
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med. , 25 March 2025
Sec. Coronary Artery Disease
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1452006
Objective: The influence of extreme sleep duration on coronary heart disease (CHD) risk across genders remains a debated topic.
Methods: This analysis gathers observational studies that explore association between varying sleep durations and CHD risks. Trend estimation employs generalized least squares, converting specific category risk estimates into relative risks (RR) per hour of sleep increase. A two-stage hierarchical regression model evaluates potential linear dose-response relationships. Data analysis utilizes random-effects restricted cubic spline models with four knots.
Results: Involving 17 studies and 906,908 participants, this meta-analysis identifies a pronounced U-shaped nonlinear relationship between sleep duration and CHD risk applicable to both genders (P < 0.01). Notably, shorter sleep durations are linked to higher CHD risks in women, whereas longer durations are more consequential for men. The optimal sleep duration for minimizing CHD risk is between 7.0–8.0 h daily for men and 7.5–8.5 h for women.
Conclusion: The influence of sleep duration on CHD risk differs significantly between genders.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/myprospero, identifier (CRD42023478235).
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including congestive heart failure (CHF), coronary heart disease (CHD), angina pectoris (AP), myocardial infarction, and stroke, pose major public health challenges and are key mortality causes globally (1). The WHO Global Burden of Disease Project highlights that coronary artery disease (CAD) caused one million deaths in East Asia and the Pacific Region, with 8.2 million angina cases and 11.8 million Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) attributed to CAD in this area (2). Stroke and CAD account for 60%–70% of CVD mortality in China (2, 3). In the U.S., around 720,000 individuals annually experience acute myocardial infarction (MI) or die from CAD, with over 335,000 facing recurrent episodes (4). Notably, older adults (aged 75 and above) form a significant portion (30%–40%) of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) hospitalizations and suffer the highest ACS-related mortality (5–7). This demographic often presents complex clinical pictures, including extensive atherosclerotic plaque, anatomical complexities, calcifications, vessel tortuosity, ostial lesions, multivessel disease, left main stenosis and concurrent geriatric syndromes, raising their overall risk (8).
Although CHD mortality rates have marginally declined, it remains a leading death cause. Risk factors for CAD fall into non-modifiable (age, gender, ethnicity, family history) and modifiable categories (hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, obesity, smoking, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, stress) (9–13). Gender is an immutable risk factor, whereas sleep duration is a modifiable one. Both have been extensively examined for their effects on health outcomes (14). Research shows notable gender disparities in the incidence and timing of CHD due to physiological, psychological, and other factors (15). Shift work, active family responsibilities, and extensive use of electronic devices lead to prevalent short and long sleep durations across gender groups (16). Sleep plays a crucial role in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases (17).
Previous studies have shown a U-shaped relationship between CHD and sleep duration across genders (18, 19). Yet, a 2018 study on cardiovascular diseases, despite its recency and breadth, did not isolate gender in its analysis, revealing a diminished link between short sleep durations and adverse events post adjustment for various factors (20). This observation suggests potential oversight in gender-specific research in earlier studies. Moreover, literature reviews indicate that after comprehensive adjustments, varying sleep durations differently affect cardiovascular disease outcomes by gender. Several studies associate short sleep durations exclusively with increased CHD risks in women (21–25), whereas others suggest similar associations in men alone after such adjustments (26, 27). Svensson's findings contradict earlier studies, showing similar correlations between short sleep durations and CHD risks in both genders (28), while Kronholm's research suggests no link between excessive sleep durations and CHD risks in males (29). Sex-specific differences may exist in the association between extreme sleep duration and CHD incidence. These differences could be attributed to distinct hormonal patterns and metabolic processes, reflecting inherent pathophysiological dimorphism in the stratification of cardiovascular risk across genders. Most recent meta-analyses have not included gender subgroup analyses (20), and those that did are considered outdated (18, 19). Since 2016, new research examining sleep durations and CHD risks by gender has emerged (23–25, 28, 30, 31). Our study incorporates this recent literature to explore potential U-shaped or J-shaped relationships between CHD and sleep duration among different genders and the differences therein. These findings have significant health implications and may inform future healthcare policies.
The study adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for reporting items and their requirements for network meta-analysis (NMA). The meta-analysis was conducted in compliance with these guidelines. The study protocol is registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (Registration Number: CRD42023478235).
Searches in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science were conducted until October 2023 using unrestricted terms related to sleep coronary artery disease, coronary artery diseases, coronary disease, coronary diseases, coronary heart disease, coronary heart diseases, multivessel coronary artery disease (details in Supplementary File). This search also included a review of studies from previous meta-analyses to identify additional relevant literature. Inclusion Criteria: (1) Observational studies examining the association between sleep duration and incident risk of CHD; (2) Studies reporting relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for different sleep durations; (3) Studies focusing on the correlation of sleep duration with CHD risk across various genders. Exclusions applied to case reports, guidelines, letters, chapters, conference abstracts, editorials, meta-analyses, reviews, and animal experiments.
Title and abstract screening were independently performed by two authors to identify relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third author. Full-text articles were then assessed against the selection criteria for final inclusion. If necessary, further information or original data were requested from study authors (first author, corresponding author, or the authors' department). Included articles contained RR values with 95% CIs for both genders and various sleep durations related to CHD risk. Data extracted included author, year, sample size, study period, type, geographical information, average age, body mass index, gender distribution, sleep groups, RR values, and follow-up duration, compiled in an Excel spreadsheet.
The quality of cohort and case-control studies will be assessed using the Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS). The NOS conducts a comprehensive evaluation from three aspects of the study: selection, comparability, and outcome (cohort studies) or exposure (case-control studies) (32, 33). Each study can earn up to one point per item in the selection and exposure categories and up to two points for comparability (Tables 1, 2). Studies will be classified as low (0–3), moderate (4–6), or high quality (7–9). For cross-sectional studies, quality assessment will use the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) 11-item checklist. Each item scores “1” for “YES” and “0” for “UNCLEAR” or “NO.” Quality categories are low (0–3), moderate (4–7), and high (8–11) (Table 3).
