- Department of Echocardiography, Beijing Chao Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Aims: This study applied exercise stress echocardiography (ESE) to identify risk factors associated with exercise intolerance in patients with chronic coronary syndrome (CCS).
Methods and results: 90 CCS patients underwent a cardiopulmonary exercise test and ESE, assessing exercise capacity, left ventricular systolic and diastolic function, and systolic reserve. The patients were divided into two groups according to the percentage of predicted oxygen consumption (VO2) at peak (≥85%, normal exercise tolerance group; <85%, exercise intolerant group). The left ventricular ejection fraction, average mitral valve S’, and left ventricular global longitudinal strain were lower in the exercise intolerant group than in the normal group, but no significant differences were observed in myocardial work parameters at rest. The average mitral valve E/e’, EDVi/E/e’, and proportion of abnormal diastolic function at the peak were higher in the exercise intolerant group than in the normal group. Moreover, the ΔSVi and flow reserve were lower, but the Δaverage mitral valve E/e’ was higher in the exercise-intolerant group. From univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, only peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi correlated independently with exercise intolerance in CCS patients. With cutoff values of 8.64 ml/m2 for peak EDVi/E/e’ and 12.17 ml/m2 for ΔSVi, the combination of these factors had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.906 (95% confidence interval, 0.820–0.960) for the prediction of exercise intolerance in CCS patients.
Conclusion: Hemodynamic changes during exercise in CCS patients were effectively evaluated using ESE. An elevated peak EDVi/E/e’ and a decreased ΔSVi are independent risk factors for exercise intolerance in patients with CCS.
Introduction
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the leading causes of death and morbidity worldwide and imposes high societal and economic burdens (1). The dynamic nature of CAD progression results in various clinical presentations that are generally categorised as either acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or chronic coronary syndrome (CCS). CCS is chronic, most often progressive, and hence severe, even in clinically apparently silent periods (2). Therefore, effective clinical management of these patients is critical.
Exercise intolerance is a common early symptom in patients with CCS and may be related to myocardial ischemic injury caused by coronary artery stenosis, left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction, functional mitral regurgitation, chronotropic insufficiency, and peripheral muscle dysfunction (3). Previous studies have found that exercise intolerance can be associated with short-term and long-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CCS (4, 5). However, the specific pathophysiological mechanism of exercise intolerance in patients with CCS remains unclear. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is a non-invasive, reliable tool for estimating global oxygen consumption (VO2), which can effectively reflect exercise capacity (6). However, CPET offers a limited ability to differentiate the responsible mechanisms when an abnormally low value is detected (7). Combining resting or stress echocardiography with CPET provides a far more informative approach, giving insights into the morphological and functional cardiac issues that may impact exercise capacity (8). To date, exercise stress echocardiography (ESE) has been rarely used to analyze the mechanism of exercise intolerance in patients with CCS. Our study aimed to evaluate the exercise capacity of CCS patients by CPET and explore whether ESE parameters can be used to predict exercise intolerance in these patients as well as to analyze its possible pathophysiological mechanism.
Methods
Study population
We prospectively enrolled 90 patients aged >18 years suspected of having CCS between September 2021 and May 2023 in our cardiology department. These patients visited our cardiology department due to chest discomfort (chest pain, tightness) or shortness of breath at rest or after activity. CCS was defined according to the 2019 European Society of Cardiology guidelines (2). The inclusion criteria were as follows: suspected CAD and “stable” anginal symptoms or dyspnea and evaluation by coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA); and prior treatment with coronary artery intervention and stable hemodynamics for at least 1 month. The selected populations were classified into the I, III, and IV clinical phenotypes of CCS. All patients were able to perform bicycle exercise. The exclusion criteria were as follows: recent occurrence of acute myocardial infarction, history or presence of symptomatic congestive heart failure, Left ventricular ejection fraction <40%, a respiratory exchange ratio (RER) <1.0 at peak on CPET, anaemia, decompensated thyroid disease, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, severe valvular disease, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, resting echocardiography suggesting pulmonary hypertension, inadequate acoustic window for echocardiography, and significant arrhythmias at rest. We collected data on demographic and clinical characteristics as well as from CCTA by querying electronic medical records, and Dr. Mingming Lin and Dr. Yunyun Qin recorded all data. The physicians who performed CPET (Dr Xi-yan Yang, Dr Wen-shu Zhao, and nurse Nian-Zhong Zhang) and ESE (Dr Weiwei Zhu and Dr Runyu Tian) were blind to the clinical data and were also blinded to the respective results.
The study was conducted in according with the Declaration of Helsinki. The institutional review board of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Affiliated with Capital Medical University, approved the study protocol, and all participants provided written informed consent.
Baseline and exercise stress echocardiography
All patients underwent a comprehensive transthoracic echocardiography examination at rest according to the latest guidelines (9), using a commercially available ultrasound system (Vivid E95, GE Healthcare, Horton, Norway). A standard multistage, symptom-limited, semi-supine exercise test was performed using a bicycle ergometer (Ergoselect 1200, Stress EchoCouch Ergometer; Ergoline, Bitz, Germany) after the resting echocardiography (10). Participants were encouraged to complete exercise to their peak (when they achieved 85% of the age-predicted maximum heart rate) or until exhaustion if someone took beta-blockers. We acquired exercise echocardiographic images at two stages: low-load effort (within the first 4 min of exercise) and peak effort. We summarized the conventional data acquisition protocol in Supplementary Table S1. All patients completed the parameter measurements in Supplementary Table S1 and underwent LV diastolic function evaluation according to the 2016 American Society of Echocardiography guidelines (11). We calculated the LVEDV/E/e′ ratio as a surrogate of LV compliance during exercise and LVEDVi/E/e′ ratio obtained after body surface area normalization (12). Flow reserve was defined as an increase in stroke volume (SV) from rest to peak effort [(SVpeak−SVbaseline)/SVbaseline] (13). Offline speckle-tracking echocardiography analysis included global longitudinal strain (GLS) and myocardial work analysis with evaluation of the myocardial work parameters global work index (GWI), global constructive work (GCW), global wasted work (GWW), global work efficiency (GWE) while ensuring a frame rate >50 Hz at rest. We analyzed all echocardiographic data offline using dedicated software (EchoPAC version 204, GE Healthcare). All parameters were measured according to the recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography (9).
