- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Rui Jin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Objective: This study compared the value of different systemic immune-inflammatory markers for evaluating coronary collateralization (CC) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and chronic total occlusion (CTO).
Methods: Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) and pan-immune-inflammation value (PIV) were calculated at admission in 1409 T2DM patients with CTO. The degree of coronary collaterals was estimated using the Rentrop scoring system and categorized into poor (Rentrop score 0 or 1) or good (Rentrop score 2 or 3) CC. The predictors of poor CC were determined by multivariate regression analysis, and the diagnostic potential of these indexes was analyzed by Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: SII, SIRI and PIV levels increased stepwise across Rentrop score 0–3, with significantly higher levels in patients with poor CC than in those with good CC (P < 0.001). After adjusting for confounders, SII, SIRI and PIV (per tertile) remained independent factors for poor CC. SII predicted poor CC better than SIRI and PIV (AUC: 0.758 vs. 0.680 and 0.698, all P < 0.001). There existed an interaction between blood concentration of HbA1c and SII (P < 0.001), with high SII levels being associated with a greater risk (OR: 5.058 vs. 2.444) and providing a better predictive ability for poor CC (AUC: 0.817 vs. 0.731) in patients with HbA1c < 6.5% compared to those with HbA1c ≥ 6.5%.
Conclusion: Our study shows that elevated SII provides a better prediction for poor CC in T2DM patients with CTO especially at good glycemic control.
Introduction
Coronary collateralization (CC) is an adaptive response to transient or permanent coronary artery occlusion (1, 2). The clinical relevance of the status of CC has been extensively investigated, showing that robust coronary collaterals are frequently associated with a favorable outcome by protecting ischemic myocardium, improving cardiac function, and decreasing future cardiovascular events and mortality (3, 4). Collateral formation is a complex multi-step process involving an array of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors (5). Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is considered as a major risk factor for severe and diffuse coronary atherosclerosis and poor clinical outcome, and T2DM patients with chronic total occlusion (CTO) are more prone to develop poor CC compared to non-diabetic counterparts (6, 7). Previous studies demonstrated that chronic low-grade inflammation, along with immune dysregulation, is a common mechanism of both atherosclerosis and T2DM, which may lead to impaired arteriogenesis and angiogenesis as well as new vessel growth in response to ischemia (8).
Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) and pan-immune-inflammation-value (PIV) have been emerged as novel markers by integrating three subtypes of white blood cell and platelets and indicate the balance between the inflammatory response and immune status (9). Numerous studies have suggested that SII and SIRI are associated with atherogenesis and cardiovascular outcome (9–11). Recently, Kelesoglu (10), Adali (12) and co-workers reported that high SII levels were correlated significantly with poor CC in patients with CTO. Yilmaz et.al demonstrated that PIV independently predicted poor CC in stable coronary artery disease patients (13). However, the value of systemic immune-inflammatory markers in the evaluation of angiographic CC in patients with T2DM and CTO remains unclear, mostly because of the small sample size and heterogenous population in the previous studies. Here, we investigated the relationship of SII, SIRI and PIV to coronary collateral formation in a large cohort of T2DM patients with CTO. The predictive value of elevated SII, SIRI and PIV for poor CC was also compared in relation to the status of glycemic control.
Methods
This study was part of the COLLECT study (COronary CoLLateralization in Type 2 diabEtic Patients with Chronic Total Occlusion) registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT06054126), which aimed to explore the risk factors and treatment options for poor collateralization in T2DM patients with CTO. All participants provided written informed consent. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao and the study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Study population
A total of 1,503 consecutive stable angina patients who had T2DM between January 2010 and March 2024 were screened. All patients were ≥18 years in age and had at least one lesion with angiographic 100% occlusion in major epicardial coronary arteries for more than 3 months. This angiographic inclusion was used based on well-established knowledge that a severe coronary artery obstruction was a prerequisite for spontaneous collateral recruitment. For the purpose of the study, 94 patients were excluded because of severe chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis (n = 13), malignant tumor and pulmonary heart disease or immune system disorders (n = 10), history of coronary artery bypass grafting (n = 30), severe chronic heart failure (New York Heart Association functional class III or IV) (n = 6), or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) within the prior 3 months (n = 35). The remaining 1,409 T2DM patients with CTO were included in the final analysis (Figure 1).
