- Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Dong E Hospital, Dong’e, China
Aims: Significant tricuspid regurgitation (TR) in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients is becoming a global issue, as it can lead to progressive right ventricular enlargement and heart failure, thereby increasing morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to evaluate potential predictors of significant TR in AF patients using open databases.
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science were searched for relevant studies from inception to September 2023. Using STATA 14.0 statistical software, hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated for data synthesis. The potential predictors included clinical characteristics, echocardiography parameters, and prior comorbidities. Evidence certainty was evaluated based on the GRADE system.
Results: In total, 12 studies involving almost 16,000 patients were included in this review. Female sex (HR = 2.14; 95% CI: 1.84–2.49; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.430), persistent atrial fibrillation (HR = 2.99; 95% CI: 2.47–3.61; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.896), left ventricular ejection fraction [standard mean difference (SMD) = −0.16; 95% CI:−0.30 to −0.03; I2 = 69.8%; p < 0.000], age (HR = 1.07; 95% CI: 1.04–1.09; I2 = 72.3%; p = 0.013), heart failure (HR = 1.86; 95% CI: 1.45–2.39; I2 = 9.0%; p = 0.348), age ≥65 years (HR = 2.30; 95% CI: 1.63–3.25; I2 = 55.1%; p = 0.108), chronic lung disease (HR = 1.33; 95% CI: 1.02–1.74; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.882), right ventricle fractional area change (SMD = 0.18; 95% CI: 0.01–0.36; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.440), systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (SMD = 0.97; 95% CI: 0.76–1.19; I2 = 41.5%; p = 0.181), and proper ventricular systolic pressure (SMD = 1.07; 95% CI: 0.54–1.59; I2 = 92.4%; p < 0.000) may negatively influence significant TR.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis identified a potential negative influence of several clinical characteristics, echocardiography parameters, and previous comorbidities on significant TR. However, due to the low level of certainty of evidence, our analysis can only provide some guidance to practitioners and researchers. Caution is advised, and further validation is needed.
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF), an epidemic disease with an increasing global public health burden, is the most common in-hospital arrhythmia in clinical practice (1) and is increasingly found to be the primary reason for morbidity and mortality in cardiovascular diseases. Recently, the prevalence of AF has been increasing, and it is estimated that one in every four to six adults will suffer from AF in their lifetime (2, 3). Clinically, AF is usually treated and controlled by drugs or ablation (4). Despite the maintenance of normal ventricular systolic function and size, a prolonged duration of illness can still result in atrial and annular dilation due to AF. This dilation may subsequently lead to a series of secondary or functional heart changes, including tricuspid (TR) and mitral regurgitation (MR) (5–7). In recent years, a large number of studies (8–10) have focused on the impact of significant TR (moderate or severe TR) in patients with AF; that is, significant TR can lead to progressive right ventricular enlargement and increased morbidity and mortality in heart failure (HF) (8–10). Currently, epidemiological evidence shows that the prevalence of TR (including significant TR) in the elderly population has markedly increased, approximately 8%–9% (10, 11), and AF was considered one of the main causes of atrial functional TR (12). Therefore, finding potential predictors of significant TR in patients with AF as early and as accurately as possible is vital for patients (especially the elderly), healthcare providers, and policymakers.
The factors associated with significant TR in AF typically include clinical characteristics, echocardiographic parameters, and prior comorbidities (13–15). Although not all of these factors, such as sex, can be changed, unchangeable predictive factors can also play a preventive and indicative role (16–18). In recent years, many studies (16, 19, 20) have reported some potential predictive factors, but most were observational studies. So far, only four published meta-analyses have focused on TR patients. Of these, three (21–23) focused on the independent risk factors of cardiac implantation (permanent pacemaker or cardioverter defibrillator) for TR, and the other (24) discussed the risk factors for TR after valve surgery. Unfortunately, no meta-analysis has reviewed the comprehensive predictive value of clinical characteristics, echocardiographic parameters, and prior comorbidities in multicenter clinical trials of a large size. Thus, this study was intended to identify the potential predictors of significant TR in AF patients based on open databases.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis was guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) statement (25).
Search strategy
PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, and the Web of Science database were comprehensively searched for relevant studies from their inception until September 2023. The study used “Atrial Fibrillations,” “Auricular Fibrillation”, “Tricuspid Valve Incompetence”, “Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation”, “Significant Tricuspid Incompetence”, “Significant Tricuspid Regurgitation”, and other relevant keywords in the medical subject heading (MeSH) terms to establish the search strategy (Supplementary Table S1).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows:
1. Population: AF patients.
2. Intervention: significant TR (patients with a clinical qualitative or quantitative diagnosis of moderate to severe TR).
3. Comparator: non-significant TR (no TR and mild TR).
4. Outcome: including at least one of the following factors: clinical characteristics (age, age ≥ 65 years, female), echocardiography parameters [left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (SPAP), right ventricle fractional area change (RV FAC), and right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP)], and previous comorbidities [persistent atrial fibrillation (PAF), coronary artery disease (CAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), HF, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, and chronic lung disease (CLD)].
The exclusion criteria were as follows:
1. Article type: conference abstracts, case reports, and reviews.
2. Duplicate reports.
Data extraction
The included studies were selected by two independent reviewers, and disagreements were resolved in consultation with a third reviewer. We extracted the author's name, publication year, country, study design, mean age, sample size, female proportion, target population, and median follow-up time from the included studies.
Quality assessment
Risk Of Bias In Non-Randomized Studies - of Interventions (ROBINS-I), a method to evaluate bias risk in non-randomized studies, was selected to assess the methodological quality of the included articles (http://www.riskofbias.info). Based on the assessment results, the bias risk of the studies was classified as “Low”, “Moderate”, “Serious”, or “Critical”.