Cardiopulmonary exercise test
All patients underwent a standard symptom-limited graded ramp bicycle exercise test in the upright position according to guideline (7) with continuous monitoring of a 12-lead electrocardiogram, brachial blood pressure, and non-invasive arterial saturation. The parameters analyzed included the peak oxygen consumption (VO2),%pred VO2 at peak, RER at peak, O2 pulse at peak, VO2 at anaerobic threshold (AT), ventilatory efficiency (VE/VCO2 slope), oxygen uptake efficiency slope (OUES) and heart rate (HR) for the first 1 min of recovery. The anaerobic threshold was calculated using a dual method approach (V-slope and ventilatory equivalent methods). OUES was derived from the relationship between VO2 (plotted on the y-axis) and the log transformation of VE (x-axis). The arteriovenous oxygen difference (A-VO2Diff) was calculated using the Fick equation: VO2/cardiac output calculated from echocardiography (13, 14). The interval between the cardiopulmonary exercise test and ESE was more than 24 h but less than seven days. With reference to the 2022 Chinese expert consensus and the 2012 EACPR/AHA joint scientific statement, we divided patients into two groups according to the percentage of predicted VO2 at peak (15, 16): those with normal exercise capacity based on ≥85% predicted VO2 at peak (normal group) and those with reduced exercise capacity based on <85% predicted VO2 at peak (exercise intolerant group).
Statistical analyses
We performed statistical analysis using SPSS Version 20 for Windows (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) and MedCalc Version 15.6.1 (MedCalc Software, Ostend, Belgium) statistical software. Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation values or median values and interquartile ranges where appropriate. Categorical data are presented as absolute numbers or percentages. Two-sample comparisons were performed using the t-test if variables were normally distributed or the Mann–Whitney U-test if variables were not normally distributed. Categorical data were compared using the chi-squared or Fisher's exact test. Either the Pearson or Spearman correlation coefficient was used to analyze the linear correlation between echocardiographic parameters, peak oxygen consumption, and %pred VO2 at peak. We used univariate or multivariate stepwise logistic regression to identify independent risk factors associated with exercise intolerance in patients with CCS. The C-statistic was used to evaluate the predictive value of the model. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to calculate the area under the curve and the cutoff point with the highest Youden index.
The same observer and an independent reader reanalyzed a random sample of 20 patients. We measured the reproducibility of the variables, including left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), SV, wall motion score index (WMSI) at rest, and during any stage of the exercise, and LVGLS at rest, by calculating intraclass correlation coefficients and coefficients of variation. All tests were two-sided, with a P value of <.05, indicating statistical significance.
Results
Baseline characteristics
Table 1 presents the demographic and clinical characteristics of the study population. Compared with the group with normal tolerance, the exercise-intolerant group showed a younger age, higher proportions of males and smokers, a larger body surface area (BSA), and a higher prevalence of previous percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). No significant differences in blood test results or therapies were observed between the groups, and CCTA showed no difference in the proportion of single vessel stenosis >50% between the patient groups.
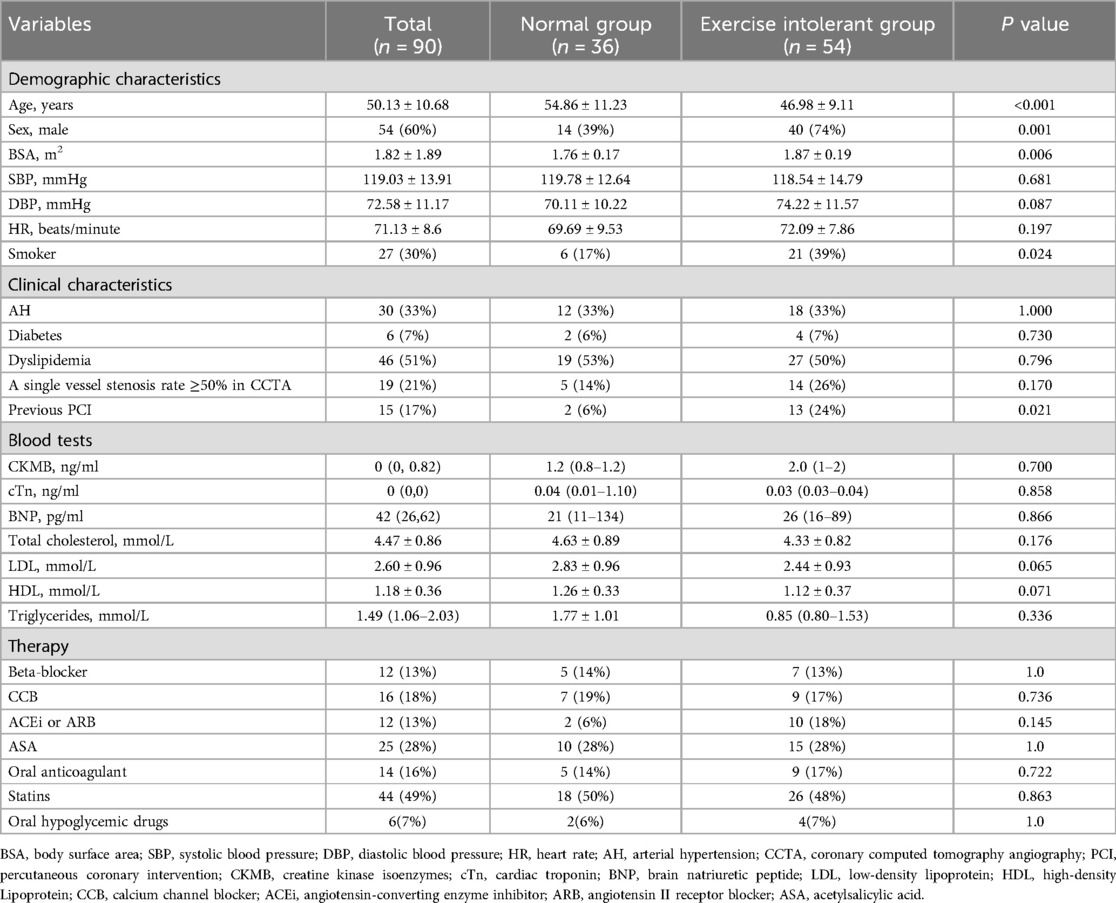
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics for patients with CCS according to the percentage of predicted oxygen uptake at peak (normal exercise capacity group, ≥85%; exercise intolerant group, <85%).
Combined stress echocardiography and cardiopulmonary exercise testing
We conducted the cardiopulmonary exercise test and exercise stress echocardiography in two separate sessions due to the limitations of the equipment. 34% of patients reached the diagnostic endpoints for ESE (85% of age-predicted maximal heart rate). The reasons for test interruption were dyspnea (8%), fatigue (23%), leg discomfort (28%) and high blood pressure [systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 250 mmHg, 7%]. No patient experienced persistent chest pain and/or syncope. Supplementary Table S2 shows a comparison of the two testing protocols.
The results for cardiopulmonary parameters are compared between the groups in Table 2. Each patient made a maximal effort during the exercise, and the mean RER at peak was 1.21. The exercise-intolerant group completed a lower workload, with a mean predicted workload at a peak of 78 W vs. 102 W in the normal group. The mean VO2 at peak in the exercise intolerant group was 20.99 ml/kg/min, which also was lower than that in the normal group (24.11 ml/kg/min), but the exercise intolerant group had a relatively preserved VO2 (peak VO2 > 20 ml/kg/min).