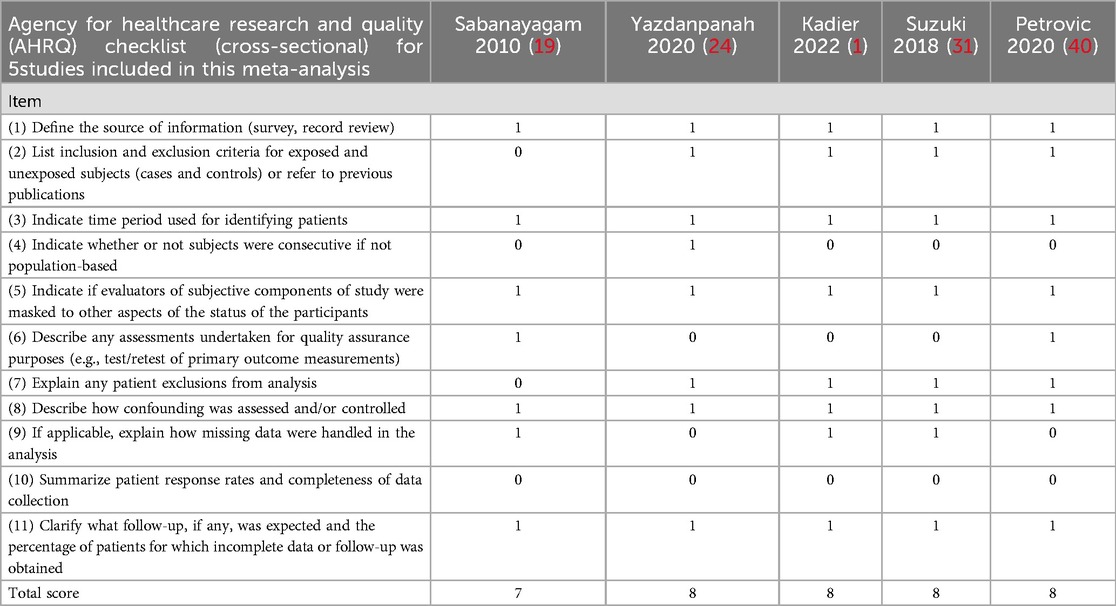
Table 3. Agency for healthcare research and quality (AHRQ) checklist (cross-sectional) for 5 studies included in this meta-analysis.
This analysis will utilize multivariate-adjusted RRs with 95% CIs. Pooled RRs and CIs will be estimated using a fixed-effects model for I² < 50% and p > 0.1; otherwise, a random-effects model is applied. Significant heterogeneity will lead to further subgroup analyses, focusing on BMI, age, region, and study type. Subgroup heterogeneity I² < 50% will indicate a major source of data variability. Sensitivity analysis will remove studies one by one to check the influence on overall results. Egger's test will assess potential publication bias. Dose-response analysis will be based on sleep duration categories, case numbers, total cases, and the logarithm of RRs and standard errors. Studies must provide data across at least three exposure categories, with median sleep durations assigned to each. For open-ended upper categories, the amplitude is assumed equal to the adjacent lower category. Using the generalized least-squares method for trend estimates, category-specific risk estimates will be converted into relative risk (RR) for each additional hour of sleep duration. A two-stage hierarchical regression model will assess the linear dose-response relationship between sleep duration and CHD, with data modeled using random-effects restricted cubic spline models with four knots.
The study identification and inclusion process are depicted in Figure 1. Searches yielded 2,236 articles from PubMed, 7,196 from Embase, 586 from Cochrane Library, and 6,387 from Web of Science as of October 11, 2023. After removing 5,092 duplicates, 11,310 articles were screened by title and abstract. Of these, 11,235 were excluded for being irrelevant, such as case reports or conference materials. Detailed full-text review of 70 articles led to the exclusion of 47 due to lack of gender differentiation, and five more (1, 35, 36, 38, 40) for insufficient data. Ultimately, 17 articles were selected for the meta-analysis.
The key data from the included studies are summarized in the provided Table 4. These studies, published between 2003 and 2021, comprise 12 cohort studies, 2 case-control studies, and 3 cross-sectional studies. Geographical distribution included 9 studies in Asia, 5 in Europe, and 3 in North America. Sample sizes ranged from 966 to 392,164, totaling 906,908 participants. All studies, except (27), adjusted for various covariates. The mean age of male participants was 41.78–64.10 years, and for females, it was 41.78–63.36 years. BMI information was provided in all but two studies (25, 28), ranging from 22.62 to 29.60 in men and 22.90–29.59 in women. The primary focus was CHD, although some studies also included stroke patients (19, 26, 29, 34). Follow-up periods varied from 1.2 to 34 years. The quality assessment scores ranged from 6 to 8, averaging 6.94, with cohort studies averaging 6.75, cross-sectional studies 7.67, and case-control studies 7.
This meta-analysis included 15 studies focusing on male participants, totaling 351,855 individuals. The dose-response analysis indicated a significant non-linear correlation between sleep duration and CHD risk in males (P < 0.01). The lowest CHD risk was observed at a sleep duration of 7.0–8.0 h per day (Figure 2B). In the heterogeneity test, the I² value was 80.9% when comparing the highest to normal sleep duration (P < 0.01). A random-effects model showed that the highest sleep duration group had a significantly increased CHD risk, with a combined RR of 1.35 (95% CI: 1.15, 1.58, P < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure S14). Similarly, the lowest sleep duration compared to normal sleep duration showed a heterogeneity I² of 93.3% (P < 0.001). Here, the lowest sleep duration group also exhibited a higher CHD risk, with a combined RR of 1.52 (95% CI: 1.16, 2.01, P < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure S9). Despite substantial heterogeneity, subgroup analyses based on study type (cohort study, cross-sectional study, case-control study), continent (Europe, Asia, North America), average age (age ≥55 years, age <55 years), and BMI (BMI ≥24, BMI <24) did not pinpoint its source. However, these analyses yielded several interesting findings, as detailed in the following sections.
