
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med. , 30 January 2025
Sec. Coronary Artery Disease
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1463170
Objective: Acupuncture combined with multiple treatment modalities has been widely employed for treating angina pectoris. This paper compared the efficacy of acupuncture combined with multiple treatment modalities for angina pectoris by network meta-analysis (NMA).
Methods: As of November 2023, this study searched eight electronic databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of acupuncture combined with multiple modalities for the treatment of angina pectoris based on antianginal therapies. Primary efficacy indicators included the number of angina episodes and duration of episodes, and secondary indicators included clinical efficacy based on symptom improvement and electrocardiographic efficacy based on ST-segment and T-wave improvement. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool 2.0 (RoB 2.0) was used for risk of bias assessment. A random-effects Bayesian NMA was performed using R (version 4.3.1) and Stata (version 16.0).
Results: 46 RCTs were enrolled, with 3976 patients with angina pectoris. In reducing the number of angina episodes, acupuncture [MD: −3.79; 95% CrI (−6.34, −1.31)] and acupuncture + TCM [MD: −3.06; 95% CrI (−5.49, −0.62)] were superior to antianginal therapies, with acupuncture having the best efficacy (SUCRA: 78.2%). In shortening the duration of angina episodes, electroacupuncture (EA) + traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) was the most effective (SUCRA: 95.1%), superior to antianginal therapies [MD: −5.04; 95% CrI (−9.18, −0.89)], adjunctive therapy [MD: 7; 95% CrI (1.58, 12.39)], rehabilitation therapy [MD: −5.38; 95% CrI (−10.75, −0.05)], and warm acupuncture + adjunctive therapy [MD: −6.71; 95% CrI (−13, −0.48)]. In terms of clinical efficacy, thumbtack needling had the best efficacy (SUCRA: 82.1%), superior to TCM [RR: 1.3; 95% CrI (1.02, 1.69)] and antianginal therapies [RR: 0.75; 95% CrI (0.6,0.91)]. In electrocardiographic efficacy, EA showed the best efficacy (SUCRA: 92.9%), superior to antianginal therapies [RR: 0.52; 95% CrI (0.35, 0.71)] and acupuncture [RR: 0.62; 95% CrI (0.39, 0.91)].
Conclusion: Acupuncture performs best in reducing anginal episodes; EA + TCM is the most effective in shortening the duration of anginal episodes; thumbtack needling is the most effective in clinical efficacy; and EA shows optimal results in electrocardiographic efficacy. To further validate these findings, multicenter and large-sample RCTs are needed.
Systematic Review Registration: PROSPERO [CRD42024505456].
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death globally. In 2019, 27% of global deaths were caused by CVD. In 2020, CVD accounted for 48.00% and 45.86% of deaths in the rural and urban areas in China, and the projected number of people living with CVD in China was 330 million, of which 11.39 million had coronary heart disease. In 2021, CVD was responsible for approximately 19.91 million deaths worldwide, and nearly half of Americans (48.6%) suffered from CVD (1, 2). Angina pectoris, a typical symptom of CVD, especially coronary artery disease, limits mobility and professional or leisure activities and has a serious impact on patients’ quality of life. The presence of angina may indicate progression of coronary artery disease, increasing the risk of myocardial infarction, heart failure, and other cardiac events (3, 4). Current clinical guidelines provide recommendations for antianginal therapy. However, it is often difficult to control symptoms with a single agent, and multiple agents are needed to maximize efficacy and avoid adverse effects. In patients with specific comorbidities, antianginal medications are limited by drug suitability, side effects, and individual differences. Patients still experience persistent angina symptoms after adequate treatment with first- and second-line drugs (3, 5). On the other hand, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) can consistently improve clinical symptoms in patients with stable angina who have severe coronary stenosis without antianginal medication. However, the efficacy of PCI in improving exercise capacity and angina symptoms has been questioned in patients receiving the best combination of pharmacologic regimens (6, 7). Moreover, 20%–40% of patients may still experience angina in the short term despite optimized PCI therapy, which places a burden on their quality of life and finances (8). Therefore, the search for safe, cost-effective, and individualized treatment strategies is the focus of current research.
Acupuncture is an integral component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with a history spanning thousands of years. By stimulating specific acupoints, it achieves therapeutic effects in treating diseases and alleviating pain. The efficacy of acupuncture has been recognized by the international medical community and has been confirmed in diverse diseases (9, 10). Acupuncture and its related therapies are widely applied clinically for angina pectoris in China as a nonpharmacologic treatment. Several meta-analyses to date have reported the efficacy of acupuncture in reducing angina attack frequency. Compared to angina medication alone, acupuncture yielded better results in improving patients’ anxiety and depression as well as better performance on the six-minute walk test, suggesting that it may improve patients’ physical fitness, mental health, and cardiac function (11–13). A randomized controlled clinical trial (RCT) by Zhao et al. revealed that electroacupuncture (EA) reduced the frequency and pain intensity of angina and improved quality of life (14). Multiple treatment modalities such as thumbtack needling, warm acupuncture, moxibustion, and acupuncture + TCM have been reported to have positive efficacy for angina (15–17). Among them, thumbtack needles are small needling tools that apply weak and prolonged stimulation to specific acupoints and are used to stimulate the skin surface without penetrating into the muscle or deeper tissue. These findings emphasize the potential and value of acupuncture combined with multiple therapeutic modalities as a nonpharmacological treatment for angina pectoris.
Clinicians frequently base their selection of an acupuncture approach for angina on their personal experiences, leading to significant variability in the treatment methods used by different physicians and resulting in diverse patient outcomes. A direct comparison of the effectiveness of acupuncture combined with multiple treatment modalities for angina is currently lacking. Therefore, we conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) to evaluate and compare the efficacy of acupuncture combined with multiple treatment modalities for angina. Using the SUCRA score, we ranked the approaches based on number of episodes, duration of episodes, clinical efficacy, electrocardiographic (ECG) efficacy, TCM symptom score, and nitroglycerin use to assist health professionals and clinicians in making evidence-based decisions.
This NMA followed the PRISMA statement (18) and was registered in the PROSPERO (CRD42024505456).
PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Web of Science, CNKI, VIP, Wanfang Data, and SinoMed were independently searched by two researchers (K.X.Y. and G.Y.) up to 7 November 2023, without restrictions in study type, date, and publication status. MeSH terms and free words of keywords, including “Angina Pectoris”, “Angina, Stable”, “Angina, Unstable”, “Acupuncture”, and “acupuncture therapy” were utilized for article retrieval. The searching strategies are displayed in Supplementary Table S1. We further looked for references to related literature to prevent omissions.
