
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med. , 04 March 2025
Sec. Heart Failure and Transplantation
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1465700
This article is part of the Research Topic Advanced Therapeutic Strategies and Safety Profiles in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction View all 5 articles
Background: Vericiguat—a novel oral soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator—was developed for the treatment of chronic heart failure (HF). Although the value of vericiguat therapy in chronic HF has been gradually recognized, its safety and efficacy in the acute phase of HF remain elusive.
Methods: 100 patients with acute HF receiving vericiguat therapy at the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University between September 2022 and June 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. An external control was built from real-world data of acute HF subjects contemporaneously hospitalized in the same hospital using a propensity score matching (PSM) method.
Results: After a median follow-up of 68 days, 80 patients completed at least one outpatient follow-up or had an endpoint event and cardiovascular death occurred in 6 patients. We matched 75 external control patients for this purpose. In single-arm study, overall, although systolic blood pressure (SBP) decreased significantly before and after treatment, there was little change in SBP in the SBP low group (baseline SBP less than 120mmHg) (from 109 mmHg to 105 mmHg, p = 0.109). Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum potassium did not change significantly (p = 0.521 and 0.070, respectively). However, compared with the renal function normal group, eGFR showed a slower downward trend in the renal insufficiency group (p = 0.025). After using the PSM method, significant improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide were seen in both groups before and after treatment. There was no significant difference between the two groups. However, the downward trend in eGFR was even less significant in the vericiguat group, with significant differences between the two groups (p = 0.024).
Conclusions: Vericiguat is feasible in acute HF, even in patients with hypotension and renal dysfunction. At the same time, vericiguat may have a potential renoprotective effect, which warrants further exploration.
Heart failure (HF) is a severe manifestation or advanced stage of various heart diseases that affects approximately 64.3 million people worldwide (1). Despite advances in therapeutic drugs, HF still leads to high mortality and hospitalization rates. Therefore, the identification of new treatment strategies is urgent.
Vericiguat—as a novel oral soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator—enhances the cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP) pathway by directly stimulating sGC through a binding site independent of nitric oxide (NO) and sensitizes sGC to endogenous NO by stabilizing NO binding to the binding site (2). Large phase III clinical trials showed that compared with placebo, vericiguat therapy reduced cardiovascular mortality and HF hospitalization in patients with stable heart failure with ejection fraction (HFrEF) accompanying a high risk of worsening HF (3). Some of the existing guidelines also acknowledge the important role of vericiguat in chronic HF (4, 5).
Based on our literature search, no clinical studies on the use of vericiguat in acute decompensated HF have been identified. Regardless of the type of HF, the safety and efficacy of vericiguat in the acute phase of HF remains uncertain. Herein, we evaluate the safety and efficacy of vericiguat therapy in decompensated HF and provide new evidence for its clinical application.
To evaluate the preliminary safety and efficacy of the vericiguat in acute phase of HF subjects, a single-arm investigator-initiated study was conducted at China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University between September 2022 and June 2023, in China. The enrolled patients had symptoms and signs of acute decompensated HF at admission, such as chest tightness, shortness of breath, dyspnea, and edema of both lower limbs. These HF patients contained a variety of categories, including HFrEF (n = 46), heart failure with mild reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF) (n = 25) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (n = 9). Patients with a first diagnosis of HF were included, besides, their common feature was that none of them had received guideline-directed medical therapy prior to this hospitalization. Patients who were lost to follow-up or did not receive vericiguat for more than one month were excluded.
All of them were treated with vericiguat before discharge and continued to outpatient follow-up. Baseline characteristics of the patients, including laboratory, echocardiographic, etiology, comorbidity, diagnosis and medication data, were collected. After a median follow-up of 68 days, a total of 20 patients were lost to follow-up. Among them, 10 patients refused outpatient follow-up due to their health status (7 patients felt they had recovered well, and 3 patients were bedridden at home due to severe illness); 6 patients refused outpatient follow-up due to time, financial, or other reasons; and 4 patients could not be contacted due to relocation, phone number changes, or death.
