
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Cardiovasc. Med. , 24 September 2024
Sec. Cardio-Oncology
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2024.1466395
This article is part of the Research Topic Case Reports in Cardio-Oncology: 2024 View all 11 articles
Introduction: Pazopanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and advanced soft-tissue sarcoma that functions by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Although the package insert and current cardio-oncology guidelines indicate a risk of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) associated with pazopanib, the causative role of pazopanib in arterial thrombosis is unclear due to a lack of focused coronary disease evaluation in oncological clinical trials prior to pazopanib initiation. Herein we present an antecedent ischemic evaluation of a patient who was prescribed pazopanib to demonstrate the first reported case of ACS directly attributable to pazopanib.
Case description: A 65-year-old woman with metastatic leiomyosarcoma presented to the hospital with ACS. Pazopanib had been initiated 8 months prior, and an ischemic evaluation 6 weeks prior to hospitalization indicated mild coronary artery disease (CAD). Emergent cardiac catheterization revealed a large thrombotic occlusion of the mid-left anterior descending coronary artery involving the secondary diagonal artery, which was treated with manual aspiration thrombectomy. Pazopanib was discontinued, and the patient was discharged from the hospital 12 days later.
Discussion: Although pazopanib is associated with ACS, there is a lack of definitive data supporting this association. This case-based demonstration of pazopanib-induced ACS provides a discrete clinical example of this phenomenon. The patient's minimal atherosclerotic burden 6 weeks prior to her presentation for ACS strongly suggests causality attributable to pazopanib. Given the increased risk for ischemic heart disease, careful attention and an individualized risk assessment for CAD should be provided to patients who are prescribed pazopanib.
Pazopanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) approved for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and advanced soft-tissue sarcoma (STS) and functions by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors (1). Although current European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Cardio-Oncology guidelines classify pazopanib as being associated with a risk for acute coronary syndrome (ACS), evidence is limited and without clear causation (2–7, 9). Herein we present the first reported case of pazopanib-induced ACS in a patient with metastatic STS.
A 65-year-old woman with a past medical history of hypertension and obesity and without any family history of coronary artery disease (CAD) was diagnosed with Stage IB leiomyosarcoma 2.5 years prior to the index hospitalization for ACS (Figure 1). Her leiomyosarcoma was initially treated with total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and bilateral pelvic lymph node dissection. Pathological examination confirmed negative margins and lymph nodes. Recurrent pulmonary metastatic disease was detected 1 year later and treated with docetaxel/gemcitabine. Due to progression of disease despite therapy, doxorubicin was initiated as a second-line treatment 15 months prior to the index hospitalization. An asymptomatic decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) from 60% to 40% with global hypokinesis was observed following doxorubicin therapy, and thus carvedilol was initiated. After a favorable response to a total anthracycline lifetime dose of 508 mg/m2, pazopanib was initiated 8 months prior to the index hospitalization due to the lifetime dose limitations of doxorubicin. Carvedilol was switched to metoprolol succinate at the time of pazopanib initiation, given the adverse drug–drug interaction between permeability glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors, such as carvedilol, and pazopanib, which can result in increased serum exposure to pazopanib (1). Due to persistently reduced LVEF on repeat evaluation, an ischemic evaluation with coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) was performed 6 weeks prior to the ACS admission. The CCTA revealed patent coronary arteries and <25% stenosis of the proximal left anterior descending artery (LAD) (Figure 2). The total coronary artery calcium score was 4. Six weeks later, the patient presented for the index ACS hospitalization.
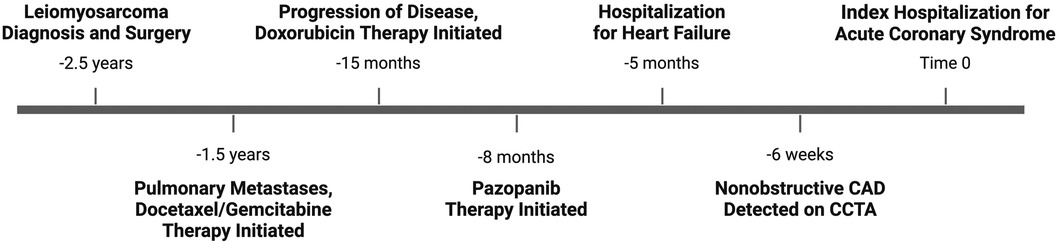
Figure 1. Timeline of clinical events. Depiction of important clinical events in chronological order, beginning with diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma and ending with index hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome.
