- 1School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Ultrasound and Key Laboratory in Cardiac Electrophysiology and Biomechanics, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Acute Care Surgery, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
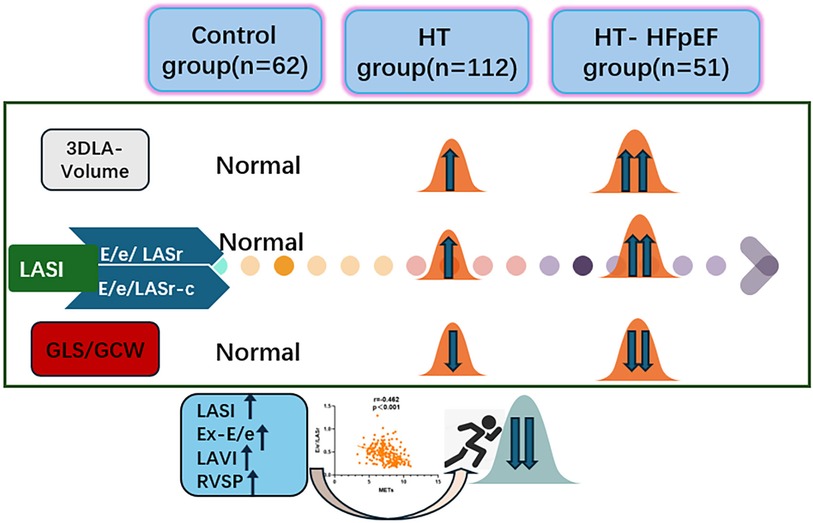
Objective: The left atrial stiffness index (LASI) holds significance in the atrioventricular coupling function and heart failure progression. To assess left atrial function and evaluate the relationship between LASI and exercise capacity in hypertension-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HT-HFpEF).
Methods: The study involved 62 healthy subjects and 163 patients with HT (112 patients in simple HT group and 51 patients in HT-HFpEF group). Each patient performed exercise stress test and standard ultrasonic images were evaluated. A comprehensive evaluation of atrioventricular function, along with investigation into the correlation between these functional parameters and exercise capacity. And further to investigate the feasibility of predicting exercise intolerance using three-dimensional derived left atrial strain index (LASI) (E/e'/LASr and E/e'/LASr-c).
Results: Compared to healthy subjects, HT group demonstrated the elevation in left atrial volume accompanied by decrease in strain value (P < 0.05). In HT-HFpEF group, further significant reductions were observed in both longitudinal (LASr) and circumferential strain (LASr-c, LASct-c) (P < 0.05). Univariate regression demonstrated that both E/e'/LASr and E/e'/LASr-c were significantly correlated with metabolic equivalents (METs) (r = −0.462, P < 0.001; r = −0.381, P < 0.001). The E/e'/LASr demonstrates comparable diagnostic efficacy to exercise-E/e' in assessing exercise intolerance in HT-HFpEF patients (AUC: 0.836 vs. 0.867, P = 0.239).
Conclusion: Progressive LA remodeling contributes to decreased atrioventricular compliance in HT and HT-HFpEF patients.E/e'/LASr serves as an independent indicator of exercise intolerance in patients with HT-HFpEF.
Introduction
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) encompasses diverse etiologies and phenotypes, with hypertension (HT) accounting for 60%–70% of cases (1), this underscoring the need for more targeted studies on this cohort. The United States with experts supporting the affirmation that asymptomatic patients with hypertension should be classified as stage A Heart Failure (2). The underlying mechanisms by which atrioventricular function affects exercise tolerance in hypertension-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HT-HFpEF) patients remain elusive.The emergence of three-dimensional speckle tracking imaging (3DSTI) technology has significantly improved reproducibility and accuracy in related assessment (3), potentially providing deeper insights into the pathophysiology underlying exercise intolerance (4). Additionally, metabolic equivalents (METs) is a standard unit used to measure the intensity of physical activity, and have been established as robust predictor of cardiovascular unfavorable outcomes (5). We hypothesized that three-dimensional left atrial(LA) speckle tracking can effectively assess atrioventricular compliance function in HT-HFpEF patients,and left atrial strain index (LASI) indices are independently associated with exercise capacity,may serve as effective tools for predicting exercise intolerance, particularly in HT-HFpEF patients.
Methods
Study subjects
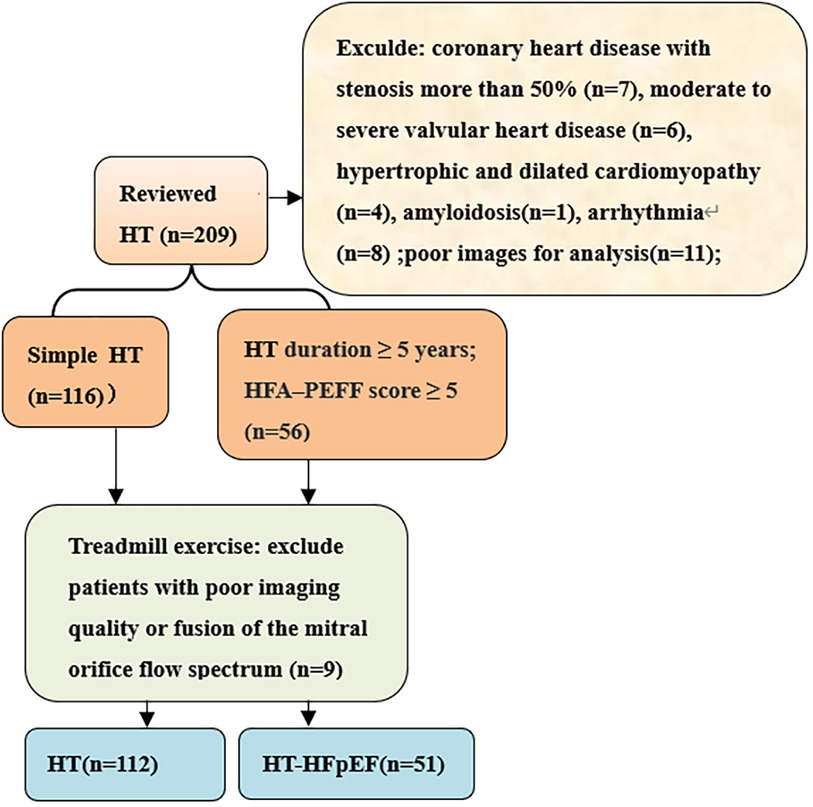
We conducted prospective cross-sectional study on hypertensive patients who received medical care at the hospital from March 2022 to October 2023. The inclusion criteria for patients diagnosed with hypertension (HT) adhered strictly to the European Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension (6), included 112 patients in HT group and 51 patients in HT-HFpEF group. The HT-HFpEF patients needed to satisfy the following criteria: duration of hypertension ≥5 years and according to the 2019 HFA–PEFF diagnostic algorithm: the consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) (7), the score ≥ 5 points implies definite HFpEF; while mean score for the HT group was 2.9 ± 1.6. Patients with poor image quality, atrial fibrillation, moderate to severe valvular heart disease,congenital heart disease, hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy,amyloidosis,coronary heart disease with stenosis more than 50%,constrictive pericarditis were excluded (Figure 1). We also included 62 normal subjects who underwent echocardiography examination during the same period with mean age of 56 ± 6 years.