Based on the outcome evaluation results and characteristics of the included studies, an evidence certainty assessment table was created using the GRADE system (26, 27).
Statistical analysis
This study used STATA 14.0 software (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). Hazard ratio (HR), standard mean difference (SMD), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to assess the clinical characteristics, echocardiography parameters, and the results of prior comorbidities. The χ2 test and I-squared (I2) statistic were used to assess the heterogeneity. The random effects model was used if p ≤ 0.10 and I2 ≥ 50%, which meant existing heterogeneity among studies model. Otherwise, the fixed-effect model was applied. Begg’s rank correlation (28), funnel plots, and Egger’s weighted regression (29) were performed to test the publication bias. Trim-and-fill analysis was conducted to judge whether the publication bias impacted the outcome synthesis if significant bias was present. Subgroup analysis was used to explore possible causes of heterogeneity if necessary. The robustness of the results in this study was determined by leave-one-out analysis. p < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
Results
Study screening
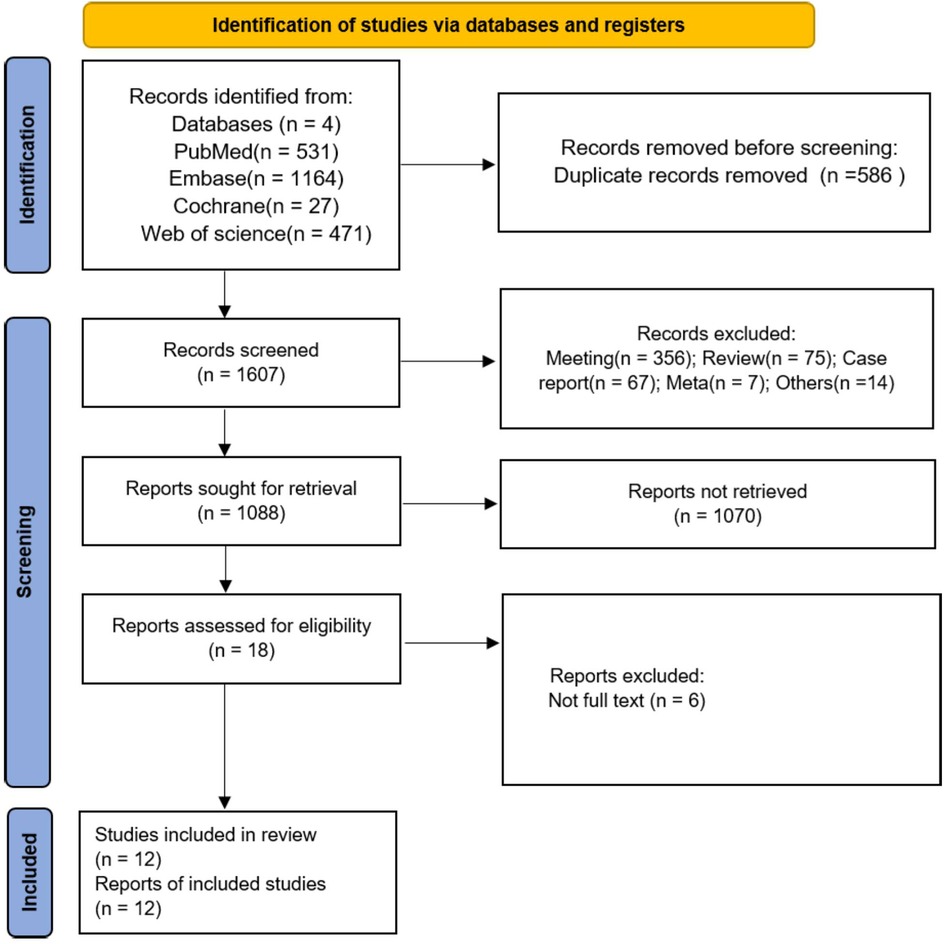
A total of 2,193 studies were retrieved as potential reports from four open databases. After the initial removal of 586 duplicate records, 1,607 articles were reserved for title and abstract review, and 519 articles with ineligible study designs were excluded. After excluding 1,070 articles, 18 articles remained for full-text review, and, ultimately, 12 studies (8, 13–20, 30–32) were included in the meta-analysis. The flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Study characteristics
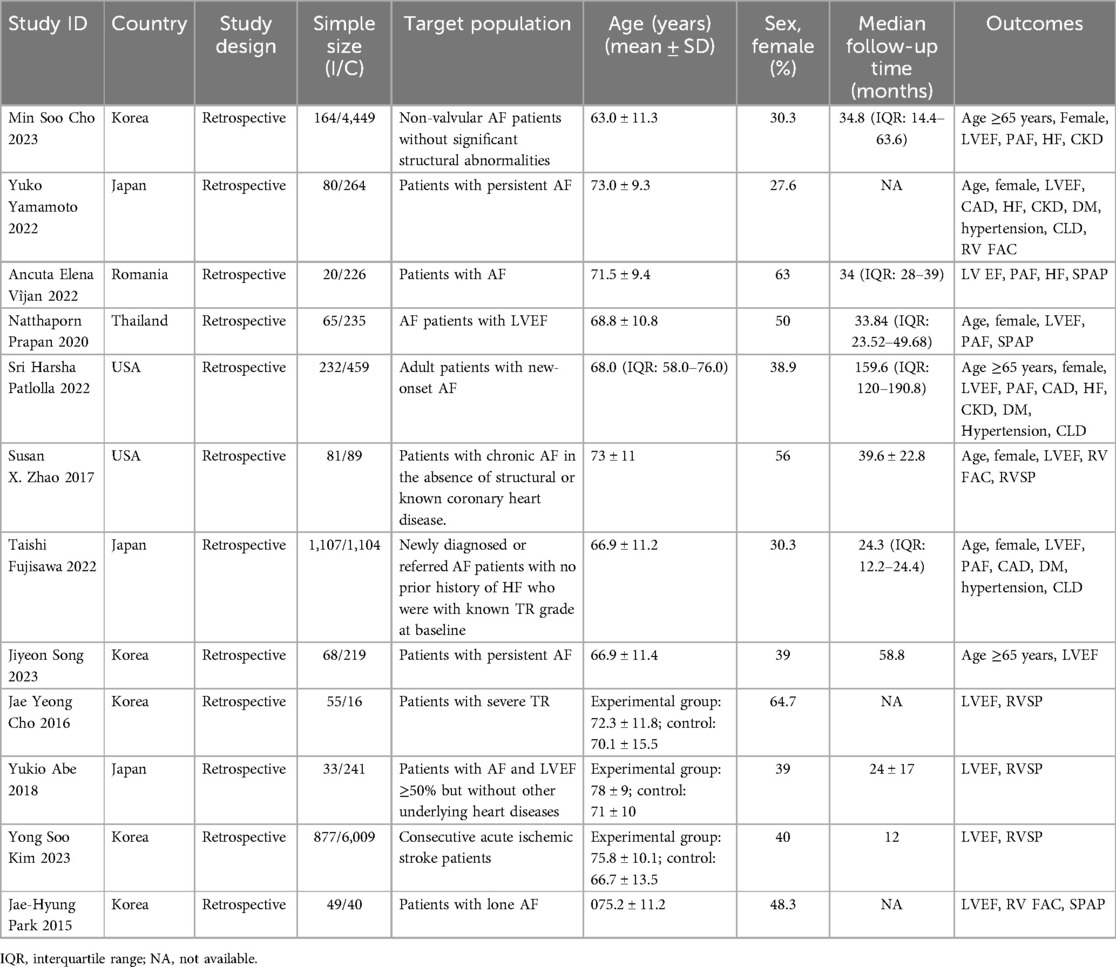
The 12 retrospective studies that met the inclusion criteria were published between 2015 and 2023, and the sample sizes ranged from 71 to 4,613. Almost 16,000 patients were included in this review. The included studies were conducted in Korea, Japan, Romania, Thailand, and