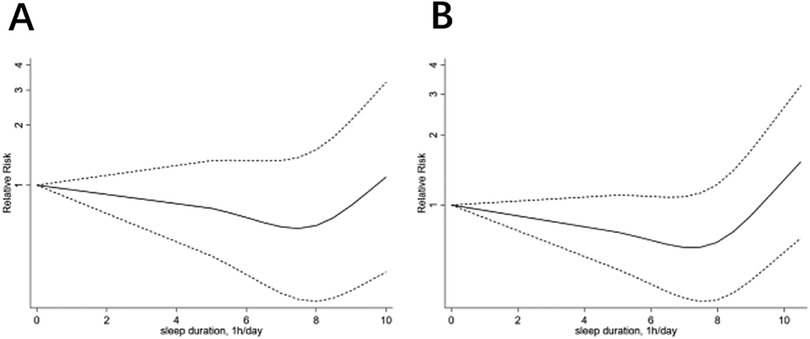
Figure 2. The dose-response analysis of coronary heart disease and sleep duration, (A) for woman, (B) for man.
In the subgroup analysis comparing the highest sleep duration to normal sleep duration in males, cohort studies showed an increased risk of CHD with an RR of 1.24 (95% CI: 1.10–1.41, P < 0.01). However, this increase was not observed in cross-sectional and case-control studies (Cross-sectional: P = 0.122, Case-control: P = 0.089) (Supplementary Figure S17). In the analysis by continent, the highest sleep duration was associated with an increased CHD risk in Europe (RR: 1.14, 95% CI: 1.01–1.28, P = 0.03), Asia (RR: 1.35, 95% CI: 1.16–1.57, P < 0.01), and North America (RR: 2.55, 95% CI: 2.11–3.09, P < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure S18). Age-based subgroup analysis revealed that males aged ≥55 years (RR: 1.34, 95% CI: 1.15–1.57, P < 0.01) and <55 years (RR: 1.37, 95% CI: 1.15–1.58, P = 0.014) both showed increased risk with the highest sleep duration (Supplementary Figure S16). In the BMI subgroup analysis, males with BMI ≥24 did not show increased CHD risk with the highest sleep duration (P = 0.056), whereas those with BMI <24 did (RR: 1.30, 95% CI: 1.11–1.52, P < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure S15).
In the subgroup analysis of study types, cohort studies showed an increase in CHD risk with the lowest sleep duration in males compared to normal (RR: 1.44, 95% CI: 1.20–1.73, P < 0.01). However, cross-sectional and case-control studies did not demonstrate a significant risk increase (Cross-sectional: P = 0.201, Case-control: P = 0.235) (Supplementary Figure S12). In the continent subgroup analysis, Asian males showed no significant association between the lowest sleep duration and CHD risk (P = 0.084). Conversely, European males (RR: 1.43, 95% CI: 1.27–1.62, P < 0.01) and North American males (RR: 2.17, 95% CI: 1.77–2.67, P < 0.01) exhibited increased CHD risk with the lowest sleep duration (Supplementary Figure S13). Age subgroup analysis indicated that for both age groups ≥55 and <55, the lowest sleep duration increased CHD risk (RR: 1.62, 95% CI: 1.23–2.14, P < 0.01 for ≥55; RR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.22–2.32, P < 0.01 for <55) (Supplementary Figure S11). Finally, in the BMI subgroup analysis, males with the lowest sleep duration showed increased CHD risk regardless of BMI being ≥24 (RR: 1.79, 95% CI: 1.18–2.72, P < 0.01) or <24 (RR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.01–1.72, P = 0.042) (Supplementary Figure S10).
In this meta-analysis, 14 articles focusing on 553,319 female participants were included. The dose-response analysis showed a significant non-linear association (P < 0.01) between sleep duration and CHD risk in females. The optimal sleep duration for the lowest CHD risk was 7.5–8.5 h per day (Figure 2A). High heterogeneity was observed in the comparison between the highest and normal sleep durations (I² = 87.8%, P < 0.01), with a significant risk increase indicated by a combined RR of 1.36 (95% CI: 1.10–1.69, P = 0.005) (Supplementary Figure S24). Similarly, the comparison between the lowest and normal sleep durations showed high heterogeneity (I² = 90.3%, P < 0.001) and a significant risk increase (combined RR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.35–2.06, P < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure S19). Despite high heterogeneity, subgroup analysis did not pinpoint its source but revealed several notable findings.
In the female cohort studies, the highest sleep duration compared to normal increased CHD risk (RR: 1.33, 95% CI: 1.14–1.54, P < 0.01). However, cross-sectional and case-control studies did not show a significant risk increase (Cross-sectional: P = 0.409, Case-control: P = 0.134) (Supplementary Figure S27). Continent-wise, European and North American females showed no significant risk association (European: P = 0.257, North American: P = 0.056), while Asian females exhibited increased risk (RR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.08–1.55, P < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure S28). Age subgroup analysis showed increased risk in females aged ≥55 (RR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.14–1.46, P < 0.01), but no significant association in females aged <55 (P = 0.066) (Supplementary Figure S26). In the BMI subgroup analysis, females with BMI ≥24 showed no significant risk association (P = 0.084), whereas those with BMI <24 had increased risk (RR: 1.34, 95% CI: 1.05–1.71, P = 0.018) (Supplementary Figure S25).