Based on previous relevant clinical studies, we ultimately selected the following indicators as observation parameters and endpoint events (6–9). Observation indices for efficacy included left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left ventricular diameter (LVD), left atrium diameter (LAD) and mitral regurgitation area (MRA) measured by echocardiography for outpatient follow-up, as well as the laboratory index N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP). Observation indices for safety included symptomatic hypotension, blood potassium and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). End events included all-cause death and cardiovascular death. Echocardiograms in this study were conducted by experienced sonographers who specialize in the heart. The LVEF values of each patient were measured three times and averaged to give a paper version of the report. A flow chart of patient selection is shown in Figure 1.
Real-world data are collected from electronic health records of patients with acute decompensated HF admitted to the same hospital and used to form an external control group. These subjects received anti-HF drug therapy with the exception of Vericiguat only and were hospitalized during the same period as the single-arm study. Their individual patient-level data (IPD) were retrospectively analyzed by applying the inclusion/exclusion criteria of the single-arm study and using the propensity score matching (PSM) method to establish the external control group.
PSM was employed in this study due to the potential for confounding variables in case-control studies, which can lead to biased results. PSM is a statistical method used to handle research data by selecting and matching baseline characteristics of the groups to balance confounding variables, thereby minimizing bias in the study outcomes (10). PSM was performed using a multivariate logistic regression model to adjust for differences in baseline characteristics [age, gender, baseline LVEF (11, 12)] in the matched analysis. A propensity score was given for each subject in both the vericiguat group and the external control group. Subjects were then matched by propensity score in a 1:1 ratio using the caliper matching and a caliper size of 0.02. The standardized mean difference (SMD) for each covariate was calculated and computed to assess the balance in baseline characteristics before and after matching. The variables with a SMD < 0.1 are considered to be well-balanced between the vericiguat group and the external control group.
The investigation conforms with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. This trial was approved by the Ethical Review Board of China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University (approval No. 2023071116) and was registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2300077292).
Continuous variables were presented as median (interquartile range), and normality tests were conducted. For normally distributed data with equal variances, t-tests were used; for data with unequal variances, Welch's t-test was applied. Non-normally distributed data were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U-test. Categorical variables were expressed as frequency (percentage) and analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test, as appropriate. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 25.0 (IBM Corp). Variables with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A total of 100 patients with prescriptions for at least 30 days were included in the analysis. Among them, 16 patients did not complete the outpatient follow-up and 4 patients were lost to follow-up. Finally, only 80 patients had at least one month of follow-up echo examination data or endpoint. These patients included a first episode of acute decompensated heart failure as well as a second acute episode of admission after multiple previous episodes.
The baseline characteristics of the study population are displayed in Table 1. The median age was 63 (55, 70) years, with males accounting for 77.5% of the entire cohort. The most common etiology for HF was ischemic cardiomyopathy (82.5%), followed by dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, peripartum cardiomyopathy, etc. At baseline, the median creatinine level was 80.69 (64.88, 101.58) μmol/L and the median eGFR was 84.27 (67.57, 98.96) ml/min/1.73 m2. The median NT-proBNP level was 3,425 (1,223, 9,865) pg/ml. For echocardiography results, the median LVEF was 35.7 (29.0, 45.0) %, with a median LVD of 56.3 (49.0, 64.2) mm, a median LAD of 42.8 (37.7, 49.4) mm and a median MRA of 4.3 (1.8, 7.8) cm2 at baseline. Regarding medication, 66 (82.5%) patients received renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, 70 (87.5%) patients received b-blockers, 71 (88.7%) received mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and 73 (91.2%) patients received sodium-dependent glucose transporters 2 inhibitors at baseline.
At the end of the study, 74 patients continued to receive vericiguat therapy, of which 13 (17.6%) patients received 10 mg, 43 (58.1%) received 5 mg and 18 (24.3%) received 2.5 mg of vericiguat.
