- 1Department of Emergency, Qingdao West Coast New Area Central Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, China
Background: To study the relationship between the monocyte/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (MHR) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and coronary artery stenosis in Non-st-elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTE-ACS) patients of different genders.
Methods: A total of 253 control and 800 NSTE-ACS patients were included, and clinic data (29 items) were also collected. NSTE-ACS patients were divided into low-risk (0–23) and high-risk (≥ 23) groups based on the Synergy between PCI with Taxus and Cardiac Surgery (SYNTAX) score. Then, Spearman correlation and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to study the associated factors of high-risk SYNTAX score in male and female NSTE-ACS patients, respectively. Finally, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to calculate the diagnostic value of MHR and NLR for predicting high-risk SYNTAX scores in male NSTE-ACS patients.
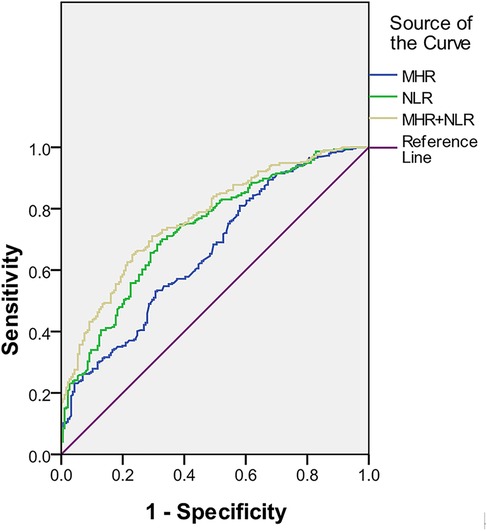
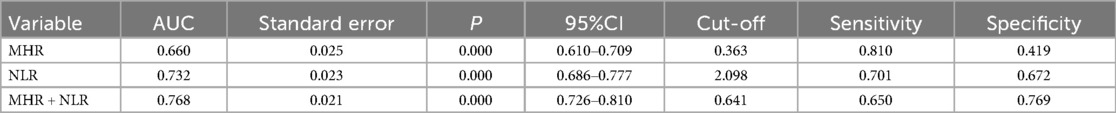
Results: Sixteen distinct factors differed between the high- and low-risk groups in male NSTE-ACS patients, a significantly higher number than female NSTE-ACS patients. Gout/hyperuricemia, smoking, NLR, and MHR are independent risk factors for arterial stenosis. At the same time, high-density lipoprotein and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are found to be protective factors in male NSTE-ACS patients. Fibrinogen, apolipoprotein B/A, and neutrophils are identified as independent risk factors for arterial stenosis in female NSTE-ACS patients, while LVEF and high-density lipoprotein are protective factors. Finally, combined NLR and MHR [p = 0.000, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.726–0.810] had better predictive efficacy on the degree of arterial vessel stenosis than NLR or MHR alone. The sensitivity and specificity of the ROC curve were 0.672 and 0.769, respectively.
Conclusion: The combination of MHR and NLR shows potential for predicting and assessing the severity of coronary artery stenosis in male patients with NSTE-ACS.
Background
In 2019, over 15 million deaths due to acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were reported globally, with 40% occurring in individuals under 70 years old (1). ACS includes ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and unstable angina pectoris. Due to their similar pathophysiology, unstable angina pectoris and NSTEMI are both known as non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS), one of the most serious and deadly forms of myocardial infarction (2, 3). Compared to STEMI, NSTE-ACS has a greater likelihood of incidence and recurrence and can cause malignant arrhythmia, cardiogenic shock, heart failure, and other complications (3). Patients with NSTE-ACS have varying degrees of coronary artery obstruction and require a more heterogeneous treatment (4).
Atherosclerosis, characterized by inflammation and lipid accumulation, is an important mechanism of ACS (5). Elevated monocytes and reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels are significant contributors to the development of atherosclerosis (6). In recent years, Monocyte/HDL cholesterol ratio (MHR) has been used to predict the severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) (7). A high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) indicates an intense inflammatory response. NLR has been identified as an autonomous risk factor for coronary heart disease and can predict the severity of ACS in coronary arteries (8–10). NLR and MHR can help to distinguish patients with ACS from those with stable angina, and their combined application can improve the sensitivity and specificity of ACS diagnosis (11). However, there are few studies on the role of MHR and NLR in NSTE-ACS patients.
The SYNTAX (Synergy Between Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Taxus and Cardiac Surgery) is a pathology-based angiographic scoring system that assesses the complexity of CAD and has been widely used to quantify the severity of CAD lesions and predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes (12). Studies have found that MHR positively correlates with SYNTAX score in ACS patients (13, 14). However, Jiang et al. (15) did not find a statistically significant correlation between MHR and SYNTAX score in NSTE-ACS patients. Therefore, the correlation between MHR and SYNTAX score in NSTE-ACS patients has not been clearly determined. Furthermore, the correlation between NLR and SYNTAX score is controversial in NSTE-ACS patients. Altun et al. found that NLR was an independent predictor for the high SYNTAX rating group of NSTE-ACS patients, and NLR was significantly correlated with the severity of ACS vascular lesions as evaluated by the SYNTAX score (16). However, Maleki et al. found that in NSTE-ACS patients, NLR was correlated with the SYNTAX score, but after adjusting the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) score, NLR had no significant predictive value for SYNTAX (17). Considering that the correlation between MHR, NLR, and SYNTAX scores in NSTE-ACS patients is controversial, it is necessary to investigate their correlation further.
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between MHR, NLR, and the degree of CAD in NSTE-ACS patients using the SYNTAX score. Similarly, to investigate the gender differences in the correlation between SYNTAX score and CAD, providing more biological indicators for predicting disease risk.
Materials and methods
Study population
This study was a retrospective analysis of patients admitted to the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University between January and December 2021 who underwent Coronary angiography (CAG) examination. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University (QYFY WZLL 28592) and followed the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines. All patients signed a written informed consent for research.
Control group inclusion criteria: Patients that were not diagnosed with ACS presenting symptoms such as chest pain, chest tightness, and other issues after a CAG test. NSTE-ACS group inclusion criteria: (1) Patients diagnosed with NSTE-ACS according to the Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of NSTE-ACS published by the Chinese Medical Association (2016). (2) Patients who underwent CAG examination and were treated in our hospital. At least two cardiovascular interventional physicians at the sub-senior level and higher determined the SYNTAX score.
Exclusion criteria: (1) People with infections, autoimmune diseases, or other stress response diseases such as recent trauma or severe ulcers; (2) Patients with malignant tumors, thyroid dysfunction, abnormal liver and kidney function, severe anemia, hypoproteinemia, malnutrition, and so on; (3) Patients with significant hematological abnormalities (white blood cell count < 3 × 109/L or >20 × 109/L, platelet count < 20 × 109/L, and so on). Moreover, for the NSTE-ACS group, patients with a history of cardiomyopathy, pericardial disease, severe valvular heart disease, congenital heart disease, severe arrhythmia, and coronary artery bypass grafting were also excluded.