America. The mean age of the included study population ranged from 63 to 78, and the female proportion ranged from 27.6% to 64.7%. The basic characteristics are outlined in Table 1.
Quality assessment
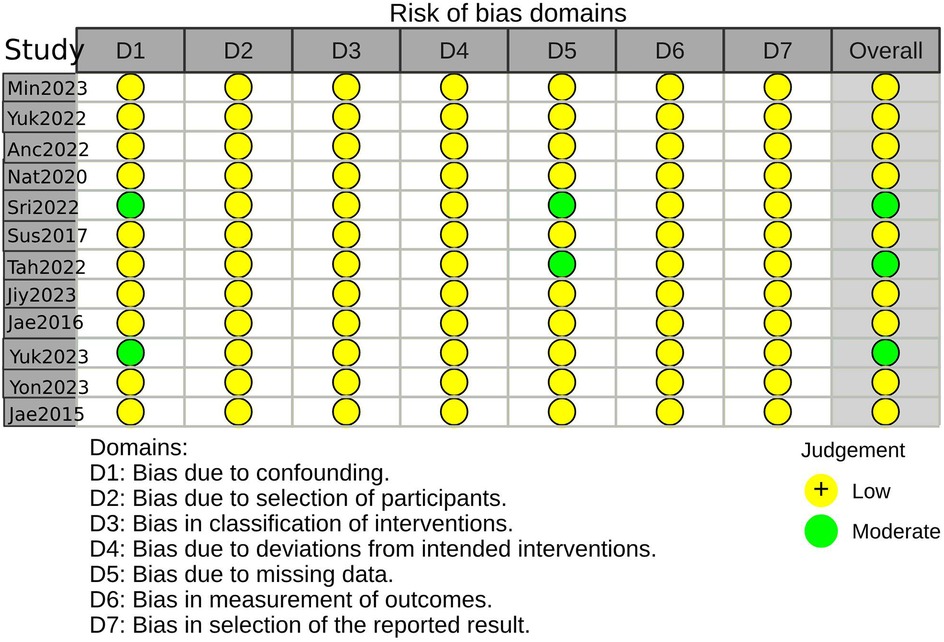
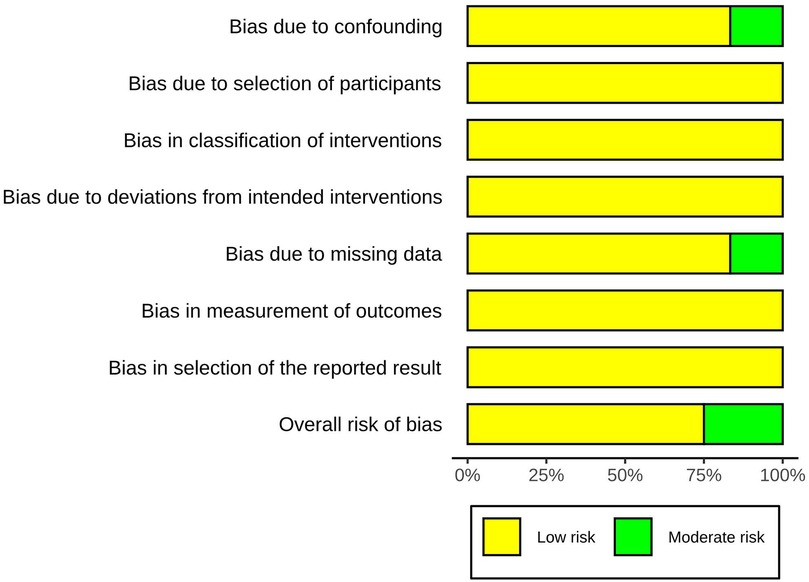
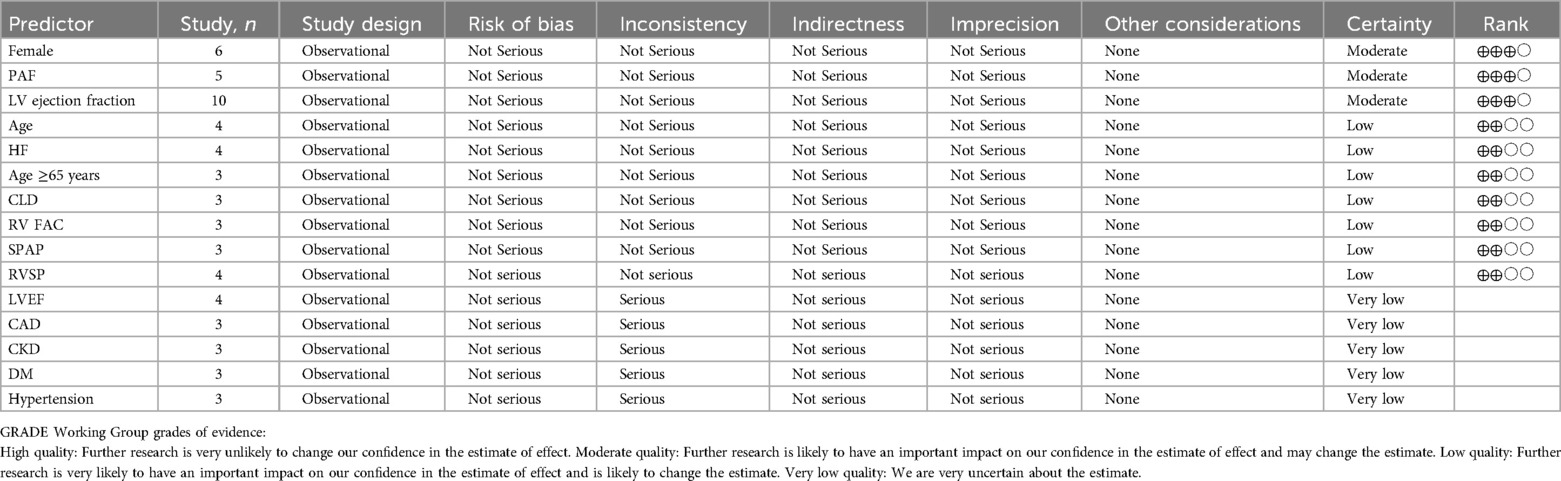
Three studies were considered to be of moderate risk due to confounding and missing data. The other nine were evaluated as low risk (Figures 2, 3, Supplementary Table S2). The certainty of evidence is summarized in Table 2 using the GRADE system. Pooled results of HR or SMD for each predictor below are also presented in order from higher to lower GRADE certainty levels.
Predictors of TR
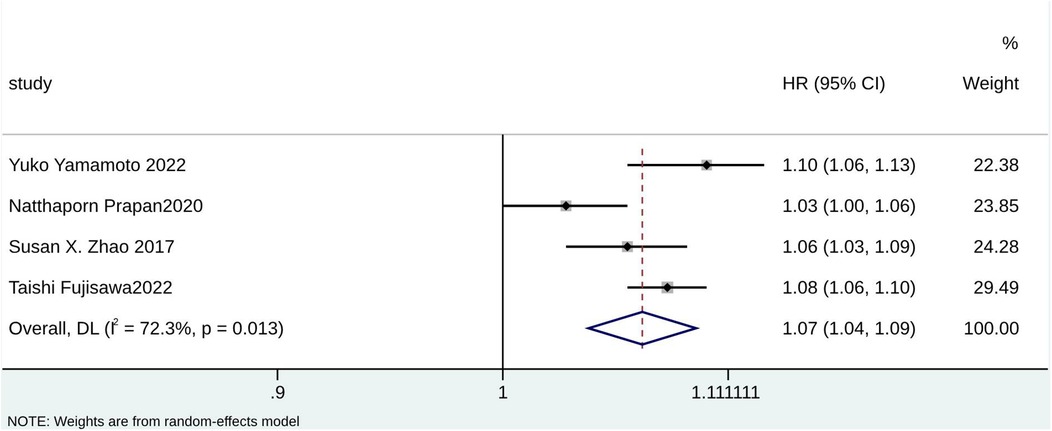
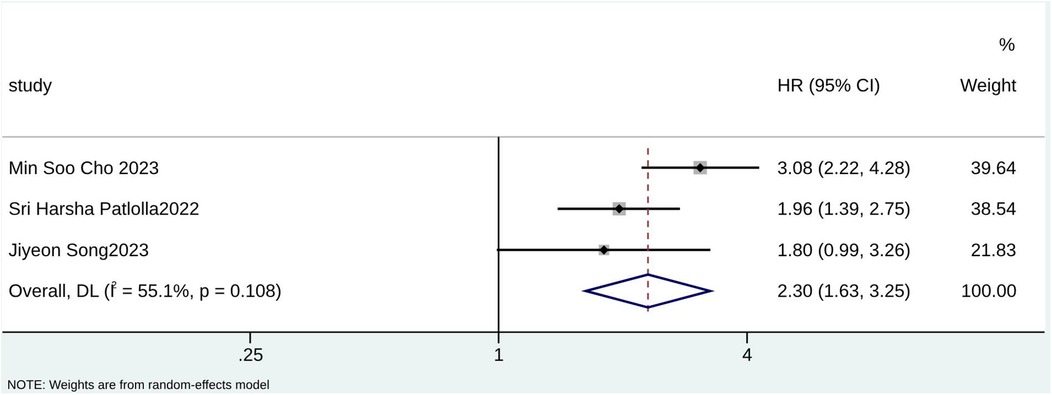
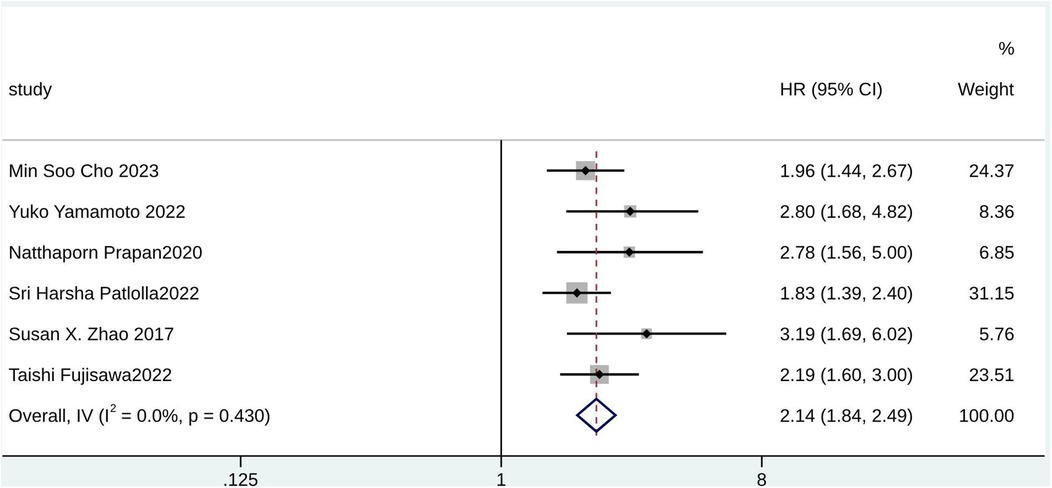
According to the pooled analysis of clinical characteristics, female sex (HR = 2.14; 95% CI: 1.84–2.49; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.430), age (HR = 1.07; 95% CI: 1.04–1.09; I2 = 72.3%; p = 0.013), and