In the female cohort studies, the lowest sleep duration compared to normal was linked to an increased CHD risk (RR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.26–1.91, P < 0.01). This pattern was also seen in case-control studies (RR: 2.12, 95% CI: 1.50–2.99, P < 0.01), but not in cross-sectional studies (P = 0.097) (Supplementary Figure S22). In continent-based subgroup analysis, European females (RR: 1.73, 95% CI: 1.24–2.41, P < 0.01) and Asian females (RR: 1.58, 95% CI: 1.21–2.05, P < 0.01) with the lowest sleep duration had increased CHD risk, unlike North American females (P = 0.145) (Supplementary Figure S23). Age-based subgroup analysis showed increased CHD risk in females aged ≥55 (RR: 1.62, 95% CI: 1.23–2.14, P < 0.01) and <55 (RR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.22–2.32, P < 0.01) with the lowest sleep duration (Supplementary Figure S21). BMI-based subgroup analysis indicated that females with BMI ≥24 (RR: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.22–2.47, P < 0.01) and <24 (RR: 1.41, 95% CI: 1.12–1.77, P < 0.01) had increased CHD risk with the lowest sleep duration (Supplementary Figure S20).
In the sensitivity analysis, excluding low-quality studies sequentially did not significantly change the combined RR values (Supplementary Figure S5–S8). Extensive Egger regression tests were conducted to check for publication bias. The results indicated no evidence of potential publication bias (P = 0.565 for men with short sleep duration and CHD; P = 0.956 for men with long sleep duration and CHD; P = 0.125 for women with short sleep duration and CHD; P = 0.632 for women with long sleep duration and CHD) (Supplementary Figure S1–S4).
This meta-analysis reveals a significant non-linear U-shaped association between sleep duration and CHD risk for both genders (both P < 0.01). Notably, short sleep duration impacts females' CHD risk more significantly, whereas long sleep duration affects males more. The ideal sleep duration is about 7.0–8.0 h daily for males and 7.5–8.5 h for females.
Sleep deprivation promotes CAD through complex pathophysiological mechanisms. A primary pathway involves elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) (41). These ROS facilitate the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) into oxidized LDL (ox-LDL). The resulting ox-LDL undergoes uptake by macrophages through scavenger receptors, leading to foam cell formation. These foam cells constitute essential components of atherosclerotic plaques and release proinflammatory cytokines, creating a pathogenic inflammatory cycle (42). ROS overproduction compromises endothelial function through multiple pathways. This process includes impairment of eNOS function (43), resulting in decreased nitric oxide availability. The activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways by ROS disrupts normal endothelial cell processes and accelerates atherogenesis (39, 44–47). The presence of ROS compromises plaque stability through dual mechanisms: inducing apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells which thins fibrous caps, and activating matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). These MMPs degrade collagen in the extracellular matrix, undermining the structural integrity of plaques (48, 49). Sleep deprivation increases interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels (50). This elevation enhances the risk of CAD through multiple pathways: stimulating hepatic C-reactive protein (CRP) production, promoting LDL oxidation through oxidative stress (51), and increasing the expression of adhesion molecules (VCAM-1/ICAM-1). These changes facilitate monocyte infiltration and subsequent foam cell development (45). Research in both animals and humans demonstrates that sleep loss reduces vagal tone (52, 53). This reduction diminishes acetylcholine-mediated suppression of proinflammatory cytokines through cholinergic receptors (54). Simultaneously, enhanced sympathetic activity increases heart rate and vascular resistance, leading to elevated blood pressure (55). Sleep deprivation disrupts leptin-ghrelin balance, characterized by decreased leptin and increased ghrelin levels. These changes promote adipocyte lipid storage and insulin resistance (56–58). The reduction in slow-wave sleep (SWS) decreases gonadotropin-releasing hormone-mediated inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. This decrease, combined with reduced cardioprotective growth hormone release, further compounds the risk of CAD.
Research on prolonged sleep duration and CAD remains limited. Studies in Spanish populations have shown that extended sleep is associated with reduced physical activity, increasing the risk of obesity (59)—a known risk factor for CAD. Longer sleep duration correlates with poorer sleep quality (60), elevating IL-6 and high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) levels, which contribute to CAD development. Prolonged sleep may also slow blood flow and increase blood viscosity, promoting thrombosis and CAD events (61). In males, the relationship may involve testosterone effects. While sleep restriction decreases testosterone levels, this reduced androgenic state might partially protect against coronary atherosclerosis through unknown mechanisms (62, 63).
Sex-specific mechanisms link short sleep duration and CAD. Females show greater leptin reduction during sleep deprivation than males, increasing weight gain susceptibility (64). Obese females have higher inflammatory marker levels than males (65), potentially explaining increased risk of CAD in women with short sleep. Rodent studies demonstrate that sleep restriction causes more prominent glucose intolerance in female mice (66), possibly due to sleep-induced estrogen disruption, as estrogen promotes glycogen synthesis through estrogen receptor alpha-mediated activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (67). Clinical studies show stronger blood pressure elevation in sleep-deprived females (68), with the Whitehall II study identifying short sleep as an independent hypertension risk factor only in females (69). These cardiovascular effects may result from increased hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis reactivity in sleep-deficient women (70). Additionally, Carter et al. found increased muscle sympathetic nerve activity after sleep deprivation, particularly in postmenopausal women (71), suggesting the modulatory effects of estrogen on sympathetic activation. Insufficient sleep also elevates low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and hsCRP specifically in women (72, 73), creating conditions favorable for CAD development.
Different mechanisms may explain sex-specific associations between prolonged sleep and CAD. Extended sleep correlates with obesity, with stronger links between abdominal adiposity and atherosclerotic processes documented in males, potentially making sleep-prolonged males with central obesity more susceptible to CAD (74). Additionally, prolonged sleep increases blood viscosity (61), affecting males disproportionately due to their naturally higher baseline blood viscosity. This sex difference results from several factors: males have higher hematocrit levels (75), while females benefit from cardioprotective high-density lipoprotein effects (76). Higher smoking rates among males further contribute to elevated blood viscosity (77). The combined effects of physical inactivity and obesity-induced viscosity elevation likely have greater cardiovascular impact on males due to their pre-existing hyperviscous state.
Further subgroup analysis yielded intriguing findings. For instance, short sleep duration does not correlate with CHD risk in Asian males (P = 0.084), possibly due to an incomplete sample or lower obesity rates in this group, which diminishes the effect of CVD caused by insufficient sleep duration related to obesity (78, 79). Conversely, excessive sleep duration shows no significant association with CHD risk in European and North American females (Europe: P = 0.257, North America: P = 0.056). These disparities suggest that gender significantly influences the relationship between long sleep duration and CHD risk. Yin et al.'s study supports this, noting higher CHD mortality and risk in males despite a higher baseline proportion of females with excessive sleep (80).