Transthoracic echocardiography
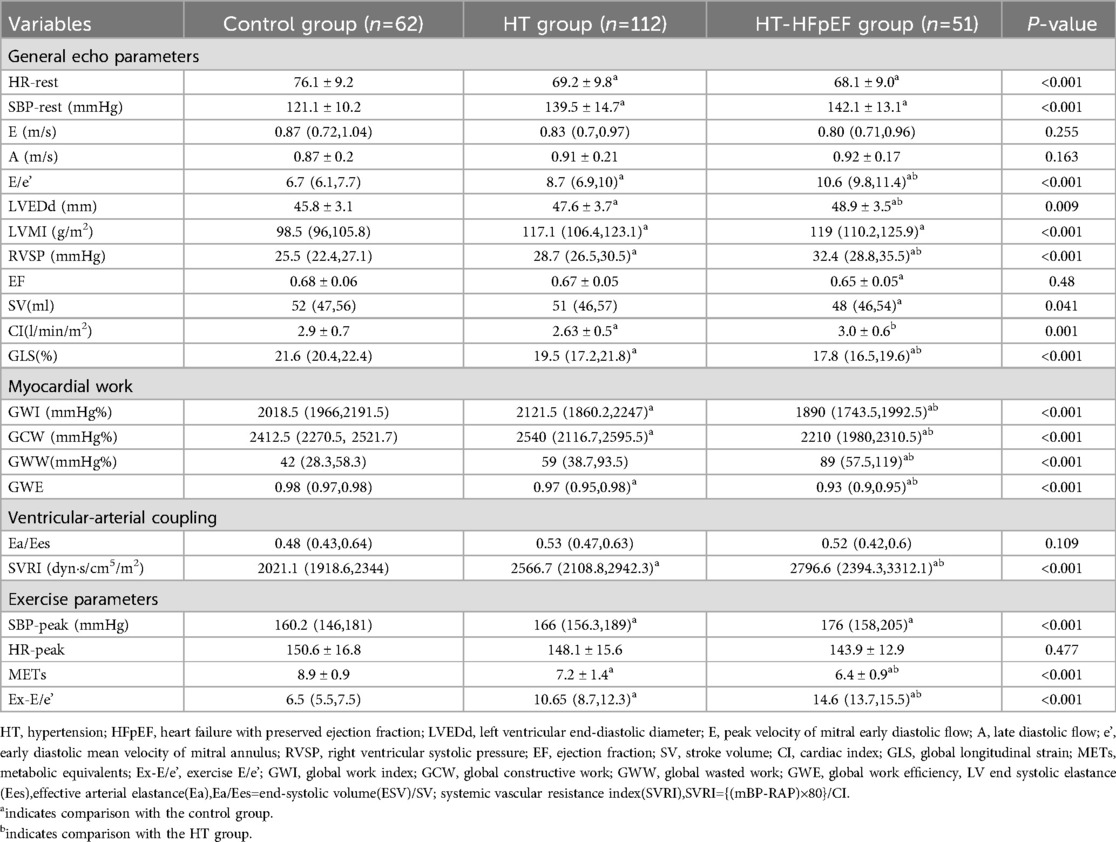
M5S and 4V1 probes of GE-vivid 95 instrument (GE Ultrasound, Horten, Norway) were utilized for the image acquisition. Patients were instructed to hold their breath for 5–7 s and the 3D image frame rate was ensured to exceed 25 frames per second. Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDd), right ventricular systolic pressure(RVSP), left ventricular mass index(LVMI), biplane-derived ejection fraction(EF), stroke volume (SV), cardiac index (CI) were obtained. From apical four-chamber views, E and A wave values were measured by transmitral flow velocity, early diastolic (e') and late diastolic (a') velocity were obtained using tissue doppler imaging (TDI),thus allowing to calculate E/e’ ratio. Auto function imaging (AFI) was applied to obtain global longitudinal strain (GLS),Global work index (GWI) represents the total workload under the pressure-strain curve, which is the product of strain and systolic pressure. Global constructive work (GCW) contributes to LV ejection and is the sum of work performed during LV systolic myocardial shortening and isovolumic diastolic myocardial lengthening.Global wasted work (GWW) is the work performed by myocardial lengthening during systole or shortening during isovolumic relaxation. Global work efficiency (GWE) is calculated as the ratio of GCW/(GCW + GWW) (8).