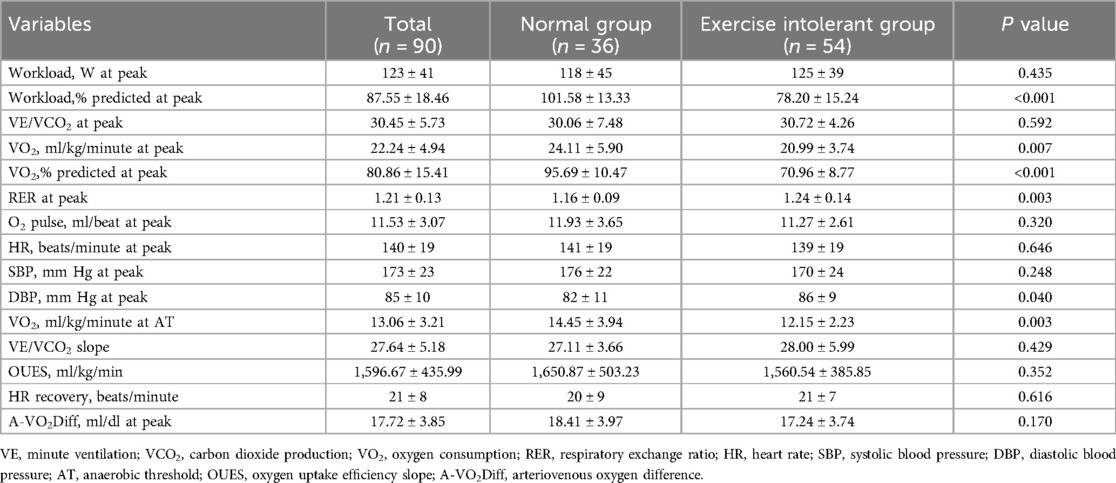
Table 2. Cardiopulmonary parameters for patients with CCS according to the percentage of predicted oxygen uptake at peak (normal exercise capacity group, ≥85%; exercise intolerant group, <85%).
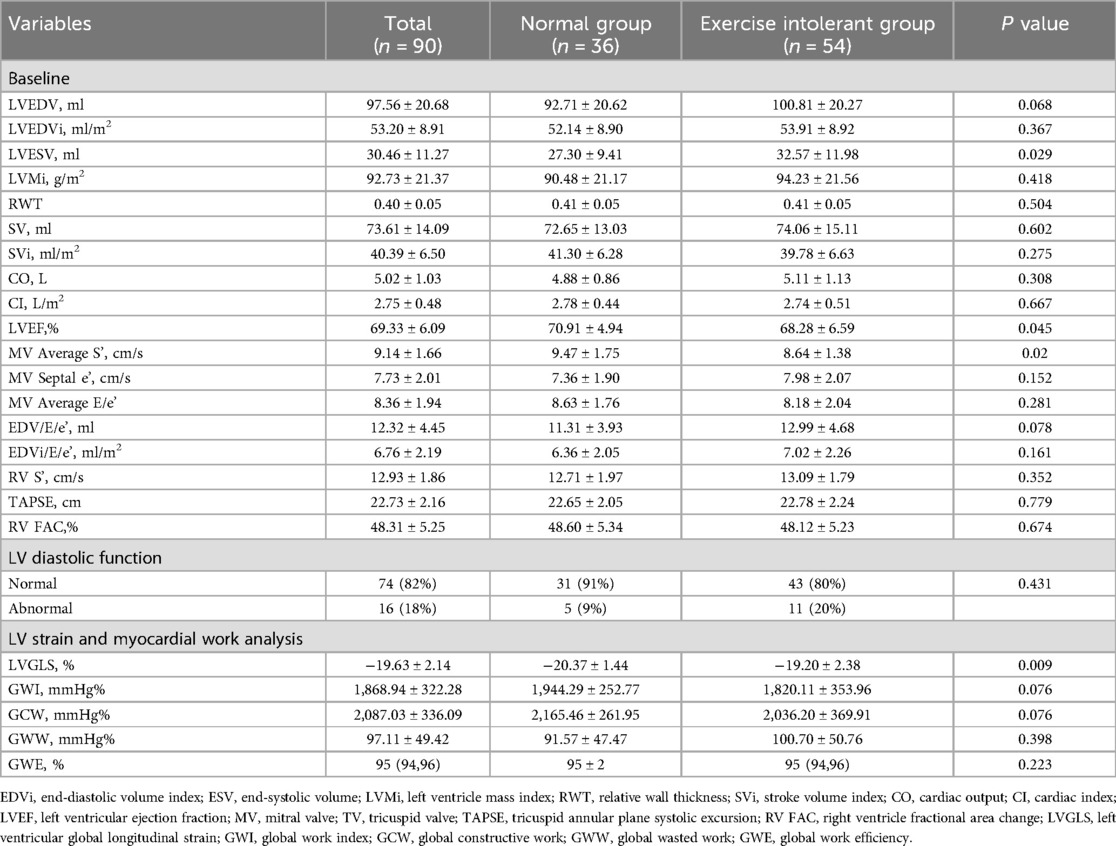
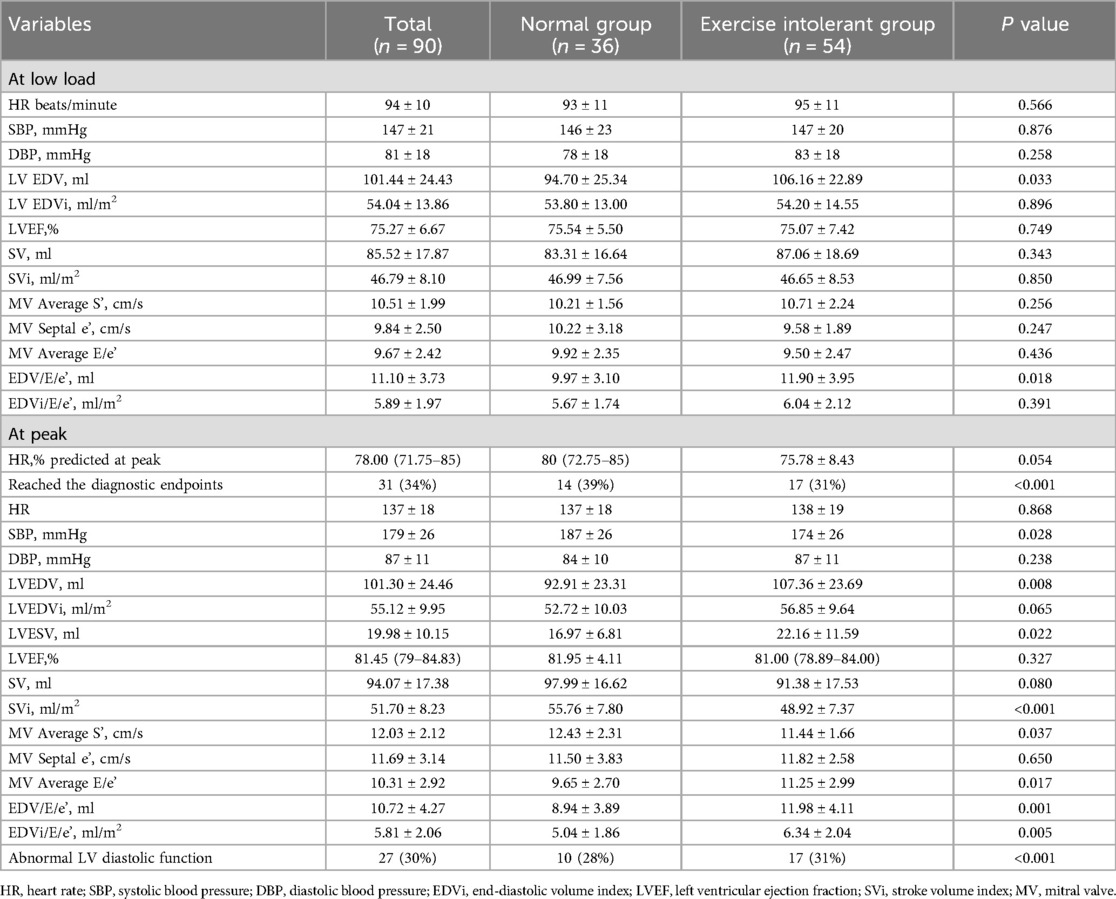
Resting myocardial strain and myocardial work analysis were completed for all patients. Tables 3, 4 displayed the results for ESE variables in the overall population and each patient group. No significant differences in most baseline and low-load echocardiography parameters, including all myocardial work parameters, were observed between the groups. Compared with the normal group, the exercise intolerant group had a lower LVEF, mitral valve (MV) average S’, and LVGLS at rest but a higher EDV/E/e’ at low load. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups after the EDV/E/e’ normalization by BSA. A lower proportion of patients with exercise intolerance completed the exercise (achieved 85% of the age-predicted maximum heart rate) compared with that in the normal group. Also, the exercise intolerant group had lower SBP, SVi, and MV average S’ values and higher MV average E/e’ and EDVi/E/e’ at peak compared with the normal group.
11 cases with normal left ventricular diastolic function at rest were reclassified as abnormal at peak. The exercise-intolerant group had a higher proportion of patients with abnormal left ventricular diastolic function. In the group with normal exercise tolerance, we did not detect segmental wall motion abnormalities at rest, even at peak. In contrast, in the exercise intolerant group, segmental wall motion abnormalities were detected in eight patients at rest [mean wall motion score index (WMSI) of 1.42], with no additional cases detected at peak. The mean WMSI of these eight patients was reduced (1.28) at peak.
Table 5 showed a comparison of exercise contractile reserve (Δ) between the two groups. Statistically significant differences in ΔSV, ΔSVi, ΔMV average E/e’, and flow reserve were observed between the two groups. The exercise intolerant group had a lower flow reserve, but the mean value (0.24) was higher than 0.20. Supplementary Table S3 reported the reproducibility analysis of echocardiographic parameters.