The safety analysis is detailed in Table 2. Overall, systolic blood pressure (SBP) declined significantly from 120 (110, 139) mmHg to 110 (104, 130) mmHg (p < 0.001). Patients were divided into a systolic-blood-pressure low (SBPL) group and a non-systolic-blood-pressure low (NSBPL) group based on whether the baseline SBP was less than 120 mmHg (Table 3). SBP before and after treatment ranged from 109 mmHg to 105 mmHg (p = 0.109) in the SBPL group and from 134 mmHg to 125 mmHg (p < 0.001) in the NSBPL group. Only one patient could not tolerate even a 2.5 mg dose of vericiguat and developed symptomatic hypotension during follow-up. Besides, two patients developed gastrointestinal symptoms with abdominal distention as the main manifestation that could be relieved by Domperidone.
Serum creatinine and eGFR remained unchanged before and after vericiguat treatment (p = 0.549 and 0.521, respectively). Meanwhile, no significant change was found in serum potassium (p = 0.070). Next, patients were divided into the renal insufficiency group (eGFR < 90 ml/min/1.73 m2) and the normal renal function group (eGFR ≥ 90 ml/min/1.73 m2) based on the baseline eGFR (Table 3). No significant change in eGFR was observed between patients with or without renal insufficiency (p = 0.162 and 0.080, respectively). However, the change in eGFR before and after treatment significantly differed between the two groups, with the renal insufficiency group showing a slower downward trend in eGFR after treatment (p = 0.025). Unfortunately, cardiovascular death occurred in six patients. The median time of death was 24 (6, 45) days.
Subsequently, we excluded populations with HFmrEF and HFpEF, and focused our safety analysis solely on individuals with HFrEF. The results demonstrated a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure, which decreased from 121 mmHg to 113 mmHg after treatment (p = 0.001). Renal function showed improvement post-treatment, as the eGFR increased from 79.13 ml/min/1.73 m² to 84.68 ml/min/1.73 m², with a significant difference observed before and after treatment (p = 0.015). Serum potassium levels, however, showed no significant change following treatment (p = 0.197).
The efficacy analysis is detailed in Table 2. After receiving vericiguat for 68 days as the median, median LVD values ranged from 56.0 mm to 55.4 mm, with no statistical significance (p = 0.383). However, the median LVEF increased significantly from 36.0% to 49.3% (p < 0.001). Meanwhile, the median LAD reduced significantly from 42.5 mm to 41.9 mm (p = 0.044). Median MRA partially increased from 4.1 cm2 to 2.5 cm2 (p = 0.013). For laboratory data, 43 patients had baseline and follow-up NT-proBNP data, with median NT-proBNP values ranging from 3,335 pg/ml to 1,270 pg/ml (p < 0.001).
Subsequently, we conducted an efficacy analysis exclusively within the HFrEF population. The results indicated that, similar to the overall heart failure cohort, there were significant differences in LVEF (p < 0.001), LAD (p = 0.010), MR (p = 0.025), and NT-proBNP (p = 0.004) before and after treatment. However, no significant difference was observed in LVD before and after treatment (p = 0.958).
The therapeutic efficacy of heart failure in different subgroups and specific populations remains unclear, including in women, the elderly, individuals with chronic kidney disease, and those with concomitant atrial fibrillation (13). Subsequently, subgroup analyses were conducted based on patient gender, age, renal function, and the presence of atrial fibrillation (AF) (Table 4).
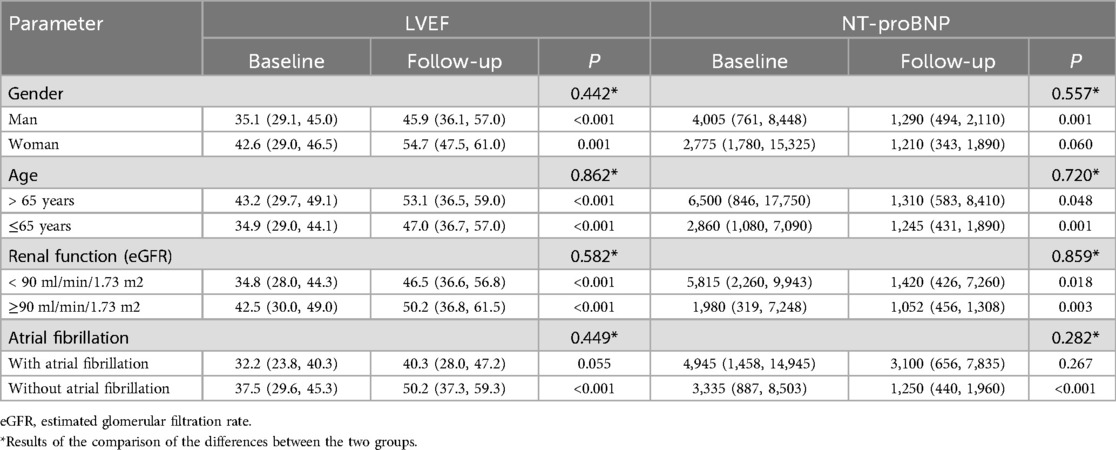
Table 4. Subgroup analysis based on gender, age, renal function and atrial fibrillation in a single-arm study.