The treadmill exercise stress test was conducted according to the Bruce protocol and the test was stopped once the target heart rate (220-age) reached 85% (9). We recorded hemodynamic parameters as peak systolic arterial pressure (SBP-peak), peak heart rate(HR-peak), METs, and echocardiography performed immediately after exercise to measure E/e'(Ex-E/e'). Effective arterial elastance (Ea) was calculated as end-systolic pressure(ESP)/SV,and LV end systolic elastance (Ees) was derived as ESP {end-systolic volume (ESV) -V0}, with V0 considered negligible compared to ESV. The Ea/Ees ratio, equivalent to ESV/SV,was used to determine ventricular-arterial coupling (10). Additionally, the total systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI) was determined using the formula{ (mean BP- right atrial pressure(RAP)} × 80/cardiac index (CI) (11), which reflects cardiac afterload,the estimation of RAP is based on the inferior vena cava diameter and its collapsibility with respiration (12).
LA volume and strain analysis
LA images were analyzed using EchoPAC 204 workstation software(4D-auto LAQ),a well-established and widely applied technique (13). Manual adjustments were made on apical four-chamber, three-chamber, and two-chamber views at end-systole and end-diastole to outline the LA border while excluding pulmonary veins and LA appendage regions, the process performed by experienced sonographers. This process generated time-volume curve for LA, and provided strain data, including longitudinal and circumferential reservoir phase strain (LASr,LASr-c), conduit phase strain (LAScd,LAScd-c), pump phase strain (LASct,LASct-c),maximum LA volume (LAVmax),minimum LA volume (LAVmin), pre-atrial contraction LA volume (LAVpreA), LA ejection volume (LAEV) and LA emptying fraction (LAEF) were automatically calculated by 3D LA analysis (14). The left atrial volume index (LAVI) was calculated by normalizing LAVmax according to body surface area (BSA),the left atrial stiffness index-LASI (E/e'/LASr, E/e'/LASr-c) was evaluated by computing the ratio of E/e' value to LA reservoir strain.We referred to previous study by snader et al. (15), who studied exercise tolerance METs to predict all-cause mortality in population of 3,400 patients; METs <6 were considered to be associated with reduced and poor long-term prognosis. Therefore, we evaluated the diagnostic value of LASI, Ex-E/e', LAVI, and RVSP in HT-HFpEF patients with METs <6,and conducted Delong test.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 26.0.Continuous variables were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni correction or the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test. General linear regression analysis was conducted to evaluate the contributions of clinical variables, echocardiographic parameters, and exercise hemodynamic measures to exercise capacity. Variables identified as significant in univariable analysis were subsequently incorporated into multivariable models to determine independent predictors. An optimized model was generated, and partial r was defined as the association between the predicted variable and achieved METs. Key parameters were utilized for receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and area under the curve (AUC) analysis, to identify HT-HFpEF patients with reduced exercise capacity,and AUC values were compared using the DeLong test. Intra/inter-observer variability for LA function measurements was determined by estimating intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) for LA longitudinal strain indices including reservoir strain, conduit strain, and contraction strain, with ICCs of 0.92(95%CI: 0.82–0.97)/0.84(95%CI:0.68–0.93); 0.91(95%CI:0.81–0.94)/0.79(95%CI:0.61–0.92), and 0.89(95%CI:0.74–0.95)/0.81(95%CI:0.69–0.94), respectively.
Results
Demographics, clinical features, and echocardiographic parameters
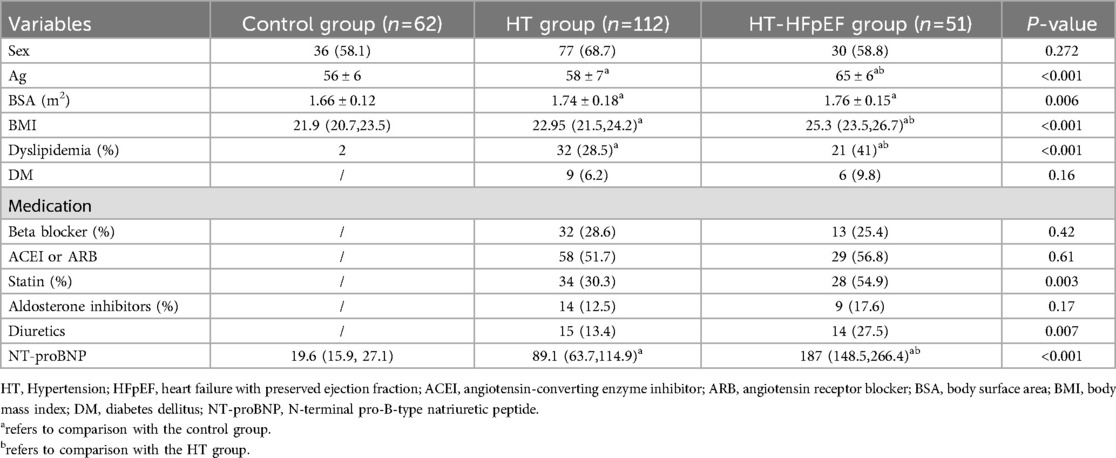
Significant differences were identified in age, body mass index (BMI), and BSA among the three groups (P < 0.05). Additionally, variations in clinical medication were observed between different HT groups, as shown in Table 1. Significant differences were found among the three groups for LVEDd, LVMI, E/e' and RVSP (P < 0.05). Similarly, SV and CI showed significant differences across the groups (P < 0.05), except for EF (P > 0.05). Baseline GLS levels were notably lower in both the HT-HFpEF and HT groups compared to the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 2).
Myocardial work and ventricular-arterial coupling
Myocardial work indices, which serve as load-independent parameters revealed decrease in GWI, GCW, and GWE in HT-HEpEF group (P < 0.05). Conversely, in the HT group, GWI/GCW exhibited a significant increase (P < 0.05), which is consistent with previous findings (16). Ea/Ees as metric indicative of ventricular-arterial coupling, did not vary significantly (P > 0.05); However, SVRI was significantly elevated in HT-HFpEF patients compared to those in HT group, with the lowest values in normal subjects. (P < 0.05). In terms of post-exercise variables, HR-peak did not differ significantly between the groups (P > 0.05). However, as expected, Ex-E/e' was significantly higher in HT-HFpEF group, and METs reflect exercise capacity was markedly lower compared to the other two groups (P < 0.05) (Table 2).