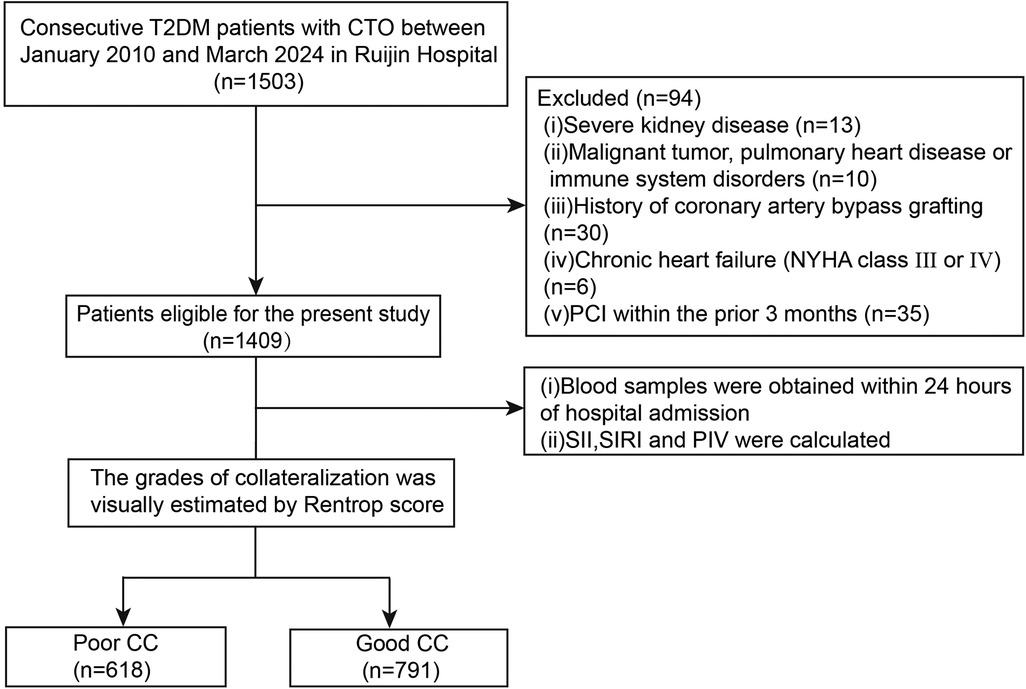
Figure 1. Flowchart of the study. T2DM type 2, diabetes mellitus; CTO, chronic total occlusion; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; SII, systemic immune-inflammation index; SIRI, systemic inflammation response index; PIV, pan-immune-inflammation value; CC, coronary collateralization.
Baseline clinical characteristics were collected from the Inpatient Medical Record Management Systems. Blood samples were obtained within 24 h of hospital admission, and hematological and biochemical data were measured by standard laboratory techniques. Laboratory personnel unaware of the patient's diagnoses analyzed the blood samples. SII, SIRI and PIV were calculated based on the following formula: SII = (neutrophil count × platelet count)/lymphocyte count; SIRI = (neutrophil count × monocyte count)/lymphocyte count; PIV = (monocyte count × neutrophil count × platelet count)/lymphocyte count (13, 14).
The diagnosis for T2DM was made according to the American Diabetes Association guidelines (14). Hypertension was diagnosed as the presence of office systolic blood pressure values ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure values ≥90 mmHg, or taking antihypertensive drugs for blood pressure control (15). Hypercholesterolemia was defined according to the Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) (16). Severe chronic kidney disease was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 15 ml/(min·1.73 m2) (17).
Coronary angiography and collateral grading
Coronary angiography was performed via the femoral or radial approach, and the degree of coronary artery narrowing was determined by quantitative coronary analysis (QCA) (18). Number of significant diseased coronary arteries (≥50% stenosis in major epicardial coronary artery) was used to assess coronary disease severity, and left main coronary stenosis was considered as 2-vessel disease (19).
Presence/absence and extent of collateral circulation were graded according to the Rentrop scoring system (20). Rentrop score 0 (no filling of any collateral vessels) and score 1 (filling of side branches of the artery by collateral vessels without visualization of the epicardial segment) were categorized into poor CC, whereas Rentrop score 2 (partial filling of the epicardial segment by collateral vessels) and score 3 (complete filling of the epicardial artery by collateral vessels) were classified into good CC. For patients with more than one chronic total occlusion, the vessel with the highest collateral grade was selected for analysis. Coronary collaterals were graded by two experienced interventional cardiologists blinded to patient's clinical characteristics. Any disagreement was resolved by a third reviewer.
Statistical analysis
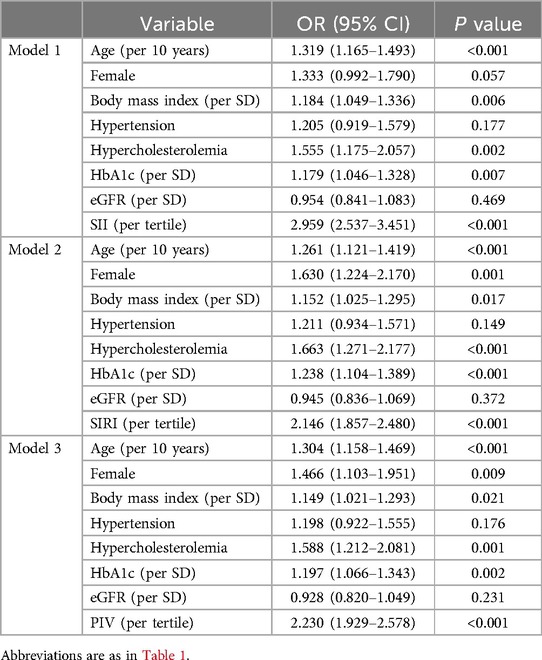
Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviations (SD) or median (interquartile range, IQR), and were compared between groups by Student's t-test and Mann–Whitney U test for normally or non-normally distributed variables, respectively. Categorical variables are expressed as absolute number with percentage and were compared between groups by Chi-square test. One-way ANOVA analysis was performed to compare the difference of SII, SIRI and PIV between groups with 0–3 Rentrop score. To determine the independent predictors for poor CC, age, female gender, body mass index (BMI), hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, hematological data, eGFR and HbA1c together with SII, SIRI or PIV were adopted in multivariate logistic regression model 1–3, respectively. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis was made, and the predictive ability of SII, SIRI and PIV for poor CC in T2DM patients with CTO was evaluated by the area under the ROC curve (AUC). The Youden index was applied to find the optimal cutoff point for maximized sensitivity and specificity. The comparisons of AUCs were performed using DeLong test. All statistical analyses were done using SPSS version 26.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and MedCalc software (Version 20.0.22; Medcalc Software, Mariakerke, Belgium). Statistical significance was set a two-tailed P value < 0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics
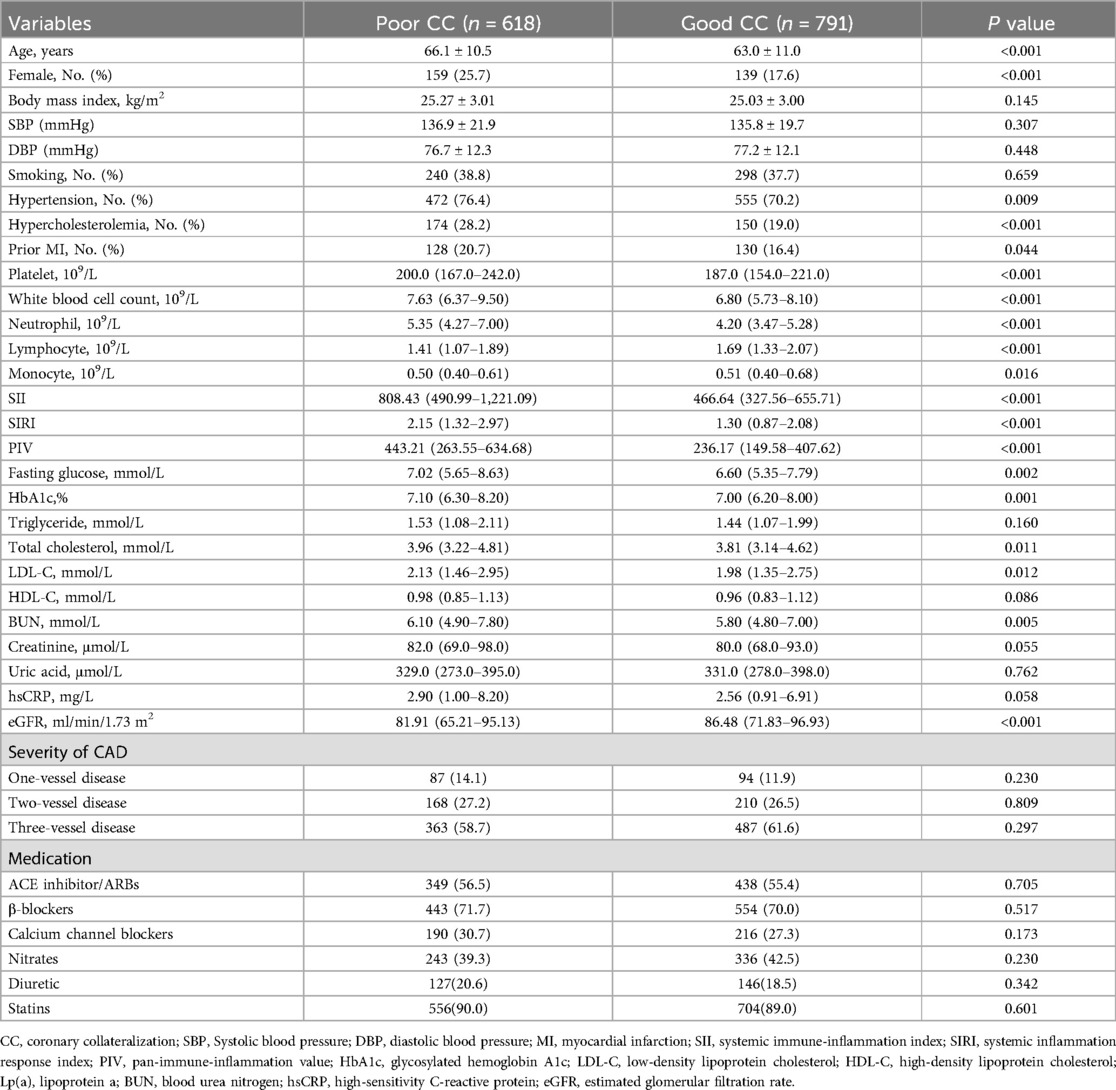
Poor and good CC were detected in 618 (43.9%) and 791 (56.1%) patients, respectively. Compared to patients with good CC, those with poor CC were older and more female in gender, and had higher incidence of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and prior myocardial infarction. As for laboratory measurements, platelet count, white blood cell count and neutrophil were higher, and fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were elevated, but monocyte, lymphocyte and eGFR were lower in patients with poor CC (P < 0.05 for all comparisons). The two groups did not significantly differ with respective to severity of coronary artery disease and medications (Table 1).
SII, SIRI and PIV with coronary collateralization
SII, SIRI and PIV levels increased stepwise across Rentrop score 0–3 (Figure 2), with significantly higher levels in patients with poor CC compared to those with good CC [SII: 808.43(490.99–1,221.09) vs. 466.64 (327.56–655.71); SIRI: 2.15(1.32–2.97) vs. 1.30 (0.87–2.08); PIV: 443.21(263.55–634.68) vs. 236.17(149.58–407.62), all P < 0.001] (Table 1). Increased SII tertiles (OR, 3.005; 95% CI, 2.589–3.489; P < 0.001), SIRI tertiles (OR, 2.111; 95% CI, 1.839–2.424; P < 0.001) and PIV tertiles (OR, 2.244; 95% CI, 1.951–2.581; P < 0.001) were associated with a higher proportion of poor CC, respectively (Figure 2).