The eligibility criteria were set based on PICOS principles, and the inclusion criteria covered (1) patients with angina pectoris of any age; (2) intervention: at least one of the following intervention modalities (any form, dose, or duration): acupuncture, EA, warm acupuncture, thumbtack needling, or a combination with these interventions. These acupuncture interventions were studied most frequently in patients with angina pectoris. (3) All patients received baseline antianginal therapies according to guideline recommendations, which included β-blockers, aspirin, statins, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Pharmacologic treatment was tailored to each patient. On this basis, additional adjunct (Adj) therapies were introduced in some control and intervention groups, respectively. (4) outcome: at least one of the following indexes: number of episodes, duration of angina episode, clinical symptom improvement rate, ECG improvement rate, TCM symptom score, and nitroglycerin use. The rates of clinical improvement and ECG improvement are defined in Supplementary Tables S2, S3. (5) The study design was an RCT. The language of these studies was limited to English or Chinese. Among them, only those Chinese studies in the “Core Journals of Peking University” or “Chinese Scientific and Technical Journal Database” were included. Articles were excluded for (1) unclear diagnostic and efficacy criteria; (2) reviews, cohort studies, case reports, opinions, descriptive studies, or abstracts; (3) incomplete or erroneous data that could not be combined; (4) publication before 2013.
Study selection was performed independently by two investigators (K.X.Y. and G.Y.) according to our predefined criteria. First, all retrieved studies were imported into EndNote 20 to remove duplicates. Then, titles and abstracts were initially screened to eliminate ineligible RCTs. Finally, the full text of the initial screened matches was further screened to identify the final included literature. Disagreements were addressed through discussion with a third researcher (Q.Z.).
The following data and information were extracted: (1) basic information such as title, first author's name, year of publication, country, and study type; (2) basic characteristics of the study population, including age, gender, number of cases, and disease type; (3) specific content of the intervention, including specific measures and time schedules; and (4) baseline and post-treatment outcome metrics, such as number of anginal episodes, duration of anginal episodes, clinical efficacy, ECG efficacy, TCM symptom score, and nitroglycerin use. One investigator (K.X.Y.) extracted the data, and then the accuracy was confirmed by another investigator (G.Y.).
The risk of bias was judged by two independent reviewers (K.X.Y. and G.Y.) using the Cochrane Risk-of-Bias Tool Version 2 (RoB 2.0) (19). Each trial was rated as “low risk”, “some concerns”, or “high risk” across the following domains: randomization; deviations from intended interventions; missing data; outcome measurement; and selective reporting of results. The trials were rated as an overall high risk of bias if one or more domains were rated as “high risk of bias” and as an overall low risk of bias if all domains were rated as “low risk of bias”.
Statistical models based on the Bayesian framework were constructed using the JAGS software (gemtc 0.8–2 and rjags 4–10 package) in R 4.3.1 (Rstudio, Boston, MA, USA). Continuous data were depicted as mean difference (MD) with a 95% credible interval (CrI) to determine the effect size, while categorical data were presented as risk ratio (RR) with a 95% CrI. Random-effect models were utilized for all NMA due to the clinical heterogeneity in the included trials. The surface under the cumulative rank curve (SUCRA) was employed to assess the relative ranking of various modalities for each outcome. The ranking of interventions is positively correlated with higher SUCRA values (20). Furthermore, the comparison between consistency and inconsistency models was conducted through deviation information criterion (DIC). A discrepancy of <5 points in DIC indicated good consistency, leading to the utilization of consistency modeling (21). To examine publication bias, funnel plots were employed. Network plots and funnel plots for NMA were generated using Stata 16.0 (StataCorp, College Station, Texas, USA).
The detailed procedure is displayed in Figure 1. Initially, 2,106 articles were retrieved. After removal of 1,045 duplicates, the title and abstract of each article were screened. Consequently, 975 articles were excluded. Following further full-text examination, 17 articles that did not have a full text and 23 articles that did not meet the criteria for RCTs and lack of data were eliminated. Ultimately, 46 articles were enrolled in the NMA.
The details of each eligible article are displayed in Table 1 (Supplementary Table S4). 46 eligible studies published in 2013–2023 were all conducted in Asia (15–17, 22–64), enrolling 3,976 patients with angina pectoris, with study sample sizes ranging from 45 to 147 and a mean age of 44.7–73.16 years. Among them, 9 articles recruited patients with unstable angina (29, 34, 37, 38, 47, 53, 57, 62, 63), 6 recruited patients with coronary heart disease with angina (28, 33, 41–43, 51), 2 enrolled patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with angina (25, 32), 1 recruited elderly patients with coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, and hyper homocysteine (46), 1 recruited patients with angina pectoris (56), 1 recruited patients with chronic stable angina pectoris (26), 1 recruited female patients with syndrome X (54), and others 27 trials recruited patients with stable angina pectoris. All patients received antianginal therapies, and 2 trials used EA (15, 51), 1 trial used EA + TCM (42), 2 trials used thumbtack needling (15, 48), 3 trials used warm acupuncture (29, 35, 54), 1 trial used acupuncture + acupressure (33), 1 trial used acupuncture + Adj therapy + moxibustion (16), 2 trials used acupuncture + moxibustion (17, 46), 1 trial used acupuncture + rehabilitation (24), 1 trial used acupuncture + TCM + moxibustion (17, 41), 1 trial used acupuncture + TCM + topical patch (49), 1 trial used acupuncture + TCM injection (36, 37), 1 trial used acupuncture + TCM injection and TCM oral administration (59), 15 trials used acupuncture (22, 25, 27, 32, 38, 40, 43, 53, 55, 57, 58, 60, 61, 63, 64), and 19 trials used acupuncture + TCM (22, 23, 26, 28, 30, 31, 34, 39, 43–45, 47, 50, 52, 55, 56, 60–62). Among the 46 trials, 6 trials involved 3 groups (15, 55, 58, 60, 61, 63), 2 trials involved 4 groups (14, 40), and the remaining 40 trials involved 2 groups. Seven efficacy indices were evaluated, namely clinical efficiency (n = 41) (15–17, 22–39, 41, 44–57, 59, 60) (62–64), ECG efficacy (n = 14) (15, 25, 44–46, 48–51, 57, 59, 60, 62, 63), number of angina attacks (n = 19) (16, 22–26, 28–31, 35, 38, 40, 42, 43), (46, 52, 53, 58), duration of anginal attacks (n = 16) (16, 22–26, 28–30, 35, 38, 42, 43, 46, 47, 52), TCM symptom score (n = 10) (25, 27, 28, 30, 31, 39, 41, 44, 49, 50), Nitroglycerin use (n = 8) (25, 30, 38, 40, 43, 47, 53, 58).