LA volume and strain analysis
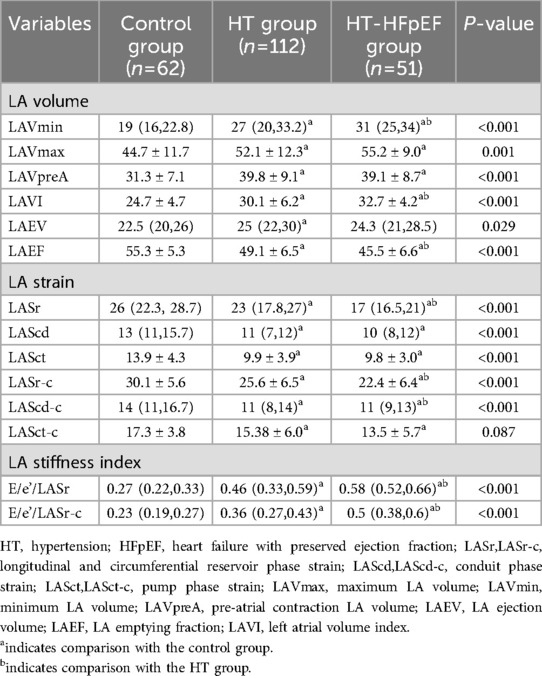
As depicted in Table 4, the values of LAVmin, LAVmax, LAVI, and LAEF were significantly elevated in HT group (P < 0.05). In the HT-HFpEF cohort, LA volume variables were increased at all time phases; however, for LAEF, longitudinal and circumferential strain were notable decreased (P < 0.05).LASr, LASr-c, LASct-c were differed significantly between the HT and HT-HFpEF groups (P < 0.05), thus indicating that these represent may serve as sensitive indicators of cardiac dysfunction in HT-HFpEF patients.
The LASI, derived from left atrial strain, showed a consistent upward trend, being significantly higher in the HT-HFpEF group (P < 0.05),specifically, the ratio of E/e' to LASr was 0.58 (0.52, 0.66) in the HT-HFpEF group vs. 0.46 (0.33, 0.59) in the HT group, similarly, the ratio of E/e' to LASr-c was 0.5 (0.38, 0.6) vs. 0.36 (0.27, 0.43). These findings emphasize LASI as key index for evaluating impaired atrioventricular compliance in HT-HFpEF patients, underscoring its critical role in detecting atrioventricular dysfunction in this population (Table 3). Conversely, no significant differences were observed in LAScd and LAScd-c between the HT and HT-HFpEF groups, indicating that conduction function remains preserved (P > 0.05). Figure 2 presents an example of different time-phase 3D LA volume and strain parameters for HT-HFpEF and control patient. Figure 3 depicts the points utilized for determining circumferential strain lines.
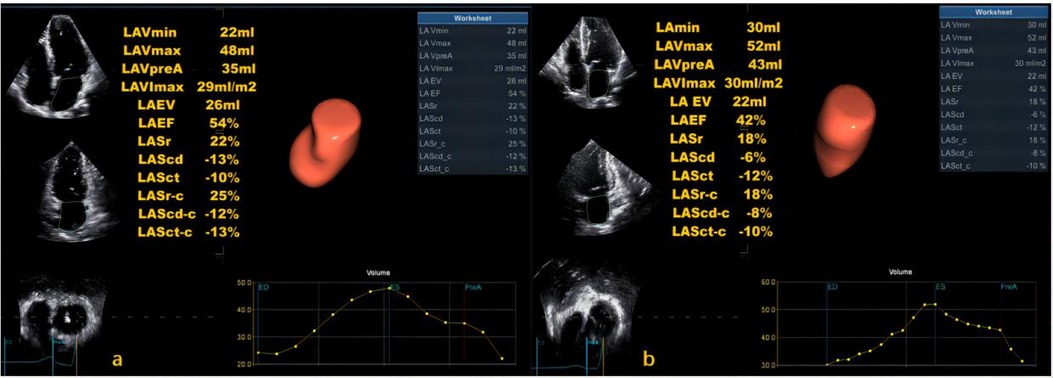
Figure 2. Three-dimensional (3D) left atrial volume and strain analysis for a control patient (a) and HT-HFpEF patient (b).
Figure 3. The points used to determine three-dimensional (3D) circumferential lines for the circumferential strain calculation.