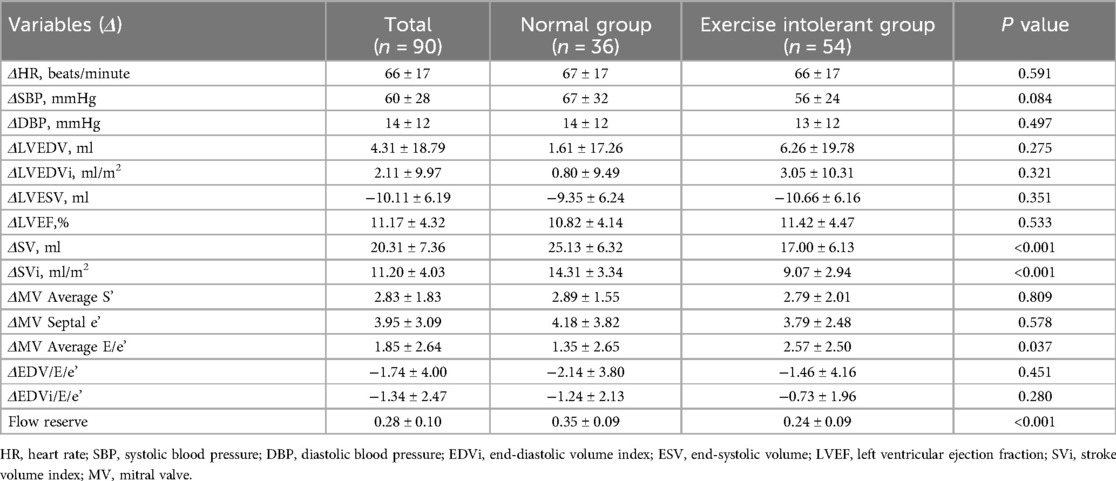
Table 5. Comparison of peak-resting echocardiographic parameters (Δ) between CCS patients with normal exercise tolerance and exercise intolerant.
Determinants of exercise capacity in patients with CCS
Supplementary Figures S1, S2 present the linear correlation analyses between echocardiographic parameters and peak oxygen consumption, as well as the %pred VO2 at peak. The correlation between flow reserve and peak oxygen consumption was the strongest, with a coefficient of 0.364 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.156–0.528]. Meanwhile, the correlation between ΔSVi and%pred VO2 at the peak was the strongest, with a correlation coefficient of 0.607 (95%CI, 0.454–0.726).
No independent correlation was found between clinical parameters, including age, gender, smoking history, previous PCI, and exercise intolerance in patients with CCS after multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis. Of all the echocardiographic parameters, only the peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi independently correlated with exercise intolerance in patients with CCS (Table 6). With a cutoff value for peak EDVi/E/e’ of 8.64 ml/m2, the sensitivity and specificity were 78.7% and 66.7%, respectively, the area under the ROC curve of 0.734 (95% CI, 0.623–0.827) for the prediction of exercise intolerance in CCS patients. With a cutoff value for ΔSVi of 12.17 ml/m2, the sensitivity and specificity were 86.3% and 82.9%, respectively, the area under the ROC curve of 0.868 (95% CI, 0.774–0.933) for the prediction of exercise intolerance in CCS patients. The combination of these two parameters with a C-statistic of 0.906 (95%CI, 0.820–0.960) showed incremental predictive value in patients with CCS over peak EDVi/E/e’ alone (0.906 vs. 0.734, P = 0.001), but not ΔSVi (0.906 vs. 0.868, P = 0.158) (Figure 1). Supplementary Figure S3 summarizes the ESE-derived parameters used in the functional model to predict%pred VO2 at peak in patients with CCS.