Clinical data
The patients' history was collected and recorded after admission, including gender, age, height, weight, smoking history (smoking for more than one year, no less than one cigarette per day, or smoking cessation for less than six months), history of hypertension, cerebral infarction, diabetes, status post coronary stent implantation, coronary heart disease/heart failure, medicine use, and so on.
Laboratory examination
A fasting venous blood sample was collected the morning after admission for blood routine and biochemical tests, including leukocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, total cholesterol, triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C, blood uric acid, creatinine, cardiac troponin T (cTnT), cystatin C, and fibrinogen. Body Mass Index, MHR, NLR, and other indices were calculated.
Ultrasonic echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is required before a CAG examination. The examining physician used the PHLIPS iE33 color Doppler echocardiography (Philips Medical Systems, Bothell, WA, USA) to examine the patients in various positions, including lying on their back and with a 30° and 45° left tilt to assess the structure and function of the heart and large blood vessels. Two clinicians performed the echocardiogram, and each patient's left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was measured.
Angiographic examination
CAG was conducted with the patient in a standard position. A percutaneous radial artery puncture was made, and an angiographic catheter was introduced into the openings of the left and right coronary arteries sequentially. At least two attending physicians and cardiologists observed the coronary vessels from multiple positions.
SYNTAX score
The SYNTAX score was calculated based on the coronary angiography results according to the website (www. SYNTAXscore.com), and the scores were reviewed by at least two experienced attending physicians or above. SYNTAX score calculation: Coronary artery dominance (left coronary dominance +0 and right coronary dominance +1), right coronary artery stage (proximal +1, middle +1, and distal +1), right coronary branch (posterior descending branch +1 and posterior lateral branch +0.5), left main artery (right coronary artery +5 and left coronary artery +6), anterior descending branch (proximal branch +3.5 and middle branch +2.5), before descending branch apex (+1), angle of branch (the first pair +1, the second to +0.5), the cyclotron branch—proximal (right +1.5, + 2.5 from left), left side (+0.5 right and left +1), and the cyclotron branch—after descending (+1) (18, 19).
Study design
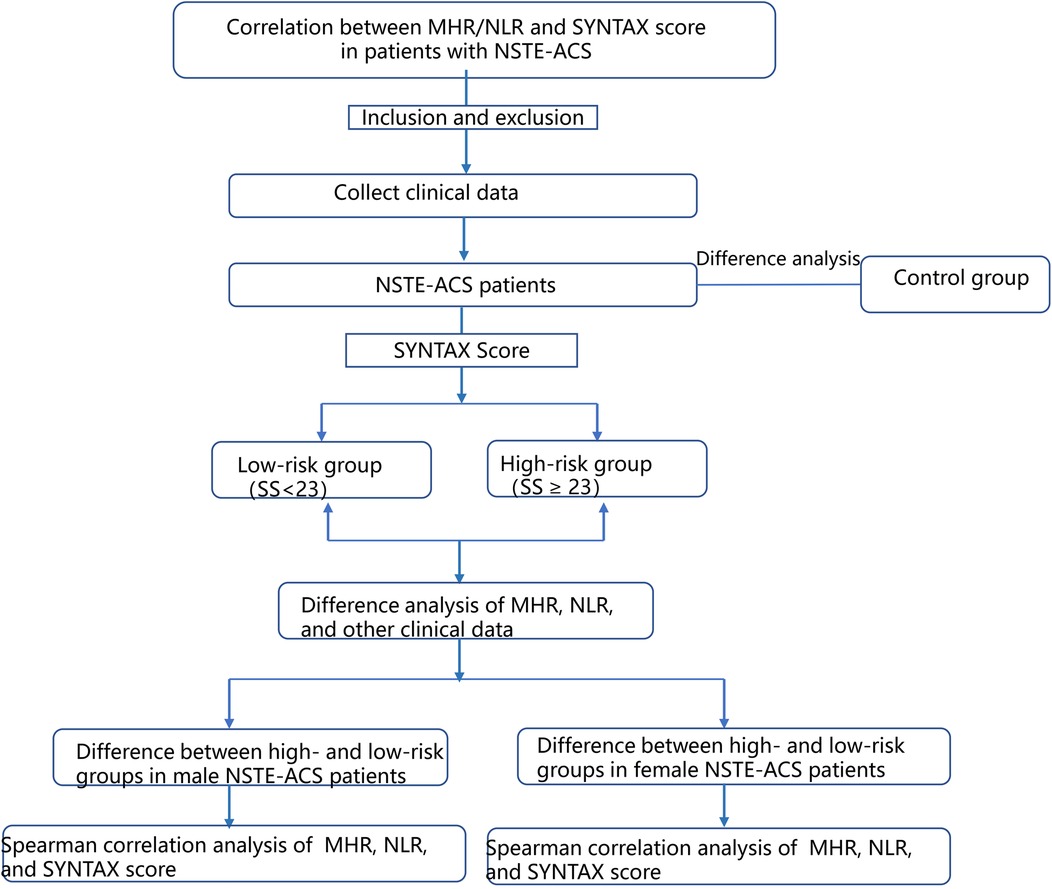
As shown in Figure 1, (1) the differences between the baseline data of the control and NSTE-ACS groups were first analyzed. (2) Patients in the NSTE-ACS group were divided into a low-risk group (0–23) and a high-risk group (≥23) based on their SYNTAX score, and the difference between the baseline data of the two groups was analyzed. (3) Patients with NSTE-ACS were then divided into two subgroups, male and female samples, and the difference in baseline data of SYNTAX scores of low-risk and high-risk groups in the two subgroups were analyzed, respectively. (4) The Spearman correlation analysis determined the correlation factors of the SYNTAX scores in different genders of patients with NSTE-ACS. (5) Logistic regression analysis was used to explore the related factors of SYNTAX scores for different genders. (6) The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to calculate the diagnostic value of MHR, NLR, and their combination in the high-risk SYNTAX score of male patients with NSTE-ACS.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20.0 statistical software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). Measurement data was tested for normalcy using the Shapiro–Wilk method. Data conforming to normal distribution was expressed by mean ± standard deviation else median and four-digit fraction spacing were used. The T-test or non-parametric (Mann–Whitney Test) was used to compare the differences between the groups. Qualitative data were presented in constituent ratios, Chi-square, or non-parametric tests to compare group differences. Correlation analysis of the two variables was performed by Pearson correlation (both variables were normally distributed) or Spearman correlation analyses. Univariate significant variables were included in multivariate logistic regression. ROC curve analysis was conducted to assess the prediction accuracy of NLR and MHR for high-risk SYNTAX scores. The appropriate threshold, sensitivity, and specificity were obtained based on the point coordinates. Bilateral p < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
Results
Comparison of the control and NSTE-ACS groups
A total of 302 participants without CAD were selected for the study, with 253 patients meeting the inclusion criteria and being included in the control group. Furthermore, 936 patients with NSTE-ACS were initially selected, and 800 met the inclusion criteria and were included in the follow-up analysis. As shown in the Supplementary Table S1, the mean age of the control group was 56.783 ± 9.793, which was significantly lower than that of the NSTE-ACS group (62.964 ± 9.055). Multiple factors in the 29 items included significantly differed between the control and NSTE-ACS groups (p < 0.05), such as age, sex, monocytes, NLR, LVEF, MHR, and so on.