Univariate and multivariate regression: independent associations of exercise capacity
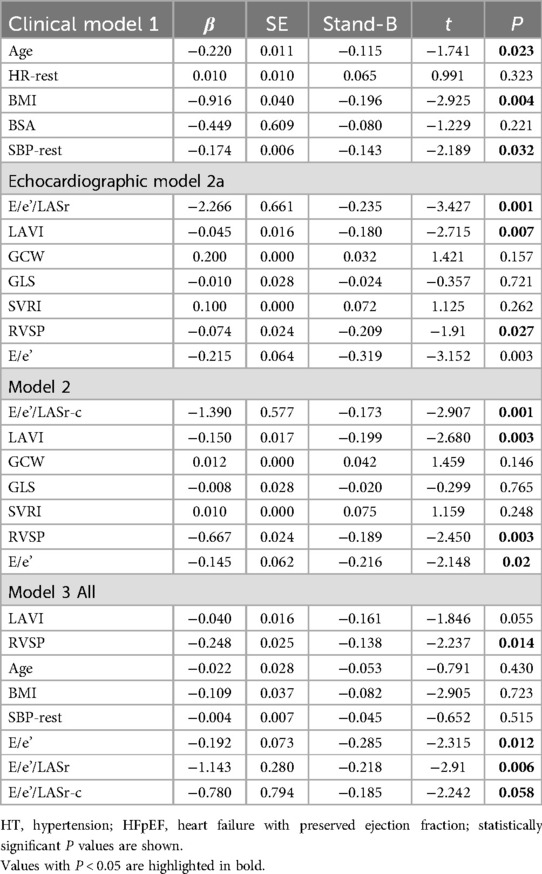
A general linear regression analysis was conducted to assess the relative contribution of each variable to exercise capacity through a heatmap,and lambda plots was used to facilitate analysis. Significant statistical correlations (P < 0.05) were observed between LA function (inclusive of volume and strain), GLS, GCW, SVRI and METs; indicated that these parameters could be considered as candidate variables in multiple regression models to determine the independent predictors of METs. Subsequently, Age, SBP-rest, and BMI emerged as independent general predictors of METs. And an analysis combining E/e'/LASr, E/e'/LASr-c with LVAI, GLS, E/e', RVSP and SVRI was conducted (referred as echocardiographic Model 2). Ultimately, a comprehensive model that integrates both general and echocardiographic predictors (Model 3) and found that E/e'/LASr still independently related, in Table 4. To assess the clinical value of E/e'/LASr, we utilized unstandardized coefficients from Model 3 to generate overlay scatter plots, comparing METs achieved during exercise with those predicted by the model, the results demonstrated strong positive linear correlation. Partial r represented the strength of association between the model variable and METs achieved (Figure 4). Notably, LASI represents the elastic modulus during diastole, and serves as a marker of myocardial stiffness or flexibility. The correlation diagram between LASI (E/e'/LASr, E/e'/LASr-c),candidate variables and METs are displayed (P < 0.05) (Figure 5). The strongest correlations were observed between Ex-E/e’ and METs (r = −0.521, P < 0.001), followed by E/e’/LASr and METs (r = −0.462, P < 0.001).
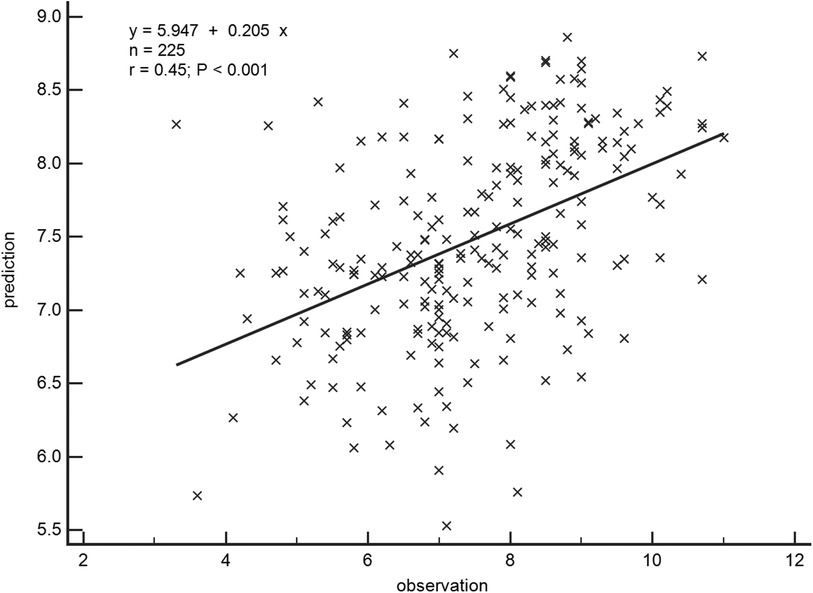
Figure 4. Overlay scatter plots of the METs achieved in comparison with the METs predicted. Partial r represented the strength of association between the variable and METs achieved, based on the predicted values derived from Model 3.
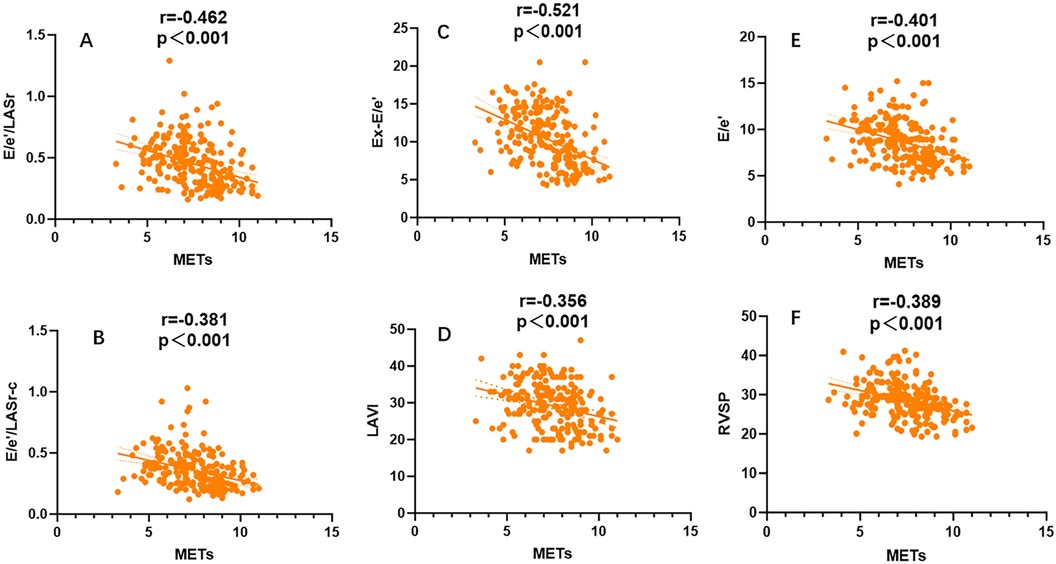
Figure 5. Univariate correlation analysis for LASI, LAVI,Ex-E/e’,RVSP,E/e’ coefficient with METs, All combinations were significantly correlated (P < 0.001).