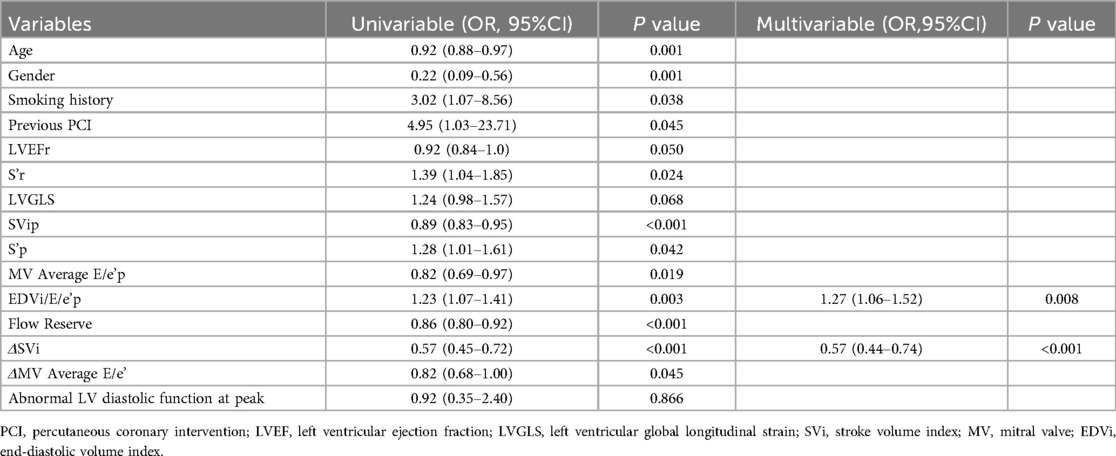
Table 6. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis for predictors of exercise intolerance in patients with CCS.
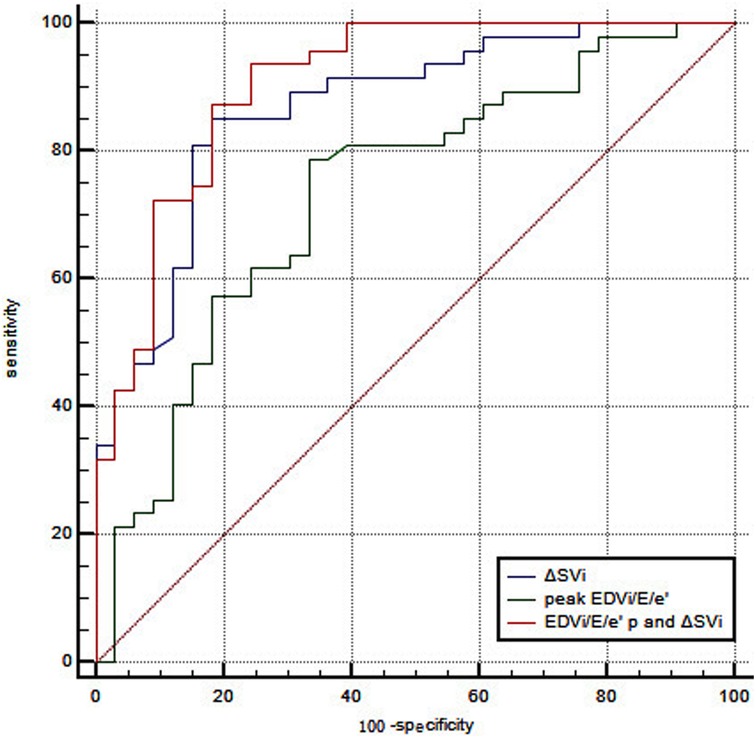
Figure 1. ROC curve analysis of peak EDVi/E/e’ combined with ΔSVi in predicting exercise intolerance in patients with CCS. With a cutoff value for peak EDVi/E/e’ of 8.64 ml/m2, the sensitivity and specificity were 78.7% and 66.7%, respectively, the area under the ROC curve of 0.734 (95% CI, 0.623–0.827). With a cutoff value for ΔSVi of 12.17 ml/m2, the sensitivity and specificity were 86.3% and 82.9%, respectively, the area under the ROC curve of 0.868 (95% CI, 0.774–0.933). The combination of these two parameters with a C-statistic of 0.906 (95%CI, 0.820−0.960) showed incremental predictive value in patients with CCS over peak EDVi/E/e’ alone (0.906 vs. 0.734, P = 0.001), but not ΔSVi (0.906 vs. 0.868, P = 0.158).
Discussion
The main findings of the present study are that peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi were identified as independent risk factors for exercise intolerance in patients with CCS, while all resting echocardiographic parameters, including myocardial work parameters and flow reserve, were not (Figure 2). Our study was a relatively rare study that combined ESE and CPET to analyze the mechanism of exercise intolerance in patients with CCS. Numerous previous studies have focused on investigating the possible causes of exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure, with the results showing that patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) presented with reduced peak VO2, mainly as a result of chronotropic incompetence and inadequate SV increase. In contrast, patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) developed multiple alterations of the cardiovascular function involving both central and peripheral components (13, 17–19). It is not uncommon for patients with CCS to have HFpEF or HFrEF, indicating the possibility of overlapping mechanisms for their exercise intolerance. Therefore, We hypothesized that CPET combined with ESE could analyze the mechanism of exercise intolerance in patients with CCS and ultimately found that ΔSVi and peak EDVi/E/e’ were independent risk factors. Rozenbaum et al. also found that a combined ESE with CPET, measuring stroke volume and AVO2 difference throughout the effort, may help diagnose significant coronary artery disease (20). However, the Smarz team (21, 22) analyzed the mechanism of exercise intolerance in patients after PCI for acute myocardial infarction and obtained different results, showing that exercise intolerance was related to slower heart rate response and decreased peak peripheral blood oxygen uptake (A-VO2Diff) during exercise, but not to stroke volume. Smarz's study involved fewer echocardiographic parameters and did not include parameters such as systolic function reserve, which reflected the hemodynamic changes during exercise. The conclusions of this study were only applicable to patients with acute myocardial infarction with LVEF ≥ 40% after PCI. Our study focuses on CCS patients, the most common type among CAD but is often overlooked due to its subtle symptoms and the limited information provided by resting echocardiography.