Comparison of the low- and high-risk groups
NSTE-ACS patients were divided into low-risk (0–23) and high-risk (≥23) groups based on the SYNTAX scores, of which 374 were in the low-risk group (188 women and 186 men), and 426 were in a high-risk group (132 women and 294 men). As shown in Table 1, gender, smoking, fibrinogen, apolipoprotein B/A, uric acid, cTnT, neutrophils, monocytes, NLR, LVEF, and MHR differed between the low-risk and high-risk groups (p < 0.05). The proportion of males (p = 0.000) and smoking history (p = 0.000) in the high-risk group were significantly different from those in the low-risk group.
Comparison of the low-risk and high-risk groups of different genders of patients with NSTE-ACS
Table 2 shows that in male NSTE-ACS patients, differences in diabetes, hyperlipidemia, gout/hyperuricemia, cerebral infarction, smoking, TG, apolipoprotein B/A, HDL-C, blood glucose, uric acid, cystatin C, cTnT, monocytes, NLR, LVEF, and MHR were statistically significant between low-risk and high-risk groups (p < 0.05). In female patients with NSTE-ACS, differences in fibrinogen, apolipoprotein B/A, HDL-C, uric acid, cTnT, neutrophils, and LVEF were statistically significant between low-risk and high-risk groups (Table 3, p < 0.05). There were significantly fewer differences between the low-risk and high-risk groups in females than in males. Besides, females with high blood pressure were more likely to develop arterial stenosis than those without high blood pressure (Table 3, p < 0.05).
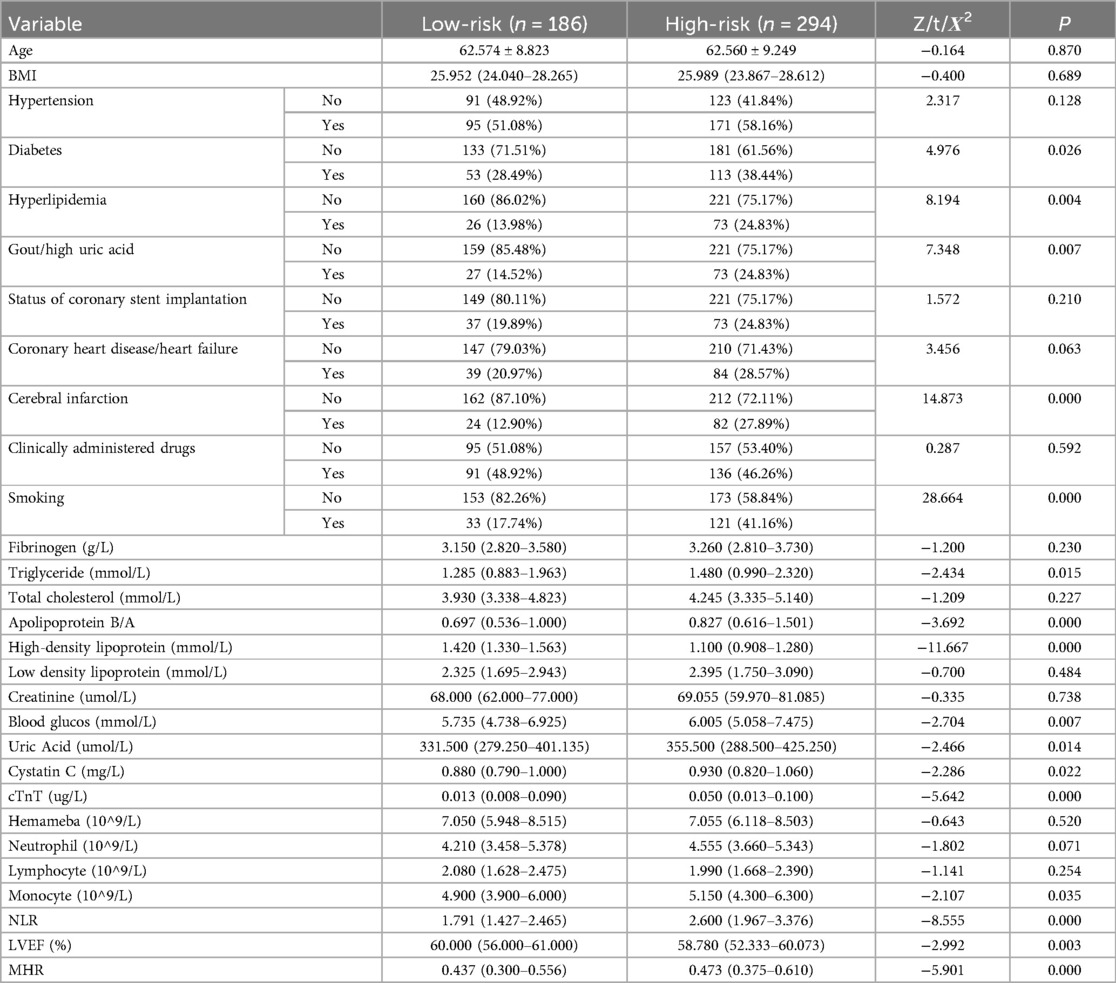
Table 2. Comparison of baseline data between the low- and high-risk group in male NSTE-ACS patients.