In terms of gender differences, LVEF improved significantly after treatment in both male and female patients. However, no significant difference in NT-proBNP levels was observed in female patients post-treatment (p = 0.060). The change in LVEF and NT-proBNP between the two groups showed no significant difference.
Regarding the population with or without AF, although no significant differences were observed in the changes of LVEF and NT-proBNP between the two groups, in the AF subgroup, the changes in both LVEF and NT-proBNP post-treatment showed no statistically significant difference (p = 0.449 and 0.282, respectively).
No significant differences in treatment outcomes were observed across different age groups (with a cutoff age of 65 years) or renal function categories (with an eGFR cutoff of 90 ml/min/1.73 m²).
For vericiguat safety and efficacy evaluation, the PSM method was used to create an external control for the vericiguat group. The real-world IPD of 75 HF subjects from the study hospital's electronic health records were collected. To balance the baseline characteristics between the vericiguat group and the external control group, the SMD for each covariate of baseline characteristics were calculated, resulting in two PSM-matched groups, with 63 participants in the vericiguat group and 63 subjects in the external control group (Figure 1). Detailed subject characteristics and a comparison of baseline characteristics between the vericiguat group and the control group are shown separately after the PSM matching in Table 5.
In terms of effectiveness evaluation, LVEF and NT-proBNP were significantly improved before and after treatment in both vericiguat group and external control group. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.367 and 0.543, respectively). Although LAD and MRA Improved in the control group but not in the vericiguat group, this may be due to the shorter follow-up period.
In terms of safety evaluation, the renal function of the vericiguat group did not change significantly before and after treatment, while the renal function of the control group worsened after treatment. eGFR was significantly different between the two groups (p = 0.024), and the deterioration was more significant in the control group. Although potassium varied significantly before and after treatment in the vericiguat group (p = 0.021), they almost all fluctuated within the normal range. The results of the case-control study are presented in Table 6.
The present study initially evaluated the safety and efficacy of vericiguat therapy in patients with acute HF in real-world practice. A partial subgroup analysis and PSM was also performed to better evaluate its role.
Symptomatic hypotension is a relatively common adverse effect of vericiguat, which is due to its vasodilatory effect. The VICTORIA trial found that the incidence of symptomatic hypotension and syncope was higher in the vericiguat group compared to the placebo group, but with no statistically significant difference (3). Subgroup analysis of the VICTORIA trial revealed that patients older than 75 years and those receiving ARNI treatment had a slight initial decrease in systolic blood pressure (SBP), which then returned to baseline levels. Additionally, the study found that patients in both the vericiguat and control groups with a baseline SBP <110 mmHg showed an increasing trend in SBP over time (14). This study also noted that although there was a significant decrease in SBP in individual treatment groups before and after treatment, this could be due to the concurrent use of other antihypertensive heart failure medications, such as ARNI and β-blockers. However, subgroup analysis in this study showed no significant change in blood pressure in the SBPL subgroup before and after treatment, which further supports the feasibility and safety of vericiguat treatment in hypotensive patients.