4 RCTs were rated at high risk due to unknown or incorrect randomization methods and missing multiple efficacy indicators. 8 RCTs were rated as some concerns, with 4 RCTs not describing randomization methods and 4 RCTs missing multiple efficacy indicators. The remaining 34 RCTs were rated at low risk of bias (Figure 2).
11 intervention modalities for angina pectoris from 19 RCTs were comprehensively assessed for their effectiveness in reducing angina episodes (Figure 3A). NMA results manifested that (Figure 3B) compared with antianginal therapies, based on antianginal therapies, acupuncture [MD: −3.79; 95% CrI (−6.34, −1.31)] and acupuncture + TCM [MD: −3.06; 95% CrI (−5.49, −0.62)] had reduced the number of angina episodes, with marked differences. Based on the SUCRA score, acupuncture was the most effective treatment (SUCRA score: 78.2%) (Supplementary Figure S1; Supplementary Table S5).
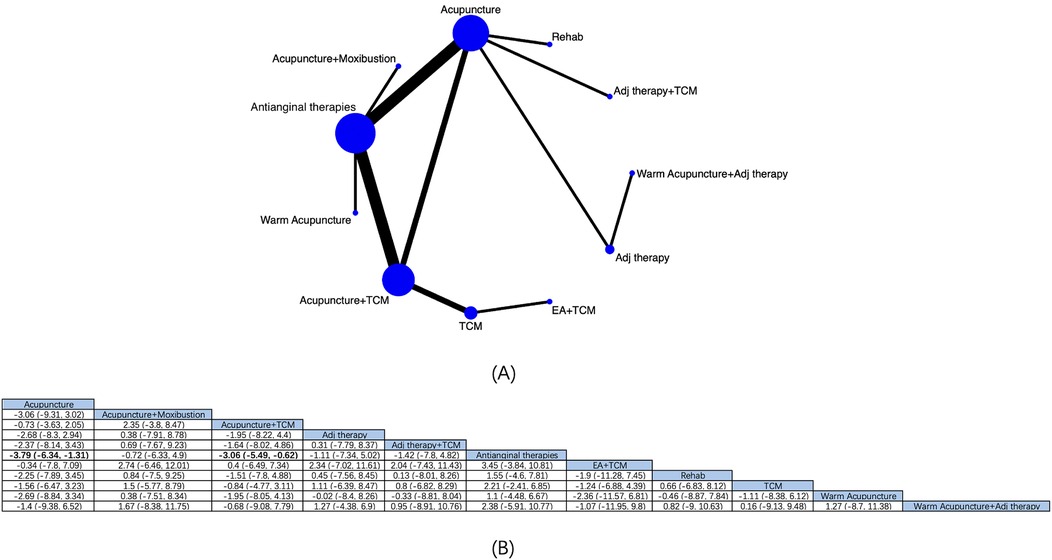
Figure 3. Network diagrams and NMA results. (A) Network plot of the number of angina episodes. (B) Relative impact of different interventions on the number of angina episodes. Estimates are depicted as MD and 95% CrI. Comparisons are interpreted by Reading from left to right. The estimates of treatment effects can be found at the point where the specified column intervention intersects with the specified row intervention. Noteworthy findings are highlighted in bold text.
10 interventions for angina pectoris from 16 RCTs were comprehensively assessed for their effectiveness in reducing the duration of angina attacks (Figure 4A). NMA results manifested that (Figure 4B) compared with antianginal therapies, based on antianginal therapies, acupuncture + TCM [MD: −3.35; 95% CrI (−4.79, −1.9)] and EA + TCM [MD −5.04; 95% CrI (−9.18, −0.89)] had reduced patients’ anginal attack durations, and EA + TCM was superior to Adj therapy [MD: 7; 95% CrI (1.58, 12.39)], rehabilitation [MD: −5.38; 95% CrI (−10.75, −0.05)], and warm acupuncture + Adj therapy [MD: −6.71; 95% CrI (−13, −0.48)], with substantial differences. Based on the SUCRA score, EA + TCM was the most effective (SUCRA score: 95.1%) (Supplementary Figure S2; Supplementary Table S6).
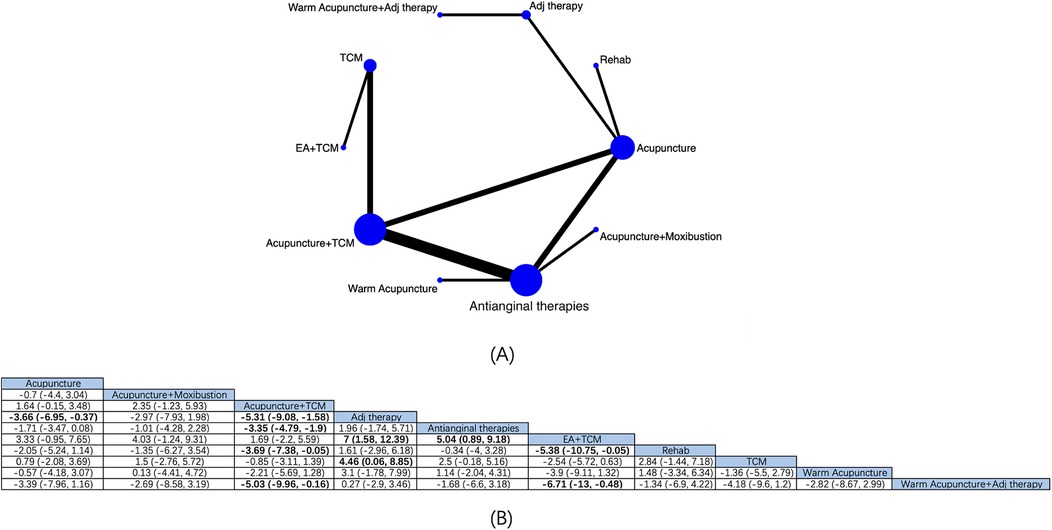
Figure 4. Network diagrams and NMA results. (A) Network plot of the duration of angina attacks. (B) Relative impact of different interventions on the duration of angina attacks. Estimates are depicted as MD and 95% CrI. Comparisons are interpreted by Reading from left to right. The estimates of treatment effects can be found at the point where the specified column intervention intersects with the specified row intervention. Noteworthy findings are highlighted in bold text.