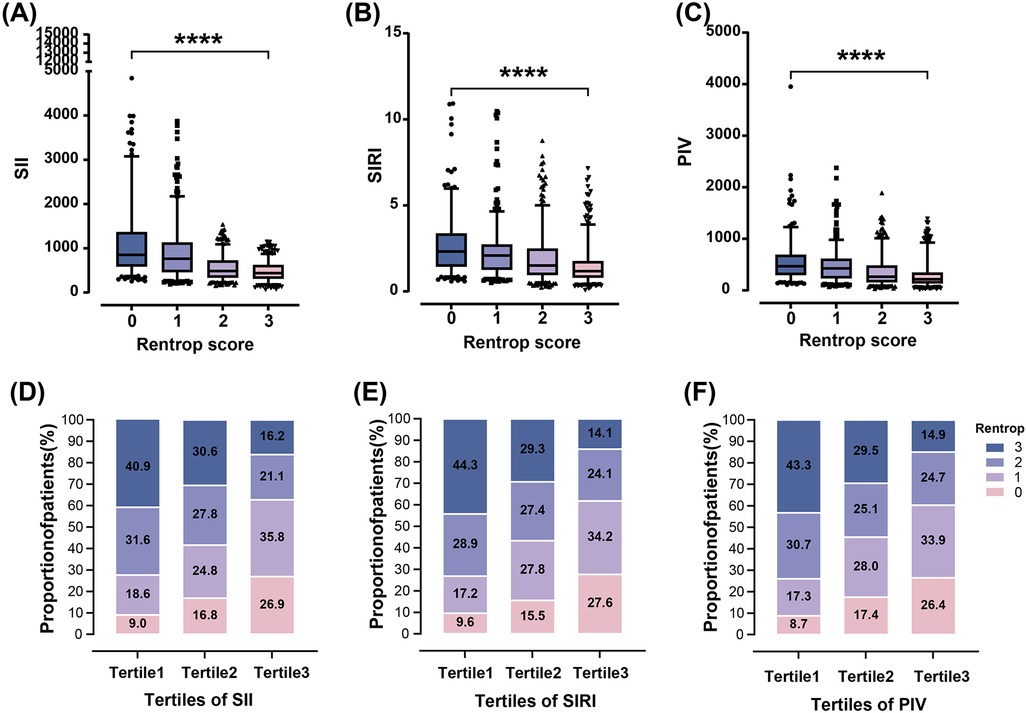
Figure 2. Relationship of SII, SIRI and PIV with rentrop score in T2DM patients with CTO. SII, SIRI and PIV decreased gradually across Rentrop score 0–3 [(A)–(C), ****P < 0.0001]. The proportion of poor CC increased from the lowest tertile to the highest tertile of SII, SIRI and PIV (D)–(F).
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that after adjustment for confounding factors including age, gender, BMI, hypercholesterolemia, hematological data, HbA1c and eGFR, high tertile of SII, SIRI and PIV levels remained independent predictors for poor CC in T2DM patients with CTO (Table 2).
In ROC analysis, the likelihood that a cutoff value of SII 703.86 could accurately differentiate patients with poor CC from those with good CC was 75.8% (95% CI, 0.735–0.781), with 61.2% sensitivity and 80.1% specificity. SII had a significantly better predictive ability for poor CC than SIRI (AUC: 0.680, 95% CI, 0.655–0.704) and PIV (AUC: 0.698, 95% CI, 0.673–0.722) (all P < 0.001) (Figure 3).
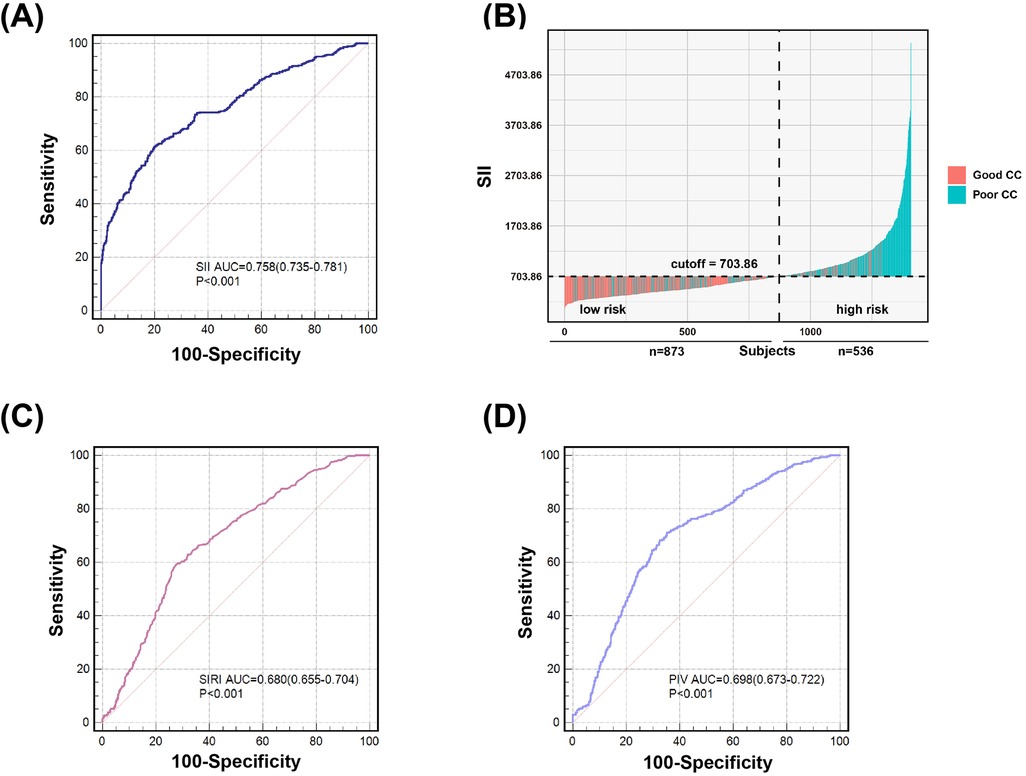
Figure 3. Value of SII (A) and (B), SIRI (C) and PIV (D) for predicting poor coronary collateralization. According to the ROC analysis, SII showed better predictive ability of poor CC compared to SIRI and PIV. The likelihood that a cutoff value of SII 703.86 could accurately differentiate patients with poor CC from those with good CC was 75.8%, with 61.2% sensitivity and 80.1% specificity (A) and (B). The likelihood that a cutoff value of SIRI 1.93 could accurately differentiate patients with poor CC from those with good CC was 68.0%, with 59.5% sensitivity and 72.1% specificity (C). The likelihood that a cutoff value of PIV 299.64 could accurately differentiate patients with poor CC from those with good CC was 69.8%, with 71.2% sensitivity and 64.6% specificity (D).