The use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, β-blockers, spironolactone and other drugs is restricted or even discontinued in patients with chronic HF due to increased creatinine levels, renal dysfunction and other reasons. All these may have adverse effects on the prognosis and condition of HF patients. The VICTORIA subgroup trial examined the relationship between the efficacy of vericiguat therapy and renal function in HFrEF patients and found that the trajectories in eGFR and creatinine with vericiguat therapy were similar to those with placebo (15). Our data showed that baseline creatinine and eGFR were 80.69 μmol/L and 84.27 ml/min/1.73 m2 respectively and remained unchanged during the vericiguat treatment. Similar observations were reported in the VICTORIA trial. Additionally, we found that eGFR did not change significantly after treatment regardless of renal insufficiency. However, a statistically significant difference in the change in eGFR was found between the two groups before and after treatment, with the renal insufficiency group exhibiting a more gradual deterioration trend after treatment (p = 0.025). In a further case-control study, we found that eGFR in the vericiguat group did not change significantly before and after treatment (p = 0.719), while eGFR in the external control group decreased significantly after treatment (p = 0.001), which was statistically significant (p = 0.024).
In recent years, several preclinical studies have suggested that sGC stimulators possess nephroprotective effects. Atteia et al. demonstrated that the long-term treatment with the sGC stimulator Iisiquiritigenin effectively and dose-dependently improved chronic renal dysfunction and endothelial dysfunction induced by adenine. This intervention not only alleviated renal fibrosis and apoptotic markers but also reduced aortic calcification (16). Lichtenberger et al. proposed that sGC activator therapy could enhance cGMP concentrations in tissues, leading to the dilation of renal microvasculature, improved blood flow, and enhanced oxygenation. This intervention significantly mitigated the reduction in renal weight, cellular damage, fibrosis, and inflammation (17). This suggested that vericiguat therapy may have a potential renoprotective mechanism, which qualifies its potential application in HF patients with renal insufficiency.
In addition, a previous study reported that vericiguat therapy neither increased nor decreased serum potassium levels and therefore, it may be safely administered to patients with elevated serum potassium concentrations (15), which is consistent with our conclusions.
The single-arm study found significant improvements in NT-proBNP, LVEF, LAD and MRA. The lack of significant changes in LVD might be due to short follow-up time or small sample size. In case-control studies, LVEF and NT-proBNP showed significant improvement after treatment in both groups. The VICTORIA subgroup trial indicated that vericiguat significantly decreased NT-proBNP levels in patients with worsening HFrEF compared with the placebo (18). This is an initial indication of the efficacy of vericiguat therapy in patients hospitalized for HF. While this was true for other drugs for patients with HF, vericiguat played a crucial role. However, large randomized controlled trials, with longer follow-up time are needed to further confirm the effectiveness of vericiguat.
In patients with HFrEF, the left atrium typically undergoes dilation due to impaired left ventricular pumping function, resulting in eccentric remodeling. Additionally, left atrial strain has been shown to be a strong predictor of recovery of ejection fraction in HFrEF patients, independent of left ventricular strain. Vericiguat, by increasing cGMP levels, can improve hemodynamic status, reduce peripheral vascular resistance, decrease the cardiac afterload, and promote vasodilation. In this study, although a significant reduction in LAD was observed, there was no significant change in LVD. This may be attributed to the fact that the effects of vericiguat on the left ventricle primarily involve improving ventricular diastolic function and hemodynamic status, rather than directly altering its anatomical structure. It can be hypothesized that vericiguat's effects on cardiac chamber size may differ, as it significantly reduces the pressure burden on the left atrium, leading to notable improvements in left atrial size. In contrast, the impact on the left ventricle primarily manifests as functional improvement, which may require a longer duration or additional therapeutic interventions before structural changes in the left ventricle can be observed.
In gender, ischemic heart disease risk in women includes biomedical, behavioral, and psychosocial contributors (19). The study found that the prevalence of heart failure is higher in women over the age of 80 compared to men (20). Similarly, in large-scale trials of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), women were older than men and exhibited more symptoms along with poorer overall health status (21). A post analysis showed that elderly, postmenopausal women with HFpEF might benefit from nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase stimulation (22). This is because comorbidities in conjunction with estradiol decline in the postmenopausal age might impair cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling to a higher extent in female patients (23). Our research found no significant differences in the changes of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and NT-proBNP between genders (p = 0.442 and 0.557, respectively), which is consistent with the results of the VICTORIA trial (24). Such a difference in mechanism may be difficult to be manifested in clinical setting either.