age ≥65 years (HR = 2.30; 95% CI: 1.63–3.25; I2 = 55.1%; p = 0.108) were potential predictors for TR in patients with AF (Figures 4–6). The GRADE evidence certainty level for female sex was the highest (moderate) of all the predictors, followed by age and age ≥65 years (low).
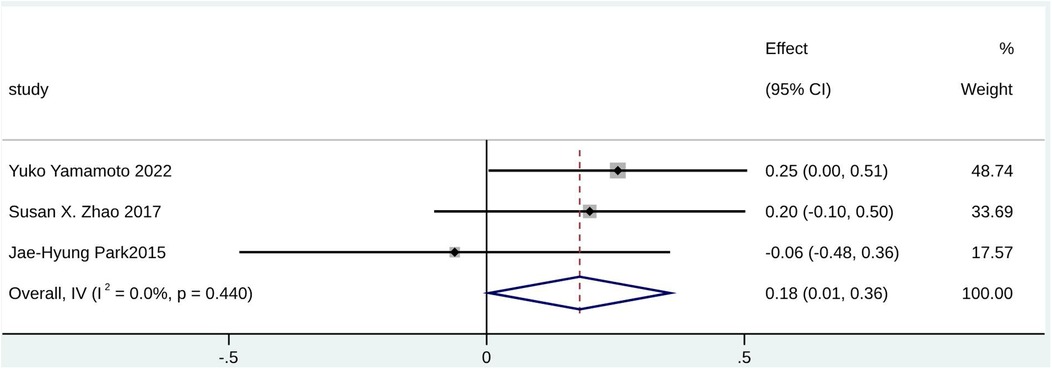
Furthermore, echocardiography parameters including RV FAC (SMD = 0.18; 95% CI: 0.01–0.36; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.440), SPAP (SMD = 0.97; 95% CI: 0.76–1.19; I2 = 41.5%; p = 0.181), and RVSP (SMD = 1.07; 95% CI: 0.54–1.59; I2 = 92.4%; p < 0.000) were potential predictors for significant TR in patients with AF (Figure 7, Supplementary Figures S32, S33). However, RVSP had high heterogeneity. A statistically significant difference was found for LVEF (SMD = −0.16; 95% CI: −0.30 to −0.03; I2 = 69.8%; p < 0.000) (Supplementary Figure S34), which may serve as a potential predictor for non-significant TR in patients with AF (HR = 1.00; 95% CI: 0.96–1.03; I2 = 71.7%; p = 0.014) (Supplementary Figure S35).