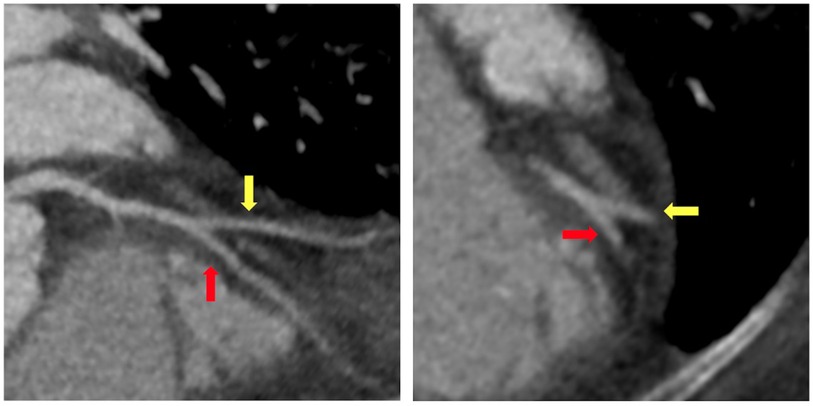
Figure 2. Coronary computed tomography angiography. Coronary computed tomography angiography performed 6 weeks prior to index hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome demonstrated minimal coronary atherosclerosis at the bifurcation of the mid-left anterior descending artery (red arrow) and secondary diagonal artery (yellow arrow).
On presentation to the index hospitalization, the patient reported nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite for 2 days. She denied a history of alcohol, tobacco, or recreational drug use. Physical examination demonstrated appropriate mentation, regular tachycardia without abnormal heart sounds, vesicular breath sounds, and no peripheral edema. An electrocardiogram showed sinus tachycardia with a heart rate of 103 beats per minute (Figure 3). High-sensitivity troponin-I was >25,000 ng/L (ref. <14 ng/L), and the lactate level was 3.4 mmol/L (ref. 0.5–2.2 mmol/L). The most recent prior measurement of high-sensitivity troponin-I was 147 ng/L 4 months prior. Liver enzyme and creatinine levels were increased from baseline. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) revealed a decrease in LVEF to 10%, left ventricular internal end-diastolic diameter (LVIDd) of 6.2 cm, severe global hypokinesis, and regional wall motion abnormalities within the LAD distribution. No left ventricular thrombus was observed. Pazopanib and carvedilol were held. Emergent cardiac catheterization revealed a large thrombotic occlusion of the mid-LAD involving the secondary diagonal artery, which was treated with manual aspiration thrombectomy (Figure 4). Right heart catheterization revealed elevated right- and left-sided filling pressures and a decreased cardiac index (Fick) of 1.36 L/min/m2. Her hemodynamic status improved following thrombectomy. The patient’s hospital course was complicated by the development of atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response, which improved with amiodarone. As the patient's cancer treatment was now limited to a fourth-line therapy with minimal chance of a favorable response, symptom control and supportive therapy were recommended. Pazopanib was discontinued, and the patient was discharged from the hospital 12 days after presentation with a slight improvement in LVEF to 15%–20%. Her discharge medications included aspirin and atorvastatin following her non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (MI); milrinone, spironolactone, and torsemide for advanced chronic systolic heart failure; and amiodarone and apixaban for atrial fibrillation. The patient was re-hospitalized 3 months later for acute decompensated heart failure following outpatient reduction of her home diuretic dose. During this hospitalization, LVEF was found to have improved to 20%–25%. Upon discharge, her previous home diuretic dose was restored. During post-hospitalization follow-up 1 month later, the patient reported that her heart failure-related symptoms and functional status had improved. Her milrinone dose remains at a stable dose, and she continues to tolerate her regimen of spironolactone, torsemide, amiodarone, and apixaban without issue.