Analysis of the LASI to identify HT-HFpEF with reduced exercise capacity
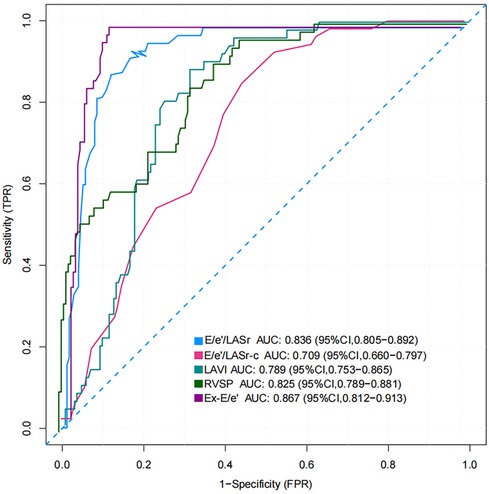
The AUC and 95% CI values for the variables are presented in Figure 6. The following cut-off values and AUCs were identified: E/e'/LASr (cut-off: 0.46; AUC: 0.836; 95% CI: 0.805–0.892), and E/e'/LASr-c (cut-off: 0.33; AUC: 0.709; 95% CI: 0.660–0.797). Additionally, the diagnostic performance for LAVI (AUC: 0.789; 95% CI: 0.753–0.865), Ex-E/e' (AUC: 0.867 95% CI: 0.812–0.913), and RVSP (AUC: 0.825; 95% CI: 0.789–0.881) were evaluated. No significant differences were found between E/e'/LASr and Ex-E/e' (Delong test, P = 0.239) (Graphical Abstract).
Discussion
In recent years, strain analysis conducted across various time periods has emerged as precise method for assessing crucial atrial function-related parameters (17), with LASI standing out as a novel and highly effective metric (18). The rapid acquisition and analysis of 3D LA images provide valuable insights into reservoir,conduit and active contraction function, serving as pivotal force in promoting blood flow into the ventricle (19). Given that a significant proportion of HFpEF patients possess prior history of hypertension (20), we conducted distinctive investigation focusing on this subset, comparing LA functional traits between individuals with HT and those suffering from HT-HFpEF. The identification of HT-HFpEF patients with reduced exercise tolerance is crucial for guiding targeted interventions and preventing progression to irreversible HFpEF (21). The key findings identified LASI analysis can be utilized as functional biomarker for evaluating HT and HT-HFpEF patients. And multiple regression analyses revealed E/e'/LASr remained an independent factor associated with exercise capacity.
There is currently no conclusive evidence regarding the association between LA function and LV mechanical abnormalities in the progression of exercise intolerance among patients with HT-HFpEF. This is primarily due to the potential coexistence or disproportionate involvement of LA and LV cardiomyopathy. Understanding the various stages of hypertensive heart disease evolution is crucial for elucidating the progression of HT-HFpEF, based on pathophysiological mechanisms (22, 23). A separate study (24) has reported that LASI is linked to the progression of HFpEF and may serve as predictor of invasive hemodynamic abnormalities.In this study, patients with the HT-HFpEF subtype were screened to exclude significant confounding factors, enabling more focused investigation of LA function changes and minimizing the influence of inherent atrial dysfunction typically observed in atrial fibrillation (25–27). This subtype is likely more associated with myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis, leading to left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and elevated left atrial pressure (28). It differs from HFpEF related to metabolic syndrome, pulmonary artery disease, highlighting the significance of our study in investigating this as a distinct subtype (29). Comparative analysis revealed no significant differences in Ea/Ees among the three groups,however, LA volume and strain were found to be impaired to varying degrees in patients with HT, suggesting that atrial dysfunction may precede the impairment of pressure-volume loop function (30).
The 3D left atrial assessment technique has been reported in previous studies and has been validated as a robust tool for evaluating left atrial function (31), myocardial deformation and arterial stiffness can detect and predict subclinical cardiotoxicity in patients with anthracyclines-induced cardiotoxicity (32, 33). The LASr, LASr-c, LASct-c differed significantly between the HT and HT-HFpEF group, which suggested that these variables serve as sensitive indicators of cardiac dysfunction, and additional research and validation are warranted in this domain (34, 35). Previous studies (36–38) have documented the association between LA function and exercise tolerance. Abnormalities in myocyte relaxation and progressive extracellular fibrosis can result in compromised ventricular filling, a process influenced by both pressure overload and neuro-endocrine factors, ultimately culminating in elevated LA pressure and dyspnea (39–41). Furthermore, multiple regression analysis model identified E/e'/LASr as an independent predictor of METs, indicating that progressive LA remodeling contributes to decreased atrioventricular compliance and is directly associated with exercise intolerance. Additionally, circumferential reserve strain also exhibited strong correlation with METs.
Kim D et al. (42) demonstrated that 2D speckle-tracking-based LASI is associated with increased all-cause mortality and higher risk of hospitalization in HFpEF patients, with its prognostic value exceeding that of LV filling pressure indices.In the present study, LASI was employed to investigate patients with HT-HFpEF and exercise intolerance,the results revealed a consistent trend in LASI (E/e'/LASr, E/e'/LASr-c), with further elevation observed in the HT-HFpEF group, highlighting its significance as key indicator of impaired atrioventricular compliance. Consequently, thorough assessment of atrioventricular compliance, combined with exercise tolerance and LA reservoir strain, may hold significant incremental value in differentiating subgroups of HT-HFpEF patients, ultimately leading to more tailored and personalized therapeutic interventions.
Limitations
In this study, we mainly focused on the hypertensive subtype of HFpEF, However,the sample size was relatively small and needs to be increased in future work. For the heterogeneity of HFpEF, including patients both with hypertension and renal dysfunction, did not entirely excluded. Despite the use of high-quality spatial and temporal resolution in our three-dimensional speckle tracking analysis, there was still inter-observer difference,and intervendor variability, image quality on loading conditions that could have theoretically impacted upon our results. In addition, long-term follow-up and large-scale prospective studies are now needed to determine the clinical predictive value of early changes in left atrial function in patients with HT.Furthermore, more in-depth analysis of pathological changes in the left atrium is required across different cardiovascular diseases to enhance our understanding of the relevant mechanisms involved. In addition, LVEDP, E/e',and LASr may be affected by volume overload and may change with the use of diuretics. We lacked objective data relating to the assessment of pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) based on invasive hemodynamics. Further studies are needed to investigate whethe increased LASI can represent an independent determinant for predicting HF hospitalization or mortality.