Regarding previous comorbidities, PAF (HR = 2.99; 95% CI: 2.47–3.61; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.896), HF (HR = 1.86; 95% CI: 1.45–2.39; I2 = 9.0%; p = 0.348), and CLD (HR = 1.33; 95% CI: 1.02–1.74; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.882) were identified as potential predictors for significant TR in patients with AF (Supplementary Figures S36–S38). However, statistically significant associations were not observed for CAD (HR = 1.10; 95% CI: 0.72–1.68; I2 = 57.7%; p = 0.094), CKD (HR = 1.11; 95% CI: 0.55–2.26; I2 = 90.7%; p < 0.000), DM (HR = 0.76; 95% CI: 0.42–1.36; I2 = 78.7%; p = 0.009), and hypertension (HR = 1.07; 95% CI: 0.87–1.32; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.688) (Supplementary Figures S39–S42).
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
The funnel plots showed that there may be a publication bias in some results, such as LVEF (HR) and RV FAC (Supplementary Figures S1–S15), but this possibility was negated by Begg’s and Egger's tests (Supplementary Table S3). The trim-and-fill results showed that bias may have impacted the pooled result for the female sex (Supplementary Figure S31). The sensitivity analysis indicated robust results (Supplementary Figures S16–S30).
Discussion
This study systematically reviewed predictors of significant TR in AF patients. We identified 10 potential predictors for significant TR in AF patients, including age, age ≥65 years, female, LVEF (SMD), RV FAC, SPAP, RVSP, PAF, HF, and CLD.
Demographic characteristics, such as age, sex, and BMI, are well-known factors associated with significant TR occurrence (33, 34). The type and number of collagen fibers in the tricuspid annulus differ with age, which may be the main reason why the gradual expansion of the tricuspid orifice and the more elliptical evolution of the triangle geometry play a role in the progression of age-affected TR (35, 36). In aging populations, the number of elderly patients with long-term AF is increasing (37–39). Therefore, it is necessary to find predictors of significant TR in AF patients over 65 years of age. A study found sex differences among clinical characteristics, valve anatomy, and morphological characteristics in AF patients with TR (40). Compared to male patients, female patients exhibited a higher circumferential index but fewer cells and less elasticity in the valve ring (41). This may indicate that sex has a predictive value for significant TR in AF patients. Consistent with existing literature, this study indicated that age, age ≥65 years, and sex were potential predictors for significant TR in AF and proved the predictive advantages of these clinical factors statistically. Moreover, significant TR in female AF patients aged ≥65 should be investigated in future clinical practice.
In addition, some echocardiographic parameters related to cardiac remodeling, such as LVEF, tricuspid annulus diameter (TAD), RV FAC, stent height, and some hemodynamic parameters, such as SPAP and RVSP, have also been confirmed to be associated with significant TR in AF in previous studies (10, 13). Several cohort studies have observed that moderate pulmonary hypertension in AF patients may be accompanied by left ventricular diastolic dysfunction or organic changes (such as tricuspid annulus changes), suggesting that SPAP may be related to the occurrence or progression of TR (42, 43). In addition, a study (31) showed that RVSP increased during the follow-up of patients with reversible TR, which may be related to respiratory variability and the inferior vena cava (IVC) size. As for parameters such as LVEF, a retrospective study (31) showed that LVEF in AF patients increasing by more than 10% may promote an improvement in reversible TR. This study showed that LVEF, RV FAC, SPAP, and RVSP were all predictive factors of significant TR in AF, proving these factors’ predictive advantages statistically. Other parameters, such as left atrial diameter (LAD), TAD, and right atrial diameter (RAD), have not been discussed in this study because it was difficult to obtain enough data. The correlation between these parameters and significant TR in patients with AF should be analyzed in subsequent research.
It is believed that the progression of AF patients with or without significant TR may be regulated by previous comorbidities (44), and the mortality of patients with simple AF was lower than that of patients with prior comorbidities (45). For AF patients with significant TR, the common comorbidities include PAF, HF, CLD, CAD, CKD, DM, and hypertension (16, 19, 20). Several studies have shown that long-term AF, a type of arrhythmia, can lead to right atrial dilatation. Maintaining sinus rhythm (rhythm control) may help prevent significant TR. This suggests a potential correlation between non-paroxysmal AF (or persistent atrial fibrillation) and significant TR in patients with AF (46, 47). In addition, 2-year follow-up data from previous studies showed that 36.9% of AF patients with significant TR developed heart failure even with preserved LVEF (9, 15), and nearly two-thirds developed new-onset lung disease (14). All the studies mentioned above demonstrate a meaningful correlation between prior comorbidities and TR in AF. This study specifically identified PAF, HF, and CLD as predictors for significant TR in AF, providing statistical evidence for the predictive value of these factors. However, our results did not support a correlation between significant TR and CAD, CKD, DM, and hypertension in patients with AF. In addition to prior comorbidities mentioned above, dyslipidemia, smoking, and alcohol abuse had not been discussed because it was difficult to obtain sufficient data. The correlation between these factors and significant TR in patients with AF should be analyzed in subsequent research.
Given the limitations of the current stage of the study, the original data only support a broad analysis of the relationship between various influencing factors and the occurrence of significant TR in patients with AF. Several limitations were identified during the study. First, potential language bias existed because only studies published in English were included. Second, due to the rarity of isolated TR and the limited number of original studies, subgroup analysis according to different AF characteristics was not performed. In subsequent research, it is necessary to discuss the predicted value of predictors of TR in AF patients according to the following subgroups: primary, secondary (caused by left valvular diseases, left ventricular systolic dysfunction, or pulmonary hypertension unrelated to any heart disease), isolated TR (accounts for 8%–10% of all TR patients approximately and there seem to be no apparent causes), persistent TR, and new-onset TR. Third, the enrolled sample size was limited. The discussion on the correlation between significant TR and more clinical characteristics, echocardiography parameters, follow-up durations, and prior comorbidities is of great clinical significance. However, the number of studies that can be included is minimal, which may make it difficult to obtain convincing results. Fortunately, no publication bias existed in most of the results, and the sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were robust.