Influence of glycemic control
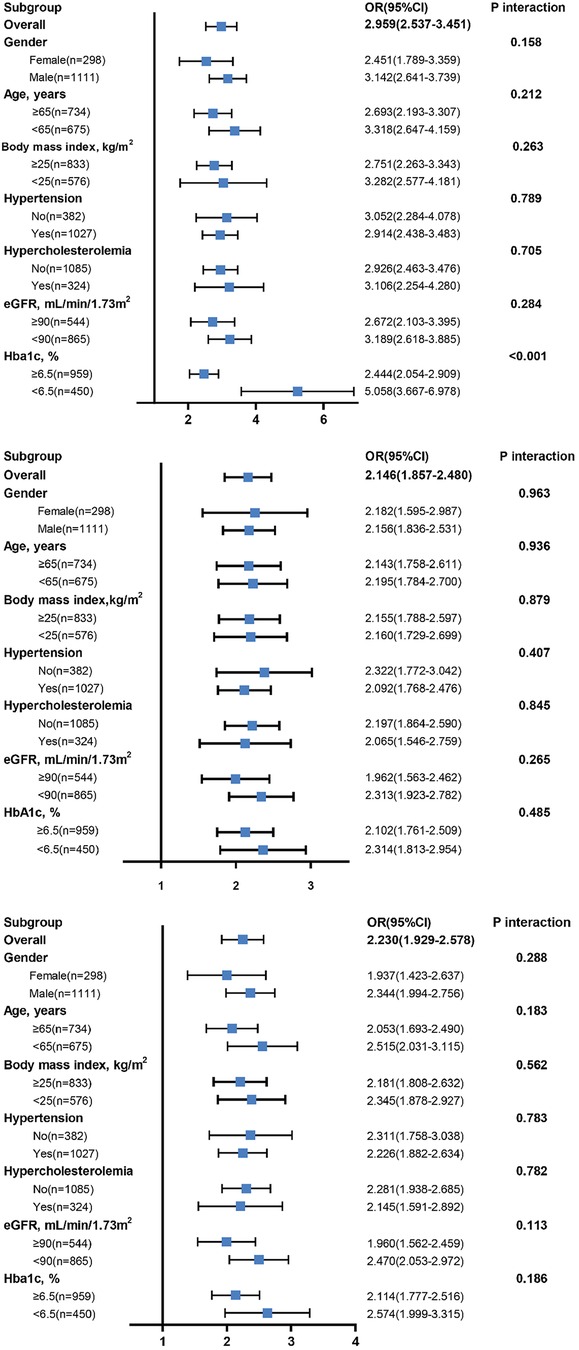
After stratifying the study population by age, gender, BMI, hypercholesterolemia, eGFR and HbA1c, increased SII, SIRI and PIV levels showed consistent predictive value for poor CC with odds ratio (OR) ranging from 1.937 to 5.058. No interactions of SII, SIRI and PIV with age, gender, BMI, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and eGFR on poor CC were observed (P for interaction >0.05). However, there existed a significant interaction between blood concentration of HbA1c and SII on poor CC (P for interaction <0.001). Compared to patients with HbA1c ≥ 6.5%, high SII values were associated with a greater risk (OR: 5.058 vs. 2.444) (Figure 4) and provided a better predictive ability (AUC: 0.817 vs. 0.731) for poor CC in those with HbA1c < 6.5% (Figure 5).