AF is one of the most common complications of HF. The mechanisms by which HF contributes to the development of AF are multifactorial, involving factors such as neurohormonal activation, cardiac stretch, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction, all of which contribute to the inflammatory state characteristic of HF (25, 26). Chronic inflammation in HF patients is marked by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory molecules, which trigger atrial fibrosis, enlargement, and cell death, thereby disrupting the normal structure and function of atrial tissue and facilitating the development and maintenance of AF (27). Previous studies have suggested that the positive effect of vericiguat on the primary composite outcome and its components remains consistent regardless of the presence of atrial fibrillation at baseline (28), which is consistent with the findings of our study. However, animal studies have shown that vericiguat can reverse atrial enlargement, reduce myocardial fibrosis, prevent the shortening of atrial effective refractory periods, and decrease the inducibility of AF, thereby significantly improving the structural and electrophysiological remodeling associated with AF (29). These findings suggest the potential of vericiguat as a therapeutic agent for AF, warranting further investigation into its effects and significance in the treatment of AF in future studies.
The SOCRATES-REDUCED Randomized Trial reported a dose-effect relationship, in which higher vericiguat doses were associated with greater reductions in NT-proBNP levels. Meanwhile, mortality and HF hospitalization rates also tended to decrease with higher vericiguat doses (30). The SOCRATES-PRESERVED phase IIb study found that vericiguat at a dose of 10 mg improved the quality of life in patients with HFpEF (31). Thus, 10 mg is conventionally recommended as a target dose of vericiguat; however, only 17.6% of patients achieved the target dose in our study. Most of our patients selected the 5 mg dose largely out of choice rather than adverse drug reaction. Therefore, future studies should pay close attention to the up-titration of vericiguat up to the maximum dose by more propaganda and education.
This study is a single-center retrospective study with a very small sample size, with a short follow-up period of only 68 days as the median. Due to the small sample size, some clinically significant differences could not reach statistical significance. There were 20 patients who did not complete outpatient follow-up for personal reasons, which may have increased selection bias. Furthermore, our study did not differentiate between patients with de novo acute HF or decompensation of chronic HF, nor did it distinguish between different HF subtypes. This introduces an additional level of uncertainty to the study results.
Previous clinical studies have mostly included patients with chronic heart failure with HFrEF or HFpEF. For example, the VICTORIA trial (3), the VITALITY-HFpEF Randomized Clinical Trial (32), the SOCRATES-REDUCED Randomized Trial (30), the SOCRATES-PRESERVED study (31) and some subgroup studies of the VICTORIA study. Several Phase Ib studies have considered the use of vericiguat for the prevention and treatment of angina pectoris in patients with chronic coronary syndromes (33, 34). Our study innovated the use of vericiguat in patients with acute decompensated heart failure and found that vericiguat is safe and contributes to the improvement of symptoms and cardiac function in these patients.