The effectiveness of 18 interventions for angina pectoris in clinical symptom improvement was assessed by a pooled analysis of 41 RCTs (Figure 5A). NMA showed (Figure 5B) that based on antianginal therapies, thumbtack needling [RR: 0.75; 95% CrI (0.6, 0.91)], EA [RR: 0.8; 95% CrI (0.66, 0.94)], acupuncture + TCM + moxibustion [RR: 0.78; 95% CrI (0.64, 0.91)], and warm acupuncture [RR: 0.81; 95% CrI (0.68, 0.93)] were more effective than antianginal therapies in alleviating angina clinical symptoms. Thumbtack needling was superior to TCM [RR: 1.3; 95% CrI (1.02, 1.69)], and TCM + acupuncture was superior to TCM [RR: 0.8; 95% CrI (0.63,0.99)] and rehabilitation [RR: 0.74; 95% CrI (0.53,0.99)], with statistically notable differences. Based on the SUCRA score, thumbtack needling was considered the most effective modality (SUCRA score: 82.1%) (Supplementary Figure S3; Supplementary Table S7).
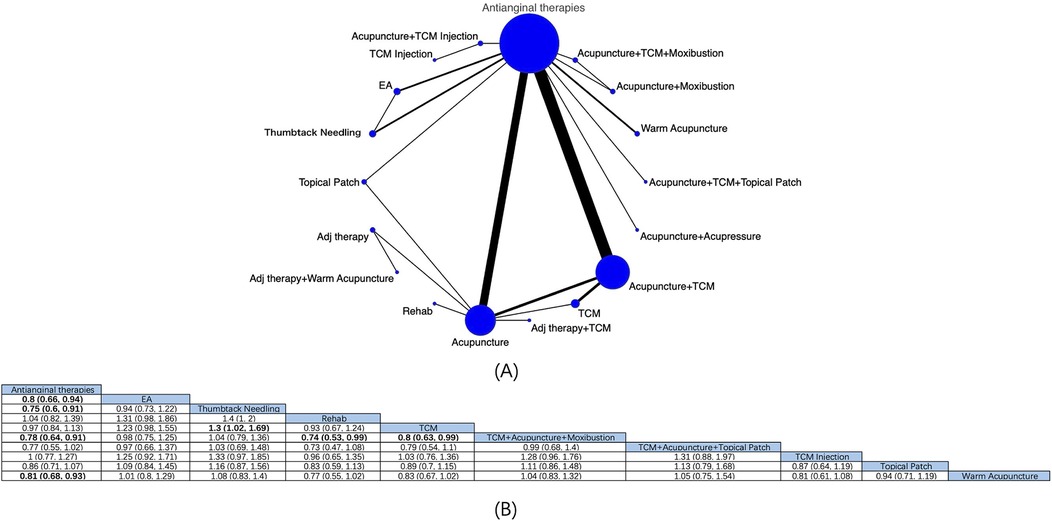
Figure 5. Network diagrams and NMA results. (A) Network diagram of clinical efficacy. (B) Relative impact of different intervention modalities on patients’ clinical efficacy. Estimates are depicted as RR and 95% CrI. Comparisons are interpreted by Reading from left to right. The estimates of treatment effects can be found at the point where the specified column intervention intersects with the specified row intervention. Noteworthy findings are highlighted in bold text. located at the intersection of the defined column intervention and the defined row intervention. Significant results are presented in bold.
8 intervention modalities for angina pectoris from 14 RCTs were comprehensively assessed for their effectiveness in ECG improvement (Figure 6A). NMA showed (Figure 6B) that based on antianginal therapies, EA [RR: 0.52; 95% CrI (0.35, 0.71)], acupuncture + TCM [RR: 1.38; 95% CrI (1.13, 1.72)], and thumbtack needling [RR 0.61; 95% CrI (0.42, 0.83)] boosted the effective rate of ECG improvement in patients with angina pectoris, and EA was superior to acupuncture [RR: 0.62; 95% CrI (0.39, 0.91)], with statistical differences. Based on the SUCRA score, EA was considered the best treatment modality (SUCRA score: 92.9%) (Supplementary Figure S4; Supplementary Table S8).
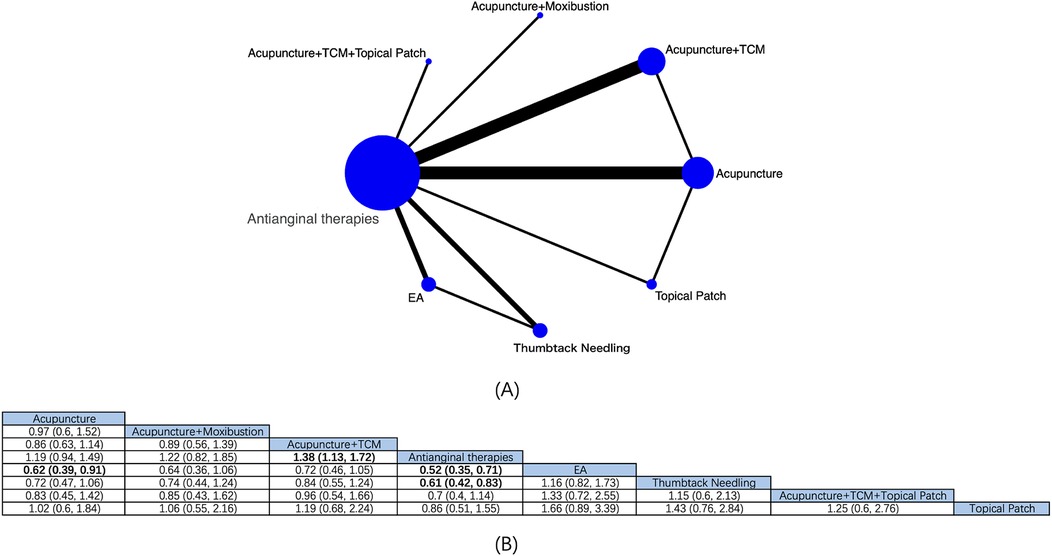
Figure 6. Network diagrams and NMA results. (A) Network plot of ECG efficiency. (B) Relative impact of different intervention modalities on the effective rate of ECG improvement. Estimates are depicted as RR and 95% CrI. Comparisons are interpreted by Reading from left to right. The estimates of treatment effects can be found at the point where the specified column intervention intersects with the specified row intervention. Noteworthy findings are highlighted in bold text.
6 interventions from 11 RCTs were comprehensively assessed (Supplementary Figure S5). Based on antianginal therapies, acupuncture + TCM [MD: −0.82; 95% CrI (−1.44, −0.22)] was superior to antianginal therapies in improving TCM symptom scores, with substantial differences. Based on the SUCRA score, acupuncture + TCM + topical patch was the most effective treatment (SUCRA score: 75.0%) (Supplementary Figure S6; Supplementary Table S9).