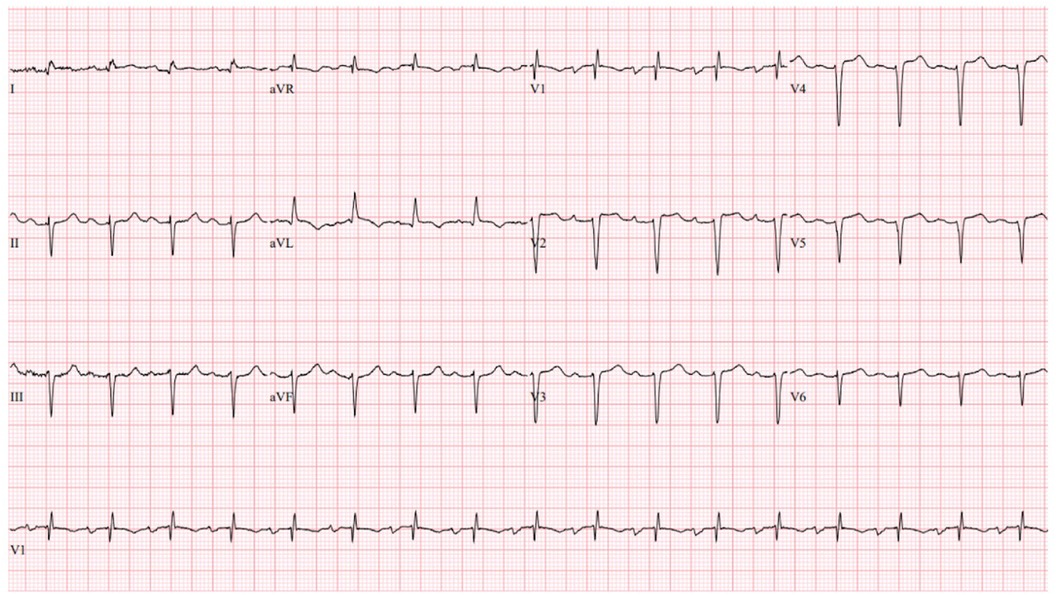
Figure 3. Index hospitalization electrocardiogram. The index hospitalization electrocardiogram demonstrated sinus tachycardia (HR 103 beats per minute), left anterior fascicular block, an RSR’ pattern in V1, and non-specific T-wave changes.
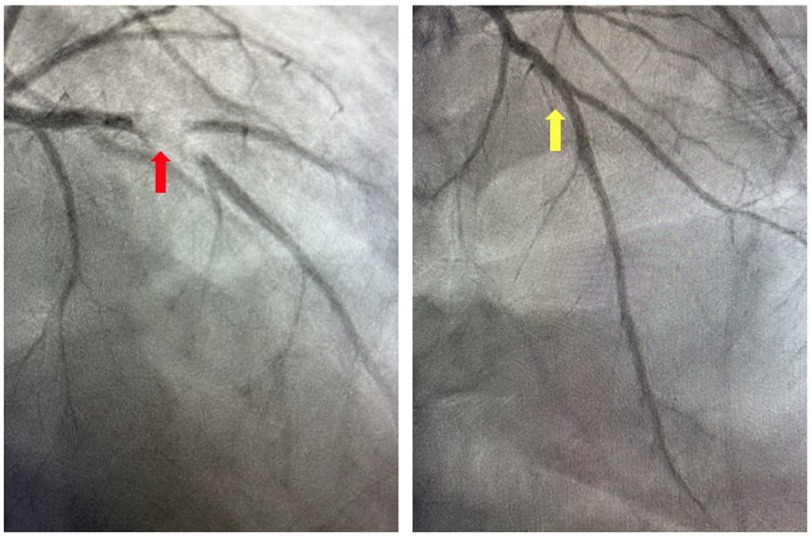
Figure 4. Coronary angiogram. Invasive coronary angiography demonstrating thrombotic occlusion of the mid-left anterior descending artery and second diagonal artery prior to manual aspiration thrombectomy (red arrow) and following manual aspiration thrombectomy (yellow arrow).
The above case represents, to our knowledge, the first causative report of pazopanib-induced ACS in a patient with metastatic STS. Although current ESC guidelines estimate a 1%–10% risk of ACS associated with pazopanib, clinical trials investigating the safety of pazopanib have not convincingly demonstrated a significant association between pazopanib therapy and ACS due to a lack of focused coronary disease evaluation in oncological clinical trials prior to pazopanib initiation (2–7). A single-arm monotherapy trial of pazopanib in patients with metastatic STS previously observed a 3% (N = 1/33) incidence of myocardial infarction incidence; however, the lack of a comparator placebo group makes this finding difficult to contextualize (4). Subsequent randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trials investigating the safety and efficacy of pazopanib in patients with metastatic STS have observed either no ACS events or an MI or ischemia incidence of 2% (N = 2/240) in the pazopanib group vs. 0% in the placebo group (Table 1) (5–7). Until now, a case demonstrating a distinct, causal relationship between pazopanib therapy and incident ACS has yet to be described.