Excessive sleep duration among Asian females associates with CHD risk, potentially exacerbated by psychosocial stressors. Mental health disorders like depression and benzodiazepine use, linked to excessive sleep, are prevalent among Asians who often face long working hours and substantial psychological stress (37, 81–83). Furthermore, the lower rate of psychological treatment in low- and middle-income Asian countries might explain the unique findings in this subgroup (84). This highlights the need for further research to dissect these complex interactions, particularly the non-association of very short sleep durations with CHD risk in North American women, possibly due to limited data inclusion from the region.
Subgroup analysis based on BMI reveals that excessive sleep duration does not correlate with CHD risk in individuals with a BMI ≥24, regardless of gender. This observation aligns with a previous meta-analysis of 40 studies, which noted that while underweight individuals (BMI <20 kg/m2) show increased overall and CVD mortality risks, those slightly overweight (BMI: 24–27.9) exhibit the lowest mortality risks. In contrast, severe obesity (BMI ≥35 kg/m2) is linked to the highest CVD mortality (85). This suggests that factors other than BMI may influence CHD risk in individuals with a BMI between 24 and 30. Given that only one included study had an average BMI ≥28, further investigation into this category is warranted.
Our findings align with those of Shankar and Sabanayagam (18, 19) but differ from the results by Meisinger, Ikehara, Lao, Yazdanpanah, Zhang, Amagai, Chandola, Svensson, Kronholm, and Strand (21–30). A detailed comparison of adjustment factors in these studies reveals that most studies showing discrepancies did not consider race and working hours as risk factors. Further research is necessary to understand how race and working hours might differently affect genders in terms of CHD risk. Nonetheless, our meta-analysis indicates that both genders face increased CHD risk with abnormal sleep durations, with the risk being particularly pronounced for short sleep durations in women and long durations in men.
Gender-specific sleep interventions are essential based on these differences. For women, maintaining 7.5–8.5 h of daily sleep is recommended, along with stress reduction through yoga and meditation to minimize stress hormone effects, and regular monitoring of blood glucose for early risk detection. For men, optimal sleep duration should be 7.0–8.0 h nightly, complemented by smoking cessation, regular exercise, and sufficient physical activity to reduce weight, improve sleep quality, and prevent obesity and metabolic risks associated with prolonged sleep.
There are three primary limitations to our paper. First, the reliance on self-reported sleep data may introduce bias compared to polysomnography, the gold standard for measuring sleep duration. Second, the number of studies within specific subgroups—such as cross-sectional, case-control, and particularly the North American subgroup—is limited, which may influence the robustness of our conclusions. Third, while our study focuses on sleep duration's correlation with CHD in men and women, some articles did not distinguish CHD from cardiovascular diseases, therefore, a few articles also included stroke patients (19, 26, 29, 34). Nonetheless, these studies passed our sensitivity analysis without issue.
In conclusion, both short and long sleep durations significantly correlate with CHD risk in both genders. Our analysis confirms a significant non-linear U-shaped relationship between sleep duration and CHD risk for both men and women (both P < 0.01). Notably, the impact of short sleep duration on CHD risk is more pronounced in women, while long sleep duration more significantly affects men. The optimal sleep duration is identified as 7.0–8.0 h daily for men and 7.5–8.5 h for women. Future longitudinal cohort studies or randomized controlled trials should evaluate the associations between sleep duration and CHD across different regions, age groups, and BMI.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. TL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. DS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JF: Conceptualization, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1452006/full#supplementary-material
1. Kadier K, Qin L, Ainiwaer A, Rehemuding R, Dilixiati D, Du YY, et al. Association of sleep-related disorders with cardiovascular disease among adults in the United States: a cross-sectional study based on national health and nutrition examination survey 2005–2008. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:954238. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.954238
2. Gaziano TA, Bitton A, Anand S, Abrahams-Gessel S, Murphy A. Growing epidemic of coronary heart disease in low- and middle-income countries. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2010) 35:72–115. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2009.10.002
3. Liu L. Cardiovascular diseases in China. Biochem Cell Biol. (2007) 85:157–63. doi: 10.1139/O07-004
4. Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 145:e153–639. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001052
5. De Luca L, Marini M, Gonzini L, Boccanelli A, Casella G, Chiarella F, et al. Contemporary trends and age-specific sex differences in management and outcome for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e004202. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004202
6. De Luca L, Olivari Z, Bolognese L, Lucci D, Gonzini L, Di Chiara A, et al. A decade of changes in clinical characteristics and management of elderly patients with non-ST elevation myocardial infarction admitted in Italian cardiac care units. Open Heart. (2014) 1:e000148. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2014-000148
7. Zaman MJ, Stirling S, Shepstone L, Ryding A, Flather M, Bachmann M, et al. The association between older age and receipt of care and outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a cohort study of the myocardial ischaemia national audit project (MINAP). Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:1551–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu039
8. O'Neill DE, Forman DE. Cardiovascular care of older adults. Br Med J. (2021) 374:n1593. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1593
9. Hajar R. Risk factors for coronary artery disease: historical perspectives. Heart Views. (2017) 18:109–14. doi: 10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_106_17
10. Mahmood SS, Levy D, Vasan RS, Wang TJ. The Framingham heart study and the epidemiology of cardiovascular disease: a historical perspective. Lancet. (2014) 383:999–1008. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61752-3