Conclusions
Progressive LA remodeling contributes to decreased atrioventricular compliance in HT and HT-HFpEF patients, and E/e'/LASr is an independent indicator of exercise capacity and can identify HT-HFpEF patients with exercise intolerance. Furthermore, the emerging metric of 3D strain offers valuable additional insights into the evaluation of atrial function in the HFpEF population.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee [Reference No. LunShen (Research) No.17, 2022]. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
QZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. SW: Investigation, Writing – original draft. HZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. WL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. GD: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft. LuY: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. CL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. YD: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Resources. LiY: Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Funded by Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Provincial Health Commission (Number:2023NSFSC0641)/Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province Project (Number: 2023NSFSC0038) Sichuan science and technology project,Number:2022NSFS0605.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.com/) for the expert linguistic services provided.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lee CJ, Park S. Hypertension and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Heart Fail Clin. (2021) 17(3):337–43. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2021.02.002
2. Oki T, Miyoshi H, Oishi Y, Mizuguchi Y, Ara N, Iuchi A. The impact of hypertension as a road to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: diagnostic value of two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography for the early impairment of left atrial-left ventricular-arterial coupling. Curr Hypertens Rev. (2014) 10(4):177–88. doi: 10.2174/1573402111666150206123245
3. Nemes A. Three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography offers complete volumetric and functional assessment of the left atrium. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2021) 37(7):22–35. doi: 10.1007/s10554-021-02220-4
4. Mohseni-Badalabadi R, Mirjalili T, Jalali A, Davarpasand T, Hosseinsabet A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the normal reference value of the longitudinal left atrial strain by three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Sci Rep. (2022) 12(1):4395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08379-7
5. Kokkinos P, Faselis C, Pittaras A, Samuel IBH, Lavie CJ, Vargas JD, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness and risk of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. (2024) 26(5):1163–71. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.3117
6. Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. (2018) 36(10):1953–2041. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001940
7. Pieske B, Tschöpe C, de Boer RA, Fraser AG, Anker SD, Donal E, et al. How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: the HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm: a consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. (2019) 40(40):3297–317. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz641
8. Chan J, Edwards NFA, Khandheria BK, Shiino K, Sabapathy S, Anderson B, et al. A new approach to assess myocardial work by non-invasive left ventricular pressure-strain relations in hypertension and dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2019) 20(1):31–9. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jey131
9. Pellikka PA, Arruda-Olson A, Chaudhry FA, Chen MH, Marshall JE, Porter TR, et al. Guidelines for performance, interpretation, and application of stress echocardiography in ischemic heart disease: from the American society of echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2020) 33(1):1–41. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.07.001
10. Chantler PD, Lakatta EG, Najjar SS. Arterial-ventricular coupling: mechanistic insights into cardiovascular performance at rest and during exercise. [published correction appears in J Appl Physiol. 2009 Mar;106(3):1027]. J Appl Physiol (1985). (2008) 105(4):1342–51. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.90600.2008
11. Lee EP, Chu SC, Hsia SH, Chen KF, Chan OW, Lin CY, et al. Comparison of predictive powers for mortality between systemic vascular resistance Index and serum lactate in children with persistent catecholamine-resistant shock. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:1341326. Published 2020 Jun 19. doi: 10.1155/2020/1341326
12. Nagata R, Harada T, Omote K, Iwano H, Yoshida K, Kato T, et al. Right atrial pressure represents cumulative cardiac burden in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. (2022) 9(2):1454–62. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13853
13. Nabeshima Y, Kitano T, Takeuchi M. Reliability of left atrial strain reference values: a 3D echocardiographic study. PLoS One. (2021) 16(4):e0250089. Published 2021 April 14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250089
14. Yafasov M, Olsen FJ, Skaarup KG, Lassen MCH, Johansen ND, Lindgren FL, et al. Normal values for left atrial strain, volume, and function derived from 3D echocardiography: the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2024) 25(5):602–12. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeae018
15. Snader CE, Marwick TH, Pashkow FJ, Harvey SA, Thomas JD, Lauer MS. Importance of estimated functional capacity as a predictor of all-cause mortality among patients referred for exercise thallium single-photon emission computed tomography: report of 3,400 patients from a single center. J Am Coll Cardiol. (1997) 30(3):641–8. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(97)00217-9
16. Jaglan A, Roemer S, Perez Moreno AC, Khandheria BK. Myocardial work in stage 1 and 2 hypertensive patients. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2021) 22(7):744–50. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeab043
17. Tanasa A, Tapoi L, Ureche C, Sascau R, Statescu C, Covic A. Left atrial strain: a novel “biomarker” for chronic kidney disease patients? Echocardiography. (2021) 38(12):2077–82. doi: 10.1111/echo.15259
18. Zhao Y, Sun Q, Han J, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Song W, et al. Left atrial stiffness index as a marker of early target organ damage in hypertension. Hypertens Res. (2021) 44(3):299–309. doi: 10.1038/s41440-020-00551-8
19. Schaaf M, Andre P, Altman M, Maucort-Boulch D, Placide J, Chevalier P, et al. Left atrial remodelling assessed by 2D and 3D echocardiography identifies paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2017) 18(1):46–53. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jew028
20. Tsioufis C, Georgiopoulos G, Oikonomou D, Thomopoulos C, Katsiki N, Kasiakogias A, et al. Hypertension and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: connecting the dots. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2017) 16(1):15–22. doi: 10.2174/1570161115666170414120532