5 intervention modalities from 8 RCTs were comprehensively assessed (Supplementary Figure S7). Based on antianginal therapies, compared with Adj therapy, acupuncture [MD: −13.8; 95%C CrI (−27.46, −0.1)] and acupuncture + TCM [MD −16.87; 95% CrI (−33.32, −0.44)] had reduced patients’ nitroglycerin use, with statistical differences. Based on the SUCRA score, acupuncture + TCM was the most effective treatment (SUCRA score: 87.9%) (Supplementary Figure S8; Supplementary Table S10).
5 interventions from the 46 RCTs included in this study reported adverse events associated with acupuncture therapies. One trial documented six cases of transient headache, dizziness, and palpitations (45). Another trial reported two cases each of gastrointestinal discomfort, liver function abnormalities, and local bleeding in the acupuncture group (54). Minor local reactions, such as bleeding at needle sites and adhesive allergies, were observed in one trial each (15). Additionally, one trial recorded two cases of vomiting and one case of fatigue in the acupuncture group (41), while another reported one case of nausea (53).
All outcome indicators were tested for publication bias (Supplementary Figure S9). According to the funnel plots, the number of angina attacks, duration of angina attacks, and clinical efficacy showed good symmetry suggesting comprehensive findings on these indicators and no significant publication bias. However, the funnel plots showed certain asymmetry in ECG improvement, nitroglycerin use, and TCM symptom score, suggesting potential publication bias.
In recent years, several clinical RCTs and meta-analyses have reported that acupuncture combined with different interventions can improve clinical symptoms and quality of life in angina patients (11, 14, 65). This NMA comprehensively evaluated acupuncture combined with multiple interventions for angina pectoris based on antianginal therapies by analyzing the most recent data from the past 10 years, including acupuncture, thumbtack needling, EA, acupuncture + TCM + moxibustion, and warm acupuncture. 46 RCTs were analyzed. The results noted that relative to antianginal therapies, these interventions demonstrated certain advantages in the number and duration of angina attacks, clinical efficacy, ECG efficacy, TCM symptom scores, and nitroglycerin use. Acupuncture alone was the most effective in reducing the frequency of angina attacks, EA + TCM was the most effective in reducing the duration of angina attacks, thumbtack needling was most significant in improving clinical symptoms of angina pectoris, and EA exhibited the best efficacy in improving ECG efficacy.
In the number of angina episodes, acupuncture + antianginal therapies was superior to antianginal therapies and was considered the optimal treatment. Nonetheless, an NMA by Li et al. concluded that acupuncture did not diminish the number of angina episodes (65). Discrepancy may be due to the heterogeneity of enrolled populations, including angina types, enrolled interventions, and the number of cases. However, the meta-analysis by Lu et al. concluded that acupuncture + antianginal therapies diminished the number of angina attacks relative to antianginal therapies alone (13), consistent with our findings. Acupuncture is one of the oldest treatment modalities in China. In reducing angina episodes, its therapeutic mechanism may involve the regulation of sympathetic nerves and the improvement of vascular endothelial function. Acupuncture regulates the activity of the sympathetic nervous system by stimulating specific acupoints, thereby reducing myocardial oxygen consumption and relieving angina symptoms. Additionally, acupuncture can improve vascular endothelial function, promote vasodilatation, and increase the blood flow of coronary arteries, thus improving myocardial blood supply and reducing angina episodes (66, 67). These mechanisms may collaborate to contribute to its significant clinical efficacy in decreasing the frequency of angina attacks.
In terms of the duration of angina attacks, EA was most effective based on antianginal therapies, while EA + TCM was the most effective in terms of electrocardiographic efficacy. EA is thought to improve myocardial function through various mechanisms. For example, by modulating the expression of energy metabolism-related ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit G1, EA enhances energy synthesis in myocardial ischemic regions. Meanwhile, by regulating the inflammation-related TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway, EA could reduce the release of inflammatory cytokines, thereby repressing inflammatory responses. EA can also reduce oxidative stress-induced myocardial injury by activating the endogenous antioxidant pathway, increasing superoxide dismutase, and decreasing malondialdehyde production. In addition, EA can prevent cardiac sympathetic activation (68–70). Although the potential efficacy of acupuncture for ECG improvement has also been reported in systematic reviews (12), suggesting that acupuncture may improve myocardial blood supply or modulate autonomic function to some extent. However, the quality of evidence from these studies is generally low. Moreover, the specific mechanism of acupuncture in improving ECG, especially in terms of ST-segment elevation and T-wave inversion improvement, is not clear. Although this study discusses the role of acupuncture on ECG improvement based on the existing literature and physiological mechanisms, these findings still need to be validated by further high-quality RCTs.
In terms of improvement in clinical symptoms of angina, the SUCRA score found that thumbtack needling performed most prominently based on antianginal therapies and significantly better than antianginal therapies and TCM. Its efficacy in treating angina pectoris may be related to its ability to improve myocardial ischemia by prolonged stimulation of acupoints and modulation of vascular growth factor expression (71). Continuous stimulation of thumbtack needles promotes the release of vascular endothelial growth factor and other angiogenesis-related factors, which are crucial in improving myocardial blood flow and reducing ischemic areas. In addition, the weak stimulation of thumbtack needles may relieve angina symptoms by reducing the inflammatory response through modulation of the neuroendocrine system (12, 72). Combined with these mechanisms, thumbtack needling not only excels in symptomatic relief but may also improve cardiac function through multiple physiologic pathways. The safety, simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and clinical applicability of thumbtack needles call for further research and clinical trials to understand its specific mechanisms and long-term effects on angina pectoris.
Acupuncture + TCM was notably better than antianginal therapies in improving TCM symptom scores (mainly including chest pain, chest tightness, palpitations, and fatigue). The difference was not statistically notable between acupuncture + TCM + topical patch and antianginal therapies in TCM symptom improvement, which may be due to the small sample size of acupuncture + TCM + topical patch, resulting in insufficient statistical efficacy. However, the SUCRA score illustrated that acupuncture + TCM + topical patch was the most effective treatment. In the future, statistical efficacy can be improved by including the latest studies to obtain more reliable results in TCM symptom scores in angina patients with acupuncture modalities.