11. Jousilahti P, Laatikainen T, Peltonen M, Borodulin K, Männistö S, Jula A, et al. Primary prevention and risk factor reduction in coronary heart disease mortality among working aged men and women in eastern Finland over 40 years: population based observational study. Br Med J. (2016) 352:i721. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i721
12. Lind L. Population-based cardiovascular cohort studies in Uppsala. Ups J Med Sci. (2019) 124:16–20. doi: 10.1080/03009734.2018.1515282
13. Pencina MJ, Navar AM, Wojdyla D, Sanchez RJ, Khan I, Elassal J, et al. Quantifying importance of major risk factors for coronary heart disease. Circulation. (2019) 139:1603–11. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031855
14. Soldatos CR, Allaert FA, Ohta T, Dikeos DG. How do individuals sleep around the world? Results from a single-day survey in ten countries. Sleep Med. (2005) 6:5–13. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2004.10.006
15. Hyvärinen M, Qiao Q, Tuomilehto J, Söderberg S, Eliasson M, Stehouwer CD. The difference between acute coronary heart disease and ischaemic stroke risk with regard to gender and age in Finnish and Swedish populations. Int J Stroke. (2010) 5:152–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-4949.2010.00423.x
16. Malik SW, Kaplan J. Sleep deprivation. Prim Care. (2005) 32:475–90. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2005.02.011
17. Wolk R, Gami AS, Garcia-Touchard A, Somers VK. Sleep and cardiovascular disease. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2005) 30:625–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2005.07.002
18. Shankar A, Koh WP, Yuan JM, Lee HP, Yu MC. Sleep duration and coronary heart disease mortality among Chinese adults in Singapore: a population-based cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. (2008) 168:1367–73. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwn281
19. Sabanayagam C, Shankar A. Sleep duration and cardiovascular disease: results from the national health interview survey. Sleep. (2010) 33:1037–42. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.8.1037
20. Kwok CS, Kontopantelis E, Kuligowski G, Gray M, Muhyaldeen A, Gale CP, et al. Self-reported sleep duration and quality and cardiovascular disease and mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7:e008552. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008552
21. Meisinger C, Heier M, Löwel H, Schneider A, Döring A. Sleep duration and sleep complaints and risk of myocardial infarction in middle-aged men and women from the general population: the MONICA/KORA Augsburg cohort study. Sleep. (2007) 30:1121–7. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.9.1121
22. Ikehara S, Iso H, Date C, Kikuchi S, Watanabe Y, Wada Y, et al. Association of sleep duration with mortality from cardiovascular disease and other causes for Japanese men and women: the JACC study. Sleep. (2009) 32:295–301. doi: 10.1093/sleep/32.3.295
23. Lao XQ, Liu X, Deng HB, Chan TC, Ho KF, Wang F, et al. Sleep quality, sleep duration, and the risk of coronary heart disease: a prospective cohort study with 60,586 adults. J Clin Sleep Med. (2018) 14:109–17. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6894
24. Yazdanpanah MH, Homayounfar R, Khademi A, Zarei F, Shahidi A, Farjam M. Short sleep is associated with higher prevalence and increased predicted risk of cardiovascular diseases in an Iranian population: Fasa PERSIAN cohort study. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:4608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61506-0
25. Zhang B, Wang Y, Liu X, Zhai Z, Sun J, Yang J, et al. The association of sleep quality and night sleep duration with coronary heart disease in a large-scale rural population. Sleep Med. (2021) 87:233–40. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.09.013
26. Amagai Y, Ishikawa S, Gotoh T, Kayaba K, Nakamura Y, Kajii E. Sleep duration and incidence of cardiovascular events in a Japanese population: the Jichi medical school cohort study. J Epidemiol. (2010) 20:106–10. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20090053
27. Chandola T, Ferrie JE, Perski A, Akbaraly T, Marmot MG. The effect of short sleep duration on coronary heart disease risk is greatest among those with sleep disturbance: a prospective study from the Whitehall II cohort. Sleep. (2010) 33:739–44. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.6.739
28. Svensson AK, Svensson T, Kitlinski M, Almgren P, Engström G, Nilsson PM, et al. Incident diabetes mellitus may explain the association between sleep duration and incident coronary heart disease. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:331–41. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4464-3
29. Kronholm E, Laatikainen T, Peltonen M, Sippola R, Partonen T. Self-reported sleep duration, all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in Finland. Sleep Med. (2011) 12:215–21. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2010.07.021
30. Strand LB, Tsai MK, Gunnell D, Janszky I, Wen CP, Chang SS. Self-reported sleep duration and coronary heart disease mortality: a large cohort study of 400,000 Taiwanese adults. Int J Cardiol. (2016) 207:246–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.01.044
31. Suzuki S, Arima H, Miyazaki S, Fujiyoshi A, Kadota A, Takashima N, et al. Self-reported sleep duration and subclinical atherosclerosis in a general population of Japanese men. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2018) 25:186–98. doi: 10.5551/jat.40527
32. Baldacci S, Santoro M, Coi A, Mezzasalma L, Bianchi F, Pierini A. Lifestyle and sociodemographic risk factors for gastroschisis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. (2020) 105:756–64. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2019-318412
33. Hu J, Dong Y, Chen X, Liu Y, Ma D, Liu X, et al. Prevalence of suicide attempts among Chinese adolescents: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Compr Psychiatry. (2015) 61:78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2015.05.001
34. Hamazaki Y, Morikawa Y, Nakamura K, Sakurai M, Miura K, Ishizaki M, et al. The effects of sleep duration on the incidence of cardiovascular events among middle-aged male workers in Japan. Scand J Work Environ Health. (2011) 37:411–7. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.3168
35. Khan H, Kella D, Kunutsor SK, Savonen K, Laukkanen JA. Sleep duration and risk of fatal coronary heart disease, sudden cardiac death, cancer death, and all-cause mortality. Am J Med. (2018) 131:1499–505.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.07.010
36. Li Y, Sato Y, Yamaguchi N. Potential biochemical pathways for the relationship between sleep duration and mortality. Sleep Med. (2013) 14:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2012.08.020
37. Cheng Y, Du CL, Hwang JJ, Chen IS, Chen MF, Su TC. Working hours, sleep duration and the risk of acute coronary heart disease: a case-control study of middle-aged men in Taiwan. Int J Cardiol. (2014) 171:419–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.12.035