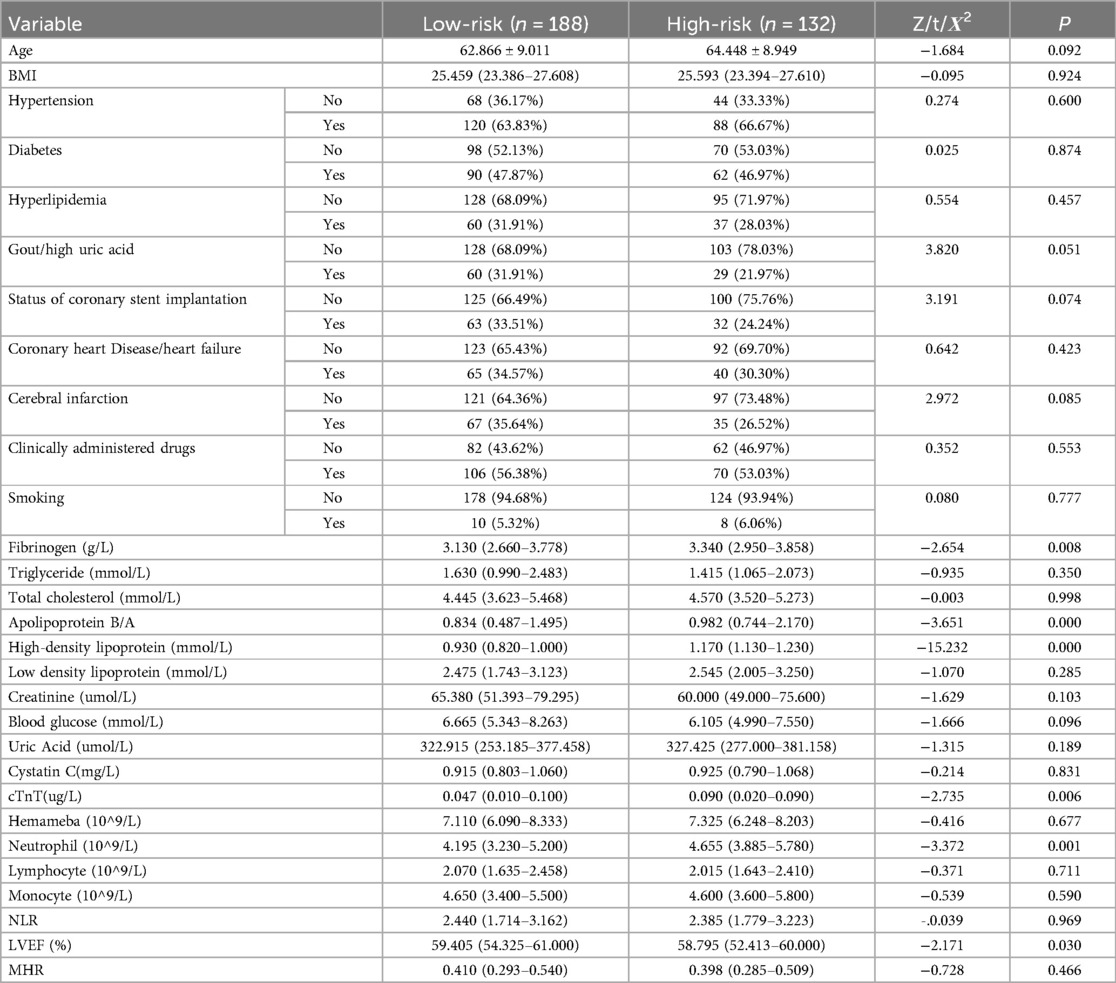
Table 3. Comparison of baseline data between the low- and high-risk group in female NSTE-ACS patients.
Upon comparing Tables 2, 3, it is evident that the presence of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, gout/hyperuricemia, and cerebral infarction significantly impact the severity of arterial stenosis in male patients with NSTE-ACS rather than in female patients. Comparing the results of biochemical tests, more factors affected the SYNTAX scores of male patients with NSTE-ACS than female patients. In male patients with NSTE-ACS, monocyte, NLR, and MHR values in high-risk groups were significantly higher than in low-risk groups (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the three values among the risk groups of female patients with NSTE-ACS.
Correlation analysis of SYNTAX scores in NSTE-ACS patients of different genders
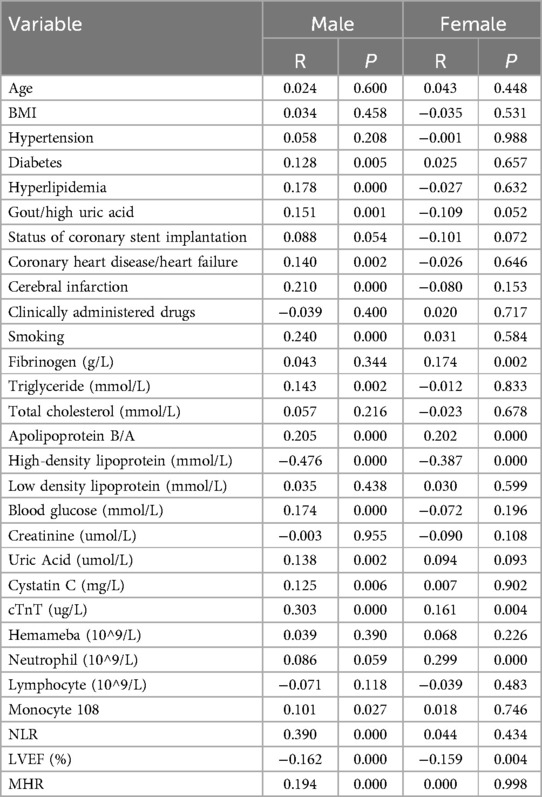
As shown in Table 4, in male patients with NSTE-ACS, SYNTAX score was positively correlated with hyperlipidemia (p = 0.000, R = 0.178), smoking (p = 0.000, R = 0.240), apolipoprotein B/A (p = 0.000, R = 0.205), uric acid (p = 0.002, R = 0.138), cTnT (p = 0.000, R = 0.303), NLR (p = 0.000, R = 0.390), and MHR (p = 0.000, R = 0.194), indicating that the higher the values, the higher the SYNTAX scores and the degree of arterial stenosis. However, HDL-C (p = 0.000, R = −0.476) and LVEF (%) (p = 0.000, R = −0.162) were negatively correlated with SYNTAX scores, indicating that high levels of HDL-C and LVEF reduced the degree of arterial stenosis (Table 4 and Figure 2). In female patients with NSTE-ACS, SYNTAX score was positively correlated with fibrinogen (p = 0.002, R = 0.174), apolipoprotein B/A (p = 0.000, R = 0.202), cTnT (p = 0.004, R = 0.161), and neutrophils (p = 0.000, R = 0.299). However, HDL-C (p = 0.000, R = −0.387) and LVEF (p = 0.004, R = −0.159) were negatively correlated with SYNTAX scores (Table 4 and Figure 3). In summary, the SYNTAX score in male patients with NSTE-ACS had more relevant factors, so we explored the risk factors for vascular stenosis in different genders.