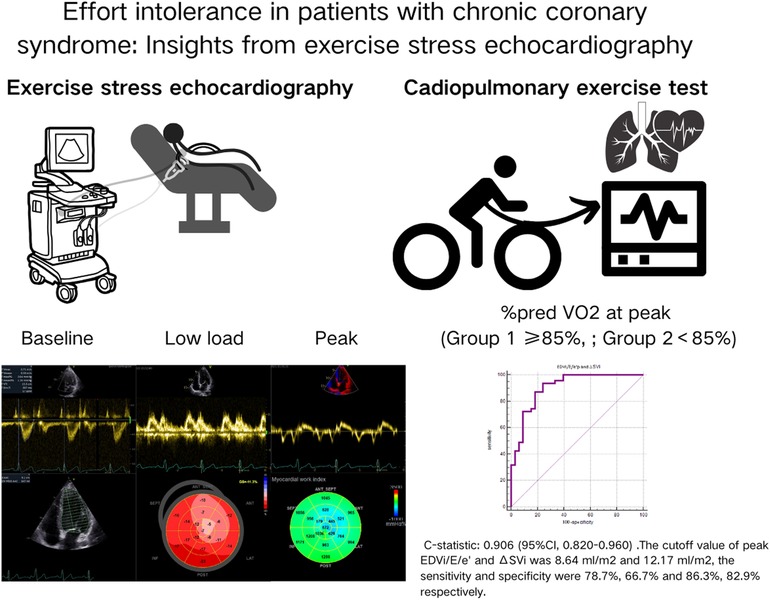
Figure 2. The main procedures and findings of our study. All patients underwent CPET and ESE. We analyzed the exercise stress echocardiography images in detail, including the traditional two-dimensional parameters, myocardial strain and myocardial work parameters. Finally, we found that only the peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi independently correlated with exercise intolerance in patients with CCS.
Several causes of exercise intolerance, leading to low%pred VO2, have been described, including Fick and non-Fick variables. We excluded patients with non-Fick variables that led to exercise termination, including pulmonary and peripheral nervous system diseases, peripheral arterial or vein pathologies, or bone and joint abnormalities. The Fick variables mainly comprise three significant elements: stroke volume, heart rate, and A-VO2Diff (23). Patients with CCS experience a series of ischemic cascade reactions triggered by coronary artery lesions (narrowing, spasm, or microvascular disease), which lead to reduced local blood flow perfusion, imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand, decreased local myocardial contractility and echocardiographic manifestations of resting or stress-induced segmental wall motion abnormalities or reduced left ventricular systolic reserve. Subsequently, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure increases, followed by a decrease in diastolic and global systolic functions, resulting in changes in the electrocardiogram, chest pain, exercise intolerance, and other clinical manifestations (24–26). In addition to segmental wall motion abnormalities, echocardiography also detects abnormal results for diastolic function parameters in patients with CCS, such as E/e’, EDV/E/e,’ as well as systolic function parameters, including LVEF, S,’ LVGLS, myocardial work parameters and SV. We observed differences in the mitral valve average E/e’ at peak, S’ at rest and peak, LVEF, and LVGLS at rest between the groups of CCS patients with and without exercise intolerance. However, on multivariate analysis, only the peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi, reflecting left ventricular compliance and contractile reserve, respectively, showed independent correlations with exercise intolerance in patients with CCS.
EDV/E/e’ was originally proposed by Shimiaie et al., reflecting the relationship between left ventricular filling pressure and volume rather than just left ventricular end-diastolic pressure or stroke volume alone (12). Changes in this ratio better represent the inability of the LV to increase its size, even with high filling pressure, suggesting a decrease in left ventricular compliance. The peak EDV/E/e’ in patients with CCS was significantly lower than at rest, regardless of exercise tolerance. Considering the differences in BSA between the two groups of patients in our study cohort, we used BSA to standardize EDV/E/e’ to obtain EDVi/E/e’. Our study showed that higher peak EDVi/E/e’ values were associated with exercise intolerance in patients with CCS, inconsistent with previous studies in HFpEF (12). We analyze the possible reasons as follows: firstly, there is a difference in age between the normal exercise tolerance and exercise intolerance groups in our study, and E/e’ gradually increases with age, which may lead to a higher EDVi/E/e’ value in the exercise intolerance group. Although we adjusted age factors in multivariate analysis, their effect on E/e’ could not be corrected. Secondly, coronary circulation dysfunction may directly lead to a gradual increase in left ventricular size, which may be another important reason. Nevertheless, these findings should be considered hypothesis-generating and tested with prospective invasive methods. Our study also showed that its sensitivity and specificity in predicting exercise intolerance are not high, and SV combined with EDVi/E/e’ has an incremental value compared to EDVi/E/e’ alone in predicting exercise intolerance in patients with CCS.
Although many previous studies have proven the value of LV GLS and myocardial work parameters in diagnosing severe CAD and predicting future cardiovascular events (27–31). Our study focused on analyzing risk factors associated with exercise intolerance in patients with CCS rather than predicting severe CAD, and only 19 patients had a single vessel stenosis rate ≥50% on CCTA. Myocardial ischemic injury may only be one factor leading to exercise intolerance in CCS patients; when left ventricular systolic function is preserved, diastolic dysfunction and reduced left ventricular systolic reserve become more critical. Among the three significant Fick variables, our study found that only ΔSVi independently correlated with reduced exercise capacity in patients with CCS, while heart rate response and A-VO2Diff did not. One possible reason is that the included cases had relatively mild coronary artery stenosis, with only 21% having single-vessel stenosis >50%. Another reason could be that our study did not strictly control the use of beta-blockers by patients on the day of examination, making the study situation closer to clinical reality. Despite this, we still observed differences in the percentages of patients who reached the predicted percentage of maximum heart rate during ESE between the normal group and exercise intolerant group. Additionally, we conducted CPET and ESE using different devices due to equipment limitations. AVO2diff, a non-invasive parameter derived from CPET-ESE, may exhibit calculation bias in our study.
Clinical implications
CCS, the most common and widely distributed type in CAD, requires long-term follow-up and management. Due to its subtle symptoms, patients may not be aware of their condition, leading to frequent neglect in clinical practice. Exercise intolerance in CCS patients poses a risk of progressing to heart failure and ACS. Conventional resting echocardiography provides minimal information and often reveals no abnormalities. The combined application of CPET and ESE allows for assessing exercise capacity and further evaluating left ventricular diastolic and systolic function and exercise systolic reserve. This combination also facilitates the investigation of the specific causes of exercise intolerance in patients with CCS, supporting the administration of targeted and timely treatment to improve patients’ exercise capacity and reduce the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
CPET acquisition can be completed while performing ESE in a semi-recumbent position for qualified cardiac centres. We recommend that patients with CCS who had exercise ability in these cardiac centres should complete these two tests. Judging from the results of our study, it seems that patients with mild coronary stenosis have more significant benefits from these two examinations. Therefore, for patients with clinically suspected CCS but no significant coronary stenosis on CCTA, CPET and ESE examinations help detect exercise tolerance and aetiology analysis. Our study revealed that peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi were identified as independent risk factors for exercise intolerance in patients with CCS. In clinical practice, targeted exercise training should be provided for these patients with exercise intolerance, and they were reexamined after some time training to observe whether peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi had improved while exercise capacity was recovered.