38. Li L, Gong S, Xu C, Zhou JY, Wang KS. Sleep duration and smoking are associated with coronary heart disease among US adults with type 2 diabetes: gender differences. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2017) 124:93–101. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.12.015
39. Zhang X, Qin Y, Ruan W, Wan X, Lv C, He L, et al. Targeting inflammation-associated AMPK//mfn-2/MAPKs signaling pathways by baicalein exerts anti-atherosclerotic action. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:4442–55. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7149
40. Petrovic D, Haba-Rubio J, de Mestral Vargas C, Kelly-Irving M, Vineis P, Kivimäki M, et al. The contribution of sleep to social inequalities in cardiovascular disorders: a multi-cohort study. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 116:1514–24. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz267
41. Vaccaro A, Kaplan Dor Y, Nambara K, Pollina EA, Lin C, Greenberg ME, et al. Sleep loss can cause death through accumulation of reactive oxygen Species in the gut. Cell. (2020) 181:1307–28.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.049
42. Sukhorukov VN, Khotina VA, Bagheri Ekta M, Ivanova EA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in macrophages: the vicious circle of lipid accumulation and pro-inflammatory response. Biomedicines. (2020) 8:210. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8070210
43. Maron BA, Michel T. Subcellular localization of oxidants and redox modulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ J. (2012) 76:2497–512. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-12-1207
44. Zhao S, Zhang L, Lian G, Wang X, Zhang H, Yao X, et al. Sildenafil attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of intracellular ROS-related MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in N9 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol. (2011) 11:468–74. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.12.017
45. Zhang J, Alcaide P, Liu L, Sun J, He A, Luscinskas FW, et al. Regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression by mast cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e14525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014525
46. Wang H, Segaran RC, Chan LY, Aladresi AAM, Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, et al. Gamma radiation-induced disruption of cellular junctions in HUVECs is mediated through affecting MAPK/NF-κB inflammatory pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2019) 2019:1486232. doi: 10.1155/2019/1486232
47. Fang C, He M, Li D, Xu Q. YTHDF2 mediates LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory response via the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Signal. (2021) 85:110060. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110060
48. Vendrov AE, Stevenson MD, Alahari S, Pan H, Wickline SA, Madamanchi NR, et al. Attenuated superoxide dismutase 2 activity induces atherosclerotic plaque instability during aging in hyperlipidemic mice. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e006775. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006775
49. Lenz M, Kaun C, Krychtiuk KA, Haider P, Brekalo M, Maier N, et al. Effects of nicorandil on inflammation, apoptosis and atherosclerotic plaque progression. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:120. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020120
50. Ferrie JE, Kivimäki M, Akbaraly TN, Singh-Manoux A, Miller MA, Gimeno D, et al. Associations between change in sleep duration and inflammation: findings on C-reactive protein and interleukin 6 in the Whitehall II study. Am J Epidemiol. (2013) 178:956–61. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwt072
51. Pang X, Liu J, Zhao J, Mao J, Zhang X, Feng L, et al. Homocysteine induces the expression of C-reactive protein via NMDAr-ROS-MAPK-NF-κB signal pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. (2014) 236:73–81. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.06.021
52. Ma SN, Liu XH, Cai WS. Preventive noninvasive vagal nerve stimulation reduces insufficient sleep-induced depression by improving the autonomic nervous system. Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 173:116344. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116344
53. Liu F, Qu B, Wang L, Xu Y, Peng X, Zhang C, et al. Effect of selective sleep deprivation on heart rate variability in post-90s healthy volunteers. Math Biosci Eng. (2022) 19:13851–60. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022645
54. Hajiasgharzadeh K, Khabbazi A, Mokhtarzadeh A, Baghbanzadeh A, Asadzadeh Z, Adlravan E, et al. Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and connective tissue diseases. Inflammopharmacology. (2021) 29:975–86. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00812-z
55. Reule S, Drawz PE. Heart rate and blood pressure: any possible implications for management of hypertension? Curr Hypertens Rep. (2012) 14:478–84. doi: 10.1007/s11906-012-0306-3
56. Spiegel K, Tasali E, Penev P, Van Cauter E. Brief communication: sleep curtailment in healthy young men is associated with decreased leptin levels, elevated ghrelin levels, and increased hunger and appetite. Ann Intern Med. (2004) 141:846–50. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-141-11-200412070-00008
57. Taheri S, Lin L, Austin D, Young T, Mignot E. Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin, elevated ghrelin, and increased body mass index. PLoS Med. (2004) 1:e62. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0010062
58. Broussard JL, Ehrmann DA, Van Cauter E, Tasali E, Brady MJ. Impaired insulin signaling in human adipocytes after experimental sleep restriction: a randomized, crossover study. Ann Intern Med. (2012) 157:549–57. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-8-201210160-00005
59. Savin KL, Patel SR, Clark TL, Bravin JI, Roesch SC, Sotres-Alvarez D, et al. Relationships of sleep duration, midpoint, and variability with physical activity in the HCHS/SOL sueño ancillary study. Behav Sleep Med. (2021) 19:577–88. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2020.1820335
60. Kalmbach DA, Buysse DJ, Cheng P, Roth T, Yang A, Drake CL. Nocturnal cognitive arousal is associated with objective sleep disturbance and indicators of physiologic hyperarousal in good sleepers and individuals with insomnia disorder. Sleep Med. (2020) 71:151–60. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2019.11.1184
61. Ahmad A, Didia SC. Effects of sleep duration on cardiovascular events. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2020) 22:18. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-1271-0