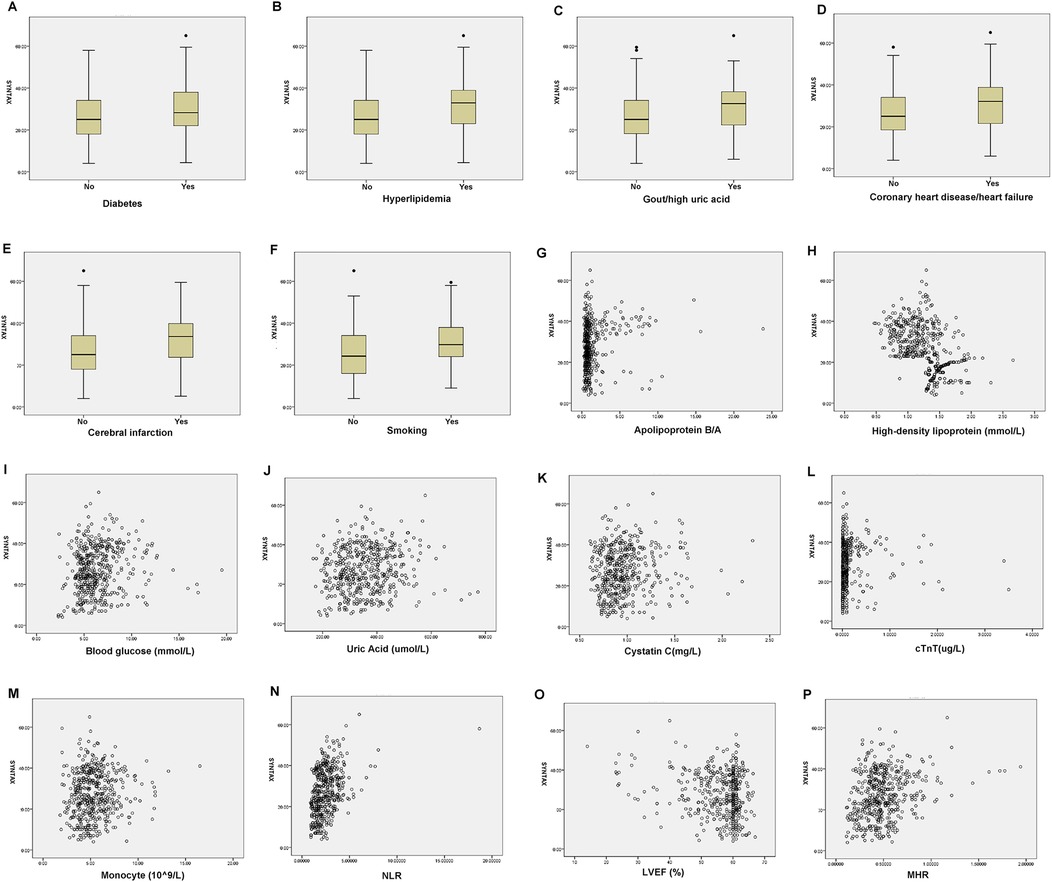
Figure 2. Box diagram and scatter plot of the related factors of SYNTAX scores in male patients with NSTE-ACS. (A) Diabetes, (B) Hyperlipidemia, (C) Gout/hyperuricemia, (D) Coronary heart disease/heart failure, (E) Cerebral infarction, (F) Smoking, (G) Apolipoprotein B/A, (H) high-density lipoprotein, (I). Blood glucose, (J). Uric Acid, (K). Cystatin C, (L). cTnT, (M). Monocyte, (N). NLR, (O). LVEF, and (P). MHR.
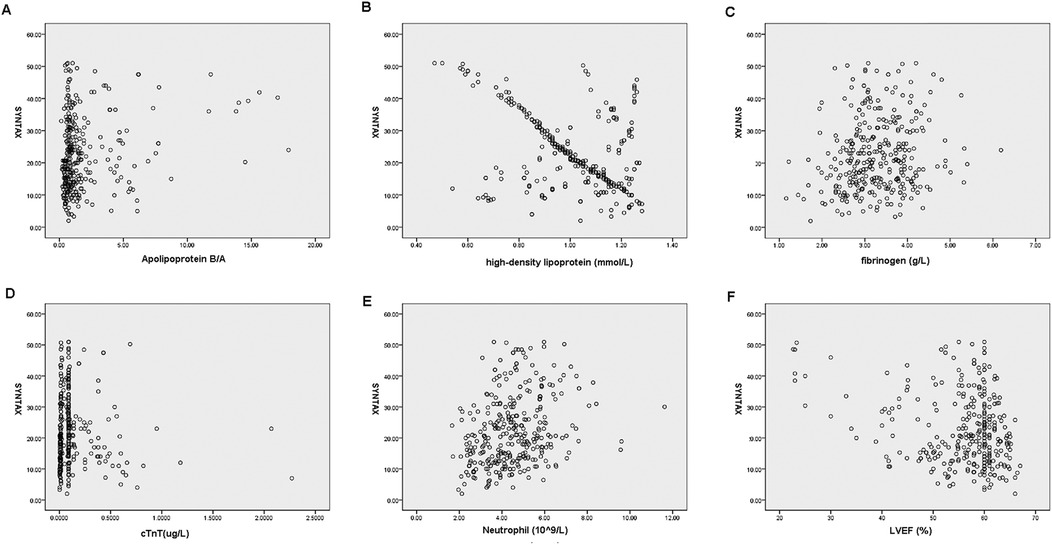
Figure 3. Scatterplot of the related factors of SYNTAX scores in female patients with NSTE-ACS. (A) Apolipoprotein B/A, (B) High-density lipoprotein, (C) fibrinogen, (D) cTnT, (E) neutrophils, and (F) LVEF.
Risk factors for vascular stenosis in different genders of patients with NSTE-ACS
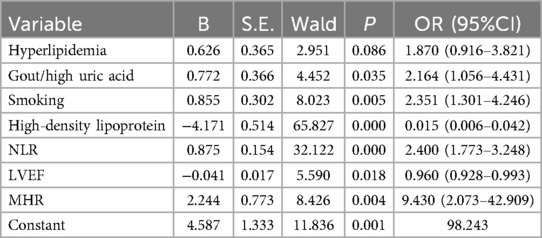
Meaningful variables in the above correlation analysis were included in the logistic regression. Table 5 shows that gout/hyperuricemia [p = 0.035, OR = 2.164 (1.056–4.431)], smoking [p = 0.005, OR = 2.351 (1.301–4.246)], NLR [p = 0.000, OR = 2.400 (1.773–3.248)], and MHR [p = 0.004, OR = 9.430 (2.073–42.909)] were risk factors for SYNTAX score in male patients with NSTE-ACS, indicating that the higher the value, the greater the degree of arterial stenosis. HDL-C [p = 0.000, OR = 0.015 (0.006–0.042)] and LVEF [p = 0.018, OR = 0.960 (0.928–0.993)] are protective factors, and low levels of HDL-C and LVEF can prevent or alleviate arterial stenosis.