Limitations
Various limitations of the current work should be noted. This was a single-centre study with a relatively small sample size. Further multicenter studies with large samples are needed to confirm our preliminary findings. Patient selection was also biased, excluding those unwilling to undergo two exercise tests. This directly led to fewer patients with LVEF of 40%–50%, so we could not conduct further subgroup analysis based on LVEF. In our study, only 19 patients (21%) had single-vessel stenosis >50%, and 5 patients in the group with normal exercise capacity. The small number of positive cases was insufficient to support further stratified analyses for plaque burden and the coronary artery affected by CAD. Our future research will focus on the impact of plaque burden on exercise capacity and prognosis of patients with CCS, but it was not the focus of this study. In addition, ESE was more challenging in obtaining coronary flow velocity reserve (CFVR) due to the hyperventilation and motion of patients during peak exercise. So, we gave up measuring CFVR, which may be related to the exercise intolerance of CCS patients. Due to equipment limitations, the separated administration of CPET and ESE could result in bias in the calculation of AVO2diff. Our study also did not specify the types of CCS. The subsequent analysis of any differences in the mechanisms of exercise intolerance among different types of CCS will be a focus of our future research. Previous studies have shown that the increased left atrial volume during exercise in CCS patients is related to decreased left ventricular systolic reserve (32). Our study did not analyze whether changes in left atrial structure and function are related to exercise intolerance in CCS patients, and this topic warrants investigation in the future. Although our study excluded patients with poor acoustic windows, challenges persist in measuring echocardiographic parameters during exercise due to gas interference.
Conclusions
CPET is a valuable tool for evaluating the exercise capacity of CCS patients, and its combination with ESE further supports the analysis of the reasons for exercise intolerance. Exercise intolerance in CCS patients is complex and may result from the combined effects of multiple mechanisms. Our study showed that only peak EDVi/E/e’ and ΔSVi were independent predictive factors for exercise intolerance in the included CCS patients. Therefore, in clinical practice, exercise stress echocardiography may be an essential addition to routine resting echocardiography for CCS patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
W-wZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Software, Validation. R-YT: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Software. D-cG: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. M-mL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. Q-zC: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. Y-yQ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. X-yD: Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. X-zL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study was funded by Beijing Key Specialists in Major Epidemic Prevention and Control Program.
Acknowledgments
We thank all subjects for their participation and other colleagues for their support. Although Dr Xi-yan Yang, Dr Wen-shu Zhao, and nurse Nian-zhong Zhang from the cardiopulmonary exercise test laboratory, Department of Cardiology were not listed as the authors of this study, the three medical staff members completed the cardiopulmonary exercise test operation and parameter measurement of all patients. We thank Dr. Xi-yan Yang, Dr. Wen-shu Zhao, and Nurse Nian-zhong Zhang for contributing to this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could potentially create a conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2024.1442263/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | The linear correlation between echocardiographic parameters and peak oxygen consumption, as well as%pred VO2 at peak. (A) The linear correlation between Sr and peak VO2, r = 0.262 (95%CI, 0.055–0.448), P value = 0.014; (B) the linear correlation between Sp and peak VO2, r = 0.311(95%CI, 0.100–0.500), P value = 0.005; (C) the linear correlation between ΔSVi and peak VO2, r = 0.356 (95%CI, 0.156–0.528), P value = 0.0008; (D) the linear correlation between EDVi/E/e’ and peak VO2, r = 0.273 (95%CI, 0.057–0.465), P value = 0.014; (E) the linear correlation between flow reserve and peak VO2, r = 0.364 (95%CI, 0.165–0.535), P value = 0.0006; (F) the linear correlation between ΔSVi and%pred VO2 at peak, r = 0.607 (95%CI, 0.404–0.720), P value < 0.0001.
Supplementary Figure 2 | The linear correlation between echocardiographic parameters and%pred VO2 at peak. (A) The linear correlation between LVESVr and%pred VO2 at peak, r = −0.218 (95%CI, −0.008 to −0.410), P value = 0.043; (B) the linear correlation between LVEFr and%pred VO2 at peak, r = 0.243(95%CI, 0.034–0.431), P value = 0.023; (C) the linear correlation between LVGLS and%pred VO2 at peak, r = −0.346 (95%CI, −0.146 to −0.519), P value = 0.001; (D) the linear correlation between SVip and%pred VO2 at peak, r = 0.512 (95%CI, 0.336–0.653), P value < 0.0001; (E) the linear correlation between EDVi/E/e’ and%pred VO2 at peak, r = −0.232 (95%CI, −0.013 to −0.430), P value = 0.039; (F) the linear correlation between flow reserve and%pred VO2 at peak, r = 0.451 (95%CI, 0.264–0.605), P value < 0.0001.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Summarizes the ESE-derived parameters used in the functional model to predict%pred VO2 at peak in patients with CCS.