62. Subramanya V, Zhao D, Ouyang P, Ying W, Vaidya D, Ndumele CE, et al. Association of endogenous sex hormone levels with coronary artery calcium progression among post-menopausal women in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. (2019) 13:41–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2018.09.010
63. Liu PY, Reddy RT. Sleep, testosterone and cortisol balance, and ageing men. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2022) 23:1323–39. doi: 10.1007/s11154-022-09755-4
64. van Egmond LT, Meth EMS, Engström J, Ilemosoglou M, Keller JA, Vogel H, et al. Effects of acute sleep loss on leptin, ghrelin, and adiponectin in adults with healthy weight and obesity: a laboratory study. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2023) 31:635–41. doi: 10.1002/oby.23616
65. Cohen E, Margalit I, Shochat T, Goldberg E, Krause I. Markers of chronic inflammation in overweight and obese individuals and the role of gender: a cross-sectional study of a large cohort. J Inflamm Res. (2021) 14:567–73. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S294368
66. Tonet NS, da Silva Marçal DF, da Silva FN, Brunetta HS, Mori M, Dos Santos GJ, et al. Moderate chronic sleep perturbation impairs glucose and lipid homeostasis in rats. Sleep. (2024) 47:zsae118. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsae118
67. Fu Q, Li T, Zhang C, Ma X, Meng L, Liu L, et al. Butyrate mitigates metabolic dysfunctions via the ERα-AMPK pathway in muscle in OVX mice with diet-induced obesity. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:95. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01119-y
68. Covassin N, Bukartyk J, Singh P, Calvin AD, St Louis EK, Somers VK. Effects of experimental sleep restriction on ambulatory and sleep blood pressure in healthy young adults: a randomized crossover study. Hypertension. (2021) 78:859–70. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17622
69. Cappuccio FP, Stranges S, Kandala NB, Miller MA, Taggart FM, Kumari M, et al. Gender-specific associations of short sleep duration with prevalent and incident hypertension: the Whitehall II study. Hypertension. (2007) 50:693–700. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.095471
70. Gao X, Yamazaki Y, Tezuka Y, Omata K, Ono Y, Morimoto R, et al. Gender differences in human adrenal cortex and its disorders. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2021) 526:111177. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111177
71. Carter JR, Fonkoue IT, Greenlund IM, Schwartz CE, Mokhlesi B, Smoot CA. Sympathetic neural responsiveness to sleep deprivation in older adults: sex differences. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2019) 317:H315–22. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00232.2019
72. Mosca M, Aggarwal B. Sleep duration, snoring habits, and cardiovascular disease risk factors in an ethnically diverse population. J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2012) 27:263–9. doi: 10.1097/JCN.0b013e31821e7ad1
73. Miller MA, Kandala NB, Kivimaki M, Kumari M, Brunner EJ, Lowe GD, et al. Gender differences in the cross-sectional relationships between sleep duration and markers of inflammation: Whitehall II study. Sleep. (2009) 32:857–64.19639748
74. Kamon T, Kaneko H, Itoh H, Kiriyama H, Mizuno Y, Morita H, et al. Possible gender difference in the association between abdominal obesity, chronic inflammation, and preclinical atherosclerosis in the general population. Int Heart J. (2021) 62:837–42. doi: 10.1536/ihj.20-654
75. Piety NZ, Reinhart WH, Stutz J, Shevkoplyas SS. Optimal hematocrit in an artificial microvascular network. Transfusion. (2017) 57:2257–66. doi: 10.1111/trf.14213
76. Kim HJ, Park HA, Cho YG, Kang JH, Kim KW, Kang JH, et al. Gender difference in the level of HDL cholesterol in Korean adults. Korean J Fam Med. (2011) 32:173–81. doi: 10.4082/kjfm.2011.32.3.173
77. Shimada S, Hasegawa K, Wada H, Terashima S, Satoh-Asahara N, Yamakage H, et al. High blood viscosity is closely associated with cigarette smoking and markedly reduced by smoking cessation. Circ J. (2011) 75:185–9. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-10-0335
78. Anujuo K, Stronks K, Snijder MB, Jean-Louis G, Rutters F, van den Born BJ, et al. Relationship between short sleep duration and cardiovascular risk factors in a multi-ethnic cohort—the helius study. Sleep Med. (2015) 16:1482–8. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2015.08.014
79. Ueshima H. Explanation for the Japanese paradox: prevention of increase in coronary heart disease and reduction in stroke. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2007) 14:278–86. doi: 10.5551/jat.E529
80. Hoevenaar-Blom MP, Spijkerman AM, Kromhout D, van den Berg JF, Verschuren WM. Sleep duration and sleep quality in relation to 12-year cardiovascular disease incidence: the MORGEN study. Sleep. (2011) 34:1487–92. doi: 10.5665/sleep.1382
81. Patel SR, Malhotra A, Gottlieb DJ, White DP, Hu FB. Correlates of long sleep duration. Sleep. (2006) 29:881–9. doi: 10.1093/sleep/29.7.881
82. Zhou Q, Zhang M, Hu D. Dose-response association between sleep duration and obesity risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Sleep Breath. (2019) 23:1035–45. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01824-4
83. Pengpid S, Peltzer K. Sedentary behaviour and 12 sleep problem indicators among middle-aged and elderly adults in South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:1422. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16081422
84. Wang PS, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Borges G, Bromet EJ, et al. Use of mental health services for anxiety, mood, and substance disorders in 17 countries in the WHO world mental health surveys. Lancet. (2007) 370:841–50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61414-7
85. Romero-Corral A, Montori VM, Somers VK, Korinek J, Thomas RJ, Allison TG, et al. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet. (2006) 368:666–78. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69251-9
86. Ayas NT, White DP, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Speizer FE, Malhotra A, et al. A prospective study of sleep duration and coronary heart disease in women. Arch Intern Med. (2003) 163:205–9. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.2.205
Keywords: extreme sleep duration, coronary heart disease, gender, BMI, continent
Citation: Li C, Luo S-x, Liang T-w, Song D and Fu J-x (2025) Gender correlation between sleep duration and risk of coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1452006. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1452006
Received: 20 June 2024; Accepted: 7 March 2025;
Published: 25 March 2025.
Edited by:
Hamidreza Goodarzynejad, North York General Hospital, CanadaReviewed by:
Jose Luis Fachi, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesCopyright: © 2025 Li, Luo, Liang, Song and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jin-xiao Fu, ZnV5YzExMDFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.