocarditis. Ann Thorac Surg. (2019) 108(4):1101–6. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2019.05.029
10. Hotchkiss RS, Opal S. Immunotherapy for sepsis–a new approach against an ancient foe. N Engl J Med. (2010) 363(1):87–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcibr1004371
11. Diab M, Lehmann T, Bothe W, Akhyari P, Platzer S, Wendt D, et al. Cytokine hemoadsorption during cardiac surgery versus standard surgical care for infective endocarditis (REMOVE): results from a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Circulation. (2022) 145(13):959–68. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056940
12. Manohar M, Jawali V, Neginahal S, Gt S, Muniraj G, Chakravarthy M. Hemoadsorption in complex cardiac surgery-A single center experience. J Clin Med. (2022) 11(23):7005. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237005
13. Nierhaus A, Morales J, Wendt D, Scheier J, Gutzler D, Jarczak D, et al. Comparison of the CytoSorb((R)) 300 ml and jafron HA380 hemoadsorption devices: an in vitro study. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. (2022) 31(7):1058–65. doi: 10.1080/13645706.2022.2104617
14. Wang J, Chen B, Xie J, Chen H, Li L, Zhang W, et al. Effects of blood hemoadsorption therapy with HA-380 in total arch replacement for acute type A aortic dissection: a retrospective observational study. Blood Purif. (2024) 53(2):138–50. doi: 10.1159/000534852
15. Callum J, Farkouh ME, Scales DC, Heddle NM, Crowther M, Rao V, et al. Effect of fibrinogen concentrate vs cryoprecipitate on blood component transfusion after cardiac surgery: the FIBRES randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2019) 322(20):1966–76. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17312
16. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315(8):801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
17. Howitt SH, Herring M, Malagon I, McCollum CN. Grant SW: incidence and outcomes of sepsis after cardiac surgery as defined by the sepsis-3 guidelines. Br J Anaesth. (2018) 120(3):509–16. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2017.10.018
18. Lorenzin A, de Cal M, Marcello M, Sorbo D, Copelli S, Ronco C, et al. Vancomycin adsorption during in vitro model of hemoperfusion with Mini-module of HA380 cartridge. Blood Purif. (2023) 52(2):174–82. doi: 10.1159/000526149
19. He Z, Lu H, Jian X, Li G, Xiao D, Meng Q, et al. The efficacy of resin hemoperfusion cartridge on inflammatory responses during adult cardiopulmonary bypass. Blood Purif. (2022) 51(1):31–7. doi: 10.1159/000514149
20. Haidari Z, Demircioglu E, Boss K, Tyczynski B, Thielmann M, Schmack B, et al. Intraoperative hemoadsorption in high-risk patients with infective endocarditis. PLoS One. (2022) 17(7):e0266820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266820
21. Bernardi MH, Rinoesl H, Dragosits K, Ristl R, Hoffelner F, Opfermann P, et al. Effect of hemoadsorption during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery—a blinded, randomized, controlled pilot study using a novel adsorbent. Crit Care. (2016) 20:96. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1270-0
22. Abdullayev R, Gul F, Bilgili B, Seven S, Cinel I. Cytokine adsorption in critically ill COVID-19 patients, a case-control study. J Intensive Care Med. (2022) 37(9):1223–8. doi: 10.1177/08850666221085185
23. Zhang G, Zhang L, Si S, Jiang T, Xia Y, Zhu Y, et al. Fibrinogen and antithrombin III are associated with in-hospital mortality among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Ren Fail. (2022) 44(1):1938–47. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2142138
24. Mori K, Tsujita Y, Yamane T, Eguchi Y. Decreasing plasma fibrinogen levels in the intensive care unit are associated with high mortality rates in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy. Clin App Thromb Hemos. (2022) 28:10760296221101386. doi: 10.1177/10760296221101386
25. Chen M, Chen X, Ling H, Bai C, Chen L, Zhong L, et al. Shi F: prognostic significance of fibrinogen levels in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: unveiling a nonlinear relationship and clinical implications. Frontiers in Nephrology. (2024) 4:1398386. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2024.1398386
26. Tang X, Shao L, Dou J, Zhou Y, Chen M, Cui Y, et al. Fibrinogen as a prognostic predictor in pediatric patients with sepsis: a database study. Mediat Inflamm. (2020) 2020:9153620. doi: 10.1155/2020/9153620
27. Cao F, Chen X, Huang G, Liu W, Zhou N, Yuan H, et al. The albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio independently predicts acute kidney injury in infants with ventricular septal defect undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Front Pediatr. (2021) 9:682839. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.682839
28. Davalos D. Akassoglou K: fibrinogen as a key regulator of inflammation in disease. Semin Immunopathol. (2012) 34(1):43–62. doi: 10.1007/s00281-011-0290-8
29. Ruot B, Breuille D, Rambourdin F, Bayle G, Capitan P, Obled C. Synthesis rate of plasma albumin is a good indicator of liver albumin synthesis in sepsis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2000) 279(2):E244–251. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2000.279.2.E244
30. Ding Y, Qi X, Li Y, Sun Y, Wan J, Luo C, et al. Albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio is an independent prognostic parameter in de novo non-M3 acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23(8):4597–608. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01241-8
31. Li L, Ban C, Ruan H, Zhang M, Wang Z, Ma M, et al. Prognostic value of albumin to fibrinogen ratio for mortality in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2023) 23(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03562-8
32. Xu J, Zhang H, Che N, Wang H. FAR In systemic lupus erythematosus: a potential biomarker of disease activity and lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23(8):4779–85. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01239-2
33. Austin PC. Type I error rates, coverage of confidence intervals, and variance estimation in propensity-score matched analyses. Int J Biostat. (2009) 5(1):Article 13. doi: 10.2202/1557-4679.1146
Keywords: infective endocarditis, HA380, blood adsorption, postoperative sepsis, cardiopulmonary bypass
Citation: Jiefei X, Lu C, Han S, Yongxu S, Shaoyan M, Kai Q, Yonghua L, Yanling Z, Yumei J and Jian R (2025) The effect of HA380 blood adsorption on patients with acute infective endocarditis undergoing cardiac surgery: a retrospective study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1512619. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1512619
Received: 17 October 2024; Accepted: 21 February 2025;
Published: 11 March 2025.
Edited by:
Lei Du, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhenxiao Jin, Air Force Medical University, ChinaXing Hao, Capital Medical University, China
Copyright: © 2025 Jiefei, Lu, Han, Yongxu, Shaoyan, Kai, Yonghua, Yanling, Yumei and Jian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rong Jian, rongjian@mail.sysu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiao Jiefei
Xiao Jiefei