There was no statistical significance in the reduction of nitroglycerin use with acupuncture, TCM, and acupuncture + TCM compared with antianginal therapies, inconsistent with the findings of Liu et al.'s meta-analysis that acupuncture + TCM can reduce nitroglycerin use in patients with angina pectoris (73). This may be related to the methodology used and the heterogeneity of the included population, as our study included cases with multiple treatment modalities. We assessed the effects of all interventions by NMA indirect comparisons (i.e., by comparison of a common control group) and evinced that acupuncture + TCM was the optimal treatment based on SUCRA scores. Combined with the study of Liu et al, we concluded that acupuncture + TCM is advantageous in reducing nitroglycerin use in patients with angina pectoris. Rigorous RCTs are warranted in the future to demonstrate the evidence-based rationale for acupuncture + TCM in reducing nitroglycerin use in patients with angina pectoris.
In terms of safety, only five studies reported a small number of adverse effects, including transient headache, nausea, and localized reactions, and serious adverse effects were not reported. The current results suggest that acupuncture combined with different therapies not only demonstrates significant efficacy based on the antianginal therapy but also has the advantage of high safety and few adverse effects.
Clinical decision-making for acupuncture-related therapies should be based on the patient's specific condition, personal wishes, and the characteristics of angina symptoms. For example, in patients with a high number of angina episodes, acupuncture therapy may provide significant benefits. In the context of precision and individualized medicine, different acupuncture therapies may further improve patient symptoms and enhance quality of life.
To our knowledge, this is the first NMA to compare the effects of acupuncture combined with multiple interventions on various outcomes in angina pectoris and to rank all interventions based on these outcomes. This study provides evidence for optimizing acupuncture-based interventions for angina pectoris. However, several limitations of this NMA should be acknowledged. First, some included studies did not clearly specify diagnostic methods (e.g., stress tests, coronary CT, or coronary angiography) and only stated that the diagnosis was based on textbooks or guidelines. The lack of clear diagnostic descriptions may have led to inconsistencies in the diagnostic standards of the study populations. Future studies should adopt clear and standardized diagnostic methods to enhance the reliability of meta-analyses. Second, the limited sample size of non-ischemic angina patients and the lack of data on revascularization rates and outcomes prevented a comprehensive analysis of treatment differences between ischemic and non-ischemic patients. Although this study primarily focuses on symptom management, the potential impact of revascularization cannot be fully excluded. Future research should explicitly document these variables for more comprehensive evaluations. However, of the 46 studies eligible for inclusion, only 19 reported the relatively internationally recognized frequency of angina attacks as an efficacy indicator, while 41 used clinical outcome improvement. Variations in the efficacy criteria used in these studies were addressed using random-effects models and consistency tests to reduce the impact of heterogeneity. Although these criteria are based on official guidelines and integrate TCM perspectives, differences in efficacy assessments and subjective measures may limit the international recognition of acupuncture in angina treatment. Future studies should adopt internationally recognized standards, such as the frequency of angina attacks, exercise tolerance tests (ETT), Seattle Angina Questionnaire (SAQ) scores, and Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) classification (6, 7), while incorporating clear and standardized diagnostic criteria along with the unique efficacy evaluation systems of TCM to enhance global acceptance. Lastly, the studies analyzed in this research were primarily published in Chinese medical journals, which may lead to regional bias and limit the generalizability of the results. Further high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to validate our findings.
No single intervention was effective for all indices in angina patients. Based on antianginal therapy in all patients, acupuncture showed the best efficacy in reducing the number of angina attacks, and EA + TCM was the most effective modality in shortening the duration of angina attacks. In addition, thumbtack needling was the most significant in improving the clinical symptoms of angina pectoris, and EA had the best efficacy in improving the electrocardiogram. In terms of TCM symptom score, acupuncture + TCM + topical patch was considered the optimal treatment modality. In terms of reducing nitroglycerin use, acupuncture + TCM showed the highest effectiveness. These results suggest that acupuncture and its combination therapies have significant clinical applications in angina pectoris. Due to some limitations of current clinical data, future research should prioritize larger sample sizes, longer follow-up duration, and more rigorous study designs to validate these findings.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XK: Writing – original draft. YG: Writing – review & editing. ZQ: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1463170/full#supplementary-material
1. Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, et al. 2024 heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2024) 149(8):e347–913. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209
2. Disease Cragocha. China Report 2022 profile of cardiovascular health and disease. Chin J Circ. (2023) 38(6):583–612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2023.06.001
3. Davies A, Fox K, Galassi AR, Banai S, Ylä-Herttuala S, Luescher TF. Management of refractory angina: an update. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42(3):269–83. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa820
4. Ferraro R, Latina JM, Alfaddagh A, Michos ED, Blaha MJ, Jones SR, et al. Evaluation and management of patients with stable angina: beyond the ischemia paradigm: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76(19):2252–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.08.078
5. Ferrari R, Camici PG, Crea F, Danchin N, Fox K, Maggioni AP, et al. Expert consensus document: a ‘diamond’ approach to personalized treatment of angina. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2018) 15(2):120–32. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.131
6. Rajkumar CA, Foley MJ, Ahmed-Jushuf F, Nowbar AN, Simader FA, Davies JR, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of percutaneous coronary intervention for stable angina. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389(25):2319–30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2310610
7. Al-Lamee R, Thompson D, Dehbi HM, Sen S, Tang K, Davies J, et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention in stable angina (ORBITA): a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2018) 391(10115):31–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32714-9
8. Crea F, Bairey Merz CN, Beltrame JF, Berry C, Camici PG, Kaski JC, et al. Mechanisms and diagnostic evaluation of persistent or recurrent angina following percutaneous coronary revascularization. Eur Heart J. (2019) 40(29):2455–62. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy857
9. Vickers AJ, Vertosick EA, Lewith G, MacPherson H, Foster NE, Sherman KJ, et al. Acupuncture for chronic pain: update of an individual patient data meta-analysis. J Pain. (2018) 19(5):455–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2017.11.005
10. Zhang JF, Williams JP, Shi WR, Qian XY, Zhao QN, Lu GF. Potential molecular mechanisms of electroacupuncture with spatial learning and memory impairment induced by chronic pain on a rat model. Pain Physician. (2022) 25(2):E271–e83.35322982
11. Yang M, Sun M, Du T, Long H, Chen J, Liang F, et al. The efficacy of acupuncture for stable angina pectoris: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2021) 28(13):1415–25. doi: 10.1177/2047487319876761
12. Yu C, Ji K, Cao H, Wang Y, Jin HH, Zhang Z, et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture for angina pectoris: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2015) 15:90. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0586-7
13. Lu L, He W, Guan D, Jiang Y, Hu G, Ma F, et al. Acupuncture in treating cardiovascular disease complicated with depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 13:1051324. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1051324
14. Zhao L, Li D, Zheng H, Chang X, Cui J, Wang R, et al. Acupuncture as adjunctive therapy for chronic stable angina. JAMA Intern Med. (2019) 179(10):1388–97. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.2407
15. Chen M, Cui J, Jiang Y. Clinical observation of different acupuncture methods for stable angina pectoris. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. (2023) 38(06):2983–7.