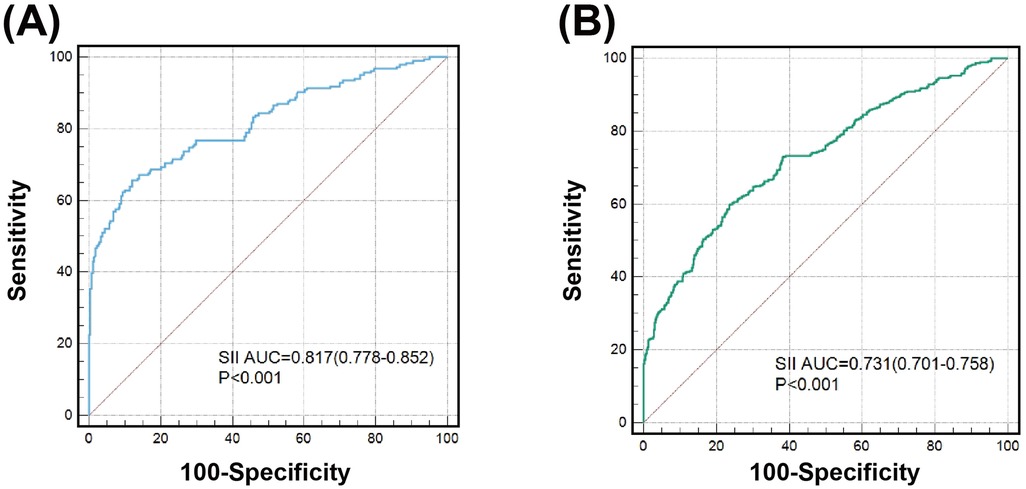
Figure 5. Value of SII for predicting poor CC in patients with good (A) or poor glycemic control (B).
Discussion
Our results showed that (1) systemic immune-inflammatory markers including SII, SIRI, and PIV were associated with angiographic CC in T2DM patients with CTO; (2) SII provided a significantly better predictive ability for poor CC than SIRI and PIV; (3) high SII levels conferred a greater risk and had a better prediction for poor CC in patients with HbA1c < 6.5% as compared to those with HbA1c ≥ 6.5%.
It is well recognized that collateral formation is impaired in T2DM patients and CTO, however, the underlying mechanism remains not fully understood. Previous studies have shown that chronic low-grade inflammation plays a central role in the pathophysiology of coronary collateral development (21). Patients with T2DM have a persistent inflammatory status, which could decrease production of nitric oxide and increase production of reactive oxygen species, leading to elevated oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction (22–24). This supports the view that inflammation-related markers might provide predictive value on CC in T2DM patients with CTO. Several readily available inflammatory biomarkers including high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), neutrophil, monocyte, platelet (PLT), neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) have been found to be associated with CC in patients with CTO (25–28). However, the inflammatory markers that are composed of a single component (neutrophil, lymphocyte, or platelet) and two components (NLR and PLR) are often affected by other confounding factors and become relatively weak predictors of prognosis. SII, SIRI and PIV are integrated markers of systemic immune-inflammation and their role in the evaluation of cardiovascular diseases has been recently studied (29–31). SII obtained by multiplying NLR and platelet increases in the presence of chronic inflammation, and it is a relatively strong inflammatory marker that may inhibit endothelial progenitor cell differentiation, survival, and function—key components of angiogenesis. SII was thought to be more reliable and representative of inflammation and thrombosis than PLR and NLR (32, 33). Dziedzic et al. demonstrated a relationship of SII values with the severity of coronary artery disease (34). Xia et al. reported that high SII was significantly associated with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality risks (9). In the present study, we found that SII levels correlated closely with Rentrop score in T2DM patients with CTO. The predictive ability of SII on poor CC performed well even after adjusting for confounding factors and was much better than other inflammation indexes (SIRI and PIV). Mechanistically, elevated SII levels indicated the increased neutrophil and platelet counts and decreased lymphocyte counts. Neutrophils release inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species, which may exacerbate endothelial dysfunction and inhibit angiogenesis (35). Low levels of lymphocytes reflect immune suppression and are associated with impaired endothelial function (36). Platelets play a vital role in new blood vessel formation by involving many angiogenesis promoters and inhibitors (37). Thus, elevated SII levels are associated with systemic inflammation, immune dysregulation, and impaired angiogenic processes. However, SIRI focuses more on monocytes and does not account for platelets, which is essential in angiogenesis and vascular remodeling. Although PIV includes platelet counts, the weights of the component are linearly distributed, which may obscure the dominant role of platelets. Taken together, it may explain why SII predicts poor CC more effectively than SIRI and PIV in T2DM patients with CTO.
In addition, the diagnostic performance of SII remained satisfied in different subgroup analysis. Interestingly, using HbA1c 6.5% as the threshold of glycemic control, a significant interaction was identified when we analyzed the predictive value of SII on poor CC. High SII was associated with a greater risk and provided a significantly better prediction for poor CC in patients with HbA1c < 6.5%, as compared to those with HbA1c > 6.5%. The reason for that remains unclear, but our findings are, at least partly, supportive of previous reports which emphasize the relationship between inflammation and the development of coronary collaterals (10, 12). We speculate that in T2DM patients with CTO and normal glycemic control, the systemic inflammatory condition is in relatively low grade. An increase in SII value could be more reliable indicator of a great risk for developing poor CC. In contrast, patients with poor glycemic control often have a high grade of inflammatory status as suggested by high baseline SII levels even in those with good CC, thus the effect of changes of SII were less remarkable for forecasting the risk of poor CC.
Study limitations
The present study had several limitations. First, this was a single center retrospective and observational study, thus the selected population may not represent the whole aimed cohort, and the causal link of SII, SIRI and PIV with poor CC was not detected. Second, although several traditional risk factors were considered, there were still some confounding factors that were not included in the analysis. Third, the degree of coronary collateral circulation was estimated according to the Rentrop scoring system, whereas measurement of collateral flow index may be more accurate.