Clinical characteristics (including age, age ≥65 years, and female sex), echocardiographic parameters (including LVEF, RV FAC, RVSP, and SPAP), and prior comorbidities (including PAF, HF, and CLD) may serve as potential predictors for significant TR. Considering the limited cumulative amount of relevant evidence, further studies are needed to determine the long-term prognostic values of the above factors in significant TR, and more attention should be paid to looking for superior predictors of this aspect in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. NZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. JF: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. DY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1428964/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. Corrigendum to: 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European association for cardio-thoracic surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European heart rhythm association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:4194. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab648
2. Staerk L, Wang B, Preis SR, Larson MG, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT, et al. Lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation according to optimal, borderline, or elevated levels of risk factors: cohort study based on longitudinal data from the Framingham heart study. Br Med J. (2018) 361:k1453. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1453
3. Magnussen C, Niiranen TJ, Ojeda FM, Gianfagna F, Blankenberg S, Njølstad I, et al. Sex differences and similarities in atrial fibrillation epidemiology, risk factors, and mortality in community cohorts: results from the BiomarCaRE consortium (biomarker for cardiovascular risk assessment in Europe). Circulation. (2017) 136:1588–97. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028981
4. Kirchhof P, Camm AJ, Goette A, Brandes A, Eckardt L, Elvan A, et al. Early rhythm-control therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1305–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2019422
5. Muraru D, Guta AC, Ochoa-Jimenez RC, Bartos D, Aruta P, Mihaila S, et al. Functional regurgitation of atrioventricular valves and atrial fibrillation: an elusive pathophysiological link deserving further attention. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2020) 33:42–53. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.08.016
6. Sanfilippo AJ, Abascal VM, Sheehan M, Oertel LB, Harrigan P, Hughes RA, et al. Atrial enlargement as a consequence of atrial fibrillation. A prospective echocardiographic study. Circulation. (1990) 82:792–7. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.82.3.792
7. Zhou X, Otsuji Y, Yoshifuku S, Yuasa T, Zhang H, Takasaki K, et al. Impact of atrial fibrillation on tricuspid and mitral annular dilatation and valvular regurgitation. Circ J. (2002) 66:913–6. doi: 10.1253/circj.66.913
8. Abe Y, Akamatsu K, Ito K, Matsumura Y, Shimeno K, Naruko T, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of functional mitral and tricuspid regurgitation despite preserved left ventricular ejection fraction in atrial fibrillation patients. Circ J. (2018) 82:1451–8. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-17-1334
9. Takahashi Y, Izumi C, Miyake M, Imanaka M, Kuroda M, Nishimura S, et al. Actual management and prognosis of severe isolated tricuspid regurgitation associated with atrial fibrillation without structural heart disease. Int J Cardiol. (2017) 243:251–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.05.031
10. Utsunomiya H, Itabashi Y, Mihara H, Berdejo J, Kobayashi S, Siegel RJ, et al. Functional tricuspid regurgitation caused by chronic atrial fibrillation: a real-time 3-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2017) 10:e004897. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.004897
11. Topilsky Y, Maltais S, Medina Inojosa J, Oguz D, Michelena H, Maalouf J, et al. Burden of tricuspid regurgitation in patients diagnosed in the community setting. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2019) 12:433–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.06.014
12. Topilsky Y, Khanna A, Le Tourneau T, Park S, Michelena H, Suri R, et al. Clinical context and mechanism of functional tricuspid regurgitation in patients with and without pulmonary hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2012) 5:314–23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.111.967919
13. Park JH, Shin SH, Lee MJ, Lee MD, Shim HI, Yoon J, et al. Clinical and echocardiographic factors affecting tricuspid regurgitation severity in the patients with lone atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. (2015) 23:136–42. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2015.23.3.136
14. Patlolla SH, Schaff HV, Nishimura RA, Stulak JM, Chamberlain AM, Pislaru SV, et al. Incidence and burden of tricuspid regurgitation in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 80:2289–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.09.045
15. Prapan N, Ratanasit N, Karaketklang K. Significant functional tricuspid regurgitation portends poor outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2020) 20:433. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01716-6
16. Cho MS, Cha MJ, Nam GB, Choi KJ, Kim J. Incidence and predictors of severe tricuspid regurgitation in atrial fibrillation patients without structural heart disease. Am J Cardiol. (2023) 203:288–94. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2023.07.005
17. Fujisawa T, Kimura T, Ikemura N, Miyama H, Katsumata Y, Ueda I, et al. Effect of tricuspid regurgitation on the reported quality of life and subsequent outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11:e022713. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022713
18. Kim YS, Jeong HG, Hwang IC, Kim BJ, Kwon JM, Bae HJ, et al. Tricuspid regurgitation: a hidden risk factor for atrial fibrillation related stroke? Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1135069. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1135069
19. Vîjan AE, Daha IC, Delcea C, Bădilă E, Dan GA. Prognostic impact of severe atrial functional tricuspid regurgitation in atrial fibrillation patients. J Clin Med. (2022) 11(23):7145. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237145
20. Yamamoto Y, Daimon M, Nakanishi K, Nakao T, Hirokawa M, Ishiwata J, et al. Incidence of atrial functional tricuspid regurgitation and its correlation with tricuspid valvular deformation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:1023732. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1023732