Regarding the above case, the patient's patent coronary arteries noted on CCTA 6 weeks prior to her presentation for ACS strongly suggest causality attributable to pazopanib. Moreover, the lack of uncontrolled traditional cardiovascular risk factors or alternative etiologies for ACS further supports this to be a case of pazopanib-induced ACS. Although pazopanib therapy has also been associated with heart failure, the patient's decline in LVEF is substantially more likely a result of anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy rather than pazopanib, given the temporal relationship with the doxorubicin therapy.
There are several proposed mechanisms for pazopanib-induced thrombosis and myocardial injury. VEGF has been linked to endothelial cell survival and proliferation, as well as the promotion of coronary angiogenesis. Given pazopanib's role in VEGF receptor inhibition, endothelial cell apoptosis and resultant thromboembolic and/or ischemic events are plausible. In addition, pazopanib-induced inhibition of VEGF can create a pro-thrombotic environment through the overproduction of erythropoietin and increased blood viscosity (8).
Although pazopanib use has been associated with ACS, evidence to support this association is lacking. This case provides a discrete example of pazopanib-induced ACS in a patient with non-obstructive CAD demonstrated 6 weeks prior to ACS presentation. Careful attention and an individualized risk assessment for CAD should be provided to patients who are prescribed pazopanib, and pazopanib should be permanently discontinued in patients who experience an arterial thromboembolic event. Future studies should examine whether a dose-response relationship exists between pazopanib therapy and adverse cardiovascular events.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
AY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WS: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. CH: Writing – review & editing. AM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. AY is supported by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award number 5T32HL007745-30.
The authors deeply appreciate the participation of the aforementioned patient. Figure 1 was created with Biorender.com.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Novartis. Votrient (pazopanib) [package insert]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. (2009). (revised 26 April 2012). Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/022465s-010S-012lbl.pdf (Accessed 16 July 2024).
2. Lyon AR, López-Fernández T, Couch LS, Asteggiano R, Aznar MC, Bergler-Klein J, et al. 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS): developed by the task force on cardio-oncology of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. (2022) 43:4229–361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac244
3. Iliescu CA, Grines CL, Herrmann J, Yang EH, Cilingiroglu M, Charitakis K, et al. SCAI expert consensus statement: evaluation, management, and special considerations of cardio-oncology patients in the cardiac catheterization laboratory (endorsed by the Cardiological Society of India, and Sociedad Latino Americana de Cardiologıa Intervencionista). Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2016) 87:E202–23. doi: 10.1002/ccd.26379
4. Lim W-T, Ng Q-S, Ivy P, Leong S-S, Singh O, Chowbay B, et al. A phase II study of pazopanib in Asian patients with recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 17:5481–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3409
5. van der Graaf WT, Blay J-Y, Chawla SP, Kim D-W, Bui-Nguyen B, Casali PG, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2012) 379:1879–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60651-5
6. Kawai A, Araki N, Hiraga H, Sugiura H, Matsumine A, Ozaki T, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study of pazopanib in patients with soft tissue sarcoma: results from the Japanese subgroup. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2016) 46:248–53. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv184
7. Justice CN, Derbala MH, Baich TM, Kempton AN, Guo AS, Ho TH, et al. The impact of pazopanib on the cardiovascular system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. (2018) 23:387–98. doi: 10.1177/1074248418769612
8. Scott SS, Greenlee AN, Schwendeman EJ, Mohammad SJ, Naughton MT, Matzko A, et al. Intracellular cardiac signaling pathways altered by cancer therapies. Cardiovasc Signal Health Dis. (2022):111–73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08309-9_4
Keywords: pazopanib, acute coronary syndrome, cardio-oncology, interventional cardiology, case report, coronary artery disease
Citation: Yadalam AK, Schultz WM, Han C and Mandawat A (2024) Case Report: Pazopanib-induced acute coronary syndrome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1466395. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1466395
Received: 17 July 2024; Accepted: 30 August 2024;
Published: 24 September 2024.
Edited by:
Reto Asmis, Wake Forest University, United StatesReviewed by:
Giulia Iannaccone, Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, ItalyCopyright: © 2024 Yadalam, Schultz, Han and Mandawat. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anant Mandawat, YW5hbnQubWFuZGF3YXRAZW1vcnkuZWR1
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.