Conclusion and perspective
This study demonstrates that SII, SIRI, and PIV are closely associated with angiographic CC, and SII provides a better prediction for poor CC than SIRI and PIV in T2DM patients with CTO, especially at good glycemic control. The good predictive ability of SII on poor CC validated its potential as a diagnostic biomarker in T2DM patients with CTO. Since there is increasing evidence that treatment decisions and indications for recanalization of a CTO should be based not only on clinical characteristics and occluded lesion morphology, but also on collateral quality and myocardial viability (38–41). SII shows CC status as a useful, simple, easily measurable, and cheap indicator, and could be used as a reference for clinicians to improve the care of diabetic patients with stable coronary artery disease. Further prospective studies with large sample size and long-term clinical follow-up are warranted to prove the diagnostic and prognostic value of SII, in relation to CC, for patients with T2DM and CTO.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Rui Jin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
LM: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Software. ZW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology. FD: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Supervision. LL: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Project administration. WS: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Validation. YD: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Software. YS: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study received support from grants provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82370409, 82170417, 81870357).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Pries AR, Badimon L, Bugiardini R, Camici PG, Dorobantu M, Duncker DJ, et al. Coronary vascular regulation, remodelling, and collateralization: mechanisms and clinical implications on behalf of the working group on coronary pathophysiology and microcirculation. Eur Heart J. (2015) 36:3134–46. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv100
2. Seiler C, Stoller M, Pitt B, Meier P. The human coronary collateral circulation: development and clinical importance. Eur Heart J. (2013) 34:2674–82. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht195
3. Allahwala UK, Kott K, Bland A, Ward M, Bhindi R. Predictors and prognostic implications of well-matured coronary collateral circulation in patients with a chronic total occlusion (CTO). Int Heart J. (2020) 61:223–30. doi: 10.1536/ihj.19-456
4. Yang ZK, Shen Y, Dai Y, Wang XQ, Hu J, Ding FH, et al. Impact of coronary collateralization on long-term clinical outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients after successful recanalization of chronic total occlusion. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19:59. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01033-4
5. Zimarino M, D'Andreamatteo M, Waksman R, Epstein SE, De Caterina R. The dynamics of the coronary collateral circulation. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2014) 11:191–7. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.207
6. Yetkin E, Topal E, Erguzel N, Senen K, Heper G, Waltenberger J. Diabetes mellitus and female gender are the strongest predictors of poor collateral vessel development in patients with severe coronary artery stenosis. Angiogenesis. (2015) 18:201–7. doi: 10.1007/s10456-015-9460-y
7. Shen Y, Ding FH, Dai Y, Wang XQ, Zhang RY, Lu L, et al. Reduced coronary collateralization in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic total occlusion. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17:26. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0671-6
8. Bao XL, Dai Y, Lu L, Wang XQ, Ding FH, Shen WF, et al. Vasostatin-2 associates with coronary collateral vessel formation in diabetic patients and promotes angiogenesis via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:1732–44. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad082
9. Xia Y, Xia C, Wu L, Li Z, Li H, Zhang J. Systemic immune inflammation index (SII), system inflammation response index (SIRI) and risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality: a 20-year follow-up cohort study of 42,875 US adults. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1128. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031128
10. Kelesoglu S, Yilmaz Y, Elcık D, Kalay N. Systemic immune inflammation index: a novel predictor for coronary collateral circulation. Perfusion. (2022) 37:605–12. doi: 10.1177/02676591211014822
11. Bian X, He J, Zhang R, Yuan S, Dou K. The combined effect of systemic immune-inflammation index and type 2 diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a large-scale cohort study. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:6415–29. doi: 10.2147/jir.S445479
12. Adali MK, Buber I, Sen G, Yilmaz S. Relationship between systemic immune-inflammation index and coronary collateral circulation in patients with chronic total occlusion. Arq Bras Cardiol. (2022) 119:69–75. doi: 10.36660/abc.20210414
13. Yilmaz Y, Kelesoglu S. The importance of pan-immune inflammation value (PIV) in predicting coronary collateral circulation in stable coronary artery patients. Angiology. (2024). doi: 10.1177/00033197241258529
14. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:S19–40. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S002
15. Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. (2018) 39:3021–104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339
16. Cleeman JI. Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). Jama. (2001) 285:2486–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.19.2486
17. Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. (2005) 67:2089–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00365.x
18. Shen Y, Lu L, Ding FH, Sun Z, Zhang RY, Zhang Q, et al. Association of increased serum glycated albumin levels with low coronary collateralization in type 2 diabetic patients with stable angina and chronic total occlusion. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2013) 12:165. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-165
19. Shen Y, Chen S, Dai Y, Wang XQ, Zhang RY, Yang ZK, et al. Lipoprotein (a) interactions with cholesterol-containing lipids on angiographic coronary collateralization in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic total occlusion. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:82. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0888-z
20. Rentrop KP, Cohen M, Blanke H, Phillips RA. Changes in collateral channel filling immediately after controlled coronary artery occlusion by an angioplasty balloon in human subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol. (1985) 5:587–92. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80380-6