In summary, the current study demonstrated that vericiguat therapy is safe, feasible and effective in patients with acute HF. Moreover, vericiguat had a better protective effect on blood pressure and renal function than other anti-HF drugs. Vericiguat may also have a unique protective mechanism for the kidneys. Nonetheless, large randomized controlled trials are warranted to further validate these conclusions.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethical Review Board of China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
ZL: Writing – original draft. TL: Writing – review & editing. TL: Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing. DS: Writing – review & editing. YH: Writing – review & editing. PY: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Science and Technology of Jilin Province [20240601011RC]. The funding body had no role in the design or writing of the study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Groenewegen A, Rutten FH, Mosterd A, Hoes AW. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. (2020) 22(8):1342–56. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1858
2. Stasch JP, Pacher P, Evgenov OV. Soluble guanylate cyclase as an emerging therapeutic target in cardiopulmonary disease. Circulation. (2011) 123(20):2263–73. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.981738
3. Armstrong PW, Pieske B, Anstrom KJ, Ezekowitz J, Hernandez AF, Butler J, et al. Vericiguat in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382(20):1883–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915928
4. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79(17):e263–421. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.12.012
5. Metra M, Tomasoni D, Adamo M, Bayes-Genis A, Filippatos G, Abdelhamid M, et al. Worsening of chronic heart failure: definition, epidemiology, management and prevention. A clinical consensus statement by the heart failure association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. (2023) 25(6):776–91. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2874
6. Tian J, Dong M, Sun X, Jia X, Zhang G, Zhang Y, et al. Vericiguat in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction patients on guideline-directed medical therapy: insights from a 6-month real-world study. Int J Cardiol. (2024) 417:132524. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2024.132524
7. Senni M, Alemayehu WG, Sim D, Edelmann F, Butler J, Ezekowitz J, et al. Efficacy and safety of vericiguat in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction treated with sacubitril/valsartan: insights from the VICTORIA trial. Eur J Heart Fail. (2022) 24(9):1614–22. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2608
8. Berg DD, Samsky MD, Velazquez EJ, Duffy CI, Gurmu Y, Braunwald E, et al. Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan in high-risk patients in the PIONEER-HF trial. Circ Heart Fail. (2021) 14(2):e007034. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.007034
9. Singh JSS, Mordi IR, Vickneson K, Fathi A, Donnan PT, Mohan M, et al. Dapagliflozin versus placebo on left ventricular remodeling in patients with diabetes and heart failure: the REFORM trial. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43(6):1356–9. doi: 10.2337/dc19-2187
10. Yang FN, Xie W, Wang Z. Effects of sleep duration on neurocognitive development in early adolescents in the USA: a propensity score matched, longitudinal, observational study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. (2022) 6(10):705–12. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00188-2
11. Lee WC, Liao TW, Chen TY, Fang HY, Fang YN, Chen HC, et al. Sacubitril/valsartan improves all-cause mortality in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction and chronic kidney disease. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2024) 38(3):505–15. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07421-0
12. Tan NY, Sangaralingham LR, Sangaralingham SJ, Yao X, Shah ND, Dunlay SM. Comparative effectiveness of sacubitril-valsartan versus ACE/ARB therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail. (2020) 8(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2019.08.003
13. Lavalle C, Mariani MV, Severino P, Palombi M, Trivigno S, D'Amato A, et al. Efficacy of modern therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in specific population subgroups: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cardiorenal Med. (2024) 14(1):570–80. doi: 10.1159/000541393
14. Lam CSP, Mulder H, Lopatin Y, Vazquez-Tanus JB, Siu D, Ezekowitz J, et al. Blood pressure and safety events with vericiguat in the VICTORIA trial. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10(22):e021094. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.021094
15. Voors AA, Mulder H, Reyes E, Cowie MR, Lassus J, Hernandez AF, et al. Renal function and the effects of vericiguat in patients with worsening heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: insights from the VICTORIA (vericiguat global study in subjects with HFrEF) trial. Eur J Heart Fail. (2021) 23(8):1313–21. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2221
16. Atteia HH, Alamri ES, Sirag N, Zidan NS, Aljohani RH, Alzahrani S, et al. Soluble guanylate cyclase agonist, isoliquiritigenin attenuates renal damage and aortic calcification in a rat model of chronic kidney failure. Life Sci. (2023) 317:121460. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121460