16. Zhang J, Wu Y. Efficacy observation of needle-warming moxibustion plus pharmaceutical treatment for stable angina pectoris coupled with depression and its effects on serum resistin and adropin levels. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2023) 42(4):342–7.
17. Sun W, Sun Q, Xu M. Effects of yangxin pingmai decoction combined with acupuncture and moxibustion on TCM symptoms and electrocardiogram indicators in treating chest stuffiness and pains(qi-yin deficiency and blood stasis type). Sh J Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 44(9):1308–11.
18. Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162(11):777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
19. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. Rob 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
20. Veroniki AA, Straus SE, Fyraridis A, Tricco AC. The rank-heat plot is a novel way to present the results from a network meta-analysis including multiple outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. (2016) 76:193–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.02.016
21. Dempster AP. The direct use of likelihood for significance testing. Stat Comput. (1997) 7:247–52. doi: 10.1023/A:1018598421607
22. Li Z, Gao H, Wen L, Zhao H. Effect of jieyu dingzhi decoction combined with acupuncture on chronic stable angina pectoris with depression. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. (2022) 40(5):85–8.
23. Zheng Y, Tai J, Liu J. Qi and blood notoginseng dan tea tong bi acupuncture method treatment of stable coronary heart disease angina pectoris clinical observation (blood stasis bizu certificate). J Emerg Tradit Chin Med. (2022) 31(1):95–7.
24. Fu Y, Liu Y, Wu W. To observe the effect of tongbuzongqi acupuncture combined with exercise rehabilitation therapy on angina pectoris of coronary heart disease and its influence on serum NO and ET levels. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. (2022) 40(2):190–2.
25. Jiang J, Chen H. Effect of Xiewei bupi tiaoxin acupuncture therapy on syndromes scores, glucose-lipid metabolism and angina onset for elderly patients with T2DM and coronary heart disease. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. (2021) 39(4):212–5.
26. Du Z, Shi K. Therapeutic cooperate to study the curative effect of acupuncture and moxibustion treatment of coronary heart disease angina pectoris. Chin Gen Pract. (2021) 24(S1):158–60.
27. Sun Y, Li B, Wang Z. Effect of acupuncture on patients with stable angina pectoris with syn-drome of blockade of phlegm-turbidity. Chin Med Herald. (2021) 18(29):68–72.
28. Liu B, Ai L, Lin H. Effect of combined acupuncture and medicine on platelet aggregation rate and heart rate variability in patients with angina pectoris. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2021) 40(6):652–7.
29. Zhang W. Efficacy observation of warm needling combined with medication for unstable angina pectoris of heart-kidney yang deficiency pattern. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2021) 40(3):258–62.
30. Liu L, Zhang D, Zou G, Sui Y, Han Y, Sun B. Observations on the efficacy of acupuncture plus wen dan decoction for stable angina pectoris of phlegm and blood stasis type. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2021) 40(4):379–84.
31. Ding L, Zhou S. Curative efficacy of modified gualou Xiebai banxia decoction combined with acupuncture on angina pectoris in coronary heart disease and its effect on serum HMGB1, CGRP and GM-CSF. Sh J Tradit Chin Med. (2021) 40(3):269–74.
32. Wang J, Zhang J, Liu Y, Gao Y, Sun J, Liu X. Acupuncture combined with western medication in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with angina pectoris of coronary heart disease: a randomized controlled study. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2021) 41(4):371–5.33909355
33. Gao J. Acupuncture in closing hole joint point massage the effect of quality of life in patients with coronary heart disease angina pectoris. J Ext Ther Tradit Chin Med. (2020) 29(4):59–60.
34. Wu B, Liu L, Yang L. Effect of acupuncture combined with Xuefu zhuyu decoction on clinical symptoms, serum CAT level and heart rate variability in patients with unstable angina pectoris. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med. (2020) 22(3):180–4.
35. Ye Y, Yang Y, Lin L, Zhu L. Therapeutic observation of warming-unblocking needling for stable angina pectoris of yang-deficiency and blood-stagnation pattern. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2020) 39(10):1230–4.
36. Zhang F. Therapeutic effect of danhong injection combined acupuncture on patients with qi deficiency and blood stasis type angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. Chin J Cardiovasc Rehabil Med. (2020) 29(2):235–40.
37. Wang K, Fu G, Wang M. Large plant rhodiola injection combined acupuncture clinical observation for the treatment of coronary heart disease unstable angina. Chin J Integr Med Cardio Cerebrovasc Dis. (2019) 17(23):3749–51.
38. Pan L. Clinical observation of acupuncture-moxibustion plus trimetazidine dihydrochloride tablets for unstable angina pectoris. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2019) 38(10):1103–8.
39. Wang L, Wu B. Effect of sanshen kuoguan decoction combined with tongbu zongqi acupuncture on uric acid, heart rate variability and inflammatory response in patients with angina pectoris with hyperuricemia and phenomenon of slow coronary flow. Modern J Integr Tradit Chin West Med. (2019) 28(24):2660–4.
40. Zhang N, Cui J, Feng L, Sun J, Ding G, Yang X. Effects of electroacupuncture therapy combined with basic drugs on the clinical symptoms in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. (2019) 34(3):1262–5.
41. Wu S, Fu W, Li R. Osmanthus close holes within three sweet soup with acupuncture treatment of coronary heart disease angina pectoris clinical efficacy and safety studies. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. (2019) 37(5):75–7.
42. Chen C, Tian J, Feng Q, Yan F. Therapeutic observation of electroacupuncture pretreatment plus medication for angina pectoris in coronary heart disease. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2019) 38(8):827–30.
43. Li Y, Liu X. Clinical observation of quyu huatan decoction combined with acupuncture in the treatment of angina pecto-ris of coronary heart disease with phlegm turbid obstruction type. Hebei J Tradit Chin Med. (2019) 41(11):1712–6.
44. Gong Q, Qi P, Shi L, Liu M, Huang L, Guo K. Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with buyang huanwu decoction on patients with SCAD. J Emerg Tradit Chin Med. (2018) 27(11):1952–5.
45. Chen H, Yang Y. Clinical observation on 52 cases of angina pectoris of coronary heart disease treated with acupuncture and medicine. Clin J Chin Med. (2018) 10(18):132–4.