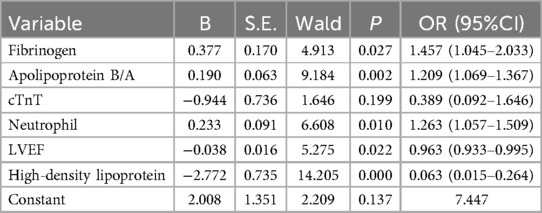
Table 6 shows that in female patients with NSTE-ACS, fibrinogen [p = 0.027, OR = 1.457 (1.045–2.033)], apolipoprotein B/A [p = 0.002, OR = 1.209 (1.069–1.367)], apolipoprotein B/A [p = 0.002, OR = 1.209 (1.069–1.367)], Neutrophils [p = 0.010, OR = 1.263 (1.057–1.509)] were independent risk factors for arterial stenosis. LVEF [p = 0.022, OR = 0.963 (0.933–0.995)] and HDL-C [p = 0.000, OR = 0.063 (0.015–0.264)] were protective factors for arterial stenosis.
NLR and MHR predict the degree of vascular stenosis in male patients with NSTE-ACS
The above results indicate that NLR and MHR are independent risk factors for SYNTAX scores. The ability of NLR and MHR to predict the high-risk SYNTAX scores was further evaluated. As shown in Figure 4 and Table 7, the area under the curve values for ROC analyses using NLR individually and combining NLR and MHR were 0.732 and 0.768, respectively. The optimal critical value of NLR was 2.098, and the corresponding sensitivity and specificity values were 0.701 and 0.672, respectively. The specificity of combined NLR and MHR in predicting the degree of arterial vessel stenosis was 0.769, higher than that of MHR and NLR individually.
Discussion
This study showed gender differences in the effects of multiple indicators on SYNTAX scores. In male patients with NSTE-ACS, gout/hyperuricemia, smoking, NLR, and MHR were independent risk factors for arterial vessel stenosis, and HDL-C and LVEF were protective factors. In female NSTE-ACS patients, fibrinogen, apolipoprotein B/A, and neutrophils were independent risk factors for arterial stenosis, and LVEF and HDL-C were protective factors for arterial stenosis. NLR combined with MHR can predict the SYNTAX score grading in male patients with NSTE-ACS.
Atherosclerotic lesions are early pathological stages of ACS. Multiple reports have shown the existence of neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in atherosclerotic lesions in both mice and humans (20, 21). NETs can damage the endothelium through the action of Interleukin 1 (IL-1) and cathepsin G and promote the expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and tissue factors related to plaque thrombosis (22). Moreover, at the site of plaque rupture, neutrophils interact with platelets to promote the development of NETs, thus accelerating thrombosis (23). Lymphocytes play a vital role in the adaptive immune response and participate in the prolonged inflammatory phase of atherosclerosis (24). It has been confirmed that there are activated T lymphocytes (such as CD4 + and CD8+ T cells) in atherosclerotic plaques (25). In addition, CD8 + T cells are negatively correlated with coronary atherosclerosis and are independent predictors of acute coronary events (26). An increase in neutrophils or a decrease in lymphocytes will result in a higher NLR value, indicating a more intense inflammatory response. During inflammation, neutrophils play a crucial role in regulating the advancement of arterial wall tissue damage, while the death of lymphocytes worsens arteriosclerosis (27). This study showed that the NLR value of the high-risk SYNTAX group was significantly higher than that of the low-risk group (p < 0.001). Furthermore, the multivariate logistic analysis showed that NLR value was an independent risk factor for a high SYNTAX score. Consistent with other studies, Arbel et al. suggested that NLR value could predict the severity of ACS coronary artery and was an independent risk factor for CAD (10). However, this study also indicated that NLR has various effects on SYNTAX grading of NSTE-ACS patients of different genders.
MHR is a novel predictor that reflects the balance between monocytes and HDL-C, inflammation, and oxidative stress (28). MHR may better predict clinical outcomes than monocyte count and HDL-C concentration alone (29). Studies have reported that the incidence of long-term major cardiovascular adverse events (MACE) in ACS patients with elevated MHR is 1.4 times higher than in ACS patients with lower MHR (30). Acikgoz et al. (31) showed that increased MHR could predict the in-hospital mortality (HR = 3.745, 95% CI: 1.304–5.950) and 5-year mortality (HR = 2.048, 95% CI: 1.225–4.091, p = 0.014). Sun et al. have comprehensively analyzed eight studies (including 6,480 ACS patients) to evaluate the prognostic role of MHR in ACS patients, and the results showed that high levels of MHR were associated with an increased risk of MACE (RR: 1.65; 95% CI: 1.36–2.02) and all-cause mortality (RR: 2.61; 95% CI: 1.29–4.89), indicating that MHR can be used as a potential prognostic indicator for ACS (32). This study has found significant differences in MHR between the control and NSTE-ACS groups and between low-risk and high-risk SYNTAX score groups. In male patients with NSTE-ACS, the MHR of the patients with high SYNTAX scores was significantly higher than that of the group with low SYNTAX scores. Moreover, MHR is an independent risk factor for SYNTAX score in male patients with NSTE-ACS, which can predict the degree of arterial vessel stenosis.
The mechanism of MHR-induced vascular stenosis may be related to the following explanations. The breakdown of endothelial cells in the blood vessel wall promotes the deposition of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and causes an oxidation reaction to produce oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL). Ox-LDL activates pattern recognition receptors, triggering immunological responses like the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the uptake of oxides by blood vessels and phagocytes, leading to atherosclerosis (33). Circulating monocytes are recruited to the inner membrane by Ox-LDL, where they transform into resident macrophages, and these macrophages consume Ox-LDL, turning into foam cells, which triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the accumulation of adipocytes (34). However, HDL-C can clear the cholesterol in the artery wall and neutralize the pro-inflammatory and pro-oxidative effects of monocytes, showing anti-atherosclerosis effects (7). Therefore, an increase in monocyte count and a decrease in HDL-C concentration will lead to a rise in MHR and atherosclerosis.
Notably, this study also showed that SYNTAX grading in patients with NSTE-ACS of different genders was affected by various factors. Multiple studies have shown that the dynamic course of CAD significantly differs between men and women. Premenopausal women are relatively resistant to CAD, while postmenopausal women have an increased risk of CAD, comparable to a 70-year-old man (35). Moreover, the manifestations of CAD are also different between men and women. In contrast to men, the etiology of ischemic heart disease in women is predominantly attributed to pathological processes, including micro embolism resulting from erosion of active atherosclerotic plaques, abnormal coronary artery response, and microvascular endothelial dysfunction, rather than anatomical blockage of the coronary arteries (35).