17. Lichtenberger FB, Xu M, Erdoğan C, Fei L, Mathar I, Dietz L, et al. Activating soluble guanylyl cyclase attenuates ischemic kidney damage. Kidney Int. (2025) 107(3):476–91. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.10.025
18. Armstrong PW, Zheng Y, Troughton RW, Lund LH, Zhang J, Lam CSP, et al. Sequential evaluation of NT-proBNP in heart failure: insights into clinical outcomes and efficacy of vericiguat. JACC Heart Fail. (2022) 10(9):677–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2022.04.015
19. Virzi NE, Krantz DS, Bittner VA, Merz CNB, Reis SE, Handberg EM, et al. Depression symptom patterns as predictors of metabolic syndrome and cardiac events in symptomatic women with suspected myocardial ischemia: the women’s ischemia syndrome evaluation (WISE and WISE-CVD) projects. Heart Mind (Mumbai). (2022) 6(4):254–61. doi: 10.4103/hm.hm_35_22
20. Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 145(8):e153–639. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001052
21. Dewan P, Rørth R, Jhund PS, Shen L, Raparelli V, Petrie MC, et al. Differential impact of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction on men and women. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2019) 73(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.081
22. Friebe A, Kraehling JR, Russwurm M, Sandner P, Schmidtko A. The 10th international conference on cGMP 2022: recent trends in cGMP research and development-meeting report. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2023) 396(8):1669–86. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02484-8
23. Sabbatini AR, Kararigas G. Menopause-Related estrogen decrease and the pathogenesis of HFpEF: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 75(9):1074–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.12.049
24. Lam CSP, Piña IL, Zheng Y, Bonderman D, Pouleur AC, Saldarriaga C, et al. Age, sex, and outcomes in heart failure with reduced EF: insights from the VICTORIA trial. JACC Heart Fail. (2023) 11(9):1246–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2023.06.020
25. Conte M, Petraglia L, Poggio P, Valerio V, Cabaro S, Campana P, et al. Inflammation and cardiovascular diseases in the elderly: the role of epicardial adipose tissue. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:844266. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.844266
26. Conte M, Petraglia L, Cabaro S, Valerio V, Poggio P, Pilato E, et al. Epicardial adipose tissue and cardiac arrhythmias: focus on atrial fibrillation. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:932262. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.932262
27. Mauriello A, Ascrizzi A, Roma AS, Molinari R, Caturano A, Imbalzano E, et al. Effects of heart failure therapies on atrial fibrillation: biological and clinical perspectives. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13(7):806. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070806
28. Ponikowski P, Alemayehu W, Oto A, Bahit MC, Noori E, Patel MJ, et al. Vericiguat in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: insights from the VICTORIA trial. Eur J Heart Fail. (2021) 23(8):1300–12. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2285
29. Lou Q, Li L, Liu G, Li T, Zhang L, Zang Y, et al. Vericiguat reduces electrical and structural remodeling in a rabbit model of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 28:10742484231185252. doi: 10.1177/10742484231185252
30. Gheorghiade M, Greene SJ, Butler J, Filippatos G, Lam CS, Maggioni AP, et al. Effect of vericiguat, a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator, on natriuretic peptide levels in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: the SOCRATES-REDUCED randomized trial. JAMA. (2015) 314(21):2251–62. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.15734
31. Pieske B, Maggioni AP, Lam CSP, Pieske-Kraigher E, Filippatos G, Butler J, et al. Vericiguat in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: results of the SOluble guanylate cyclase stimulatoR in heArT failurE patientS with PRESERVED EF (SOCRATES-PRESERVED) study. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38(15):1119–27. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw593
32. Armstrong PW, Lam CSP, Anstrom KJ, Ezekowitz J, Hernandez AF, O'Connor CM, et al. Effect of vericiguat vs placebo on quality of life in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: the VITALITY-HFpEF randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2020) 324(15):1512–21. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.15922
33. Boettcher M, Mikus G, Trenk D, Düngen HD, Donath F, Werner N, et al. Vericiguat in combination with isosorbide mononitrate in patients with chronic coronary syndromes: the randomized, phase ib, VISOR study. Clin Transl Sci. (2022) 15(5):1204–14. doi: 10.1111/cts.13238
Keywords: vericiguat, heart failure, heart failure hospitalization, safety, efficiency
Citation: Li Z, Li T, Liu T, Liu Y, Si D, He Y and Yang P (2025) Short-term outpatient follow-up of vericiguat treatment in patients hospitalized for heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1465700. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1465700
Received: 16 July 2024; Accepted: 17 February 2025;
Published: 4 March 2025.
Edited by:
Paolo Severino, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyReviewed by:
Nicola Pierucci, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyCopyright: © 2025 Li, Li, Liu, Liu, Si, He and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Daoyuan Si, c2lkYW95dWFuQGpsdS5lZHUuY24=; Yuquan He, aGV5cUBqbHUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.