21. Allahwala UK, Khachigian LM, Nour D, Ridiandres A, Billah M, Ward M, et al. Recruitment and maturation of the coronary collateral circulation: current understanding and perspectives in arteriogenesis. Microvasc Res. (2020) 132:104058. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104058
22. Rocic P. Why is coronary collateral growth impaired in type II diabetes and the metabolic syndrome? Vascul Pharmacol. (2012) 57:179–86. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2012.02.001
23. Waltenberger J. Impaired collateral vessel development in diabetes: potential cellular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc Res. (2001) 49:554–60. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00228-5
24. Wang Y, Li F, Mao L, Liu Y, Chen S, Liu J, et al. Promoting collateral formation in type 2 diabetes mellitus using ultra-small nanodots with autophagy activation and ROS scavenging. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:85. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02357-z
25. Fan Y, Li S, Li XL, Zhu CG, Guo YL, Wu NQ, et al. C-reactive protein as a predictor for poor collateral circulation in patients with chronic stable coronary heart disease. Ann Med. (2016) 48:83–8. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2015.1136429
26. Uysal OK, Turkoglu C, Sahin DY, Duran M, Yildirim A, Elbasan Z, et al. The relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and coronary collateral circulation. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. (2015) 21:329–33. doi: 10.1177/1076029613503399
27. Nacar AB, Erayman A, Kurt M, Buyukkaya E, Karakaş MF, Akcay AB, et al. The relationship between coronary collateral circulation and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with coronary chronic total occlusion. Med Princ Pract. (2015) 24:65–9. doi: 10.1159/000365734
28. Akdag S, Akyol A, Asker M, Ozturk F, Gumrukcuoglu HA. The relation of platelet-lymphocyte ratio and coronary collateral circulation in patients with non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. (2016) 12:224–30. doi: 10.5114/aic.2016.61644
29. Liu Y, Liu J, Liu L, Cao S, Jin T, Chen L, et al. Association of systemic inflammatory response index and pan-immune-inflammation-value with long-term adverse cardiovascular events in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients after primary percutaneous coronary intervention. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:3437–54. doi: 10.2147/jir.S421491
30. Bayramoğlu A, Hidayet Ş. Association between pan-immune-inflammation value and no-reflow in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. (2023) 83:384–9. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2023.2241131
31. Xiang J, He L, Li D, Wei S, Wu Z. Value of the systemic immune-inflammation index in predicting poor postoperative outcomes and the short-term prognosis of heart valve diseases: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e064171. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064171
32. Yang YL, Wu CH, Hsu PF, Chen SC, Huang SS, Chan WL, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) predicted clinical outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Invest. (2020) 50:e13230. doi: 10.1111/eci.13230
33. Zhou YX, Li WC, Xia SH, Xiang T, Tang C, Luo JL, et al. Predictive value of the systemic immune inflammation index for adverse outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:836595. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.836595
34. Dziedzic EA, Gąsior JS, Tuzimek A, Paleczny J, Junka A, Dąbrowski M, et al. Investigation of the associations of novel inflammatory biomarkers-systemic inflammatory index (SII) and systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI)-with the severity of coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome occurrence. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:9553. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179553
35. Margraf A, Lowell CA, Zarbock A. Neutrophils in acute inflammation: current concepts and translational implications. Blood. (2022) 139:2130–44. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021012295
36. Gimbrone MA J, García-Cardeña G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118:620–36. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.115.306301
37. Matsunaga T, Chilian WM, March K. Angiostatin is negatively associated with coronary collateral growth in patients with coronary artery disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2005) 288:H2042–6. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00669.2004
38. Jang WJ, Yang JH, Choi SH, Song YB, Hahn JY, Choi JH, et al. Long-term survival benefit of revascularization compared with medical therapy in patients with coronary chronic total occlusion and well-developed collateral circulation. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2015) 8:271–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2014.10.010
39. Choi SY, Choi BG, Rha SW, Baek MJ, Ryu YG, Park Y, et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus optimal medical therapy for chronic total coronary occlusion with well-developed collaterals. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e006357. doi: 10.1161/jaha.117.006357
40. Khan MF, Wendel CS, Thai HM, Movahed MR. Effects of percutaneous revascularization of chronic total occlusions on clinical outcomes: a meta-analysis comparing successful versus failed percutaneous intervention for chronic total occlusion. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2013) 82:95–107. doi: 10.1002/ccd.24863
Keywords: systemic immune-inflammation index, coronary collateral circulation, type 2 diabetes mellitus, stable coronary artery disease, chronic total occlusion
Citation: Mao LS, Wang YX, Wu ZM, Ding FH, Lu L, Shen WF, Dai Y and Shen Y (2024) Elevated systemic immune-inflammatory index predicts poor coronary collateralization in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic total occlusion. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1490498. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1490498
Received: 3 September 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 12 December 2024.
Edited by:
Vladimir M. Pisarev, V.A.Negovsky Research Institute of General Reanimatology, RussiaReviewed by:
Jie Wu, Mayo Clinic Arizona, United StatesJayanta Gupta, Florida Gulf Coast University, United States
Copyright: © 2024 Mao, Wang, Wu, Ding, Lu, Shen, Dai and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Shen, cmpzaGVueWluZzhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lin Shuang Mao
Lin Shuang Mao Yi Xuan Wang
Yi Xuan Wang Zhi Ming Wu1
Zhi Ming Wu1 Feng Hua Ding
Feng Hua Ding Lin Lu
Lin Lu Wei Feng Shen
Wei Feng Shen Yang Dai
Yang Dai Ying Shen
Ying Shen