References
1. Townsend N, Nichols M, Scarborough P, Rayner M. Cardiovascular disease in Europe–epidemiological update 2015. Eur Heart J. (2015) 36:2696–705. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv428
2. Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato E, Funck-Brentano C, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:407–77. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz425
3. Kaminsky LA, Myers J, Arena R. Determining cardiorespiratory fitness with precision: compendium of findings from the FRIEND registry. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. (2019) 62:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2018.10.003
4. Kiviniemi AM, Lepojarvi S, Kentta TV, Junttila MJ, Perkiomaki JS, Piira OP, et al. Exercise capacity and heart rate responses to exercise as predictors of short-term outcome among patients with stable coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. (2015) 116:1495–501. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.08.014
5. Hung RK, Al-Mallah MH, McEvoy JW, Whelton SP, Blumenthal RS, Nasir K, et al. Prognostic value of exercise capacity in patients with coronary artery disease: the FIT (henry ford ExercIse testing) project. Mayo Clin Proc. (2014) 89:1644–54. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.07.011
6. Guazzi M, Bandera F, Ozemek C, Systrom D, Arena R. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 70:1618–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.08.012
7. Guazzi M, Arena R, Halle M, Piepoli MF, Myers J, Lavie CJ. 2016 focused update: clinical recommendations for cardiopulmonary exercise testing data assessment in specific patient populations. Circulation. (2016) 133:e694–711. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000406
8. Santoro C, Sorrentino R, Esposito R, Lembo M, Capone V, Rozza F, et al. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing and echocardiographic exam: an useful interaction. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. (2019) 17:29. doi: 10.1186/s12947-019-0180-0
9. Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2015) 28:1–39.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.10.003
10. Pellikka PA, Arruda-Olson A, Chaudhry FA, Chen MH, Marshall JE, Porter TR, et al. Guidelines for performance, interpretation, and application of stress echocardiography in ischemic heart disease: from the American society of echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2020) 33:1–41.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.07.001
11. Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, Byrd BF 3rd, Dokainish H, Edvardsen T, et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: an update from the American society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2016) 29:277–314. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2016.01.011
12. Shimiaie J, Sherez J, Aviram G, Megidish R, Viskin S, Halkin A, et al. Determinants of effort intolerance in patients with heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. (2015) 3:803–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2015.05.010
13. Pugliese NR, De Biase N, Conte L, Gargani L, Mazzola M, Fabiani I, et al. Cardiac reserve and exercise capacity: insights from combined cardiopulmonary and exercise echocardiography stress testing. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2021) 34:38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2020.08.015
14. Bugge-Asperheim B, Kiil F. Preload, contractility, and afterload as determinants of stroke volume during elevation of aortic blood pressure in dogs. Cardiovasc Res. (1973) 7:528–41. doi: 10.1093/cvr/7.4.528
15. Guazzi M, Adams V, Conraads V, Halle M, Mezzani A, Vanhees L, et al. EACPR/AHA scientific statement. Clinical recommendations for cardiopulmonary exercise testing data assessment in specific patient populations. Circulation. (2012) 126:2261–74. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31826fb946
16. Cardiovascular Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Professional Committee of Cardiopulmonary Prevention and Rehabilitation of China Rehabilitation Medicine Association, Editorial Committee of Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Disease. Chinese expert consensus on standardized clinical application of cardiopulmonary exercise testing. J Chin Cardiovasc Dis. (2022) 50:973–86. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20220316-00180
17. Obokata M, Olson TP, Reddy YNV, Melenovsky V, Kane GC, Borlaug BA. Haemodynamics, dyspnoea, and pulmonary reserve in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. (2018) 39:2810–21. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy268
18. Pugliese NR, Fabiani I, Santini C, Rovai I, Pedrinelli R, Natali A, et al. Value of combined cardiopulmonary and echocardiography stress test to characterize the haemodynamic and metabolic responses of patients with heart failure and mid-range ejection fraction. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2019) 20:828–36. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez014
19. Pugliese NR, Mazzola M, Fabiani I, Gargani L, De Biase N, Pedrinelli R, et al. Haemodynamic and metabolic phenotyping of hypertensive patients with and without heart failure by combining cardiopulmonary and echocardiographic stress test. Eur J Heart Fail. (2020) 22:458–68. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1739
20. Rozenbaum Z, Khouri S, Aviram G, Gura Y, Sherez J, Man A, et al. Discriminating circulatory problems from deconditioning. Chest. (2017) 151:431–40. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.09.027
21. Smarz K, Jaxa-Chamiec T, Zaborska B, Tysarowski M, Budaj A. Combined use of stress echocardiography and cardiopulmonary exercise testing to assess exercise intolerance in patients treated for acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0255682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255682
22. Smarz K, Jaxa-Chamiec T, Zaborska B, Tysarowski M, Budaj A. Mechanisms of exercise capacity improvement after cardiac rehabilitation following myocardial infarction assessed with combined stress echocardiography and cardiopulmonary exercise testing. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:4083. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184083
23. Houstis NE, Lewis GD. Causes of exercise intolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: searching for consensus. J Card Fail. (2014) 20:762–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2014.07.010
24. Nesto RW, Kowalchuk GJ. The ischemic cascade: temporal sequence of hemodynamic, electrocardiographic and symptomatic expressions of ischemia. Am J Cardiol. (1987) 59:23C–30C. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)90192-5
25. Chinese Society of Echocardiography, Shallow Tissue and Vascular Group of Chinese Medical Association Ultrasound Medicine Branch, Ultrasound Medicine Professional Committee of China Medical Education Association. Clinical practice guidelines for stress echocardiography in chronic coronary artery syndrome (2023 edition). Chin J Ultrason. (2023) 32:921–45. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn131148-20230511-00267
26. Gaibazzi N, Ciampi Q, Cortigiani L, Wierzbowska-Drabik K, Zagatina A, Djordjevic-Dikic A, et al. Multiple phenotypes of chronic coronary syndromes identified by ABCDE stress echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2024) 37:477–85. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2023.12.003
27. Brainin P, Hoffmann S, Fritz-Hansen T, Olsen FJ, Jensen JS, Biering-Sorensen T. Usefulness of postsystolic shortening to diagnose coronary artery disease and predict future cardiovascular events in stable angina pectoris. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2018) 31:870–879.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2018.05.007
28. Pastore MC, Mandoli GE, Contorni F, Cavigli L, Focardi M, D'Ascenzi F, et al. Speckle tracking echocardiography: early predictor of diagnosis and prognosis in coronary artery disease. Biomed Res Int. (2021) 2021:1. doi: 10.1155/2021/6685378
29. Borrie A, Goggin C, Ershad S, Robinson W, Sasse A. Noninvasive myocardial work index: characterizing the normal and ischemic response to exercise. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2020) 33:1191–200. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2020.05.003
30. Edwards NFA, Scalia GM, Sabapathy S, Anderson B, Chamberlain R, Khandheria BK, et al. Resting global myocardial work can improve interpretation of exercise stress echocardiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2021) 37:2409–17. doi: 10.1007/s10554-021-02216-0
31. Gaibazzi N, Bergamaschi L, Pizzi C, Tuttolomondo D. Resting global longitudinal strain and stress echocardiography to detect coronary artery disease burden. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2023) 24:e86–8. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jead046
Keywords: chronic coronary syndrome, exercise stress echocardiography, exercise intolerance, stroke volume, oxygen consumption
Citation: Zhu W-w, Tian R-Y, Guo D-c, Lin M-m, Cai Q-z, Qin Y-y, Ding X-y and Lv X-z (2024) Exercise intolerance in patients with chronic coronary syndrome: insights from exercise stress echocardiography. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1442263. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1442263
Received: 1 June 2024; Accepted: 13 November 2024;
Published: 28 November 2024.
Edited by:
Attila Kardos, Milton Keynes University Hospital, United KingdomReviewed by:
Luca Bergamaschi, University of Bologna, ItalyJet Van Zalen, Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust, United Kingdom
Copyright: © 2024 Zhu, Tian, Guo, Lin, Cai, Qin, Ding and Lv. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiu-zhang Lv, bHh6X2VjaG9AMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Wei-wei Zhu
Wei-wei Zhu Qi-zhe Cai
Qi-zhe Cai Xiu-zhang Lv
Xiu-zhang Lv