There are also differences in sex hormones and immune responses between men and women. The anti-inflammatory effects of estrogen on macrophages help prevent atherosclerosis. Moreover, estrogen has been reported to promote the polarization of the immune response towards antibody-mediated humoral immunity, mainly involving the Th2 (auxiliary) and Treg (regulatory) types of CD4+ T lymphocytes (36). Estrogen stimulates B cells and enhances antibody production by B lymphocytes, whereas androgens inhibit B-cell development, decreasing antibody synthesis in humans (37, 38). Androgens are believed to stimulate cell-mediated and Th1 responses (39). So, women have an increased antibody response to infections and vaccines compared to men. In men, testosterone increases the activation of mast cells and macrophages, leading to the development of TLR2+/TLR4+/M2b macrophages and foam cells within the atherosclerotic plaques. Besides, cytokines, enzymes, and other mediators remodeled the vessel wall, resulting in a thrombus formation (38). This regulation of the immune system by androgens, combined with early exposure to behavioral factors such as smoking, early onset of hypertension, or multiple sclerosis, may lead to inconsistencies in the factors affecting the degree of vascular stenosis in patients of different genders with NSTE-ACS.Gender differences in performance, sex hormones, immune response characteristics, and risk factors of CHD patients may lead to gender differences in MHR and NLR. Pan et al. found that NLR was associated with high SYNTAX scores in men with CAD and was an independent risk factor and predictor of CAD in men but not women (40). Xu et al. found that MHR was positively correlated with SYNTAX scores in males with stable CAD, which could help interventional cardiologists detect high-risk patients before coronary artery catheterization, but its application may only be limited to men (41). Similar results were also found in this study. Only in male patients with NSTE-ACS, NLR and MHR differed significantly between low-risk and high-risk SYNTAX score groups and were independent correlated factors for high SYNTAX scores. MHR and NLR had different abilities to predict stenosis severity in CAD of different sexes, which may be related to the immune mechanism of varying sex hormones. Estrogen can act directly on monocytes, reducing their ability to migrate to the artery wall, thereby reducing the inflammatory response of arteriosclerosis. Besides, estrogen can increase T and B cells' tolerance, reducing their accumulation within the artery wall. At the same time, estrogen may also increase the number of anti-inflammatory lymphocytes (such as regulatory T cells Tregs), promote immune tolerance, and reduce arteriosclerosis inflammation (42, 43). While, testosterone is associated with an increase in the inflammatory response of immune cells, particularly the activity of monocytes and the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6). Besides, testosterone can stimulate the activity of neutrophils, enhancing their aggregation, which further exacerbates arterial inflammation and promotes plaque formation and instability (44, 45). In summary, the different effects of sex hormones make men and women differ in immune response and progression of arteriosclerosis, which may also explain the gender-related differences in the impact of MHR and NLR on the SYNTAX scores in CAD patients.
Conclusion
NLR paired with MHR can effectively predict SYNTAX scores in male patients with NSTE-ACS, offering a theoretical foundation for assessing coronary artery stenosis in this patient population.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. XL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. KT: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. SL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XM: Resources, Writing – review & editing. YC: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. FW: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. HX: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2024.1469730/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Dziedzic EA, Gasior JS, Tuzimek A, Paleczny J, Junka A, Dabrowski M, et al. Investigation of the associations of novel inflammatory biomarkers-systemic inflammatory Index (SII) and systemic inflammatory response Index (SIRI)-with the severity of coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome occurrence. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(17):1–14. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179553
2. Hedayati T, Yadav N, Khanagavi J. Non-ST-segment acute coronary syndromes. Cardiol Clin. (2018) 36(1):37–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2017.08.003
3. Bhatt DL, Lopes RD, Harrington RA. Diagnosis and treatment of acute coronary syndromes: a review. JAMA. (2022) 327(7):662–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0358
4. Jneid H, Addison D, Bhatt DL, Fonarow GC, Gokak S, Grady KL, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC clinical performance and quality measures for adults with ST-elevation and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on performance measures. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. (2017) 10(10):3–7. doi: 10.1161/HCQ.0000000000000032
5. Ahmadi A, Argulian E, Leipsic J, Newby DE, Narula J. From subclinical atherosclerosis to plaque progression and acute coronary events: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2019) 74(12):1608–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.08.012
6. Ganjali S, Gotto AM Jr, Ruscica M, Atkin SL, Butler AE, Banach M, et al. Monocyte-to-HDL-cholesterol ratio as a prognostic marker in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233(12):9237–46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27028
7. Karim K, Aulia MS, Pradisa IS, Huda MF, Setyasari A, Yosephina S, et al. Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as highly predictive marker in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Future Cardiol. (2023) 19(5):261–70. doi: 10.2217/fca-2023-0001
8. Li Q, Ma X, Shao Q, Yang Z, Wang Y, Gao F, et al. Prognostic impact of multiple lymphocyte-based inflammatory indices in acute coronary syndrome patients. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:811790. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.811790
9. Bajari R, Tak S. Predictive prognostic value of neutrophil-lymphocytes ratio in acute coronary syndrome. Indian Heart J. (2017) 69 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S46–s50. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.01.020
10. Arbel Y, Finkelstein A, Halkin A, Birati EY, Revivo M, Zuzut M, et al. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is related to the severity of coronary artery disease and clinical outcome in patients undergoing angiography. Atherosclerosis. (2012) 225(2):456–60. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.009
11. Liang LZH. Clinical value of MHR and NLR in the diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome (Chinese). Nurs Res. (2021) 35(24):4372–5.
12. Bae KH, Kim SW, Choi YK, Seo JB, Kim N, Kim CY, et al. serum levels of PCSK9 are associated with coronary angiographic severity in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Diabetes Metab J. (2018) 42(3):207–14. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.0081
13. Kundi H, Kiziltunc E, Cetin M, Cicekcioglu H, Cetin ZG, Cicek G, et al. Association of monocyte/HDL-C ratio with SYNTAX scores in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Herz. (2016) 41(6):523–9. doi: 10.1007/s00059-015-4393-1
14. Akboga MK, Balci KG, Maden O, Ertem AG, Kirbas O, Yayla C, et al. Usefulness of monocyte to HDL-cholesterol ratio to predict high SYNTAX score in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Biomark Med. (2016) 10(4):375–83. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2015-0050
15. Jiang Z, Pan X, Xie X. Serum monocyte/HDL ratio was correlated with GRACE score and SYNTAX score in patients with non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (Chinese). Chin J Gerontol. (2019) 39(15):5.
16. Altun B, Turkon H, Tasolar H, Beggi H, Altun M, Temiz A, et al. The relationship between high-sensitive troponin T, neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and SYNTAX score. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. (2014) 74(2):108–15. doi: 10.3109/00365513.2013.860619
17. Maleki M, Tajlil A, Separham A, Sohrabi B, Pourafkari L, Roshanravan N, et al. Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) with angiographic SYNTAX score in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS). J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. (2021) 13(3):216–21. doi: 10.34172/jcvtr.2021.40
18. Wang Z. Prognostic Significance of SYNTAX/SYNTAX II Score and ApoB/ApoA1 Ratio in Patients After Coronary Stenting. Jilin: JiLin University (2019).
19. Zhu X, Hu Z, Feng J. Correlation between lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, lipoprotein (a) and SYNTAX score in patients with coronary heart disease (Chinese). J Anhui Medical University. (2022) 010:057.