21. Alnaimat S, Doyle M, Krishnan K, Biederman RWW. Worsening tricuspid regurgitation associated with permanent pacemaker and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 66,000 subjects. Heart Rhythm. (2023) 20:1491–501. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2023.07.064
22. Tatum R, Maynes EJ, Wood CT, Deb AK, Austin MA, O'Malley TJ, et al. Tricuspid regurgitation associated with implantable electrical device insertion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. (2021) 44:1297–302. doi: 10.1111/pace.14287
23. Zhang XX, Wei M, Xiang R, Lu YM, Zhang L, Li YD, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of tricuspid regurgitation after cardiac implantable electronic device implantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. (2022) 36:1741–55. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2021.06.025
24. Zhu TY, Min XP, Zhang HB, Meng X. Preoperative risk factors for residual tricuspid regurgitation after isolated left-sided valve surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiology. (2014) 129:242–9. doi: 10.1159/000367589
25. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev. (2021) 10:89. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
26. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Br Med J. (2008) 336:924–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
27. Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Br Med J. (2004) 328:1490. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1490
28. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. (1994) 50:1088–101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
29. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br Med J. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
30. Cho JY, Kim KH, Choi GH, Lee N, Song J, Park H, et al. Predictors of progression of tricuspid regurgitation in patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2023) 81:1519. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(23)01963-0
31. Cho JY, Kim KH, Kim JY, Sim DS, Yoon HJ, Yoon NS, et al. Predictors of reversible severe functional tricuspid regurgitation in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Cardiol. (2016) 68:419–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2015.11.010
32. Zhao SX, Soltanzad N, Swaminathan A, Ogden WD, Schiller NB. Frequency and associated clinical features of functional tricuspid regurgitation in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. (2017) 119:1371–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.01.037
33. Najib MQ, Vinales KL, Vittala SS, Challa S, Lee HR, Chaliki HP. Predictors for the development of severe tricuspid regurgitation with anatomically normal valve in patients with atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography. (2012) 29:140–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2011.01565.x
34. Shiran A, Najjar R, Adawi S, Aronson D. Risk factors for progression of functional tricuspid regurgitation. Am J Cardiol. (2014) 113:995–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.11.055
35. Keller F, Leutert G. Age dependence of collagen structures of the human heart. Z Gerontol. (1994) 27:186–93.8091837
36. Skwarek M, Hreczecha J, Dudziak M, Jerzemowski J, Szpinda M, Grzybiak M. Morphometric features of the right atrioventricular orifice in adult human hearts. Folia Morphol (Warsz). (2008) 67:53–7.18335414
37. Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2017) 135:e146–603. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485
38. Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation. (2014) 129:837–47. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119
39. Krijthe BP, Kunst A, Benjamin EJ, Lip GY, Franco OH, Hofman A, et al. Projections on the number of individuals with atrial fibrillation in the European union, from 2000 to 2060. Eur Heart J. (2013) 34:2746–51. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht280
40. Gual-Capllonch F, Cediel G, Ferrer E, Teis A, Juncà G, Vallejo N, et al. Sex-related differences in the mechanism of functional tricuspid regurgitation. Heart Lung Circ. (2021) 30:e16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2020.06.018
41. El-Busaid H, Hassan S, Odula P, Ogeng'o J, Ndung'u B. Sex Variations in the Structure of Human Atrioventricular Annuli. Folia Morphol (Warsz). (2012) 71:23–7.22532181
42. Oren M, Oren O, Feldman A, Bloch L, Turgeman Y. Permanent lone atrial fibrillation and atrioventricular valve regurgitation: may the former lead to the latter? J Heart Valve Dis. (2014) 23:759–64.25790624
43. Topilsky Y, Tribouilloy C, Michelena HI, Pislaru S, Mahoney DW, Enriquez-Sarano M. Pathophysiology of tricuspid regurgitation: quantitative Doppler echocardiographic assessment of respiratory dependence. Circulation. (2010) 122:1505–13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.941310
44. Jahangir A, Lee V, Friedman PA, Trusty JM, Hodge DO, Kopecky SL, et al. Long-term progression and outcomes with aging in patients with lone atrial fibrillation: a 30-year follow-up study. Circulation. (2007) 115:3050–6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.644484
45. Kim EJ, Yin X, Fontes JD, Magnani JW, Lubitz SA, McManus DD, et al. Atrial fibrillation without comorbidities: prevalence, incidence and prognosis (from the Framingham heart study). Am Heart J. (2016) 177:138–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.03.023
46. Fender EA, Zack CJ, Nishimura RA. Isolated tricuspid regurgitation: outcomes and therapeutic interventions. Heart. (2018) 104:798–806. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2017-311586
47. Itakura K, Hidaka T, Nakano Y, Utsunomiya H, Kinoshita M, Susawa H, et al. Successful catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation is associated with improvement in functional tricuspid regurgitation and right heart reverse remodeling. Heart Vessels. (2020) 35:842–51. doi: 10.1007/s00380-019-01546-3
Keywords: significant tricuspid regurgitation, atrial fibrillation, echocardiography parameters, predictors, meta-analysis
Citation: Zhang X, Zhang N, Fu J and Yu D (2025) Predictors of significant tricuspid regurgitation in atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1428964. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1428964
Received: 7 May 2024; Accepted: 24 January 2025;
Published: 6 March 2025.
Edited by:
Sri Harsha Patlolla, Mayo Clinic, United StatesReviewed by:
Aravind Reddy Kuchkuntla, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, United StatesKartik Andi, Mayo Clinic, United States
Copyright: © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Fu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dapeng Yu, ZGV5dWRwQDE2My5jb20=
 Xiuxiu Zhang
Xiuxiu Zhang Dapeng Yu
Dapeng Yu