46. Sun Q, Guan Y, Zhang W. Warming acupuncture was used in the treatment of 44 elderly patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease and hyperhomocysteinemia. Glob Tradit Chin Med. (2018) 11(9):1436–8.
47. Lu Z, Sun Z. Clinical effect of acupuncture combined with huoxue recipe on 89 cases of unstable angina pectoris and its influence on vascular endothelial function. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. (2018) 36(5):1177–80.
48. Deng J, Fei L, Zhou J, Wu S, Huang W, Chen X. Needle-embedding therapy combined with basic treatment for stable angina pectoris. World J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2018) 28(2):81–5. doi: 10.1016/j.wjam.2018.05.004
49. Deng L. Clinical observation of Trinity combination therapy of traditional Chinese medicine on treating coronary heart disease with stable angina pectoris (qi deficiency and blood stasis type). J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med. (2017) 19(4):121–3.
50. Shi L, Du X, Zhao F, Yang D, Liu M, Tan Y. Effect of acupuncture combined with buyang huanwu decoction on stable angina pectoris with syndrome of qi deficiency and blood stasis and blood lipid level. Modern J Integr Tradit Chin West Med. (2017) 26(35):3880–2966.
51. Wang B, Wu S, Xie J. Electric acupuncture treatment of blood stasis resistance type of coronary heart disease angina pectoris clinical observation. J Hubei Univ Chin Med. (2017) 19(3):77–9.
52. Wu T. Fructus scallions bai guizhi tonga subtraction auxiliary acupuncture for the treatment of heart yang type of coronary heart disease angina pectoris observation. World Tradit Chin Med. (2017) 12(0):412–3.
53. Yan P. Clinical observation of acupuncturing neiguan point combined with wenyang huoxue method and alprostadil for treating unstable angina. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. (2017) 35(2):191–4.
54. Wang B, Na W, Han S. Effect of warm needling plus atorvastatin on cardiac syndrome X in women. Sh J Acupunct Moxibustion. (2016) 35(12):1432–5.
55. Jia D, Wang Y, Fan X. Clinical therapeutic effect of combination of acupuncture with Xuefu zhuyu decoction in the patient of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease with heart-blood stagnation syndrome. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med. (2016) 18(3):117–9.
56. Fu C. Curative observation of using yiqi huayu decoction combined with acupuncture in the treatment of acute coronary syndrome complicated with angina pectoris and the impact on heart function. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. (2016) 34(11):61–4.
57. Li X, Cao J, Jiang A, Wei L. Acupuncture combined with western medicine in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris clinical curative effect and dynamic electrocardiogram observation. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2015) 35(9):895–6.
58. Wang N, Chen H, Lu S, Wang J, Zhang W, Zhu B. Impacts on neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients of chronic stable angina pectoris treated with acupuncture at neiguan (PC 6). Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2015) 35(5):417–21.
59. Jin H, Qi F, Cui X, Jiang L. Evaluation on clinical therapeutic effect of acupuncture method in treatment of stable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease based on theory of latent phlegm and blood stasis theory. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. (2015) 33(3):549–51.
60. Huang J, Liu Y, Xie S, Hu W, Liu M, Wang C, et al. Effect of acupuncture combined with medicine on stable angina pectoris ET and NO. J Emerg Tradit Chin Med. (2014) 23(2):206–8.
61. Xie S, Huang J, Liu Y, Hu W, Liu M, Wang C. Clinical observation on stable angina pectoris with the treatment of acupuncture combined with medicine. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. (2014) 29(7):2385–7.
62. Zhao J, Shi X, Zheng M, Chen S. 30 Cases of angina pectoris of heart blood stasis type were treated with acupuncture and medication. Sh J Tradit Chin Med. (2013) 47(05):50–1.
63. Jin H, Qi F, Cui X, Jiang L. Evaluation on clinical therapeutic effect of acupuncture method in treatment of stable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease based on theory of latent phlegm and blood stasis theory. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. (2013) 33(3):523–4.
64. Qiu Y, Li C. Clinical observation of acupuncture with conventional western medicine therapy stable angina. J Emerg Tradit Chin Med. (2013) 22(6):1002.
65. Li R, Wan L, Zi M, Duan W, He L, Gao R. Stable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease treated with different acupuncture and moxibustion therapies: a network meta-analysis. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2022) 42(12):1431–8.36484199
66. Park JM, Shin AS, Park SU, Sohn IS, Jung WS, Moon SK. The acute effect of acupuncture on endothelial dysfunction in patients with hypertension: a pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. J Altern Complement Med. (2010) 16(8):883–8. doi: 10.1089/acm.2009.0427
67. Teragawa H, Oshita C, Orita Y, Kihara Y. Acupuncture: could it be a treatment for angina pectoris? Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2021) 28(14):e3–4. doi: 10.1177/2047487319885198
68. Zhang J, Zhu L, Li H, Tang Q. Electroacupuncture pretreatment as a novel avenue to protect heart against ischemia and reperfusion injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2020) 2020:9786482. doi: 10.1155/2020/9786482
69. Shao M, Li Y, Cui H, Jiang M, Tan Q. Protective effect of acupuncture preconditioning on oxidative stress injury induced by myocardial is chemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2017) 37(3):285–90.
70. Li W, Zhong M, Yang J, Zhao W. Effects of electroacupuncture preconditioning at “neiguan"(PC 6)on gene expression of myocardial opioid receptors in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2011) 31(05):441–5.
71. Yang X, Cui J, Liu X, Zhang X, Feng L, Wang X. Expression profile of vascular growth functional genes in miniature pigs with myocardial ischemia injury induced by acupuncture at neiguan point. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. (2012) 16(37):6857–62.
72. Yu J, Jiang Y, Tu M, Liao B, Fang J. Investigating prescriptions and mechanisms of acupuncture for chronic stable angina pectoris: an association rule mining and network analysis study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2020) 2020:1931839. doi: 10.1155/2020/1931839
Keywords: acupuncture, multiple therapies, angina pectoris, systematic review, network meta-analysis
Citation: Kong X, Gu Y and Qiu Z (2025) Acupuncture combined with multiple therapies for angina pectoris: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1463170. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1463170
Received: 12 July 2024; Accepted: 17 January 2025;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Seokhun Yang, Seoul National University Hospital, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Jianli jimmy Zhao, University of Alabama at Birmingham, United StatesCopyright: © 2025 Kong, Gu and Qiu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangyu Kong, S2V2aW5feHlLb25nQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.