21. Tam MC, Lee R, Cascino TM, Konerman MC, Hummel SL. Current perspectives on systemic hypertension in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Curr Hypertens Rep. (2017) 19(2):12. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0709-2
22. Slivnick J, Lampert BC. Hypertension and heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. (2019) 15(4):531–41. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2019.06.007
23. Nedeljkovic I, Banovic M, Stepanovic J, Giga V, Djordjevic-Dikic A, Trifunovic D, et al. The combined exercise stress echocardiography and cardiopulmonary exercise test for identification of masked heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in patients with hypertension. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2016) 23(1):71–7. doi: 10.1177/2047487315604836
24. Ma CS, Liao YP, Fan JL, Zhao X, Su B, Zhou BY. The novel left atrial strain parameters in diagnosing of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Echocardiography. (2022) 39(3):416–25. doi: 10.1111/echo.15304
25. Ginelli P, Bella JN. Treatment of diastolic dysfunction in hypertension. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2012) 22(8):613–8. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2012.04.016
26. Shen L, Jhund PS, Anand IS, Carson PE, Desai AS, Granger CB, et al. Developing and validating models to predict sudden death and pump failure death in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Clin Res Cardiol. (2021) 110(8):1234–48. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01786-8
27. Uziȩbło-Życzkowska B, Jurek A, Witek P, Zieliński G, Gielerak G, Krzesiński P. Left heart dysfunction in acromegaly revealed by novel echocardiographic methods. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:418. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00418
28. Sorrentino MJ. The evolution from hypertension to heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. (2019) 15(4):447–53. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2019.06.005
29. Levine AR, Simon MA, Gladwin MT. Pulmonary vascular disease in the setting of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Trends Cardiovasc Med. (2019) 29(4):207–17. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2018.08.005
30. Bonnet B, Jourdan F, du Cailar G, Fesler P. Noninvasive evaluation of left ventricular elastance according to pressure-volume curves modeling in arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2017) 313(2):237–43. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00086.2017
31. Mohty D, Petitalot V, Magne J, Fadel BM, Boulogne C, Rouabhia D, et al. Left atrial function in patients with light chain amyloidosis: a transthoracic 3D speckle tracking imaging study. J Cardiol. (2018) 71(4):419–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2017.10.007
32. Santoro C, Arpino G, Esposito R, Lembo M, Paciolla I, Cardalesi C, et al. 2D And 3D strain for detection of subclinical anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients: a balance with feasibility. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2017) 18(8):930–6. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jex033
33. Tarr A, Stoebe S, Tuennemann J, Baka Z, Pfeiffer D, Varga A, et al. Early detection of cardiotoxicity by 2D and 3D deformation imaging in patients receiving chemotherapy. Echo Res Pract. (2015) 2(3):81–8. doi: 10.1530/ERP-14-0084
34. Liu M, Sun M, Li L, Li P, Hou S, Li Z, et al. Left atrial function in young strength athletes: four-dimensional automatic quantitation study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2022) 38(9):1929–37. doi: 10.1007/s10554-022-02585-0
35. Ran H, Schneider M, Wan LL, Ren JY, Ma XW, Zhang PY. Four-Dimensional volume-strain expression in asymptomatic primary hypertension patients presenting with subclinical left atrium-ventricle dysfunction[J]. Cardiology. (2020) 145(9):578–88. doi: 10.1159/000508887
36. Hawkins NM, Wang D, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, Granger CB, et al. Prevalence and prognostic implications of electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy in heart failure: evidence from the CHARM programme. Heart. (2007) 93(1):59–64. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2005.083949
37. Thomas L, Marwick TH, Popescu BA, Donal E, Badano LP. Left atrial structure and function, and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2019) 73(15):1961–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.059
38. Elliott AD, Ariyaratnam J, Howden EJ, La Gerche A, Sanders P. Influence of exercise training on the left atrium: implications for atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and stroke. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2023) 325(4):822–36. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00322.2023
39. Singleton MJ, Nelson MB, Samuel TJ, Kitzman DW, Brubaker P, Haykowsky MJ, et al. Left atrial stiffness index independently predicts exercise intolerance and quality of life in older, obese patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J Card Fail. (2022) 28(4):567–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2021.10.010
40. Soullier C, Niamkey JT, Ricci JE, Messner-Pellenc P, Brunet X, Schuster I. Hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy have global left atrial dysfunction and impaired atrio-ventricular coupling. J Hypertens. (2016) 34(8):1615–20. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000971
41. Bruun Pedersen K, Madsen C, Sandgaard NCF, Hey TM, Diederichsen ACP, Bak S, et al. Left atrial volume index and left ventricular global longitudinal strain predict new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with transient ischemic attack. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2019) 35(7):1277–86. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01586-w
Keywords: three-dimensional speckle tracking, left atrial, hypertension, stiffness, heart failure
Citation: Zhang Q, Wang S, Zhang H, Wang K, Li W, Ding G, Ye L, Li C, Deng Y, Wang Y and Yin L (2024) Evaluation of left atrial function and the relationship between left atrial stiffness index and exercise capacity in hypertension-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1501004. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1501004
Received: 24 September 2024; Accepted: 3 December 2024;
Published: 17 December 2024.
Edited by:
Nikolaos Papageorgiou, Barts Heart Centre, United KingdomReviewed by:
Ionut Donoiu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, RomaniaAndrea Sonaglioni, IRCCS MultiMedica, Italy
Copyright: © 2024 Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Wang, Li, Ding, Ye, Li, Deng, Wang and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Wang, d2FuZ3lpaGRsQDEyNi5jb20=; Lixue Yin, eWlubGl4dWVfY2FyZGlhY0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qingfeng Zhang1,2,†
Qingfeng Zhang1,2,† Hongmei Zhang
Hongmei Zhang Kai Wang
Kai Wang Wenhua Li
Wenhua Li Luwei Ye
Luwei Ye Chunmei Li
Chunmei Li Yan Deng
Yan Deng Yi Wang
Yi Wang Lixue Yin
Lixue Yin