20. Megens RT, Vijayan S, Lievens D, Döring Y, van Zandvoort MA, Grommes J, et al. Presence of luminal neutrophil extracellular traps in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. (2012) 107(3):597–8. doi: 10.1160/TH11-09-0650
21. Pertiwi KR, van der Wal AC, Pabittei DR, Mackaaij C, van Leeuwen MB, Li X, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps participate in all different types of thrombotic and haemorrhagic complications of coronary atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. (2018) 118(6):1078–87. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1641749
22. Folco EJ, Mawson TL, Vromman A, Bernardes-Souza B, Franck G, Persson O, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induce endothelial cell activation and tissue factor production through interleukin-1α and cathepsin G. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2018) 38(8):1901–12. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311150
23. Wu Y, Wei S, Wu X, Li Y, Han X. Neutrophil extracellular traps in acute coronary syndrome. J Inflamm (Lond). (2023) 20(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12950-023-00344-z
24. Hedrick CC. Lymphocytes in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35(2):253–7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.305144
25. van Duijn J, Kritikou E, Benne N, van der Heijden T, van Puijvelde GH, Kröner MJ, et al. CD8+ T-cells contribute to lesion stabilization in advanced atherosclerosis by limiting macrophage content and CD4+ T-cell responses. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115(4):729–38. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy261
26. Zidar DA, Mudd JC, Juchnowski S, Lopes JP, Sparks S, Park SS, et al. Altered maturation Status and possible immune exhaustion of CD8T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients presenting with acute coronary syndromes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2016) 36(2):389–97. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306112
27. Yuan S, Pu T, Wang Z, Li L, Gao P, Zhang L, et al. [Correlation between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome]. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. (2022) 34(3):274–9.35574745
28. Eyyupkoca F, Yildirim O, Sivri S, Ali-Felekoglu M, Demirtas B, Sait-Altintas M, et al. Admission monocyte/HDL ratio predicts adverse cardiac remodeling after st-elevation myocardial infarction. Rev Invest Clin. (2022) 74(2):104–12. doi: 10.24875/RIC.21000599
29. Villanueva DLE, Tiongson MD, Ramos JD, Llanes EJ. Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR) as a predictor of mortality and Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01242-6
30. Cetin MS, Ozcan Cetin EH, Kalender E, Aydin S, Topaloglu S, Kisacik HL, et al. Monocyte to HDL cholesterol ratio predicts coronary artery disease severity and future Major cardiovascular adverse events in acute coronary syndrome. Heart Lung Circ. (2016) 25(11):1077–86. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2016.02.023
31. Açikgöz SK, Açikgöz E, Sensoy B, Topal S, Aydogdu S. Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is predictive of in-hospital and five-year mortality in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiol J. (2016) 23(5):505–12. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2016.0026
32. Sun M, Zhao D, Zhang Y, Zhai Y, Ye M, Wang X, et al. Prognostic utility of monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a meta-analysis. Am J Med Sci. (2020) 359(5):281–6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2020.01.018
33. Bergmark BA, Mathenge N, Merlini PA, Lawrence-Wright MB, Giugliano RP. Acute coronary syndromes. Lancet. (2022) 399(10332):1347–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02391-6
34. Puig N, Montolio L, Camps-Renom P, Navarra L, Jiménez-Altayó F, Jiménez-Xarrié E, et al. Electronegative LDL promotes inflammation and triglyceride accumulation in macrophages. Cells. (2020) 9(3):1–20. doi: 10.3390/cells9030583
35. Reynolds HR, Srichai MB, Iqbal SN, Slater JN, Mancini GB, Feit F, et al. Mechanisms of myocardial infarction in women without angiographically obstructive coronary artery disease. Circulation. (2011) 124(13):1414–25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.026542
36. Sameer AS, Nissar S, Aziz R. Telomeres and estrogens: the unholy nexus in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cardiol Res. (2014) 5(3-4):85–90. doi: 10.14740/cr335e
37. Quintero OL, Amador-Patarroyo MJ, Montoya-Ortiz G, Rojas-Villarraga A, Anaya JM. Autoimmune disease and gender: plausible mechanisms for the female predominance of autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. (2012) 38(2-3):J109–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.10.003
38. Fairweather D. Sex differences in inflammation during atherosclerosis. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. (2014) 8(Suppl 3):49–59. doi: 10.4137/CMC.S17068
39. Girón-González JA, Moral FJ, Elvira J, García-Gil D, Guerrero F, Gavilán I, et al. Consistent production of a higher TH1:TH2 cytokine ratio by stimulated T cells in men compared with women. Eur J Endocrinol. (2000) 143(1):31–6. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1430031
40. Pan Q, Zhang W, Li X, Chen Z, Yang Y, Wang G. Sex difference in the association between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and severity of coronary artery disease. Angiology. (2022) 73(5):470–7. doi: 10.1177/00033197211070884
41. Xu W, Guan H, Gao D, Pan J, Wang Z, Alam M, et al. Sex-specific association of monocyte count to high-density lipoprotein ratio with SYNTAX score in patients with suspected stable coronary artery disease. Medicine (Baltimore). (2019) 98(41):e17536. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017536
42. Aryan L, Younessi D, Zargari M, Banerjee S, Agopian J, Rahman S, et al. The role of estrogen receptors in cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(12):4314. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124314
43. Meng Q, Li Y, Ji T, Chao Y, Li J, Fu Y, et al. Estrogen prevent atherosclerosis by attenuating endothelial cell pyroptosis via activation of estrogen receptor α-mediated autophagy. J Adv Res. (2020) 28:149–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.08.010
44. Gencer B, Bonomi M, Adorni MP, Sirtori CR, Mach F, Ruscica M. Cardiovascular risk and testosterone–from subclinical atherosclerosis to lipoprotein function to heart failure. Rev Endocr Metabol Disord. (2021) 22:257–74. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09628-2
Keywords: non ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome, monocyte/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (MHR), neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), SYNTAX score, receiver operating characteristic (ROC)
Citation: Yang Y, Lv X, Tan K, Li K, Li S, Meng X, Chen Y, Wang F and Xin H (2025) The correlation between serum MHR and NLR and the severity of coronary lesions in NSTE-ACS patients of different genders. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1469730. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1469730
Received: 24 July 2024; Accepted: 24 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Federico Biscetti, Agostino Gemelli University Polyclinic (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Larisa Anghel, Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, RomaniaJorgo Kostov, Saints Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje, North Macedonia
Copyright: © 2025 Yang, Lv, Tan, Li, Li, Meng, Chen, Wang and Xin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Xin, eGluaHVpcWluZ3lpQDE2My5jb20=
 Yanping Yang1
Yanping Yang1 Kai Tan
Kai Tan Hui Xin
Hui Xin